- 1Police Dog Technology College, Criminal Investigation Police University of China, Shenyang, China
- 2Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changsha, China
- 3The Second Affiliated Hospital of Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang, China
Introduction: This study examines the detrimental effects of high-temperature environments on canine testicular function and reproductive health, and investigates the potential of Epimedii Folium, particularly its active component icariin, in alleviating these effects and improving testicular function.
Methods: A completely randomized single-factor design was employed, involving 24 adult male Beagle dogs (9.82 ± 0.73 kg) assigned randomly to four treatment groups, with six dogs in each group. The groups included a negative control group (“Control”), a positive control group exposed to testicular heat stress (“Model”), and two icariin-treated groups receiving daily doses of 0.5 g/kg (Icariin-L) and 1.0 g/kg (Icariin-H), respectively. All groups, except the negative control, underwent a testicular heat stress model to induce damage and assess the effects of icariin on sperm quality, testicular function, hormone levels, protein expression, and testicular histological changes.
Results: Icariin supplementation improved sperm quality under heat stress, as indicated by increased total sperm count and motility, along with a reduction in sperm malformation rate (p < 0.01). It also restored adenosine triphosphate (ATPase) activities (Na+-K+-ATPase, Mg2+-ATPase, and Ca2+-ATPase) and serum hormone levels (GnRH, LH, and E2) (p < 0.01). Western blot analysis revealed that icariin upregulated steroidogenic proteins (STAR, 17βHSD, and CYP450) and the tight junction protein ZO-1 (p < 0.01), while downregulating the BAX expression (a key regulator of mitochondrial apoptosis) and enhancing the BCL-2 expression (a major anti-apoptotic factor in the BCL-2 family) (p < 0.01). Histological assessments demonstrated that icariin mitigated heat-induced damage to seminiferous tubules, epithelial thinning, and spermatogonia degeneration. Furthermore, molecular docking analysis confirmed a strong binding affinity between icariin and 17βHSD, mediated by hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that icariin may alleviate testicular heat stress by modulating testosterone synthesis, enhancing ATPase function, restoring blood–testis barrier integrity, and inhibiting apoptosis. The dose-dependent efficacy (1.0 g/kg > 0.5 g/kg) supports the potential of icariin as a possible therapeutic agent for improving reproductive health in dogs exposed to high-temperature environments.
1 Introduction
Dogs residing in high-temperature environments, particularly southern regions of China or during the intense summer months, are frequently exposed to elevated ambient temperatures, which pose a considerable risk of heat stress to their testes. This exposure poses a significant challenge to maintaining reproductive health in dogs. The testes, as the primary organ of the male reproductive system, play a crucial role in maintaining the reproductive capacity of dogs through their normal physiological functions (1, 2). However, studies have shown that high-temperature environments can cause spermatogenic dysfunction in the testes, resulting in reduced sperm quality and quantity, and ultimately affecting the reproductive performance of dogs (3). Therefore, exploring effective strategies to mitigate testicular heat stress in dogs, along with elucidation of the underlying mechanisms, holds immense theoretical and practical importance.
Epimedii Folium has been found to contain more than 379 compounds, among which are flavonoids, lignans, organic acids, terpenoids, dihydrophenanthrene derivatives, alkaloids, and other compounds. Flavonoid compounds, such as epimedin A, B, C, icariin, baohuoside I, icariside I, and icaritin, are acknowledged as the leading chemical and pharmacologically active components in Epimedii Folium (4, 5). In recent years, icariin, a compound derived from traditional Chinese medicine and the primary active ingredient in Epimedii Folium, has shown extensive potential in enhancing testicular function. Chen et al. reported that a dosage of 200 mg/kg of icariin significantly increased epididymal sperm count and testosterone levels in male rats by modulating the expression of specific genes, including peripheral benzodiazepine receptors (PBR) and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (STAR) (6). Similarly, Zhao et al. found that the administration of 50 mg/kg body weight (BW) of icariin for 80 consecutive days significantly improved the reproductive performance of male dairy goats, manifesting as increased serum levels of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and testosterone, enhanced spermatogenesis and sperm motility, and improved testicular organ coefficients (7). Furthermore, icariin has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in ameliorating age-related declines in spermatogenic function, safeguarding the junctional function of testicular Sertoli cells, and upregulating ERα/c-fos signaling and the PKR pathway. Its mechanism of action is contingent upon the presence of these signaling molecules (8). Additionally, icariin exerts protective effects against testicular damage in diabetic rats by markedly improving the morphology of the seminiferous tubules, increasing the number of spermatogenic cells, and effectively inhibiting cell apoptosis (9).
While Epimedii Folium contains multiple bioactive compounds, icariin is its primary flavonoid component and has demonstrated significant effects in enhancing testicular function and spermatogenesis across rodent and caprine models (6, 7, 9). Given icariin’s dominant concentration and prior evidence of spermatoprotective effects, we focused on its specific mechanisms in mitigating canine testicular heat stress. Particularly under high-temperature conditions, the manner in which icariin regulates the testosterone synthesis pathway and alleviates spermatogenic dysfunction by influencing the expression of related proteins in testicular tissue warrants further elucidation. Consequently, the present study aims to investigate the therapeutic effects and underlying mechanisms of icariin in dogs with testicular heat stress. It is expected that this study will elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which icariin alleviates heat stress in canine testes and provide a scientific basis for the application of icariin in protecting the reproductive health of dogs.
2 Materials and methods
All experimental procedures involving Beagle dogs were approved by the Animal Care and Welfare Committee of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Ethical Approval No. ISA-2024-0031). The study strictly adhered to institutional guidelines for the humane use of animals, and all participating institutions obtained informed consent for the experimental protocols.
2.1 Experimental materials
This study utilized icariin standard reagent (B9520, purity ≥ 98%, analytical reagent (AR) grade) obtained from Meilun Biotech Co., Ltd. (MB2189-S, Dalian, Liaoning, China). An ultramicro-ATPase kit was procured from Enzyme-Linked Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (ml093096, Wuhan, Hubei, China). Additionally, the GnRH kit (E-EL-0071), LH kit (E-EL-M3053), and E2 kit (E-OSEL-C0001) were sourced from Elabscience Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, Hubei, China). For antibody-based analyses, the following antibodies were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific: ZO-1 (33–9100), BAX (MA5-14003), BCL-2 (13–8800), STAR (MA5-47013), 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (17βHSD) (MA5-25937), and CYCP450 (PA1-343).
