- 1Collaborative Innovation Center for Zoonosis Prevention and Control, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou, China
- 2College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China
- 3Xiangtan Animal Disease Prevention and Control Center, Xiangtan, China
- 4College of Veterinary Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China
- 5College of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, Shenyang, China
- 6Jilin Genet-Med Biotechnological Co., Ltd., Changchun, China
- 7Genet-Med (Dezhou) Biotechnological Co., Ltd., Dezhou, China
Background and objective: Weaning stress can cause decreased immunity and intestinal flora imbalance, leading to diarrhea and even death of the rabbits. The present study aimed to investigate the benefits from Trollius chinensis Bunge residues (TCBR) on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, intestinal health and cecal microbiota in weaned rabbits.
Methods: Through the ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) technology, the main active ingredients from TCBR were analyzed. And then, 48 30-day-old rabbits were randomly allocated into 4 groups, with 12 replicates per group. Four diets were formulated with graded levels of TCBR: 2.0, 4.0, and 6.0% represented as TCBR2, TCBR4, and TCBR6 groups alongside a Mock group without TCBR.
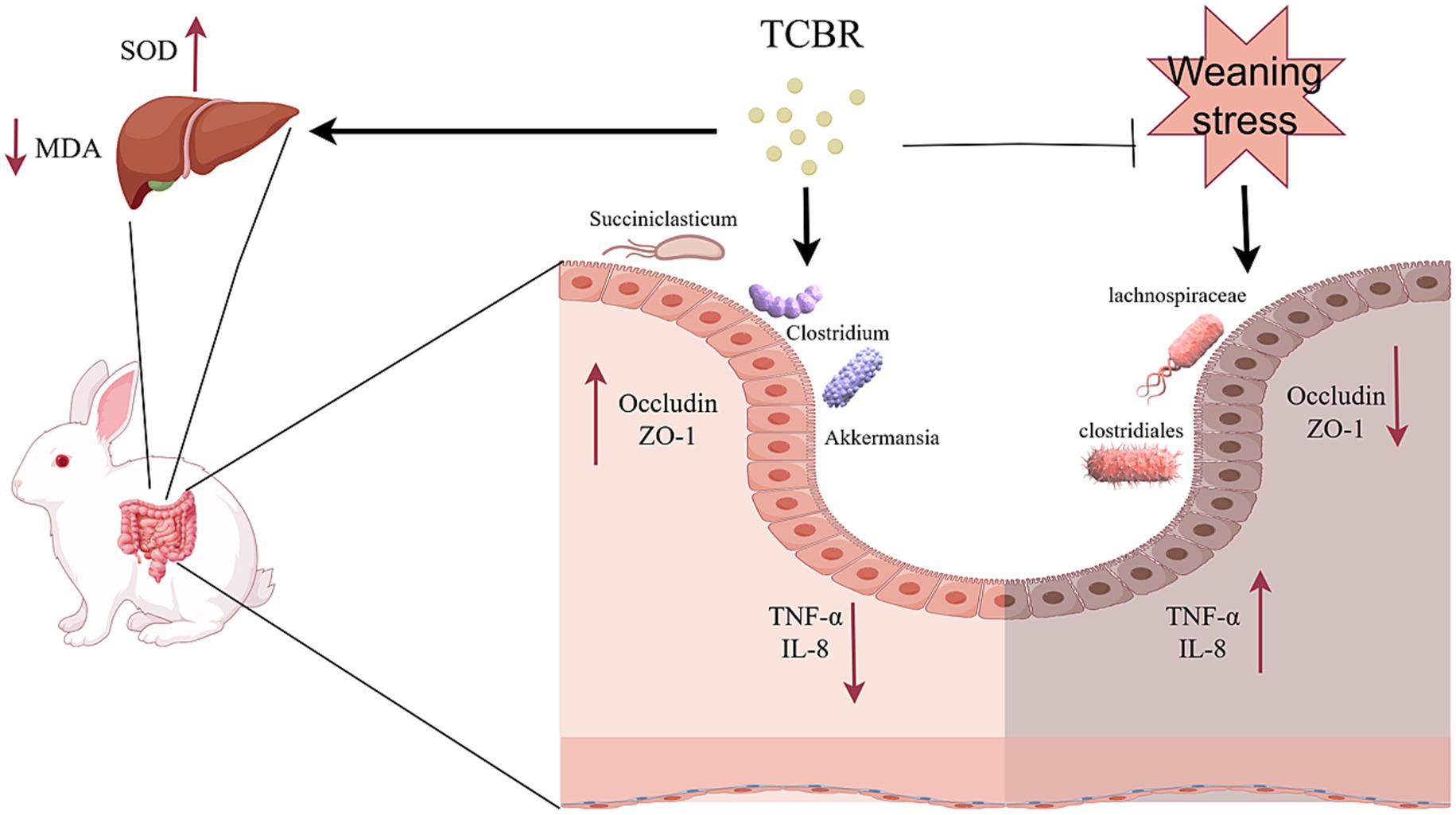
Results: Our results showed that TCBR2 significantly alleviated adverse clinical manifestations in weaned rabbits and improved survival rate, growth performance, and reduced the feed conversion ratio compared with the Mock group. TCBR2 also enhanced carcass yield, partial-eviscerated carcass yield, and antioxidant capacity, and increased jejunal villus height and villus/crypt ratio compared with that in the Mock group, whereas no differences were observed between the TCBR4 and TCBR6 groups. Furthermore, TCBR2 significantly increased the expression levels of Occludin and ZO-1 in jejunal tissue while reducing the expression levels of TNF-α and IL-8. Notably, 16S RNA analysis revealed that Bacteroidota levels were significantly elevated in the TCBR2 groups, with Akkermansia, Clostridium, and Succiniclasticum also up-regulated in the TCBR2 group.
Conclusion: TCBR2 supplementation improved growth performance and attenuated adverse clinical symptoms in rabbits, suggesting the potential of low-dose TCBR as a feed additive.
1 Introduction
Rabbit meat is highly nutritious and healthy, containing high levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids, proteins, and essential amino acids, which benefit the human diet (1). Rabbit meat production primarily occurs in Asia, Europe, the Americas, and Africa, with Asia accounting for 70% of global production. China leads the Asian rabbit meat market (2). The first 10–15 days after weaning are the most critical period of postnatal development for rabbits. During this period, weaned rabbits are susceptible to gastrointestinal infections, leading not only to increased mortality but also to growth retardation and consequently severe economic losses (3). Especially, the implementation of the “Prohibition of Antibiotic Use,” policy has worsened health issues in Chinese rabbit farms (4, 5). Therefore, nutritional regulation using exogenous supplements to promote the healthy development of the livestock and poultry industry, has become a research focus (6–9).
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), natural substances known for their safety, simple preparation, affordability, and minimal side effects (10, 11), has been widely used to prevent and treat various diseases in humans and animals, including as herbal antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antiparasitic, and antidiarrheal agents (12–15). Several studies have suggested that herbal ingredients in animal feed can promote growth, intestinal integrity, antioxidant effects, nutrient absorption, and immunity (16–20). Researchers demonstrated that residues of TCM are abundant in bioactive compounds, offering numerous nutritional and health benefits to animals. Animal health is intricately linked to immune homeostasis, with the removal and suppression of inflammatory factors being crucial for maintaining health. The NF-κB pathway is a critical regulator of the expression of various pro-inflammatory factors and serves as a key mediator of the inflammatory response. Several studies indicated that TCM residues modulated the expression of inflammatory factors via the NF-κB pathway, thereby exerting a beneficial effect on animal physiology (21–23). Furthermore, some TCM residues mixture showed to reduce the expression levels of inflammatory markers such as IL-4, IL-1β, and TNF-α, which in turn enhances the egg production of chickens (24). Additionally, the intestinal tract, the body’s largest immune organ, plays a significant role in immune modulation through its resident intestinal flora. Dietary supplementation with Isatidis root residue showed to reduce the prevalence of detrimental intestinal bacteria, such as Campylobacter, Actinobacillus minor, and Ralstonia pickettii. These reduction contributes to the enhancement of intestinal barrier integrity and mitigates diarrhea associated with early weaning (25). Furthermore, Sun et al. demonstrated that Xiasangju residue increased the relative abundance of beneficial bacteria, including Lactobacillus johnsonii and Weissella jogaeotgali, while decreasing the relative abundance of harmful bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Treponema porcinum. Additionally, this supplementation led to an increased expression of IL-10 and a decreased expression of IL-1β in the ileum, thereby improving the integrity of the intestinal tight junction barrier (26). Trollius chinensis Bunge, a perennial herb of the buttercup family, has high medicinal value owing to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antibacterial, and antiviral properties. These benefits are attributed to its rich bioactive compounds, such as flavonoids, organic acids, and alkaloids, evaluated the toxicity of T. chinensis, confirming its low toxicity and safety in animal feed (27–29). However, To date, no studies have evaluated the effects of Trollius chinensis Bunge residues (TCBR) in meat rabbit production.
This study aimed to investigate the effects of TCBR supplementation on the growth performance, serum biochemical indexes, antioxidant capacity, and cecal microbiota of weaned rabbits, providing a theoretical basis for using TCBR as a feed additive to promote healthy rabbit breeding.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Trollius chinensis Bunge residues composition assay
The dried residues of Trollius chinensis Bunge were pulverized and placed into a medicinal bag for a 2-h soak. Subsequently, the contents were brought to a boil and decocted twice, followed by concentration to obtain the aqueous extract of Trollius chinensis Bunge residues. A 200 μL aliquot of the drug solution was mixed with 800 μL of methanol, subjected to vortex mixing for 10 min, and then centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was collected for analysis. Chromatographic separation was performed using a Welch AQ-C18 column with a mobile phase comprising 0.1% formic acid in water (solvent A) and methanol (solvent B). The elution was executed under the following gradient conditions: 0–10 min, 2–20% B; 10–15 min, 50–80% B; 15–20 min, 80–95% B; 20–27 min, 95% B; 27–28 min, 95–2% B; and 28–30 min, 2% B. The injection volume was 5 μL, with a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min, and the detection wavelength was set at 254 nm. Additionally, a Q Exactive high-resolution mass spectrometer was employed for analysis, utilizing an electrospray ionization (ESI) source and operating in both positive and negative ion modes. Furthermore, a Q Exactive high-resolution mass spectrometer was employed for the analytical procedures. This instrument utilizes an electrospray ionization (ESI) source and is capable of operating in both positive and negative ionization modes. Data acquisition was conducted using data-dependent acquisition (DDA), with dynamic background subtraction (DBS) performed at 30-s intervals, and a high sensitivity mode set at 70,000 resolution. Preliminary organization of the high-resolution liquid chromatography data was facilitated by Compound Discoverer 3.3 (CD 3.3, Thermo Fisher), followed by database searching against mzCloud.
2.2 Experimental design, diets, growth performance, and clinical records
In total, 48 weaned (30-days-old) weaned rabbits were used in a 42-day experiment. Each rabbit was housed individually, with each cage representing a replicate experimental unit. After assessing their initial body weight (BW), the weaned rabbits were randomly assigned to one of four dietary groups (n = 12/group), with TCBR added to their diets as follows: (1) Mock without TCBR, (2) TCBR2 containing 2% TCBR, (3) TCBR4 containing 4% TCBR, and (4) TCBR6 containing 6% TCBR. The basal diet, containing corn and soybean meal, was formulated to meet or exceed the nutrient requirements for growing rabbits. The ingredients and proximate composition of the basic diets are provided in Table 1. Rabbits had free access to feed and water without any vaccinations during the experiment. Individual feed intake was recorded daily, and BW was recorded once every 5 days daily feed intake, body weight gain, and feed conversion ratio (FCR = feed intake/body weight gain) were calculated. Clinical scores were based on the Vesikari rating system with slight modifications (30). A five-point scale from 1 to 5 was used, reflecting normality (0 score), non-feeding (1 score), mild diarrhea (2 score), severe diarrhea (3 score), and death (5 score).
