- 1Feed Research Institute, Xinjiang Academy of Animal Sciences, Urumqi, China
- 2Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Herbivorous Livestock Feed Biotechnology, Urumqi, China
Introduction: The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of a preparation of black goji berry branches (Lycium ruthenicum) on growth performance, meat quality, amino acid and fatty acid content of sheep.
Methods: The experiment was a one-way completely randomized trial, in which 40 male sheep of the F1 generation of Dupo × Lake sheep crosses at four months of age were randomly divided into four groups of ten lambs each. Each group was fed an isoenergetic and isonitrogenous total mixed pellet ration containing 0% (CON), 10% (H1), 20% (H2) and 30% (H3) of Lycium ruthenicum branches. The experimental period included a pre-test adaptation of 10 d and an experimental test period of 60 d.
Results: The Luminosity of each experimental group was highly significantly higher than that of the CON (p < 0.01). The values for Redness of the H2 and H3 groups were significantly higher than that of the CON (p < 0.05). The gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) concentration in the longest back muscle first increased and then decreased (p < 0.01), and the H2 group was extremely significantly higher than the CON and the other experimental groups. The H1 and H2 groups were significantly lower than the control group, decreasing by 6.87% and 7.07%, respectively (p < 0.05). The c20:0, c20:1 content showed a linear increase with increasing addition of Lycium ruthenicum, but the difference was not significant (p > 0.05).
Discussion: Thus, dietary feed supplementation with 20% of dried, ground Lycium ruthenicum branches can improve sheep meat quality and culture benefit.
1 Introduction
The rapid development of animal farming has led to insufficient high-fiber forage resources and shortages of grass for animals. This scarcity together with the dependence on only a few types of forage have become more serious and have begun to limit the development of animal husbandry (1). One solution of this problem is to test non-conventional types of roughage as replacements in conventional feeds (2). Increasing the proportion of ground-sourced, non-conventional roughage in the feed can alleviate the resource shortage and reduce feed costs.
Lycium ruthenicum (L. ruthenicum) is a deciduous shrub in the Solanaceae family, valuable as a food plant but also medicinally useful because of its antioxidant (3), antitumor, lipid-lowering (4), and immune-enhancing properties. Its by-products (stalks, branches, leaves, leftover fruit, etc.) contain beneficial compounds like proanthocyanidins, flavonoids, polysaccharides, alkaloids, amino acids, betaine and other active ingredients (5). These compounds make L. ruthenicum by-products promising candidates for use as functional feed additives with bioactive properties (6). L. ruthenicum leaf flavonoids inhibit the proteolysis of minced meat and enhance its gelatinous and chewy properties by delaying muscle pH changes, lowering fat peroxide value (POV) and total volatile base nitrogen (TVB-N) content, and altering pancreatic lipase secondary structure by non-covalent reversible binding to trypsin, thereby reducing fat synthesis (7, 8).
Adding a mixture of wolfberry leaves and astragalus to the diets of pigs increased the content of unsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E in pork, which in turn improved meat quality and nutritional value (9). A study by Zhang et al. (10) found that wolfberry by-products and their fermentation products could significantly improve the fatty acid and organic acid contents of lamb by regulating valine, leucine, and isoleucine biosynthesis, linoleic acid metabolism, and glycerophospholipid metabolic pathways, which could affect meat quality. Hou et al. (11) found that the addition of 5% black wolfberry residual fruits to replace part of the roughage significantly increased the growth performance and improved rumen fermentation parameters and gross profit of Dolan sheep.