2.2 Experimental design and diet composition
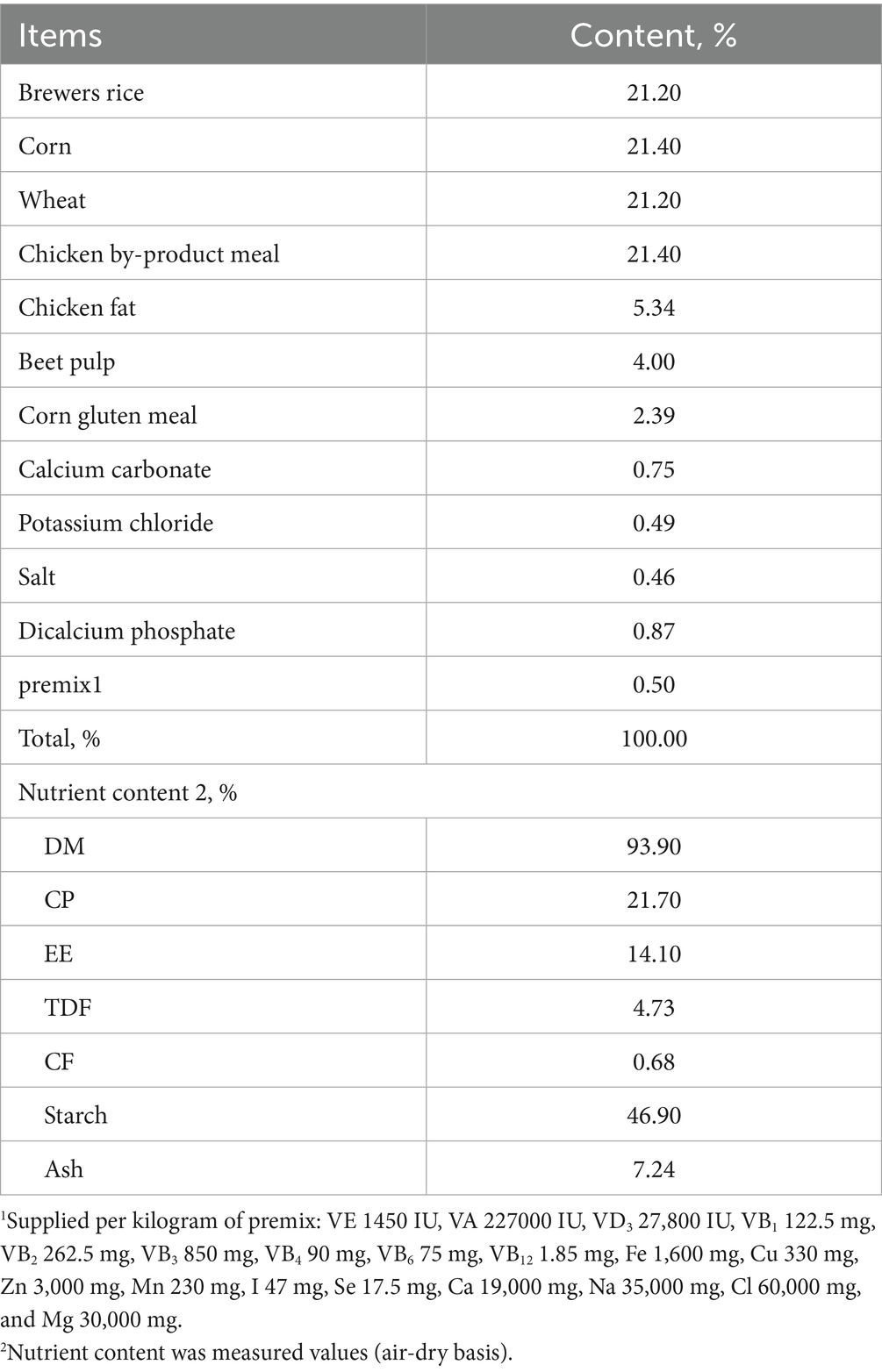
This study employed a single-factor completely randomized design, utilizing 24 2-year-old adult male Beagle dogs procured from Changchun Fenglong Biotechnology Co., Ltd.—a nationally certified laboratory animal provider (Unified Social Credit Code: 91220122MACQ0YWB6G). The animals, with a mean body weight of 9.82 ± 0.73 kg, were randomly allocated into four treatment groups, each consisting of six replicates with one dog per replicate. The treatments included the following: (1) a negative control group (“Control” group), (2) a positive control group (“Model” group), (3) a group receiving a daily dose of 0.5 g/kg icariin (icariin-L group), and (4) a group receiving a daily dose of 1.0 g/kg icariin (Icariin-H group). The diet formulation and nutrient composition, presented in Table 1, met the nutrient requirements for dogs, as outlined by the National Research Council (NRC) (10). All groups received the same basal diet, with icariin supplementation only in the treatment groups. The experimental period spanned 21 days, consisting of a 7-day pre-feeding phase and a 14-day main experimental phase. On day 18, a testicular heat stress model was established by exposing dogs in the Model, Icariin-L, and Icariin-H groups to a 45°C water bath for approximately 30 min/day, for 4 consecutive days, following the methodology described by Henning et al. (11). The experimental procedure is illustrated in Figure 1.
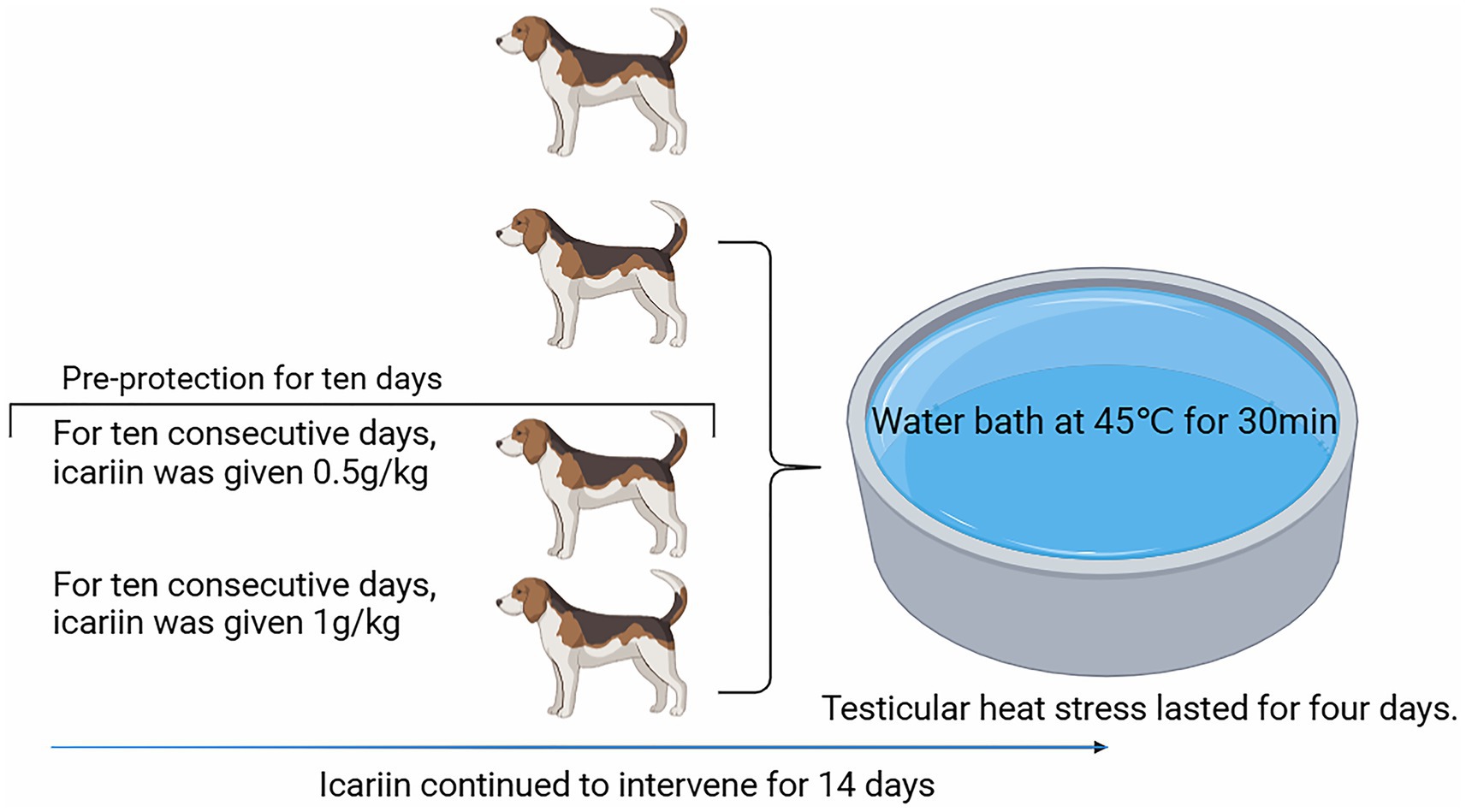
Figure 1. Flowchart of procedural operations for each treatment group during the formal experimental period.
