- 1Tranditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine Laboratory, College of Veterinary Medicine, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China
- 2Lanzhou Center for Animal Disease Prevention & Control, Lanzhou, China
Background: This study addresses the global challenge of subclinical bovine mastitis (SCBM) in dairy cows, a prevalent disease causing substantial economic losses, by investigating the mechanistic basis of Astragali Radix, a traditional herbal remedy with empirically validated efficacy but incompletely understood modes of action.
Methods: Initially, the active components of Astragali Radix were identified using LC-MS/MS. Dose-response trials were conducted in Holstein cows (n = 24 SCBM cases; n = 6 healthy controls), along with multi-omics integration, including 16S rRNA sequencing for rumen/feces microbiota and UHPLC-MS metabolomics for serum analysis. The therapeutic effects of Astragali Radix water decoction (ARWD) on milk production, inflammatory markers, immune parameters, and oxidative stress were systematically evaluated.
Results: ARWD administration dose-dependently improved milk yield and protein content while reducing somatic cell counts. Serum pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β) decreased, contrasting with increases in immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM, IgG) and enhanced superoxide dismutase activity. Microbiota restructuring featured ruminal enrichment of Bifidobacterium and fecal dominance of Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group, coupled with suppression of pro-inflammatory taxa (e.g., Christensenellaceae_R-7_group). Metabolomic analysis identified four ARWD-responsive biomarkers, notably Spirotaccagenin and Pelanin, operating through linoleic acid metabolism and phospholipase D signaling pathways. Strong correlations linked microbial shifts to improved lactation parameters and reduced inflammation.
Conclusion: The findings establish that ARWD alleviates SCBM through coordinated microbiota remodeling and metabolic reprogramming, specifically enhancing antioxidant defenses, restoring mammary barrier integrity, and modulating immune-inflammation crosstalk, with optimal efficacy at 0.4 g·kg−1·d−1 dosage. This mechanistic validation positions ARWD as a scientifically grounded, eco-friendly alternative for sustainable mastitis management, reconciling therapeutic effectiveness with agricultural economic priorities.
1 Introduction
In recent years, subclinical bovine mastitis (SCBM) has emerged as a significant issue in the dairy industry, second only to clinical mastitis. This condition has a profound impact on milk yield and quality, negatively affecting overall herd health and ultimately reducing the profitability of dairy farms (1). Veterinary experts agree that controlling somatic cell count (SCC) is crucial for sustainable dairy production. SCBM is characterized by the gradual onset, high contagion rates, and increased SCC levels in milk, often going unnoticed until it causes considerable economic losses (2). Therefore, it is vital to implement preventive measures during the SCBM phase to ensure the health of bovine mammary glands. While traditional antibiotic treatments are commonly employed, they can adversely affect milk quality and pose risks to human health due to the potential for antimicrobial resistance, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable alternatives (3).
According to traditional Chinese veterinary medicine (TCVM), deficiencies in qi and blood contribute to the development of SCBM, increasing cows' susceptibility to bacterial colonization in the mammary tissues. Key pathogens involved include Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus agalactiae, which take advantage of weakened immune states to establish persistent infections (4).
The mammary gland serves as an essential component of the immune system, employing intricate mechanisms to protect against bacterial infections, which are vital for managing infections. Recent research indicates that the gastrointestinal microbiota, often called the “second genome,” significantly contributes to the immune defenses of the mammary gland through interactions along the gut-mammary axis (5). This microbial community is crucial for the immune system, particularly in identifying pathogens within the mammary glands and regulating inflammation.
The gut-immune axis has emerged as a significant area of research, with compelling evidence indicating a bidirectional communication between gut microbiota and host immunity (6). An imbalance in gut microbiota is linked to various health problems, including infections and inflammatory diseases. In dairy cows, changes in gut microbiota composition can heighten the risk of mastitis, even in subclinical cases (7). This microbial dysregulation impacts the production of immunomodulatory metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which plays a crucial role in regulating the immune system throughout the body (8). In this regard, herbal medicines have shown promising immunomodulatory properties without adverse effects. For instance, Astragali Radix, a prominent herb known for boosting qi, has been found to modulate immune responses and affect gut microbiota. Experimental studies indicate that this herb promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium while inhibiting harmful pathogens such as Escherichia and Salmonella (9). Additionally, bioactive compounds found in Astragalus, including polysaccharides and saponins, significantly enhance macrophage phagocytosis, promote the maturation of dendritic cells, and stimulate T-lymphocyte proliferation (10). Moreover, advanced technologies like high-throughput 16S rRNA gene sequencing and metabolomics are shedding light on the interactions between traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), gut microbiota, and immune function. By influencing microbial communities and regulating metabolic pathways, these innovative methods help clarify the mechanisms underlying TCM interventions (11, 12).
This study explored the therapeutic effectiveness and underlying mechanisms of Astragali Radix water decoction (ARWD) in treating bovine SCBM by utilizing fecal 16S rRNA sequencing and serum untargeted metabolomics. Additionally, the research identified the bioactive components of ARWD decoction through LC-MS/MS analysis. The findings provide a scientific foundation for clinical application of ARWD in SCBM prevention and control within veterinary practice.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials and reagents
Astragali Radix was purchased from Lanzhou Yellow River medicine market. Origin: Liupanshan Region, China. The following kits were used in this study: malondialdehyde (MDA) test kit (catalog No. YJ016824), superoxide dismutase (SOD) test kit (catalog No. YJ036559), myeloperoxidase (MPO) test kit (catalog No. YJ300741), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) test kit (catalog No. YJ520026), immunoglobulin A (IgA) ELISA kit (catalog No. YJ542063), immunoglobulin G (IgG) ELISA kit (catalog No. YJ330698), immunoglobulin M (IgM) ELISA kit (catalog No. YJ627279), Interleukin-2 (IL-2) ELISA kit (catalog No. YJ002498), interleukin-1 β (IL-1 β) ELISA kit (catalog No. YJ064295), interleukin-6 (IL-6) ELISA kit (catalog No. YJ064296) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF- α) ELISA kit (catalog No. YJ077389), all the above were purchased from Shanghai Meilian Biotechnology Company.
2.2 Preparation of ARWD
Astragali Radix were mixed with distilled water at a 1:10 (w/v) ratio. The mixture was vigorously boiled, then simmered at low heat for 30 min and filtered through four-layer sterile gauze. The residue underwent re-extraction with an 8-fold volume of distilled water following identical boiling/simmering conditions, followed by gauze filtration. Both filtrates were combined for subsequent experiments.
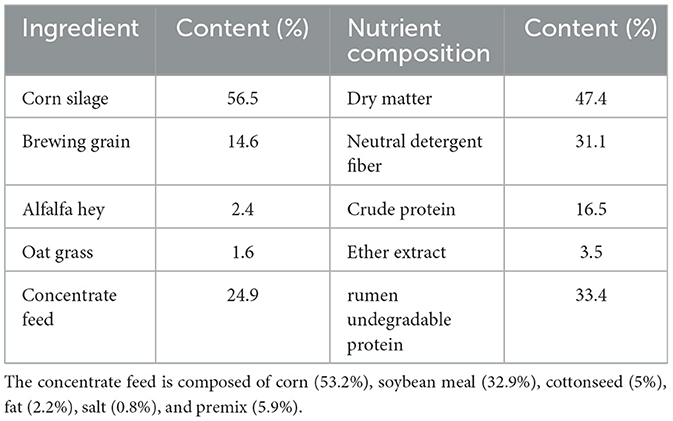
2.3 Experimental animals and grouping
All experimental cows were obtained from the Gansu Holstein Dairy Cattle Breeding Center and selected as multiparous, mid-lactation individuals (3–9 years old) with comparable body weights. The animals were fed mixed ration (TMR) three times a day at 8:00, 16:00, and 21.30 respectively (Table 1). Mammary health was assessed via SCC and clinical mastitis evaluation. Based on established criteria (13, 14), cows with SCC < 200,000 cells/ml were considered healthy, while those with SCC > 200,000 cells/ml without clinical symptoms were diagnosed with SCBM. Untreated positive cows with SCBM for 3–5 days (n = 24) were randomly assigned to four experimental groups (n = 6 per group): Astragali Radix water decoction High-dose group (0.4 g·kg−1·d−1, AR_H), Astragali Radix water decoction Medium-dose group (0.2 g·kg−1·d−1, AR_M), Astragali Radix water decoction Low-dose group (0.1 g·kg−1·d−1, AR_L). Model group: untreated SCBM controls (MOD). Six additional healthy cows received equivalent volumes of water as negative controls (NC). All ARWD treatments were administered orally via force-feeding for seven consecutive days. Sample Collection: 5 ml of blood were collected from each cow through the tail vein 1 h after feeding on the morning of day 8. The blood samples were then centrifuged at 3,000 r/min for 15 min at 4°C to separate the serum. Rumen fluid was extracted by inserting a rumen sampler via the mouth into the rumen and using a syringe. The first two tubes of rumen fluid were discarded to prevent salivary contamination. Approximately 150 ml of rumen fluid was sampled from each cow. Fecal samples were collected from the rectum using sterile long-arm gloves, 3 h after feeding, and placed in sterile, sealed plastic bags. Fecal and rumen fluid samples were immediately snap frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C. Milk samples were collected and transported on ice for somatic cell count (SCC) analysis and milk composition testing.
2.4 LC-MS/MS analysis of ARWD samples
The LC-MS/MS analysis was performed using a UHPLC-Q Exactive system (Thermo Scientific) equipped with a UPLC BEH C18 column (2.1 × 100 mm i.d., 1.7 μm). The mobile phase consisted of (A) 2% acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid and (B) acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid. Full-scan MS data were acquired in both positive and negative ionization modes over a mass range of 70–1,050 m/z at a resolution of 70,000. Data processing, including peak alignment, extraction, and quantification, was conducted using Compound Discoverer QI v3.0 (WatersCorporation, Milford, USA) software. Metabolite identification was achieved by matching accurate mass and MS/MS spectra against the Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China) database with (mass accuracy threshold of <10 ppm).
2.5 Milk yield statistical analysis
Milking was performed using rotary milking parlors pre- and post-treatment, with individual milk yields recorded for each cow.
2.6 Somatic cell count and milk composition analysis
SCC and milk composition parameters [fat, protein, lactose, total milk solids (TS), milk urea nitrogen (MUN)] were analyzed using a CombiFoss™ 7 analyzer (Foss Analytical, Denmark).
2.7 Detection of serum oxidative stress markers
The biochemical test kit was used to measure the levels of LDH, MPO, MDA, and SOD in serum. All experimental procedures were strictly conducted according to the manufacturer's instructions for the reagents.
2.8 Detection of serum inflammatory cytokines
The levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-2, and TNF-α in serum were measured using ELISA test kits. All experimental procedures were strictly carried out according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer for the reagents.
2.9 Detection of serum immunoglobulin
The levels of IgA, IgM, and IgG in serum were measured using biochemical test kits. All experimental procedures were strictly followed according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer for the reagents.
2.10 Rumen and fecal microbiota analysis
After drug administration, rumen fluid and rectal content were collected and stored at −80°C. According to the manufacturer's instructions, total microbial genomic DNA was extracted from 18 gastric juice samples and 18 fecal samples using the E.Z.N.A.® soil DNA Kit (Omega Bio-tek, Norcross, GA, U.S.). The mass and concentration of DNA were determined by 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis and NanoDrop2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, United States), and were stored at −80°C for further use. The hypervariable region V3–V4 of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene were amplified with primer pairs 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT3′) by T100 Thermal Cycler PCR thermocycler (BIO-RAD, USA). The PCR reaction mixture included 4 μl of 5 × Fast Pfu buffer, 2 μl of 2.5 mm dNTPs, 0.8 μl (5 μm) for each primer, 0.4 μl of Fast Pfu polymerase, 10 ng of template DNA, and ddH2O up to a final volume of 20 μl. The PCR amplification cycle conditions are as follows: initial denaturation at 95°C for 3 min, denaturation at 95°C for 30 s, annealing at 55°C for 30 s, extension at 72°C for 45 s, single extension at 72°C for 10 min, and conclusion of 27 cycles at 4°C. The PCR product was extracted from 2% agarose gel and purified using the PCR Clean-Up Kit (Yuhua, Shanghai, China) according to manufacturer's instructions and quantified using Qubit 4.0 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA), and the purified amplifiers were aggregated in equal molar amounts. 2 × 300 bp paired-end sequencing was performed on the Illumina Nextseq2000 platform (Illumina, San Diego, USA) according to the standard protocols by Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2.11 Serum untargeted metabolomics analysis
Serum samples from blank control, model, and astragalus intervention groups (n = 6/group) were extracted with methanol:acetonitrile (1:1, v/v). After ultrasonication (5°C, 40 kHz, 30 min) and incubation (−20°C, 30 min), supernatants were collected by centrifugation (13,000 g, 4°C, 15 min), dried under nitrogen, and reconstituted in acetonitrile:water (1:1, v/v). Quality control (QC) samples were processed identically.