2.3 Sample collection and calculation of slaughter performance
After 42 days of feeding, the rabbits were fasted overnight before sampling and slaughter. The 8 rabbits were randomly selected from 12 rabbits per group and sacrificed via intravenous air injection at the ear margin. Blood samples were collected via heart puncture, centrifuged to collect serum, and stored at −20°C for further analysis. Eight rabbits from each group were selected to assess slaughter performance. The rabbits were sequentially skinned, limbed, decapitated, and eviscerated. The following measurements were recorded: carcass weight, semi-eviscerated carcass weight, and eviscerated carcass weight. Carcass traits were calculated relative to live BW based on previous studies and slightly revision (31).
2.4 Measurement of serum biochemistry
Serum levels of glucose (GLU), triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (T-CHO), albumin (ALB), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and total protein (TP) were assayed using ELISA kits (F006-1-1, A110-1-1, A111-1-1, A028-2-1, C009-2-1, C013-2-1, A059-2-2, and A045-2-2; Nanjing Jiancheng Institute of Bioengineering, Nanjing, PRC) and a microplate reader (Tecan Austria GmbH, Vienna, Austrian).
2.5 Determination of antioxidant parameters
Serum and liver antioxidant parameters were measured using a previously described method (6). Briefly, serum samples were directly analyzed, whereas liver samples were homogenized with precooled phosphate-buffered saline (1:10, v/v) and centrifuged (8,000 rpm and 4°C for 10 min) to obtain clarified homogenates. The activities of total superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), along with the concentration of malondialdehyde (MDA), were assayed using ELISA kits (A001-3-2, A007-1-1, A005-1-2, and A003-1-1; Nanjing Jiancheng Institute of Bioengineering) and a spectrophotometer, as described above.
2.6 Morphological observation of the ileum wall
Fixed ileum samples were dehydrated, embedded in overheated paraffin, and cut into 4-μm-thick sections (RM2235, Leica Microsystems, Germany). After drying, dewaxing, and staining with hematoxylin and eosin, the sections were scanned using a Pannoramic Scanner (C13210-01, HAMAMATSU, Japan). Villus height and crypt depth were measured using ImageJ software (version 1.54), and the villus-to-crypt (V/C) ratio was calculated.
2.7 RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis, and quantitative real-time PCR
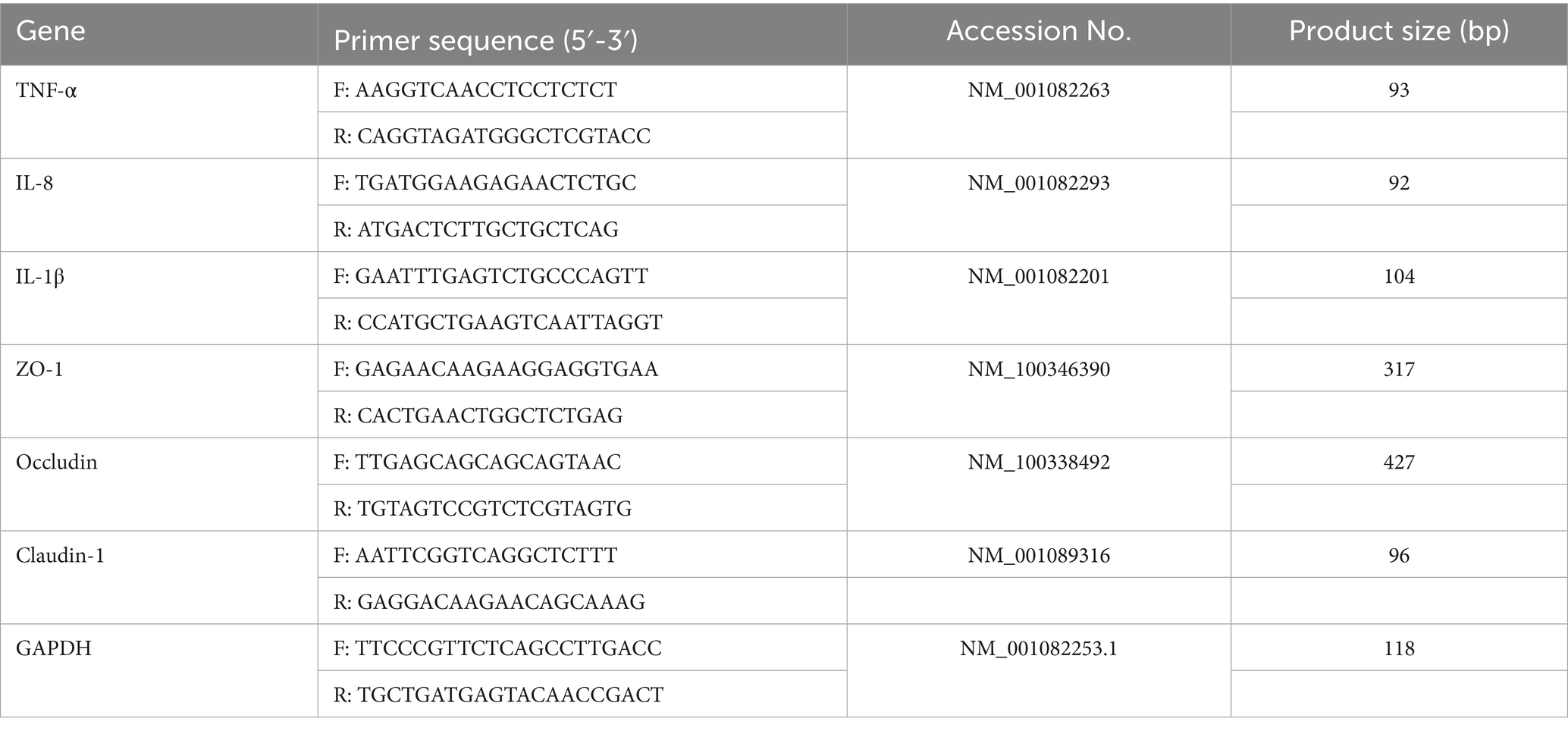
Tissue RNA was extracted according to methods described in a previous study (32). Ileum tissues were homogenized with precooled phosphate buffered saline (PBS), and the homogenates were lysed using RNA isolator total RNA extraction reagent (Vazyme Biotech, Nanjing, China). RNA concentration was measured using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA). Subsequently, a cDNA template was synthesized from 1,000 ng of RNA using the HiScript®II Q RT SuperMix for quantitative PCR (qPCR; +gDNA wiper; Vazyme Biotech). Real-time qPCR was performed on an ABI system (Thermo Fisher Scientific) using the ChamQTM SYBR® qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme Biotech). PCR conditions comprised 40 cycles of 95°C for 5 s, 60°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 60 s. The sequences of the primers used are listed in Table 2. Gene relative expression was calculated using the 2−∆∆Ct method.
2.8 Analysis of the cecal microbial community
Total DNA from cecal samples was extracted using the Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide (CTAB) method according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Sequences of the 16S rRNA genes from the V3–V4 hypervariable regions were amplified using the universal primers 341F (5′-CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3′) and 805R (5′- GACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC-3′). PCR products were confirmed via 2% agarose gel electrophoresis, purified using AMPure XT beads (Beckman Coulter Genomics, Danvers, MA, USA), and quantified using Qubit (Invitrogen, CA, USA). Amplicon pools were prepared for sequencing, and the size and quantity of the amplicon library were assessed using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent, USA) and the Library Quantification Kit for Illumina (Kapa Biosciences, MA, USA), respectively. Libraries were sequenced on the NovaSeq PE250 platform. Paired-end reads were merged using FLASH, filtered, and replicated to obtain the feature table and feature sequence. Alpha and beta diversity were calculated by normalizing to the same sequences randomly. Feature abundance was normalized using the SILVA database (release 138) based on relative sample abundance. Sequence alignment was performed using BLAST, and feature sequences were annotated using the SILVA database for each representative sequence.
2.9 Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS software (version 16.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Prior to conducting a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), the Shapiro–Wilk test for normality and Levene’s test for homogeneity of variances were applied to each dataset group. If the data adhered to a normal distribution and exhibited homogeneity of variance, standard ANOVA procedures were employed. In instances where ANOVA revealed statistically significant differences among groups, Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference (HSD) test was subsequently utilized for post hoc multiple comparisons. p < 0.05 indicated that the differences were statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Analysis of major components in TCBR
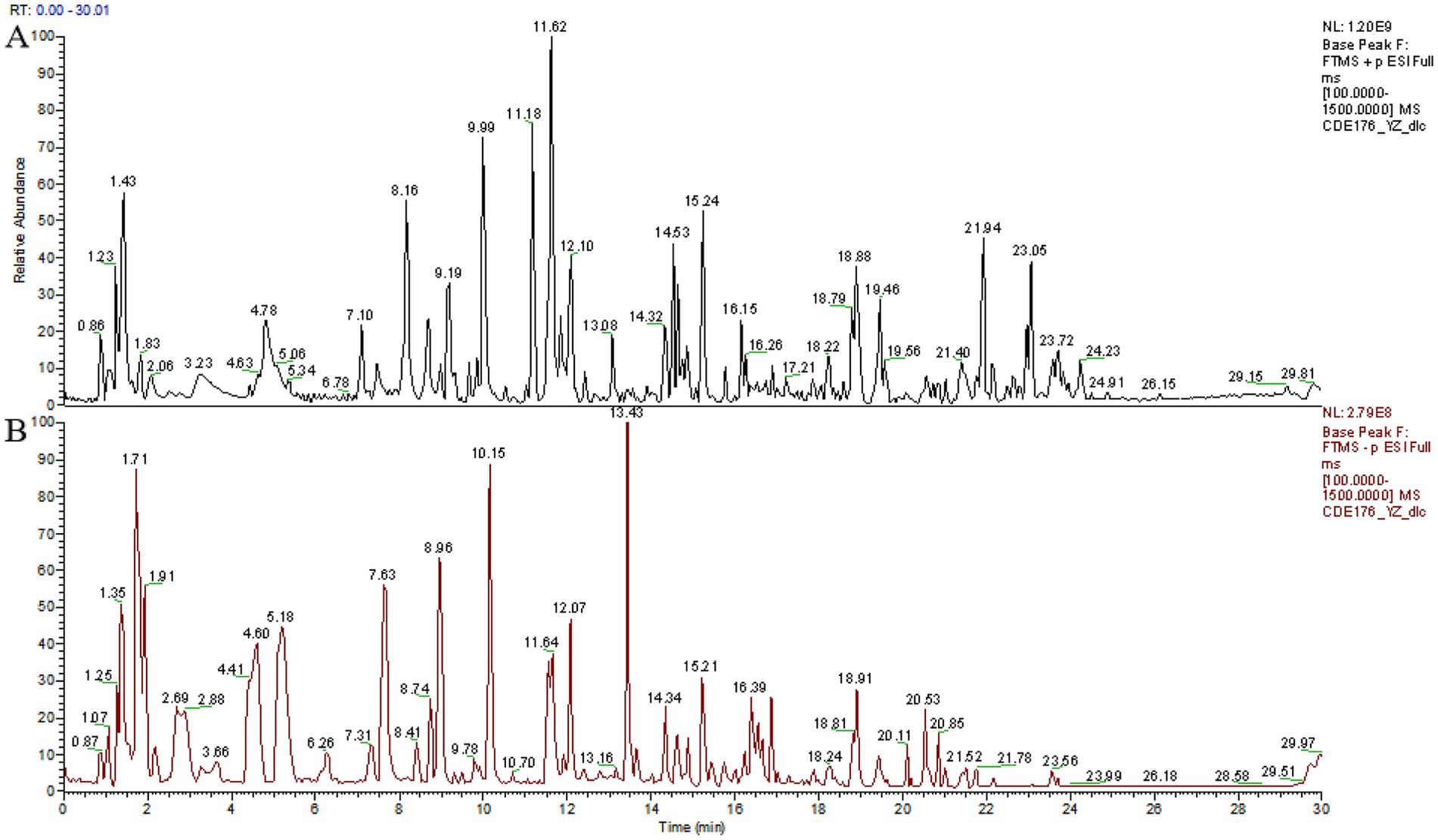
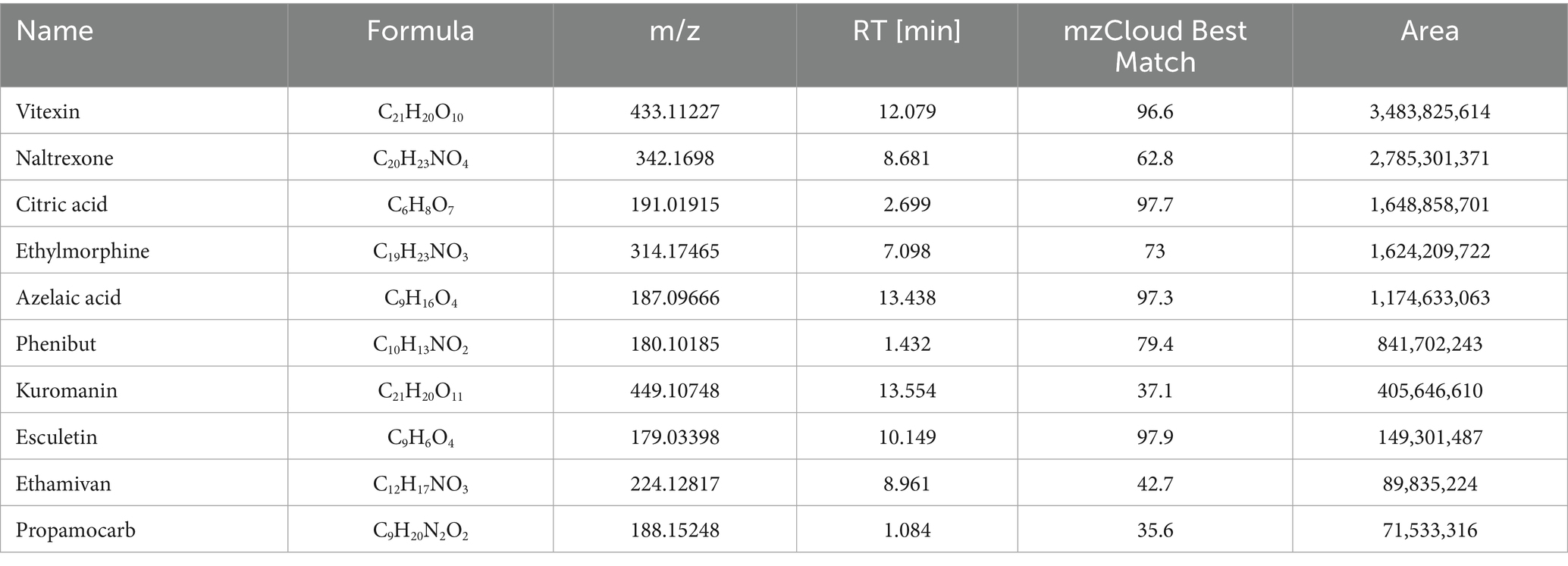
To evaluate the potential of TCBR as a functional feed, our study employed the UPLC technique to identify the constituents of TCBR (Figures 1A,B). The results revealed that the top10 primary active ingredients in TCBR are Vitexin, Naltrexone, Citric Acid, Ethylmorphine, Azelaic Acid, Phenibut, Kuromanin, Esculetin, and Ethamivan (Table 3).
