- Key Laboratory for Animal Disease-resistance Nutrition of China Ministry of Education, Animal Nutrition Institute, Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
The antioxidants were found to improve inflammatory responses and redox status. This study investigated the effects of maternal and post-weaning supplementation with microbe-derived antioxidants (MA) on sow performance, redox status, and fecal microorganisms, as well as the growth performance, inflammatory responses and intestinal microbiota of weaned piglets. Sixty multiparous sows were randomly allocated to the control group (CON, basal diet) and the MA group (basal diet supplemented with 2.0 g MA/kg) from d 90 of gestation to d 24 of lactation, according to the parity and body condition. At weaning, a total of 80 piglets per group were selected and randomly assigned to either the basal diet or the MA-supplemented diet, with 10 pens per group and 4 piglets per pen, for a period of 21-day trial. Results showed that maternal MA supplementation increased litter size at weaning (p < 0.05) and the milk contents of dry matter (p = 0.08) and fat (p = 0.09), while decreasing the plasma activities of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase in sows on d 24 of lactation (p < 0.05). Moreover, maternal MA supplementation reduced plasma malondialdehyde concentration (p ≤ 0.01) in sows at farrowing and weaning, as well as catalase activity at weaning (p = 0.01), and tended to increase total antioxidant capacity at farrowing (p = 0.08). Additionally, the fecal contents of butyrate (p = 0.04) and propionate (p = 0.09) were higher in sows receiving the MA diet at d 24 of lactation. In post-weaning piglets, maternal MA supplementation increased average daily gain (p = 0.07) and average daily feed intake (p < 0.05) throughout the period, and increased plasma immunoglobulin G and interleukin-10 concentrations (p < 0.05). Additionally, either maternal or post-weaning MA supplementation positively influenced the gut microbiome of both sows and weaned piglets. In conclusion, maternal MA supplementation during late gestation and lactation increased litter size at weaning, which may be associated with the improved milk quality and redox status. Furthermore, maternal MA supplementation may enhance the growth performance of post-weaning piglets, potentially linking to the improvements in immunological parameters and gut microbiome.
1 Introduction
During late gestation and lactation, sows experience stress due to environmental and physiological changes, which include feeding restrictions, housing modifications, and farrowing transitions. The perinatal period is particularly critical for both dam and offspring, as it brings significant changes to maternal metabolism, redox status, and microbiota (1, 2). Physiological changes that occur in sows during farrowing, such as the production of prostaglandins, prostacyclin, and tissue damage, can lead to inflammatory reactions in sows (3). Additionally, the levels of pro-inflammatory factors during early lactation are significantly higher than those during early pregnancy or late lactation (4). Furthermore, oxidative stress is observed during late gestation and lactation, which would adversely affect milk production, reproductive efficiency, and sow longevity (5).
Weaning represents a pivotal stage for the growth and development of piglets. Weaning stress, which includes dietary changes, maternal separation, environmental alterations, and more, can lead to a series of issues in piglets, such as diarrhea, morbidity, growth check etc. (6, 7). Various feed additives, such as cysteamine, plant extracts, probiotics, and postbiotics, had been shown to alleviate weaning stress by reducing diarrhea, improving redox status and microbiota composition (8–10). Recent studies have demonstrated that maternal nutrition or supplementation with functional components (such as postbiotics) can promote improvements in both the growth performance and health of offspring (11–13).
Postbiotics, also called inactivated probiotics, are a complex mixture of inactivated bacterial cells generated through fermentation and probiotic metabolites, such as secreted proteins, peptides, enzymes, proteins, vitamins, and exopolysaccharides (EPSs), which provide overall health benefits to animal (14, 15). Studies have shown that maternal supplementation with yeast-derived postbiotics can decrease piglet mortality and the diarrhea index (16). The postbiotic consisting of heat-inactivated Lactobacillus fermentum and Lactobacillus delbrueckii improved the growth performance of nursery pigs, which was related to enhanced intestinal health and increased diversity and abundance of beneficial microbiota in pigs challenged with F18+ E. coli (17). Meanwhile, Lactobacillus reuteri postbiotics can also improve antioxidant function and reduce piglet mortality by regulating the gut microbiota (18).
Microbe-derived antioxidants (MA) are a mixture of fermented and inactivated Sea buckthorn and Rosa roxburghii combined with probiotics, containing numerous bioactive compounds such as isoflavones, flavone, glutathione, and polyphenols etc. (19, 20). As a type of postbiotic, studies have been reported that MA exhibits free radical scavenging ability (21), inhibits oxidative stress and inflammation (22), possesses hypolipidemic and anti-inflammatory properties (12, 23). Dietary supplementation with MA during gestation and lactation in rats can alleviate high-fat diet-induced production of hepatic nitrogen radical, increase antioxidant enzyme activity, and attenuate lipid accumulation and NLRP3 inflammasome levels (12). Considering these potential benefits, we hypothesized that MA could enhance the productive performance and health status of sows and their offspring. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effects of maternal and post-weaning MA supplementation on the productive performance of sows and their offspring, gut microbiota, redox status and immunology-related parameters.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental materials
Microbe-derived antioxidants was provided by Shanghai Chuangbo Ecological Engineering Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Briefly, it was produced through a multi-stage complex fermentation process involving Rosa roxburghii and Sea buckthorn with Bacillus Subtilis, Lactobacillus, Clostridium Butyricum, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The process included extraction, concentration, inactivation, and freeze-drying. MA exhibited a fermented taste, with the main bioactive compounds being 1.37% isoflavones, 194,000 U/100 g superoxide dismutase, 886 mg/100 g glutathione, and 82.4 mg/100 g total saponins (19, 20).
2.2 Animals, experiment design and management
Sixty Landrace × Yorkshire sows (LY, parity 4.06 ± 0.24) at 90 days of gestation were randomly assigned to two groups based on parity and body condition, with 30 replicates for each group and one sow per replicate (n = 30). The control group (CON) received basal diet, whereas the treatment group (MA) received the basal diet supplemented with 2.0 g MA/kg. The nutritional requirements for the basal diet of sows during gestation and lactation were based on the National Research Council (2012) (NRC, United States), and the compositions and nutritional levels of the diets were detailed in Supplementary Table S1. The sow trial extended from d 90 of gestation to d 24 of lactation.
At weaning, a total of 80 Duroc × Landrace × Yorkshire (DLY) piglets were selected from each group based on their litter (2–3 piglets per litter) and body weight (BW, the average weight per litter). The 80 piglets from each group of sows were then randomly assigned to receive either a basal diet or a basal diet supplemented with 2.0 g MA/kg. The two factors, maternal diet and post-weaning diet, were arranged in a 2 × 2 factorial design, resulting in four treatment groups, with 10 pens for each group (n = 10) and 4 piglets per pen, as follows: CON. CON (basal diet for both sows and piglets), CON. MA (basal diet for sows and MA diet for piglets), MA. CON (MA diet for sows and basal diet for piglets) and MA. MA (MA diet for both sows and piglets). The basal diet was formulated according to the nutritional requirements of 5–7 kg and 7–11 kg piglets, as outlined by the NRC (2012), and the ingredients and nutrient composition were provided in Supplementary Table S1. After 3 days of pre feeding, the piglets trial lasted 21 days until 24 d post-weaning.
The feeding, management, and immunization procedures were conducted according to the farm’s standards for gestating and lactating sows and weaned piglets. During gestation, all the sows were housed in individual stalls and fed 3 kg/d of gestation-period diet twice a day (08: 00 and 15:00), with access to water ad libitum throughout the study. On d 110 of gestation, the sows were moved to the farrowing room and the day of parturition was defined as d 0 of lactation. The sows were no feed on the day of farrowing, 2 kg/d of diet on the following 3 days, and then feed freely twice a day (8:00, 16:00). Feed allocation and refusals were recorded daily during lactation. At farrowing, the numbers of live, stillborn, and mummified piglets, along with their birth weight, were recorded. Cross-fostering occurred within 48 h post-farrowing and the litters were adjusted to consist of 11–12 piglets within the same treatment. The numbers and weights of piglets were recorded after standardizing the litters and again at weaning. Two sows in the CON were eliminated due to fever and illness before production. Additionally, the piglets had free access to water throughout lactation but did not have access to creep feed. Weaned piglets were fed ad libitum four times a day (08:00, 12:00, 16:00, and 20:00). During the trial, weaned piglets had free access to water; pens were regularly cleaned, disinfected, and dewormed, with stable air circulation and temperature maintained. Fecal scores of pigs were recorded daily following observations of the individual piglet and signs of stool consistency in the pen. The calculation of fecal scoring criteria and diarrhea index was performed as previously described by our group (24). On days 0, 7, 14, and 21 of formal trial, all piglets were weighed and feed intake was recorded. The average daily gain (ADG), average daily feed intake (ADFI) and feed to gain ratio (F/G) were calculated for each pen.
2.3 Samples collection
Colostrum samples (15 mL) were collected from 8 sows per group (n = 8) before any piglets sucked, and milk samples (15 mL) were obtained from the same sows (n = 8) on d 10 of lactation. The milk samples were collected using 2 mL of oxytocin via the ear vein, as previously described (11). All samples were stored at −20°C for subsequent analysis.
