- 1Graduate School of Horticulture, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan
- 2Faculty of Horticulture, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan
- 3Chongqing Jianzhu College, Chongqing, China
Introduction: Urban parks in crowded cities like Tokyo face challenges such as limited space and declining resident participation in park activities. This study examines how participatory events held in community parks affect residents’ park use, satisfaction, and place attachment. The goal is to develop strategies to enhance user participation in parks located in densely populated areas.
Methods: This study focused on three community parks in Toshima Ward, Tokyo. Data were collected from a survey answered by 176 local residents. The research analyzed how residents’ demographic and socioeconomic affect their participation, identified differences in park use motivations between those who joined events and those who did not, and explored how events affected park visits, satisfaction with park facilities, and place attachment.
Results: Participation varied by age, family size and length of residence. Younger people and families were more likely to participate. Participants tended to use parks for social or family activities. Non-participants tended to choose activities such as walking alone. Participants visited the park more often. They also preferred park features such as rest areas, open space and easy access. Events such as fairs and community meetings encourage more interaction and strengthened residents’ emotional bonds with the parks.
Discussion: The results show that regular participatory events and better park facilities lead to more park visits. They also increase residents’ satisfaction and place attachment to parks. Urban park managers should consider the diverse needs of different user groups and provide a variety of activities for families and young people.
1 Introduction
Urban parks are an important component of urban living in terms of recreational activity, social interaction opportunity, and psychological and physical health promotion (Lin et al., 2022). Community parks are publicly accessible and open spaces where people engage in recreation, social contact, and psychological restoration. In densely populated urban areas, such as Tokyo, where per capita outdoor space is minimal, the role of well-designed public parks becomes even more significant. Prior literature has confirmed that parks are good for mental health, sociality, and the environment (Liu et al., 2017; Rastkhadiv et al., 2024). Research has shown that access to parks and park environments has a direct influence on mental health, citing that well-equipped parks are psychologically better than just having access to them (Sturm and Cohen, 2014). Yet, the ongoing loss of green space and the decreasing use of parks in Tokyo have caused growing concern about the physical and mental wellbeing of residents and their social ties. Limited park access often results in reduced physical activity, heightened stress and anxiety, fewer chances for social interaction, and greater differences in park usage among age groups and family types (Liu et al., 2017; Sturm and Cohen, 2014).
Public participation has been an increasing concern in urban park planning in the past decades. Participatory activities—defined in this study as community-driven events including games, nature-related activities, art events, markets, educational events, cultural festivals, and exchange of views—have been launched by cities to foster people’s interaction with the parks. These activities support park visitation, social capital, and place attachment (Romolini et al., 2019; Stevinson and Hickson, 2014). Empirical studies suggest that social, environmental, and economic factors influence place attachment. They also show that public space plays a role in local identity construction and affective place attachment (Lin et al., 2022). In aging societies, including Japan, participatory activities offer valuable opportunities for older adults to connect with others. These activities lessen isolation and support interaction across generations (Murayama et al., 2024;Abbott, 2010). Still, research on how participatory activities shape park use patterns, satisfaction, and place attachment in Japanese cities remains scarce (Yang et al., 2023).
Previous studies have predominantly been concerned with the physical characteristics of parks—such as facilities, vegetation, and spatial layout—and their impact on visitors’ satisfaction. While these are undoubtedly important, less attention has been paid to understanding how participatory activities can enhance the social and emotional value of parks, particularly in space-constrained environments like Tokyo (Ramkissoon et al., 2011). In addition, studies have proved environmental justice concerns, revealing socioeconomic inequalities can contribute to inequalities in park quality and availability (Bojorquez and Ojeda-Revah, 2018). Japanese park revitalization has also focused on participatory governance and public-private partnerships to expand park facilities and improve administration (Zhao et al., 2024). While this kind of research undoubtedly demonstrates the role of equitable park planning, few studies have explicitly analyzed how sustained participatory activities affect satisfaction and attachment among diverse user groups in Asian megacities. Additionally, most research in Tokyo has not explored how participatory activities could address challenges common in high-density urban areas, including limited green space, an aging population, and social isolation (Murayama et al., 2024). Comparative findings between the UK and China report that park use reflects social and cultural differences in both access and the purposes for which parks are used, with wide variations depending on context (Wang et al., 2020). Green space and crime have also been discussed from the viewpoint of Global South scholarship, whose research creates a relationship whereby inner-city green space will reduce violent crime, and measurements such as distance to a park and tree canopy might be linked with variability in property crime (Zhao et al., 2024). Similarly, age-friendly neighborhood park policy was trendy with inclusive park planning being given the priority as a way of dealing with diverse demographic demands (Shobri, 2024). Studies on Japanese neighborhood parks confirm that people from varied demographic groups, especially the elderly, do use these parks, highlighting the need for park designs that respond to diverse users (Wang et al., 2020).
There is also a study that investigated social interaction in parks, and the results showed that clean and well-maintained green spaces facilitate social interaction and reduce social isolation (Koynova et al., 2019). Utah studies have shown that park design is instrumental to attaining social cohesion and mental health gains (Schwartz et al., 2018). Furthermore, Yokohama case studies attest to the success of local community involvement in the management of parks, showing that effective members of the local community ensure better utilization and maintenance of parks (Zhou et al., 2024). Singapore lessons remind us of park design responsiveness to a diverse range of users, ranging from children to older persons. In Japan, studies on small park redevelopment note that when facilities are upgraded and spaces reorganized, user satisfaction and park visitation often rise.
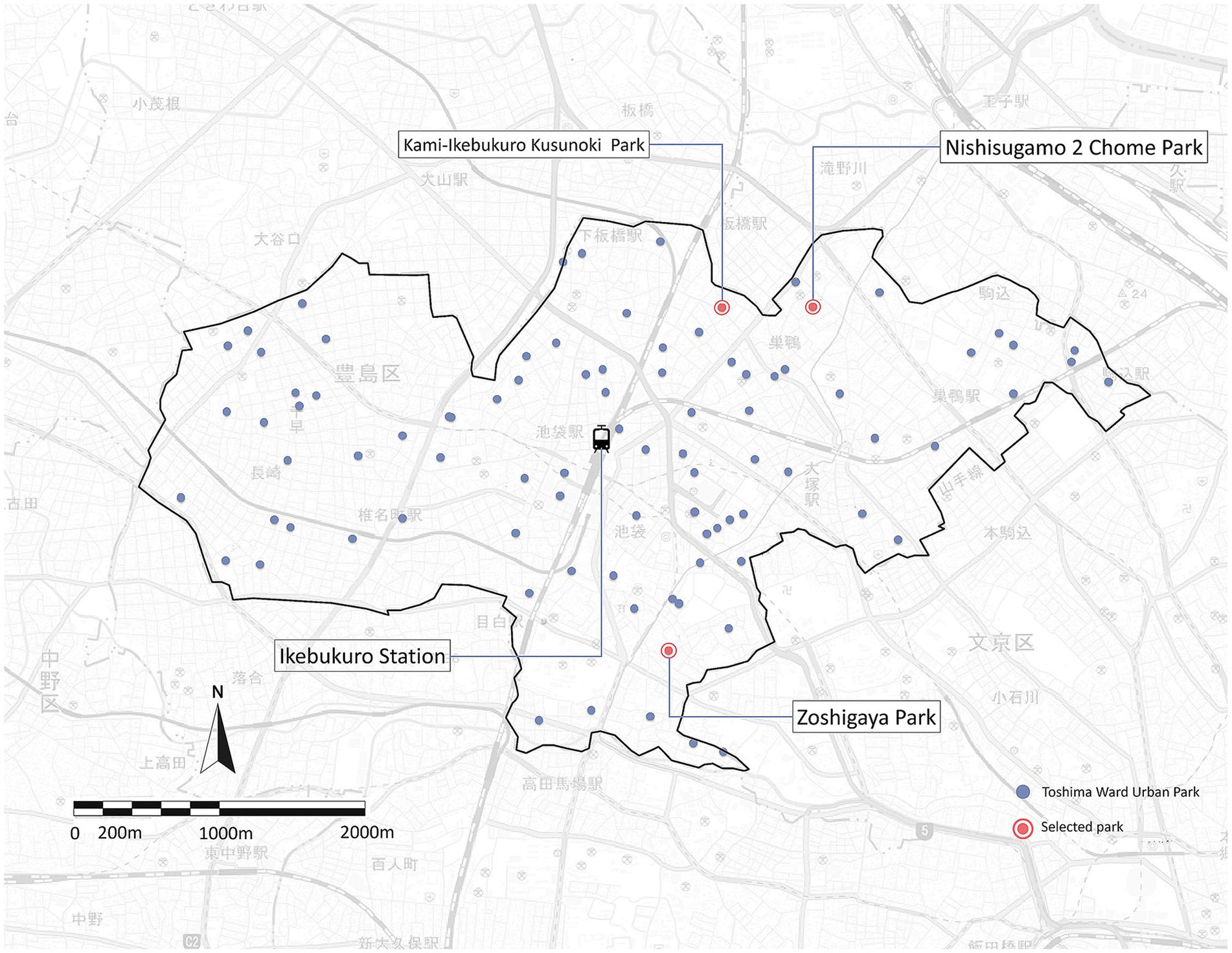
To address these research gaps, this study focuses on community parks in Toshima Ward. Toshima was chosen because of its high population density, limited park space, and the local government’s active promotion of participatory park activities to improve social connection and address aging and social isolation. The three block parks—Zoshigaya Park, Kami-Ikebukuro Kusunoki Park, and Nishisugamo 2-Chome Park—host regular events and engage diverse stakeholders. Their characteristics made them suitable for investigating how participatory activities relate to park use and user perceptions (Toshima Ward, 2023a, 2023b).
This study examines how participatory activities affect visit frequency, satisfaction, and place attachment in Tokyo community parks. It also analyzes differences in park visits between participants and non-participants. This study focuses on the following main questions:
1. What demographic and motivational factors influence participation in park activities?
2. What reasons lead participants and non-participants to visit parks differently?
3. How does park usage frequency vary between user groups?
4. How do participants and non-participants differ in park facility experience and satisfaction?
5. Does taking part in activities strengthen place attachment among park users?
In offering these solutions, the study aids in the formulation of knowledge as a key variable for participatory management of a city park. The findings present evidence empirically to back the enhancement of event planning, improvement of people’s involvement, and the enhancement of general park management policies. Given the unique challenges faced by dense Asian cities, this study provides practical lessons for developing more diverse and active public spaces beyond Tokyo.
2 Study area and methods
2.1 Study area
Toshima Ward is one of Tokyo’s densest areas. It is a good case to study how community parks improve livability in cities with limited space. The 13.01 km2 ward has the largest population density in Tokyo’s 23 wards with 23,356 residents per km2 in April 2023. For all its population density, green space per person in Toshima Ward continues to be urgently low at merely 0.77 hectares, the lowest rate in all the wards of Tokyo (Toshima Ward, 2023a, 2023b). This sharp gap between green space supply and population calls for new efforts to create planned green spaces that support social cohesion and improve wellbeing (Zong et al., 2024).