In order to improve the yield of Lycium barbarum, Lycium barbarum trees need to be artificially shaped and pruned, producing a large number of Lycium barbarum branches. The hypothesis of this paper is that the applicantion of L. ruthenicum branches and leaves as livestock feed in animal husbandry can effectively alleviate the problem of insufficient sources of forage, reduce the cost of animal husbandry, improve the production performance of livestock, and improve the economic benefits of farming.
Therefore, this study investigated how different amounts of L. ruthenicum by-products added to sheep feed affect carcass characteristics, meat quality, amino acid and fatty acid composition. The goal was to provide scientific evidence for the application of L. ruthenicum branches to improve production in an actual sheep farm.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental location and ethical statement
The experiments were conducted from Jun 9 to Aug2, 2023 at the sheep farm of Xinjiang Taihe Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Technology Co., Ltd., Bachu County, Kashgar Prefecture, Xinjiang (Kashgar, China). The study was carried out in accordance with the procedures sanctioned for this research, which were approved by the Science and Technology Ethics Committee of Xinjiang Academy of Animal Sciences, China (Approval No. 20230508). These procedures adhere to the principles and regulations for ethical protection in human and animal biological science and technology in China.
2.2 Experimental materials
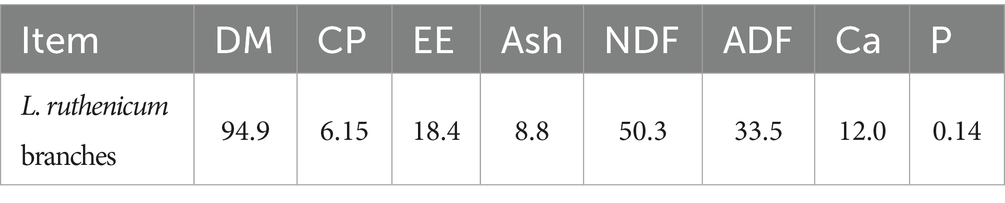
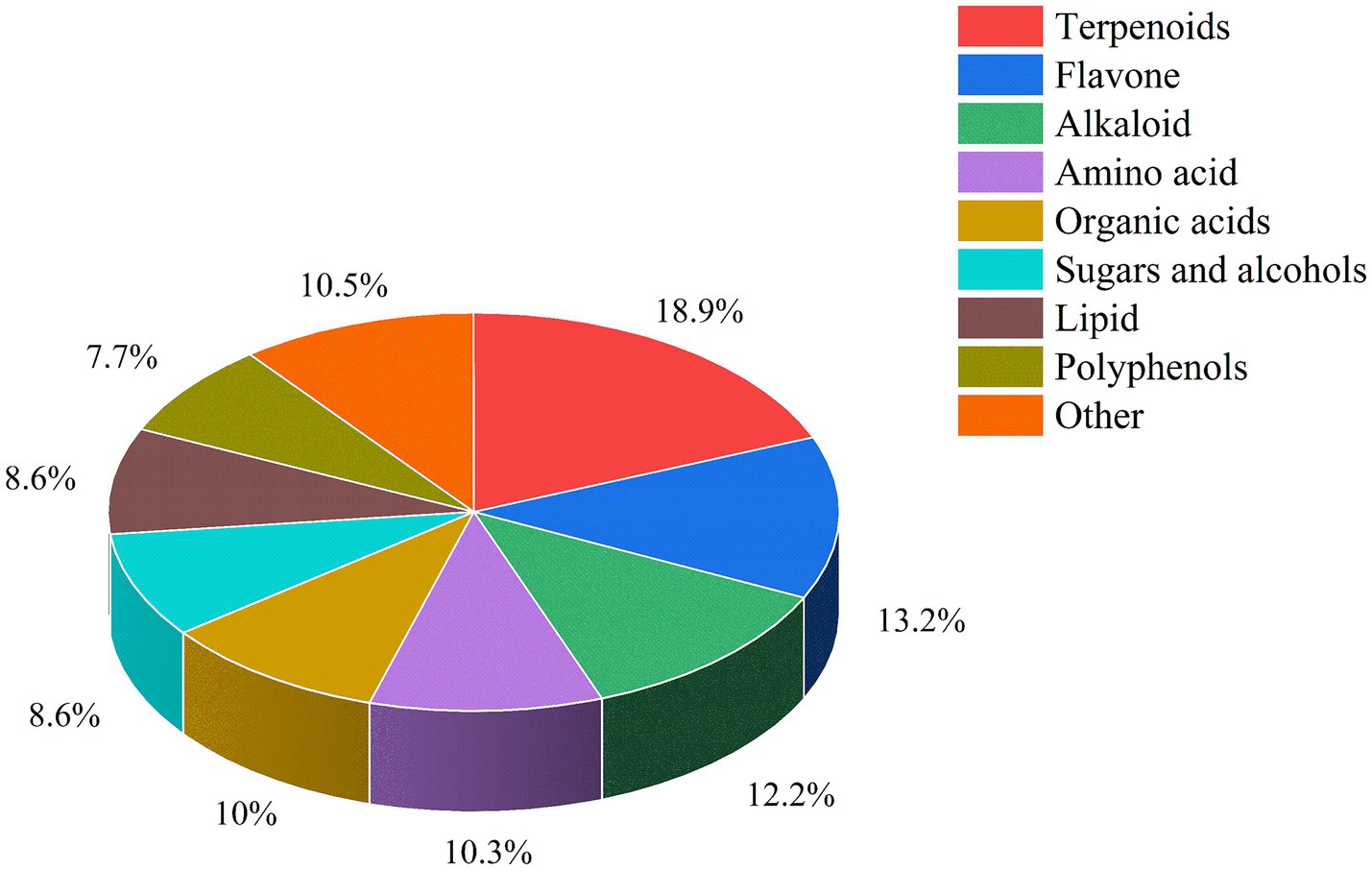
Air-dried L. ruthenicum branches remaining after picking fresh fruit were provided by Xinjiang black fruit goji berry Biotechnology Company, Ltd., and their nutrient composition is shown in Table 1. The detection and quantitation of the bioactive ingredients in L. ruthenicum branches was performed by the Baimaike Biological Company, Ltd., using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC–MS), and the results are shown in Figure 1. The main active components included terpenoids, flavonoids, alkaloids, amino acids, organic acids, sugars, alcohols, lipids and polyphenols. The top five most abundant compounds were terpenoids (18.90%), flavonoids (13.20%), alkaloids (12.20%), organic acids (10.00%), and amino acids (10.30%).
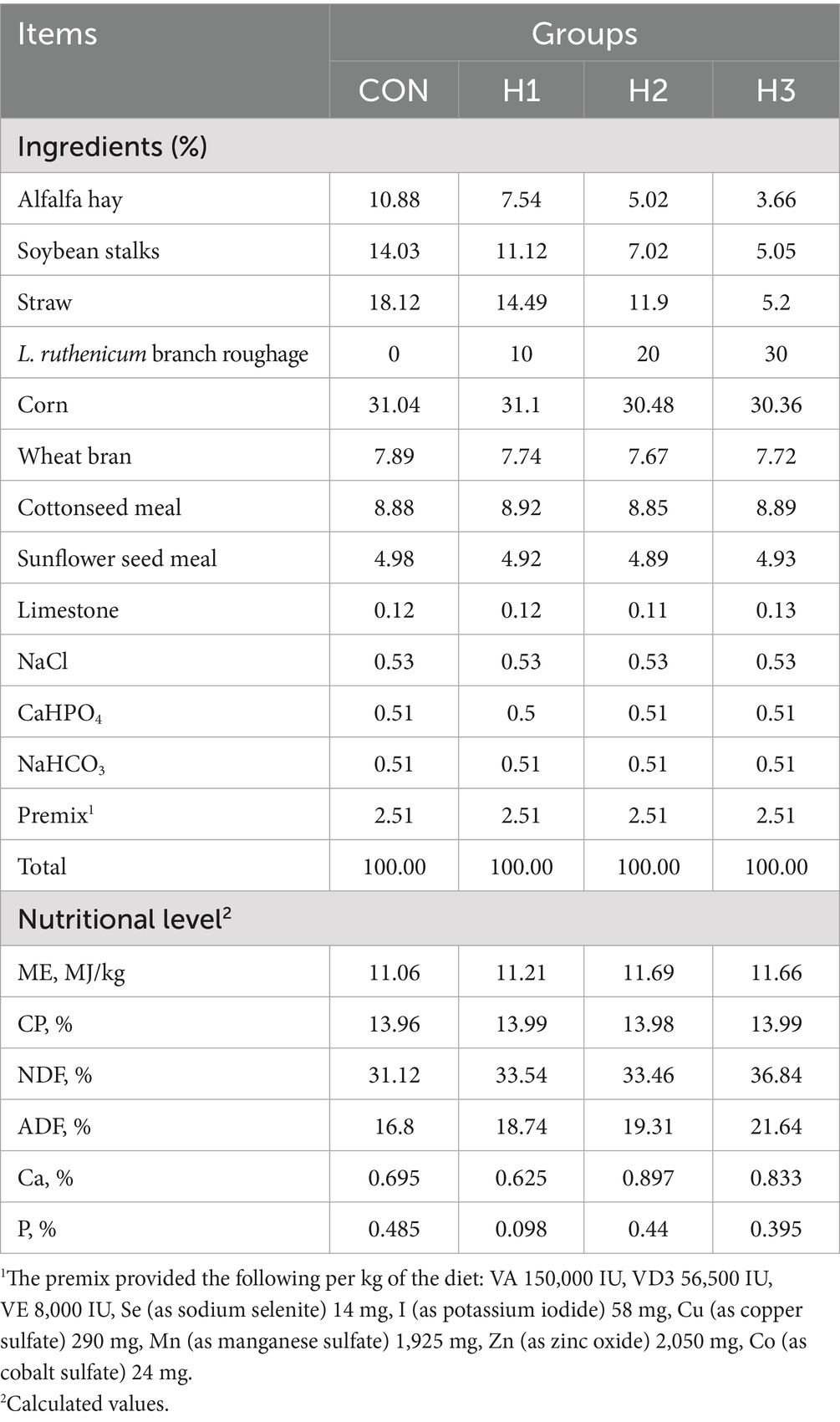
This study employed a completely randomized design to investigate the effects of incorporating L. ruthenicum into the diet of sheep. Forty male sheep (4 months old, 30 ± 2 kg body weight) were dewormed and randomly assigned to four treatment groups (n = 10 sheep per group),they are CON, H1, H2, H3 groups. The control group (CON) received the standard diet, while groups H1, H2 and H3 received the same diet supplemented with 10, 20 and 30% L. ruthenicum branch roughage [referring to Hou et al. and Duan et al. with minor modifications (11, 12)], respectively (see Table 2 for the composition and nutrient analysis of the diet). The 70-day experimental period included a ten-day acclimation period followed by a 60-day feeding trial. Bedding material selection straw, hay, etc. initial laying thickness 15–20 cm, subsequent weekly replenishment. Adjusted according to humidity, usually 1–2 weeks partial replacement, once a month thoroughly cleaned. The temperature inside the sheep house is 10–24°C. A ridged roof with adjustable skylights is used. The eaves are 3–4 meters high to promote air convection and relative humidity is maintained at 60–70%.
2.3 Experimental design and animal feeding
Before the test, the sheep pens were cleaned and disinfected, and the test sheep were sheared, dewormed, and bathed. During the test period, the sheep were kept in separate pens and fed twice a day, at 10:00 a.m. and 18:00 p.m. The pens were equipped with a single water trough and a feed trough, and the sheep were free to feed and drink during the period.
