- 1Laboratory of Animal Etiology and Epidemiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi, China
- 2State Key Laboratory for Zoonotic Diseases, Key Laboratory for Zoonosis Research of the Ministry of Education, Institute of Zoonosis, College of Veterinary Medicine, Jilin Universitygrid, Changchun, China
- 3Changchun Research Veterinary Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Changchun, China
- 4State Key Laboratory for Animal Disease Control and Prevention, College of Veterinary Medicine, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Lanzhou, China
- 5Xinjiang Key Laboratory of New Drug Research and Development for Herbivores, Urumqi, China
Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) is commonly detected in biological products such as tissues and serum. This study identified BVDV contamination in a commercially available fetal bovine serum (FBS) sample. To determine whether the detected virus was infectious or merely genetic material, the FBS was inoculated into Madin-Darby bovine kidney (MDBK) cells. Following six serial passages, both indirect immunofluorescence assay results and electron microscopic visualization of viral particles confirmed the presence of infectious BVDV. The isolated strain, designated BI-2023, had a complete genome length of 12,273 nucleotides. Comparative sequence analysis showed that the 5′ untranslated region (UTR) and full genome of BI-2023 shared 87.4–97.1% and 92.4–95.2% nucleotide identity, respectively, with reference strains of BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b. Phylogenetic analyses based on the 5′UTR and whole genome placed BI-2023 within the genotype 1b cluster of Pestivirus bovis. Several amino acid substitutions were identified in the E2 and Erns proteins of the BI-2023 regions involved in immune evasion and viral secretion. This suggests this strain may represent a distinct variant within the genotype 1b group. These results highlight the critical need for routine viral screening in commercial FBS preparations.
Introduction
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) is an essential supplement in cell culture media, widely used in manufacturing vaccines and other biologics. However, the adventitious agents, particularly viruses, can significantly compromise the safety and quality of these biological products (1–3). Bovine serum is known to potentially carry a variety of contaminating viruses, including bluetongue virus (BTV), adenovirus (BAV), poliovirus (BPV), respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV), viral diarrhea virus (BVDV), rabies virus (RV), parainfluenza virus type III (PIV III), and infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus (IBRV), among others. BVDV is one of the most commonly detected contaminants in bovine serum samples (1–13).
The BVDV is a member of the Flaviviridae family and belongs to the genus Pestivirus. It is the primary causative agent of bovine viral diarrhea and mucosal disease in cattle, conditions characterized by clinical signs such as fever, diarrhea, decreased milk yield, and reproductive dysfunctions (14). BVDV is a single-stranded, positive-sense RNA virus with a genome approximately 12.3 kb in length (15). Globally, two major genotypes of BVDV have been identified: BVDV-1 and BVDV-2. According to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), these are now classified as Pestivirus bovis (BVDV-1) and Pestivirus tauri (BVDV-2), respectively (15). Within Pestivirus bovis, at least 25 distinct genotypes (designated 1a to 1.25) have been recognized (16–22). Furthermore, BVDV exists in two biotypes: cytopathogenic (CP) and non-cytopathogenic (NCP), differentiated by their ability to induce cytopathic effects (CPE) in cultured cells.
In this study, a non-cytopathogenic strain of BVDV was successfully isolated from commercially available fetal bovine serum. Multiple amino acid substitutions were identified in the E2 and Erns protein regions that play key roles in immune evasion and viral secretion. These mutations suggest the isolate may represent a novel BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b group variant. This discovery underscores the genetic diversity of circulating BVDV strains and highlights the critical need for routine surveillance to ensure the safety of bovine-derived biological materials.
Materials and methods
BVDV detection
Four commercial fetal bovine serum (FBS) samples originating from Israel were obtained from Biological Industries (LOT: 2153440) and ExCell Bio (LOT: 12B052). Viral RNA was extracted from 200 μL of each FBS sample using the Geneaid extraction kit, following the manufacturer’s protocol. Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized using PrimeScript II Reverse Transcriptase (Takara, China) under the following thermal conditions: 65°C for 5 min, 42°C for 60 min, and 95°C for 5 min. The 5′-UTR of BVDV was then amplified by PCR using the primer pair 1F1 and 1R462 (Table 1). Amplification was performed with 2 × TransStart® FastPfu Fly PCR SuperMix (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China) under the following cycling parameters: initial denaturation at 95°C for 2 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 20 s, annealing at 52°C for 20 s, and extension at 72°C for 30 s, with a final extension step at 72°C for 5 min. The PCR products were analyzed via electrophoresis on a 1% agarose gel.