2.3 Housing management and sample collection procedures
Prior to the experiment, dogs were housed individually and underwent standard procedures, including vaccination, deworming, and labeling (1–24). During the pre-feeding phase, all dogs were fed the same diet. In the main experiment phase, dogs were fed their respective treatment diets. Each dog received 600 g of diet per day, divided into two equal feedings (morning and evening), with ad libitum access to water. Dogs were allowed at least 60 min of free activity, which started 40 min after each feeding. The experimental facility was regularly cleaned and disinfected throughout the study duration. On day 22, venous blood was collected from all dogs. Five milliliters of blood were placed in a coagulation-promoting tube, allowed to stand for 30 min, and subsequently centrifuged at 2,500 rpm for 10 min. The serum was separated and stored at −20°C. All surgical interventions (orchiectomy) were performed under general anesthesia using isoflurane inhalation (3% induction, 2% maintenance). Pre- operative and postoperative analgesia was administered via subcutaneous buprenorphine (0.02 mg/kg) and oral meloxicam (0.1 mg/kg). No animals were euthanized, and all dogs fully recovered post-surgery under veterinary supervision.
2.4 Sperm quality, testicular function, and hormone level determination
After testicle removal, the epididymal portion was excised and rinsed with PBS buffer to obtain spermatozoa. The collected spermatozoa were stained and then analyzed using a sperm motility analyzer (HT-Motility™, Hamilton Thorne, Inc, Beverly, MA) to assess their density, viability, and abnormality rate. The testicular tissue was homogenized, and the activities of Na+-K+-ATPase, Mg2+-ATPase, and Ca2+-ATPase were measured using standard kit procedures. The collected serum was assayed for GnRH, LH, and E2 levels using the respective standard kits.
2.5 Testicular histopathology and protein expression analysis
Testicular tissue specimens (0.5 cm3) from dogs were fixed by immersion in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA, pH 7.4) at 4°C for 48 h, followed by graded ethanol dehydration and xylene clearing. The processed tissues were embedded in paraffin and sectioned at a thickness of 5 μm using a rotary microtome (RM2235, Leica Microsystems). Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) according to standard protocols and then mounted with neutral balsam for histomorphological examination under a light microscope (DM4000B, Leica Microsystems). For Western blot analysis, parallel samples were homogenized in ice-cold RIPA lysis buffer (Catalog No. R0020, Solarbio Life Sciences) containing a 1% protease inhibitor cocktail (Catalog No. 04693132001, Roche Diagnostics) using a Polytron homogenizer. Lysates were centrifuged at 14,000 g for 15 min at 4°C, and the supernatants were collected for protein quantification via BCA assay (Catalog No. 23225, Pierce™, Thermo Fisher Scientific) with bovine serum albumin standards. Protein extracts (30 μg per lane) were separated on 12% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gels and transferred to activated polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (0.22 μm, Catalog No. IPVH00010, MilliporeSigma) using a wet transfer system. Membranes were blocked with 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) (w/v) in tris-buffered saline (TBST) with 0.1% Tween-20 for 2 h at room temperature and then incubated with primary antibodies at 4°C for 16 h with gentle agitation: ZO-1 (1:1,000), BAX (1:1,000), BCL-2 (1:1,000), STAR (1:800), 17βHSD (1:1,000), and CYP450 (1:1,000). After five 5-min TBST washes, membranes were incubated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG) secondary antibody (1:10,000) for 1 h at 25°C. Protein bands were visualized using SuperSignal™ West Femto Chemiluminescent Substrate (Catalog No. 34095, Thermo Fisher Scientific) and captured using a FUSION FX Spectra imaging system (Vilber Lourmat). Densitometric analysis was performed using ImageJ 1.53 k with β-actin (1:5000, Catalog No. AC004, ABclonal, Wuhan, Hubei, China) as the loading control.
2.6 Molecular docking and visualization analysis
Small molecule ligand two-dimensional (2D) structures were retrieved from the PubChem CID database (http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), converted into three-dimensional (3D) structures using ChemOffice 20.0 software (PerkinElmer, Inc., Waltham, MA), and subsequently saved as mol2 files. High-resolution crystal structures of protein targets were selected from the Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics – Protein Data Bank (RCSB PDB) database (http://www.rcsb.org/) to serve as molecular docking receptors. PyMOL 2.6.0 software was employed to remove water molecules and phosphates from the protein, add hydrogen atoms to the ligand and the protein, and prepare them for docking. These were saved as Protein Data Bank identification (PDB ID) files. The Molecular Operating Environment (MOE, Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA, San Diego, CA) 2019 software was used to minimize the energy of compounds, preprocess target proteins, and identify active sites. MOE 2019 was chosen for docking, and docking was performed with 50 iterations to ensure thorough exploration of the binding space. The binding activity was evaluated based on binding energy, and the results were visualized using PyMOL 2.6.0 and Discovery Studio 2019 software (Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY).
2.7 Statistical analysis
All data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD), and fundamental statistical analyses were performed using the MEANS module of the Statistical Analysis System (SAS Institute Inc. Cary, NC) 9.4. The Generalized Linear Model (GLM) module was employed for the analysis of variance (ANOVA) of sperm quality, testicular function, hormone levels, and expression of heat stress-related proteins among different treatments. Duncan’s multiple comparison test was used to assess the effect of icariin on the ability of canine testes to resist heat stress-induced damage. A significance level of p of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant, and a p-value of < 0.01 indicated a highly significant difference. Statistical graphs were generated using GraphPad Prism 8.0 (GraphPad Software, LLC, San Diego, CA).
3 Results
3.1 Impact of icariin on canine sperm quality
As shown in Figure 2, the heat-stressed dogs (Model group) exhibited a significant decline in total sperm count and motility compared with the Control group (p < 0.01) and were accompanied by a marked increase in the sperm abnormality rate (p < 0.01). Dietary supplementation with icariin has led to significant improvements in these parameters. Specifically, compared with the Model group, both Icariin-L and Icariin-H groups demonstrated a significant increase in total sperm count and sperm motility rate (p < 0.01), while also significantly reducing sperm malformation rate (p < 0.01). Furthermore, high-dose icariin addition demonstrated superior efficacy in canine sperm quality (p < 0.01).