Historically, Toshima Ward has many residential buildings, and about 40% are traditional wooden houses. The area has seen rapid urbanization, increasing the need for better green spaces. The ward has started several projects to use its limited green areas well. These projects focus on participatory activities and community involvement (Clarke et al., 2023).
Toshima Ward’s community parks comprise 86.88% of its whole park and green space and are the essential spaces for social engagement, recreation, and community. Participatory events are actively promoted by the ward in such parks, with an approximately 216 events being arranged in 2020 from flea markets and street festivals in the neighborhood to education sessions. Plans to increase such events to over 350 per annum demonstrate growing interest in the development of community engagement through urban green spaces (Zhou et al., 2024). These events are an ideal place to analyze the impact of participatory events on park usage, resident satisfaction, and place attachment.
This study examines three municipal community parks in Toshima Ward: Zoshigaya Park, Kami-Ikebukuro Kusunoki Park, and Nishi-Sugamo 2-Chome Park (Figure 1). The selection followed several key points:
1. Range of participatory activities—Each park offers different participatory activities. These activities allow a clear analysis of how they influence user groups, park use patterns, and place attachment (Sánchez et al., 2021).
2. Programming consistency—Regular programmed events in these parks provide a consistent data set, with the ability to test long-term participation trends in this way.
3. Community engagement—Resident use of park activities is high, supporting local identity and place attachment, making these parks suitable for investigating the effects of community engagement on park use and satisfaction.
4. Practical considerations—Other parks were excluded because they lacked regular participatory activities, had lower user numbers.
Zoshigaya Park (Figure 2), the largest of the three parks, has an area of 8,653.75 m2 and is situated near Kishibojin-mae Station. It serves as a cultural and social events hub and draws a diverse group of visitors. The park is renowned for its communal markets and recreational games, which are very popular among locals and university students (Zoshigaya Hiroba Club, 2023). Additionally, the park also has well-equipped facilities, including seating spaces, playgrounds, and a tennis court (Appendix 1). These features allow for the analysis of the relationship between park facilities, participatory activities, and users’ satisfaction.

Figure 2. Photos of the three selected parks (from left to right, the parks are Zoshigaya Park, Kami-Ikebukuro Kusunoki Park, and Nishi-Sugamo 2-Chome Park. The photos were taken by the author).
Kami-Ikebukuro Kusunoki Park, with a size of 3,088.80 m2, is situated at the Ikebukuro Honcho and Kami-Ikebukuro district. The park is renowned for having a strong presence of educational and cultural activities, particularly through workshops organized by local universities and seasonal community events. All these features qualify it as an ideal location to evaluate the impact of participatory activities on the motivation and frequency of residents visiting parks. Amenities in the park are benches, a children’s playground, and a promenade, providing essential facilities for studying factors influencing resident satisfaction with urban parks (Borland, 2019).
The smallest of the three, measuring 1,357.83 m2, Nishi-Sugamo 2-Chome Park, is important to the Nishi-Sugamo and Sugamo community. This park is also actively used for community-driven initiatives such as periodic workshops for park revitalization and “Park Track” scheme, through which facilities such as mobile snack vans and library services are enabled. These activities are especially helpful for understanding how community participation relates to place attachment and why participatory activities matter for the long-term success of urban parks is well supported by Romolini et al. (2019).
The demographic heterogeneity of Toshima Ward also supports the applicability of this research. The ward populace in January 2023 consisted of 288,704 persons with a respectable 1.9% growth year on year. Furthermore, the ward further consists of 28,933 foreign inhabitants, roughly 10% of the population, and an impressive 19.6% year on year growth (Toshima Ward, 2023a, 2023b). This variety of people provides a strong base for studying how age, gender, job type, family size, and years living in the area affect park visits, user satisfaction, and joining social activities (Murayama et al., 2024).
By comparing of these three parks, this research aims to provide empirical data on how participatory activities in urban parks improve attachment in the community, residents’ satisfaction, and place attachment. The research will also contribute to the overall literature of the management of urban parks and provide practical information on how to optimize the functionality and social values of neighborhood parks in high-density cities (Clarke et al., 2023). As cities keep growing and the population changes, this study looks at the urgent need for well-designed, accessible, and community-friendly green spaces. In brief, the selected parks in Toshima Ward are natural components of the city system that provide an ideal setting to examine inter-dependent relationships among the urban green space, societies’ daily life, and determinants of park use, satisfaction, and place attachment.
2.2 Questionnaires
2.2.1 Questionnaire design and ethical considerations
The questionnaire was structured to collect data in a systematic manner in line with the study goals. It covered five main parts: demographic characteristics, park use behaviors, participation in park activities, user satisfaction, and place attachment (Cohen et al., 2010). First, the demographic section asked about gender, age, occupation, years of residence, family members, and housing type. Next, the park use section collected information on how people accessed the park, how long the journey took, how often they visited, how long they stayed, and what activities they did in the park. The participation section asked about awareness of park events, attendance, participation frequency, and types of social interaction at participatory activities. The satisfaction and place attachment section used five-point scales. These measured overall satisfaction, satisfaction with park features, perceptions of the park’s environment, and place attachment. The survey aimed to examine how citizens’ socioeconomic backgrounds and their participation in park activities influence their motivation to visit community parks and their general satisfaction (Giles-Corti et al., 2005).
Before collecting data, ethical clearance was obtained to ensure compliance with research integrity and ethical principles (Resnik, 2018). Informed consent was collected, and all answers were kept anonymous. No personal information was collected (Bryman, 2012).
2.2.2 Data collection
The survey was distributed through direct mailing to randomly chosen households within 250 meters of the three specified community parks in Toshima Ward, Tokyo. Studies show that proximity to green spaces is strongly linked to park usage frequency and residents’ satisfaction with their urban environment (Chen et al., 2024; Schipperijn et al., 2017; Zhang and Tan, 2019). Questionnaires were sent to all the houses with a free return envelope so that they could respond without incurring additional costs. This method aligns with strategies recommended for increasing participation in neighborhood-based surveys (Dillman et al., 2014).
The questionnaires were sent in November 2023, with a submission deadline set for December 2023. A total of 900 questionnaires were sent out, with 300 distributed to the neighborhood surrounding each park. During data screening, 176 valid responses were kept. This resulted in a 19.6% response rate. The number of responses from each park was as follows: Zoshigaya Park (83), Kami-Ikebukuro Kusunoki Park (38), and Nishisugamo 2-Chome Park (55). Although the response rate was relatively low, past studies have shown that urban environmental surveys often face similar challenges. Despite this, they can still provide valid analytical insights (Baruch and Holtom, 2008). Sample sizes are sufficient for reliable statistical analysis.
2.2.3 Data analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics version 29.0.1.0. Descriptive statistics were employed to reflect respondents’ demographic profile and to provide a general description of their park use behavior.
To understand differences between groups and how key factors are related, we used several statistical tests. We used chi-square tests to check how participants were spread across different groups, such as age and gender. We also used these tests to compare the main reasons why participants and non-participants visit the park. Chi-square tests are widely applied in social and environmental studies for categorical data comparison (Field, 2013). In addition to testing further differences in user satisfaction, independent sample t-tests were run considering differences in overall satisfaction, facility satisfaction, and safety satisfaction across the two groups. The data satisfied the normal distribution assumption for t-tests. The t-test method is commonly employed in environmental research to test mean differences between two distinct groups (Cohen et al., 2010). Also, binary logistic regression was applied to determine whether participation in engagement activities increased the probability of visiting parks frequently. Binary logistic regression is commonly used to predict categorical outcomes in behavioral studies (Hosmer et al., 2013). To test the effect of activity participation on place attachment, ordinal logistic regression was used (Agresti, 2018). This combined analytical approach allowed a detailed examination of the factors influencing park usage behavior, user satisfaction, and place attachment. This research design allowed a close examination of the factors influencing park use, user satisfaction, and place attachment. It also made it possible to explore how participatory activities shape residents’ perceptions, behaviors, and place attachment in urban community parks (Cohen et al., 2010;Chen et al., 2024).
2.3 Socioeconomic characteristics of park visitors
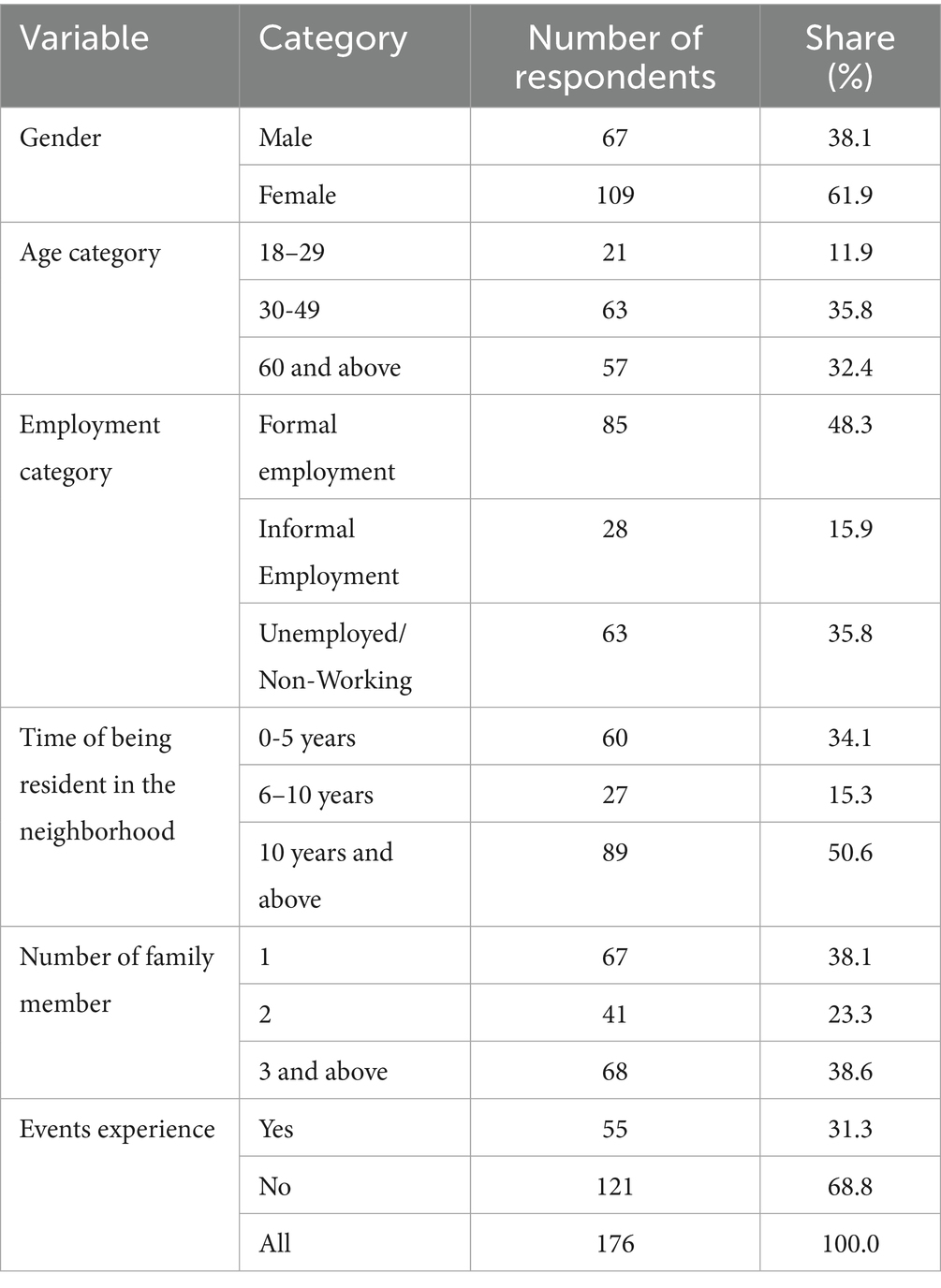
The socio-economic and demographic attributes of the 176 survey respondents provide an important context for understanding park use and attitudes in the study area. The sample consisted of 38.1% male and 61.9% female and the age distribution across the life cycle was comparable: 11.9% were 18–29 years old, 35.8% were 30–49 years old, 19.9% were 50–59 years old, and 32.4% were 60 years and above. This classification reflects important differences in family roles, work-life balance, and leisure preferences (Veitch et al., 2018).