Cell culture and virus isolation
Madin-Darby bovine kidney (MDBK) cells, confirmed to be free of BVDV by the PCR described above, were kindly provided by the laboratory of Tu Changchun. MDBK cells were exposed to BVDV-positive fetal bovine serum for 2 h at 37°C in a humidified incubator for viral inoculation with 5% CO2. Following incubation, the inoculum was removed, and the cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 2% BVDV-negative FBS. The cultures were maintained under these conditions for 96 h, after which the cells underwent three freeze–thaw cycles to release intracellular virus particles. Six additional cell passages were performed to enhance viral propagation. For electron microscopy, virus particles were purified via sucrose density gradient centrifugation and negatively stained using 2% phosphotungstic acid.
Indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA)
MDBK cells were seeded into 12 wells of a 96-well culture plate and allowed to grow until they reached 70–80% confluency. Four wells were inoculated with the previously prepared virus solution, while the remaining eight were negative controls. The cells were then incubated for 48 h. Following incubation, the cells were fixed with 4% formaldehyde for 30 min, then blocked with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) at room temperature for 30 min. A mouse monoclonal antibody targeting the BVDV E2 protein (IgG2a isotype; kindly provided by Prof. Changchun Tu) was applied at a 1:1000 dilution, and the plates were incubated for 1 h at 37°C. After washing with phosphate-buffered saline containing Tween 20 (PBST), the cells were incubated with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated donkey anti-mouse IgG (Invitrogen) at a 1:500 dilution for 2 h at 37°C. Following a final wash with PBST, fluorescence was visualized using an Olympus CKX53 fluorescence microscope at 5 × magnification.
Complete genomic amplification and sequencing
The PCR assays were established to amplify the BVDV genomic sequence using primer pairs detailed in Table 1. RNA extraction and reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) were carried out following the same protocol described previously for BVDV detection. Positive PCR products were cloned into the pESI-T vector (Yeasen Biotech) and transformed into E. coli DH5α chemically competent cells (Weidi Biotech). Three independent clones from each amplicon were selected for Sanger sequencing (Sangon Biotech).
Phylogenetic analyses
A total of 23 BVDV reference strains representing diverse genotypes from the United States, Japan, Germany, and China were retrieved from GenBank. Detailed information, including GenBank accession numbers, is presented in Figures 3, 4. Sequence similarity analyses were performed using MegAlign software (Lasergene v7.1). Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the maximum-likelihood method based on the Tamura–Nei model. To assess the robustness of the inferred tree topologies, bootstrap analysis with 1,000 replicates was conducted (23).

Figure 3. Phylogenetic analysis of the new isolates with 23 BVDV reference strains based on the 5′-UTR nucleotide sequences. The 5′-UTR nucleotide sequences of the new isolates were aligned with 23 reference BVDV strains, and phylogenetic analysis was carried out by the maximum-likelihood (ML) method using MEGA7 software (1,000 bootstrap replicates). Fixed circles represent the BVDV BI-2023 strain isolated in this study. The 5′-UTR nucleotide sequences of the reference BVDV strains were obtained from the GenBank data.
Results
Virus isolation and identification
RT-PCR analysis revealed a specific 462 bp amplicon corresponding to BVDV in all FBS samples obtained from Biological Industries, but not in those from ExCell Bio. The two BVDV-positive commercial FBS was then used to inoculate MDBK cells, which were monitored daily. After six successive passages, no apparent cytopathic effects were observed in the infected cells. However, BVDV RNA was detected by RT-PCR in one of the two culture supernatant, indicating the presence of an NCP BVDV strain. This isolate was designated BVDV BI-2023. The presence of BVDV BI-2023 in the commercial FBS was further confirmed by indirect immunofluorescence assay (Figures 1A,B), and its identity was validated via transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (Figure 2).

Figure 1. IFA for BVDV. (A) IFA detection of BVDV-infected MDBK cells using an anti-BVDV monoclonal antibody. (B) MDBK cells negative for BVDV were used as the control.
