Abstract
Planning, governing processes, and making decisions are crucial elements for any societal change and the development of an urban circular economy. The fight for urban resources, environmental sustainability, maintaining the urban ecosystem, promoting a circular economy, and fulfilling public service demands has put pressure on existing governments to increase their efficiency and collaborative abilities to work in a smarter way. This study aims to explore various enablers that can improve city administration for smart cities. The factors are identified from the literature. The study follows the decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL) approach. The experts have been consulted for the finalization of factors and for the establishment of the causal relationships using the DEMATEL technique to study the cross-inter-relationship among factors. The findings suggest the rankings of factors and classify them into cause-and-effect groups. The study finds influencing enablers that improve policy implementation, e-services, transparency, monitoring, and control abilities for smart city administration. The development of smart cities facilitates an established, interconnected, and sustainable urban system for a circular economy. The policymakers, officials, service providers, and urban planners would get benefit from the outcomes to plan the right initiatives for improvements in governance structure for the development of the smart cities. Although there has been a widespread literature on factors for improving governance, cause-and-effect relationships have not been explored. This study proposes a strategic framework for smart city governance and sustainable social change.
1 Introduction
Planning and governing processes are crucial elements for any societal change and urban development initiatives in this digital era (Sharifi et al., 2024). Nam and Pardo (2014) have defined smart governance as the management of public services and local administration. The smartness can be infused by integrating and interconnecting the real-time data, sensor-based analytics, innovations, sharing information, citizens' participation, and engagement in the decision process (Gil-Garcia et al., 2016). A global call to action, the sustainable development goals (SDGs) aim to ensure that no one is left behind and to build a fairer and equitable world (Dai et al., 2023). Cities are home to half of the world's population (Hui et al., 2023). By 2050, this is expected to increase to 70 percent. The emergence of megacities in developing countries is attributed to the swift pace of urbanization coupled with increasing migration from rural areas to urban centers. In 1990, there were 10 megacities, each with a population exceeding 10 million. In 2014, there were 28 megacities with a population of 453 million (https://www.un.org/). Slums and comparable conditions have grown as a result of rapid urbanization, which is outpacing the construction of housing, infrastructure, and services. In 2020, it was estimated that ~1.1 billion individuals residing in urban areas were either living in slums or conditions similar to slums. Furthermore, it is projected that an additional 2 billion people will inhabit these types of settlements over the next three decades (https://www.un.org/). Sustainable growth cannot be achieved without significant changes in metropolitan planning, design, and management. Ensuring access to secure and affordable housing, modernizing slum settlements, investing in public transit, creating green spaces, and improving inclusive and participatory urban planning and administration are all crucial to make cities smart and sustainable (https://www.un.org/).
In India, most of the cities are facing complex and difficult conditions such as rapid sprawling, pollution, inadequate infrastructure, unplanned urban agglomeration, shortages of affordable housing, mobility challenges, aging, and limited resources. There is a huge pressure on city authorities to become a smart city by optimizing the use of available resources for providing quality life, delivery of services, and efficient infrastructure (Novotný et al., 2014; Gue et al., 2022).
The word “smart city” can be defined as an urban place that is metamorphosed through the integration of advanced technologies and participatory processes to manage and improve the city's resources, service deliveries, and quality of life of citizens. The development of smart cities promotes a sustainable urban system (Debnath et al., 2014; Cesario et al., 2022; Gupta et al., 2022; Cai et al., 2023). The citizens' needs and measures have been focused on enhancing policy making and effective administration structure in the vision of a smart city (Eskelinen et al., 2015; Cardullo and Kitchin, 2018).
The accountability of the government of India has been questioned for a long time due to overlapping functions, lack of expertise, and poor inter-agency coordination. The governments are still lacking efficiency, effectiveness, and sustainability in terms of implementation. Traditional governance has already been criticized thoroughly for its inefficiency, low-quality outcomes (Zamanifard et al., 2018), and under-performing capabilities. For the effective execution of government schemes, significant advancements are required (Nam and Pardo, 2014) in the administrative structure. To understand the public demand and to incorporate local issues, a structured administration is required to execute the urban policies (Novotný et al., 2014) through participatory mechanisms.
Smart city transformation requires massive efforts (Borsekova et al., 2018) from multiple stakeholders to maximize socioeconomic performance. To achieve this, the improvement in city administration is an imperative need to plan urban strategies in a better way. In developing countries like India, Bangladesh, and Pakistan, the smart city concept is still in its nascent phase in terms of understanding and implementation (Tan and Taeihagh, 2020). Therefore, the study has the following objectives:
-
a. To identify the enablers for the administration of smart cities to create sustainable social change.
-
b. To develop contextual cause and effect relationships between the enablers from a policy perspective.
In view of the theoretical contribution, this study set out to gain an understanding of various enablers to ameliorate the administrative structure for the smart city. The research contributes to the previous literature in terms of aggregated knowledge about various enablers. The study explores and proposes the contextual relationships among the enablers to plan initiatives for improving the administration. From the perspectives of decision makers and urban planners, the study presents the classification of cause group enablers and effect group enablers, which can enhance the in-depth understanding for improvement of the city administration.
The article is organized into eight sections. The study background and research objective have been set in the Introduction (Section 1). The literature survey (Section 2) provides insights on various forms of adopted governance models and previous viewpoints on city administration for smart cities. Section 3 (methodology) explains the identification of enablers and methodological steps for the decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL). Section 4 (Results and Discussions) comprises the empirical evidence and calculated matrices. The implications have been discussed in Section 5 (Implications of the study). The conclusions have been made in Section 6. Finally, Section 7 presents study limitations and further directions.
2 Review of literature
This section provides relevant literature on sustainable social change through smart cities in the global and Indian scenarios.
The increasing population, scarcity of resources, pollution, and climate change are primary concerns for the whole world. The technological transformation of city administration will not occur in isolation; it will affect societal changes such as infrastructure, norms, and industrial regulations. Therefore, the importance of social acceptability in the implementation of emerging technology needs to be analyzed. The automation, computation, connectivity, and integration can transform a traditional system into a smart administration system (Gupta and Kumar, 2022). As per the theory of socio-technical transition, the transition of technologies will not emerge alone but will also influence changes in society, such as changes in infrastructure, norms, and industrial regulations (Tijan et al., 2021). Moreover, social cognition theory defines three elements of social integration as personal behavior, individual cognition, and social behavior (Liu et al., 2018). Social integration is an important aspect that should be considered for the adoption of any new technologies by citizens (Kumar et al., 2022).
It is crucial to comprehend a few directions that directly impact the growth of smart cities before outlining the research hypotheses. Among these, we emphasize the shift from the idea of governance to the idea of smart governance.
Effective governance is crucial in the evolution of smart cities, integrating technology and sustainable development. It ensures inclusive decision-making processes, resilient infrastructure investment, and stakeholder collaboration for urban prosperity (Olubunmi et al., 2024). In the 1990s, the phrase “smart city” was first used to describe urban areas that used modern information and communication technologies (ICT) to improve the efficiency of their infrastructure (Albino et al., 2015; Gupta et al., 2024). The smart city approach consists of a number of synergistic elements that combine the social, environmental, and technical aspects of the city with technological solutions (Nam and Pardo, 2011).
Analyzing governance in smart cities necessitates the adaptation of public and social models to address challenges related to digitalization, service delivery, decision-making, and transparency, thereby enabling effective and interoperable urban operations.
2.1 Types of adopted governance
The concept of Smart cities from so many years has gained significant attention in urban governance and policy around the world (Xu et al., 2024). Pierre (2005) has elaborated urban governance as “the processes of control, coordination and regulation of the urban affairs; and steering urban society toward collectively defined goals.” Strategic planning is required to create synergies between digital infrastructure and administration capacity building (Kumar et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2023). For this, clarification is needed about the enablers for the city governance structure.
While exploring the various forms of adopted governance models worldwide, the governance coupled with information technology (e-governance) has improved the transparency and accountability of government functionalities through online services. Mobile governance facilitates mobile-enabled services to enhance connectivity with the end users. Collaborative governance is a form of networked governance that allows participants to get engaged in the development of novel solutions to emerging problems (Baldwin et al., 2018). Good governance refers to measures that enhance the overall governance by improving its effectiveness and legitimacy (Carrington et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2024).
In addition to these, Misuraca et al. (2012) have classified governance into four types, namely, open, leviathan, privatized, and self-service governance, based on government openness, transparency, and integration of policies. While looking minutely in terms of urban development, some operational deficiencies have been found in this governance structure. The open governance may increase the online engagement of citizens and various stakeholders (Misuraca et al., 2012), but to assess the local issues and development priorities, citizens' participation and engagement in governance are essential. In leviathan governance, active citizens' participation is not required in the everyday decision-making process (Misuraca et al., 2012). The diversity of opinions and cultural differences among different communities would increase social exclusions and public divide in self-service governance due to a lack of engagement culture. Therefore, a more robust, structured governance is required for smart administration.
2.2 Factors for smart city administration
Gil-Garcia (2012) has elaborated smart administration as “An advanced form of electronic governance that uses information technologies to interconnect and integrate information, processes, institutions, and physical infrastructure.” Smart administration can be attained by adopting a community-based governance model with higher technological connectivity.
Gil-Garcia et al. (2016) have argued that three elements are associated with smartness and innovation in administration. They emphasized on (i) e-governance to include information and knowledge sharing between multiple stakeholders and government entities for collective decision-making, (ii) engagement of communities and multiple stakeholders, and (iii) networks, partnerships, and collaboration among multiple actors.
The citizens' participation enhances the legitimacy of public policy decisions. Arnstein (1969) has proposed a citizen participation ladder to improve the process. The social media presence in public sectors enhances government responsiveness toward citizens (Eom et al., 2018). Transparency can be considered a crucial element to reduce government corruption (Li et al., 2017). The e-services delivery was important for better accessibility, ease of use, time savings, and to reduce the cost. The differences between visions for smart initiatives and their implementation may create crucial gaps to the success of smart cities (Fernandez-Anez et al., 2018).
The frameworks or models discussed previously do not furnish a clear essence about various enablers to improve the city administration for smart cities. The study attempts to fill this gap and suggests enablers for smart city administration.
Nam and Pardo (2014) have argued that smart governance is the management of public services and local administration. The smartness can be infused by integrating and interconnecting the real-time data, sensors-based analytics, innovations, sharing information, citizens' participation, and engagement in the decision process (Gil-Garcia et al., 2016).
Important factors for the administration of a smart city are described in the following sections.
