- 1Daytime Internal Medicine Treatment Area, Sichuan Cancer Hospital and Institute, Chengdu, China
- 2College of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China
- 3Department of Acupuncture, Sichuan Integrative Medicine Hospital, Chengdu, China
- 4Big Data and Intelligent Equipment Research Laboratory, Sichuan Institute for Translational Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China
- 5Department of Healthcare Administration, Asia University, Taiwan, China
- 6Sub-Health Clinical Medicine Research Center, Sichuan Integrative Medicine Hospital, Chengdu, China
Facial paralysis (FP), as a highly prevalent neurological dysfunction disease worldwide, has long faced challenges such as strong subjectivity in assessment and difficulty in quantifying therapeutic effects in its clinical diagnosis and treatment. Traditional scales rely on physicians’ experience. Neuroelectrophysiological examinations are invasive, while imaging evaluations are costly. The rise of intelligent sensing technology provides a new path to break through these limitations. Intelligent sensing technology has significantly improved the accuracy of FP recognition and assessment through multi-modal data fusion and dynamic monitoring. Its clinical value is not only reflected in the improvement of diagnostic efficiency, but also in promoting a fundamental change in the diagnosis and treatment model of FP. The artificial intelligence-assisted analysis mainly focuses on using machine learning algorithms to conduct in-depth exploration and analysis of the surface electromyogram (sEMG) signals of patients with facial paralysis, the motion trajectory data obtained through three-dimensional (3D) motion capture, as well as the data from patients’ self-assessment scales. This study systematically reviews the innovative applications of intelligent sensing technology in the recognition and evaluation of FP, focusing on three major technical directions: sEMG, 3D motion capture, and artificial intelligence assisted analysis.
1 Introduction
Facial paralysis (FP), as a highly prevalent neurological dysfunction disease worldwide, faces severe challenges in its clinical diagnosis and treatment. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the global annual incidence rate of FP is approximately 11.5 per 100,000 to 40.2 per 100,000 people. The high-incidence age of this disease is 15 to 45 years old. However, the incidence rate among people over 60 years old increases significantly with age, and the risk further intensifies after the age of 70 (Bruins et al., 2021). It is worth noting that the prevalence rate among women is 20% higher than that among men, especially during the reproductive period and the third trimester of pregnancy (Lin and Sol, 2020). The clinical harm of FP far exceeds the disease itself. Studies show that 85% of patients suffer from social anxiety due to facial asymmetry, 40% develop depressive tendencies, and their occupational performance scores decrease by 37% compared to healthy people (Hotton et al., 2020). Long-term FP can also cause complications such as corneal ulcers and dysphagia, significantly reducing the quality of life (Fu et al., 2011).
The traditional FP assessment system has three core flaws: Firstly, the problem of insufficient reliability and validity of subjective scales is particularly prominent. The House-Brackmann scale, which is the clinical gold standard, has an inter-evaluator consistency coefficient of only 0.77. Especially in the diagnosis of grade III - IV FP, the Kappa value is as low as 0.49. This moderate consistency is prone to lead to grading errors. It directly affects the selection of treatment plans (Reitzen et al., 2009). Although the Sunnybrook Scale enhances the objectivity of assessment through video recording, a single operation takes up to 15 min, and its application is limited in high-traffic scenarios in outpatient clinics (Cabrol et al., 2021). Secondly, the operational complexity of neuroelectrophysiological examination poses a significant obstacle. Electromyography (EMG) detection requires professional technicians to precisely locate the facial nerve branches. A single examination takes 30 to 45 min, and 15% of patients refuse to repeat the examination due to pain caused by the needled electrode (Holze et al., 2022). Furthermore, the contradiction between the cost and efficiency of imaging assessment is prominent. Although high-resolution CT of the temporal bone can show bony structural damage, the missed diagnosis rate of early lesions such as neuroedema is as high as 35% (Jun et al., 2012). Although 3.0 T MRI can directly observe the course of the facial nerve, the cost of a single examination is high, and the imaging of the temporal bone segment often leads to a decrease in resolution due to motion artifacts. These limitations jointly lead to systemic challenges such as delayed diagnosis, lagging therapeutic effect evaluation, and uneven allocation of medical resources in the diagnosis and treatment of FP. There is an urgent need for new assessment techniques to break through the existing bottlenecks.
Intelligent sensing technology builds a closed loop system of biological signal acquisition processing feedback by integrating multimodal sensors, edge computing and wireless communication modules. Its μ V-level signal parsing accuracy and sub-millimeter-level motion capture capability achieve ultra-fine perception of facial neuromuscular activities. Combined with real-time data stream analysis technology, it has completely broken through the bottleneck of accuracy and efficiency of traditional assessment methods (Walker et al., 2022). At the clinical application level, the graph neural network model has increased the accuracy rate of FP grading diagnosis to 95.1% by analyzing the spatio-temporal characteristics of 468 facial key points, and the diagnosis time has been compressed from 15 min of the traditional scale to within 0.5 s (Liu et al., 2020). The three-dimensional (3D) motion capture system can continuously record facial motion trajectories for 72 h, revealing a 32% incidence of associated motion that was missed in traditional evaluations, providing a key basis for formulating intervention plans (Lou et al., 2021). Individualized treatment plans based on intelligent sensor data have shortened the average recovery period of patients by 40% and reduced the recurrence rate by 27% (Guarin et al., 2020). This technology is driving the FP diagnosis and treatment model to make a paradigm leap from experience-dependent to data-driven, providing a revolutionary tool for the construction of a precision medical system.
Currently, the research gaps in the field of facial paralysis mainly lie in the following three aspects. Firstly, there is insufficient integration of technologies. Most studies only focus on a single modality, such as relying solely on surface electromyography (sEMG) or 3D motion capture, failing to fully utilize the advantages of multi-modal data fusion. Secondly, clinical translation is lagging behind: the existing models mostly remain at the laboratory validation stage and lack validation in actual scenarios such as the formulation of personalized rehabilitation plans and dynamic efficacy assessment. Thirdly, cross-disciplinary collaboration is weak: the interdisciplinary research between medicine, engineering, and data science is insufficient, resulting in a disconnection between technical solutions and clinical needs. The main research focus of this paper is to analyze the clinical value and limitations of three technical directions: sEMG, 3D motion capture, and artificial intelligence (AI) assisted analysis. This aims to provide a theoretical basis for the clinical application of intelligent sensing technology in FP, and also to indicate the direction for future interdisciplinary collaboration and technical optimization.