Metabolites were analyzed using UHPLC-Q Exactive Focus MS (Thermo Fisher) with an ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 column (100 × 2.1 mm, 1.8 μm). Mobile phases: (A) 95% water/5% acetonitrile (0.1% formic acid); (B) 47.5% acetonitrile/47.5% isopropanol/5% water (0.1% formic acid). Flow rate: 0.40 ml/min, injection volume: 5 μl, column temperature: 40°C. MS parameters: ±3.50 kV spray voltage, 325°C capillary temperature, full scan at 81–1,000 m/z (70,000 resolution), HCD fragmentation (30 eV).
Raw data were processed in Progenesis QI v3.0 for peak alignment. Metabolites were identified by matching MS/MS spectra against HMDB, Metlin, and Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) in-house databases (MS error < 10 ppm, spectral score filtering). Differential metabolites underwent pathway enrichment analysis (P < 0.05).
2.12 Correlation analysis
Spearman's rank correlation analysis was performed to investigate relationships between differential metabolites and gut microbiota among NC, MOD, and AR_H groups. Additionally, pairwise correlations were analyzed between metabolites/gastrointestinal microbiota and dairy parameters (SCC, milk yield, milk composition), inflammatory factors, immune/antioxidant indices.
2.13 Statistical analysis
Gastrointestinal flora alpha diversity was statistically determined using the Kruskal–Wallis test, and beta-diversity was statistically determined using the ANOSIM test. Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA in GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software), with significance levels defined as P < 0.05 (significant), P < 0.01 (highly significant), and P > 0.05 (not significant).
3 Results
3.1 LC-MS/MS analysis of ARWD
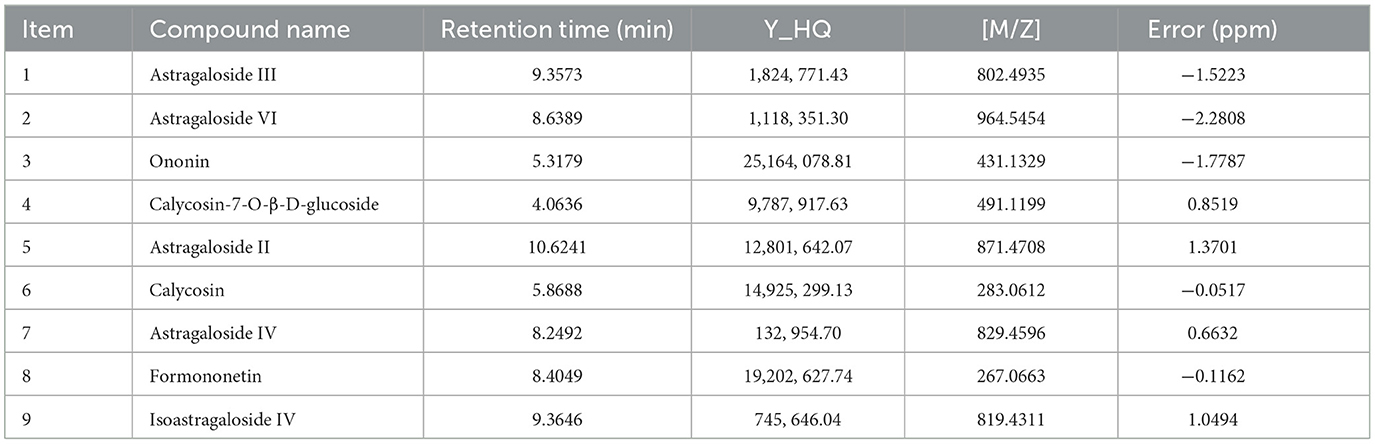
Total ion chromatograms were acquired in both positive and negative ion modes. As shown in Figure 1, well-resolved peaks with uniform distribution were observed under the current analytical conditions. Qualitative analysis was performed by matching the mass spectrometry data matrix (retention time, m/z, and peak intensity) against the MJBIOTCM database. Nine compounds were identified, including flavonoids, steroids, and their derivatives (Table 2).
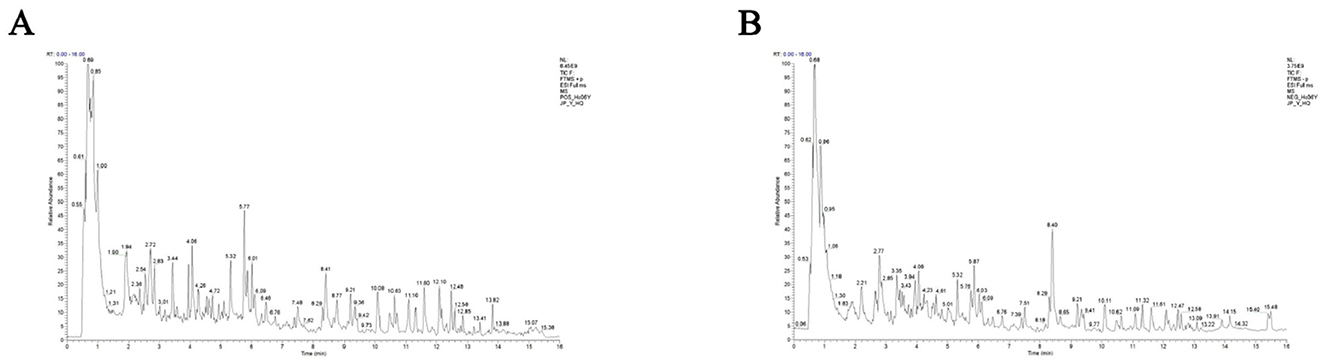
Figure 1. LC-MS/MS total ion chromatograms of ARWD in positive and negative ion modes. (A) Positive ion mode (POS); (B) negative ion mode (NEG).
3.2 Effects of ARWD on milk yield in SCBM cows
Analysis of milk yield before and after oral administrations revealed significant intergroup differences. Pretreatment milk yield in the MOD group was significantly lower than the NC group (P < 0.01). Post-intervention, all ARWD treated groups (AR_L, AR_M, AR_H) exhibited increased milk yields compared to baseline levels. Notably, the AR_H group showed marked improvement vs. the MOD group (P < 0.01), approaching NC group values. AR_L and AR_M groups demonstrated moderate milk yield increases post-treatment, though these changes lacked statistical significance (P > 0.05) (Figure 2).
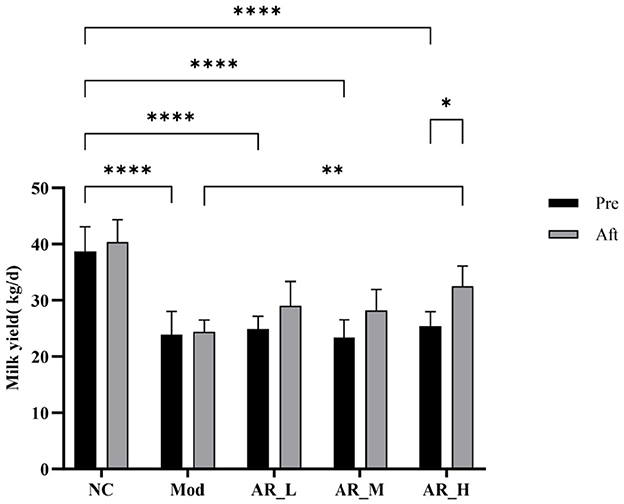
Figure 2. Milk yield changes. Differences between the two groups are indicated by (*), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
3.3 Effects of ARWD on SCC and milk composition in SCBM cows
Post-treatment SCC analysis demonstrated significant reduction in the AR_H group vs. baseline (P < 0.01) and MOD group (P < 0.01). The AR_M group showed moderate SCC decrease compared to MOD (P < 0.05), while AR_L exhibited no significant change (Figure 3A).
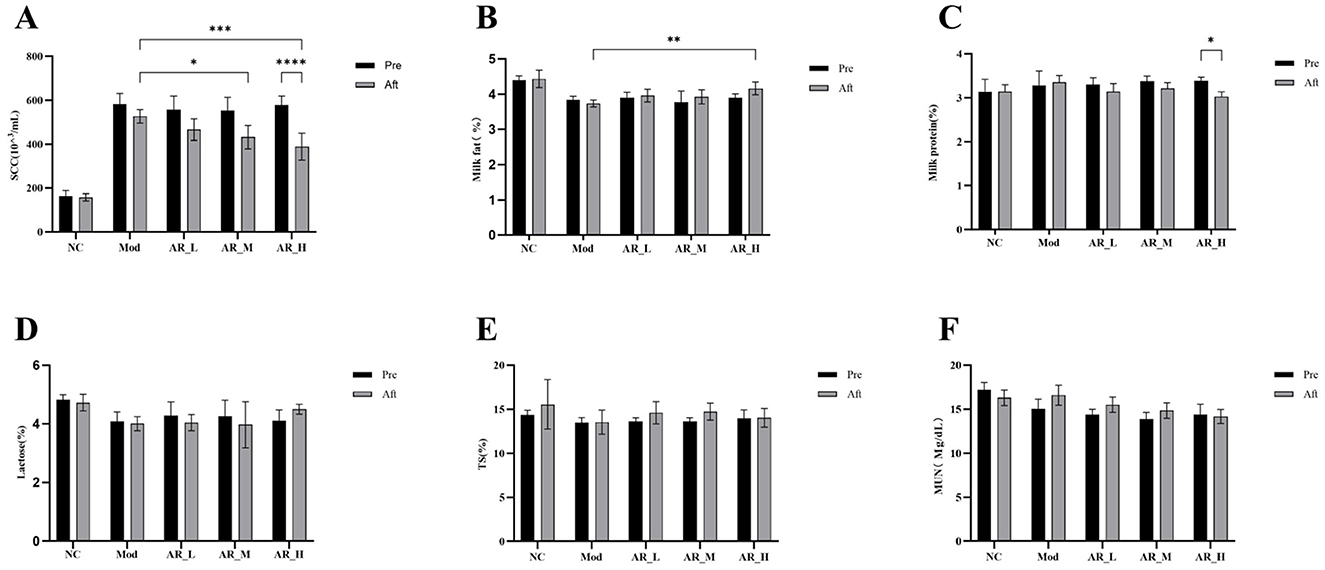
Figure 3. Changes of the somatic cells and milk components. (A) SCC; (B) milk fat; (C) milk protein; (D) latctose; (E) TS; (F) MUN. The differences between the two groups are indicated by (*), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
Milk fat content analysis showed that after ARWD intervention, the fat content in the AR_H group was significantly higher than that in the MOD group (P < 0.01). Compared with before treatment, the fat content in the AR_H, AR_M, and AR_L groups increased after ARWD intervention, but the increase was not significant (Figure 3B).
Milk protein content analysis indicated that the protein levels in the AR_H group after treatment were significantly lower than before treatment (P < 0.05). Compared with the MOD group, the protein contents in the AR_H, AR_M, and AR_L groups were all lower than those in the MOD group and lower than before administration (Figure 3C).
Lactose, Total Solids, and Milk Urea Nitrogen analysis revealed that no statistically significant differences in lactose, total solids (TS), or milk urea nitrogen (MUN) were detected among experimental groups relative to NC (P > 0.05). Slight increases in lactose and TS were observed in AR_H and AR_M groups, though these trends did not reach statistical significance (Figures 3D–F).
3.4 Effects of ARWD on serum inflammatory cytokines in SCBM cows
As shown in Figure 4, IL-6 expression in the AR_H group was significantly reduced post-intervention compared to pre-treatment (P < 0.01). Similarly, IL-1β levels showed marked reduction in AR_H vs. both pre-treatment (P < 0.05) and MOD group (P < 0.05). TNF-α expression in AR_H group was significantly lower than MOD group (P < 0.05). In contrast, AR_M and AR_L groups exhibited no significant alterations in IL-6, IL-1β, or TNF-α levels compared to NC or MOD groups (P > 0.05). IL-2 expression remained unchanged across all experimental phases (Figure 4).