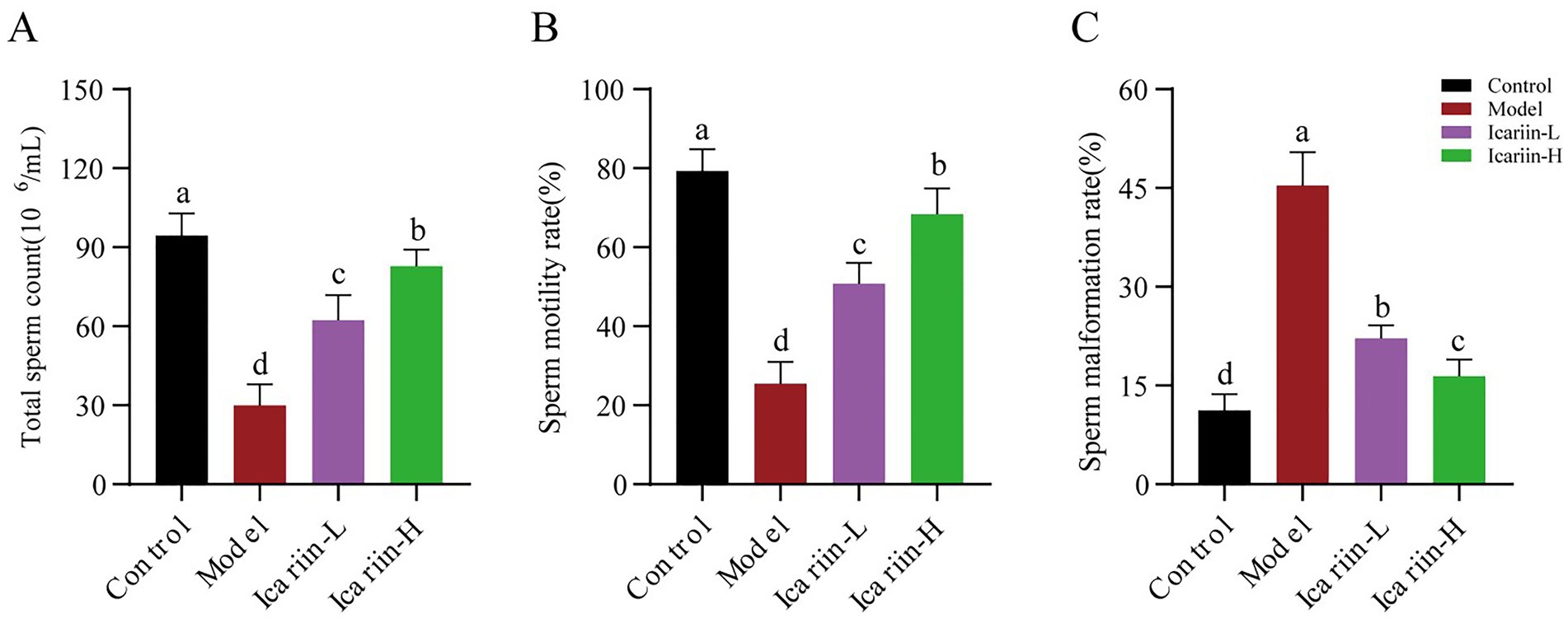
Figure 2. Effects of icariin on canine sperm quality under heat stress. (A), Total sperm count; (B) Sperm motility rate; (C) Sperm malformation rate. Letters labeled differently represent significant differences, p < 0.05.
3.2 Impact of icariin on reproductive function status
The activities of P-type ATPases (Na+-K+-ATP, Mg2+-ATP, and Ca2+-ATP) of testicular tissue are presented in Figure 3. According to the findings, heat stress treatment significantly reduced the activity of Na+-K+-ATP, Mg2+-ATP, and Ca2+-ATP enzymes in test dogs (p < 0.01). In the icariin-supplemented groups (Icariin-L and Icariin-H), there was a significant improvement in the activities of Na+-K+-ATP, Mg2+-ATP, and Ca2+-ATP enzymes (p < 0.01). Nevertheless, compared to the Control group, the activity of P-type ATPases was still significantly reduced (p < 0.01). In terms of serum sex hormones, the contents of GnRH, LH, and E2 were decreased considerably in the Model group (p < 0.01). In contrast, both Icariin-L and Icariin-H groups exhibited partial restoration of hormone contents (p < 0.01). Notably, the high-dose icariin supplement had a more pronounced impact on restoring hormone contents (p < 0.01).
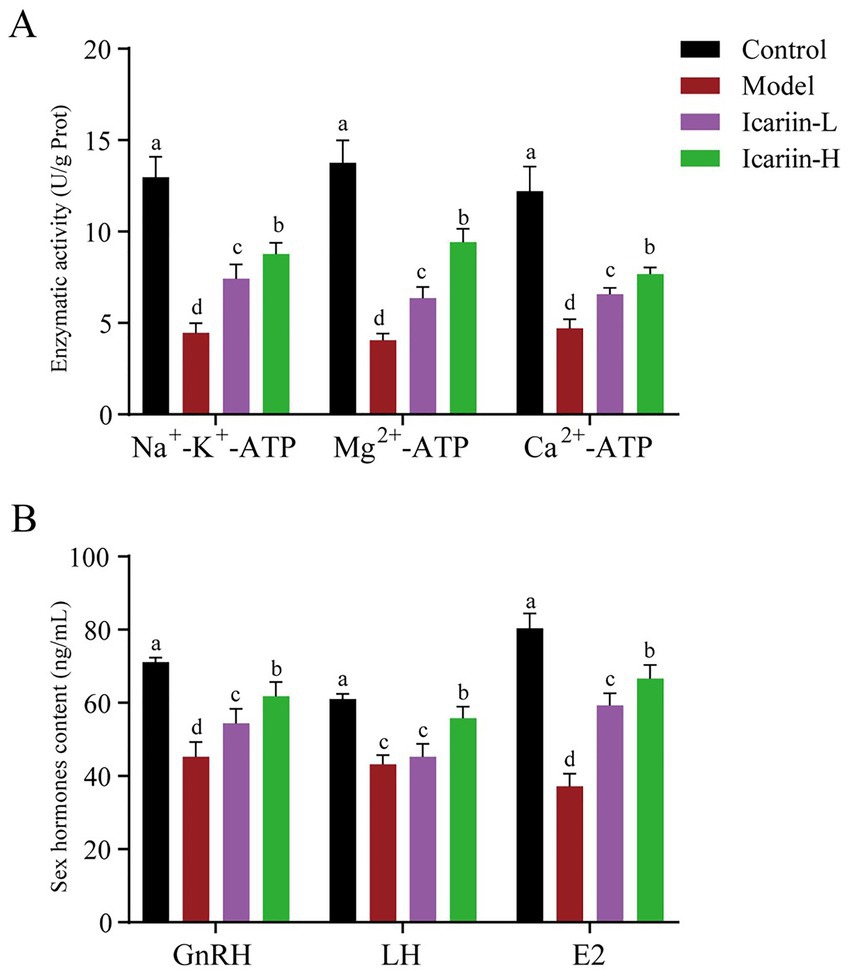
Figure 3. Impact of icariin on testicular ATPase activity and serum hormone levels. (A) Enzymatic activity; (B) Sex hormones content. Letters labeled differently represent significant differences, p < 0.05.
3.3 Modulation of protein expression related to canine testicular heat stress resistance by icariin
As shown in Figure 4, the expression of STRA, 17βHSD, and CYP450 in heat-stressed dogs (Model group) was significantly decreased compared to the Control group (p < 0.01). Nevertheless, icariin administration significantly upregulated the expression of these rate-limiting enzymes in both the Icariin-L and Icariin-H groups, with expression levels considerably higher than those in the Model group (p < 0.01). Moreover, a significant reduction in ZO-1 protein expression was observed in the testicular tissue of the Model group compared to the Control group. Notably, icariin intervention significantly increased ZO-1 protein expression in both the Icariin-L and Icariin-H groups compared to the Model group (p < 0.01). With regard to testicular cell apoptosis, the Model group demonstrated a significant increase in BAX protein expression and a corresponding reduction in BCL-2 protein expression compared to the Control group (p < 0.01). However, dietary supplemented with icariin suppressed BAX expression, a key regulator of mitochondrial apoptosis, and enhanced BCL-2 expression, a major anti-apoptotic factor in the BCL-2 family, compared to the Model group (p < 0.01). Furthermore, the Icariin-H group exhibited significantly greater efficacy than the Icariin-L group in enhancing resistance to testicular heat stress among dogs and modulating the expression of relevant rate-limiting enzymes and apoptotic proteins (p < 0.05).