Employment status shows the social and economic differences among respondents (Table 1). About 48.3% have formal jobs, 15.9% have informal jobs, and 35.8% are unemployed or not working. More than half of the respondents (50.6%) have lived in the area for over 10 years, indicating a stable community. This may affect their connection to local parks and their participation in park events. Research shows that economic factors like household income and job stability strongly influence park use and spending habits (Choi and Jeon, 2021).
Household size differs among respondents. About 38.1% live alone, while 38.6% live in households with three or more people. These differences may affect what they need and how they use the park. Research shows that larger households are more likely to join social or group activities in parks (Walker and Crompton, 2012).
Event participation is low, with only 31.3% of respondents having joined park events. This suggests that while community activities are available, there is still a big opportunity to encourage more participation. Studies highlight that better outreach and event planning are key to boosting community engagement and increasing park use (Flyr and Koontz, 2024). However, the low participation rate may limit the comparison between participants and non-participants. More details are discussed in the limitations section. Overall, the demographic and socioeconomic differences provide a clear basis for studying park use, satisfaction, and community activities. However, the relatively low response rate (19.6%) may cause some sampling bias. This possible limitation is discussed further in the limitations section.
3 Results
We present here the results of the study on a variety of different domains (all analyses based on N = 176 survey respondents): (1) sociodemographic correlates of community park activity participation, (2) motivational distinctions in park use among event participants and non-participants, (3) impacts of event participation on park visitation frequency, (4) impact of participatory activities on park satisfaction and key determinants, and (5) participatory activities and social interaction in fostering place attachment.
3.1 Sociodemographic correlates of community park activity participation
In our sample (N = 176), a number of socio-demographic variables were significantly associated with whether residents participated in community park activities (Figure 3). Middle-aged adults (30–49 years old) had the highest participation rate (~48%), significantly higher than younger adults (18–29 years old: ~10%, p < 0.01); older adults (60 years and above) had intermediate participation rates (~30%). Similar patterns have been reported in other studies. Middle-aged people tend to participate more because of family roles and social ties (Mowen et al., 2012). In Japan, many middle-aged adults manage both work and family while joining social activities to support their wellbeing and social connection (Monma et al., 2016). Gender differences also exist: about 38% of women participate, compared to 21% of men (p < 0.05). This aligns with research showing that women are more active in community events, possibly due to caregiving roles or social orientation (Carlson et al., 2010). Household size was also important (p < 0.001): single-household dwellings comprised just 13% of park event attendance, compared to ~50% of three-or-more-person households. Larger households may attend more frequently because they seek social or family-friendly environments (Goyder et al., 2018). Length of time in the community was non-linearly related to participation (p < 0.05): 6–10 year residents had highest participation (~56%), higher than new arrivals (0–5 years: ~27%) and extremely long-term residents (10 + years: ~27%). This pattern supports the idea that stronger social ties formed over time promote community involvement (Bruton et al., 2011). Social capital and community connections, which grow with longer residence, have been identified as key motivators for participation in community activities (Abbott, 2010).
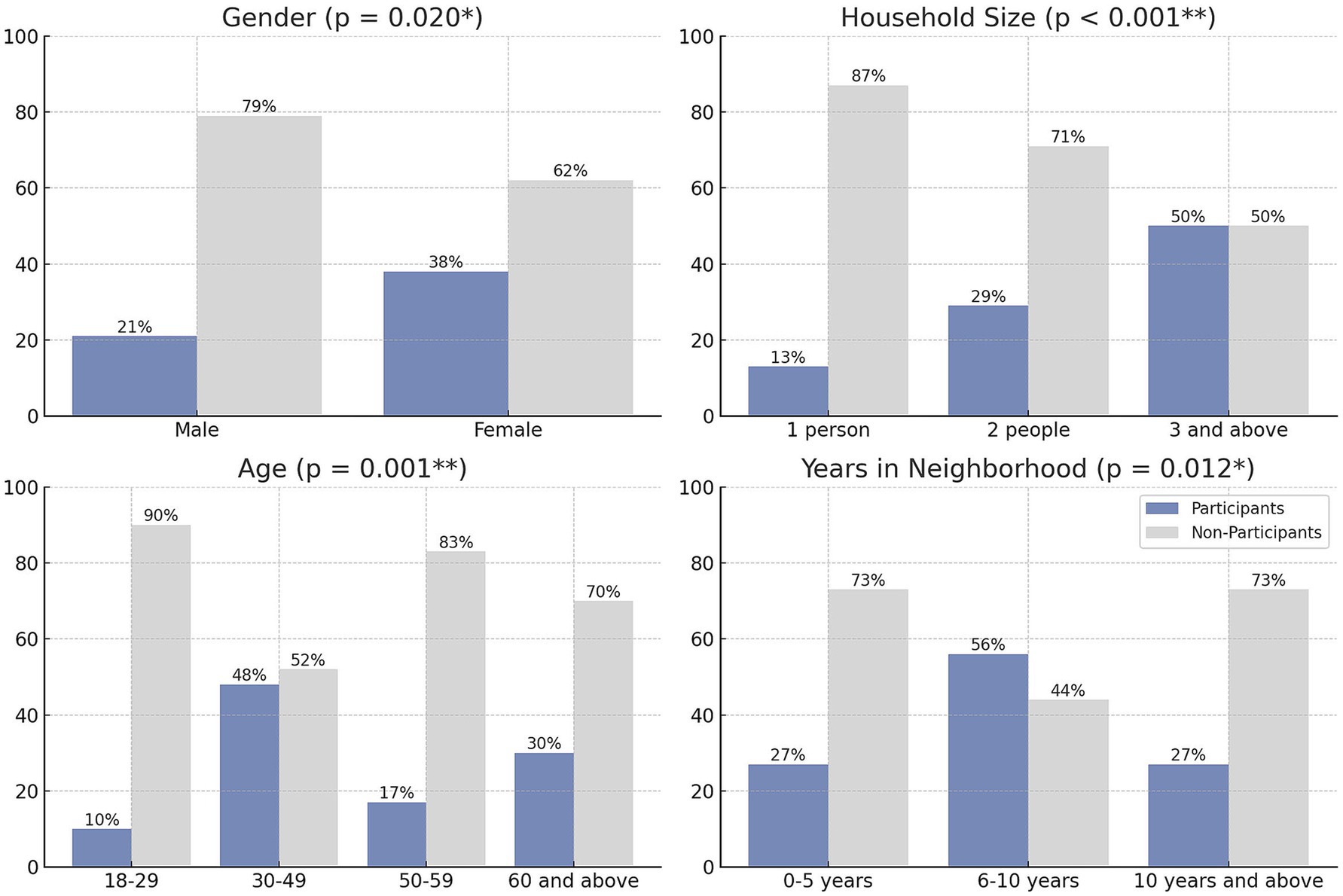
Figure 3. Sociodemographic profiles of participants and non-participants in community park activities.
These trends reflect that life cycle and social setting influence community involvement. Briefly, middle-aged adults (often with families) were the most active participating in park events, while young, unmarried, and newly settled residents were the least active.
3.2 Comparison of park use motivations among participants and non-participants
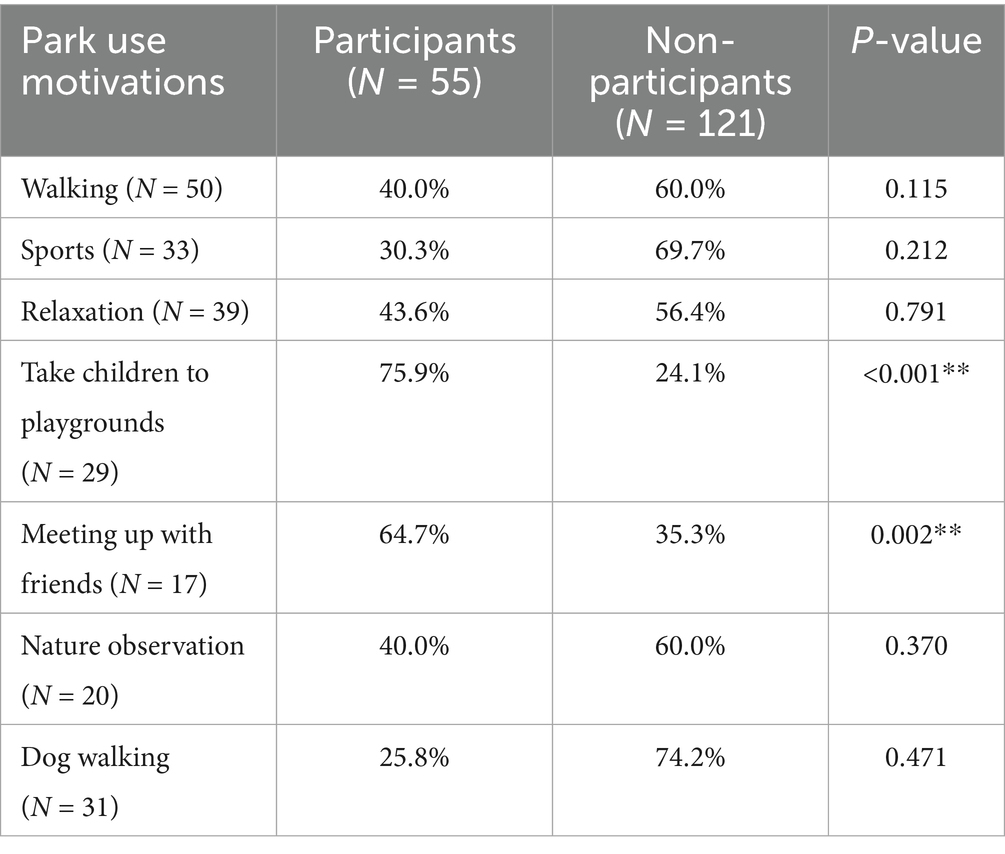
Park use motivations showed differences between participants and non-participants. Event attendees were more likely to mention social or family reasons for park visits, while non-attendees mentioned individual or practical reasons (Table 2) (Stanis and Schneider, 2010). For instance, among child visitors to the playground, 76% were event attendees, and only 24% were not (p < 0.001). Likewise, 65% of those who said “meeting friends” was a reason were event participants, compared to 35% non-participants (p = 0.002). More dog walkers and recreational walkers did not join the activities (about 74 and 60%). But these differences were not significant (p > 0.1). This shows that people who come to the park for walking or dog walking often choose to do activities alone, even when community events are available. Both groups often mentioned relaxation and enjoying nature; about 31% of participants and 18% of non-participants reported “relaxation,” with no significant difference. Some individual motives, such as walking or observing nature, also showed no significant variation (p > 0.3), suggesting quiet park use is common regardless of event attendance. These results suggest that park motivations can differ between social and personal interests. Some people are drawn to social activities, while others prefer nature, relaxation, or outdoor exercise (Zafeiroudi and Kouthouris, 2020). Social identity and a sense of belonging are also linked to activities like the popular “parkrun” (Grunseit et al., 2024). People who join community events often visit parks for social reasons, family time, or to meet others. Organized activities are good at attracting those who want shared experiences and social ties (Goyder et al., 2018).