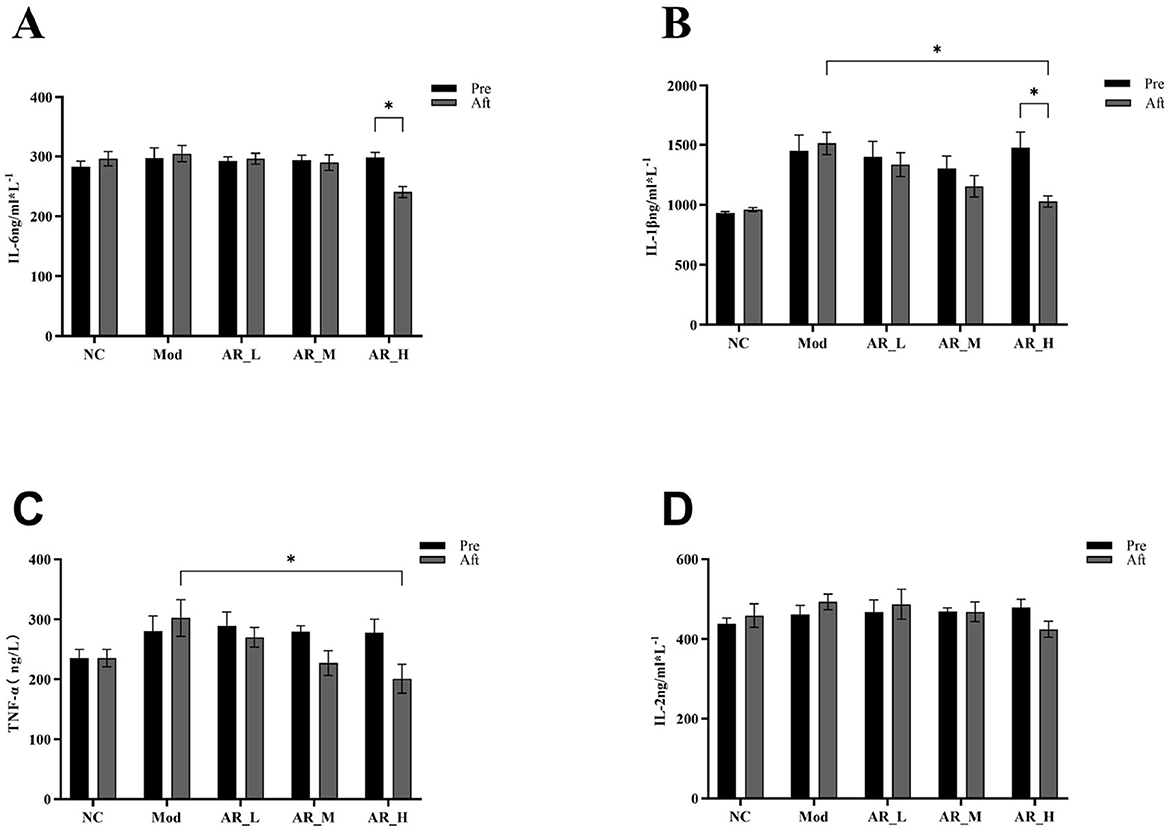
Figure 4. Changes of the serum inflammatory cytokines. (A) IL-6; (B) IL-1β; (C) TNF-α; (D) IL-2. The differences between the two groups are indicated by (*), *P < 0.05.
3.5 Effects of ARWD on oxidative stress in SCBM cows
Post-intervention analysis revealed significant increases in SOD activity (P < 0.01) and marked reductions in MDA (P < 0.01), LDH (P < 0.05), and MPO (P < 0.05) levels in the AR_H group. Notably, AR_H group MPO levels were significantly lower than MOD group (P < 0.01). No significant differences were observed between AR_M and AR_L groups (Figure 5). These findings demonstrate that Astragalus supplementation, particularly at high doses, significantly enhanced antioxidant capacity and alleviated oxidative stress, while lower doses exhibited moderate effects.
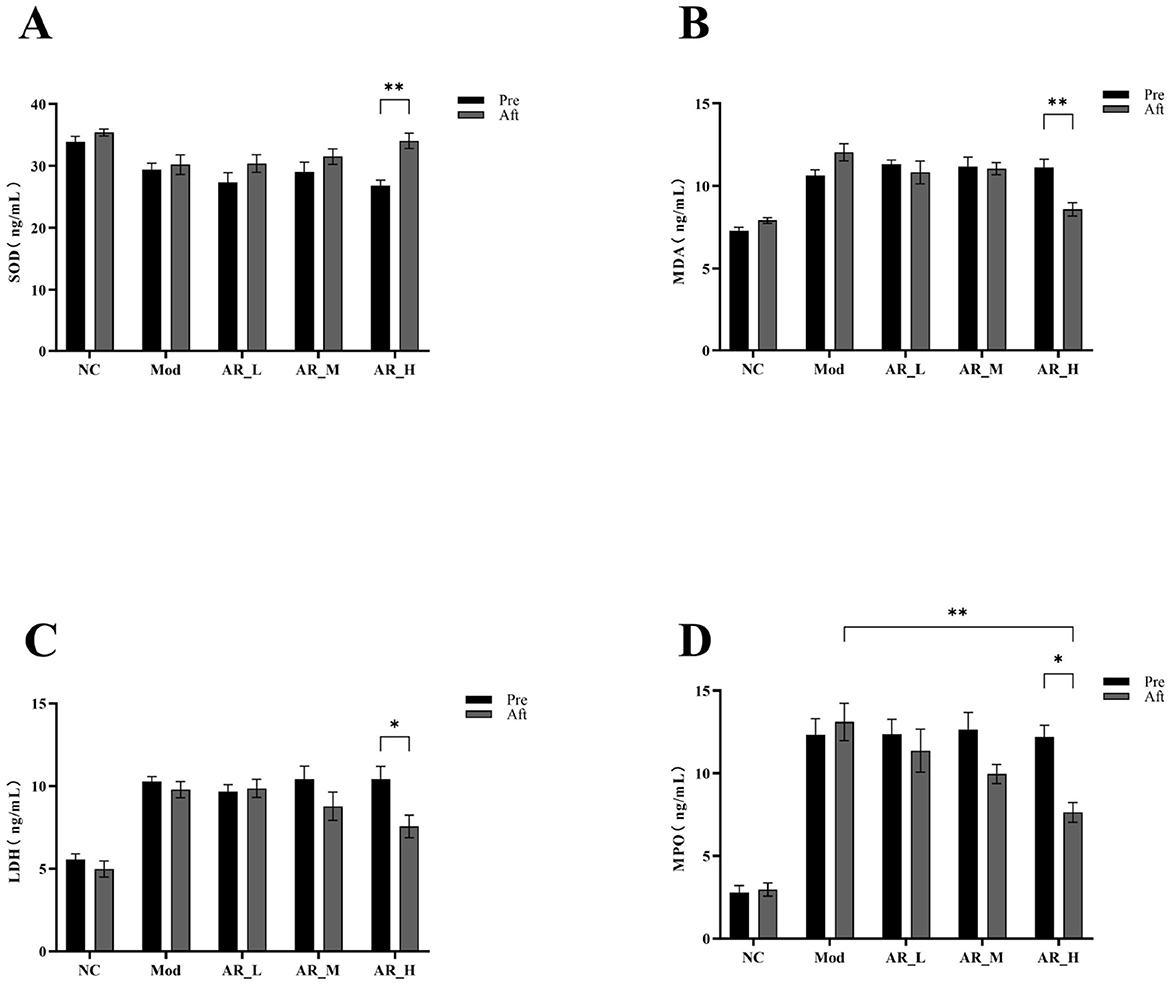
Figure 5. Changes of the serum oxidative stress markers. (A) SOD; (B) MDA; (C) LDH; (D) MPO. The differences between the two groups are indicated by (*), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
3.6 Effects of ARWD on immunoglobulins in SCBM cows
ARWD exerted significant modulatory effects on the immunoglobulin profiles in experimental groups. In the AR_H group, post-treatment levels of IgA, IgG, and IgM were significantly elevated compared to pre-treatment (P < 0.05). Furthermore, AR_H exhibited marked increases in IgM and IgG vs. the MOD group (P < 0.05). In contrast, AR_M and AR_L groups demonstrated no significant alterations in immunoglobulin levels relative to MOD (P > 0.05) (Figure 6). These findings indicate that high-dose Astragalus supplementation enhanced immune function through immunoglobulin modulation, while medium- and low-dose groups showed marginal efficacy.
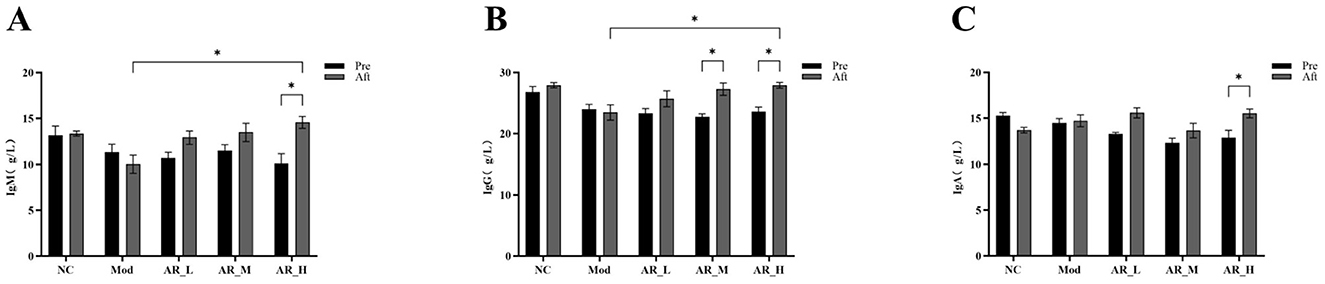
Figure 6. Changes of the serum Immunoglobulin. (A) IgM; (B) IgG; (C) IgA. The differences between the two groups are indicated by (*), *P < 0.05.
3.7 Effects of ARWD on rumen and gut microbiota in SCBM cows
3.7.1 Rumen fluid microbiota sequencing
A total of 4, 323 valid 16S rRNA sequences were obtained from 18 rumen fluid samples. Clustering analysis of non-redundant sequences at 97% similarity threshold identified 2,058 operational taxonomic units (OTUs). Rarefaction curves approached saturation with increasing sequencing depth, indicating adequate sequencing coverage (Figure 7A).
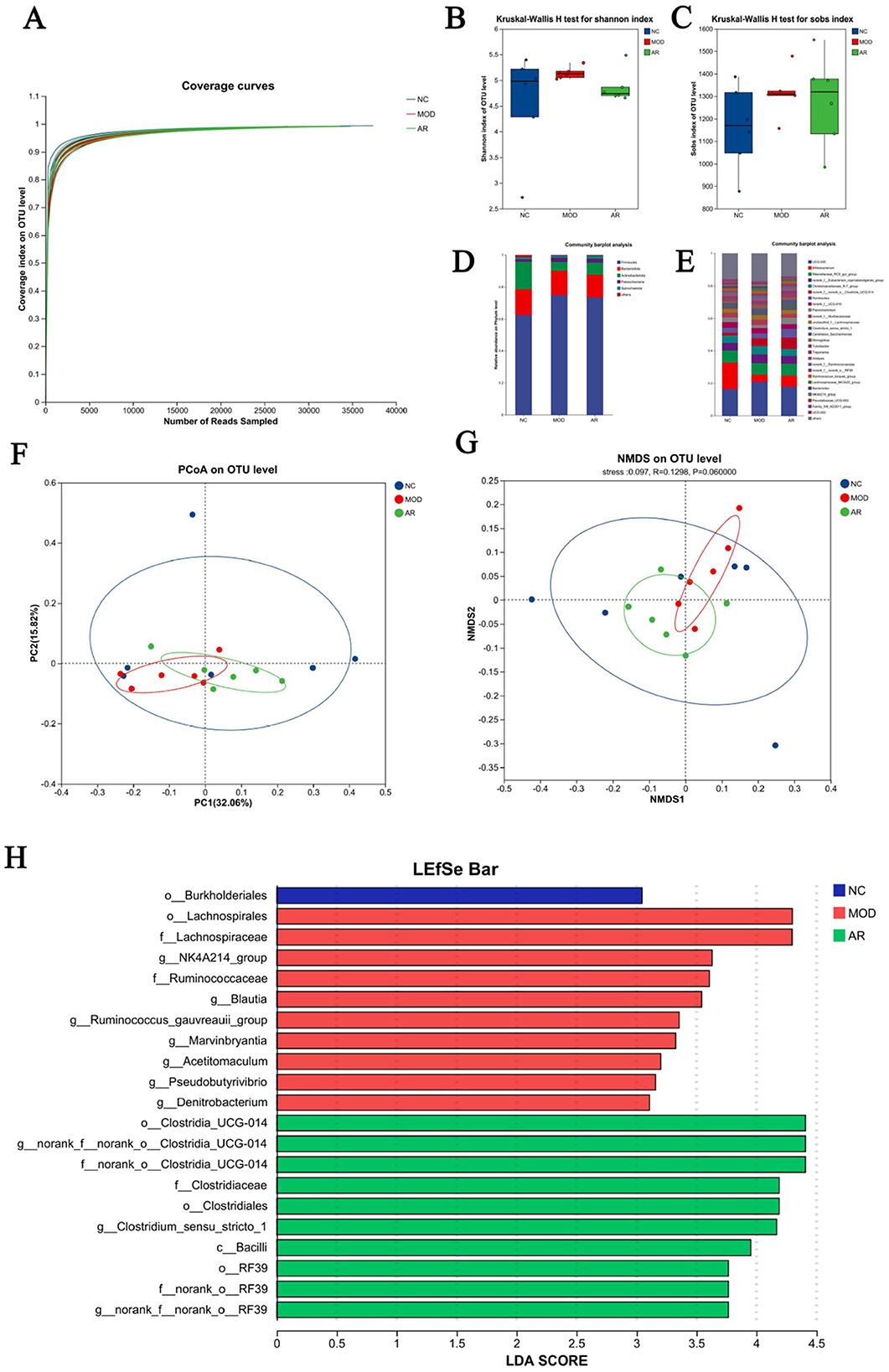
Figure 7. Diversity of the rumen bacterial flora. (A) Microbial species rarefaction curve; (B) Shannon; (C) Sobs; (D) phylum level; (E) genus levels; (F) PCoA; (G) NMDS; (H) LDA.