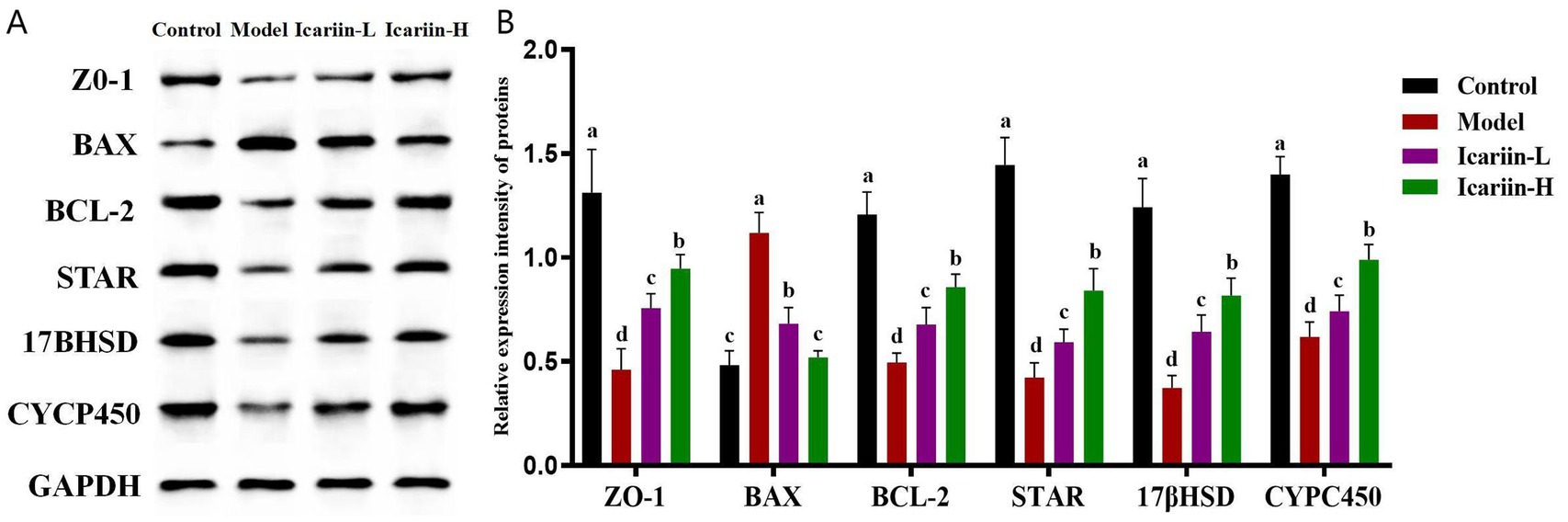
Figure 4. Effects of icariin on the modulation of protein expression related to canine resistance to testicular heat stress. (A,B) western blot analysis of ZO-1, BAX, BCL-2, STAR, 17βHSD, CYCP450, and GAPDH. Letters labeled differently represent significant differences, p < 0.05.
3.4 Influence of icariin on canine testicular tissue structure
The seminiferous tubules and testicular epithelium constitute essential elements of the testicular physiological architecture. The testicular epithelium of dogs in the Model group exhibited a significant decrease in thickness compared to the Control group (Figure 5). This reduction was accompanied by a disruption in the epithelial structure of the seminiferous tubules, as well as pronounced degeneration, detachment, and a marked decrease in the number of spermatogonia. Following dietary supplementation with icariin, notable improvements were observed in the testicular epithelium, structural integrity of the seminiferous tubule epithelium, and spermatogonia count in the Icariin-L and Icariin-H groups compared to the Model group. Notably, a discernible disparity remains in the restoration of testicular tissue connectivity and the resolution of surrounding fragmented tissue within the seminiferous tubules in these two treatment groups, as compared to the Control group.
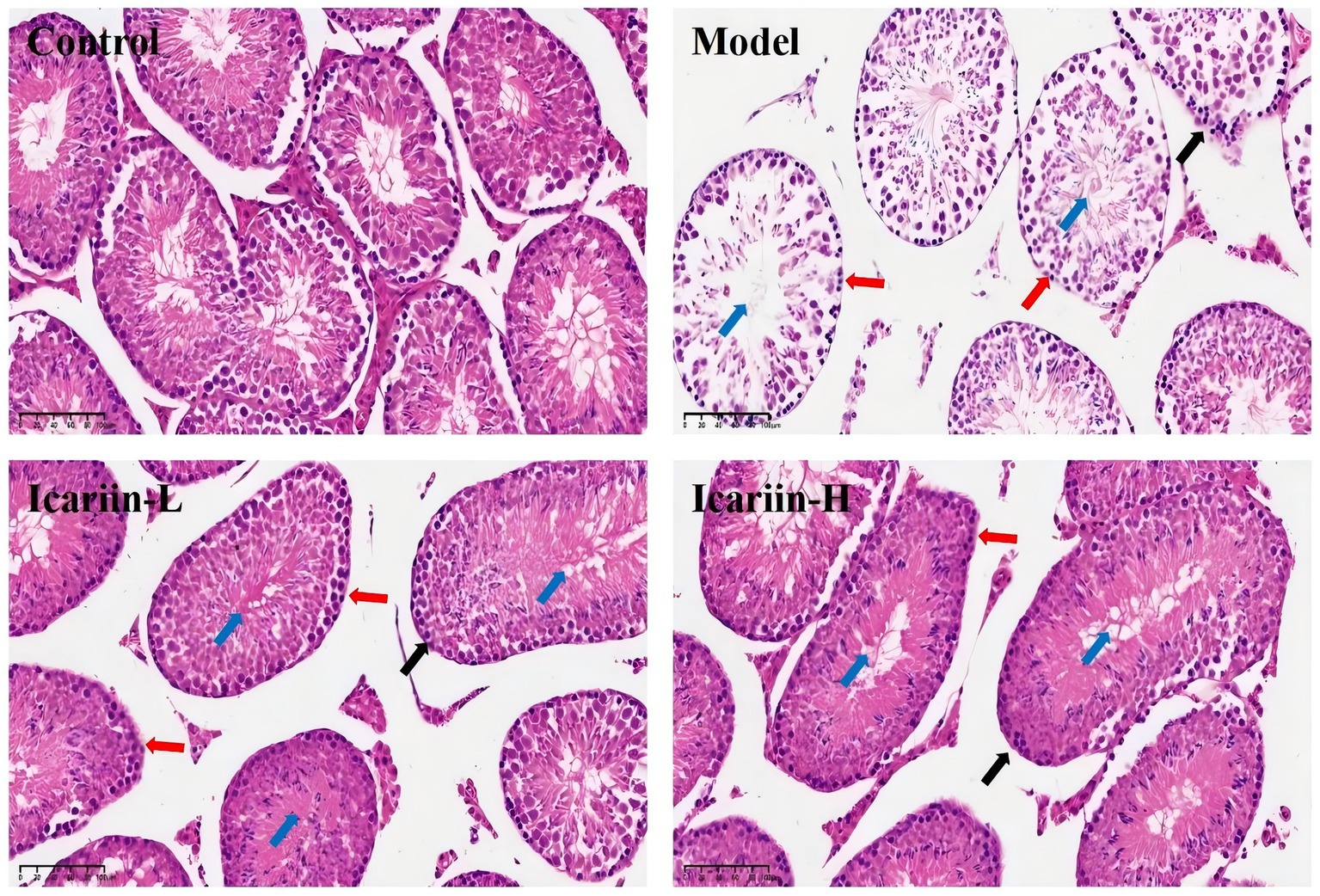
Figure 5. Histopathological effects of icariin on canine testicular tissue under heat stress. Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections of testicular tissue from the Control, Model, Icariin-L (0.5 g/kg), and Icariin-H (1.0 g/kg) groups. In the Model group, heat stress-induced disorganization of the seminiferous tubule (blue arrow), epithelial thinning (black arrow), and spermatogonia degeneration of spermatogonia (red arrows). icariin supplementation mitigated these lesions, with the Icariin-H group showing improved tubular architecture and reduced cellular damage. Scale bars: 100 μm.
