- 1College of Life Science, Baicheng Normal University, Baicheng, China
- 2Changchun Borui Science & Technology Co., Ltd, Changchun, China
- 3College of Animal Science and Technology, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun, China
Ginsenoside, as the pivotal bio-active constituents derived from ginseng, exhibit multifunctional biological properties including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immune regulation and stress-alleviating effects. Ginsenosides modulate immune responses, enhance metabolic regulation, and exert antioxidant effects through multiple pathways, improving animal health, meat quality and productivity. The purpose of this article is to provide solutions for the development of new feed additives under the premise of a complete ban on the use of antibiotics. Consequently, ginsenosides represent a premium botanical resource for feed additive applications in modern livestock and poultry production. This paper reviews the structural classification, source, biological function and application of ginsenoside in animals, in order to provide a reference for the rational use of ginsenoside in animal husbandry.
1 Introduction
Ginseng, discovered in China more than 5,000 years ago, is a perennial herb which is called the “king of the herb” (1, 2). In China, Changbai Mountain in Jilin Province is the area where the natural growth yields is the highest (3). In recent years, with the continuous optimization of the extraction and separation technology of Chinese herbal medicine, ginsenoside, the main medicinal active ingredient in ginseng, has also attracted much attention from researchers. Ginsenosides are a kind of natural steroid glycosides and triterpenoid saponins, which are often used as markers to determine the medicinal value of ginseng (4, 5). Ginsenosides have multiple biologically active functions, including immune regulation (6), protection of the central nervous system and cardiovascular health (7, 8), anti-inflammatory (9), antioxidant (10) and even anti-cancer (11), but suffer from drawbacks including poor water solubility, short half-life, and low bioavailability. Currently, the specific mechanisms of action for many ginsenosides remain were unclear, and many researchers are also working in this area to solve these problems. At present, relevant research reports have been published on the application of ginsenosides in animal production (12). Based on the research reports, this article summarizes the chemical structure, classification and sources, biological functions, and applications of ginsenosides in animal production, in order to develop a new natural green feed additive in utilizing animal husbandry.
2 Chemical structure and classification of ginsenosides
The basic structure of ginsenosides is similar, consisting of a 17-carbon-atomic paeonol steroid nucleus, the structure of which was first discovered by a Japanese researcher in the 1960s (1). According to their mobility on thin layer chromatography plates, they can be divided into four major categories: 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol (PPD), 20(S)-Protopanaxatriol (PPT), C17 Side-chain Varied (C17SCV) and oleanolic acid (OA). PPD, PPT and C17SCV are the main types of ginsenosides, and their compositions vary significantly in different parts of ginseng (12). Sun et al. (13) identified a total of 408 ginsenosides by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-TOF-MS) qualitative analysis, of which 8 common saponins were found in all parts of the whole ginseng plant (12), as shown in Figure 1, including 3 types of PPD (ginsenoside Rb1, ginsenoside Rb2, ginsenoside Rc), 4 types of PPT (ginsenoside Re, ginsenoside Rg1, ginsenoside Rg2, Notoginsenoside R1), and 1 oleanolic acid type (ginsenoside Ro).