3.7.2 Rumen microbiota Alpha diversity analysis
No significant differences in Ace, Chao, Coverage, Shannon, Simpson, or Sobs indices were observed between Astragalus-treated and MOD groups (P > 0.05). However, downward trends in Shannon and Sobs indices were noted in the intervention group (Figures 7B, C). These results suggest potential modulatory effects of ARWD on rumen microbial richness and diversity in SCBM cows, though statistical significance was not achieved.
3.7.3 Rumen fluid microbial composition at phylum and genus levels
Analysis of 18 rumen fluid samples revealed distinct microbial compositions at phylum and genus levels. Phylum-level composition identified 15 phyla. Firmicutes dominated across groups (62.5% in NC, 74.8% in MOD, 73.5% in AR_H group), followed by Bacteroidota (16.0%, 15.3%, 14.2%) and Actinobacteriota (17.2%, 5.4%, 7.4%). Minor phyla including Patescibacteria and Spirochaetota showed substantially lower abundances (< 2% collectively) (Figure 7D). Genus-level analysis detected 294 genera. Dominant genera in NC included UCG-005 (16.2%), Bifidobacterium (16.6%), Romboutsia (3.1%), and Paeniclostridium (2.8%). MOD group exhibited altered profiles: UCG-005 (20.8%), Bifidobacterium (4.6%), Romboutsia (3.0%), and Paeniclostridium (1.9%). Astragalus intervention induced notable compositional shifts vs. MOD group: increased abundances of Bifidobacterium (6.8%), Romboutsia (5.3%), and Paeniclostridium (4.0%), with reduced UCG-005 (17.9%) (Figure 7E). These phylum- and genus-level microbial restructuring patterns suggest potential mechanistic links to Astragalus' therapeutic effects on SCBM in dairy cows.
3.7.4 Rumen microbiota β-diversity analysis
Bray-Curtis distance-based PCoA and NMDS analyses revealed partial separation of microbial communities among groups. The AR_H group exhibited distinct clustering from the MOD group, with closer proximity to the NC group, suggesting partial restoration of rumen microbiota structure in SCBM cows (Figures 7F, G). However, limited effects were observed on fecal microbiota β-diversity indices.
3.7.5 LEfSe analysis of rumen microbiota
LEfSe analysis with linear discriminant analysis (LDA) revealed significant microbial shifts between the MOD and AR_H groups (P < 0.05, Figure 7H). Compared to the MOD group, the AR_H group showed significant enrichment in beneficial genera such as Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 (P = 0.016), Turicibacter (P = 0.037), Erysipelotrichaceae_UCG-008 (P = 0.028), and fiber-degrading taxa including Cellulosilyticum (P = 0.004) Clostridium_sensu_stricto_6 (P = 0.036) hoa5-07d05_gut_group (P = 0.007). Conversely, Blautia (P = 0.006), Ruminococcus_gauvreauii_group (P = 0.016), Roseburia (P = 0.004) and other inflammation-associated genera, and Brevibacillus (P = 0.028), Pseudobutyrivibrio (P = 0.006), Marvinbryantia (P = 0.006) and other Potential pathobionts were significantly reduced. These microbiota alterations suggest that ARWD may alleviate SCBM by modulating microbial communities linked to immune regulation and metabolic balance.
3.7.6 Fecal microbiota sequencing
A total of 5,216 high-quality 16S rRNA sequences were obtained from 18 fecal samples. Clustering at 97% similarity threshold yielded 2, 290 OTUs. The rarefaction curve plateaued with increasing sequencing depth (Figure 8A), confirming adequate sampling coverage to capture microbial diversity.
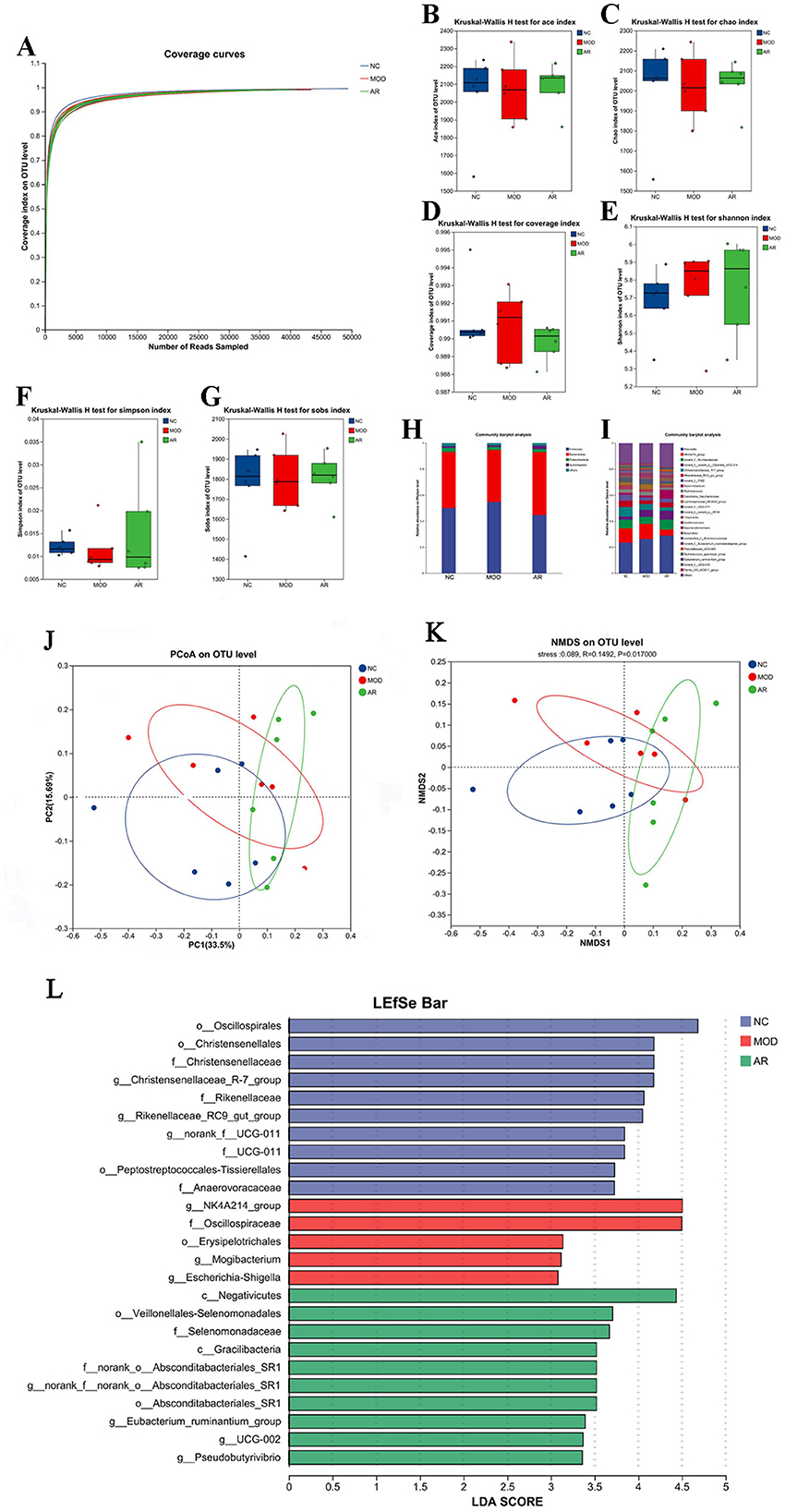
Figure 8. Diversity of the fecal microflora. (A) Feces microbial species rarefaction curve; (B) ACE; (C) Chao; (D) coverage; (E) Shannon; (F) Simpson; (G) Sobs;(H) phylum level; (I) genus levels; (J) NMDS; (K) PCoA; (L)LDA.
3.7.7 Fecal microbiota Alpha diversity
Alpha diversity indices (Ace, Chao, Shannon, Simpson, Sobs, and Coverage) showed increased trends in the AR_H group compared to MOD, though without statistical significance (P > 0.05, Figures 8B–G). This non-significant elevation in richness (Ace/Chao) and evenness (Shannon/Simpson) suggests a potential but modest modulatory effect of Astragalus intervention on microbial community structure in SCBM cows.
3.7.8 Fecal microbial composition at phylum and genus levels
Taxonomic classification using the RDP classifier and Bayesian algorithm identified 19 phyla and 320 genera across 18 fecal samples. Phylum-level analysis revealed dominant taxa across groups: Firmicutes: 50.1% (NC), 54.7% (MOD), 44.7% (AR_H). Bacteroidota: 43.1% (NC), 39.95% (MOD), 48.25% (AR_H). Minor phyla: Patescibacteria (3.2%, 2.3%, 2.5%) and Spirochaetota (1.2%, 1.04%, 2.5%) (Figure 8H). Genus-level profiling demonstrated group-specific dominance: NK4A214_group: 10.94% (NC), 11.52% (MOD), 4.57% (AR_H). Christensenellaceae_R-7_group: 7.13% (NC), 4.49% (MOD), 2.5% (AR_H). Functional shifts: Succiniclasticum increased to 6.69% in AR_H (vs. 1.44% in MOD), while Ruminococcus_gauvreauii_group declined to 0.68% (vs. 1.27% in MOD) (Figure 8I). These results highlight distinct fecal microbiota restructuring at both taxonomic levels following Astragalus intervention in SCBM cows.
3.7.9 Fecal microbiota Beta-diversity analysis
Beta-diversity analysis based on Bray-Curtis distance revealed partial compositional shifts among NC, MOD, and AR_H groups. PCoA and NMDS plots demonstrated distinct clustering of AR_H group from MOD, with a convergence trend toward CON (Figures 8J, K). These findings suggest Astragalus intervention partially restored microbial richness and diversity in SCBM cows, though its effects on β-diversity metrics remained statistically non-significant, indicating limited structural reorganization of the fecal microbiota community.
3.7.10 LEfSe analysis of fecal microbiota across groups
LEfSe analysis with LDA identified significant microbial biomarkers between MOD and AR_H groups (P < 0.05, Figure 8L). Compared to MOD, the AR_H group exhibited enrichment of fiber-degrading genera (e.g., Treponema, P = 0.037; Selenomonas, P = 0.01) and metabolic regulators (Anaerovibrio, P = 0.025), alongside suppression of mastitis-associated taxa (Ruminococcus_gauvreauii_group, P = 0.037; Corynebacterium, P = 0.007). Notably, opportunistic pathogens (Brevibacillus, P = 0.002) and inflammation-linked genera (Roseburia, P = 0.037) were reduced. These findings highlight Astragalus-induced remodeling of gut microbiota, potentially mediating systemic anti-inflammatory effects via the gut-mammary axis in SCBM cows.