Sequence analyses of 5’-UTR
To determine the genotype of BVDV BI-2023, phylogenetic analysis was performed using the maximum likelihood method based on its 5’-UTR sequence, alongside 20 BVDV reference strains (Figure 3). The results showed that BVDV BI-2023 clustered within the BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b group. Sequence alignment revealed that the new isolate shared 87.4–97.1% nucleotide identity with known BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b strains, including USMARC/PI-91-21/CD46GE, USMARC/PI-91-21/MDBK, AU526, CP7, CC13B, and JL-1. However, its similarity with other BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype ranged from 68.1 to 88.6% (Table 2). These findings support the classification of BVDV BI-2023 as a member of the BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b lineage.
Whole-genome sequence comparisons and phylogenetic analyses
To investigate the molecular characteristics of the isolate, the full-length genome of BVDV BI-2023 was amplified and sequenced, yielding a sequence of 12,273 nucleotides, which has been submitted to GenBank under accession number OR753412. Comparative analysis revealed that BI-2023 shared 92.4–95.2% nucleotide identity with BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b reference strains (Table 3). In particular, it showed 95.2% identity with the BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b reference strain CP7, confirming its classification as a BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b group member (Table 3). Further multiple sequence alignments revealed that BVDV BI-2023 isolated in the present study shared 90.7–97.0% nucleotide (Table 4) and 90.1–100% amino acid (Table 5) identities for the Npro, Core, Erns, E1, E2, p7, NS2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B genes, with BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b reference strain CC13B, CP7, JL-1, USMARC/PI-91-21/CD46GE, USMARC/PI-91-21/MDBK, and TJ2018 etc.
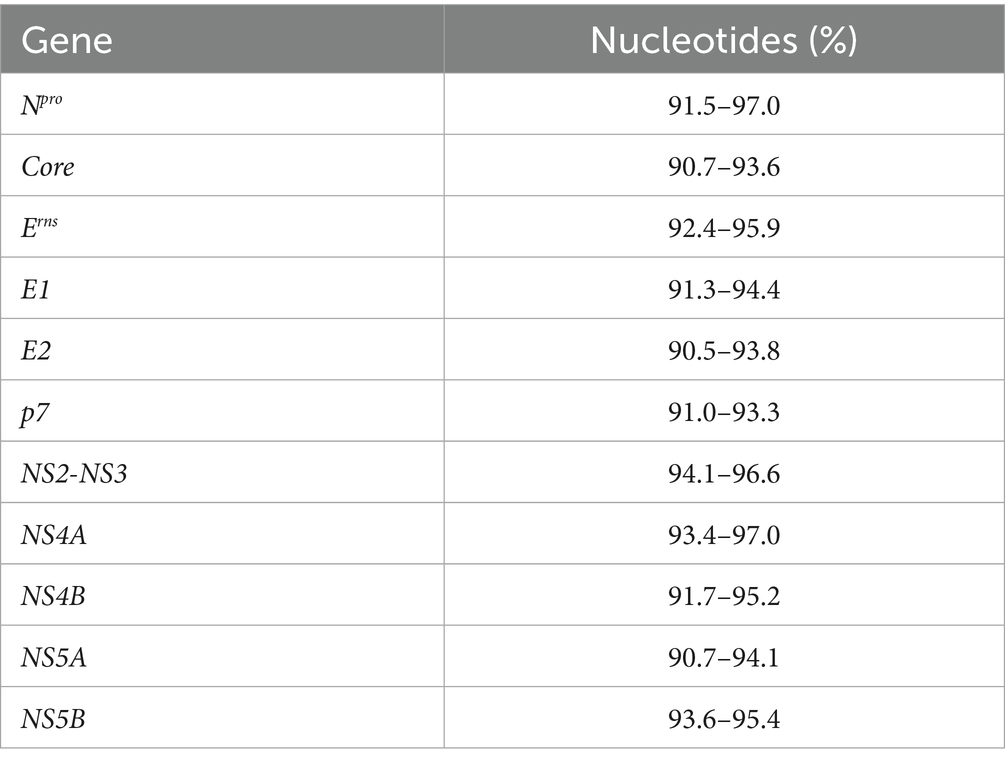
Table 4. Homology analysis of the BVDV BI-2023 and BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b reference strains 11 genes in this study.

Table 5. Homology analysis of the BVDV BI-2023 and BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b reference strains 11 proteins in this study.
