- 1Heilongjiang Agricultural Economy Vocational College, Mudanjiang, China
- 2Department of Cell Biology, School of Life Science, Central South University, Changsha, China
- 3Department of Clinical Laboratory Sciences, College of Applied Medical Sciences, King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia
- 4Department of Clinical Laboratories Sciences, College of Applied Medical Sciences, Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia
- 5College of Agriculture and Biology, Liaocheng University, Liaocheng, China
Bovine mastitis, an inflammatory condition of the mammary glands caused by diverse etiological agents, represents a significant economic challenge to the global dairy industry, resulting in annual losses of approximately $35 billion. While antibiotic therapy remains the conventional intervention for both prophylaxis and treatment, the increasing prevalence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), particularly the emergence of multidrug-resistant and methicillin-resistant strains, has compromised therapeutic efficacy. These developments pose substantial concerns regarding milk safety and public health implications. Consequently, research attention has shifted toward alternative therapeutic modalities, encompassing phytotherapeutic interventions, nutritional modifications, and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). Numerous plant species demonstrate significant antimicrobial properties while maintaining favorable safety profiles for humans, animals, and ecological systems. Complementary therapeutic approaches, including acupuncture and traditional herbal formulations, have exhibited promising potential in enhancing treatment outcomes and improving milk quality parameters. This review synthesizes current evidence on the integration of traditional Chinese medicine and plant-derived bioactive compounds into sustainable, holistic strategies for mastitis management, with implications for animal welfare, economic sustainability, and public health safety.
1 Introduction
The dairy industry is a fundamental pillar of global agricultural systems, contributing significantly to food security and economic stability worldwide (1). Mastitis, an inflammatory condition affecting the mammary glands, is one of the most economically devastating diseases in dairy production, characterized by distinct pathological alterations in mammary tissues accompanied by pronounced physical and chemical modifications in milk composition (2–4). This complex, multifactorial disease predominantly affects dairy cattle during the periparturient period, resulting from intricate interactions among host susceptibility factors, pathogenic microorganisms, and environmental management practices (5–7). The etiology of mastitis encompasses a diverse spectrum of more than 200 microbial agents, with Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria serving as the primary causative pathogens. At the same time, additional contributing factors include udder morphology, animal age, genetic predisposition (8–11), and environmental conditions (5, 12).
The economic ramifications of mastitis on the global dairy sector are profound, with conservative estimates indicating annual losses of approximately $35 billion worldwide (13). Regional economic assessments reveal similarly substantial impacts, with the United States sustaining approximately US$2 billion in annual losses, Canada experiencing Can$400 million (US$318 million) in economic damage, and China reporting financial losses ranging between 15 and 45 billion CNY (14, 15). These comprehensive financial impacts encompass multiple direct and indirect costs, including diminished milk yield, mandatory milk disposal due to antibiotic residues, veterinary intervention expenses, premature culling of chronically infected animals, and occasional mortality (5, 16–19). Detailed economic analyses reveal that approximately 60% of losses are attributable to decreased milk production, 16% to increased labor requirements, 9% to discarded milk, 7% to elevated animal replacement costs, 4% to reduced milk market value, 3% to medication expenses, and 1% to veterinary consultation fees (20).
The predominant bacterial pathogens associated with mastitis include Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Streptococcus agalactiae (S. agalactiae), Streptococcus uberis (S. uberis), Escherichia coli (E. coli), and Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) (21, 22). A growing concern is the rising incidence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) among these pathogens, as documented in various global studies. Research from Ethiopia and Estonia has revealed high rates of penicillin-resistant S. aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci (23, 24). At the same time, investigations in West Bengal, India, have identified Gram-negative bacteria resistant to β-lactams and tetracyclines (25). Comparable resistance patterns have been systematically documented in Central Mexico, where coagulase-negative Staphylococci represented 42% of udder pathogens, followed by Streptococci at 17%. Notable isolates included S. aureus, Brevibacterium stationis (B. stationis), Brevibacterium conglomeratum (B. conglomeratum), and Raoultella species, each comprising 8% of the total isolates. Critically, 72.7% of these isolates demonstrated multidrug resistance to three or more antimicrobial agents, with the highest resistance frequencies observed against penicillin, clindamycin, and cefotaxime (26). Parallel studies in Southern Taiwan revealed that E. coli isolates exhibited complete resistance to cloxacillin (100%) and demonstrated moderate resistance (50%) to tetracycline, neomycin, gentamicin, ampicillin, ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, and ceftazidime. Approximately 70% of isolates displayed resistance to at least two distinct antibiotics. In comparison, 28.1% harbored both AmpA and AmpC resistance genes simultaneously, with blaTEM representing the most frequently detected beta-lactamase gene, followed by blaCMY, blaCTX, blaSHV, and blaDHA (27). Advanced whole-genome sequencing analyses conducted in Canada on S. uberis and S. dysgalactiae isolates have revealed direct correlations between specific AMR genes and elevated minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs), particularly for tetracyclines and lincosamides. In contrast, subclinical isolates continued to harbor AMR genes acquired through horizontal gene transfer mechanisms, emphasizing their critical role in resistance dissemination within dairy herds (28).
The evolutionary development of AMR, initially documented with penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae (S. pneumoniae), occurs through sophisticated mechanisms involving the horizontal transfer of resistance genes via mobile genetic elements, including bacteriophages, plasmids, naked DNA, and transposable elements (29). While antimicrobial intervention remains indispensable for maintaining economic viability, ensuring animal welfare, and preserving mammary gland health in commercial dairy operations, the emergence and proliferation of resistant bacterial strains constitute a significant threat to global public health, food security, and sustainable agricultural development (29, 30). This concerning development has prompted increased interest in alternative therapeutic approaches (15), including nutritional interventions, bioactive compound therapies, and evidence-based plant-derived treatments (31–35).
From a broader public health perspective, the increasing incidence of bovine mastitis frequently necessitates intensive antibiotic usage, consequently elevating the risk of antibiotic residues in milk products and contributing to the global AMR burden, ultimately increasing healthcare costs and threatening therapeutic efficacy. To address these multifaceted challenges and reduce dependence on conventional antimicrobials, researchers worldwide are systematically investigating alternative treatment strategies, including homeopathic approaches, with a rigorous emphasis on ensuring therapeutic efficacy and safety for both animals and consumers (36).
Medicinal plants represent a vast repository of bioactive compounds with demonstrated therapeutic potential, containing diverse phytochemical constituents that exhibit beneficial effects on human and animal health. The encouraging empirical evidence supporting plant-based therapies has generated substantial scientific interest in exploring these natural substances for developing innovative therapeutic interventions. Plant extracts and essential oils, renowned for their broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties, represent up-and-coming alternatives that are generally recognized as safe for animals, humans, and environmental systems (30). Plants synthesize a diverse array of secondary metabolites as integral components of their natural defense mechanisms, many of which possess potent antimicrobial properties and have maintained significant roles in traditional medicinal systems throughout human history. The antimicrobial efficacy of plant-derived compounds is primarily attributed to diverse classes of bioactive phytochemicals, including flavonoids (such as quercetin, kaempferol, and catechins), alkaloids (including berberine, quinine, and morphine), terpenoids and terpenes (encompassing monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and triterpenes), phenolic acids (such as gallic acid, caffeic acid, and ferulic acid), saponins, tannins, and essential oil components (including thymol, carvacrol, eugenol, and linalool). These phytochemicals exhibit antimicrobial activity through multiple mechanisms, including disruption of bacterial cell wall synthesis, interference with cytoplasmic membrane integrity, inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis, disruption of metabolic pathways, and interference with bacterial communication systems (quorum sensing). Flavonoids demonstrate antimicrobial efficacy by forming complexes with extracellular proteins and bacterial cell walls, while alkaloids exert their effects through DNA intercalation and enzyme inhibition. Terpenoids compromise membrane integrity and interfere with respiratory processes, whereas phenolic compounds disrupt cellular metabolism and protein function (37). The therapeutic application of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in mastitis management, including established formulations such as Yanghe decoction (38), Danggui buxue decoction (39), Medulla tetrapanacis water extract (31), and Red ointment (40), has demonstrated considerable clinical success and therapeutic efficacy (41–44). Beyond TCM, bioactive phytocompounds have emerged as promising alternatives to conventional antibiotics for treating bovine mastitis (15, 45–50). This review critically evaluates the current evidence base for the therapeutic application of TCM and plant-derived bioactive compounds in bovine mastitis management.
2 Methodology for literature search
This review aims to explore the role of TCM and plant-derived bioactive compounds in the treatment of mastitis. To achieve this, a comprehensive literature search spanning 2014–2025 (11 years) was conducted using reputable databases including Google Scholar, PubMed, Web of Science, X-MOL, and additional Chinese databases (CNKI, Wanfang, VIP). Keywords such as TCM, plant-derived bioactive compounds, Chinese herbal medicine, bovine mastitis, udder health, herbal formulations, mastitis risk factors, and antimicrobial resistance were employed to find relevant studies. The inclusion criteria for this review were as follows: articles published between 2014 and 2025 were considered, with a specific focus on the application of TCM and plant-derived bioactive compounds for mastitis treatment. Studies published as book chapters, conference papers, abstracts, or in newspapers were excluded from this review.
3 Mastitis classification and possible risk factors
The etiological agents of mastitis are delineated into three distinct categories based on the nature and origin of the causative pathogens: contagious, environmental, and opportunistic agents (Figure 1) (51).
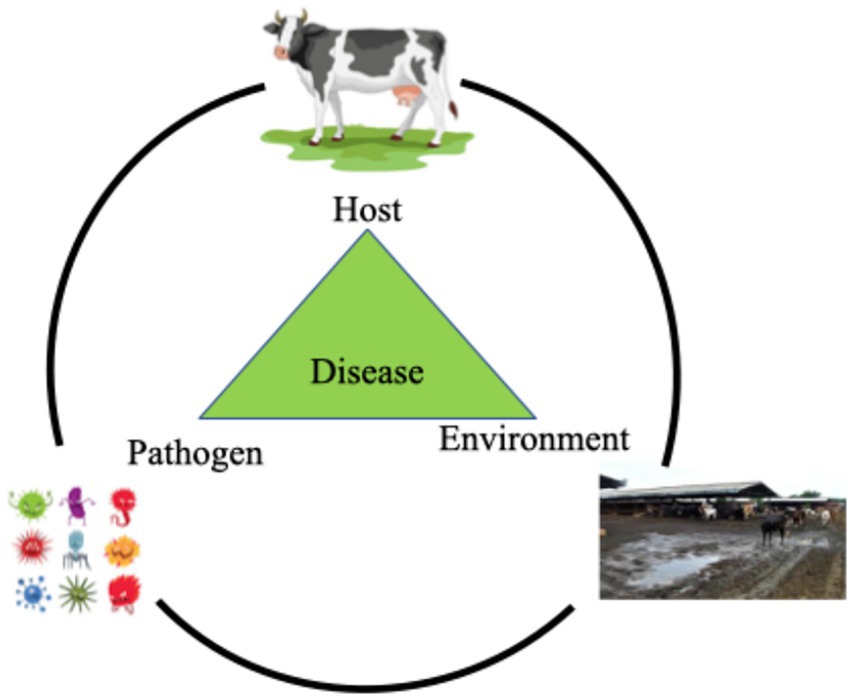
Figure 1. Host-pathogen-environment interactions and their association with mastitis. This diagram illustrates the disease triangle model, showing how mastitis develops through the interaction of three key factors. The host (in this case, a cow) represents the susceptible animal, with factors such as age, immunity, and genetics influencing susceptibility to mastitis. The pathogen shows various disease-causing agents, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, that can cause mastitis. The environment (farm setting) depicts conditions influencing transmission, such as temperature, humidity, housing, milking practices, and sanitation. The central green triangle represents mastitis occurring at the intersection where all three factors align - when a susceptible host encounters a virulent pathogen under favorable environmental conditions (85).
3.1 Type of mastitis
Broadly, mastitis can be categorized into two types: lactational and non-lactational mastitis (as shown in Figure 2). The most common form is lactational mastitis, which typically occurs during breastfeeding. This condition is infectious and presents with localized pain and swelling, accompanied by systemic symptoms. Although it can develop at any time during the lactation period, it most frequently occurs during the second or third week of postpartum. Non-lactational mastitis includes two primary forms: idiopathic granulomatous and periductal mastitis. Periductal mastitis, though rare, can affect non-lactating individuals, particularly those of reproductive age. It’s often linked to bacterial infection (52).
