Abstract
Pharmacotherapy variability is defined as the variability in drug response among and within individuals that is attributed to the inter and intra-individual differences in the action and disposition of drugs. Neurological and medical complications in neurocritical care contribute significantly to the overall disease prognosis. Pharmacological management plays a key role in managing many of those complications such as cerebral vasospasm, delayed cerebral ischemia, hyponatremia, infections, and seizures. However, pathophysiologic changes secondary to neurological and critical illnesses make the medical management of these patients challenging, contributing to pharmacotherapy variability. Interindividual differences in disease pathophysiology, altered organ function, systemic inflammation, hemodynamic instability, and common interventions employed in intensive care settings could alter the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of medications. The use of potentially ineffective treatments and suboptimal dosing of medications to manage patients can lead to poor outcomes as the understanding of the effect of neurological injury on the action and disposition of drugs is limited. This narrative review highlights the factors contributing to pharmacotherapy variability in neurocritical care, equipping clinicians with critical insights to refine patient management strategies. In conclusion, pharmacotherapy variability within neurocritical care introduces additional layers of complexity that may significantly contribute to therapy failure, adverse drug reactions, and setbacks in drug development. Understanding these variations is essential for identifying subpopulations that may derive the greatest benefit from specific therapies, representing a critical step toward achieving precision medicine in neurocritical care, ensuring the administration of the appropriate medication to the right patient at the correct dosage regimen.
1 Introduction
Pharmacotherapy is essential in managing complications within neurocritical care, where timely and targeted interventions are crucial for patient survival and recovery. Neurocritical care includes a range of acute neurological conditions, including subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), traumatic brain injury (TBI), ischemic stroke (IS), and status epilepticus (SE). These conditions often present with secondary complications such as cerebral edema, seizures, vasospasm, delayed cerebral ischemia (DCI), electrolyte abnormalities, venous thromboembolism, infections, hemodynamic instability, and altered organ functions. The pharmacological management of these complications is vital for improving patient outcomes. However, pathophysiologic changes secondary to neurological and critical illnesses make the medical management of these patients challenging, contributing to pharmacotherapy variability. Interindividual differences in disease pathophysiology, altered organ function, systemic inflammation, hemodynamic instability, and common interventions employed in intensive care settings could alter the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of medications, potentially resulting in lack of efficacy or increased toxicity. The use of potentially ineffective or toxic treatments and suboptimal dosing of medications to manage patients may increase poor outcomes as the understanding of the influence of neurological injury on the action and disposition of drugs is limited. Therefore, it is essential to investigate factors affecting pharmacotherapy variability.
The aim of this review is to highlight the factors contributing to pharmacotherapy variability in neurocritical care, equipping clinicians with critical insights to refine patient management strategies. We summarized our research and other studies investigating the variability in pharmacotherapy and its link to patient outcomes. Understanding these variations is essential for identifying subpopulations that may derive the greatest benefit from specific therapies, representing a critical step toward achieving precision medicine in neurocritical care.
2 Pharmacotherapy variability
2.1 Definition and significance
Pharmacotherapy variability is defined as the variability in drug response among and within individuals that is attributed to the inter and intra-individual differences in the action and disposition of drugs. Variability arises from differences in drug PK (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion) and pharmacodynamics (drug action) among patients. In neurocritical care, where patients often present with altered physiology due to severe neurological injury, systemic inflammation, altered organ function, or concurrent therapies, these differences become even more pronounced. Tables 1, 2 summarize the PK and PD alterations in neurocritical care, respectively.
Table 1
| Pharmacokinetic alterations | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption | ||
| Reduced gut motility (Gastroparesis) | Neurological injury, sedation, and opioid use can delay the GIT transit time, resulting in reduced and/or delayed drug absorption. |
|
| Impaired perfusion | Hypotension and vasopressor use (e.g., catecholamines) can alter blood flow to the GIT, affecting drug absorption. | |
| Enteral feeding | Continuous enteral feeding can interact with drug formulations, altering their absorption. | |
| Vomiting and diarrhea | Vomiting and diarrhea are common in the ICU, potentially reducing drug bioavailability. | |
| pH changes | Frequent administration of PPIs or other acid-suppressing agents elevates gastric pH, which can consequently influence the ionization state and subsequent gastrointestinal absorption. | |
| Distribution | ||
| Hypoalbuminemia | Critical illness often leads to decreased serum albumin levels, resulting in a higher free drug fraction, potentially increasing the pharmacological effect and the risk of toxicity, but also clearance. |
|
| Altered BBB permeability | Neurological injury can disrupt the BBB, affecting the penetration of drugs into the CNS. | |
| Increased extracellular fluid volume | Cerebral edema and systemic fluid overload can increase the Vd of hydrophilic drugs, potentially leading to lower plasma concentrations. | |
| Metabolism | ||
| Hepatic dysfunction | Critical illness can lead to hepatic hypoperfusion and dysfunction, impairing the activity of CYP450 enzymes responsible for metabolizing many drugs. |
|
| Systemic inflammation | Systemic inflammation can inhibit CYP enzyme activity. | |
| Drug interactions | Polypharmacy in neurocritical care increases the risk of drug–drug interactions. | |
| Genetic polymorphism | Individual genetic variations in CYP enzymes can lead to significant variability in drug metabolism rates. | |
| Excretion | ||
| Acute kidney injury | AKI is a common complication in neurocritical care, reducing glomerular filtration rate and impairing the elimination of renally cleared drugs and their active metabolites. |
|
| Augmented renal clearance | ARC has been frequently seen in neurocritical care population, resulting in subtherapeutic levels of renally eliminated drugs. | |
| Changes in renal blood flow | Hypotension and vasopressor use (e.g., catecholamines) can alter renal perfusion, affecting drug excretion. | |
| Renal replacement therapy | Patients with severe AKI may require RRT, which can significantly remove certain drugs from the circulation. | |
| Therapeutic hypothermia | Therapeutic hypothermia induces a systemic reduction in both metabolic and excretory processes, consequently diminishing the functional capacity of CYP450 enzymes and drug transporters. | |
Pharmacokinetic alterations in neurocritical care.
AKI, acute kidney injury; ARC, augmented renal clearance; ASMs, antiseizure medications; BBB, blood brain barrier; CNS, central nervous system; CYP450: cytochrome p450; GIT, gastrointestinal tract; ICU, intensive care unit; PD, pharmacodynamics; PK, pharmacokinetics; PPI, proton pump inhibitors; RRT, renal replacement therapy; UGT, Uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase; Vd, volume of distribution.
Table 2
| Pharmacodynamic alterations | Description | Examples | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altered drug sensitivity/toxicity | Patients with brain injuries or other neurological illnesses often exhibit altered pharmacodynamics. The involvement of the CNS can lead to significant pharmacotherapy variability due to several factors:
|
|
||
Pharmacodynamic alterations in neurocritical care.
ASMs, antiseizure medications; BBB, blood brain barrier; CNS, central nervous system; GABA, Gamma-aminobutyric acid; SAH, subarachnoid hemorrhage.
This pharmacotherapy variability directly influences patient outcomes by affecting the balance between therapeutic efficacy and the risk of adverse events. For example, subtherapeutic levels of antiseizure medications (ASM) in SE could result in uncontrolled seizures, worsening neurological outcomes (1, 2). Another example is the increased risk for hyponatremia in SAH patients receiving exogenous vasopressin infusion due to increased sensitivity in this patient population (3).
Pharmacotherapy variability contributes to the heterogeneity of treatment effect observed in clinical trials within neurocritical care (4, 5). Variability in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion driven by patient-specific factors such as organ dysfunction, genetic polymorphisms, disease severity, and concurrent therapies can lead to wide inter-individual differences in drug exposure and response. This variability can mask true drug effects or falsely attribute outcomes to the intervention, leading to inconclusive or misleading trial results. To illustrate, in studies investigating the effect of hypothermia combined with standard of care versus standard of care alone, hypothermia alone can reduce the clearance of many standard of care drugs, potentially leading to toxicity if doses are not adjusted accordingly. In other words, the standard of care ceases to be truly standard if variability in pharmacotherapy is not taken into account. Recognizing and accounting for pharmacotherapy variability is therefore essential for accurately interpreting trial findings, optimizing therapy, and advancing precision medicine in neurocritical care.
The economic implications of pharmacotherapy variability within neurocritical care settings have not been extensively studied. Nevertheless, the overall economic burden in these settings can be inferred by considering the implications of pharmacotherapy variability. Notable factors include adverse drug reactions, toxicity, and treatment failures, all of which contribute to treatment escalation and extended hospital stays. These outcomes significantly increase healthcare costs (6–8). Therefore, addressing pharmacotherapy variability and precision medicine could potentially reduce the economic impact and improve patient outcomes (9).
In summary, pharmacotherapy variability in neurocritical care is a critical factor that can significantly impact patient outcomes. Current clinical guidelines have not fully taken into consideration drug variability in neurocritical care. Therefore, understanding and addressing this variability is essential to optimize drug efficacy and minimize adverse effects.
2.2 Factors contributing to pharmacotherapy variability
There are several factors that contribute to pharmacotherapy variability. Figure 1 illustrates the Neuro-CPK Pharmaco-variability Wheel. It outlines the main factors affecting pharmacotherapy variability in neurocritical care, including comorbid conditions, drug interactions, practice variations, patient characteristics, pharmacogenomics, and co-interventions. Comorbid conditions could lead to physiological changes that affects how the body handle drugs (10). Moreover, drug interactions play a significant role in pharmacotherapy variability as neurocritical care patients usually receive multiple drugs (11, 12). Furthermore, variations in practice within the same health care facility or between different facilities could result in significant discrepancies in pharmacotherapy (13). Patient’s specific characteristics such as age, sex and body weight are major well-known factors contributing to variability (14). Additionally, monogenic and polygenic variability substantially contribute to the diverse PK and PD effects observed across individuals receiving the same medications (15). And finally, neurocritical care patients receive different co-interventions which create a highly variable environment for pharmacotherapy that may be overlooked in practice. In the following sections we discuss each factor in detail, providing examples and discussing the implications of these factors on pharmacotherapy variability. It is crucial to consider all potential factors that influence drug PK and PD, as the observed drug response in patients is essentially the result of the interplay among all these factor.
Figure 1

Hanafy’s Neuro-CPK Pharmaco-variability Wheel illustrates the factors influencing the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of drugs in neurocritical care. Pharmacogenomics contribute to inter-individual variability in drug responses, affecting PK through mechanisms such as cytochrome P450 (CYP) polymorphisms and altered transporter expression, and PD through drug tolerance and structural/functional changes at the drug-target level. Co-interventions in neurocritical care, including renal replacement therapies, therapeutic hypothermia, fluid resuscitation, and therapeutic plasma exchange, can result in pharmacotherapy variability. Comorbid conditions like systemic inflammation, ARC, and neurological injury impact the body’s drug response, leading to erratic and unpredictable drug levels. Practice variations between institutions and health care teams are critical factors often underemphasized. Different formulations and administration techniques result in variable drug plasma levels. Drug dosing practices may also vary. Concomitant medication administration is prevalent among ICU patients, resulting in drug–drug interactions, with many drugs classified as CYP inducers or inhibitors. Drug-food interactions may also occur through adsorption, chelation, or complexation. Patient characteristics, including age, sex, race and socioeconomic status are important factors affecting drug concentrations in the body. Despite efforts to identify factors causing drug variability, gaps remain that are currently unexplainable. Neuro-CPK, Neurotherapeutics and Clinical Pharmacokinetic laboratory; PK, pharmacokinetics; PD, pharmacodynamics; CYP, Cytochrome P450 enzymes. Created in BioRender. Lab, Neuro-CPK. (2025) https://biorender.com/bu0h3tj.
3 Drug-disease interaction (effect of comorbid conditions)
Drug-disease interactions are important factors affecting pharmacotherapy variability in neurocritical care. Critical illness and neurological conditions can significantly change drug PK and PD through systemic physiological changes, such as altered organ function (e.g., augmented renal clearance), systemic inflammation, hemodynamic instability, changed plasma protein levels, and disrupted blood–brain barrier integrity. These disease-induced changes can result in unpredictable subtherapeutic or toxic drug levels, and increased risk of adverse effects. Understanding drug-disease interactions is therefore essential for minimizing variability, optimizing individualized therapy, and improving outcomes in this highly vulnerable patient population.
3.1 Augmented renal clearance
Augmented renal clearance (ARC), a state of renal hyperfiltration, is a clinical phenomenon observed in critically ill patients (16). First described by Udy et al. (17) following observations of unexpectedly high creatinine clearance (CLCR) values during investigating antimicrobials PK in critical care population. ARC is primarily defined by elevated CLCR. However, the exact threshold remains debated. The most commonly cited definition utilizes CLCR normalized to body surface area (BSA), with a threshold of >130 mL/min/1.73 m2 (16). ARC significantly enhances the elimination of renally excreted medications, potentially leading to subtherapeutic drug levels and compromised treatment outcomes. Notably, commonly used estimated CLCR equations, such as Cockcroft-Gault, often underestimate ARC occurrence (18). This underestimation, coupled with the infrequent use of measured CLCR in clinical practice, contributes to the frequent oversight of ARC. The reported prevalence of ARC varies considerably across studies, largely due to differences in the patient populations examined. A meta-analysis by Hefny et al. (19) indicated an overall ARC prevalence of approximately 36% in mixed intensive care unit (ICU) patients. However, the percentage rises significantly in neurocritical care, with reported prevalence of 74%, highlighting the significance of this phenomenon in neurocritical care.
The pathophysiology of ARC remains incompletely understood (Figure 2). The hyperdynamic state characteristic of critical illness, driven by increased sympathetic response, increased renal blood flow, and the use of vasopressors or aggressive fluid resuscitation, contribute to ARC development. Emerging research also highlights the role of inflammatory mediators in augmenting kidney functions. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), common in critical care, has been implicated in increasing glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and subsequently inducing ARC (20). Specifically, atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) has been identified as a potential mediator. Studies have demonstrated an association between elevated ANP levels and ARC development in patients with TBI (21). Regarding the underlying renal mechanisms, Udy et al. (22) demonstrated that ARC is characterized by concurrent increases in GFR, tubular reabsorption, and active tubular anion secretion. These combined effects result in enhanced excretion of renally cleared drugs.
