- Lee-Klingemann Canine Cancer Research Foundation, Boston, MA, United States
Immunotherapy for humans has enjoyed a recent boost of treatment options that, however, has not translated into the veterinary field. Developments like monoclonal antibodies against immune checkpoint inhibitors and tumor-specific CAR-T cells have broadened treatment options for human cancer patients but the canine space has not benefited from those advancements. These novel treatments are expensive to develop for the canine market and are not necessarily promising a significant financial return for the pharmaceutical industry. Hence the question is whether there are immunotherapies that work for humans and that also have some cross-species (xenogeneic) activity in dogs, but at the same time have only minimal side effects and are affordably priced. Can such an approach be considered at all assuming that the disparity could result in an immediate rejection of the administered ‘product’ with all the potential side effects? Maybe this assumption is not necessarily founded on solid data and this brief review attempts to summarize of what is actually known on the treatment of canine cancers with human immuno-therapeutics.
Introduction
Cancer is the most common cause of death in dogs with an estimated incidence of 30–40% and increasing with age. Almost half of dogs over the age of 10 years will develop cancer and aggressive treatments (chemotherapy and radiation) are less well tolerated at that age group (1, 2).
Immunotherapy of cancer has seen some encouraging developments for humans but this has not translated to the same extent into progress for dogs. Hampel et al. (3) recently reviewed the current options and potential opportunities. Treatments like CAR-T cells, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and checkpoint inhibitors for canines are in their infancies and there is concern that they will ever find an accepted place in the spectrum of therapies for canine cancer (4, 5). Those treatments are expensive because of their more complex manufacturing process and lengthy path to regulatory approval. Most dog owners also have limitations as to what they can and will pay for the treatment of their beloved dog. Only some 10–15% of dog owners in the US carry health insurance for their pet and it cannot be assumed that insurance companies will pay for those more advanced and often experimental treatments. Likewise, pharmaceutical companies are not particularly motivated to invest in the development of biologics that will not promise a significant financial return. Hence immunotherapy for dogs with cancer has made limited progress (6).
There is, however, a clear need for immuno-therapeutics that are well tolerated by dogs as cancer is so much more prevalent in older dogs that tolerate chemotherapy and radiation less well (7). In fact, a recent survey suggested that about two-thirds of dog owners would not elect to treat their dog with chemotherapy or radiation due to the negative impact on their quality of life (8). Considering the limited spectrum of available immuno-therapeutics for dogs, the question is whether there are immune-active biologics that have been or are being used for human cancer treatment and that—because of crossreactivity—could also be used to treat cancer in dogs? In addition of the need for crossreactivity, there is also the concern that the xenogeneic cells, cytokines and biologics will induce a rejection response with neutralizing antibodies and/or xenoreactive immune cells. Such concerns go back to the data on the infusion of human serum albumin into dogs for a protein losing enteropathy (9, 10). It appears though that infusions of 5% albumin had less side effects than 25% albumin preparations. Also, a single infusion was relatively safe with anti-HLA antibodies forming only after one to two weeks. A reaction occurs mostly with the second and following infusions although it needs to be considered that about 8–10% of dogs already have antibodies against human serum albumin (11).
There are not a lot of data that would tell us how often a more severe immune reaction occurs especially in situations where there is high structural homology between human and canine proteins. Moreover, canine cancer patients, like humans, have a compromised immune reactivity which may allow for the human therapeutic to have some effect before it is “rejected.” The Toronto group has shown that the infusion of allogeneic NK cells into (human) patients with lymphoma or myeloma did not trigger HLA-antibodies in any of the 12 patients and allo-reactive T-lymphocytes (as detected in a mixed lymphocyte culture) were formed in only half of the patients (12). Even if there is a humoral and/or cellular anti-human immune response after systemic administration, could the local (intra-tumor) injection of the therapeutic be an effective alternative simply because of the higher effector concentration at the tumor site?
The objective of this review is to summarize immunotherapeutics developed for humans that have been given to dogs because of their potential crossreactivity. This review does not attempt to cover the entire field of immunotherapy for dogs as this has been done comprehensively by Hampel et al. (3).
Human monoclonal antibodies
With protein-based biologics like antibodies, there are two potential considerations: First, is the canine target molecule at the sequence level sufficiently identical to the human equivalent for the antibody to recognize and bind the canine target antigen? Secondly, will the canine immune system mount an immune response against the human (xenogenic) protein that will not only result in the loss of activity but could also induce some side effects.