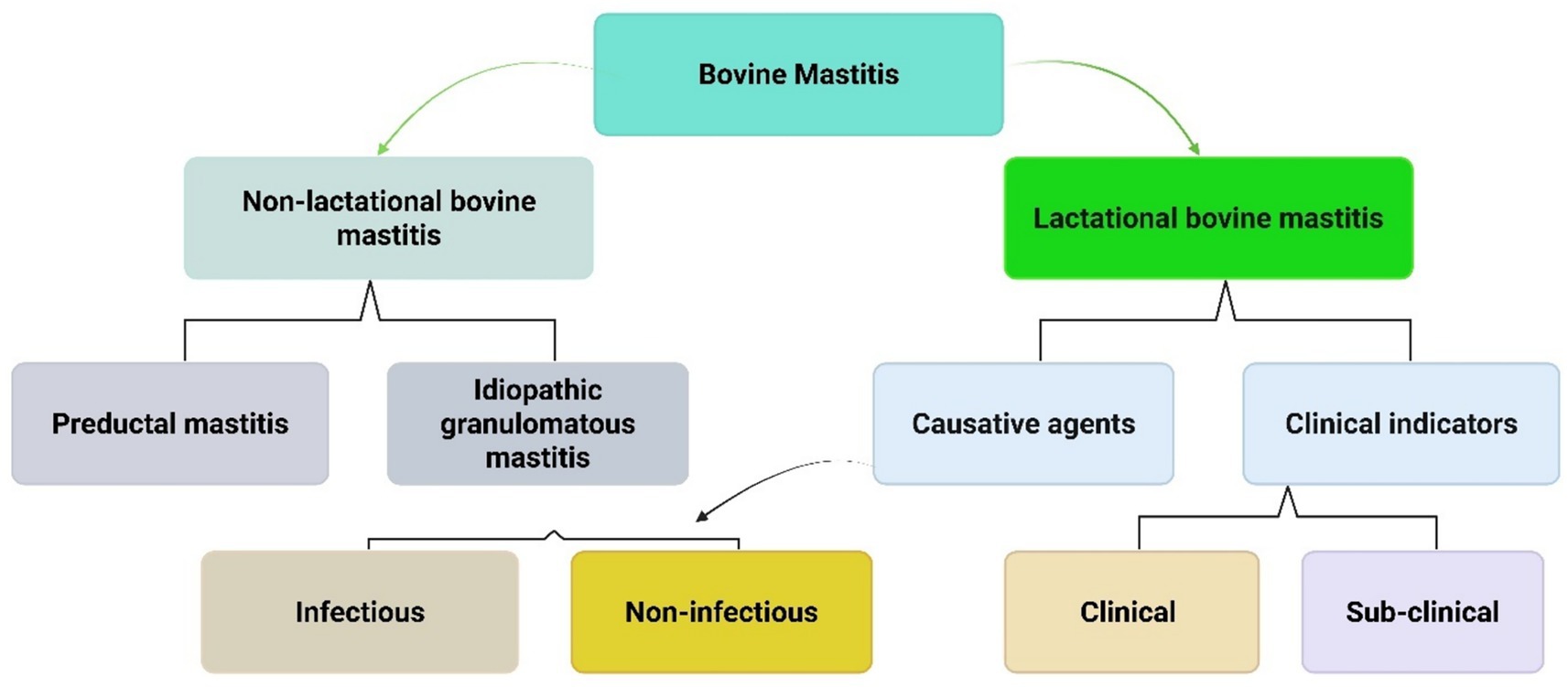
Figure 2. Classification of mastitis types. This flowchart classifies bovine mastitis (mammary gland inflammation in cattle) into two main categories. Non-lactational mastitis occurs when cows aren’t producing milk and includes preductal and idiopathic granulomatous types. Lactational mastitis occurs during milk production and is classified by cause (infectious vs. non-infectious) and symptoms (clinical with visible signs vs. sub-clinical with hidden infection).
Lactational mastitis can be further classified as either clinical or subclinical intramammary inflammation, based on the presence or absence of visible symptoms. The primary causative agents in clinical cases are Gram-negative bacteria, with E. coli being the most common (53). Clinical condition is primarily categorized into two main presentations: acute and chronic. Acute mastitis is characterized by overt inflammatory signs, including erythema, localized hyperthermia, and tissue tumefaction at the affected site. In severe manifestations, systemic complications may emerge, including pyrexia, septicemia, and abscess formation. Conversely, chronic mastitis exhibits a more insidious progression, typically characterized by recurrent infections and progressive tissue deterioration (2).
In contrast, subclinical mastitis (SCM) represents a pathogenic infection that proceeds without overt clinical manifestations or systemic symptomatology. However, it is distinguished by diminished milk production, compromised quality parameters, and a marked increase in somatic cell count (SCC) (54, 55). This form is predominantly associated with Gram-positive bacterial infections, most notably S. aureus (53). Clinical mastitis is generally easy to diagnose due to visible symptoms, but SCM lacks obvious signs of inflammation, making it more challenging to detect. Diagnostic tools such as the California mastitis test (CMT), elevated SCC in milk, and microbial isolation and culture from milk samples aid in identifying SCM. Early detection is crucial in the dairy industry to minimize financial losses. Numerous microorganisms, primarily bacteria, have been identified as the causative agents of mastitis (56). SCC is a key marker for evaluating udder health and serves as a reliable method for detecting mastitis by quantifying immune cells, such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, and macrophages, in milk (57). When SCC levels exceed 200,000 cells/ml, it often indicates a bacterial infection. Both clinical and SCM can lead to significant changes in SCC level, highlighting the ongoing inflammatory response in the udder (58).
3.2 Pathogenic factors
Environmental pathogens constitute a diverse group of microorganisms that originate from multiple reservoirs within the agricultural environment, including bedding substrates, arthropod vectors, housing infrastructure, and the bovine enteric microbiome, with E. coli representing a predominant example (59). The proliferation and transmission of these pathogens are significantly influenced by suboptimal husbandry conditions, including excessive stocking density, inadequate floor sanitation, insufficient ventilation systems, and elevated ambient temperatures coupled with high relative humidity (60). Contagious pathogens, primarily represented by S. aureus and S. agalactiae, exhibit host-adapted characteristics and are transmitted through direct inter-animal contact or via contaminated milking apparatus (2). Opportunistic pathogens demonstrate dual behavioral characteristics, functioning as either contagious or environmental agents depending on circumstances, and typically exploit periods of immunocompromised host status to establish intramammary infections (51).
Recent epidemiological studies have documented increased morbidity associated with mycotic mastitis in bovines. Notable fungal pathogens include zoonotic yeasts such as C. albicans and Kodamaea ohmeri, along with other Candida species: C. guilliermondii, C. famata, C. tropicalis, C. colliculosa, C. krusei, C. rugosa, C. glabrata, C. parapsilosis, and C. inconspicua. Additional fungal agents encompass Trichosporon species, Rhodotorula glutinis, Saccharomyces fragilis, Pichia kudriavzevii, and Cyberlindnera rhodanensis. Mold species, including Aspergillus amstelodami, A. fumigatus, and Geotrichum candidum, have also been implicated (61). Furthermore, yeast-like algae, specifically Prototheca zopfii and Prototheca blaschkeae, have been identified as causative agents (21). Yeast-like algae, including Prototheca zopfii and Prototheca blaschkeae, have also been implicated (62).
Viral infections contribute significantly to mastitis pathogenesis through direct and indirect mechanisms (63). Direct viral mastitis occurs with bovine herpesvirus 1 and 4 (clinical and subclinical presentations, respectively) (64–66), parainfluenza virus, and foot-and-mouth disease virus (67–69). Indirect viral contributions result from teat epithelial lesions caused by bovine herpesvirus 2, cowpox virus, pseudo-cowpox virus, vesicular stomatitis virus, papillomavirus, and bovine leukemia virus, which compromise barrier defenses and predispose to secondary bacterial invasion (21, 63, 70–72).
3.3 Non-pathogenic factors
Mechanical trauma associated with automated milking systems represents a critical predisposing factor, as it disrupts the anatomical integrity of the udder quarter. Specifically, compromised keratin plug formation and mucosal damage to the teat sinus create portals of entry for pathogenic microorganisms (21, 73). Suboptimal milking hygiene protocols demonstrate a significant positive correlation with mastitis incidence, emphasizing the importance of standardized sanitation procedures (21). In addition to mechanical factors, genetic and phenotypic characteristics substantially influence mastitis susceptibility through multiple interconnected pathways. Breed-specific variations reveal differential susceptibility patterns, with high-producing Holstein-Friesian cattle exhibiting increased vulnerability relative to medium-yielding Jersey cattle (74), while low-yielding Rendena cattle demonstrate superior disease resistance (60). Moreover, parity effects indicate a heightened susceptibility in multiparous compared to primiparous animals, reflecting cumulative exposure and potential immunological changes (75).
Beyond genetic predisposition, immunological determinants play a fundamental role in disease susceptibility through variations in cytokine expression profiles and humoral immune responses (76). Critical immune effector mechanisms include antimicrobial peptides (such as lysozyme and lactoferrin), cellular immune components (macrophages and neutrophils), and hormonal receptor expression patterns, which collectively modulate the host defense capacity (77). Concurrently, anatomical predispositions include specific udder conformations, particularly pendulous udder structure and funnel-shaped teat morphology, which facilitate pathogen entry and retention (12). Additionally, age-related physiological changes in geriatric animals contribute to increased susceptibility through progressive teat canal dilation and enhanced mammary epithelial permeability (60).
Temporal physiological changes further complicate these intrinsic factors, as the periparturient transition period represents a critical vulnerability window characterized by profound metabolic and immunological alterations. During this phase, nutritional status has a significant influence on mastitis susceptibility, particularly given the substantial metabolic demands associated with colostrum synthesis and lactogenesis in dairy cattle (12). Consequently, a negative energy balance can precipitate deficiencies in essential proteins, trace minerals, and vitamins that are fundamental to optimal immune function (78). Therefore, maintaining an adequate nutritional status, including sufficient selenium, iron, copper, zinc, cobalt, chromium, essential amino acids, and vitamins A, E, and C, is paramount for both mastitis prevention and sustained lactational performance (79).
4 Factors involved in antibiotic resistance
The primary approach to treating bovine mastitis involves the use of antibiotics. However, the effectiveness of this treatment is diminishing due to the rising incidence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which is now recognized as a significant global health concern (80). While antimicrobials have considerably improved animal health and yield, the improper or unnecessary use of antimicrobials in food-producing animals is believed to play a significant role in the development of AMR (81). Moreover, the presence of residues in milk poses potential risks to both animal and human health (82). The utilization of antimicrobial agents in animal husbandry has been a longstanding practice, primarily for therapeutic purposes and occasionally for production enhancement. These agents are also employed prophylactically to prevent infections. In dairy cattle management, antimicrobials are predominantly used to control mastitis, a prevalent and economically significant disease, during two crucial phases: lactation therapy and dry cow therapy (30).
Specifically, lactation therapy presents a significant challenge as antimicrobial use necessitates extended milk withdrawal periods due to the risk of drug residues. These residues present multiple concerns for human health, including potential adverse reactions in hypersensitive individuals, promotion of antimicrobial resistance, and interference with dairy product manufacturing processes (30). In contrast, dry cow therapy, which involves administering long-acting antimicrobials to all mammary quarters at the end of lactation, serves both therapeutic and preventive purposes. Although this approach has been fundamental to mastitis control programs, concerns about increasing AMR have prompted many nations to re-evaluate the use of prophylactic antimicrobials in livestock (83).
Unfortunately, the excessive and inappropriate use of antibiotics in mastitis treatment has substantially contributed to the emergence of antimicrobial and multidrug resistance, thereby complicating disease management (84). Consequently, prolonged or excessive antibiotic administration disrupts the internal microbial equilibrium, promotes the development of resistance, and results in antibiotic residues in milk (85). The underlying bacterial resistance mechanisms encompass the presence of resistant variants, selective reproductive advantages under antibiotic pressure, and the heritability of resistance traits, potentially leading to resistant strain dominance within populations (86).