3.2 Clinical records, growth performance and slaughter performance
To investigate whether TCBR showed a positive effect on weaned rabbits, we recorded clinical symptoms, growth performance and slaughter performance of weaned rabbits. TCBR2 significantly increased the BW of rabbits (13.4%) compared with those in the Mock group (p < 0.05). However, the TCBR4 and TCBR6 groups did not show significant differences (Figure 2A). TCBR2 also improved the rabbit survival rate and reduced their adverse clinical manifestations (diarrhea and death; Figures 2B,C). The Mock group had the highest diarrhea index (Figure 2B), whereas the TCBR6 group had the highest mortality rate (33.3%) (Figure 2C).
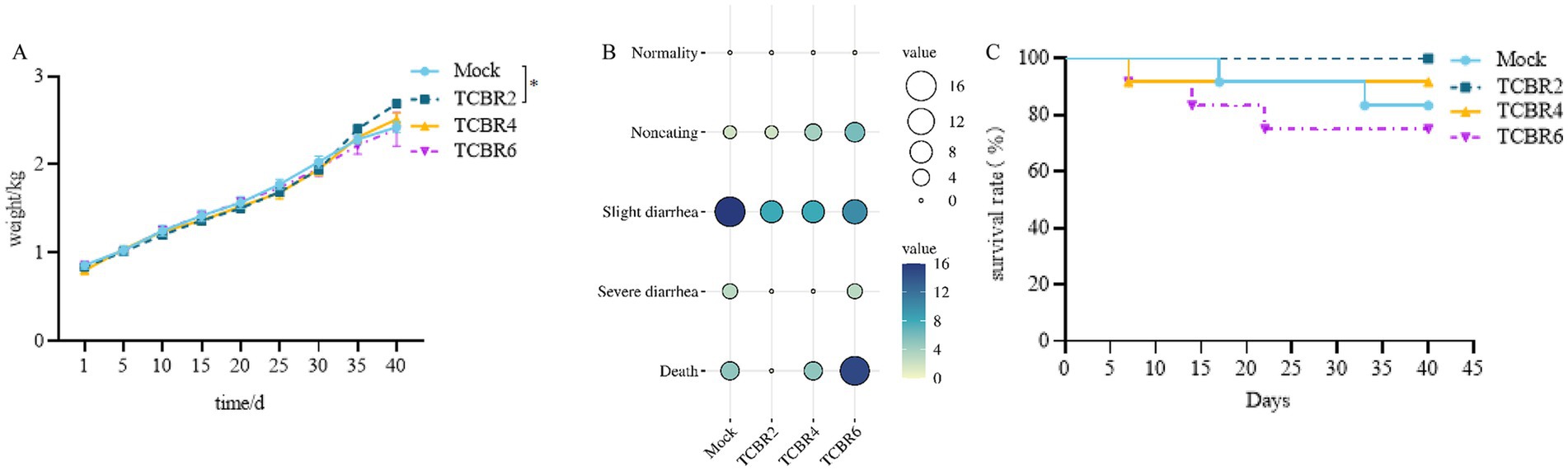
Figure 2. Clinical condition documentation for rabbits. (A) Recorded body weights of rabbits. Values represent means of eight replicate samples. *p < 0.05 compared to the Mock group. (B) Clinical performance score statistics: scores range from 0 to 5, with higher scores indicating more severe disease; darker colors represent more disease cases. (C) Survival rates of rabbits.
Compared with that in the Mock group, TCBR2 increased the BW, average daily BW gain, and FCR of rabbits between 37 and 72 days of age (p < 0.05; Table 4). However, TCBR4 and TCBR6 showed no notable benefits. TCBR2 significantly increased carcass yield and half-eviscerated carcass yield by 3.1 and 4.1%, respectively, compared with the Mock group (p < 0.05; Table 4). No significant differences were observed in the carcass yield and half-eviscerated carcass yield between the TCBR4 and TCBR6 groups (p > 0.05).
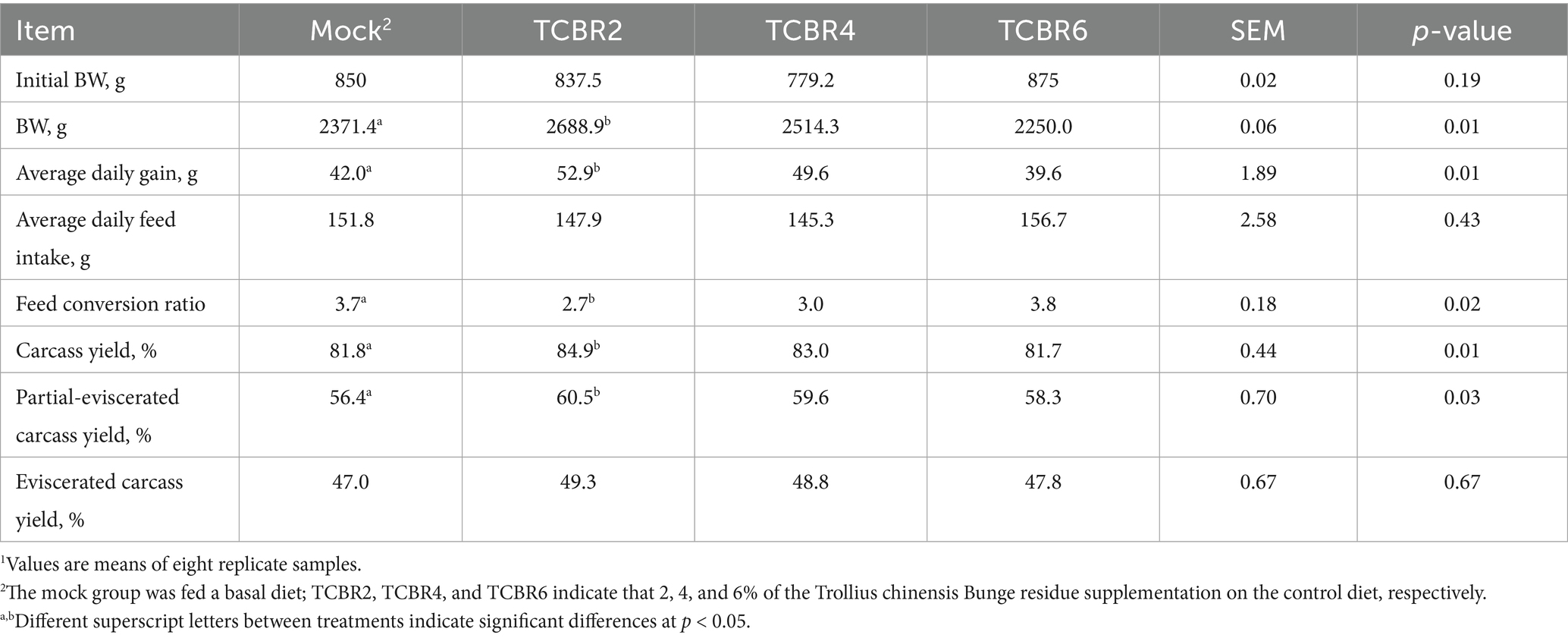
Table 4. Effects of Trollius chinensis Bunge residue supplementation on the growth and slaughter performance of rabbits1.
3.3 Serum biochemistry
To assess the toxicity of TCBR, rabbit serum was analyzed for biochemical indices. Different levels of TCBR supplementation reduced the serum glucose levels in 72-day-old rabbits (Table 5). TCBR2 and TCBR4 lowered the activities of ALP and ALT, as well as the blood urea nitrogen concentration in serum, compared with the Mock treatment. TCBR2 also increased the levels of total protein compared with the Mock treatment. Additionally, TCBR6 significantly increased serum total cholesterol concentration (p < 0.05).
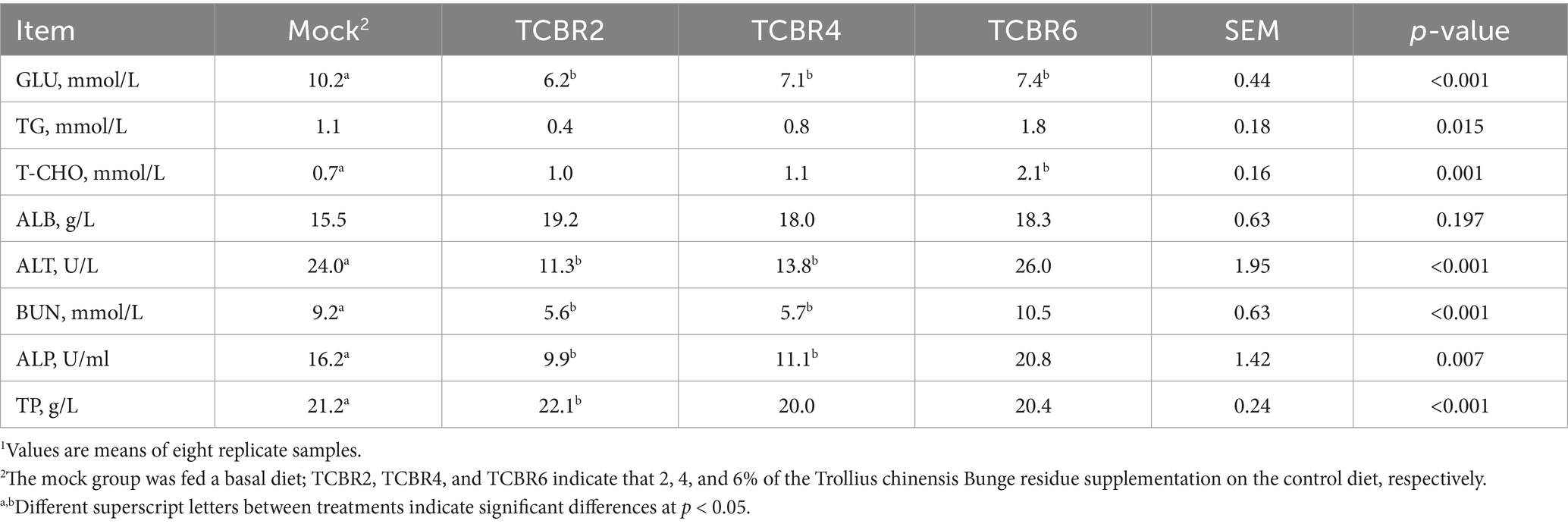
Table 5. Effects of Trollius chinensis Bunge residues on the serum biochemical indexes of rabbits1.
