Abstract
Background:
The neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHR) has emerged as a novel inflammatory marker with prognostic significance. This study aims to explore the association between NHR and adverse prognosis in patients with acute large vessel occlusion (LVO) stroke who achieved complete recanalization after mechanical thrombectomy (MT).
Methods:
This retrospective study analyzed acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients with LVO who underwent MT at three stroke centers in Dalian, China, between January 2016 and November 2023. Complete recanalization was defined as achieving a modified Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction (mTICI) grade 3. Blood parameters were assessed within 24 h after MT. We compared intergroup differences based on NHR tertiles and employed the multivariate logistic regression analysis to assess the relationship between NHR and adverse outcomes.
Results:
This study included 348 AIS patients with LVO, of whom 215 (61.8%) had adverse clinical outcomes at 90 days. The multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed a significant association between an elevated NHR and 90-day adverse outcomes (OR 2.311, 95% CI 1.248–4.278, p = 0.008). A restricted cubic spline curve demonstrated a linear dose–response relationship between NHR and adverse outcomes, with a p-value of 0.348 for non-linearity.
Conclusion:
Our findings revealed that an elevated NHR could increase the risk of adverse prognosis following complete recanalization after MT in acute LVO stroke patients, which indicated that NHR could serve as a potential inflammatory marker for identifying high risk patients.
Introduction
Mechanical thrombectomy (MT) has been established as an effective treatment for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) caused by large vessel occlusion (LVO) (1). Successful recanalization is typically defined as achieving modified Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction (mTICI) grade 2b-3 (2). Previous studies have demonstrated that successful recanalization can be achieved in over 83% of patients after MT (3, 4). Despite successful recanalization, nearly half of the patients still exhibit unfavorable clinical outcomes at 90 days, a phenomenon termed futile recanalization (5–7). Current studies on futile recanalization primarily focus on patients who achieve successful recanalization (mTICI 2b-3) after MT; however, the understanding of potential factors associated with poor outcomes in patients who achieve complete recanalization (mTICI 3) remains limited. A systematic review and meta-analysis indicated that mTICI 3 is associated with better outcomes and safety compared to mTICI 2b, and the recanalization grade represents the most important modifiable predictor of patient prognosis (8). VanHorn et al. found that patients with complete recanalization still had a high proportion of adverse outcomes (9). Therefore, actively exploring the factors associated with futile recanalization in patients with mTICI grade 3 may help optimize patient management and improve clinical outcomes.
The inflammatory immune response plays a crucial role in the pathophysiology, treatment outcomes, and prognosis of ischemic stroke (10). Among leukocytes, neutrophils are the first immune cells to increase in circulation shortly after the onset of ischemic stroke (11). Neutrophils in the blood infiltrate ischemic or infarcted tissue through the compromised blood–brain barrier (BBB) and release inflammatory mediators, thereby increasing the risk of BBB disruption, reperfusion injury, hemorrhagic transformation, and malignant brain edema (12). High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) regulates macrophages and adipocytes via cholesterol transporters, exerting anti-inflammatory (13) and anti-atherosclerosis effects (14). As a potential inflammatory marker, the neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHR) has demonstrated certain prognostic value. This blood indicator is inexpensive and readily available. Huang et al. found that an elevated NHR is a potential predictor of long-term mortality and recurrence rates in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction (15). A previous study indicated that NHR may be associated with an increased risk of adverse short-term outcomes following intravenous thrombolysis in AIS patients (16). However, its correlation with futile recanalization at mTICI3 remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between NHR and adverse prognosis in LVO patients who achieved complete recanalization after MT.
Methods
This multicenter retrospective study consecutively enrolled patients with AIS who underwent MT at three stroke centers: the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, the First Hospital of Dalian Medical University, and the Central Hospital of Dalian University of Technology, between January 2016 and November 2023. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) age ≥18 years, (2) received MT within 24 h and achieved complete recanalization with mTICI grade 3, and (3) occlusion of the internal carotid artery or M1/M2 segments of the middle cerebral artery. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) pre-onset modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score >2; (2) severe infection, malignant tumor, or immune dysfunction; (3) severe cardiac, hepatic, renal, or other major organ diseases; (4) missing medical records or data; and (5) 90-day loss to follow-up. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University.