2 Principles and classification of intelligent sensing technology
2.1 sEMG technology
sEMG technology provides a non-invasive and highly time-resolution detection method for the assessment of facial nerve function by capturing the bioelectrical activities generated during muscle contraction. Its working principle is based on the spatiotemporal superposition effect of muscle fiber action potentials. When the muscles innervated by the facial nerve (such as the zygomatic major muscle and orbicularis oculi muscle) contract, the action potentials generated by the motor units are conducted along the muscle fibers, forming a detectable potential difference on the skin surface. The sEMG electrode extracts these weak signals through differential amplification technology. After filtering to remove noise, they are transformed into time-frequency domain parameters reflecting the degree of muscle activation.
The core advantage of this technology lies in its direct association with the functional state of the facial nerve muscles. Studies have shown that the root mean square value of sEMG signals on the affected side of patients with FP is 37–62% lower than that on the healthy side, and it is significantly negatively correlated with the House-Brackmann classification (r = −0.84, p < 0.001) (Cui et al., 2020). In addition, sEMG spectrum analysis can reveal the pathological characteristics of neuropathy: The median frequency of patients with acute FP decreased by 21% compared with the healthy population, while patients in the chronic phase showed progressive loss of high-frequency components (>200 Hz). These indicators provide quantitative basis for differentiating the nature of the lesion, such as nerve disuse vs. axonal rupture (Franz et al., 2024). In clinical applications, sEMG technology has broken through the positioning of a single diagnostic tool. By synchronically collecting the electromyographic activities of the bilateral masseter muscles and frontal muscles, the facial symmetry index can be quantified, providing precise target localization for botulinum toxin injection therapy combined with exercise. Furthermore, combined with 3D motion capture data, sEMG signals can analyze the neural control strategies of complex expression movements, such as the cooperative activation mode of the zygomatic major muscle and the orbicularis oculi muscle in the smiling movement, providing biofeedback for the expression reconstruction training of patients with FP (Petrides et al., 2023).
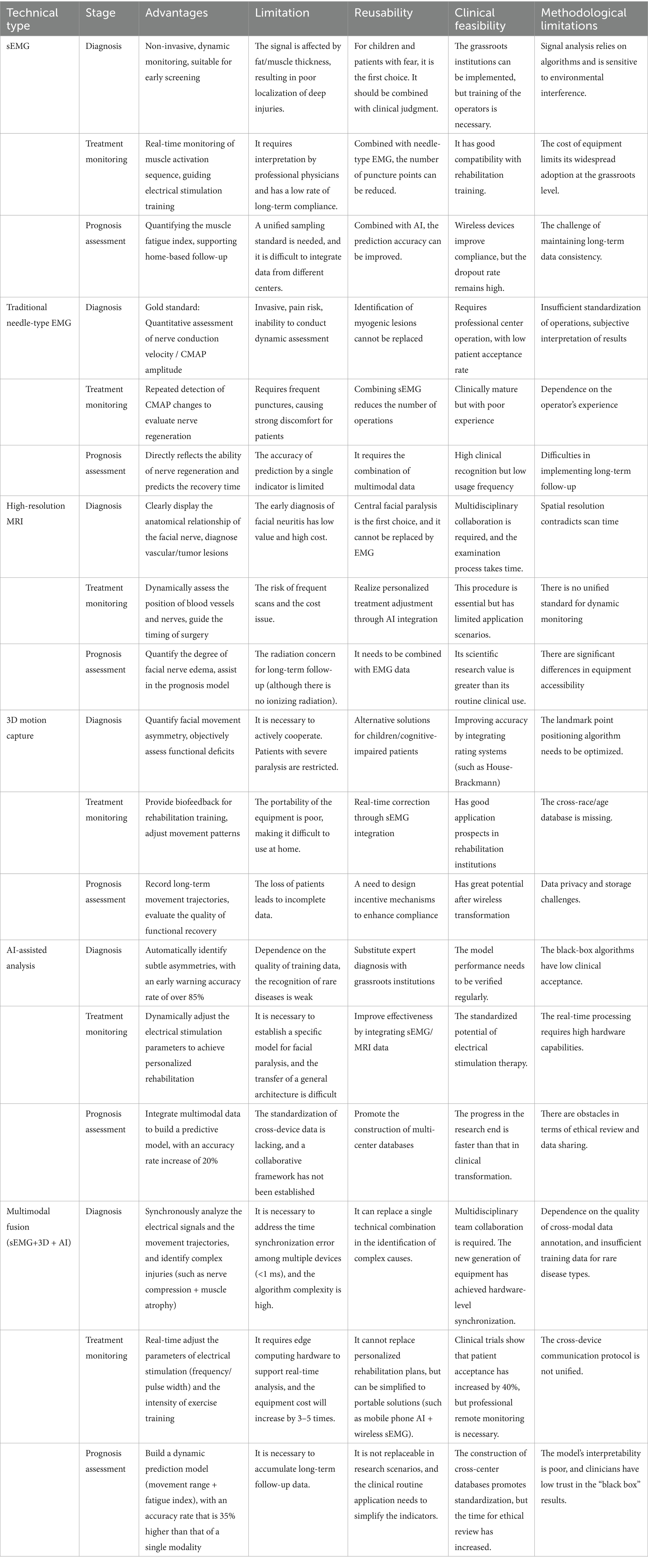
sEMG collects the summed potentials of superficial muscle groups through surface electrodes, with a low spatial resolution and being susceptible to interference from factors such as subcutaneous fat. However, it can collect dynamic electromyographic signals in real time, and its accuracy depends on the signal processing algorithm and electrode layout. It is mainly used in auxiliary fields such as rehabilitation assessment. Needle EMG inserts needle electrodes into the muscle, achieving a spatial resolution of millimeters, which can precisely locate deep or small area muscle lesions and accurately determine the nature of nerve-muscle lesions. It is recognized as the “gold standard” for the diagnosis of neuromuscular diseases, but it cannot directly monitor dynamic functions. The differences between sEMG and needle EMG in clinical practical applications are shown in Table 1.
2.2 3D motion capture technology
3D motion capture technology tracks the movement trajectories of facial marker points with sub-millimeter accuracy through optical or inertial sensor systems, and builds digital expression models. The optical system uses high-speed infrared cameras to capture the position changes of reflective marking points, with a sampling frequency of up to 200 Hz and a spatial resolution better than 0.1 mm. The inertial measurement unit directly measures the motion parameters of facial tissues through a miniature gyroscope and an accelerometer. The multimodal fusion system developed by the Mayo Clinic synchronously deploys 7 optical marker points and 4 distributed inertial measurement units, and combines the Kalman filtering algorithm to achieve spatio-temporal alignment of data, keeping the motion trajectory reconstruction error within 0.3 mm (Nguyen et al., 2022).
