- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Western Theater General Hospital, Chengdu, China
- 2College of Medicine, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, China
- 3Department of Hyperbaric Oxygen Medicine, Western Theater General Hospital, Chengdu, China
Ferroptosis is a distinctive form of regulated cell death that is closely associated with various neurodegenerative disorders. In recent years, an increasing number of studies have demonstrated the crucial role of ferroptosis in the development and progression of epilepsy. Firstly, this article will review the existing research on the specific biological mechanism of ferroptosis in nerve injury, particularly in epilepsy, encompassing iron metabolism disorders and alterations in the expression of ferroptosis-related proteins. Secondly, with regards to treatment, this article will explore the application of ferroptosis inhibitors in antiepileptic therapy and their potential therapeutic effects. Additionally, it will focus on investigating the interaction between ferroptosis and existing antiepileptic drugs as well as the potential impact of strategies regulating ferroptosis on epilepsy treatment. Finally, we will evaluate both the progress made and limitations encountered in current research while proposing possible future directions for further exploration at the intersection of ferroptosis and epilepsy fields. These studies not only contribute to a better understanding of epileptic pathological mechanisms but also hold promise for providing novel insights and strategies for treating epilepsy.
1 Introduction
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures, which arise from aberrant and generalized electrical activity in the brain (1). Globally, epilepsy affects approximately 50 million individuals and has a prevalence of 0.5 to 1% among children, significantly impairing their quality of life. Epilepsy remains insufficiently understood by many, with certain social contexts stigmatizing it as “abnormal” or “defective.” Moreover, apart from the individual level impact, the resource-intensive nature of epilepsy treatment and necessary support services during rehabilitation substantially contribute to the social and economic burden (2). The etiology of epilepsy is intricate and diverse, encompassing genetic factors, brain injury, infection, and structural abnormalities of the central nervous system. However, despite significant advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy, approximately 30–40% of patients remain unresponsive to existing antiepileptic drugs (3). Consequently, there exists an urgent imperative to explore novel therapeutic targets and strategies.
Ferroptosis, characterized as an iron-dependent form of programmed cell death, represents a regulated mechanism of cellular demise triggered by iron-catalyzed lethal lipid damage. It significantly diverges from conventional pathways of cell death (such as apoptosis and autophagy) and was initially reported and elucidated by Dixon et al. (4, 5). The regulation of ferroptosis signaling pathways encompasses the control of iron homeostasis, RAS pathway, and cystine transport pathway. Dysregulation in these pathways can contribute to the occurrence of ferroptosis. Although the underlying mechanism remains elusive, ferroptosis exhibits several distinctive features: ① Alterations in cell morphology are prominent during ferroptosis, characterized by reduced mitochondrial size, increased membrane density, diminished or absent mitochondrial cristae, and potential disruption of the outer membrane. However, discernible changes in nuclear morphology are not observed (6). ② Metabolic perturbations: Enhanced lipid peroxidation leading to excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation represents a hallmark feature of ferroptosis. Concurrently, intracellular levels of ferric ions also accumulate (7). ③ Impaired glutathione peroxidase function: Deficiency in the membrane lipid repair enzyme glutathione peroxidase (GPX4) results in ROS buildup on membrane lipids (8). Although the specific regulatory networks governing these features remain elusive, ferroptosis primarily encompasses three factors: aberrant iron ion metabolism, depletion of REDOX glutathione (GSH)/ GPX4/ cystine-glutamate transporter system (System Xc−), and dysregulated lipid peroxidation (9, 10). In recent years, the involvement of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of various neurological disorders has garnered significant attention, encompassing traumatic brain injury, stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and brain tumors (11–16). Ferroptosis has also been implicated in epilepsy (17); however, its precise role and underlying mechanisms in epileptogenesis remain elusive. Elucidating the regulatory mechanisms governing iron-induced cell death in epilepsy could offer novel avenues for prevention and treatment strategies. This review article aims to comprehensively explore the mechanistic aspects of ferroptosis and its implications in epilepsy to provide valuable insights into potential therapeutic targets.
2 Biochemical features of ferroptosis
Ferroptosis is characterized by three core pathological processes: iron dysregulation, glutathione depletion, and lipid peroxidation.
2.1 Iron metabolism dyshomeostasis
Cellular iron homeostasis is maintained through transferrin (Tf)-mediated transport. Fe3+ binds to Tf forming holo-Tf, which undergoes endocytosis via TfR1 on brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs). After reduction to Fe2+ by STEAP3/DCYTB, iron enters the cytoplasm via DMT1, forming the labile iron pool (LIP). Excess Fe2+ catalyzes hydroxyl radical (•OH) generation through Fenton reactions, driving peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). Iron chelators (e.g., deferoxamine) and suppression of iron-regulatory genes (IREB2, TFRC) inhibit ferroptosis by reducing iron availability (18–25). The signaling mechanism is illustrated in Figure 1.
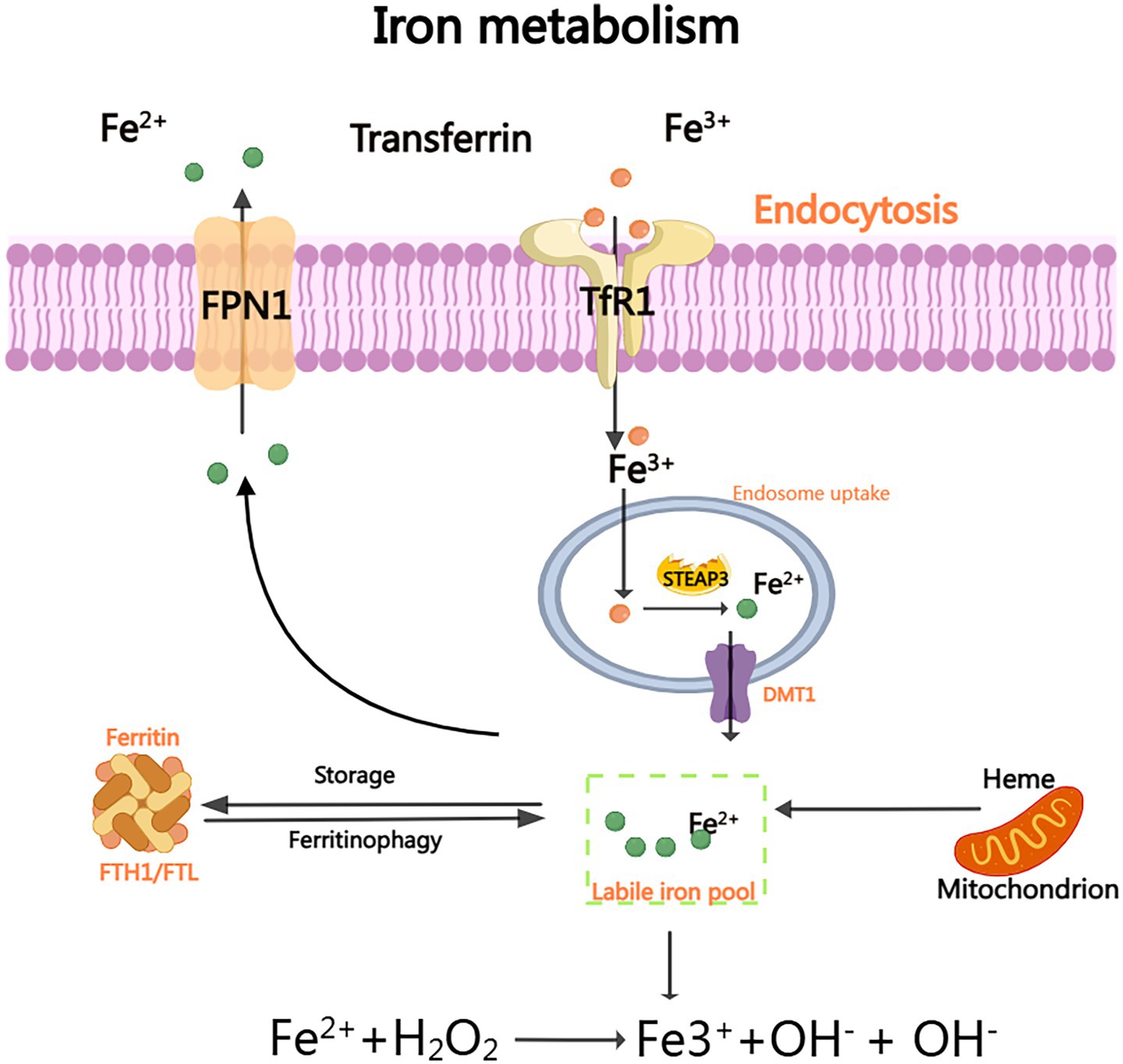
Figure 1. Iron metabolism: The efficient delivery of Fe3+ to various organs is facilitated by the binding of plasma transporter TF. Upon binding to TFR1, TF facilitates the smooth transfer of iron ions into the cell interior and subsequent release of Fe3+. Subsequently, STEAP3 reduces Fe3+ and converts it to accessible Fe2+ within the cytoplasm. Through the DMT1 channel, Fe2+ can enter the cytoplasm and form a stable iron pool (LIP). Excess unbound Fe3+ can be exported outside the cell via FPN and subsequently oxidized back to Fe3+. As a crucial substrate for generating hydroxyl radical (OH) and hydroxide ion (OH-) through Fenton reaction, Fe2+ plays a pivotal role.