Data collection included patient demographics and clinical characteristics such as age, sex, medical history (including hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and atrial fibrillation), smoking status, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score, Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS), intravenous thrombolysis, stroke subtype according to the Trial of Org 10,172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) criteria, anesthesia type, retriever passes, time from onset to puncture (OTP), and time from onset to recanalization (OTR). Laboratory tests conducted within 24 h after MT measured neutrophil, lymphocyte, and platelet counts, as well as cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), HDL-C, and NHR. ASPECTS was evaluated using non-contrast computed tomography (NCCT). The site of vascular occlusion was confirmed using digital subtraction angiography (DSA). All neuroimaging data were independently reviewed by two experienced neurointerventionists who were blinded to the patients’ clinical information, and discrepancies were resolved by consensus. Recanalization was assessed using the mTICI score, with complete recanalization defined as an mTICI score of 3 (17). Each center followed up with postoperative patients via telephone or outpatient clinic visits to assess the 90-day mRS score. An mRS score of 0–2 was defined as a good outcome, while a score of 3–6 was considered a poor outcome.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were presented as means with standard deviations or medians with interquartile ranges (IQRs). The normality of the distribution was assessed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Categorical variables were reported as frequencies and percentages. Group differences in continuous variables were evaluated using the Wilcoxon test, whereas the chi-squared or Fisher’s exact test was used for categorical variables. The study population was stratified into tertiles based on the NHR range, and continuous variables were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) or the Kruskal-Wallis test. Confounding factors included in the multivariate logistic regression models were those that showed statistical significance in the univariate analysis. Model 1 remained unadjusted, Model 2 was adjusted for demographic factors, and Model 3 accounted for clinically relevant factors. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Version 27.0 software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) and R version 4.2.3 (R Core Team, Vienna, Austria). A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant (Figure 1).
Figure 1

Flowchart showing the number (n) of patients included in the analysis. LVO, large vessel occlusion; MT, mechanical thrombectomy; mTICI, modified Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction; NHR, neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio.
Results
A total of 917 patients with anterior circulation and LVO who underwent MT were included in this study, of whom 348 met the eligibility criteria. The median age was 70 years (IQR, 62–76), with 228 (65.5%) being male and 215 (61.8%) experiencing adverse clinical outcomes at 90 days. Patients were stratified into three NHR tertiles: first (<6.29), second (6.29–9.50), and third (>9.50). Higher NHR tertiles were associated with a higher proportion of male participants (p < 0.001), hyperlipidemia (p < 0.001), poor 90-day prognosis (p < 0.005), elevated platelet counts (p = 0.014), elevated neutrophil counts (p < 0.001), elevated TG levels (p < 0.001), and lower HDL-C levels (p < 0.001) (Table 1). Ordered logistic regression analysis demonstrated significant differences in mRS scores across NHR tertiles, with an adjusted OR of 0.4897 (95% CI: 0.3021–0.7945, p = 0.004) between the lowest and highest tertiles (Figure 2). To explore the association between NHR and prognosis, patients were divided into good and adverse prognosis groups for the univariate analysis. Patients with adverse prognoses tended to be older (p < 0.001), had a higher prevalence of diabetes mellitus (p = 0.014), had elevated baseline NIHSS scores (p < 0.001), had reduced ASPECTS scores (p < 0.001), had higher baseline systolic blood pressure (p = 0.026), and had a higher incidence of general anesthesia use (p = 0.012). Laboratory findings indicated that these patients also had higher neutrophil counts (p < 0.001), lower lymphocyte counts (p = 0.001), and elevated NHR levels (p = 0.004) (Table 2). Three models were developed for the multivariate logistic regression analysis. Model 1, which was unadjusted, revealed that the highest NHR group was significantly associated with an increased risk of adverse prognosis after thrombectomy (OR 2.371, 95% CI: 1.368–4.112, p = 0.002). Model 2, which was adjusted for demographic factors such as age, demonstrated that NHR remained a significant risk factor for adverse prognosis (OR 2.887, 95% CI: 1.618–5.151, p < 0.001). Model 3, further adjusted for clinically relevant confounders (diabetes, general anesthesia, baseline NIHSS, ASPECTS, baseline systolic blood pressure, and lymphocyte count) based on Model 2, confirmed the persistence of this association (OR 2.311, 95% CI: 1.248–4.278, p = 0.008). When analyzed as a continuous variable, NHR yielded consistent results (OR 1.445 per 1-SD increase, 95% CI: 1.095–1.908, p = 0.009) (Table 3). A restricted cubic spline curve analysis demonstrated a positive linear dose–response relationship between the NHR and adverse prognosis (A p-value of 0.348 for non-linearity) (Figure 3). A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted to evaluate the predictive performance of NHR. The results demonstrated that the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.592 (95% CI: 0.531–0.653; p = 0.004), with an optimal cutoff value of 9.486 (Figure 4). The logistic curve demonstrated that the probability of adverse prognosis gradually increased with elevated NHR levels (Figure 5). Subgroup analyses revealed that factors such as age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, smoking, intravenous thrombolysis, number of passes, baseline NIHSS, baseline ASPECTS, and stroke subtyping did not significantly influence the correlation between NHR and adverse prognosis (all p-values for interaction >0.05) (Figure 6).