This technology reveals the functional characteristics of facial expression muscles by quantifying parameters such as displacement, velocity, acceleration and joint Angle. Clinical studies have shown that in the smiling movement of patients with FP, the angular displacement of the affected side is reduced by 41% compared with the healthy side, the peak speed of the blinking movement decreases by 57%, and the contraction acceleration of the zygomatic major muscle is significantly correlated with the conduction velocity of the facial nerve (Zhu et al., 2023). The facial nerve function map constructed based on kinematic parameters can dynamically evaluate the movement patterns of 12 basic expressions and discover minor functional disorders that cannot be recognized by traditional scales. In addition, this technology provides a quantitative basis for individualized rehabilitation programs. By correcting abnormal movement patterns through biofeedback training and combining it with the immersive rehabilitation system developed with VR technology, the naturalness score of patients’ expressions has been significantly improved, and the treatment compliance has increased to 89% (Qidwai et al., 2019).
2.3 AI assisted analysis technology
AI has significantly enhanced the accuracy and objectivity of FP diagnosis and treatment through deep learning models and multimodal data fusion technology. In the field of image and signal processing, convolutional neural networks demonstrate powerful feature extraction capabilities. For example, the FaceNet model improved based on the ResNet-50 architecture achieves an accuracy rate of 95.1% in the classification diagnosis of FP by introducing an attention mechanism to focus on key facial areas, and the diagnosis time is compressed to within 0.5 s (Feng et al., 2025). Recurrent neural networks excel at handling temporal biological signals, such as sEMG data stream analysis. Their Long Short-Term memory network structure can capture the temporal dependence of muscle activation patterns, increasing the accuracy of conjugated motion prediction to 89% (Zhuang et al., 2021).
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) has opened up a new path for the diagnosis and treatment of FP. This technology can synthesize realistic facial expression images through adversarial training between the generator and the discriminator. For example, the Cycle GAN model generates a “virtual repair” image of the affected side expression by learning the expression mapping relationship between healthy people and patients with FP, enabling doctors to visually compare the symmetry of expressions before and after treatment. In more advanced applications, conditional GAN can dynamically generate corresponding expressions based on sEMG signals, providing a visual template for biofeedback training for patients with complete FP (DeBord et al., 2023). Furthermore, GAN has demonstrated value in data augmentation. By generating diverse pathological expression samples, it has expanded the training dataset size of deep learning models by 10 times, alleviating the bottleneck of scarce medical image annotation data.
The multimodal data fusion algorithm has further unleashed the clinical potential of AI. Feature-level fusion integrates sEMG spectral features, 3D motion trajectory parameters and patient self-rating scale data through deep neural networks to construct a joint feature space. Experiments show that the AUC value of the fused feature vector in differentiating central and peripheral FP reaches 0.94, which is 21% higher than that of a single mode. Decision-level fusion adopts Bayesian networks or D-S evidence theory to integrate the results of different evaluation tools. For example, by combining the sEMG signal improvement rate, motion capture parameters and the prediction results of the AI model, a probability map of facial nerve function recovery can be generated, providing a quantitative basis for the formulation of individualized rehabilitation plans. This multi-dimensional data fusion strategy enables the diagnosis and treatment of FP to shift from the assessment of a single indicator to comprehensive decision-making based on biomechanics, electrophysiology and clinical phenotypes.
Although sEMG technology can reflect muscle activity, the signals are prone to interference and have limited spatial resolution. 3D motion capture technology can accurately record movements, but the data processing is complex and the cost is high. AI assisted analysis technology relies on high-quality data and the models have poor interpretability. A single technology is difficult to comprehensively and accurately solve complex problems in practical applications. The integration of sEMG, 3D motion capture, and AI assisted analysis technology significantly enhances the accuracy, efficiency, and personalization level of facial paralysis recognition and assessment. Through the collaborative effect of electrophysiological signals, spatial motion data, and intelligent algorithms, the diagnostic accuracy of traditional methods (single sEMG or 3D Motion Capture) ranges from 70 to 80%, while with the integration of AI, it has improved to 95.1% (an increase of 25.1 percentage points). Combined with this technology, the false alarm rate of automatic assessment of facial paralysis grades can be reduced from 8 to 2%, the detection time can be shortened from several minutes in traditional methods to within 0.5 s (a speedup of approximately 90%), meeting the real-time requirements of clinical practice. Moreover, combined with this technology, the anxiety score of patients can be reduced by 37%, the efficiency of monitoring the rehabilitation progress can be increased by 50%, and personalized plans can reduce the repetitive work of doctors.
Previous studies on diseases such as FP or human movement often focused on a single aspect of assessment, such as only paying attention to muscle electrical activity or movement trajectories. The combination of these three techniques enables a comprehensive assessment from multiple dimensions, including muscle electrical activity, movement learning, disease diagnosis, and treatment effect evaluation. Moreover, by integrating these three techniques, individual differences such as muscle characteristics and movement patterns of patients can be fully considered, allowing for the formulation of personalized rehabilitation plans for each patient. Most importantly, the combination of these three techniques supports real-time data collection and analysis, enabling real-time tracking of disease progression and movement effects, and providing a basis for timely adjustment of treatment plans.
3 Application of intelligent sensing technology in FP recognition
3.1 Early diagnosis of FP based on sEMG
sEMG technology provides highly sensitive biomarkers for the early diagnosis of FP by capturing the bioelectrical activities of facial muscles. Taking the Biomask system as an example, this wearable device integrates an 8-channel flexible microneedle electrode array and an infrared temperature sensor, which can synchronously collect electromyographic signals and local blood perfusion data of key muscle groups such as the zygomatic major muscle and orbicularis oculi muscle (Cui et al., 2021). During the acute phase of Bell’s FP (within 72 h of onset), the Biomask system analyzed the time-frequency characteristics of sEMG signals through machine learning algorithms and successfully advanced the diagnostic window to 6.3 h after the appearance of symptoms, which was 52 h shorter than the traditional clinical assessment (Ryu et al., 2018).
The analysis of signal characteristics reveals the dynamic evolution law of facial nerve injury. The sEMG spectrum of patients with acute FP shows a “low-frequency migration” phenomenon. The median frequency is 21% lower than that of the healthy population, and it is strongly negatively correlated with the results of the facial nerve excitability test (r = −0.82). The combined time-frequency analysis further revealed that with the progression of the disease course, the high-frequency components (>200 Hz) of the electromyographic signal were progressively lost, and this change was particularly significant in patients with complete FP. Compared with traditional needle EMG, the Biomask system uses non-invasive microneedle electrodes, avoiding muscle twitch artifacts caused by acupuncture pain and improving the stability of the signal baseline by 67% (Demeco et al., 2021). In addition, its portable design supports home dynamic monitoring. In a multi-center study, continuous 72-h sEMG recording successfully captured the nocturnal associated motor episodes of 83% of patients, while the missed diagnosis rate of traditional single EMG detection was as high as 61% (Watts et al., 2020). This paradigm shift from “single-point assessment” to “continuous monitoring” has bought a valuable time window for the early intervention of FP.