Blood samples were collected in sodium heparin-anticoagulated vacuum tubes. Fasting blood samples (10 mL) were collected from marginal ear vein of 8 sows per group (n = 8) at 1 h post-farrowing and on d 24 of lactation, before the morning meal. Fasting blood samples (5 mL) were collected from the anterior vena cava of 8 piglets (one per pen, n = 8) per group on days 0 and 21 of formal trial. The blood was maintained at room temperature for 30 min, then centrifuged at 3,000 × g and 4°C for 10 min. The supernatant plasma was collected and stored at −20°C for later analysis.
Eight healthy sows (n = 8) were randomly selected from each group, and fresh fecal samples were collected immediately after defecation (one sample per pig). The samples were collected in sterile centrifuge tubes 1 h after the first piglet was born and on d 24 of lactation, placed in liquid nitrogen, and then stored at −80°C for microbial analysis. At the end of the weaned piglet trial, 8 pigs per group (one per pen, n = 8) were selected and anaesthetized with a lethal injection of sodium pentobarbital (200 mg/kg BW) following an overnight fast. The abdomen was then immediately opened, the jejunum was removed, emptied, and washed with normal saline. The middle section of the jejunum (1.5 cm) was collected and fixed in a 4% paraformaldehyde solution for histological analysis. Additionally, colonic chyme from the mid-region of the colon was collected in sterile centrifuge tubes, quickly placed in liquid nitrogen, and then stored at −80°C for microbial analysis.
2.4 Milk and plasma indicators analysis
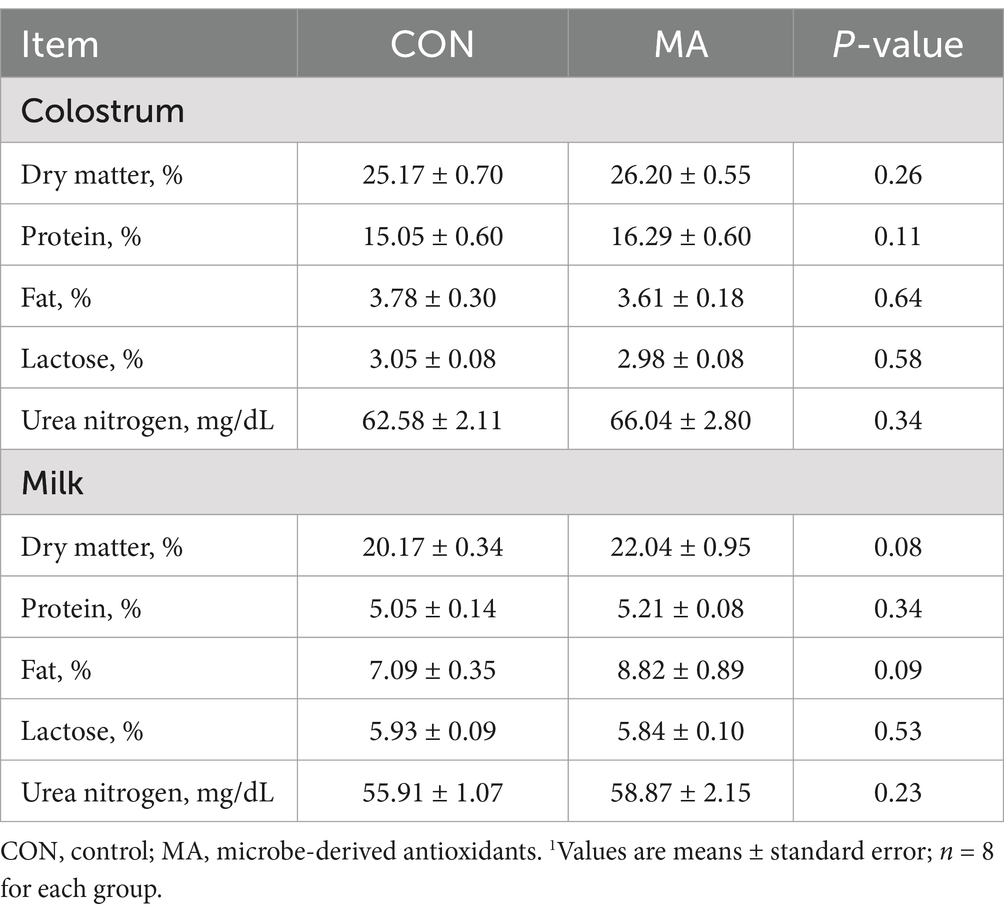
The contents of fat, protein, urea nitrogen and lactose were determined using a multifunctional dairy analyzer (MilkoScan FT+, FOSS, Sweden). The dry matter (DM) was measured using method (930.15) of AOAC (2019) (25).
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and gamma glutamyl transferase (γ-GGT) in sow plasma were measured using reagent kits (CH0101201, CH0101202, CH0101204; Maccura, Chengdu, China) on an automatic biochemistry analyzer (3,100, HITACHI, Tokyo, Japan). The activities of catalase (CAT), total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD), along with the concentrations of malondialdehyde (MDA), protein carbonyl (PCO) and inhibition and produce superoxide anion (O2−), were quantified using corresponding assay kits (No. A007-1-1, A015-1-2, A001-1-2, A003-1-2, A087-1-2 and A052-1-1; Jiancheng Bioengineering, Nanjing, China), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The concentration of protein was determined using the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) method with a BCA protein assay kit (No. A045-3-2, Jiancheng Bioengineering, Nanjing, China).
In piglet plasma, IgG, IgM and complement 3 (C3) were measured using reagent kits (CH0105306, CH0105308, CH0105309; Maccura, Chengdu, China) on an automatic biochemistry analyzer (3,100, HITACHI, Tokyo, Japan). The levels of interleukin-10 (IL-10), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) were measured using ELISA kits (No. P1000, PTA00 and PLB00B; R&D Systems China Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), following the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.5 Histomorphology measurements
Jejunum samples of the piglets, preserved in 4% paraformaldehyde solution, were dehydrated and infiltrated with paraffin wax. This procedure was performed as previously described by our group (24). The samples were sectioned to a thickness of 5 μm using a microtome (HistoCore MULTICUT, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) and stained with periodic acid-Schiff. Crypt depth (CD) and villus height (VH) of each sample were measured using Image-Pro Plus 6.0 software (Media Cybernetics, Maryland, United States) with a digital trinocular microscope camera (BX43F, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). At least 10 well-oriented villi and crypt columns were counted for each sample, and the ratio of villus height to crypt depth (VH/CD) was calculated. Simultaneously, goblet cells and the corresponding villus area were measured, and the density of goblet cells was calculated.
2.6 Short-chain fatty acids analysis
Sow feces were prepared using methods previously described by our group (24). Briefly, approximately 2 g of feces was mixed with ultra-pure water (1:1, w/v) and then centrifuged for 10 min at 12,000 × g and 4°C. The supernatant was mixed with 25% metaphosphoric acid and crotonic acid, incubated and recentrifuged. Subsequently, the supernatant was mixed with methanol and recentrifuged again. Finally, the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter membrane, and the short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) concentrations were determined using a gas chromatograph system (CP-3800, Varian, Palo Alto, United States).
2.7 Microbial analysis
The microflora structure in sow feces and piglet colonic chyme was analyzed using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing technology. This procedure was performed as previously described by our group (24). Total DNA was extracted from the samples using the Fecal DNA Isolation Kit (No. D4015-01, Omega, Norcross, United States) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA purity and concentration were analyzed using 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis and a spectrophotometer (Nanodrop 2000, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, United States). The qualified DNA samples were sent to Novogene Bioinformatics Technology (Beijing, China) for sequence analysis. The V4 hypervariable regions of the 16S rRNA gene were amplified with primers 515F (5′-GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′). Pyrosequencing of bacterial 16S rDNA was performed using the Illumina NovaSeq platform to generate 250 bp paired-end reads. The paired-end reads were merged using FLASH (V1.2.11), quality filtering was performed, and chimera sequences were removed to obtain effective tags. The effective tags were assigned to operational taxonomic units (OTUs) using the Uparse software (V7.0.1001) with 97% sequence similarity. Subsequent analysis of a-diversity and b-diversity was based on these normalized output data. Species annotation and α-diversity analysis were performed using QIIME software (V1.7.0). The LEfSe analysis was performed using LEfSe software (V1.0).
2.8 Statistical analysis
The data were normally distributed after testing homogeneity of variances and normal distribution using the Shapiro–Wilk method in SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC). The measurement data from sows were analyzed using the T-test procedure in SAS 9.4. Reproductive performance was measured in litters, while other indicators of sows were assessed in duplicate individuals. The data from weaned piglets were analyzed using the MIXED procedure in SAS 9.4 for split-plot analysis of variance and significance testing. The statistical models included the effects of sow diet MA levels (0 or 2.0 g/kg), piglet diet MA levels (0 or 2.0 g/kg), and their interaction. Piglet weaning BW was treated as a random effect, and the Tukey method was used for multiple comparisons. Except for growth performance and the diarrhea index, measured in pens, all other indicators were assessed in individual subjects. Data were presented as means ± SE, and differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05, while results with 0.05 ≤ p < 0.1 were defined as trends.