Table 1
| Variable | Total (n = 348) |
NHR<6.29 (n = 115) |
6.29 ≤ NHR≤9.50 (n = 116) |
NHR>9.50 (n = 117) |
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (IQR) | 70.0 (62.0–76.0) | 71.0 (63.8–77.3) | 68.0 (60.0–75.0) | 70.0 (61.0–76.0) | 0.053 |
| Sex, n (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Male | 228 (65.5) | 60 (52.2) | 79 (68.1) | 89 (76.1) | |
| Female | 120 (34.5) | 55 (45.8) | 37 (30.8) | 28 (23.3) | |
| HTN, n (%) | 199 (57.2) | 74 (66.1) | 56 (46.6) | 69 (59.0) | 0.010 |
| DM, n (%) | 94 (27.0) | 31 (27.0) | 28 (24.1) | 35 (29.9) | 0.611 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 155 (44.5) | 30 (26.1) | 47 (40.5) | 78 (66.7) | <0.001 |
| AF, n (%) | 154 (44.3) | 59 (51.3) | 50 (43.1) | 45 (38.5) | 0.137 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 117 (33.6) | 36 (31.3) | 31 (26.7) | 50 (42.7) | 0.029 |
| Intravenous thrombolysis, n (%) | 155 (44.5) | 55 (47.8) | 58 (50.0) | 42 (35.9) | 0.066 |
| NIHSS, median (IQR) | 16 (13–20) | 16 (13–20) | 16 (12–20) | 18 (14–22) | 0.015 |
| ASPECTS, median (IQR) | 8 (7–10) | 9 (7–10) | 9 (8–10) | 8 (6–9) | 0.004 |
| Baseline SBP, median (IQR) | 146 (130–165) | 144 (130–165) | 143 (123–160) | 151 (133–169) | 0.034 |
| Baseline DBP, median (IQR) | 81 (73–90) | 82 (72–89) | 80 (70–90) | 85 (75–96) | 0.059 |
| OTP, median (IQR) | 245.0 (185.3–340.0) | 235.0 (170.8–317.5) | 270.0 (205.0–350.0) | 246.0 (195.0–344.0) | 0.031 |
| OTR, median (IQR) | 325.0 (254.5–420.0) | 291.0 (231.5–400.1) | 345.0 (265.0–438.0) | 330.0 (267.0–440.0) | 0.011 |
| Occlusion site, n (%) | 0.883 | ||||
| ICA | 122 (35.1) | 39 (33.9) | 41 (35.3) | 42 (35.9) | |
| MCA-M1 | 161 (46.3) | 56 (48.7) | 54 (46.6) | 51 (43.6) | |
| MCA-M2 | 31 (10.1) | 13 (11.3) | 11 (9.5) | 11 (9.4) | |
| Tandem | 30 (8.6) | 7 (6.1) | 10 (8.6) | 13 (11.1) | |
| TOAST, n (%) | 0.888 | ||||
| LAA | 165 (44.8) | 51 (44.3) | 45 (38.8) | 60 (51.3) | |
| Cardioembolic | 183 (52.6) | 61 (53.0) | 69 (59.5) | 53 (45.3) | |
| Others | 9 (2.6) | 3 (2.6) | 2 (3.7) | 4 (1.4) | |
| Neutrophils, 109/L, median (IQR) | 8.47 (6.58–10.34) | 6.15 (5.05–7.31) | 8.54 (7.10–9.75) | 11.02 (9.17–13.53) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocytes, 109/L, median (IQR) | 1.14 (0.80–1.54) | 1.07 (0.76–1.51) | 1.20 (0.90–1.60) | 1.11 (0.80–1.51) | 0.179 |
| Platelets, 109/L, median (IQR) | 186 (150–224) | 176 (140–214) | 188 (160–228) | 191 (161–232) | 0.014 |
| TC, mmol/L, median (IQR) | 4.30 (3.66–5.05) | 4.23 (3.72–5.16) | 4.41 (3.82–5.23) | 4.16 (3.51–4.81) | 0.067 |
| TG, mmol/L, median (IQR) | 1.13 (0.81–1.51) | 0.94 (0.69–1.25) | 1.16 (0.92–1.53) | 1.24 (0.91–1.65) | <0.001 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L, median (IQR) | 1.08 (0.90–1.27) | 1.27 (1.10–1.49) | 1.08 (0.90–1.25) | 0.93 (0.77–1.06) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L, median (IQR) | 2.60 (2.05–3.28) | 2.40 (1.95–3.22) | 2.79 (2.12–3.45) | 2.52 (2.03–3.22) | 0.065 |
| General anesthesia, n (%) | 62 (17.8) | 17 (14.8) | 14 (12.1) | 31 (26.5) | 0.009 |
| Passes of retriever ≥3, n (%) | 83 (23.9) | 25 (21.7) | 33 (28.4) | 25 (21.4) | 0.362 |
| 90-day mRS 3–6, n (%) | 215 (61.8) | 62 (53.9) | 67 (57.8) | 86 (73.5) | 0.005 |
Demographic and clinical characteristics based on NHR tertiles.
HTN, hypertension; DM, diabetes mellitus; AF, atrial fibrillation; NIHSS, National Institute of Health Stroke Scale; ICA, internal carotid artery; MCA, middle cerebral artery.