2.4 Sample collection
2.4.1 Growth
Each sheep was weighed on an empty stomach before morning feeding on d 0 and d 60 (9.00 AM) of the positive trial period, and the amount of feed and leftover material was recorded. Initial body weight, final body weight, average daily gain (ADG), average daily feed intake (ADFI) and feed/gain (F/G) ratio were calculated. According to the following formulas:
.
2.4.2 Carcass traits
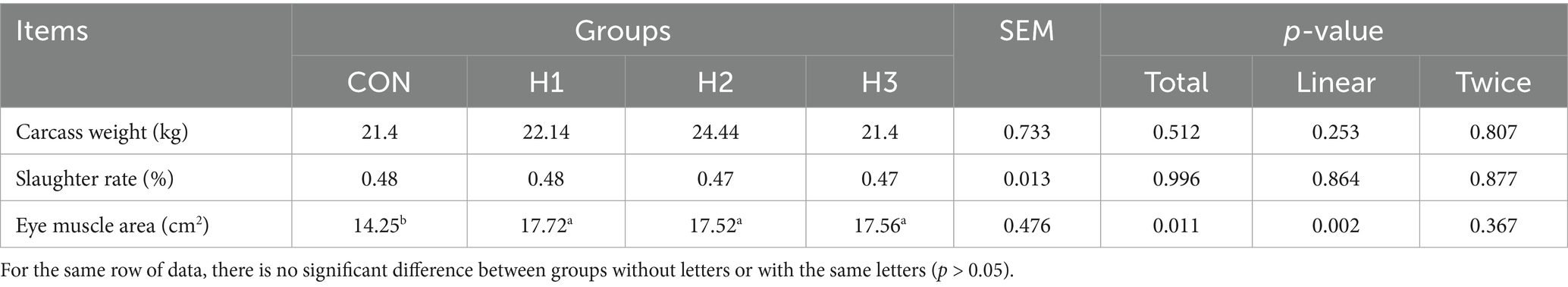
The live weight (kg) of each experimental sheep was measured and recorded just before slaughter. The test sheep were bled through the carotid jugular vein, and the head, hoof, skin, and viscera of the test sheep were removed, while the kidneys were retained. The carcass weight was measured and recorded immediately after slaughter, and slaughter percentage was calculated as carcass wgt/live wgt × 100. A longitudinal incision was made on the longissimus dorsi (LD) muscle between the 12th and 13th ribs to obtain the area of the eye muscle. A Vernier caliper was used to measure the length of the longest and widest parts of the eye muscle. The eye muscle area (cm2) was calculated as the longest value of the eye muscle cross section (cm) × the widest value (cm) × 0.7 (13).
2.4.3 Meat quality
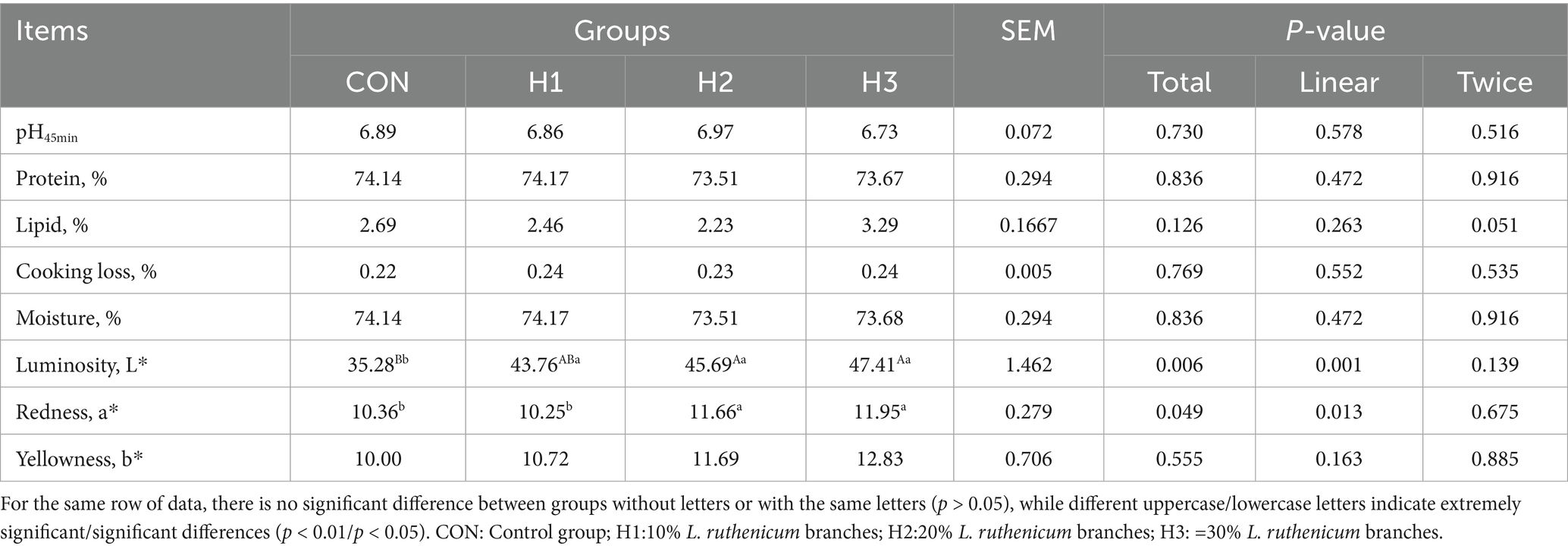
Meat quality measurements included physical indicators (pH, color, water loss and cooking loss) and chemical indicators (water, protein, fat and ash contents). Muscle pH was measured using a calibrated portable muscle tissue pH meter (HI99163, Shanghai Jiahui Instrumentation Co.). Meat color indices were measured in the dark 45 min after slaughter using a carcass meat color meter (Meat-5; Beijing Tianxiang Feiyu Technology Co.) and the determinations included L* (brightness), a* (redness), and b* (yellowness). A 1-cm-thick sample was cut vertically along the longest muscle fiber of the back using a circular sampling tool with a diameter of 3 cm (DL-100; Shandong Shunsheng Zhongshi, Shandong, China). To measure the loss in weight from cooking, a 3 × 3 × 5-cm sample of meat was dried with a paper towel, weighed (W1, g), placed into a bag, sealed, and heated in a water bath at 85°C for 40 min. After cooling to room temperature, it was patted dry with a paper towel and then weighed (W2, g). Cooking loss was calculated by subtracting W2 from W1. AOAC (14) methods were used to quantitate the moisture content (Method 950.46), crude protein (Method 928.08), crude fat (Method 960.39), and ash (Method 920.153) in the meat.
