- 1College of Food Science, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Food Quality and Safety, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China
- 2College of Veterinary Medicine, Guangdong Key Laboratory for Veterinary Drug Development and Safety Evaluation, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China
Introduction: Tenvermectin (TVM) is a novel avermectin-class drug that has attracted attention for its superior antiparasitic potency, low toxicity, and broad-spectrum activity. However, uncertainty about its interaction with cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) has raised concerns about potential therapeutic failure, increased risk of toxicity, dangerous drug combinations, and prolonged discontinuation periods.
Method: To address these critical safety concerns, we conducted a systematic comparative study using a highly selective and quantitatively accurate substrate conversion assay to assess and compare the effects of TVM and ivermectin (IVM) on the activities of key CYPs (CYP1A1/2, 2B1, 2C6, 2D2, and 3A1/2).
Results: TVM induced CYP1A, 2C, 2D and 3A activities only at high therapeutic doses (2.5 mg/kg), and its induction was significantly weaker than that of IVM at all doses tested, with the most pronounced difference for CYP3A1/2. Although TVM had weak inhibitory effects on CYP2B1 and 2D2, at therapeutic concentrations these effects are presumably unlikely to cause clinically significant CYP-mediated drug interactions.
Conclusion: As the first study to report the effects of TVM on CYP enzyme activity, these findings provide important experimental evidence and a theoretical framework for its clinical safety assessment, development of optimal dosing regimens, and rational polypharmacy strategies.
1 Introduction
Tenvermectin (TVM) is a novel avermectin-class drug produced by the genetically engineered bacterium Streptomyces avermitilis MHJ110 (1), which has a promising application in the treatment of gastrointestinal nematode infections and ectoparasites (2, 3). Compared with ivermectin (IVM), TVM has lower toxicity (3), rapid metabolism, and its area under the drug-time curve (AUC) and maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) are only 50% of those of IVM (4), and it has a better anthelmintic efficacy against Ascaris suum (pig roundworm) and Trichuris suis (pig whipworm) (3). As a drug candidate, systematic preclinical studies are essential to ensure the efficacy and safety of TVM in clinical applications (5). In particular, it is important to elucidate the mechanism of interaction between TVM and cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) (6). Hepatic CYPs are involved in ~95% of drug metabolism (5, 7), and abnormalities in these enzymes during drug metabolism can lead to therapeutic failures, enhanced toxicity, risk of coadministration, and prolonged withdrawal times, ultimately jeopardizing efficacy, animal welfare, and food safety (7–10). However, no studies on the interaction of TVMs with CYPs have been reported to date. In addition, given the homology of CYP genes between rats and humans, dogs and pigs (9, 11), the study of the effects of TVMs on CYPs in rats may provide an important reference for predicting their rational use in other animal species.
Currently, a series of drugs similar to TVM have been reported in relevant studies: doramectin (0.3 mg/kg BW, subcutaneous injection (SC) or intramuscular injection) administered as a single dose has a low risk of inhibition of porcine hepatic CYPs (12). IVM is a moderate to weak inhibitor of human recombinant CYPs (CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4) (13). However, the level of inhibition of CYPs by IVM at clinically recommended doses is unlikely to result in drug-drug interactions (DDI) (13). On the other hand, IVM significantly induced CYP1A activity in rats when administered at a dose 20–30 times the veterinary therapeutic dose (35 mg/kg BW, oral administration (PO), single dose), as well as CYP1A, CYP2B, and CYP3A1/2 activity in mouflon (0.5 mg/kg BW, PO, single dose) (14, 15). In humans, moxidectin (8 mg, PO, single dose) does not affect the activity of CYP3A4 (16). These studies indicate that despite their similar chemical structures, these drugs have different effects on the activity of CYPs due to dosage differences, different affinities with CYPs, and species differences (17). Therefore, in order to avoid the potential risk of DDI and promote the rational clinical application of TVMs, the results of similar drugs can only be used as a reference, and comprehensive and detailed experimental studies must be conducted for TVMs to obtain reliable data support. In addition, rat modeling studies may provide important insights to further explore the effects of TVM on CYPs in other species and help to reveal potential safety and efficacy issues.
In this study, we used a highly specific and quantitatively accurate substrate conversion assay to measure the activity of CYPs and determined the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) under in vitro to assess the inhibitory effect of TVM on the activity of CYPs (Scheme 1). In addition, we compared the changes in CYPs activity after SC of different doses of TVM to assess its induction of CYPs activity. IVM was used as an experimental control to further validate the effect of TVM on CYPs. These findings provide a scientific basis for the safe use of TVM in clinical practice and optimization of dosing strategies.
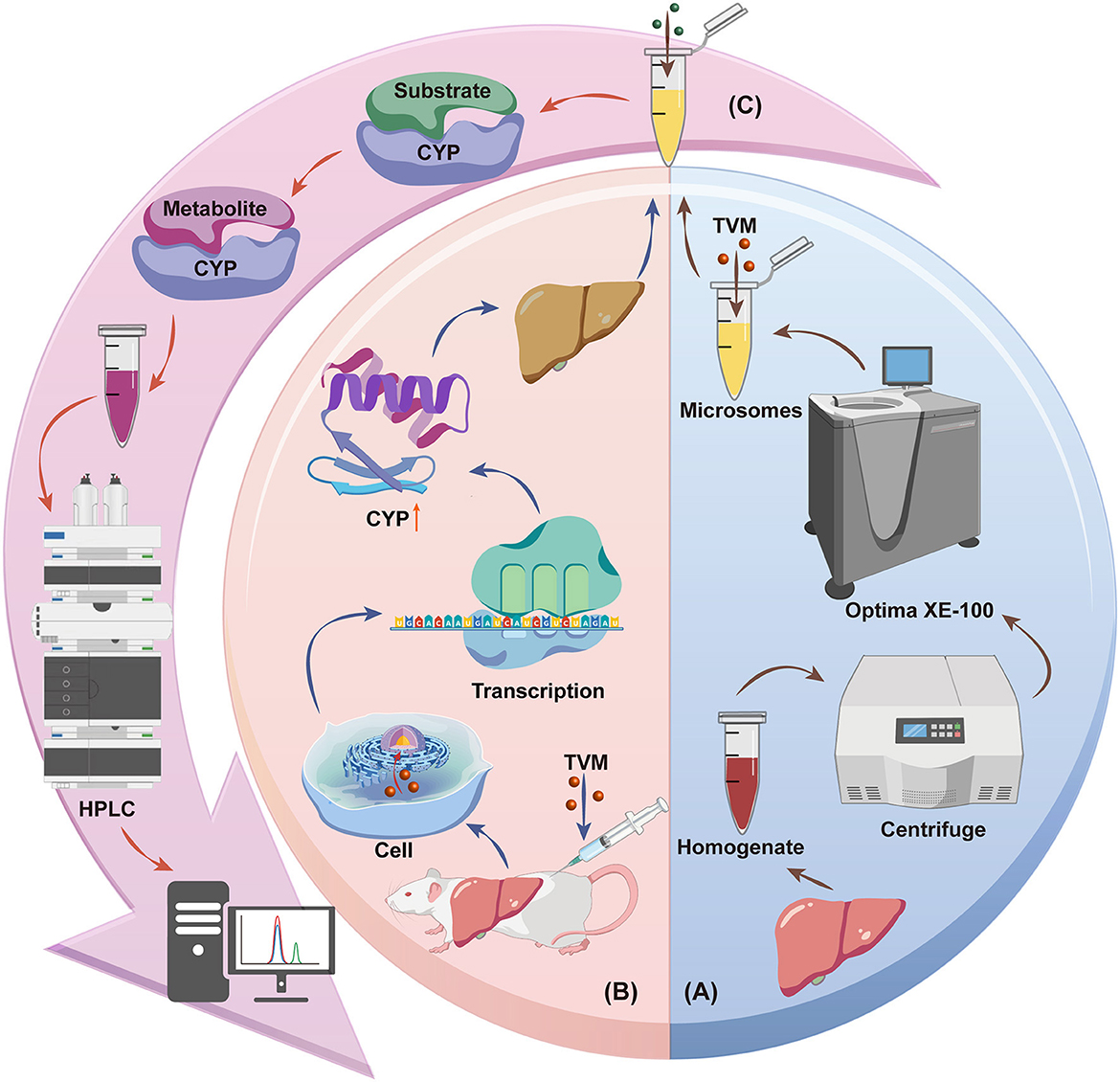
Scheme 1. Schematic diagram of the effect of TVM on liver CYPs in rats: (A) Inhibition of CYPs by TVM, (B) Induction of CYPs by TVM, (C) Substrate conversion assay. Source: Created by the authors, using a generic diagram platform (GDP) by Jiang et al. (44).
