- 1Center for Precision Medicine, School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, Huaqiao University, Xiamen, China
- 2GeneYoung Biopharmaceuticals, Shenzhen, China
Anxiety and insomnia are prevalent global mood disorders, and affect approximately 4 and 10 out of every 100 individuals, respectively. Common abnormal brain activity and altered neural circuitries are detected in patients with anxiety disorders and insomnia, suggesting overlapping pathogenesis in these two disorders. Promisingly, GABA from dietary supplements and GABA produced by gut microbiota have shown significant treatment effects in anxiety and insomnia. This review summarizes neurological mechanisms causing anxiety and insomnia, reveals cellular pathways transferring GABA from the gut to the brain, and delivers the therapeutic potential of gut derived GABA for anxiety and insomnia. Moreover, this review proposes emerging therapeutic strategies utilizing engineered GABA-producing bacteria to target anxiety and insomnia, and highlights the potential of live biotherapeutics as novel interventions for mood disorders.
1 Introduction
The global prevalence of anxiety disorder is increasing, particularly in cities with greater levels of stress and fast-paced lifestyles. In 2024, nearly 275 million people are suffering from anxiety disorders, accounting for approximately 3.5% of the global population (Calm, 2024). Moreover, about 10% of adults are affected by insomnia disorders, and an additional 20% experiences occasional insomnia symptoms worldwide (Morin and Jarrin, 2022). Anxiety disorders and sleep disturbances exhibit a bidirectional relationship, where anxiety-induced hyperarousal disrupts sleep architecture, and sleep deprivation amplifies emotional vulnerability (Bragantini et al., 2019; Pillai et al., 2014; Sadeh et al., 2004). Specifically, sleep deprivation increases cortisol levels, amplifies emotional procession of the limbic system and the salience network involved in cognitive control (dorsal anterior cingulate cortex and anterior insula), and creates a vicious cycle of hyperarousal and anxious apprehension (Carlisi et al., 2017; Palmer and Alfano, 2020; Yoo et al., 2007). Conversely, anxiety disorders disrupt sleep architecture by reducing slow-wave sleep and increase nocturnal awakenings through noradrenergic hyperactivity in the locus coeruleus (Chellappa and Aeschbach, 2022; Gong et al., 2021).
Pathogenic studies have shown that anxiety and insomnia share similar biological mechanisms (Morris et al., 2020; Van Someren, 2021). The locus coeruleus (LC) can activate the amygdala by releasing norepinephrine (NE), thereby inducing anxiety and triggering the body’s anxious response (Suárez-Pereira et al., 2022). The locus coeruleus also acts as the control center for wakefulness. Its specialized nerve cells release norepinephrine when one is awake, like an internal “alarm system.” During deep and slow-wave sleep, these cells quiet down significantly, and fall silent completely during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, the stage mostly associated with vivid dreaming (Verret et al., 2006). Thus, the LC serves as a pivotal point where the two disorders converge.
Another potential pivotal point is the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis. Anxiety and insomnia patients commonly exhibit activation of the HPA axis, characterized by elevated hormone levels such as cortisol (Juruena et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2014). Elevated cortisol levels enhance the amygdala’s sensitivity to threat signals (Roberts et al., 2022). Prolonged high cortisol exposure keeps it in “hyper-vigilance,” causing continuous anxiety even without real threats. Moreover, high cortisol can activate the amygdala, and reduce slow-wave sleep (Buckley and Schatzberg, 2005; Wong et al., 2000). Additionally, increased cortisol damages prefrontal cortex neurons and weakens its inhibitory function on the amygdala, impairing one’s emotion regulation ability (Ren et al., 2022).
Currently, besides behavioral interventions such as mental therapy and exercise, medication remains an effective treatment for anxiety and insomnia (Kandola and Stubbs, 2020; Riedel et al., 2024; Shaha, 2023; Vu and Conant-Norville, 2021). Many medications have been developed, with several already commercialized and available on the market. For example, classic medications such as barbiturates and benzodiazepines are known to possess sedative and hypnotic effects (Bormann, 1988; Bowery et al., 1979; Sigel and Ernst, 2018). However, the current medications for anxiety and insomnia often cause various side effects. For instance, benzodiazepines can cause sedation, slowed reaction time, and impaired memory and psychomotor function (Greenblatt et al., 2020). Therefore, the development of a more natural and less harmful medication holds significant promise for the treatment of anxiety and insomnia.
As a natural neurotransmitter, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is promoted for its benefits in addressing anxiety and insomnia (Hepsomali et al., 2020; Ngo and Vo, 2019). The efficacy of orally administered GABA is supported by positive consumer reviews and clinical experiments, suggesting its promising therapeutic effects on anxiety and insomnia symptoms (Ngo and Vo, 2019). Dietary sources that are rich in GABA and GABA-producing probiotics also display significant therapeutic effects on anxiety and insomnia (Liwinski et al., 2023; Strandwitz, 2018).
Because the association of gut microbiota in human health and diseases is well recognized, it is timely to better understand how gut derived GABA may function in humans. Moreover, in this review, orally administered GABA, GABA from GABA-rich food, and GABA from GABA-producing probiotics are collectively referred to as “gut derived GABA.” This review explores production, absorption and transmission of gut derived GABA, clarifies its potential mechanisms in alleviating anxiety and insomnia, and discusses future applications for optimized production and clinical use.
2 Anxiety and insomnia
2.1 Anxiety
Anxiety disorder represents a prevalent category of mood disorders (Byrd and Brook, 2014). While acute anxiety involves a sudden onset of intense fearful experiences, chronic anxiety is the most common presentation of anxiety disorders, with symptoms including persistent and unwarranted worries, fatigue, insomnia and profound distress (Nutt, 2005; Robinson et al., 2019). A variety of risk factors, including family issues, environmental exposures, and perceived threats, can contribute to the development of anxiety (Warner and Strawn, 2023).
The neural circuitry associated with anxiety has been studied. The amygdala plays a crucial role in emotion generation, recognition and regulation, as well as in controlling learning and memory, and fear response through receiving and responding information from the locus coeruleus (LC) and other sensory inputs (Krettek and Price, 1978; Suárez-Pereira et al., 2022). For transient panic, the basolateral amygdala (BLA) integrates sensory information from the environment and activates the central amygdala (CE). Subsequently, the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) triggers defensive responses by projecting to brain regions such as the ventral striatum, hippocampus, lateral hypothalamus (LH) and surrounding areas (LeDoux, 2000). For persistent anxiety, the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), which is part of an extended amygdala, is more directly involved and closely coupled with the CE (Zhu et al., 2024).
Under high-pressure conditions, the LC enhances amygdala function while simultaneously attenuates the prefrontal cortex (PFC) function to facilitate fear learning. Conversely, under low-pressure conditions, the LC enhances PFC function, thereby increasing the inhibitory effect of the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) on the amygdala from top to bottom, and subsequently promoting fear extinction (Giustino and Maren, 2018).
Moreover, the hippocampus receives signals from the BLA and stores fear and long-term anxiety signals (Hajisoltani and Meftahi, 2024). These memories persist for a period and can be reactivated by a similar context, even if the individual is no longer directly in that situation (Chaaya et al., 2018). In addition to anxiety signals from the locus coeruleus, sensory information from visceral changes, such as heart rate, gastrointestinal responses and blood pressure, can be transmitted to the mPFC via the anterior insula, thereby contributing to the maintenance of anxiety (Vertes, 2004). Disrupted limbic-hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (LHPA), commonly referred to as the HPA axis, is also involved in anxiety disorders. Patients with anxiety exhibit elevated levels of plasma cortisol, which is released from the adrenal gland, potentially intensifying feelings of fatigue due to the acceleration of glycogen metabolism (Juruena et al., 2020).
2.2 Insomnia
Insomnia is the most prevalent sleep disorder in industrialized countries, characterized by symptoms such as dissatisfaction with sleep quality or duration, difficulty falling asleep at bedtime, waking up in the middle of the night or too early in the morning (Morin and Benca, 2012). Although symptoms of insomnia primarily occur at night, many individuals also experience daytime cognitive impairments, such as difficulties with attention, concentration and memory, as along with mood disturbances like irritability and dysphoria (Buysse et al., 2007). Even though a significant number of adults are suffering from severe insomnia, less than 15% of those receive proper treatment (Bhat et al., 2008).
Dysfunction of the wakefulness and sleep neural systems is the major cause of insomnia (Riemann et al., 2010). The wakefulness regulatory system comprises two pathways (Saper et al., 2005). One pathway involves NA neurons in the LC, serotonin (5-HT) neurons in the raphe nuclei, histaminergic (His) neurons in the tuberomammillary nucleus (TMN) and dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the ventral periaqueductal gray (vPAG) (John et al., 2004; Ko et al., 2003; Verret et al., 2006). This pathway receives signals from neurons in the LH, including orexin (ORX) and melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH), and acetylcholine (ACh) and GABA from neurons in the basal forebrain (BF), and leads to cortical activation and wakefulness. The second ascending arousal pathway includes cholinergic neurons in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus (PPT) and laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (LDT). Their activation stimulates thalamic relay neurons, resulting in cortical activation and maintenance of conscious wakefulness (Morin et al., 2015).
In addition, the sleep-promoting system includes the hypothalamic ventrolateral preoptic area, basal ganglia, cerebral cortex, limbic system, BF, and the brainstem and thalamus (Saper et al., 2005). Activation of GABAergic neurons in the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO) and inhibition of NA activity mediated sleep are the core sleep-promoting cluster (Dubourget et al., 2017). Moreover, VLPO GABAergic neurons can inhibit the activation of wakefulness systems, including the LDT, dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), and locus coeruleus (LC), causing a transition to sleep (Morin et al., 2015).
Sleep–wake homeostasis is maintained by the “Flip-Flop Switch” model, in which transition between sleep and arousal depends on interactions among the VLPO, monoaminergic cell groups (nuclei) and ORX neurons (Morin et al., 2015; Saper et al., 2005). Dysregulation of the arousal system, characterized by heightened physiological arousal during both sleep and wakefulness, results in a state known as hyperarousal, which is a significant contributor to insomnia (Riemann et al., 2010).
3 An association of GABA with anxiety and insomnia
Insomnia is considered to exacerbate anxiety, since inadequate sleep can increase negative emotions, diminish positive emotions, and alter adolescents’ comprehension, expression and modulation of emotions (Blake et al., 2018; Palmer and Alfano, 2017). Conversely, anxiety can contribute to the onset of insomnia, and stress exposure disrupts sleep, leading to difficulties in both falling asleep and staying asleep (Kalmbach et al., 2018).
It appears that both anxiety disorder and insomnia are associated with decreased levels of GABA. Significantly reduced GABA levels have been observed in brains of individuals with anxiety disorders, particularly in the thalamus and the amygdala, as detected by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) analysis (Babaev et al., 2018; Streeter et al., 2010). GABA levels in plasma of patients with anxiety have shown notable decreases (Lydiard, 2003; Shutta et al., 2021). Moreover, reduced expression levels of GABAA receptor α1 and α2 subunits have also been detected in the serum of insomnia patients (Xiang et al., 2023). On the other hand, the GABAA receptor agonist, such as benzodiazepine, can effectively alleviate symptoms of anxiety and treat insomnia, and the antagonist of GABAB and GABAC receptors, like CGP-36742, can reduce a patient’s slow-wave sleep (Deschaux et al., 2006; Nutt, 2005; Sternbach, 1978).
4 Synthesis and functions of GABA
GABA is a prominent neurotransmitter within the brain, and also functions as a regulatory hormone in peripheral organs, which holds significant importance for the human body (Jin and Korol, 2023; Zhang et al., 2021). GABA, also known as 4-aminobutyric acid, is a compound represented by the chemical formula C₄H₉NO₂ (Figure 1A). It is an amino acid that is widely distributed among vertebrates, plants, and microorganisms (Sarasa et al., 2020). In living organisms, GABA is primarily synthesized by glutamate decarboxylase (GAD), an enzyme that uses glutamate (L-Glu) as the raw material in the presence of coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate and protons (Figure 1A) (Soghomonian and Martin, 1998).