2.2.1 Digital infrastructure
The technological development opens advanced approaches to tackle societal problems (Dameri et al., 2019). The connectivity of physical, IT, and social infrastructure is required to make the government advanced and smart. The usage of advanced IT infrastructure, technology savviness (Gil-Garcia et al., 2016), digitization of information, and incorporation of ICT has been focused to support and running smart applications. The IoT and sensors can share data to control and manage the activities remotely with the use of smart devices (Shin, 2014). The most recent intelligent systems integrated with a citywide network of connectivity enable the safe real-time interchange of data throughout the city, making it accessible to businesses and residents alike (Yoon et al., 2020; Hu et al., 2023). The quality, dependability, and cost of services are increased by cloud computing and storage, which also presents new possibilities for managing data and services.
2.2.2 Ubiquitous information
Information sharing and exchange over a large, heterogeneous network can reduce the gaps between citizens and governments. The government should provide information to citizens in an easy and accessible manner (Baud et al., 2015). The provided information must be complete, accurate, concise, relevant (Scupola and Zanfei, 2016), linked, integrated, organized, and have timelines to create awareness among the citizens (Kim et al., 2005). The users must be aware of available e-services (Verdegem and Verleye, 2009; Koca et al., 2021) and policies to access, participate, and provide feedback to the government.
2.2.3 Public participation
Public participation is essential to improve the efficacy of government processes (Sæbø et al., 2008). The participation of citizens is required in decision-making (Kim et al., 2005; Giffinger et al., 2007) and deciding development priorities. It improves the confidence between the citizens and government (Gagliardi et al., 2017; Braga et al., 2021).
2.2.4 E-consultation
The government must understand the problems of citizens (de Oliveira et al., 2013). The citizens should be able to speak to a live person in case of facing a problem (e.g., toll-free number, live chat facility, blogs, and social platforms). The government should facilitate online platforms for citizens' complaints (Porwol et al., 2016a) and e-consultation. The primary goals of the e-consultation system are to provide advice and valuable recommendations to the citizens without meeting face to face with an area specialist to save time, money, and personal efforts in commuting.
2.2.5 Citizens' engagement
Most of the societies, tribes, and citizens may not be aware of their rights and political conditions. Citizens' engagement process can develop civic and political knowledge among the citizens, awareness of their rights, and citizens' sense of ownership, which would reshape the citizen–government relationships (Abu-Shanab, 2015) in an intelligent and stronger way. Engagement of multiple stakeholders in policy planning, implementation, and evaluations can improve the city governance, especially at the implementation level (Criado et al., 2013; de Hoop et al., 2021).
2.2.6 Transparency
Government transparency is essential in providing information, decision processes, and various operations (Gil-Garcia et al., 2016; Petersson, 2022). The transparency is an important element in government processes (Picazo-Vela et al., 2012; Kumar et al., 2016; Arkorful et al., 2021) to improve its accountability. The use of open data platforms can provide transparent, efficient, and cost-effective public services and utilities to improve the city operations, serviceability, and citizens' satisfaction (Abu-Shanab, 2015).
2.2.7 E-service delivery
Extensive digital services, also known as e-services, facilitate convenient access and prompt handling of requests for both citizens and businesses, whereas digitized public administration enhances accountability, efficiency, and transparency (Yoon et al., 2020; Bhuiyan and Abrar, 2022). The services must be extended and available over internet platforms to improve the ease of utility. The deployment of technologies can reduce duplication in data collection and data storage. The electronic data storage and e-service delivery can reduce the processing costs of services (Gil-Garcia et al., 2016). The government should facilitate e-services deliveries to the citizens in a cost-effective and personalized manner with greater satisfaction, higher efficiency (Verdegem and Verleye, 2009), and quality. In order to enhance their present and future service delivery capabilities, they need to optimize their core systems (public safety, transport, government services, and health) “smarter” (Koca et al., 2021).
2.2.8 Strategic implementations of policies
Strategic urban planning (Baud et al., 2015), quality of policy making, regional development, and responsible resource consumption (de Oliveira et al., 2013) are important for a city governance to increase its efficiency in government processes outcomes (Kim et al., 2005; Baud et al., 2015; Retnandari, 2022).
2.2.9 Innovative solutions
Innovations are needed for advancements in governance, society, and culture (Kagan et al., 2018). Change management, innovation, spatial intelligence, and sensor integration can provide new urban solutions. Criado et al. (2013) have focused on government innovations, crowdsourcing solutions, and people-led innovations for developing a smart city. The advancement of smart cities necessitates a novel approach to configuration, which includes collaboration among public and private sectors as well as active participation from citizens. It also demands new drivers, encompassing both economic and social factors, along with a diverse array of resources, both technological and non-technological, throughout its development and execution (Leite, 2022).
2.2.10 Monitoring and control
Hall (2000) has defined a smart city in terms of the integration and monitoring of the critical infrastructure of a city. The technology-oriented auto analysis of real-time data can support city authorities in managing events in an organized manner and to respond accordingly. The government should implement interactive monitoring to control the city resources, policy implementations, and unusual events happening in a city (Javed et al., 2022). The sensory data can be collected through the participants' smartphones or embedded sensors for effective monitoring (Khan et al., 2015).
2.2.11 Inclusion of social media
Over social media platforms, citizens and government can participate together to co-create (Picazo-Vela et al., 2012; Kumar et al., 2016) and collaborate in development plans. Porwol et al. (2016b) have found that social media usage in the political process. Stewart (2006) has supported the use of public forums over social media, whereas Kavanaugh et al. (2012) have discussed social media benefits for extremely unusual situations like natural or man-made calamities to inform citizens in a fast manner. The social media usage can improve the responsiveness of city government toward its citizens (Kumar et al., 2016; Ledesma-Gumasing and Mendoza-Armiendo, 2021).
The experts given in Annexure 1 with diverse relevant expertise, such as urban developers, academicians, service providers, planning advisors, solutions consultants, and architects, were consulted personally in different sittings. Some factors were merged due to relevance, and some were discarded due to inappropriateness based on the opinion and consensus of the experts. This process helps to reduce the duplicity and increases the comprehensiveness of taken concept. The final selected determinants are represented in Table 1.
Table 1
| Constructs | Description | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Digital infrastructure (DI) | The use of ICT, digitization of information, and connectivity of physical, IT, and social infrastructure to make the government advanced and smart | Verdegem and Verleye, 2009; Nam and Pardo, 2011; Gil-Garcia et al., 2016; Hu et al., 2023 |
| Ubiquitous Information facility (UI) | The complete, accurate, concise, relevant, integrated, organized, and timelines information availability to citizens via all mediums of communication | |
| Public participation (PP) | Citizens' participation in decision-making and policy design for effective planning by utilizing multiple communication channels | Macintosh, 2004; Stewart, 2006; Giffinger et al., 2007; Picazo-Vela et al., 2012; Baud et al., 2015; Sæbø et al., 2008; Porwol et al., 2016a,b; Cardullo and Kitchin, 2019; Braga et al., 2021 |
| E-consultation (EC) | The two-way communication relationships among multiple stakeholders. The government should facilitate online platforms for citizens' complaints, feedback processes, and co-creation for citizen-driven development | Macintosh, 2004; Porwol et al., 2016a; Baud et al., 2015; Rochdane and Assaber, 2022 |
| Citizen Engagement (CE) | Engagement of multi-stakeholders in crowd-sourcing solutions, policy implementation, and policy evaluations to improve the city administration and to empower the citizens using multi-channel communications | Sæbø et al., 2008; Gil-Garcia et al., 2016; Porwol et al., 2016a,b; Gagliardi et al., 2017; Appio et al., 2019; de Hoop et al., 2021 |
| Transparency in governance (TG) | The transparency in government processes, policy, functionality, and activities improves the city operations, services, and citizens' satisfaction | Macintosh, 2004; Kim et al., 2005; Stewart, 2006; Baud et al., 2015; Gil-Garcia et al., 2016; Appio et al., 2019; Arkorful et al., 2021; Petersson, 2022 |
| e-Service delivery (SD) | The facility of e- service delivery to the residents in a cost-effective, faster, and personalized manner with greater satisfaction, higher efficiency, and service quality | Giffinger et al., 2007; Verdegem and Verleye, 2009; Gil-Garcia et al., 2016; Scupola and Zanfei, 2016; Bhuiyan and Abrar, 2022 |
| Strategic implementation of policies (IP) | Strategic urban planning to increase implementation efficiency in government processes and outcomes | Kim et al., 2005; Preuss, 2009; Baud et al., 2015; Retnandari, 2022 |
| Innovative solutions (IS) | The government's innovative solutions, crowdsourcing solutions, and people-led new suggestions for developing a smart city | Criado et al., 2013; Gil-Garcia et al., 2016; Kumar et al., 2016; Appio et al., 2019; Bours et al., 2022 |
| Monitoring and Control (MC) | The interactive monitoring of critical infrastructure and resources of a city with the use of sensing and tracking devices, and to identify unusual events in a city | Sæbø et al., 2008; de Oliveira et al., 2013; Baud et al., 2015; Appio et al., 2019; Javed et al., 2022 |
| Inclusion of social media (SM) | Social media for public participation, engagement, and to increase the responsiveness of city government toward its citizens, to improve government processes and public services | Stewart, 2006; Kavanaugh et al., 2012; Kumar et al., 2016; Ledesma-Gumasing and Mendoza-Armiendo, 2021 |
The factors for improving city administration with respect to smart cities.
3 Methodology
Decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL) approach has been used in this study to prioritize enabling factors for the administration of smart cities. The “Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM)” techniques facilitate decision-makers' abilities to make the best choice from a complex set of alternatives.
3.1 DEMATEL approach
The “Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM)” techniques facilitate decision-making abilities to make the best choice from a complex set of alternatives. The “decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory” (DEMATEL) technique was developed at the “Research Center of the Battelle Memorial Institute,” Geneva. DEMATEL builds and evaluates models and relations among various enablers selected for a particular purpose (Si et al., 2018). It classifies all the factors into cause-and-effect depending on their influencing abilities (Parmar and Desai, 2020; Yadav et al., 2021).
The DEMATEL approach has advantages over other MCDM techniques such as TOPSIS, AHP, ANP, ELECTRE, and VIKOR, as DEMATEL helps to visualize the cause–effect relationships between all the selected factors (Gardas et al., 2019). Though AHP, TOPSIS, and ANP can prioritize or provide weights for the best alternative selection, these methods do not provide any relational diagram (Sharma et al., 2020). In comparison to interpretive structural modeling (ISM), DEMATEL obtains the contextual relationships between variables and emphasizes the influencing impact of their relationships. ISM cannot provide quantified relationships (Singh et al., 2020). Compared with other modeling techniques, such as “total interpretive structural modeling (TISM),” the DEMATEL determines the effects of interrelationships (Singh et al., 2020).