Furthermore, phylogenetic analysis based on the complete genome sequence demonstrated that BVDV BI-2023 is closely aligned with established BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b reference strains, including CC13B, CP7, JL-1, USMARC/PI-91-21/CD46GE, and TJ2018. As depicted in Figure 4, BI-2023 clusters within the genotype 1b lineage, highlighting its strong genetic relatedness to these strains and further supporting its classification as a member of BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b (Figure 4).
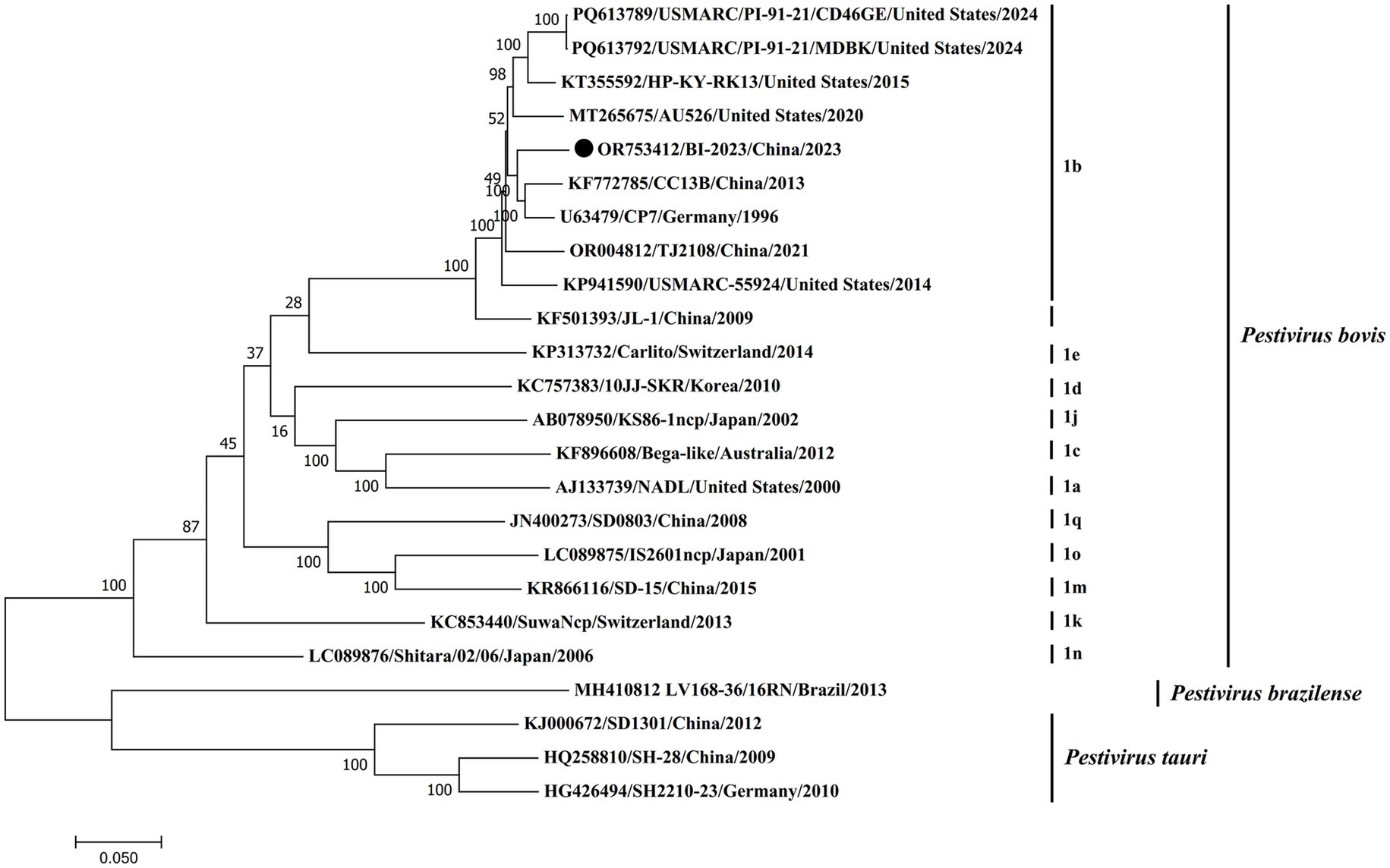
Figure 4. Phylogenetic analysis of the new isolates with pestiviruses based on the full-length nucleotide sequences. The genomic sequences of the new isolates with pestiviruses were based on the full-length nucleotide sequences. The genomic sequences of the new isolates were generated and aligned with representative pestiviruses, including Pestivirus bovis, Pestivirus tauri, and Pestivirus brazilense, in this study. Phylogenetic analysis was carried out using the maximum-likelihood (ML) method using MEGA7 software (1,000 bootstrap replicates). Fixed circles represent the BVDV BI-2023 strain isolated in this study.