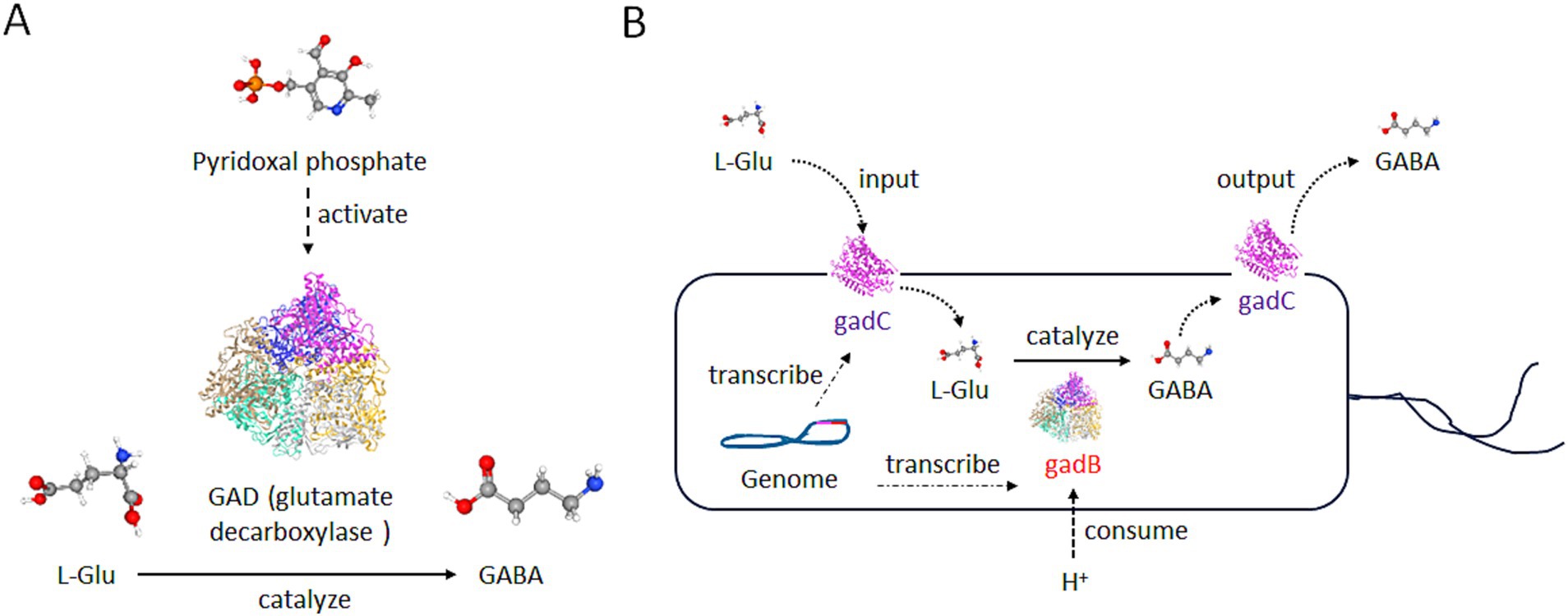
Figure 1. Structure and production of GABA. (A) The production diagram of GABA. With the assistance of pyridoxal phosphate, the glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) enzyme is transformed into an active structure and then converts L-Glu into GABA. L-Glu, GABA, and Pyridoxal phosphate are illustrated by PubChem. White ball: the hydrogen atom; red ball: the oxygen atom; gray ball: the carbon atom; blue ball: the nitrogen atom; yellow ball: the phosphorus atom. (B) The diagram of GABA’s production by gut microbiota. The genome of many bacteria carries the gadB and gadC genes. The gadB is a type of GAD in (A), and functions in the same manner as GAD. GABA produced by gadB can be transported extracellularly through gadC. Meanwhile, the raw material L-Glu can also enter the cell through gadC, and this process can consume H+ ions outside the environment.
In bacteria, GABA is primarily involved in the survival ability in an acidic environment. Escherichia coli and other enterobacteria utilize the H+ consuming reaction catalyzed by gad to reduce the concentration of H+ around the microorganism itself, and survive in the stomach acidity before reaching the intestine (Figure 1B) (Sarasa et al., 2020). In the vertebrates, GABA primarily acts on GABA receptors, triggering ion exchange across the neuronal membrane, altering current signals, and generating inhibitory potentials, thereby inhibiting neuronal excitation (Taylor et al., 2003). Particularly, GABA can act on ionotropic receptors such as GABAA and GABAC receptors, as well as the metabotropic receptor GABAB receptor in the brain (Figure 2) (Felice et al., 2022).
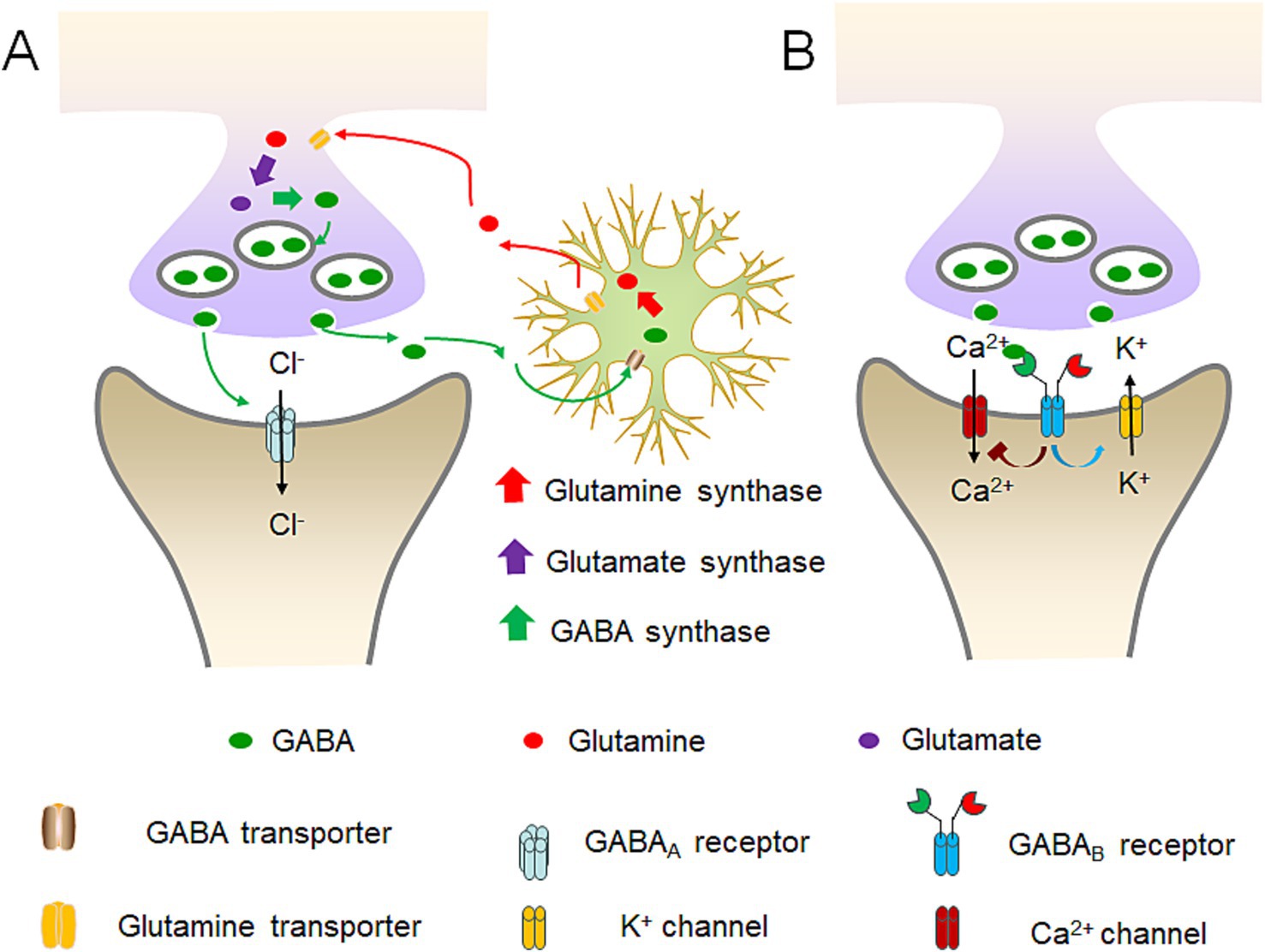
Figure 2. Diagram of GABA receptors’ workflow and GABA’s conversion balance. (A) GABAA receptors’ workflow and the balance among GABA, glutamine and glutamate. GABA neurons can convert the absorbed glutamine into glutamate, and then into GABA. Subsequently, GABA is excreted and acts on the next neuron. Upon the binding of GABA to the GABAA receptor, it prompts the opening of chloride ion channels within the receptor, thereby giving rise to either the inward or outward flow of chloride ions. The predominant direction of movement is the inward flow. (B) GABAB receptors’ workflow. GABAB receptors are capable of anchoring to Ca2+ and K+ channels on the cell membrane. Through the dynamic modulation of the closure of these ion channels, it restricts the influx of Ca2+ and augments the influx of K+, thereby attaining an inhibitory hyperpolarized state of the membrane potential.
GABAA receptors are pentameric ligand-gated ion channels widely expressed throughout the central and peripheral nervous system (Luo and Balle, 2022). When GABA binds to the GABAA receptor, it causes the chloride ion channels on the receptor to open, and leads to either the influx or efflux of chloride ions, with the predominant movement being the influx (Figure 2A) (Kim and Hibbs, 2021). The opening of the chloride ion channels by GABA helps stabilize the resting potential of cells during the activation of excitatory receptors and makes it more difficult for neurons to generate excitatory action potentials and release neurotransmitters (Bormann, 1988; Kim and Hibbs, 2021).
GABAB receptors are G-protein coupled receptors and primarily exist in a heterodimeric form. Different from the GABAA ion channels, GABAB receptors can anchor to Ca2+ and K+ channels on the cell membrane (Figure 2B) (Bormann, 1988). By dynamically regulating the closure of these ion channels, it inhibits the influx of Ca2+ and promotes the influx of K+ to achieve an inhibitory hyperpolarized state of the membrane potential. Additionally, it can dynamically regulate the switches of the G-proteins it anchors to, realizing the activation of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins and indirectly producing the second messenger cAMP to exert its effects (Bettler et al., 2004).
The GABAC receptor is a subclass of the GABAA receptor, and is often referred to as the GABAA rho receptor with three different subtypes ρ1-3 (Olsen and Sieghart, 2008). Its structure and function are largely similar to those of GABAA receptors. It is categorized separately due to being insensitive to both bicuculline and baclofen (Johnston, 2013).
In the brain, GABA primarily plays a role in intermediate neurons, which are notably rich in the enzyme GAD. Experimental findings have revealed that the removal of the GAD enzyme from the mouse brain tissue results in a significant reduction in detectable GABA levels (Ji et al., 1999).
In the synaptic cleft, any excess GABA that remains unabsorbed after transmission is re-uptaken by astrocytes, where it is converted into glutamine (Figure 2A). This glutamine is then utilized by glutamatergic neurons to synthesize glutamate. Subsequently, the released glutamate is taken up by GABAergic neurons to regenerate GABA. Through the coordinated activity of glutamatergic neurons, GABAergic neurons and astrocytes, GABA stays at a balanced level, and the neural network maintains a state of equilibrium, which is essential for the proper functioning of the brain (Mazzoli and Pessione, 2016; Steel et al., 2020).