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
TVM (98.3%) was provided by Tianwei Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen, China). IVM (97.9%) was purchased from Qifa Drug Co., Ltd (Shandong, China). ER, resorufin (RF), diclofenac (DF), β-BNF, ketoconazole (KCZ), and quinine (QUI) were purchased from Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). DEX and α-BNF were purchased from Merck Sharp & Dohm (German). 4′-hydroxy diclofenac was ordered from Sigma Aldrich Corporation (USA). Dextromethorphan (DOM) and metyrapone (MTY) were purchased from Aladdin Holdings Group Co., Ltd. Benzyloxyresorufin (BR) was purchased from Saan Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Testosterone (TS), ordered from Ron Shanghai Lin'en Technology Development Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Dextrorphan (DOR) was purchased from Quality Control Solutions (QCS) Standard Material Research and Development Center (Shenzhen, China). 6β-hydroxytestosterone (6β-OH-TS) was purchased from Weikeqi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Sichuan, China). PB-Na subscribed from Yanzhe Technology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China). All other chemicals and reagents were of analytical grade and commercially available.
2.2 Animal
Male SD rats, each weighing 250–320 g (11 weeks old), were purchased from the Laboratory Animal Management Center of Southern Medical University. The experiment was conducted at the Laboratory Animal Center of South China Agricultural University (2024-b134) following the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals issued by the National Science Council's Animal Center (18). Rats were euthanized by CO2 inhalation (flow rate: 30%−70% of chamber volume/min, no prefilled chambers). After respiratory arrest, CO2 was continued to be released for at least 1 min. To reduce hepatic glycogen content, no food was given for 24 h prior to euthanasia (18). The livers were then perfused with cold saline through the inferior vena cava to flush out the blood. The livers were harvested after the blood was thoroughly flushed out, and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. The liver tissues should be stored at −80°C.
2.3 Preparation of microsomes
The livers were washed two–three times in cold 0.05 M Tris-HCl solution (pH 7.4) and then homogenized with four volumes of homogenization buffer (0.25 M sucrose, 1 mM EDTA-2Na, and 0.05 M Tris-HCl solution) using a glass homogenizer kept in an ice bath. The resulting liver homogenate was centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 20 min at 4°C. The supernatant was further centrifuged in an ultracentrifuge (Optima XE-100) at 100,000 × g for 60 min at 4°C to obtain the liver microsomes as the pellet. The liver microsomes were then diluted to a concentration of liver weight to Tris-HCl buffer (1:1), aliquoted proportionally, and stored at −80°C for future use (19). The protein concentration of all samples was determined using a BCA Protein Assay Kit.
2.4 Substrate conversion assays
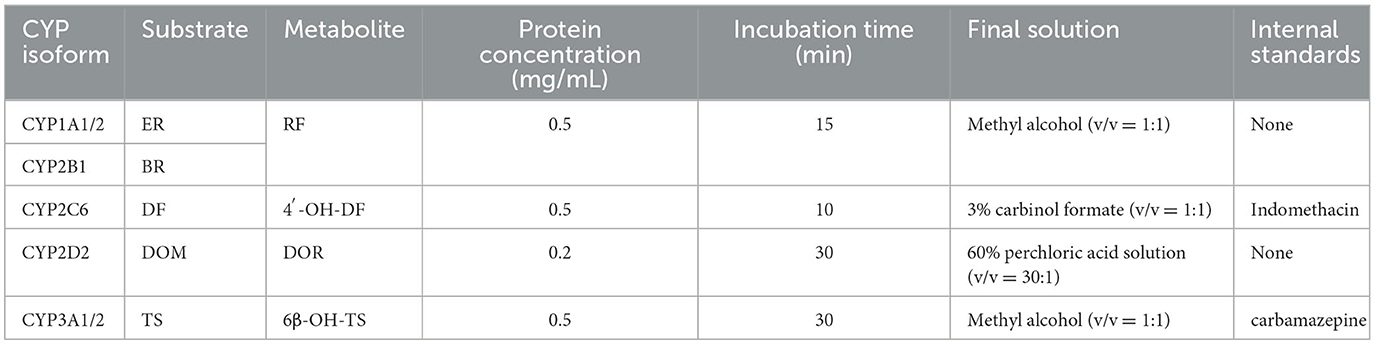
2.4.1 Incubation conditions
The incubation system included: 0.05 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.4), a certain concentration of liver microsomal protein, and an NADPH regeneration system (3.3 mM magnesium chloride, 0.05 mM sodium citrate, 3.3 mM glucose-6-phosphate, 1.3 mM NADP+, and 0.4 U/mL glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase). After pre-incubation for 3 min, the reaction was initiated by adding the respective substrate solutions (Table 1). Upon completion of the incubation, the corresponding stop solution was added to quench the reaction. For CYP2C6 and CYP3A1/2 incubation samples, IS [0.2 mM indomethacin (20), 0.4 mM carbamazepine (21)] were added. The samples were then vortexed for 5 min, followed by centrifugation at 4°C, 12,000 × g for 15 min. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter for instrumental analysis.