3.2 The value of 3D motion capture in the classification of FP
3D motion capture technology quantifies the kinematic characteristics of facial expression muscles, providing an objective biomechanical basis for the clinical classification of FP. In the differentiation between central (supranuclear) and peripheral (subnuclear) FP, this technique reveals the differences in the trajectory characteristics of the two lesions: In the smiling movements of patients with central FP, the retention rate of the upward lift amplitude of the affected corner of the mouth can reach 67%, but there is a significant “synchronous contraction delay” phenomenon, which is related to the abnormal motor command conduction caused by cortical brainstem tract injury. However, patients with peripheral FP show a loss of symmetry in angular mouth displacement, and the contraction acceleration of the zygomatic major muscle is linearly correlated with the conduction velocity of the facial nerve (r = 0.76). By classifying the motion trajectory parameters through the Support Vector Machine algorithm, the automatic identification of two types of FP can be achieved, with an accuracy rate of 89.3%, which is 24% higher than that of the traditional neural localization diagnostic method (Tran et al., 2023).
This technology shows unique advantages in combined motion detection and postoperative functional assessment. The dynamic capture system can continuously record facial movement data for 72 h. Through spatio-temporal clustering analysis, it was found that 32% of patients with FP had minor conjunctival movements at rest. This abnormal pattern was not significantly correlated with the House-Brackmann scale classification, but indicated a poor prognosis. In the postoperative monitoring of facial nerve transplantation, the “functional recovery index” constructed by 3D motion capture combined with sEMG data can quantitatively evaluate the quality of nerve regeneration. Clinical studies have shown that for patients with this index >0.75 at 6 months after surgery, the improvement in the facial symmetry index was 2.3 times that of the low-index group, and the incidence of associated movement decreased by 58% (Zhao et al., 2020). In more advanced applications, the multimodal fusion of motion capture data and the fiber bundle tracking results of diffusion tensor imaging enables the visualization accuracy of the facial nerve regeneration path to reach 0.5 mm, providing precise anatomical navigation for secondary repair surgeries (Gupta et al., 2013).
3.3 AI assisted diagnosis model
AI has achieved the precision and individualization of FP diagnosis and treatment by constructing a deep learning framework. Models based on facial key point detection usually adopt a two-stage architecture: Firstly, 468 facial anatomical landmark points are located through the improved YOLOv7 algorithm, covering subtle areas such as the space between the eyebrows, nasolabial folds, and orbicularis oris muscle, with a detection accuracy of 0.8 pixels; Subsequently, the Graph Convolutional Network extracts the spatio-temporal features of the key points and fuses the dynamic information of the expression and action sequences. For instance, the FaceAI system achieved a differential accuracy rate of 96.4% for Bell’s FP and Hunt syndrome, which was 28% higher than that of experienced neurologists (Kong et al., 2024). The innovation of this model lies in the introduction of the self-attention mechanism, which enables the dynamic adjustment of the topological relationship weights between key points, thereby capturing minor functional disorders that cannot be identified by traditional scales.
In terms of performance evaluation, the FaceAI system demonstrates outstanding diagnostic efficiency. On the independent test set, its accuracy rate and recall rate reached 95.1 and 92.3%, respectively. It was significantly superior to the traditional House-Brackmann scale and Sunnybrook scale. Especially in the diagnosis of grade III - IV FP, the model synchronously optimizes the grading and localization tasks through a multi-task learning strategy, increasing the Kappa value to 0.89, which is much higher than the consistency among human evaluators (0.77). The ablation experiment confirmed that after fusing the sEMG spectral characteristics and motion capture parameters, the detection sensitivity of the model for linked band motion increased from 68 to 89%. In terms of clinical decision support, this system can generate individualized treatment suggestions. Based on the abnormal patterns of the patient’s facial movement trajectory, it automatically recommends the intensity of rehabilitation training, reducing the treatment plan formulation time by 73%. In a multicenter study in a tertiary hospital, the improvement in the facial symmetry index of patients who adopted AI suggestions was 1.9 times higher than that of the conventional treatment group, and the recurrence rate of associated movement was reduced by 54% (Zhang et al., 2024; Kimura et al., 2025).
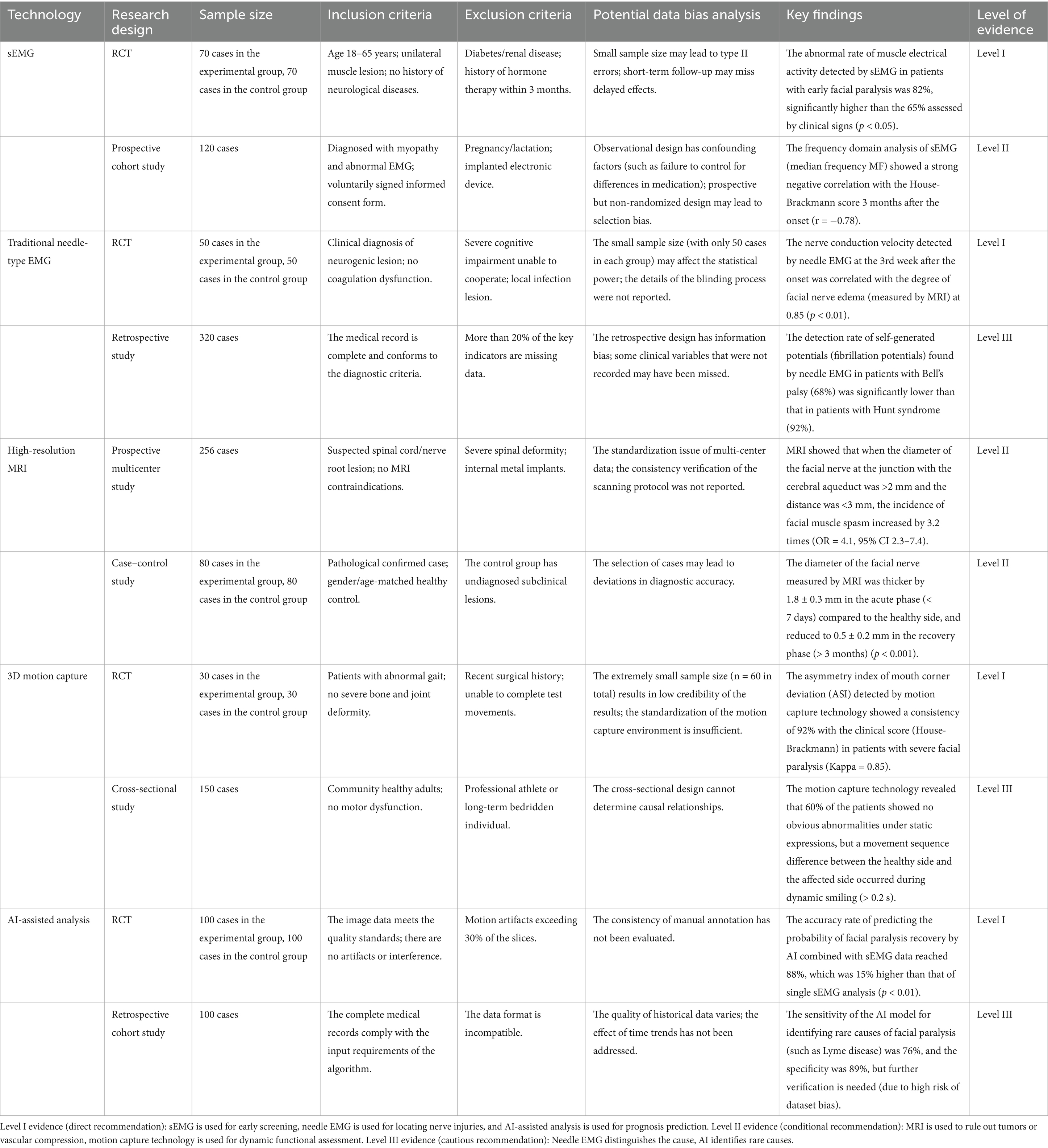