3.4 Antioxidant capacity
As the intervention of low-dose TCBR improved the clinical performance of rabbits, we hypothesized that TCBR may have antioxidant effects. TCBR4 and TCBR6 significantly increased CAT activity in serum (p < 0.05; Table 6). However, no significant differences were observed in the serum activities of SOD, GSH-Px, and MDA among treatments. In the liver, different levels of TCBR supplementation increased SOD activity, with TCBR6 also enhancing GSH-Px activity. But TCBR2 and TCBR4 decreased the concentration of MDA in the liver. However, TCBR supplementation had no effect on CAT activity in the liver.
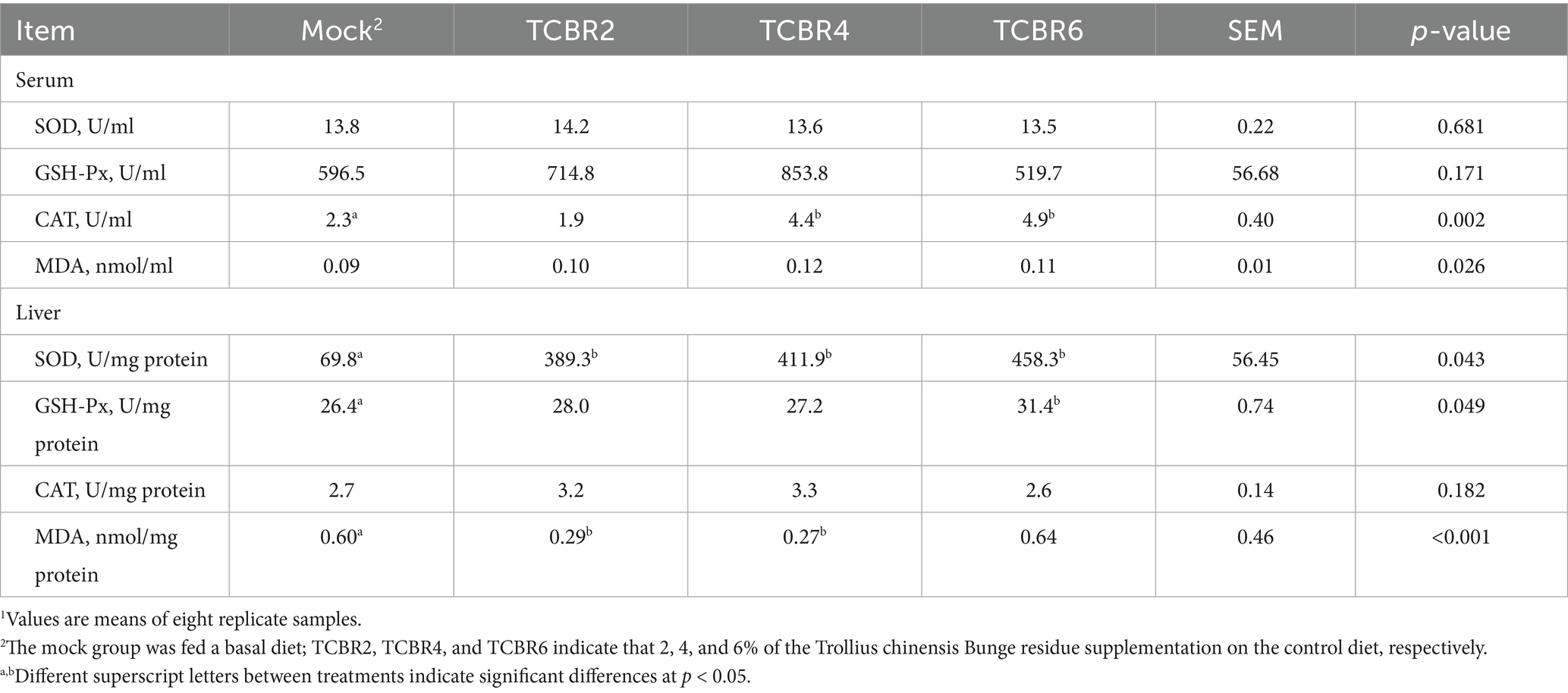
Table 6. Effects of Trollius chinensis Bunge residues on the antioxidant capacity of rabbits1.
3.5 Jejunal morphology
In addition, supplementation of low-dose TCBR increased body weight in rabbits, and we speculated that perhaps TCBR showed a positive effect on rabbits intestinal tissues. The jejunal morphology of tested rabbit is shown in Figure 3. Compared with Mock rabbits, those supplemented with TCBR2 showed significantly increased villus height and V/C ratio (p < 0.001; Figure 3A). However, no significant differences were found in villus height or the V/C ratio with TCBR4 and TCBR6 supplementation (p > 0.05) compared with the Mock treatment. Jejunal sections, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, are shown in Figure 3B.
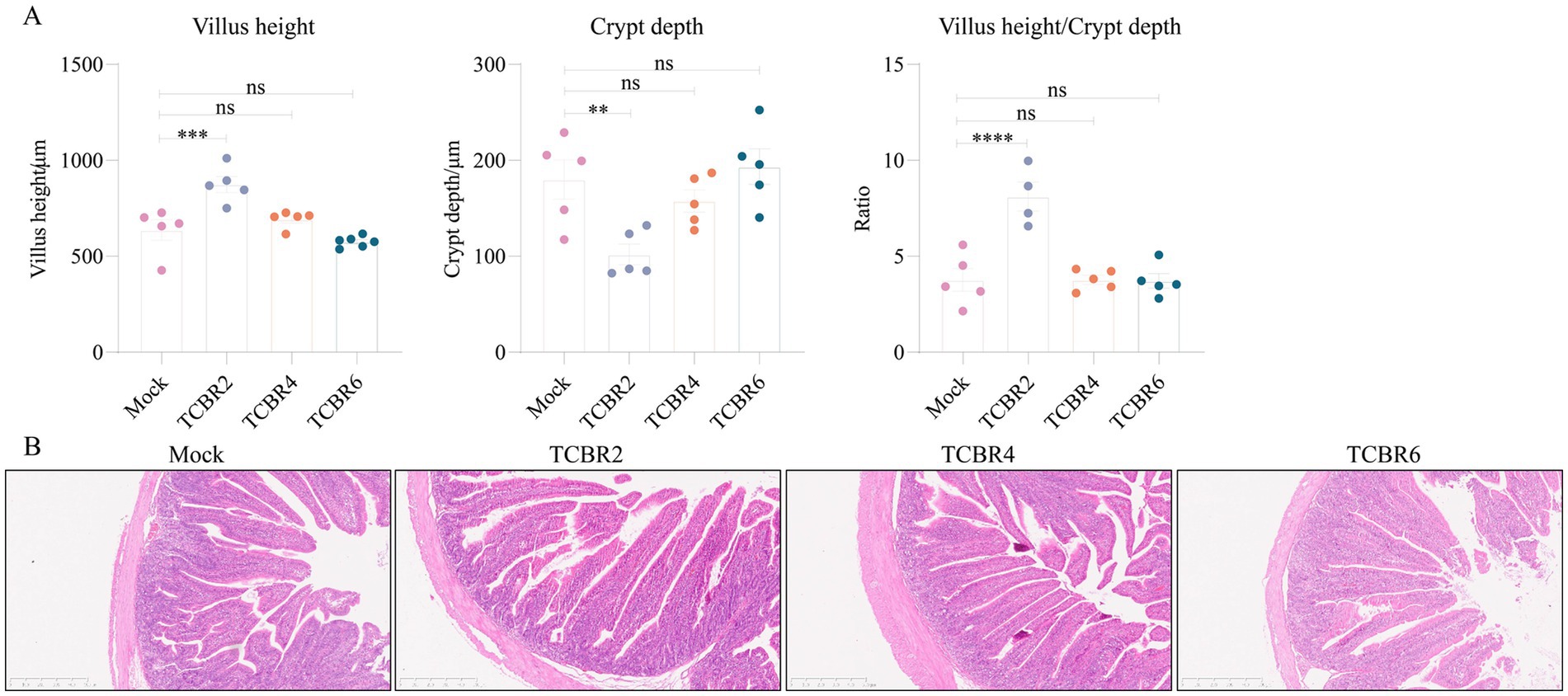
Figure 3. Effects of Trollius chinensis Bunge residue supplementation on the jejunal morphology of rabbits. (A) Villus height, crypt depth, and the villus-to-crypt ratio among treatments. Values represent means of eight replicate samples. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 compared to the Mock group. (B) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin–stained jejunal tissue. Scale bar: 500 μm.
3.6 Gene expression
Meanwhile, we also evaluated inflammatory factors and gut barrier in the gut. The effects of TCBR supplementation on gene transcript levels in the jejunal tissue of rabbits are shown in Figure 4. Compared with the Mock treatment, TCBR2 supplementation significantly up-regulated the expression levels of occludin and ZO-1 but had no significant effect on claudin-1 expression. In contrast, TCBR4 and TCBR6 supplementation down-regulated the expression levels of occludin, ZO-1, and claudin-1 in the jejunal tissue. Additionally, TCBR2 and TCBR4 supplementation significantly down-regulated the relative expression levels of TNF-α and IL-8 (p < 0.05).