2.4.4 Amino acids
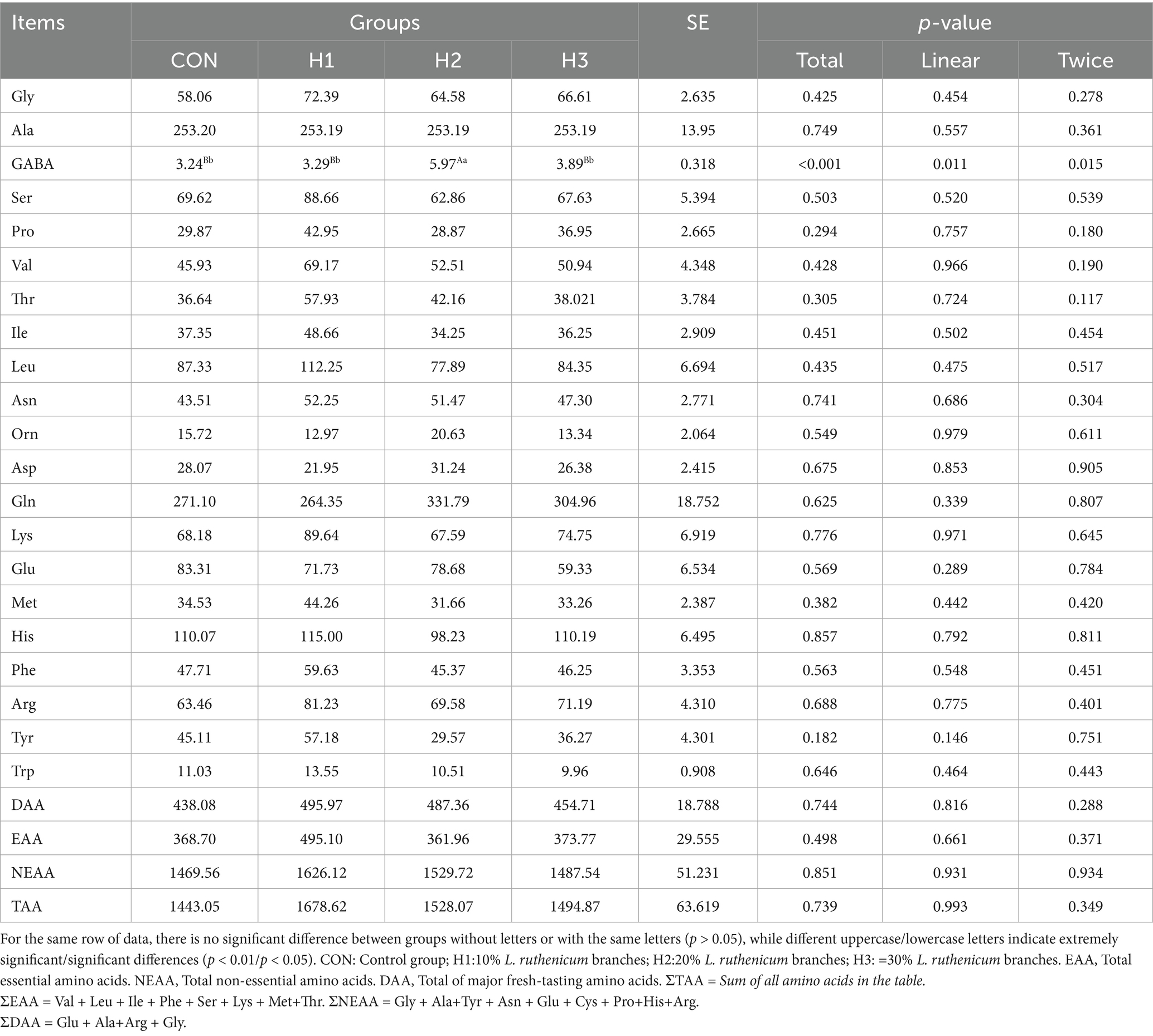
For determination of amino acid composition and concentrations, 100 mg samples of lyophilized tissues were homogenized in 1.2 mL of 10% sulfosalicylic acid, then centrifuged at 13,500 × g for 15 min at 4°C. Supernatants were removed and filtered through a 0.22 μm membrane filter into a 2.0 mL glass vial, and amino acid composition and concentration were determined with a high-speed amino acid analyzer (L-8900, Hitachi High-Tech Corporation, TKY, Japan).
2.4.5 Fatty acids
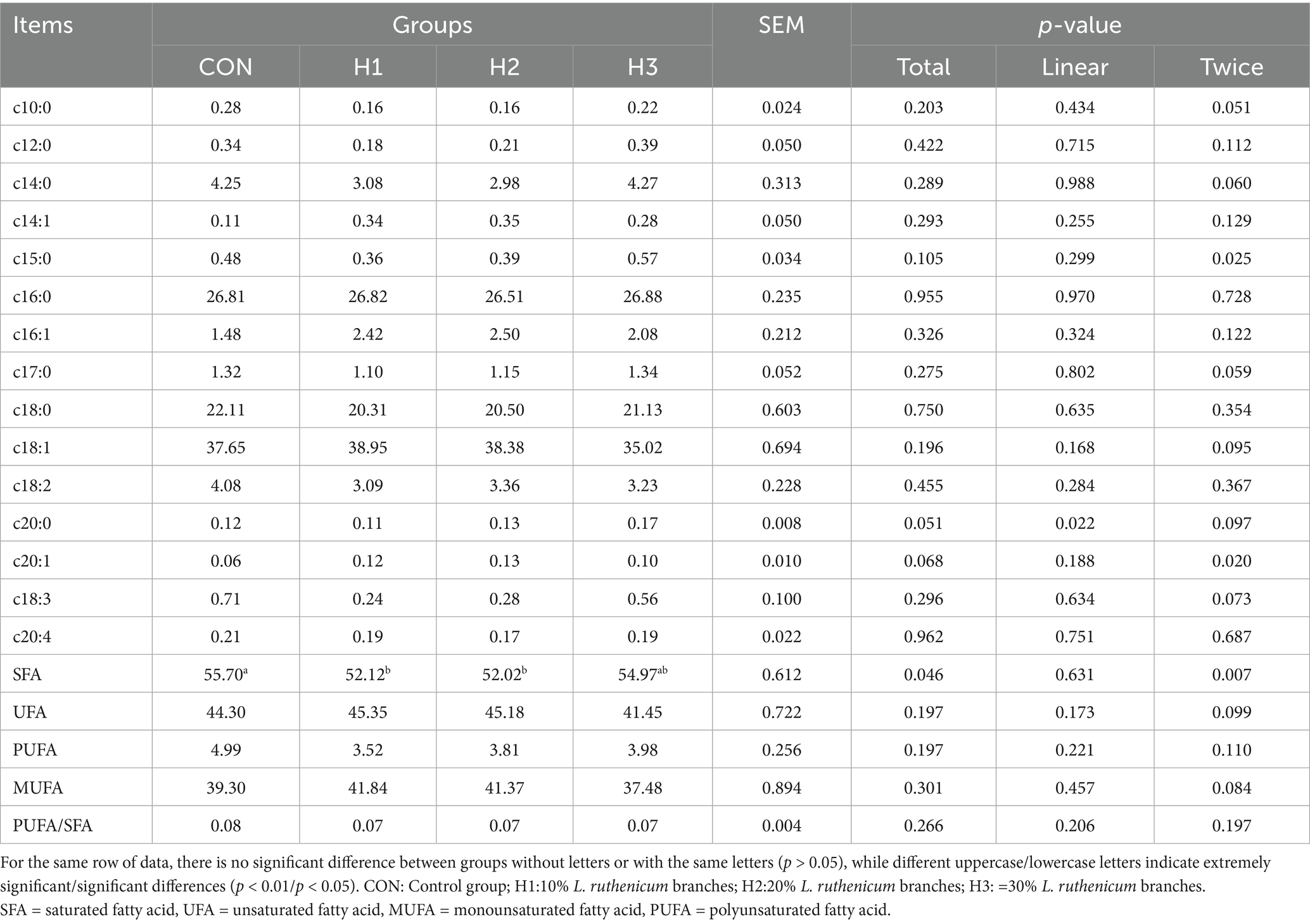
Total fatty acids (TFAs) in frozen meat samples were extracted according to the method of Liang et al. (15). The fatty acids (FAs) were separated by gas chromatography (GC-450, Varian Co., Walnut Creek, CA, USA), and the sample peaks were identified by retention time. The concentrations of individual FAs were determined using standard curves generated from known standard compounds (mixture of C4-C24 methyl esters; Sigma-Aldrich, Inc., St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.5 Statistical analysis of data
Data were organized using Excel 2016, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed using the ANOVA procedure of SPSS 26.0 statistical software. Multiple comparisons were performed using Duncan’s method if the differences were significant. The results were expressed as the mean and standard error of the mean (SEM) and regression analysis was done to test for linearity of the effects of increasing amounts of L. ruthenicum branches added to feed. The differences were taken as significant at the p < 0.05 level and highly significant at p < 0.01. Among them, the overall p-value refers to testing whether there is a significant difference between the means of all groups to determine the effect of the overall effect on the corresponding detection indexes with the increase in the addition of L. ruthenicum branches; the linear p-value refers to testing whether the corresponding detection indexes show a linear trend with the level of L. ruthenicum branches added when the amount of L. ruthenicum branches added increases; and the quadratic p-value refers to whether the corresponding detection indexes show a nonlinear (quadratic) trend.