TOAST, Trial of Org 10,172 in Acute Stroke Treatment classification; LAA, large artery atherosclerosis; OTP, time from onset to puncture; OTR, time from onset to recanalization.
IQR, interquartile range.
Figure 2

Distribution of modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores at 90 days stratified by NHR tertiles.
Table 2
| Variable | Total (n = 348) |
Poor outcome (mRS3-6) (n = 215) |
Good outcome (mRS0-2) (n = 133) |
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (IQR) | 70.0 (62.0–76.0) | 72.0 (64.0–78.0) | 66.0 (58.5–72.5) | <0.001 |
| Gender, n (%) | 0.507 | |||
| Male | 228 (65.5) | 138 (64.2) | 90 (67.7) | |
| Female | 120 (34.5) | 77 (35.8) | 43 (32.3) | |
| HTN, n (%) | 199 (57.2) | 129 (60.0) | 70 (52.9) | 0.177 |
| DM, n (%) | 94 (27.0) | 68 (31.6) | 26 (19.5) | 0.014 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 155 (44.5) | 102 (47.4) | 53 (39.8) | 0.166 |
| AF, n (%) | 154 (44.3) | 102 (47.4) | 52 (39.1) | 0.128 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 117 (33.6) | 66 (30.7) | 51 (38.3) | 0.142 |
| Intravenous thrombolysis, n (%) | 155 (44.5) | 94 (43.7) | 61 (45.9) | 0.696 |
| NIHSS, median (IQR) | 16 (13–20) | 18 (14–22) | 16 (12–18) | <0.001 |
| ASPECTS, median (IQR) | 8 (7–10) | 8 (6–9) | 9 (7–10) | <0.001 |
| Baseline SBP, median (IQR) | 146 (130–165) | 150 (132–166) | 141 (125–160) | 0.026 |
| Baseline DBP, median (IQR) | 81 (73–90) | 82 (75–90) | 80 (70–92) | 0.398 |
| OTP, median (IQR) | 245.0 (185.3–340.0) | 247.0 (195.0–340.0) | 240.0 (172.5–341.5) | 0.447 |
| OTR, median (IQR) | 325.0 (254.5–420) | 330.0 (260.0–428.0) | 305.0 (239.0–413.0) | 0.158 |
| Occlusion site, n (%) | 0.740 | |||
| ICA | 122 (35.1) | 81 (37.7) | 41 (30.8) | |
| MCA-M1 | 161 (46.3) | 88 (40.9) | 73 (54.9) | |
| MCA-M2 | 31 (10.1) | 24 (11.2) | 11 (8.3) | |
| Tandem | 30 (8.6) | 22 (10.2) | 8 (6.0) | |
| TOAST, n (%) | 0.436 | |||
| LAA | 165 (44.8) | 94 (43.7) | 62 (46.6) | |
| Cardioembolic | 183 (52.6) | 117 (54.4) | 66 (49.6) | |
| Others | 9 (2.6) | 4 (1.9) | 5 (3.8) | |
| Neutrophils, 109/L, median (IQR) | 8.47 (6.58–10.34) | 8.82 (7.08–11.18) | 7.58 (5.95–9.50) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocytes,109/L, median (IQR) | 1.14 (0.80–1.54) | 1.07 (0.73–1.45) | 1.28 (0.96–1.69) | 0.001 |
| Platelets, 109/L, median (IQR) | 186 (150–223) | 183 (148–217) | 195 (155–235) | 0.054 |
| TC, mmol/L, median (IQR) | 4.30 (3.66–5.05) | 4.32 (3.66–5.07) | 4.30 (3.64–5.06) | 0.780 |
| TG, mmol/L, median (IQR) | 1.13 (0.81–1.51) | 1.08 (0.78–1.50) | 1.15 (0.86–1.58) | 0.751 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L, median (IQR) | 1.08 (0.90–1.27) | 1.10 (0.92–1.29) | 1.06 (0.89–1.26) | 0.221 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L, median (IQR) | 2.60 (2.05–3.28) | 2.59 (2.01–3.25) | 2.63 (2.08–3.32) | 0.348 |
| NHR, median (IQR) | 7.74 (5.70–10.53) | 7.92 (6.09–11.33) | 7.23 (5.10–9.43) | 0.004 |
| General anesthesia, n (%) | 62 (17.8) | 47 (21.9) | 15 (11.3) | 0.012 |
| Passes of retriever ≥3, n (%) | 83 (23.9) | 50 (23.3) | 33 (24.8) | 0.741 |
Comparison of demographics and clinical characteristics between poor and good outcome groups.
HTN, hypertension; DM, diabetes mellitus; AF, atrial fibrillation; NIHSS, National Institute of Health Stroke Scale; ICA, internal carotid artery; MCA, middle cerebral artery.
TOAST, the Trial of Org 10,172 in Acute Stroke Treatment classification; LAA, large artery atherosclerosis; OTP, time from onset to puncture; OTR, time from onset to recanalization.