3.8 Identification of serum characteristic metabolites and analysis of related metabolic pathways in cows with SCBM
Orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) was employed to investigate metabolic disparities. As shown in Figure 9A, score plots in both positive and negative ion modes revealed distinct clustering patterns among groups (NC, MOD, and AR_H), with tight intra-group sample aggregation, indicating significant intergroup differences (P < 0.05) and robust data reproducibility. Differential metabolites were screened using criteria of variable importance in projection (VIP) > 1.0 and P < 0.05, identifying 270 metabolites between MOD and NC groups and 198 metabolites between AR_H and MOD groups (Figures 9B, C). The OPLS-DA/PLS-DA models, validated by seven-fold cross-validation, highlighted metabolites critical for group classification via VIP analysis.
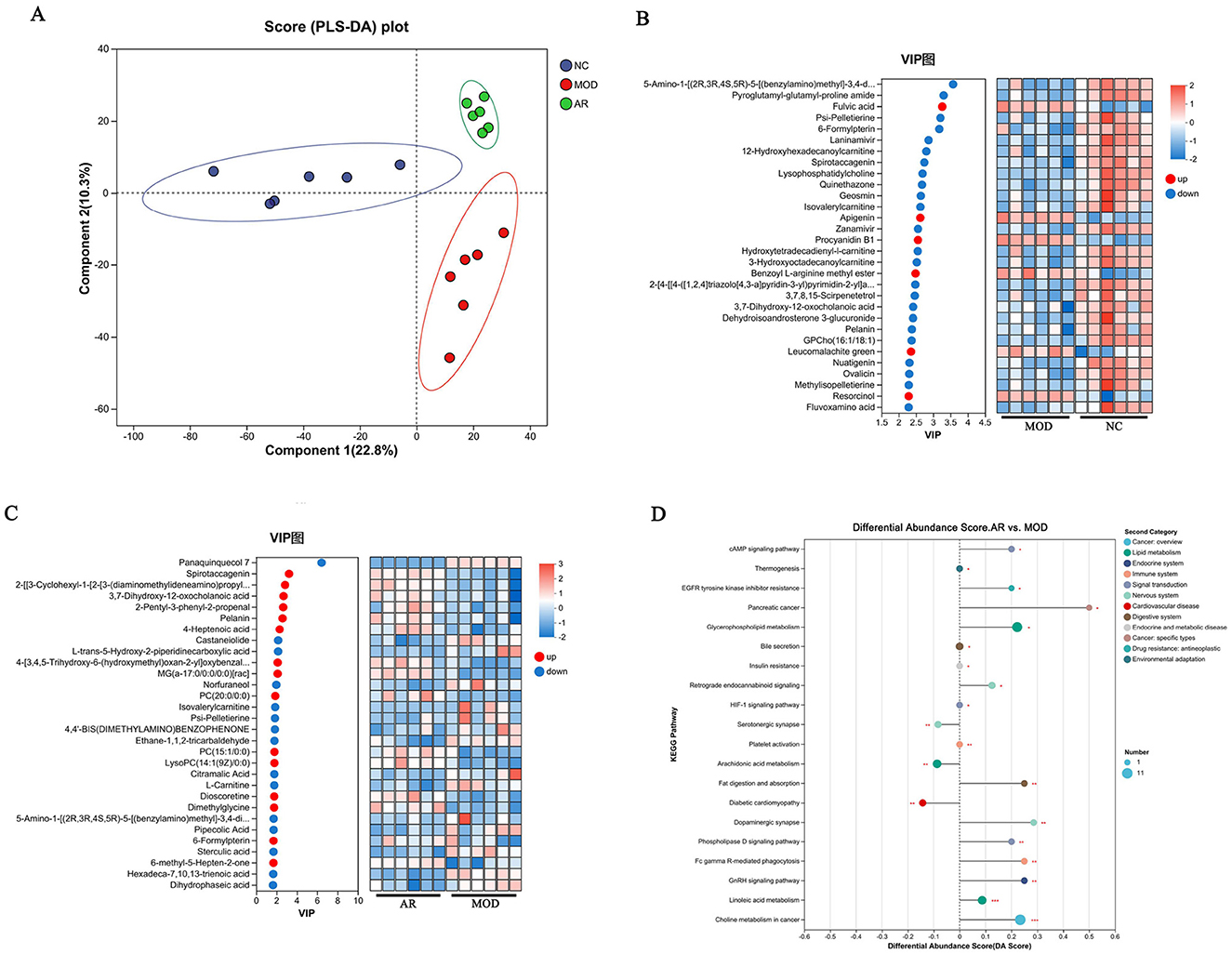
Figure 9. Effects of AR_H on the serum metabolites. (A) PLS-DA score plot; (B) heatmap of MOD vs. NC; (C) heatmap of AR vs. MOD; (D) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis.
MOD vs. NC comparisons showed 24 significantly downregulated and 6 upregulated metabolites. In AR_H vs. MOD, 15 metabolites were downregulated and 15 upregulated. Notably, MOD exhibited marked reductions in 3, 7-dihydroxy-12-oxocholanoic acid, pelanin, and 6-formylpterin compared to NC (P < 0.05), while AR_H restored these metabolites to near-normal levels (P < 0.05). Pathway analysis identified five dysregulated pathways in MOD vs. NC: linoleic acid metabolism (P = 0.003), choline metabolism in cancer (P = 0.007), retrograde endocannabinoid signaling (P = 0.012), cAMP signaling pathway (P = 0.018), and phospholipase D signaling (P = 0.023). AR_H significantly restored these pathways (Figure 9D), suggesting its therapeutic role in modulating lipid-associated inflammation and cellular signaling cascades in SCBM.
3.9 Correlation analysis between serum metabolites and gastrointestinal microbiota
In this study, seven differential metabolites significantly associated with rumen microbiota (R > 0.5, P < 0.05) were identified (Figure 10A). Among them, betaine exhibited a positive correlation with norank_f__norank_o__WCHB1-41, cyclohexane with Christensenellaceae_R-7_group, and 3-guanidinopropanoate with Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group, suggesting that these metabolites may promote or be linked to the abundance or activity of these bacterial taxa. Conversely, PC (17:0/0:0) and indoxyl showed negative correlations with Christensenellaceae_R-7_group, lauryldiet with norank_f__F082, and betaine with norank_f__Muribaculaceae, indicating potential inhibitory effects on the growth or function of these microbial populations. These findings highlight the complex interactions between distinct metabolites and rumen microbiota, which may play a pivotal role in modulating host rumen microbial communities and providing a foundation for further exploration of underlying mechanisms.
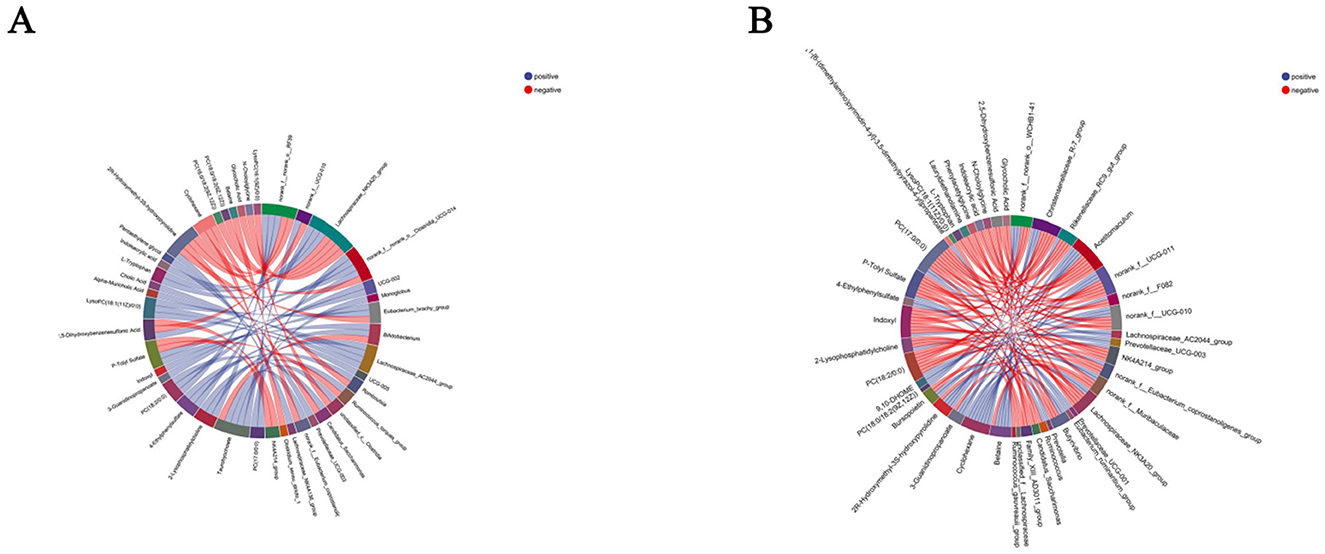
Figure 10. Correlation analysis results between serum differential metabolites and gastrointestinal microbiota. (A) Serum differential metabolites-rumen microbiota correlation; (B) serum differential metabolites-intestinal microbiota correlation. Red and blue lines indicate positive and negative correlations, respectively.
Four differential metabolites displayed strong correlations with fecal microbiota (R > 0.5, P < 0.05) (Figure 10B). Specifically, PC (17:0/0:0) was positively correlated with norank_f__norank_o__RF39, whereas p-tolyl sulfate showed a negative correlation with NK4A214_group, taurohyocholate with Bifidobacterium, and lysoPC (16:1(9Z)/0:0) with unclassified_c__Clostridia. These results suggest that these metabolites may influence the composition and activity of fecal microbiota, underscoring the potential role in regulating the fecal microbial dynamics.
3.10 Correlation analysis between gastrointestinal microbiota and SCC, milk yield, milk composition, and serum parameters
Spearman correlation analysis was performed to evaluate the associations between the relative abundance of gastrointestinal microbiota at the genus level and 18 metrics, including SCC, milk yield, milk composition, and serum parameters.
As illustrated in Figure 11A, 29 OTUs displayed significant correlations with at least one metric. Notably, Acetitomaculum, Ruminococcus_gauvreauii_group, Pseudobutyrivibrio, norank_f__norank_o__RF39, and Monoglobus in the rumen showed significant positive correlations with SCC, whereas UCG-014 exhibited a negative correlation with SCC (P < 0.05), suggesting its potential protective role. Conversely, Pseudobutyrivibrio and Ruminococcus_gauvreauii_group were negatively correlated with milk yield, indicating detrimental associations with lactation performance.
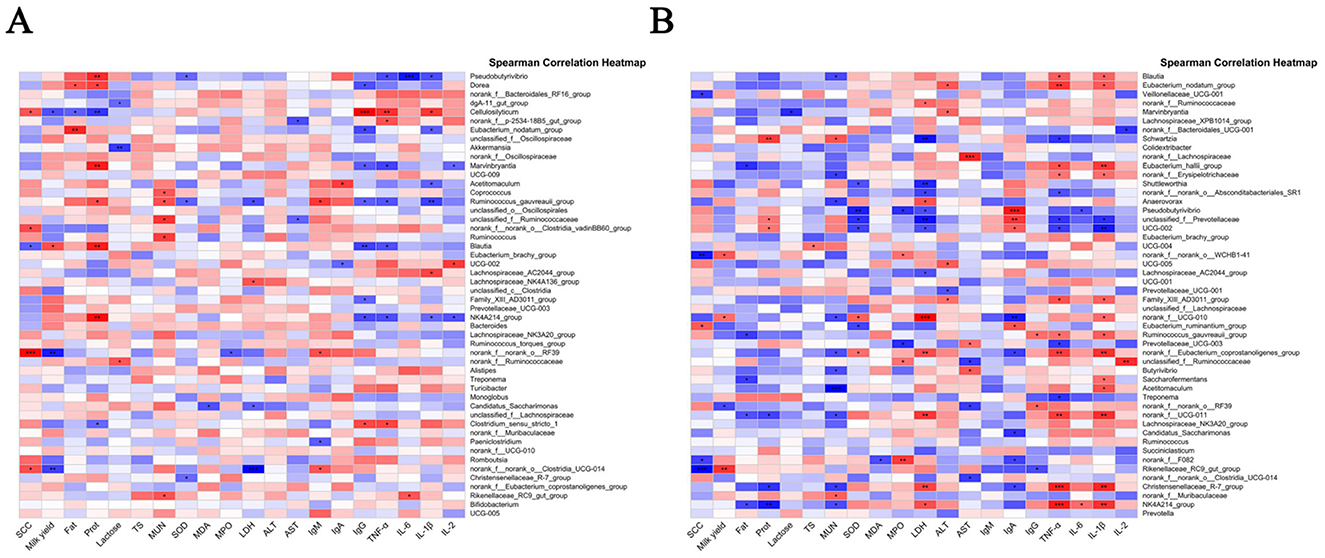
Figure 11. Correlation analysis results between gastrointestinal microbiota and clinical parameters. (A) Correlation between rumen microbiota and clinical parameters; (B) correlation between intestinal microbiota and clinical parameters. Red and blue colors indicate positive and negative correlations, respectively.