In the previous research, DEMATEL technique has been applied in various fields to visualize the cause-and-effect groups like developing supplier selection criteria (Chang et al., 2011); green supply chain management (Lin, 2013); Sponge city project in China; logistics enterprises in Iran (Ahmad Alinejad et al., 2018); knowledge management (Abdullah and Zulkifli, 2019); e-waste remanufacturing; adoption of sustainable-supply-chain (Li and Mathiyazhagan, 2018); manufacturing organizations; mobile app issues; and hospital management performance (Jiang et al., 2020) and so on.
3.1.1 Steps of the DEMATEL approach
Step 1. Develop a direct-relationship matrix between the selected factors on a scale of 0 to 4 by considering “0” for “no relationship”; “1” for “low influence;” “2” for “moderate influence;” “3” for “high influence;” and “4” for “very high influence.” The matrix Az is developed based on the influence of “i” over “j” received from each expert. The diagonal pairwise value will be 0, which states no effect on itself when i = j.
Step 2. Based on the consensus of experts, develop an overall direct-relationship matrix A -
where A = overall direct-relation matrix, aij =consensus of all experts.
Step 3. Develop a normalized direct-relation matrix X -
Step 4. Calculate Total-relation matrix (T) –
where I denote an “Identity matrix.”
Step 5. From the Total-relation matrix, calculate the row sum (R) and column sum (C) -
Sum of elements in rows:
Sum of elements in columns:
Step 6. Calculate threshold value (α) as:
where n2 = total number of elements in T. For “n” enablers, the total elements in matrix T= nxn = n2
Step 7. Draw a connecting diagram by plotting (R+C) on the x-axis and (R-C) on the y-axis.
Step 8. Develop a cause-effect directed graph based on values greater than α and significant influential strength.
4 Results and discussion
In the qualitative decision-making process, 5 to 30 experts can be considered a good range to get opinions (Sharma et al., 2020). In this study, 22 experts (Annexure 1) were asked to assess the causal relationships between 11 enablers. On a scale of 0 to 4, each expert has responded to the influence of i on the j variable (Singh and Acharya, 2014). Based on the consensus of the experts, the direct-relation matrix has been developed. The normalized matrix (Table 2) is calculated by using Equation 3. The total relation matrix (Table 3) is calculated by using Equation 4. The row sum and column sum have been calculated by using Equations 5, 6. The threshold value (α = 0.303) has been calculated by using Equation 7. The threshold value helps to identify significant cause-effect relations as shown in the inner dependence matrix (Table 4).
Table 2
| (DI) | (UI) | (PP) | (EC) | (CE) | (TG) | (SD) | (IP) | (IS) | (MC) | (SM) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (DI) | 0.000 | 0.118 | 0.088 | 0.059 | 0.118 | 0.118 | 0.118 | 0.088 | 0.088 | 0.118 | 0.088 |
| (UI) | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.088 | 0.088 | 0.088 | 0.088 | 0.118 | 0.059 | 0.088 | 0.088 | 0.118 |
| (PP) | 0.029 | 0.059 | 0.000 | 0.118 | 0.088 | 0.118 | 0.059 | 0.029 | 0.118 | 0.118 | 0.088 |
| (EC) | 0.059 | 0.088 | 0.088 | 0.000 | 0.088 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.118 | 0.088 | 0.088 |
| (CE) | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.088 | 0.088 | 0.000 | 0.088 | 0.088 | 0.118 | 0.118 | 0.088 | 0.059 |
| (TG) | 0.059 | 0.029 | 0.029 | 0.088 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.118 | 0.088 | 0.029 | 0.118 | 0.059 |
| (SD) | 0.118 | 0.088 | 0.000 | 0.029 | 0.029 | 0.118 | 0.000 | 0.059 | 0.088 | 0.118 | 0.029 |
| (IP) | 0.088 | 0.029 | 0.088 | 0.118 | 0.029 | 0.118 | 0.088 | 0.000 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.059 |
| (IS) | 0.088 | 0.029 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.088 | 0.059 | 0.000 | 0.118 | 0.088 |
| (MC) | 0.059 | 0.088 | 0.118 | 0.000 | 0.059 | 0.088 | 0.000 | 0.118 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| (SM) | 0.059 | 0.118 | 0.088 | 0.118 | 0.118 | 0.088 | 0.118 | 0.059 | 0.088 | 0.088 | 0.000 |
Normalization of direct matrix.
Table 3
| (DI) | (UI) | (PP) | (EC) | (CE) | (TG) | (SD) | (IP) | (IS) | (MC) | (SM) | R | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (DI) | 0.258 | 0.379 | 0.365 | 0.344 | 0.373 | 0.468 | 0.429 | 0.375 | 0.390 | 0.491 | 0.337 | 4.208 |
| (UI) | 0.253 | 0.236 | 0.324 | 0.330 | 0.312 | 0.391 | 0.383 | 0.306 | 0.349 | 0.413 | 0.327 | 3.625 |
| (PP) | 0.241 | 0.279 | 0.235 | 0.343 | 0.302 | 0.399 | 0.318 | 0.272 | 0.361 | 0.424 | 0.292 | 3.466 |
| (EC) | 0.265 | 0.303 | 0.315 | 0.236 | 0.302 | 0.348 | 0.318 | 0.293 | 0.361 | 0.395 | 0.293 | 3.429 |
| (CE) | 0.279 | 0.286 | 0.324 | 0.329 | 0.226 | 0.390 | 0.355 | 0.356 | 0.371 | 0.410 | 0.275 | 3.600 |
| (TG) | 0.227 | 0.210 | 0.215 | 0.264 | 0.201 | 0.237 | 0.313 | 0.274 | 0.228 | 0.356 | 0.217 | 2.743 |
| (SD) | 0.286 | 0.268 | 0.199 | 0.221 | 0.211 | 0.354 | 0.222 | 0.260 | 0.286 | 0.371 | 0.203 | 2.881 |
| (IP) | 0.276 | 0.236 | 0.292 | 0.324 | 0.231 | 0.378 | 0.324 | 0.218 | 0.288 | 0.347 | 0.249 | 3.164 |
| (IS) | 0.270 | 0.231 | 0.263 | 0.261 | 0.250 | 0.318 | 0.312 | 0.269 | 0.222 | 0.385 | 0.263 | 3.044 |
| (MC) | 0.202 | 0.234 | 0.276 | 0.178 | 0.209 | 0.295 | 0.192 | 0.277 | 0.208 | 0.223 | 0.155 | 2.449 |
| (SM) | 0.301 | 0.367 | 0.351 | 0.381 | 0.362 | 0.423 | 0.412 | 0.333 | 0.379 | 0.447 | 0.245 | 4.000 |
| C | 2.857 | 3.028 | 3.160 | 3.212 | 2.979 | 4.000 | 3.579 | 3.233 | 3.444 | 4.260 | 2.857 |
Total relation matrix.
The last column (R) and last row (C) could represent row-wise totals (R) and column-wise averages (C).
Table 4
| (DI) | (UI) | (PP) | (EC) | (CE) | (TG) | (SD) | (IP) | (IS) | (MC) | (SM) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (DI) | 0.258 | 0.379 | 0.365 | 0.344 | 0.373 | 0.468 | 0.429 | 0.375 | 0.390 | 0.491 | 0.337 |
| (UI) | 0.253 | 0.236 | 0.324 | 0.330 | 0.312 | 0.391 | 0.383 | 0.306 | 0.349 | 0.413 | 0.327 |
| (PP) | 0.241 | 0.279 | 0.235 | 0.343 | 0.302 | 0.399 | 0.318 | 0.272 | 0.361 | 0.424 | 0.292 |
| (EC) | 0.265 | 0.303 | 0.315 | 0.236 | 0.302 | 0.348 | 0.318 | 0.293 | 0.361 | 0.395 | 0.293 |
| (CE) | 0.279 | 0.286 | 0.324 | 0.329 | 0.226 | 0.390 | 0.355 | 0.356 | 0.371 | 0.410 | 0.275 |
| (TG) | 0.227 | 0.210 | 0.215 | 0.264 | 0.201 | 0.237 | 0.313 | 0.274 | 0.228 | 0.356 | 0.217 |
| (SD) | 0.286 | 0.268 | 0.199 | 0.221 | 0.211 | 0.354 | 0.222 | 0.260 | 0.286 | 0.371 | 0.203 |
| (IP) | 0.276 | 0.236 | 0.292 | 0.324 | 0.231 | 0.378 | 0.324 | 0.218 | 0.288 | 0.347 | 0.249 |
| (IS) | 0.270 | 0.231 | 0.263 | 0.261 | 0.250 | 0.318 | 0.312 | 0.269 | 0.222 | 0.385 | 0.263 |
| (MC) | 0.202 | 0.234 | 0.276 | 0.178 | 0.209 | 0.295 | 0.192 | 0.277 | 0.208 | 0.223 | 0.155 |
| (SM) | 0.301 | 0.367 | 0.351 | 0.381 | 0.362 | 0.423 | 0.412 | 0.333 | 0.379 | 0.447 | 0.245 |
Inner dependence matrix.
Bold values showing effect side and non-bold values reflects cause side.
The results have been divided into three sections, i.e., rankings of enablers, cause-and-effect groups, and enablers for decision-making.
4.1 Rankings of the enablers
Based on the degree of importance (R+C) score, the rankings of enablers (Table 5) have been assigned. The rankings are helpful to find the relative importance of enablers.
Table 5
| R | C | R+C | R-C | Rankings | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (DI) | 4.208 | 2.857 | 7.065 | 1.351 | 1 |
| (UI) | 3.625 | 3.028 | 6.653 | 0.597 | 5 |
| (PP) | 3.466 | 3.160 | 6.626 | 0.306 | 7 |
| (EC) | 3.429 | 3.212 | 6.641 | 0.217 | 6 |
| (CE) | 3.600 | 2.979 | 6.579 | 0.621 | 8 |
| (TG) | 2.743 | 4.000 | 6.743 | −1.257 | 3 |
| (SD) | 2.881 | 3.579 | 6.460 | −0.698 | 10 |
| (IP) | 3.164 | 3.233 | 6.397 | −0.070 | 11 |
| (IS) | 3.044 | 3.444 | 6.488 | −0.400 | 9 |
| (MC) | 2.449 | 4.260 | 6.710 | −1.811 | 4 |
| (SM) | 4.000 | 2.857 | 6.857 | 1.143 | 2 |
Degree of influence (rankings based on R+C score).