Statistical analysis was performed using bivariate correlation analysis in SPSS 26.0 statistical software, the Pearson algorithm was used to calculate the correlation coefficients, and heat maps of the correlation were created using the heat map tool in Hiplot Pro (https://hiplot.com.cn/). Red color indicates a positive correlation, and blue color indicates a negative correlation. The color shade indicates the magnitude of the correlation. * represents 0.01 < p ≤ 0.05, and ** represents p ≤ 0.01.
3 Results
3.1 Growth performance
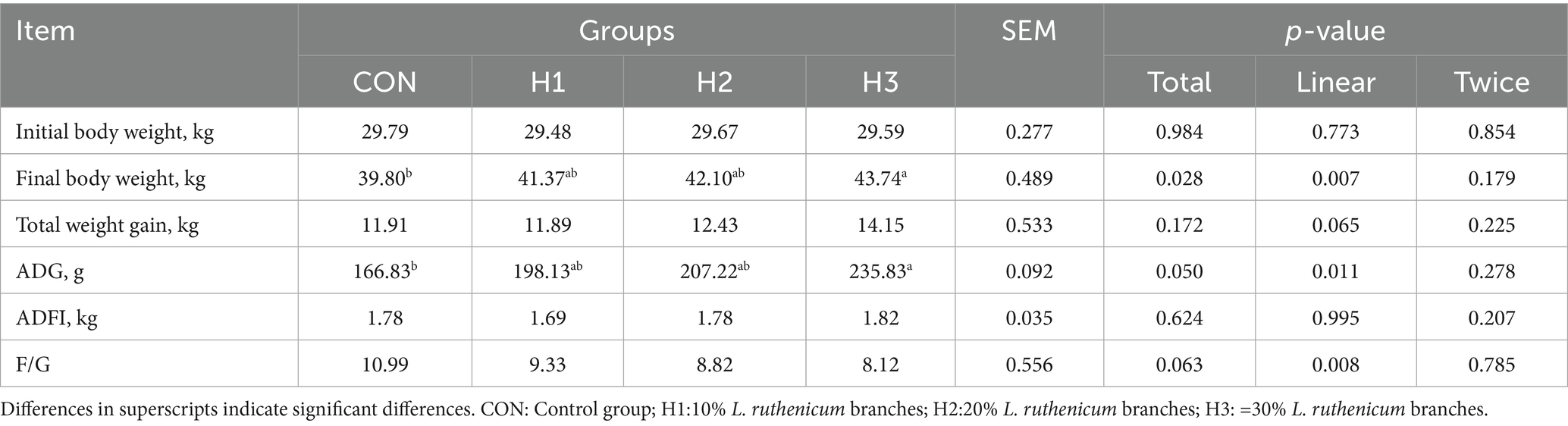
As can be seen in Table 3, the final weight, ADG of the sheep increased linearly with increasing amounts of L. ruthenicum branches added to the feed (p = 0.007); the H3 group was significantly higher than the CON, with an increase of 9.89, 41.34% (p < 0.05).
3.2 Carcass traits
As shown in Table 4, the eye muscle area of H1, H2, H3 groups was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than that of the CON group, with increases of 24.35, 22.95, 23.23%, respectively.
3.3 Meat quality
As can be seen in Table 5, supplementation with L. ruthenicum branches resulted in L* and a* values that were linearly highly significantly or significantly higher (p < 0.01or p < 0.05). The L* of H1, H2, H3 groups was highly significantly higher than that of the CON group, with increases of 24.04, 29.51, and 34.38%, respectively (p < 0.01). The values for a* of the H2 and H3 groups were significantly higher than that of the CON group by 12.55, 15.35% (p < 0.05).
3.4 Amino acid contents
As can be seen in Table 6, with increasing addition of L. ruthenicum branches, the GABA content showed a tendency to increase and then decrease (p < 0.01). The H2 group was extremely significantly higher (p < 0.01) than theH1, H2, CON groups, respectively, with increases of 81.46, 53.47, 84.26%. The other indices were not significantly different (p > 0.05).
3.5 Fatty acid content
As can be seen in Table 7, the increase in L. ruthenicum branches added to feed resulted in a trend of decreasing and then increasing SFA content. The H1 and H2 groups were significantly lower than the control group, decreasing by 6.87 and 7.07%, respectively (p < 0.05). The c20:0, c20:1 content showed a linear increase with increasing addition of black wolfberry branches, but the difference was not significant (p > 0.05).
3.6 Relationship between meat quality and content of amino acids and fatty acids
As shown in Figure 2, b* was significantly positively correlated with L* and SFA, and significantly negatively correlated with EAA, NEAA, and TAA (p < 0.05). DAA was significantly negatively correlated with a*, and significantly positively correlated with, EAA, NEAA, TAA, MUFA, UFA, PUFA, and PUFA/SFA (p < 0.05). EAA was significantly positively correlated with NEAA, TAA and significantly negatively correlated with SFA (p < 0.05). NEAA was significantly positively correlated with TAA, UFA, PUFA, PUFA/SFA (p < 0.05). TAA was significantly positively correlated with UFA, PUFA, PUFA/SFA (p < 0.05). UFA was significantly positively correlated with PUFA, PUFA/SFA (p < 0.05). PUFA was significantly positively correlated with PUFA/SFA (p < 0.05).