Key correlations with inflammatory markers were also observed: Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group, Balautia, unclassified_f_Lachnospiraceae, and Dorea displayed positive correlations with TNF-α, while Balautia, NK4A214_group, Bacteroides, and unclassified_f_Oscillospirales were positively correlated with IL-6 (P < 0.05), highlighting their involvement in inflammatory responses. Intriguingly, Acetitomaculum and Ruminococcus_gauvreauii_group showed positive correlations with IL-1β, LDH, and MPO—markers of inflammation and cellular damage—but negative correlations with SOD, lactose, IgG, and milk fat (P < 0.05), linking these genera to oxidative stress and milk quality deterioration. These findings reveal significant associations between specific rumen microbial taxa and critical clinical/biochemical parameters, identifying potential microbial targets for improving host health and productivity.
In the fecal microbiota (Figure 11B), Eubacterium_ruminantium_group was positively correlated with SCC, whereas Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group, norank_f__norank_o__WCHB1-41, norank_f__F082, and Veillonellaceae_UCG-001 exhibited negative correlations with SCC (P < 0.05), implying potential anti-inflammatory properties. Notably, norank_f__UGG-010, norank_f__norank_o__WCHB1-41, and Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group demonstrated positive correlations with milk yield, highlighting their potential role in yield enhancement. Norank_f__norank_o__RF39 and Eubacterium_ruminantium_group were positively correlated with LDH, linking them to tissue damage and inflammatory states. Additionally, genera such as Eubacterium_nodatum_group, Eubacterium_hallii_group, norank_f__Eubacterium_coprostanoligenes_group, norank_f__UCG-011, Christensenellaceae_R-7_group, and NK4A214_group showed positive correlations with TNF-α (P < 0.05), emphasizing their participation in systemic inflammation.
The therapeutic efficacy of ARWD in SCBM might largely stem from its ability to modulate gastrointestinal microbiota, particularly by influencing microbial taxa associated with inflammation, milk production, and systemic health. These results underscore the pivotal role of gastrointestinal microbiota in both the pathophysiology and treatment of SCBM.
3.11 Correlation analysis between serum metabolites and SCC, milk yield, milk composition, and serum parameters
Correlation analysis between serum metabolites (AR_H vs. MOD) and clinical indicators, milk composition, and serum parameters (Figure 12) revealed significant changes in metabolite levels associated with SCC, serum parameters, and milk composition following ARWD intervention. Notably, serum D-fructose exhibited positive correlations with SCC, LDH, and MDA, but negative correlations with milk yield, fat, and lactose (P < 0.05), suggesting its association with inflammation and impaired milk quality. Furthermore, metabolites such as 6-oxopiperidine-2-carboxylic acid, 2, 3-dihydroxybenzoic acid, L-carnitine, decanedioic acid, and (3S, 5R, 6R, 7E)-3, 5, 6-trihydroxy-7-megastigmen-9-one showed significant positive correlations with SCC, MDA, and MPO, but negative correlations with milk yield, fat, lactose, and IgG (P < 0.05), implicating their roles in inflammatory responses, oxidative stress, and immune dysfunction. Conversely, PE (20:1/0:0) demonstrated a negative correlation with TNF-α and IL-6 (P < 0.05), highlighting the potential anti-inflammatory properties.
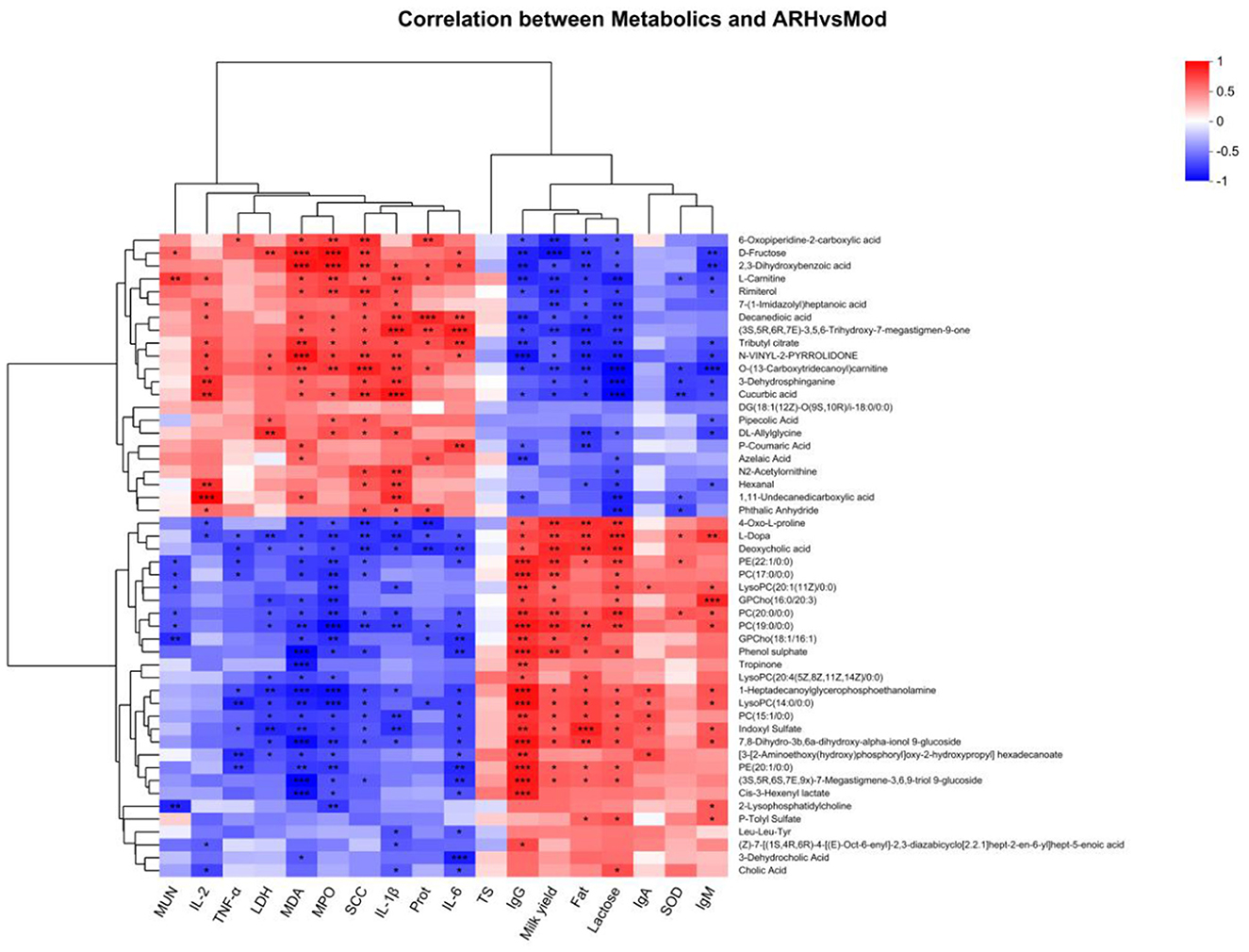
Figure 12. Correlation analysis results between serum metabolites and clinical parameters. Red and green colors indicate positive and negative correlations, respectively; P values are denoted as * < 0.05, ** < 0.01, *** < 0.001.
These results indicate that AR_H effectively modulates serum metabolites, reduces SCC, alleviates inflammation and oxidative stress, and improves milk yield and immune function. Taken together, these results highlight Astragali Radix as a promising traditional herbal formulation for the treatment of SCBM in dairy cows.
4 Discussion
SCBM in dairy cows remains a critical health challenge requiring urgent resolution in modern livestock farming. With increasing antibiotic resistance and evolving veterinary drug regulations, there is a pressing need to develop greener and healthier alternatives (15). In this study, untargeted metabolomic was employed to analyze the bioactive components of ARWD and integrated serum metabolomics with 16S rRNA sequencing were used to elucidate the therapeutic mechanism on SCBM of ARWD.
To clarify the bioactive basis of ARWD in treating bovine mastitis, LC-MS/MS analysis identified nine active compounds, including Astragalosides III, VI, and IV, ononin, formononetin, and their derivatives. These compounds were found to exhibit anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory properties. Notably, Astragaloside III demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory activity by reducing inflammatory responses and accumulating in immune organs such as the thymus and spleen, highlighting its immunomodulatory potential (16). Furthermore, Astragaloside polysaccharides and Astragaloside IV markedly suppressed the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and apoptosis in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced bovine mammary epithelial cell models, underscoring their pivotal role in mitigating mastitis (17). Other components, such as ononin and formononetin, also showed therapeutic promise. Ononin reduced ROS generation and inhibited pro-inflammatory factors, suggesting broad applications in anti-inflammatory and anticancer therapies (18). Similarly, formononetin alleviated LPS-induced mastitis symptoms by enhancing the integrity of the lactation barrier and suppressing AhR-Src signaling pathway activation (19). Additionally, bioactin A demonstrated robust anti-inflammatory and immune-enhancing properties, further supporting its development as a therapeutic agent for mastitis (20).
SCC serves as a critical biomarker for assessing udder health in dairy cows, where significant elevation in SCC levels typically indicates mastitis. The increase in SCC is primarily attributed to immune cell infiltration into mammary tissues, triggering inflammatory responses. Studies have shown that mastitis pathogenesis involves LPS and pathogenic microorganisms stimulating the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α, leading to inflammatory damage in mammary tissues and marked increases in SCC (21, 22). Elevated SCC levels are often associated with impaired mammary barrier function, resulting in sustained pathogenic stimulation and exacerbated inflammation. Clinical studies further reveal significant differences in lactation performance between cows with varying SCC levels (23). In healthy cows, milk proteins predominantly comprise casein, whey proteins, and minor non-protein nitrogen components. During mastitis, inflammatory mediators disrupt mammary epithelial cell function and increase barrier permeability, causing an imbalance in protein composition and reduced total protein content. Notably, the proportion of casein declines significantly, while concentrations of whey proteins such as lactoferrin and lactoglobulin rise substantially. These shifts likely reflect the activation of mammary immune defenses, which enhance the secretion of whey proteins, particularly antimicrobial proteins, to combat infection (24, 25).
Mastitis-induced changes in osmotic gradients facilitate the leakage of plasma proteins such as albumin and fibrinogen into milk, further altering milk protein composition and potentially compromising dairy processing quality. Studies also indicate that cows with elevated SCC levels typically have lower milk protein content, which is associated with the metabolic burden of inflammation as well as physical damage and functional decline in mammary tissues (25).
The development of bovine mastitis is closely associated with the overexpression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, particularly IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, which play pivotal roles in inflammatory cascades (26). IL-1β acts as a critical initiator of inflammatory responses by activating NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways, thereby inducing the release of other pro-inflammatory cytokines and significantly enhancing neutrophil migration into mammary tissues, exacerbating tissue damage (27). Elevated IL-1β levels in milk from mastitic cows correlate positively with increased SCC (26). IL-6, a key mediator of acute-phase responses, enhances antimicrobial defenses by stimulating lactoferrin and C-reactive protein production. However, its role in increasing vascular permeability may also promote inflammatory dissemination (28). Prolonged IL-6 overexpression further impairs mammary barrier function and is strongly associated with reduced lactose secretion. TNF-α, another central regulator of pro-inflammatory responses, induces apoptosis and oxidative stress, aggravating mammary tissue lesions (29). Our findings demonstrate that ARWD significantly reduces IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α expression levels in milk from mastitic cows. These results suggest that ARWD alleviates mammary inflammation and tissue damage by disrupting cytokine-triggered inflammatory cascades. Consistent with this, Khan et al. (30) reported that certain natural plant-derived bioactive compounds regulate mastitis-associated cytokines. By suppressing the overexpression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, ARWD effectively mitigates mastitis symptoms, preserves mammary tissue integrity, and improves lactation performance in dairy cows.