In patients with anxiety and insomnia, signs of excessive consumption of GABA were detected. This may be related to the overactivity of GABA transaminase, which causes excessive conversion of GABA into succinic semialdehyde (SSA), reducing the neuroinhibitory effect of GABA (Liu M. Q. et al., 2022). Adding some GABA transaminase inhibitors can be effective in the treatment of anxiety and insomnia (Di Pierro et al., 2024; Liu M. Q. et al., 2022; Srichomphu et al., 2022).
5 Therapeutic effects of gut derived GABA on anxiety and insomnia
5.1 Anxiety
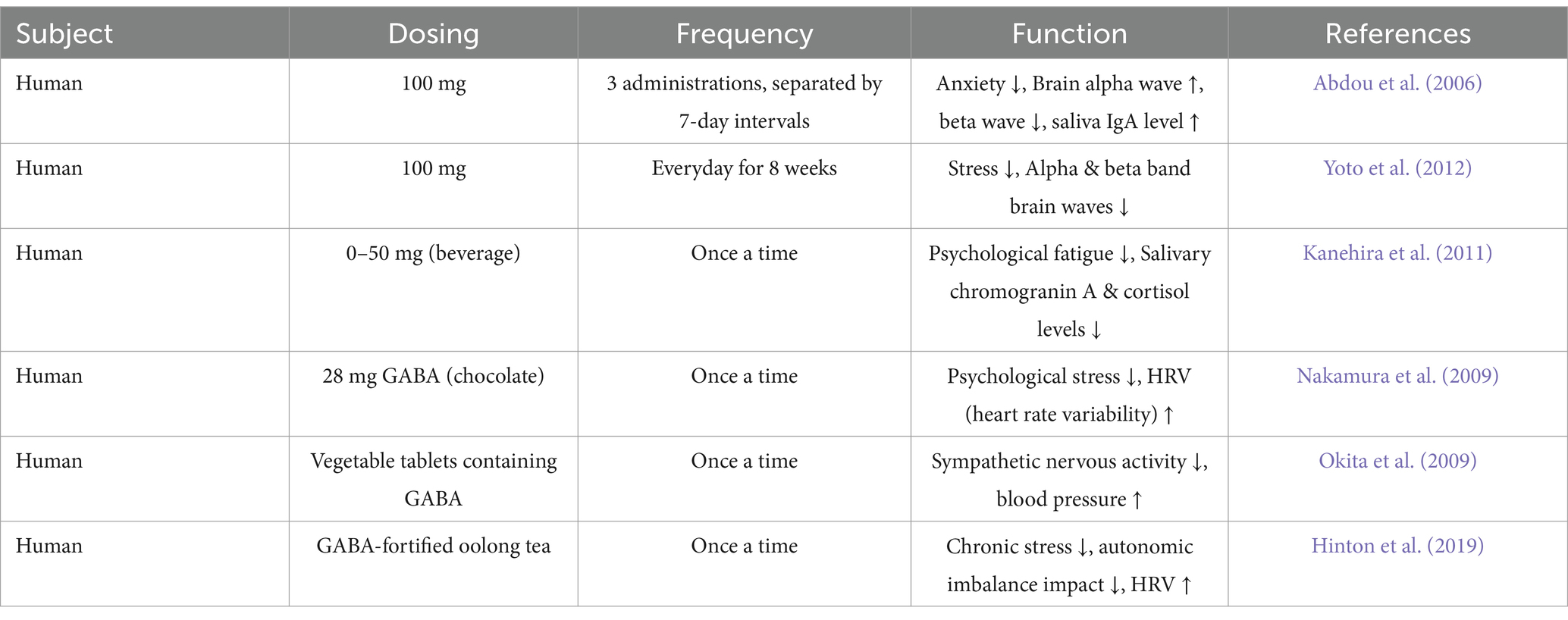
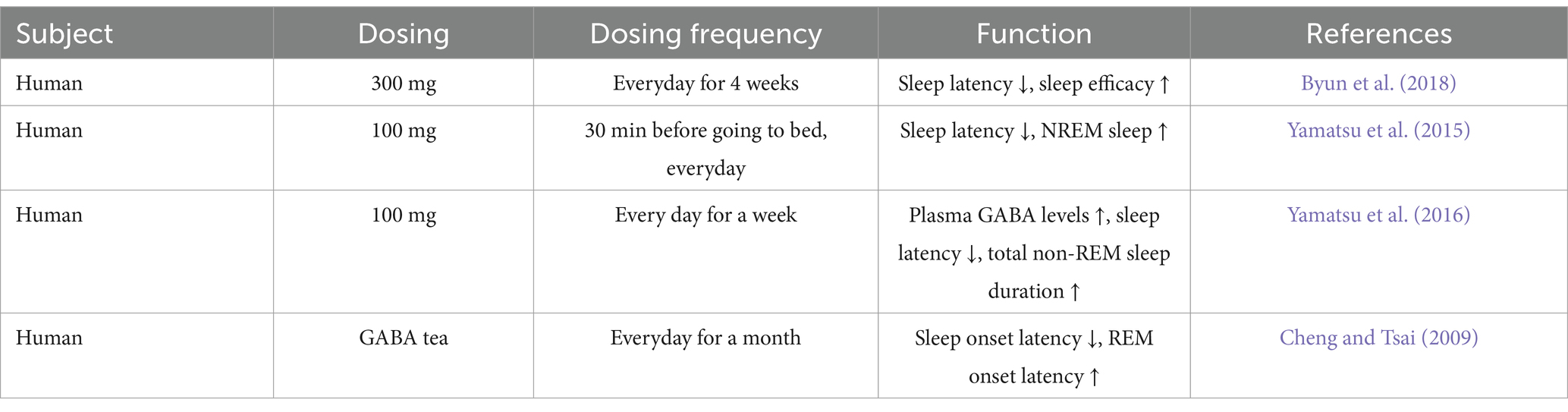
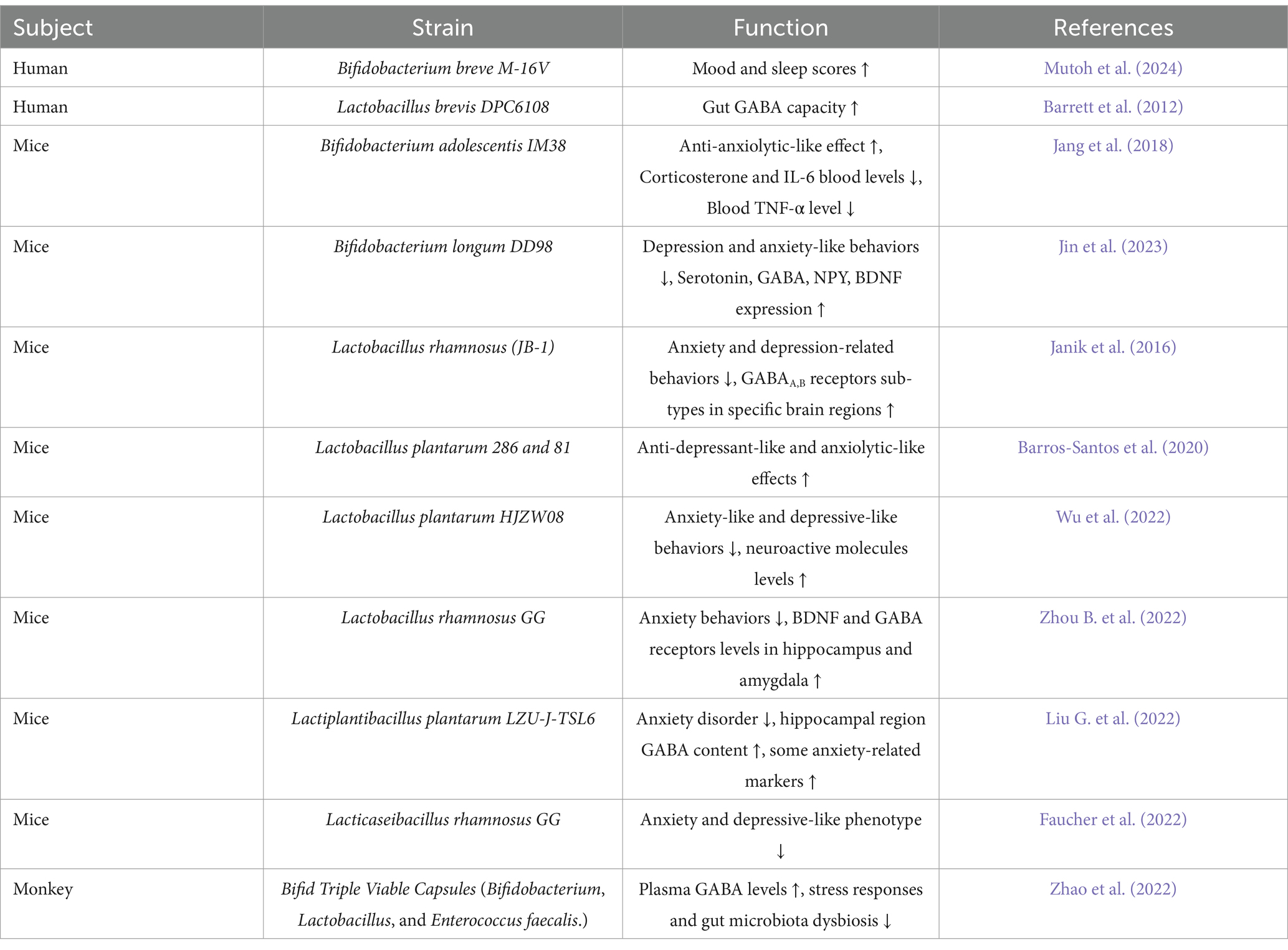
Gut derived GABA encompasses GABA obtained from dietary sources as well as GABA produced by the resident gut microbiota, and represents a significant source of GABA in the human body (Duranti et al., 2020; Liwinski et al., 2023). Direct oral GABA supplements and dietary food, for instance potatoes, tomatoes, rice, tea and beans, are primary sources of gut derived GABA (Tables 1, 2) (Cai et al., 2014; Hinton and Johnston, 2020; Kim et al., 2015; Lei et al., 2023; Liwinski et al., 2023; Vann et al., 2020; Yan et al., 2021). Moreover, bacteria can convert glutamate into GABA through a process that utilizes protons (Feehily and Karatzas, 2013). Probiotic bacteria such as Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus and Lactiplantibacillus can produce GABA and significantly increase the GABA level in the intestines (Table 3) (Barrett et al., 2012; Duranti et al., 2020; Luck et al., 2021; Watanabe et al., 2022). Notably, studies have shown that gut derived GABA can treat anxiety and insomnia by exerting a widespread influence on hormone levels, secretion of signaling molecules, gene expression, and various other physiological changes (Abdou et al., 2006; Liwinski et al., 2023; Yamatsu et al., 2015).
Studies indicate that both the direct administration of 100 mg of GABA and the consumption of GABA-containing foods exhibit a certain therapeutic effect on anxiety-related behaviors (Table 1) (Barros-Santos et al., 2020; Faucher et al., 2022; Yoto et al., 2012). The administration of the GABA-producing strain Bifidobacterium adolescentis IM38 significantly improved anxiety-like behaviors in mice, and this effect was blocked by flumazenil, a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist (Jang et al., 2018). This finding suggests that gut derived GABA exerts their influence through GABA-regulated sites, potentially acting on GABA receptors in the brain. Moreover, administering probiotics Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SNK12, which produces GABA, has been shown to alleviate anxiety and reduce salivary cortisol levels in humans (Watanabe et al., 2022). Similar phenomena are also observed in animal models (Cai et al., 2022).