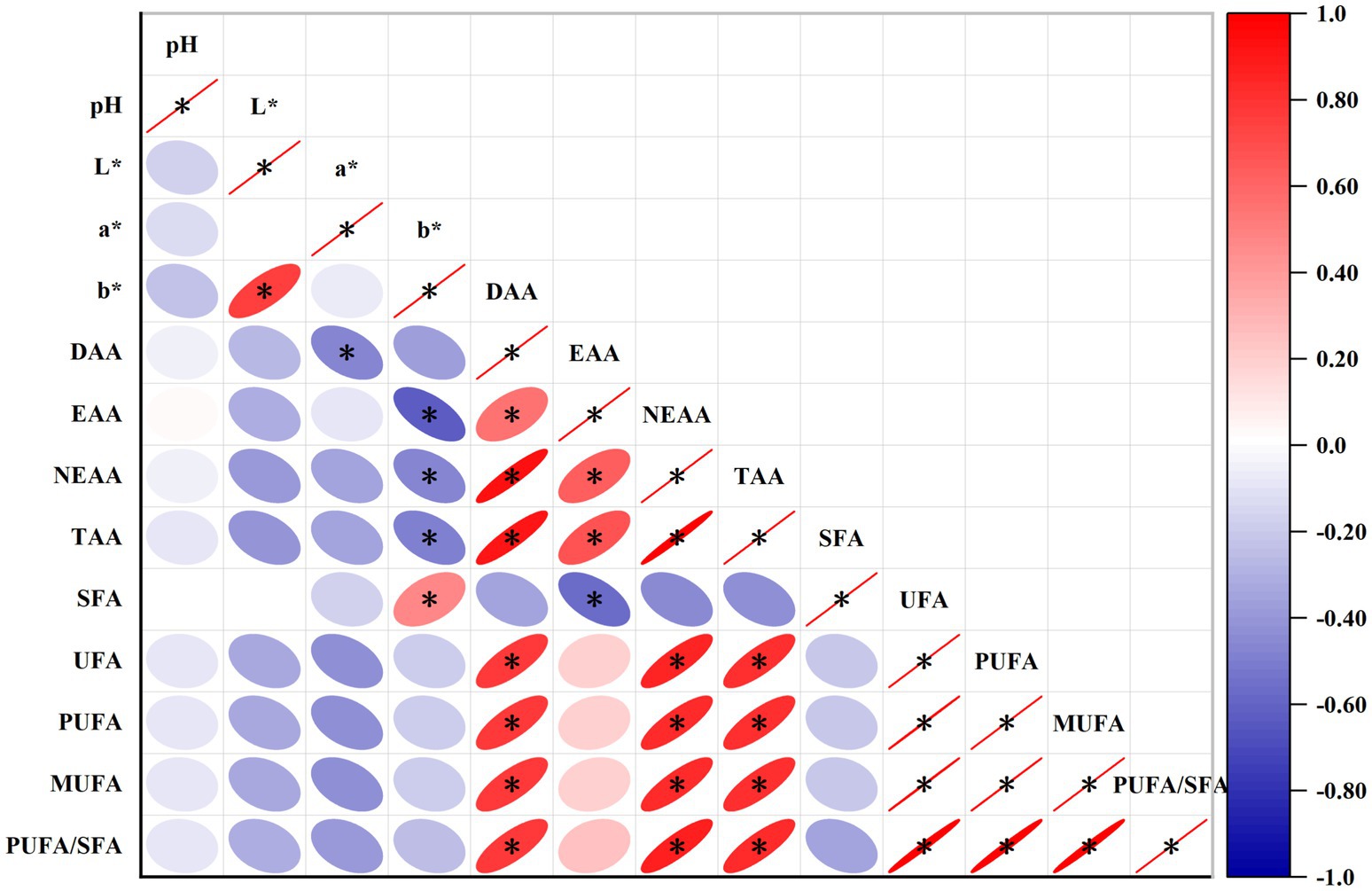
Figure 2. Heat map showing correlation between muscle amino acids, fatty acids and meat quality indicators. * represents 0.01 < p ≤ 0.05, and ** represents p ≤ 0.01.
3.7 Economic benefits
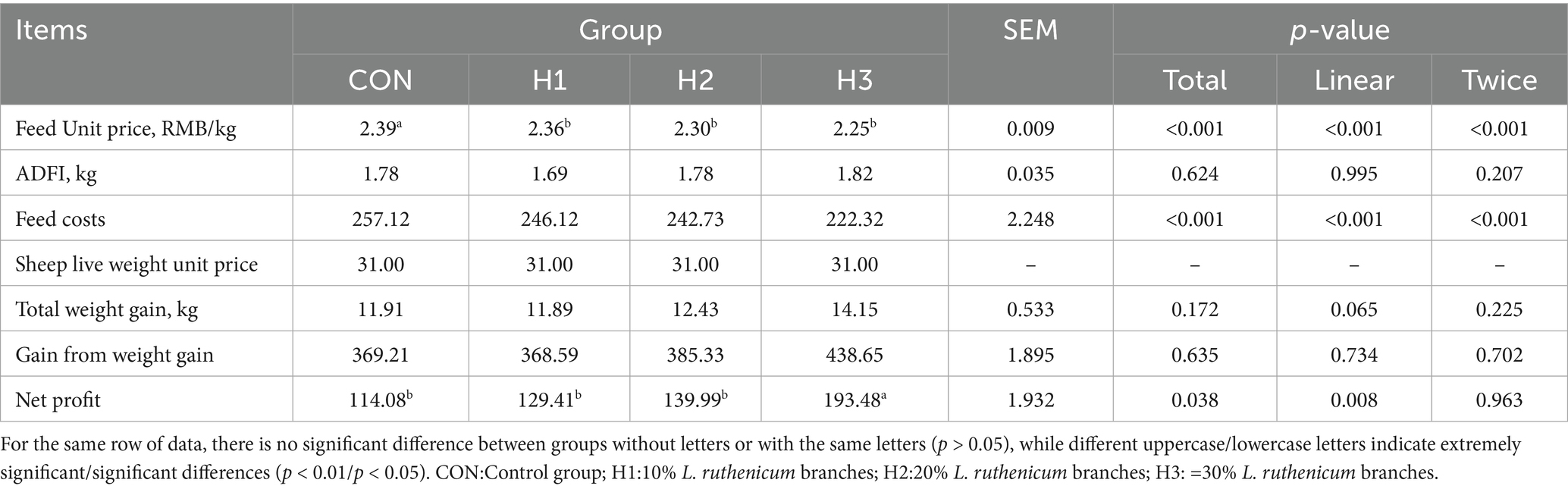
As can be seen in Table 8, the unit price for feed in each group ranged from 2.25–2.39 RMB/kg, and gradually decreased with increasing addition of L. ruthenicum branches. The gross profit of group H3 increased by 79.4% compared to CON.
4 Discussion
Feed intake, average daily gain, feed-to-weight ratio and final body weight are key indicators of growth performance. Among them, feed intake is significantly correlated with feed conversion efficiency (FCE), which is closely related to growth performance (16). The results of this study showed that the addition of up to 30% L. ruthenicum branch roughage to a standard diet could significantly increase the final weight of sheep. This was consistent with the findings of Duan et al. (12). Reflecting the fact that roughage made from L.ruthenicum branches is rich in polysaccharides, flavonoids, polyphenols and other biologically active substances, which could improve the growth performance of sheep by enhancing the digestion and absorption of nutrients. Through the analysis of economic benefits, H2 weight gain and economic returns were higher than the control group indicating that the LBP branch all-mixed pellet diet can improve the economic benefits of meat goats, can be applied in the practical production of meat goats and has a certain value of popularization.
The pH of muscle can reflect the speed and intensity of muscle glycolysis after slaughter, which affects its water holding capacity and color (17). Higher pH significantly improves the storage stability of meat by inhibiting the rate of glycolysis of myoglycogen, reducing water mobility, and maintaining protein conformational stability (18). As a reflection of muscle physiology and biology, meat color is an important indicator of appearance and economic value. Good color and luster can stimulate consumers’ desire to buy (19). Meat color (the a* value) is mainly influenced by hemoglobin and myoglobin, which turns bright red when oxygenated. The value of b* is affected by the intake of carotenoids in the rations as well as the inter- and intramuscular fat content. An increase in a* corresponds to a brighter red color, while a decrease in b* (yellow color) makes the meat appear more reddish, improving its sensory qualities and consumer appea (20).