3.5 Molecular docking analysis of icariin with the 17βHSD protein target
The molecular docking outcomes of icariin with the 17βHSD protein target are shown in Figure 6. Icariin effectively penetrates the binding pocket of the 17βHSD protein, engaging in hydrogen bonding interactions with the Ile34, Gly15, Ser12, Thr190, and Val188 residues of the protein receptor. Moreover, icariin exhibits carbon-hydrogen interactions with the Thr140, Gly92, and Val188 residues, with Thr190 notably participating in multiple interaction types. A specific Pi-Sigma interaction is observed between the Pro187 residue and icariin. Additionally, significant hydrophobic interactions are established between icariin and the Tyr155, Leu149, and Val188 residues of the protein receptor, with Val188 playing a pivotal role in multiple interaction networks.
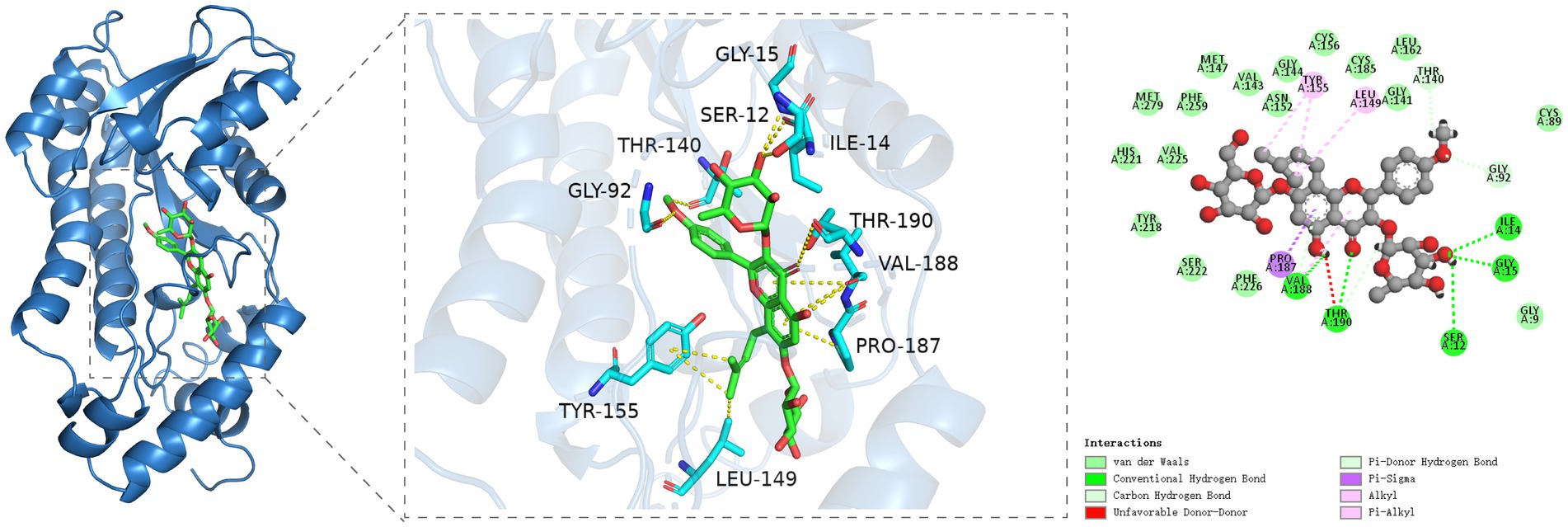
Figure 6. Molecular docking analysis of icariin with 17βHSD reveals binding interactions critical for testosterone synthesis. (A) Three-dimensional (3D) structure of the 17βHSD protein (ribbon diagram). (B) Direct interaction sites: icariin forms hydrogen bonds with Ile34, Gly15, Ser12, Thr190, and Val188 (dashed lines) and carbon-hydrogen bonds with Thr140, Gly92, and Val188. (C) Hydrophobic interactions (van der Waals forces) between icariin and Tyr155, Leu149, Val188, and Pro187 (Pi-Sigma interaction).
4 Discussion
In mammals, prolonged exposure to hyperthermic environments disrupts systemic homeostasis by exceeding physiological thermoregulatory thresholds (12). The testes, which require a temperature of 2 to 8°C below core body temperature for normal spermatogenesis, are particularly vulnerable in dogs due to compromised scrotal cooling mechanisms (13, 14). To model this pathology, we subjected dogs to scrotal immersion in a 45°C water bath for 30 min, a protocol adapted from Henning et al. (11) that minimizes confounding stressors through non-invasive thermal exposure. Histopathological analyses revealed seminiferous epithelial thinning, disorganization of spermatogenic cell layers, and sloughing of spermatogonia in heat-stressed testes, concomitant with significant declines in sperm concentration (a 68.4% reduction compared to the control) and progressive motility (67.9% reduction). These morphological and functional impairments correlated with suppressed serum testosterone levels, suggesting partial mediation through the androgen signaling pathways. The observed reproductive dysfunction aligns with previous reports of heat-induced testicular atrophy and steroidogenic suppression in mammals (15). Plant saponins, including icariin, have shown promise in ameliorating high-temperature-induced spermatogenesis disorders in various animal models (14, 16, 17). Icariin, in particular, has demonstrated significant effects in regulating testosterone synthesis, protecting testicular tissue structure, and inhibiting cell apoptosis (6, 7, 9). Therefore, we selected icariin as the intervention in this study and, based on the metabolic body weight of the experimental animals (18), set the dietary icariin supplementation level between 0 and 1 g/kg to systematically evaluate its effects on canine sperm quality, testicular function, hormone levels, related protein expression, and testicular tissue structure.
Thermal stress induces mitochondrial oxidative damage through reactive oxygen species (ROS) overproduction, particularly superoxide anion (O₂−) and hydroxyl radical (OH−), which preferentially target electron transport chain complexes (19–21). This oxidative insult disrupts ATP synthesis, leading to substrate limitation for ATP-dependent membrane transporters. Specifically, Na+-K+-ATPase and Ca2+-ATPase activities in testicular tissue decreased by 65.6 and 61.5%, respectively, in heat-stressed dogs. Given the critical role of these enzymes in maintaining membrane potential and calcium homeostasis, their functional impairment is likely to contribute to the observed deficits in sperm motility. Notably, icariin supplementation restored testicular ATPase activities in a dose-dependent manner (22.9 and 15.4% recovery at 0.5 g/kg; 33.2 and 24.3% at 1 g/kg for Na+-K+-ATPase and Ca2+-ATPase, respectively), paralleling improvements in sperm motility parameters. The dose-dependent efficacy of icariin (1.0 g/kg > 0.5 g/kg) aligns with its role in modulating testosterone synthesis and cellular resilience. Higher doses more robustly enhanced ATPase activity, restored blood–testis barrier integrity via ZO-1 upregulation, and suppressed apoptosis (reduced BAX/BCL-2 ratio), collectively explaining superior spermatogenic recovery in the Icariin-H group. These data suggest that icariin mitigates oxidative damage through ion transport modulation, potentially via direct ROS scavenging or upregulation of antioxidant enzymes, as demonstrated in murine models (22).
Hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis dysregulation has emerged as a key mechanism underlying heat-induced reproductive failure (23). Nevertheless, this axis can be perturbed by external stimuli, such as inflammation and oxidative stress, which can impair spermatogenesis. Our data corroborate previous reports of HPG axis dysregulation under thermal stress. Specifically, heat-exposed dogs exhibited suppressed hypothalamic GnRH release, resulting in decreased pituitary LH production and subsequent reductions in E2 synthesis. Post-treatment, serum GnRH and LH levels recovered to baseline values, while E2 levels showed a gradual increase. Heat stress activates the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, leading to elevated cortisol levels. Cortisol exerts a negative feedback effect on hypothalamic GnRH synthesis, thereby reducing the synthesis of GnRH. Since GnRH is critical for pituitary LH production, this suppression consequently diminishes LH synthesis. The restoration of HPG axis function coincided with improved blood–testis barrier (BTB) integrity. Immunoblotting revealed that ZO-1 expression increased by 2.1-fold, while the BAX/BCL-2 ratio decreased from 2.4 to 0.6, suggesting dual mechanisms of junctional stabilization and apoptosis suppression. The restoration of these proteins’ expression levels is likely instrumental in the recovery of testicular physiological function (23–25). Moreover, our study revealed that, under heat stress conditions, the testes of the Model group exhibited considerable structural damage, manifested by the emergence of large gaps and morphological distortions in the seminiferous tubules. Western blot analysis validated that the expression levels of ZO-1 and BCL-2 were substantially decreased, while the level of BAX was significantly increased in the testicular tissue of the experimental dogs. Notably, following icariin intervention, the expression levels of ZO-1 and BCL-2 recovered to varying extents, suggesting a potential restoration of the BTB structure. These findings imply that icariin not only modulates testosterone secretion but also effectively ameliorates testicular heat stress injury by rejuvenating the integrity of the BTB (26). Speculatively, icariin may activate Nrf2/HO-1 signaling or directly scavenge hydroxyl radicals, as its flavonoid structure contains phenolic hydroxyl groups capable of donating protons to neutralize ROS. These mechanisms could synergize with ion transport regulation to reduce oxidative injury to spermatogenic cells. Notably, BAX and BCL-2 extend beyond apoptotic regulation. BCL-2 family proteins also modulate autophagy via interactions with Beclin-1, and BAX has been associated with mitochondrial dynamics and cellular metabolism (27, 28).
The maintenance of a stable testosterone concentration within the seminiferous tubules is crucial for the differentiation of spermatogonia into mature spermatozoa (29–31). Heat stress significantly suppressed key steroidogenic enzymes (STAR: 70.7% reduction; 17βHSD: 69.9%; CYP450: 55.8%), with these reductions mirroring concomitant declines in testosterone levels, a pattern consistent with the findings from Ji et al. (2024) (32). Molecular docking studies revealed a strong binding affinity between icariin and 17βHSD, consistent with the observed upregulation of steroidogenic proteins post-treatment. Concomitant increases in STAR and CYP450 expression (key regulators of testosterone biosynthesis) suggest a coordinated enhancement of the steroidogenic pathway, where icariin’s binding to 17βHSD serves as a mechanistic trigger. These findings align with the restoration of serum testosterone levels (implied by GnRH/LH recovery) and testicular ATPase activities, collectively indicating that icariin modulates both enzyme structure and pathway dynamics to mitigate heat stress–induced steroidogenic dysfunction. Importantly, the high-dose icariin group (1 g/kg) exhibited complete restoration of sperm count (82.9 × 106 vs. 94.5 × 106/mL in controls). This finding was further corroborated by Western blot analysis, which showed a significant increase in the expression levels of STAR, 17βHSD, and CYP450 following icariin treatment. These results suggest that icariin may have a direct modulatory effect on the expression of these key proteins involved in testosterone biosynthesis. These findings align with murine studies demonstrating icariin’s safety profile at 200 mg/kg (6), while extending dose–response evidence to dogs. In the current study, we administered a higher dose of icariin (Icariin-H group: 1 g/kg) to experimental dogs, which was well within their maximum tolerable dose. Our therapeutic findings indicate that the effectiveness of icariin in mitigating heat stress-induced damage to the reproductive system increased with higher dosages. This dose-dependent response suggests that icariin is not only efficacious in protecting the reproductive system from heat stress-induced damage but also safe and devoid of side effects within the normal dosage range for dogs (33). Collectively, these preclinical data support further investigation of icariin as a therapeutic candidate for mitigating heat stress-induced reproductive dysfunction in dogs. The observed dose-dependent efficacy (up to 1 g/kg) and absence of adverse effects within the tested range warrant translational studies to establish clinical safety and optimal dosing regimens.
5 Conclusion
The study provides preliminary evidence suggesting that icariin may exert a multifaceted protective effect against heat stress-induced damage in canine testes. Specifically, our data indicate that it upregulates the expression of proteins crucial for testosterone synthesis, enhances ATPase activity, regulates hormone levels, promotes repair of the blood–testis barrier, and inhibits cell apoptosis. These findings contribute to the scientific basis for exploring the use of icariin in preserving canine reproductive health and highlight its potential therapeutic relevance for managing reproductive disorders associated with environmental heat stress.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by all experimental procedures involving Beagle dogs were approved by the Animal Care and Welfare Committee of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, with the ethical approval number ISA-2024-0031. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
BL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Writing – original draft. LX: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. MS: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Formal analysis. XZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. CY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. WG: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. WW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YY: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Science and Technology Program of the Ministry of Public Security of the People’s Republic of China, “Research on Cold-Resistant Pedigree Breeding and Support Technologies for Police Service Dogs in High-Altitude and Cold Regions” [Grant No. 2024JSZ12], and by the Liaoning Provincial Department of Education’s project, “Ginsenoside Rg1 regulates D-Gal-induced autophagy to delay liver injury in mice” [Grant No. JYTMS/20231403].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Velasco, A, and Ruiz, S. New approaches to assess fertility in domestic animals: relationship between arterial blood flow to the testicles and seminal quality. Animals. (2020) 11:12. doi: 10.3390/ani11010012
2. Li, S, and Yang, QE. Hypobaric hypoxia exposure alters transcriptome in mouse testis and impairs spermatogenesis in offspring. Gene. (2022) 823:146390. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146390
3. Ilkhani, S, Moradi, A, Aliaghaei, A, Norouzian, M, Abdi, S, Rojhani, E, et al. Spatial arrangement of testicular cells disrupted by transient scrotal hyperthermia and subsequent impairment of spermatogenesis. Andrologia. (2020) 52:e13664. doi: 10.1111/and.13664
4. Lin, Y, Chen, WW, Ding, B, Guo, M, Liang, M, Pang, H, et al. Highly efficient bioconversion of icariin to icaritin by whole-cell catalysis. Microb Cell Factories. (2023) 22:64. doi: 10.1186/s12934-023-02068-4
5. Qian, HQ, Wu, DC, Li, CY, Liu, XR, Han, XK, Peng, Y, et al. A systematic review of traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicity of Epimedium koreanum Nakai. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 318:116957. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116957
6. Chen, M, Hao, J, Yang, Q, and Li, G. Effects of icariin on reproductive functions in male rats. Molecules. (2014) 19:9502–14. doi: 10.3390/molecules19079502
7. Zhao, FE, Chen, H, Wang, S, Zhang, X, Chen, N, Chen, H, et al. Effects of icariin as a feed additive on the reproductive function in bucks (Capra hircus). Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1467947. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1467947
8. Ma, X, Zhu, K, Yao, Z, Yuan, D, Wu, J, Zhang, C, et al. Icariin alleviates the injury of Sertoli cell junction function by upregulating PKR pathway via ERα/c-fos signaling in aged mice. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 335:118673. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118673
9. Liu, F, Liao, B, Ling, YL, Meng, XZ, Wang, JL, Hu, LL, et al. Icariin protects testicular damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through regulation of glycolysis pathway. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. (2024) 38:03946320241279525. doi: 10.1177/03946320241279525
10. National Research Council (NRC). Nutritional requirements of dogs and cats. Washington, DC: National Academic Press (2006).