A prominent example of this resistance challenge is S. aureus, a major pathogen of mastitis, which exemplifies this problem through its persistent and recurrent infections that often resist treatment. Notably, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was first identified as a causative agent of mastitis in cows in 1972 (87). These methicillin-resistant S. aureus strains, which carry the mecA gene encoding penicillin-binding protein 2a, demonstrate resistance to all β-lactam antibiotics, including penicillin, cephalosporins, and carbapenems. Furthermore, MRSA frequently exhibits resistance to multiple antibiotic classes, including aminoglycosides, macrolides, tetracyclines, and fluoroquinolones (30).
The rapid evolution of bacterial resistance, driven by the widespread use of antimicrobials, has emerged as a global public health crisis (88). This situation is further exacerbated by limited research and development of new antimicrobial agents. Addressing this challenge requires a comprehensive understanding of resistance mechanisms and the development of novel antimicrobial strategies (30). As a result, there is an urgent need to identify and develop alternative therapeutic approaches that address these concerns while maintaining high standards of animal welfare and public health (89). In response to this critical need, the development of new alternative therapies and treatments presents a significant opportunity that requires collaborative efforts between veterinary practitioners and researchers. Traditional Chinese herbs offer several advantages over conventional antibiotics, including reduced side effects, a lower risk of bacterial resistance, minimal toxicity, and negligible residue levels. Additionally, they are used in the treatment of mastitis, as seen in the use of TCM and its extracts in treating mastitis (89–91).
5 Use of TCM and plant-derived bioactive compounds as an alternative treatment for bovine mastitis
5.1 TCM formulations and therapeutic approaches
TCM has garnered significant attention as an effective alternative to conventional antibiotic treatments for mastitis, demonstrating therapeutic efficacy while minimizing risks associated with antimicrobial resistance and secondary complications. The comprehensive antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and antioxidant properties of TCM, developed over centuries of use, position it as a viable alternative therapy for mastitis treatment (32, 41, 92, 93). Building upon this foundation, numerous TCM formulations have been systematically introduced for the treatment of various types of mastitis (94). These include a comprehensive range of therapeutic options, such as Chai Hu Qing Gan Tang (95), Yanghe decoction (96), and Chaihu Qinggan (38). Furthermore, other notable formulations include Tuoli Tounong Decoction (97), Yiqi Heying (98) and Gong Ying San (99).
Among the most extensively studied traditional formulations, Jingfang Granules (JF’s) demonstrate remarkable efficacy in treating LPS-induced mastitis through multiple therapeutic pathways. Specifically, these granules operate through nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), Akt, mitogen-activated protein kinase/Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/ERK), p38, and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine-rich-containing family, pyrin domain-containing-3 (NLRP3) signaling cascades. Moreover, they maintain milk barrier integrity through the regulation of tight junction proteins and prevent cell apoptosis by modulating Bcl-2 and Bax expression (100). In parallel, Qicao Rukang powder has demonstrated comparable effectiveness in treating SCM, showing notable improvements in SCC, milk composition, and bacteriological cure rates. The powder’s therapeutic efficacy is attributed to its diverse active constituents, including polysaccharides, saponins, flavonoids, and terpenoids (101). Complementing these oral formulations, Pulsatilla saponin B4 injection protocols have shown significant effectiveness in treating clinical mastitis. These protocols achieve therapeutic benefits by reducing SCC, eliminating pathogenic bacteria, and lowering inflammatory markers, including CRP, SAA, HP, and various pro-inflammatory cytokines (102). Notably, the integration of traditional approaches has shown auspicious results when combined with modern therapeutic techniques. For instance, combined therapy using intramammary antibiotics and complementary acupuncture has demonstrated substantial efficacy in reducing bovine mammary inflammation in cases of SCM. This innovative approach, which targets specific points on affected mammary quarters, resulted in a significant reduction of N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAGase) activity, thereby indicating improved healing of mammary epithelial cells (103).
Expanding beyond traditional Chinese formulations, a comprehensive evaluation of Tibetan herbal medicines has revealed additional therapeutic options. These include Swertia bimaculata, Gentiana urnula, Uncaria rhynchophylla, Aconitum flavum, Dracocephalum tanguticum, and Lagotis brachystachy, all of which demonstrated significant antibacterial activity against mastitis-causing Staphylococcus strains. Particularly noteworthy is Lagotis brachystachy, which demonstrated exceptional efficacy against MDR strains (104). Ultimately, clinical studies have provided robust validation of the benefits of TCM in the treatment of acute mastitis. These investigations have demonstrated significant improvements across multiple parameters, including clinical effectiveness, lactation rates, symptom relief, quality of life, and emotional well-being. Collectively, these findings provide strong evidence supporting the efficacy of TCM external therapy in both symptom alleviation and promoting recovery (105).
5.2 Plant-derived bioactive compounds
Contemporary research has increasingly focused on identifying and characterizing plant-derived bioactive compounds with substantial therapeutic potential for managing mastitis. Among the most promising candidates are Dimethyl itaconate, Polydatin, Sinomenine hydrochloride, and Jiawei Tounong powder, which have demonstrated significant efficacy through various molecular mechanisms (106–109). Of particular significance is Shikonin (SHI), a bioactive natural naphthoquinone constituent extracted from Lithospermum erythrorhizon, which shows remarkable anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Initially utilized in TCM for treating wounds and various skin conditions, SHI has subsequently emerged as a viable therapeutic alternative to conventional antibiotics in managing inflammatory conditions, most notably lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis. The underlying mechanism of action involves the systematic inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway through the targeted suppression of p-IκBα and p-p65 proteins, thereby achieving a substantial reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 (110). Furthermore, SHI effectively alleviates oxidative stress through the activation of the Nrf2/HO1 signaling pathway (111).
Complementing these findings, comprehensive essential oil studies have revealed significant bacteriostatic activity of traditional extracts, particularly those from lemon balm and peppermint oil, against prevalent mastitis pathogens, including S. aureus and E. coli (112). In parallel, Sodium houttuynia (SH), derived from Houttuynia cordata, has demonstrated considerable efficacy in inhibiting LPS-induced inflammatory responses in bovine mammary epithelial cells (bMECs). The therapeutic mechanism involves the sophisticated modulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, resulting in markedly reduced pro-inflammatory cytokine expression (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) and decreased levels of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B (IκBα), and NF-κB p65 (113).
Building upon these observations, Zhang et al. (114) conducted comprehensive investigations into the protective effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza polysaccharides (SMPs) in S. aureus-induced mastitis models. Their findings convincingly demonstrated that SMP treatment significantly reduced bacterial load, inflammatory cell infiltration, and cytokine levels while simultaneously inhibiting activation of the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. These therapeutic effects were substantiated by notable histopathological improvements and significant reductions in MPO and NAGase activity (114). Correspondingly, quercetin, extracted from Ligustrum lucidum, has exhibited considerable promise in both the prevention and treatment of mastitis. Through sophisticated network pharmacological analysis, researchers identified seven active ingredients and 42 key molecular targets, with tumor necrosis factor (TNF), alpha serine/threonine kinase 1 (AKT1), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) serving as core therapeutic targets. Subsequent in vivo studies validated quercetin’s capacity to alleviate pathological changes and downregulate inflammatory markers through the modulation of the PI3K-AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways (115).
Furthermore, geraniol has emerged as an up-and-coming therapeutic alternative, demonstrating effective pathogen inhibition, probiotic enhancement, and maintenance of gut microbial diversity. Notably, geraniol treatment exhibited no detectable milk residues after four days of administration and, significantly, did not induce drug resistance during prolonged exposure periods (116). Concomitantly, Taraxacum mongolicum has been shown to exhibit substantial protective effects against S. aureus-induced mastitis through well-characterized anti-inflammatory mechanisms, including the targeted downregulation of TLR2 and the systemic inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways (117).
Of exceptional interest, Forsythiaside A (FTA) has established a pivotal role in mastitis treatment through multiple comprehensive studies (118–121). Recent research has successfully elucidated FTA’s sophisticated protective mechanisms, particularly its capacity to modulate mitophagy through the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway. This pathway represents a crucial component for maintaining mitochondrial integrity, cellular energy production, and cell viability under conditions of mastitis-induced stress. FTA’s selective activation of mitophagy facilitates the targeted removal of dysfunctional mitochondria, thereby preserving mitochondrial integrity and reducing inflammatory responses. Additionally, FTA demonstrates remarkable effectiveness in lowering both cellular and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby mitigating oxidative damage, associated inflammation, and tissue injury. These synergistic mechanisms collectively contribute to reduced mastitis severity and improved dairy cow health and productivity (122).
Beyond these extensively characterized compounds, various other traditional therapeutic agents have demonstrated promising potential. Specifically, Tanshinone I and Tanshinone IIA/B exhibit significant inhibition of NF-κB activation in nMECs, proving particularly effective when combined with conventional antibiotics such as cephalosporins (123). Similarly, Artemisia argyi Leaves (ALE) have shown substantial therapeutic potential in LPS-induced mouse mastitis models, demonstrating the capacity to alleviate tissue damage, reduce oxidative stress, and regulate inflammation-associated gene expression (124). Moreover, Broadleaf Mahonia has been shown to exhibit significant anti-inflammatory properties by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, CCL-5, and IL-6, in RAW264.7 cell cultures. This therapeutic effect is primarily mediated through systematic inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways, which represent crucial regulators of inflammatory responses. In cases of granulomatous lobular mastitis, preventive treatment with Broadleaf mahonia effectively reduces inflammation and promotes tissue homeostasis (125).
To comprehensively understand the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms, investigations into mastitis caused by S. aureus have revealed significant inflammatory responses characterized by elevated levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and MPO activity, alongside increased ferroptosis markers such as Fe2+ and MDA levels. Decreased protective factors, including GSH, GPX4, and ferritin in mammary tissues, accompany these pathological changes (126). Remarkably, the strategic integration of traditional therapeutic approaches has yielded promising clinical results. In this context, Schisandrin B (SB) treatment has demonstrated considerable effectiveness in mitigating pathological changes by reducing both inflammation and ferroptosis. The underlying therapeutic mechanism involves the upregulation of SIRT1 and SLC7A11 expression, the inhibition of p53 and NF-κB activation, and the restoration of antioxidant defense systems. These therapeutic effects were confirmed through comprehensive histological analysis, demonstrating reduced tissue damage in SB-treated groups, thereby suggesting that SB’s therapeutic action occurs through the SIRT1/p53/SLC7A11 and NF-κB pathways (127). The molecular mechanisms underlying the protective effects of traditional Chinese medicine and plant-derived bioactive compounds against mastitis are schematically represented in Figure 3. Additionally, a comprehensive overview of research developments on traditional Chinese medicine and plant-derived bioactive compounds in mastitis therapy is summarized in Table 1 and Figure 4.