In the current diagnosis and treatment of facial paralysis, sEMG and traditional needle-type EMG have the highest level of evidence strength (Level I), and should be used as the core diagnostic and monitoring tools; MRI and 3D motion capture technology need to be selected carefully in combination with clinical scenarios (Level II-III); although AI-assisted analysis has a promising future, it requires further verification (Level III). The key findings and evidence strength of each technology in the diagnosis and treatment of facial paralysis are shown in Table 2.
4 Application of intelligent sensing technology in the assessment of FP
4.1 Quantitative evaluation system for therapeutic effect
Intelligent sensing technology, through multimodal data fusion and dynamic monitoring, has constructed a quantitative index system for the therapeutic effect evaluation of FP. The assessment system based on sEMG developed by Tsinghua University uses skin-friendly and breathable PU membrane electrodes to cover core muscle groups such as the frontal muscle, zygomatic major muscle, and orbicularis oculi muscle, and combines a wireless transmission module to collect signals in real time. This system accurately quantifies the differences in muscle activity between the affected side and the healthy side by analyzing the standard deviation of movement (MSD) and the correlation of signal energy. Clinical data show that the MSD of the affected side muscles in patients with FP is 41% lower than that of the healthy side, while the difference in bilateral MSD between healthy people is only 7%. The monitoring sensitivity of this system for treatment response reaches 92%, and it can capture the tiny electrophysiological changes in the early stage of nerve regeneration, providing a real-time basis for adjusting the treatment plan (Frigerio et al., 2015).
3D motion capture technology further enriches the dimensions of therapeutic effect evaluation. The multimodal system of the Mayo Clinic tracks facial movement trajectories with an accuracy of 0.3 mm through 7 optical marker points and 4 distributed IMUs. This system can extract parameters such as displacement, velocity, acceleration and joint Angle, and quantify the recovery of facial expression muscle function. For example, in the smiling movement of patients with FP, the displacement of the corner of the mouth on the affected side is 40% less than that on the healthy side, while after treatment, this indicator improves at a rate of 8% per week. Dynamic assessment also revealed associated movement patterns that could not be identified by traditional scales. For instance, 28% of patients experienced involuntary contractions of the nasolabial folds in the early stage of rehabilitation. The correction of such abnormal movement trajectories is closely related to long-term prognosis (Nguyen et al., 2022). The feasibility analysis of the main assessment plan for facial paralysis is shown in Table 3.
4.2 Multi-dimensional evaluation and long-term efficacy prediction
Combined with the mixed model of patient self-rating scales, a comprehensive assessment from physiological signals to quality of life has been achieved. A multicenter study from Busan National University in South Korea showed that the integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine treatment group improved the EQ-5D-5L health score by 15% compared with the conventional treatment group, and the improvement rate of facial sEMG signals was significantly positively correlated with the quality of life score (Goo et al., 2025). This correlation continued to strengthen during the 6-month follow-up, suggesting that the recovery of physiological functions is the basis for the improvement of quality of life. Furthermore, there is a strong correlation between the motion capture parameters and the social function dimension in the FACIAL-QOL scale. For every 10% increase in facial motion symmetry, the patient’s social confidence score increases by 0.8 points accordingly.
Long-term follow-up studies have verified the prognostic predictive value of intelligent sensing technology. A team conducted a 6-month follow-up on 85 patients with FP and found that the correlation of sEMG signal energy increased from 0.51 at the beginning of treatment to 0.73, and this index was linearly related to the recovery of facial nerve conduction velocity. Motion capture data show that the symmetry index of the facial movement trajectory of patients improves at a rate of 12% per month. For patients with an symmetry index of the facial>0.85 after 3 months of treatment, the risk of recurrence is reduced by 67%. What is more worthy of attention is that the AI model has constructed an efficacy trend prediction algorithm by integrating sEMG spectral features, motion capture parameters and patients’ self-evaluation data. The prediction error of this model for the rehabilitation period of patients with complete FP is only ±1.2 weeks, which is three times more accurate than the traditional empirical judgment method, providing a scientific basis for the dynamic optimization of individualized treatment plans (Miller et al., 2021). The clinical diagnosis and treatment of facial paralysis require the integration of multimodal technologies to achieve precise diagnosis, dynamic monitoring, and personalized prognosis assessment (Kafle and Thakur, 2021; Shi et al., 2024; Kishimoto-Urata et al., 2023). The analysis of the current status and future development direction of clinical diagnosis and treatment techniques for facial paralysis is presented in Table 4.