As an example for the first consideration: the human anti-CD20 antibody (RituximabR) is effective for the treatment of human lymphoma but a single amino acid difference in the CD20 binding region prevents the binding of RituximabR to the canine malignant B-cells (Figure 1) (13).
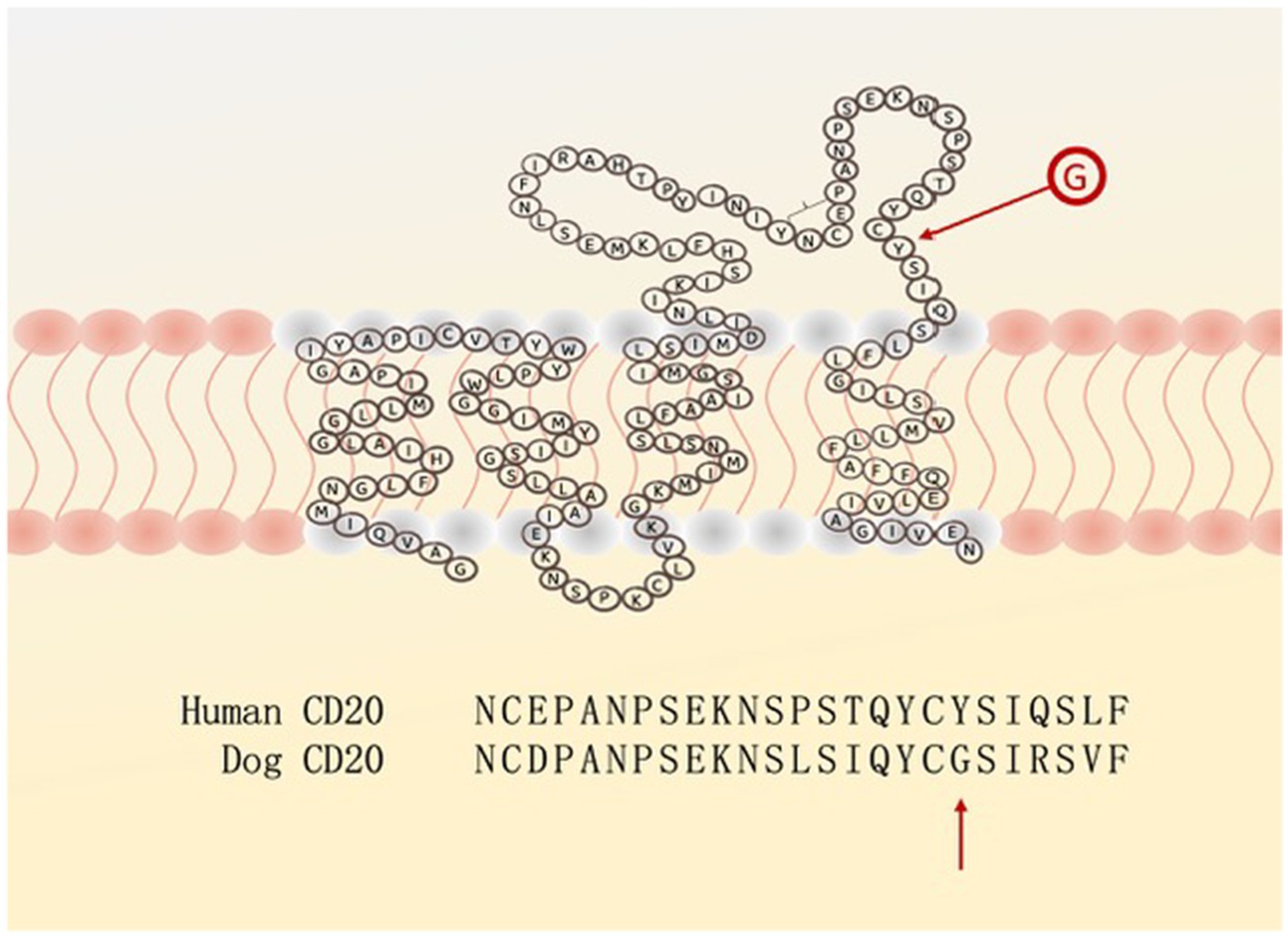
Figure 1. The extra-cellular loop of the CD20 surface antigen on human and canine B-cells differs in (only) one amino acid: Y (tyrosine) versus G (glycine), preventing rituximab from having its blocking activity.
Pantelyushin et al. (14) tested seven FDA approved human immune checkpoint inhibitors targeting CTLA-4 or PD/PD-L1 against various canine tumor cell lines. Only one of the antibodies (AtezolizumabR) recognized the canine PD-L1 equivalent and showed some blocking effect in vitro of canine PBMC. Its potential clinical relevance for treatment in dogs was not further explored.