Digital infrastructure (DI) has been found to as the most important enabler (Table 5). The technological development opens advanced approaches to tackle urban problems (Toppeta, 2010; Dameri et al., 2019; Calzada et al., 2023). The connectivity of physical, IT, and social infrastructure is required to make the government advanced and smart. Over social media platforms, citizens and government can participate together to co-create (Kumar et al., 2016) and collaborate in development plans. Transparency is an important enabler in government processes (Macintosh, 2004; Kumar et al., 2016) to improve their accountability. Hall (2000) has defined a smart city as the integration and monitoring of the critical infrastructure of a city. The technology-oriented auto analysis of real-time data can support city authorities in managing events in an organized manner and responding accordingly.
Ubiquitous information exchange over a large, heterogeneous network can reduce the gaps between citizens and governments. For e-consultation, the city government should understand the problems (de Oliveira et al., 2013) and queries of its citizens. Public participation is essential to improve the efficacy of government processes (Sæbø et al., 2008; Rahman et al., 2023). Most of the societies, tribes, and citizens may not be aware of their rights and political conditions. Citizens' engagement process can develop civic and political knowledge among the citizens, awareness of their rights, and citizens' sense of ownership, which would reshape the citizen–government relationships. Criado et al. (2013) have focused on government innovations, crowdsourcing solutions, and people-led innovations for smart cities. The services must be extended and available over internet platforms to improve the ease of utility. The electronic data storage and e-service delivery can reduce the processing costs of services (Gil-Garcia et al., 2016; Peldon et al., 2024). Preuss (2009) has highlighted the importance of strategy and flexibility in public policies.
4.2 Cause-and-effect group
The enablers possessing the positive value of R–C scores (Table 6) are influencing enablers and put into the cause group (Figure 1). The effect group consists of enablers that have a negative value of R–C scores (Figure 2). The effect group enablers are getting influenced by the cause group.
Table 6
| Criteria | Description of factors |
|---|---|
| Highest influential impact power (R) | DI–Digital Infrastructure has the highest influential impact power R = 4.208, which indicates that DI is highly influential in the cause group |
| Highest R-C Score | DI–Digital Infrastructure has the highest score of (R-C) in this group (=1.351), which indicates DI is the least influenced |
| Lowest R-C score | EC–the e-consultation has the lowest score of R-C in this group (=0.217), which indicates EC is highly influenced by any other enablers in this group |
| Highest R+C in this group | DI–Digital Infrastructure has the highest R+C score (=7.605), which indicates DI has high potential to revamp the system. The concerned authorities should pay attention to digital infrastructure |
Criteria check—cause group enablers.
Figure 1
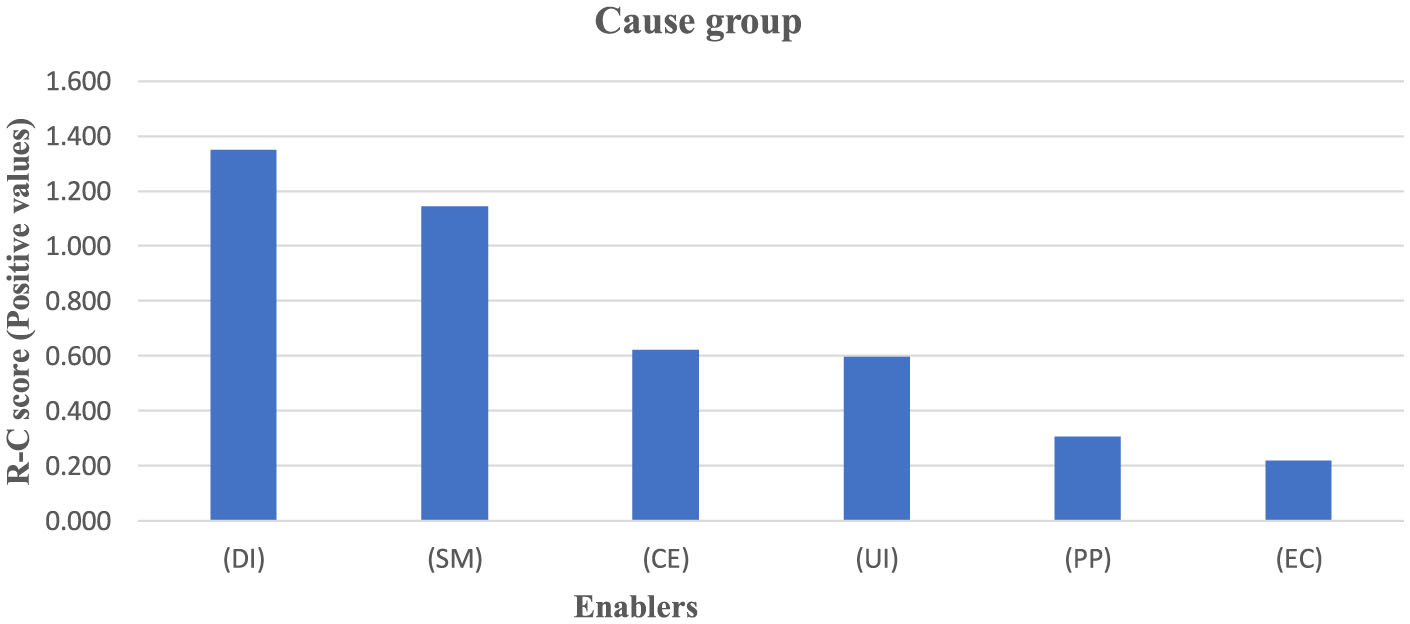
Cause group enablers for city administration.
Figure 2
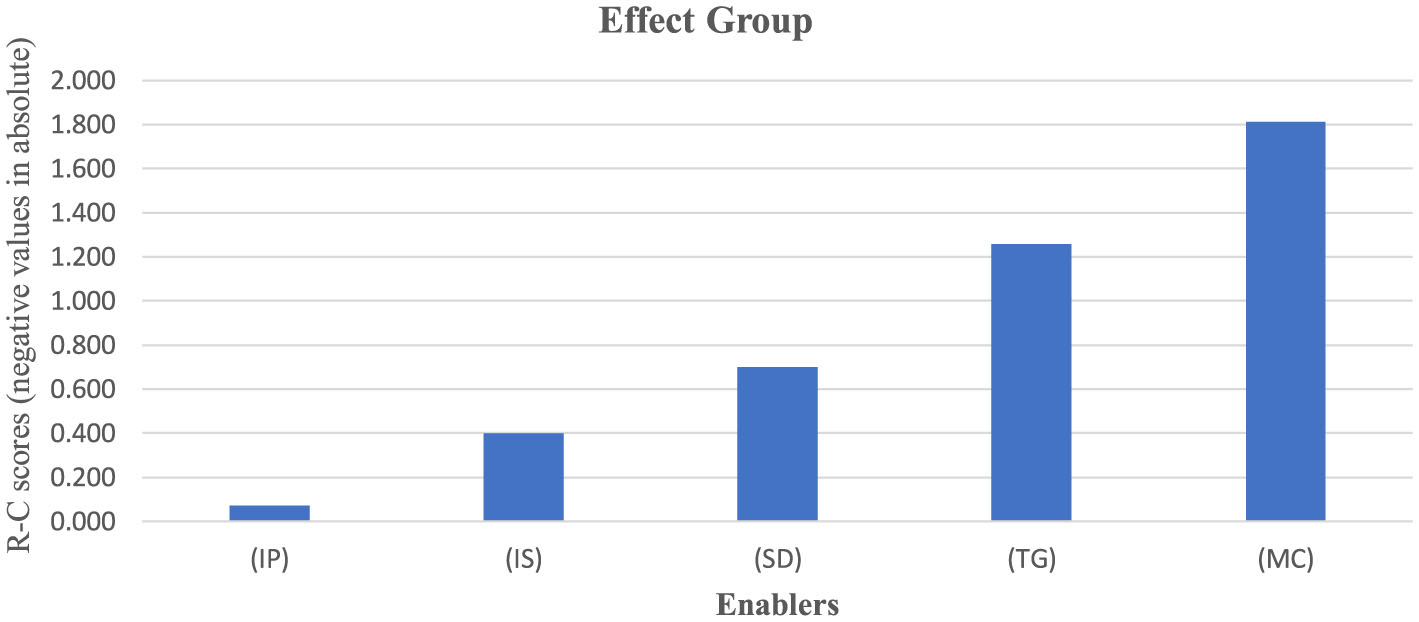
Effect group enablers for city administration.
The use of digital infrastructure (DI) can advance government decision processes. The usage of advanced IT infrastructure, technology savviness (Gil-Garcia et al., 2016; Calzada et al., 2023), digitization of information, and incorporation of ICT has been focused to support and run smart applications. The social media (SM) reduces the information asymmetry among the stakeholders. Social platforms can be used to raise the administrative and development issues to the concerned authorities. The engagement of multiple stakeholders in policy planning, implementation, and evaluations (Criado et al., 2013) can improve the city administration, especially at the implementation level.
The facility of ubiquitous information (UI) to inform citizens about city planning and operations. The government should provide information (Macintosh, 2004; Baud et al., 2015) to citizens in an easy and accessible manner. The provided information must be complete, accurate, concise, relevant (Scupola and Zanfei, 2016), linked, integrated, organized, and have timelines to create awareness (Kim et al., 2005) among the citizens. Public participation (PP) is essential for prioritizing the development and building confidence among citizens to believe in governments (Gagliardi et al., 2017; Janowski, 2015). The citizens should be able to speak to a live person in case of facing a problem (e.g., toll-free number, live chat facility, blogs, and social platforms). Table 6 highlights a few important points for cause group enablers.
To execute the smart city progress process, the strategic alignment is necessary for the implementation of policies (IP). Innovative services (IS) are needed for advancements in administration, society, and culture. Change management, innovation, spatial intelligence, and sensors integration can provide new urban solutions. The e-services delivery (SD) reduces operating costs and enhances system performance. The transparency (TG) is strongly linked to government accountability. Advanced ICT, high-speed networks, and integration of mobile devices and sensors can offer the capability of monitoring and controlling (MC) events and real-time access. Table 7 highlights a few important points for effect group enablers.
Table 7
| Criteria | Description of factors |
|---|---|
| Highest influential impact power (R) | IP–Strategic implementation of Policies has the highest influential impact power R (=3.164), which indicates IP is highly effective for the improvement |
| Highest R-C Score | IP–Strategic implementation of Policies has (highest R-C) score (minus 0.070), which indicates IP is mostly determined by other enablers |
| Lowest R-C score | MC–Monitoring and control enabler has the lowest score of R-C (minus 1.811), which indicates that MC is the least influenced |
| Highest R+C in this group | TG–Transparency in group has the highest score of R+C (=6.743), which signifies that TG is the most important enabler in this group |
Criteria check—effect group.