2.4.2 HPLC and HPLC-MS/MS conditions
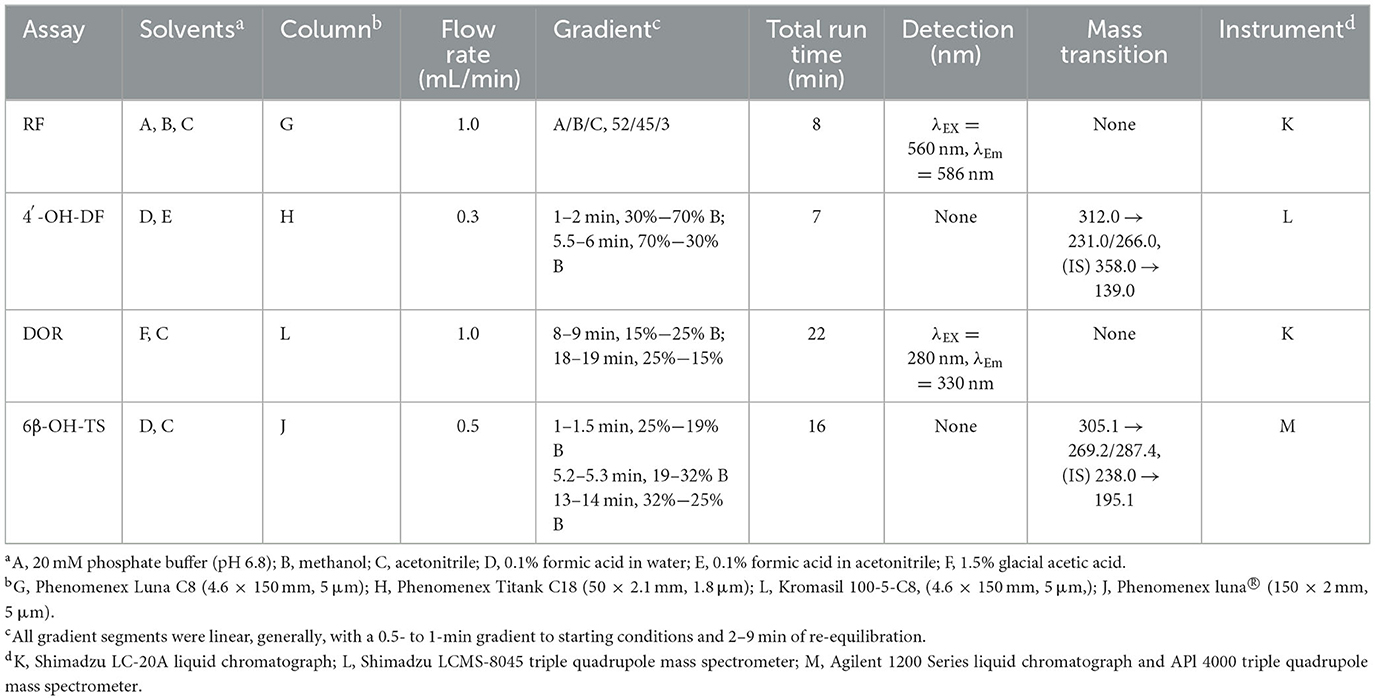
Summary of HPLC and HPLC-MS/MS methods for measuring various CYPs activities (Table 2). The HPLC methods for detecting CYP1A1/2 and CYP2B1 are based on the protocols described by Pegolo et al. (22). The method for assessing CYP2D2 activity is similar to those reported by Tian et al. (23) and Albassam et al. (24). Both methods were carried out on a Shimadzu LC-20A liquid chromatograph. The instrument is equipped with the following components: an LC-20AD quaternary pump, an RF-20A fluorescence detector, a DGU-20A5R degasser, a SIL-20ACXR autosampler, and a CTO-40C column oven. For CYP2C6, the HPLC system employed is the Shimadzu LC-20A liquid chromatograph. Samples are prepared by mixing with a mobile phase composed of water containing 0.1% formic acid and acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid, followed by injection into a C18 column for gradient elution at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. Analysis is performed using a Shimadzu LCMS-8045 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer with an electrospray ionization (ESI+) source in multiple reaction monitoring mode. The transitions monitored include m/z 266.0 → 231.0 (CE = −13 eV) for 4'-OH-DF and m/z 195.0 (CE = −19 eV) for indomethacin as IS. For CYP3A4, the HPLC-MS/MS system comprises an Agilent 1200 Series liquid chromatograph coupled with an API 4,000 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer. The mobile phase is delivered at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min for gradient elution. Mass spectrometric analysis is conducted in multiple reaction monitoring mode under positive ion conditions, with the ion spray voltage set to 5,500 V and the ion source temperature maintained at 550°C. The collision gas, curtain gas, nebulizer gas, and auxiliary gas are set to 12, 35, 55, and 55 psi, respectively. The qualitative and quantitative ions for 6β-OH-TS are m/z 287.4 → 269.2 (CE = 20/19 eV), and the Q3 transition for the carbamazepine is m/z 195.1 (CE = 25 eV).
2.4.3 Methodological validation
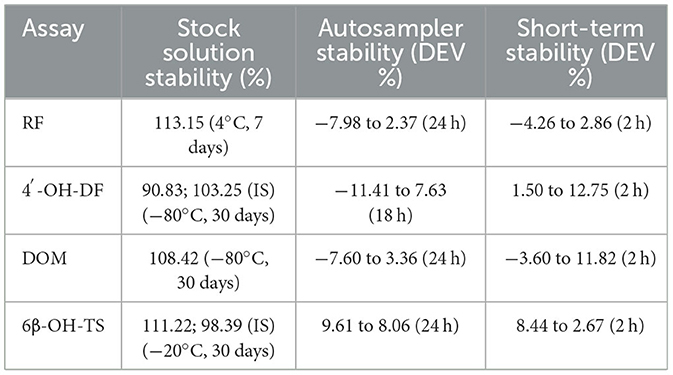
According to the guidelines for bioanalytical method validation of the US Food and Drug Administration, the methodological validation was performed for the above four analytical methods (selectivity, calibration curve, carryover, sensitivity, accuracy and precision, recovery, and stability). Accuracy and precision were obtained using a linear equation from six-point calibration. Stability encompasses stock solution stability, autosampler stability and short-term stability (25). When testing samples, each batch is accompanied by calibration curves and quality control samples at high, medium, and low levels to ensure the stability of the instrument.
2.5 Inhibition of CYPs by TVM and IVM
To determine the inhibitory potential (IC50) of TVM and IVM on the activity of CYPs (CYP1A1/2, 2B1, 2C6, 2D2, and 3A1/2), substrates at concentrations approximately equal to their respective Km values were mixed with different concentrations of TVM or IVM (0.5–150 μM), with the total organic solvent content not exceeding 1%, and then incubated according to the microsome protein concentration and incubation time in Table 1. The blank control group was replaced with an equal volume of methanol and TVM or IVM was added, and corresponding positive groups were designed: α-BNF (CYP1A1/2), MTY (CYP2B1) (26), QUI (CYP2D2), and KCZ (CYP3A1/2) (27).
2.6 Induction of CYPs by TVM and IVM
To investigate the induction of CYPs by TVM, low, medium (equivalent to the standard veterinary therapeutic dose), and high doses of TVM or IVM were administered and subsequent changes in the activity of liver microsomal CYPs were monitored (28). Rats were randomly divided into 12 groups and five rats in each group. These groups were Blank, TVM-0.5, TVM-1.25, TVM-2.5, IVM-0.5, IVM-1.25, IVM-2.5, Oil, Salt, β-BNF, PB-Na, and DEX. The blank control group was a mixture of propylene glycol, PEG 4000, and water (the blank solvent for TVM and IVM); TVM-0.5, TVM-1.25, and TVM-2.5 groups were administered with a single SC at a dose of 0.5, 1.25, and 2.5 mg/kg BW; the same was true for IVM-0.5, IVM-1.25, and IVM-2.5 groups. β-BNF, PB-Na, and DEX are all chemical inducer groups: β-BNF (CYP1A1/2) dissolved in corn oil solution, 80 mg/kg BW intraperitoneal injection (IP), once a day, for 3 days (29); PB-Na (CYP2B1 and CYP2C) dissolved in normal saline solution, 80 mg/kg BW, IP, once a day, for 4 days (30); DEX (CYP3A) dissolved in corn oil solution, 100 mg/kg BW, IP, once a day, for 4 days (31).
2.7 Data processing
Michaelis-Menten kinetic data, including Km and Vmax, were fitted by nonlinear regression analysis using GraphPad Prism 9, and Eadie-Hofstee plots were obtained to determine the kinetic type. The enzyme inhibition function of the dose-response was used to calculate the IC50. All data were obtained from triplicate reactions and are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Two-tailed Student's t-test was used to determine the significance of differences in CYPs activity after drug treatment. p < 0.05 was considered significant, p < 0.01 was very significant, and p < 0.001 was extremely significant.
3 Results
3.1 Substrate conversion assays
In order to quantitatively assess the effects of TVM on the activities of key CYPs, HPLC and HPLC-MS/MS analytical methods based on the principle of substrate conversion assay were developed for the quantitative determination of the metabolites (resorufin, 4'-hydroxydiclofenac, dextrorphan and 6β-hydroxytestosterone). Specifically, the reaction rates of ethoxyresorufin O-deethylation (EROD) and benzyloxyresorufin O-dealkylation (BROD), diclofenac 4'-hydroxylation (DFH), dextromethorphan N-demethylation (DMOD), and testosterone 6β-hydroxylation (T-6β-OH), were used as indicators for assessing the activity of CYP 1A1/2, 2B1, 2C6, 2D2, and 3A1/2, respectively.