One of the main mechanisms of action for mAbs is through antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) which requires an intact Fc-receptor on immune effector cells. The primary effector cells of ADCC—NK cells—are still relatively poorly described in dogs (3, 15, 16). It is also largely unknown which of the four IgG subclasses effectively mediate ADCC in dogs. Studies by Mizuno et al. (17) and Hullsiek et al. (18) have shown that the human NK cell line NK-92 can be transfected with a canine Fc-receptor which will allow to test canine mAb candidates for their target specificity and ADCC. Those observations also confirm that human perforin and granzymes are cross-reactive and kill canine cancer cells (19).
Even if there is some reasonable evidence for a human mAb to be cross-reactive with a specific canine cancer, the costs for such an antibody may be a significant issue for dog owners. For example, GilvetmabR, a mAb against (canine) PD-1 was recently conditionally approved for treatment of melanoma and mast cell tumors in dogs. At a price of $ 1,200–1,500 per infusion (depending on the weight of the dog and the overhead charges of the practice/hospital) and the recommendation for 10 infusions, treatment costs can be substantial.
Human T-lymphocytes
Isolating T-cells from canine blood, expanding them to significant numbers and ultimately making them tumor-specific, is a formidable challenge that so far has not translated into clinical practice. The alternative, to use T-cells from humans, has not been explored out of concern of graft-versus-host and host-versus-graft reactions. In addition, the lack of known targetable surface antigens on canine cancer cells has also stalled this potential option.
Some 30 years ago, the Philadelphia group used a broadly human cytotoxic T-cell line (TALL-104) to treat dogs with advanced cancers including osteosarcoma and histiocytosis (20, 21). In the initial trial, the cells were administered as intravenous bolus over 30 min, on alternate days for 2 weeks followed by a once weekly infusion for 3 weeks (total of nine injections) (20). Since the dogs developed anti-human antibodies after about 2 weeks into TALL-104 treatment, a follow up trial treated dogs with a modified protocol, which consisted of daily cell infusions for five consecutive days followed by monthly cell boosts (21). PCR amplification of the mini-satellite region YNZ.22 could confirm that the TALL-104 cells stayed in the dogs’ circulation for a few days after infusion.
Despite the immune response against TALL-104 cells, their effect on canine cancer was encouraging with 7/19 dogs showing some tumor regression and one dog having a complete remission. A graft-versus host reaction was not observed and none of the dogs experienced any significant side effect after the infusion. The main reason why the TALL-104 treatment did not get developed further (even for human treatment) was based on the fact that the cells were somewhat difficult to maintain in culture and to expand to numbers sufficient for multiple infusions. The study however taught us that human immune cells can be infused into dogs without any significant side effects and that some anti-tumor effect is achievable.
CAR-T cell therapy has enriched the treatment spectrum for human cancer patients particularly with lymphoma and myeloma. The CAR-T cell field for canine cancer treatment has been slow to develop largely due to a lack of targetable tumor antigens and low efficacy (5, 22). This has led investigators to explore human CAR constructs that are cross-reactive with canine antigens (14). Zhang et al. (23) reported preliminary results on canine CAR-T cells recognizing the human B7-H3 molecule. The CAR was engineered based on the sequence of the human mAb MGA271 (enoblituzumab) which the investigators confirmed to be cross-reactive with canine B7-H3. The cells were expanded in the presence of human recombinant IL-2. Two healthy beagles received lymphodepleting chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide and fludarabine) followed by infusions of B7-H4 specific CAR cells with no significant side effects.
The Flint Animal Cancer Center generated a dual CAR comprised of the human B7-H3 and the human CXCR2 sequence for canine T-cells to improve homing of those cells to osteosarcoma sites (24). For the ex vivo expansion and activation, the investigators used the human cytokines IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15 and noted that those human cytokines resulted in better ex vivo CAR-T cell generation and function than the corresponding canine cytokines.
Human natural killer cells
In contrast to human natural killer (NK) cells which can be quite reliably identified as CD3 negative cells expressing the CD56 antigen, canine NK cells are not as well characterized and lack specific antigens (3, 4). The UC Davis group could characterize a subpopulation of canine lymphocytes that expresses CD5 as having NK-like activity and they were able to isolate and expand those cells from PMBC (15, 25). Clinical trials will have to show whether those cells provide an effective treatment for canine cancers. Alternatively, could there be a place for human NK cell lines, that have been immortalized and can be grown up in unlimited quantities? Although several human NK cell lines have been established (26), only NK-92 cells have consistent and broad cytotoxicity and have been given to (human) cancer patients [reviewed in Klingemann (27)]. The cells have also been genetically engineered to express a high affinity Fc-receptor, able to serve as effector cells for mAbs and with IL-2 to make their expansion independent of exogenous IL-2 (27, 28). Various CAR expressing NK-92 cell variants have been developed targeting PD-L1 and Her-2 and clinical trials in human cancer patients have been completed or are ongoing with those engineered cells (27).