Figure 2
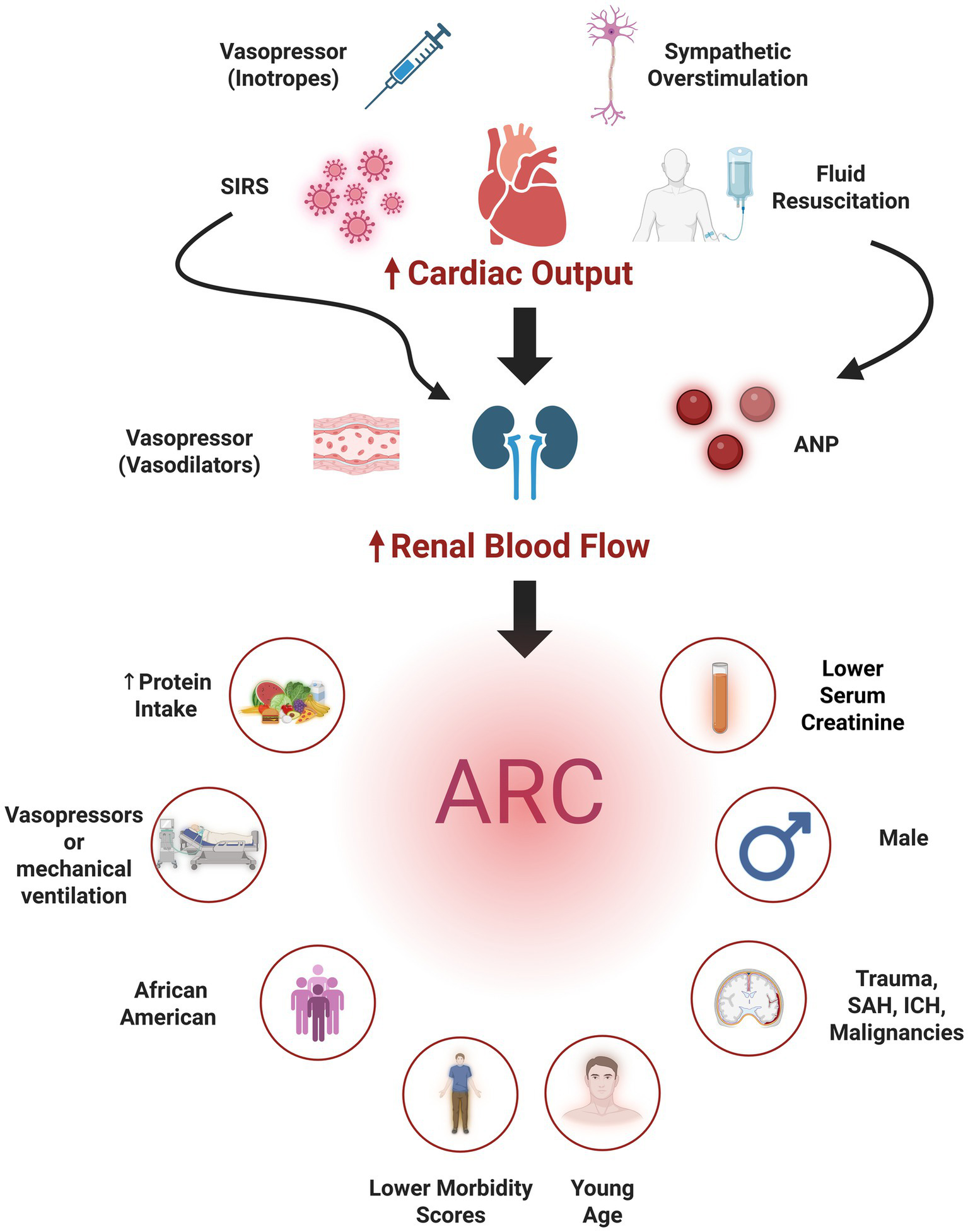
Pathophysiology of augmented renal clearance (ARC) (top) the use inotropes, autonomic dysregulation, fluid resuscitation, and systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) contribute to increasing cardiac output and hence renal blood flow. Other mechanisms (e.g., vasodilatory vasopressors, atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) secreted secondary to hypervolemia, or SIRS directly increase renal blood flow), also contribute subsequently leading to ARC development. Independent predictors of ARC (bottom) comprise patient demographics (young age, male sex), neurological illnesses [traumatic brain injury, intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) and subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)], and clinical factors (e.g., lower morbidity scores, lower serum creatinine, increased protein intake, and vasopressor administration). Created in BioRender. Lab, Neuro-CPK. (2025) https://BioRender.com/0fuwuz5.
Younger age, particularly below 50 years, and male sex are consistently identified demographic risks (17, 23–25), with a single study also identifying African American race as a risk factor (26). Other reported risk factors include trauma (24), hematological malignancies (27), ICH (28), the absence of cardiovascular comorbidities and lower morbidity scores (28–31). Low baseline serum creatinine concentrations (25), the use of mechanical ventilation and vasopressors (30, 32), and increased protein intake (26) were also reported as ARC risk factors. One study identified SAH, especially when accompanied by younger age, higher mean arterial pressure, absence of prior hypertension, and increased nitrogen loss significantly elevate ARC risk (33).
Current research focuses on optimizing drug dosing regimens in the context of ARC (34). Strategies to mitigate the risk of subtherapeutic drug exposure include escalating drug doses, shortening dosing intervals, administering drugs via continuous infusion, or prolonging infusion durations.
3.1.1 Impact of ARC on renally eliminated antiseizure medications
Seizures are common following acute neurological illnesses, necessitating immediate initiation of adequately dosed ASMs (35–37). ARC can significantly increase the clearance of renally eliminated ASMs, potentially resulting in reduced drug exposure, therapeutic failure, and breakthrough seizures (24).
Levetiracetam is a first line ASM that is commonly used to control seizures in neurocritical care, with reference range of 12–46 mg/L. Levetiracetam is predominantly renally eliminated, with ~66% of the administered dose excreted unchanged in urine (24). The remaining portion is eliminated by non-cytochrome P450 enzymes, mainly by hydrolysis. Several studies have reported the positive correlation between CLCR and levetiracetam clearance (38–40). Consequently, ARC significantly decrease levetiracetam exposure, which necessitates an increase in the dosage to achieve concentrations within the reference range (24, 41). The recommended initial dose of levetiracetam of 500 mg twice daily was clearly proven to result in subtherapeutic concentrations in patients with ARC, necessitating at least 1,500 mg to be administered twice daily to achieve concentrations within the reference range (24, 34, 42).
Lacosamide is utilized in the management of focal and generalized seizures, typically as adjunctive therapy or for seizures refractory to first-line agents and status epilepticus (43). Exhibiting linear PK, approximately 40% of lacosamide is eliminated unchanged via renal excretion (44). Studies have also demonstrated a positive correlation between CLCR and lacosamide clearance in patients with renal impairment, highlighting the impact of renal function on drug elimination (44–46). There is a gap in the literature about ARC’s impact on lacosamide pharmacokinetics, more research is needed (47).
Other antiseizure medications such as pregabalin and gabapentin are commonly used in neurocritical care primarily for neuropathic pain; they are less frequently employed for seizure control in the ICU. Both drugs are predominantly eliminated by the kidneys, with almost 100% of gabapentin and approximately 90% of pregabalin excreted renally (48, 49). Their clearance strongly correlates with CLCR (50–54). Further research is needed to establish appropriate administration strategies for these medications in this patient population. Topiramate is another medication less commonly used in the ICU. Research has demonstrated a correlation between its clearance and renal function (55). While studies have extensively investigated dose adjustments for reduced kidney function (48, 56, 57), the impact of ARC on ASM exposure in neurocritical care remains unstudied.
3.1.2 Impact of ARC on renally eliminated antimicrobials
Neurocritical patients are highly prone to hospital acquired infections (HAI) due to prolonged ICU stay, invasive procedures and compromised neurological function (58). HAI occurs in approximately 11% of neurosurgical ICU patients, however, the rate increases to 36% for those who stays for more than 48 h (59). Examples of HAI include ventilator-associated pneumonia, catheter- associated urinary tract infection, central line- associated blood stream infections and surgical site infections (60). A wide range of antimicrobials are used to treat these infections, and the majority are renally eliminated (61). ARC may lead to sub-therapeutic-drug concentrations of renally eliminated antimicrobials, treatment failure and the development of antimicrobial resistance (17). It is essential to achieve therapeutic concentrations as early as possible because the time is a significant factor in infections, as for example each one hour delay in the start of antimicrobials may result in 9% increase in mortality in sepsis (62). Among the most used antimicrobials to treat HAI are vancomycin, piperacillin-tazobactam and meropenem. Around 60–90% of these antibiotics are excreted unchanged through the kidney, thus any alterations in the kidney function could have a crucial impact on their systemic exposure (63, 64).
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic used to treat infections caused by gram positive bacteria especially those caused by methicillin resistant staphylococcus aurous (MRSA) (65). Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is recommended for vancomycin. It is recommended to achieve a target area under the curve/minimum inhibitory concentration (AUC/MIC) ≥ 400 (66), or if difficult to obtain AUC, a trough concentration within the range of 10–20 mg/L is to be targeted as a surrogate measure. ARC patients on standard vancomycin dosing have been reported to achieve below-target trough concentrations, requiring higher doses (67–70).
Piperacillin-tazobactam is a broad spectrum β-lactam antibiotic that used to treat infections secondary to gram negative bacteria especially Pseudomonas aeruginosa (71). Since TDM of piperacillin is not a part of the standard care, ensuring target therapeutic concentrations is essential. It was found that around 37% of patients who have CLCR > 120 mL/min had insufficient piperacillin concentrations (72). Moreover, around 31% of patients with ARC had underexposures to piperacillin versus 0% in the non-ARC patients (defined using a target of MIC>16 mg/L) (73).
Meropenem is a broad spectrum carbapenem antibiotic that exhibits coverage against a wide range of organisms (74). It was reported that around 55% of patients with CLCR > 200 mL/min and received 2 grams every 8 h, had sub-therapeutic concentrations (target 8 mg/mL) (75). A recommended approach to achieve target meropenem concentration in ARC patients is either to increase the dose or administer it via prolonged continuous infusion (76).
It is challenging to administer the right dose to patients with ARC to achieve therapeutic concentrations and avoid any undesirable consequences of sub therapeutic concentrations and treatment failure (67). TDM in such population might be valuable tool to guide the dosing (77), however, there is a clear need for further research to guide specific dosing recommendations in neurocritical care.
3.2 Inflammation in neurocritical care
Inflammation is a complex biological response initiated by the immune system following exposure to a range of adverse stimuli in the body, including pathogens, exogenous toxins, ischemia, and tissue injury (78). It is characterized by the activation of immune cells and inflammatory mediators such as cytokines, chemokines, histamines, and acute-phase proteins to coordinate further immune responses, vascular permeability, and tissue remodeling (79). Although localized inflammation is protective against damaging physiological stressors, downstream systemic effects or maladaptive responses can lead to pathophysiological consequences that may impair innate cellular function, compromise vascular integrity, or heighten organ stress (80). Inflammation in neurocritical care patients is consistently linked to worse clinical outcomes, such as neurological deficits, prolonged hospital stays, and higher rates of morbidity and mortality (81).
Many conditions in neurocritical care have been associated with inflammation, including SAH, TBI, IS, ICH, SE and infections of the central nervous system (82–86). For example, patients with SAH have elevated inflammatory markers, resulting in the activation of various inflammatory pathways (81). Animal models of SAH investigated the inflammatory pathways, including the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway responsible for regulating the expression of pro-inflammatory genes such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin 6 (IL-6). Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK–ERK) pathway within the MAPK signaling cascade is also implicated in SAH models, elevating the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines that regulate cellular responses to stress and inflammation (87–89). Similarly, in patients with TBI, neuroinflammation is associated with both the acute and chronic phases of the condition. Immune cell activation occurs at the point of injury, releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines that can disrupt the blood–brain barrier and exacerbate neuronal damage. In the chronic phase, inflammation is linked to ongoing neuronal injury and long-term cognitive and behavioral deficits (90).
Inflammation often complicates neurocritical care by altering drug metabolism and overall clearance, thereby affecting the PK and PD of commonly used therapies in this setting. In Humans and animal models of inflammation, inflammatory cytokines modulate the activity of cytochrome P450 (CYP) drug metabolizing enzymes such as CYP3A4 and CYP2C9, and drug transporters such as P-glycoprotein. This results in decreased drug metabolism, altered drug distribution, and impaired transport across the blood brain barrier (BBB), increasing patient susceptibility to drug toxicity or reduced drug efficacy. Inflammation can also downregulate or alter the conformation of drug targets, such as L-type calcium channels and β-adrenergic receptors, diminishing drug binding affinity (91–94). Table 3 summarizes the preclinical evidence of inflammation-induced pharmacotherapy variability in drugs relevant to neurocritical care. For example, nimodipine, a calcium channel blocker utilized to improve outcomes in SAH patients, is metabolized by CYP3A4. Inflammation-induced suppression of this enzyme can lead to reduced nimodipine clearance, causing elevated systemic concentrations and a heightened risk of hypotension in SAH patients (95). Concurrently, the upregulation of P-glycoprotein at the blood–brain barrier seen in preclinical models may limit nimodipine’s ability to penetrate the central nervous system, potentially reducing its therapeutic efficacy despite higher plasma levels (96, 97).
Table 3
| Drug | Primary metabolism / Transport/Target | Inflammation impacts | PK changes | PD changes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nimodipine | CYP3A4 L-type calcium channels |
IL-6/IL-2 suppress CYP3A4; upregulation of P-glycoprotein at BBB Inflammatory suppression of calcium channel expression |
Decreased clearance, increased systemic levels, decreased CNS penetration | Potential for decreased CNS efficacy despite increased concentrations Potential for decreased CNS efficacy due to reduced receptor binding |
| Phenytoin | CYP2C9, CYP2C19 | Cytokine-mediated suppression of metabolic enzymes | Increased variability in serum levels (increased risk of toxicity) | Unpredictable therapeutic response |
| Midazolam | CYP3A4 | IL-6 suppresses CYP3A4 activity | Drug accumulation; prolonged sedation | Increased sedative effects; delayed emergence from sedation |
| Levetiracetam | Renal (OCTN1 transporter) | Cytokine effects on transporter activity | Potential changes in CNS distribution | Possible alteration in CNS availability |
| Propofol | Hepatic (non-specific enzymes), protein binding | Inflammation reduces clearance and alters protein binding | Increased Free drug fraction; prolonged action and risk of toxicity | Increased risk of cardiopulmonary depression |
| Propranolol | β-adrenergic receptor | Downregulation of β-receptors in inflammatory states | - | Decreased response to beta-blockade |
| Nicardipine | L-type calcium channels | Inflammatory suppression of calcium channel expression | - | Decreased vasodilatory efficacy |
Preclinical evidence of inflammation-induced pharmacotherapy variability for drugs relevant to neurocritical care (93, 228–236).
BBB, blood brain barrier; CNS, central nervous system; CYP, cytochrome P450; IL, interleukin.
These interactions emphasize the need for personalized dosing regimens in neurocritical care, considering both the patient’s inflammatory status and the pharmacodynamics of each drug. Systemic inflammation not only worsens the primary injury but also introduces variability in pharmacotherapy, complicating treatment and outcomes. This highlights the importance of targeted anti-inflammatory strategies to optimize therapeutic effectiveness. Future research should focus on developing PK-PD models that address the impact of inflammation, leading to more precise and individualized treatments in neurocritical care.
3.3 Neurologic injury and altered drug actions
Neurologic injury itself is a major driver of pharmacotherapy variability in neurocritical care due to its profound effects on both systemic and cerebral physiology as shown in (Table 2) (98–101).
Increased sensitivity to exogenous vasopressin infusion in SAH patients is an example of altered PD of drugs secondary to neurological injury. In critically ill patients with septic shock, exogenous vasopressin administration is infrequently associated with the development of hyponatremia (102). In contrast, Marr et al. reported that the administration of exogenous vasopressin in SAH patients may lead to the development of hyponatremia, which is already the most common electrolyte imbalance encountered after SAH (3). They concluded that vasopressin is an independent predictor of hyponatremia in SAH patients. A possible explanation for this could be that SAH patients have higher serum levels of endogenous vasopressin due to the syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone (SIADH), where exogenous vasopressin further enhances the action of the endogenous hormone (103, 104).