4.3 Causal diagram for decision-making
DEMATEL builds and evaluates models and relations among various enablers selected for a particular purpose (Si et al., 2018). It classifies all the factors into cause-and-effect depending on their influencing abilities (Parmar and Desai, 2020; Yadav et al., 2021). The causal diagram (Figure 3) has been developed by plotting R+C scores on the x-axis and R-C scores on the y-axis. The causal diagram shows the importance of enablers and illustrates the directional relational effects for implementation (Figure 4).
Figure 3
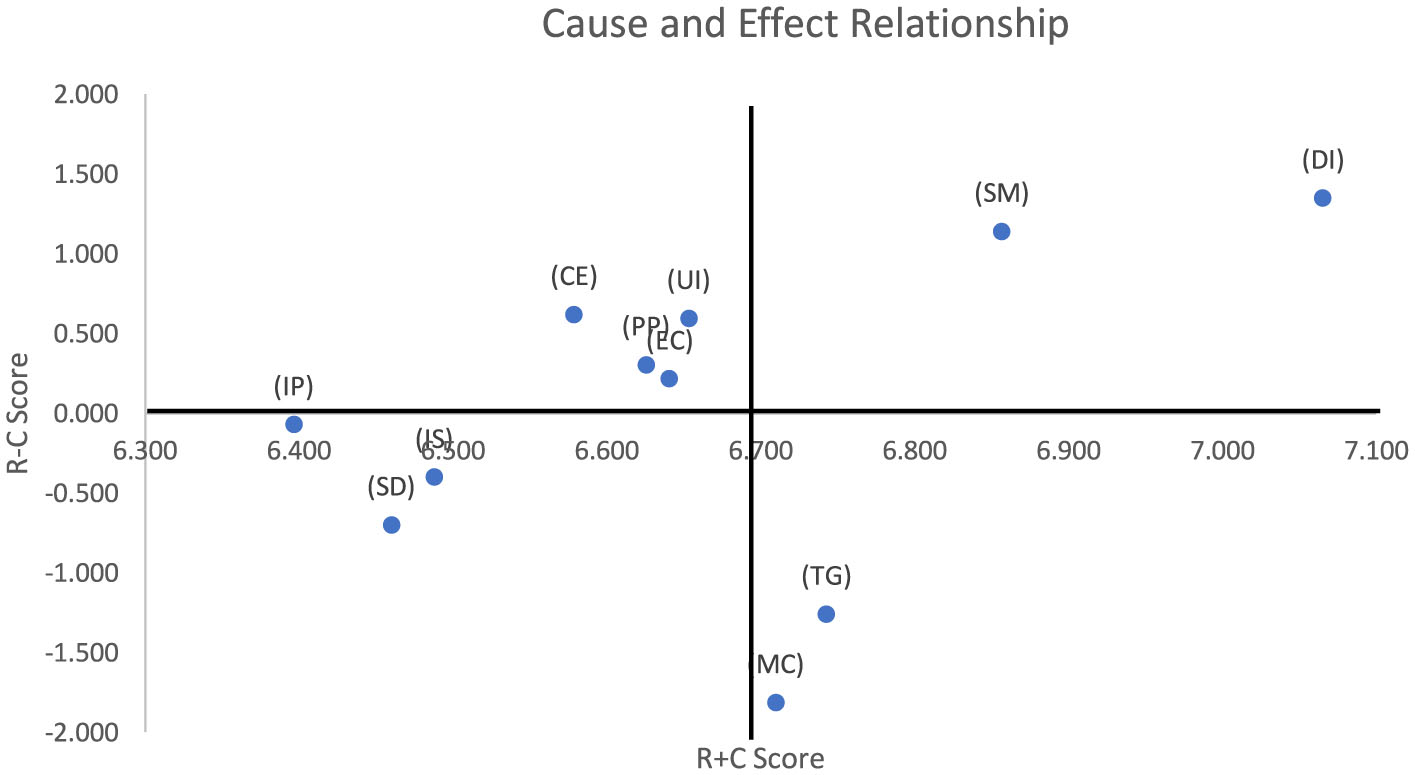
Cause-and-effect relationships between enablers.
Figure 4
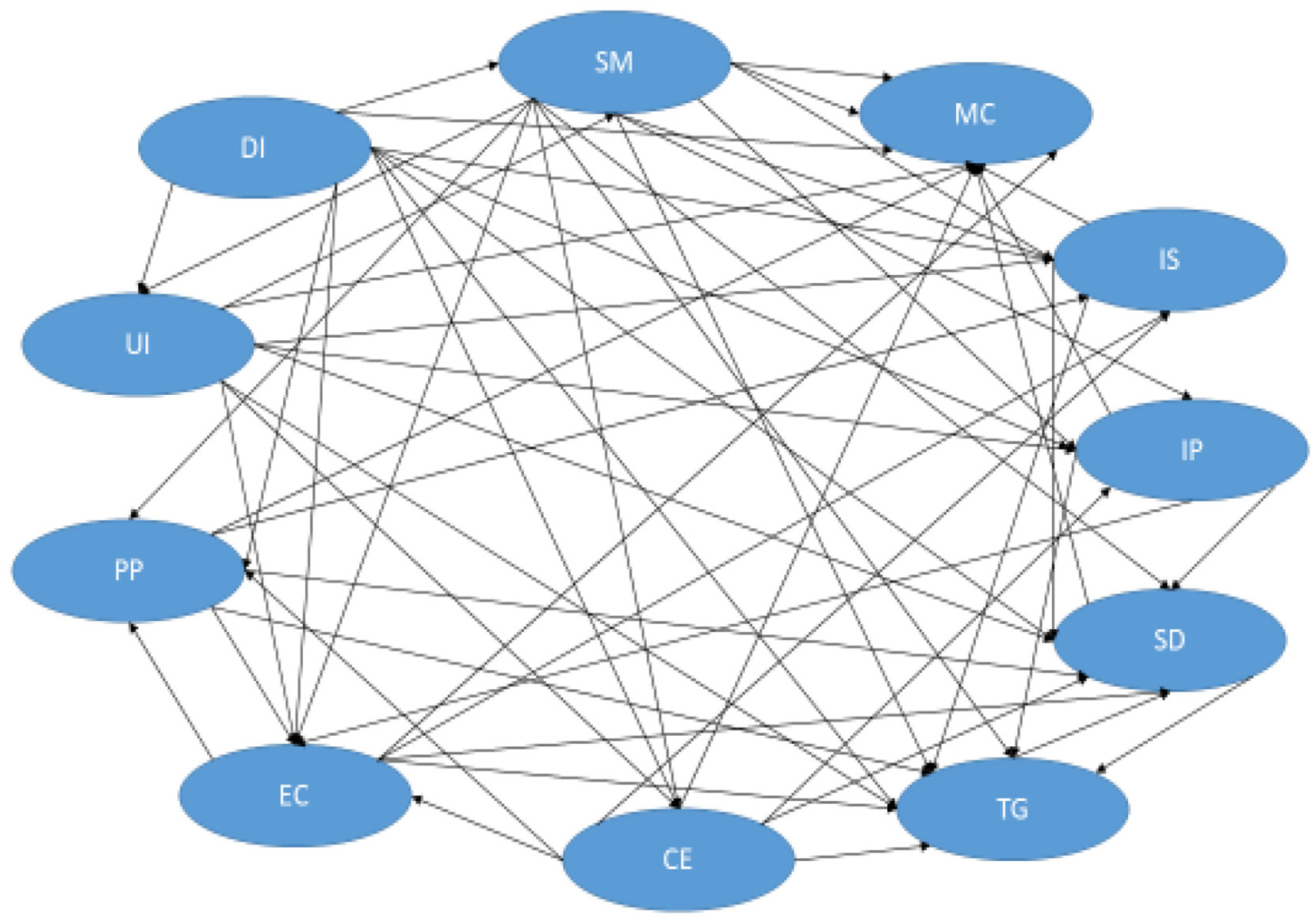
Cause-and-effect relationships between enablers.
To develop the digital infrastructure (DI), the role of technologies has been emphasized to design interconnected networks, service-oriented architectures (Nam and Pardo, 2011). DI influences SM, IS, IP, TG, and MC. The social media (SM) usage can improve the responsiveness of the city government toward its citizens (Kumar et al., 2016). The increased usage of social media can make a city administration more efficient and collaborative (Nam and Pardo, 2014) to manage the city operations. Stewart (2006) has supported the use of public forums over social platforms. Kavanaugh et al. (2012) have elaborated social media benefits for extremely unusual situations, such as natural or man-made calamities, to inform citizens in a fast manner. The SM is getting influenced by DI. SM and UI can influence each other. The usage of SM can improve IP, EC, and MC.
Circular economy (CE) principles are increasingly becoming vital for transforming urban systems into sustainable and regenerative models. In the context of smart cities, integrating digital enablers with circular approaches allows for intelligent planning, participatory governance, and responsible resource management. Ubiquitous information (UI) acts as a catalyst in enhancing Public Participation (PP), E-Consultation (EC), Citizen Engagement (CE), Innovative Solutions (IS), Transparency in Governance (TG), and Monitoring and Control (MC). Active citizen participation in decision-making not only strengthens the bond between government and citizens (Kim et al., 2005; Giffinger et al., 2007; Gagliardi et al., 2017) but also supports the development of circular strategies such as local repair networks, shared mobility, and community-led reuse initiatives. UI and CE promote PP, which in turn strengthens IS and Sustainable Delivery (SD) of services aligned with circular values like reuse, remanufacturing, and waste-to-resource conversion.
Governments must deploy inclusive digital platforms for citizen feedback and e-consultation (Kavanaugh et al., 2012; de Oliveira et al., 2013; Porwol et al., 2016a). Such systems can gather community insights for more adaptive, efficient policies in areas like energy, water, mobility, and waste—core sectors of circular transformation. EC directly enhances IS and SD enablers by facilitating citizen-driven innovation in local resource loops.
Smart city services should be designed to be innovative, circular, and environmentally responsible. Multi-sensory environments, location-based services, and open data can support the circular economy by enabling real-time tracking of resources, predictive maintenance, and demand-based service delivery (Kumar et al., 2016). IS further enhances SD and MC, enabling closed-loop models of urban services. Efficient implementation of circular policies (IP) improves PP, SD, and MC by aligning development with reuse, regeneration, and sustainable consumption.