2.2 System xc−-GPX4 axis failure and lipid peroxidation
The System Xc−-GPX4 axis plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular redox homeostasis (26). System Xc− is responsible for importing cystine, which is subsequently reduced to cysteine, facilitating the synthesis of GSH. This GSH serves as a critical cofactor for GPX4, an enzyme that converts toxic lipid hydroperoxides, such as polyunsaturated fatty acid hydroperoxides (PUFA-OOH), into benign alcohols. When GPX4 is inhibited (for example, by RSL3) or when System Xc− becomes dysfunctional, GSH levels are depleted (27, 28) (Figure 2). This depletion leads to the accumulation of lipid ROS through Fe2+-catalyzed peroxidation reactions (29). Additionally, it causes mitochondrial damage, characterized by the loss of cristae and membrane rupture, ultimately resulting in the collapse of membrane integrity through alkoxyl radical chain reactions (30). Notably, PUFAs in neuronal membranes are primary targets for lipid peroxidation, with ROS derived from mitochondrial metabolism and NADPH oxidases further amplifying oxidative stress (28) (Figure 3).
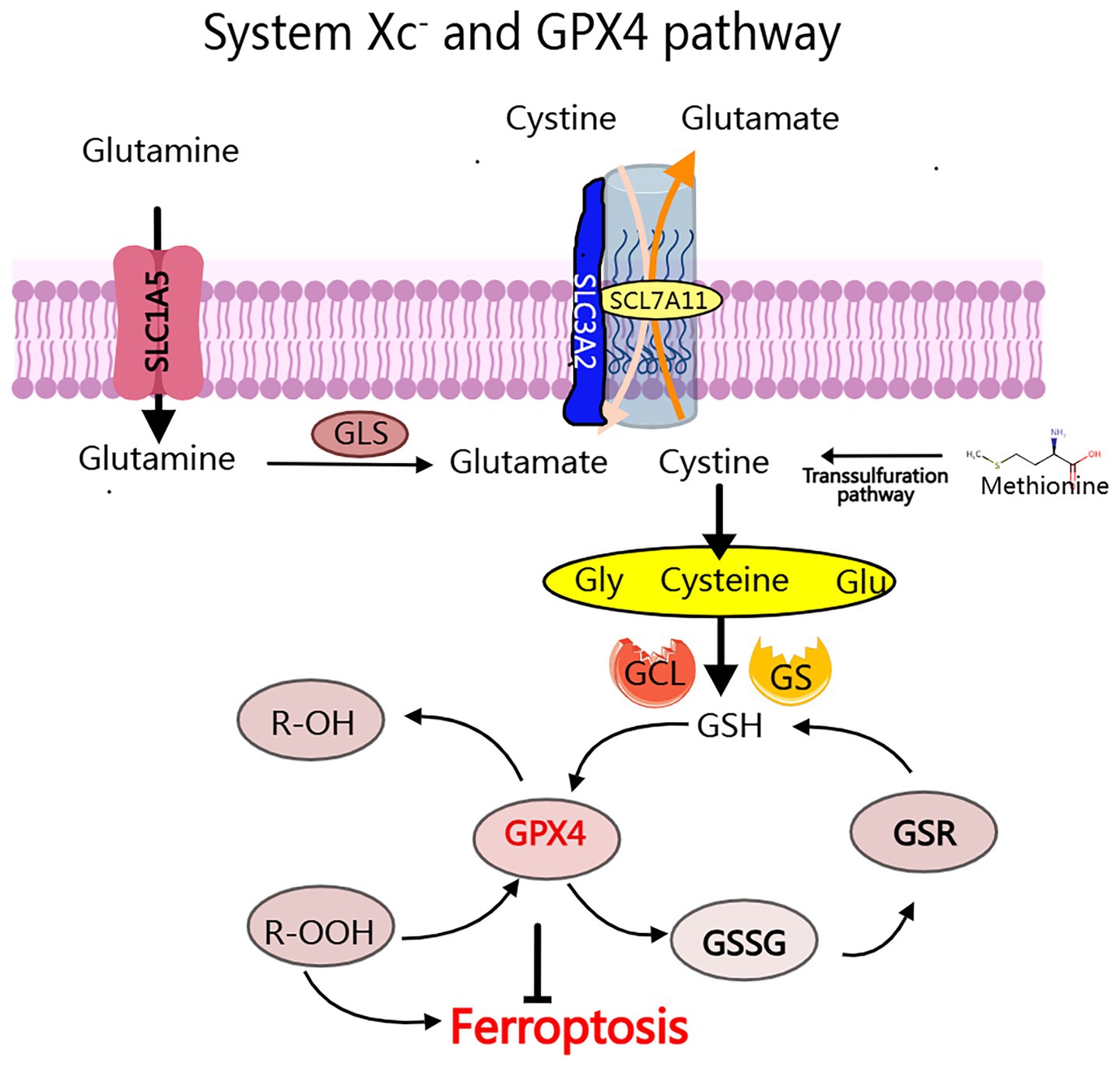
Figure 2. The System Xc- and GPX4 pathway: The conversion of cytoplasmic cysteine to glutathione (GSH) for tripeptide synthesis primarily occurs through the process ocess of glutamate-cysteine exchange, which involves a two-step enzymatic reaction: (1) Glutamic acid cysteine transaminase (GCL), also known as y-glutamyl cysteine synthetase (y-GCS); (2) Glutathione synthetase (GS). The major regulators of iron ptosis include GPX4, GSH, and System Xc-.
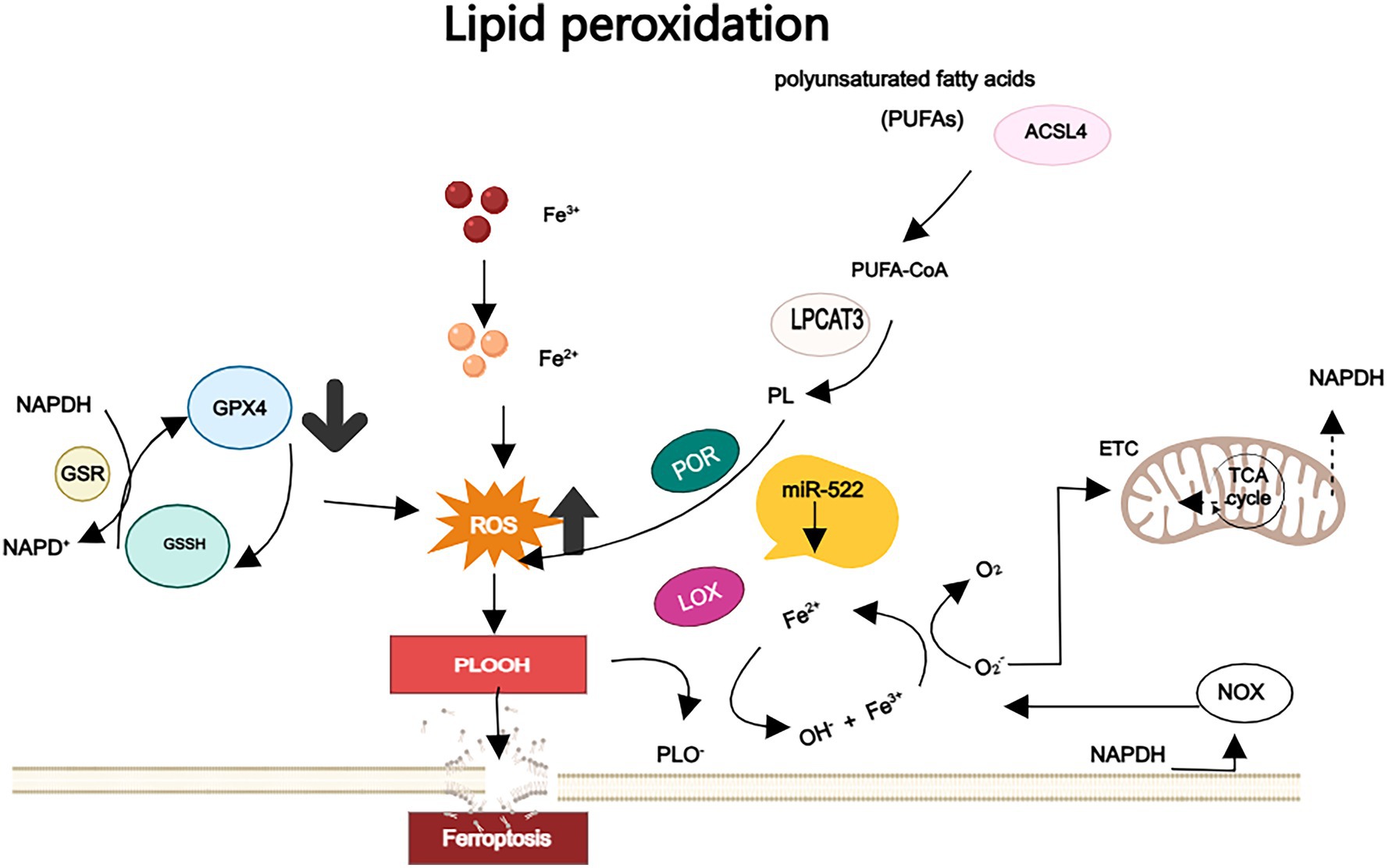
Figure 3. The lipid peroxidation: PUFAs are esterified to membrane phospholipids and subsequently react with ROS, thereby promoting cell ferroptosis. GPX4 uses GSH as a cofactor to enzymically reduce the lipid peroxides of polyunsaturated fatty acids to non-toxic lipid alcohols. Loss or inactivation of GPX4 results in the accumulation of lipid peroxides above normal levels, and in the presence of Fe2+ these lipid peroxides generate highly oxidized alkoxy groups. These alkoxy groups have the ability to directly damage adjacent PUFAs through free radical-mediated chain reactions, resulting in severe membrane damage.