In contrast, those who do not attend events may use the park mainly for walking, exercise, or enjoying a quiet space by themselves. This reading aligns with both environmental psychology principles and social capital theory: event participants may be seeking social interaction, whereas non-participants may pursue the restorative qualities of the natural environment. However, these explanations will be examined further in the Discussion section. The results show that while community events were successful in attracting residents seeking social interaction, they have not succeeded in reaching those who use the park primarily for solitary escape or routine personal activities. In general, community events attracted people for social and family-oriented use of the park, while non-participants used the park mainly for individual purposes.
3.3 Impact of event participation on park usage frequency
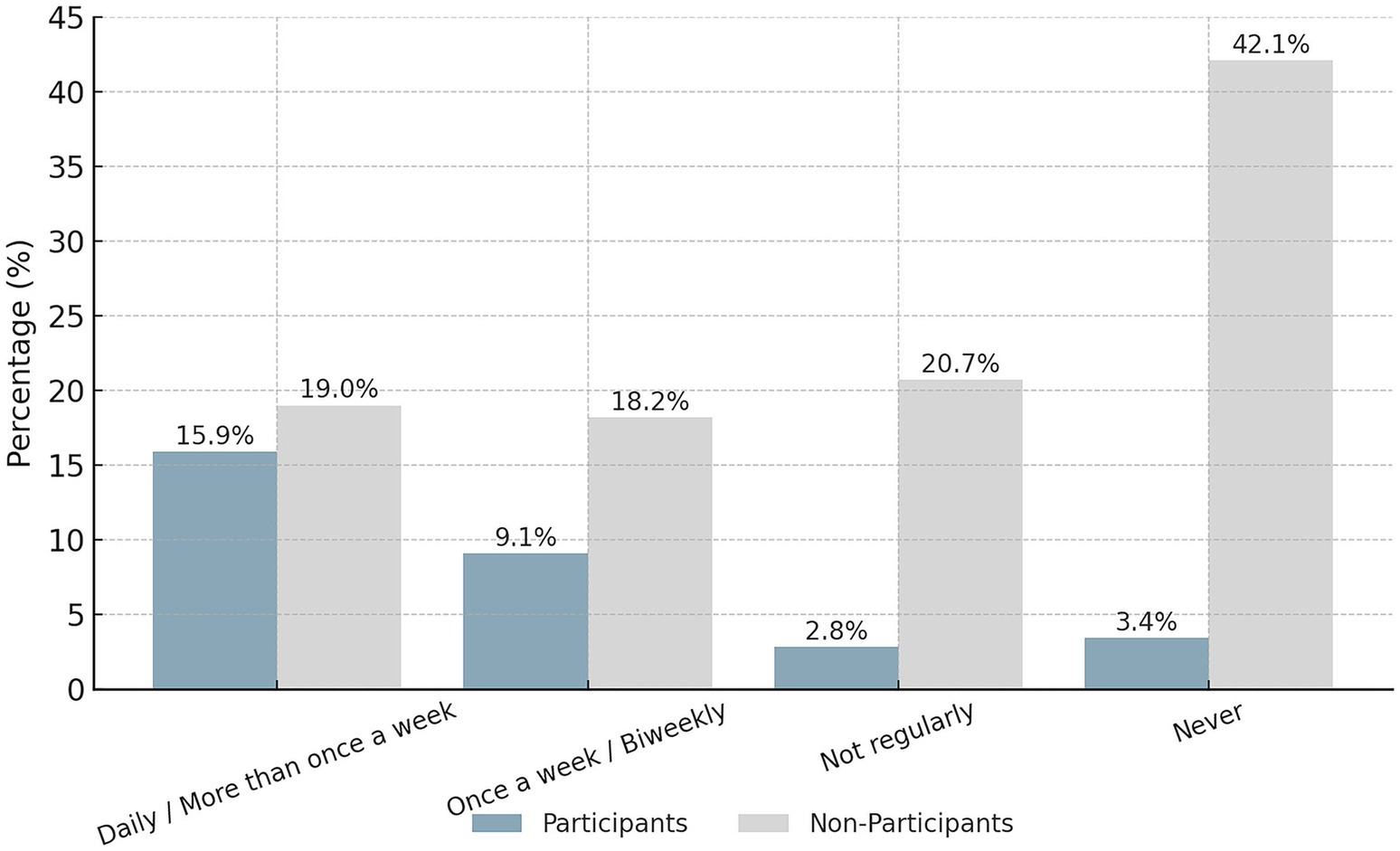
Participants in our survey came to the park much more frequently than non-participants. The frequency of visits was quite dissimilar between the two groups. Nearly no event participants never visited the park: only 3% of participants said they went “never,” compared to 42% of non-participants who never visit (Figure 4). That is, an extremely high proportion of participants visited the park at least somewhat frequently, whereas a considerable proportion of non-participants did not visit the park at all. Recurring use was also more prevalent among participants—roughly half of event participants used the park weekly or every other week—whereas non-participants were concentrated toward making minimal use. These trends suggest a positive relationship between attending park activities and frequent park visits. In order to capture the relationship, considering other forces upon it, we conducted a binary logistic regression as a prediction for high frequency park usage.
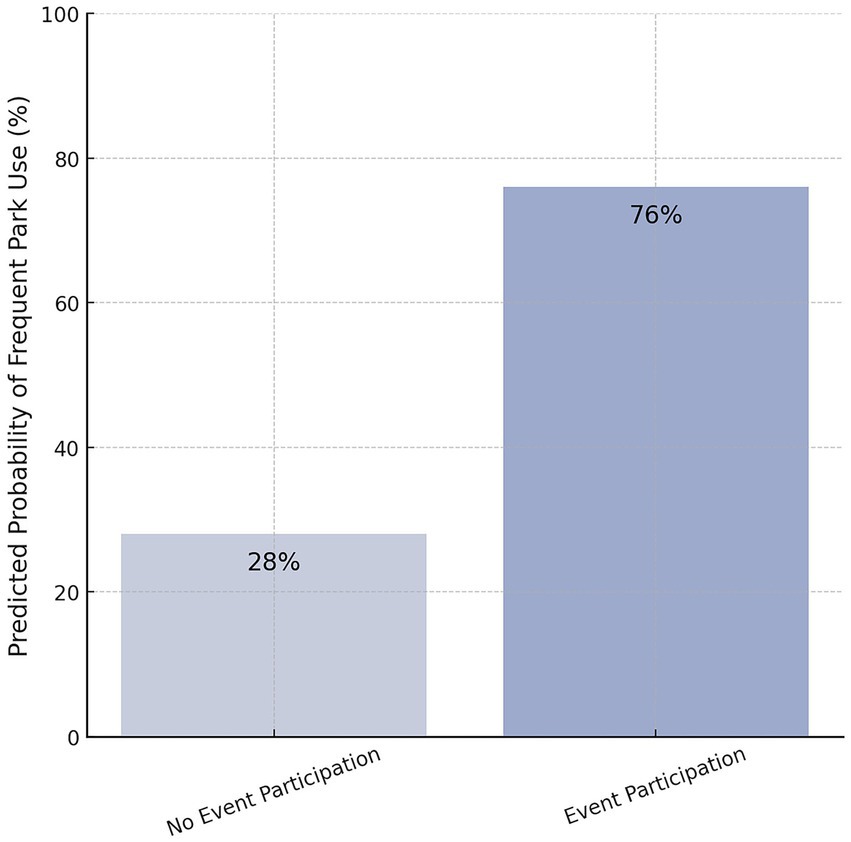
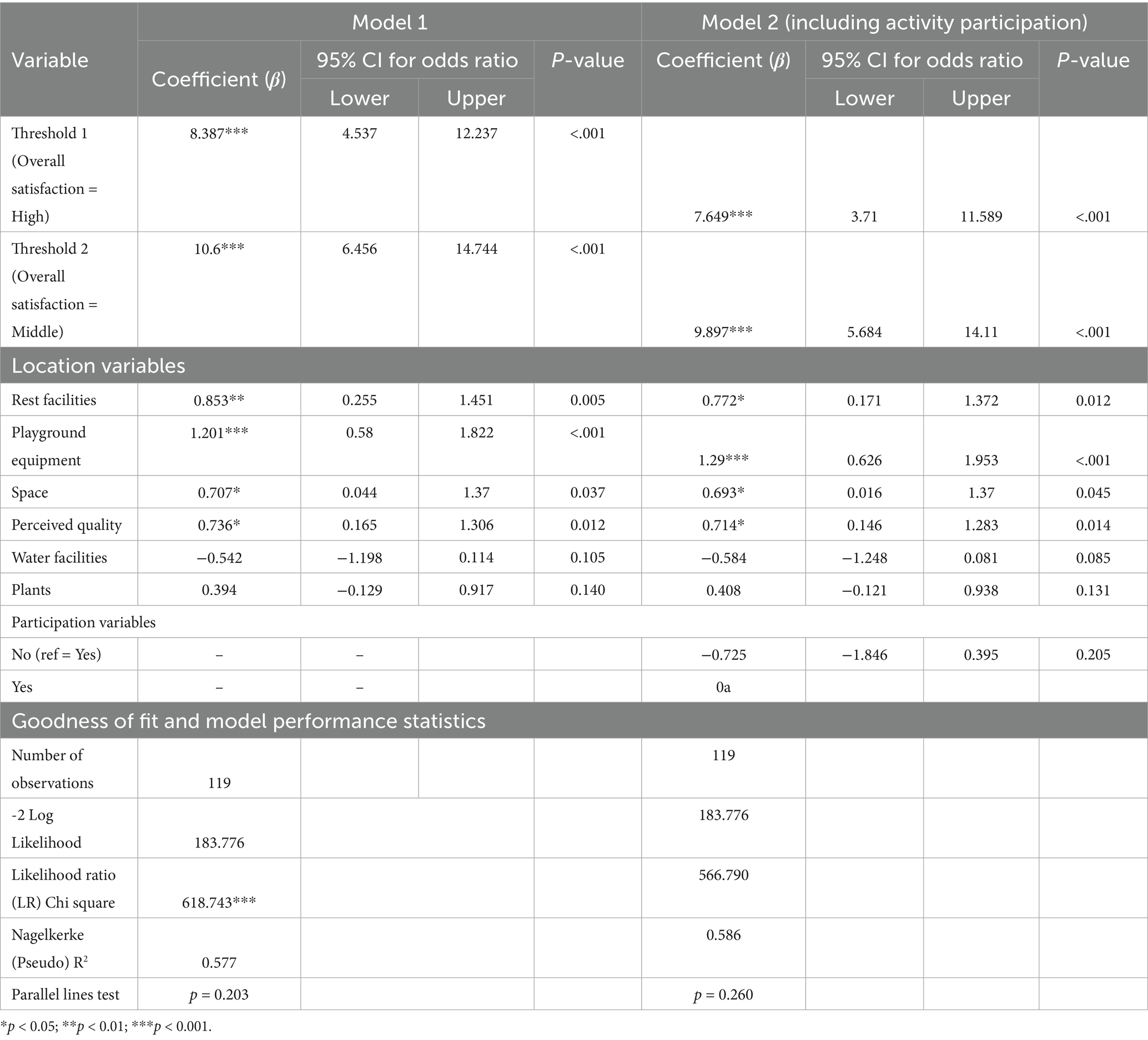
Attendance at events was also the strongest predictor of repeat visits to the park (β = 2.09, p < 0.001). This meant that participants had about eight times higher odds of repeat visits, with model-simulated frequent visit probability going up from about 28% if one does not attend events to about 76% if one does (Figure 5). Notably, the impact of participation persisted even when controlling for demographic and perceptual covariates. Moreover, the model (Appendix 2) revealed a number of other predictors of high park use. Perceiving the park as safe was related to higher usage (β = 0.76, p < 0.01), as would be expected if individuals are more likely to use public places when they perceive them as safe.