To further test the extent and relevance of cross-species reactivity, NK-92 cells engineered with a murine CD20 CAR were injected into the lymphoma of immune-competent C57BL/6 mice which resulted in significantly longer survival compared to the control group (29). Likewise intra-tumor injection of (murine) Her2 + expressing CAR NK-92 cells into immunocompetent mice with glioma (GL261) resulted in tumor control and greatly extended their survival (30). Importantly, in both studies, the intra-tumor injection of CAR-specific NK-92 cells was able to induce a vaccine-like effect: when NK-92 treated mice were re-challenged with the same cancer cells after several weeks at a different body site, no tumor growth occurred.
NK-92 cells have cytotoxic activity against various canine cancer cell lines (Figure 2). Lysate generated from NK-92 cells generated by repeat freeze/thawing not only contains perforin/granzymes but also the entire spectrum of immune-active cytokines and chemokines able to control canine cancer cells (19).
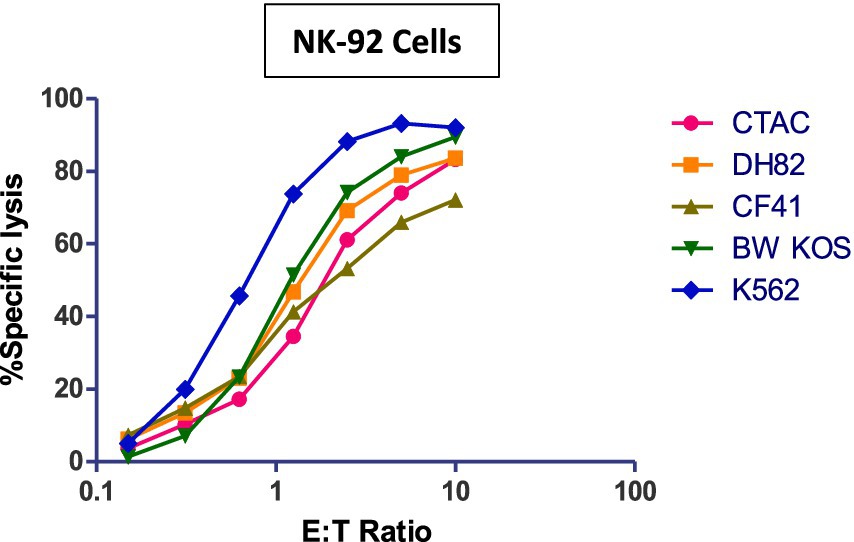
Figure 2. Cytotoxicity (4 h) of NK-92 cells against various canine tumor cell lines. Human K562 cells serve as positive control. Canine cell lines; CTAC: thyroid adenocarcinoma, DH82: malignant histiocytosis, CF41: mammary carcinoma, BW KOS: osteosarcoma.
Human cytokines
Interleukin-2
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) has been available in recombinant form for some time and has been given systemically or via intra-tumor injection to human cancer patients with documented efficacy. Since there is about 80% sequence homology between human and canine IL-2, investigators have administered the human version to dogs (31, 32). Human IL-2—as a liposomal preparation and with human serum albumin (HAS) as a solvent-was given via inhalation to seven dogs with pulmonary metastases and two dogs with lung cancer (33). Responses were encouraging with 2/4 dogs with pulmonary metastases from osteosarcoma having complete remissions lasting for more than 12 and 20 months, respectively. Those therapeutic effects were seen despite the fact that antibodies against human IL-2 and human serum albumin were detected in all dogs. Ziekman et al. (32) reported on 10 dogs with non-resectable cutaneous mastocytoma (three dogs with metastases) who were given one intra-tumor injection of 4.5 million IU of human IL-2 (AldesleukinR). Five of seven animals with non-metastatic disease either had a partial or a complete response. Importantly, no significant side effects were reported. The same group also reported some responses in dogs with transmissible venereal tumors (TVT) after intra- and peri-tumoral injection of 2.0 million IU of human IL-2 (34). Of 13 dogs treated, two dogs entered a complete remission, the tumor regressed partially in one dog, and four dogs had stable disease.