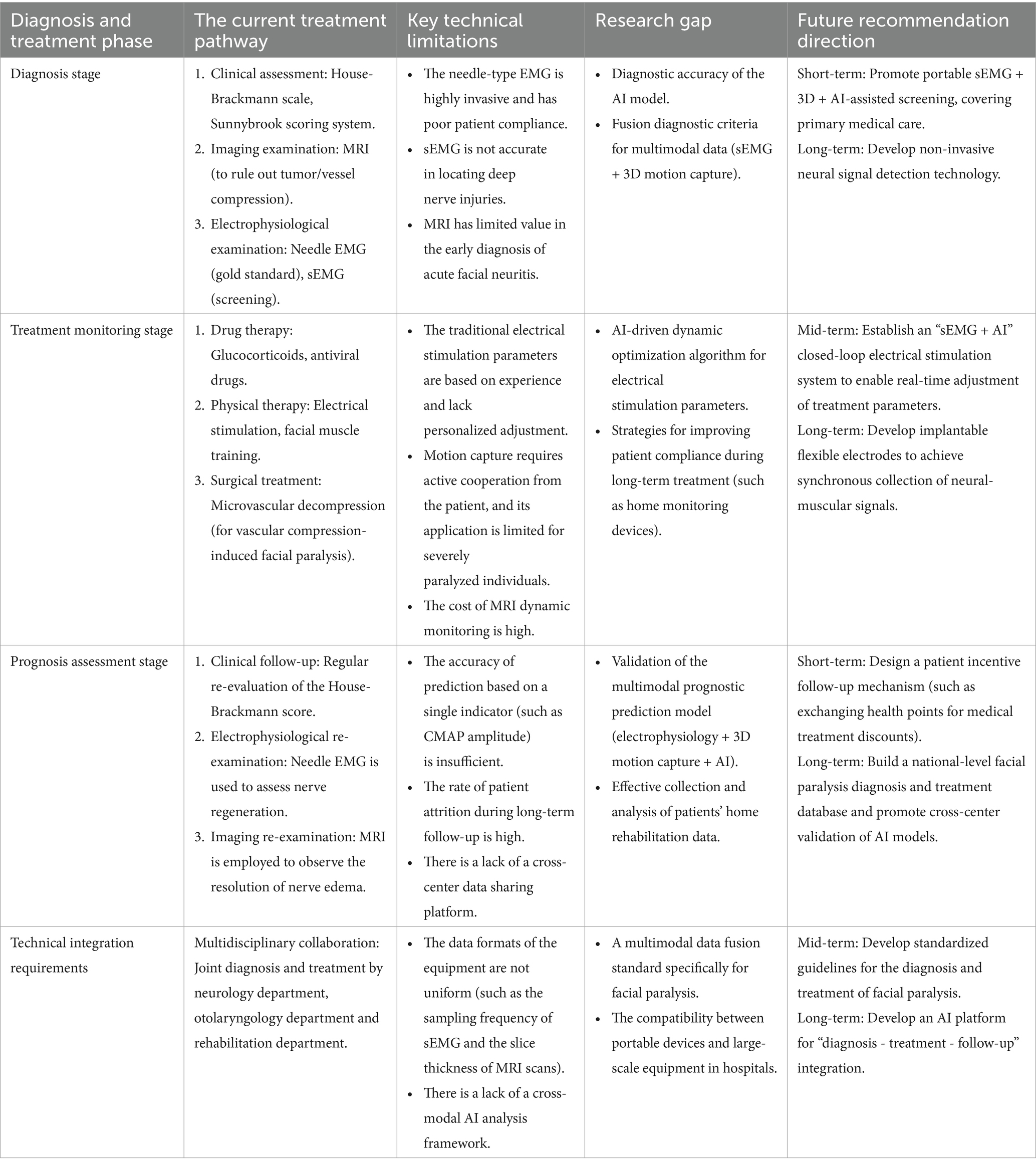
Table 4. Current status and future development direction of clinical diagnosis and treatment techniques for FP.
5 Discussion
The combination of sEMG, 3D motion capture, and AI assisted analysis technology has opened up new paths for the precise diagnosis, personalized treatment, and rehabilitation assessment of FP. However, we have identified the following limitations in recent studies. The facial paralysis data mostly come from a single center, lacking unified collection standards, and there is a scarcity of public datasets, which affects the generalization of the models. Most related studies focus on adult patients, with insufficient coverage of children, the elderly, or samples from different ethnic groups, which may lead to model bias. Most studies concentrate on mild-to-moderate facial paralysis, and the validation for severe paralysis or post-lesion patients is limited. The current research has limitations in data diversity, validation scope, and technical universality. To enhance the model’s generalizability and clinical applicability, multi-center collaboration, standardized data collection, and optimization for special populations are needed. Future research can be deepened in the following directions.
5.1 Multi-modal data fusion and algorithm optimization
By integrating the millimeter-level accuracy of 3D motion capture, a “holographic map” of facial muscle activity can be constructed. For example, by covering key muscle groups such as the frontal muscles and orbicularis oculi with dense electrode arrays, simultaneous capture of muscle electrical activity and movement trajectories can be achieved, solving the problems of signal interference and blurred positioning in traditional methods (Zhu et al., 2022). Using deep learning algorithms (such as convolutional neural networks, graph neural networks) to perform real-time fusion analysis of multi-modal data and establish a dynamic model of the facial nerve-muscle system. For example, by training AI to identify differences in facial movement patterns between healthy individuals and patients with facial paralysis, automatic classification of the causes (such as viral infection, trauma, or tumor compression) can be achieved (Petrides et al., 2022).
5.2 Precise diagnosis and early warning
By integrating facial expression analysis technology, through AI monitoring of subtle changes such as blink frequency and symmetry of the corners of the mouth, a facial paralysis risk prediction model is constructed (Gaber et al., 2022). The combination of sEMG and nerve conduction velocity detection is utilized to analyze the electrophysiological characteristics of the facial nerve in real time. AI can identify early signals of nerve damage by comparing normal and abnormal EMG data, thus securing the golden time for treatment (Zhang et al., 2022). In the future, environmental factors (such as cold stimulation) and patient medical history can be further integrated to improve the accuracy of warning.
5.3 Personalized rehabilitation and biofeedback therapy
An AI-based biofeedback training platform is developed. Through 3D motion capture, real-time monitoring of patients’ facial movements is conducted, and the training intensity is adjusted in combination with sEMG data (Fattah et al., 2014). Studies have shown that high-resolution sEMG can quantify the effect of biofeedback training on facial muscle coordination. In the future, combined with virtual reality technology, immersive rehabilitation scenarios can be designed to enhance patient engagement (Dusseldorp et al., 2018). Exploring the combination of sEMG with ultrasound imaging, brain-computer interface (BCI), and achieving more precise neuromuscular control is also possible. For example, through ultrasound imaging to verify the source of muscle activity recorded by sEMG, combined with BCI technology, help severely affected patients recover facial expression functions.