3 Results
3.1 Reproductive performance
As shown in Table 1, maternal MA supplementation did not significantly alter the number of piglets born alive, stillborn piglets and total born piglets, the litter weight of total born and born alive piglets, or the duration of farrowing. However, the litter size at weaning was significantly increased in the MA group compared to the CON group (p < 0.05).
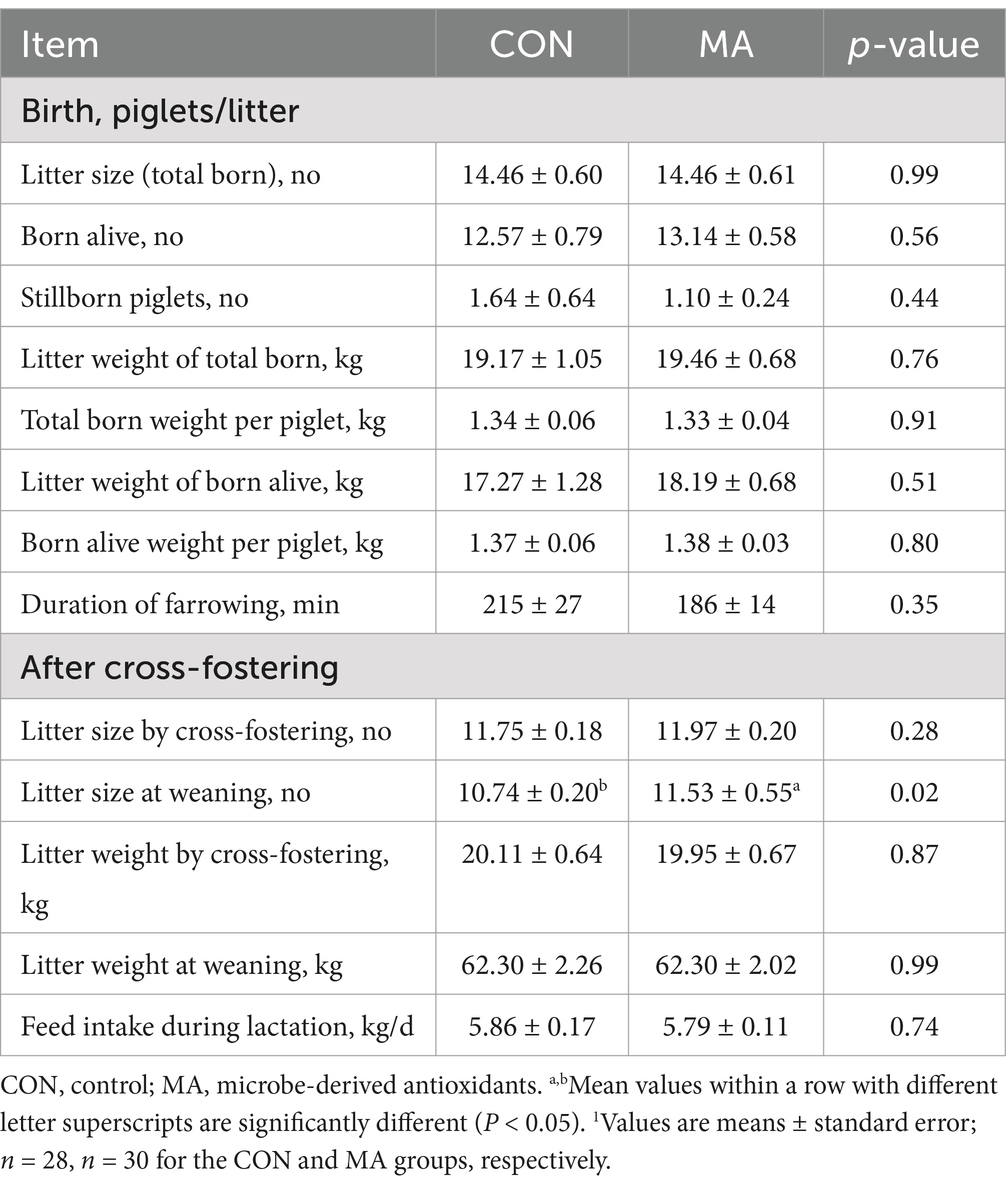
Table 1. Effect of maternal MA supplementation on reproductive performance of sows and growth performance of suckling piglets1.
3.2 Composition of colostrum and milk
Maternal MA supplementation tended to increase the contents of dry matter (p = 0.08) and fat (p = 0.09) in the milk compared to the CON group (Table 2).
3.3 Plasma metabolites and antioxidant enzyme activities
Maternal MA supplementation significantly reduced the levels of ALT (p = 0.01), AST (p = 0.03), MDA (p < 0.01), and CAT activity (p = 0.01) in the plasma of sows at weaning, as well as the level of MDA in the plasma at farrowing (p = 0.01). Additionally, it tended to increase T-AOC activity in the plasma of sows at farrowing (p = 0.08) (Table 3).
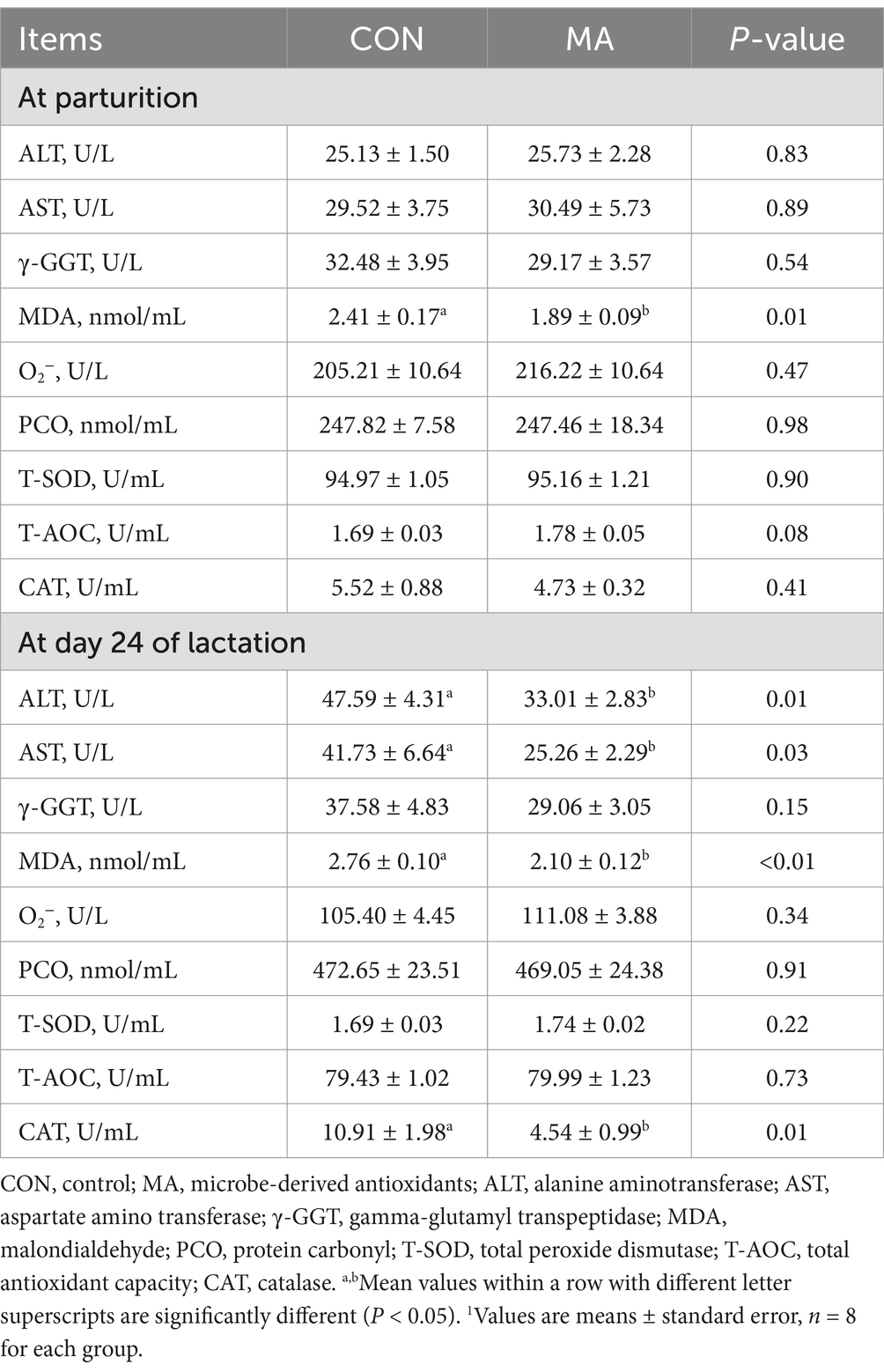
Table 3. Effect of maternal MA supplementation on metabolic and redox status-related parameters in plasma of sows1.
3.4 Short-chain fatty acids
Maternal MA supplementation significantly increased (p < 0.05) butyrate levels and tended to increase (p = 0.09) propionate levels in sow feces at weaning (Figure 1B), but had no significant effect on acetate, propionate, or butyrate levels in feces at farrowing (Figure 1A).