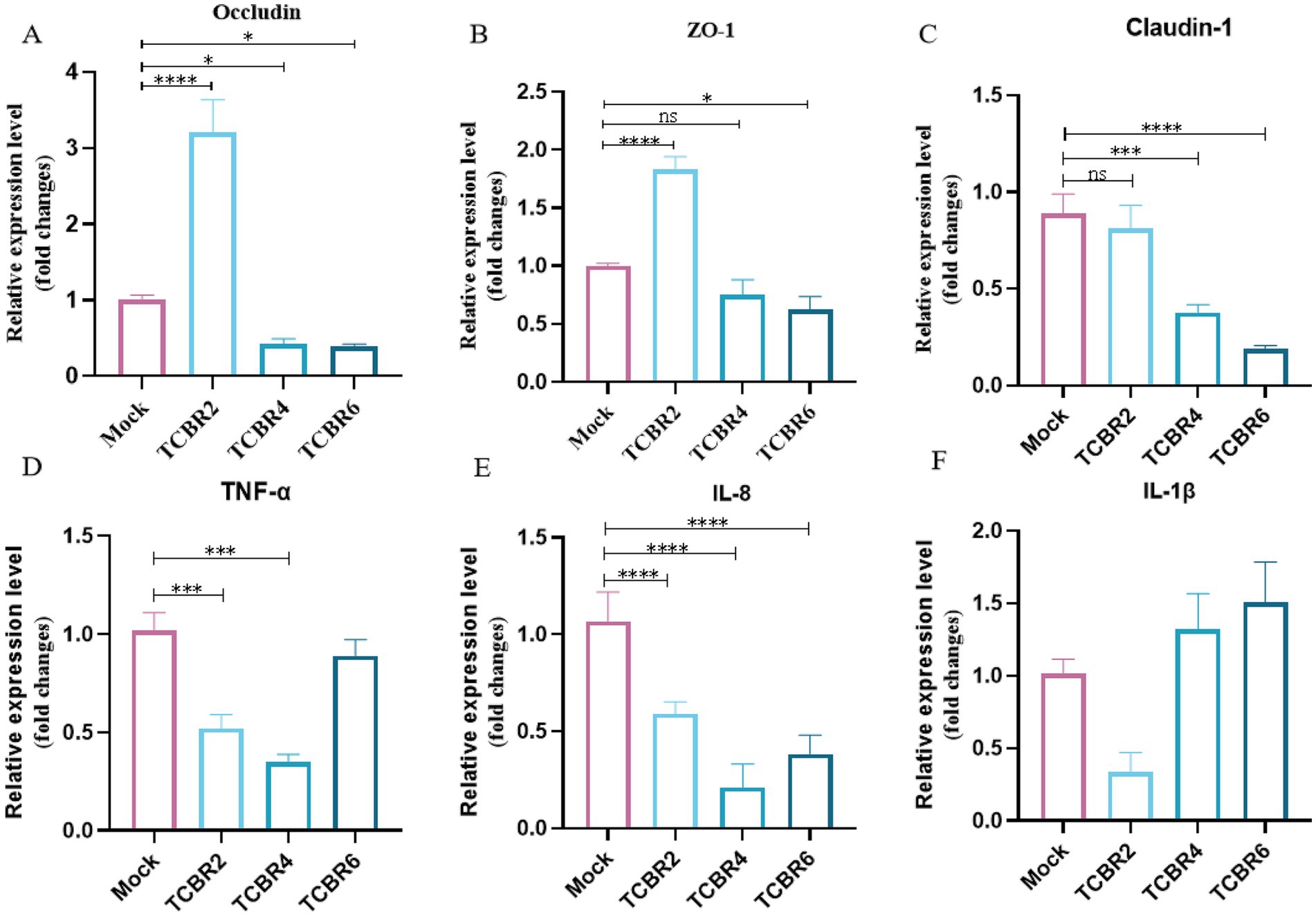
Figure 4. Relative mRNA expression levels of genes in the jejunal mucosa of rabbits. (A–C) Show jejunal mechanical barrier gene expression levels. (D–F) Indicate jejunal inflammatory gene expression levels. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 compared with the Mock group.
3.7 Cecal microbiota analysis
In our study, 8,081 ASV were obtained through sequencing, with the number of operational taxonomic units decreasing as TCBR concentration increased (Figure 5). ASV Venn analysis identified 2,174, 2,169, 1948, and 451 unique ASV in the Mock, TCBR2, TCBR4, and TCBR6 groups, respectively (Figure 5A). Compared with the Mock group, both the ACE and Chao1 indexes were reduced in the TCBR6 groups (p < 0.05). The Shannon and Simpson indexes were lower in all TCBR-treated groups relative to the Mock group (p < 0.05). Moreover, the goods_coverage index is above 0.98 for all samples. That indicated high coverage of species in the samples and reasonable sequencing depths. Principal coordinate analysis indicated a progressive shift in the microbial community with increasing dietary TCBR levels (Figure 5C).
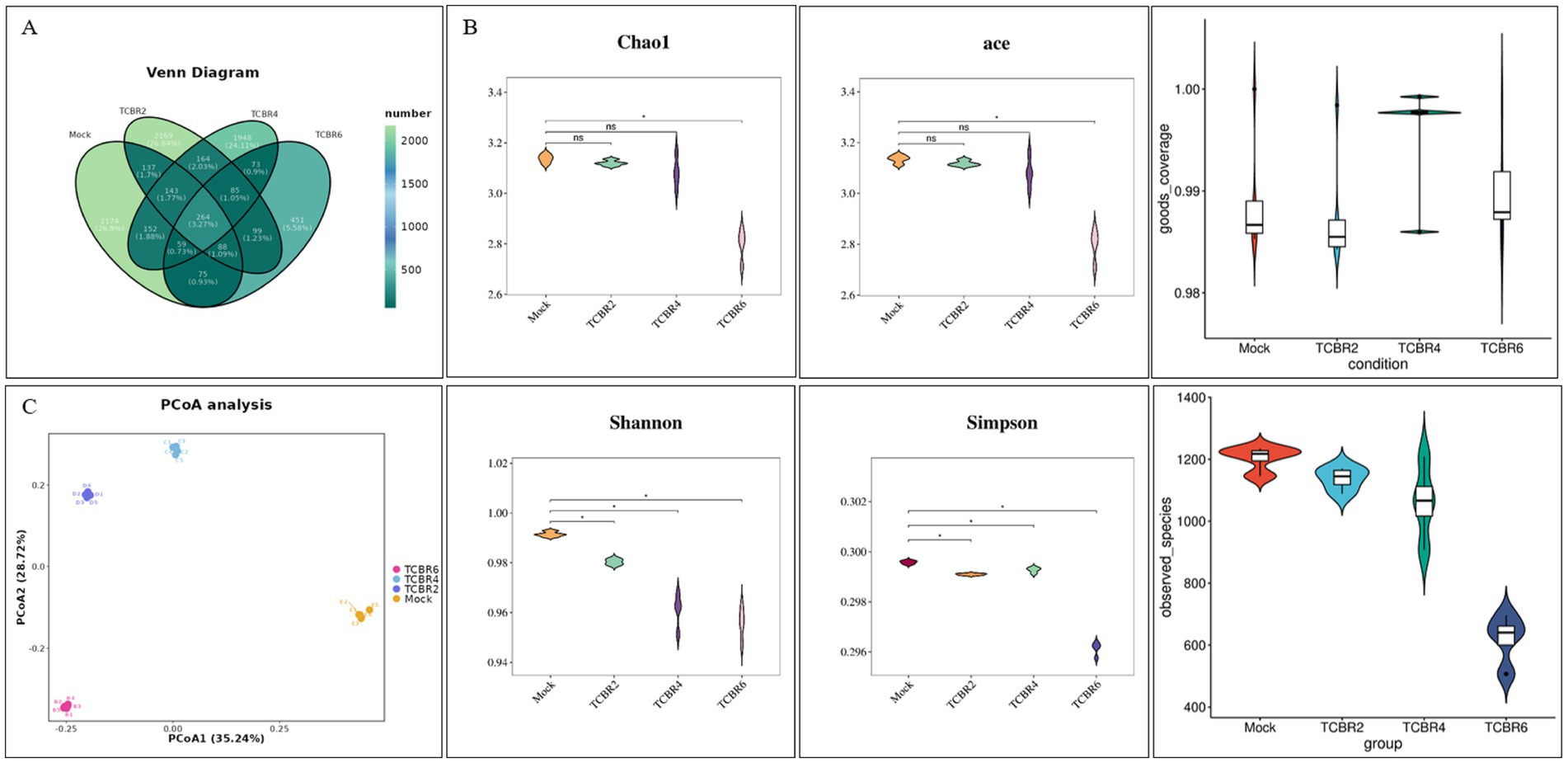
Figure 5. Cecal microbiota richness and diversity. (A) ASV Venn diagram. (B) Comparison of alpha diversity indexes presented as box plots. (C) β-diversity analysis. n = 5, *Significant difference at p < 0.05.
TCBR2 and TCBR4 supplementation reduced the relative abundance of the cecal Firmicutes phylum while increasing the relative abundance of the cecal Bacteroidota phylum (p < 0.0001; Figure 6). TCBR2 also increased the relative abundance of the cecal Verrucomicrobiota phylum (p < 0.0001). All TCBR levels increased the relative abundance of the cecal Akkermansia genus (p < 0.001). TCBR2 further increased the relative abundance of the cecal Clostridium, Alistipes, and Succiniclasticum genera (p < 0.05), whereas TCBR4 reduced the relative abundance of the cecal Clostridium genus (p < 0.05).
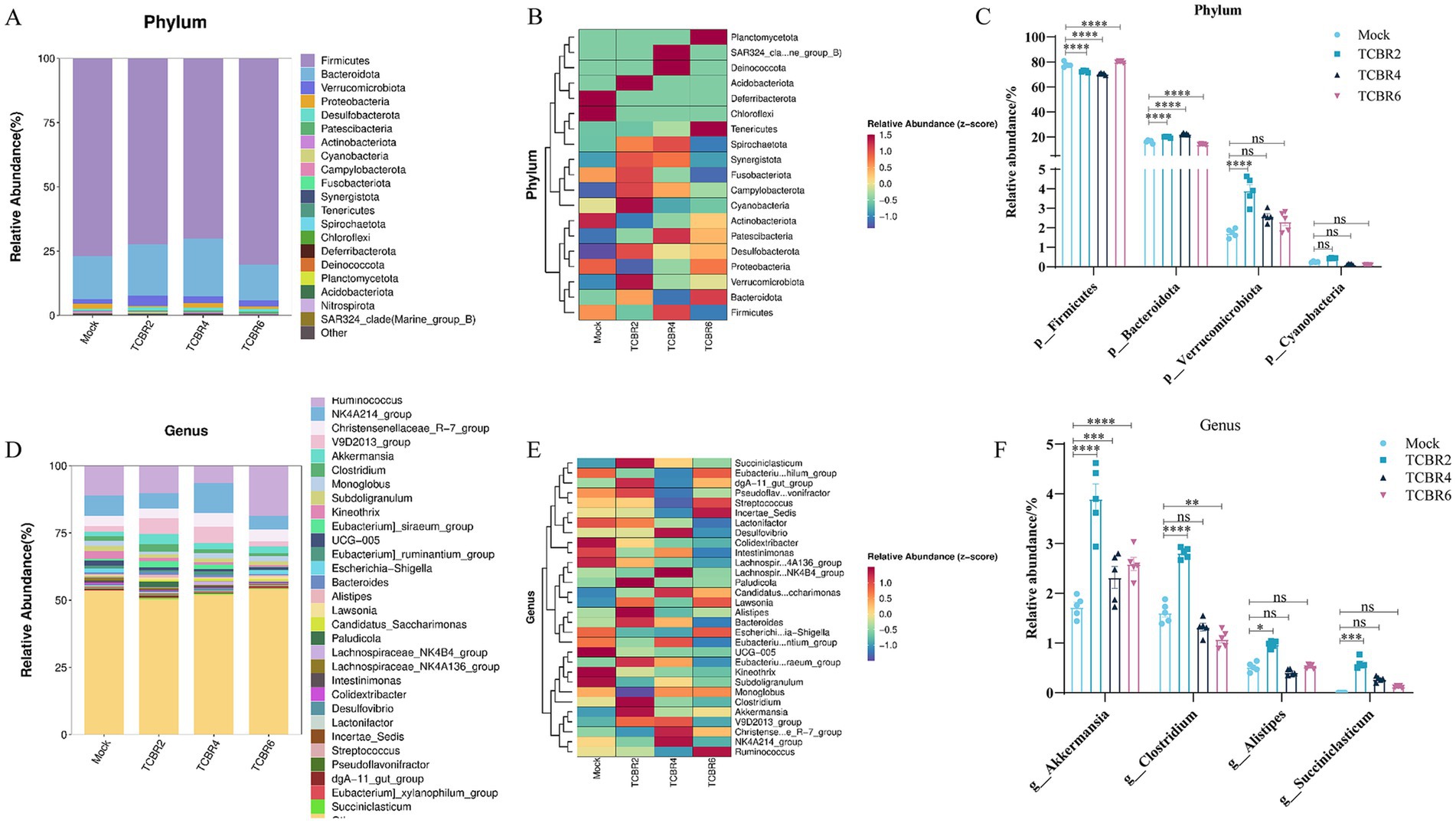
Figure 6. Relative abundance and differences in cecal microbiota. (A) Relative abundance of the top 20 phyla. (B) Heatmap of the top 20 phyla. (C) Differences in microbiota composition at the phylum levels. (D) Relative abundance of the top 30 genera. (E) Heatmap of the top 30 genera. (F) Differences in microbiota composition at the genus levels. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 compared to the Mock group.
We conducted LefSe analysis to elucidate the differences in microbial abundance between the Mock and TCBR-treated groups. As exhibited in Figures 7A,B, a total of 42 branching taxa showed significant differences in abundance (LDA Score > 4; p < 0.05). Among these, 10 branch taxa were evaluated to be significantly affected in the Mock group, including o_clostridiales, f_lachnospiraceae, o_firmicutes, and others. Subsequently, the TCBR2 group showed considerable consequences for 10 branch taxa, comprising c_verrucomicrobiae, f_akkermansiaceae, g_paludicola, and others. But 13 branch taxa were exhibited to be significantly affected in the TCBR4 group, containing f_oscillospiraceae, p_firmicutes, c_clostridia, and others. In addition, TCBR6 group demonstrated substantial influence on 9 branch taxa, consisting of f_ruminococcaceae, g_muribaculaceae, o_bacteroidales, and others.