BVDV BI-2023 encodes E2, and Erns has several unique mutations in functional domains
A comparative analysis of the E2 and Erns amino acid sequences among BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b strains revealed distinct differences in BVDV BI-2023. Residues F6, I16, I/T55, V77, and D/N83 within domain DA, as well as L/T/R252 and O263 in domain DC of the E2 protein, were conserved across all analyzed BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b reference strains except in BVDV BI-2023 (Figure 5A). Furthermore, two unique substitutions were identified in the Erns protein: Q150K within one of the seven known linear epitopes, and S190R in the C-terminal domain. These findings suggest that BVDV BI-2023 may represent a novel variant within the BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b group (Figure 5B).

Figure 5. Analysis of the E2 and Erns protein sequence. Analysis of the BVDV1b BI-2023 E2 protein sequence (A). Analysis of the BVDV1b BI-2023 Erns protein sequence (B). Sequence identity with the BVDV1b BI-2023 isolate (CLC Sequence Viewer 8) is indicated by dots.
Discussion
Bovine serum has been an essential component in cell culture systems for over five decades, yet it continues to be frequently contaminated with adventitious viruses. There are numerous viral agents in bovine serum and its derivatives, with BVDV being the most commonly detected contaminant (1–13). In this study, an NCP strain of BVDV was successfully detected and isolated from commercial FBS. However, this analysis did not extend to other possible adventitious agents or pathogens, which may also pose significant risks to the safety of biological products. This highlights the critical importance of thorough screening for viral contaminants in commercial serum and related biological materials before using.
While PCR offers specific and sensitive detection for known viruses, it may fail to identify uncharacterized variants or closely related viral species. Commercial serum products may harbor undetected contaminants without comprehensive testing, adversely affecting experimental reliability. NCP-type BVDV, in particular, can persistently infect cultured cells without producing overt cytopathic effects, making it difficult to detect and potentially compromising experimental results, diagnostic assays, and clinical trial outcomes. Advanced techniques such as next-generation sequencing provide a more robust approach for identifying these hidden viral contaminants.
Based on 5′-UTR sequence comparisons, BVDV strains are classified into two species: Pestivirus bovis (BVDV-1) and Pestivirus tauri (BVDV-2). Pestivirus bovis has been subdivided into 25 genotypes (1a to 1.25) (16–22). Previous unpublished sequence data have reported the presence of BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b in various regions of Israel (24). In the current study, a putative BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b strain was identified in commercial FBS sourced from Israel, suggesting that this virus may be circulating within Israeli cattle populations. Further investigations are warranted to screen additional batches or sources of FBS to assess the extent of viral contamination.
The FBS is an essential raw material for cell culture applications (1–3). However, if contaminated with viruses, it can transmit these pathogens into cell culture-derived vaccines and other biological products (1–3). Previous studies have demonstrated that commercial bovine serum products from various regions in China frequently contain at least one type of viral contaminant (4–9). In a 1991 investigation, the National Animal Disease Center identified 93 viral isolates from 190 batches of commercial FBS (5). Multiple reports have also documented the presence of BVDV1 in imported commercial FBS, highlighting the widespread issue of BVDV contamination in both domestic and imported serum sources (4, 6–9).
Furthermore, a novel putative pestivirus species provisionally named “HoBi-like” and currently classified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses as Pestivirus brazilense was initially detected in Europe in FBS imported from Brazil (25, 26). Contaminated serum can interfere with the diagnosis of viral infection, and using such contaminated serum to produce vaccines can lead to seroconversion or illness in vaccinated animals (4–6). These findings underscore the frequent occurrence of BVDV contamination in cattle-derived materials.