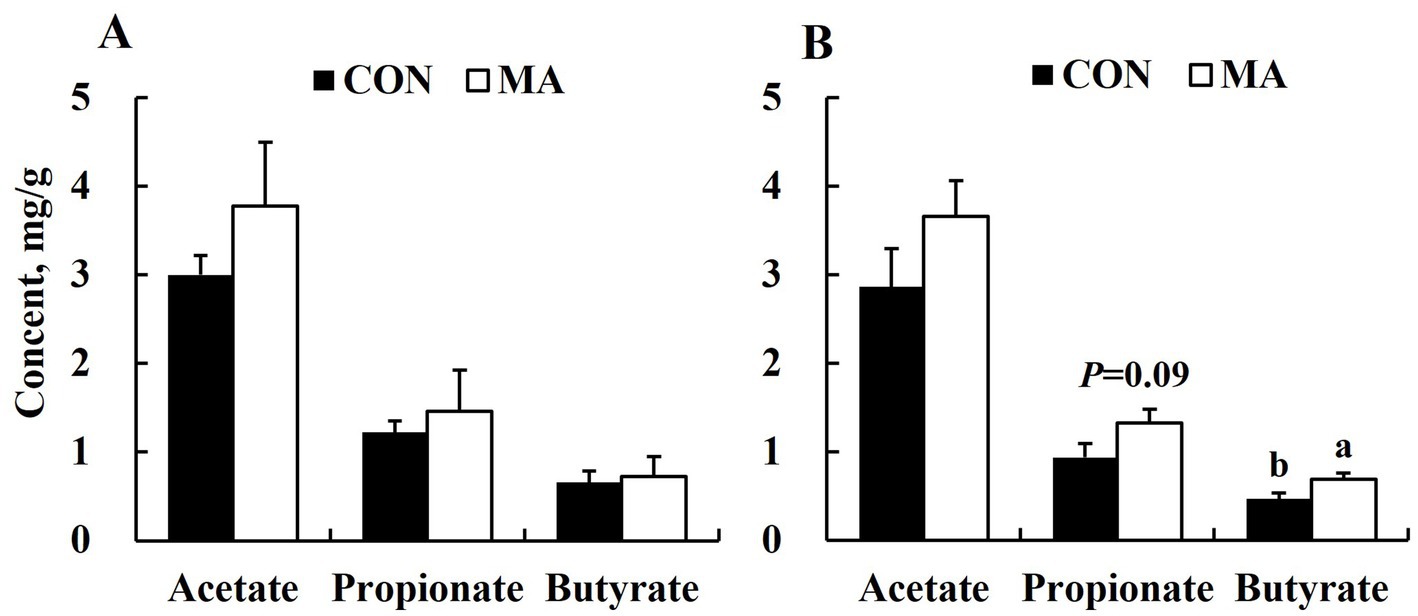
Figure 1. Effects of maternal MA supplementation on short-chain fatty acids of feces at farrowing and weaning. (A) At farrowing. (B) At weaning.
3.5 Microbiota composition
A total of 1800 and 1933 OTUs were assigned at farrowing (Figure 2A) and 2,230 and 2,182 OTUs were assigned at weaning (Figure 2C) in the CON and MA groups, respectively. Compared to the CON group, which had 500 unique OTUs, the MA group had more unique OTUs (633) at farrowing (Figure 2A). However, at d 24 of lactation, the MA group had 645 unique OTUs, which was 48 fewer than the 693 unique OTUs in the CON group (Figure 2C). Maternal MA supplementation had no effect on the α-diversity indices (Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson) at both farrowing and weaning (Supplementary Table S2).
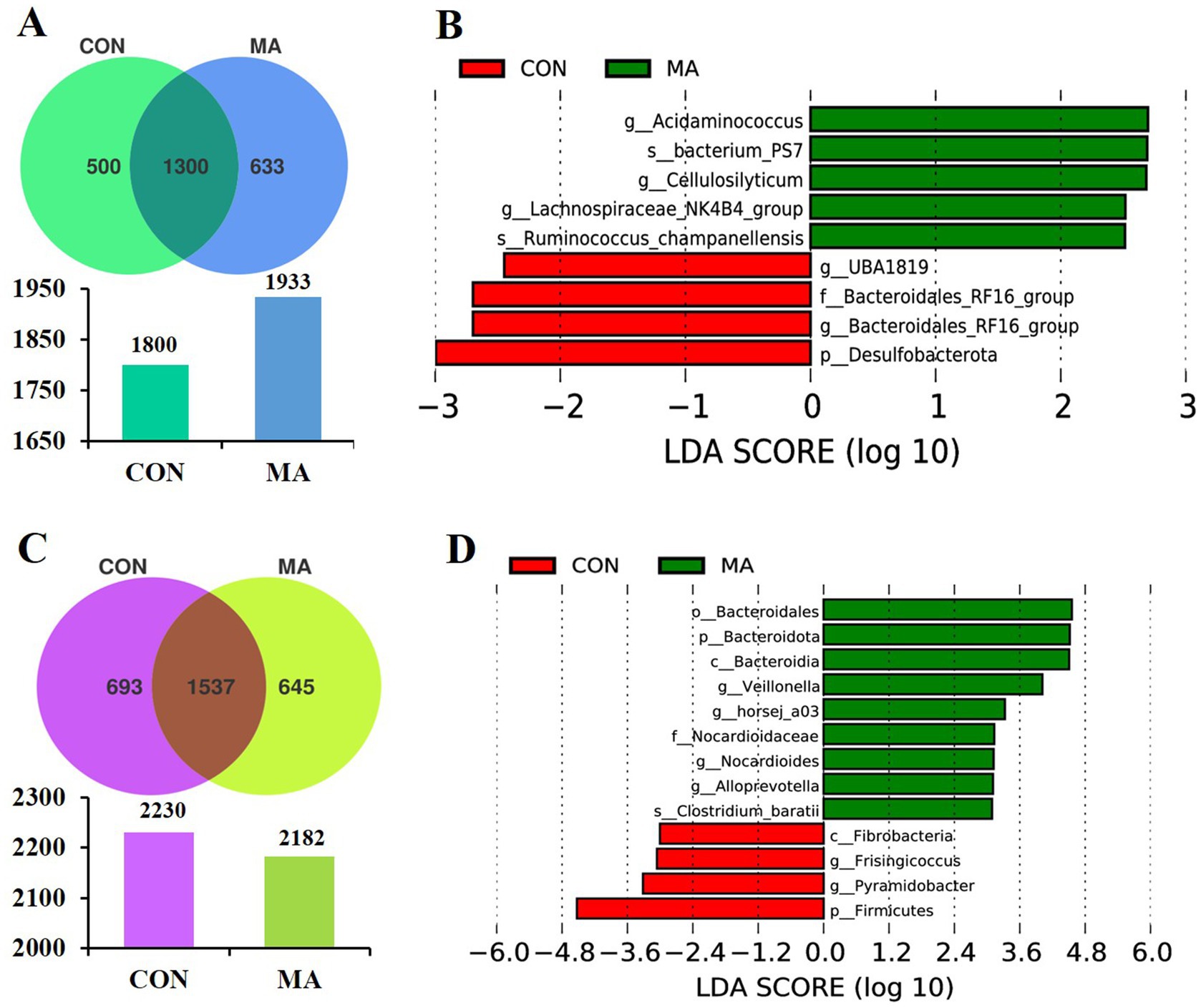
Figure 2. Effects of maternal MA supplementation on fecal microbial characteristics of sows at farrowing and weaning (n = 8). (A) The unique and shared OTUs in each group at farrowing. (B) LDA scores show the significant bacterial differences between the groups at farrowing (p < 0.05, LDA Score > 2.5). (C) The unique and shared OTUs in each group at weaning. (D) LDA scores show the significant bacterial differences between the groups at weaning (p < 0.05, LDA Score > 3.0). LDA, linear discriminant analysis; MA, microbe-derived antioxidants; OTUs, operational taxonomic units.
LEfSe analysis (LDA Score > 2.5) identified 4 species (p_Desulfobacterota, f_Bacteroidales_RF16_group, g_UBA1819, and g_Bacteroidales_RF16_group) and 5 species (g_Acidaminococcus, g_Lachnospiraceae_NK4B4_group 7, g_Cellulosilyticum, s_bacterium_PS and s_Ruminococcus_champanellensis) enriched in the sows of CON and MA groups at farrowing, respectively (Figure 2B). In contrast, at d 24 of lactation, 9 enriched species were identified in the MA group compared to 4 species (p_Firmicutes, c_Fibrobacteria, g_Frisingicoccus, and g_Pyramidobacter) in the CON group (LDA Score > 3.0) (Figure 2D). Among the 9 species, 4 belonged to p_Bacteroidota (p_Bacteroidota, c_Bacteroidia, o_Bacteroidales, and g_Alloprevotella), 2 belonged to o_Propionibacteriales (f_Nocardioidaceae and g_Nocardioides), 2 belonged to p_Firmicutes (g_Veillonella and s_Clostridium_baratii), and g_horsej_a03 belonged to f_Oligosphaeraceae.
3.6 Growth performance of piglets
As shown in Table 4, maternal MA supplementation increased the BW of piglets on d 7 (p = 0.05) and d 21 (p = 0.08) post-weaning, increased the ADG on days 1–7 (p < 0.05) and for the entire period (1–21 d, p = 0.07), also increased the ADFI on days 8–14, 15–21 and across the entire period (p < 0.05).