The onset of bovine mastitis is accompanied by exacerbated oxidative stress, characterized by dysregulated levels of oxidative biomarkers such as MPO, LDH, SOD, and MDA. MPO, a key oxidative enzyme released by neutrophils, reflects the intensity of inflammatory responses and neutrophil hyperactivation. Elevated MPO activity is recognized as a marker of inflammatory severity in mastitic cows (31, 32). LDH, an indicator of cellular damage, increases significantly during mastitis due to inflammation and necrosis in mammary tissues, signifying impaired tissue metabolism and compromised mammary barrier integrity (33). Concurrently, reduced SOD activity—a critical antioxidant enzyme counteracting oxidative stress—leads to free radical accumulation, aggravating tissue damage. MDA, a lipid peroxidation byproduct, exhibits elevated concentrations indicative of oxidative membrane damage (34). Our results demonstrate that ARWD significantly reduced MPO and LDH activities in mastitis models while elevating SOD levels and reducing MDA concentrations. These findings highlight ARWD's efficacy in mitigating oxidative stress-induced tissue damage, underscoring its potential as a therapeutic agent for bovine mastitis.
The pathogenesis of bovine mastitis is accompanied by immune system activation (35), with immunoglobulins IgM, IgG, and IgA playing critical roles in mammary immune defense. During mastitis, LPS translocation from the rumen to the bloodstream enhances pro-inflammatory cytokine release and elevates serum immunoglobulin levels (36). IgM, the primary antibody in the initial immune response, rapidly recognizes mastitis-associated pathogens and facilitates pathogen clearance by activating the complement system. IgG, the predominant antibody in bovine mammary immunity, provides protection by neutralizing pathogen toxins and enhancing phagocyte functionality. The marked increase in milk IgG levels during mastitis reflects sustained immune responses to mammary infections (28). Additionally, IgA, a key component of local mucosal immunity, prevents pathogen adhesion to mammary epithelial cells, thereby reducing tissue damage. Studies indicate that elevated IgA levels in bovine milk strengthen local immune barriers and enhance protective functions (28). In this study, ARWD significantly elevated serum IgM, IgG, and IgA levels in mastitic cows, indicating its dual role in augmenting systemic primary immune responses and suppressing inflammatory progression via improved local mammary immunity. These findings align with reports by Khan et al. (30), who demonstrated that certain herbal components effectively upregulate immunoglobulin expression linked to bovine mammary immunity. Collectively, this underscores the protective effects and theoretical rationale for using traditional Chinese medicine in mastitis management.
The rumen microbiota plays a pivotal role in both the development and therapeutic management of bovine mastitis by modulating systemic immune functions during inflammatory responses (29, 37). Our study revealed significant shifts in microbial diversity within the rumen and intestines of mastitic cows, with ARWD intervention promoting a restorative trend in microbiota composition. Notably, key genera such as Turicibacter, Cellulosilyticum, Brevibacillus, Roseburia, and Saccharofermentans were implicated in these dynamics.
Turicibacter is a strictly anaerobic, Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium typically abundant in the gut and rumen of healthy animals. It critically maintains microbial balance, supports host metabolic health, and regulates immune functions (38). Cellulosilyticum is a cellulolytic genus essential for degrading plant fibers in the rumen, producing volatile fatty acids (VFAs) vital for energy metabolism. Mastitis-induced reductions in its abundance impair energy homeostasis and compromise immune defenses (39). Brevibacillus is a Gram-positive, spore-forming, thermotolerant genus within the Bacillaceae family, exhibiting aerobic/facultative anaerobic traits. Brevibacillus strains demonstrate resistance to 67% of tested antibiotics, suggesting potential interference with mastitis treatment (40). Roseburia is a strictly anaerobic, Gram-positive genus prevalent in mammalian intestines. Zhao et al. (41) reported that citrus flavonoid extracts reduce its abundance, improving inflammatory and immune-metabolic functions in cows. Saccharofermentans is an acid-producing bacterium critical for mammary barrier integrity. Its depletion correlates with metabolic dysregulation and reduced milk protein levels in lactating cows (42). Our findings demonstrate that ARWD significantly restored the abundance of beneficial rumen microbiota, particularly Turicibacter and Cellulosilyticum. These results suggest that ARWD alleviates mastitis by rebalancing rumen microbiota and enhancing metabolic functions, thereby mitigating inflammation and supporting mammary health.
The onset of bovine mastitis is frequently accompanied by significant gut microbiota disruption, which not only alters microbial diversity but also directly impacts host immunometabolic and inflammatory responses. Our study identified marked changes in the abundance of Roseburia, Treponema, Selenomonas, Prevotellaceae_UCG-004, Corynebacterium, Staphylococcus, Microbacterium, and Eubacterium_nodatum_group in the gut microbiota of mastitic cows. Roseburia, a primary producer of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) via butyrate metabolism, plays a pivotal role in maintaining intestinal barrier integrity and suppressing systemic inflammation. Its depletion in mastitic cows is strongly associated with exacerbated immune dysfunction (41). Conversely, Treponema, a Gram-negative spirochete linked to chronic inflammation and tissue damage, exhibited elevated abundance, potentially exacerbating mastitis through lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated immune hyperactivation (43). Similarly, increased Selenomonas (a Gram-negative genus involved in metabolic regulation) abundance may disrupt metabolic homeostasis and inflammatory control, aggravating mammary tissue injury (44). Prevotellaceae_UCG-004, enriched in high-fiber diets, was modulated by dietary calcium propionate to improve energy metabolism and hypocalcemia (45). Pathogenic roles were observed for Corynebacterium (46) and Staphylococcus/Microbacterium (47) with Astragalus supplementation specifically inhibiting Microbacterium to exert anti-inflammatory effects. Notably, Eubacterium_nodatum_group, a Gram-positive anaerobic commensal linked to metabolic regulation, showed reduced abundance in Astragalus-treated buffalo with mastitis, suggesting its role in microbiota-driven therapeutic modulation (39). These findings underscore the potential of Astragalus to alleviate mastitis by restoring gut microbiota balance and targeting pathogenic taxa, highlighting its dual role in metabolic and immune regulation.
ARWD significantly increased the abundance of the gut microbiota genus Roseburia while reducing Treponema and Selenomonas levels, suggesting its ability to alleviate mastitis by restoring gut microbial equilibrium, suppressing pro-inflammatory bacteria, and improving systemic immune-metabolic homeostasis. These findings highlight ARWD potential to mitigate clinical manifestations of bovine mastitis.
Serum metabolomics identified four key differential metabolites in cows with SCBM: spirotaccagenin, 3, 7-dihydroxy-12-oxocholanoic acid, pelanin, and 6-formylpterin. These metabolites were linked to dysregulated pathways, including linoleic acid metabolism, choline metabolism in cancer, retrograde endocannabinoid signaling, cAMP signaling, and phospholipase D signaling, which collectively influence inflammatory responses, oxidative stress, and immune regulation. Spirotaccagenin is a steroidal compound hypothesized to exert anti-inflammatory and immunostimulatory effects via downstream steroidal glycosides, which modulate cell proliferation and antimicrobial activity (48, 49). 3,7-Dihydroxy-12-oxocholanoic acid is a bile acid derivative critical for lipid digestion and absorption, with potential roles in gut microbiota modulation and immune function (50). Pelanin is an anthocyanin derivative renowned for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, attenuating chronic inflammation via inhibition of NF-κB and STAT1/3 signaling pathways (51). 6-Formylpterin: Suppresses lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide (NO) production in macrophages, demonstrating anti-inflammatory potential (52). Pathway analysis revealed that linoleic acid metabolism—a dual modulator of pro- and anti-inflammatory responses through its role as a precursor for arachidonic acid—enhances bacterial clearance in macrophages, suggesting lipid-mediated immune defense (53). Similarly, the phospholipase D signaling pathway regulates cellular stress and inflammation during mastitis by modulating secondary messengers involved in proliferation and anti-apoptosis (54, 55). ARWD significantly elevated these metabolites and restored pathway activity, particularly in linoleic acid metabolism, thereby enhancing anti-inflammatory and antioxidant capacity. These findings elucidate ARWD molecular mechanisms in SCBM management, emphasizing its dual role in microbiota restoration and metabolic reprogramming to combat inflammation and oxidative stress.
5 Conclusion
ARWD effectively mitigates SCBM by modulating rumen-gut microbiota interactions and regulating linoleic acid metabolism and phospholipase D signaling. This intervention significantly reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α), enhanced immunoglobulins (IgM/IgG/IgA), and improved antioxidant capacity, achieving dual therapeutic benefits of lowered somatic cell counts and increased milk yield. These findings highlight ARWD's multi-target anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms, offering a sustainable alternative to antibiotics for mastitis management.
Data availability statement
The data presented in the study is deposited in the https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ repository, accession number: SRP589200 and SRP589088.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Animal Ethics Committee of Gansu Agricultural University (GSAU-Eth-VMC-2021-020). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
JY: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. KZ: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing. TM: Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. PJ: Project administration, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YW: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: U21A20262), the Science and Technology Plan of Gansu Province (24ZDNA001), 2025 Project for Outstanding Graduate Students in Science and Technology of Gansu Province (No. 25CXZX-76).
Acknowledgments
We thank all authors for their contributions and support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
ARWD, Astragali Radix water decoction; SCBM, subclinical bovine mastitis; SCC, somatic cell count; TCVM, traditional Chinese veterinary medicine; SCFAs. short-chain fatty acids; TCM, traditional Chinese medicine; MDA, malondialdehyde; SOD, superoxide dismutase; MPO, myeloperoxidase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; IgA, immunoglobulin A; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IgM, immunoglobulin M; IL-2, interleukin-2; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; AR_H, Astragali Radix water decoction high-dose; AR_M, Astragali Radix water decoction medium-dose; AR_L, Astragali Radix water low-dose; MOD, model group; NC, negative controls; TS, total milk solids; MUN, milk urea nitrogen; OTUs, operational taxonomic units; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PCA, principal component analysis.