2.3 Mevalonate pathway: a metabolic gatekeeper of ferroptosis
The mevalonate (MVA) pathway—best known for cholesterol synthesis—is also a pivotal brake on ferroptosis. HMG-CoA reductase generates isopentenyl pyrophosphate that fuels two anti-ferroptotic arms: ① synthesis of coenzyme Q10, whose reduced form, recycled by FSP1 at the plasma membrane, scavenges lipid-peroxyl radicals independently of GPX4; inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase depletes CoQ10, weakens FSP1 activity and markedly increases ferroptotic sensitivity (31, 32); ② isopentenylation of tRNA^Sec, a modification required for efficient GPX4 translation, so limiting MVA flux lowers GPX4 and elevates lipid-ROS (33). In addition, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate prenylates small GTPases that regulate iron uptake and phospholipid remodeling; loss of prenylation disrupts iron homeostasis and further primes cells for ferroptosis (34). Hence, intact MVA metabolism sustains both the FSP1-CoQ10 shield and GPX4 abundance, acting as a central metabolic checkpoint that dictates ferroptosis sensitivity.
3 Association between ferroptosis and epilepsy
Epilepsy is a chronic, recurrent disorder of brief transient dysfunction of brain function, which seriously affects the quality of life of patients and has the risk of causing unexpected death and sudden death (35, 36). Since current anti-epileptic drugs are mainly used for the control of seizures, there is still a great urgency for basic pathophysiological research (37, 38). Studies have shown that epileptiform seizures may initially originate from ion channel dysfunction caused by various stress events such as central nervous system injury, and that astrocyte proliferation and inflammatory responses play important roles in the pathological process of neuronal network excitation and inhibition imbalance, which is a self-perpetuating process. Regularly occurring excessive synchronized abnormal discharges of cortical neurons indicate the formation of epilepsy. Repetitive abnormal neuronal discharges can further lead to various pathological changes at the cellular level, including excessive oxidation. This process forms a “hypoxia, oxidative stress and inflammation” triad, which is a vicious cycle of neuronal activation, leading to systemic brain dysfunction (39, 40).
3.1 Potential involvement of ferroptosis mechanisms in the pathogenesis of epilepsy
Iron is an indispensable trace element for human growth and development, playing crucial roles in various REDOX reactions such as oxygen transportation, cellular oxidative respiratory chain, tricarboxylic acid cycle, and DNA biosynthesis (41, 42). Additionally, iron closely associates with myelin formation and catecholamine neurotransmitter metabolism in the nervous system (43, 44). Henceforth, meticulous regulation of iron metabolism is imperative within the human body. The most prevalent neurological disorders associated with abnormal iron metabolism are hemorrhagic stroke and post-traumatic epilepsy (PTE) (45, 46), which also exhibit the highest incidence of secondary epilepsy among neurological diseases. Ferroptosis, a newly recognized form of regulated cell death characterized by excessive lipid peroxidation and ROS production due to iron overload, has been observed in various neurological disorders including epilepsy (47). Therefore, based on chronological extrapolation, ferroptosis can be considered a significant pathological link leading to iron overload-induced epilepsy.
Iron overload is frequently implicated when conducting a comprehensive patient history of epilepsy and examining the impact of stressful brain events, such as PTE, which is characterized by vascular extravasation of red blood cells and elevated hemoglobin levels within the central nervous system. The breakdown of hemoglobin releases a substantial quantity of iron ions, leading to significant reduction in cell viability, superoxide dismutase and glutathione levels, increased generation of reactive oxygen species, lipid peroxidation and malondialdehyde levels, as well as upregulation in the expression of ferroptosis-related proteins that induce mitochondrial ultrastructural changes. Ultimately, this cascade culminates in the exacerbation of ferroptosis process (48–50).
Animal studies suggest that iron overload may underlie the pathophysiology of epilepsy and correlate with seizure onset and severity. For instance, cortical injection of hemoglobin or iron salts (FeCl3) into rats can induce chronic seizures, effectively replicating the characteristics of PTE in humans (51). On one hand, iron accumulation can upregulate the expression of Nav1.1 and Nav1.6 in the cortex and hippocampus, thereby modulating neuronal excitability (52, 53). On the other hand, excessive iron levels within cells after FeCl3 injection in the rat cerebral cortex can aberrantly activate the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation pathway. Excess Fe2+ can donate electrons to H2O2 and O2, resulting in substantial production of O2 − and OH free radicals which may cause lipid peroxidation of neuronal membranes as well as accelerated generation of guanidine compounds in the brain, ultimately leading to epileptic conditions (51). Injection of nanoscale iron into the cerebral cortex can induce chronic epilepsy in mice and replicate brain damage caused by microbleeds, resulting in varying degrees of spontaneous epileptiform events (51). The severity of epileptiform events is correlated with the reduction of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurons and impairment of cerebral blood flow autoregulation in the hemisphere injected with iron (54). In the human study, researchers analyzed transferrin saturation in 130 patients with epilepsy compared to 128 sex- and age-matched control subjects without epilepsy to investigate whether iron overload is a predisposing factor for epilepsy. The results revealed that the mean transferrin saturation of the epilepsy group was significantly higher than that of the control group (55). Zimmer’s study also identified overexpression of iron regulatory genes in TSC patients, FCD IIb patients, and Tsc1GFAP − / − mice, suggesting that early and persistent activation of antioxidant signaling and disruption in iron metabolism are pathological markers for FCDIIb and TSC (56). A retrospective study found significantly elevated levels of transferrin in epileptic children with a history of encephalitis compared to normal controls, indicating that ferroptosis plays a crucial role in oxidative stress-induced epileptiform activity during infantile brain inflammation due to high oxygen consumption, low antioxidant capacity, increased brain iron content, and abundant PUFAs in neuronal membranes (55). Kobrinsky et al. (57) through a case–control study, demonstrated that anemia can raise the threshold for first febrile seizures (FS), while iron deficiency may prevent their onset.
The MVA pathway provides a basis for exploring the potential involvement of ferroptosis in the development of epilepsy. Children with hereditary mevalonate kinase deficiency frequently exhibit febrile or afebrile seizures, underscoring the in vivo relevance of this metabolic pathway (34). Clinical studies on patients with drug-resistant epilepsy have demonstrated a significant negative correlation between serum CoQ10 levels and seizure frequency. Notably, the administration of either mevalonate or coenzyme Q10 has been shown to mitigate simvastatin-induced exacerbation of epileptic seizures and associated neuronal damage (58).
In this article, we review disorders of iron metabolism may underlie the mechanisms linking ferroptosis and seizures. However, how would ferroptosis function as a repeated seizure event of abnormal nervous system stress? Or, how might ferroptosis affect epilepsy progression?
3.2 The exacerbation of disease deterioration and adverse outcomes is facilitated by the progression of ferroptosis induced by epilepsy
It is crucial to clarify that iron overload does not solely manifest prior to the onset of epilepsy, and seizures often exacerbate the disruption of iron metabolism. Research has demonstrated that the ferroptosis inhibitor Fer-1 exhibits potential in ameliorating epileptiform seizures in rats with PTE, while also significantly safeguarding against seizure-induced cognitive impairment. These findings provide support for the pivotal role of ferroptosis in epilepsy pathology (59).
Firstly, seizure-induced chronic neuronal iron uptake may contribute to neuronal loss in temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis (TLE-HS). Several studies have reported that seizures can activate the hif-1a/HO-1 pathway, leading to abnormal iron metabolism and increased Fe2+ accumulation in hippocampal neurons. Excessive Fe2+ accumulation can induce oxidative stress and cell damage, thereby triggering ferroptosis of hippocampal neurons and further promoting seizures (60). Secondly, sensitivity weighted imaging was employed to investigate alterations in whole-brain iron levels in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE) from central China. The findings revealed a redistribution of iron between subcortical and cortical structures, influenced by the progression of seizures (61). Microinjection of Fe3+ into the brain of an animal model for epilepsy resulted in glutamate release, which is known to be a systemic Xc− inhibitor (62). However, it is well-established that elevated extracellular glutamate levels during seizures contribute to relapse and facilitate seizure onset as well as status epilepticus (SE) (63).