The results of methodological validation (Tables 3, 4 and Supplementary Figure S1–S4) showed that the constructed method could effectively separate the target analytes (metabolites), internal standards (IS) and endogenous components in the matrix with high sensitivity, which satisfied the requirements of the determination; the linearity was good within the set concentration range (R2 > 0.99); and the residual effect did not interfere with the accuracy and precision. The deviation of accuracy (DEV) ranged from −14.83% to 13.05%, the coefficient of variation (CV) ranged from 1.10% to 8.29%, and the extraction recoveries ranged from 88.75% to 107.30%, which enabled the precise quantification. Under the analytical conditions in Table 4, the stability of the methods was good and suitable for the analysis of real samples, which fully verified their reliability and accuracy.
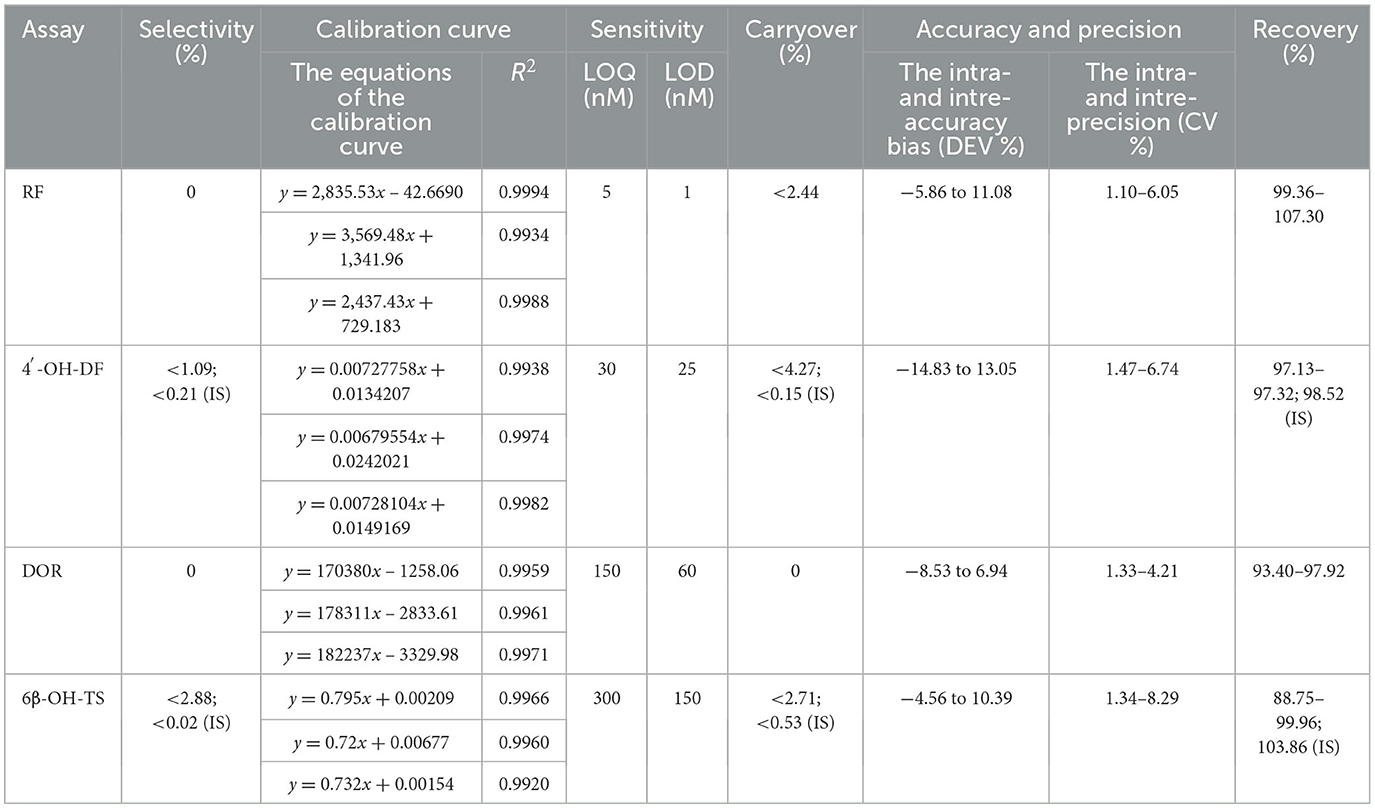
Table 3. HPLC and HPLC-MS/MS method's selectivity, calibration curve, sensitivity, carryover, accuracy, precision, and recovery.
The Michaelis–Menten kinetic model is the classic theoretical model describing the relationship between the rate of an enzymatic reaction and the substrate concentration. Eadie-Hofstee plots are commonly used to estimate Km and Vmax from experimental data, and when the plots show a linear trend, it implies that the reaction is catalyzed by a single enzyme rather than by the synergistic action of multiple enzymes (32). As shown in Figure 1, the enzyme kinetic curves of the five CYP isozyme reactions saturated with increasing substrate concentration, and the corresponding Eadiehofstee plots were all linear, indicating that these reactions are simple single-substrate-single-product reactions that can accurately reflect the activities of the corresponding CYPs.
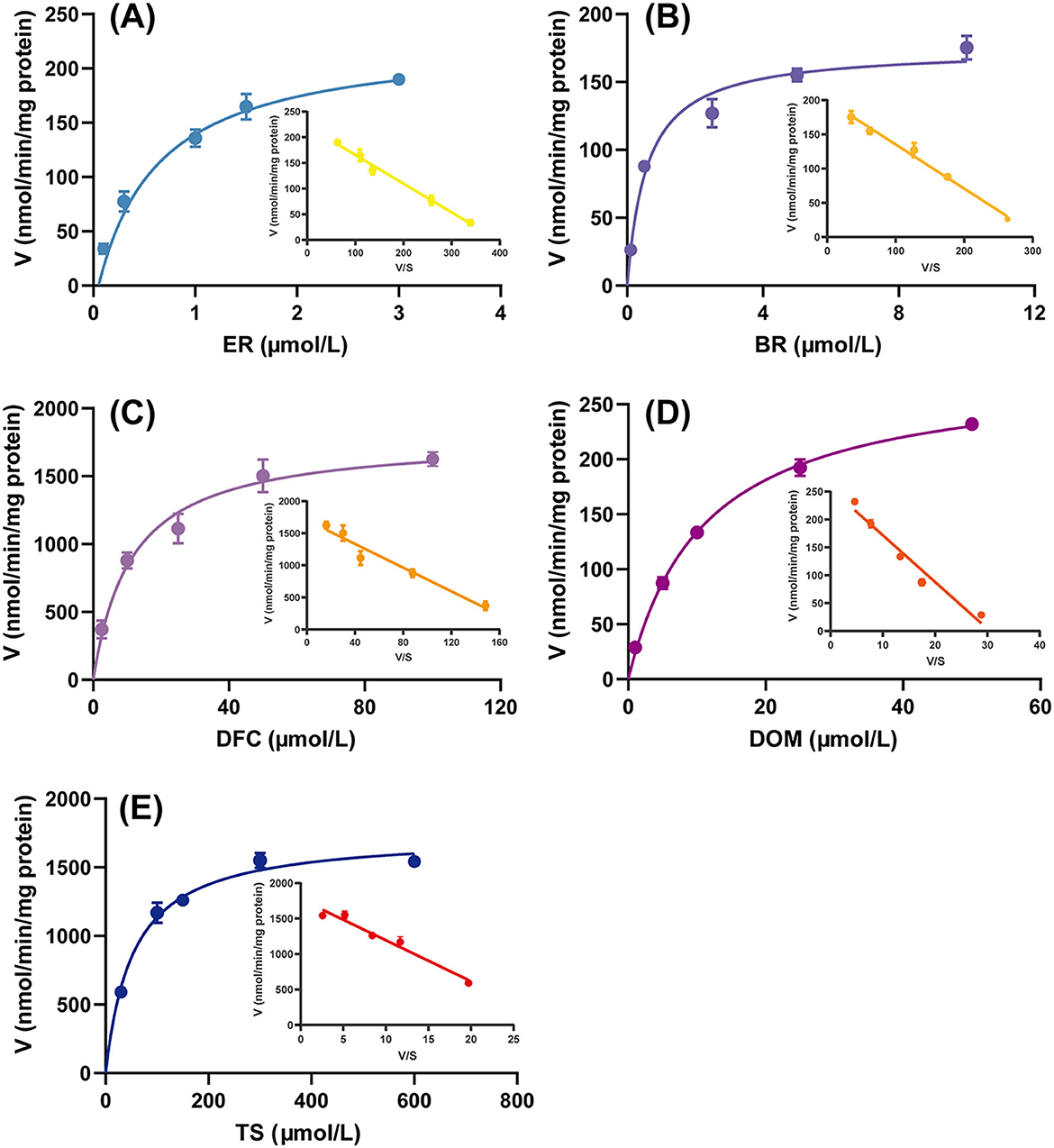
Figure 1. Michaelis-Menten kinetic data and Eadie-Hofstee plots for the metabolism of (A) ethoxyresorufin (ER) (CYP1A1/2), (B) benzyloxyresorufin (BR) (CYP2B1), (C) diclofenac (DF) (CYP2C6), (D) dextromethorphan (DOM) (CYP2D2), and (E) testosterone (TS) (CYP3A1/2) to resorufin (RF), 4′-hydroxydiclofenac (4′-OH-DF), dextromethorphan (DOR), and 6β-hydroxytestosterone (6β-OH-TS), respectively, in rat liver microsomes. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, n = 3.