Currently, China restricts the import of FBS to countries certified free of bovine spongiform encephalopathy, such as Australia, New Zealand, and Uruguay. However, the circulation of American FBS with unverified origins in the domestic market raises concerns about the effectiveness of animal disease prevention and control efforts in China (6). In this study, the BVDV BI-2023 strain identified in the FBS was an NCP type, posing a potential risk of widespread infection and the birth of persistently infected animals. As a result, laboratories must screen FBS for exogenous viruses and determine their genotypes before use.
Genome sequencing of the BVDV BI-2023 strain revealed a total of 12,273 nucleotides encoding a polyprotein comprising four structural and seven non-structural proteins. Based on 5’-UTR sequence comparison, this isolate was classified as a BVDV1b genotype. A previous study by Zhu et al. proposed that the dominant BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b strains circulating in China (e.g., CC13B and JL-1) likely originated from Europe (27). In the present study, alignment analyses using the full genome, 5’-UTR, structural, and non-structural protein sequences showed that BVDV BI-2023 shared high sequence identity with several foreign reference strains, including USMARC/PI-91-21/CD46GE, USMARC/PI-91-21/MDBK, and AU526, all originally isolated in the United States. Phylogenetic analysis of the full genome and the 5’-UTR further confirmed a closer genetic relationship between BVDV BI-2023 and these United States-derived strains than with other BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b isolates. These findings support the hypothesis that the BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b strains currently reported in China may have been introduced abroad, highlighting the need to monitor this genotype in imported FBS and domestic cattle populations.
Glycoprotein E2 is the primary envelope protein displayed on the surface of BVDV virions and plays a key role in eliciting neutralizing antibody responses during infection (28). Structurally, the E2 protein is organized into four domains: DA (residues 4–87), DB (residues 88–164), DC (residues 165–271), and DD (residues 272–333) (28). There are three immunodominant regions in the BVDV E2 protein, located at residues 16–26, 71–74, and 142–150 (29–31), all of which are within the DC domain and contribute to neutralization. In this study, a comparison of BVDV BI-2023 with other BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b reference strains indicated that the BVDV BI-2023 E2 protein had one unique mutations located at residue I16V of immunodominant regions (Figure 5A). The unique mutation may reduce antibody-binding affinity, potentially enabling BVDV BI-2023 to evade host immune recognition.
Erns is another envelope glycoprotein involved in virus neutralization and is distinguished by its intrinsic ribonuclease (RNase) activity (28). Seven linear epitopes of the Erns protein from BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b reference strains 31GIWPEKIC38, 65NYTCCKLQ72, 127QARNRPTT134, 145SFAGTVIE152, 161VEDILY166, 114CRYDKNTDVNV124, and 116YDKNTDVNV124 have been identified as key antibody-interacting regions (28). In the current study, BVDV BI-2023 showed a unique mutation within the fourth linear epitope, altering 145SFAGTVIE152 to 145SFAGTVQ151KE152 (Figure 5B), implying potential differences in antibody-binding properties between BVDV BI-2023 and reference genotype 1b strains. Furthermore, the C-terminal region of Erns is critical for its secretion and intracellular retention, with residues 183, 190, and 208 playing important roles (28). Sequence analysis revealed a unique R190S substitution in BVDV BI-2023 (Figure 5B), suggesting that this mutation might affect the protein’s secretion dynamics. These findings indicate that BVDV BI-2023 shows molecular differences in Erns compared to established genotype 1b reference strains.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study identified a potentially novel strain of BVDV1 (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b from commercially imported FBS. Given the risk of viral contamination in cell cultures and biological products and the potential for broader dissemination, the implicated serum batch should be discarded. These findings highlight the urgent need for regulatory authorities to implement routine viral screening protocols for all imported serum batches to safeguard laboratory research and animal health.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Author contributions