NHR, neutrophil-high-density lipoprotein ratio; IQR, interquartile range.
Table 3
| NHR | Model 1 OR (95% CI) |
p value | Model 2 OR (95% CI) |
p value | Model 3 OR (95% CI) |
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NHR as a continuous variable | ||||||
| Per 1-SD increase | 1.46 (1.151–1.853) | 0.002 | 1.620 (1.259–2.084) | <0.001 | 1.445 (1.095–1.908) | 0.009 |
| NHR tertile | ||||||
| Tertile1 (<6.29) | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||
| Tertile2 (6.29–9.50) | 1.169 (0.695–1.966) | 0.556 | 1.436 (0.833–2.476) | 0.193 | 1.618 (0.913–2.865) | 0.099 |
| Tertile3 (>9.50) | 2.371 (1.368–4.112) | 0.002 | 2.887 (1.618–5.151) | <0.001 | 2.311 (1.248–4.278) | 0.008 |
Multivariable logistic regression models for poor outcome after MT.
Figure 3

The positive linear relationship between NHR and adverse prognosis 90 days after RCS analysis.
Figure 4

ROC curve analysis of NHR in predicting poor prognosis at 90 days.
Figure 5
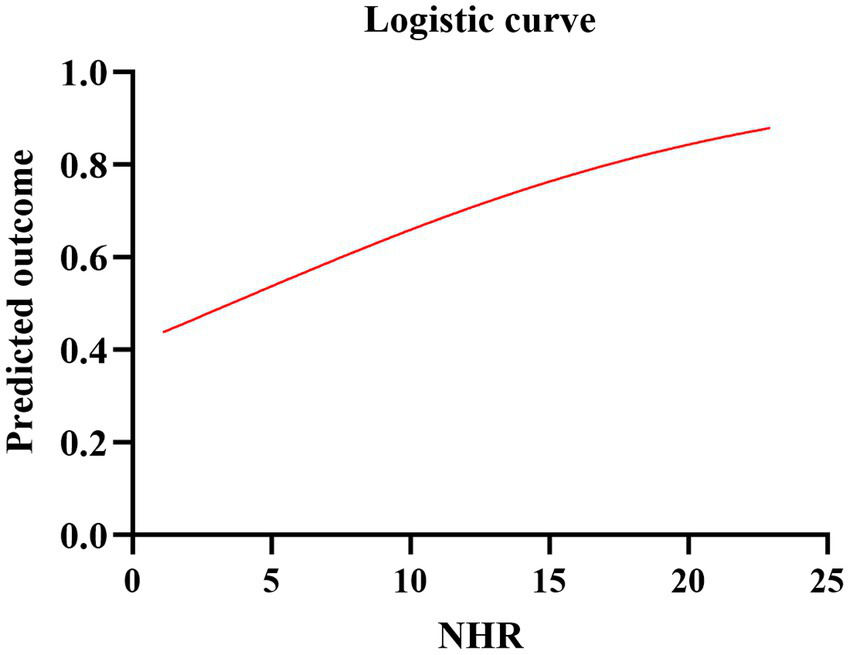
Logistic curve of the predicted probability of poor prognosis and NHR.
Figure 6

Stratified analysis of the relationship between the NHR and adverse prognosis at 90 days. The model was adjusted for age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, smoking, intravenous thrombolysis, number of passes, baseline NIHSS score, baseline ASPECTS, and stroke subtype. In each subgroup analysis, separate stratified variables were not included.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first study to evaluate the correlation between NHR and futile recanalization after MT in acute LVO stroke patients. It was found that elevated NHR levels within 24 h post-surgery were significantly associated with adverse prognosis in patients achieving complete recanalization.
Neuroinflammation is associated with BBB disruption, neuronal damage, and worse clinical outcomes following ischemic stroke (18). After the initial cerebral ischemic injury, the inflammatory response exacerbates the damage. Neutrophils are identified as pivotal drivers of ischemic brain injury development (19, 20). Research indicates that neutrophils are the first peripheral blood cells to cross the BBB following ischemic stroke, with their numbers increasing rapidly within hours of stroke onset (21). By releasing reactive oxygen species, proteases (e.g., metalloproteinases, elastase, and cathepsin G), cytokines (e.g., IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α), and chemokines (e.g., CCL2, CCL3, and CCL5), the BBB is compromised, thereby aggravating ischemic damage and cerebral edema (22). Moreover, neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) formed due to excessive neutrophil activation can trap other blood cells, resulting in pathological thrombosis and amplifying neuroinflammatory responses (23). Angiogenesis and vascular remodeling are essential for post-stroke brain repair (24). Kang et al. found that peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 (PAD4), an enzyme required for NETs formation, is upregulated in peri-ischemic brain tissue. Overexpression of PAD4 exacerbates vascular damage and impedes angiogenesis and vascular repair by releasing additional NETs (25). Several clinical studies have confirmed the potentially detrimental effects of neutrophils on ischemic brain tissue. Cui et al. reported that an increase in neutrophil counts on the second day after the onset of large hemispheric infarction (LHI) was associated with brain herniation and early death (26). Meanwhile, Semerano et al. demonstrated that higher neutrophil counts at admission and on the first day following thrombectomy were significantly associated with poor functional outcomes and increased mortality at 90 days (27).