3.2 Inhibition of CYPs by TVM and IVM
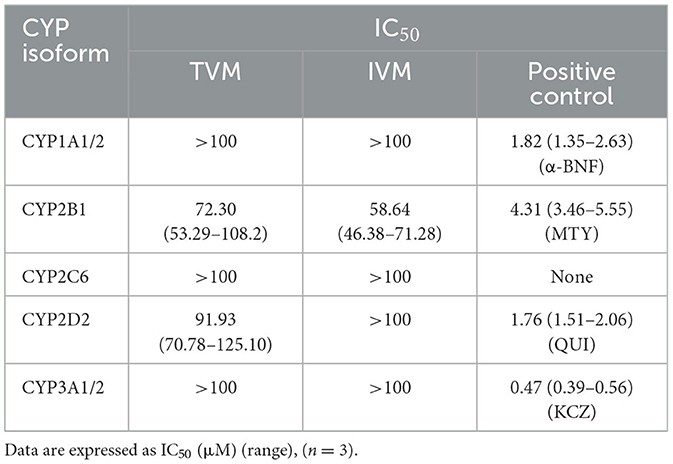
The inhibition function curves of TVM and IVM on the activity of CYPs at different doses are shown in Figure 2, and the IC50 values obtained are listed in Table 5. The results showed that the IC50 values were above 100 μM (Figures 2A, C, E), which indicated that TVM and IVM had no inhibit CYP 1A1/2, CYP 2C6, and CYP 3A1/2. According to the inhibition law of drugs on the activity of CYPs, the lower IC50 value means the stronger inhibition effect. In this theoretical framework, both drugs showed a slight inhibitory effect (50 μM < IC50 < 100 μM) against CYP2B1 (Figure 2B), with IC50 values of 72.30 and 58.64 μM, respectively. For CYP2D2, although the inhibitory function curves of TVM and IVM were similarly obtained (Figure 2D), the TVM showed a weak inhibitory effect IC50 = 91.93 μM. To verify the reliability of the experiment, the positive control group showed strong inhibition in all tests (IC50 < 10 μM, Figure 2F). This result provides strong evidence that the experimental system is capable of accurately and reliably assessing inhibition of the target CYPs and ensures the validity of the TVM and IVM inhibition data.
![Six graphs labeled A through F display the inhibition rates (IR%) against the logarithm of concentration (Log [C (μmol/L)]). Each graph shows data trends with error bars: (A) Red circles (TVM) and blue triangles (IVM) show a downward trend from 95% to 60%. (B) Similar symbols as A, starting at 95% dropping to 30%. (C) Ranges from 100% to 60%, both following a similar downward pattern. (D) Starts at 100% moving down to 50%. (E) Shows a decline from 100% to 50%. (F) Has four lines: yellow squares (α-BNF), red triangles (MTY), purple circles (QUI), and green triangles (KCZ), each exhibiting varied downward trends ending below 50%.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1647697/fvets-12-1647697-HTML-r1/image_m/fvets-12-1647697-g002.jpg)
Figure 2. Enzyme inhibition rates of TVM and IVM for five rat CYPs: (A) CYP1A1/2, (B) CYP2B1, (C) CYP2C6, (D) CYP2D2, (E) CYP3A1/2; and (F) Inhibition rates of four positive inhibitors for four rat CYPs: α-naphthoflavone (α-BNF; CYP1A1/2), metyrapone (MTY; CYP2B1), quinine (QUI; CYP2D2), ketoconazole (KCZ; CYP3A1/2). The inhibition rate is expressed as relative activity compared to the control group. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, n = 3.
3.3 Induction of CYPs by TVM and IVM
In the present study, we systematically evaluated the potential of drug candidates to induce CYP activity by comparing enzymatic activity levels across experimental, blank, and positive control groups (Figure 3). The positive control group (β-BNF, PB-Na, DEX) increased the activities of CYP1A1/2, CYP2B1, CYP2C6, and CYP3A1/2 by 11.64-, 44.18-, 11.71-, and 14.50-fold, respectively, as compared with the solvent control (corn oil/saline). The obvious activity-inducing effect verified the validity and reliability of the animal experiments.