Since the half life of IL-2 in the circulation is short requiring more frequent administration, the intra-tumor administration is an attractive option. Stinson et al. (35) developed a method to link IL-2 (and IL-12) to collagen which prolongs their presence in the tumor microenvironment after intra-tumor injection.
Interleukin-12
Clinical use of this cytokine has been limited by concerns around its short half-life and narrow therapeutic index. Even when given intra-tumor, is it rapidly cleared from the tumor site requiring more frequent injections which has led to efforts to bind it in a stable complex. Options include binding interleukin-12 (IL-12) to tumor collagen (35) or “anchor” it with aluminum hydroxyte (36). Human IL-12 has also been administered locally by electrogene therapy (37).
The immunocytokine NHS-IL-12 consists of the heavy-chains of a human mAb raised against DNA released by necrostic tumor cells which is fused to two molecules of a genetically modified human IL-12 (38). It is currently not in trials or part of clinical practice.
Interleukin 15 (IL-15) and IL-15:IL-15R (AnktivaR)
A recent study at the University of Davis administered human IL-15 to dogs (n = 21) via inhalation through a fitted nebulizer twice daily for two weeks (39). Dogs had lung lesions of their osteosarcoma or melanoma. Response rates were encouraging with stable disease (n = 5), partial response (n = 1) and one dog with a complete remission. Importantly, no side effects to the xenogeneic IL-15 were observed. As part of that study, four dogs received the human IL-15 superagonist AnktivaR which was well tolerated.
The same group recently showed that the number of NK cells that can be obtained from unmanipulated canine PBMC is equal or even better than the yield after CD5 depletion of PBMC (16). Both fractions were expanded on an irradiated K562 feeder layer engineered to produce human IL-21 and human IL-2. Using this approach, the investigators conducted two feasibility trials with NK cells expanded from canine PBMC: autologous cells were injected on days 0 and 7 supported by a two week twice daily inhalation of human IL-15. A second trial treated dogs with advanced melanoma with allogeneic (canine) NK cells supported by two subcutaneous injections of human IL-15. No serious side effects occurred in either study and some promising responses were observed (25).
The University of Davis group is currently leading a multicenter study with inhaled human IL-15 in the adjuvant setting for dogs after amputation and chemotherapy for osteosarcoma [R. Rebhuhn, personal communication]. With the recent FDA approval of AnktivaR for bladder cancer in humans and its cross-reactivity with canine cancer tissue, it is hoped that there will be studies testing efficacy of this unique cytokine more broadly against canine tumors.
Hematopoietic growth factors (G-CSF and GM-CSF)
Human preparations for both cytokines have been administered to dogs to accelerate neutrophil recovery after chemotherapy and/or radiation. Safety and efficacy for both preparations have been confirmed (40, 41).
Human gene engineered tumor vaccines
Gene delivery methods include both viral and non-viral vectors, such as transfer of plasmid DNA injected directly into the tumor via gene gun or electroporation. CSPG4 is a cell surface proteoglycan overexpressed in a wide range of human and canine tumors that has been tested with the rationale to overcome unresponsiveness to “self” antigen (42). Although there was an immune response against the human CSPG4 in dogs with melanoma, a convincing benefit of this treatment has not been shown (43). The same is true for intradermal injection of human tyrosinase DNA in a bacterial plasmid (Oncept®). It is suggested to induce a humoral and cytotoxic T-cell response against canine melanoma cells that express tyrosinase (44). The product is USDA—approved for the treatment of dogs with stage II or III oral melanoma. Although a popular therapy among veterinarians, its efficacy has not conclusively shown in well-designed clinical trials (45).
Oncolytic viruses are receiving some attention as they could make tumors more immunogeneic or modulate the tumor microenvironment. Studies in humans with different viruses are ongoing (46) T-VEC, also known as ImlygicR, is a genetically modified herpes simplex virus, approved by the FDA for the treatment of unresectable melanoma in humans (47). T-VEC has not been studied yet in canines although administration of some experimental oncolytic viruses (i.e., adenovirus based) have suggested the occasional benefit (48). One challenge in using oncolytic viruses in dogs is the potential for neutralizing antibodies against the virus, especially if the dog has been vaccinated against a similar virus.