Longer residence in the neighborhood also grew use: inhabitants of 6–10 years (β = 1.95, p = 0.004) or more than 10 years (β = 1.47, p = 0.003) visited more than those living fewer than 5 years. This suggests that as people stay longer in a community, they develop more regular park visiting habits. Unemployed people were more likely to be repeat visitors than full-time employed people (β = 1.08, p = 0.023), as would be expected given more time off. Significantly, female was associated with odds of less frequent attendance (β = −0.93, p = 0.036), suggesting that men (although less engaged in events) could visit the park more casually (e.g., regular exercise or casual meetings).
Park characteristics was also problematic: both smaller parks that were part of the study showed dramatically lower levels of frequent visitation than Tokyo’s largest park, Zoshigaya (β = −2.1 for each, p < 0.001). This was probably because the larger park offered more amenities and scheduled activities to attract regular visitors, while the smaller parks had fewer such features (Smith, 2018).
Overall, these results indicate programmed community events as a powerful driver of repeat park visits. By offering organized activities, events help people make regular park visits part of their routine. In general, attendees at community events were far more likely to be frequent park visitors (Bostock et al., 2016).
3.4 Impact of participatory activities on park satisfaction and key determinants
Besides usage, our research also investigated whether engaging in community activities affected how individuals assess their park experience. Event attendees did not report being more satisfied overall with the park compared to non-attendees, but they did rate higher on several specific park amenities.
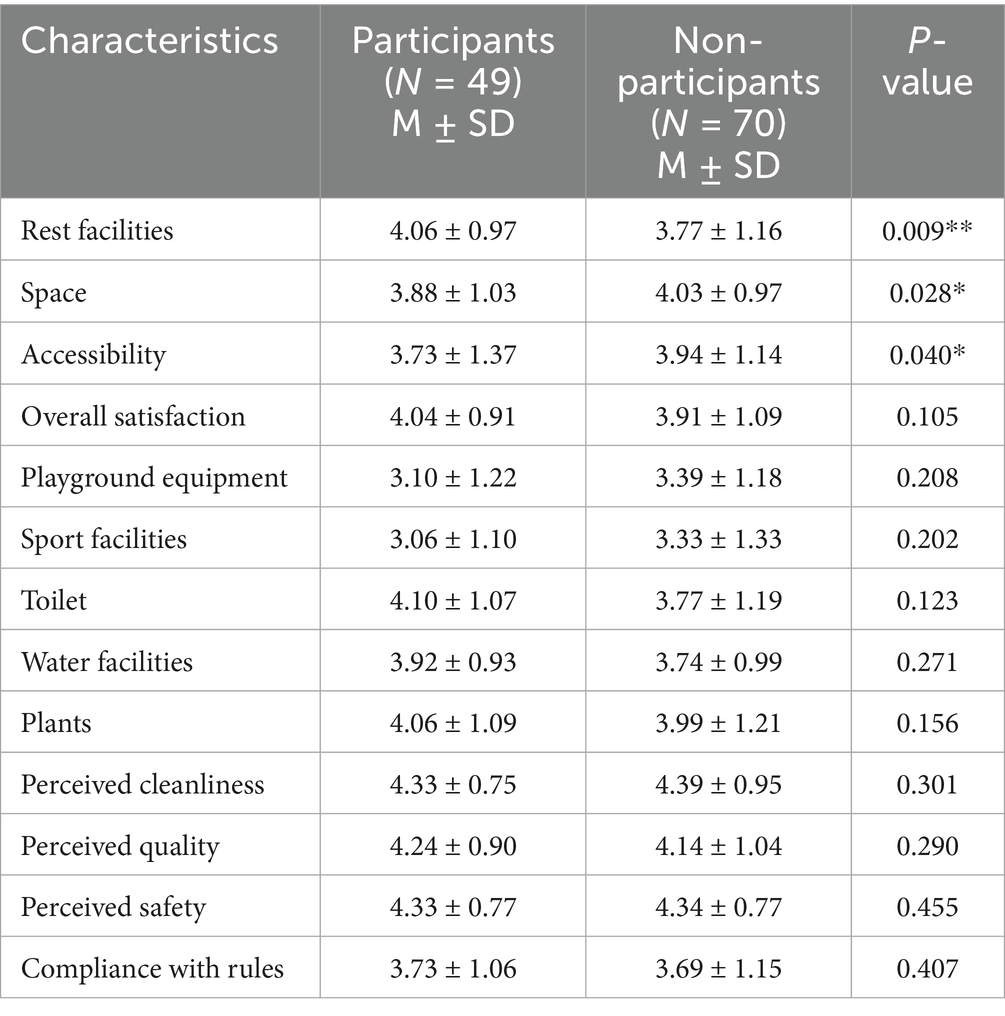
Specifically, the participants were satisfied more with places such as rest areas (mean ~4.06 vs. 3.77 among non-participants, p = 0.009), perceived accessible area (~4.0 vs. 3.9, p = 0.028), and access (~3.9 vs. 3.7, p = 0.040). This suggests that participants may appreciate certain features that support both social and leisure use. Similar findings have been supported by research indicating that diverse park features, such as increased amenities and usability, are strongly associated with park satisfaction (Roberts et al., 2019).
Overall satisfaction measure for subjects was 4.04 on average (Table 3), almost indistinguishable from the 3.91 obtained for non-participants (p = 0.105). Thus, participation in park activities did not significantly increase overall satisfaction, although it was linked to higher ratings for some park features. An ordered logistic regression (Table 4) confirmed that physical park attributes, not participation itself, were the main predictors of overall satisfaction. In the model, the participation indicator (yes/no) was not a predictor of higher satisfaction (β = −0.73, p = 0.205) when other variables were considered.
This aligns with findings that amenities such as rest areas, playground equipment, and well-maintained facilities significantly improve user satisfaction (Arowosafe and Ajayi, 2018). Furthermore, research has shown that cleanliness, size, and upkeep play pivotal roles in enhancing park satisfaction (Wu et al., 2025).
Observing that the park was sufficient in size to possess a great deal of space (β = 0.69, p = 0.045) and good ambiance (β = 0.71, p = 0.014) were significant positive factors. Cleanliness and safety did not appear as predictors because they were consistently rated highly by most respondents, leaving little variation to explain. Overall, event participation elevated satisfaction with certain facilities but was not a large influence on general park satisfaction, which was mainly influenced by physical park attributes.
3.5 Participatory activities and social interaction in fostering place attachment
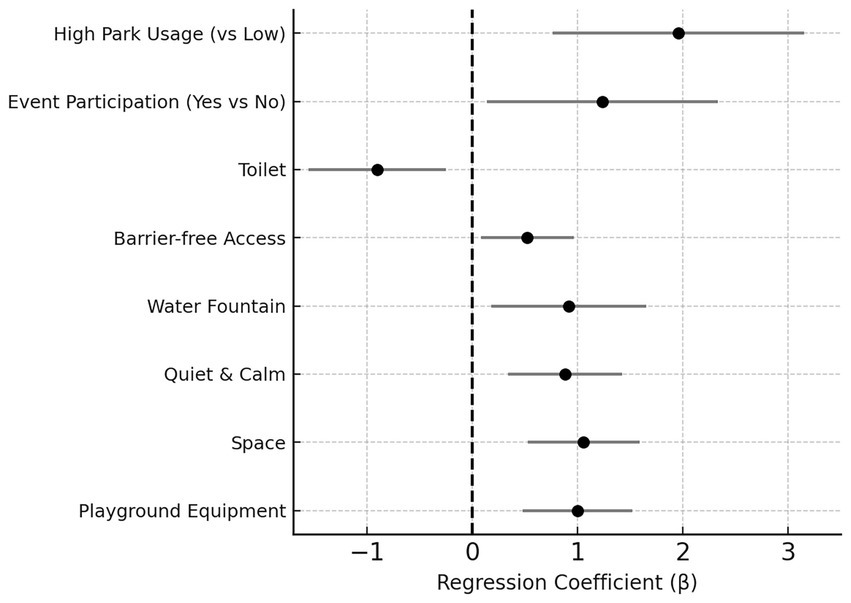
One of the main questions was whether taking part in activities in the local park contributes towards the development of a stronger emotional connection to the park (place attachment). Our results suggest that it does: taking part in events, and the social contact involved, was associated with much stronger place attachment. An ordered logistic regression (Figure 6) showed that, controlling for other variables, event participants had greater odds of having high attachment to the park than non-participants. In other words, the participation coefficient (yes/no) was about 1.24 (p = 0.027), which is equivalent to about a 3.4-fold higher odds of high attachment for those who attend events (Appendix 3). In the same way, park use frequency was associated with higher attachment: park frequent users exhibited a large positive coefficient (β = 1.96, p = 0.001), approximately a seven-fold higher odds of high attachment compared to less frequent users (Plunkett et al., 2019). These patterns support the idea that greater involvement with a place, through both use and participation, strengthens emotional connection.