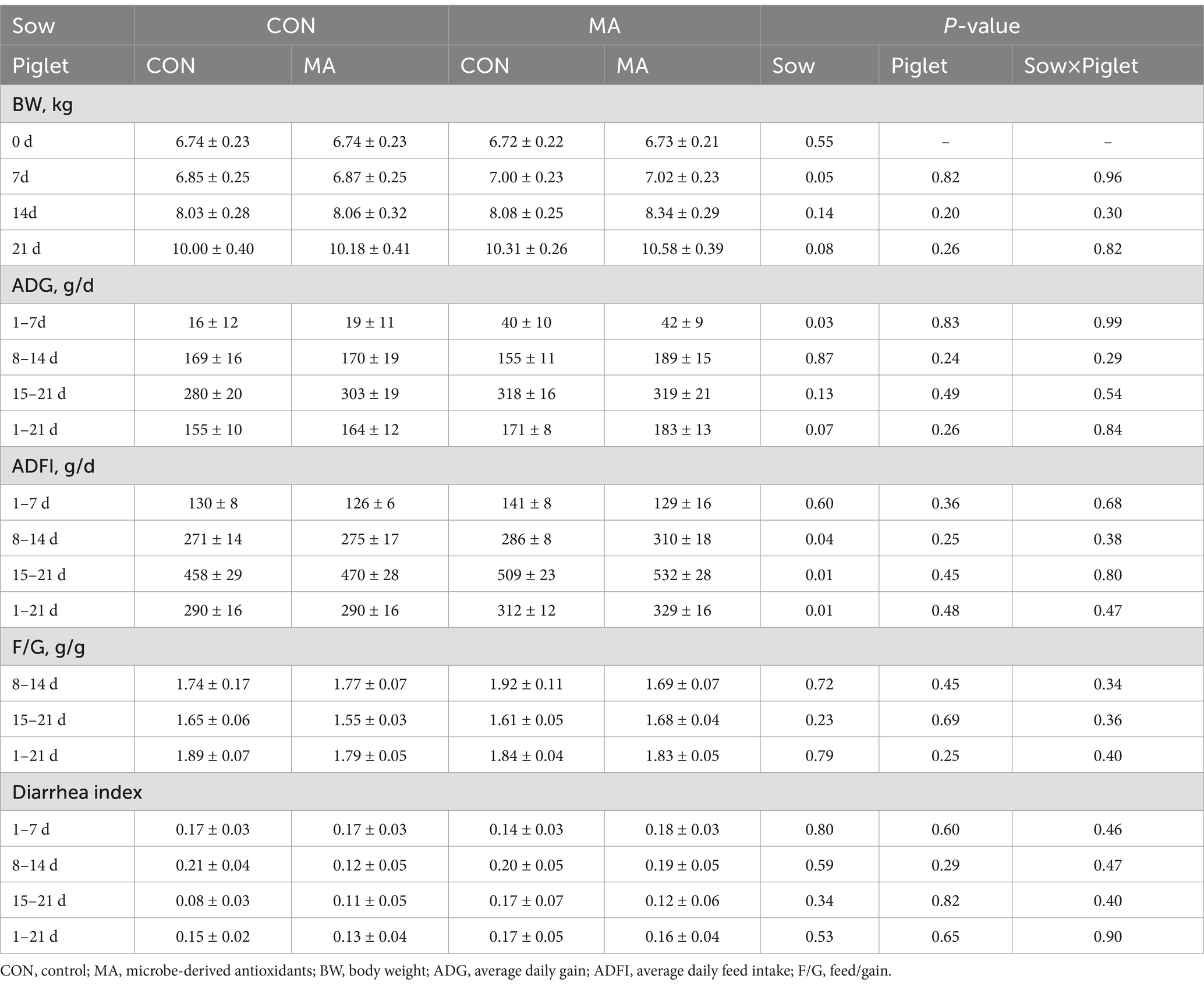
Table 4. Effects of maternal and post-weaning supplementation with MA on the growth performance and diarrhea index in piglets (n = 10).
3.7 Immunological and inflammatory parameters
As shown in Table 5, maternal MA supplementation tended to increase the levels of C3 (p = 0.07) and IL-10 (p = 0.06) and reduce the level of TNF-α (p = 0.07) in the plasma of piglets at weaning. Regardless of post-weaning MA supplementation, maternal MA supplementation significantly increased (p < 0.05) the levels of IgM and IL-10 in the plasma of piglets on d 24 post-weaning. Compared to the CON. CON group, the levels of IgM and IL-10 were markedly increased by 54.5 and 188.5% in the MA. MA group, respectively.
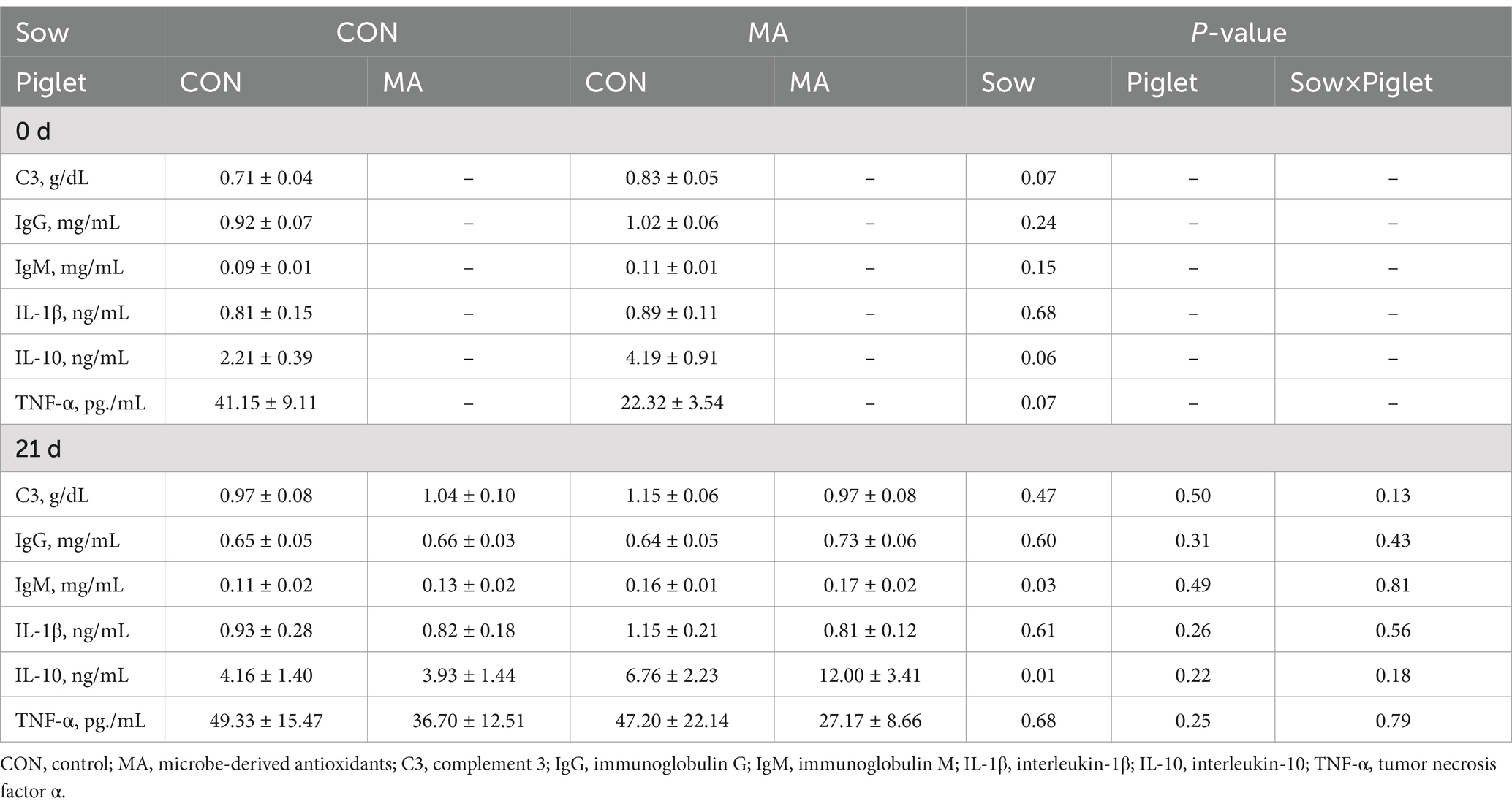
Table 5. Effects of maternal and post-weaning supplementation with MA on inflammatory parameters in plasma of piglets (n = 8).
3.8 Intestinal morphology
Maternal or post-weaning MA supplementation had no significant effect on the VH, CD, VH/CD ratio, or the number of goblet cells in the jejunum of the weaned piglets (Supplementary Table S3).
3.9 Microbial composition of colonic chyme of piglets
A total of 1,204, 1,519, 1,244, and 1,270 OTUs were assigned to the weaned offspring in the CON. CON, CON. MA, MA. CON and MA. MA groups, respectively. The four groups shared 772 OTUs, with the groups of CON. CON, CON. MA, MA. CON and MA. MA having 144, 406, 127, and 158 unique OTUs, respectively (Figure 3A). There were no significant differences in microbial α-diversity indices (Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson) of colonic chyme among the four groups (Supplementary Table S4).