Conclusion
Veterinarians should not be overly concerned that a human (xenogeneic) immune-based therapeutic will cause significant side effects in dogs or may be ineffective because of an immediate or delayed immunological rejection. Especially the intra-tumor injection or inhalation of a human cytokine (IL-2, IL-12, IL-15) could be an attractive treatment option for certain canine cancers with minimal side effects and the possibility of inducing a vaccine-like effect. Cytokines offer the opportunity to be combined with radiation or low dose chemotherapy as recently shown for IL-2 and IL-12 (49) with the rationale to induce local tumor cell apoptosis/necrosis and exposing tumor antigens to become targets for cytokine activated lymphocytes. The costs for such treatment protocols should be reasonable compared to the more significant costs of monoclonal antibodies or cell-engineered treatments. A general challenge though in immunotherapy trials in dogs and arriving at conclusions is the widespread use of corticosteroids in veterinary practices which can make it difficult to assess the contribution of a specific therapeutic (50).
Author contributions
HK: Resources, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Software, Visualization, Investigation, Project administration, Validation, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Lee-Klingemann Canine Cancer Research Foundation (https://www.canine-cancer-research.org).
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Fleming, JM, Creevy, KE, and Promislow, DE. Mortality in North American dogs from 1984 to 2004: an investigation into age-, size-, and breed-related causes of death. J Vet Intern Med. (2011) 25:187–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-1676.2011.0695.x
2. Thamm, DH. Canine cancer: strategies in experimental therapeutics. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:1257. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01257
3. Hampel, JM, Cheuk, N, Barbosa, MMP, and Fan, TM. The promise of immunotherapeutic strategies to advance cancer treatment in pet dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2024) 262:1583–93. doi: 10.2460/javma.24.08.0532
4. Klingemann, H. Immunotherapy for dogs: still running behind humans. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:665784. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.665784
5. Cockey, JR, and Leifer, CA. Racing CARs to veterinary immune-oncology. Front Vet Sci. (2023) 10:1130182. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1130182
6. Richtel, M. (2024). Cancer kills millions of dogs. Will immunotherapy prolong their lives?. New York Times. Available online at: https://www.nytimes.com/2024/06/21/science/dogs-cancer-immunotherapy.html (Accessed June 21, 2024).
7. Stephens, T. The use of chemotherapy to prolong the life of dogs suffering from cancer: the ethical dilemma. Animals. (2019) 9:441. doi: 10.3390/ani9070441
8. Williams, J, Phillips, C, and Byrd, HM. Factors which influence owners when deciding to use chemotherapy in terminally ill pets. Animals. (2017) 7:18. doi: 10.3390/ani7030018
9. Viganó, F, Perissinotto, L, and Bosco, VR. Administration of 5% human serum albumin in critically ill small animal patients with hypoalbuminemia: 418 dogs and 170 cats (1994–2008). J Vet Emerg Crit Care. (2010) 20:237–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-4431.2010.00526.x
10. Loyd, KA, Cocayne, CG, Cridland, JM, and Hause, WR. Retrospective evaluation of the administration of 25% human albumin to dogs with protein-losing enteropathy: 21 cases (2003–2013). J Vet Emerg Crit Care. (2016) 4:587–92. doi: 10.1111/vec.12484
11. Trow, AV, Rozanski, EA, Delaforcade, AM, and Chan, DL. Evaluation of use of human albumin in critically ill dogs: 73 cases (2003–2006). J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2008) 233:607–12. doi: 10.2460/javma.233.4.607
12. Williams, BA, Law, AD, Routy, B, denHollander, N, Gupta, V, Wang, XH, et al. A phase I trial of NK-92 cells for refractory hematological malignancies relapsing after autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation shows safety and evidence of efficacy. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:89256–68. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19204
13. Impellizeri, JR, Howell, K, McKeever, KP, and Crow, SE. The role of rituximab in the treatment of canine lymphoma: an ex vivo evaluation. Vet J. (2006) 171:556–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2005.03.005
14. Pantelyushin, S, Ranninger, E, Guerrera, D, Hutter, G, Maake, C, Markkanen, E, et al. Cross-reactivity and functionality of approved human immune checkpoint blockers in dogs. Cancers. (2021) 13:785. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040785
15. Razmara, AM, Gingrich, AA, Toedebusch, CM, Rebhun, RB, Murphy, WJ, Kent, MS, et al. Improved characterization and translation of NK cells for canine immunotherapy. Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1336158. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1336158
16. Addissie, S, and Klingemann, H. Cellular immunotherapy of canine cancer. Vet Sci. (2018) 5:100. doi: 10.3390/vetsci50401100
17. Mizuno, T, Takeda, Y, Tsukui, T, and Igase, M. Development of a cell line-based assay to measure the antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of a canine therapeutic antibody. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. (2021):240. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2021.110315
18. Hullsiek, R, Li, Y, Snyder, KM, Wang, S, Di, D, Borgatti, A, et al. Examination of IgG Fc receptor CD16A and CD64 expression by canine leukocytes and their ADCC activity in engineered NK cells. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:841859. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.841859
19. Chinnapen, H, Boissel, L, Bickett, T, Fleenor, C, Godbole, V, Saxena, M, et al. NK-92 (aNK) whole cell lysate exerts potent cytotoxic and anti-proliferative activity on tumor cells. Cell Immunol. (2025) 413:104951. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2025.104951
20. Cesano, A, Visonneau, S, Jeglum, KA, Owen, J, Wilkinson, K, Carner, K, et al. Phase I clinical trial with a human major histocompatibility complex nonrestricted cytotoxic T-cell line (TALL-104) in dogs with advanced tumors. Cancer Res. (1996) 56:3021–9.