HDL-C exerts anti-atherosclerotic and anti-inflammatory effects, thereby reducing BBB disruption in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) (28). Atherosclerosis is a common cause of ischemic stroke and is characterized by the accumulation of macrophages and T lymphocytes in the arterial intima (29, 30). Macrophages take up oxidized low-density lipoprotein and transform it into foam cells. In contrast, HDL-C can promote cholesterol efflux from foam cells and exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties (31). In addition to its role in reverse cholesterol transport, HDL-C interacts with platelets, the coagulation cascade, and the vascular endothelium. Native HDL-C prevents platelet hyperreactivity by restricting cholesterol overload within platelets and modulating platelet signaling pathways after binding to platelet HDL receptors such as scavenger receptor B and apolipoprotein E receptor 2. Its anti-thrombotic properties are also associated with the inhibition of coagulation cascade reactions and the promotion of clot fibrinolysis. Moreover, HDL-C stimulates endothelial cells to produce nitric oxide and prostacyclin, which are potent inhibitors of platelet activation (32). In a cohort study of Chinese community-based hypertensive patients, higher HDL-C levels were identified as an important protective factor against first-time ischemic stroke (33). Li et al. found that reduced HDL-C levels were independently associated with an increased adverse prognosis at 3 months after AIS and cerebral hemorrhage (34).
Furthermore, HDL-C and neutrophil levels demonstrated reciprocal functional inhibition. Animal experiments conducted by Scanu et al. showed that HDL-C can reduce neutrophil infiltration by inhibiting cytokine synthesis, including IL-6 and IL-1β, thereby alleviating inflammatory responses (35). Apolipoprotein A-I, the primary component of HDL-C (36), decreases neutrophil production by reducing granulocyte colony-stimulating factor levels and restricts neutrophil chemotaxis to localized inflammatory sites by inhibiting IL-8 synthesis in activated neutrophils (37, 38). Previous studies have indicated that activated neutrophils can mediate the oxidation of HDL through oxidant-generating enzymes, such as myeloperoxidase, NADPH oxidase, and nitric oxide synthase. This process impairs the cholesterol efflux capacity and promotes atherosclerosis and inflammatory responses (39, 40). In addition, Carlucci et al. found that low-density granulocytes, a distinct neutrophil subset present in systemic lupus erythematosus, interact with modified HDL to promote foam cell formation and contribute to the progression of inflammatory high-risk plaques (41). Thus, elevated NHR levels may be associated with increased neutrophil count or decreased HDL-C levels. Inflammation and dyslipidemia are key factors influencing the pathophysiology of ischemic stroke (42). As a comprehensive indicator, NHR could better reflect patients’ inflammatory status and lipid metabolism throughout the entire pathological process of stroke.
Our study has several limitations. First, as a retrospective study, the exclusion of participants with missing data may have resulted in the loss of valuable information and introduced some bias into the results. Second, although this was a multicenter study, the sample size was relatively small and did not account for the potential effects of diet, medication, and health status on lipid levels. Therefore, future prospective studies with larger sample sizes and more centers are required to validate our findings. Third, the relationship between NHR and early functional deterioration or related complications (such as symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage, malignant brain edema, post-stroke pneumonia, and urinary tract infection) was not explored. Finally, this study only included NHR within 24 h after MT, and the relatively low AUC of NHR indicated its limited predictive performance. Future studies should explore dynamic changes in NHR and compare its predictive performance with other inflammatory markers to comprehensively evaluate the prognostic value of NHR as an inflammatory predictor.
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that an elevated NHR is associated with an increased risk of adverse prognosis following complete recanalization after MT in acute LVO stroke patients. NHR could, therefore, serve as a potential inflammatory marker for identifying high-risk patients. Early intervention targeting the inflammatory state may help improve clinical outcomes following thrombectomy.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University Clinical Research Ethics Committee. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
SC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. FW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. KL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LY: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2025.1536535/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Goyal M Menon BK van Zwam WH Dippel DW Mitchell PJ Demchuk AM et al . Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet. (2016) 387:1723–31. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00163-X
2.
Badhiwala JH Nassiri F Alhazzani W Selim MH Farrokhyar F Spears J et al . Endovascular Thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: a Meta-analysis. JAMA. (2015) 314:1832–43. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.13767
3.
Nogueira RG Jadhav AP Haussen DC Bonafe A Budzik RF Bhuva P et al . Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:11–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1706442
4.