5.2 Insomnia
Clinical trials have provided evidence that the administration of 100 mg of GABA significantly improves sleep quality, which is reflected by a reduction in sleep latency and an increase in the duration of non-REM sleep (Table 2) (Yamatsu et al., 2015; Yamatsu et al., 2016). Similar positive effects on sleep quality have been observed in clinical trials involving the consumption of GABA tea (Cheng and Tsai, 2009). In animal studies, a significant decrease in peripheral blood GABA concentration of sleep-deprived monkeys, accompanied by a substantial increase in peripheral blood NE and cortisol, both indicative of HPA axis upregulation (Zhao et al., 2022). Supplementation with probiotics producing GABA significantly reduced the levels of hormones associated with the HPA axis and increased peripheral blood GABA levels, suggesting a therapeutic effect. Similar findings were also reported in mouse experiments. Mice fed GABA black tea exhibited a significant decrease in sleep latency period induced by pentobarbital sodium, accompanied by a substantial increase in the duration of effective sleep (Zhao et al., 2015). Administration of 100 mg/kg GABA not only significantly reduced sleep latency and increased sleep duration, but also elevated the expression levels of GABA receptor mRNA in the mouse brain, proving that supplementing with gut derived GABA can indeed enhance GABAergic signaling in the brain and improve sleep (Chen et al., 2021; Kim et al., 2019; Liu D. et al., 2022).
5.3 Dosage and side effects
Studies indicated that a direct administration of 100 mg of GABA represents an appropriate dosage for the treatment of anxiety and insomnia. This dosage can exert positive effects in terms of alleviating anxiety, shortening sleep latency, and enhancing sleep quality (Abdou et al., 2006; Yamatsu et al., 2015; Yamatsu et al., 2016; Yoto et al., 2012). Research has demonstrated that even when a relatively high dose, such as 6 g of GABA per day, is administered, no obvious side effects are observed in volunteers, suggesting the favorable biosafety of GABA (Li et al., 2015). However, it is noteworthy that current studies have revealed that GABA is not conducive to the anti-tumor response. Multiple investigations have elucidated that GABA can inhibit dendritic cell mediated T-cell recruitment and activation (Huang et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2021). Therefore, it is not advisable to use gut derived GABA as a drug treatment for cancer patients.
5.4 Probiotics and engineered bacteria
It is worth noting that in addition to the dietary and orally administered GABA presented in Tables 1, 2, the utilization of GABA-producing bacteria has emerged as an innovative therapeutic strategy for anxiety and insomnia (Table 3). A substantial body of research demonstrates that GABA-producing bacteria can effectively mitigate these disorders. These bacteria exert diverse effects on the body, such as diminishing stress factor levels, augmenting GABA concentrations, and modulating the levels of GABA receptors and their corresponding mRNAs in the brain (Janik et al., 2016; Jin et al., 2023; Liu G. et al., 2022; Zhou B. et al., 2022).
Unlike orally ingested GABA, which is rapidly eliminated from the body, GABA-producing gut bacteria can colonize the host’s gastrointestinal tract for an extended period. This persistent colonization enables continuous GABA synthesis, thereby conferring prolonged therapeutic benefits (Pokusaeva et al., 2017). Additionally, the impact of these bacteria on the gut’s ecological environment is persistent over time. Significantly, the employment of probiotic strains has the significant advantage of imposing a lower metabolic burden on organs such as the liver compared to traditional small molecule drugs (Li et al., 2015; Oketch-Rabah et al., 2021).
Moreover, through microbiome sequencing, it has been found that some bacteria can either promote or inhibit the growth of GABA-producing bacteria. Supplementation with Limosilactobacillus fermentum L18 can significantly increase the abundance of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus (Kaur et al., 2023). This might be due to that these strains can optimize the acidic environment for GABA production by regulating the intestinal pH value and metabolite exchange. However, some strains, such as Enterobacteriaceae, can reduce the abundance of GABA-producing bacteria. This could be due to the production of substances like lipopolysaccharides by these strains, which hinder the growth of GABA-producing bacteria (Zeng et al., 2024). Thus, the supplementation of GABA-producing bacteria is still an effective method. In the future, the administration of combined bacterial agents could be considered (Zhao et al., 2022).
Apart from certain natural probiotic strains like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, genetically engineered bacterial strains have also been harnessed in the treatment of anxiety. To date, numerous studies have endeavored to employ engineered probiotics to express GABA and address anxiety (Lebovich and Andrews, 2022, 2023; Pan et al., 2022; Pokusaeva et al., 2017). The advantage of using engineered bacteria for anxiety treatment resides in the precise regulation of GABA production, for instance treating anxious mice using an engineered Lactococcus lactis strain (Pan et al., 2022).
Moreover, the majority of these studies have adopted Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) (Lebovich and Andrews, 2022, 2023). EcN is a renowned probiotic strain of Escherichia coli. Owing to its probiotic properties and well-defined manipulable genetic background, it is currently extensively utilized as a vector in engineered bacteria therapy (Lynch et al., 2022). When engineered EcN is employed to produce GABA, the GABA yield can attain as high as 17.9 g/L (Lan et al., 2021). Another benefit of engineered bacteria is their proficiency in GABA production, as they can overexpress gadB and gadC proteins within the bacteria. Nevertheless, at present, research articles on the application of EcN that produces GABA to treat neurological diseases remain relatively scarce, presenting an area worthy of future exploration.
There are several issues regarding probiotics that need to be addressed. The introduction of gut microbiota can alter intestinal metabolic activities in the host, which may have adverse effects on a very small number of individuals. For example, the probiotics L. acidophilus and Bifidobacterium can convert primary bile salts into secondary bile salts (Ruseler-van Embden et al., 1995). Most secondary bile salts are reabsorbed to enter the liver for metabolism. If the liver function is abnormal and unable to metabolize secondary bile salts properly, it may lead to their accumulation in the liver, exerting toxic effects on liver cells and further aggravating liver damage (Zawistowska-Rojek and Tyski, 2018). Moreover, some probiotics may carry antibiotic-resistance genes, which poses a risk of potential transfer of these genes within the gut microbiota (Merenstein et al., 2023). These issues need to be considered and addressed in the future studies.
5.5 Gut microbiota
To optimize the application of gut derived GABA, it is crucial to summarize and investigate the underlying mechanisms of its effects. When GABA is taken orally and enters the intestinal tract, it will first be affected by the body’s intestinal microbiota (Figure 3). GABA is reported to act as a critical growth factor for certain strains of intestinal bacteria in the human gut microbiota, leading to an increase of these specific microbial communities within the host (Strandwitz et al., 2019). GABA also serves as a carbon and nitrogen source for the gut microbiota. Within bacteria, GABA can be further converted into succinic semialdehyde (SSA) by GABA transaminase. Subsequently, SSA is transformed into succinate by the enzyme succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase, which then enters the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle for further metabolic processing (Sarasa et al., 2020).
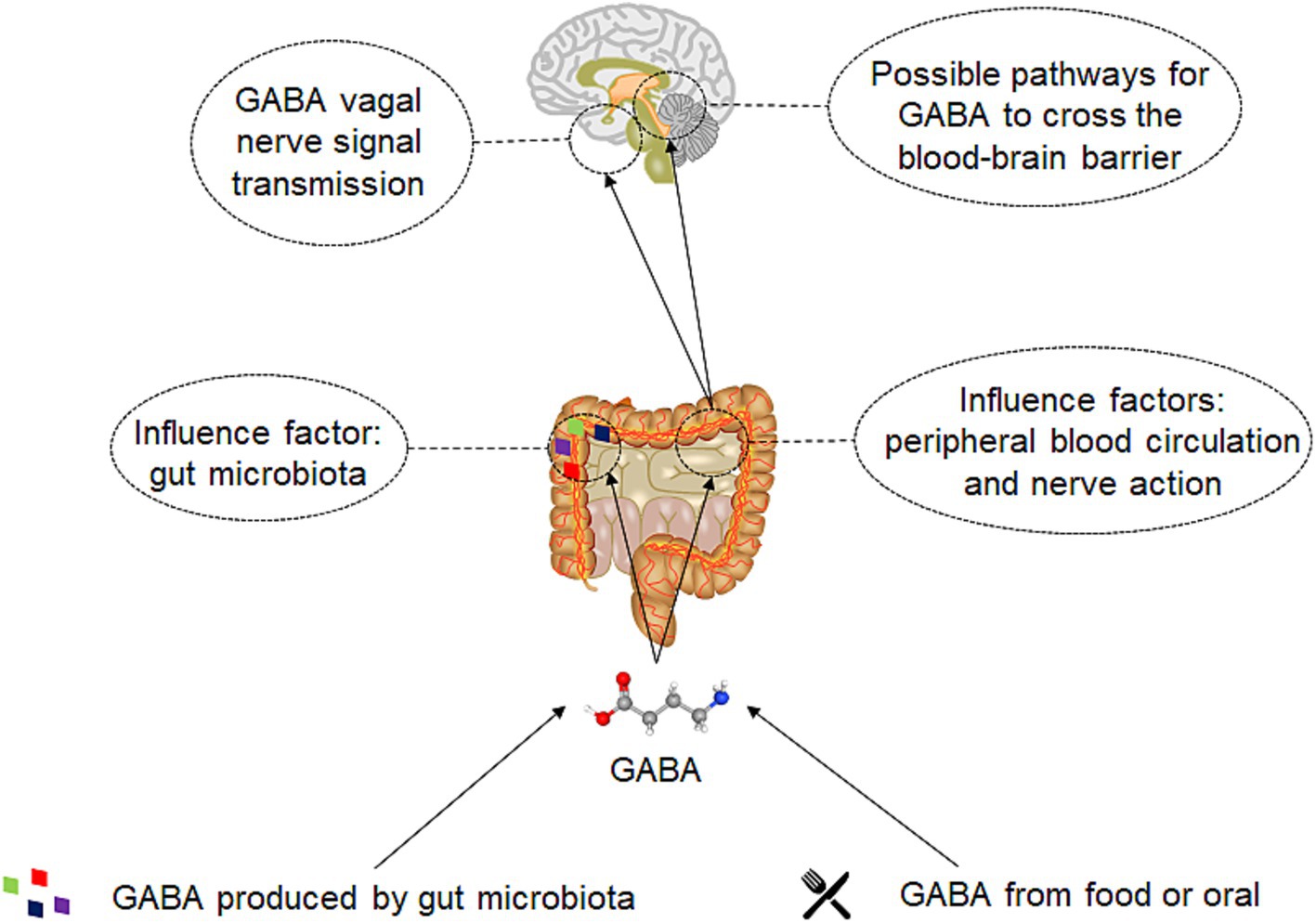
Figure 3. The mechanism of gut derived GABA on human body. Two sources gut derived GABA: one is obtained through direct oral intake or via food, and the other is generated by the gut microbiota. Subsequently, GABA will directly act on the gut microbiota and have a direct impact on its metabolism. A significant portion will also be absorbed by the gut, enter the bloodstream, or act on enteric neurons and the vagus nerve. GABA that acts on the enteric nerves and vagus nerve can be transmitted through neural signals and affect the brain. GABA that enters the bloodstream may eventually interact with the brain by crossing the blood–brain barrier.
5.6 GABA absorption
5.6.1 Small intestine epithelial cell transport: SLC family
The initial site of interaction between gut derived GABA and the human body is the intestinal tract. In the intestine, gut derived GABA is absorbed by intestine epithelial cells (Figure 4). The intestine normally employs passive absorption to transport small-molecule substances, such as amino acids (Nácher et al., 1994; Thwaites et al., 2000). GABA transporters in the intestines of both rodents and humans facilitate both active and passive absorption of GABA (Nácher et al., 1994; Thwaites et al., 2000). Proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 (PAT1) has been confirmed as the GABA transporter responsible for transporting GABA across the apical membrane of intestinal epithelial cells into the cells (Figure 4B) (Chen et al., 2003).