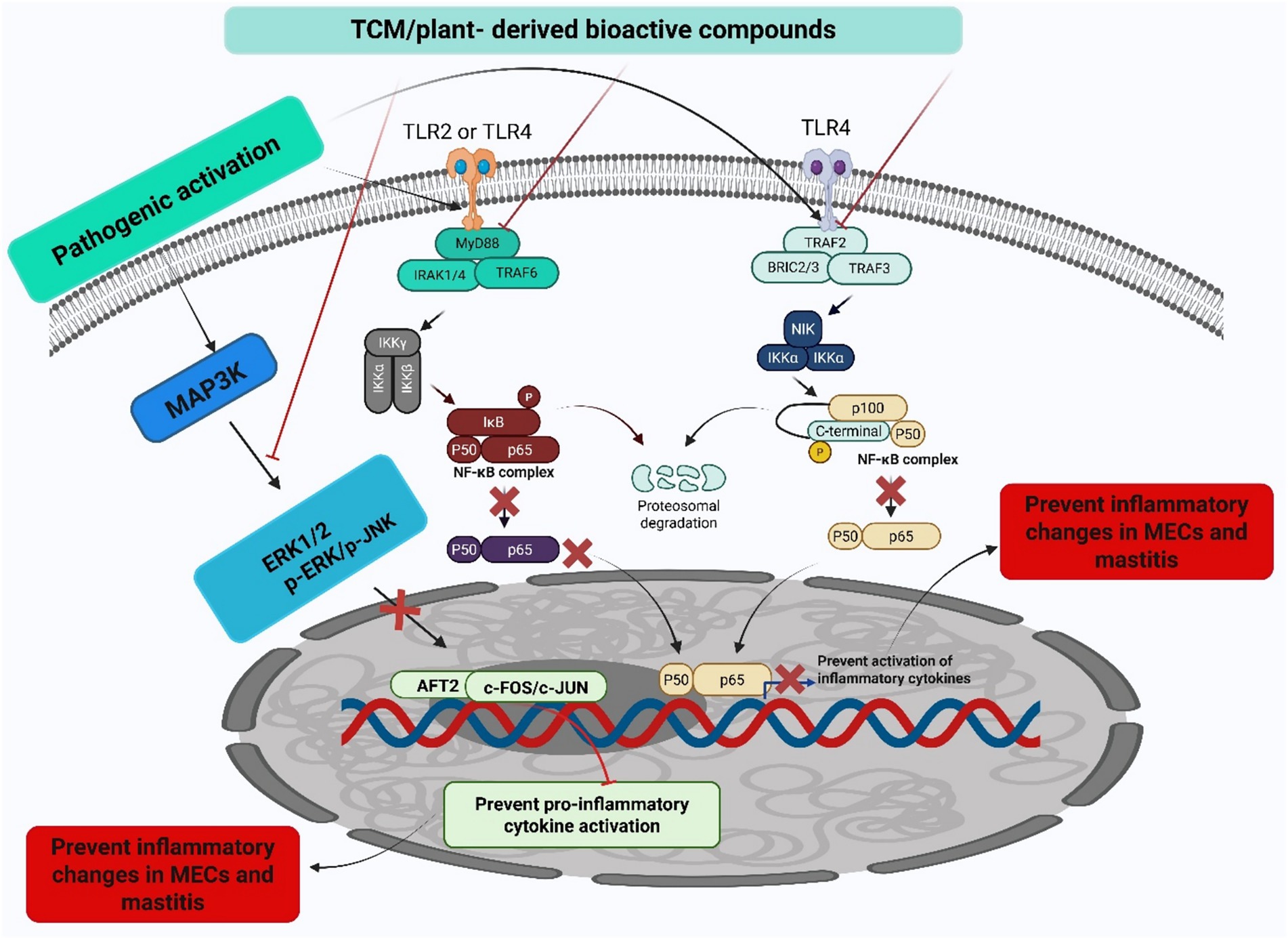
Figure 3. Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of TCM and plant-derived bioactive compounds. This figure illustrates the mechanism by which conventional TCM and plant-derived bioactive compounds exert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting key inflammatory signaling pathways, specifically the MAPK and NF-κB pathways, ultimately leading to the prevention of mastitis. The conceptual framework presented in this figure is adapted from findings reported in previously published literature (12, 77, 88).
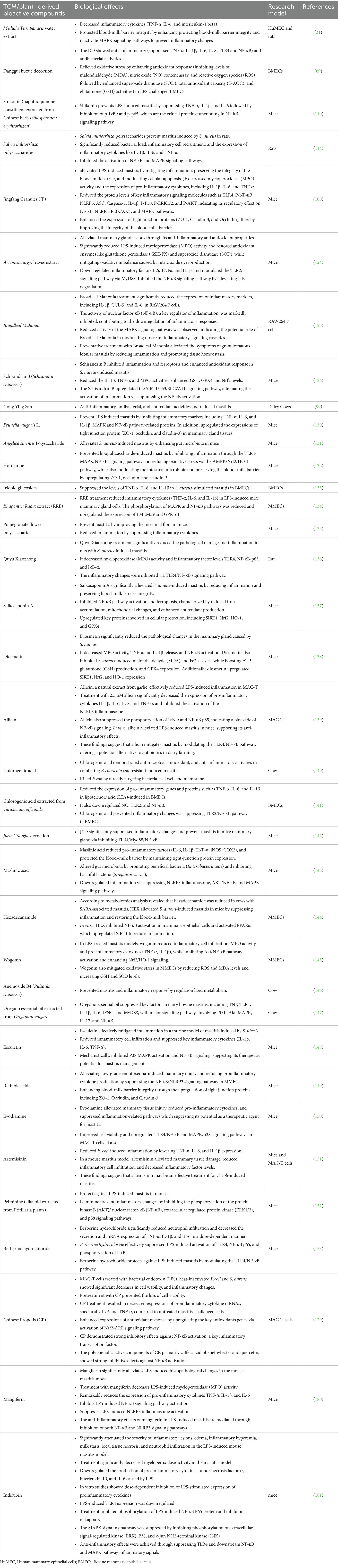
Table 1. Summary of research on TCM and plant- derived bioactive compounds for mastitis treatment (2014–2025).
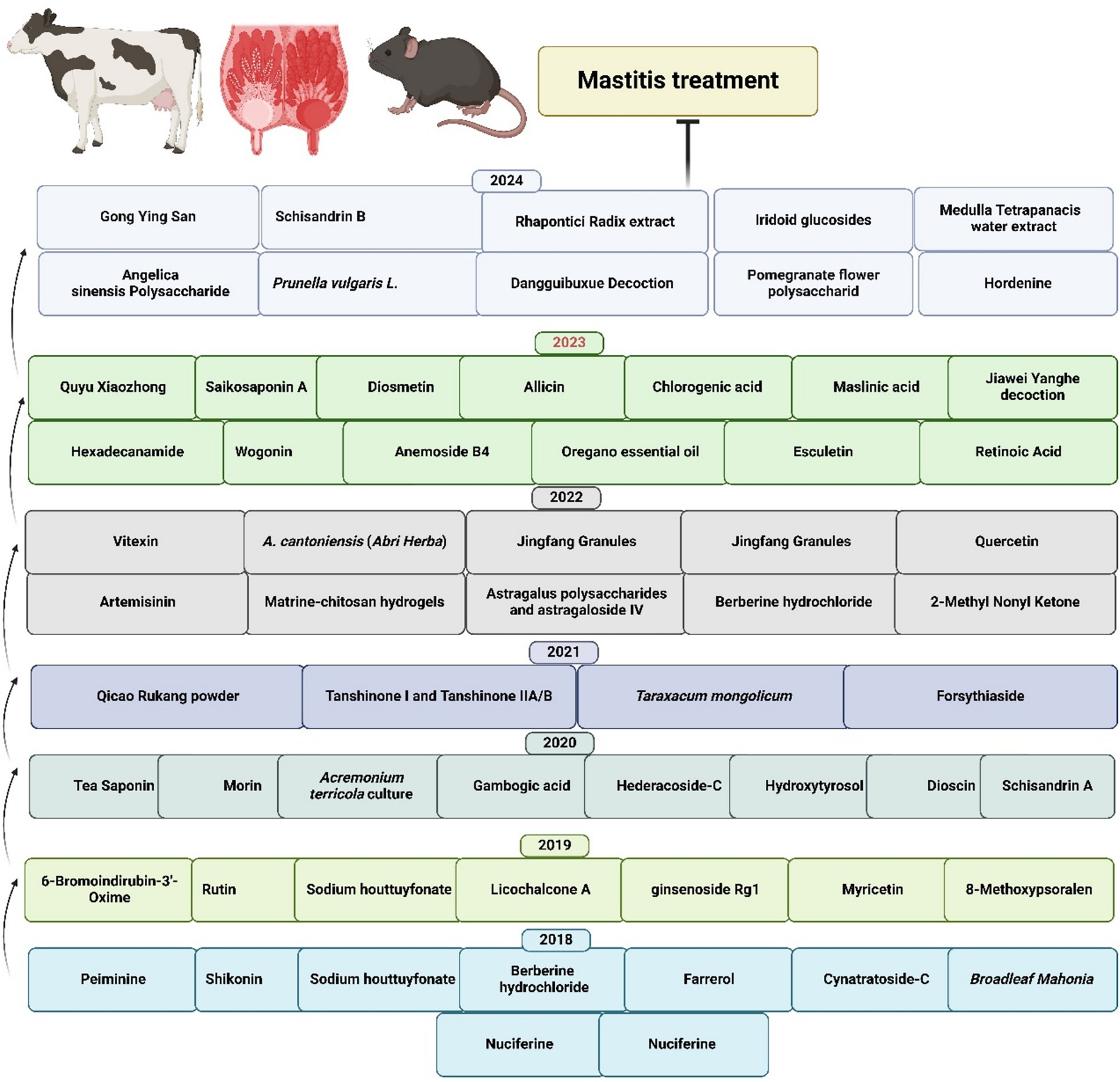
Figure 4. Recent advances in TCM and plant-derived bioactive compounds for mastitis treatment (31, 89, 99–101, 110, 113, 115, 117, 120, 123, 125, 130–178).
While plant-derived bioactive compounds show promising antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects against bovine mastitis pathogens in vitro and in mouse models (128), their use in dairy cattle remains limited due to several inherent barriers in large animal research. Research on Traditional Chinese Medicine and plant-derived compounds for mastitis treatment is still in its early stages, with most trials still in development using mouse models, resulting in insufficient foundational data to support progress to large animal studies. Conducting controlled clinical trials in dairy cattle involves significant economic challenges, requiring much larger sample sizes, longer observation periods, and higher operational costs compared to mouse models, often surpassing available research budgets.
The regulatory framework governing veterinary pharmaceuticals in food-producing animals requires comprehensive safety evaluations, including pharmacokinetic studies, tissue residue analyses, and the establishment of withdrawal periods for milk and meat products, leading to lengthy approval processes that deter initial research investments. The physiological complexity of ruminant digestive systems adds further challenges, as plant-derived compounds undergo extensive ruminal metabolism that can alter bioavailability and therapeutic effectiveness compared to monogastric models. Additionally, dairy industry stakeholders usually prioritize rapid-acting, standardized antimicrobial treatments that work with existing automated milking protocols and quality systems, which creates market resistance to traditional plant-based therapies that need more complex preparation, administration, and monitoring. These economic, regulatory, physiological, developmental, and practical factors collectively explain why the translation of Traditional Chinese Medicine and plant-derived compounds from promising laboratory results to field use in dairy cattle is limited, despite their demonstrated anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory properties in experimental studies (129).
6 Conclusion and future perspective
Based on available literature, we concluded that TCM and plant-derived bioactive compounds present a sustainable and effective alternative to conventional antibiotics for managing mastitis, addressing critical challenges such as antimicrobial resistance, drug residue in milk, and environmental impact. Plant-derived bioactive compounds and TCM have demonstrated efficacy in targeting key inflammatory and immune pathways (e.g., NF-κB, PI3K-AKT, MAPK) and improving milk quality without inducing remedies, which holds significant promise. Therefore, Plant- derived bioactive compounds and TCM require future efforts and concentration to elucidate its molecular mechanisms, standardize formulations, and conduct large-scale clinical trials to validate its efficacy and safety. Integrative approaches that combine plant- derived bioactive compounds and TCM with conventional therapies and advanced technologies, such as omics and artificial intelligence, can enhance therapeutic precision. Collaboration among researchers, policymakers, and farmers is essential to ensure scalability, farmer acceptance, and the establishment of harmonized regulatory frameworks, ultimately promoting plant-derived bioactive compounds and TCM as a mainstream, eco-friendly solution for mastitis control.