The delivery of circular public services must be cost-effective, citizen-centric, and high in quality (Verdegem and Verleye, 2009). Public awareness and accessibility to circular services—such as digital waste exchange platforms or green product registries—can transform citizens into co-creators of circular value. SD is closely linked to PP, UI, CE, EC, IS, and IP and operates as a mutual influencer with TG and MC.
Transparency in governance (TG) plays a crucial role in the circular transition by making information on resource flows, recycling systems, and environmental impacts openly available (Gil-Garcia et al., 2016). TG is enhanced by DI, UI, PP, EC, CE, IP, IS, and SD, fostering accountability and collective responsibility.
Monitoring and control (MC) systems, powered by sensors and big data, enable cities to track energy, water, emissions, and waste in real-time. This facilitates adaptive management of city resources and effective policy execution aligned with circularity. Data from smartphones, IoT devices, and public interfaces helps detect anomalies and optimize urban metabolism (Khan et al., 2015).
Integrating these enablers enhances urban efficiency and promotes circular outcomes, such as reduced resource extraction, minimized waste, and maximized reuse. These contribute directly to sustainable urban planning, quality policymaking, and resilient infrastructure. When designed around the principles of a circular economy, smart cities significantly support Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 6 (Clean Water), SDG 7 (Clean Energy), SDG 9 (Industry and Innovation), SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities), SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
5 Implications and recommendations for sustainable social change
5.1 Theoretical implications
The study enhances the theoretical understanding by linking the enablers of smart governance (such as digital infrastructure, citizen engagement, and transparency) to the operationalization of circular economy principles in urban settings. It contributes to the socio-technical transition theory by showcasing how administrative and digital enablers can drive systemic transformations needed for circular practices in cities. Through the DEMATEL approach, the study provides a theoretical framework for understanding interdependencies among enablers. This methodologically reinforces the systems thinking perspective, which is central to the circular economy. It fills a gap in existing literature by quantifying and classifying administrative drivers of circular city transformations. Most circular economy literature is based in the context of developed nations. This study offers a contextual theoretical model applicable to the urban realities of developing economies, where governance inefficiencies, infrastructure gaps, and socio-political complexities demand adaptive and inclusive frameworks.
5.2 Practical implications
The findings provide urban planners and city administrators with a roadmap to design smart cities that are inherently circular, emphasizing resource optimization, waste minimization, and closed-loop systems enabled through ICT and real-time data. The identified enablers (e.g., ubiquitous information, e-services, and monitoring systems) equip municipal bodies with practical strategies to educate citizens, streamline services, and promote behavioral change toward sustainability, critical for the success of circular practices like recycling, reusing, and sharing. The study highlights digital infrastructure not only as a technological asset but also as a practical enabler for tracking resource flows, enabling circular logistics, and automating public systems (such as smart waste management and energy grids), thereby reinforcing the circular economy on the ground.
5.3 Policy implications
Policymakers can leverage the proposed strategic framework to embed circular economy principles within smart city governance policies. This includes integrating urban sustainability goals (e.g., SDG 11 and SDG 12) with digital innovation and administrative reform. With smart monitoring and control as key enablers, the study recommends that governments develop data-centric policies, utilizing real-time analytics to evaluate circular performance indicators (waste reduction, material reuse, and energy savings) and inform adaptive regulations. The importance of citizen participation, social media engagement, and e-consultation underlines the need for inclusive governance structures. Policymakers should institutionalize participatory platforms to co-create circular policies and ensure legitimacy and responsiveness in circular transitions.
Smart urban areas have the potential to enhance the accessibility and quality of urban services for residents, enterprises, and governmental bodies by leveraging digital technologies (Yoon et al., 2020). Municipal authorities and local stakeholders ought to be granted the authority to lead their city's smart initiatives and guarantee the responsible application of technology. Establishing well-defined governance structures, regulatory frameworks, and urban policies that support a unified vision or strategy for the city can enhance the guidance for smart city technologies and initiatives. The expansion of urban areas, their economic significance, and the competitive edge they possess are contingent upon the skills of the populace, as well as the creativity, knowledge, and innovative capabilities inherent within the economy (Koca et al., 2021).
Smart governance can significantly influence society by enabling more effective remote monitoring and management of conventional public services, including transportation, parking, public lighting, education, and healthcare, among others (Leite, 2022). Digital technology integration into city management to support sustainable urban development may also open up commercial potential for businesses while enhancing social wellbeing. It is essential for socio-political actors to be informed about the conditions within the city. By sharing information regarding the city's current needs, they can facilitate the generation of ideas, promote citizen engagement, and enhance the utilization of technology-driven services. Citizens may be regarded as socio-political participants in smart cities, playing a significant role in the innovation process. In order to provide services in a more citizen-centric manner, cities must implement more sophisticated information technology (Koca et al., 2021).
Based on the sustainable city goals, policy, and strategy, assessed planning for harmonizing with nature, and promoting disaster resilience, sustainable economies, social inclusion, equitable basic services, and improving service quality (Choi and Song, 2023). Planning capacity assesses practical considerations for the implementation of the strategy, such as budget, coordination, and timeline for various domains of the city, such as energy management, clean energy, education for all, health services, intelligent monitoring, enhanced agricultural systems, early warning system for disasters, effective management of environmental pollution, and waste management.
The study strengthens the preceding research with respect to the gathered knowledge about enablers for the smart administration. The policy makers and urban planners can make use of the study outcomes to understand the cause-and-effect enablers to plan initiatives accordingly. The digital infrastructure (DI) is an important enabler to facilitate the auto response and faster system in the smart city. The online portals, social media platforms, app-based services, citizens' helplines, mobile messages, and toll-free voice facility can deliver the necessary information to citizens to make them aware.
The collaborative environments, e-consultation, campaigning, polling, and voting process can increase the citizens' engagement and participation in the administrative process. The social media and open data platforms can enable more transparency and accountability in governments. The setup of innovation labs and fostering high-tech industries can provide opportunities to develop innovative solutions for smart cities. The interactive monitoring and management of resources can enable the government to control resource consumption and the real-time tracking process. Therefore, the improvements in digital infrastructure, raising awareness among the citizens, increased usage of mobile devices, social media, enhanced citizens' engagement, public participation, and e-consultation can influence the implementation of policies, innovative solutions, e-services delivery, transparency, monitoring, and control to reshape the city administration into a smart administration for smart cities.
6 Conclusion
With the rapid urbanization and increasing population, cities are grappling with complex challenges such as strained resources, unemployment, and deteriorating urban infrastructure. To address these issues in a sustainable manner, cities are adopting smarter and more circular approaches to governance and development. The concept of the circular economy, which emphasizes resource efficiency, waste minimization, and regeneration of natural systems, aligns seamlessly with the goals of smart city administration.
This study identifies enablers that support the transition toward smart and circular urban governance. Drawing from literature and expert insights, the DEMATEL method was employed to analyze and rank these enablers, categorizing them into cause and effect groups. These enablers not only facilitate digital transformation but also embed circular principles into city operations.
The findings highlight that digital infrastructure (DI), social media (SM), citizens' engagement (CE), ubiquitous information (UI), public participation (PP), and e-consultation (EC) form the foundational “cause group.” These drivers enable the “effect group” elements such as innovative solutions (IS), implementation of circular policies (IP), e-service delivery (SD), transparency in governance (TG), and monitoring and control (MC).
The causal analysis suggests that digital infrastructure, when integrated with social media and smart technologies, enables data-driven circular innovations and automated decision-making in public services. Enhanced accessibility of information, participatory governance, and citizen-centric planning are vital to creating closed-loop urban systems. Intelligent systems, IoT, and data analytics facilitate real-time monitoring of waste, energy, mobility, and other urban flows—enabling cities to design out waste and maximize resource recovery.
These advancements lead to more efficient policy implementation, transparent governance, and cost-effective service delivery, all of which are essential to the circular economy. The result is a resilient, inclusive, and regenerative urban ecosystem where citizens actively co-create value. The alignment of digital and circular strategies ensures that smart cities not only become technologically advanced but also environmentally restorative and socially inclusive.
7 Limitations and future scope
The research is focused on identifying the various enablers to improve the city administration. The article does not address the barriers to participatory planning such as age, educational attainment, unequal access to capital, public expertise, and racial and gender biases. The digital divide is least discussed while advocating the use of digital infrastructure. The study does not provide any procedural orders among the suggested enablers. In this article, the layers of IT security, and failure of technology are not discussed thoroughly.
In future research, solutions to reduce the digital divide, models for public participation, frameworks for policy implementation and monitoring, and service delivery models can be proposed and interlinked together to explain a more robust concept of city administration for smart cities. The more adaptive solutions can be explored in case of rapid changes in technologies as well as requirements for a smart city environment.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RS: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AS: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Abdullah L. Zulkifli N. (2019). A new DEMATEL method based on interval type-2 fuzzy sets for developing causal relationship of knowledge management criteria. Neural Comput. Appl.31, 4095–4111. 10.1007/s00521-017-3304-1
2
Abu-Shanab E. A. (2015). Reengineering the open government concept: an empirical support for a proposed model. Gov. Inf. Q.32, 453–463. 10.1016/j.giq.2015.07.002
3
Ahmad Alinejad E. Pishvaee M. S. Bonyadi Naeini A. (2018). Key success factors for logistics provider enterprises: an empirical investigation in Iran. Kybernetes47, 426–440.