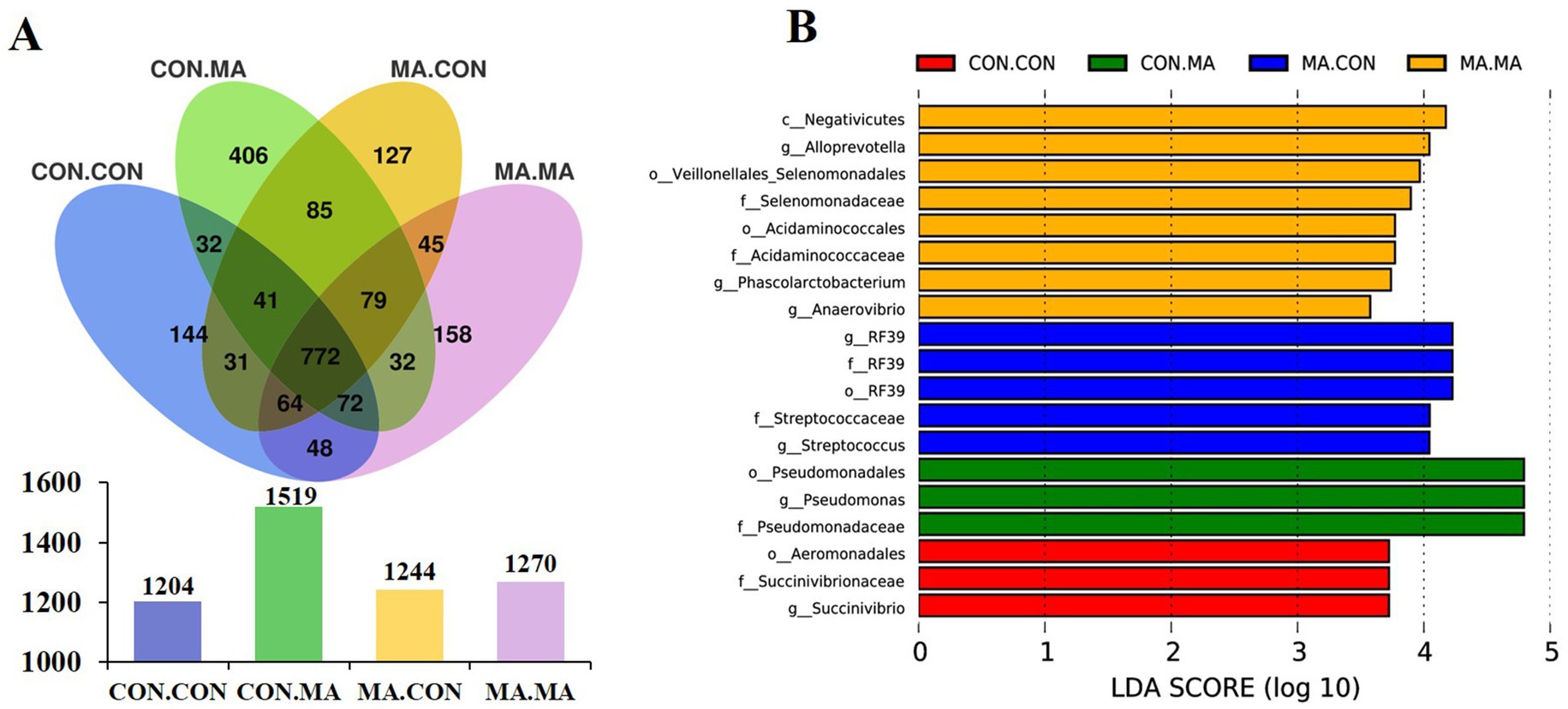
Figure 3. Effects of maternal and post-weaning MA supplementation on colonic chyme microbial characteristics of piglets on day 21 post-weaning (n = 8). (A) The unique and shared OTUs in each group. (B) LDA scores show the significant bacterial differences among the groups (p < 0.05, LDA Score > 3.5). LDA, linear discriminant analysis; MA, microbe-derived antioxidants; OTUs, operational taxonomic units. CON. CON, basal diet for both sows and piglets; MA. CON, 2.0 g MA/kg diet for sows and basal diet for piglets; CON. MA, basal diet for sows and 2.0 g MA/kg diet for piglets; MA. MA, 2.0 g MA/kg diet for both sows and piglets.
LEfSe analysis (LDA Score > 3.5) identified 3 species (o_Aeromonadales, f_Succinivibrionaceae, and g_Succinivibrio), 3 species (o_Pseudomonadales, f_Pseudomonadaceae, and g_Pseudomonas), 5 species (o_RF39, f_RF39, f_Streptococcaceae, g_RF39, and g_Streptococcus), and 8 species enriched in the CON. CON, CON. MA, MA. CON and MA. MA groups, respectively (Figure 3B). Among the 8 species, 7 belonged to c_Negativicutes (c_Negativicutes, o_Veillonellales_Selenomonadales, o_Acidaminococcales, f_Selenomonadaceae, f_Acidaminococcaceae, g_Anaerovibrio, and g_Phascolarctobacterium), while g_Alloprevotella belonged to f_Prevotellaceae.
4 Discussion
In an intensive feeding system, hyperprolific sows experience metabolic burdens during late gestation and lactation, which may lead to oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory responses (13, 26). The oxidative stress is recognized as imbalanced redox status, an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and their elimination by antioxidant system, can lead to chronic inflammation (26). It has been reported that sows exhibited imbalanced redox status during late gestation and lactation, which is associated with lower levels of antioxidant components and total antioxidant capacity (5). To eliminate excessive ROS, the body produces antioxidant enzymes to maintain redox balance, such as T-SOD, CAT, GSH-Px, and nonenzymatic antioxidants. As a mixture of Rosa roxburghii and Sea buckthorn fermented by probiotics, MA contains bioactive ingredients with antioxidant properties, such as polyphenols, isoflavones, and flavones (19, 20). In this study, MA decreased MDA concentrations in the plasma of sows at farrowing and weaning, while tended to increase T-AOC at farrowing. As a byproduct of lipid peroxidation caused by ROS attacking cell membrane lipids, MDA increases with elevated oxidative stress (27). When the antioxidant status is imbalanced, a higher T-AOC indicates a stronger ability to combat oxidative stress by neutralizing excess ROS. Therefore, the higher levels of antioxidant indicators in sows receiving MA diet suggest these sows had greater antioxidant system to resist oxidative damage. Studies have shown that microbial antioxidants can enhance antioxidant capacity of sows during late pregnancy and/or lactation (11, 28). Similarly, maternal supplementation with antioxidant polyphenols (200–300 mg/kg), a class of compounds with multiple phenolic hydroxyl groups (such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, stilbenes, etc.), reduced MDA concentrations and increased the serum activities of GSH-Px and T-AOC (13).
In this study, we found that MA supplementation during late gestation and lactation significantly improved the litter size at weaning, which may be attributed to its beneficial effects on the redox status of sows. The better redox status by MA diet could be one of the factors contributing to the better milk quality, as indicated by the increasing the contents of dry matter and fat of milk from MA-supplemented sows. Similar results have been found that maternal supplementation with polyphenols, a typical antioxidant component, can increase the levels of colostrum immunoglobulins and milk composition, thereby improving pre-weaning survivability (13). Additionally, serum biochemical parameters are important indicators for evaluating the physical status of animals. ALT and AST are enzymes involved in amino acid metabolism and indicators of liver function and nutritional recovery, and their elevation in serum usually indicates liver cell damage, which is often associated with oxidative stress (29). In this study, maternal MA supplementation reduced the activities of ALT and AST in the plasma of sows at weaning, indicating a potential improvement of MA diet on liver function of sows.
The complex community of microbiota, serving as the microbial barrier of the gastrointestinal tract, plays a crucial role in the intestinal functions of pigs, including nutrient absorption, maintenance of dynamic balance of the intestinal barrier, immune regulation, and resistance to pathogen attacks (30). The composition of intestinal microbiota is influenced by multiple factors, such as diet, physiological stage, and health status. During gestation and lactation, changes in the immune system and metabolism of sows are related to the compositional dynamics of microbiota (31). Postbiotics, including enzymes, EPS, bacterial lysates, and cell wall fragments, exert beneficial effects on gut microorganisms (32, 33). In this study, maternal MA supplementation improved the composition of beneficial bacteria in the intestines of sows, such as significantly increasing the abundances of p_Bacteroidota, c_Bacteroidia, o_Bacteroidales, f_Nocardioidaceae, g_Alloprevotella, g_Nocardioides, g_horsej_a03, g_Veillonella and s_Clostridium_baratii at weaning, but had no effect on the α-diversity indices. Among these, Bacteroidota contributes to intestinal metabolism and homeostasis (34). Bacteroidetes is rich in carbohydrate metabolites and polysaccharide-degrading enzymes that breakdown complex nutrients into simpler forms for absorption by the animal’s intestine (35). Alloprevotella, a branch of Prevotella, can break down complex carbohydrates and dietary fibers, producing SCFAs such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate (36). In the weaned piglets, the combination of maternal and post-weaning MA supplementation significantly increased the abundances of c_Negativicutes, o_Veillonellales_Selenomonadales, o_Acidaminococcales, f_Selenomonadaceae, f_Acidaminococcaceae, g_Anaerovibrio, g_Phascolarctobacterium, and g_Alloprevotella. As a gram-negative genus producing SCFAs, Phascolarctobacterium plays a positive role in maintaining intestinal health (37). Some studies have found that a strong correlation between the enrichment of Anaerovibrio and the enhancement of host amino acid metabolism and nucleosides/nucleotides biosynthesis (38).