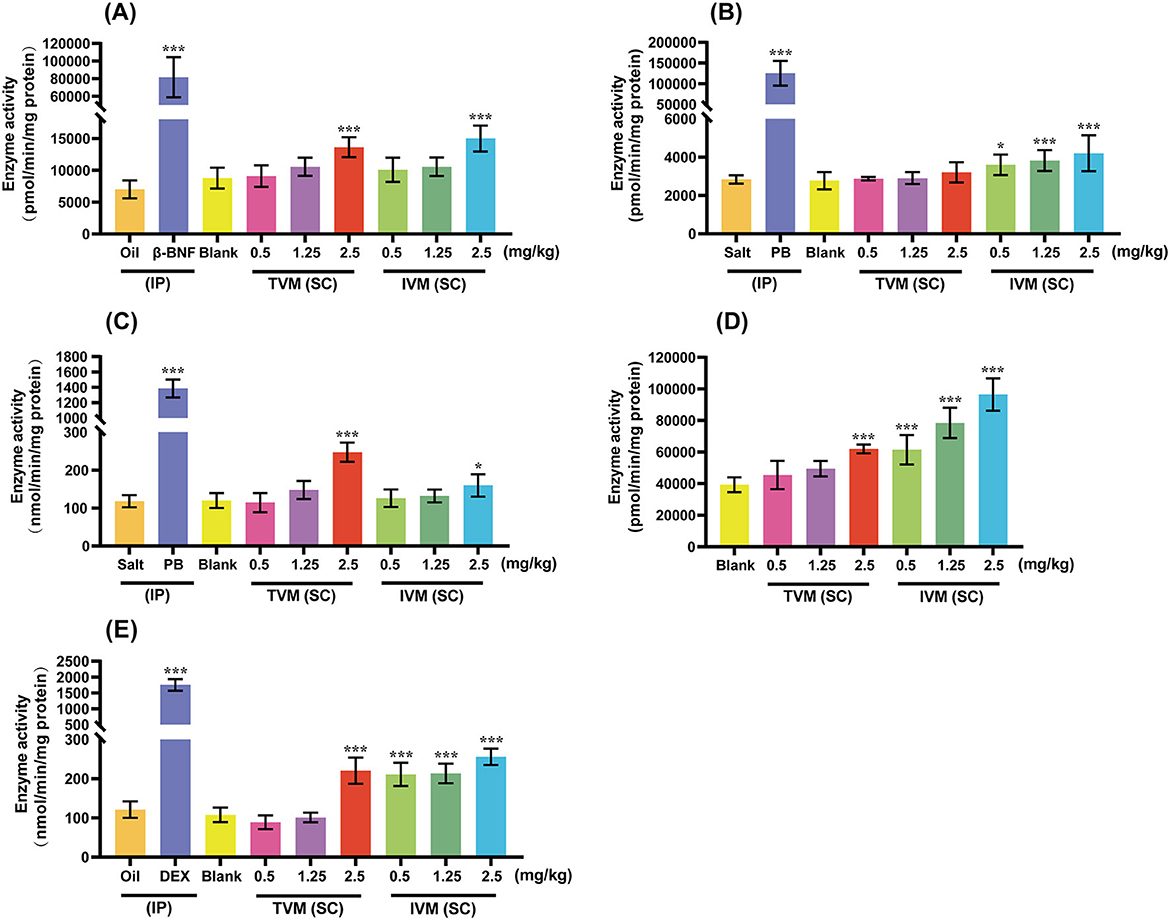
Figure 3. The induction effects of TVM and IVM on CYP1A1/2 (A), CYP2B1 (B), CYP2C6 (C), CYP2D2 (D), and CYP3A1/2 (E) in rat liver. TVM/IVM was administered at single doses of 0.5, 1.25, and 2.5 mg/kg BW (SC), β-naphthoflavone (β-BNF) at 80 mg/kg BW/day for 3 days (IP), Phenobarbital Sodium (PB-Na) at 80 mg/kg BW/day for 4 days (IP), and dexamethasone (DEX) at 100 mg/kg BW/day for 4 days (IP). Inhibition rate is relative to enzyme activity, calculated as 100% of control activity. Each value represents the mean ± standard deviation of five rats. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001, TVM/IVM vs. Blank; Positive control vs. Oil/Salt. Due to the lack of a clinically recognized or mechanistically clear CYP2D inducer, no positive control group was set up for CYP2D2 induction.
The induction of CYPs activity by IVM showed a clear dose-dependent and isoform-selective effect. As shown in Figure 3, different doses of IVM significantly increased the activities of CYP2B1 (1.30-, 1.38-, and 1.52-fold), CYP2D2 (1.56-, 2.00-, and 2.46-fold), and CYP3A1/2 (1.96-, 1.98-, and 2.37-fold). High-dose IVM (2.5 mg/kg BW) also induced other CYPs to varying degrees: CYP1A1/2 (1.70-fold) and CYP2C6 (1.33-fold). In summary, IVM had the most pronounced induction of CYP3A1/2, followed by CYP2D2 and CYP2B1, and relatively weak induction of CYP1A1/2 and CYP2C6. The weaker induction of CYPs by the drug candidate TVM reduced the risk of DDI compared to IVM. CYPs (CYP1A, 2C, 2D, and 3A) activity was induced by TVM only at high doses, with 1.55-, 2.06-, 1.57-, and 2.04-fold increase in enzyme activity, respectively, compared to the blank control (Figure 3).
4 Discussion
In drug metabolism studies, EROD, BROD, DFH, DMOD, and T-6β-OH are the classic substrate probes for the assessment of CYPs activity. It has been shown that in the rat liver metabolic system, CYP1A1/2 is the predominant isoenzyme affecting EROD activity (Figure 1A), although other CYPs may be involved in the process, but with relatively low contributions (33). For the BROD reaction, although it is commonly used to assess CYP2B1 activity, CYP1A1/2 also catalyzing the reaction can confuse the assessment of CYP2B1 activity (26). To solve this problem, the optimized incubation system significantly improved the accuracy of CYP2B1 activity determination by adding 5 μM α-BNF to specifically inhibit the CYP1A1/2-mediated metabolic pathway (Figure 1B). In addition, DFH, DMOD and T-6β-OH have been shown to be predominantly catalyzed by CYP2C6, CYP2D2, and CYP3A1/2, respectively (34). The specificity of these substrate probe reactions for the characterization of the corresponding CYPs activities was further validated by the linear characterization of the Eadie-Hofstee plots (Figure 1) in this study.
From a clinical risk perspective, inhibitory effects of drugs on CYPs are usually more potentially harmful than inducible effects (35), as they can reduce drug metabolism and lead to enhanced potency or adverse effects (36). Previous studies have shown that IVM moderately inhibits human recombinant CYP 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, and 3A4 (13), but in the present study, we found that IVM only weakly inhibited rat CYP2B1 (IC50 = 58.64 μM). Notably, the Cmax of IVM under different routes of administration (SC, intramuscular injection, intramuscular injection, and PO) in a variety of animals (cattle, sheep, pigs, canines, and horses) were lower than 150 ng/mL (~0.2 μM) (37). Similarly, TVM although weakly inhibiting CYP2B1 and CYP2D2 (IC50 of 72.30 and 91.93 μM, respectively), had a Cmax of only 245.89 ng/mL (~0.3 μM) in rats (unpublished data from our laboratory), again suggesting a low risk of inhibition in vivo.
In the field of research on the induction of CYPs activity by avermectins, no relevant studies have been reported on the effect of TVM and IVM on the enzyme activity of CYPs after SC. Previous studies have shown that when rats were administered IVM (35 mg/kg BW, PO) at doses 20–30 times the veterinary therapeutic dose, EROD activity significantly increased, while a dose of 0.3 mg/kg BW had no effect on this activity (14). Following a single dose of IVM (0.5 mg/kg BW, PO) in mouflons, the activity of CYP1A, 2B, and 3A1/2 significantly increased, while the activity of CYP2E1 remained unchanged (15). In this study, the induction of rat CYPs by IVM also exhibited a similar dose-dependent pattern (Figure 3). At a dose of 2.5 mg/kg BW, IVM significantly induced the activity of CYP1A, 2B1, 2C6, 2D2, and 3A1/2, while the two lower doses had no significant effect on the activity of CYP1A and 2C6. However, the induction effect of TVM was much lower than that of IVM, with weak induction of CYP1A, 2C, 2D, and 3A only at high doses, suggesting that the problem of attenuation of efficacy of conventional avermectin analogs due to self-induction of the CYPs can be circumvented. The reduced induction effect may be due to the weaker lipophilic structure of TVM than IVM (4), its shorter accumulation time in adipose tissue and higher plasma clearance (13, 14), which in turn reduces the possibility of TVM's induction of CYPs. The reasons for this need to be further studied.