4
Albino V. Berardi U. Dangelico R. M. (2015). Smart cities: definitions, dimensions, performance, and initiatives. J. Urban Technol. 22, 3–21. 10.1080/10630732.2014.942092
5
Appio F. P. Lima M. Paroutis S. (2019). Understanding smart cities: innovation ecosystems, technological advancements, and societal challenges. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change142, 1–14. 10.1016/j.techfore.2018.12.018
6
Arkorful V. E. Lugu B. K. Hammond A. Basiru I. (2021). “Decentralization and citizens' participation in local governance: does trust and transparency matter?–an empirical study,” in Forum for Development Studies, Vol. 48 (Routledge), 199–223. 10.1080/08039410.2021.1872698
7
Arnstein S. R. (1969). A ladder of citizen participation. J. Am. Inst. Plann.35, 216–224. 10.1080/01944366908977225
8
Baldwin E. Rountree V. Jock J. (2018). Distributed resources and distributed governance: stakeholder participation in demand side management governance. Energy Res. Soc. Sci.39, 37–45. 10.1016/j.erss.2017.10.013
9
Baud I. S. A. Scott D. Pfeffer K. Sydenstricker-Neto J. Denis E. (2015). Reprint of: digital and spatial knowledge management in urban governance: emerging issues in India, Brazil, South Africa, and Peru. Habitat Int.46, 225–233. 10.1016/j.habitatint.2015.01.018
10
Bhuiyan A. R. Abrar M. (2022). Role of one stop shop for e-service delivery: case study on union digital center in Bangladesh. Soc. Sci. Rev. 39, 91–102. 10.3329/ssr.v39i1.64876
11
Borsekova K. Koróny S. Vanová A. Vitálišová K. (2018). Functionality between the size and indicators of smart cities: a research challenge with policy implications. Cities78, 17–26. 10.1016/j.cities.2018.03.010
12
Bours S. A. Wanzenböck I. Frenken K. (2022). Small wins for grand challenges. A bottom-up governance approach to regional innovation policy. Eur. Plan. Stud. 30, 2245–2272. 10.1080/09654313.2021.1980502
13
Braga I. F. Ferreira F. A. Ferreira J. J. Correia R. J. Pereira L. F. Falcão P. F. (2021). A DEMATEL analysis of smart city determinants. Technol. Soc.66:101687. 10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101687
14
Cai M. Kassens-Noor E. Zhao Z. Colbry D. (2023). Are smart cities more sustainable? An exploratory study of 103 US cities. J. Clean. Prod.416:137986. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137986
15
Calzada I. Pérez-Batlle M. Batlle-Montserrat J. (2023). People-centered smart cities: an exploratory action research on the cities' coalition for digital rights. J. Urban Aff.45, 1537–1562. 10.1080/07352166.2021.1994861
16
Cardullo P. Kitchin R. (2018). Being a ‘citizen'in the smart city: up and down the scaffold of smart citizen participation in Dublin, Ireland. GeoJournal84, 1–13. 10.1007/s10708-018-9845-8
17
Cardullo P. Kitchin R. (2019). Smart urbanism and smart citizenship: the neoliberal logic of ‘citizen-focused'smart cities in Europe. Environ. Plan. C Polit. Space37, 813–830. 10.1177/0263774X18806508
18
Carrington W. DeBuse J. Lee H. (2008). The Theory of Governance and Accountability. University of Iowa Center for International Finance and Development.
19
Cesario E. Uchubilo P. I. Vinci A. Zhu X. (2022). Multi-density urban hotspots detection in smart cities: a data-driven approach and experiments. Pervasive Mob. Comput.86:101687. 10.1016/j.pmcj.2022.101687
20
Chang B. Chang C. W. Wu C. H. (2011). Fuzzy DEMATEL method for developing supplier selection criteria. Expert Syst. Appl.38, 1850–1858. 10.1016/j.eswa.2010.07.114
21
Choi H. S. Song S. K. (2023). Direction for a transition toward smart sustainable cities based on the diagnosis of smart city plans. Smart Cities6, 156–178. 10.3390/smartcities6010009
22
Criado J. I. Sandoval-Almazan R. Gil-Garcia J. R. (2013). Government innovation through social media. Gov. Inf. Q.30, 319–326. 10.1016/j.giq.2013.10.003
23
Dai Y. Hasanefendic S. Bossink B. (2023). A systematic literature review of the smart city transformation process: the role and interaction of stakeholders and technology. Sustain. Cities Soc.101:105112. 10.1016/j.scs.2023.105112
24
Dameri R. P. Benevolo C. Veglianti E. Li Y. (2019). “Understanding smart cities as a glocal strategy: a comparison between Italy and China,” in Technological Forecasting and Social Change, Vol. 142, 26–41. 10.1016/j.techfore.2018.07.025
25
de Hoop E. Moss T. Smith A. Löffler E. (2021). Knowing and governing smart cities: four cases of citizen engagement with digital urbanism. Urban Gov.1, 61–71. 10.1016/j.ugj.2021.12.008
26
de Oliveira J. A. P. Doll C. N. Balaban O. Jiang P. Dreyfus M. Suwa A. et al . (2013). Green economy and governance in cities: assessing good governance in key urban economic processes. J. Clean. Prod.58, 138–152. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.07.043
27
Debnath A. K. Chin H. C. Haque M. M. Yuen B. (2014). A methodological framework for benchmarking smart transport cities. Cities37, 47–56. 10.1016/j.cities.2013.11.004
28
Eom S. J. Hwang H. Kim J. H. (2018). Can social media increase government responsiveness? A case study of Seoul, Korea. Gov. Inf. Q. 35, 109–122. 10.1016/j.giq.2017.10.002
29
Eskelinen J. Robles A. G. Lindy I. Marsh J. Muente-Kunigami A. (eds.). (2015). Citizen-Driven Innovation. World Bank Publications.
30
Fernandez-Anez V. Fernández-Güell J. M. Giffinger R. (2018). Smart City implementation and discourses: an integrated conceptual model. The case of Vienna. Cities78, 4–16. 10.1016/j.cities.2017.12.004
31
Gagliardi D. Schina L. Sarcinella M. L. Mangialardi G. Niglia F. Corallo A. (2017). Information and communication technologies and public participation: interactive maps and value added for citizens. Gov. Inf. Q.34, 153–166. 10.1016/j.giq.2016.09.002
32
Gardas B. B. Mangla S. K. Raut R. D. Narkhede B. Luthra S. (2019). Green talent management to unlock sustainability in the oil and gas sector. J. Clean. Prod.229, 850–862. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.018
33
Giffinger R. Fertner C. Kramar H. Kalasek R. Pichler-Milanović N. Meijers E. (2007). Smart Cities: Ranking of European Medium-Sized Cities. Vienna, Austria: Centre of Regional Science (SRF), Vienna University of Technology.
34
Gil-Garcia J. R. (2012). Enacting electronic government success: an integrative study of government-wide websites, organizational capabilities, and institutions (Vol. 31). Springer Science and Business Media: New York. 10.1007/978-1-4614-2015-6
35
Gil-Garcia J. R. Zhang J. Puron-Cid G. (2016). Conceptualizing smartness in government: an integrative and multi-dimensional view. Gov. Inf. Q.33, 524–534. 10.1016/j.giq.2016.03.002
36
Gue I. H. V. Tan R. R. Ubando A. T. (2022). Causal network maps of urban circular economies. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy24, 261–272. 10.1007/s10098-021-02117-9
37
Gupta A. Gupta A. Memoria M. Kumar R. Kumar S. Singh D. (2022). “Artificial intelligence and smart cities: a bibliometric analysis,” in 2022 International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data, Cloud and Parallel Computing (COM-IT-CON), Faridabad, India, 540–544. 10.1109/COM-IT-CON54601.2022.9850656
38
Gupta A. Kumar H. (2022). Multi-dimensional perspectives on electric vehicles design: a mind map approach. Clean. Eng. Technol.8:100483. 10.1016/j.clet.2022.100483
39
Gupta A. Singh R. K. Paul J. Sharma M. Joshi S. (2024). Battery-operated electric vehicles (BOEVs) adoption in India: analysis of barriers and strategies. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 71, 7076–7087. 10.1109/TEM.2023.3253621
40
Hall R. E. (2000). “The vision of a smart city,” in Proceedings of the 2nd International Life Extension Technology Workshop, Paris, France.
41
Hu J. Zhang H. Irfan M. (2023). How does digital infrastructure construction affect low-carbon development? A multidimensional interpretation of evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod.396:136467. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136467
42
Hui C. X. Dan G. Alamri S. Toghraie D. (2023). Greening smart cities: an investigation of the integration of urban natural resources and smart city technologies for promoting environmental sustainability. Sustain. Cities Soc.99:104985. 10.1016/j.scs.2023.104985
43
Janowski T. (2015). Digital government evolution: from transformation to contextualization. Gov. Inf. Q.32, 221–236. 10.1016/j.giq.2015.07.001
44
Javed A. R. Shahzad F. ur Rehman S. Zikria Y. B. Razzak I. Jalil Z. et al . (2022). Future smart cities: Requirements, emerging technologies, applications, challenges, and future aspects. Cities129:103794. 10.1016/j.cities.2022.103794
45
Jiang S. Shi H. Lin W. Liu H. C. (2020). A large group linguistic Z-DEMATEL approach for identifying key performance indicators in hospital performance management. Appl. Soft Comput.86:105900. 10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105900
46
Kagan S. Hauerwaas A. Holz V. Wedler P. (2018). Culture in sustainable urban development: practices and policies for spaces of possibility and institutional innovations. City Cult. Soc.13, 32–45. 10.1016/j.ccs.2017.09.005
47
Kavanaugh A. L. Fox E. A. Sheetz S. D. Yang S. Li L. T. Shoemaker D. J. et al . (2012). Social media use by government: from the routine to the critical. Gov. Inf. Q.29, 480–491. 10.1016/j.giq.2012.06.002
48
Khan A. Imon S. K. A. Das S. K. (2015). A novel localization and coverage framework for real-time participatory urban monitoring. Pervasive Mob. Comput.23, 122–138. 10.1016/j.pmcj.2015.07.001
49
Kim P. S. Halligan J. Cho N. Oh C. H. Eikenberry A. M. (2005). Toward participatory and transparent governance: report on the Sixth Global Forum on Reinventing Government. Public Adm. Rev.65, 646–654. 10.1111/j.1540-6210.2005.00494.x
50
Koca G. Egilmez O. Akcakaya O. (2021). Evaluation of the smart city: applying the dematel technique. Telemat. Inform.62:101625. 10.1016/j.tele.2021.101625
51
Kumar A. Agrawal R. Wankhede V. A. Sharma M. Mulat-Weldemeskel E. (2022). A framework for assessing social acceptability of industry 4.0 technologies for the development of digital manufacturing. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change174:121217. 10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121217
52
Kumar H. Singh M. K. Gupta M. P. (2016). “Smart governance for smart cities: a conceptual framework from social media practices,” in Conference on e-Business, e-Services and e-Society (Springer International Publishing: New York), 628–634. 10.1007/978-3-319-45234-0_56
53
Kumar H. Singh M. K. Gupta M. P. Madaan J. (2020). Moving towards smart cities: solutions that lead to the smart city transformation framework. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change153:119281. 10.1016/j.techfore.2018.04.024
54
Ledesma-Gumasing R. Mendoza-Armiendo R. (2021). Popular, accessible, inclusive: social media as an ideal for decision-making in a democracy. J. Public Policy Adm. 5, 131–138. 10.11648/j.jppa.20210504.12
55
Leite E. (2022). Innovation networks for social impact: an empirical study on multi-actor collaboration in projects for smart cities. J. Bus. Res.139, 325–337. 10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.09.072
56
Li Y. Mathiyazhagan K. (2018). Application of DEMATEL approach to identify the influential indicators towards sustainable supply chain adoption in the auto components manufacturing sector. J. Clean. Prod.172, 2931–2941. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.120
57
Li Z. Ouyang X. Du K. Zhao Y. (2017). Does government transparency contribute to improved eco-efficiency performance? An empirical study of 262 cities in China. Energy Policy110, 79–89. 10.1016/j.enpol.2017.08.001
58
Lin R. J. (2013). Using fuzzy DEMATEL to evaluate the green supply chain management practices. J. Clean. Prod.40, 32–39. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.06.010
59
Liu J. Feng Y. Zhu Q. Sarkis J. (2018). Green supply chain management and the circular economy: reviewing theory for advancement of both fields. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 48, 794–817. 10.1108/IJPDLM-01-2017-0049
60
Liu Z. Qu J. Wu X. Niu X. Feng S. (2024). Improving member satisfaction with cooperatives: the role of participation in governance. Ann. Public Cooper. Econ.95, 703–722.