Another example is the altered drug absorption secondary to neurological injury-induced gastrointestinal dysfunction. Kranawetter et al. (105) investigated the effect of SAH on the gut function using esomeprazole as a probe. All SAH patients in this study received esomeprazole via feeding tube while the control group swallowed it orally. Median esomeprazole AUC was eight-folds lower in the SAH group compared to the control group (24.8 vs., 208 mg.min/L, respectively, p- value < 0.001), suggested significantly reduced oral bioavailability. This aligns with previous results suggesting reduced bioavailability of nimodipine in SAH with increased disease severity (high grade) (106–108). Disease severity itself may be associated with bleeding, gastric reflux, decreased peristalsis, poor perfusion to the splanchnic region potentially contributing to reduced bioavailability of orally administered drugs (105).
In summary, it is important to consider how neurological injury may alter the safety and effectiveness of pre-existing treatments that were previously well-tolerated, as dose adjustments, route change or alternative therapies may be necessary.
4 Drug–drug interactions
Drug interactions are common in neurocritical care secondary to polypharmacy, presence of impaired organs function and altered protein binding (109). Interpatient variability, including genetic polymorphisms affecting the activity of multiple CYP enzymes, transporters, and other relevant proteins, also plays a crucial role. Additionally, patient-specific characteristics such as age, sex, race, and social habits can influence drug interactions (109). Mechanistically, these interactions can affect any stage of drug disposition, including any of the PK processes. PD interactions, such as synergism, antagonism, or receptor competition, are also common. Finally, physical incompatibilities, such as the formation of insoluble complexes, can occur, leading to a loss of drug activity (110).
A significant proportion of drug–drug interactions (DDI) occur at the level of hepatic drug metabolism mediated by CYP enzymes (11, 111). Many administered medications are substrates for specific CYPs while simultaneously exhibiting inhibitory or inducing effects on the same or different CYP isoforms. Consequently, the co-administration of drugs impacting CYP enzyme activity frequently results in altered PK of other medications, often necessitating dosage optimization to maintain therapeutic efficacy. For instance, carbamazepine, a commonly used ASM, acts as a potent inducer of CYP3A4 and CYP2B6. Given the broad substrate specificity of CYP3A4, carbamazepine can lead to increased clearance and potentially subtherapeutic concentrations of numerous co-administered drugs (112). Conversely, CYP inhibitors, such as the azole antifungal ketoconazole, certain calcium channel blockers like verapamil, and proton pump inhibitors such as omeprazole, can inhibit the metabolism of their respective substrate drugs (113–115). This inhibition can result in elevated drug plasma concentrations, increasing the risk of adverse drug reactions and toxicity.
Several classes of medications frequently used in neurocritical care warrant careful consideration for potential DDIs, including ASMs (e.g., phenytoin, valproic acid, carbamazepine, benzodiazepines, barbiturates), antimicrobials (e.g., certain beta-lactams and quinolones), calcium channel blockers (e.g., nimodipine, diltiazem, verapamil), sedatives (e.g., dexmedetomidine), and opioids (e.g., fentanyl, morphine) (11).
Therefore, careful assessment and continuous monitoring of DDIs are crucial for reducing pharmacotherapy variability and enhancing patient safety. Adopting a strategy of prioritizing medications with a safer DDI profile, such as drugs primarily eliminated renally with minimal CYP involvement (e.g., levetiracetam compared to other ASMs, certain beta-lactam antimicrobials like piperacillin/tazobactam and cefepime, and the anticoagulant enoxaparin), can contribute to reducing the risk of interactions. However, medication selection in neurocritical care necessitates case-by-case approach to achieve an individualized therapy plan that optimizes therapeutic outcomes while minimizing the risk of DDIs.
5 Drug-food interactions
The interaction between drugs and nutrients is a significant concern in hospitalized patients, particularly in the ICU, where the number of prescribed medications is high (116). Drug-food interactions are one of the factors contributing to pharmacotherapy variability and is usually undermined or unrecognized.
The interaction between phenytoin and nutritional feeds is a well-documented example of drug-food interactions that is particularly relevant to neurocritical care. The absorption of phenytoin is influenced by the nutrient composition of the meal. Specifically, high-carbohydrate meals can enhance its absorption, whereas high-protein diets can diminish it (117, 118). Furthermore, binding feeds significantly reduce phenytoin bioavailability. To address this issue, it is recommended to withhold enteral feeding 2 h prior to and following the administration of the drug to ensure optimal bioavailability (118, 119).
The oral administration of certain antimicrobials can be associated with altered bioavailability secondary drug-food interactions. For instance, fluoroquinolones such as ciprofloxacin may form complexes with divalent cations, thereby reducing their absorption and subsequent bioavailability (120, 121). Consequently, it is recommended that ciprofloxacin be taken 1–2 h before meals and vitamin supplementation. Similarly, tetracyclines bind to calcium to form precipitates, which result in sub-therapeutic drug levels, extended hospital stays, and additional economic burdens (122). Furthermore, the bioavailability of azithromycin, a macrolide, is reduced by 43% when taken with food (122).
Nimodipine is another example. The nimodipine monograph notes a 40% reduction in nimodipine peak concentrations and double time to peak concentration, though overall absorption remains consistent, recommending administration with or without meals but consistently (123). In the ICU, crushing tablets for feeding tube delivery leads to erratic concentrations and low bioavailability (95, 106–108, 124). Holding feeds before or after nimodipine dose is impractical for SAH patients who need dosing every two to 4 h. Further research is needed to determine the optimal nimodipine dosing and administration technique to maximize its benefits.
The studies assessing the clinical impact of drug-nutrient interactions are limited, and existing recommendations are based on weak evidence (125). There is a need for well-designed studies. Standardizing drug administration protocols in conjunction with enteral nutrition and developing monitoring methods are crucial steps.
6 Co-interventions
Co-interventions, therapies or procedures administered alongside the primary treatment, may contribute to pharmacotherapy variability in neurocritical care. Patients in this setting often undergo a range of concurrent interventions, such as mechanical ventilation, targeted temperature management, continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT), or the use of vasopressors and sedatives, all of which can influence drug PK and PD. For instance, hypothermia can reduce hepatic enzyme activity and slow drug metabolism, while CRRT can increase drug clearance, particularly for hydrophilic agents with low protein binding. Additionally, fluid resuscitation, altered pH, and hemodynamic instability can further modulate drug distribution and efficacy. These co-interventions can modify drug exposure independently of the primary treatment, contributing to variability in therapeutic outcomes and complicating the interpretation of clinical trial data. Recognizing and adjusting for the impact of co-interventions is essential for accurate dosing, minimizing variability, and ensuring effective, individualized care in neurocritical patients.
6.1 Therapeutic plasma exchange
Therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) is an extracorporeal treatment where blood is withdrawn from a patient’s vein, the plasma is separated, and the blood is subsequently returned to the patient with or without fluid or plasma replacement. TPE is employed in neurocritical care for various conditions, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome and myasthenic crisis. Furthermore, it can be utilized for drug filtration in cases of intoxication.
TPE may affect drug exposure by removing protein-bound drug fractions, which could potentially lead to treatment failure. The PK characteristics of the drug, as well as the specific attributes of the TPE procedure, determine the extent of drug removal during TPE. The volume of distribution (Vd) and plasma protein binding (PPB) are essential in predicting the impact of TPE on drug plasma concentrations (126, 127). A high Vd indicates that the drug is widely distributed throughout the body, resulting in a lower amount of the drug present in the plasma to be removed. Conversely, drugs with a low Vd (0.2–0.3 L/kg) are extensively extracted during the TPE procedure (126–128). PPB defines the fraction of the drug that is bound to plasma proteins and the free unbound fraction remaining. Highly bound drugs (>80%) are readily removed by TPE. For drugs exhibiting multi-compartment PK models, which feature distinctive distribution and elimination phases, the timing of the TPE procedure is critical. Conducting TPE during the drug’s distribution phase results in a higher likelihood of drug removal. The half-life (t1/2) and drug clearance are important intrinsic factors for drug removal from plasma. As drug clearance is not always mentioned in monographs, t1/2 serves as a surrogate marker for clearance (127–130). TPE-specific factors include the timing of TPE initiation, procedure duration, exchanged plasma volume, and frequency of the procedure. One TPE session typically lasts 2 to 3 h, making drugs with a t1/2 longer than 2 h more liable to extraction. The number of plasma volume exchanges correlates directly with the percentage of plasma components removed. The number of TPE sessions impacts drug removal, with most of the drug being removed in the first session, followed by a decrease in the extraction percentage in subsequent sessions due to the exponential nature of drug removal (127, 131).
Evidence reporting drug removal by TPE is scarce; however, utilizing the drug PK characteristics can help estimate the likelihood of drug extraction by TPE. Figure 3 depicts a conceptual proposed tool to determine how likely drugs are removed by TPE based on the PK characteristics of the drug and the current evidence at the time of the study (127). However, this developed tool needs to be validated in future research.
Figure 3
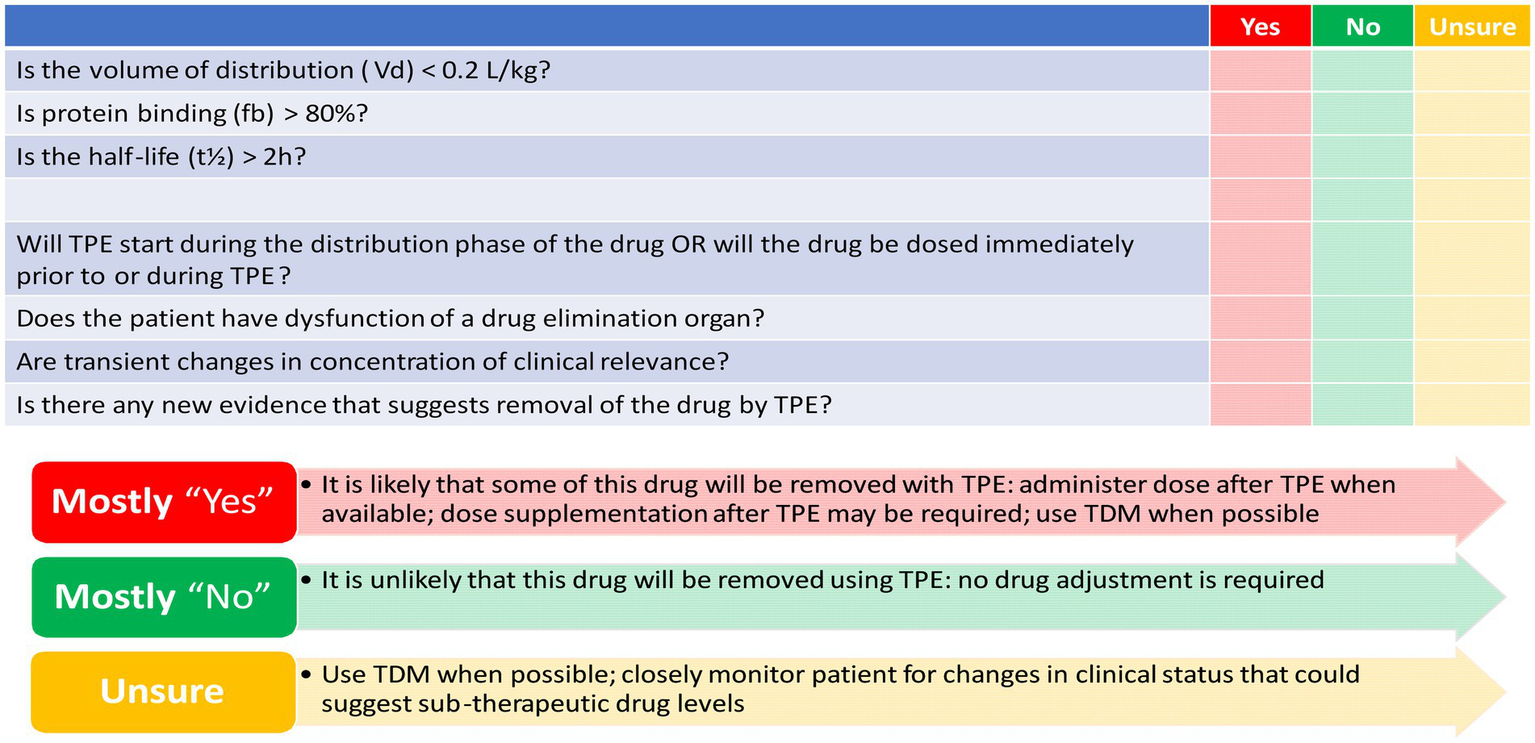
Checklist to determine how likely drugs are removed by therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE). Mahmoud et al. (127) reproduced with permission from Springer Nature.
6.2 Renal replacement therapies
Renal replacement therapies (RRTs) are not uncommon in neurocritical care (132). Neurological conditions often lead to systemic inflammatory responses and hemodynamic instability, predisposing patients to acute kidney injury (AKI) and necessitating RRT to maintain electrolyte balance, remove metabolic waste, and control fluid overload (133). In this context, RRT serves not only to support renal function but also to optimize neurological recovery by preventing complications like cerebral edema and electrolyte-induced seizures (134–136). The primary RRT modalities used include CRRT, preferred for hemodynamically unstable patients due to its gradual fluid and solute removal, intermittent hemodialysis (IHD), suitable for stable patients requiring efficient solute removal over a shorter time period, and peritoneal dialysis (PD), less common in acute neurocritical care but a possible alternative in some cases (135, 137, 138).
CRRT is a form of extracorporeal blood purification employed in hemodynamically unstable critically ill patients, where IHD is poorly tolerated (139). It operates on the principles of convection and diffusion, continuously removing solutes and fluids across a semipermeable membrane via a slow, controlled process (139). Indications include AKI complicated by hemodynamic instability, severe electrolyte imbalances, and conditions necessitating strict fluid management, such as cerebral edema (140, 141). The gradual nature of CRRT minimizes rapid shifts in solute concentrations and intravascular volume, thus reducing the risk of cerebral perfusion pressure fluctuations and elevated intracranial pressure (141). However, CRRT can potentially lead to unintended consequences, including the removal of certain medications, necessitating careful drug dosing adjustments (142). Therefore, subtherapeutic levels of medications are frequently encountered, arising from the combined effects of altered PK in critically ill patients and the extracorporeal clearance provided by CRRT. Antimicrobials (e.g., vancomycin, meropenem and piperacillin-tazobactam) and ASMs (e.g., levetiracetam) demonstrate significant susceptibility to CRRT mediated removal (143). These drugs share PK characteristics, including low protein binding, small volumes of distribution and/or significant renal clearance (144). Consequently, initial recommended dosing regimens often result in subtherapeutic drug levels, potentially compromising therapeutic efficacy and increasing the risk of treatment failure. PK studies are increasingly focused on optimizing drug dosing during CRRT (143, 145–147).
IHD is an another blood purification technique that removes waste products and excess fluids over a shorter period, typically 3–4 h (139). It relies primarily on diffusion to clear solutes across a semipermeable membrane, driven by a concentration gradient between the blood and dialysate (139). In neurocritical care, IHD can be utilized when rapid correction of electrolyte imbalances or significant fluid removal is needed, provided the patient can tolerate the hemodynamic shifts associated with the procedure. However, IHD can cause rapid changes in blood volume and electrolyte concentrations, potentially leading to hypotension and disequilibrium syndrome (neurological symptoms due to rapid solute shifts), potentially resulting in increased intracranial pressure (148, 149). Medications, especially those with low volumes of distribution and low protein binding may be significantly cleared during IHD, necessitating careful monitoring and post-dialysis dosing adjustments to maintain therapeutic levels and prevent neurological complications. Similar to CRRT, significant research has been dedicated to optimizing medication dosing regimens in IHD (146).