References
1. Pakrashi A, Ryan C, Gueret C, Berry DP, Corcoran M, Keane MT, et al. Early detection of subclinical mastitis in lactating dairy cows using cow-level features. J Dairy Sci. (2023) 106:4978–90. doi: 10.3168/jds.2022-22803
2. Cavero D, Tölle KH, Rave G, Buxadé C, Krieter J. Analysing serial data for mastitis detection by means of local regression. Livest Sci. (2007) 110:101–10. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2006.10.006
3. Sindhu S, Saini T, Rawat HK, Chahar M, Grover A, Ahmad S, et al. Beyond conventional antibiotics approaches: global perspectives on alternative therapeutics including herbal prevention, and proactive management strategies in bovine mastitis. Microb Pathog. (2024) 196:106989. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106989
4. Bittante G, Amalfitano N, Bergamaschi M, Patel N, Haddi ML, Benabid H, et al. Composition and aptitude for cheese-making of milk from cows, buffaloes, goats, sheep, dromedary camels, and donkeys. J Dairy Sci. (2022) 105:2132–52. doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-20961
5. Belkaid Y, Harrison OJ. Homeostatic immunity and the microbiota. Immunity. (2017) 46:562–76. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.04.008
6. Wiertsema SP, van Bergenhenegouwen J, Garssen J, Knippels LMJ. The interplay between the gut microbiome and the immune system in the context of infectious diseases throughout life and the role of nutrition in optimizing treatment strategies. Nutrients. (2021) 13:886. doi: 10.3390/nu13030886
7. Derakhshani H, Fehr KB, Sepehri S, Francoz D, De Buck J, Barkema HW, et al. Invited review: Microbiota of the bovine udder: contributing factors and potential implications for udder health and mastitis susceptibility. J Dairy Sci. (2018) 101:10605–25. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-14860
8. Silva YP, Bernardi A, Frozza RL. The role of short-chain fatty acids from gut microbiota in gut-brain communication. Front Endocrinol. (2020) 11:25. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00025
9. Che Y, Li L, Kong M, Geng Y, Wang D, Li B, et al. Dietary supplementation of Astragalus flavonoids regulates intestinal immunology and the gut microbiota to improve growth performance and intestinal health in weaned piglets. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1459342. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1459342
10. Li CX, Liu Y, Zhang YZ, Li JC, Lai J. Astragalus polysaccharide: a review of its immunomodulatory effect. Arch Pharm Res. (2022) 45:367–89. doi: 10.1007/s12272-022-01393-3
11. Kim J, Zhang S, Zhu Y, Wang R, Wang J. Amelioration of colitis progression by ginseng-derived exosome-like nanoparticles through suppression of inflammatory cytokines. J Ginseng Res. (2023) 47:627–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.01.004
12. Tian S, Zheng N, Zu X, Wu G, Zhong J, Zhang J, et al. Integrated hepatic single-cell RNA sequencing and untargeted metabolomics reveals the immune and metabolic modulation of Qing-Fei-Pai-Du decoction in mice with coronavirus-induced pneumonia. Phytomedicine. (2022) 97:153922. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153922
13. Ma C, Sun Z, Zeng B, Huang S, Zhao J, Zhang Y, et al. Cow-to-mouse fecal transplantations suggest intestinal microbiome as one cause of mastitis. Microbiome. (2018) 6:200. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0578-1
14. Hiitiö H, Vakkamäki J, Simojoki H, Autio T, Junnila J, Pelkonen S, et al. Prevalence of subclinical mastitis in Finnish dairy cows: changes during recent decades and impact of cow and herd factors. Acta Vet Scand. (2017) 59:22. doi: 10.1186/s13028-017-0288-x
15. Cheng WN, Han SG. Bovine mastitis: risk factors, therapeutic strategies, and alternative treatments - a review. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. (2020) 33:1699–713. doi: 10.5713/ajas.20.0156
16. Liu XH, Guo L, Yang YL, Hu F, Chen XY, Feng SL. Development and validation of a rapid and simple UPLC-ESI-MS method for pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of Astragaloside III in rats. J Chromatogr Sci. (2016) 54:811–8. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmw021
17. Jiaqi F, Fang J, Yusi L, Xuezhang Z. Effects of astragalus polysaccharide and astragaloside IV on lipopolysaccharides-induced inflammation of bovine mammary epithelial cells. J South China Agric Univ. (2022) 43:16–28. doi: 10.7671/j.issn.1001-411X.202106034
18. Bhuia MS, Aktar MA, Chowdhury R, Ferdous J, Rahman MA, Hasan MSA, et al. Therapeutic potentials of ononin with mechanistic insights: a comprehensive review. Food Biosci. (2023) 56:103302. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2023.103302
19. Xiang K, Shen P, Gao Z, Liu Z, Hu X, Liu B, et al. Formononetin protects LPS-induced mastitis through suppressing inflammation and enhancing blood-milk barrier integrity via AhR-induced Src inactivation. Front Immunol. (2022) 13. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.814319
20. Yuan Z, Li F, Zhang W, Wei Y, Hua Y. Exploring the potential role of Sophora alopecuroides L. in inflammation of bovine mammary epithelial cells induced by lipoteichoic acid based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. (2024). doi: 10.2174/0113862073313036240829070704
21. Li K, Zhang L, Xue J, Yang X, Dong X, Sha L, et al. Dietary inulin alleviates diverse stages of type 2 diabetes mellitus via anti-inflammation and modulating gut microbiota in db/db mice. Food Funct. (2019) 10:1915–27. doi: 10.1039/C8FO02265H
22. Zhao XH, Gong JM, Zhou S, Liu CJ, Qu MR. The effect of starch, inulin, and degradable protein on ruminal fermentation and microbial growth in rumen simulation technique. Ital J Anim Sci. (2016) 13:3123. doi: 10.4081/ijas.2014.3121
23. Schepers AJ, Lam TJ, Schukken YH, Wilmink JB, Hanekamp WJ. Estimation of variance components for somatic cell counts to determine thresholds for uninfected quarters. J Dairy Sci. (1997) 80:1833–40. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(97)76118-6
24. Ma C, Zhao J, Xi X, Ding J, Wang H, Zhang H, et al. Bovine mastitis may be associated with the deprivation of gut Lactobacillus. Benef Microbes. (2016) 7:95–102. doi: 10.3920/BM2015.0048
25. Vojinovic D, Radjabzadeh D, Kurilshikov A, Amin N, Wijmenga C, Franke L, et al. Relationship between gut microbiota and circulating metabolites in population-based cohorts. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:5813. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13721-1
26. Bannerman DD, Paape MJ, Lee JW, Zhao X, Hope JC, Rainard P. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus elicit differential innate immune responses following intramammary infection. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. (2004) 11:463–72. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.11.3.463-472.2004
27. He X, Wei Z, Zhou E, Chen L, Kou J, Wang J, et al. Baicalein attenuates inflammatory responses by suppressing TLR4 mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced mastitis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. (2015) 28:470–6. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.07.012
28. Gabay C, Kushner I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med. (1999) 340:448–54. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199902113400607
29. Hu X, Li S, Mu R, Guo J, Zhao C, Cao Y, et al. The rumen microbiota contributes to the development of mastitis in dairy cows. Microbiol Spectr. (2022) 10:e0251221. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02512-21
30. Khan W, Khan SA, Khan FA, Khan S, Ullah I, Shah A, et al. Therapeutic potential of natural products and antibiotics against bovine mastitis pathogen of cows and buffaloes. Vet Med. (2023) 68:271–80. doi: 10.17221/80/2022-VETMED
31. Raulo SM, Sorsa T, Tervahartiala T, Latvanen T, Pirilä E, Hirvonen J, et al. Increase in milk metalloproteinase activity and vascular permeability in bovine endotoxin-induced and naturally occurring Escherichia coli mastitis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. (2002) 85:137–45. doi: 10.1016/S0165-2427(01)00423-8
32. Liu Y, Jiang Y, Yang Y, Wang H, Ye J, Liu D, et al. Houttuynia essential oil and its self-microemulsion preparation protect against LPS-induced murine mastitis by restoring the blood-milk barrier and inhibiting inflammation. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:842189. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.842189
33. Wall SK, Wellnitz O, Hernández-Castellano LE, Ahmadpour A, Bruckmaier RM. Supraphysiological oxytocin increases the transfer of immunoglobulins and other blood components to milk during lipopolysaccharide- and lipoteichoic acid-induced mastitis in dairy cows. J Dairy Sci. (2016) 99:9165–73. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-11548
34. Özkan H, Keçeli HH, Kaya U, Dalkiran S, Yüksel M, Tek E, et al. Considering potential roles of selected MicroRNAs in evaluating subclinical mastitis and Milk quality in California mastitis test (+) and infected bovine milk. Anim Sci J. (2024) 95:e13959. doi: 10.1111/asj.13959
35. Sordillo LM, Streicher KL. Mammary gland immunity and mastitis susceptibility. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. (2002) 7:135–46. doi: 10.1023/A:1020347818725
36. Dong G, Liu S, Wu Y, Lei C, Zhou J, Zhang S. Diet-induced bacterial immunogens in the gastrointestinal tract of dairy cows: impacts on immunity and metabolism. Acta Vet Scand. (2011) 53:48. doi: 10.1186/1751-0147-53-48
37. Xu Q, Qiao Q, Gao Y, Hou J, Hu M, Du Y, et al. Gut microbiota and their role in health and metabolic disease of dairy cow. Front Nutr. (2021) 8:701511. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.701511
38. Tan YJ, Koh SP, Khoizirah S, Rozaihan M, Manthan J, Khirrol NAW, et al. Genomic mapping milk microbiota from healthy, sub-clinical and clinical mastitis of Jersey Friesian cattle in a Malaysian farm. Food Res. (2023) 56:103302. doi: 10.26656/fr.2017.6(S4).006
39. Chen X, An M, Zhang W, Li K, Kulyar MF, Duan K, et al. Integrated bacteria-fungi diversity analysis reveals the gut microbial changes in buffalo with mastitis. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:918541. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.918541
40. Gutiérrez-Chávez AJ, Martínez-Ortega EA, Valencia-Posadas M, León-Galván MF, de la Fuente-Salcido NM, Bideshi DK, et al. Potential use of Bacillus thuringiensis bacteriocins to control antibiotic-resistant bacteria associated with mastitis in dairy goats. Folia Microbiol. (2016) 61:11–9. doi: 10.1007/s12223-015-0404-0
41. Zhao Y, Yu S, Li L, Zhao H, Li Y, Jiang L, et al. Feeding citrus flavonoid extracts decreases bacterial endotoxin and systemic inflammation and improves immunometabolic status by modulating hindgut microbiome and metabolome in lactating dairy cows. Anim Nutr. (2023) 13:386–400. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2023.03.007
42. Li M, Zhong H, Li M, Zheng N, Wang J, Zhao S. Contribution of ruminal bacteriome to the individual variation of nitrogen utilization efficiency of dairy cows. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:815225. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.815225
43. Jin W, Xue C, Liu J, Yin Y, Zhu W, Mao S. Effects of disodium fumarate on in vitro rumen fermentation, the production of lipopolysaccharide and biogenic amines, and the rumen bacterial community. Curr Microbiol. (2017) 74:1337–42. doi: 10.1007/s00284-017-1322-y
44. Xie T, Kong F, Wang W, Wang Y, Yang H, Cao Z, et al. In vitro and in vivo studies of soybean peptides on milk production, rumen fermentation, ruminal bacterial community, and blood parameters in lactating dairy cows. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:911958. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.911958
45. Zhang F, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Wang H, Nan X, Guo Y, et al. Dietary supplementation with calcium propionate could beneficially alter rectal microbial composition of early lactation dairy cows. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:940216. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.940216
46. Johnstone KJ, Robson J, Cherian SG, Wan Sai Cheong J, Kerr K, Bligh JF. Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis associated with Corynebacterium including Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii. Pathology. (2017) 49:405–12. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2017.01.006
47. Gryaznova MV, Syromyatnikov MY, Dvoretskaya YD, Solodskikh SA, Klimov NT, Mikhalev VI, et al. Microbiota of cow's milk with udder pathologies. Microorganisms. (2021) 9:1974. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9091974
48. Nguyen DH, Bruguière A, Miyamoto T, Dias AMM, Bellaye P-S, Collin B, et al. Steroidal glycosides from Yucca rostrata and Dracaena braunii and their cytotoxic and antimicrobial evaluation. Biochem Syst Ecol. (2024) 113:104791. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2024.104791
49. da Silva Leite JM, Barros Araújo CB, Alves LP, Bezerra Pereira MR, Guedes GG, de Carvalho Moreira LMC, et al. Trends and application of analytical methods for the identification and quantification of dexamethasone in drug delivery system. Curr Pharm Anal. (2023) 19:1–19. doi: 10.2174/1573412918666221004122046
50. Vítek L, Haluzík M. The role of bile acids in metabolic regulation. J Endocrinol. (2016) 228:R85–96. doi: 10.1530/JOE-15-0469
51. Lee HH, Lee SG, Shin JS, Lee HY, Yoon K, Ji YW, et al. p-coumaroyl anthocyanin mixture isolated from tuber epidermis of solanum tuberosum attenuates reactive oxygen species and pro-inflammatory mediators by suppressing NF-κB and STAT1/3 signaling in LPS-induced RAW2647 macrophages. Biol Pharm Bull. (2017) 40:1894–902. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00362
52. Mori H, Arai T, Hirota K, Ishii H, Endo N, Makino K, et al. Effects of 6-formylpterin, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor and a superoxide scavenger, on production of nitric oxide in RAW 2647 macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2000) 1474:93–9. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4165(99)00210-X
53. Yan B, Fung K, Ye S, Lai PM, Wei YX, Sze KH, et al. Linoleic acid metabolism activation in macrophages promotes the clearing of intracellular Staphylococcus aureus. Chem Sci. (2022) 13:12445–60. doi: 10.1039/D2SC04307F
54. Nabih AM, Hussein HA, El-Wakeel SA, Abd El-Razik KA, Gomaa AM. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis mastitis in Egyptian dairy goats. Vet World. (2018) 11:1574–80. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2018.1574-1580
Keywords: Astragali Radix, subclinical bovine mastitis, phytochemical untargeted metabolomics, metabolomics, 16S rRNA
Citation: Yan J, Zhou K, Ma T, Ji P and Wei Y (2025) Gastrointestinal flora and serum metabolomic elucidation of Astragali Radix water decoction intervention in subclinical bovine mastitis. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1611467. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1611467
Received: 14 April 2025; Accepted: 17 July 2025;
Published: 18 August 2025.
Edited by:
Shuaiyu Wang, China Agricultural University, ChinaReviewed by:
Hongxu Du, Southwest University, ChinaRuonan Bo, Yangzhou University, China
Patipan Hnokaew, Chiang Mai University, Thailand
Copyright © 2025 Yan, Zhou, Ma, Ji and Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanming Wei, d2VpeW1AZ3NhdS5lZHUuY24=; Peng Ji, amlwQGdzYXUuZWR1LmNu
 Jianpeng Yan
Jianpeng Yan Ke Zhou
Ke Zhou Ting Ma
Ting Ma Peng Ji
Peng Ji Yanming Wei
Yanming Wei