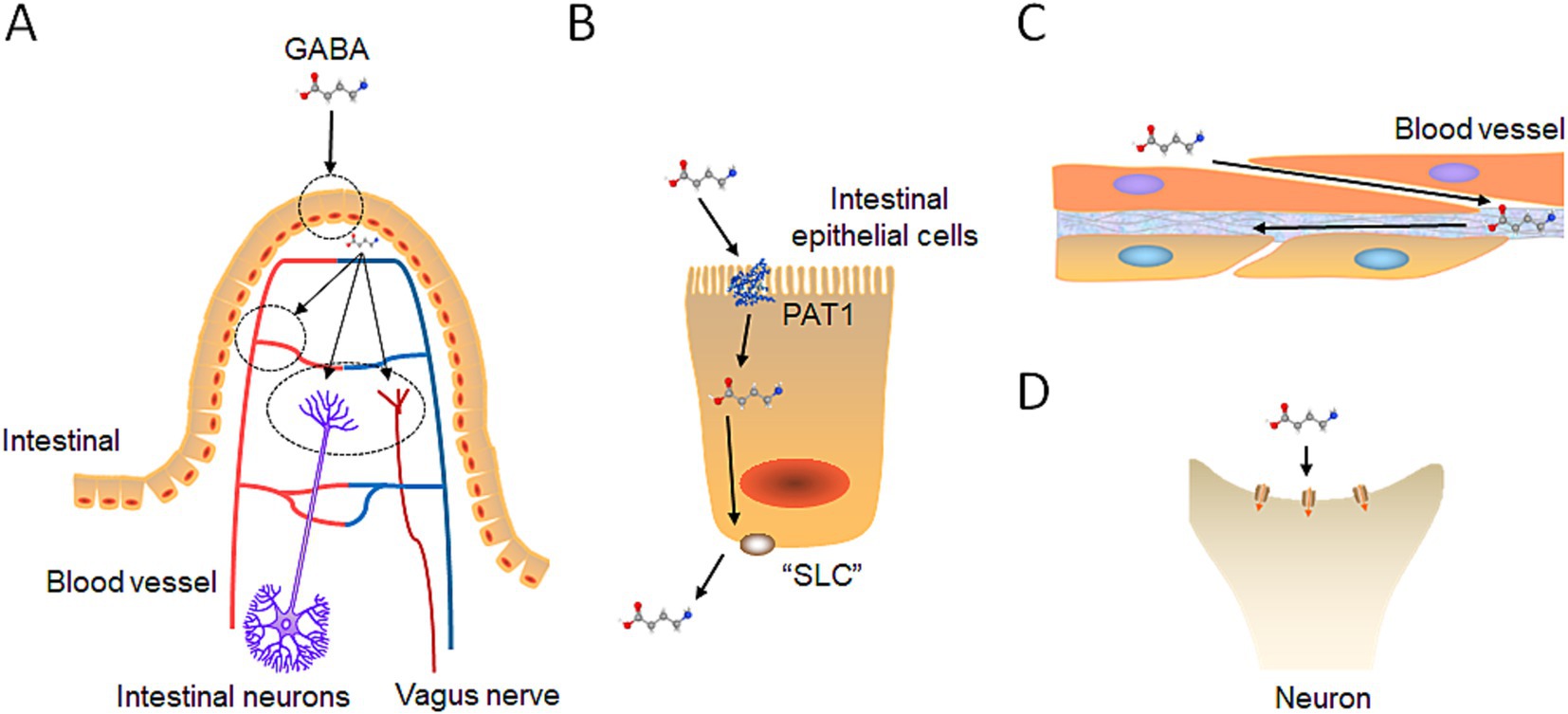
Figure 4. Exogenous GABA intestinal absorption pathway. (A) GABA intestinal absorption diagram: Initially, GABA is taken up by intestinal epithelial cells. Then, it diverges into three pathways: bloodstream entry, interaction with enteric neurons, and connection with the vagus nerve. (B) GABA intestinal transport: GABA crosses the small intestine membrane via the PAT protein on the basolateral side and exits through a probable SLC family protein on the apical side. (C) GABA integrates into the blood circulation: GABA penetrates the fenestrated capillaries within the intestinal lining to join the bloodstream. (D) GABA binds to receptors: GABA interacts with GABA receptors on intestinal neurons and the vagus nerve, as previously described, to exert its effects.
It is speculated that small intestinal epithelial cells exclude GABA from the basal membrane into the extracellular space of the submucosal layer through one of the solute carrier transporters (SLC) family proteins (Figure 4B). SLC transporters comprise approximately 350 members belonging to 55 families, with some SLC proteins exhibit bidirectional transport functions (Kristensen et al., 2011). For example, SLC6A1 (GAT1) mediates the transport of GABA together with sodium and chloride ions, and is responsible for the reuptake of GABA from the synapse. The direction and magnitude of GABA transport are determined by thermodynamic conditions, influenced by factors such as membrane potential and the concentrations of Na+, Cl−, and GABA (Mattison et al., 2018). SLC family proteins with bidirectional transport mechanisms or one that transports GABA from intracellular to extracellular spaces may exist at the basal membrane of small intestinal epithelial cells, facilitating the transport of GABA (Zafar and Jabeen, 2018). Further research is necessary to confirm this possibility.
5.6.2 Capillary absorption
When GABA is transported by small intestinal epithelial cells to the lamina propria, it partially enters the capillaries to participate in blood circulation (Figure 4C). The capillaries in the lamina propria are fenestrated, called “fenestrated capillary,” meaning that they have intracellular pores or “windows” with a diaphragm that penetrate the endothelial lining (Augustin and Koh, 2017). These pores facilitate the exchange of water and allow the passage of solutes, such as small peptides, between plasma and interstitial fluid. Fenestrated capillaries are found throughout various tissues, including the choroid plexus of the brain, certain endocrine organs, kidney filtration sites, and intestinal absorptive regions (Augustin and Koh, 2017). Given that GABA is significantly smaller than peptides, it can theoretically pass through the pores of fenestrated capillaries. Consequently, research has demonstrated that GABA derived from the gut can effectively elevate GABA levels in the bloodstream of both humans and animal models (Yamatsu et al., 2016; Zhao et al., 2022).
5.6.3 Vagus nerve absorption
GABA is transported by small intestinal epithelial cells to the lamina propria, where some enter the bloodstream, and some act on the intestinal nerve plexus, which causes intestinal muscles and glands to respond and transmit signals to other parts such as the brain through the vagus nerve (Figure 4D). Interestingly, administering Lactobacillus rhamnosus (JB-1), a probiotic strain producing GABA, has been shown to improve anxiety-and depression-related behaviors in mice (Bravo et al., 2011). However, after surgically removing the vagus nerves in mice fed with the probiotic, the behavioral improvements were lost, indicating that the vagus nerve serves as a major modulatory constitutive communication pathway between gut-exposed bacteria and the brain.
5.6.4 Hypothalamus—hormone secretion
After receiving the signals of gut derived GABA, the afferent fibers of the vagus nerve in the gastrointestinal tract transmit the messages through neuronal synapses, converting them into cholinergic signals (Qu et al., 2024). These signals are then transmitted to the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) in the medulla oblongata. Subsequently, the NTS communicates with the locus coeruleus, which sends signals onward to either the amygdala or the thalamus (Breit et al., 2018). Additionally, the hypothalamus directly receives signals from GABA in the peripheral blood. Structurally, it is closely connected to the primary capillary plexus within the pituitary portal system (Ilgin, 2020). Studies have shown that injecting competitive antagonists of GABAA receptors into the PVN significantly increases stress-induced cortisol secretion, whereas selective GABA receptor antagonists notably reduce it (Cullinan et al., 2008). Moreover, supplementation with GABA-producing probiotics inhibits the activated HPA axis. Indeed, this indirectly provides evidence that GABA in peripheral blood can act on the hypothalamus to regulate the HPA axis (Cai et al., 2022; Watanabe et al., 2022).
5.7 Brain
5.7.1 The pathway of gut derived GABA entering the brain
The impact of gut derived GABA on the brain has been a contentious topic, with a central question being the permeability of the blood–brain barrier (BBB). While some studies suggest that GABA cannot penetrate the BBB in mammals, other research indicates that GABA can traverse it, albeit in modest quantities (Boonstra et al., 2015; Frey and Löscher, 1980; Knudsen et al., 1988; Toth and Lajtha, 1981; Van Gelder and Elliott, 1958). Analyzing the structural aspects of the BBB could provide a theoretical basis to support the potential passage of GABA through this barrier.
The BBB consists of adjacent capillary endothelial cells interconnected by impermeable tight junctions, requiring molecules to enter through active uptake by specialized transporter proteins or by diffusing into the BBB cells (Abbott et al., 2010; Brightman and Reese, 1969; Pardridge, 2005, 2007). Among these transporters, a crucial group is the SLC6 family, one of the largest SLC families comprising 20 genes that encode highly similar transporter proteins. The SLC6 family, abundantly expressed in the brain, includes GABA transporters such as GAT1 (SLC6A1), GAT2 (SLC6A13), GAT3 (SLC6A11), and BGT1 (SLC6A12). These transporters are responsible for the transport of neurotransmitters into and out of the brain, thereby regulating neurotransmitter homeostasis (Abbott et al., 2010). Studies have shown that GAT2/BGT-1 expressed in epithelial cells serve as GABA transporters at the BBB to transport GABA (Takanaga et al., 2001). In addition, GAT2/BGT-1 has been found to be widely expressed in the mouse brain. Notably, GAT2 is expressed on both the apical and basal membranes of epithelial cells, exhibiting bidirectional transport capability. In contrast, BGT1 is expressed solely on the basal membrane. GAT2 at the BBB facilitates the transport of GABA.
Extensive studies have observed increased concentrations of brain GABA and mRNA expression levels of GABA receptors following administration of gut derived GABA (Jin et al., 2023; Watanabe et al., 2022; Zhou H. et al., 2022). These findings collectively support that gut derived GABA can modulate the brain’s GABAergic system, potentially alleviating neurological disorders by enhancing GABAergic signaling in the brain.
6 Future direction
Currently, a large portion of the global population is suffering from anxiety and insomnia, grappling with the challenges posed by these mental health disorders. The current sedatives and sleep aids available for treating anxiety and insomnia often come with side effects like physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms (Shyken et al., 2019). Hence, the development of novel interventions that address anxiety and insomnia without such drawbacks remains necessary.
GABA, as a natural neurotransmitter in the human body, poses minimal harm even in high doses (Li et al., 2015). The supplementation of GABA through gut derived sources holds great promise. Oral GABA, GABA-enriched diets, and probiotic strains producing GABA have demonstrated positive and effective outcomes in treating anxiety and insomnia. However, oral GABA has several limitations, which include: First, low blood–brain barrier permeability: Unlike benzodiazepines, GABA does not efficiently cross the blood–brain barrier, limiting its ability to exert strong pharmacological effects. Overall, the efficiency of GABA crossing the blood–brain barrier is not very high. Second, low bioavailability: The bioavailability of GABA when ingested is relatively low, and it is quickly eliminated from the body, which makes it challenging to sustain therapeutic efficacy. Third, non-specific effects: GABA is widely distributed throughout the body, not only in the central nervous system but also in many other tissues and organs. This wide distribution may lead to non-specific effects rather than targeting specific diseases or symptoms. An increasing amount of research has found that GABA functions as a signal molecule in the immune system. Several studies have clarified that GABA is not beneficial for the anti-tumor response. So, it is not recommended to provide gut derived GABA as a drug treatment for cancer patients.
Probiotic and engineered bacteria capable of producing GABA present promising avenues for the treatment of anxiety and insomnia. These bacteria can colonize in the human gut and release GABA promptly. There remain several aspects that warrant further exploration. For instance, determining the optimal drug dosage of probiotics for human treatment and, notably, laying particular emphasis on considering the safety of engineered foreign genes. Future research efforts should be intensified to not only optimize the drug dosage regimens but also to conduct rigorous and systematic investigations into the safety of foreign genes. Only through such meticulous exploration can we hope to translate these promising approaches into reliable and effective therapeutic solutions, thereby offering a new ray of hope for the countless individuals suffering from anxiety and insomnia, and revolutionizing the landscape of mental health treatment.