6.3 Therapeutic hypothermia
Therapeutic hypothermia is a treatment strategy that lowers the body temperature intentionally to 32–34°C over a period of 12–24 h (150). It is used in certain conditions such as cardiac arrest, ischemic stroke and traumatic brain injury to limit or restore brain damage (150–153). It has a neuroprotective function as it decreases the brain damage after reduced blood flow (154). There are several hypothesized mechanisms by which therapeutic hypothermia could reduce brain injury. For example, it reduces the metabolic rate by 6–8% per 1°C decrease in the temperature which in turn reduces the brain demand for oxygen. Moreover, it suppresses inflammation, as excessive and continuous inflammation could lead to further brain damage (155). Conversely, some randomized controlled trials did not show any outcome differences if therapeutic hypothermia was applied (156, 157). Therapeutic hypothermia is a three phases process: induction, maintenance and re-warming (155). However, each of these phases carries its risks, and close monitoring of the patient is important. In the induction phase, immediate risks such as electrolyte disturbance, hyperglycemia and shivering could result. On the other hand, monitoring of nosocomial infections and pressure ulcers are important in the maintenance phase. And the rewarming phase should be done very slowly to avoid again electrolytes disturbances and risks of hypoglycemia (155). Therapeutic hypothermia slows down all the processes inside the body which in turn alters the PK and PD of some drugs variably between patients. From the PK point of view, it mainly affects the drugs metabolism and results in increasing the drug concentrations which in turn leads to prolonged response (158). And from the PD aspects it could affect target sensitivity (158).
ASMs such as phenytoin and phenobarbital could be affected by hypothermia (159, 160). A study examined phenytoin PK during and after mild hypothermia (34°C), found that phenytoin metabolism is inhibited by hypothermia. Additionally, phenytoin concentrations were higher during hypothermia compared to concentrations after hypothermia. In addition, there was an 180% increase in AUC and 67% decrease in phenytoin clearance (159). This should be carefully monitored given that phenytoin is a drug with a narrow therapeutic range and any increased serum concentrations could lead to toxicity.
Sedatives and analgesics are commonly used in neurocritical care and therapeutic hypothermia could also impact their disposition in the body. To illustrate, it has been shown that hypothermia (30°C) significantly resulted in increased morphine concentrations in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. Moreover, it increased the mean residence time and lowered its clearance significantly (161). Hypothermia also increases the sensitivity to morphine, which could expose the patient to toxicity risks. As such, hypothermia has dual effects on morphine disposition in the body and may lead to morphine toxicity. Additionally, there was a significant decrease in the metabolism of midazolam in healthy volunteers treated with hypothermia. There is a positive correlation between body temperature and inter-compartmental clearance of midazolam, with an 11.1% decrease in clearance for each degree Celsius decrease in temperature (162).
Therapeutic hypothermia has the potential to not only limit cerebral damage but also impact the entire body. Consequently, it is essential to carefully monitor patients undergoing this treatment, and adjustments to medication dosages may be required.
6.4 Fluid resuscitation
Fluid resuscitation, a common intervention in neurocritical care, significantly contributes to pharmacotherapy variability by altering the PK of many drugs. Aggressive fluid administration can expand the extracellular fluid volume, leading to dilutional effects and increased volume of distribution, particularly for hydrophilic drugs such as beta-lactam antibiotics (163, 164). This can result in lower plasma drug concentrations and potentially subtherapeutic effects unless dosing is appropriately adjusted (164). Changes in renal perfusion and function caused by fluid resuscitation may also modify drug clearance, either increasing elimination in hyperdynamic states (e.g., ARC) or reducing it in cases of fluid overload and renal impairment (16). These changes necessitate close therapeutic drug monitoring and dose adjustment to ensure effective and safe pharmacotherapy in neurocritical care patients.
7 Practice variations
Practice variation in neurocritical care significantly impacts pharmacotherapy variability and clinical outcomes. Differences in institutional protocols, clinician preferences, and resource availability often lead to inconsistent prescribing practices, affecting the quality and uniformity of care. For instance, variations in the choice, dosing and administration of sedatives, ASMs, antimicrobials or anticoagulants can result in diverse pharmacological responses and safety profiles. This inconsistency can lead to underdosing, resulting in therapeutic failure, or overdosing, increasing the risk of adverse drug reactions. Reducing practice variation is critical to optimizing pharmacotherapy and improving outcomes in neurocritical care. Standardized protocols, enhanced communication across multidisciplinary teams, and the integration of decision-support tools into clinical workflows can minimize variability and ensure consistent application of best practices. Such measures, combined with ongoing education and research, can help mitigate the impact of practice variation, fostering more reliable and equitable patient outcomes. In this section we present two examples from our research, highlighting the impact of practice variations on patient outcomes.
7.1 Nimodipine administration techniques and formulations
An example of how practice variations could contribute to pharmacotherapy variability is the variability in nimodipine administration in SAH. Nimodipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker, characterized by being the only member of this class to cross the blood brain barrier and act on the cerebral vascular smooth muscles. Nimodipine inhibits L-type voltage gated calcium channels, hindering the calcium ions influx and hence a vasodilator effect (165, 166). Nimodipine was found to improve outcomes in SAH patients, therefore guidelines recommend that all SAH patients receive a fixed dose of oral nimodipine administered as 60 mg every 4 h for 21 days from ictus (36, 167). To date, nimodipine is the only drug approved for this indication.
Many studies have indicated variability in plasma concentrations of nimodipine, potentially resulting in pharmacotherapy variability (Figure 4). These variations have led to questions regarding whether all patients are receiving the optimal benefit from the administered dose (95, 106, 107, 168). Multiple factors could contribute to nimodipine pharmacotherapy variability such as: age, sex, comorbid conditions, drug–drug interactions, disease severity on admission, genetic polymorphisms, and nimodipine formulations and administration techniques (97). Practice variations in the administration techniques may result in differences in patient outcomes. In a single-center retrospective study comparing the outcomes of administering nimodipine tablets orally (PO) to conscious patients versus delivering the crushed tablet through a feeding tube (FT) to dysphagic, unconscious, or mechanically ventilated patients. The study found that patients who received the crushed tablet via the FT had a higher prevalence of moderate to severe vasospasm and DCI following adjustment for disease severity (124). A multicenter retrospective study conducted across North America included 727 patients from 21 hospitals to compare different nimodipine formulations administered enterally in terms of efficacy and safety. Various oral dosage forms were tested since the oral tablet is the only dosage form marketed in Canada, while capsules and oral solution are available in US institutions. For unconscious, mechanically ventilated, or dysphagic patients, tablets were crushed and administered through FT. Similarly, capsule contents were withdrawn from the gelatin shell using a syringe, either by pharmacists or nurses at the bedside, followed by emptying the syringe content into the FT. Thirty one percent of the patients included in the study developed DCI. The highest prevalence was among the group receiving the crushed tablet via the FT followed by the group receiving the liquid withdrawn from the capsule at bedside (108). From both studies, it is plausible to say that different formulations/administration techniques may not be equivalent. Factors such as differences in excipient formulations, inconsistencies in medication delivery due to institutional practices, and altered drug bioavailability may contribute at least in part to the observed differences (108, 124).
Figure 4
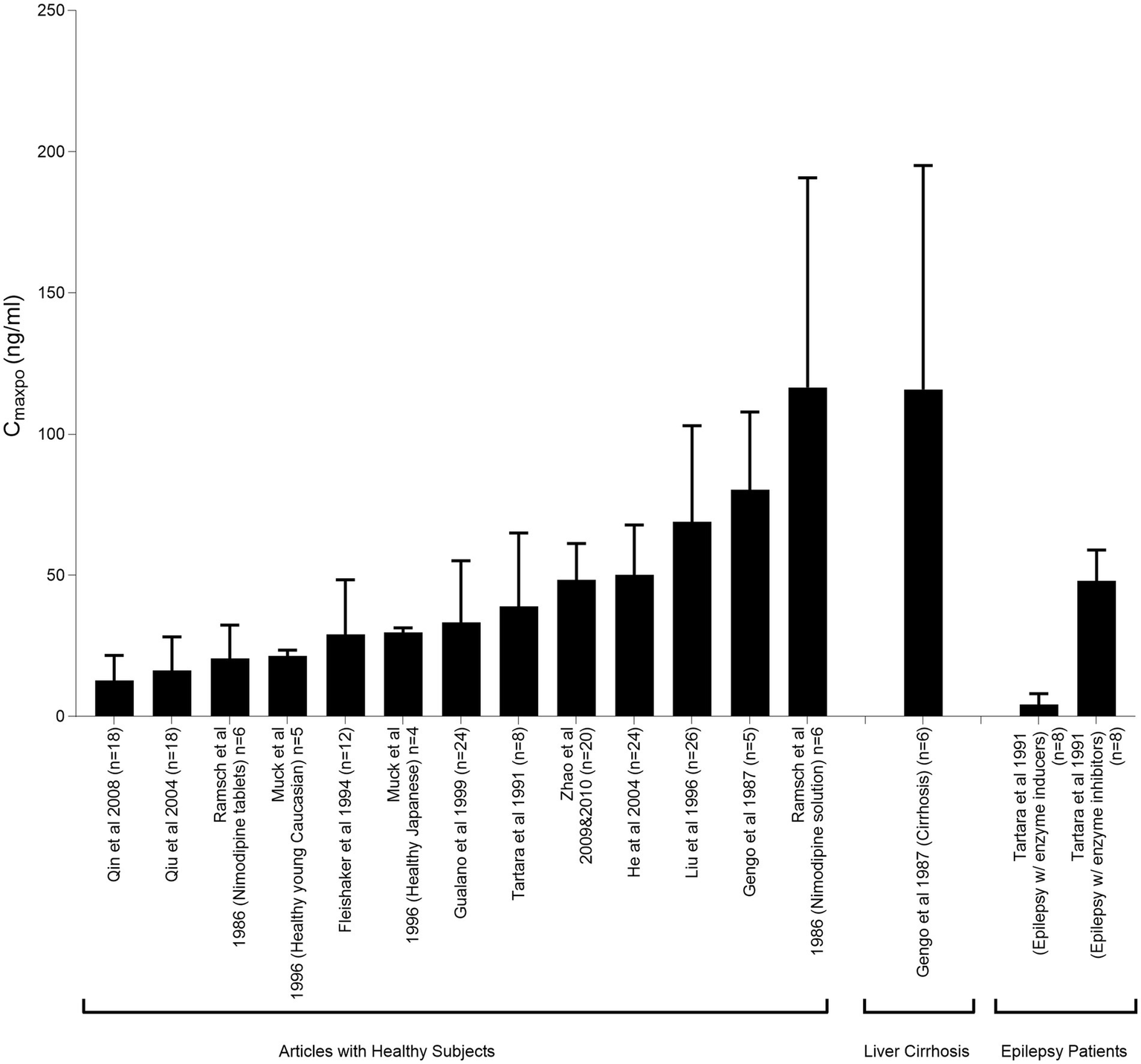
Peak plasma nimodipine concentrations following oral administration (CmaxPO) of a single 60-mg nimodipine dose in healthy individuals and patients with liver cirrhosis and epilepsy. This figure illustrates the pharmacokinetic variability of nimodipine across studies. Mahmoud et al. (97) reproduced from Springer Nature under a creative commons attribution-non commercial 4.0 international license.
7.2 Herpes encephalitis and acyclovir dosing
Herpes encephalitis is a fatal viral infection caused by viruses of the Herpesviridae family specifically herpes simplex virus and varicella zoster virus. It has high mortality rate of 70% without treatment, however, even with treatment the mortality rate is 20% (169, 170). Herpes encephalitis diagnosis is confirmed through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the cerebrospinal fluid to detect the presence of the virus (171). Given the severity of herpes encephalitis, it is crucial to start adequate antiviral therapy as early as possible to improve the morbidity and mortality (172, 173).
Acyclovir is the standard treatment of herpes encephalitis, given intravenously as 10 mg/kg every 8 h for 14–21 days (174, 175). It was first discovered in 1974 to treat cutaneous and genital herpes infection (176, 177); however, in 1994 it was recommended to be started in all patients with suspected encephalitis (172). High acyclovir concentrations in the body could lead to acyclovir nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity (178). Acyclovir nephrotoxicity is observed as AKI due to precipitation of acyclovir crystals in the kidney tubules (178). Acyclovir induced neurotoxicity observed as hallucination, confusion and other neurological symptoms that also mimic herpes encephalitis (179).
There is a wide practice variations on what body weight to be used in calculating the dose specifically in obese patients (180). An abstract published in 1991, recommended that clinicians should use ideal body weight in calculating the dose to be given to obese patients (181). However, a pharmacist survey reported that there is a clear lack of uniformity to agree on a specific body weight to be used in calculating acyclovir dose in obese patients (182). Pharmacists tend to use adjusted body weight, which is the ideal body weight in addition to the water content of the extra fat in the patient, in overweight patients (182, 183). In obese patients, using actual body weight results in high acyclovir plasma concentrations, which may lead to toxicity (184). On the other hand, using ideal bodyweight could result in lower concentrations compared to using actual body weight in non-obese patients (185). There is no evidence reporting the outcomes associated with using different body weight. Few studies suggest that adjusted body weight could be used in calculating acyclovir dose in obese patients. In our comprehensive literature review, we suggested to use adjusted body weight in obese and actual body weight in non-obese (180).
Another important consideration when dosing acyclovir is the kidney function. The dosing of acyclovir in impaired kidney function patient is well reported, however, its dosing in adult patients with ARC is not well studied. A study conducted on pediatrics patients, suggests that patients with ARC (CLCR > 250 mL/min/1.73m2) require larger doses of acyclovir to get effective concentrations (186). However, there is a need for larger prospective studies to confirm the dosing proposals based on the main factors affecting acyclovir concentrations which are body weight to be used and kidney function.
8 Pharmacogenomics in neurocritical care
Pharmacogenomics, the study of how genetic variations impact drug response, plays a critical role in optimizing medication therapy (187). Neurocritical care patients often require complex treatment regimens involving high-risk medications with narrow therapeutic ranges such as sedatives, ASMs, analgesics, anticoagulants, and antimicrobials. As time is crucial, the proper choice of drugs considering any genetic variations is important to prevent any secondary brain injury and improve outcomes. Practitioners can improve drug safety and effectiveness in neurocritically ill patients by considering the genetics behind drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity. Of the three main areas of pharmacogenomics is metabolism, transporters and targets. Pharmacogenomics variations could be at the level of single gene involvement (monogenic) or more complex involving more than one gene (polygenic) (187, 188).