Significantly, physical elements of the park environment also played an important part in attachment. Multiple park feature satisfaction measures had positive coefficients within the model (each p < 0.05), and this means people who felt that the park exceeded expectations on those scales were more likely to feel connected. For example, play equipment satisfaction was a significant predictor (β = 1.00, p < 0.001), and viewing the park as peaceful and quiet was also (β = 0.88, p = 0.001). Perceptions of spaciousness, functional facilities like water fountains, and barrier-free design were all positively associated with attachment (β-values ~0.5–1.1, p < 0.05). Interestingly, one of the variables had a negative effect: high value on toilets in the park was associated with lower attachment (β = −0.90, p = 0.007). This may suggest that dissatisfaction with restrooms reduces comfort, or that visitors who depend heavily on these facilities (such as older adults) feel less attached due to mobility or health constraints. These results indicate that both park use and satisfaction with physical features contribute to emotional attachment.
We also examined the role of the quality of social engagement in park activities. Survey return feedback from activity participants was categorized by their level of social interaction (from minimal to high involvement), and the differences in attachment were large. Those participants who socially engaged actively and established new relationships in park activities reported significantly greater levels of attachment than those who were less active (Amine, 2018). As indicated in Figure 7, the average place attachment score increased from around 3.76 (on a scale of 5) for low social interaction participants to around 4.67 for high social interaction participants. Even among event attendees, those who attended events but did not interact with others had much weaker attachment than those who socialized, volunteered, or made new friends.
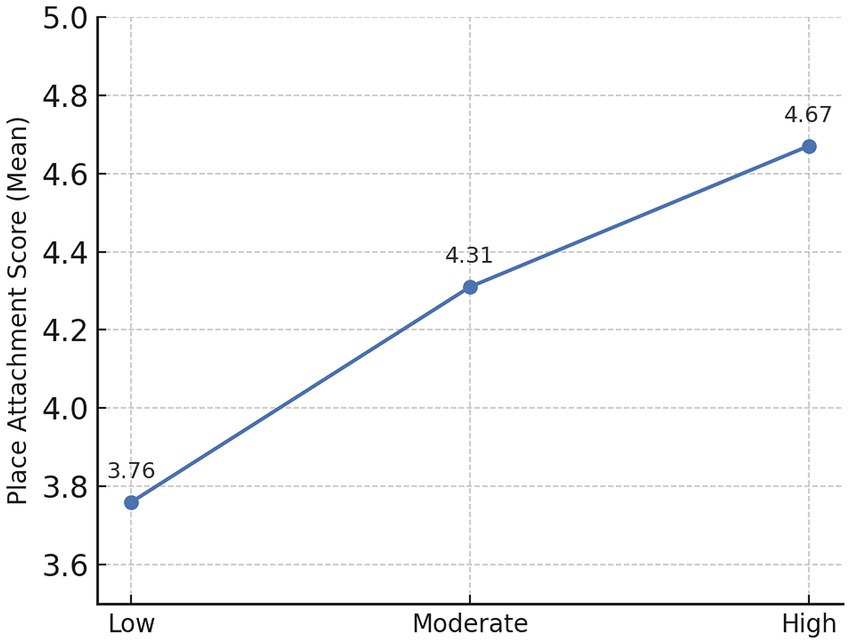
Figure 7. Relationship between social interaction level and place attachment: mean scores across interaction levels.
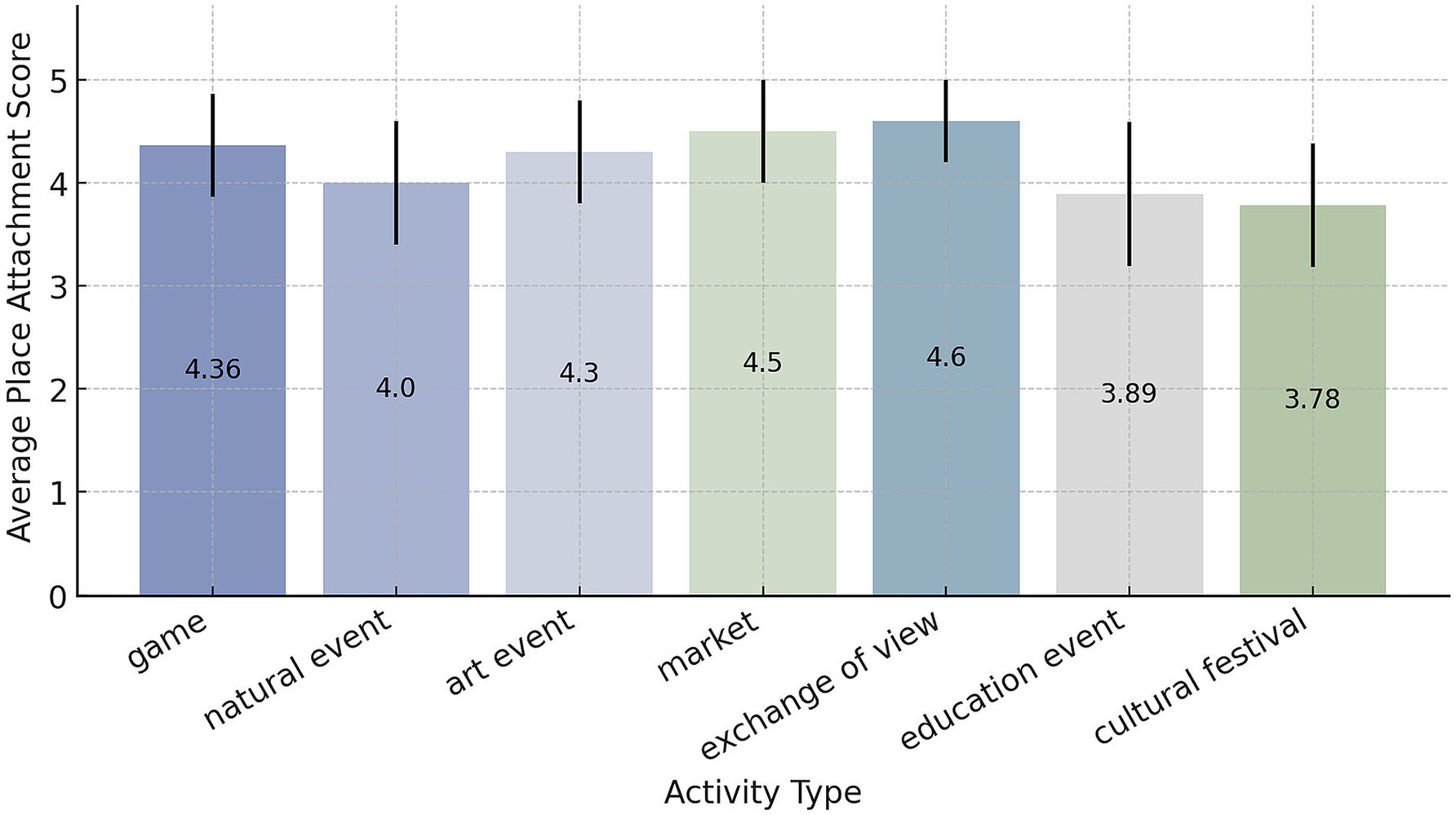
The type of activity also mattered. Highly interactive activities, such as neighborhood markets (mean ~4.5) and community discussion forums (~4.6), were linked to stronger attachment (Figure 8). Lower attachment was observed for more passive activities such as attending performances or lectures (mean scores ~3.8–3.9). These results suggest that activities promoting active social interaction are more effective at fostering place attachment. In general, our results suggest that both social interaction and positive park features contribute to stronger place attachment. This corresponds with the theoretical perspectives of social capital and sense-of-community theories (Yang et al., 2023), which emphasize the role of social bonding and trust in creating valued community spaces. At the same time, a welcoming and well-equipped physical environment provides the conditions necessary for positive experiences and attachments. Both factors — active community participation and a high-quality park environment — combined to generate the strongest attachment results.
4 Discussion
The current research offers a detailed exploration of the sociodemographic and socioeconomic determinants of motivation, frequency, satisfaction, and place attachment in park use. These findings relate to the multidimensionality of park use behavior and offer significant implications for urban planners and policymakers in a bid to make community parks more usable and appealing.
4.1 Sociodemographic factors influencing park activity participation
We observed strong sociodemographic determinants of community participation in park activities. As shown in Figure 3, participation rates were highest among residents aged 30–49 (48%), while much lower rates were observed among younger adults aged 18–29 (10%) and older adults aged 60 and above (30%) (p = 0.001). This pattern reflects life stage influences, consistent with the literature on the role played by life stage and family obligations in facilitating community participation (Fermino et al., 2015). The much higher participation of women is consistent with recent findings of variation in active participation in local community activity by gender, perhaps a reflection of women’s predominance in informal care work and local social networking (Valenzuela et al., 2019). Family size was the second determinant variable, larger families being more involved, showing the significance of parks as a public place for families (Vaughan et al., 2018). Similarly, previous studies have shown that age, family size, education, and employment status are important factors shaping park usage and perceptions, including in Asian park settings (Zhao et al., 2024).
Specifically, we identified a nonlinear correlation between length of residence and participation, as Social Capital Theory would predict, where residents seem to become more participative after having established denser social networks after several years. Participation was highest among those living in the neighborhood for 6–10 years (56%), while those with shorter (0–5 years) or longer residence (10 years and above) had lower rates (both 27%), as shown in Figure 3. City planners and policy makers should, therefore, create specially designed community programs directed at the specific interests of young residents, single-family households, and recent migrants to the area with the intention of fostering general community participation and social cohesion (Kim et al., 2024).
4.2 Park use motivations: balancing social interaction and solitary preferences
Motivational differences between park users and non-users were evident. As shown in Table 2, participants undertook mainly socially and family-centered leisure, such as taking children to playgrounds (75.9 vs. 24.1%, p < 0.001) and meeting up with friends (64.7 vs. 35.3%, p = 0.002). Participants undertook mainly socially and family-centered leisure, whereas non-participants engaged in solo-centered leisure activities such as dog-walking and relaxation. Findings affirm double roles of parks as social spaces and restorative environments according to Social Capital Theory and Restorative Environment Theory principles (Chen et al., 2024).
It should be noted that motivations such as dog-walking (p = 0.471) and relaxation (p = 0.791) did not show significant differences between participants and non-participants. This likely reflects the limited availability of walking areas in dense urban neighborhoods (Koohsari et al., 2020) and housing restrictions on pet ownership common in rental housing. These environmental and policy factors may limit the role of pet-related activities in differentiating between park participants and non-participants. According to these results, future park planning needs to program passive, restorative and social spaces to accommodate the diversity of user preference appropriately. In this way, parks’ increased community value as well as social and psychological value can be optimized (Roberts et al., 2019).
4.3 Impact of organized events on park visitation frequency
Our study provides firm evidence in support of the argument that resident park visit frequency was significantly higher among those attending community events. As shown in Table 3, attendees at visiting parks had higher park visiting and reduced disengagement than non-attendees (p < 0.01), suggesting the contributions of planned events to developing habitual use of the park (Moyle and Weiler, 2017).