The intestinal microbiome provides an extensive repertoire of molecules and metabolites that influence host health. Among these molecules, SCFAs, derived from bacteria-dependent hydrolysis of fibers, have attracted considerable attention because of their role in host health (39). As products of the fermentation of plant polysaccharides by intestinal microbiota, SCFAs serve as important fuels for intestinal epithelial cells, enhancing gut barrier functions as well as host metabolism (40). In this study, maternal MA supplementation increased the concentrations of butyrate and propionate in the sows on d 24 of lactation. Butyrate modulates the immune response by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines, while supports intestinal epithelial cell proliferation as the primary energy source (40, 41). As the primary substrate for liver gluconeogenesis, propionate influences carbohydrate metabolism, exhibits a statin-like effect by inhibiting cholesterol synthesis pathways, and demonstrates anti-inflammatory activity comparable to butyrate (42).
Weaning stress often accompanies with serious diarrhea, infection and poor growth performance due to the immature immune system during early life of pigs (43). Previous studies have shown that supplementing with inactivated (heat-killed) Lactobacillus can improve growth performance and feed efficiency, reduce the occurrence of diarrhea, and positively influence gut microbiota (44–46). In this study, post-weaning MA supplementation did not significantly improve diarrhea index of piglets, which is consistent with the results of intestinal morphology. However, weaned piglets from sows receiving MA diet exhibited relatively faster growth rate, which could be perhaps ascribed to the optimal redox status and maternal transfer of probiotic bacteria to their offspring. In this study, we found that the enriched g_Alloprevotella in sow feces at weaning was also enriched in the colonic chyme of piglets at d 24 post-weaning. Likewise, previous studies have shown that maternal supplementation with yeast-derived postbiotics positively affects the gut microbiome and immunological parameters of offspring (16, 47).
The positive effect of maternal MA supplementation on offspring piglets is also reflected by its beneficial effect on the immunity-related parameters of offspring. In this study, maternal MA supplementation tended to increase the levels of C3 and IL-10, reduce TNF-α at weaning, and increase IgM and IL-10 at d 24 post-weaning. It has been reported that C3 participates in the clearance of microorganisms and mediates the occurrence of inflammation (48). As an anti-inflammatory cytokine produced by inflammatory cells, IL-10 is known to prevent excessive inflammatory responses at the maternal-fetal interface (49). As a pro-inflammatory cytokine, TNF-α had been found to be decreased in MA-supplemented mouse (22). In RAW264.7 cells, MA also significantly down-regulated the level of TNF-α together with the lower accumulation of ROS (23). Similarly, several heat-killed Lactobacillus probiotics have shown immunomodulatory abilities by enhancing anti-inflammatory cytokines and suppressing oxidative stress in both in vitro and in vivo experimental models (50). It can be seen that the enhancement of immune function in weaned piglets should be closely related to the maternal supplementation of MA to enhance their own immune function.
5 Conclusion
In summary, the present results demonstrated that maternal MA supplementation during late gestation and lactation increased the number of weaned piglets, which may be associated with the improved redox status and milk composition of sows. Additionally, maternal MA supplementation increased the growth rate of post-weaning piglets, which is likely related to the improved immunological parameters and gut microbiome of both sows and weaned piglets.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Sichuan Agricultural University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
JT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YW: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. QZ: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. ZF: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. YL: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. SX: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. BF: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. XJ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. DW: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. LC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the foundations from Research Center of Microbial Fermentation Metabolites and Cell health of Chuangbo Biotechnology Inc. And Sichuan Agricultural University (Grant2022), Sichuan Science and Technology Program (No. 2021ZDZX0011), and the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System (No. CARS-35). The authors declare that this study received funding from Chuangbo Biotechnology Inc. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2025.1574259/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Newbern, D, and Freemark, M. Placental hormones and the control of maternal metabolism and fetal growth. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. (2011) 18:409–16. doi: 10.1097/med.0b013e32834c800d
2. Zhou, P, Zhao, Y, Zhang, P, Li, Y, Gui, TT, Wang, J, et al. Microbial mechanistic insight into the role of inulin in improving maternal health in a pregnant sow model. Front Microbiol. (2017) 8:2242. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02242
3. Kaiser, M, Jacobson, M, Andersen, PH, Bækbo, P, Cerón, JJ, Dahl, J, et al. Inflammatory markers before and after farrowing in healthy sows and in sows affected with postpartum dysgalactia syndrome. BMC Vet Res. (2018) 14:83. doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1382-7
4. Cheng, CS, Wei, HK, Yu, HC, Xu, CH, Jiang, SW, and Peng, J. Metabolic syndrome during perinatal period in sows and the link with gut microbiota and metabolites. Front Microbiol. (2018) 9:1989. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01989
5. Berchieri-Ronchi, CB, Kim, SW, Zhao, Y, Correa, CR, Yeum, KJ, and Ferreira, ALA. Oxidative stress status of highly prolific sows during gestation and lactation. Animal. (2011) 5:1774–9. doi: 10.1017/S1751731111000772
6. Boudry, G, Péron, V, Huerou-Luron, IL, Lallès, JP, and Sève, B. Weaning induces both transient and long-lasting modifications of absorptive, secretory, and barrier properties of piglet intestine. J Nutr. (2004) 134:2256–62. doi: 10.1093/jn/134.9.2256
7. Hu, CH, Xiao, K, Luan, ZS, and Song, J. Early weaning increases intestinal permeability, alters expression of cytokine and tight junction proteins, and activates mitogen-activated protein kinases in pigs. J Anim Sci. (2013) 91:1094–101. doi: 10.2527/jas.2012-5796
8. Huang, SB, Wu, ZF, Huang, ZH, Hao, XY, Zhang, LM, Hu, CJ, et al. Maternal supply of cysteamine alleviates oxidative stress and enhances angiogenesis in porcine placenta. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. (2021) 12:91. doi: 10.1186/s40104-021-00609-8
9. Lan, RX, and Kim, I. Enterococcus faecium supplementation in sows during gestation and lactation improves the performance of sucking piglets. Vet Med Sci. (2020) 6:92–9. doi: 10.1002/vms3.215
10. Ali, MS, Lee, E, Hsu, WH, Suk, K, Sayem, SAJ, Ullah, HMA, et al. Probiotics and postbiotics as an alternative to antibiotics: an emphasis on pigs. Pathogens. (2023) 12:874. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12070874
11. Zhang, QQ, Li, J, Cao, M, Li, Y, Zhuo, Y, Fang, ZF, et al. Dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis PB6 improves sow reproductive performance and reduces piglet birth intervals. Anim Nutr. (2020) 6:278–87. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2020.04.002
12. Luo, Z, Xu, X, Zhao, S, Sho, T, Luo, WL, Zhang, J, et al. Inclusion of microbe-derived antioxidant during pregnancy and lactation attenuates high-fat diet-induced hepatic oxidative stress, lipid disorders, and NLRP3 inflammasome in mother rats and offspring. Food Nutr Res. (2019) 63:3504. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v63.3504
13. Wang, XR, Jiang, GT, Kebreab, E, Yu, QF, Li, JH, Zhang, X, et al. Effects of dietary grape seed polyphenols supplementation during late gestation and lactation on antioxidant status in serum and immunoglobulin content in colostrum of multiparous sows. J Anim Sci. (2019) 97:2515–23. doi: 10.1093/jas/skz128
14. Deshpande, G, Athalye-Jape, G, and Patole, S. Para-probiotics for preterm neonates-the next frontier. Nutrients. (2018) 10:871. doi: 10.3390/nu10070871
15. Malashree, L, Angadi, V, Yadav, KS, and Prabha, R. “Postbiotics”-one step ahead probiotics. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci. (2019) 8:2049–53. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2019.801.214
16. Xu, SY, Jia, XL, Liu, YL, Pan, XJ, Chang, JL, Wei, WY, et al. Effects of yeast-derived postbiotic supplementation in late gestation and lactation diets on performance, milk quality, and immune function in lactating sows. J Anim Sci. (2023) 101:skad201. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad201
17. Xu, X, Duarte, ME, and Kim, SW. Postbiotic effects of Lactobacillus fermentate on intestinal health, mucosa-associated microbiota, and growth efficiency of nursery pigs challenged with F18+ Escherichia coli. J Anim Sci. (2022) 100:skac210. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac210