Around 75% of drugs are metabolized by CYP, where genetic variations could greatly result in drugs PK variation (189). Clopidogrel, an antiplatelet agent commonly used in the ICU, is metabolized by CYP2C19. There are 2 genetic variations in the CYP2C19, specifically the 2* and 3* alleles, that lead to reduced drug activation and increased risk of thrombotic events (190, 191). Another example of a drug that CYP genetic variations affect its PK and PD is codeine, an opioid analgesic often prescribed in neurocritical care (192). CYP2D6 polymorphisms could lead to either poor metabolism or extensive metabolism. Poor metabolism of codeine impairs its activation to morphine and subsequently decreases the analgesic effect. On the other hand, ultra rapid metabolism could lead to morphine toxicity (193). Moreover, in sedatives such as midazolam where CYP3A4/3A5 plays a significant role in its metabolism, genetic variations can change drug clearance, necessitating dose adjustments to avoid either prolonged or inadequate sedation (194).
Genetic variations in drug transporters also play a role in pharmacotherapy variability. For example, polymorphisms in the SLCO1B1 gene affect the transport of statins, which can lead to an increased risk of myopathy (195). Moreover, genetic variations in ABCB1, a p-glycoprotein transporter, could influence the transport of ondansetron and therefore it will result in variability in its antiemetic activity (196). Polygenic variations are common given the complexity and the interplay of several genes to drug disposition in the body. Warfarin, an anticoagulant medication, genetic markers like VKORC1 (target receptor) and CYP2C9 (metabolizing enzyme) are critical for optimizing its anticoagulation (197, 198). Another example is phenytoin. CYP2C9 (metabolizing enzyme) and HLA-B (involved in hypersensitivity reaction) genes play a significant role in phenytoin toxicity (199, 200).
The integration of pharmacogenomics into neurocritical care holds great promise for transforming neurocritical care by enabling a precision-based approach to drug therapy, ultimately aiming to improve the outcomes and prevent toxicity of patients with severe neurological illnesses. However, this is limited by the availability and applicability of genetic testing in acute neurocritical care settings because of the time sensitivity of the setting, the cost of the testing and the complexity of pharmacogenomics data. Overcoming these barriers will require multidisciplinary collaboration, the development of enhanced clinical decision-support tools, and continued research to create a solid pharmacogenomics knowledge base for neurocritical care relevant medications.
9 Patient characteristics
Patient-specific characteristics such as age, sex, race, body mass index (BMI), socioeconomic status and social history play a critical role in pharmacotherapy variability in neurocritical care. Clinicians are vigilant to take these characteristics into consideration when making treatment decisions especially for drugs that known to cause adverse effects in patients with specific characteristics. However, less attention is given to the PK/PD changes caused by variable patients’ characteristics.
Age-related physiological changes can significantly impact drug metabolism and clearance. It is not only the elderly patients have reduced renal and hepatic function, but also young adults who are admitted with neurological illness such as TBI are highly prone to have ARC (16).
Many factors could contribute to sex-based differences, such as hormonal and genetic factors. Pharmacotherapy variability could be attributed to different enzyme expression, drug transport, and receptor sensitivity among males and females (201). For example, higher prevalence of ARC was observed in males (16).
Understanding the role of race in pharmacotherapy variability in the neurocritical illness presentations and therapy response is crucial to provide the best care to patients. Because of genetic variations in CYP3A5, an enzyme involved in nimodipine metabolism, different populations could have variable drug exposure depending on the enzyme genotype (extensive, normal, intermediate and poor metabolizers) (202).
Body weight and composition affect Vd and clearance of drugs. For drugs with Vd similar to the total body weight, dosing should carefully consider the type of body weight used. Using ideal body weight may result in lower concentrations due to the water content of fat tissues, while using actual body weight could lead to higher, potentially toxic concentrations. Acyclovir is an example of a drug requiring weight-based dosing, where the choice of weight calculation significantly impacts toxicity, especially in obese patients (180).
Social history such as smoking and alcoholism could greatly impact the drugs PK/PD in the body. Chronic alcohol intake is well known for its induction of CYP2E1enzyme which is involved in metabolizing some drugs such as acetaminophen to its hepatotoxic metabolite (203, 204). Gathering such information is important to be considered as one source of variability.
In neurocritical care, where therapeutic windows are limited and treatment responses can vary, it is important to consider patient-specific characteristics to ensure safe and effective pharmacotherapy.
10 Limitations, research gaps, and future directions
This review is limited by its narrative format. The absence of a systematic search methodology may result in subjectivity and restricts the evaluation of the quality of the included studies. Additionally, some studies mentioned in this review do not provide high levels of evidence and their results should be interpreted with caution. Significant research gaps persist in understanding pharmacotherapy variability in neurocritical care. Limited studies have systematically characterized these alterations or translated findings into individualized dosing strategies. The use of potentially ineffective or toxic treatments, as well as suboptimal medication dosing, may contribute to poor patient outcomes due to the limited understanding of how neurological injury influences drug action and disposition. There is a need for precision pharmacotherapy research tailored to neurocritical care to optimize patient outcomes and minimize adverse effects. Further research is required to enhance data capture, characterize clinical phenotypes and their impact on pharmacotherapy variability, and identify biomarkers that predict and guide treatment. Moreover, decision-making tools need to be developed to assist clinicians in making timely decisions within the fast-paced environment of neurocritical care. It will be valuable to incorporate pharmacotherapy variability insights into clinical decision support system. For instance, an electronic health record integrated alert for dosing antimicrobials in a patient with high-risk factors for ARC will efficiently help the clinician to optimize the care. The integration of evidence generated from pharmacotherapy variability research with clinical, genomic, metabolomic, and proteomic data, utilizing machine learning, represents the future of precision medicine in neurocritical care. Table 4 summarizes research focus areas relevant to pharmacotherapy variability and precision medicine in neurocritical care.
Table 4
| Research focus | Details |
|---|---|
| Prioritize research on PK/PD Alterations | Need for systematic and longitudinal studies on neurological injuries’ effects on drug PK and PD |
| Develop and validate individualized dosing strategies | Translate PK/PD study findings into practical dosing algorithms and guidelines for clinicians |
| Enhance data capture and integration | Adopt standardized data collection, leverage Electronic Health Records, integrate multi-modal neuromonitoring and “omics” data |
| Focus on clinical phenotyping | Identify and validate clinically relevant phenotypes in neurocritical care patients and their association with pharmacotherapy variability |
| Investigate and validate predictive biomarkers | Identify and validate biomarkers that predict drug response in neurocritically ill patients |
| Develop and implement clinical decision support tools | Create user-friendly decision support systems that integrate patient data and algorithms for pharmacotherapy decisions |
| Innovative clinical trial designs | Implement innovative clinical trial designs that address pharmacotherapy variability as contributors for heterogeneity of treatment effect such as adaptive clinical trial designs |
| Implementation research | Uptake the findings of the evidence-based research and implement it to the routine clinical practice Implement medication safety programs with clinical pharmacists |
Research focus areas relevant to pharmacotherapy variability and precision medicine in neurocritical care.
PK, pharmacokinetics; PD, pharmacodynamics.
11 Conclusion
Pharmacotherapy variability within neurocritical care introduces additional layers of complexity that may significantly contribute to therapy failure, adverse drug reactions, and setbacks in drug development. By investigating these unique complexities inherent to neurocritical care, we can advance precision pharmacotherapy, ensuring the administration of the appropriate medication to the right patient at the correct dosage regimen. This approach aims to ultimately enhance clinical outcomes in this vulnerable population.
Clinical implications
-
Pharmacotherapy variability, the variability in drug response among and within individuals, complicates management in neurocritical care by potentially contributing to therapy failure, adverse drug reactions, and setbacks in drug development.
-
Clinicians should be cognizant of factors that may contribute to pharmacotherapy variability, including comorbid conditions, drug interactions, practice variations, patient characteristics, pharmacogenomics, and co-interventions.
-
Augmented renal clearance (ARC) in neurocritical care accelerates the elimination of renally excreted medications, risking subtherapeutic drug levels and poor treatment outcomes. Proper dosing for those with ARC risk factors is essential.
-
Systemic inflammation and neurological injury introduce variability in pharmacotherapy, complicating treatment and outcomes. Further research is needed in this area.
-
Clinicians should be vigilant of drug–drug and drug-food interactions in neurocritical care and take appropriate measures to mitigate those interactions, such as holding feeds prior to medication administration, using alternate non-interacting medications, and performing therapeutic drug monitoring.
-
Co-interventions, such as therapeutic plasma exchange and renal replacement therapies, may reduce the systemic exposure of drugs, potentially leading to treatment failures. Clinicians should consult available evidence to determine the appropriate dosing and measures to mitigate the effects of co-interventions.
-
Incorporating pharmacotherapy variability into treatment guidelines is key to reducing practice variation and advancing personalized care.
-
Pharmacists serve as invaluable resources in neurocritical care, offering drug expertise that is essential for managing and minimizing pharmacotherapy variability.
-
Until decision-making tools become broadly accessible, individualized patient assessment and monitoring are essential to ensure the delivery of optimal care to patients.
Statements
Author contributions
SM: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Project administration, Funding acquisition. MK: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Writing – original draft. AA: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AE: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. EG: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Investigation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) -Funding Reference Number (192195).
Acknowledgments
We extend our appreciation to all former members of the Neurotherapeutics and Clinical Pharmacokinetics (Neuro-CPK) Laboratory for their valuable contributions to the research on pharmacotherapy variability.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Mahmoud SH Marette V Lindqvist T Ahmed SN . Critical Care Management of Status Epilepticus at a tertiary care university hospital. Can J Neurol Sci. (2019) 46:702–10. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2019.278
2.
Holtkamp M Othman J Buchheim K Meierkord H . Predictors and prognosis of refractory status epilepticus treated in a neurological intensive care unit. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2005) 76:534–9. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2004.041947
3.
Marr N Yu J Kutsogiannis DJ Mahmoud SH . Risk of hyponatremia in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage treated with exogenous vasopressin infusion. Neurocrit Care. (2016) 26:182–90. doi: 10.1007/s12028-016-0300-8
4.
Iwashyna TJ Burke JF Sussman JB Prescott HC Hayward RA Angus DC . Implications of heterogeneity of treatment effect for reporting and analysis of randomized trials in critical care. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2015) 192:1045–51. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201411-2125CP
5.
Yarnell CJ Fralick M . Heterogeneity of treatment effect - an evolution in subgroup analysis. NEJM Evid. (2024) 3:EVIDe2400054. doi: 10.1056/EVIDe2400054
6.
Sendekie AK Kasahun AE Limenh LW Dagnaw AD Belachew EA . Clinical and economic impact of adverse drug reactions in hospitalised patients: prospective matched nested case-control study in Ethiopia. BMJ Open. (2023) 13:e073777. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-073777
7.
Seo B Yang MS Park SY Park BY Kim JH Song WJ et al . Incidence and economic burden of adverse drug reactions in hospitalization: a prospective study in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. (2023) 38:e56. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e56
8.
Cullen DJ Sweitzer BJ Bates DW Burdick E Edmondson A Leape LL . Preventable adverse drug events in hospitalized patients: a comparative study of intensive care and general care units. Crit Care Med. (1997) 25:1289–97. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199708000-00014
9.
Kasztura M Richard A Bempong NE Loncar D Flahault A . Cost-effectiveness of precision medicine: a scoping review. Int J Public Health. (2019) 64:1261–71. doi: 10.1007/s00038-019-01298-x
10.
Morales Castro D Dresser L Granton J Fan E . Pharmacokinetic alterations associated with critical illness. Clin Pharmacokinet. (2023) 62:209–20. doi: 10.1007/s40262-023-01213-x
11.
Spoelhof B Farrokh S Rivera-Lara L . Drug interactions in Neurocritical care. Neurocrit Care. (2017) 27:287–96. doi: 10.1007/s12028-016-0369-0
12.
Aleksic DZ Jankovic SM Mlosavljevic MN Toncev GL Miletic Drakulic SD Stefanovic SM . Potential drug-drug interactions in acute ischemic stroke patients at the neurological intensive care unit. Open Med. (2019) 14:813–26. doi: 10.1515/med-2019-0093
13.
Ilan R Fowler RA Geerts R Pinto R Sibbald WJ Martin CM . Knowledge translation in critical care: factors associated with prescription of commonly recommended best practices for critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. (2007) 35:1696–702. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000269041.05527.80
14.
Tejerina EE Goncalves G Gomez-Mediavilla K Jaramillo C Jimenez J Frutos-Vivar F et al . The effect of age on clinical outcomes in critically ill brain-injured patients. Acta Neurol Belg. (2023) 123:1709–15. doi: 10.1007/s13760-022-01987-0
15.
Acosta JN Brown SC Falcone GJ . Genetic variation and response to Neurocritical illness: a powerful approach to identify novel pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Neurotherapeutics. (2020) 17:581–92. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00837-2
16.
Mahmoud SH Shen C . Augmented renal clearance in critical illness: an important consideration in drug dosing. Pharmaceutics. (2017) 9:36. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics9030036
17.
Udy AA Roberts JA Boots RJ Paterson DL Lipman J . Augmented renal clearance: implications for antibacterial dosing in the critically ill. Clin Pharmacokinet. (2010) 49:1–16. doi: 10.2165/11318140-000000000-00000
18.
Baptista JP Neves M Rodrigues L Teixeira L Pinho J Pimentel J . Accuracy of the estimation of glomerular filtration rate within a population of critically ill patients. J Nephrol. (2014) 27:403–10. doi: 10.1007/s40620-013-0036-x
19.
Hefny F Stuart A Kung JY Mahmoud SH . Prevalence and risk factors of augmented renal clearance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmaceutics. (2022) 14:445. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020445
20.
Katsube T Echols R Wajima T . Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of cefiderocol, a novel siderophore cephalosporin. Clin Infect Dis. (2019) 69:S552–8.
21.
Udy AA Jarrett P Lassig-Smith M Stuart J Starr T Dunlop R et al . Augmented renal clearance in traumatic brain injury: a single-center observational study of atrial natriuretic peptide, cardiac output, and creatinine clearance. J Neurotrauma. (2017) 34:137–44. doi: 10.1089/neu.2015.4328
22.
Udy AA Jarrett P Stuart J Lassig-Smith M Starr T Dunlop R et al . Determining the mechanisms underlying augmented renal drug clearance in the critically ill: use of exogenous marker compounds. Crit Care. (2014) 18:1–9. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0657-z
23.
Nazer LH AbuSara AK Kamal Y . Augmented renal clearance in critically ill patients with cancer (ARCCAN study): a prospective observational study evaluating prevalence and risk factors. Pharmacol Res Perspect. (2021) 9:e00747. doi: 10.1002/prp2.747
24.
Kharouba M Aboelezz A Kung JY Mahmoud SH . The impact of augmented renal clearance on the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam in critically ill patients: a literature review. J Clin Pharmacol. (2025) 65:815–834. doi: 10.1002/jcph.70007
25.
Bing E Archambault K Sananikone A Nguyen K-D Fang YT Jabamikos C et al . Risk factors associated with augmented renal clearance in a mixed intensive care unit population: a retrospective study. Int J Clin Pharm. (2022) 44:1277–86. doi: 10.1007/s11096-022-01458-9
26.
Dickerson RN Crawford CN Tsiu MK Bujanowski CE Van Matre ET Swanson JM et al . Augmented renal clearance following traumatic injury in critically ill patients requiring nutrition therapy. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1681. doi: 10.3390/nu13051681
27.
Saito K Kamio S Ito K Suzuki N Abe K Goto T . A simple scoring method to predict augmented renal clearance in haematologic malignancies. J Clin Pharm Ther. (2020) 45:1120–6. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13193
28.