Lapergue B Blanc R Gory B Labreuche J Duhamel A Marnat G et al . Effect of endovascular contact aspiration vs stent retriever on revascularization in patients with acute ischemic stroke and large vessel occlusion: the ASTER randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2017) 318:443–52. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.9644
5.
Zhou T Yi T Li T Zhu L Li Y Li Z et al . Predictors of futile recanalization in patients undergoing endovascular treatment in the DIRECT-MT trial. J Neurointerv Surg. (2022) 14:752–5. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2021-017765
6.
Lattanzi S Norata D Divani AA Di Napoli M Broggi S Rocchi C et al . Systemic inflammatory response index and futile recanalization in patients with ischemic stroke undergoing endovascular treatment. Brain Sci. (2021) 11:1164. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11091164
7.
Deng G Xiao J Yu H Chen M Shang K Qin C et al . Predictors of futile recanalization after endovascular treatment in acute ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg. (2022) 14:881–5. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2021-017963
8.
Kaesmacher J Dobrocky T Heldner MR Bellwald S Mosimann PJ Mordasini P et al . Systematic review and meta-analysis on outcome differences among patients with TICI2b versus TICI3 reperfusions: success revisited. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2018) 89:910–7. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2017-317602
9.
van Horn N Kniep H Leischner H McDonough R Deb-Chatterji M Broocks G et al . Predictors of poor clinical outcome despite complete reperfusion in acute ischemic stroke patients. J Neurointerv Surg. (2021) 13:14–8. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-015889
10.
Feng Y Bai X Li W Cao W Xu X Yu F et al . Postoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts unfavorable outcome of acute ischemic stroke patients who achieve complete reperfusion after thrombectomy. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:963111. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.963111
11.
Castellanos M Leira R Serena J Pumar JM Lizasoain I Castillo J et al . Plasma metalloproteinase-9 concentration predicts hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. (2003) 34:40–6. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000046764.57344.31
12.
Batra A Latour LL Ruetzler CA Hallenbeck JM Spatz M Warach S et al . Increased plasma and tissue MMP levels are associated with BCSFB and BBB disruption evident on post-contrast FLAIR after experimental stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2010) 30:1188–99. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.1
13.
De Nardo D Labzin LI Kono H Seki R Schmidt SV Beyer M et al . High-density lipoprotein mediates anti-inflammatory reprogramming of macrophages via the transcriptional regulator ATF3. Nat Immunol. (2014) 15:152–60. doi: 10.1038/ni.2784
14.
Sacks FM Jensen MK . From high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to measurements of function: prospects for the development of tests for high-density lipoprotein functionality in cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2018) 38:487–99. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.307025
15.
Huang JB Chen YS Ji HY Xie WM Jiang J Ran LS et al . Neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein ratio has a superior prognostic value in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction: a comparison study. Lipids Health Dis. (2020) 19:59. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01238-2
16.
Chen G Yang N Ren J He Y Huang H Hu X et al . Neutrophil counts to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio: a potential predictor of prognosis in acute ischemic stroke patients after intravenous thrombolysis. Neurotox Res. (2020) 38:1001–9. doi: 10.1007/s12640-020-00274-1
17.
Zaidat OO Yoo AJ Khatri P Tomsick TA von Kummer R Saver JL et al . Recommendations on angiographic revascularization grading standards for acute ischemic stroke: a consensus statement. Stroke. (2013) 44:2650–63. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.001972
18.
Candelario-Jalil E Dijkhuizen RM Magnus T . Neuroinflammation, stroke, blood-brain barrier dysfunction, and imaging modalities. Stroke. (2022) 53:1473–86. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.122.036946
19.
Gelderblom M Leypoldt F Steinbach K Behrens D Choe CU Siler DA et al . Temporal and spatial dynamics of cerebral immune cell accumulation in stroke. Stroke. (2009) 40:1849–57. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.534503
20.
Wu L Walas S Leung W Sykes DB Wu J Lo EH et al . Neuregulin1-β decreases IL-1β-induced neutrophil adhesion to human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Transl Stroke Res. (2015) 6:116–24. doi: 10.1007/s12975-014-0347-9
21.
Ao LY Yan YY Zhou L Li CY Li WT Fang WR et al . Immune cells after ischemic stroke onset: roles, migration, and target intervention. J Mol Neurosci. (2018) 66:342–55. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1173-4
22.
Jickling GC Liu D Ander BP Stamova B Zhan X Sharp FR . Targeting neutrophils in ischemic stroke: translational insights from experimental studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2015) 35:888–901. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.45
23.
Sorvillo N Cherpokova D Martinod K Wagner DD . Extracellular DNA NET-works with dire consequences for health. Circ Res. (2019) 125:470–88. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.314581
24.
Kang L Yu H Yang X Zhu Y Bai X Wang R et al . Neutrophil extracellular traps released by neutrophils impair revascularization and vascular remodeling after stroke. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:2488. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16191-y
25.