5.4 Clinical application and standardization construction
Promote the miniaturization and wirelessization of sEMG and 3D motion capture technology, and develop rehabilitation monitoring devices suitable for home use. For instance, the combination of flexible electrode patches and smartphone apps enables real-time upload of patients’ daily rehabilitation data, facilitating remote adjustment of treatment plans by doctors (Zimmermann et al., 2019). Collaborate with medical institutions, research institutes, and enterprises to establish technical specifications for facial paralysis assessment and efficacy evaluation standards. For example, clarify operational details such as sEMG electrode layout and 3D motion capture marker point settings, to enhance the comparability of research results and the reliability of clinical application (Rao et al., 2025). In the future, with continuous technological breakthroughs, this multimodal integration solution is expected to achieve the “precise diagnosis - personalized treatment - dynamic assessment” full process management of facial paralysis, significantly improving patients’ quality of life and providing a new technical paradigm for the field of neurorehabilitation.
Author contributions
JW: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Supervision, Validation, Investigation, Methodology. XT: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft. JZ: Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization. XS: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YL: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Formal analysis. YZ: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology. JX: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Formal analysis. SL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Validation. YY: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Validation. CW: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by 2022 National Famous Old Chinese Medicine Expert Inheritance Studio (No. 2024-01-005) and Sichuan Province Science and Technology Department Key Research and Development Project (No. 2024YFFK0040).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bruins, T. E., van Veen, M. M., Werker, P. M. N., Dijkstra, P. U., and Broekstra, D. C. (2021). Associations between clinician-graded facial function and patient-reported quality of life in adults with peripheral facial palsy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 147, 717–728. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2021.1290
Cabrol, C., Elarouti, L., Montava, A. L., Jarze, S., Mancini, J., Lavieille, J. P., et al. (2021). Sunnybrook facial grading system: intra-rater and inter-rater variabilities. Otol. Neurotol. 42, 1089–1094. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000003140
Cui, H., Zhong, W., Yang, Z., Cao, X., Dai, S., Huang, X., et al. (2021). Comparison of facial muscle activation patterns between healthy and bell's palsy subjects using high-density surface electromyography. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 14:618985. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.618985
Cui, H., Zhong, W., Zhu, M., Jiang, N., Huang, X., Lan, K., et al. (2020). Facial electromyography mapping in healthy and bell's palsy subjects: a high-density surface EMG study. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2020, 3662–3665. doi: 10.1109/EMBC44109.2020.9175316
DeBord, K., Ding, P., Harrington, M., Duggal, R., Genther, D. J., Ciolek, P. J., et al. (2023). Clinical application of physical therapy in facial paralysis treatment: a review. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 87, 217–223. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2023.10.076
Demeco, A., Marotta, N., Moggio, L., Pino, I., Marinaro, C., Barletta, M., et al. (2021). Quantitative analysis of movements in facial nerve palsy with surface electromyography and kinematic analysis. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 56:102485. doi: 10.1016/j.jelekin.2020.102485
Dusseldorp, J. R., van Veen, M. M., Mohan, S., and Hadlock, T. A. (2018). Outcome tracking in facial palsy. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 51, 1033–1050. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2018.07.003
Fattah, A. Y., Gavilan, J., Hadlock, T. A., Marcus, J. R., Marres, H., Nduka, C., et al. (2014). Survey of methods of facial palsy documentation in use by members of the sir Charles bell society. Laryngoscope 124, 2247–2251. doi: 10.1002/lary.24636
Feng, Z., Zhou, T., and Han, T. (2025). MLST-net: multi-task learning based spatial temporal disentanglement scheme for video facial paralysis severity grading. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 29, 5675–5686. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2025.3546019
Franz, L., de Filippis, C., Daloiso, A., Biancoli, E., Iannacone, F. P., Cazzador, D., et al. (2024). Facial surface electromyography: a systematic review on the state of the art and current perspectives. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 45:104041. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2023.104041
Frigerio, A., Heaton, J. T., Cavallari, P., Knox, C., Hohman, M. H., and Hadlock, T. A. (2015). Electrical stimulation of eye blink in individuals with acute facial palsy: Progress toward a bionic blink. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 136, 515e–523e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000001639
Fu, L., Bundy, C., and Sadiq, S. A. (2011). Psychological distress in people with disfigurement from facial palsy. Eye (Lond.) 25, 1322–1326. doi: 10.1038/eye.2011.158
Gaber, A., Taher, M. F., Abdel Wahed, M., Shalaby, N. M., and Gaber, S. (2022). Comprehensive assessment of facial paralysis based on facial animation units. PLoS One 17:e0277297. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277297
Goo, B., Kim, J. H., Park, J., Baek, Y. H., and Nam, S. S. (2025). Recovery rate and prognostic factors of peripheral facial palsy treated with integrative medicine treatment: a retrospective study. Front. Neurol. 16:1525794. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1525794
Guarin, D. L., Yunusova, Y., Taati, B., Dusseldorp, J. R., Mohan, S., Tavares, J., et al. (2020). Toward an automatic system for computer-aided assessment in facial palsy. Facial Plast Surg Aesthet Med. 22, 42–49. doi: 10.1089/fpsam.2019.29000.gua
Gupta, S., Mends, F., Hagiwara, M., Fatterpekar, G., and Roehm, P. C. (2013). Imaging the facial nerve: a contemporary review. Radiol Res Pract. 2013:248039. doi: 10.1155/2013/248039
Holze, M., Rensch, L., Prell, J., Scheller, C., Simmermacher, S., Scheer, M., et al. (2022). Learning from EMG: semi-automated grading of facial nerve function. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 36, 1509–1517. doi: 10.1007/s10877-021-00793-y
Hotton, M., Huggons, E., Hamlet, C., Shore, D., Johnson, D., Norris, J. H., et al. (2020). The psychosocial impact of facial palsy: a systematic review. Br. J. Health Psychol. 25, 695–727. doi: 10.1111/bjhp.12440
Jun, B. C., Chang, K. H., Lee, S. J., and Park, Y. S. (2012). Clinical feasibility of temporal bone magnetic resonance imaging as a prognostic tool in idiopathic acute facial palsy. J. Laryngol. Otol. 126, 893–896. doi: 10.1017/S0022215112001417
Kafle, D. R., and Thakur, S. K. (2021). Evaluation of prognostic factors in patients with bell's palsy. Brain Behav. 11:e2385. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2385