It has been previously demonstrated that the addition of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides (LBPs) in the diet can enhance the appearance and sensory qualities of meat. Addition of LBPs improved meat quality by increasing the tethering force of the longest back muscles of lambs, increasing a* and decreasing b*; thus, it is reasonable to suppose that the polysaccharides in L. ruthenicum branch roughage could also have strong antioxidant functions, which could reduce glycogen fermentation and the accumulation of lactic acid in muscle, preventing the drop in pH that negatively affects quality (21). In this study, the value of L*, a* in the H2 and H3 groups was also significantly higher than that in the CON group. This suggests that the bioactive components of L. ruthenicum branches can prevent myoglobin oxidation and that phenols in flavonoid compounds with hydroxyl and carbonyl groups can bind metal ions and block the production of free radicals, thus enhancing the activity of iron myoglobin reductase and delaying the oxidation of myoglobin (22). Therefore, the improvement of meat quality by L. ruthenicum may be related to its strong antioxidant properties.
Certain amino acids (AAs), especially the four fresh-flavor AAs (Glu, Ala, Arg, Gly), are important flavoring substances, and the amino acid content in lamb directly affects its appeal to consumers (23). Studies have shown that the higher the content of flavor-enhancing AAs, the more delicious the meat (24). Currently, there are few reports on the effect of L. ruthenicum branches on the amino acid content of animal muscle. In this study, the addition of L. ruthenicum branch roughage improved the fresh-flavor AAs, but the difference was not significant. However, the L. ruthenicum-supplemented feed did significantly improve the nutritional value of the meat and this may be related to the fact that L. ruthenicum branches are rich in digestible protein and have a high EAA content. L. ruthenicum also provides beneficial gut bacteria to improve the gut microbial composition, which promotes the deposition of amino acids in the muscle (25). L. ruthenicum branches are also rich in flavonoids, as well as dietary fiber and active enzymes (26). GABA is effective in promoting protein metabolism, growth hormone mediator production, chondrocyte division and matrix proliferation, and in promoting glucose uptake and the synthesis of proteins in muscle (27). The addition of 20% of L. ruthenicum branches significantly increased GABA content in this study, which may be a result of its high flavonoid content. The strong antioxidant properties of flavonoids inhibit lipid oxidation and free radical generation in lamb, thereby protecting the activity of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD), a key enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of glutamate to GABA and whose activity is significantly affected by oxidative stress. Studies have shown that flavonoids can maintain the structural stability of GAD and promote the efficiency of GABA synthesis by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reducing malondialdehyde (MDA) levels (28).
The most fatty acids in lamb meat are not only an important factor affecting the flavor, but also play a crucial role in human health and physiological well-being (29). Intramuscular fat content is one of the most important indicators for assessing meat quality and is closely associated with tenderness, flavor, and juiciness. It has been shown that flavonoids can significantly increase the fat content of the longest dorsal muscle of sheep, affecting the flavor of the meat (30). It was found that excessive SFA content in ingested meat increases the probability of coronary heart disease and can also lead to fat storage and inflammation in the human body, whereas in the present study, a significant decrease in the content of SFA in the longest muscle of the dorsum was found, which suggests that the extract of L. nigra is effective in improving the composition of the fat and decreasing the proportion of SFA, which has a positive impact on the improvement of the nutritional and health attributes of the meat.
The longest muscle of the back is very active in fatty acid oxidative metabolism and is dependent on fatty acids for energy, and the decrease in saturated fatty acid content of the longest muscle of the sheep’s back may be related to the flavonoid content in the branches of L. ruthenicum (31). Kwiecien et al. found that the bioactive components in alfalfa could increase the activity of SFA enzymes and promote the conversion of SFA to UFA (32). L. ruthenicum branches may also have the potential to improve the conversion and distribution of FAs in the dorsal muscle of sheep and have a positive effect on the nutritional value and flavor of the lamb meat. The potent active components (flavonoids, polysaccharides and polyphenols) in L. ruthenicum have antioxidant activities and reduce rumen microbial hydrogenation, leading to higher deposition of MUFA and PUFA in the muscles of meat sheep (33). Secondly, the high content of polyphenols in L. ruthenicum is also likely to be responsible for the improvement in fatty acid content. High doses of polyphenols may maintain the stability of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the meat by inhibiting lipid peroxidation and protecting the integrity of the muscle cell membranes, while promoting the efficiency of energy metabolism and significantly enhancing the end weight of sheep (Table 3) (1).
5 Conclusion
The results of this study show that Lycium ruthenicum branches can improve the growth performance of sheep and positively affect the amino acid and fatty acid composition of sheep muscle, thus improving meat quality and increasing profits for sheep farmers. Our data show that the optimal amount of Lycium ruthenicum branches for feed supplementation to achieve this goal is 20%.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Xinjiang Academy of Animal Sciences. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Supervision, Methodology, Data curation. YY: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LH: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Conceptualization. JL: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation. PD: Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Data curation. TG: Data curation, Visualization, Methodology, Investigation, Conceptualization, Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Li, J, Tuo, Y, He, L, Ma, Y, Zhang, Z, Cheng, Z, et al. Effects of chili straw on rumen fermentation, meat quality, amino acid and fatty acid contents, and rumen bacteria diversity in sheep. Front Microbiol. (2025) 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1525612
2. Martin, G, Barth, K, Benoit, M, Brock, C, Destruel, M, Dumont, B, et al. Potential of multi-species livestock farming to improve the sustainability of livestock farms: a review. Agric Syst. (2020) 181. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2020.102821
3. Yun, D, Yan, Y, and Liu, J. Isolation, structure and biological activity of polysaccharides from the fruits of Lycium ruthenicum Murr: a review. Carbohydr Polym. (2022) 291:119618. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119618
4. Magalhães, V, Silva, AR, Silva, B, Zhang, X, and Dias, ACP. Comparative studies on the anti-neuroinflammatory and antioxidant activities of black and red goji berries. J Funct Foods. (2022) 92. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2022.105038
5. Xu, M-L, He, Y-F, Xie, L, Qu, L-B, Xu, G-R, and Cui, C-X. Research Progress on active ingredients and product development of Lycium ruthenicum Murray. Molecules. (2024) 29. doi: 10.3390/molecules29102269
6. Dong, Y, Yang, C, Zhong, W, Shu, Y, Zhang, Y, and Yang, D. Antibacterial effect and mechanism of anthocyanin from Lycium ruthenicum Murr. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.974602
7. Nie, C, Hu, Y, Chen, R, Guo, B, Li, L, Chen, H, et al. Effect of probiotics and Chinese medicine polysaccharides on meat quality, muscle fibre type and intramuscular fat deposition in lambs. Ital J Anim Sci. (2022) 21:811–20. doi: 10.1080/1828051x.2022.2067489