Furthermore, seizures induce an excessive production of ROS and promote ferroptosis, thereby exacerbating oxidative stress. This oxidative stress is particularly pronounced in brain tissues during epilepsy due to their high oxygen consumption, leading to increased generation of free radicals compared to other tissues and consequently aggravating neuronal cell death in various brain regions. It is closely associated with the development of comorbidities in epilepsy (64). For instance, researchers have observed activation of the ferroptosis process in a mouse model of Epilepsy-associated cognitive disorder (ECD), and inhibition of ferroptosis through pharmacological intervention or genetic manipulation targeting Lox can ameliorate ECD-related damage.
The alarming aspect is that Ferroptosis, which is believed to be exacerbated by seizures, is associated with sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) (65). Seizures are accompanied by elevated levels of intracellular free Fe2+ ions and deposition of hemosiderin. Existing reports suggest significant iron buildup in the brain and heart that is connected to epilepsy (66). Generalized tonic–clonic seizures (GTCS) present a considerable risk for SUDEP, affecting not only the brain but also causing cardiogenic dysfunction characterized by excessive iron accumulation and cardiomyopathy (IOC), along with electrical and mechanical abnormalities referred to as ‘epileptic heart,’ which carries a high likelihood of malignant bradycardia (67). Researchers induced SE in rats using pilocarpine and observed substantial accumulation of hemosiderin within cardiomyocytes, which was also correlated with an increase in spontaneous mortality (66). Therefore, hypoxia-ischemia–reperfusion secondary to status epilepticus can not only induce up-regulation of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and down-regulation of Kir channels, but also impact cardiac repolarization associated with epileptic heart and iron accumulation as well as ptosis associated with ischemic optic neuropathy (ION). These two mechanisms, triggered by the same convulsive stress, can simultaneously lead to severe cardiac dysfunction. Furthermore, ferroptosis is a common consequence of both brain and cardiac hypoxia. This dual effect induces neurodegeneration and epileptogenesis in heart failure (epileptic heart) while increasing the high risk of SUDEP (68, 69).
As mentioned earlier, our discussion highlights an important point: it is not advisable to overemphasize the direct causal relationship between epilepsy and ferroptosis. The reason is that ferroptosis may act as an auxiliary factor in the pathogenesis of epilepsy, potentially promoting the occurrence of epilepsy; at the same time, the repeated attacks of epilepsy may exacerbate the ferroptosis process, thus forming a vicious cycle of mutual causation, which may further worsen the clinical outcomes of the disease. Figure 4 illustrates the bidirectional pathological interaction between ferroptosis and epilepsy. This discovery actually reveals the huge potential and feasibility of ferroptosis process in epilepsy as a diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target.
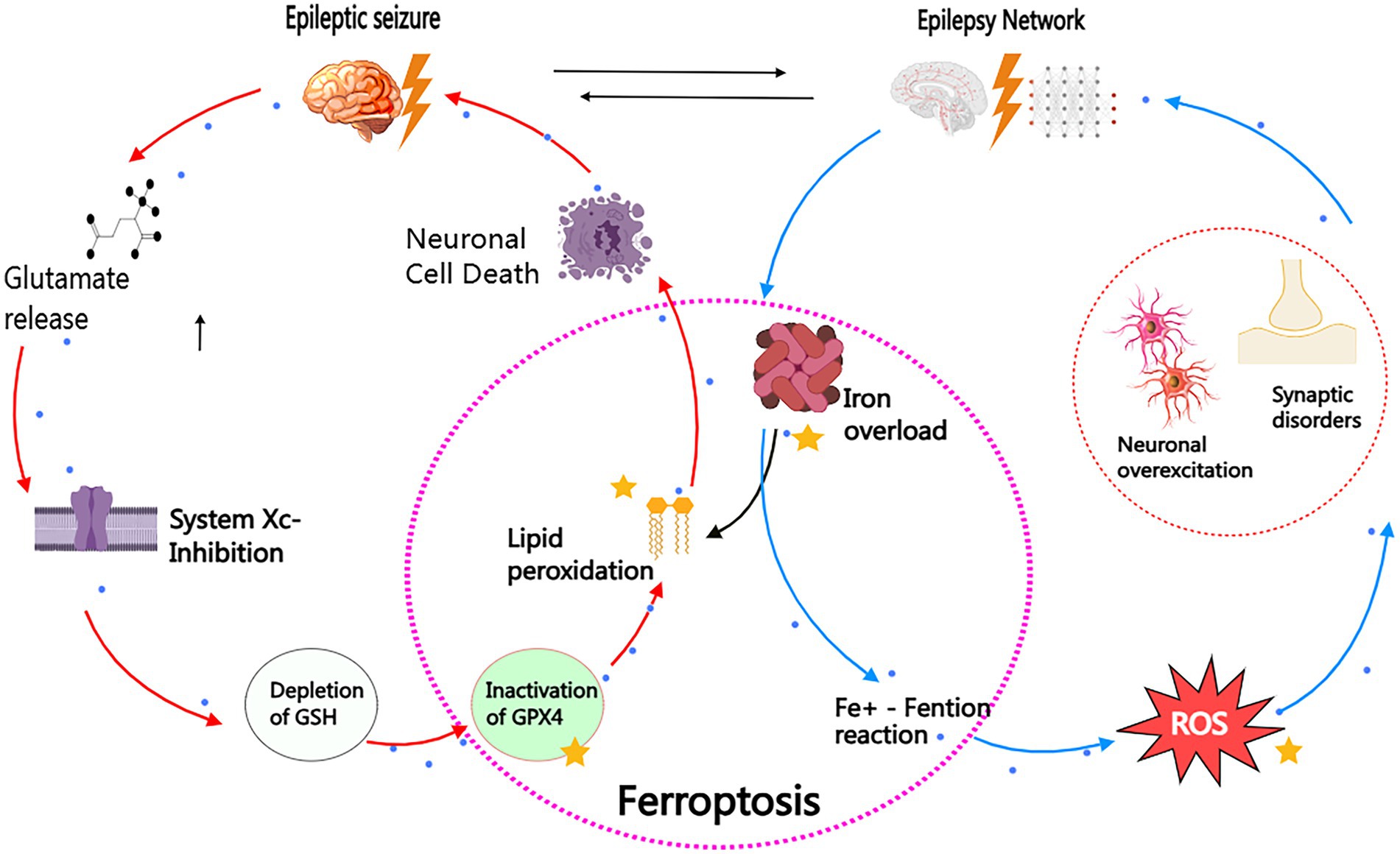
Figure 4. Bidirectional pathogenic loop between ferroptosis and epilepsy. This schematic illustrates the self-reinforcing cycle linking ferroptosis and epilepsy through two interconnected axes: I. Epilepsy. Ferroptosis Pathway (Red Arrows) Seizure activity triggers glutamate excitotoxicity, inhibiting the cystine/glutamate antiporter (System Xc-). This depletes glutathione (GSH), inactivating GPX4 and enabling iron-dependent lipid peroxidation. Subsequent membrane rupture and neuronal death further potentiate epileptogenesis. II. Ferroptosis Epilepsy Pathway (Blue Arrows) Iron overload (e.g., post-hemorrhagic or metabolic) generates hydroxyl radicals (OH) via Fenton reactions. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) hyperexcite neurons through Nav channel dysregulation and mitochondrial dysfunction, establishing hyper-synchronous networks that lower seizure thresholds. Therapeutic Intervention Points (Yellow Stars): (1) Iron chelators (e.g., DFO): Block Fe2−-mediated ROS production. (2) GPX4 activators (e.g., Selenium): Restore lipid peroxide detoxification. (3) Radical-trapping antioxidants (e.g. Fer-1): Terminate lipid peroxidation chain reactions. The vicious cycle highlights ferroptosis as both cause and consequence of epilepsy, providing mechanistic targets for clinical intervention.
3.3 Clinical evidence of ferroptosis in human epilepsy
Emerging clinical studies have begun to reveal potential ferroptosis signatures in patients with epilepsy, though evidence remains preliminary. For instance, SWI has identified abnormal iron accumulation in the hippocampus and cortex of patients with MTLE, correlating with seizure frequency and disease duration (70, 71). Victoria Martella et al. further demonstrated visual biomarkers of iron deposition within the pulvinar region of the thalamus in epilepsy patients using SWI (72). Metabolomic analyses of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from drug-resistant epilepsy patients show alterations in oxidative stress markers (e.g., lipid peroxidation products), suggesting possible ferroptotic activity (73, 74). Additionally, hematological studies in pediatric epilepsy patients report GSH depletion and GPX4 inactivation (75).
However, critical limitations must be acknowledged: ① Spatiotemporal Gaps: Current imaging detects iron accumulation but cannot confirm dynamic ferroptosis progression. The causal relationship between iron deposition and epileptogenesis requires longitudinal studies. ② Biomarker Specificity: Altered oxidative markers in CSF/blood may reflect general neurodegeneration rather than ferroptosis specifically. Validation with direct ferroptosis indicators (e.g., ACSL4, PUFA-OOH) is needed. ③ Therapeutic Translation: No clinical trials have yet tested ferroptosis inhibitors in epilepsy patients, leaving human efficacy unproven despite promising preclinical data.
Despite these challenges, existing evidence provides crucial foundations. Iron deposition patterns observed on SWI may serve as non-invasive prognostic tools for epilepsy progression. Additionally, deficits in GSH and GPX4 highlight testable hypotheses for the personalization of antioxidant therapy. Furthermore, multi-omics approaches that integrate iron-metabolomics, lipidomics, and epigenomics could uncover definitive ferroptosis signatures. Future studies should prioritize brain tissue biopsies, obtained from epilepsy surgery, to map the molecular drivers of ferroptosis and launch phase I/II trials of repurposed iron chelators, such as deferiprone, in drug-resistant cohorts.