Nei AM Kashani KB Dierkhising R Barreto EF . Predictors of augmented renal clearance in a heterogeneous ICU population as defined by creatinine and cystatin C. Nephron. (2020) 144:313–20. doi: 10.1159/000507255
29.
Egea A Dupuis C de Montmollin E Wicky P-H Patrier J Jaquet P et al . Augmented renal clearance in the ICU: estimation, incidence, risk factors and consequences—a retrospective observational study. Ann Intensive Care. (2022) 12:88. doi: 10.1186/s13613-022-01058-w
30.
Zhao J Fan Y Yang M Liang X Wu J Chen Y et al . Association between augmented renal clearance and inadequate vancomycin pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic targets in Chinese adult patients: a prospective observational study. Antibiotics. (2022) 11:837. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11070837
31.
Udy AA Roberts JA Shorr AF Boots RJ Lipman J . Augmented renal clearance in septic and traumatized patients with normal plasma creatinine concentrations: identifying at-risk patients. Crit Care. (2013) 17:1–9. doi: 10.1186/cc12544
32.
Mikami R Hayakawa M Imai S Sugawara M Takekuma Y . Onset timing and duration of augmented renal clearance in a mixed intensive care unit. J Intensive Care. (2023) 11:13. doi: 10.1186/s40560-023-00660-9
33.
de Courson H Cane G d’Auzac A Barbieri A Derot S Carrie C et al . Augmented renal clearance: prevalence, risk factors and underlying mechanism in critically ill patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care. (2024) 42:1–7. doi: 10.1007/s12028-024-02144-6
34.
Hefny F Sambhi S Morris C Kung JY Stuart A Mahmoud SH . Drug dosing in critically ill adult patients with augmented renal clearance. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. (2022) 47:607–20. doi: 10.1007/s13318-022-00779-4
35.
Rey E Tréluyer J-M Pons G . Pharmacokinetic optimisation of benzodiazepine therapy for acute seizures: focus on delivery routes. Clin Pharmacokinet. (1999) 36:409–24. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199936060-00003
36.
Hoh BL Ko NU Amin-Hanjani S Chou SH-Y Cruz-Flores S Dangayach NS et al . 2023 guideline for the management of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2023) 54:e314–70. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000436
37.
Mahmoud SH Buxton J . Seizures and choice of antiepileptic drugs following subarachnoid hemorrhage: a review. Can J Neurol Sci. (2017) 44:643–53. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2017.206
38.
Bilbao-Meseguer I Barrasa H Asín-Prieto E Alarcia-Lacalle A Rodríguez-Gascón A Maynar J et al . Population pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam and dosing evaluation in critically ill patients with normal or augmented renal function. Pharmaceutics. (2021) 13:1690. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13101690
39.
Sime FB Roberts JA Jeffree RL Pandey S Adiraju S Livermore A et al . Population pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam in patients with traumatic brain injury and subarachnoid hemorrhage exhibiting augmented renal clearance. Clin Pharmacokinet. (2021) 60:655–64. doi: 10.1007/s40262-020-00979-8
40.
Spencer DD Jacobi J Juenke JM Fleck JD Kays MB . Steady-state pharmacokinetics of intravenous levetiracetam in neurocritical care patients. Pharmacotherapy. (2011) 31:934–41. doi: 10.1592/phco.31.10.934
41.
Jarvie D Mahmoud SH . Therapeutic drug monitoring of Levetiracetam in select populations. J Pharm Pharm Sci. (2018) 21:149s–76s. doi: 10.18433/jpps30081
42.
Drust A Luchtmann M Firsching R Troger U Martens-Lobenhoffer J Bode-Boger SM . Recurrent seizures in a levetiracetam-treated patient after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a matter of enhanced renal function?Epilepsy Behav. (2012) 23:394–5. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2011.12.016
43.
He Z Li J . The therapeutic effects of lacosamide on epilepsy-associated comorbidities. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1063703. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1063703
44.
Curia G Biagini G Perucca E Avoli M . Lacosamide: a new approach to target voltage-gated sodium currents in epileptic disorders. CNS Drugs. (2009) 23:555–68. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200923070-00002
45.
Cawello W Fuhr U Hering U Maatouk H Halabi A . Impact of impaired renal function on the pharmacokinetics of the antiepileptic drug lacosamide. Clin Pharmacokinet. (2013) 52:897–906. doi: 10.1007/s40262-013-0080-7
46.
Iwasaki T Kobayashi T Miyamoto Y Imaizumi T Kaku S Udagawa N et al . Efficacy and blood levels of Lacosamide in patients with focal epilepsy. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:6958. doi: 10.3390/jcm13226958
47.
Schultz L Mahmoud SH . Is therapeutic drug monitoring of lacosamide needed in patients with seizures and epilepsy?Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. (2020) 45:315–49. doi: 10.1007/s13318-019-00601-8
48.
Beydoun A Uthman BM Sackellares JC . Gabapentin: pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and safety. Clin Neuropharmacol. (1995) 18:469–81. doi: 10.1097/00002826-199512000-00001
49.
Toth C . Pregabalin: latest safety evidence and clinical implications for the management of neuropathic pain. Therap Adv Drug Safety. (2014) 5:38–56. doi: 10.1177/2042098613505614
50.
Blum RA Comstock TJ Sica DA Schultz RW Keller E Reetze P et al . Pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in subjects with various degrees of renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther. (1994) 56:154–9. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1994.118
51.
Carlsson KC van de Schootbrugge M Eriksen HO Moberg ER Karlsson MO Hoem NO . A population pharmacokinetic model of gabapentin developed in nonparametric adaptive grid and nonlinear mixed effects modeling. Ther Drug Monit. (2009) 31:86–94. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0b013e318194767d
52.
Chew M Ma G Xie R Bockbrader H Chapel S Marshall S . Population pharmacokinetics of pregabalin extended-release in healthy volunteers and patients with postherpetic neuralgia, fibromyalgia, and partial-onset seizures. J Clin Pharmacol. (2019) 59:1527–42. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1450
53.
Shoji S Suzuki M Tomono Y Bockbrader HN Matsui S . Population pharmacokinetics of pregabalin in healthy subjects and patients with post-herpetic neuralgia or diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. (2011) 72:63–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.03932.x
54.
Bockbrader HN Burger P Knapp L Corrigan BW . Population pharmacokinetics of pregabalin in healthy subjects and patients with chronic pain or partial seizures. Epilepsia. (2011) 52:248–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02933.x
55.
Manitpisitkul P Curtin CR Shalayda K Wang S-S Ford L Heald DL . Pharmacokinetics of topiramate in patients with renal impairment, end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis, or hepatic impairment. Epilepsy Res. (2014) 108:891–901. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2014.03.011
56.
Cross AL Viswanath O Sherman AL . Pregabalin. Internet: StatPearls Publishing (2024).
57.
Bae E-K Lee J Shin J-W Moon J Lee K-J Shin Y-W et al . Factors influencing topiramate clearance in adult patients with epilepsy: a population pharmacokinetic analysis. Seizure. (2016) 37:8–12. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2016.02.002
58.
Frontera JA Fernandez A Schmidt JM Claassen J Wartenberg KE Badjatia N et al . Impact of nosocomial infectious complications after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. (2008) 62:80–7. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000311064.18368.ea
59.
Laborde G Grosskopf U Schmieder K Harders A Klimek L Hardenack M et al . Nosocomial infections in a neurosurgical intensive care unit. Anaesthesist. (1993) 42:724–31.
60.
Stone PW Glied SA McNair PD Matthes N Cohen B Landers TF et al . CMS changes in reimbursement for HAIs: setting a research agenda. Med Care. (2010) 48:433–9. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e3181d5fb3f
61.
Eyler RF Shvets K . Clinical pharmacology of antibiotics. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2019) 14:1080–90. doi: 10.2215/CJN.08140718
62.
Fielding-Singh V Iwashyna TJ Bhattacharya J Escobar GJ . Reply: the timing of early antibiotics and hospital mortality in Sepsis: playing devil's advocate. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2017) 196:935–6. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201704-0774LE
63.
Harrison MP Haworth SJ Moss SR Wilkinson DM Featherstone A . The disposition and metabolic fate of 14C-meropenem in man. Xenobiotica. (1993) 23:1311–23. doi: 10.3109/00498259309059441
64.
Vandecasteele SJ De Vriese AS . Recent changes in vancomycin use in renal failure. Kidney Int. (2010) 77:760–4. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.35
65.
Nagarajan R . Antibacterial activities and modes of action of vancomycin and related glycopeptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (1991) 35:605–9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.35.4.605
66.
Rybak MJ Lomaestro BM Rotschafer JC Moellering RC Craig WA Billeter M et al . Vancomycin therapeutic guidelines: a summary of consensus recommendations from the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Clin Infect Dis. (2009) 49:325–7. doi: 10.1086/600877
67.
Tesfamariam NS Aboelezz A Mahmoud SH . The impact of augmented renal clearance on vancomycin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in critically ill patients. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:317. doi: 10.3390/jcm13082317
68.
Yu YX Lu J Lu HD Li L Li JJ Shi L et al . Predictive performance of reported vancomycin population pharmacokinetic model in patients with different renal function status, especially those with augmented renal clearance. Eur J Hosp Pharm. (2022) 29:e6–e14. doi: 10.1136/ejhpharm-2020-002477
69.
Hirai K Ishii H Shimoshikiryo T Shimomura T Tsuji D Inoue K et al . Augmented renal clearance in patients with febrile neutropenia is associated with increased risk for subtherapeutic concentrations of vancomycin. Ther Drug Monit. (2016) 38:706–10. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000346
70.
Sahraei Z Saffaei A Alavi Darazam I Salamzadeh J Shabani M Shokouhi S et al . Evaluation of vancomycin pharmacokinetics in patients with augmented renal clearances: a randomized clinical trial. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:1041152. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1041152
71.
Holmes B Richards DM Brogden RN Heel RC . Piperacillin. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. (1984) 28:375–425. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198428050-00002
72.
Jacobs A Taccone FS Roberts JA Jacobs F Cotton F Wolff F et al . Beta-lactam dosage regimens in septic patients with augmented renal clearance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2018) 62:e02534–17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02534-17
73.
Carrie C Legeron R Petit L Ollivier J Cottenceau V d'Houdain N et al . Higher than standard dosing regimen are needed to achieve optimal antibiotic exposure in critically ill patients with augmented renal clearance receiving piperacillin-tazobactam administered by continuous infusion. J Crit Care. (2018) 48:66–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2018.08.026
74.
Hurst M Lamb HM . Meropenem: a review of its use in patients in intensive care. Drugs. (2000) 59:653–80. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200059030-00016
75.
Scharf C Paal M Schroeder I Vogeser M Draenert R Irlbeck M et al . Therapeutic drug monitoring of meropenem and piperacillin in critical illness-experience and recommendations from one year in routine clinical practice. Antibiotics. (2020) 9:31. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9030131
76.
Sjovall F Alobaid AS Wallis SC Perner A Lipman J Roberts JA . Maximally effective dosing regimens of meropenem in patients with septic shock. J Antimicrob Chemother. (2018) 73:191–8. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx330
77.
Casu GS Hites M Jacobs F Cotton F Wolff F Beumier M et al . Can changes in renal function predict variations in beta-lactam concentrations in septic patients?Int J Antimicrob Agents. (2013) 42:422–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2013.06.021
78.
Medzhitov R . Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature. (2008) 454:428–35. doi: 10.1038/nature07201
79.
Chen L Deng H Cui H Fang J Zuo Z Deng J et al . Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget. (2018) 9:7204–18. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23208
80.
Ransohoff RM Brown MA . Innate immunity in the central nervous system. J Clin Invest. (2012) 122:1164–71. doi: 10.1172/JCI58644
81.
Bjerkne Wenneberg S Odenstedt Herges H Svedin P Mallard C Karlsson T Adiels M et al . Association between inflammatory response and outcome after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Acta Neurol Scand. (2021) 143:195–205. doi: 10.1111/ane.13353
82.
Simon DW McGeachy MJ Bayir H Clark RSB Loane DJ Kochanek PM . The far-reaching scope of neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury. Nat Rev Neurol. (2017) 13:572. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2017.13
83.
Anttila JE Whitaker KW Wires ES Harvey BK Airavaara M . Role of microglia in ischemic focal stroke and recovery: focus on toll-like receptors. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2017) 79:3–14. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2016.07.003
84.
Irisa K Shichita T . Neural repair mechanisms after ischemic stroke. Inflamm Regen. (2025) 45:7. doi: 10.1186/s41232-025-00372-7
85.
Wang J . Preclinical and clinical research on inflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. Prog Neurobiol. (2010) 92:463–77. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.08.001
86.
Khey KMW Huard A Mahmoud SH . Inflammatory pathways following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cell Mol Neurobiol. (2020) 40:675–93. doi: 10.1007/s10571-019-00767-4
87.
Hanafy KA . The role of microglia and the TLR4 pathway in neuronal apoptosis and vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neuroinflammation. (2013) 10:83. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-10-83
88.
Fassbender K Hodapp B Rossol S Bertsch T Schmeck J Schutt S et al . Inflammatory cytokines in subarachnoid haemorrhage: association with abnormal blood flow velocities in basal cerebral arteries. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2001) 70:534–7. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.70.4.534
89.
Allan SM Rothwell NJ . Cytokines and acute neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2001) 2:734–44. doi: 10.1038/35094583
90.
Bramlett HM Dietrich WD . Long-term consequences of traumatic brain injury: current status of potential mechanisms of injury and neurological outcomes. J Neurotrauma. (2015) 32:1834–48. doi: 10.1089/neu.2014.3352
91.
Morgan ET . Impact of infectious and inflammatory disease on cytochrome P450-mediated drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. (2009) 85:434–8. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2008.302
92.
Renton KW . Alteration of drug biotransformation and elimination during infection and inflammation. Pharmacol Ther. (2001) 92:147–63. doi: 10.1016/S0163-7258(01)00165-6
93.
Abdallah YEH Chahal S Jamali F Mahmoud SH . Drug-disease interaction: clinical consequences of inflammation on drugs action and disposition. J Pharm Pharm Sci. (2023) 26:11137. doi: 10.3389/jpps.2023.11137
94.
Hanafy S El-Kadi AO Jamali F . Effect of inflammation on molecular targets and drug transporters. J Pharm Pharm Sci. (2012) 15:361–75. doi: 10.18433/j30300
95.
Mahmoud SH Hefny F Isse FA Farooq S Ling S O'Kelly C et al . Nimodipine systemic exposure and outcomes following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a pilot prospective observational study (ASH-1 study). Front Neurol. (2024) 14:1233267. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1233267
96.
Zhang L Liu XD Xie L Wang GJ . P-glycoprotein restricted transport of nimodipine across blood-brain barrier. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2003) 24:903–6.
97.
Mahmoud SH Ji X Isse FA . Nimodipine pharmacokinetic variability in various patient populations. Drugs R D. (2020) 20:307–18. doi: 10.1007/s40268-020-00322-3
98.
Chen S Xu P Fang Y Lenahan C . The updated role of the blood brain barrier in subarachnoid hemorrhage: from basic and clinical studies. Curr Neuropharmacol. (2020) 18:1266–78. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200914161231
99.