The strong induction of CYP3A by IVM further exacerbates the clinical risk of drug use. As a key CYP enzyme involved in the metabolism of ~60% of human drugs (38), up-regulation of CYP3A activity may accelerate the metabolism of co-administered drugs, triggering widespread DDI, and, according to Barber, S. et al., the combination of IVM (SC) and moxidectin (whose main metabolizing enzyme is CYP3A) produced higher AUC in sheep than moxidectin alone, a phenomenon likely related to the relatively high 6β-TOH activity in the sheep microsomes (39). From this point of view, TVM should be more suitable for combination therapy with moxidectin than IVM. On the other hand, IVM show better suitability when combined with anthelmintics that have metabolites as their main pharmacodynamic effect, albendazole being a typical example [CYP3A4 is a key factor in the formation of albendazole sulfoxide (40)]. In a report by Alvarez et al. (41), the combination of albendazole + IVM (SC) was compared with albendazole administered alone to lambs, and a 40% increase in the AUC of albendazole sulfoxide was found in the former compared to the latter. Taken together, it is likely that the induction of CYP3A by IVM (SC) is responsible for the increase in plasma levels of albendazole sulfoxide in sheep. In addition, anthelmintic treatment with a combination of IVM and albendazole may also be a more appropriate option for some animals with high intrinsic CYP 3A activity, such as miniature pigs (42).
On the other hand, the induction of CYP1A1/2, which is mainly responsible for catalyzing the biotransformation of organic environmental pollutants (which include pro-carcinogens such as PAHs and PCBs), is also associated with the activation of the protein kinase cascade as well as with the increase of mitosis and cellular proliferation, a complex with toxic effects (14). In the present study, a weak induction of CYP1A1/2 activity was observed using both IVM (SC) and TVM (SC) at two-fold veterinary doses. Of interest, the EROD activity of bovine microsomes was five-fold higher than that of microsomes from other farm species (e.g., pigs, goats, and sheep) (42). Based on this difference, when treating cattle with IVM and TVM, high-dose regimens should be carefully selected and utilized in order to effectively reduce the potential risk of mutagenicity and carcinogenesis. In addition, special care should be taken to avoid combining IVM and TVM with drugs metabolized by CYP1A, such as estradiol, during clinical treatment (42).
In addition to the potential for DDI in the treatment of domestic animals, IVM administered via SC may have some impact in companion animal applications. In canines, the clinical substrates of CYP 2B and CYP 2D have been relatively well studied and described. Canine CYP 2B plays an important role in drug metabolism by facilitating the bioclearance process of cyclophosphamide (a commonly used chemotherapeutic drug) and propofol (an anesthetic drug) (9, 43). Meanwhile, CYP 2B is also involved in the metabolism of various endogenous substrates (e.g., androstenedione and progesterone) as well as toxic environmental chemicals (e.g., polychlorinated biphenols) (43). CYP 2D, on the other hand, possesses the ability to catalyze the biotransformation of antiemetic drugs (e.g., maropitant, metoclopramide) in addition to its ability to efficiently scavenge a number of antidepressants (e.g., clomipramine, fluoxetine) and opioid derivatives (e.g., tramadol) (43). This implies that the effects of IVM on CYP2B and CYP2D, as well as possible interactions with other drugs, need to be taken into account when treating canine companion animals, so as to formulate a more scientific and rational therapeutic regimen and to ensure the safety and efficacy of the medication.
5 Conclusion
This study is the first to systematically assess the effect of TVM on the activity of CYPs. The study showed that the inhibitory effect of TVM on CYPs is very unlikely to occur in vivo, and that the induction of CYPs by TVM was dose-dependent and significantly weaker than that of IVM, with a more pronounced induction of CYPs only at doses up to twice the usual veterinary dose. The induction of CYPs is significantly weaker with TVM than with IVM—only at doses up to twice the usual veterinary dosage. Therefore, TVM is feasible for combination therapy with most drugs. These findings validate the superior clinical safety and therapeutic potential of TVM, provide key evidence in support of its metabolic properties, and lay a solid foundation for subsequent translational clinical studies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Laboratory Animal Center of South China Agricultural University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
JL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. WR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. LLi: Conceptualization, Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. LLv: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. XH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2022YFD1802105).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2025.1647697/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Zhu LY, Zhang SY, Lu F, Zhang K, Han QQ, Ying QW, et al. Cross-resistance, fitness costs, and biochemical mechanism of laboratory-selected resistance to tenvermectin A in Plutella xylostella. Pest Manag Sci. (2021) 77:2826–35. doi: 10.1002/ps.6317
2. Wan X, Zhang SY, Zhang H, Zhai J, Huang J, Chen AL, et al. Two new tenvermectins from a genetically engineered strain Streptomyces avermitilis MHJ1011. J Asian Nat Prod Res. (2017) 19:327–32. doi: 10.1080/10286020.2016.1197911
3. Fei CZ, She RF Li GY, Zhang LF, Fan WS, Xia SH, et al. Safety and clinical efficacy of tenvermectin, a novel antiparasitic 16-membered macrocyclic lactone antibiotics. Eur J Pharm Sci. (2018) 117:154–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2018.02.010
4. Li G, Cao X, Liao J, Wei Y. Pharmacokinetics of tenvermectin in swine, a novel antiparasitic drug candidate-comparison with ivermectin. Vet Med Sci. (2023) 9:1211–6. doi: 10.1002/vms3.1085
5. Spatzenegger M, Jaeger W. Clinical importance of hepatic cytochrome P450 in drug metabolism. Drug metab rev. (1995) 27:397–417. doi: 10.3109/03602539508998329
6. Thompson TN. Optimization of metabolic stability as a goal of modern drug design. Med Res Rev. (2001) 21:412–49. doi: 10.1002/med.1017
7. Trepaluier LA. Cytochrome P450 and its role in veterinary drug interactions. Vet Clin N Am-Small. (2006) 36:975–85. doi: 10.1016/j.cvsm.2006.05.003
8. Antonovic L, Martinez M. Role of the cytochrome P450 enzyme system in veterinary pharmacokinetics: where are we now? Where are we going?. Future Med Chem. (2011) 3:855–79. doi: 10.4155/fmc.11.37
9. Fink-Gremmels J. Implications of hepatic cytochrome P450-related biotransformation processes in veterinary sciences. Eur J Pharmacol. (2008) 585:502–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.03.013
10. Lin JH, CYP. induction-mediated drug interactions: in vitro assessment and clinical implications. Pharm Res-dordr. (2006) 23:1089–116. doi: 10.1007/s11095-006-0277-7
11. Bogaards JJ, Bertrand M, Jackson P, Oudshoorn MJ, Weaver RJ, van Bladeren PJ, et al. Determining the best animal model for human cytochrome P450 activities: a comparison of mouse, rat, rabbit, dog, micropig, monkey and man. Xenobiotica. (2000) 30:1131–52. doi: 10.1080/00498250010021684
12. Hu SX, Mazur CA, Feenstra KL, Lorenz JK, Merritt DA. Assessment of inhibition of porcine hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes by 48 commercial drugs. Vet J. (2016) 211:26–31. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2016.03.011
13. Neodo A, Schulz JD, Huwyler J, Keiser J. In vitro and in vivo drug-drug interaction study of the effects of ivermectin and oxantel pamoate on tribendimidine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2019) 63:e00762-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00762-18
14. Skalova L, Szotakova B, Machala M, Neca J, Lamka J, Duchacek L, et al. Effect of ivermectin on induction of cytochromes P450 in male rats. Chem Pap. (2000) 54:249−53. Available online at: https://chempap.org/?id=7&paper=2892
15. Skalova L, Szotakova B, Machala M, Neca J, Soucek P, Havlasova J, et al. Effect of ivermectin on activities of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes in mouflon (Ovis musimon) and fallow deer (Dama dama). Chem-biol interact. (2001) 137:155–67. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2797(01)00227-7