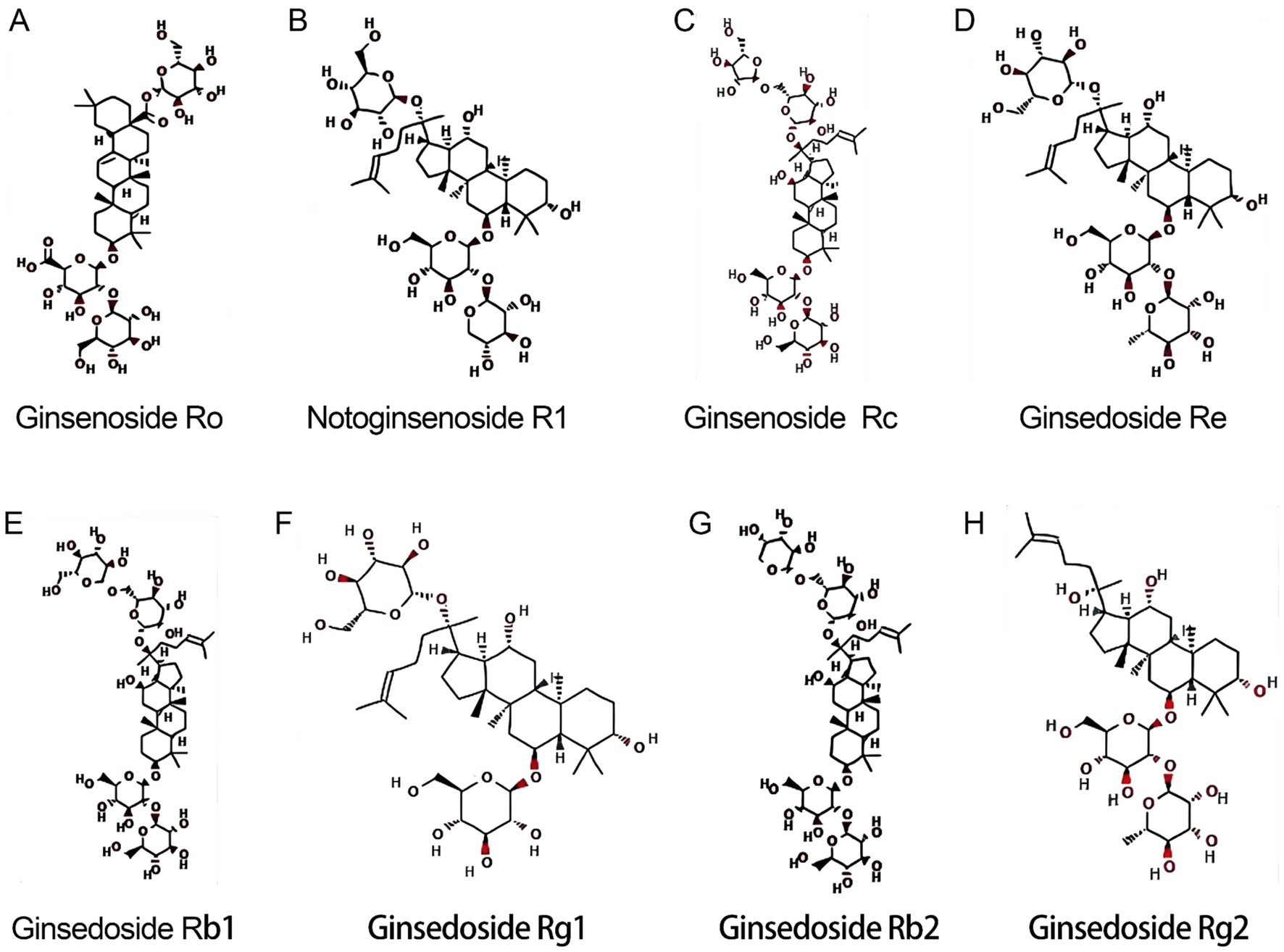
Figure 1. Molecular structures of 8 common ginsenosides. (A) Ginsenoside Ro. (B) Notoginsenoside R1. (C) Ginsenoside Rc. (D) Ginsenoside Re. (E) Ginsenoside Rb1. (F) Ginsenoside Rg1. (G) Ginsenoside Rb2. (H) Ginsenoside Rg2.