21. Visonneau, S, Cesano, A, Jeglum, KA, and Santoli, D. Adjuvant treatment of canine osteosarcoma with the human cytotoxic T-cell line TALL-104. Clin Cancer Res. (1999) 7:1868–75.
22. Panjwani, MK, Atherton, MJ, MaloneyHuss, MA, Haran, KP, Xiong, A, Gupta, M, et al. Establishing a model system for evaluating CART cell therapy using dogs with spontaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Onco Targets Ther. (2019) 9:1676615. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2019.1676615
23. Zhang, S, Black, RG, Kohli, K, Hayes, BJ, Miller, C, Koehne, A, et al. B7-H3 specific CAR T cells for the naturally occurring, spontaneous canine sarcoma model. Mol Cancer Ther. (2022) 21:999–1009. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-21-0726
24. Cao, JW, Lake, J, Impastato, R, Chow, L, Perez, L, Chubb, L, et al. Targeting osteosarcoma with canine B7-H3 CAR T cells and impact of CXCR2 co-expression on functional activity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2024) 73:77. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03642-4
25. Razmara, AM, Farley, LE, Harris, RM, Judge, SJ, Lammers, M, Iranpur, KR, et al. Preclinical evaluation and first-in-dog clinical trials of PBMC-expanded natural killer cells for adoptive immunotherapy in dogs with cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2024) 12:e007963. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007963
26. Klingemann, H. Chapter twelve—development and testing of NK cell lines In: MT Lotze and AW Thomson, editors. Natural killer cells. London: Academic Press (2010). 169–75.
27. Klingemann, H. The NK-92 cell line-30 years later: its impact on natural killer cell research and treatment of cancer. Cytotherapy. (2023) 25:451–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2022.12.003
28. Jochems, C, Hodge, JW, Fantini, M, Fujii, R, Morillon, Y II, Greiner, JW, et al. An NK cell line (haNK) expressing high levels of granzyme and engineered to express the high affinity CD16 allele. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:86359–73. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13411
29. Boissel, L, Klingemann, H, Khan, J, and Soon-Shiong, P. Intra-tumor injection of CAR-engineered NK cells induces tumor regression and protection against tumor re-challenge. Blood. (2016) 128:466. doi: 10.1182/blood.V128.22.466.466
30. Burger, MC, Forster, MT, Romanski, A, Straßheimer, F, Macas, J, Zeiner, PS, et al. Intracranial injection of natural killer cells engineered with a HER2-targeted chimeric antigen receptor in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncol. (2023) 25:2058–71. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noad087
31. Helfand, SC, Soergel, SA, MacWilliams, PS, Hank, JA, and Sondel, P. Clinical and immunological effects of human recombinant interleukin-2 given by repetitive weekly infusion to normal dogs. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (1994) 39:84–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01525313
32. Ziekman, PG, Den Otter, W, Tan, JF, Teske, E, Kirpensteijn, J, Koten, JW, et al. Intratumoral interleukin-2 therapy can induce regression of non-resectable mastocytoma in dogs. Anticancer Res. (2013) 33:161–6.
33. Khanna, C, Anderson, PM, Hasz, DE, Katsanis, E, Neville, M, and Klausner, JS. Interleukin-2 liposome inhalation therapy is safe and effective for dogs with spontaneous pulmonary metastases. Cancer. (1997) 79:1409–21. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19970401)79:7<1409::AID-CNCR19>3.0.CO;2-3
34. Den Otter, W, Hack, M, Jacobs, JJL, Tan, JFV, Rozendaal, L, and van Moorselaar, RJA. Treatment of transmissible venereal tumors in dogs with intratumoral interleukin-2 (IL-2). A pilot study. Anticancer Res. (2015) 35:713–8.