Denorme F Portier I Rustad JL Cody MJ de Araujo CV Hoki C et al . Neutrophil extracellular traps regulate ischemic stroke brain injury. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132:e154225. doi: 10.1172/JCI154225
26.
Cui LL Zhang Y Chen ZY Su YY Liu Y Boltze J . Early neutrophil count relates to infarct size and fatal outcome after large hemispheric infarction. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2020) 26:829–36. doi: 10.1111/cns.13381
27.
Semerano A Laredo C Zhao Y Rudilosso S Renú A Llull L et al . Leukocytes, collateral circulation, and reperfusion in ischemic stroke patients treated with mechanical Thrombectomy. Stroke. (2019) 50:3456–64. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026743
28.
Wang Y Cheng Y Song Q Wei C Liu J Wu B et al . The association between monocyte to high-density lipoprotein ratio and hemorrhagic transformation in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Aging. (2020) 12:2498–506. doi: 10.18632/aging.102757
29.
Xu Q Wu Q Chen L Li H Tian X Xia X et al . Monocyte to high-density lipoprotein ratio predicts clinical outcomes after acute ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2023) 29:1953–64. doi: 10.1111/cns.14152
30.
Osterud B Bjorklid E . Role of monocytes in atherogenesis. Physiol Rev. (2003) 83:1069–112. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00005.2003
31.
Barter PJ Nicholls S Rye KA Anantharamaiah GM Navab M Fogelman AM . Antiinflammatory properties of HDL. Circ Res. (2004) 95:764–72. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000146094.59640.13
32.
van der Stoep M Korporaal SJ Van Eck M . High-density lipoprotein as a modulator of platelet and coagulation responses. Cardiovasc Res. (2014) 103:362–71. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu137
33.
Zhang Y Li J Liu C Yu H Chen C Bi C et al . High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and the risk of first ischemic stroke in a Chinese hypertensive population. Clin Interv Aging. (2021) 16:801–10. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S295252
34.
Li W Liu M Wu B Liu H Wang LC Tan S . Serum lipid levels and 3-month prognosis in Chinese patients with acute stroke. Adv Ther. (2008) 25:329–41. doi: 10.1007/s12325-008-0045-7
35.
Scanu A Luisetto R Oliviero F Gruaz L Sfriso P Burger D et al . High-density lipoproteins inhibit urate crystal-induced inflammation in mice. Ann Rheum Dis. (2015) 74:587–94. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203803
36.
Nazir S Jankowski V Bender G Zewinger S Rye KA van der Vorst EPC . Interaction between high-density lipoproteins and inflammation: function matters more than concentration!Adv Drug Deliv Rev. (2020) 159:94–119. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.10.006
37.
Dai C Yao X Keeran KJ Zywicke GJ Qu X Yu ZX et al . Apolipoprotein A-I attenuates ovalbumin-induced neutrophilic airway inflammation via a granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-dependent mechanism. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2012) 47:186–95. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0322OC
38.
Smythies LE White CR Maheshwari A Palgunachari MN Anantharamaiah GM Chaddha M et al . Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic 4F alters the function of human monocyte-derived macrophages. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2010) 298:C1538–48. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00467.2009
39.
Smith CK Vivekanandan-Giri A Tang C Knight JS Mathew A Padilla RL et al . Neutrophil extracellular trap-derived enzymes oxidize high-density lipoprotein: an additional proatherogenic mechanism in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2014) 66:2532–44. doi: 10.1002/art.38703
40.
Smith CK Seto NL Vivekanandan-Giri A Yuan W Playford MP Manna Z et al . Lupus high-density lipoprotein induces proinflammatory responses in macrophages by binding lectin-like oxidised low-density lipoprotein receptor 1 and failing to promote activating transcription factor 3 activity. Ann Rheum Dis. (2017) 76:602–11. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209683
41.
Carlucci PM Purmalek MM Dey AK Temesgen-Oyelakin Y Sakhardande S Joshi AA et al . Neutrophil subsets and their gene signature associate with vascular inflammation and coronary atherosclerosis in lupus. JCI Insight. (2018) 3:e99276. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.99276
42.
Libby P . Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. (2002) 420:868–74. doi: 10.1038/nature01323
Summary
Keywords
neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio, adverse prognosis, complete recanalization, mechanical thrombectomy, large vessel occlusion
Citation
Ci S, Li D, Wang F, Li K and Yin L (2025) Correlation between neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHR) and adverse prognosis in patients who achieve complete recanalization after thrombectomy for acute large vessel occlusion stroke. Front. Neurol. 16:1536535. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1536535
Received
29 November 2024
Accepted
12 May 2025
Published
04 June 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Pradeep Kumar, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, India
Reviewed by
Dongwei Sun, University of California, Riverside, United States
Koji Tanaka, Fujita Health University, Japan
Jayanta Gupta, Florida Gulf Coast University, United States
Kerollos Abdelsayed, Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation (MHIF), United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Ci, Li, Wang, Li and Yin.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lin Yin, lyin_neuro@126.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.