11. Henning, H, Masal, C, Herr, A, Wolf, K, Urhausen, C, Beineke, A, et al. Effect of short-term scrotal hyperthermia on spermatological parameters, testicular blood flow and gonadal tissue in dogs. Reprod Domest Anim. (2014) 49:145–57. doi: 10.1111/rda.12244
12. Johnson, JS, Boddicker, RL, Sanz-Fernandez, MV, Ross, JW, Selsby, JT, Lucy, MC, et al. Effects of mammalian in utero heat stress on adolescent body temperature. Int J Hyperth. (2013) 29:696–702. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2013.843723
13. Steinberger, A. Effects of temperature on the biochemistry of the testis. Temp Environ Eff Testis. (1991) 286:33–47. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5913-5-4
14. Leng, J, Hou, JG, Fu, CL, Ren, S, Jiang, S, Wang, YP, et al. Platycodon grandiflorum saponins attenuate scrotal heat-induced spermatogenic damage via inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice. J Funct Foods. (2019) 54:479–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.01.050
15. Wang, K, Li, Z, Li, Y, Li, X, Suo, Y, and Li, C. Impacts of elevated temperature on morphology, oxidative stress levels, and testosterone synthesis in ex vivo cultured porcine testicular tissue. Theriogenology. (2023) 212:181–8. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2023.09.015
16. Kim, KJ, Yoon, KY, Hong, HD, and Lee, BY. Role of the red ginseng in defense against the environmental heat stress in Sprague Dawley rats. Molecules. (2015) 20:20240–53. doi: 10.3390/molecules201119692
17. Liu, W, Leng, J, Hou, JG, Jiang, S, Wang, Z, Liu, Z, et al. Saponins derived from the stems and leaves of panax ginseng attenuate scrotal heat-induced spermatogenic damage via inhibiting the MAPK mediated oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice. Phytother Res. (2021) 35:311–23. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6801
18. Arrington, KA, Legendre, AM, Tabeling, GS, and Frazier, DL. Comparison of body surface area-based and weight-based dosage protocols for doxorubicin administration in dogs. Am J Vet Res. (1994) 55:1587–92. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.1994.55.11.1587
19. Agarwal, A, Hamada, A, and Esteves, SC. Insight into oxidative stress in varicocele-associated male infertility: part 1. Nat Rev Urol. (2012) 9:678–90. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2012.197
20. Shiraishi, K, Matsuyama, H, and Takihara, H. Pathophysiology of varicocele in male infertility in the era of assisted reproductive technology. Int J Urol. (2012) 19:538–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.02982.x
21. Lin, C, Choi, YS, Park, SG, Gwon, LW, Lee, JG, Yon, JM, et al. Enhanced protective effects of combined treatment with β-carotene and curcumin against hyperthermic spermatogenic disorders in mice. Bio Med Res Int. (2016) 2016:2572073. doi: 10.1155/2016/2572073
22. Jing, J, Peng, Y, Fan, W, Han, S, Peng, Q, Xue, C, et al. Obesity-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction negatively affect sperm quality. FEBS Open Bio. (2023) 13:763–78. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13589
23. Chen, Y, Tian, P, Li, Y, Tang, Z, and Zhang, H. Thiram exposure: disruption of the blood–testis barrier and altered apoptosis-autophagy dynamics in testicular cells via the Bcl-2/Bax and mTOR/Atg5/p62 pathways in mice. Pestic Biochem Physiol. (2024) 203:106010. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2024.106010
24. Li, XW, Li, S, Yang, Y, Talukder, M, Xu, XW, Li, CX, et al. The FAK/occludin/ZO-1 complex is critical for cadmium-induced testicular damage by disruption of the integrity of the blood–testis barrier in chickens. J Hazard Mater. (2024) 470:134126. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134126
25. Acısu, TC, Akarsu, SA, Sönmez, M, Yüce, A, Çeribaşı, S, Dayan Cinkara, S, et al. Ameliorative effects of ganoderma lucidum (Reishi) on testicular tissue of rats exposed to bisphenol a. Pol J Vet Sci. (2024) 27:459–67. doi: 10.24425/pjvs.2024.151741
26. Lasiene, K, Kleina, R, Dabuzinskiene, A, Gasiliunas, D, Juodziukyniene, N, Zilaitiene, B, et al. A model for estimation of testicular volume in different age male rats–suitability of various testicular volume calculation formulas for living animals. Pol J Vet Sci. (2025) 28:103–10. doi: 10.24425/pjvs.2025.154018
27. Gross, A, and Katz, SG. Non-apoptotic functions of BCL-2 family proteins. Cell Death Differ. (2017) 24:1348–58. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.22
28. Naim, S, and Kaufmann, T. The multifaceted roles of the BCL-2 family member BOK. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:574338. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.574338
29. Jorban, A, Huleihel, M, and Lunenfeld, E. O-264 testosterone potentiates the effect of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) in the maturation of spermatogonial cells in vitro from prepubertal mice. Hum Reprod. (2022) 37:deac106.046. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deac106.046
30. Strzeżek, R, Lecewicz, M, Orzeł, I, and Siemieńczuk, J. Effect of repeated semen ejaculation on sperm quality and selected biochemical markers of canine semen. Pol J Vet Sci. (2024) 27:203–10. doi: 10.24425/pjvs.2024.149350
31. Casao, A, Peña-Delgado, V, and Pérez-Pe, R. From spermatogenesis to fertilisation: the role of melatonin on ram spermatozoa. Domest Anim Endocrinol. (2025) 91:106916. doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2025.106916
32. Ji, H, Fan, W, Kakar, M, Alajmi, RA, Bashir, MA, and Shakir, Y. Effect of cadmium on the regulatory mechanism of steroidogenic pathway of Leydig cells during spermatogenesis. J Exp Zool A Ecol Integr Physiol. (2024) 341:31–40. doi: 10.1002/jez.2758
Keywords: icariin, dog testicular heat stress, testosterone synthesis pathway, spermatogenic dysfunction, cellular apoptosis
Citation: Li B, Xie L, Song M, Zhang X, Yan C, Gao W, Wang W and Yang Y (2025) Evaluation of the efficacy of icariin against heat stress-induced spermatogenic dysfunction in the testes of dogs. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1631149. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1631149
Edited by:
Izhar Hyder Qazi, South China Agricultural University, ChinaReviewed by:
Xueming Zhao, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), ChinaBaichuan Deng, South China Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Li, Xie, Song, Zhang, Yan, Gao, Wang and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yang Yang, eWFuZ195YW5nOTEzQDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Baoan Li1†
Baoan Li1† Liuwei Xie
Liuwei Xie Mingqiang Song
Mingqiang Song