18. Sun, DF, Tong, WF, Han, SC, Wu, MJ, Li, P, Li, YG, et al. Effects of dietary supplementation with Lactobacillus reuteri postbiotics on growth performance, intestinal flora structure and plasma metabolome of weaned piglets. Animals. (2025) 15:204. doi: 10.3390/ani15020204
19. Cai, X, Chen, XL, Yang, F, Xu, JX, Gu, J, and Zhang, C. A preliminary research of antioxidant capacity by micro-derived antioxidants in vitro. Biotechnology. (2011) 21:84–7. doi: 10.1007/s11518-011-5154-1
20. Luo, Z, Gao, QY, Zhang, HC, Zhang, YT, Zhou, SJ, Zhang, J, et al. Microbe-derived antioxidants attenuate cobalt chloride-induced mitochondrial function, autophagy and BNIP3-dependent mitophagy pathways in BRL3A cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2022) 232:113219. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113219
21. Zhu, LH, Zhao, KL, Chen, XL, and Xu, JX. Impact of weaning and an antioxidant blend on intestinal barrier function and antioxidant status in pigs. J Anim Sci. (2012) 90:2581–9. doi: 10.2527/jas.2012-4444
22. Gao, QY, Luo, Z, Ma, S, Yu, CB, Shen, C, Xu, WN, et al. Microbe-derived antioxidants alleviate liver and adipose tissue lipid disorders and metabolic inflammation induced by high fat diet in mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:3269. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043269
23. Shen, C, Luo, Z, Ma, S, Yu, CB, Gao, QY, Zhang, MJ, et al. Microbe-derived antioxidants reduce lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses by activating the Nrf2 pathway to inhibit the ROS/NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:12477. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012477
24. Tang, JY, Li, WT, Zhou, Q, Fang, ZF, Lin, Y, Xu, SY, et al. Effect of heating, microbial fermentation, and enzymatic hydrolysis of soybean meal on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and intestinal microbiota of weaned piglets. J Anim Sci. (2023) 101:skad384. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad384
26. Hussain, T, Tan, B, Yin, YL, Blachier, F, Tossou, MCB, and Rahu, N. Oxidative stress and inflammation: what polyphenols can do for us? Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2016) 2016:7432797. doi: 10.1155/2016/7432797
27. Ji, Y, Gao, Y, Chen, H, Yin, Y, and Zhang, WZ. Indole-3-acetic acid alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice via attenuation of hepatic lipogenesis, and oxidative and inflammatory stress. Nutrients. (2019) 11:2062. doi: 10.3390/nu11092062
28. Tan, CQ, Li, JY, Ji, YC, Yang, YY, Zhao, XC, Chen, MX, et al. Effects of dietary supplementation of different amounts of yeast extract on oxidative stress, milk components, and productive performance of sows. Anim Feed Sci Technol. (2021) 274:114648. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2020.114648
29. Lee, J, Kwon, CHD, Kim, JM, Shin, M, and Joh, J. Effect of early enteral nutrition after hepatectomy in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. (2012) 16:129–33. doi: 10.14701/kjhbps.2012.16.4.129
30. He, W, Gao, YN, Guo, ZQ, Yang, Z, Wang, XX, Liu, HG, et al. Effects of fermented wheat bran and yeast culture on growth performance, immunity, and intestinal microflora in growing-finishing pigs. J Anim Sci. (2021) 99:skab308. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab308
31. Kong, XF, Ji, YJ, Li, HW, Zhu, Q, Blachier, F, Geng, MM, et al. Colonic luminal microbiota and bacterial metabolite composition in pregnant Huanjiang minipigs: effects of food composition at different times of pregnancy. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:37224. doi: 10.1038/srep37224
32. Tsilingiri, K, and Rescigno, M. Postbiotics: what else? Benef Microbes. (2013) 4:101–7. doi: 10.3920/BM2012.0046
33. Żółkiewicz, J, Marzec, A, Ruszczyński, M, and Feleszko1, W. Postbiotics - a step beyond pre-and probiotics. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2189. doi: 10.3390/nu12082189
34. Lapébie, P, Lombard, V, Drula, E, Terrapon, N, and Henrissat, B. Bacteroidetes use thousands of enzyme combinations to break down glycans. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:2043. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10068-5
35. Xu, XX, Dai, M, Lao, F, Chen, F, Hu, XS, Liu, YP, et al. Effect of glucoraphanin from broccoli seeds on lipid levels and gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice. J Funct Foods. (2020) 68:103858. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.103858
36. Precup, G, and Vodnar, DC. Gut Prevotella as a possible biomarker of diet and its eubiotic versus dysbiotic roles: a comprehensive literature review. Br J Nutr. (2019) 122:131–40. doi: 10.1017/S0007114519000680
37. Wu, FF, Guo, XF, Zhang, JC, Zhang, M, Ou, ZH, and Peng, YZ. Phascolarctobacterium faecium abundant colonization in human gastrointestinal tract. Exp Ther Med. (2017) 14:3122–6. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4878
38. Chen, HC, Cheng, YC, Hsieh, ML, Lin, PJ, Wissel, EF, Steward, T, et al. Gut microbiota modulation in cardiac cell therapy with immunosuppression in a nonhuman primate ischemia/reperfusion model. NPJ Regen Med. (2025) 10:2. doi: 10.1038/s41536-025-00390-6
39. Martin-Gallausiaux, C, Marinelli, L, Blottière, HM, Larraufie, P, and Lapaque, N. SCFA: mechanisms and functional importance in the gut. Proc Nutr Soc. (2021) 80:37–49. doi: 10.1017/S0029665120006916
40. D’Souza, WN, Douangpanya, J, Mu, S, Jaeckel, P, Zhang, M, Maxwell, JR, et al. Differing roles for short chain fatty acids and GPR43 agonism in the regulation of intestinal barrier function and immune responses. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0180190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180190
41. Donohoe, DR, Collins, LB, Wali, A, Bigler, R, Sun, W, and Bultman, SJ. The Warburg effect dictates the mechanism of butyrate-mediated histone acetylation and cell proliferation. Mol Cell. (2012) 48:612–26. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.08.033
42. Tedelind, S, Westberg, F, Kjerrulf, M, and Vidal, A. Anti-inflammatory properties of the short-chain fatty acids acetate and propionate: a study with relevance to inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. (2007) 13:2826–32. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i20.2826
43. Han, M, Song, PX, Huang, C, Rezaei, A, Farrar, S, Brown, MA, et al. Dietary grape seed proanthocyanidins (GSPs) improve weaned intestinal microbiota and mucosal barrier using a piglet model. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:80313–26. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13450
44. Kang, J, Lee, JJ, Cho, JH, Choe, J, Kyoung, H, Kim, SH, et al. Effects of dietary inactivated probiotics on growth performance and immune responses of weaned pigs. J Anim Sci Technol. (2021) 63:520–30. doi: 10.5187/jast.2021.e44
45. Tartrakoon, W, Charoensook, R, Incharoen, T, Numthuam, S, Pechrkong, T, Onoda, S, et al. Effects of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum L-137 supplementation on growth performance, blood profiles, intestinal morphology, and immune gene expression in pigs. Vet Sci. (2023) 10:87. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10020087
46. Liu, H, Ji, HF, Zhang, DY, Wang, SX, Wang, J, Shan, DC, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus brevis preparation on growth performance, fecal microflora and serum profile in weaned pigs. Livest Sci. (2015) 178:251–4. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2015.06.002
47. Chang, JL, Jia, XL, Liu, YL, Jiang, XM, Che, LQ, Lin, Y, et al. Microbial mechanistic insight into the role of yeast-derived postbiotics in improving sow reproductive performance in late gestation and lactation sows. Animals. (2024) 14:162. doi: 10.3390/ani14010162
48. Ehrenstein, MR, and Notley, CA. The importance of natural IgM: scavenger, protector and regulator. Nat Rev Immunol. (2010) 10:778–86. doi: 10.1038/nri2849
49. Kalkunte, S, Nevers, T, Norris, WE, and Sharma, S. Vascular IL-10: a protective role in preeclampsia. J Reprod Immunol. (2011) 88:165–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2011.01.009
Keywords: sows, piglets, reproductive performance, antioxidant, microorganisms
Citation: Tang J, Wang Y, Zhou Q, Fang Z, Lin Y, Xu S, Feng B, Zhuo Y, Jiang X, Zhao H, Wu D and Che L (2025) Effects of maternal and post-weaning supplementation with microbe-derived antioxidants on sow and piglet performance, oxidative status, and gut microbiota. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1574259. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1574259
Edited by:
Sadarman Sadarman, State Islamic University of Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau, IndonesiaReviewed by:
Yong Su, Nanjing Agricultural University, ChinaXihong Zhou, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), China
Moyosore Joseph Adegbeye, University of Africa, Bayelsa State, Nigeria
Copyright © 2025 Tang, Wang, Zhou, Fang, Lin, Xu, Feng, Zhuo, Jiang, Zhao, Wu and Che. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lianqiang Che, Q2hlLmxpYW5xaWFuZ0BzaWNhdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jiayong Tang
Jiayong Tang Yifan Wang
Yifan Wang Qiang Zhou
Qiang Zhou Zhengfeng Fang
Zhengfeng Fang Yan Lin
Yan Lin Shengyu Xu
Shengyu Xu Bin Feng
Bin Feng Yong Zhuo
Yong Zhuo De Wu
De Wu Lianqiang Che
Lianqiang Che