61
Macintosh (2004). “Characterizing e-participation in policy-making. In System Sciences, 2004,” in 37th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (Big Island, HI: IEEE), 10. 10.1109/HICSS.2004.1265300
62
Misuraca G. Broster D. Centeno C. (2012). Digital Europe 2030: designing scenarios for ICT in future governance and policy making. Gov. Inf. Q.29, S121–S131. 10.1016/j.giq.2011.08.006
63
Nam T. Pardo T. A. (2011). “Conceptualizing smart city with dimensions of technology, people, and institutions,” in Proceedings of the 12th Annual International Digital Government Research Conference: Digital Government Innovation in Challenging Times (ACM), 282–291. 10.1145/2037556.2037602
64
Nam T. Pardo T. A. (2014). The changing face of a city government: a case study of Philly311. Gov. Inf. Q.31, S1–S9. 10.1016/j.giq.2014.01.002
65
Novotný R. Kuchta R. Kadlec J. (2014). Smart city concept, applications and services. J. Telecommun. Syst. Manag.3:1. 10.4172/2167-0919.1000117
66
Olubunmi A. A. Chinedu E. Excel G. C. (2024). The evolution of smart cities: Integrating technology, governance, and sustainable development. Int. J. Appl. Res. Soc. Sci.6, 891–902. 10.51594/ijarss.v6i5.1131
67
Parmar P. S. Desai T. N. (2020). Evaluating sustainable lean six sigma enablers using fuzzy DEMATEL: a case of an Indian manufacturing organization. J. Clean. Prod.265:121802. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121802
68
Peldon D. Banihashemi S. LeNguyen K. Derrible S. (2024). Navigating urban complexity: the transformative role of digital twins in smart city development. Sustain. Cities Soc. 111:105583. 10.1016/j.scs.2024.105583
69
Petersson M. T. (2022). Transparency in global fisheries governance: the role of non-governmental organizations. Marine Policy136:104128. 10.1016/j.marpol.2020.104128
70
Picazo-Vela S. Gutierrez-Martinez I. Luna-Reyes L. F. (2012). Understanding risks, benefits, and strategic alternatives of social media applications in the public sector. Gov. Inf. Q.29, 504–511. 10.1016/j.giq.2012.07.002
71
Pierre J. (2005). Comparative urban governance: uncovering complex causalities. Urban Aff. Rev.40, 446–462. 10.1177/1078087404273442
72
Porwol L. Ojo A. Breslin J. G. (2016a). An ontology for next generation e-Participation initiatives. Gov. Inf. Q.33, 583–594. 10.1016/j.giq.2016.01.007
73
Porwol L. Ojo A. Breslin J. G. (2016b). Social software infrastructure for e-participation. Gov. Inf. Q. 35, S88–S98. 10.1016/j.giq.2016.01.002
74
Preuss L. (2009). Addressing sustainable development through public procurement: the case of local government. Supply Chain Manag.14, 213–223. 10.1108/13598540910954557
75
Rahman M. H. Albaloshi S. A. Sarker A. E. (2023). “From e-governance to smart governance: policy lessons for the UAE,” in Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 5075–5087. 10.1007/978-3-030-66252-3_2482
76
Retnandari N. D. (2022). Implementation of strategic planning in regional/municipal governments, obstacles and challenges. Policy Gov. Rev. 6, 155–175. 10.30589/pgr.v6i2.556
77
Rochdane H. Assaber O. (2022). Informal collaboration: building a smart city through self-organized stakeholders. Smart Cities Reg. Dev.6, 9–17.
78
Sæbø Ø. Rose J. Flak L. S. (2008). The shape of eParticipation: characterizing an emerging research area. Gov. Inf. Q.25, 400–428. 10.1016/j.giq.2007.04.007
79
Scupola A. Zanfei A. (2016). Governance and innovation in public sector services: the case of the digital library. Gov. Inf. Q.33, 237–249. 10.1016/j.giq.2016.04.005
80
Sharifi A. Allam Z. Bibri S. E. Khavarian-Garmsir A. R. (2024). Smart cities and sustainable development goals (SDGs): a systematic literature review of co-benefits and trade-offs. Cities146:104659. 10.1016/j.cities.2023.104659
81
Sharma M. Joshi S. Kannan D. Govindan K. Singh R. Purohit H. C. (2020). Internet of Things (IoT) adoption barriers of smart cities' waste management: An Indian context. J. Clean. Prod.270, 122047. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122047
82
Shin D. (2014). A socio-technical framework for internet-of-things design: a human-centered design for the internet of things. Telemat. Inform. 31, 519–531. 10.1016/j.tele.2014.02.003
83
Si S. L. You X. Y. Liu H. C. Zhang P. (2018). DEMATEL technique: a systematic review of the state-of-the-art literature on methodologies and applications. Math. Probl. Eng. 3696457. 10.1155/2018/3696457
84
Singh C. Singh D. Khamba J. S. (2020). Analyzing barriers of green lean practices in manufacturing industries by DEMATEL approach. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 32, 176–198. 10.1108/JMTM-02-2020-0053
85
Singh R. K. Acharya P. (2014). Identification and evaluation of supply chain flexibilities in Indian FMCG sector using DEMATEL. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag.15, 91–100. 10.1007/s40171-013-0050-9
86
Stewart K. (2006). Designing good urban governance indicators: the importance of citizen participation and its evaluation in Greater Vancouver. Cities23, 196–204. 10.1016/j.cities.2006.03.003
87
Tan S. Y. Taeihagh A. (2020). Smart city governance in developing countries: a systematic literature review. Sustainability12:899.
88
Tijan E. Jović M. Aksentijević S. Pucihar A. (2021). Digital transformation in the maritime transport sector. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change170:120879. 10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120879
89
Toppeta D. (2010). The smart city vision: how innovation and ICT can build smart, “livable”, sustainable cities. Innov. Knowl. Found.5, 1–9.
90
Verdegem P. Verleye G. (2009). User-centered e-government in practice: a comprehensive model for measuring user satisfaction. Gov. Inf. Q.26, 487–497. 10.1016/j.giq.2009.03.005
91
Xu Y. Cugurullo F. Zhang H. Gaio A. Zhang W. (2024). The emergence of Artificial Intelligence in anticipatory urban governance: multi-scalar evidence of China's transition to city brains. J. Urban Technol.44, 1–25. 10.1080/10630732.2023.2292823
92
Yadav H. Soni U. Kumar G. (2021). Analysing challenges to smart waste management for a sustainable circular economy in developing countries: a fuzzy DEMATEL study. Smart Sustain. Built Environ.12, 361–384. 10.21203/rs.3.rs-263855/v1
93
Yoon S. Y. Hong S. L. Zelt T. (2020). Smart City Pathways for DevelopingAsia: An Analytical Framework and Guidance. 10.22617/WPS200342-2
94
Zamanifard H. Alizadeh T. Bosman C. (2018). Towards a framework of public space governance. Cities78, 155–165. 10.1016/j.cities.2018.02.010
95
Zhang W. H. Yuan Q. Cai H. (2023). Unravelling urban governance challenges: objective assessment and expert insights on livability in Longgang District, Shenzhen. Ecol. Indic.155:110989. 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110989
Appendix
Annexure 1
| Expert profile/designation (experience, Years) | Category | Expert profile/designation (experience, Years) | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Professor, e-governance (>22 Years) | Academician, Delhi, India | Technical Adviser (>20 Years) | Government Official, India |
| CEO, Planning and IT (>20 Years) | Private industry, India | Solution Architect, Green technology (>18 Years) | Government Official, India |
| Professor, Public administration (>17 Years) | Academician, Delhi, India | Chairperson, Municipality (>15 Years) | Government Official, India |
| Public works department (PWD) officer (>14 Years) | Government Officials, India | General Manager (Telecom and network infrastructure; >14 Years) | Government official, India |
| Architect, construction (>14 Years) | Government Official, India | Officer, Cyber security (>14 Years) | Government Officials, India |
| Manager- IT (>13 Years) | Telecom Industry, India | Consultant (Urban economy; >13 Years) | Service providing firm, India |
| Associate Professor, Competitiveness (>11 Years) | Academician, State University, India | CEO, Smart city projects (>10 Years) | Government officials, India |
| Consultant, Planning (>10 Years) | Government Officials, India | Project manager, Operations (>9 Years) | Consulting firm, India |
| Technology consultant, IT Applications (>8 Years) | Private firm, India | Developer (Internet services; >8 Years) | Private firm, India |
| Building Architect (>8 Years) | Private firm, India | Engineer, Road development (>8 Years) | Government officials, India |
| Officer, Urban services (>7 Years) | Government officials, India | Consultant, Urban business (>7 Years) | Private firm, India |
List of experts.
The experts who were consulted for finalization of the factors and to get input for DEMATEL process. The name and affiliation are kept hidden to maintain the data and information privacy laws.
Summary
Keywords
smart administration, city governance, smart city, urban societies, DEMATEL, circular economy
Citation
Kumar H, Gupta A, Singh R and Sayal A (2025) Toward sustainable social change: strategic approaches to smart city development in developing nations. Front. Sustain. Cities 7:1592534. doi: 10.3389/frsc.2025.1592534
Received
12 March 2025
Accepted
22 July 2025
Published
25 August 2025
Volume
7 - 2025
Edited by
Dillip Das, University of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
Reviewed by
Muhammad Mushahid Anwar, University of Gujrat, Pakistan
Richard Kotter, Northumbria University, United Kingdom
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Kumar, Gupta, Singh and Sayal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Anu Sayal anu.sayal@taylors.edu.my
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.