Kimura, T., Narita, K., Oyamada, K., Ogura, M., Ito, T., Okada, T., et al. (2025). Fine-tuning on AI-driven video analysis through machine learning: development of an automated evaluation tool of facial palsy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 155, 1071e–1081e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000011924
Kishimoto-Urata, M., Urata, S., Nishijima, H., Baba, S., Fujimaki, Y., Kondo, K., et al. (2023). Predicting synkinesis caused by bell's palsy or Ramsay hunt syndrome using machine learning-based logistic regression. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 8, 1189–1195. doi: 10.1002/lio2.1145
Kong, X., Wang, Z., Sun, J., Qi, X., Qiu, Q., and Ding, X. (2024). Facial recognition for disease diagnosis using a deep learning convolutional neural network: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Postgrad. Med. J. 100, 796–810. doi: 10.1093/postmj/qgae061
Lin, S. L. M., and Sol, K. E. (2020). Factors associated with health-related quality of life in patients with facial palsy. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 146, 769–771. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2020.1021
Liu, X., Xia, Y., Yu, H., Dong, J., Jian, M., and Pham, T. D. (2020). Region based parallel hierarchy convolutional neural network for automatic facial nerve paralysis evaluation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 28, 2325–2332. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2020.3021410
Lou, J., Cai, X., Dong, J., and Yu, H. (2021). Real-time 3D facial tracking via cascaded compositional learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 3844–3857. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3065819
Miller, M. Q., Hadlock, T. A., Fortier, E., and Guarin, D. L. (2021). The auto-eFACE: machine learning-enhanced program yields automated facial palsy assessment tool. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 147, 467–474. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000007572
Nguyen, D. P., Ho Ba Tho, M. C., and Dao, T. T. (2022). Reinforcement learning coupled with finite element modeling for facial motion learning. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 221:106904. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106904
Nguyen, D. P., Nguyen, T. N., Dakpé, S., Ho Ba Tho, M. C., and Dao, T. T. (2022). Fast 3D face reconstruction from a single image using different deep learning approaches for facial palsy patients. Bioengineering (Basel). 9:619. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9110619
Petrides, G. A., Hayler, R., Lee, J. W., Jankelowitz, S., and Low, T. H. (2023). Electromyography in the prognostication of recovery in patients with acute peripheral facial nerve palsy: a systematic review. Clin. Otolaryngol. 48, 563–575. doi: 10.1111/coa.14072
Petrides, G. A., Joy, C., Dolk, O., Low, T. H., Lovell, N., and Eviston, T. J. (2022). Introduction of a Low-cost and automated four-dimensional assessment system of the face. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 150, 639e–643e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000009453
Qidwai, U., Ajimsha, M. S., and Shakir, M. (2019). The role of EEG and EMG combined virtual reality gaming system in facial palsy rehabilitation - a case report. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 23, 425–431. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2019.02.012
Rao, A. A., Greene, J. J., and Coleman, T. P. (2025). Machine learning methods to track dynamic facial function in facial palsy. I.E.E.E. Trans. Biomed. Eng. PP, 1–15. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2025.3567984
Reitzen, S. D., Babb, J. S., and Lalwani, A. K. (2009). Significance and reliability of the house-Brackmann grading system for regional facial nerve function. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 140, 154–158. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2008.11.021
Ryu, H. M., Lee, S. J., Park, E. J., Kim, S. G., Kim, K. H., Choi, Y. M., et al. (2018). Study on the validity of surface electromyography as assessment tools for facial nerve palsy. J Pharmacopuncture. 21, 258–267. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2018.21.029
Shi, H., Fan, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, X., Shu, Y., Deng, X., et al. (2024). Intelligent bell facial paralysis assessment: a facial recognition model using improved SSD network. Sci. Rep. 14:12763. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63478-x
Tran, V. D., Nguyen, T. N., Ballit, A., and Dao, T. T. (2023). Novel baseline facial muscle database using statistical shape modeling and in silico trials toward decision support for facial rehabilitation. Bioengineering (Basel). 10:737. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10060737
Walker, S., Firouzeh, A., Robertson, M., Mengüç, Y., and Paik, J. (2022). 3D printed motor-sensory module prototype for facial rehabilitation. Soft Robot. 9, 354–363. doi: 10.1089/soro.2020.0010
Watts, P., Breedon, P., Nduka, C., Neville, C., Venables, V., and Clarke, S. (2020). Cloud computing Mobile application for remote monitoring of bell's palsy. J. Med. Syst. 44:149. doi: 10.1007/s10916-020-01605-7
Zhang, N., Bogart, K., Michael, J., and McEllin, L. (2022). Web-based sensitivity training for interacting with facial paralysis. PLoS One 17:e0261157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261157
Zhang, Y., Gao, W., Yu, H., Dong, J., and Xia, Y. (2024). Artificial intelligence-based facial palsy evaluation: a survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 32, 3116–3134. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2024.3447881
Zhao, Y., Feng, G., Wu, H., Aodeng, S., Tian, X., Volk, G. F., et al. (2020). Prognostic value of a three-dimensional dynamic quantitative analysis system to measure facial motion in acute facial paralysis patients. Head Face Med 16:15. doi: 10.1186/s13005-020-00230-6
Zhu, P., Wang, H., Zhang, L., and Jiang, X. (2022). Deep learning-based surface nerve electromyography data of E-health Electroacupuncture in treatment of peripheral facial paralysis. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 1–12. doi: 10.1155/2022/8436741
Zhu, H., Yang, H., Guo, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Huang, M., et al. (2023). Face scape: 3d facial dataset and benchmark for single-view 3d face reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45, 14528–14545. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3307338
Zhuang, Y., McDonald, M. M., Aldridge, C. M., Hassan, M. A., Uribe, O., Arteaga, D., et al. (2021). Video-based facial weakness analysis. I.E.E.E. Trans. Biomed. Eng. 68, 2698–2705. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2021.3049739
Keywords: intelligent sensing technology, facial paralysis, surface electromyogram, three-dimensional motion capture, artificial intelligence
Citation: Wang J, Tang X, Zhang J, Shao X, Liu Y, Zhai Y, Xu J, Lan S, Yen Y and Wang C (2025) A review of the application of intelligent sensing technology in the recognition and evaluation of facial paralysis. Front. Neurosci. 19:1646485. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1646485
Edited by:
Shaoxiong Sun, The University of Sheffield, United KingdomReviewed by:
Bhanu Priya Dandumahanti, SRM University, IndiaDong Cao, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Tang, Zhang, Shao, Liu, Zhai, Xu, Lan, Yen and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chao Wang, ODUyNTE3MTNAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Jingyao Wang1
Jingyao Wang1 Xing Tang
Xing Tang Yan Zhai
Yan Zhai Jili Xu
Jili Xu