Author contributions
XF: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Data curation. AQ: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. MA: Funding acquisition, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. FMA: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. KJA: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. KFA: Funding acquisition, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. MK: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Visualization, Supervision. XJ: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Data curation, Conceptualization, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the Liaocheng Municipal Bureau of Science and Technology, High-talented Foreign Expert Introduction Program (GDWZ202401), and the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through the large research group program under grant number (R.G.P.02/709/46).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Tomanić, D , Samardžija, M , Kladar, N , Pećin, M , Ružić, Z , and Kovačević, Z . Assessment of antibiotic use patterns in bovine mastitis treatment in the dairy sector in Serbia. Reprod Domest Anim. (2023) 58:1756–65. doi: 10.1111/rda.14494
2. Zaatout, N . An overview on mastitis-associated Escherichia Coli: pathogenicity, host immunity and the use of alternative therapies. Microbiol Res. (2022) 256:126960. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2021.126960
3. Khan, MZ , Wang, J , Ma, Y , Chen, T , Ma, M , Ullah, Q, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in immune- and inflammation-associated genes and their association with bovine mastitis resistance/susceptibility. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1082144. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1082144
4. Khan, M , Belhan, S , Cetin, N , Khan, A , Ahmad, I , Ma, Y, et al. Mining for the association of bovine mastitis linked genes to pathological signatures and pathways. Ann Anim Sci. (2021) 22:000010247820210049. doi: 10.2478/aoas-2021-0049
5. Zhang, Z , Chen, Y , Li, X , Wang, X , and Li, H . Detection of antibiotic resistance, virulence gene, and drug resistance gene of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from bovine mastitis. Microbiol Spectr. (2022) 10:e0047122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00471-22
6. Khan, MZ , Huang, B , Kou, X , Chen, Y , Liang, H , Ullah, Q, et al. Enhancing bovine immune, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory responses with vitamins, rumen-protected amino acids, and trace minerals to prevent Periparturient mastitis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1290044. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1290044
7. Khan, MZ , Ma, Y , Xiao, J , Chen, T , Ma, J , Liu, S, et al. Role of selenium and vitamins E and B9 in the alleviation of bovine mastitis during the Periparturient period. Antioxidants. (2022) 11:657. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040657
8. Khan, MZ , Dari, G , Khan, A , and Yu, Y . Genetic polymorphisms of Trappc9 and Cd4 genes and their association with Milk production and mastitis resistance phenotypic traits in Chinese Holstein. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:1008497. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1008497
9. Khan, MZ , Khan, A , Xiao, J , Ma, J , Ma, Y , Chen, T, et al. Overview of research development on the role of Nf-Κb signaling in mastitis. Animals. (2020) 10:625. doi: 10.3390/ani10091625
10. Wang, D , Wei, Y , Shi, L , Khan, MZ , Fan, L , Wang, Y, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation pattern in a mouse model reveals two novel genes associated with Staphylococcus Aureus mastitis. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2020) 33:203–11. doi: 10.5713/ajas.18.0858
11. Khan, MZ , Wang, D , Liu, L , Usman, T , Wen, H , Zhang, R, et al. Significant genetic effects of Jak2 and Dgat1 mutations on milk fat content and mastitis resistance in Holsteins. J Dairy Res. (2019) 86:388–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022029919000682
12. Nelson, VK , Nuli, MV , Ausali, S , Gupta, S , Sanga, V , Mishra, R, et al. Dietary anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial medicinal plants and its compounds in bovine mastitis associated impact on human life. Microb Pathog. (2024) 192:106687. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106687
13. Tomanić, D , Božić, DD , Kladar, N , Samardžija, M , Apić, J , Baljak, J, et al. Clinical evidence on expansion of essential oil-based formulation's pharmacological activity in bovine mastitis treatment: antifungal potential as added value. Antibiotics. (2024) 13:575. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070575
14. Khan, MZ , Li, L , Wang, T , Liu, X , Chen, W , Ma, Q, et al. Bioactive compounds and probiotics mitigate mastitis by targeting Nf-Κb signaling pathway. Biomolecules. (2024) 14:11. doi: 10.3390/biom14081011
15. Khan, MZ , Li, L , Zhan, Y , Binjiang, H , Liu, X , Kou, X, et al. Targeting Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway using bioactive compounds to combat mastitis. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1425901. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1425901
16. Benić, M , Maćešić, N , Cvetnić, L , Habrun, B , Cvetnić, Ž , Turk, R, et al. Bovine mastitis: a persistent and evolving problem requiring novel approaches for its control - a review. Vet Arh. (2018) 88:535–57. doi: 10.24099/vet.arhiv.0116
17. Kovačić, M , Samardžija, M , Đuričić, D , Vince, S , Flegar, Z , Perkov, S, et al. Paraoxonase-1 activity and lipid profile in dairy cows with subclinical and clinical mastitis. J Appl Anim Res. (2018) 47:1–4. doi: 10.1080/09712119.2018.1555090
18. Lamari, I , Mimoune, N , and Khelef, D . Effect of feed additive supplementation on bovine subclinical Mastitisučinak Dodatka Prehrani Na Supklinički mastitis Krava. Vet Stanica. (2021) 52:12. doi: 10.46419/vs.52.4.12
19. Nedić, S , Vakanjac, S , Samardžija, M , and Borozan, S . Paraoxonase 1 in bovine Milk and blood as marker of subclinical mastitis caused by Staphylococcus Aureus. Res Vet Sci. (2019) 125:323–32. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2019.07.016
20. Cvetnic, L , Samardžija, M , Habrun, B , Kompes, G , and Benić, M . Microbiological monitoring of mastitis pathogens in the control of udder health in dairy cows. Slov Vet Res. (2016) 53:131–40.
21. Morales-Ubaldo, AL , Rivero-Perez, N , Valladares-Carranza, B , Velázquez-Ordoñez, V , Delgadillo-Ruiz, L , and Zaragoza-Bastida, A . Bovine mastitis, a worldwide impact disease: prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and viable alternative approaches. Vet Anim Sci. (2023) 21:100306. doi: 10.1016/j.vas.2023.100306
22. Saddam, JM , Rahman, SU , Khan, M , Qadeer, A , and Mahmoud, MH . Genomic diversity and nutritional analysis of multi-drug resistant extended spectrum Β-lactamase producing-Klebsiella pneumoniae genes isolated from mastitic cattle milk in district Peshawar, Pakistan. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e35876. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35876
23. Beyene, T , Hayishe, H , Gizaw, F , Beyi, AF , Abunna, F , Mammo, B, et al. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profile of Staphylococcus in dairy farms, abattoir and humans in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. (2017) 10:171. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-2487-y
24. Kalmus, P , Aasmäe, B , Kärssin, A , Orro, T , and Kask, K . Udder pathogens and their resistance to antimicrobial agents in dairy cows in Estonia. Acta Vet Scand. (2011) 53:4. doi: 10.1186/1751-0147-53-4
25. Das, A , Guha, C , Biswas, U , Jana, PS , Chatterjee, A , and Samanta, I . Detection of emerging antibiotic resistance in Bacteria isolated from subclinical mastitis in cattle in West Bengal. Vet World. (2017) 10:517–20. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2017.517-520
26. León-Galván, MF , Barboza-Corona, JE , Lechuga-Arana, AA , Valencia-Posadas, M , Aguayo, DD , Cedillo-Pelaez, C, et al. Molecular detection and sensitivity to antibiotics and Bacteriocins of pathogens isolated from bovine mastitis in family dairy herds of Central Mexico. Biomed Res Int. (2015) 2015:615153. doi: 10.1155/2015/615153
27. Su, Y , Yu, CY , Tsai, Y , Wang, SH , Lee, C , and Chu, C . Fluoroquinolone-resistant and extended-Spectrum Β-lactamase-producing Escherichia Coli from the Milk of cows with clinical mastitis in southern Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. (2016) 49:892–901. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2014.10.003
28. Vélez, JR , Cameron, M , Rodríguez-Lecompte, JC , Xia, F , Heider, LC , Saab, M, et al. Whole-genome sequence analysis of antimicrobial resistance genes in Streptococcus Uberis and Streptococcus Dysgalactiae isolates from Canadian dairy herds. Front Vet Sci. (2017) 4:63. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2017.00063
29. Li, X , Xu, C , Liang, B , Kastelic, JP , Han, B , Tong, X, et al. Alternatives to antibiotics for treatment of mastitis in dairy cows. Front Vet Sci. (2023) 10:10. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1160350
30. Lopes, TS , Fontoura, PS , Oliveira, A , Rizzo, FA , Silveira, S , and Streck, AF . Use of plant extracts and essential oils in the control of bovine mastitis. Res Vet Sci. (2020) 131:186–93. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2020.04.025
31. Kwok, CTK , Hu, Y , Tsoi, B , Wong, F , Hau, PT , Tam, EWT, et al. Medulla Tetrapanacis water extract ameliorates mastitis by suppressing bacterial internalization and inflammation via mapks signaling in vitro and in vivo. Food Front. (2024) 6:500–15. doi: 10.1002/fft2.476
32. Hua, C , Li, F , Shi, Y , Xu, Y , Zhu, M , Wang, Y, et al. Long-term outcomes of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of granulomatous lobular mastitis: a two-year follow-up study on recurrence and new occurrence rates with analysis of risk factors. J Inflamm Res. (2024) 17:7389–99. doi: 10.2147/jir.S485589
33. Xiao, J , Khan, MZ , Ma, Y , Alugongo, GM , Ma, J , Chen, T, et al. The antioxidant properties of selenium and vitamin E; their role in periparturient dairy cattle health regulation. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:555. doi: 10.3390/antiox10101555
34. Khan, MZ , Khan, A , Xiao, J , Dou, J , Liu, L , and Yu, Y . Overview of folic acid supplementation alone or in combination with vitamin B12 in dairy cattle during Periparturient period. Meta. (2020) 10:263. doi: 10.3390/metabo10060263
35. Khan, MZ , Zhang, Z , Liu, L , Wang, D , Mi, S , Liu, X, et al. Folic acid supplementation regulates key immunity-associated genes and pathways during the Periparturient period in dairy cows. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2020) 33:1507–19. doi: 10.5713/ajas.18.0852
36. Kovačević, Z , Mihajlović, J , Mugoša, S , Horvat, O , Tomanić, D , Kladar, N, et al. Pharmacoeconomic analysis of the different therapeutic approaches in control of bovine mastitis: Phytotherapy and antimicrobial treatment. Antibiotics. (2023) 12:11. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010011
37. Ashraf, MV , Pant, S , Khan, MAH , Shah, AA , Siddiqui, S , Jeridi, M, et al. Phytochemicals as antimicrobials: prospecting Himalayan medicinal plants as source of alternate medicine to combat antimicrobial resistance. Pharmaceuticals. (2023) 16:881. doi: 10.3390/ph16060881
38. Ma, LWJ , Ye, M , Wang, B , Yin, Y , Zhou, Y , Zhong, Y, et al. Intervention study of Yanghe decoction on plasma cell mastitis based on mammary microecology and metabolomics investigation. Classic Chinese Med Prescript. (2024) 56:16–24. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2024.23.003
39. Wang, J , Cheng, C , Gao, Y , Li, Y , Zhang, X , Yao, D, et al. Danggui Buxue decoction alleviates inflammation and oxidative stress in mice with Escherichia Coli-induced mastitis. Vet Sci. (2025) 12:227. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12030227
40. Feng, J , Chen, Z , Sun, J , Shao, S , Xie, L , Qu, W, et al. Efficacy of red ointment in wound cavity repair following non-puerperal mastitis debridement. Hereditas. (2025) 162:82. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00451-2
41. Lou, Y , Xu, H , Lu, Z , Wang, B , and Liu, X . Immune regulation: a new strategy for traditional Chinese medicine-based treatment of granulomatous lobular mastitis. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1494155. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1494155
42. Zhang, S , Ren, J , Liu, B , Wang, M , Huang, L , Mao, Y, et al. Proteome-wide mendelian randomization study of plasma proteins associated with mastitis and prediction of potential candidates from herbal medicine. Clinic Trad Med Pharmacol. (2025) 6:200205. doi: 10.1016/j.ctmp.2025.200205
43. Meng, T , Chu, ML , Wang, B , Ye, MN , Cheng, YQ , and Chen, HF . Granulomatous lobular mastitis treated by a combined internal and external treatment of traditional Chinese medicine: a case report. World J Clin Cases. (2024) 12:4748–54. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4748
44. Fang, YW , Chen, SF , Wang, ML , and Wang, MH . Effects of traditional Chinese medicine-assisted intervention on improving postpartum lactation: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e27154. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27154
45. Wang, X , Lai, J , Xu, F , and Liu, M . Network pharmacology and molecular docking: exploring the mechanism of peppermint in mastitis prevention and treatment in dairy cows. Vet Sci. (2025) 12:129. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12020129