Author contributions
CJ: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YC: Writing – review & editing. TS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Scientific Research Funds of Huaqiao University (Z16Y0017, TS), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32271002, TS).
Acknowledgments
We thank members of the Sun laboratory and members of GeneYoung Biopharmaceuticals for their valuable discussions and advice.
Conflict of interest
YC is employed by GeneYoung Biopharmaceuticals.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Chengji Jiang polished the paper with ChatGPT.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbott, N. J., Patabendige, A. A., Dolman, D. E., Yusof, S. R., and Begley, D. J. (2010). Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 37, 13–25. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.07.030
Abdou, A. M., Higashiguchi, S., Horie, K., Kim, M., Hatta, H., and Yokogoshi, H. (2006). Relaxation and immunity enhancement effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) administration in humans. Biofactors 26, 201–208. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520260305
Augustin, H. G., and Koh, G. Y. (2017). Organotypic vasculature: from descriptive heterogeneity to functional pathophysiology. Science 357:eaal2379. doi: 10.1126/science.aal2379
Babaev, O., Piletti Chatain, C., and Krueger-Burg, D. (2018). Inhibition in the amygdala anxiety circuitry. Exp. Mol. Med. 50, 1–16. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0063-8
Barrett, E., Ross, R. P., O'Toole, P. W., Fitzgerald, G. F., and Stanton, C. (2012). γ-Aminobutyric acid production by culturable bacteria from the human intestine. J. Appl. Microbiol. 113, 411–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05344.x
Barros-Santos, T., Silva, K. S. O., Libarino-Santos, M., Elisangela Gouveia, C.-P., Reis, H. S., Tamura, E. K., et al. (2020). Effects of chronic treatment with new strains of Lactobacillus plantarum on cognitive, anxiety-and depressive-like behaviors in male mice. PLoS One 15:e0234037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234037
Bettler, B., Kaupmann, K., Mosbacher, J., and Gassmann, M. (2004). Molecular structure and physiological functions of GABA(B) receptors. Physiol. Rev. 84, 835–867. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00036.2003
Bhat, A., Shafi, F., and El Solh, A. A. (2008). Pharmacotherapy of insomnia. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 9, 351–362. doi: 10.1517/14656566.9.3.351
Blake, M. J., Trinder, J. A., and Allen, N. B. (2018). Mechanisms underlying the association between insomnia, anxiety, and depression in adolescence: implications for behavioral sleep interventions. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 63, 25–40. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2018.05.006
Boonstra, E., de Kleijn, R., Colzato, L. S., Alkemade, A., Forstmann, B. U., and Nieuwenhuis, S. (2015). Neurotransmitters as food supplements: the effects of GABA on brain and behavior. Front. Psychol. 6:1520. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01520
Bormann, J. (1988). Electrophysiology of GABAA and GABAB receptor subtypes. Trends Neurosci. 11, 112–116. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90156-7
Bowery, N. G., Doble, A., Hill, D. R., Hudson, A. L., Shaw, J. S., and Turnbull, M. J. (1979). Baclofen: a selective agonist for a novel type of GABA receptor proceedings. Br. J. Pharmacol. 67, 444–445.
Bragantini, D., Sivertsen, B., Gehrman, P., Lydersen, S., and Güzey, I. C. (2019). Differences in anxiety levels among symptoms of insomnia. The HUNT study. Sleep Health 5, 370–375. doi: 10.1016/j.sleh.2019.01.002
Bravo, J. A., Forsythe, P., Chew, M. V., Escaravage, E., Savignac, H. M., Dinan, T. G., et al. (2011). Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 16050–16055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102999108
Breit, S., Kupferberg, A., Rogler, G., and Hasler, G. (2018). Vagus nerve as modulator of the brain-gut Axis in psychiatric and inflammatory disorders. Front. Psych. 9:44. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00044
Brightman, M. W., and Reese, T. S. (1969). Junctions between intimately apposed cell membranes in the vertebrate brain. J. Cell Biol. 40, 648–677. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.3.648
Buckley, T. M., and Schatzberg, A. F. (2005). On the interactions of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and sleep: normal HPA axis activity and circadian rhythm, exemplary sleep disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90, 3106–3114. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-1056
Buysse, D. J., Thompson, W., Scott, J., Franzen, P. L., Germain, A., Hall, M., et al. (2007). Daytime symptoms in primary insomnia: a prospective analysis using ecological momentary assessment. Sleep Med. 8, 198–208. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2006.10.006
Byrd, J. B., and Brook, R. D. (2014). Anxiety in the "age of hypertension". Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 16:486. doi: 10.1007/s11906-014-0486-0
Byun, J. I., Shin, Y. Y., Chung, S. E., and Shin, W. C. (2018). Safety and efficacy of gamma-aminobutyric acid from fermented Rice germ in patients with insomnia symptoms: a randomized, double-blind trial. J. Clin. Neurol. 14, 291–295. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2018.14.3.291
Cai, S., Gao, F., Zhang, X., Wang, O., Wu, W., Zhu, S., et al. (2014). Evaluation of γ-aminobutyric acid, phytate and antioxidant activity of tempeh-like fermented oats (Avena sativa L.) prepared with different filamentous fungi. J. Food Sci. Technol. 51, 2544–2551. doi: 10.1007/s13197-012-0748-2
Cai, L., Tao, Q., Li, W., Zhu, X., and Cui, C. (2022). The anti-anxiety/depression effect of a combined complex of casein hydrolysate and γ-aminobutyric acid on C57BL/6 mice. Front. Nutr. 9:971853. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.971853
Calm, C. C. (2024). Mental health 2024 statistics: the growing impact of anxiety. Available online at: https://www.laurageftman.com/blog/mental-health-2024-statistics-anxiety.
Carlisi, C. O., Hilbert, K., Guyer, A. E., and Ernst, M. (2017). Sleep-amount differentially affects fear-processing neural circuitry in pediatric anxiety: a preliminary fMRI investigation. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 17, 1098–1113. doi: 10.3758/s13415-017-0535-7
Chaaya, N., Battle, A. R., and Johnson, L. R. (2018). An update on contextual fear memory mechanisms: transition between amygdala and Hippocampus. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 92, 43–54. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.05.013
Chellappa, S. L., and Aeschbach, D. (2022). Sleep and anxiety: from mechanisms to interventions. Sleep Med. Rev. 61:101583. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101583
Chen, Z., Fei, Y. J., Anderson, C. M., Wake, K. A., Miyauchi, S., Huang, W., et al. (2003). Structure, function and immunolocalization of a proton-coupled amino acid transporter (hPAT1) in the human intestinal cell line Caco-2. J. Physiol. 546, 349–361. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.026500
Chen, X., Jia, X., Zhang, Y., Zhao, Z., Hao, J., Li, H., et al. (2021). The combined use of gamma-aminobutyric acid and walnut peptide enhances sleep in mice. Ann. Palliat. Med. 10, 11074–11082. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2798
Cheng, T. C., and Tsai, J. F. (2009). GABA tea helps sleep. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 15, 697–698. doi: 10.1089/acm.2009.0023
Cullinan, W. E., Ziegler, D. R., and Herman, J. P. (2008). Functional role of local GABAergic influences on the HPA axis. Brain Struct. Funct. 213, 63–72. doi: 10.1007/s00429-008-0192-2
Deschaux, O., Froestl, W., and Gottesmann, C. (2006). Influence of a GABA(B) and GABA(C) receptor antagonist on sleep-waking cycle in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 535, 177–181. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.01.066
Di Pierro, F., Sisti, D., Rocchi, M., Belli, A., Bertuccioli, A., Cazzaniga, M., et al. (2024). Effects of Melissa officinalis Phytosome on sleep quality: results of a prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled, and cross-over study. Nutrients 16:4199. doi: 10.3390/nu16234199
Dubourget, R., Sangare, A., Geoffroy, H., Gallopin, T., and Rancillac, A. (2017). Multiparametric characterization of neuronal subpopulations in the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus. Brain Struct. Funct. 222, 1153–1167. doi: 10.1007/s00429-016-1265-2
Duranti, S., Ruiz, L., Lugli, G. A., Tames, H., Milani, C., Mancabelli, L., et al. (2020). Bifidobacterium adolescentis as a key member of the human gut microbiota in the production of GABA. Sci. Rep. 10:14112. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70986-z
Faucher, P., Dries, A., Mousset, P. Y., Leboyer, M., Dore, J., and Beracochea, D. (2022). Synergistic effects of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG, glutamine, and curcumin on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression in a mouse model. Benef Microbes 13, 253–264. doi: 10.3920/bm2021.0188
Feehily, C., and Karatzas, K. A. (2013). Role of glutamate metabolism in bacterial responses towards acid and other stresses. J. Appl. Microbiol. 114, 11–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05434.x
Felice, D., Cryan, J. F., and O'Leary, O. F. (2022). GABA(B) receptors: anxiety and mood disorders. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 52, 241–265. doi: 10.1007/7854_2020_171
Frey, H. H., and Löscher, W. (1980). Cetyl GABA: effect on convulsant thresholds in mice and acute toxicity. Neuropharmacology 19, 217–220. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(80)90141-0
Giustino, T. F., and Maren, S. (2018). Noradrenergic modulation of fear conditioning and extinction. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 12:43. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00043
Gong, L., Shi, M., Wang, J., Xu, R., Yu, S., Liu, D., et al. (2021). The abnormal functional connectivity in the locus Coeruleus-norepinephrine system associated with anxiety symptom in chronic insomnia disorder. Front. Neurosci. 15:678465. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.678465
Greenblatt, D. J., Harmatz, J. S., and Shader, R. I. (2020). Diazepam in the elderly: looking Back, ahead, and at the evidence. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 40, 215–219. doi: 10.1097/jcp.0000000000001213
Hajisoltani, R., and Meftahi, G. H. (2024). Epinephrine injected into the basolateral amygdala affects anxiety-like behavior and memory performance in stressed rats. Neurosci. Lett. 819:137590. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2023.137590
Hepsomali, P., Groeger, J. A., Nishihira, J., and Scholey, A. (2020). Effects of Oral gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) administration on stress and sleep in humans: a systematic review. Front. Neurosci. 14:923. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00923
Hinton, T., Jelinek, H. F., Viengkhou, V., Johnston, G. A., and Matthews, S. (2019). Effect of GABA-fortified oolong tea on reducing stress in a university student cohort. Front. Nutr. 6:27. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00027
Hinton, T., and Johnston, G. A. R. (2020). GABA-enriched teas as neuro-nutraceuticals. Neurochem. Int. 141:104895. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104895
Huang, D., Wang, Y., Thompson, J. W., Yin, T., Alexander, P. B., Qin, D., et al. (2022). Cancer-cell-derived GABA promotes β-catenin-mediated tumour growth and immunosuppression. Nat. Cell Biol. 24, 230–241. doi: 10.1038/s41556-021-00820-9
Ilgin, S. (2020). The adverse effects of psychotropic drugs as an endocrine disrupting chemicals on the hypothalamic-pituitary regulation in male. Life Sci. 253:117704. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117704
Jang, H. M., Jang, S. E., Han, M. J., and Kim, D. H. (2018). Anxiolytic-like effect of Bifidobacterium adolescentis IM38 in mice with or without immobilisation stress. Benef Microbes 9, 123–132. doi: 10.3920/bm2016.0226
Janik, R., Thomason, L. A. M., Stanisz, A. M., Forsythe, P., Bienenstock, J., and Stanisz, G. J. (2016). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals oral Lactobacillus promotion of increases in brain GABA, N-acetyl aspartate and glutamate. NeuroImage 125, 988–995. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.11.018
Ji, F., Kanbara, N., and Obata, K. (1999). GABA and histogenesis in fetal and neonatal mouse brain lacking both the isoforms of glutamic acid decarboxylase. Neurosci. Res. 33, 187–194. doi: 10.1016/s0168-0102(99)00011-5