3 The biological functions of ginsenosides
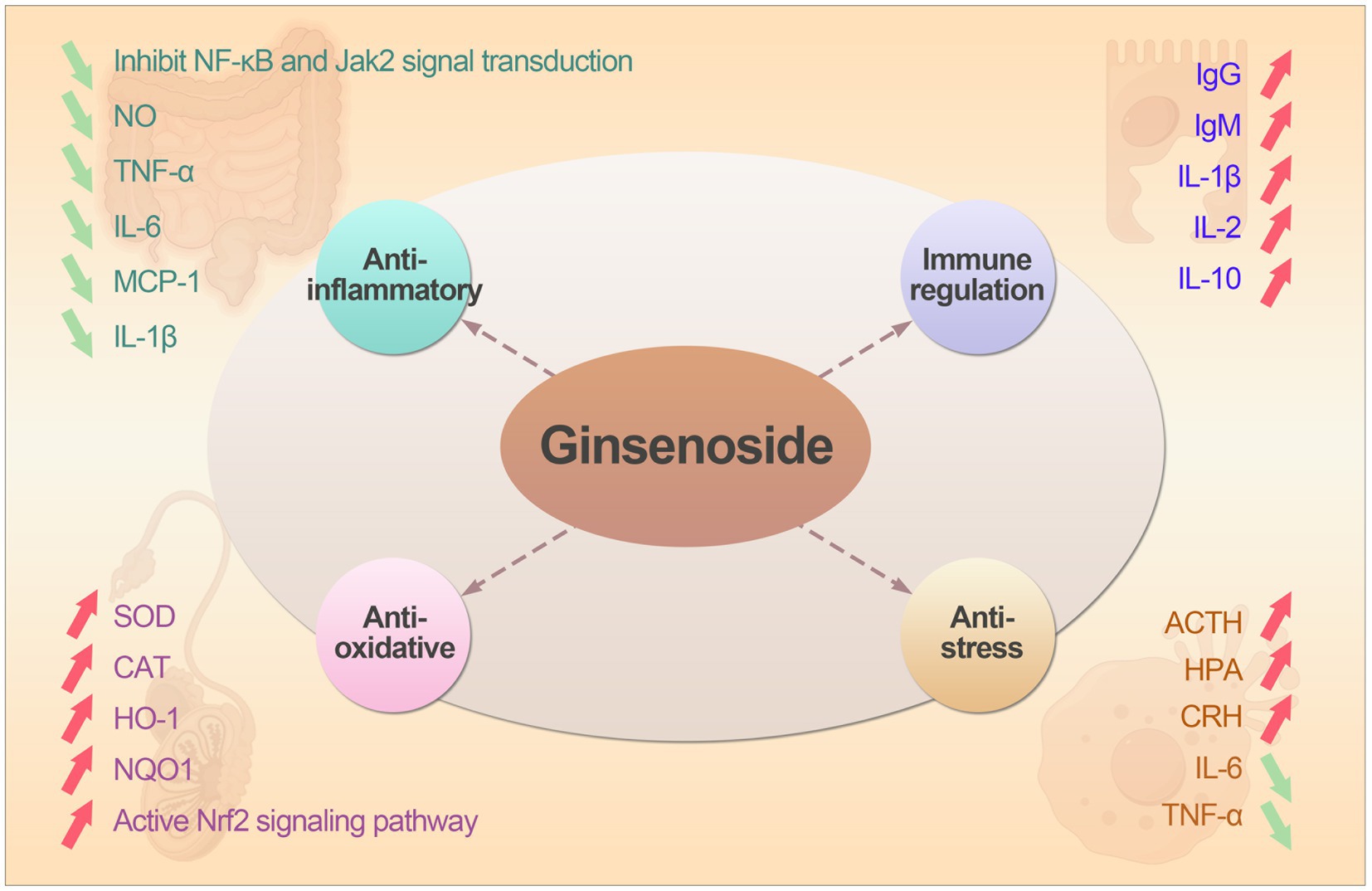
Ginsenosides exert multifaceted regulatory effects on animals primarily through modulation of critical signaling pathways and interaction with cellular receptors. Ginsenosides can activate Nrf2 signal pathway, promoting its nuclear translocation and binding to the Antioxidant Response Element (ARE), leading to up-regulated expression of antioxidant enzymes (HO-1, SOD, CAT, GSH-Px) (14). Ginsenosides can also suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) by inhibiting IκBα degradation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB (15, 16). As well as modulate c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) (17), ERK (18), and p38 signaling pathways (19), reducing inflammation and cellular stress responses. In the part of anti-stress, ginsenosides can regulate unfolded protein response (UPR) sensors and reducing excessive ER stress-induced apoptosis (20). The main biological functions of ginsenosides was shown as followed.