Kumar P McBride DW Dash PK Matsumura K Rubi A Blackburn SL . Endothelial cell dysfunction and injury in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mol Neurobiol. (2019) 56:1992–2006. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1213-7
100.
Haruwaka K Ikegami A Tachibana Y Ohno N Konishi H Hashimoto A et al . Dual microglia effects on blood brain barrier permeability induced by systemic inflammation. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:5816. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13812-z
101.
Thurgur H Pinteaux E . Microglia in the neurovascular unit: blood–brain barrier–microglia interactions after central nervous system disorders. Neuroscience. (2019) 405:55–67. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.06.046
102.
Russell JA Walley KR Singer J Gordon AC Hebert PC Cooper DJ et al . Vasopressin versus norepinephrine infusion in patients with septic shock. N Engl J Med. (2008) 358:877–87. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa067373
103.
Hannon MJ Behan LA O'Brien MM Tormey W Ball SG Javadpour M et al . Hyponatremia following mild/moderate subarachnoid hemorrhage is due to SIAD and glucocorticoid deficiency and not cerebral salt wasting. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2014) 99:291–8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3032
104.
Mather HM Ang V Jenkins JS . Vasopressin in plasma and CSF of patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (1981) 44:216–9. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.3.216
105.
Kranawetter B Brockmöller J Sindern J Hapke A Bruns E Harnisch L-O et al . Intestinal drug absorption after subarachnoid hemorrhage and elective neurosurgery: insights from esomeprazole pharmacokinetics. Crit Care Med. (2025) 53:e140–50. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000006512
106.
Soppi V Kokki H Koivisto T Lehtonen M Helin-Tanninen M Lehtola S et al . Early-phase pharmacokinetics of enteral and parenteral nimodipine in patients with acute subarachnoid haemorrhage–a pilot study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (2007) 63:355–61. doi: 10.1007/s00228-007-0267-7
107.
Abboud T Andresen H Koeppen J Czorlich P Duehrsen L Stenzig J et al . Serum levels of nimodipine in enteral and parenteral administration in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir. (2015) 157:763–7. doi: 10.1007/s00701-015-2369-9
108.
Mahmoud SH Hefny FR Panos NG Delucilla L Ngan Z Perreault MM et al . Comparison of nimodipine formulations and administration techniques via enteral feeding tubes in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. Pharmacotherapy. (2023) 43:279–90. doi: 10.1002/phar.2791
109.
Romac DR Albertson TE . Drug interactions in the intensive care unit. Clin Chest Med. (1999) 20:385–99. doi: 10.1016/S0272-5231(05)70148-9
110.
Sun L Mi K Hou Y Hui T Zhang L Tao Y et al . Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic drug–drug interactions: research methods and applications. Meta. (2023) 13:897. doi: 10.3390/metabo13080897
111.
Papadopoulos J Smithburger PL . Common drug interactions leading to adverse drug events in the intensive care unit: management and pharmacokinetic considerations. Crit Care Med. (2010) 38:S126–S35. doi: 10.1097/ccm.0b013e3181de0acf
112.
Baciewicz AM . Carbamazepine drug interactions. Ther Drug Monit. (1986) 8:305–17. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198609000-00012
113.
Brüggemann RJ Alffenaar J-WC Blijlevens NM Billaud EM Kosterink JG Verweij PE et al . Clinical relevance of the pharmacokinetic interactions of azole antifungal drugs with other coadministered agents. Clin Infect Dis. (2009) 48:1441–58. doi: 10.1086/598327
114.
McKeever RG Patel P Hamilton RJ . Calcium channel blockers. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing (2024).
115.
Shirasaka Y Sager JE Lutz JD Davis C Isoherranen N . Inhibition of CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 by omeprazole metabolites and their contribution to drug-drug interactions. Drug Metab Dispos. (2013) 41:1414–24. doi: 10.1124/dmd.113.051722
116.
Heldt T Loss SH . Drug-nutrient interactions in the intensive care unit: literature review and current recommendations. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. (2013) 25:162–7. doi: 10.5935/0103-507X.20130028
117.
Johansson O Wahlin-Boll E Lindberg T Melander A . Opposite effects of carbohydrate and protein on phenytoin absorption in man. Drug Nutr Interact. (1983) 2:139–44. PMID:
118.
Asadi-Pooya AA Johannessen Landmark C Mirzaei Damabi N Fazelian K . Interactions between antiseizure medications and foods and drinks: a systematic review. Epilepsia Open. (2024) 9:475–85. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12918
119.
Ozuna J Friel P . Effect of enteral tube feeding on serum phenytoin levels. J Neurosci Nurs. (1984) 16:289–91. doi: 10.1097/01376517-198412000-00002
120.
Pitman SK Hoang UT Wi CH Alsheikh M Hiner DA Percival KM . Revisiting oral fluoroquinolone and multivalent cation drug-drug interactions: are they still relevant?Antibiotics. (2019) 8:108. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8030108
121.
Radkowski P Derkaczew M Mazuchowski M Moussa A Podhorodecka K Dawidowska-Fidrych J et al . Antibiotic–drug interactions in the intensive care unit: a literature review. Antibiotics. (2024) 13:503. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13060503
122.
Mirtallo JM . Drug–Nutrient Interactions in Patients Receiving Parenteral Nutrition. In: Boullata, J., Armenti, V. (eds) Handbook of Drug-Nutrient Interactions. Nutrition and Health. Humana Press. (2010). doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-362-6_14
123.
Bayer Pharmaceuticals . NIMOTOP (nimodipine) tablets for oral use monograph 2022. Available online at: https://www.bayer.com/sites/default/files/2020-11/nimotop-tab-pm-en.pdf (Accessed March 15, 2025).
124.
Isse FA Abdallah YEH Mahmoud SH . The impact of nimodipine administration through feeding tube on outcomes in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Pharm Pharm Sci. (2020) 23:100–8. doi: 10.18433/jpps30960
125.
Forsberg J Bedard E Mahmoud SH . Bioavailability of orally administered drugs in critically ill patients. J Pharm Pract. (2023) 36:967–79. doi: 10.1177/08971900221100205
126.
Bauer PR Ostermann M Russell L Robba C David S Ferreyro BL et al . Plasma exchange in the intensive care unit: a narrative review. Intensive Care Med. (2022) 48:1382–96. doi: 10.1007/s00134-022-06793-z
127.
Mahmoud SH Buhler J Chu E Chen SA Human T . Drug dosing in patients undergoing therapeutic plasma exchange. Neurocrit Care. (2021) 34:301–11. doi: 10.1007/s12028-020-00989-1
128.
Fauvelle F Petitjean O Tod M Guillevin L . Clinical pharmacokinetics during plasma exchange. Therapie. (2000) 55:269–75.
129.
Ibrahim RB Balogun RA . Medications in patients treated with therapeutic plasma exchange: prescription dosage, timing, and drug overdose. Semin Dial. (2012) 25:176–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-139x.2011.01030.x
130.
Cheng CW Hendrickson JE Tormey CA Sidhu D . Therapeutic plasma exchange and its impact on drug levels: an ACLPS critical review. Am J Clin Pathol. (2017) 148:190–8. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqx056
131.
Shelat SG . Practical considerations for planning a therapeutic apheresis procedure. Am J Med. (2010) 123:777–84. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2010.01.022
132.
Ramírez-Guerrero G Baghetti-Hernández R Ronco C . Acute kidney injury at the neurocritical care unit. Neurocrit Care. (2022) 36:640–9. doi: 10.1007/s12028-021-01345-7
133.
Goyal A Daneshpajouhnejad P Hashmi MF Bashir K . Acute kidney injury. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls (2017).
134.
Patel P Nandwani V McCarthy PJ Conrad SA Keith SL . Continuous renal replacement therapies: a brief primer for the neurointensivist. Neurocrit Care. (2010) 13:286–94. doi: 10.1007/s12028-010-9386-6
135.
Ronco C . Continuous dialysis is superior to intermittent dialysis in acute kidney injury of the critically ill patient. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. (2007) 3:118–9. doi: 10.1038/ncpneph0423
136.
Diringer M . Neurologic manifestations of major electrolyte abnormalities. Handb Clinic Neurol. (2017) 141:705–13. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-444-63599-0.00038-7
137.
Ronco C Bellomo R Ricci Z . Continuous renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2001) 16:67–72. doi: 10.1093/ndt/16.suppl_5.67
138.
Cullis B Abdelraheem M Abrahams G Balbi A Cruz DN Frishberg Y et al . Peritoneal dialysis for acute kidney injury. Perit Dial Int. (2014) 34:494–517. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2013.00222
139.
Kanji S Roger C Taccone FS Muller L . Practical considerations for individualizing drug dosing in critically ill adults receiving renal replacement therapy. Pharmacotherapy. (2023) 43:1194–205. doi: 10.1002/phar.2858
140.
Baeg SI Lee K Jeon J Jang HR . Management for electrolytes disturbances during continuous renal replacement therapy. Electr Blood Pressure. (2022) 20:64–75. doi: 10.5049/EBP.2022.20.2.64
141.
Saunders H Rehan A Hashmi MF Sanghavi DK . Continuous renal replacement therapy. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing (2024).
142.
Morsch CMF Haas JS Plotnick R Cavalcanti TC Cardoso PC Pilger T et al . Hypothermia related to continuous renal replacement therapy: incidence and associated factors. Rev Brasil Terapia Intens. (2005) 33:111–8. doi: 10.5935/0103-507x.20210012
143.
Bouajram RH Awdishu L . A clinician’s guide to dosing analgesics, anticonvulsants, and psychotropic medications in continuous renal replacement therapy. Kidney Int Rep. (2021) 6:2033–48. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.05.004
144.
Böhler J Donauer J Keller F . Pharmacokinetic principles during continuous renal replacement therapy: drugs and dosage. Kidney Int. (1999) 56:S24–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.56.s.72.2.x
145.
Jang SM Infante S Abdi Pour A . Drug dosing considerations in critically ill patients receiving continuous renal replacement therapy. Pharmacy. (2020) 8:18. doi: 10.3390/pharmacy8010018
146.
Pistolesi V Morabito S Di Mario F Regolisti G Cantarelli C Fiaccadori E . A guide to understanding antimicrobial drug dosing in critically ill patients on renal replacement therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2019) 63:19. doi: 10.1128/aac.00583-19
147.
Mahmoud SH . Antiepileptic drug removal by continuous renal replacement therapy: a review of the literature. Clin Drug Investig. (2017) 37:7–23. doi: 10.1007/s40261-016-0457-0
148.
Bhandari B Komanduri S . Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL) (2020).
149.
Sitprija V Holmes J . Preliminary observations on the change in intracranial pressure and intraocular pressure during hemodialysis. ASAIO J. (1962) 8:300–8. doi: 10.1097/00002480-196204000-00061
150.
Callaway CW . Targeted temperature management with hypothermia for comatose patients after cardiac arrest. Clin Exp Emerg Med. (2023) 10:5–17. doi: 10.15441/ceem.23.012
151.
Hypothermia after Cardiac Arrest Study G . Mild therapeutic hypothermia to improve the neurologic outcome after cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med. (2002) 346:549–56. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa012689
152.
Schwab S Schwarz S Spranger M Keller E Bertram M Hacke W . Moderate hypothermia in the treatment of patients with severe middle cerebral artery infarction. Stroke. (1998) 29:2461–6. doi: 10.1161/01.str.29.12.2461
153.
McIntyre LA Fergusson DA Hebert PC Moher D Hutchison JS . Prolonged therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic brain injury in adults: a systematic review. JAMA. (2003) 289:2992–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.22.2992
154.
Karnatovskaia LV Wartenberg KE Freeman WD . Therapeutic hypothermia for neuroprotection: history, mechanisms, risks, and clinical applications. Neurohospitalist. (2014) 4:153–63. doi: 10.1177/1941874413519802
155.
Moore EM Nichol AD Bernard SA Bellomo R . Therapeutic hypothermia: benefits, mechanisms and potential clinical applications in neurological, cardiac and kidney injury. Injury. (2011) 42:843–54. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2011.03.027
156.
Andrews PJ Sinclair HL Rodriguez A Harris BA Battison CG Rhodes JK et al . Hypothermia for intracranial hypertension after traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:2403–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1507581
157.
Dankiewicz J Cronberg T Lilja G Jakobsen JC Levin H Ullen S et al . Hypothermia versus Normothermia after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:2283–94. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2100591
158.
van den Broek MP Groenendaal F Egberts AC Rademaker CM . Effects of hypothermia on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: a systematic review of preclinical and clinical studies. Clin Pharmacokinet. (2010) 49:277–94. doi: 10.2165/11319360-000000000-00000
159.
Iida Y Nishi S Asada A . Effect of mild therapeutic hypothermia on phenytoin pharmacokinetics. Ther Drug Monit. (2001) 23:192–7. doi: 10.1097/00007691-200106000-00002
160.
Schaible DH Cupit GC Swedlow DB Rocci ML . High-dose pentobarbital pharmacokinetics in hypothermic brain-injured children. J Pediatr. (1982) 100:655–60. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80780-4
161.
Bansinath M Turndorf H Puig MM . Influence of hypo and hyperthermia on disposition of morphine. J Clin Pharmacol. (1988) 28:860–4. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1988.tb03229.x
162.
Hostler D Zhou J Tortorici MA Bies RR Rittenberger JC Empey PE et al . Mild hypothermia alters midazolam pharmacokinetics in normal healthy volunteers. Drug Metab Dispos. (2010) 38:781–8. doi: 10.1124/dmd.109.031377
163.
Svensen CH Rodhe PM Prough DS . Pharmacokinetic aspects of fluid therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. (2009) 23:213–24. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2008.11.003
164.
Veiga RP Paiva JA . Pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics issues relevant for the clinical use of beta-lactam antibiotics in critically ill patients. Crit Care. (2018) 22:233. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2155-1
165.
Birks J López-Arrieta J Dementia C Group CI . Nimodipine for primary degenerative, mixed and vascular dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (1996) 2010:CD000147. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000147
166.
Wessell A Kole MJ Badjatia N Parikh G Albrecht JS Schreibman DL et al . High compliance with scheduled nimodipine is associated with better outcome in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients cotreated with heparin infusion. Front Neurol. (2017) 8:268. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00268
167.
Treggiari MM Rabinstein AA Busl KM Caylor MM Citerio G Deem S et al . Guidelines for the neurocritical care management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care. (2023) 39:1–28. doi: 10.1007/s12028-023-01713-5
168.
Kumana C Kou M Yu Y Fong K Fung C Chang C et al . Investigation of nimodipine pharmacokinetics in Chinese patients with acute subarachnoid haemorrhage. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (1993) 45:363–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00265956
169.
Bradshaw MJ Venkatesan A . Herpes simplex Virus-1 encephalitis in adults: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Neurotherapeutics. (2016) 13:493–508. doi: 10.1007/s13311-016-0433-7
170.
Hartley L Evans J MacDermott NE . Management and outcome in viral meningo-encephalitis. Paediatr Child Health. (2011) 21:488–94. doi: 10.1016/j.paed.2011.07.007
171.
Davis LE . Diagnosis and treatment of acute encephalitis. Neurologist. (2000) 6:145–59. doi: 10.1097/00127893-200006030-00001
172.
Gleadle J Dixon C Brown MM Schon F . The use of acyclovir in suspected encephalitis. J R Soc Med. (1994) 87:7–8. doi: 10.1177/014107689408700105
173.