16. Tan BS, Opoku N, Attah SK, Awadzi K, Kuesel AC, Lazdins-Helds J, et al. Pharmacokinetics of oral moxidectin in individuals with Onchocerca volvulus infection. PLoS Neglect Trop D. (2022) 16:e0010005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010005
17. Lewis DF, Modi S, Dickins M. Structure–activity relationship for human cytochrome P450 substrates and inhibitors. Drug Metab Rev. (2002) 34:69–82. doi: 10.1081/DMR-120001391
18. Le Bon AM, Vernevaut MF, Guenot L, Kahane R, Auger J, Arnault I, et al. Effects of garlic powders with varying alliin contents on hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes in rats. J Agric Food Chem. (2003) 51:7617–23. doi: 10.1021/jf0346758
19. Wang X, Wang Y, Wang Y, Sun L. Gooneratne R. Preparation of T-2-glucoronide with rat hepatic microsomes and its use along with T-2 for activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in RAW2647 cells. J Agric Food Chem. (2017) 65:4811–8. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b01250
20. Kumar S, Samuel K, Subramanian R, Braun MP, Stearns RA, Chiu SHL, et al. Extrapolation of diclofenac clearance from in vitro microsomal metabolism data: role of acyl glucuronidation and sequential oxidative metabolism of the acyl glucuronide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2002) 303:969–78. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.038992
21. Wang GF, Hsieh Y, Cui XM, Cheng KC, Korfmacher WA. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometric determination of testosterone and its metabolites in in vitro samples. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrum. (2006) 20:2215–21. doi: 10.1002/rcm.2580
22. Pegolo S, Merlanti R, Giantin M, Dacasto M, Montesissa C, Capolongo F. High performance liquid chromatography determination of cytochrome P450 1A and 2C activities in bovine liver microsomes. Vet J. (2010) 183:81–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2008.08.006
23. Tian X, Cheng ZY, He J, Jia LJ, Qiao HL. Concentration-dependent inhibitory effects of baicalin on the metabolism of dextromethorphan, a dual probe of CYP2D and CYP3A, in rats. Chem-Biol Interact. (2013) 203:522–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2013.02.005
24. Albassam AA, Ahad A, Alsultan A, Al-Jenoobi FI. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes by thymoquinone in human liver microsomes. Saudi Pharm J. (2018) 26:673–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2018.02.024
25. Kadian N, Raju KSR, Rashid M, Malik MY, Taneja I, Wahajuddin M. Comparative assessment of bioanalytical method validation guidelines for pharmaceutical industry. J Pharmaceut Biomed. (2016) 126:83–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2016.03.052
26. Pekthong D, Desbans C, Martin H, Richert L. Bupropion hydroxylation as a selective marker of rat CYP2B1 catalytic activity. Drug Metab Dispos. (2012) 40:32–8. doi: 10.1124/dmd.111.041368
27. Guengerich FP. Comparisons of catalytic selectivity of cytochrome P450 subfamily enzymes from different species. Chem-biol Interact. (1997) 106:161–82. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2797(97)00068-9
28. Jiang B, Meng LY, Zhang F, Jin XL, Zhang GL. Enzyme-inducing effects of berberine on cytochrome P450 1A2 in vitro and in vivo. Life Sci. (2017) 189:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.09.011
29. Xiao Y, Xue X, Wu YF, Xin GZ, Qian Y, Xie TP, et al. β-Naphthoflavone protects mice from aristolochic acid-I-induced acute kidney injury in a CYP1A dependent mechanism. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2009) 30:1559–65. doi: 10.1038/aps.2009.156
30. Minamiyama Y, Takemura S, Toyokuni S, Imaoka S, Funae Y, Hirohashi K, et al. CYP3A induction aggravates endotoxemic liver injury via reactive oxygen species in male rats. Free Radical Bio Med. (2004) 37:703–12. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.05.022
31. Li L, Li ZQ, Deng CH, Ning MR Li HQ, Bi SS, et al. A mechanism-based pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model for CYP3A1/2 induction by dexamethasone in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2012) 33:127–36. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.161
32. Hu N, Huang YJ, Gao XJ Li S, Yan ZX, Wei B, et al. Effects of dextran sulfate sodium induced experimental colitis on cytochrome P450 activities in rat liver, kidney and intestine. Chem-Biol Interact. (2017) 271:48–58. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.04.018
33. Burke MD, Thompson S, Weaver RJ, Wolf CR, Mayer RT. Cytochrome P450 specificities of alkoxyresorufin O-dealkylation in human and rat liver. Biochem pharmacol. (1994) 48:923–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90363-8
34. Kobayashi K, Urashima K, Shimada N, Chiba K. Substrate specificity for rat cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms: screening with cDNA-expressed systems of the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. (2002) 63:889–96. doi: 10.1016/S0006-2952(01)00843-7
35. Huang J, Chen AL, Zhang H, Yu Z, Li MH, Li N, et al. Gene replacement for the generation of designed novel avermectin derivatives with enhanced acaricidal and nematicidal activities. Appl Environ Microb. (2015) 81:5326–34. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01025-15
36. Monbaliu J, Gonzalez M, Bernard A, Jiao J, Sensenhauser C, Snoeys J, et al. In vitro and in vivo drug-drug interaction studies to assess the effect of abiraterone acetate, abiraterone, and metabolites of abiraterone on CYP2C8 activity. Drug Metab Dispos. (2016) 44:1682–91. doi: 10.1124/dmd.116.070672
37. Canga AG, Prieto AMS, Liébana MJD, Martínez NF, Vega MS, Vieitez JJG. The pharmacokinetics and metabolism of ivermectin in domestic animal species. Vet J. (2009) 179:25–37. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.07.011
38. Wang X, Cheung CM, Lee WYW, Or PMY, Yeung JHK. Major tanshinones of Danshen Salvia miltiorrhiza exhibit different modes of inhibition on human CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4 activities in vitro. Phytomedicine. (2010) 17:868–75. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2010.05.003
39. Zeng Z, Andrew NW, Woda JM, Halley BA, Crouch LS, Wang RW. Role of cytochrome P450 isoforms in the metabolism of abamectin and ivermectin in rats. J Agric Food Chem. (1996) 44:3374–8. doi: 10.1021/jf960222+
40. Velík J, Baliharová V, Fink-Gremmels J, Bull S, Lamka J, Skálová L. Benzimidazole drugs and modulation of biotransformation enzymes. Res Vet Sci. (2004) 76:95–108. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2003.08.005
41. Alvarez L, Lifschitz A, Entrocasso C, Manazza J, Mottier L, Borda B, et al. Evaluation of the interaction between ivermectin and albendazole following their combined use in lambs. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. (2008) 31:230–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.2008.00953.x
42. Szotáková B, Baliharová V, Lamka J, Nozinová E, Wsól V, Velík J, et al. Comparison of in vitro activities of biotransformation enzymes in pig, cattle, goat and sheep. Res Vet Sci. (2004) 76:43–51. doi: 10.1016/S0034-5288(03)00143-7
43. Martinez MN, Antonovic L, Court M, Dacasto M, Fink-Gremmels J, Kukanich B, et al. Challenges in exploring the cytochrome P450 system as a source of variation in canine drug pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab Rev. (2013) 45:218–30. doi: 10.3109/03602532.2013.765445
Keywords: tenvermectin, cytochrome P450 enzymes, ivermectin, rats, inhibition and induction
Citation: Liang J, Cui C, Ren W, Li L, Lv L, Huang X and Li X (2025) Dose-dependent modulation of hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes by tenvermectin: implications for medication safety and combination therapy. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1647697. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1647697
Received: 16 June 2025; Accepted: 25 July 2025;
Published: 25 August 2025.
Edited by:
Fan Yang, Henan University of Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Yingchun Liu, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaYiming Liu, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, China
Copyright © 2025 Liang, Cui, Ren, Li, Lv, Huang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiangmei Li, bGl4aWFuZ21laTEyQDE2My5jb20=; Xianhui Huang, eGhodWFuZ0BzY2F1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Jianping Liang1,2
Jianping Liang1,2 Xianhui Huang
Xianhui Huang Xiangmei Li
Xiangmei Li