Additionally, Table 3 shows that residential tenure and perceived safety were also significant factors influencing visit frequency. Longer-term residents and those who perceived the park as safe were more likely to visit regularly (p < 0.05). This underlines the need for programmed activities suitable for long-term residents and flexible work cohorts as well as for safety factors in whole-of-community engagement programs (Powers et al., 2024). Effective programs would involve regular, varied programming aimed at facilitating regular visitation and ongoing community engagement with public open spaces (Khazaei et al., 2019).
4.4 Role of park facilities in enhancing user satisfaction
As shown in Table 4, park event attendance did not make significant contributions to overall satisfaction (p = 0.238) but did positively influence resident ratings for some amenities, including restrooms (p = 0.016), availability of space (p = 0.022), and accessibility (p = 0.031). These findings highlight the critical role that specific park facilities play in shaping user satisfaction and are consistent with previous findings on the significance of tangible park attributes (Song and Wei, 2024; Xiao et al., 2024). This pattern suggests that while participatory activities may not directly enhance overall satisfaction, they can promote greater awareness and use of park amenities, leading to higher ratings for those features (Song and Wei, 2024).
Therefore, park planners can strive for the development of major amenities—particularly playground facilities, comfortable benches, and large open spaces—to ensure the highest level of visitors’ satisfaction effectively. Moreover, involving participatory activities along with targeted improvements in infrastructure can also improve the attitudes and affection of residents toward park amenities and, in turn, contribute indirectly to overall satisfaction (Lu et al., 2024).
4.5 Enhancing place attachment through social interaction
Among the strongest findings of our study is that participatory events have a powerful effect on enhancing residents’ affective attachment to parks. As shown in Appendix 1, event participants had significantly higher place attachment than non-participants (β = −1.236, p = 0.027). In addition, residents with high park use frequency also exhibited significantly greater place attachment (β = 1.958, p = 0.001). Strongest was the robust positive association between high social interaction at events and enhanced place attachment (Rout and Nesbitt, 2024).
This supports theoretical models of community bonding and social capital formation. Most interactive activities, such as discussion forums and community markets, generated the strongest level of emotional bonds (Veitch et al., 2015). Park programming in the future must therefore concentrate on interactive forms that engage people directly with one another and, in the process, create social cohesion and sense of belonging to community (Lee et al., 2024).
However, it is also important to note that while social interaction and activities promoted place attachment, satisfaction with certain functional amenities, especially restrooms, showed a weak inverse relationship with attachment. This may reflect the difference between functional use and emotional connection. Users who focus on practical needs, such as clean restrooms, may have more task-oriented visits and spend less time forming emotional ties to the park (Ramkissoon et al., 2011).
4.6 Limitations and future research directions
In addition to its strengths, the study has several limitations, most notably a somewhat small sample and geographical clustering within particular parks in Tokyo, which may limit generalizability. The response rate was relatively low (19.6%), raising the possibility of sampling bias if non-respondents differed systematically from respondents (Hansen and Hurwitz, 2004).
Future research would be strengthened through geographic extension and through the use of longitudinal designs to investigate longer-term effects of community park use on resident satisfaction and participation. The modest participation rate in park events (31.3%) may also affect the strength of conclusions regarding the effects of event participation (Refisch et al., 2024). Some variables, such as satisfaction and place attachment, relied on self-reported data, which may be influenced by individual expectations and subjective perceptions of park quality (Bai et al., 2013). To reduce potential bias, combining subjective evaluations with objective assessments of park features is recommended.
Seasonal effects, cultural heterogeneity, and some design factors also deserve to be examined to better understand urban park use and management practices. Additionally, environmental factors, such as soil and water conditions, though beyond this study’s scope, may influence park user experiences (Sivasankar et al., 2023). In conclusion, this study adds to the urban park literature by portraying demographic and motivational determinants of visitation to parks, describing the roles of programmed events in bridging visitation and attachment, and recording strategic implications towards achieving user satisfaction. These findings provide valuable insights for urban planners and policymakers, especially those seeking to develop inclusive, engaging, and sustainable urban parks.
5 Implications and conclusion
This study provides applied implications to optimize the performance of urban community parks in more dense cities like Tokyo. Based on an analysis of participatory interventions’ effectiveness in influencing park use, satisfaction, and place attachment, this study determines adaptive design, inclusive facilities, and ongoing maintenance as main strategies. Parks specifically need to include adaptive zones that meet multiple requirements, offer focused amenities such as seating space with shade and accessible routes, and offer open maintenance to create user trust and visitation.
The findings, particularly the positive association between participatory event attendance and increased park use frequency, satisfaction with specific amenities, and stronger place attachment, directly inform these recommendations. Also, the study supports the central role of active community life like markets, cross-cultural encounters, and park discussions in enhancing emotional ties and social solidarity, specifically among seniors and multicultural community members. However, given the study’s limitations—including sample size, response rate, and the reliance on self-reported data—these implications should be applied cautiously and adapted to the specific demographic and cultural contexts of other urban settings.
The research provides an immediate basis by which managers and policymakers may plan participatory parks with potential for inclusivity. Future research should further explore strategies tailored to different user groups, including younger adults, elderly residents, and culturally diverse populations, and should employ longitudinal and mixed-method designs to validate and expand upon the current findings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Graduate School of Horticulture, Faculty of Horticulture. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
MZ: Project administration, Supervision, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Validation, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Visualization, Formal Analysis, Resources. SY: Project administration, Validation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. RW: Visualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research has received support through All Directional Innovative Challenger Ph. D. Project by the JST SPRING (Grant number J24HJ00001).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frsc.2025.1599193/full#supplementary-material
References
Abbott, S. (2010). Social capital and health: The role of participation. Soc Theory Health. 8, 51–65. doi: 10.1057/sth.2009.19
Amine, M. (2018). Place attachment process and its influence on neighborhood park utilization in Putrajaya, Malaysia (Doctoral thesis). Seri Kembangan: Universiti Putra Malaysia.
Arowosafe, F., and Ajayi, A. (2018). Visitors’ satisfaction and intention to revisit Agodi parks and garden Ibadan, Oyo state. J. Res. For. Wildl. Environ. 10, 110–117. Available at: https://www.ajol.info/index.php/jrfwe/article/view/182020
Bai, H., Wilhelm Stanis, S. A., Kaczynski, A. T., and Besenyi, G. M. (2013). Perceptions of neighborhood park quality: associations with physical activity and body mass index. Ann. Behav. Med. 45, 39–48. doi: 10.1007/s12160-012-9448-4
Baruch, Y., and Holtom, B. C. (2008). Survey response rate levels and trends in organizational research. Hum. Relat. 61, 1139–1160. doi: 10.1177/0018726708094863
Bojorquez, I., and Ojeda-Revah, L. (2018). Urban public parks and mental health in adult women: mediating and moderating factors. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 64, 637–646. doi: 10.1177/0020764018795198
Borland, J. (2019). Small parks, big designs: reconstructed Tokyo’s new green spaces, 1923–1931. Urban Hist. 47, 106–125. doi: 10.1017/S0963926819000567
Bostock, J., Cooper, R. J., and Roberts, G. (2016). Rising to the challenge of sustainability: Community events by the community, for the community. London: Palgrave Macmillan, 16–33.
Bruton, C. M., Floyd, M., Bocarro, J., Henderson, K., Casper, J. M., and Kanters, M. (2011). Physical activity and health partnerships among park and recreation departments in North Carolina. J. Park. Recreat. Adm. 29, 23–36. Available at: https://js.sagamorepub.com/index.php/jpra/article/view/1092
Carlson, S., Brooks, J. D., Brown, D. R., and Buchner, D. (2010). Racial/ethnic differences in perceived access, environmental barriers to use, and use of community parks. Prev. Chronic Dis. 7:A49.
Chen, S., Sleipness, O., Christensen, K., Yang, B., Park, K., Knowles, R., et al. (2024). Exploring associations between social interaction and urban park attributes: Design guideline for both overall and separate park quality enhancement. Cities. 145:104714. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2023.104714
Choi, J., and Jeon, H. (2021). Economic impacts of local park visitor spending on local communities: a case of Mississippi parks. Int. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 5, 37–44. doi: 10.11648/j.ijhtm.20210502.12
Clarke, M., Wallace, C., Cadaval, S., Anderson, E. C., Egerer, M. H., Dinkins, L., et al. (2023). Factors that enhance or hinder social cohesion in urban greenspaces: a literature review. Urban For. Urban Green. 80:128456. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2023.127936
Cohen, D. A., McKenzie, T. L., Sehgal, A., Williamson, S., Golinelli, D., and Lurie, N. (2010). Contribution of public parks to physical activity. Am. J. Public Health 97, 509–514. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2005.072447
Dillman, D. A., Smyth, J. D., and Christian, L. M. (2014). Internet, phone, mail, and mixed mode surveys: The tailored design method. 4th Edn. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Fermino, R., Reis, R., Hallal, P., and Kaczynski, A. (2015). Who are the users of urban parks? A study with adults from Curitiba, Brazil. J. Phys. Act. Health 12, 58–67. doi: 10.1123/jpah.2012-0482
Flyr, M., and Koontz, L. (2024). 2023 national park visitor spending effects: Economic contributions to local communities, states, and the nation. Science report NPS/SR—2024/174. National Park Service, U.S. Department of the Interior, Fort Collins, Colorado. doi: 10.36967/2305351
Giles-Corti, B., Broomhall, M. H., Knuiman, M., Collins, C., Douglas, K., Ng, K., et al. (2005). Increasing walking: how important is distance to, attractiveness, and size of public open space? Am. J. Prev. Med. 28, 169–176. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2004.10.018
Goyder, E. C., Edmonds, C., Sabey, A., Lawrence, D., Bullas, A., Taylor, M., et al. (2018). What factors predict participation in a mass community physical activity programme? The case of the five Sheffield ‘parkruns’. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 72, A61–A62. doi: 10.1136/jech-2018-SSMabstracts.128
Grunseit, A., Huang, B.-H., Merom, D., Cranney, L., Bauman, A. E., and Rogers, K. (2024). Coming back for more: individual participation patterns in the physical activity initiative parkrun in Australia. Health Promot. Int. 39:daac045. doi: 10.1093/heapro/daae098
Hansen, M. H., and Hurwitz, W. N. (2004). The problem of nonresponse in sample surveys. Am. Stat. 58, 292–294. doi: 10.1198/000313004X6328
Hosmer, D. W., Lemeshow, S., and Sturdivant, R. X. (2013). Applied logistic regression. New York, NY: Wiley.