Defres S Navvuga P Hardwick H Easton A Michael BD Kneen R et al . Health economic impact of early versus delayed treatment of herpes simplex virus encephalitis in the UK. medRxiv. (2024). doi: 10.1101/2024.02.14.24302706
174.
Tunkel AR Glaser CA Bloch KC Sejvar JJ Marra CM Roos KL et al . The management of encephalitis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. (2008) 47:303–27. doi: 10.1086/589747
175.
Lexicomp Acyclovir (systemic) (Lexi-drugs) - Lexicomp Available online at: https://online.lexi.com/lco/action/doc/retrieve/docid/patch_f/1763800?cesid=1GYbi0RBBcN&searchUrl=%2Flco%2Faction%2Fsearch%3Fq%3Dacyclovir%26t%3Dname%26acs%3Dtrue%26acq%3Dacyclo (Accessed April 1, 2025).
176.
Schaeffer HJ Beauchamp L de Miranda P Elion GB Bauer DJ Collins P . 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine activity against viruses of the herpes group. Nature. (1978) 272:583–5. doi: 10.1038/272583a0
177.
Schaeffer HJ . Acyclovir chemistry and spectrum of activity. Am J Med. (1982) 73:4–6. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90054-7
178.
Balfour HH Jr . Acyclovir therapy for herpes zoster: advantages and adverse effects. JAMA. (1986) 255:387–8. doi: 10.1001/jama.1986.03370030107039
179.
Brandariz-Nunez D Correas-Sanahuja M Maya-Gallego S Martin Herranz I . Neurotoxicity associated with acyclovir and valacyclovir: a systematic review of cases. J Clin Pharm Ther. (2021) 46:918–26. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13464
180.
Aboelezz A Mahmoud SH . Acyclovir dosing in herpes encephalitis: a scoping review. J Am Pharm Assoc. (2024) 64:102040. doi: 10.1016/j.japh.2024.02.013
181.
Davis R Quenzer R Weller S Blum R Acyclovir pharmacokinetics in morbid obesity. Interscience conference on antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy; (1991).
182.
Wong A Pickering AJ Potoski BA . Dosing practices of intravenous acyclovir for herpes encephalitis in obesity: results of a pharmacist survey. J Pharm Pract. (2017) 30:324–8. doi: 10.1177/0897190016642689
183.
Schwartz SN Pazin GJ Lyon JA Ho M Pasculle AW . A controlled investigation of the pharmacokinetics of gentamicin and tobramycin in obese subjects. J Infect Dis. (1978) 138:499–505. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.499
184.
Aboelezz A Kharouba M Mahmoud SH . Acyclovir dosing strategies in herpes encephalitis: a retrospective charts review. J Clin Neurosci. (2025) 136:111230. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2025.111230
185.
Turner RB Cumpston A Sweet M Briggs F Slain D Wen S et al . Prospective, controlled study of acyclovir pharmacokinetics in obese patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2016) 60:1830–3. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02010-15
186.
Abdalla S Briand C Oualha M Bendavid M Beranger A Benaboud S et al . Population pharmacokinetics of intravenous and Oral acyclovir and Oral Valacyclovir in pediatric population to optimize dosing regimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2020) 64:20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01426-20
187.
Zhou S Skaar DJ Jacobson PA Huang RS . Pharmacogenomics of medications commonly used in the intensive care unit. Front Pharmacol. (2018) 9:1436. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01436
188.
Khera AV Chaffin M Aragam KG Haas ME Roselli C Choi SH et al . Genome-wide polygenic scores for common diseases identify individuals with risk equivalent to monogenic mutations. Nat Genet. (2018) 50:1219–24. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0183-z
189.
Zhao M Ma J Li M Zhang Y Jiang B Zhao X et al . Cytochrome P450 enzymes and drug metabolism in humans. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:808. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312808
190.
Hulot JS Collet JP Cayla G Silvain J Allanic F Bellemain-Appaix A et al . CYP2C19 but not PON1 genetic variants influence clopidogrel pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and clinical efficacy in post-myocardial infarction patients. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. (2011) 4:422–8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.111.963025
191.
Cavallari LH Lee CR Beitelshees AL Cooper-DeHoff RM Duarte JD Voora D et al . Multisite investigation of outcomes with implementation of CYP2C19 genotype-guided antiplatelet therapy after percutaneous coronary intervention. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2018) 11:181–91. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2017.07.022
192.
Hassouneh B Centofanti JE Reddy K . Pain management in post-craniotomy patients: a survey of Canadian neurosurgeons. Can J Neurol Sci. (2011) 38:456–60. doi: 10.1017/S0317167100011872
193.
Dean L Kane M . Codeine therapy and CYP2D6 genotype In: PrattVMScottSAPirmohamedMEsquivelBKattmanBLMalheiroAJ, editors. Medical genetics summaries. National Center of Biotechnology Information (US), Bethesda, MD: (2012)
194.
Kuehl P Zhang J Lin Y Lamba J Assem M Schuetz J et al . Sequence diversity in CYP3A promoters and characterization of the genetic basis of polymorphic CYP3A5 expression. Nat Genet. (2001) 27:383–91. doi: 10.1038/86882
195.
Voora D Shah SH Spasojevic I Ali S Reed CR Salisbury BA et al . The SLCO1B1*5 genetic variant is associated with statin-induced side effects. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2009) 54:1609–16. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.053
196.
He H Yin JY Xu YJ Li X Zhang Y Liu ZG et al . Association of ABCB1 polymorphisms with the efficacy of ondansetron in chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Clin Ther. (2014) 36:1242–1252.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.06.016
197.
Lee CR Goldstein JA Pieper JA . Cytochrome P450 2C9 polymorphisms: a comprehensive review of the in-vitro and human data. Pharmacogenetics. (2002) 12:251–63. doi: 10.1097/00008571-200204000-00010
198.
Limdi NA Wadelius M Cavallari L Eriksson N Crawford DC Lee MT et al . Warfarin pharmacogenetics: a single VKORC1 polymorphism is predictive of dose across 3 racial groups. Blood. (2010) 115:3827–34. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-12-255992
199.
Chung WH Chang WC Lee YS Wu YY Yang CH Ho HC et al . Genetic variants associated with phenytoin-related severe cutaneous adverse reactions. JAMA. (2014) 312:525–34. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.7859
200.
Grover S Kukreti R . HLA alleles and hypersensitivity to carbamazepine: an updated systematic review with meta-analysis. Pharmacogenet Genomics. (2014) 24:94–112. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0000000000000021
201.
Yang L Li Y Hong H Chang CW Guo LW Lyn-Cook B et al . Sex differences in the expression of drug-metabolizing and transporter genes in Human liver. J Drug Metab Toxicol. (2012) 3:1000119. doi: 10.4172/2157-7609.1000119
202.
Peacock SH James C Turnbull MT Cowart JB Reid JM Freeman WD . Pharmacogenomics of cytochrome P450 of Nimodipine metabolism after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosci Nurs. (2019) 51:238–42. doi: 10.1097/JNN.0000000000000464
203.
Lu Y Cederbaum AI . CYP2E1 and oxidative liver injury by alcohol. Free Radic Biol Med. (2008) 44:723–38. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.11.004
204.
Sinclair JF Szakacs JG Wood SG Walton HS Bement JL Gonzalez FJ et al . Short-term treatment with alcohols causes hepatic steatosis and enhances acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in Cyp2e1(−/−) mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (2000) 168:114–22. doi: 10.1006/taap.2000.9023
205.
Wheless JW Richardson B Rubinos C Faught E Vuong M . Dysphagia in epilepsy patients: the silent enemy. Neurol Clin Pract. (2025) 15:e200362. doi: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000200362
206.
Zhou W Nightingale C Davis G Nicolau D . Absolute bioavailability of fluconazole suspension in intensive care unit patients. Journal of Infectious Disease Pharmacotherapy. (2001) 5:27–35.
207.
Barquist ES Gomez-Fein E Block EF Collin G Alzamel H Martinez O . Bioavailability of oral fluconazole in critically ill abdominal trauma patients with and without abdominal wall closure: a randomized crossover clinical trial. J Trauma Injury Infect Crit Care. (2007) 63:159–63. doi: 10.1097/01.ta.0000232011.59630.93
208.
Sukumar S Cabero M Tiu S Fang MC Kogan SC Schwartz JB . Anti–factor Xa activity assays of direct-acting oral anticoagulants during clinical care: an observational study. Res Pract Thrombosis Haemost. (2021) 5:e12528. doi: 10.1002/rth2.12528
209.
Maynard GA Jones KM Guidry JR . Phenytoin absorption from tube feedings. Arch Intern Med. (1987) 147:1821.
210.
Markowsky SJ Skaar DJ Christie JM Eyer SD Ehresman DJ . Phenytoin protein binding and dosage requirements during acute and convalescent phases following brain injury. Ann Pharmacother. (1996) 30:443–8. doi: 10.1177/106002809603000501
211.
Idasiak-Piechocka I Lewandowski D Świgut W Kalinowski J Mikosza K Suchowiejski P et al . Effect of hypoalbuminemia on drug pharmacokinetics. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1546465. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1546465
212.
Brar T Mahmoud SH . Role of free Valproic acid levels in a patient with severe hypoalbuminemia: a case report. Can J Hosp Pharm. (2022) 75:239–42. doi: 10.4212/cjhp.3179
213.
Kawai M Harada M Motoike Y Koshikawa M Ichikawa T Watanabe E et al . Impact of serum albumin levels on supratherapeutic PT-INR control and bleeding risk in atrial fibrillation patients on warfarin: a prospective cohort study. IJC Heart Vasc. (2019) 22:111–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2019.01.002
214.
Sime FB Roberts MS Tiong IS Gardner JH Lehman S Peake SL et al . Adequacy of high-dose cefepime regimen in febrile neutropenic patients with hematological malignancies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2015) 59:5463–9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00389-15
215.
Levy RH . Cytochrome P450 isozymes and antiepileptic drug interactions. Epilepsia. (1995) 36:S8–S13. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1995.tb06007.x
216.
Gunes A Bilir E Zengil H Babaoglu MO Bozkurt A Yasar U . Inhibitory effect of valproic acid on cytochrome P450 2C9 activity in epilepsy patients. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. (2007) 100:383–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2007.00061.x
217.
Shah RR Smith RL . Inflammation-induced phenoconversion of polymorphic drug metabolizing enzymes: hypothesis with implications for personalized medicine. Drug Metab Dispos. (2015) 43:400–10. doi: 10.1124/dmd.114.061093
218.
Shaikh SA Regal RE . Dosing of enoxaparin in renal impairment. Pharm Ther. (2017) 42:245.
219.
Chappell K Kimmons LA Haller JT Canada RB He H Hudson JQ . Levetiracetam pharmacokinetics in critically ill patients undergoing renal replacement therapy. J Crit Care. (2021) 61:216–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2020.10.032
220.
Claisse G Zufferey PJ Trone JC Maillard N Delavenne X Laporte S et al . Predicting the dose of vancomycin in ICU patients receiving different types of RRT therapy: a model-based meta-analytic approach. Br J Clin Pharmacol. (2019) 85:1215–26. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13904
221.
Chaijamorn W Charoensareerat T Srisawat N Pattharachayakul S Boonpeng A . Cefepime dosing regimens in critically ill patients receiving continuous renal replacement therapy: a Monte Carlo simulation study. J Intensive Care. (2018) 6:1–11. doi: 10.1186/s40560-018-0330-8
222.
Zhou J Poloyac SM . The effect of therapeutic hypothermia on drug metabolism and response: cellular mechanisms to organ function. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. (2011) 7:803–16. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2011.574127
223.
Empey PE De Mendizabal NV Bell MJ Bies RR Anderson KB Kochanek PM et al . Therapeutic hypothermia decreases phenytoin elimination in children with traumatic brain injury. Crit Care Med. (2013) 41:2379–87. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318292316c
224.
Kang Y Jamison K Jaywant A Dams-O’Connor K Kim N Karakatsanis NA et al . Longitudinal alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAA) receptor availability over∼ 1 year following traumatic brain injury. Brain Commun. (2022) 4:fcac159. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac159
225.
Lee C-Y Perez FM Wang W Guan X Zhao X Fisher JL et al . Dynamic temporal and spatial regulation of mu opioid receptor expression in primary afferent neurons following spinal nerve injury. Eur J Pain. (2011) 15:669–75. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2010.11.018
226.
Goodkin HP Sun C Yeh JL Mangan PS Kapur J . GABAA receptor internalization during seizures. Epilepsia. (2007) 48:109–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01297.x
227.
Oh CY Bainbridge J . Lowering the seizure threshold associated with antidepressants, stimulants, antipsychotics, and others. Ment Health Clin. (2012) 2:127–8. doi: 10.9740/mhc.n127568
228.
Aitken AE Morgan ET . Gene-specific effects of inflammatory cytokines on cytochrome P450 2C, 2B6 and 3A4 mRNA levels in human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. (2007) 35:1687–93. doi: 10.1124/dmd.107.015511
229.
Morgan ET Goralski KB Piquette-Miller M Renton KW Robertson GR Chaluvadi MR et al . Regulation of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters in infection, inflammation, and cancer. Drug Metab Dispos. (2008) 36:205–16. doi: 10.1124/dmd.107.018747
230.
Dickmann LJ Patel SK Rock DA Wienkers LC Slatter JG . Effects of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and an anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibody on drug-metabolizing enzymes in human hepatocyte culture. Drug Metab Dispos. (2011) 39:1415–22. doi: 10.1124/dmd.111.038679
231.
Sunman JA Hawke RL LeCluyse EL Kashuba AD . Kupffer cell-mediated IL-2 suppression of CYP3A activity in human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. (2004) 32:359–63. doi: 10.1124/dmd.32.3.359
232.
Renton KW . Regulation of drug metabolism and disposition during inflammation and infection. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. (2005) 1:629–40. doi: 10.1517/17425255.1.4.629
233.
Khatsenko OG Gross SS Rifland AB Vane JR . Nitric oxide is a mediator of the decrease in cytochrome P450-dependent metabolism caused by immunostimulants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1993) 90:11147–51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11147
234.
Aitken AE Richardson TA Morgan ET . Regulation of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters in inflammation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2006) 46:123–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.46.120604.141059
235.
Ho RH Kim RB . Transporters and drug therapy: implications for drug disposition and disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. (2005) 78:260–77. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2005.05.011
236.
Hanafy S Dagenais NJ Dryden WF Jamali F . Effects of angiotensin II blockade on inflammation-induced alterations of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of calcium channel blockers. Br J Pharmacol. (2008) 153:90–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707538
Summary
Keywords
precision medicine, neurocritical care, pharmacotherapy, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics
Citation
Mahmoud SH, Kharouba M, Aboelezz A, Elshamy A and Gunn E (2025) Pharmacotherapy variability and precision medicine in neurocritical care. Front. Neurol. 16:1630163. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1630163
Received
17 May 2025
Accepted
24 June 2025
Published
18 July 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Cina Sasannejad, Duke University, United States
Reviewed by
Pedro Grille, Hospital Maciel, Uruguay
Esteban Zavaleta, Hospital Clinica Biblica, Costa Rica
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Mahmoud, Kharouba, Aboelezz, Elshamy and Gunn.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sherif Hanafy Mahmoud, smahmoud@ualberta.ca
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.