4 Potential role of ferroptosis mechanism in the treatment of epilepsy
4.1 Application of ferroptosis inhibitors and associated agents in the treatment of epilepsy
Firstly, the exploration of the application of ferroptosis inhibitors in the treatment of epilepsy can be traced back to some fundamental research. Deferoxamine (DFO), which is an iron chelator capable of effectively scavenging iron, has been found that its treatment of epilepsy induced by ferric chloride can reduce local transferrin and significantly inhibit epilepsy (76). Secondly, considering the inseparable relationship between ferroptosis and ROS, the use of antioxidants (e.g., vitamin E, melatonin, etc.) (77–79), ferroptosis inhibitors such as ferrostain-1 (Fer − 1), and/or iron chelators can prevent brain iron accumulation and the neuroprotective role of ROS, thereby blocking the pathological process of epilepsy to a certain extent (80).
For instance, in a mouse model of PTZ-induced seizures and pilocarpine-induced seizures, the administration of Fer-1 significantly mitigated seizure severity and frequency while reducing iron accumulation in the hippocampus (81). In another experimental model of post-traumatic epilepsy induced by stereotactic injection of 50 mM FeCl3 into the somatosensory cortical area, Fer-1 exhibited a notable protective effect against acute seizures and memory decline (59). Moreover, in a previously described rat model of pilocarpine-induced TLE, Klotho overexpression was induced in the hippocampus using an adeno-associated viral vector delivery system. This approach not only inhibited ferroptosis and iron overload but also regulated the expression of divalent metal transporter 1 and ferrotransporter, both associated with iron accumulation in the hippocampus. Consequently, it effectively ameliorated cognitive deficits and demonstrated neuroprotective effects. Importantly, Klotho significantly elevated GPX4 and GSH levels while suppressing ROS levels. In summary, this protein alleviates cognitive deficits and exerts neuroprotective effects by inhibiting ferroptosis in a rat model of TLE (82, 83). Coenzyme Q10 (CQ 10) is a compound renowned for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Studies have demonstrated that appropriate CQ 10 supplementation also exhibits an inhibitory effect on ferroptosis (84). Furthermore, a separate study confirmed the involvement of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of epilepsy associated with mitochondrial disease and revealed that alpha-tocotrienol quinone (EPI-743) effectively ameliorated ferroptosis in cells derived from patients with five distinct childhood epilepsy syndromes in a dose-dependent manner by reducing lipid peroxidation (LPO) and 15-hydroxyditetraenoic acid (15-HETE) levels (17).
Furthermore, it is crucial to consider the interaction between ferroptosis inhibitors and traditional antiepileptic drugs. The mechanism of action of traditional antiepileptic drugs is intricate, encompassing enhancement of GABA-mediated inhibitory neurotransmission, inhibition of excitatory amino acid release or function, blockade of voltage-dependent sodium channels, and regulation of calcium channels. However, emerging evidence suggests that apart from these conventional mechanisms, iron metabolism imbalance and ferroptosis may significantly impact the efficacy of antiepileptic drugs. For instance, certain antiepileptic drugs like sodium valproate (VPA) exhibit notable antioxidant activity which effectively reduces free radical generation and consequently inhibits ferroptosis. In a mouse model with kainic acid-induced epilepsy, VPA not only markedly decreased lipid peroxide levels but also suppressed Ptgs2 mRNA expression. Importantly, the positive correlation observed between VPA’s inhibitory effect on ferroptosis and its antiepileptic effect strongly indicates that modulation of ferroptosis might be an important avenue for harnessing the therapeutic potential of antiepileptic drugs (85). Conversely, the occurrence of ferroptosis could impair the effectiveness of certain antiepileptic drugs as well. Specifically, excessive iron accumulation and subsequent induction of ferroptosis can trigger lipid peroxidation in neuronal membranes leading to alterations in their physical and chemical properties. Such changes undoubtedly influence drug penetration and targeting within cells thereby posing a potential threat to therapeutic efficacy (86).
Furthermore, numerous studies have revealed that specific antiepileptic drugs may exert their unique pharmacological effects by directly or indirectly interfering with the signaling pathway of ferroptosis. For instance, topiramate, a widely recognized broad-spectrum antiepileptic drug, not only possesses significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties but also effectively mitigates cellular oxidative stress, which is one of the key triggers of ferroptosis (87). Additionally, lamotrigine not only inhibits excitatory synaptic transmission but also fine-tunes intracellular iron ion concentration to potentially reduce the occurrence of ferroptosis events (88). Table 1 provides a comprehensive summary of drugs that have the potential to enhance epilepsy treatment through their impact on ferroptosis.
In conclusion, there exists an intricate and interconnected network between ferroptosis and antiepileptic drugs. A comprehensive exploration into the role of the ferroptosis mechanism within this network in epilepsy treatment will undoubtedly unveil novel strategies and targets while promoting more efficient and precise therapeutic approaches. Therefore, future research should focus on elucidating the specific molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction between ferroptosis and antiepileptic drugs to provide a robust scientific foundation and practical guidance for enhancing treatment efficacy and improving quality of life among epilepsy patients.
4.2 Implications of AMD research for ferroptosis-targeted epilepsy treatment
When exploring the potential role of ferroptosis mechanisms in epilepsy treatment, valuable insights can be gained from the study of ferroptosis in other neurodegenerative diseases. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a neurodegenerative condition, is closely associated with ferroptosis and provides important references for epilepsy treatment (89) (Shared ferroptotic pathways are illustrated in Figure 5). The pathological features of AMD, including iron accumulation in the retina, lipid peroxidation, and decreased GPX4 activity, are highly consistent with the mechanisms of ferroptosis (89). Interventions used in AMD research, such as iron chelators, ferroptosis inhibitors, and activation of the Nrf2 pathway, offer potential strategies for epilepsy treatmen.
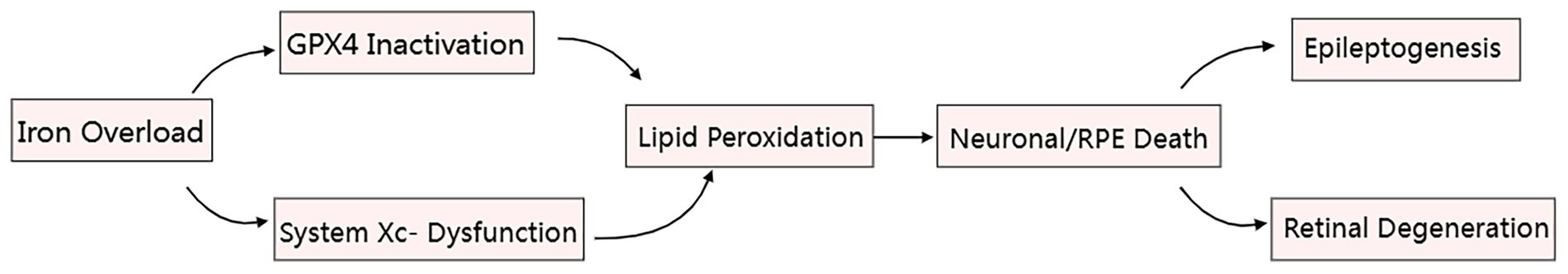
Figure 5. Iron-mediated ferroptosis core pathways in epilepsy (hippocampal neurons) and AMD (retinal pigment epithelium). Therapeutic targets (red stars): ① Iron chelation, ② GPX4 activation, ③ Antioxidant delivery.
Moreover, the experience gained from AMD research also provides important references for developing epilepsy treatments targeting ferroptosis. In terms of diagnosis, a hippocampal iron quantification MRI standard could be developed, for example, setting an iron concentration threshold of >1.2 mg/g to identify high-risk epilepsy patients. Regarding drug delivery strategies, a cranial sustained-release system loaded with ferroptosis inhibitors (such as Ferrostatin-1) could be developed, mimicking the intravitreal injections used in AMD, to achieve localized drug release and enhance therapeutic efficacy (90). In clinical trial design, a composite endpoint approach used in AMD research could be adopted to evaluate both seizure frequency (primary endpoint) and changes in SWI iron signals (secondary endpoint), providing more comprehensive evidence for the study of ferroptosis mechanisms. Although these measures have not yet been validated in epilepsy, these translational concepts have the potential to offer new ideas and methods for epilepsy treatment targeting ferroptosis, from diagnostic assessment to therapeutic strategies, and to promote the clinical application of relevant treatment approaches.
5 Research status and challenges
Although there has been some progress in exploring the role of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of epilepsy in recent years, the current research still faces many limitations, which greatly limit our depth and breadth of our comprehensive cognition and practice application in this area. The first problem is that a large number of studies focus on external and animal models, and the direct clinical evidence of epilepsy patients is inadequate. It is true that the experiment and animal model of vitro provides us with valuable mechanism exploration and drug screening platform, but these results often face many uncertainties in the transformation of the complex human physiological environment. Especially in the context of epilepsy, a multi-factor disease, the exploration of a single mechanism is difficult to fully reveal its intricate pathological process. Second, existing research tends to focus on a specific link or signaling pathway of iron death, and the interaction between it and its disease mechanism is not enough. For example, iron death, inflammatory response, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction may be synergistic in the onset of epilepsy, but the correlation and impact of these factors have not been systematically studied. The fragmentation of this study undoubtedly prevents our understanding of the comprehensive and systematic understanding of iron deaths in the mechanism of epilepsy.