Jin, X., Hu, Y., Lin, T., Gao, F., Xu, Z., Hou, X., et al. (2023). Selenium-enriched Bifidobacterium longum DD98 relieves irritable bowel syndrome induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in mice. Food Funct. 14, 5355–5374. doi: 10.1039/d2fo03408e
Jin, Z., and Korol, S. V. (2023). GABA signalling in human pancreatic islets. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 14:1059110. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1059110
John, J., Wu, M. F., Boehmer, L. N., and Siegel, J. M. (2004). Cataplexy-active neurons in the hypothalamus: implications for the role of histamine in sleep and waking behavior. Neuron 42, 619–634. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(04)00247-8
Johnston, G. A. (2013). Advantages of an antagonist: bicuculline and other GABA antagonists. Br. J. Pharmacol. 169, 328–336. doi: 10.1111/bph.12127
Juruena, M. F., Eror, F., Cleare, A. J., and Young, A. H. (2020). The role of early life stress in HPA Axis and anxiety. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1191, 141–153. doi: 10.1007/978-981-32-9705-0_9
Kalmbach, D. A., Anderson, J. R., and Drake, C. L. (2018). The impact of stress on sleep: pathogenic sleep reactivity as a vulnerability to insomnia and circadian disorders. J. Sleep Res. 27:e12710. doi: 10.1111/jsr.12710
Kandola, A., and Stubbs, B. (2020). Exercise and anxiety. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1228, 345–352. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1792-1_23
Kanehira, T., Nakamura, Y., Nakamura, K., Horie, K., Horie, N., Furugori, K., et al. (2011). Relieving occupational fatigue by consumption of a beverage containing γ-amino butyric acid. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 57, 9–15. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.57.9
Kaur, S., Sharma, P., Mayer, M. J., Neuert, S., Narbad, A., and Kaur, S. (2023). Beneficial effects of GABA-producing potential probiotic Limosilactobacillus fermentum L18 of human origin on intestinal permeability and human gut microbiota. Microb. Cell Factories 22:256. doi: 10.1186/s12934-023-02264-2
Kim, J. J., and Hibbs, R. E. (2021). Direct structural insights into GABA(a) receptor pharmacology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 46, 502–517. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.01.011
Kim, S., Jo, K., Hong, K. B., Han, S. H., and Suh, H. J. (2019). GABA and l-theanine mixture decreases sleep latency and improves NREM sleep. Pharm. Biol. 57, 65–73. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2018.1557698
Kim, H. S., Lee, E. J., Lim, S. T., and Han, J. A. (2015). Self-enhancement of GABA in rice bran using various stress treatments. Food Chem. 172, 657–662. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.107
Knudsen, G. M., Poulsen, H. E., and Paulson, O. B. (1988). Blood-brain barrier permeability in galactosamine-induced hepatic encephalopathy. No evidence for increased GABA-transport. J. Hepatol. 6, 187–192. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(88)80030-8
Ko, E. M., Estabrooke, I. V., McCarthy, M., and Scammell, T. E. (2003). Wake-related activity of tuberomammillary neurons in rats. Brain Res. 992, 220–226. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2003.08.044
Krettek, J. E., and Price, J. L. (1978). A description of the amygdaloid complex in the rat and cat with observations on intra-amygdaloid axonal connections. J. Comp. Neurol. 178, 255–279. doi: 10.1002/cne.901780205
Kristensen, A. S., Andersen, J., Jørgensen, T. N., Sørensen, L., Eriksen, J., Loland, C. J., et al. (2011). SLC6 neurotransmitter transporters: structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol. Rev. 63, 585–640. doi: 10.1124/pr.108.000869
Lan, Y. J., Tan, S. I., Cheng, S. Y., Ting, W. W., Xue, C., Lin, T. H., et al. (2021). Development of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 derivative by CRISPR/Cas9 and application for gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) production in antibiotic-free system. Biochem. Eng. J. 168:107952. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2021.107952
Lebovich, M., and Andrews, L. B. (2022). Surveying the genetic design space for transcription factor-based metabolite biosensors: synthetic gamma-aminobutyric acid and propionate biosensors in E. coli Nissle 1917. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10:938056. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.938056
Lebovich, M., and Andrews, L. B. (2023). Genetic circuits for feedback control of gamma-aminobutyric acid biosynthesis in probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917. bioRxiv. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.09.544351
LeDoux, J. E. (2000). Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 155–184. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.23.1.155
Lei, J., Shen, L., Zhang, W., Ma, F., Wang, J., Wei, T., et al. (2023). Comparative chemical characterization of potato powders using (1)H NMR spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 78, 590–596. doi: 10.1007/s11130-023-01088-0
Li, J., Zhang, Z., Liu, X., Wang, Y., Mao, F., Mao, J., et al. (2015). Study of GABA in healthy volunteers: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Front. Pharmacol. 6:260. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00260
Liu, G., Khan, I., Li, Y., Yang, Y., Lu, X., Wang, Y., et al. (2022). Overcoming anxiety disorder by probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LZU-J-TSL6 through regulating intestinal homeostasis. Food Secur. 11:3596. doi: 10.3390/foods11223596
Liu, M. Q., Wang, T., Wang, Q. L., Zhou, J., Wang, B. R., Zhang, B., et al. (2022). Structure-guided discovery of food-derived GABA-T inhibitors as hunters for anti-anxiety compounds. Food Funct. 13, 12674–12685. doi: 10.1039/d2fo01315k
Liu, D., Zhang, J., Chen, J., Zhang, C., Yi, H., and Liu, D. (2022). Carrot-based fermentation juice rich in sleep-promoting components improved sleep in mice. Front. Nutr. 9:1043055. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1043055
Liwinski, T., Lang, U. E., Brühl, A. B., and Schneider, E. (2023). Exploring the therapeutic potential of gamma-aminobutyric acid in stress and depressive disorders through the gut-brain Axis. Biomedicines 11:3128. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123128
Luck, B., Horvath, T. D., Engevik, K. A., Ruan, W., Haidacher, S. J., Hoch, K. M., et al. (2021). Neurotransmitter profiles are altered in the gut and brain of mice mono-associated with Bifidobacterium dentium. Biomol. Ther. 11:1091. doi: 10.3390/biom11081091
Luo, Y., and Balle, T. (2022). GABA(a) receptors as targets for anaesthetics and analgesics and promising candidates to help treat coronavirus infections: a mini-review. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 131, 443–451. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13798
Lynch, J. P., Goers, L., and Lesser, C. F. (2022). Emerging strategies for engineering Escherichia coli Nissle 1917-based therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 43, 772–786. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2022.02.002
Mattison, K. A., Butler, K. M., Inglis, G. A. S., Dayan, O., Boussidan, H., Bhambhani, V., et al. (2018). SLC6A1 variants identified in epilepsy patients reduce γ-aminobutyric acid transport. Epilepsia 59, e135–e141. doi: 10.1111/epi.14531
Mazzoli, R., and Pessione, E. (2016). The neuro-endocrinological role of microbial glutamate and GABA signaling. Front. Microbiol. 7:1934. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01934
Merenstein, D., Pot, B., Leyer, G., Ouwehand, A. C., Preidis, G. A., Elkins, C. A., et al. (2023). Emerging issues in probiotic safety: 2023 perspectives. Gut Microbes 15:2185034. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2185034
Morin, C. M., and Benca, R. (2012). Chronic insomnia. Lancet 379, 1129–1141. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60750-2
Morin, C. M., Drake, C. L., Harvey, A. G., Krystal, A. D., Manber, R., Riemann, D., et al. (2015). Insomnia disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 1:15026. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2015.26
Morin, C. M., and Jarrin, D. C. (2022). Epidemiology of insomnia: prevalence, course, risk factors, and public health burden. Sleep Med. Clin. 17, 173–191. doi: 10.1016/j.jsmc.2022.03.003
Morris, L. S., McCall, J. G., Charney, D. S., and Murrough, J. W. (2020). The role of the locus coeruleus in the generation of pathological anxiety. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 4:2398212820930321. doi: 10.1177/2398212820930321
Mutoh, N., Moriya, M., Xu, C., Kato, K., Arai, S., Iwabuchi, N., et al. (2024). Bifidobacterium breve M-16V regulates the autonomic nervous system via the intestinal environment: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Behav. Brain Res. 460:114820. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114820
Nácher, A., Polache, A., Moll-Navarro, M. J., Plá-Delfina, J. M., and Merino, M. (1994). Intestinal absorption pathway of gamma-aminobutyric acid in rat small intestine. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 15, 359–371. doi: 10.1002/bdd.2510150503
Nakamura, H., Takishima, T., Kometani, T., and Yokogoshi, H. (2009). Psychological stress-reducing effect of chocolate enriched with gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in humans: assessment of stress using heart rate variability and salivary chromogranin a. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 60, 106–113. doi: 10.1080/09637480802558508
Ngo, D. H., and Vo, T. S. (2019). An updated review on pharmaceutical properties of gamma-aminobutyric acid. Molecules 24:2678. doi: 10.3390/molecules24152678
Nutt, D. J. (2005). Overview of diagnosis and drug treatments of anxiety disorders. CNS Spectr. 10, 49–56. doi: 10.1017/s1092852900009901
Oketch-Rabah, H. A., Madden, E. F., Roe, A. L., and Betz, J. M. (2021). United States Pharmacopeia (USP) safety review of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Nutrients 13:2742. doi: 10.3390/nu13082742
Okita, Y., Nakamura, H., Kouda, K., Takahashi, I., Takaoka, T., Kimura, M., et al. (2009). Effects of vegetable containing gamma-aminobutyric acid on the cardiac autonomic nervous system in healthy young people. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 28, 101–107. doi: 10.2114/jpa2.28.101
Olsen, R. W., and Sieghart, W. (2008). International Union of Pharmacology. LXX. Subtypes of gamma-aminobutyric acid(a) receptors: classification on the basis of subunit composition, pharmacology, and function. Update. Pharmacol. Rev. 60, 243–260. doi: 10.1124/pr.108.00505
Palmer, C. A., and Alfano, C. A. (2017). Sleep and emotion regulation: an organizing, integrative review. Sleep Med. Rev. 31, 6–16. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2015.12.006
Palmer, C. A., and Alfano, C. A. (2020). Anxiety modifies the emotional effects of sleep loss. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 34, 100–104. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2019.12.001
Pan, H., Sun, T., Cui, M., Ma, N., Yang, C., Liu, J., et al. (2022). Light-sensitive Lactococcus lactis for microbe-gut-brain Axis regulating via Upconversion Optogenetic Micro-Nano system. ACS Nano 16, 6049–6063. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c11536
Pardridge, W. M. (2005). The blood-brain barrier: bottleneck in brain drug development. NeuroRx 2, 3–14. doi: 10.1602/neurorx.2.1.3
Pardridge, W. M. (2007). Blood-brain barrier delivery. Drug Discov. Today 12, 54–61. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2006.10.013
Pillai, V., Roth, T., Mullins, H. M., and Drake, C. L. (2014). Moderators and mediators of the relationship between stress and insomnia: stressor chronicity, cognitive intrusion, and coping. Sleep 37, 1199–1208A. doi: 10.5665/sleep.3838
Pokusaeva, K., Johnson, C., Luk, B., Uribe, G., Fu, Y., Oezguen, N., et al. (2017). GABA-producing Bifidobacterium dentium modulates visceral sensitivity in the intestine. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 29:e12904. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12904
Qu, S., Yu, Z., Zhou, Y., Wang, S., Jia, M., Chen, T., et al. (2024). Gut microbiota modulates neurotransmitter and gut-brain signaling. Microbiol. Res. 287:127858. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2024.127858
Ren, X., Zhao, X., Li, J., Liu, Y., Ren, Y., Pruessner, J. C., et al. (2022). The hippocampal-ventral medial prefrontal cortex Neurocircuitry involvement in the Association of Daily Life Stress with Acute Perceived Stress and Cortisol Responses. Psychosom. Med. 84, 276–287. doi: 10.1097/psy.0000000000001058
Riedel, A., Benz, F., Deibert, P., Barsch, F., Frase, L., Johann, A. F., et al. (2024). The effect of physical exercise interventions on insomnia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 76:101948. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2024.101948