JP: Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. JJ: Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. SM: Investigation, Writing – original draft. XC: Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. RD: Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. SG: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition. LK: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Resources. JX: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PT:Investigation, Software, Resources, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The Major Special Science and Technology Project of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (grant no. 2023A02007-2) and the Key Research and Development Program of Gansu Province (grant no. 22YF7NA030).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Pastoret, PP . Human and animal vaccine contaminations. Biologicals. (2010) 38:332–4. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2010.02.015
2. Gómez-Romero, N, Velazquez-Salinas, L, Ridpath, JF, Verdugo-Rodríguez, A, and Basurto-Alcántara, FJ. Detection and genotyping of bovine viral diarrhea virus found contaminating commercial veterinary vaccines, cell lines, and foetal bovine serum lots originating in Mexico. Arch Virol. (2021) 166:1999–2003. doi: 10.1007/s00705-021-05089-9
3. Nuttal, PA, Luther, PD, and Stott, EJ. Viral contamination of bovine foetal serum and cell cultures. Nature. (1977) 266:835–7. doi: 10.1038/266835a0
4. Zhang, Q, Li, SQ, Li, J, Xiong, W, Wang, QQ, Li, CY, et al. Detection of bovine viral diarrhoea virus contamination in imported foetal calf serum. Chin Anim Health Inspect. (2013) 30:55–7 (In Chinese). doi: 1005-944X(2013)02-0055-03
5. Xia, HY, Vijayaraghavan, B, Belák, S, and Liu, LH. Detection and identification of the atypical bovine pestiviruses in commercial foetal bovine serum batches. PLoS One. (2011) 6:e28553. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028553
6. Wang, JH, Li, S, He, WR, Zhao, Q, and Qiu, HJ. Isolation and identification of bovine viral diarrhea virus from imported foetal bovine serum. Chin J Biol. (2016) 29:308–11. (In Chinese). doi: 10.13200/j.cnki.cjb.001281
7. Liu, Z, Dong, QQ, Wu, AD, Wang, KY, Liang, CZ, Adnan, A, et al. Isolation, identification, and mouse pathogenicity analysis of a strain of bovine viral diarrhea virus from imported fetal bovine serum. Chin Anim Husband Vet Med. (2024) 51:4052–9. (In Chinese). doi: 10.16431/j.cnki.1671-7236.2024.09.033
8. Wen, SB, Song, Y, Meng, XG, Chen, Z, Meng, LH, Wang, MS, et al. Isolation and identification of a BVDV strain from imported fetal bovine serum. J Pathog Biol. (2024) 16:743–6. (In Chinese). doi: 10.13350/j.cjpb.210701
9. Zhang, SQ, Tan, B, Guo, L, Wang, FX, Zhu, HW, Wen, YJ, et al. Genetic diversity of bovine viral diarrhea viruses in commercial bovine serum batches of Chinese origin. Infect Genet Evol. (2014) 27:230–3. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2014.07.021
10. Bolin, SR, Matthews, PJ, and Ridpath, JF. Methods for detection and frequency of contamination of foetal calf serum with bovine viral diarrhoea virus and antibodies against bovine viral diarrhoea virus. J Vet Diagn Invest. (1991) 3:199–203. doi: 10.1177/104063879100300302
11. Bolin, SR, and Ridpath, JF. Prevalence of bovine viral diarrhoea virus genotypes and antibody against those viral genotypes in foetal bovine serum. J Vet Diagn Invest. (1998) 10:135–9. doi: 10.1177/104063879801000203
12. Makoschey, B, van Gelder, PT, Keijsers, V, and Goovaerts, D. Bovine viral diarrhoea virus antigen in foetal calf serum batches and consequences of such contamination for vaccine production. Biologicals. (2003) 31:203–8. doi: 10.1016/s1045-1056(03)00058-7
13. Zhang, P, Cao, L, Ma, YY, Su, B, Zhang, CY, and Li, YP. Metagenomic analysis reveals the presence of different animal viruses in commercial fetal bovine serum and trypsin. Zool Res. (2022) 43:756–66. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.093
14. Chi, SS, Chen, S, Jia, WJ, He, YJ, Ren, LZ, and Wang, XL. Non-structural proteins of bovine viral diarrhea virus. Virus Genes. (2022) 58:491–500. doi: 10.1007/s11262-022-01914-8
15. Hugues, F, Cabezas, I, Garigliany, M, Rivas, F, Casanova, T, González, EE, et al. First report of bovine viral diarrhea virus subgenotypes 1d and 1e in southern Chile. Virol J. (2023) 20:205. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02170-4