Khazaei, A., Joppe, M., and Elliot, S. (2019). Mapping a diverse community’s engagement in parks planning. Leis. Sci. 41, 294–312. doi: 10.1080/01490400.2017.1410740
Kim, J., Kim, C., Lee, S., and Jeong, J. Y. (2024). Race, poverty, and space: a spatial intersectional approach to equity of urban park access. Cities 147:104819. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2024.104819
Koohsari, M. J., Nakaya, T., McCormack, G. R., Shibata, A., Ishii, K., Yasunaga, A., et al. (2020). Dog-walking in dense compact areas: the role of neighbourhood built environment. Health Place 61:102242. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2019.102242
Koynova, T., Koleva, V., Dragoeva, A., and Natchev, N. (2019). Peri-urban National Parks as green spaces for recreation. Int. J. Soc. Ecol. Sustain. Dev. 10, 46–58. doi: 10.4018/IJSESD.2019010104
Lee, J. H., Ahn, Y., Kang, D., and Kim, H. (2024). Disparities in urban park visitation patterns among socioeconomically vulnerable communities during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sustain. For. 16:1070. doi: 10.3390/su16031070
Lin, D., Sun, Y., Yang, Y., Han, Y., and Xu, C. (2022). Urban park use and self-reported physical, mental, and social health during the COVID-19 pandemic. Urban For. Urban Green. 79:127804. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2022.127804
Liu, H., Li, F., Li, J., and Zhang, Y. (2017). The relationships between urban parks, residents’ physical activity, and mental health benefits. J. Environ. Manag. 190, 223–230. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.12.058
Lu, J., Xiao, X., Huang, X., Chuai, X., Li, Z., Wei, H., et al. (2024). Big data insights into urban park use in the pandemic: Changes in visitation patterns and exacerbated social inequalities in the U.S. Cities 152:105204. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2024.105204
Monma, T., Takeda, F., Noguchi, H., Takahashi, H., and Tamiya, N. (2016). The Impact of Leisure and Social Activities on Activities of Daily Living of Middle-Aged Adults: Evidence from a National Longitudinal Survey in Japan. PLoS One. 11:e0165106. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165106
Mowen, A., Trauntvein, N. E., Graefe, A., and Son, J. S. (2012). The influence of visitor characteristics on state park physical activity levels. J. Park. Recreat. Adm. 30, 19–40. Available at: https://www.js.sagamorepub.com/index.php/jpra/article/view/2651
Moyle, B., and Weiler, B. (2017). Revisiting the importance of visitation: public perceptions of park benefits. Tour. Hosp. Res. 17, 105–191. doi: 10.1177/1467358416638918
Murayama, H., Sugiyama, M., Inagaki, H., Edahiro, A., Miyamae, F., Ura, C., et al. (2024). Community social capital and all-cause mortality in Japan: findings from the Adachi cohort study. J. Epidemiol. 34, 45–56. doi: 10.2188/jea.JE20240277
Plunkett, D., Fulthorp, K., and Paris, C. M. (2019). Examining the relationship between place attachment and behavioral loyalty in an urban park setting. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tourism. 25:006. doi: 10.1016/j.jort.2018.11.006
Powers, S. L., Mowen, A., and Rodgers, E. B. D. (2024). Belonging and welcomeness in state and community parks: visitation impacts and strategies for advancing environmental justice. Geoforum 157:104149. doi: 10.1016/j.geoforum.2024.104149
Ramkissoon, H., Weiler, B., and Smith, L. (2011). Place attachment and pro-environmental behaviour in national parks: the development of a conceptual framework. J. Sustain. Tour. 20, 257–276. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2011.602194
Rastkhadiv, A., Hami, A., and Pouya, S. (2024). Effects of nature-based solutions on mental well-being—the case of urban parks in Marivan, Iran. Arboric. Urban For. 50, 301–323. doi: 10.48044/jauf.2024.012
Refisch, M., Kurz, K., and Hartmann, J. (2024). Urban green space usage and life satisfaction during the Covid-19 pandemic. Appl. Res. Qual. Life 19, 1139–1171. doi: 10.1007/s11482-024-10279-z
Resnik, D. B. (2018). The ethics of research with human subjects: Protecting people, advancing science, promoting trust. Cham: Springer.
Roberts, H., Kellar, I., Conner, M., Gidlow, C., Kelly, B., Nieuwenhuijsen, M., et al. (2019). Associations between park features, park satisfaction and park use in a multi-ethnic deprived urban area. Urban For. Urban Green. 46:126485. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2019.126485
Romolini, M., Ryan, R. L., Simso, E. R., and Strauss, E. G. (2019). Visitors’ attachment to urban parks in Los Angeles, CA. Urban For. Urban Green. 41, 118–126. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2019.03.015
Rout, A., and Nesbitt, L. (2024). Equity, travel, and park visitation in 10 US metro areas: a smartphone mobility study. Urban For. Urban Green. 101:128557. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2024.128557
Sánchez, D. M., Tsukamoto, Y., and Lobo, N. G. (2021). Tokyo metropolitan parks as urban forestry assemblages: reframing more-than-human commons in the city. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 21, 2636–2651. doi: 10.1080/13467581.2021.1974455
Schipperijn, J., Cerin, E., Adams, M. A., Reis, R., Smith, G., Cao, C., et al. (2017). Access to parks and physical activity: An eight country comparison. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 27, 253–263. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2017.08.010
Schwartz, A., Dodds, P., O’Neil-Dunne, J., Danforth, C., and Ricketts, T. (2018). Exposure to urban parks improves affect and reduces negativity on twitter. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1807.07982.
Shobri, N. I. M. (2024). Urban park design for mental health restoration via different ages in Malaysia. Planning Malaysia 22, 45–58. doi: 10.21837/pm.v22i34.1658
Sivasankar, V., Omine, K., Zhang, Z., Shi, S., Sano, H., and Chicas, S. D. (2023). Plaster board waste (PBW) – a potential fluoride leaching source in soil/water environments and, fluoride immobilization studies using soils. Environ. Res. 218:115005. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.115005
Smith, A. (2018). Paying for parks: ticketed events and the commercialisation of public space. Leis. Stud. 37, 533–546. doi: 10.1080/02614367.2018.1497077
Song, Y., and Wei, Q. (2024). Impact of apparent temperatures on park visitation behavior: a comprehensive analysis using large-scale mobility data. Sci. Total Environ. 940:173388. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173388
Stanis, S. W., and Schneider, I. (2010). Park physical activity motivations, constraints and negotiation: generational differences. J. Outdoor Recreat. Educ. Leadersh. 2, 181–185. doi: 10.7768/1948-5123.1064
Stevinson, C., and Hickson, M. (2014). Exploring the public health potential of a mass community participation event. J. Public Health 36, 268–274. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdt082
Sturm, R., and Cohen, D. (2014). Proximity to urban parks and mental health. J. Ment. Health Policy Econ. 17, 19–24. doi: 10.1186/1476-072X-12-26
Toshima Ward (2023a). Toshima Ward basic plan for greening. Available online at: https://www.city.toshima.lg.jp/339/kuse/shisaku/shisaku/kekaku/008450/index.html (Accessed March 25, 2025).
Toshima Ward (2023b). Toshima policy data book 2023. Available online at: https://www.city.toshima.lg.jp/001/kuse/shisaku/shisaku/hakusho/008287/documents/2309121137.html (Accessed March 25, 2025).
Valenzuela, A. L. E. M., Santos, A. C. B., Justina, M., Kuhn, T. S., Pazin, J., and Rech, C. R. (2019). Environmental factors to promote the use of a public park in adults. Rev. Bras. Ativ. Fis. Saude 23:e0049. doi: 10.12820/RBAFS.23E0049
Vaughan, C., Colabianchi, N., Hunter, G. P., Beckman, R., and Dubowitz, T. (2018). Park use in low-income urban neighborhoods: who uses the parks and why? J. Urban Health 95, 222–231. doi: 10.1007/s11524-017-0221-7
Veitch, J., Carver, A., Abbott, G., Giles-Corti, B., Timperio, A., and Salmon, J. (2015). How active are people in metropolitan parks? An observational study of park visitation in Australia. BMC Public Health 15:1960. doi: 10.1186/s12889-015-1960-6
Veitch, J., Wang, W., Salmon, J., Carver, A., Giles-Corti, B., and Timperio, A. (2018). Who goes to metropolitan parks? A latent class analysis approach to understanding park visitation. Leis. Sci. 40, 343–355. doi: 10.1080/01490400.2017.1325798
Walker, J., and Crompton, J. (2012). The relationship of household proximity to park use. J. Park. Recreat. Adm. 30, 79–98. Available at: https://js.sagamorepub.com/index.php/jpra/article/view/2808
Wang, Z., Zhang, C., Chen, Y., Liu, X., and Guo, J. (2020). The effects of urban park on residents’ health: an empirical study based on Tangxi River park in Hefei. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 544:012020. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/569/1/012073
Wu, H., Gong, C., Wang, R., Niu, X., Cao, Y., Cao, C., et al. (2025). Moderating effects of park accessibility and external environment on park satisfaction in a mountainous city. Land 14:77. doi: 10.3390/land14010077
Xiao, Z., Zhang, C., Li, Y., and Chen, Y. (2024). Community park visits determined by the interactions between built environment attributes: an explainable machine learning method. Appl. Geogr. 172:103423. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2024.103423
Yang, C., Shi, S., and Runeson, G. (2023). Towards sustainable urban communities: investigating the associations between community parks and place attachment in master-Planned Estates in Sydney. Sustain. Cities Soc. 96:104659. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2023.104659
Zafeiroudi, A., and Kouthouris, C. (2020). Segmenting visitors of a Greek recreational theme park using factors that motivate attendance. Manag. Sport Leis. 28, 120–134. doi: 10.1080/23750472.2020.1860802
Zhang, J., and Tan, P. (2019). Demand for parks and perceived accessibility as key determinants of urban park use behavior. Urban For. Urban Green. 44:126420. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2019.126420
Zhao, J., Abdul Aziz, F., Song, M., Zhang, H., Ujang, N., Xiao, Y., et al. (2024). Evaluating visitor usage and safety perception experiences in National Forest Parks. Land 13:1341. doi: 10.3390/land13091341
Zhou, Y., Guan, C., Wu, L., Li, Y., Nie, X., Song, J., et al. (2024). Visitation-based classification of urban parks through mobile phone big data in Tokyo. Appl. Geogr. 160:103456. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2024.103300
Zong, M., Xu, G., and Yanai, S. (2024). Building local partnership through community parks in Central Tokyo: perspectives from different participants. Front. Sustain. Cities 6:102345. doi: 10.3389/frsc.2024.1445754
Zoshigaya Hiroba Club (2023). The development of Zoshigaya Park. Toshima: Zoshigaya Hiroba Club. Available at: https://zoshigaya.club/zoshigayapark.html (Accessed March 25, 2025).
Keywords: participatory events, user satisfaction, place attachment, public engagement, urban green spaces
Citation: Zong M, Yanai S and Wang R (2025) Exploring the use and perceptions of community parks with engagement activities: a case study of Tokyo, Japan. Front. Sustain. Cities. 7:1599193. doi: 10.3389/frsc.2025.1599193
Edited by:
Esther Oreofeoluwa Esho, The Australian New Zealand Society for Ecological Economics (ANZSEE), AustraliaReviewed by:
Irfan Ahmed Memon, Mehran University of Engineering and Technology, PakistanZiyi Cheng, The University of Manchester, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2025 Zong, Yanai and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Min Zong, MjJoZDA2MDFAc3R1ZGVudC5ncy5jaGliYS11Lmpw
 Min Zong
Min Zong Shigeto Yanai2
Shigeto Yanai2