46. de Aguiar, SC , Cottica, SM , dos Santos, ST , da Fonseca, JM , da Silva Leite, L , and Silva, ML . Antioxidant activity, phenolic acid, and flavonoid composition of an antiseptic ointment based on Aloe and green propolis and its potential for preventing mastitis in dairy cows. Vet Sci. (2025) 12:248. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12030248
47. Li, K , Ran, X , Han, J , Ding, H , Wang, X , Li, Y, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide alleviates mastitis disrupted by Staphylococcus Aureus infection by regulating gut microbiota and Scfas metabolism. Int J Biol Macromol. (2025) 286:138422. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.138422
48. Pang, Y , Ke, Y , Amona, FM , Chen, X , Liu, Z , Chen, J, et al. Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside mitigates Staphylococcus Aureus-induced mastitis by suppressing inflammatory responses and Ferroptosis mediated by Sesn2/Nrf2. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 159:114868. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114868
49. Silva, C , Vidal, CS , Filho, SMA , Agatão, IM , Berbert, LC , Salles, JB, et al. Rapid bactericidal activity of Punica granatum L. peel extract: a natural alternative for mastitis prevention in dairy cattle. Molecules. (2025) 30:387. doi: 10.3390/molecules30112387
50. Moreira, AJS , de Araújo Domingues, KC , Camargo, KDV , Aulik, NA , Oyama, LB , Huws, SA, et al. Synergistic antimicrobial activity of Lynronne-1 and Edta against bovine mastitis pathogens. J Antimicrob Chemother. (2025) 80:427–38. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkae425
51. Ndahetuye, JB , Persson, Y , Nyman, AK , Tukei, M , Ongol, MP , and Båge, R . Aetiology and prevalence of subclinical mastitis in dairy herds in Peri-urban areas of Kigali in Rwanda. Trop Anim Health Prod. (2019) 51:2037–44. doi: 10.1007/s11250-019-01905-2
52. Gondkar, P , Kumar, H , and Patel, K . Incidence and risk factors associated with human mastitis. Health Sci Rev. (2024) 12:100191. doi: 10.1016/j.hsr.2024.100191
53. Khan, MZ , Khan, A , Xiao, J , Ma, Y , Ma, J , Gao, J, et al. Role of the Jak-stat pathway in bovine mastitis and milk production. Animals. (2020) 10:107. doi: 10.3390/ani10112107
54. Yang, J , Tang, Y , Liu, X , Zhang, J , Zahoor Khan, M , Mi, S, et al. Characterization of peripheral white blood cells transcriptome to unravel the regulatory signatures of bovine subclinical mastitis resistance. Front Genet. (2022) 13:949850. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.949850
55. S, M , Khan, M , Jamal, M , Rahman, SU , Qadeer, A , Khan, I, et al. Nutritional analysis and characterization of carbapenemase producing-Klebsiella pneumoniae resistant genes associated with bovine mastitis infected cow's milk. PLoS One. (2023) 18:e0293477. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293477
56. Đuričić, D , Sukalić, T , Marković, F , Kočila, P , Žura Žaja, I , Menčik, S, et al. Effects of dietary Vibroactivated Clinoptilolite supplementation on the Intramammary microbiological findings in dairy cows. Animals. (2020) 10:202. doi: 10.3390/ani10020202
57. Gantner, V , Jozef, I , Samardžija, M , Steiner, Z , Gantner, R , Solić, D, et al. The variability in the prevalence of subclinical and clinical mastitis and its impact on milk yield of Holstein and Simmental cows as a result of parity. Vet Arh. (2024) 94:269–84. doi: 10.24099/vet.arhiv.2518
58. Tomanić, D , Samardžija, M , Stancic, I , Kladar, N , Mačešić, N , and Kovacevic, Z . Mastitis challenges in Serbian dairy farming: a study on somatic cell counts and pathogen distribution. Mljekarstvo. (2024) 74:239–48. doi: 10.15567/mljekarstvo.2024.0307
59. Klaas, IC , and Zadoks, RN . An update on environmental mastitis: challenging perceptions. Transbound Emerg Dis. (2018) 65:166–85. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12704
60. Cheng, WN , and Han, SG . Bovine mastitis: risk factors, therapeutic strategies, and alternative treatments - a review. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2020) 33:1699–713. doi: 10.5713/ajas.20.0156
61. Turner, SA , and Butler, G . The Candida pathogenic species complex. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. (2014) 4:a019778. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a019778
62. Ricchi, M , De Cicco, C , Buzzini, P , Cammi, G , Arrigoni, N , Cammi, M, et al. First outbreak of bovine mastitis caused by Prototheca Blaschkeae. Vet Microbiol. (2013) 162:997–9. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.11.003
63. Wellenberg, GJ , van der Poel, WH , and Van Oirschot, JT . Viral infections and bovine mastitis: a review. Vet Microbiol. (2002) 88:27–45. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(02)00098-6
64. Ataseven, VS , Ambarcıoğlu, P , and Doğan, F . Serum and Milk levels of antibodies to bovine viral Diarrhoea virus, bovine Herpesvirus-1 and -4, and circulation of different bovine Herpesvirus-4 genotypes in dairy cattle with clinical mastitis. J Vet Res. (2023) 67:33–40. doi: 10.2478/jvetres-2023-0010
65. Kálmán, D , Jánosi, S , and Egyed, L . Role of bovine herpesvirus 4 in bacterial bovine mastitis. Microb Pathog. (2004) 37:125–9. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2004.06.011
66. Izumi, Y , Tsuduku, S , Murakami, K , Tsuboi, T , Konishi, M , Haritani, M, et al. Characterization of bovine herpesvirus type 4 isolated from cattle with mastitis and subclinical infection by the virus among cattle. J Vet Med Sci. (2006) 68:189–93. doi: 10.1292/jvms.68.189
67. Çomakli, S , and Özdemir, S . Comparative evaluation of the immune responses in cattle mammary tissues naturally infected with bovine parainfluenza virus type 3 and bovine Alphaherpesvirus-1. Pathogens. (2019) 8:26. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8010026
68. Gorden, PJ , Magstadt, DR , Baker, AL , Arruda, BL , Bell, TM , and Nelli, RK . Viral mastitis associated with influenza a in dairy cattle. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. (2025) 41:271–83. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2025.02.010
69. Lyons, NA , Alexander, N , Stӓrk, KD , Dulu, TD , Rushton, J , and Fine, PE . Impact of foot-and-mouth disease on mastitis and culling on a large-scale dairy farm in Kenya. Vet Res. (2015) 46:41. doi: 10.1186/s13567-015-0173-4
70. Cuesta, LM , Liron, JP , Nieto Farias, MV , Dolcini, GL , and Ceriani, MC . Effect of bovine leukemia virus (Blv) infection on bovine mammary epithelial cells Rna-Seq transcriptome profile. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0234939. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234939
71. Watanabe, A , Maeda, Y , Murakami, H , Miyoshi, S , Miura, M , Murao, K, et al. Evaluation of the therapeutic effect of levamisole on subclinical mastitis in bovine leukemia virus-infected cows classified by Proviral load. Animals. (2025) 15:145. doi: 10.3390/ani15142145
72. Nakada, S , Fujimoto, Y , Kohara, J , and Makita, K . Economic losses associated with mastitis due to bovine leukemia virus infection. J Dairy Sci. (2023) 106:576–88. doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-21722
73. Ashraf, A , and Imran, M . Causes, types, etiological agents, prevalence, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, effects on human health and future aspects of bovine mastitis. Anim Health Res Rev. (2020) 21:36–49. doi: 10.1017/s1466252319000094
74. Lim, DH , Mayakrishnan, V , Lee, HJ , Ki, KS , Kim, TI , and Kim, Y . A comparative study on Milk composition of Jersey and Holstein dairy cows during the early lactation. J Anim Sci Technol. (2020) 62:565–76. doi: 10.5187/jast.2020.62.4.565
75. Fodor, I , Gábor, G , Lang, Z , Abonyi-Tóth, Z , and Ózsvári, L . Relationship between reproductive management practices and fertility in primiparous and multiparous dairy cows. Can J Vet Res. (2019) 83:218–27.
76. Thompson-Crispi, K , Atalla, H , Miglior, F , and Mallard, BA . Bovine mastitis. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:493. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00493
77. Vlasova, AN , and Saif, LJ . Bovine immunology: implications for dairy cattle. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:643206. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.643206
78. Oz, HS . Nutrients, infectious and inflammatory diseases. Nutrients. (2017) 9:1085. doi: 10.3390/nu9101085
79. Libera, K , Konieczny, K , Witkowska, K , Żurek, K , Szumacher-Strabel, M , Cieslak, A, et al. The association between selected dietary minerals and mastitis in dairy cows-a review. Animals. (2021) 11:330. doi: 10.3390/ani11082330
80. Tomanić, D , Samardžija, M , and Kovačević, Z . Alternatives to antimicrobial treatment in bovine mastitis therapy: a review. Antibiotics. (2023) 12:683. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12040683
81. Kovačević, Z , Samardžija, M , Horvat, O , Tomanić, D , Radinović, M , Bijelić, K, et al. Is there a relationship between antimicrobial use and antibiotic resistance of the most common mastitis pathogens in dairy cows? Antibiotics. (2022) 12:3. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010003
82. Mimoune, N , Saidi, R , Benadjel, O , Khelef, D , and Kaidi, R . Alternative Treatment of Bovine Mastitisalternativno Liječenje Mastitisa Krava. Vet Stanica. (2021) 52:9. doi: 10.46419/vs.52.6.9
83. Derakhshani, H , Plaizier, JC , De Buck, J , Barkema, HW , and Khafipour, E . Composition of the Teat Canal and Intramammary microbiota of dairy cows subjected to antimicrobial dry cow therapy and internal teat sealant. J Dairy Sci. (2018) 101:10191–205. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-14858
84. Deng, J , Liu, K , Wang, K , Yang, B , Xu, H , Wang, J, et al. The prevalence of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus associated with bovine mastitis in China and its antimicrobial resistance rate: a Meta-analysis. J Dairy Res. (2023) 90:158–63. doi: 10.1017/s0022029923000365
85. Ajose, DJ , Oluwarinde, BO , Abolarinwa, TO , Fri, J , Montso, KP , Fayemi, OE, et al. Combating bovine mastitis in the dairy sector in an era of antimicrobial resistance: ethno-veterinary medicinal option as a viable alternative approach. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:800322. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.800322
86. Baquero, F . The 2010 Garrod lecture: the dimensions of evolution in antibiotic resistance: ex Unibus Plurum et ex pluribus Unum. J Antimicrob Chemother. (2011) 66:1659–72. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr214
87. Cvetnić, L , Samardžija, M , Duvnjak, S , Habrun, B , Cvetnić, M , Jaki Tkalec, V, et al. Multi locus sequence typing and Spa typing of Staphylococcus Aureus isolated from the Milk of cows with subclinical mastitis in Croatia. Microorganisms. (2021) 9:725. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9040725
88. Munita, JM , and Arias, CA . Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol Spectr. (2016) 4:16. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.VMBF-0016-2015
89. Wang, J , Gao, Y , Cheng, C , Li, Y , Zhang, X , Yao, D, et al. Dangguibuxue decoction protects against lipopolysaccharides-induced mastitis in bovine mammary epithelial cells in vitro. J Anim Sci Technol. (2024). doi: 10.5187/jast.2024.e63
90. Nawaz, S , Wajid, A , Nawaz, A , Ullah, H , Arbab, S , Khan, S, et al. Calotropis procera: a review of molecular mechanisms, bioavailability, and potential anticancer property. Biomed Eng Commun. (2024) 3:17–22. doi: 10.53388/BMEC2024021
91. Babar, M , Buzdar, JA , Zaheer, A , Nizam-ud-din, M , Mustafa, G , Khan, BA, et al. Carotenoids as a nutraceutical and health-promoting dietary supplement for human and animals: an updated review. Tradit Med Res. (2025) 10:13–8. doi: 10.53388/TMR20240831001
92. Yuan, J , Cheng, X , Wang, B , and Wang, Z . Correlation between granulomatous mastitis and autoimmune function and the immune-regulating role of traditional Chinese medicine. Chinese Med Nat Prod. (2024) 04:e88–92. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1790539
93. Zhang, J , Xu, J , Zhang, J , and Ren, Y . Chinese herbal compound combined with Western medicine therapy in the treatment of plasma cell mastitis: a protocol for systematic review and Meta-analysis. Medicine. (2020) 99:e22858. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022858
94. Zhang, MPD , Meng, F , Shi, G , and Li, J . Alterations in signaling pathways and therapeutic strategies of traditional Chinese medicine in granulomatous lobular mastitis. J Inflamm Res. (2025) 18:9185–97. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S535195
95. Li, H , Li, B , Chen, H , Liu, X , Wang, H , and Zhang, G . Application of microwave ablation combined with Chai Hu Qing Gan Tang in the treatment of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Breast J. (2025) 2025:2731494. doi: 10.1155/tbj/2731494
96. Ma, F , Xiao, Y , Qian, L , and Zhang, S . Intervention study of Yanghe decoction on plasma cell mastitis based on mammary microecology and metabolomics investigation. J Pharm Biomed Anal. (2025) 262:116870. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2025.116870
97. Zhao, Z , Zuo, XM , Wang, TS , Liu, JL , Yang, ZR , and Gao, S . Effect of Tuoli tounong decoction on Caspase-1/Gsdmd signaling pathway in granulomatous lobular mastitis. Global Traditional Chin Med. (2022) 15:1537–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1749.2022.09.003
98. Ziwei, DQS , and Xiaofei, L . Mechanism study of Yiqi Heying traditional Chinese medicine in regulating Tnf-Α-induced immune status and Nfκb signaling pathway expression in granulomatous lobular mastitis. Lishizhen Med Mater Res. (2024) 35:2614–8.