3.1 Antioxidant
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) are highly reactive molecules containing oxygen, generated through both normal cellular metabolism and exposure to external factors. This complex interplay of metabolic byproducts, enzymatic reactions, conversions, and environmental exposures constitutes the major pathways of ROS formation within biological systems (21, 22). They are unstable compounds that mainly originate from the oxidative phosphorylation process in the mitochondrial electron transport chain. They are usually produced as a byproduct of cellular metabolism and always play an important role in signal transduction. However, their excessive production can cause cellular oxidative damage (23). Under the condition of intensive farming process in recent years, animals are easily affected by external factors such as weaning, vaccination and temperature, which cause ROS to accumulate in vivo, damaging macro-molecules such as lipids and proteins (24, 25), leading to an imbalance of oxidative and antioxidant homeostasis, finally ultimately causing oxidative stress (26). A study has found that ginsenosides can relieve oxidative stress by scavenging free radicals, inhibiting the production of nitric oxide (NO), inducing catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene expression and reducing lipid peroxidation (27). Similarly, ginsenoside Rb1 can exert antioxidant effects in ischemic hippocampal neurons by increasing endogenous antioxidant enzymes, thereby protecting the central nervous system (28). Anti-NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) plays a key role in regulating the expression of antioxidant-related genes (29). Under normal physiological conditions, Nrf2 usually exists in the cytoplasm together with Kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1 (Keap1). When animals are under oxidative stress, Nrf2 binds to the antioxidant response element (ARE) to initiate the transcription of antioxidant enzyme genes, up-regulating the expression of genes encoding the second type of enzymes and antioxidant proteins, including NAD (P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLc) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), further enhancing the antioxidant capacity of cells escaping from oxidative damage (30). A study by Liu et al. (31) showed that 25 μM ginsenosides can significantly activate the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway, enhance the activity of various antioxidant enzymes such as GSH-Px and SOD, and effectively alleviate cellular oxidative stress damage. The above studies showed that ginsenosides can exert antioxidant effects by activating the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway in vivo and up-regulating the gene expression of various antioxidant enzymes such as SOD, CAT, HO-1, NQO1 and GCLc.
3.2 Anti-inflammatory
Inflammation is an immune response to infection in animals. When animals are infected by pathogens, cell surface receptors (such as TLRs) activate the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and activator protein 1 (AP-1) signaling pathways, releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines and inducing inflammatory responses (32, 33). Studies have shown that ginsenoside Rb1 can inhibit the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) pathway and protect mice from LPS induced liver damage (34), it alleviated hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammatory response in rats (35). Ginsenosides significantly inhibits LPS-induced NO release in RAW264.7 macrophages in a dose-dependent manner (0–100 μmol/L), achieving near-complete suppression at 100 μmol/L, while downregulating mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory mediators (36). Similarly, 20 mg/kg ginsenoside reduces chronic inflammatory pain in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-κB signaling, decreasing spinal expression of IL-1β, TLR4, and NF-κB by 40–50%, while elevating mechanical pain thresholds by 2.5-fold and prolonging rotarod endurance by 80% (37). Ginsenoside Rk1 can also inhibit NF-κB and Janus kinase 2 (Jak2) signal transduction, meanwhile inhibit the production of NO, tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), MCP-1, and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) induced by LPS in the mouse mononuclear macrophage cell line RAW264.7, thereby alleviating the inflammatory response (38). NF-κB is a transcription factor associated with inflammatory response (30). It interacts with the Nrf2 pathway. Nrf2 up-regulation can inhibit NF-κB activation, at the same time NF-κB mediated transcription can also inhibit Nrf2 activation and reduce antioxidant capacity (39). As an exogenous regulatory factor, ginsenosides can activate the Nrf2 antioxidant defense system through the PI3K/Akt pathway and inhibit the NF-κB inflammatory signaling pathway, thereby alleviating LPS induced blood–brain barrier (BBB) damage (40). Ginsenoside Ro can increase the expression of HO-1 in macrophages, activate the Nrf2 signaling pathway, and reduce the expression of LPS induced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), thereby improving the antioxidant capacity (41). In summary, ginsenosides can exert anti-inflammatory effects by activating the antioxidant defense system to inhibit inflammatory responses or directly acting on inflammatory signaling pathways.