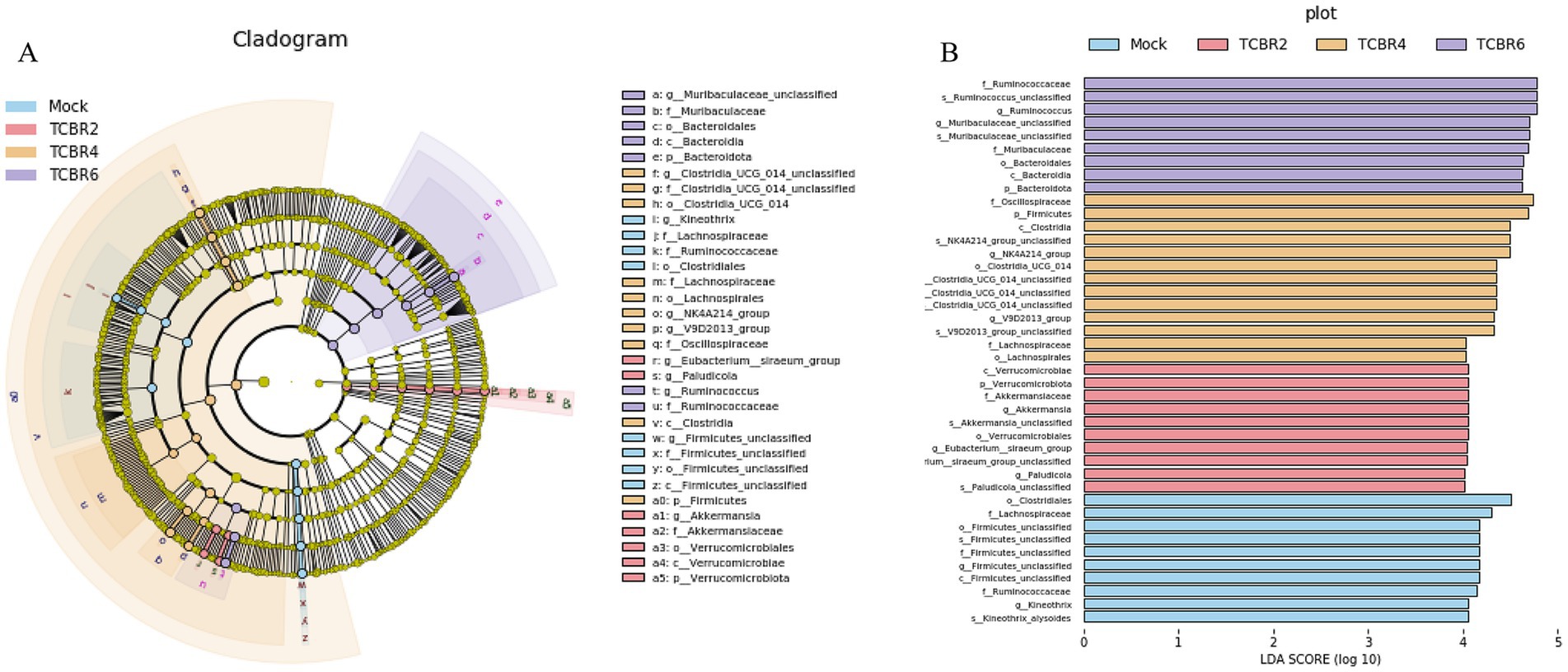
Figure 7. Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) effect size (LEfSe) in cecal microbiota. (A) Evolutionary branching diagram. Circles radiating from inside to outside represent taxonomic levels from phylum to genus (or species). Each small circle at a different taxonomic level represents a taxon at that level, and the size of the diameter of the circle is proportional to the relative abundance size. (B) LDA value distribution histogram. The different colored zones represent different groups, with the four colors indicating microbial taxa that are significant in the four groups, respectively. Only species with an LDA Score > 4 are displayed in the diagram, and the length of the bars represents the magnitude of the LDA values. Method: Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test.
4 Discussion
Rabbits are considered ideal meat-producing animals owing to their short life cycle, short gestation period, high reproductive rates, and efficient feed conversion. As an important source of meat protein, the rabbit farming industry is receiving increasing attention (1). However, gut health of weaned rabbits is important for rabbit growth, with the growing emphasis on reducing antibiotic use in the livestock industry, there are higher demands for the sustainable and healthy development of rabbit farming. Previous study suggested that Taxus chinensis Rehder fruit extract (TCFE) demonstrated significant anti-aging properties by reducing microglia activation, decreasing oxidative stress, and influencing inflammatory pathways (33). meanwhile, Canna x generalis extract (CGE) improved the integrity of the intestinal mucosal barrier and lessened oxidative stress and inflammation (34, 35). Which indicated that Traditional Chinese medicine plays a role in promoting animal health and improving production efficiency. Their byproducts, residues left after the extraction of active herbal ingredients, may still contain active compounds beneficial to livestock (9, 36, 37). However. The specific role of TCBR as a feed additive for weaned rabbits remains to be elucidated. A previous study showed that adding turmeric residue improved survival rates in Chinese soft-shelled turtles exposed to high ambient temperatures (38). He et al. found that supplementing Shengxuebao herbal residues in the diets of heat-stressed New Zealand rabbits increased BW (39). Similarly, our study found that adding 2% TCBR significantly increased final BW, reduced adverse clinical symptoms, and improved survival rates in weaned rabbits. TCBR2 also significantly increased the average daily BW gain of the rabbits. These effects may be linked to the presence of bioactive substances, such as brassinoids, organic acids, and alkaloids, in TCBR. However, high dose of Trollius chinensis Bunge residues, with 6% in the rabbits diet, showed adverse clinical syndrome, suggesting potential toxicity at highier dose. The study found that flavonoids produced cellular damage at 450 μM cellular viability, causing a 12–60% reduction in cellular viability in isolated guinea pig enterocytes and lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) leakage 28–41% greater (40). Moreover, the total flavonoids (TFs) from Rosa laevigata Michx fruit could cause side effects at the dose of 2000 mg/kg/day in males and females, such as increased intercellular space of myocardial cells and the relative cardiac weight (41). In addition, Aconitine, a component of traditional Chinese medicine, showed to induce cardiotoxicity and neurotoxicity at high doses, resulting the destruction of neuronal cells (42). Concurrently, Excessive exposure to Tripterygium hypoglaucum and Myrica rubra pomace polyphenols (MRPP) has been linked to damage in hepatocytes and the intestines (43, 44). meanwhile, pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) derived from Eupatorium fortunei demonstrated to cause significant hepatotoxicity by disrupting glycerophospholipid metabolism at a dosage of 25 mg/(kg-day) in mouse model (45). Therefore, Our study provided an experimental basis for the use of TCBR as a feed additive, and its practical application needs to be further verified by a larger-scale sample.
Slaughter rate is a key indicator of growth and performance. A previous study found that supplementation with TCM significantly increased the slaughter and evisceration rates of broiler chickens (46). Similarly, supplementation on Eucommia ulmoides polysaccharides to diets improved growth and carcass performance in Songliao black pigs (47). Moreover, dietary supplementation of Litsea cubeba essential oil (LCO) and Alpinia oxyphylla essential oil (AEO) to fattening pigs improves growth performance and the efficiency of digestion and absorption of nutrients (48, 49). In our study, TCBR2 supplementation significantly increased the carcass and partial-eviscerated carcass yield in rabbits, consistent with findings from previous studies.
Blood biochemical markers, such as sugars, fats, and proteins, provide insight into an animal’s growth, nutrient digestion, absorption, and metabolism. For instance, albumin, total protein, and urea nitrogen levels reflect protein and amino acid utilization and metabolism, whereas blood glucose levels indicate an animal’s glucose regulation and overall health, and triglyceride and total cholesterol levels suggest the efficiency of fat metabolism (50, 51). Our study revealed that TCBR2 supplementation significantly increased serum total protein levels while decreasing urea nitrogen and triglyceride levels. Moreover, TCBR supplementation lowered serum glucose levels. And the Chinese medicine Tongxinluo significantly reduced lipid levels in rabbits (52). However, Some studies indicated that Ligustrum lucidum supplementation does not significantly impact glucose, total protein, or albumin levels in Hy-Line Brown hens during the late laying period (53), which may be attributed to differences in the animal species and herbs.
The host metabolism is regulated by the gut microbiome. Short-chain fatty acids, branched-chain amino acids and bile acids synthesized by the gut microbiome are a direct source of energy for the host cells and also affect the energy metabolism of its host (54). Previous study showed that Portulaca oleracea increased the metabolic tryptophan and some vitamins in the intestinal flora, thereby promoting intestinal health and growth performance in Hu Lambs (55). Wei et al. also demonstrated that supplementation of dairy cows with low crude protein (CP) and rumen-protected lysine (RPL) balanced the amino acid supply, increased the efficiency of nitrogen utilization, and altered the intestinal flora composition, which was beneficial to the lactation performance of the cows (56). ALT and ALP are cytokines of liver metabolism and important indicators of liver injury (57). Researcher suggested that Gegen-Qinlian decoction (GQD) alleviated liver injury and metabolic disorders in Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) mice by correcting intestinal dysbiosis and modulating the bile acid (BA) profile in a mouse model of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (58). TCBR2 supplementation in rabbits reduced serum ALT and ALP levels but significantly increased the liver SOD activity; however, it had no significant effect on GSH-Px and catalase levels. A previous study showed that supplementing with Ilicis Chinensis folium extract significantly reduced ALT levels and increased SOD activity in broiler chickens (59). Similarly, acidic polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis significantly reduced ALT levels and increased SOD activity in cases of liver injury (60). Additionally, researcher verified that hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA) treated traumatic brain injury (TBI) mice mainly through affecting the functions of blood vessels, increased brain microvessel density and the expression of angiogenic marker proteins VEGFA and CD34 (61). Moreover, Qiwei Tiexie pills (QWTX) effectively attenuates acetaminophen (APAP) overdose-induced elevation of serum AST, ALT and inflammatory factors in a mouse model (62). Furthermore, supplementation with 4 and 6% TCBR significantly increased serum CAT levels. These results indicated that TCBR maybe possess antioxidant properties.