8. Patra, A, Abdullah, S, and Pradhan, RC. Review on the extraction of bioactive compounds and characterization of fruit industry by-products. Bioresour Bioprocess. (2022) 9:14. doi: 10.1186/s40643-022-00498-3
9. Hao, Z, Li, Z, Huo, J, Chu, Y, Li, J, Yu, X, et al. Effects of Chinese wolfberry and astragalus extracts on growth performance, pork quality, and unsaturated fatty acid metabolism regulation in Tibetan fragrant pigs. Anim Sci J. (2021) 92:e13581. doi: 10.1111/asj.13581
10. Chen, Z, Wang, G, Wang, W, Wang, X, Huang, Y, Jia, J, et al. Relationship between jejunum ATPase activity and antioxidant function on the growth performance, feed conversion efficiency, and jejunum microbiota in Hu sheep (Ovis aries). BMC Vet Res. (2024) 20:242. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04100-0
11. Hou, L, Duan, P, Yang, Y, Shah, AM, Li, J, Xu, C, et al. Effects of residual black wolfberry fruit on growth performance, rumen fermentation parameters, microflora and economic benefits of fattening sheep. Front Vet Sci. (2025) 11:1528126. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1528126
12. Duan, P, Rehemujiang, H, Zhang, L, Lu, M, Li, C, Hu, L, et al. Lycium barbarum (wolfberry) branches and leaves enhance the growth performance and improve the rumen microbiota in Hu sheep. Animals. (2024) 14. doi: 10.3390/ani14111610
13. Yar, MK, Jaspal, MH, Ali, S, Ijaz, M, Badar, IH, and Hussain, J. Carcass characteristics and prediction of individual cuts and boneless yield of Bos indicus and Bos indicus × Bos taurus bulls differing in age. Livest Sci. (2022) 264:105041. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2022.105041
14. Broderick, GA, and Jinhe, K. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. J Dairy Sci. (1980) 63:64–75. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(80)82888-8
15. Liang, Y, Jiao, D, Du, X, Zhou, J, Degen, AA, Ran, F, et al. Effect of dietary Agriophyllum squarrosum on average daily gain, meat quality and muscle fatty acids in growing tan lambs. Meat Sci. (2023) 201:109195. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2023.109195
16. Wang, M, Han, H, Shang, Y, Zhang, L, Zhang, Y, Su, C, et al. Effect of the replacement of maize silage and Soyabean meal with mulberry silage in the diet of Hu lambs on growth performance, serum biochemical indices, slaughter performance, and meat quality. Animals. (2022) 12:3164. doi: 10.3390/ani12223164
17. Menchetti, L, Brecchia, G, Branciari, R, Barbato, O, Fioretti, B, Codini, M, et al. The effect of goji berries (Lycium barbarum) dietary supplementation on rabbit meat quality. Meat Sci. (2020) 161:108018. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.108018
18. Xu, M, Chen, X, Huang, Z, Chen, D, Li, M, He, J, et al. Effects of dietary grape seed proanthocyanidin extract supplementation on meat quality, muscle fiber characteristics and antioxidant capacity of finishing pigs. Food Chem. (2022) 367:130781. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130781
19. Liu, W, Ding, H, Erdene, K, Chen, R, Mu, Q, Ao, C, et al. Effects of flavonoids from Allium mongolicum regel as a dietary additive on meat quality and composition of fatty acids related to flavor in lambs. Can J Anim Sci. (2019) 99:15–23. doi: 10.1139/cjas-2018-0008
20. de Sousa, SV, Diogenes, LV, Oliveira, RL, Souza, MNS, Mazza, PHS, da Silva Júnior, JM, et al. Effect of dietary Buriti oil on the quality, fatty acid profile and sensorial attributes of lamb meat. Meat Sci. (2022) 186:108734. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2022.108734
21. Xu, X, Chen, X, Chen, D, Yu, B, Yin, J, and Huang, Z. Effects of dietary apple polyphenol supplementation on carcass traits, meat quality, muscle amino acid and fatty acid composition in finishing pigs. Food Funct. (2019) 10:7426–34. doi: 10.1039/c9fo01304k
22. Chen, S, Li, X, Liu, X, Wang, N, An, Q, Ye, XM, et al. Investigation of chemical composition, antioxidant activity, and the effects of alfalfa flavonoids on growth performance. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2020/8569237
23. Ding, W, Lu, Y, Xu, B, Chen, P, Li, A, Jian, F, et al. Meat of sheep: insights into mutton evaluation, nutritive value, influential factors, and interventions. Agriculture-Basel. (2024) 14:1060. doi: 10.3390/agriculture14071060
24. Wang, L-w, Su, S-f, Zhao, J, He, X-l, Fu, S-y, Wang, B, et al. Effects of dietary oat supplementation on carcass traits, muscle metabolites, amino acid profiles, and its association with meat quality of small-tail Han sheep. Food Chem. (2023) 411:135456. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.135456
25. Cremonesi, P, Curone, G, Biscarini, F, Cotozzolo, E, Menchetti, L, Riva, F, et al. Dietary supplementation with goji berries (Lycium barbarum) modulates the microbiota of digestive tract and Caecal metabolites in rabbits. Animals. (2022) 12:121. doi: 10.3390/ani12010121
26. Zhao, L, Sun, X, Wu, J, Su, L, Yang, F, Jin, Y, et al. Effects of Allium mongolicum regel and its extracts on the quality of fermented mutton sausages. Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 10:169–78. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2657
27. Bi, C, Yin, J, Yang, W, Shi, B, and Shan, A. Effects of dietary γ-aminobutyric acid supplementation on antioxidant status, blood hormones and meat quality in growing-finishing pigs undergoing transport stress. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr. (2019) 104:590–6. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13280
28. Lucio-Ruíz, F, Godina-Rodríguez, JE, Granados-Rivera, LD, Orzuna-Orzuna, JF, Joaquín-Cancino, S, and Hernández-García, PA. Meta-analysis of dietary supplementation with flavonoids in small ruminants: growth performance, antioxidant status, nutrient digestibility, ruminal fermentation, and meat quality. Small Rumin Res. (2024) 241:107401. doi: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2024.107401
29. Ma, JS, Chang, WH, Liu, GH, Zhang, S, Zheng, AJ, Li, Y, et al. Effects of flavones of sea buckthorn fruits on growth performance, carcass quality, fat deposition and lipometabolism for broilers. Poult Sci. (2015) 94:2641–9. doi: 10.3382/ps/pev250
30. Liu, W, and Ao, C. Effect of dietary supplementation with Allium mongolicum regel extracts on growth performance, carcass characteristics, and the fat color and flavor-related branched-chain fatty acids concentration in ram lambs. Animal Biosci. (2021) 34:1134–45. doi: 10.5713/ajas.20.0246
31. Zhang, Y, Chang, X, Wang, B, Wei, D, Zhong, R, Guo, Y, et al. Supplementation of Lycium barbarum residue increases the growth rate of tan sheep by enhancing their feed intake and regulating their rumen microbiome and metabolome. J Integr Agric. (2024) 23:3129–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jia.2023.10.008
32. Kwiecień, M, Winiarska-Mieczan, A, Danek-Majewska, A, Kwiatkowska, K, and Krusiński, R. Effects of dietary alfalfa protein concentrate on lipid metabolism and antioxidative status of serum and composition and fatty acid profile and antioxidative status and dietetic value of muscles in broilers. Poult Sci. (2021) 100:100974. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.12.071
Keywords: Lycium barbarum (black goji berry), meat quality, amino acids, fatty acid composition, sheep
Citation: Ma Y, Yang Y, Hou L, Li J, Duan P and Guo T (2025) Effects of dietary Lycium ruthenicum (black goji berry) branches supplementation on growth performance, meat quality, and muscle amino acid and fatty acid composition in sheep. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1616612. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1616612
Edited by:
Yafeng Huang, Anhui Agricultural University, ChinaReviewed by:
Ping Li, Guizhou University, ChinaXianwen Dong, Chongqing Academy of Animal Science, China
Copyright © 2025 Ma, Yang, Hou, Li, Duan and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tongjun Guo, Z3VvdGFveGpAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Yan Ma
Yan Ma Yuxia Yang1,2
Yuxia Yang1,2 Jinlong Li
Jinlong Li Pingping Duan
Pingping Duan Tongjun Guo
Tongjun Guo