Riemann, D., Spiegelhalder, K., Feige, B., Voderholzer, U., Berger, M., Perlis, M., et al. (2010). The hyperarousal model of insomnia: a review of the concept and its evidence. Sleep Med. Rev. 14, 19–31. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2009.04.002
Roberts, A. G., Peckins, M. K., Gard, A. M., Hein, T. C., Hardi, F. A., Mitchell, C., et al. (2022). Amygdala reactivity during socioemotional processing and cortisol reactivity to a psychosocial stressor. Psychoneuroendocrinology 144:105855. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2022.105855
Robinson, O. J., Pike, A. C., Cornwell, B., and Grillon, C. (2019). The translational neural circuitry of anxiety. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 90, jnnp-2019-321400–jnnp-2019-321360. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2019-321400
Ruseler-van Embden, J. G., van Lieshout, L. M., Gosselink, M. J., and Marteau, P. (1995). Inability of Lactobacillus casei strain GG, L. acidophilus, and Bifidobacterium bifidum to degrade intestinal mucus glycoproteins. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 30, 675–680. doi: 10.3109/00365529509096312
Sadeh, A., Keinan, G., and Daon, K. (2004). Effects of stress on sleep: the moderating role of coping style. Health Psychol. 23, 542–545. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.23.5.542
Saper, C. B., Scammell, T. E., and Lu, J. (2005). Hypothalamic regulation of sleep and circadian rhythms. Nature 437, 1257–1263. doi: 10.1038/nature04284
Sarasa, S. B., Mahendran, R., Muthusamy, G., Thankappan, B., Selta, D. R. F., and Angayarkanni, J. (2020). A brief review on the non-protein amino acid, gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA): its production and role in microbes. Curr. Microbiol. 77, 534–544. doi: 10.1007/s00284-019-01839-w
Shaha, D. P. (2023). Insomnia management: a review and update. J. Fam. Pract. 72, S31–s36. doi: 10.12788/jfp.0620
Shutta, K. H., Balasubramanian, R., Huang, T., Jha, S. C., Zeleznik, O. A., Kroenke, C. H., et al. (2021). Plasma metabolomic profiles associated with chronic distress in women. Psychoneuroendocrinology 133:105420. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2021.105420
Shyken, J. M., Babbar, S., Babbar, S., and Forinash, A. (2019). Benzodiazepines in Pregnancy. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 62, 156–167. doi: 10.1097/grf.0000000000000417
Sigel, E., and Ernst, M. (2018). The benzodiazepine binding sites of GABAA receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 39, 659–671. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.03.006
Soghomonian, J. J., and Martin, D. L. (1998). Two isoforms of glutamate decarboxylase: why? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 19, 500–505. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(98)01270-x
Srichomphu, P., Wattanathorn, J., Thukham-Mee, W., and Muchimapura, S. (2022). Anxiety, insomnia, and memory impairment in metabolic syndrome rats are alleviated by the novel functional ingredients from Anacardium occidentale. Antioxidants (Basel) 11:2203. doi: 10.3390/antiox11112203
Steel, A., Mikkelsen, M., Edden, R. A. E., and Robertson, C. E. (2020). Regional balance between glutamate+glutamine and GABA+ in the resting human brain. NeuroImage 220:117112. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117112
Sternbach, L. H. (1978). The benzodiazepine story. Prog. Drug Res. 22, 229–266. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7102-0_5
Strandwitz, P. (2018). Neurotransmitter modulation by the gut microbiota. Brain Res. 1693, 128–133. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.03.015
Strandwitz, P., Kim, K. H., Terekhova, D., Liu, J. K., Sharma, A., Levering, J., et al. (2019). GABA-modulating bacteria of the human gut microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 396–403. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0307-3
Streeter, C. C., Whitfield, T. H., Owen, L., Rein, T., Karri, S. K., Yakhkind, A., et al. (2010). Effects of yoga versus walking on mood, anxiety, and brain GABA levels: a randomized controlled MRS study. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 16, 1145–1152. doi: 10.1089/acm.2010.0007
Suárez-Pereira, I., Llorca-Torralba, M., Bravo, L., Camarena-Delgado, C., Soriano-Mas, C., and Berrocoso, E. (2022). The role of the locus Coeruleus in pain and associated stress-related disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 91, 786–797. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.11.023
Takanaga, H., Ohtsuki, S., Hosoya, K., and Terasaki, T. (2001). GAT2/BGT-1 as a system responsible for the transport of gamma-aminobutyric acid at the mouse blood-brain barrier. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 21, 1232–1239. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200110000-00012
Taylor, M., Bhagwagar, Z., Cowen, P. J., and Sharp, T. (2003). GABA and mood disorders. Psychol. Med. 33, 387–393. doi: 10.1017/s0033291702006876
Thwaites, D. T., Basterfield, L., McCleave, P. M., Carter, S. M., and Simmons, N. L. (2000). Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transport across human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cell monolayers. Br. J. Pharmacol. 129, 457–464. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703069
Toth, E., and Lajtha, A. (1981). Elevation of cerebral levels of nonessential amino acids in vivo by administration of large doses. Neurochem. Res. 6, 1309–1317. doi: 10.1007/bf00964352
Van Gelder, N. M., and Elliott, K. A. (1958). Disposition of gamma-aminobutyric acid administered to mammals. J. Neurochem. 3, 139–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12620.x
Van Someren, E. J. W. (2021). Brain mechanisms of insomnia: new perspectives on causes and consequences. Physiol. Rev. 101, 995–1046. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00046.2019
Vann, K., Techaparin, A., and Apiraksakorn, J. (2020). Beans germination as a potential tool for GABA-enriched tofu production. J. Food Sci. Technol. 57, 3947–3954. doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04423-4
Verret, L., Fort, P., Gervasoni, D., Léger, L., and Luppi, P. H. (2006). Localization of the neurons active during paradoxical (REM) sleep and projecting to the locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurons in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 495, 573–586. doi: 10.1002/cne.20891
Vertes, R. P. (2004). Differential projections of the infralimbic and prelimbic cortex in the rat. Synapse 51, 32–58. doi: 10.1002/syn.10279
Vu, V., and Conant-Norville, D. (2021). Anxiety: recognition and treatment options. Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 44, 373–380. doi: 10.1016/j.psc.2021.04.005
Warner, E. N., and Strawn, J. R. (2023). Risk factors for pediatric anxiety disorders. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 32, 485–510. doi: 10.1016/j.chc.2022.10.001
Watanabe, T., Hayashi, K., Takara, T., Teratani, T., Kitayama, J., and Kawahara, T. (2022). Effect of Oral Administration of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SNK12 on temporary stress in adults: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:8936. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19158936
Wong, M. L., Kling, M. A., Munson, P. J., Listwak, S., Licinio, J., Prolo, P., et al. (2000). Pronounced and sustained central hypernoradrenergic function in major depression with melancholic features: relation to hypercortisolism and corticotropin-releasing hormone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 325–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.1.325
Wu, Y., Wang, Y., Hu, A., Shu, X., Huang, W., Liu, J., et al. (2022). Lactobacillus plantarum-derived postbiotics prevent Salmonella-induced neurological dysfunctions by modulating gut-brain axis in mice. Front. Nutr. 9:946096. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.946096
Xiang, T., Liao, J., Cai, Y., Fan, M., Li, C., Zhang, X., et al. (2023). Impairment of GABA inhibition in insomnia disorders: evidence from the peripheral blood system. Front. Psych. 14:1134434. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1134434
Yamatsu, A., Yamashita, Y., Maru, I., Yang, J., Tatsuzaki, J., and Kim, M. (2015). The improvement of sleep by Oral intake of GABA and Apocynum venetum leaf extract. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 61, 182–187. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.61.182
Yamatsu, A., Yamashita, Y., Pandharipande, T., Maru, I., and Kim, M. (2016). Effect of oral γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) administration on sleep and its absorption in humans. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 25, 547–551. doi: 10.1007/s10068-016-0076-9
Yan, L., Zheng, H., Liu, W., Liu, C., Jin, T., Liu, S., et al. (2021). UV-C treatment enhances organic acids and GABA accumulation in tomato fruits during storage. Food Chem. 338:128126. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128126
Yoo, S. S., Gujar, N., Hu, P., Jolesz, F. A., and Walker, M. P. (2007). The human emotional brain without sleep--a prefrontal amygdala disconnect. Curr. Biol. 17, R877–R878. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.08.007
Yoto, A., Murao, S., Motoki, M., Yokoyama, Y., Horie, N., Takeshima, K., et al. (2012). Oral intake of γ-aminobutyric acid affects mood and activities of central nervous system during stressed condition induced by mental tasks. Amino Acids 43, 1331–1337. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-1206-6
Zafar, S., and Jabeen, I. (2018). Structure, function, and modulation of γ-aminobutyric acid transporter 1 (GAT1) in neurological disorders: a Pharmacoinformatic prospective. Front. Chem. 6:397. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00397
Zawistowska-Rojek, A., and Tyski, S. (2018). Are probiotic really safe for humans? Pol. J. Microbiol. 67, 251–258. doi: 10.21307/pjm-2018-044
Zeng, Y., Hu, H., He, Y., Deng, Z., Guo, Y., and Zhou, X. (2024). Multi-omics reveal the improvements of nutrient digestion, absorption, and metabolism and intestinal function via GABA supplementation in weanling piglets. Animals (Basel) 14:3177. doi: 10.3390/ani14223177
Zhang, J., Lam, S. P., Li, S. X., Ma, R. C., Kong, A. P., Chan, M. H., et al. (2014). A community-based study on the association between insomnia and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: sex and pubertal influences. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 99, 2277–2287. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3728
Zhang, B., Vogelzang, A., Miyajima, M., Sugiura, Y., Wu, Y., Chamoto, K., et al. (2021). B cell-derived GABA elicits IL-10(+) macrophages to limit anti-tumour immunity. Nature 599, 471–476. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04082-1
Zhao, W., Li, Y., Ma, W., Ge, Y., and Huang, Y. (2015). A study on quality components and sleep-promoting effects of GABA black tea. Food Funct. 6, 3393–3398. doi: 10.1039/c5fo00265f
Zhao, N., Shu, Y., Jian, C., Zhou, Z., Bao, H., Li, X., et al. (2022). Lactobacillus ameliorates SD-induced stress responses and gut Dysbiosis by increasing the absorption of gut-derived GABA in Rhesus monkeys. Front. Immunol. 13:915393. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.915393
Zhou, B., Jin, G., Pang, X., Mo, Q., Bao, J., Liu, T., et al. (2022). Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG colonization in early life regulates gut-brain axis and relieves anxiety-like behavior in adulthood. Pharmacol. Res. 177:106090. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106090
Zhou, H., Zhang, S., Zhang, X., Zhou, H., Wen, T., and Wang, J. (2022). Depression-like symptoms due to Dcf1 deficiency are alleviated by intestinal transplantation of Lactobacillus murine and Lactobacillus reuteri. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 593, 137–143. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.01.026
Keywords: GABA, anxiety, insomnia, gut microbiota, probiotics, genetic engineered bacteria
Citation: Jiang C, Chen Y and Sun T (2025) From the gut to the brain, mechanisms and clinical applications of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on the treatment of anxiety and insomnia. Front. Neurosci. 19:1570173. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1570173
Edited by:
Avinash Veerappa, University of Nebraska Medical Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Sushil Shakyawar, University of Nebraska Medical Center, United StatesNana Zhang, Xiamen University, China
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Chen and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tao Sun, dGFvc3VuQGhxdS5lZHUuY24=
 Chengji Jiang1
Chengji Jiang1 Tao Sun
Tao Sun