16. Vilcek, S, Paton, DJ, Durkovic, B, Strojny, L, Ibata, G, Moussa, A, et al. Bovine viral diarrhoea virus genotype 1 can be separated into at least eleven genetic groups. Arch Virol. (2001) 146:99–115. doi: 10.1007/s007050170194
17. Vilcek, S, Durkovic, B, Kolesarova, M, and Paton, DJ. Genetic diversity of BVDV: consequences for classification and molecular epidemiology. Prev Vet Med. (2005) 72:31–5. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2005.08.004
18. Booth, RE, Thomas, CJ, El-Attar, LMR, Gunn, G, and Brownlie, J. A phylogenetic analysis of bovine viral Diarrhoea virus (BVDV) isolates from six different regions of the UK and links to animal movement data. Vet Res. (2013) 44:43. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-44-43
19. Yeşilbağ, K, Alpay, G, and Becher, P. Variability and global distribution of subgenotypes of bovine viral diarrhea virus. Viruses. (2017) 9:128. doi: 10.3390/v9060128
20. Giangaspero, M, Yesilbag, K, and Apicella, C. Who's who in the bovine viral diarrhea virus type 1 species: genotypes L and R. Virus Res. (2018) 256:50–75. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2018.07.009
21. Shi, HF, Li, H, Zhang, Y, Yang, LL, Hu, Y, Wang, ZC, et al. Genetic diversity of bovine pestiviruses detected in backyard cattle farms between 2014 and 2019 in Henan Province, China. Front Vet Sci. (2020) 7:197. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00197
22. Giangaspero, M, and Zhang, SQ. Pestivirus a, bovine viral diarrhea virus type 1 species genotypes circulating in China and Turkey. Open Vet J. (2023) 13:903–31. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2023.v13.i7.12
23. Kumar, S, Stecher, G, and Tamura, K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. (2016) 33:1870–4. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054
24. Friedgut, O, Rotenberg, D, Brenner, J, Yehuda, S, Paz, R, Alpert, N, et al. Description of the first acute bovine diarrhea virus-2 outbreak in Israel. Vet J. (2011) 189:108–10. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2010.06.007
25. Lescoat, C, Perrotte, D, Barry, S, Oden, É, Herbet, V, Beaunée, G, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution and international context of bovine viral diarrhoea virus genetic diversity in France. Vet Res. (2024) 55:129. doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01377-9
26. Bauermann, FV, Ridpath, JF, Weiblen, R, and Flores, EF. HoBi-like viruses: an emerging group of pestiviruses. J Vet Diagn Invest. (2013) 25:6–15. doi: 10.1177/1040638712473103
27. Wang, FI, Deng, MC, Huang, YL, and Chang, CY. Structures and functions of pestivirus glycoproteins: not simply surface matters. Viruses. (2015) 7:3506–29. doi: 10.3390/v7072783
28. Deregt, D, van Rijn, PA, Wiens, TY, and van den Hurk, J. Monoclonal antibodies to the E2 protein of a new genotype (type 2) of bovine viral diarrhea virus define three antigenic domains involved in neutralization. Virus Res. (1998) 57:171–82. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1702(98)00095-1
29. Ciulli, S, Galletti, E, Battilani, M, Galligioni, V, and Prosperi, S. Analysis of variability and antigenic peptide prediction of E2 BVDV glycoprotein in a mucosal-disease affected animal. Vet Res Commun. (2009) 33:125–7. doi: 10.1007/s11259-009-9267-7
30. Wang, W, Shi, XC, Chen, CY, and Wu, H. Genetic characterization of a noncytopathic bovine viral diarrhea virus 2b isolated from cattle in China. Virus Genes. (2014) 49:339–41. doi: 10.1007/s11262-014-1067-7
Keywords: Pestivirus bovis , genotype 1b, fetal bovine serum, contamination, novel strain
Citation: Pan J, Jiang J, Mi S, Chen X, Duan R, Gao S, Kuang L, Tong P and Xie J (2025) Molecular characteristics of a potentially novel BVDV (Pestivirus bovis) genotype 1b isolate from commercial fetal bovine serum. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1629211. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1629211
Edited by:
Veasna Duong, Institut Pasteur du Cambodge, CambodiaReviewed by:
Massimo Giangaspero, Independent Researcher, Teramo, ItalyJames McConville, Agri-Food and Biosciences Institute, United Kingdom
Florence Hugues, University of Concepcion, Chile
Copyright © 2025 Pan, Jiang, Mi, Chen, Duan, Gao, Kuang, Tong and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jinxin Xie, eGllamlueGluMTk4NjgzQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Juanjuan Pan1†
Juanjuan Pan1† Shijiang Mi
Shijiang Mi Shandian Gao
Shandian Gao Panpan Tong
Panpan Tong Jinxin Xie
Jinxin Xie