In addition, the complexity of the protein and signaling pathways of iron deaths increased the difficulty of the study. Currently, the study focuses on several major proteins and molecular markers, such as GPX4, Ferritin and ROS, but do not explore other potential key molecules. Because iron death is a process of multi-step, multi-signal channel participation, the neglect of any link can lead to misunderstanding of the overall mechanism. Moreover, the study of iron death in epilepsy treatment is still in the preliminary exploration phase, and there is a lack of systematic clinical trial data. Although some iron death inhibitors show certain therapeutic potential in animal models, the applicability, side effects and long-term effects of different types of epilepsy are not fully verified. Moreover, most studies have focused on a particular drug or treatment strategy, but failed to provide multiple strategies for comparison and combined application research data.
5.1 Prospects for future research directions
Although ferroptosis research has demonstrated promising prospects in the field of epilepsy, scientists still need to overcome current limitations and adopt diversified and interdisciplinary comprehensive research methods. These include integrating in vitro and in vivo experiments, conducting extensive clinical research, and fostering collaboration among multidisciplinary teams. By doing so, we can gradually unravel the intricate mechanisms underlying ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of epilepsy, thereby establishing a more robust theoretical foundation for its diagnosis and treatment. Future investigations should prioritize several core directions:
1. To investigate the distinct role of ferroptosis in various types of epilepsy: Given the substantial heterogeneity observed in epilepsy, different types may exhibit diverse pathogenic mechanisms (91, 92). Therefore, it is imperative to comprehensively explore whether discrepancies exist in the involvement of ferroptosis across different types of epilepsy, aiming to unveil the universal principles governing ferroptosis action and its specific efficacy for particular epileptic conditions.
2. Investigating the combined effect of ferroptosis inhibitors and existing antiepileptic drugs aims to explore the potential benefits of comprehensive treatment in terms of improving drug efficacy and reducing side effects. This research not only contributes to optimizing clinical treatment plans but also sheds light on the underlying role of ferroptosis in epilepsy therapy.
3. Discovery and application of biomarkers: Future studies should aim to identify biomarkers associated with ferroptosis for early diagnosis, disease progression monitoring, and evaluation of treatment efficacy in epilepsy (93). This will provide valuable insights for personalized treatment strategies and may also unveil novel therapeutic targets.
4. Clinical trials and translational research: Despite significant progress in animal models regarding ferroptosis-related studies, further validation is required before clinical application can be realized. Large-scale clinical trials are essential to generate robust evidence that can determine the actual effectiveness and safety profile of ferroptosis inhibitors in patients with epilepsy.
Through comprehensive exploration and meticulous research in the aforementioned fields, we aim to unveil the fundamental mechanisms underlying ferroptosis throughout the entire trajectory of epilepsy onset, progression, and treatment. Moreover, our endeavors will pave the way for unprecedented therapeutic perspectives for individuals with epilepsy while fostering the development of more efficient and targeted treatment protocols.
Author contributions
JX: Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Data curation. XD: Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft, Supervision. MY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XC: Validation, Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization. HS: Software, Visualization, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Resources, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Supervision, Validation. SY: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Software, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Data curation, Project administration, Conceptualization, Formal analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province [grant number 2024NSFSC0619]; Medical Innovation Project [grant number 21WQ040].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Fisher, RS. Final comments on the process: ILAE definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia. (2014) 55:492–3. doi: 10.1111/epi.12585
2. Falco-Walter, JJ, Scheffer, IE, and Fisher, RS. The new definition and classification of seizures and epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. (2018) 139:73–9. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2017.11.015
4. Fearnhead, HO, Vandenabeele, P, and Vanden Berghe, T. How do we fit ferroptosis in the family of regulated cell death? Cell Death Differ. (2017) 24:1991–8. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.149
5. Dixon, SJ, Lemberg, KM, Lamprecht, MR, Skouta, R, Zaitsev, EM, Gleason, CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. (2012) 149:1060–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
6. Xie, L, Zhou, C, Wu, Y, Fu, X, Zhang, G, Han, X, et al. Wenqingyin suppresses ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of sepsis-induced liver injury by activating the Nrf2-mediated signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. (2023) 114:154748. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154748
7. Stockwell, BR, Friedmann Angeli, JP, Bayir, H, Bush, AI, Conrad, M, Dixon, SJ, et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death Nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. (2017) 171:273–85. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.021
8. Chen, H, Qi, Q, Wu, N, Wang, Y, Feng, Q, Jin, R, et al. Aspirin promotes RSL3-induced ferroptosis by suppressing mTOR/SREBP-1/SCD1-mediated lipogenesis in PIK3CA-mutant colorectal cancer. Redox Biol. (2022) 55:102426. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102426
9. Liu, L, Liu, R, Liu, Y, Li, G, Chen, Q, Liu, X, et al. Cystine-glutamate antiporter xCT as a therapeutic target for cancer. Cell Biochem Funct. (2021) 39:174–9. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3581
10. Tang, B, Zhu, J, Wang, Y, Chen, W, Fang, S, Mao, W, et al. Targeted xCT-mediated ferroptosis and protumoral polarization of macrophages is effective against HCC and enhances the efficacy of the anti-PD-1/L1 response. Adv Sci. (2023) 10:e2203973. doi: 10.1002/advs.202203973
11. Do Van, B, Gouel, F, Jonneaux, A, Timmerman, K, Gelé, P, Pétrault, M, et al. Ferroptosis, a newly characterized form of cell death in Parkinson's disease that is regulated by PKC. Neurobiol Dis. (2016) 94:169–78. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.05.011
12. Geng, Z, Guo, Z, Guo, R, Ye, R, Zhu, W, and Yan, B. Ferroptosis and traumatic brain injury. Brain Res Bull. (2021) 172:212–9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2021.04.023
13. Guo, J, Tuo, QZ, and Lei, P. Iron, ferroptosis, and ischemic stroke. J Neurochem. (2023) 165:487–520. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15807
14. Wang, F, Wang, J, Shen, Y, Li, H, Rausch, WD, and Huang, X. Iron Dyshomeostasis and Ferroptosis: a new Alzheimer's disease hypothesis? Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:830569. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.830569
15. Mahoney-Sánchez, L, Bouchaoui, H, Ayton, S, Devos, D, Duce, JA, and Devedjian, JC. Ferroptosis and its potential role in the physiopathology of Parkinson's disease. Prog Neurobiol. (2021) 196:101890. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101890
16. Li, J, Jia, B, Cheng, Y, Song, Y, Li, Q, and Luo, C. Targeting molecular mediators of Ferroptosis and oxidative stress for neurological disorders. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:3999083. doi: 10.1155/2022/3999083
17. Kahn-Kirby, AH, Amagata, A, Maeder, CI, Mei, JJ, Sideris, S, Kosaka, Y, et al. Targeting ferroptosis: a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of mitochondrial disease-related epilepsy. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0214250. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214250
18. Ganz, T. Iron homeostasis: fitting the puzzle pieces together. Cell Metab. (2008) 7:288–90. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.03.008
19. Burkhart, A, Skjørringe, T, Johnsen, KB, Siupka, P, Thomsen, LB, Nielsen, MS, et al. Expression of Iron-related proteins at the neurovascular unit supports reduction and Reoxidation of Iron for transport through the blood-brain barrier. Mol Neurobiol. (2016) 53:7237–53. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9582-7
20. Ohgami, RS, Campagna, DR, Greer, EL, Antiochos, B, McDonald, A, Chen, J, et al. Identification of a ferrireductase required for efficient transferrin-dependent iron uptake in erythroid cells. Nat Genet. (2005) 37:1264–9. doi: 10.1038/ng1658
21. Hassannia, B, Van Coillie, S, and Vanden Berghe, T. Ferroptosis: biological rust of lipid membranes. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2021) 35:487–509. doi: 10.1089/ars.2020.8175
22. Yan, B, Ai, Y, Sun, Q, Ma, Y, Cao, Y, Wang, J, et al. Membrane damage during Ferroptosis is caused by oxidation of phospholipids catalyzed by the oxidoreductases POR and CYB5R1. Mol Cell. (2021) 81:355–369.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.11.024