As a crucial organ for nutrient absorption, the intestines play a key role in maintaining overall health through their structure, mucosal barrier, and microbial composition. We hypothesize that components within TCBR can regulate intestinal flora and modify the intestinal index. Previous research has shown that various compounds, such as patchouli alcohol, luteolin, and other therapeutic agents, can regulate gut flora and reduce intestinal inflammation and damage (63–65). Our findings suggested that TCBR2 supplementation significantly increased jejunal villus height and decreased crypt depth compared with the Mock treatment. The intestinal barrier, consisting of microbial, mechanical, and chemical components, plays a key role in preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream and maintaining the body’s internal stability (66). TCBR2 supplementation in our study significantly up-regulated the relative expression of occludin-1 and ZO-1 while down-regulating the relative expression of TNF-α and IL-8. The tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1 are vital for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal mucosa. Modified Gegen Qinlian decoction has been shown to improve symptoms and pathological damage in ulcerative colitis model mice by up-regulating occludin and ZO-1 expression (67). Mulberry extract was found to attenuate colonic damage and inflammation, suppress colonic oxidative stress, and restore intestinal tight junction protein expression in mice with DSS-induced colitis (18). Our research showed that TCBR2 supplementation significantly increased the relative abundance of the Bacteroidetes and Verrucomicrobiota phylum, particularly the Akkermansia genus. Bacteroidetes, a prominent bacterial group within the animal gut microbiome, significantly influence host growth by facilitating food digestion and nutrient absorption (68). These bacteria function as intestinal symbionts by providing protection against pathogens and supporting other gut microorganisms (69). Researcher demonstrated that mouse pretreated with Mycobacterium anthropophilum spp. and its metabolites enhanced survival rates, reducing brainstem inflammation after infection HSV-1 (70). Additionally, Akkermansia, a genus of anaerobic Gram-negative bacteria from the Verrucomicrobiota phylum, resides in the gut lining and plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health (71). The presence of Akkermansia muciniphila is strongly associated with positive effects on host metabolism, efficacy of cancer treatment checkpoints, and the maintenance of immune stability. Research demonstrated that TLR2-TLR1 heterodimers play a regulatory role in modulating lipid diacylphosphatidylethanolamine within the cell membranes of Akkermansia, thereby promoting a preference for TNF-α production (72). In a murine sepsis model, the administration of Akkermansia significantly reduced sepsis-induced mortality. The Arg-Lys-His (RKH) protein secreted by Akkermansia binds directly to Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), inhibiting TLR4 signaling in immune cells. This interaction results in decreased activation of inflammatory cells and a reduction in the overproduction of pro-inflammatory factors associated with sepsis (73). Similarly, The gut flora can secrete SCFA, potent anti-inflammatory agents, inhibited neutrophils and macrophages from releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines, to maintain epithelial integrity, thereby contributing to immune system stability. Previous study demonstrated that butyrate enhances the expression of the tight-junction proteins claudin-1 and ZO-1 and upregulate the expression of mucin 2 (MUC2) to reinforce the mucous layer against luminal pathogens (74). Through multi-omics sequencing and correlation analysis, it was found that butyric acid (BA) produced by Faecalibacterium prausnitzii plays a crucial role in improving valve function in calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) (75). Interestingly, TCM is not only effective in disease through the gut-liver axis, but can also positively affect disease through the gut-brain axis. Yu et al. demonstrated the significant regulatory impact of Ginkgo biloba extract on intestinal microflora and microbial metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) model mice, reducing the Firmicutes/Bacteroides ratio and increasing Bacteroidetes abundance (76). and Lonicerae Japonicae Flos (LJF) may have a therapeutic effect in AD (77). Importantly, Astragaloside IV likely prevents the proliferation and migration of microglia/macrophages after intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) by binding its transformed products to CDC42, PTK2, and CSF1R in C57 BL/6 mice model (78). Moreover, ASIV altered the gut microbiota, and inhibited the production of conditional pathogenic bacteria. Li et al. suggested that gut microbiota and its metabolites may be the key regulator of AS-IV in treating ICH (79). In brief, TCM showed promising prospects in the treatment of various diseases and multiple applications.
5 Conclusion
The inclusion of 2% TCBR in the diets of growing rabbits alleviated adverse clinical symptoms and improved survival rates, growth performance, and meat quality by increasing BW and BW gain while decreasing the FCR. These benefits may be attributed to enhanced antioxidant activity in the liver, improved jejunal morphology, and a higher relative abundance of beneficial intestinal flora (Figure 8). These findings highlight the potential of TCBR as an effective feed additive in rabbit production.
Data availability statement
The data presented in the study are deposited in the NCBI repository, accession number BioProject: PRJNA1322195.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Jilin Genet-Med Biotechnological Co., Ltd. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
LD: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. JF: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft. JY: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YD: Validation, Writing – review & editing. KH: Software, Writing – review & editing. XY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. DF: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. XH: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MM: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. JB: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Collaborative Innovation Center for Zoonosis prevention and control, Jinzhou Medical University (182231506003).
Conflict of interest
XY and JB were employed by Jilin Genet-Med Biotechnological Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Cullere, M, and Dalle Zotte, A. Rabbit meat production and consumption: state of knowledge and future perspectives. Meat Sci. (2018) 143:137–46. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2018.04.029
2. Li, S, Zeng, W, Li, R, Hoffman, LC, He, Z, Sun, Q, et al. Rabbit meat production and processing in China. Meat Sci. (2018) 145:320–8. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2018.06.037
3. Bivolarski, BL, and Vachkova, EG. Morphological and functional events associated to weaning in rabbits. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). (2014) 98:9–18. doi: 10.1111/jpn.12058
4. Sun, C, Wang, Z, Li, Y, and Huang, J. Antibiotic resistance spectrums of Escherichia coli and Enterococcus spp. strains against commonly used antimicrobials from commercial meat-rabbit farms in Chengdu City, Southwest China. Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1369655. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1369655
5. Elghandour, MMY, Tan, ZL, Abu Hafsa, SH, Adegbeye, MJ, Greiner, R, Ugbogu, EA, et al. Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a probiotic feed additive to non and pseudo-ruminant feeding: a review. J Appl Microbiol. (2020) 128:658–74. doi: 10.1111/jam.14416
6. Jiang, SQ, Chen, ZL, Zhang, S, Ye, JL, and Wang, YB. Protective effects of protocatechuic acid on growth performance, intestinal barrier and antioxidant capacity in broilers challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Animal. (2023) 17:100693. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2022.100693
7. Song, Z, Xie, K, Zhang, Y, Xie, Q, He, X, and Zhang, H. Effects of dietary Ginsenoside Rg1 supplementation on growth performance, gut health, and serum immunity in broiler chickens. Front Nutr. (2021) 8:705279. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.705279
8. Abdelatty, AM, Mandouh, MI, Mousa, MR, Mansour, HA, Ford, H, Shaheed, IB, et al. Sun-dried Azolla leaf meal at 10% dietary inclusion improved growth, meat quality, and increased skeletal muscle ribosomal protein S6 kinase β1 abundance in growing rabbit. Animal. (2021) 15:100348. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2021.100348
9. Abdallah, A, Zhang, P, Zhong, Q, and Sun, Z. Application of traditional Chinese herbal medicine by-products as dietary feed supplements and antibiotic replacements in animal production. Curr Drug Metab. (2019) 20:54–64. doi: 10.2174/1389200219666180523102920
10. Yu, W, Ma, M, Chen, X, Min, J, Li, L, Zheng, Y, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine and constitutional medicine in China, Japan and Korea: a comparative study. Am J Chin Med. (2017) 45:1–12. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X1750001X
11. Su, Y, Bai, Q, Tao, H, and Xu, B. Prospects for the application of traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology in food science research. J Sci Food Agric. (2023) 103:5183–200. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12541
12. Huang, K, Zhang, P, Zhang, Z, Youn, JY, Wang, C, Zhang, H, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in the treatment of COVID-19 and other viral infections: efficacies and mechanisms. Pharmacol The r. (2021) 225:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107843
13. Dai, YJ, Wan, SY, Gong, SS, Liu, JC, Li, F, and Kou, JP. Recent advances of traditional Chinese medicine on the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Chin J Nat Med. (2020) 18:881–9. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(20)60031-0
14. Hongzhi, D, Xiaoying, H, Yujie, G, Le, C, Yuhuan, M, Dahui, L, et al. Classic mechanisms and experimental models for the anti-inflammatory effect of traditional Chinese medicine. Animal Model Exp Med. (2022) 5:108–19. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12224
15. Li, P, Ju, H, Zhang, Y, Achi, JG, Kang, D, Zou, J, et al. Discovery of ligustrazine and chalcone derivatives as novel viral nucleoprotein nuclear export inhibitors against influenza viruses. J Med Virol. (2023) 95:e28968. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28968
16. Song, X, Luo, J, Fu, D, Zhao, X, Bunlue, K, Xu, Z, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions enhance growth performance of heat stressed beef cattle by relieving heat stress responses and increasing apparent nutrient digestibility. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2014) 27:1513–20. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2014.14058
17. Li, D, Wang, Y, Liu, N, Chen, S, Liu, H, Wang, P, et al. Modified Sijunzi granule decreases post-weaning diarrhea in rex rabbits via promoting intestinal development. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:972326. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.972326
18. Mo, J, Ni, J, Zhang, M, Xu, Y, Li, Y, Karim, N, et al. Mulberry anthocyanins ameliorate DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by improving intestinal barrier function and modulating gut microbiota. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11:1674. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091674
19. Zhu, M, Song, Y, Xu, Y, and Xu, H. Manipulating microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease treatment: clinical and natural product interventions explored. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:11004. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311004
20. Wang, Y, Zhang, Q, Chen, Y, Liang, CL, Liu, H, Qiu, F, et al. Antitumor effects of immunity-enhancing traditional Chinese medicine. Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 121:109570. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109570
21. Yu, H, Lin, L, Zhang, Z, Zhang, H, and Hu, H. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2020) 5:209. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00312-6
22. Huang, B, An, H, Gui, M, Qiu, Y, Xu, W, Chen, L, et al. Qingjie fuzheng granule prevents colitis-associated colorectal cancer by inhibiting abnormal activation of NOD2/NF-κB signaling pathway mediated by gut microbiota disorder. Chinese Herbal Medicines. (2025) 17:500–12. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2025.04.001
23. Xu, Z, Li, J, Liu, X, Liu, L, Lin, W, Sun, D, et al. Curcuma longa L. extract and residue prevent Alzheimer's disease in mice by regulating microglia and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2025) 77:593–608. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgaf034
24. Li, Z, Ma, N, Gong, X, Shi, W, Meng, X, Yan, J, et al. Effects of herbal dregs supplementation of salvia miltiorrhiza and Isatidis Radix residues improved production performance and gut microbiota abundance in late-phase laying hens. Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1381226. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1381226
25. Chen, Z, Yan, Z, Xia, S, Wang, K, Han, Q, Zhou, M, et al. Dietary Isatidis root residue improves diarrhea and intestinal function in weaned piglets. Animals (Basel). (2024) 14:2776. doi: 10.3390/ani14192776
26. Sun, W, Chen, Z, Huang, Z, Wan, A, Zhou, M, and Gao, J. Effects of dietary traditional Chinese medicine residues on growth performance, intestinal health and gut microbiota compositions in weaned piglets. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1283789. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1283789
27. He, L, Wang, Z, Lu, J, Qin, C, He, J, Ren, W, et al. Trollius chinensis Bunge: a comprehensive review of research on botany, Materia Medica, Ethnopharmacological use, Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and quality control. Molecules. (2024) 29:421. doi: 10.3390/molecules29020421
28. Guo, L, Qiao, S, Hu, J, Li, D, Zheng, S, Shi, D, et al. Investigation of the effective components of the flowers of Trollius chinensis from the perspectives of intestinal bacterial transformation and intestinal absorption. Pharm Biol. (2017) 55:1747–58. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2017.1321023
29. Yang, K, Wang, Z, Wang, P, Wang, L, Li, Y, He, L, et al. A comprehensive research review of herbal textual research, Phytochemistry, pharmacology, traditional uses, clinical application, safety evaluation, and quality control of Trollius chinensis Bunge. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). (2024) 17:800. doi: 10.3390/ph17060800