99. Gao, S , Tang, L , Ma, J , Wang, K , Yao, H , Tong, J, et al. Evaluation of the mechanism of Gong Ying san activity on dairy cows mastitis by network pharmacology and metabolomics analysis. PLoS One. (2024) 19:e0299234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299234
100. Li, S , Li, X , Yang, T , Pan, L , Xu, Y , Wang, L, et al. Jingfang granules alleviate Lps-induced mastitis by inhibiting inflammation, protecting the blood-milk barrier structure and regulating cell apoptosis. Pharmacol Res. (2022) 2:100072. doi: 10.1016/j.prmcm.2022.100072
101. Imam, BH , Oladejo, AO , Wu, X , Yang, J , Ma, X , Shen, W, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial potential of Qicao Rukang powder in bovine subclinical mastitis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2021/2148186
102. Shen, L , Qian, B , Shangkui, L , You, L , Zhang, Y , Shen, Y, et al. Effect of a natural plant ingredient — Pulsatilla saponin B4 on clinical mastitis and serum inflammatory indices in dairy cows (2020). doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-48799/v1,
103. Ryan, EL , Klopfenstein, JJ , and Kutzler, MA . Intramammary antibiotics with complementary acupuncture decreases Milk serum N-acetyl-Beta-D-Glucosaminidase concentrations in dairy cattle with subclinical mastitis. Reprod Domest Anim. (2020) 55:1747–55. doi: 10.1111/rda.13835
104. Liu, X , Qiu, F , Hou, S , Guo, J , and Liu, L . In vitro antibacterial activities of the Tibetan herbal medicines against the Staphylococcus isolated from mastitis of Guanzhong dairy goat (2021). doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-655812/v1,
105. Zhu, S , and Li, L . The initial efficacy of comprehensive treatment of external treatment of traditional Chinese medicine on acute mastitis during lactation and its influence on patients' symptoms. Altern Ther Health Med. (2024) 30:31–7.
106. Zhao, C , Jiang, P , He, Z , Yuan, X , Guo, J , Li, Y, et al. Dimethyl Itaconate protects against Lippolysacchride-induced mastitis in mice by activating Mapks and Nrf2 and inhibiting Nf-Κb signaling pathways. Microb Pathog. (2019) 133:103541. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.05.024
107. Jiang, K-f , Zhao, G , Deng, G-z , Wu, H-c , Yin, N-n , Chen, X-y, et al. Polydatin ameliorates Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in mice via inhibiting TLR2-mediated activation of the P38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2017) 38:211–22. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.123
108. Liu, Y , Sun, Y , Zhou, Y , Tang, X , Wang, K , Ren, Y, et al. Sinomenine hydrochloride inhibits the progression of plasma cell mastitis by regulating Il-6/Jak2/Stat3 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 81:106025. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106025
109. Sserunkuma, P , McGaw, L , Nsahlai, I , and Van Staden, J . Selected southern African medicinal plants with low cytotoxicity and good activity against bovine mastitis pathogens. S Afr J Bot. (2017) 111:242–7.
110. Yang, C , Liu, P , Wang, S , Zhao, G , Zhang, T , Guo, S, et al. Shikonin exerts anti-inflammatory effects in Lps-induced mastitis by inhibiting Nf-Κb signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2018) 505:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.198
111. Fanfan, LYX , and Xiaoxu, W . Therapeutic effect of Shikonin on experimental rat granulomatous lobular mastitis by regulating Nrf2/ho-1 signaling pathway. Chin J Clin Anat. (2024) 42:26–32.
112. Arbab, S , Ullah, H , Bano, I , Li, K , Ul Hassan, I , Wang, W, et al. Evaluation of in vitro antibacterial effect of essential oil and some herbal plant extract used against mastitis pathogens. Vet Med Sci. (2022) 8:2655–61. doi: 10.1002/vms3.959
113. Liu, P , Yang, C , Lin, S , Zhao, G , Zhang, T , Guo, S, et al. Sodium Houttuyfonate inhibits Lps-induced mastitis in mice via the Nf-Κb Signalling pathway. Mol Med Rep. (2019) 19:2279–86. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9846
114. Zhang, D , Jin, G , Liu, W , Dou, M , Wang, X , Shi, W, et al. Salvia Miltiorrhiza polysaccharides ameliorates Staphylococcus Aureus-induced mastitis in rats by inhibiting activation of the Nf-Κb and Mapk signaling pathways. BMC Vet Res. (2022) 18:201. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03312-6
115. Cao, L , Wang, T , Mi, X , Ji, P , Zhao, X , and Zhang, Y . Exploring the action mechanism of the active ingredient of quercetin in Ligustrum Lucidum on the mouse mastitis model based on network pharmacology and molecular biology validation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2022) 2022:4236222. doi: 10.1155/2022/4236222
116. Guo, W , Qiu, M , Pu, Z , Long, N , Yang, M , Ren, K, et al. Geraniol-a potential alternative to antibiotics for bovine mastitis treatment without disturbing the host microbial community or causing drug residues and resistance. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1126409. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1126409
117. Ge, BJ , Zhao, P , Li, HT , Sang, R , Wang, M , Zhou, HY, et al. Taraxacum Mongolicum protects against Staphylococcus Aureus-infected mastitis by exerting anti-inflammatory role via Tlr2-Nf-Κb/Mapks pathways in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. (2021) 268:113595. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113595
118. Gao, Y , Hao, Z , Zhang, H , Liu, J , Zhou, G , Wen, H, et al. Forsythiaside a attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced mouse mastitis by activating autophagy and regulating gut microbiota and metabolism. Chem Biol Interact. (2024) 396:111044. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111044
119. Zhang, X , Zhang, H , Gao, Y , Hao, Z , Liu, J , Zhou, G, et al. Forsythoside a regulates autophagy and apoptosis through the Ampk/Mtor/Ulk1 pathway and alleviates inflammatory damage in mac-T cells. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 118:110053. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110053
120. Tong, C , Chen, T , Chen, Z , Wang, H , Wang, X , Liu, F, et al. Forsythiaside a plays an anti-inflammatory role in Lps-induced mastitis in a mouse model by modulating the Mapk and Nf-Κb signaling pathways. Res Vet Sci. (2021) 136:390–5. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2021.03.020
121. Zhang, J , Zhang, Y , Huang, H , Zhang, H , Lu, W , Fu, G, et al. Forsythoside a Inhibited S. aureus stimulated inflammatory response in primary bovine mammary epithelial cells. Microb Pathog. (2018) 116:158–63. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.01.002
122. Liu, J , Gao, Y , Zhang, H , Hao, Z , Zhou, G , Wen, H, et al. Forsythiaside a attenuates mastitis via Pink1/Parkin-mediated Mitophagy. Phytomedicine. (2024) 125:155358. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155358
123. Yang, L , Zhou, G , Liu, J , Song, J , Zhang, Z , Huang, Q, et al. Tanshinone I and Tanshinone Iia/B attenuate Lps-induced mastitis via regulating the Nf-Κb. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 137:111353. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111353
124. Ma, Q , Wei, Y , Meng, Z , Chen, Y , and Zhao, G . Effects of water extract from Artemisia Argyi leaves on Lps-induced mastitis in mice. Animals. (2022) 12:907. doi: 10.3390/ani12070907
125. Wang, Z , Wang, N , Liu, X , Wang, Q , Xu, B , Liu, P, et al. Broadleaf Mahonia attenuates granulomatous lobular mastitis-associated inflammation by inhibiting ccl-5 expression in macrophages. Int J Mol Med. (2018) 41:340–52. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3246
126. Zhou, D , Sun, L , Li, J , and Yang, Y . Schisandrin B inhibits inflammation and ferroptosis in S.Aureus-induced mastitis through regulating Sirt1/P53/Slc7a11 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 137:112430. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112430
127. Shi, M , and Ning, Z . In vivo and in vitro investigations of Schisandrin B against angiotensin ii induced Ferroptosis and atrial fibrosis by regulation of the Sirt1 pathway. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:6200. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89895-0
128. Ananda Baskaran, S , Kazmer, GW , Hinckley, L , Andrew, SM , and Venkitanarayanan, K . Antibacterial effect of plant-derived antimicrobials on major bacterial mastitis pathogens in vitro. J Dairy Sci. (2009) 92:1423–9. doi: 10.3168/jds.2008-1384
129. Siddiqui, SA , Bahmid, NA , Taha, A , Abdel-Moneim, AE , Shehata, AM , Tan, C, et al. Bioactive-loaded nanodelivery systems for the feed and drugs of livestock; purposes, techniques and applications. Adv Colloid Interf Sci. (2022) 308:102772. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2022.102772
130. Luo, H , Li, Y , Xie, J , Xu, C , Zhang, Z , Li, M, et al. Extract on alleviating lipopolysaccharide-induced acute mastitis in protecting the blood-Milk barrier and reducing inflammation. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 328:117998. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117998
131. Ran, X , Li, Y , Guo, W , Li, K , Guo, W , Wang, X, et al. Angelica Sinensis polysaccharide alleviates Staphylococcus Aureus-induced mastitis by regulating the intestinal Flora and gut metabolites. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:24504–17. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c06094
132. Xie, Y , Li, X , Xu, D , He, D , Wang, J , Bi, J, et al. Hordenine alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress, modulating intestinal microbiota, and preserving the blood–milk barrier. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:21503–19. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c02867
133. Zhang, Y , and Xu, P . Iridoid glucosides against Staphylococcus aureus infection and inhibit inflammation on bovine mammary epithelial cells. Thai J Vet Med. (2024) 54:1–10. doi: 10.56808/2985-1130.3729
134. Lv, X , Xie, Z , Wang, H , Lu, G , Li, M , Chen, D, et al. In vivo and in vitro anti-inflammation of Rhapontici Radix extract on mastitis via Tmem59 and Gpr161. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 333:118462. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118462
135. Li, J , Yin, W , Liang, Y , Yang, Z , Li, L , Mai, Z, et al. Pomegranate flower polysaccharide improves mastitis in mice by regulating intestinal Flora and Restoring the blood-Milk barrier. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1427355. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1427355
136. Wang, M , and Jin, L . Quyu xiaozhong recipe exerts anti-inflammatory effect in acute mastitis by inhibiting Tlr4/Nf-Κb signal pathway. Trop J Pharm Res. (2023) 22:981–6. doi: 10.4314/tjpr.v22i5.7
137. Zhao, L , Jin, L , and Yang, B . Saikosaponin a alleviates Staphylococcus Aureus-induced mastitis in mice by inhibiting Ferroptosis via Sirt1/Nrf2 pathway. J Cell Mol Med. (2023) 27:3443–50. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17914
138. Zhao, L , Jin, L , and Yang, B . Diosmetin alleviates S. aureus-induced mastitis by inhibiting Sirt1/Gpx4 mediated ferroptosis. Life Sci. (2023) 331:122060. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122060
139. Che, H-Y , Zhou, C-H , Lyu, C-C , Meng, Y , He, Y-T , Wang, H-Q, et al. Allicin alleviated Lps-induced mastitis via the Tlr4/Nf-Κb signaling pathway in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:3805. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043805
140. Feng, S , Zhang, Y , Fu, S , Li, Z , Zhang, J , Xu, Y, et al. Application of Chlorogenic acid as a substitute for antibiotics in multidrug-resistant Escherichia Coli-induced mastitis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 114:109536. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109536
141. Xu, P , Xu, X , Fotina, H , and Fotina, T . Anti-inflammatory effects of Chlorogenic acid from Taraxacum Officinale on Lta-stimulated bovine mammary epithelial cells via the Tlr2/Nf-Κb pathway. PLoS One. (2023) 18:e0282343. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282343
142. Zhao, J , Xu, L , Lv, L , Wang, L , Wang, X , Liang, C, et al. Network pharmacology and in vivo and in vitro experiments to determine the mechanism behind the effects of Jiawei Yanghe decoction via Tlr4/Myd88/Nf-Κb against mastitis. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e21219. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21219