23. Ding, H, Chen, S, Pan, X, Dai, X, Pan, G, Li, Z, et al. Transferrin receptor 1 ablation in satellite cells impedes skeletal muscle regeneration through activation of ferroptosis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2021) 12:746–68. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12700
24. Song, J, Liu, T, Yin, Y, Zhao, W, Lin, Z, Yin, Y, et al. The deubiquitinase OTUD1 enhances iron transport and potentiates host antitumor immunity. EMBO Rep. (2021) 22:e51162. doi: 10.15252/embr.202051162
25. Yu, X, Guo, Q, Zhang, H, Wang, X, Han, Y, and Yang, Z. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α can reverse the Adriamycin resistance of breast cancer adjuvant chemotherapy by upregulating transferrin receptor and activating ferroptosis. FASEB J. (2024) 38:e23876. doi: 10.1096/fj.202401119R
26. Parker, JL, Deme, JC, Kolokouris, D, Kuteyi, G, Biggin, PC, Lea, SM, et al. Molecular basis for redox control by the human cystine/glutamate antiporter system xc(). Nat Commun. (2021) 12:7147. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27414-1
27. Hider, RC, and Kong, XL. Glutathione: a key component of the cytoplasmic labile iron pool. Biometals. (2011) 24:1179–87. doi: 10.1007/s10534-011-9476-8
28. Noordergraaf, IW, Witono, JR, and Heeres, HJ. Grafting starch with acrylic acid and Fenton's initiator: the selectivity challenge. Polymers. (2024) 16:255. doi: 10.3390/polym16020255
29. Trommer, S, Leimert, A, Bucher, M, and Schumann, J. Polyunsaturated fatty acids induce ROS synthesis in microvascular endothelial cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2018) 1072:393–7. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-91287-5_63
30. Cadenas, S. Mitochondrial uncoupling, ROS generation and cardioprotection. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. (2018) 1859:940–50. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2018.05.019
31. Tan, Q, Fang, Y, and Gu, Q. Mechanisms of modulation of Ferroptosis and its role in central nervous system diseases. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:657033. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.657033
32. Hernández-Camacho, JD, García-Corzo, L, Fernández-Ayala, DJM, Navas, P, and López-Lluch, G. Coenzyme Q at the hinge of health and metabolic diseases. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:1785. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111785
33. Lee, JY, Kim, WK, Bae, KH, Lee, SC, and Lee, EW. Lipid metabolism and ferroptosis. Biology. (2021) 10:184. doi: 10.3390/biology10030184
34. Xu, N, Shen, N, Wang, X, Jiang, S, Xue, B, and Li, C. Protein prenylation and human diseases: a balance of protein farnesylation and geranylgeranylation. Sci China Life Sci. (2015) 58:328–35. doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-4836-1
35. Manford, M. Recent advances in epilepsy. J Neurol. (2017) 264:1811–24. doi: 10.1007/s00415-017-8394-2
36. Beghi, E, Giussani, G, and Sander, JW. The natural history and prognosis of epilepsy. Epileptic Disord. (2015) 17:243–53. doi: 10.1684/epd.2015.0751
37. Hakami, T. Neuropharmacology of Antiseizure drugs. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. (2021) 41:336–51. doi: 10.1002/npr2.12196
38. Sisodiya, SM. Precision medicine and therapies of the future. Epilepsia. (2021) 62:S90–s105. doi: 10.1111/epi.16539
39. Fu, J, Tao, T, Li, Z, Chen, Y, Li, J, and Peng, L. The roles of ER stress in epilepsy: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 131:110658. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110658
40. Ramazi, S, Fahanik-Babaei, J, Mohamadi-Zarch, SM, Tashakori-Miyanroudi, M, Nourabadi, D, Nazari-Serenjeh, M, et al. Neuroprotective and anticonvulsant effects of sinomenine in kainate rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy: involvement of oxidative stress, inflammation and pyroptosis. J Chem Neuroanat. (2020) 108:101800. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2020.101800
41. Lynch, SR. Interaction of iron with other nutrients. Nutr Rev. (1997) 55:102–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1997.tb06461.x
42. Abbina, S, Gill, A, Mathew, S, Abbasi, U, and Kizhakkedathu, JN. Polyglycerol-based macromolecular Iron Chelator adjuvants for antibiotics to treat drug-resistant Bacteria. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. (2020) 12:37834–44. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c06501
43. David, S, Jhelum, P, Ryan, F, Jeong, SY, and Kroner, A. Dysregulation of Iron homeostasis in the central nervous system and the role of Ferroptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2022) 37:150–70. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0218
44. Vallée, L. Iron and neurodevelopment. Arch Pediatr. (2017) 24:5s18–15s22. doi: 10.1016/S0929-693X(17)24005-6
45. Sun, Y, Li, Q, Guo, H, and He, Q. Ferroptosis and iron metabolism after intracerebral hemorrhage. Cells. (2022) 12:90. doi: 10.3390/cells12010090
46. Tang, S, Gao, P, Chen, H, Zhou, X, Ou, Y, and He, Y. The role of iron, its metabolism and ferroptosis in traumatic brain injury. Front Cell Neurosci. (2020) 14:590789. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.590789
47. Cai, Y, and Yang, Z. Ferroptosis and its role in epilepsy. Front Cell Neurosci. (2021) 15:696889. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.696889
48. Yang, L, Wang, H, Yang, X, Wu, Q, An, P, Jin, X, et al. Auranofin mitigates systemic iron overload and induces ferroptosis via distinct mechanisms. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2020) 5:138. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00253-0
49. Gu, K, Wu, A, Yu, B, Zhang, T, Lai, X, Chen, J, et al. Iron overload induces colitis by modulating ferroptosis and interfering gut microbiota in mice. Sci Total Environ. (2023) 905:167043. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167043
50. Jiang, Z, Wang, H, Qi, G, Jiang, C, Chen, K, and Yan, Z. Iron overload-induced ferroptosis of osteoblasts inhibits osteogenesis and promotes osteoporosis: an in vitro and in vivo study. IUBMB Life. (2022) 74:1052–69. doi: 10.1002/iub.2656
51. Mori, A, Hiramatsu, M, Yokoi, I, and Edamatsu, R. Biochemical pathogenesis of post-traumatic epilepsy. Pavlov J Biol Sci. (1990) 25:54–62. doi: 10.1007/BF02964604
52. Prakash, C, Mishra, M, Kumar, P, Kumar, V, and Sharma, D. Response of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels subtypes on Dehydroepiandrosterone treatment in Iron-induced epilepsy. Cell Mol Neurobiol. (2021) 41:279–92. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00851-0
53. Pico, RM, and Gall, CM. Hippocampal epileptogenesis produced by electrolytic iron deposition in the rat dentate gyrus. Epilepsy Res. (1994) 19:27–36. doi: 10.1016/0920-1211(94)90085-X
54. Jyoti, A, Sethi, P, and Sharma, D. Aging accelerates the progression and manifestation of seizures in post-traumatic model of epilepsy. Neurosci Lett. (2009) 453:86–91. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.01.082
55. Ikeda, M. Iron overload without the C282Y mutation in patients with epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2001) 70:551–3. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.70.4.551
56. Zimmer, TS, Ciriminna, G, Arena, A, Anink, JJ, Korotkov, A, Jansen, FE, et al. Chronic activation of anti-oxidant pathways and iron accumulation in epileptogenic malformations. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. (2020) 46:546–63. doi: 10.1111/nan.12596
57. Kobrinsky, NL, Yager, JY, Cheang, MS, Yatscoff, RW, and Tenenbein, M. Does iron deficiency raise the seizure threshold? J Child Neurol. (1995) 10:105–9. doi: 10.1177/088307389501000207
58. Liao, WC, Huang, CW, Hsiao, YH, Sung, PS, Fu, TF, Chang, AYW, et al. Association between the serum coenzyme Q10 level and seizure control in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy. Healthcare. (2021) 9:118. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9091118
59. Chen, KN, Guan, QW, Yin, XX, Wang, ZJ, Zhou, HH, and Mao, XY. Ferrostatin-1 obviates seizures and associated cognitive deficits in ferric chloride-induced posttraumatic epilepsy via suppressing ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. (2022) 179:109–18. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.12.268
60. Liang, Z, Zheng, Z, Guo, Q, Tian, M, Yang, J, Liu, X, et al. The role of HIF-1α/HO-1 pathway in hippocampal neuronal ferroptosis in epilepsy. iScience. (2023) 26:108098. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108098
61. Liu, X, and Chen, J. Research progress on ferroptosis and its role in epilepsy. J Physiol Pharmacol. (2022) 73:2. doi: 10.26402/jpp.2022.6.02
62. Fricker, M, Tolkovsky, AM, Borutaite, V, Coleman, M, and Brown, GC. Neuronal cell death. Physiol Rev. (2018) 98:813–80. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00011.2017
63. Albrecht, J, and Zielińska, M. Mechanisms of excessive extracellular glutamate accumulation in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurochem Res. (2017) 42:1724–34. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2105-8
64. Walker, MC. Reactive oxygen species in status epilepticus. Epilepsia Open. (2023) 8:S66–s72. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12691
65. Moscovicz, F, Taborda, C, Fernández, F, Borda, N, Auzmendi, J, and Lazarowski, A. Ironing out the links: Ferroptosis in epilepsy and SUDEP. Epilepsy Behav. (2024) 157:109890. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2024.109890
66. Akyuz, E, Doganyigit, Z, Eroglu, E, Moscovicz, F, Merelli, A, Lazarowski, A, et al. Myocardial Iron overload in an experimental model of sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. Front Neurol. (2021) 12:609236. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.609236