30. Kabue, JP, Khumela, R, Meader, E, Baroni de Moraes, MT, Traore, AN, and Potgieter, N. Norovirus-associated gastroenteritis Vesikari score and pre-existing salivary IgA in young children from rural South Africa. Viruses. (2023) 15:2185. doi: 10.3390/v15112185
31. Zhou, X, Zhang, H, Li, S, Jiang, Y, Kang, L, Deng, J, et al. The effects of fermented feedstuff derived from Citri Sarcodactylis Fructus by-products on growth performance, intestinal digestive enzyme activity, nutrient utilization, meat quality, gut microbiota, and metabolites of broiler chicken. Front Vet Sci. (2023) 10:1231996. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1231996
32. Deng, L, Min, W, Guo, S, Deng, J, Wu, X, Tong, D, et al. Interference of pseudorabies virus infection on functions of porcine granulosa cells via apoptosis modulated by MAPK signaling pathways. Virol J. (2024) 21:25. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02289-y
33. Chen, M, Zhang, F, Xu, W, Lei, H, Hong, Z, Yu, R, et al. Taxus chinensis (Pilg.) Rehder fruit attenuates aging behaviors and neuroinflammation by inhibiting microglia activation via TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. (2025) 337:118943. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118943
34. Mahmoud, TN, El-Maadawy, WH, Kandil, ZA, Khalil, H, El-Fiky, NM, and El Alfy, TSMA. Canna x generalis L H. Bailey rhizome extract ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via modulating intestinal mucosal dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and TLR4/NF-ҡB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. (2021) 269:113670. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113670
35. Li, H, Zhou, Y, Liao, L, Tan, H, Li, Y, Li, Z, et al. Pharmacokinetics effects of chuanxiong rhizoma on warfarin in pseudo germ-free rats. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 13:1022567. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1022567
36. Niu, K, Wang, H, Kim, SK, Wassie, T, and Wu, X. Stepwise co-fermented traditional Chinese medicine byproducts improve antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in a piglet model. J Sci Food Agric. (2024) 104:1166–77. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13002
37. Yu, F, Yu, X, Liu, R, Guo, D, Deng, Q, Liang, B, et al. Dregs of Cardamine hupingshanensis as a feed additive to improve the egg quality. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:915865. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.915865
38. Chen, Y, Zhang, YF, Qian, HC, Wang, JL, Chen, Z, Ordovas, JM, et al. Supplementation with turmeric residue increased survival of the Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) under high ambient temperatures. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. (2018) 19:245–52. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1600451
39. He, Y, Yu, J, Song, Z, Tang, Z, Duan, JA, Zhu, H, et al. Anti-oxidant effects of herbal residue from Shengxuebao mixture on heat-stressed New Zealand rabbits. J Therm Biol. (2024) 119:103752. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2023.103752
40. Canada, AT, Watkins, WD, and Nguyen, TD. The toxicity of flavonoids to guinea pig enterocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (1989) 99:357–61. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(89)90018-5
41. Zhang, S, Zheng, L, Xu, L, Sun, H, Li, H, Yao, J, et al. Subchronic toxicity study of the total flavonoids from Rosa laevigata Michx fruit in rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. (2012) 62:221–30. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2011.12.009
42. Gao, Y, Fan, H, Nie, A, Yang, K, Xing, H, Gao, Z, et al. Aconitine: a review of its pharmacokinetics, pharmacology, toxicology and detoxification. J Ethnopharmacol. (2022) 293:115270. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115270
43. Zhao, J, Zhang, F, Xiao, X, Wu, Z, Hu, Q, Jiang, Y, et al. Tripterygium hypoglaucum (Lévl.) hutch and its main bioactive components: recent advances in pharmacological activity, pharmacokinetics and potential toxicity. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:715359. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.715359
44. Chang, G, Tian, S, Luo, X, Xiang, Y, Cai, C, Zhu, R, et al. Hypoglycemic effects and mechanisms of polyphenols from Myrica rubra pomace in type 2 diabetes (db/db) mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2025) 69:e202400523. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202400523
45. Zan, K, Lei, W, Li, Y, Wang, Y, Liu, L, Zuo, T, et al. Integrative metabolomics and proteomics detected hepatotoxicity in mice associated with alkaloids from Eupatorium fortunei Turcz. Toxins (Basel). (2022) 14:765. doi: 10.3390/toxins14110765
46. Xie, Z, Zhang, J, Ma, S, Huang, X, and Huang, Y. Effect of Chinese herbal medicine treatment on plasma lipid profile and hepatic lipid metabolism in Hetian broiler. Poult Sci. (2017) 96:1918–24. doi: 10.3382/ps/pew456
47. Liang, Y, Tang, Z, Wang, H, Liu, M, Zhao, F, Wang, L, et al. Effect of dietary Eucommia ulmoides oliver polysaccharide on immune function and meat quality of Songliao black pigs. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:13901. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64257-4
48. Chen, F, Liu, Z, Xie, C, He, J, Chen, J, Peng, K, et al. The effect of Alpinia oxyphylla essential oil on growth performance, immune, antioxidant functions and gut microbiota in pigs. Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1468520. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1468520
49. Chen, F, Wang, Y, Wang, K, Chen, J, Jin, K, Peng, K, et al. Effects of Litsea cubeba essential oil on growth performance, blood antioxidation, immune function, apparent digestibility of nutrients, and fecal microflora of pigs. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1166022 2023 Jul 3. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1166022
50. Tang, H, Zhang, H, Liu, D, Wang, Z, Yu, D, Fan, W, et al. Genome-wide association study reveals the genetic determinism of serum biochemical indicators in ducks. BMC Genomics. (2022) 23:856. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-09080-9
51. Zhang, QQ, Chang, C, Chu, Q, Wang, HH, Zhang, J, Yan, ZX, et al. Dietary calcium and non-phytate phosphorus levels affect the performance, serum biochemical indices, and lipid metabolism in growing pullets. Poult Sci. (2023) 102:102354. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102354
52. Chen, WQ, Zhong, L, Zhang, L, Ji, XP, Zhao, YX, Zhang, C, et al. Chinese medicine tongxinluo significantly lowers serum lipid levels and stabilizes vulnerable plaques in a rabbit model. J Ethnopharmacol. (2009) 124:103–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.04.009
53. Li, XL, He, WL, Yang, ML, Yan, YM, Xue, YH, and Zhao, ST. Effect of dietary supplementation of Ligustrum lucidum on performance, egg quality and blood biochemical parameters of Hy-line Brown hens during the late laying period. Animal. (2017) 11:1899–904. doi: 10.1017/S1751731117000532
54. Cani, PD, Van Hul, M, Lefort, C, Depommier, C, Rastelli, M, and Everard, A. Microbial regulation of organismal energy homeostasis. Nat Metab. (2019) 1:34–46. doi: 10.1038/s42255-018-0017-4
55. Li, S, Li, S, Liu, S, Lu, S, Li, J, Cheng, S, et al. Portulaca oleracea exhibited anti-coccidian activity, fortified the gut microbiota of Hu lambs. AMB Express. (2024) 14:50. doi: 10.1186/s13568-024-01705-4
56. Wei, X, Wu, H, Wang, Z, Zhu, J, Wang, W, Wang, J, et al. Rumen-protected lysine supplementation improved amino acid balance, nitrogen utilization and altered hindgut microbiota of dairy cows. Anim Nutr. (2023) 15:320–31. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2023.08.001
58. Shu, X, Cao, Y, Wu, Y, Chen, M, Zhao, W, Ji, G, et al. Gegen-Qinlian decoction alleviates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis by modulating the microbiota-bile acid axis in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. (2025) 347:119719. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119719
59. Zhong, Y, Li, L, Chen, W, Xing, D, and Wu, X. Effects of Ilicis Chinensis folium extract supplementation on growth performance, serum parameters, intestinal morphology, and antioxidant capacity of broiler chickens. BMC Vet Res. (2023) 19:94. doi: 10.1186/s12917-023-03667-4
60. Yuan, R, Tao, X, Liang, S, Pan, Y, He, L, Sun, J, et al. Protective effect of acidic polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis on acute ethanol-induced liver injury through reducing CYP2E1-dependent oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother. (2018) 99:537–42. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.079
61. Li, T, Zhang, L, Cheng, M, Hu, E, Yan, Q, Wu, Y, et al. Metabolomics integrated with network pharmacology of blood-entry constituents reveals the bioactive component of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction and its angiogenic effects in treating traumatic brain injury. Chin Med. (2024) 19:131. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-01001-0
62. Bian, X, Chen, L, Bian, X, Li, L, Liu, D, Liu, S, et al. Protective effect of Tibetan medicine Qiwei Tiexie pills on liver injury induced by acetaminophen overdose: an integrated strategy of network pharmacology, metabolomics and transcriptomics. Phytomedicine. (2024) 123:155221. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155221
63. Wu, J, Gan, Y, Li, M, Chen, L, Liang, J, Zhuo, J, et al. Patchouli alcohol attenuates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis via TLR2/MyD88/NF-kB pathway and regulation of microbiota. Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 124:109883. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109883
64. Li, B, Du, P, Du, Y, Zhao, D, Cai, Y, Yang, Q, et al. Luteolin alleviates inflammation and modulates gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis rats. Life Sci. (2021) 269:119008. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.119008
65. Wang, L, Lei, J, Zhao, Z, Jia, J, and Wang, L. Therapeutic effects of paeoniflorin on irritable bowel syndrome in rats. J Vet Sci. (2023) 24:e23. doi: 10.4142/jvs.22083
66. Che, Q, Luo, T, Shi, J, He, Y, and Xu, DL. Mechanisms by which traditional Chinese medicines influence the Intestinal Flora and Intestinal barrier. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2022) 12:863779. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.863779
67. Wang, Y, Zhang, J, Zhang, B, Lu, M, Ma, J, Liu, Z, et al. Modified Gegen Qinlian decoction ameliorated ulcerative colitis by attenuating inflammation and oxidative stress and enhancing intestinal barrier function in vivo and in vitro. J Ethnopharmacol. (2023) 313:116538. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116538
68. Pan, X, Raaijmakers, JM, and Carrión, VJ. Importance of Bacteroidetes in host-microbe interactions and ecosystem functioning. Trends Microbiol. (2023) 31:959–71. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2023.03.018
69. Zafar, H, and Saier, MH Jr. Gut Bacteroides species in health and disease. Gut Microbes. (2021) 13:1–20. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1848158
70. Mancini, M, and Vidal, SM. Insights into the pathogenesis of herpes simplex encephalitis from mouse models. Mamm Genome. (2018) 29:425–45. doi: 10.1007/s00335-018-9772-5
71. Ioannou, A, Berkhout, MD, Geerlings, SY, and Belzer, C. Akkermansia muciniphila: biology, microbial ecology, host interactions and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2025) 23:162–77. doi: 10.1038/s41579-024-01106-1
72. Bae, M, Cassilly, CD, Liu, X, Park, SM, Tusi, BK, Chen, X, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila phospholipid induces homeostatic immune responses. Nature. (2022) 608:168–73. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04985-7
73. Xie, S, Li, J, Lyu, F, Xiong, Q, Gu, P, Chen, Y, et al. Novel tripeptide RKH derived from Akkermansia muciniphila protects against lethal sepsis. Gut. (2023) 73:78–91. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-329996
74. Liu, P, Wang, Y, Yang, G, Zhang, Q, Meng, L, Xin, Y, et al. The role of short-chain fatty acids in intestinal barrier function, inflammation, oxidative stress, and colonic carcinogenesis. Pharmacol Res. (2021) 165:105420. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105420
75. Wang, C, Liu, Z, Zhou, T, Wu, J, Feng, F, Wang, S, et al. Gut microbiota-derived butyric acid regulates calcific aortic valve disease pathogenesis by modulating GAPDH lactylation and butyrylation. iMeta. (2025):e70048. doi: 10.1002/imt2.70048
76. Yu, T, Xing, Y, Gao, Q, Wang, D, Chen, H, Wang, H, et al. Ginkgo biloba extract drives gut Flora and Microbial metabolism variation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15:2746. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122746
77. Xiang, Q, Xiang, Y, Liu, Y, Chen, Y, He, Q, Chen, T, et al. Revealing the potential therapeutic mechanism of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos in Alzheimer’s disease: a computational biology approach. Front Med. (2024) 11:1468561. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1468561
78. Hu, E, Li, Z, Li, T, Yang, X, Ding, R, Jiang, H, et al. A novel microbial and hepatic biotransformation-integrated network pharmacology strategy explores the therapeutic mechanisms of bioactive herbal products in neurological diseases: the effects of Astragaloside IV on intracerebral hemorrhage as an example. Chin Med. (2023) 18:40. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00745-5
Keywords: traditional Chinese medicine residues, Trollius chinensis Bunge, rabbit, cecal microbiota, antioxidant capacity, blood biochemistry
Citation: Deng L, Fang J, Yu J, Dong Y, Han K, Yang X, Fei D, Han X, Ma M and Bai J (2025) Effects of dietary Trollius chinensis Bunge residue supplementation on growth performance, antioxidant status, intestinal morphology, and cecal microbiota in weaned rabbits. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1640419. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1640419
Edited by:
Yeni Widiawati, National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), IndonesiaReviewed by:
Baseer Ahmad, Muhammad Nawaz Shareef University of Agriculture, PakistanAsghar Abbas, Muhammad Nawaz Shareef University of Agriculture, Pakistan
Copyright © 2025 Deng, Fang, Yu, Dong, Han, Yang, Fei, Han, Ma and Bai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jieying Bai, YmFpamlleWluZ0AxMjYuY29t; Mingxiao Ma, bG5qem1teEAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Lingcong Deng
Lingcong Deng Juan Fang3†
Juan Fang3† Dongliang Fei
Dongliang Fei Mingxiao Ma
Mingxiao Ma Jieying Bai
Jieying Bai