143. Li, K , Ran, X , Zeng, Y , Li, S , Hu, G , Wang, X, et al. Maslinic acid alleviates Lps-induced mice mastitis by inhibiting inflammatory response, maintaining the integrity of the blood-Milk barrier and regulating intestinal Flora. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 122:110551. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110551
144. Bao, L , Sun, H , Zhao, Y , Feng, L , Wu, K , Shang, S, et al. Hexadecanamide alleviates Staphylococcus Aureus-induced mastitis in mice by inhibiting inflammatory responses and restoring blood-Milk barrier integrity. PLoS Pathog. (2023) 19:e1011764. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011764
145. He, X , Wang, J , Sun, L , Ma, W , Li, M , Yu, S, et al. Wogonin attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress in lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis by inhibiting Akt/Nf-Κb pathway and activating the Nrf2/ho-1 signaling. Cell Stress Chaperones. (2023) 28:989–99. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01391-4
146. Shen, L , Shen, Y , Zhang, Y , Cao, S , Yu, S , Zong, X, et al. Effects of Anemoside B4 on plasma metabolites in cows with clinical mastitis. Vet Sci. (2023) 10:437. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10070437
147. Cao, G , Liu, J , Liu, H , Chen, X , Yu, N , Li, X, et al. Integration of network pharmacology and molecular docking to analyse the mechanism of action of oregano essential oil in the treatment of bovine mastitis. Vet Sci. (2023) 10:350. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10050350
148. Zhou, G , Zhang, W , Wen, H , Su, Q , Hao, Z , Liu, J, et al. Esculetin improves murine mastitis induced by Streptococcus isolated from bovine mammary glands by inhibiting Nf-Κb and Mapk signaling pathways. Microb Pathog. (2023) 185:106393. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106393
149. Wu, K , Shang, S , Bao, L , Zhao, Y , Guan, Z , Xu, J, et al. Retinoic acid ameliorates low-grade Endotoxemia-induced mastitis by limiting inflammatory responses in mice. Microb Pathog. (2023) 185:106426. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106426
150. Yang, Y , Ran, X , Wang, H , Chen, Y , Hou, S , Yang, Z, et al. Evodiamine relieve Lps-induced mastitis by inhibiting Akt/Nf-Κb P65 and Mapk signaling pathways. Inflammation. (2022) 45:129–42. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01533-9
151. Li, Z , Hu, J , Wang, X , Du, Y , Yin, J , Gao, J, et al. Effects of artemisinin on Escherichia Coli–induced mastitis in bovine mammary epithelial cells and mice. Vet Sci. (2022) 9:381. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9080381
152. Gong, Q , Li, Y , Ma, H , Guo, W , Kan, X , Xu, D, et al. Peiminine protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis by inhibiting the Akt/Nf-Κb, Erk1/2 and P38 signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:2637. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092637
153. Wang, X , Feng, S , Ding, N , He, Y , Li, C , Li, M, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Berberine hydrochloride in an Lps-induced murine model of mastitis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2018) 2018:5164314. doi: 10.1155/2018/5164314
154. Lyu, C-C , Ji, X-Y , Che, H-Y , Meng, Y , Wu, H-Y , Zhang, J-B, et al. Cga alleviates Lps-induced inflammation and Milk fat reduction in Bmecs through the Nf-Κb signaling pathway. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e25004. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25004
155. Chen, Y , Yang, J , Huang, Z , Yin, B , Umar, T , Yang, C, et al. Vitexin mitigates Staphylococcus Aureus-induced mastitis via regulation of Ros/Er stress/Nf-Κb/Mapk pathway. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:7977433. doi: 10.1155/2022/7977433
156. Sun, W-J , Wu, E-Y , Zhang, G-Y , Xu, B-C , Chen, X-G , Hao, K-Y, et al. Total flavonoids of Abrus Cantoniensis inhibit Cd14/Tlr4/Nf-Κb/Mapk pathway expression and improve gut microbiota disorders to reduce lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis in mice. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:985529. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.985529
157. Zhang, H , Wang, Z , Yao, H , Jiang, L , and Tong, J . Intramammary infusion of Matrine-chitosan hydrogels for treating subclinical bovine mastitis—effects on Milk microbiome and metabolites. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:950231. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.950231
158. Tong, J , Hou, X , Cui, D , Chen, W , Yao, H , Xiong, B, et al. A Berberine hydrochloride-Carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel protects against Staphylococcus Aureus infection in a rat mastitis model. Carbohydr Polym. (2022) 278:118910. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118910
159. Fan, J , Jia, F , Liu, Y , and Zhou, X . Astragalus polysaccharides and Astragaloside iv alleviate inflammation in bovine mammary epithelial cells by regulating Wnt/Β-catenin signaling pathway. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0271598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271598
160. Wang, N , Zhu, Y , Li, D , Basang, W , Huang, Y , Liu, K, et al. 2-methyl Nonyl ketone from Houttuynia Cordata Thunb alleviates Lps-induced inflammatory response and oxidative stress in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Front Chem. (2022) 9:793475. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.793475
161. Chen, Z , Zhang, Y , Zhou, J , Lu, L , Wang, X , Liang, Y, et al. Tea tree oil prevents mastitis-associated inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated bovine mammary epithelial cells. Front Vet Sci. (2020) 7:496. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00496
162. Jiang, A , Zhang, Y , Zhang, X , Wu, D , Liu, Z , Li, S, et al. Morin alleviates Lps-induced mastitis by inhibiting the Pi3k/Akt, Mapk, Nf-Κb and Nlrp3 signaling pathway and protecting the integrity of blood-Milk barrier. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 78:105972. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105972
163. Li, Y , Jiang, X , Xu, H , Lv, J , Zhang, G , Dou, X, et al. Acremonium Terricola culture plays anti-inflammatory and antioxidant roles by modulating Mapk signaling pathways in rats with lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis. Food Nutr Res. (2020) 64:64. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v64.3649
164. Tang, X , Liu, C , Li, T , Lin, C , Hao, Z , Zhang, H, et al. Gambogic acid alleviates inflammation and apoptosis and protects the blood-Milk barrier in mastitis induced by Lps. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 86:106697. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106697
165. Akhtar, M , Shaukat, A , Zahoor, A , Chen, Y , Wang, Y , Yang, M, et al. Hederacoside-C inhibition of Staphylococcus Aureus-induced mastitis via Tlr2 & Tlr4 and their downstream signaling Nf-Κb and Mapks pathways in vivo and in vitro. Inflammation. (2020) 43:579–94. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01139-2
166. Fusco, R , Cordaro, M , Siracusa, R , Peritore, AF , D’Amico, R , Licata, P, et al. Effects of Hydroxytyrosol against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in bovine mammary epithelial cells: a natural therapeutic tool for bovine mastitis. Antioxidants. (2020) 9:693. doi: 10.3390/antiox9080693
167. Xu, D , Liu, J , Ma, H , Guo, W , Wang, J , Kan, X, et al. Schisandrin a protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis through activating Nrf2 signaling pathway and inducing autophagy. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 78:105983. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105983
168. Ran, X , Zhang, Y , Yang, Y , Hu, G , Liu, J , Hou, S, et al. Dioscin improves pyroptosis in Lps-induced mice mastitis by activating Ampk/Nrf2 and inhibiting the Nf-Κb signaling pathway. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:8845521. doi: 10.1155/2020/8845521
169. Wang, Y , Ma, Y , Bi, S , Ma, X , Guan, R , Wang, S, et al. Therapeutic effect of Ginsenoside Rg1 on mastitis experimentally induced by lipopolysaccharide in lactating goats. J Dairy Sci. (2019) 102:2443–52. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15280
170. Guo, W , Liu, B , Yin, Y , Kan, X , Gong, Q , Li, Y, et al. Licochalcone a protects the blood–milk barrier integrity and relieves the inflammatory response in Lps-induced mastitis. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:287. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00287
171. Su, S , Li, X , Li, S , Ming, P , Huang, Y , Dong, Y, et al. Rutin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis by inhibiting the activation of the Nf-Κb signaling pathway and attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Inflammopharmacology. (2019) 27:77–88. doi: 10.1007/s10787-018-0521-x
172. Liu, C , Tang, X , Zhang, W , Li, G , Chen, Y , Guo, A, et al. 6-Bromoindirubin-3′-oxime suppresses Lps-induced inflammation via inhibition of the Tlr4/Nf-Κb and Tlr4/Mapk signaling pathways. Inflammation. (2019) 42:2192–204. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01083-1
173. Kan, X , Liu, B , Guo, W , Wei, L , Lin, Y , Guo, Y, et al. Myricetin relieves Lps-induced mastitis by inhibiting inflammatory response and repairing the blood–milk barrier. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:16252–62. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28288
174. Li, J , Yin, P , Gong, P , Lv, A , Zhang, Z , and Liu, F . 8-Methoxypsoralen protects bovine mammary epithelial cells against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury via suppressing Jak/stat and Nf-Κb pathway. Microbiol Immunol. (2019) 63:427–37. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12730
175. Li, Y , Gong, Q , Guo, W , Kan, X , Xu, D , Ma, H, et al. Farrerol relieve lipopolysaccharide (Lps)-induced mastitis by inhibiting Akt/Nf-Κb P65, Erk1/2 and P38 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:1770. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061770
176. Hu, G , Hong, D , Zhang, T , Duan, H , Wei, P , Guo, X, et al. Cynatratoside-C from Cynanchum Atratum displays anti-inflammatory effect via suppressing Tlr4 mediated Nf-Κb and Mapk signaling pathways in Lps-induced mastitis in mice. Chem Biol Interact. (2018) 279:187–95. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.10.017
177. Chen, X , Zheng, X , Zhang, M , Yin, H , Jiang, K , Wu, H, et al. Nuciferine alleviates Lps-induced mastitis in mice via suppressing the Tlr4-Nf-Κb signaling pathway. Inflamm Res. (2018) 67:903–11. doi: 10.1007/s00011-018-1183-2
178. Wang, W , Hu, X , Shen, P , Zhang, N , and Fu, Y . Sodium Houttuyfonate inhibits Lps-induced inflammatory response via suppressing Tlr4/Nf-ĸb signaling pathway in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Microb Pathog. (2017) 107:12–6. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.03.011
179. Wang, K , Jin, XL , Shen, XG , Sun, LP , Wu, LM , Wei, JQ, et al. Effects of Chinese Propolis in protecting bovine mammary epithelial cells against mastitis pathogens-induced cell damage. Mediat Inflamm. (2016) 2016:1–12. doi: 10.1155/2016/8028291
180. Qu, S , Wang, W , Li, D , Li, S , Zhang, L , Fu, Y, et al. Mangiferin inhibits mastitis induced by Lps via suppressing Nf-ĸb and Nlrp3 signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. (2017) 43:85–90. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.11.036
Keywords: mastitis, antimicrobial resistance, antibiotics, inflammatory changes, bioactive compounds, traditional Chinese medicine
Citation: Fan X, Qadeer A, Asiri M, Alzahrani FM, Alzahrani KJ, Alsharif KF, Khan MZ and Jiang X (2025) Traditional Chinese medicine and plant-derived bioactive compounds as sustainable alternatives to antibiotics in bovine mastitis: a review. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1642647. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1642647
Edited by:
Ibukun Michael Famuyide, Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), South AfricaReviewed by:
Jyoti Ranjan Rout, AIPH University, IndiaAbosede Tomilola Abolude, Alcorn State University, United States
Tunde Emmanuel Ogundare, North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Fan, Qadeer, Asiri, Alzahrani, Alzahrani, Alsharif, Khan and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xuewei Fan, ZmFueHVld2VpOEAxMjYuY29t; Abdul Qadeer, cWFkZWVya3RrODQ4QHlhaG9vLmNvbQ==
 Xuewei Fan
Xuewei Fan Abdul Qadeer
Abdul Qadeer Mohammed Asiri
Mohammed Asiri Fuad M. Alzahrani4
Fuad M. Alzahrani4
 Khalid J. Alzahrani
Khalid J. Alzahrani Khalaf F. Alsharif
Khalaf F. Alsharif Muhammad Zahoor Khan
Muhammad Zahoor Khan