67. Ryvlin, P, Ciumas, C, Wisniewski, I, and Beniczky, S. Wearable devices for sudden unexpected death in epilepsy prevention. Epilepsia. (2018) 59:61–6. doi: 10.1111/epi.14054
68. Auzmendi, J, Buchholz, B, Salguero, J, Cañellas, C, Kelly, J, Men, P, et al. Pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus is associated with P-glycoprotein induction in cardiomyocytes, electrocardiographic changes, and sudden death. Pharmaceuticals. (2018) 11:21. doi: 10.3390/ph11010021
69. Akyüz, E, Mega Tiber, P, Beker, M, and Akbaş, F. Expression of cardiac inwardly rectifying potassium channels in pentylenetetrazole kindling model of epilepsy in rats. Cell Mol Biol. (2018) 64:47–54. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2017.64.15.8
70. Zhang, Z, Liao, W, Bernhardt, B, Wang, Z, Sun, K, Yang, F, et al. Brain iron redistribution in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: a susceptibility-weighted magnetic resonance imaging study. BMC Neurosci. (2014) 15:117. doi: 10.1186/s12868-014-0117-3
71. Zimmer, TS, David, B, Broekaart, DWM, Schidlowski, M, Ruffolo, G, Korotkov, A, et al. Seizure-mediated iron accumulation and dysregulated iron metabolism after status epilepticus and in temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol. (2021) 142:729–59. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02348-6
72. Martella, V, Ludovichetti, R, Nierobisch, N, Obermüller, C, Gunzer, F, Maibach, F, et al. The hypointense pulvinar sign on susceptibility weighed magnetic resonance imaging: a visual biomarker for iron deposition in epilepsy. Neuroradiol J. (2025) 38:337–45. doi: 10.1177/19714009241303050
73. Zhao, Z, Xing, N, and Hou, L. Cerebrospinal fluid metabolites as potential biomarkers for epilepsy: insights from genome-wide association studies. Epilepsia Open. (2025) 10:233–42. doi: 10.1002/epi4.13101
74. Wang, T, Li, C, Ma, Y, Zhou, H, Du, X, Li, Y, et al. Metabolomics of cerebrospinal fluid reveals prognostic biomarkers in pediatric status epilepticus. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2023) 29:3925–34. doi: 10.1111/cns.14312
75. Jin, Y, Ren, L, Jing, X, and Wang, H. Targeting ferroptosis as novel therapeutic approaches for epilepsy. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1185071. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1185071
76. Zou, X, Jiang, S, Wu, Z, Shi, Y, Cai, S, Zhu, R, et al. Effectiveness of deferoxamine on ferric chloride-induced epilepsy in rats. Brain Res. (2017) 1658:25–30. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.01.001
77. Upaganlawar, AB, Wankhede, NL, Kale, MB, Umare, MD, Sehgal, A, Singh, S, et al. Interweaving epilepsy and neurodegeneration: vitamin E as a treatment approach. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 143:112146. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112146
78. Ambrogini, P, Torquato, P, Bartolini, D, Albertini, MC, Lattanzi, D, Di Palma, M, et al. Excitotoxicity, neuroinflammation and oxidant stress as molecular bases of epileptogenesis and epilepsy-derived neurodegeneration: the role of vitamin E. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis. (2019) 1865:1098–112. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.01.026
79. Verma, N, Maiti, R, Mishra, BR, Jha, M, Jena, M, and Mishra, A. Effect of add-on melatonin on seizure outcome, neuronal damage, oxidative stress, and quality of life in generalized epilepsy with generalized onset motor seizures in adults: a randomized controlled trial. J Neurosci Res. (2021) 99:1618–31. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24820
80. Ye, Q, Zeng, C, Luo, C, and Wu, Y. Ferrostatin-1 mitigates cognitive impairment of epileptic rats by inhibiting P38 MAPK activation. Epilepsy Behav. (2020) 103:106670. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.106670
81. Mao, XY, Zhou, HH, and Jin, WL. Ferroptosis induction in Pentylenetetrazole kindling and pilocarpine-induced epileptic seizures in mice. Front Neurosci. (2019) 13:721. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00721
82. Xiang, T, Luo, X, Zeng, C, Li, S, Ma, M, and Wu, Y. Klotho ameliorated cognitive deficits in a temporal lobe epilepsy rat model by inhibiting ferroptosis. Brain Res. (2021) 1772:147668. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147668
83. Ranjbar, N, Raeisi, M, Barzegar, M, Ghorbanihaghjo, A, Shiva, S, Sadeghvand, S, et al. The possible anti-seizure properties of klotho. Brain Res. (2023) 1820:148555. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2023.148555
84. Costa, I, Barbosa, DJ, Silva, V, Benfeito, S, Borges, F, Remião, F, et al. Research models to study Ferroptosis's impact in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15:1369. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051369
85. Li, Q, Huang, YH, Li, QQ, Jia, JN, Liu, ZQ, Zhou, HH, et al. Sodium valproate ablates ferroptosis in kainic acid-induced epileptic seizure via suppressing lysyl oxidase. Neuroreport. (2024) 35:1090–7. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000002103
86. Ralhan, I, Chang, J, Moulton, MJ, Goodman, LD, Lee, NYJ, Plummer, G, et al. Autolysosomal exocytosis of lipids protect neurons from ferroptosis. J Cell Biol. (2023) 222:7130. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202207130
87. Chen, QW, Meng, RT, and Ko, CY. Modulating oxidative stress and neurogenic inflammation: the role of topiramate in migraine treatment. Front Aging Neurosci. (2024) 16:1455858. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1455858
88. Onishi, K, Kamida, T, Fujiki, M, Momii, Y, and Sugita, K. Anticonvulsant and antioxidant effects of lamotrigine on pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in mice. Neuroreport. (2023) 34:61–6. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001859
89. Zhao, T, Guo, X, and Sun, Y. Iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation in the aging retina: implication of Ferroptosis in age-related macular degeneration. Aging Dis. (2021) 12:529–51. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.0912
90. Zhao, J, Li, X, Tang, S, Xu, G, Xu, X, Zhang, F, et al. EXTEND II: an open-label phase III multicentre study to evaluate efficacy and safety of ranibizumab in Chinese patients with subfoveal choroidal neovascularization secondary to age-related macular degeneration. BioDrugs. (2014) 28:527–36. doi: 10.1007/s40259-014-0106-1
91. Falco-Walter, J. Epilepsy-Definition, Classification, Pathophysiology, and Epidemiology. Semin Neurol. (2020) 40:617–623.
92. Sarmast, ST, Abdullahi, AM, and Jahan, N. Current classification of seizures and epilepsies: scope, limitations and recommendations for future action. Cureus. (2020) 12:e10549.
93. Yuan, H, Li, X, Zhang, X, Kang, R, and Tang, D. Identification of ACSL4 as a biomarker and contributor of ferroptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. (2026) 478:1338–1343.
Glossary
ROS - Reactive Oxygen Species
Tf - Transferrin
TfR1 - Transferrin Receptor 1
BMECs - Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
DCYTB - Duodenal Cytochrome B
STEAP3 - Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of Prostate 3
DMT1 - Divalent Metal Transporter 1
LIP - Labile Iron Pool
FPN - Ferroportin
GSH - Glutathione
GPX4 - Glutathione Peroxidase 4
PUFAs - Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
NADPH - Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate
GSSG - Oxidized Glutathione
RSL3 - RAS-Selective Lethal compound 3
PTE - Post-Traumatic Epilepsy
GABA - Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid
TSC - Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
FCD - Focal Cortical Dysplasia
TLE - Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
HS - Hippocampal Sclerosis
LPCAT3 - Lysophosphatidylcholine Acyltransferase 3
MTLE - Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
SE - Status Epilepticus
SUDEP - Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy
GTCS - Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
IOC - Iron Overload Cardiomyopathy
P-gp - P-glycoprotein
ION - Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
DFO - Deferoxamine
VPA - Valproic Acid
NTBI - Non-Transferrin Bound Iron
Fer-1 - Ferrostatin-1
CQ10 - Coenzyme Q10
LPO - Lipid Peroxidation
15-HETE - 15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid
AEDs - Antiepileptic Drugs
SWI - Susceptibility Weighted Imaging
AMD - Age-related Macular Degeneration
RPE - Retinal Pigment Epithelium
OCT - Optical Coherence Tomography
CoQ10 - Coenzyme Q10
ACSL4 - Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long Chain Family Member 4
MVA - mevalonate
Keywords: ferroptosis, epilepsy, iron metabolism, lipid peroxidation, reactive oxygen species
Citation: Xu J, Dong X, Yuan M, Chen X, Shu H and Yu S (2025) Ferroptosis and epilepsy: bidirectional pathogenic links and therapeutic implications. Front. Neurol. 16:1635441. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1635441
Edited by:
Vassiliy Tsytsarev, University of Maryland, United StatesReviewed by:
Mikhail Inyushin, Central University of the Caribbean, Puerto RicoMegha Mete, Srinath University, India
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Dong, Yuan, Chen, Shu and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xin Chen, OTQ0NjEwMDM4QHFxLmNvbQ==; Haifeng Shu, c2h1aGFpZmVuZ0Bzd2p0dS5lZHUuY24=; Sixun Yu, YmluZ3l1dGlhbjE5ODJAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Jing Xu
Jing Xu Xinning Dong
Xinning Dong Mu Yuan
Mu Yuan Xin Chen
Xin Chen Haifeng Shu
Haifeng Shu Sixun Yu
Sixun Yu