35. Stinson, JA, Sheen, A, Momin, N, Hampel, J, Bernstein, R, Kamerer, R, et al. Collagen-anchored interleukin-2 and interleukin-12 safely reprogram the tumor microenvironment in canine soft-tissue sarcomas. Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 29:2110–22. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-0006
36. Passos Barbosa, MM, Kamerer, RL, Schmit, J, Lopez, AJ, Uyehara, R, Tighe, R, et al. Preclinical evaluation of an anchored immunotherapy strategy with aluminum hydroxide-tethered interleukin-12 in dogs with advanced malignant melanoma. Mol Cancer Ther. (2024). doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-24-0317
37. Pavlin, D, Cemazar, M, Sersa, G, and Tozon, N. IL-12 based gene therapy in veterinary medicine. J Transl Med. (2012) 10. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-234
38. Paoloni, M, Mazcko, C, Selting, K, Lana, S, Barber, L, Phillips, J, et al. Defining the pharmacodynamic profile and therapeutic index of NHS-IL12 immunocytokine in dogs with malignant melanoma. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e0129954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129954
39. Rebhun, RB, York, D, Cruz, SM, Judge, SJ, Razmara, AM, Farley, LE, et al. Inhaled recombinant human IL-15 in dogs with naturally occurring pulmonary metastases from osteosarcoma or melanoma: a phase 1 study of clinical activity and correlates of response. J Immunother Cancer. (2022) 10:e004493. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004493
40. Schuening, FG, Storb, R, Goehle, S, Graham, TC, Appelbaum, FR, Hackman, R, et al. Effect of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on hematopoiesis of normal dogs and on hematopoietic recovery after otherwise lethal total body irradiation. Blood. (1989) 74:1308–13.
41. Schuening, FG, Storb, R, Goehle, S, Nash, R, Graham, TC, Appelbaum, FR, et al. Stimulation of canine hematopoiesis by recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Exp Hematol. (1989) 17:889–94.
42. Rolih, V, Barutello, G, Iussich, S, De Maria, R, Quaglino, E, Buracco, P, et al. CSPG4: a prototype oncoantigen for translational immunotherapy studies. J Transl Med. (2017) 15:151. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1250-4
43. Giacobino, D, Camerino, M, Riccardo, F, Cavallo, F, Tarone, L, Martano, M, et al. Difference in outcome between curative intent vs marginal excision as a first treatment in dogs with oral malignant melanoma and the impact of adjuvant CSPG4-DNA electrovaccination: a retrospective study on 155 cases. Vet Comp Oncol. (2021) 19:651–60. doi: 10.1111/vco.12690
44. Pellin, MA. The use of Oncept melanoma vaccine in veterinary patients: a review of the literature. Vet Sci. (2022) 9:597. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9110597
45. Ottnod, JM, Smedley, RC, Walshaw, R, Hauptman, JG, Kiupel, M, and Obradovich, JE. A retrospective analysis of the efficacy of Oncept vaccine for the adjunct treatment of canine oral malignant melanoma. Vet Comp Oncol. (2013) 11:219–29. doi: 10.1111/vco.12057
46. Hemminki, O, Dos Santos, JM, and Hemminki, A. Oncolytic viruses for cancer immunotherapy. J Hematol Oncol. (2020) 13:84. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00922-1
47. Ferrucci, PF, Pala, L, Conforti, F, and Cocorocchio, E. Talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC): an intralesional cancer immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. Cancers. (2021) 13:1383. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061383
48. Sánchez, D, Cesarman-Maus, G, Amador-Molina, A, and Lizano, M. Oncolytic viruses for canine cancer treatment. Cancers. (2018) 10:404. doi: 10.3390/cancers10110404
49. Stinson, JA, Barbosa, MMP, Sheen, A, Momin, N, Fink, E, Hampel, J, et al. Tumor-localized interleukin-2 and interleukin-12 combined with radiation therapy to safely potentiate regression of advanced malignant melanoma in pet dogs. Clin Cancer Res. (2024) 30:4029–43. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0861
Keywords: immunotherapy, dogs, NK cells, lymphocytes, crossreactivity, cytokines
Citation: Klingemann H (2025) Human immuno-therapeutics for cancer treatment of dogs? Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1593333. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1593333
Edited by:
Felisbina Luisa Queiroga, University of Trás-os-Montes and Alto Douro, PortugalReviewed by:
Robert J. Canter, University of California, Davis, United StatesJohannes vom Berg, University of Zurich, Switzerland
Copyright © 2025 Klingemann. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hans Klingemann, aGFucy5rbGluZ2VtYW5uQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Hans Klingemann
Hans Klingemann