3.3 Immune regulation
Ginsenosides play an important role in enhancing humoral immunity and cellular immunity. Immunoglobulin is the main mediator of humoral immunity. Immunoglobulin is the main mediator of humoral immunity. Ginsenosides can promote the production of serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) and immunoglobulin M (IgM) in mice. When the feeding dose was 60 mg/kg, 120 mg/kg and 240 mg/kg, the serum IgG content was significantly increased by 23.39, 24.29 and 26.39%, respectively, compared with the control group, and the IgM content was increased by 32.47, 33.17 and 38.33%, respectively, compared with the control group (42). In addition, ginsenosides are also widely used in vaccine adjuvants. Oral administration of ginseng stem and leaf saponins (GSLS) can significantly enhance the immune efficacy of infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) vaccines and Newcastle disease virus (NDV) vaccines in chickens (43). A study by Su et al. (44) showed that ginsenoside Re, as a vaccine adjuvant, can enhance the immune response of mice to inactivated rabies vaccine (RV) by enhancing cellular and humoral immune responses, thereby increasing the serum antibody level after vaccination. Yuan et al. (45) found that ginsenoside Rg1 had adjuvant properties in stimulating IgG, splenocyte proliferation, and mRNA expression of cytokines IFN-γ and IL-4, as well as the expression of cell surface marker TLR4 in the HBsAg-immunized mice. Therefore, ginsenosides can improve immune function by increasing serum immunoglobulin levels and related cytokine production.
3.4 Anti-stress
In large-scale farming environments, stress often occurs in early weaning piglets, heat stress in dairy cows and immune stress in broiler chicken. These stress from the external environment can cause an increase in ROS produced by the mitochondrial respiratory chain in animals, leading to imbalance between the oxidative and antioxidant systems (46). Therefore, whether weaning stress or heat stress, it is ultimately cellular oxidative stress. Li et al. (47) showed that ginsenoside Rg1 can protect H9c2 cells from Hypoxia/Re-oxygenation induced apoptosis by alleviating oxidative stress injury, which depended largely on subsequent Nrf2 nuclear translocation and up-regulation of HO-1. Similarly, ginsenoside Rb1 can also reduce oxidative stress and cell apoptosis caused by Staphylococcus aureus by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway and inhibiting the mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway (48). Immune stress can also have adverse effects on the health of livestock and poultry (49), the mechanism is that immune stress induced by adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) increased directly. When animals are under stress, the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA) is activated, the hypothalamus can secrete corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and ACTH (50). A study has shown that ginsenoside Rg3 can reduce serum ACTH levels in broiler chickens under immune stress (51). The mechanism of action may be that ginsenoside Rg3 acts on the HPA axis, stimulating the hypothalamic thermoregulatory center to lower the body temperature of broilers, shorten the fever period, and inhibit the release of pro-inflammatory factors such as IL-6 and TNF-α (39), thereby alleviating the immune stress caused by LPS. The biological functions of ginsenosides was shown in Figure 2.
4 The application of ginsenosides in animal production
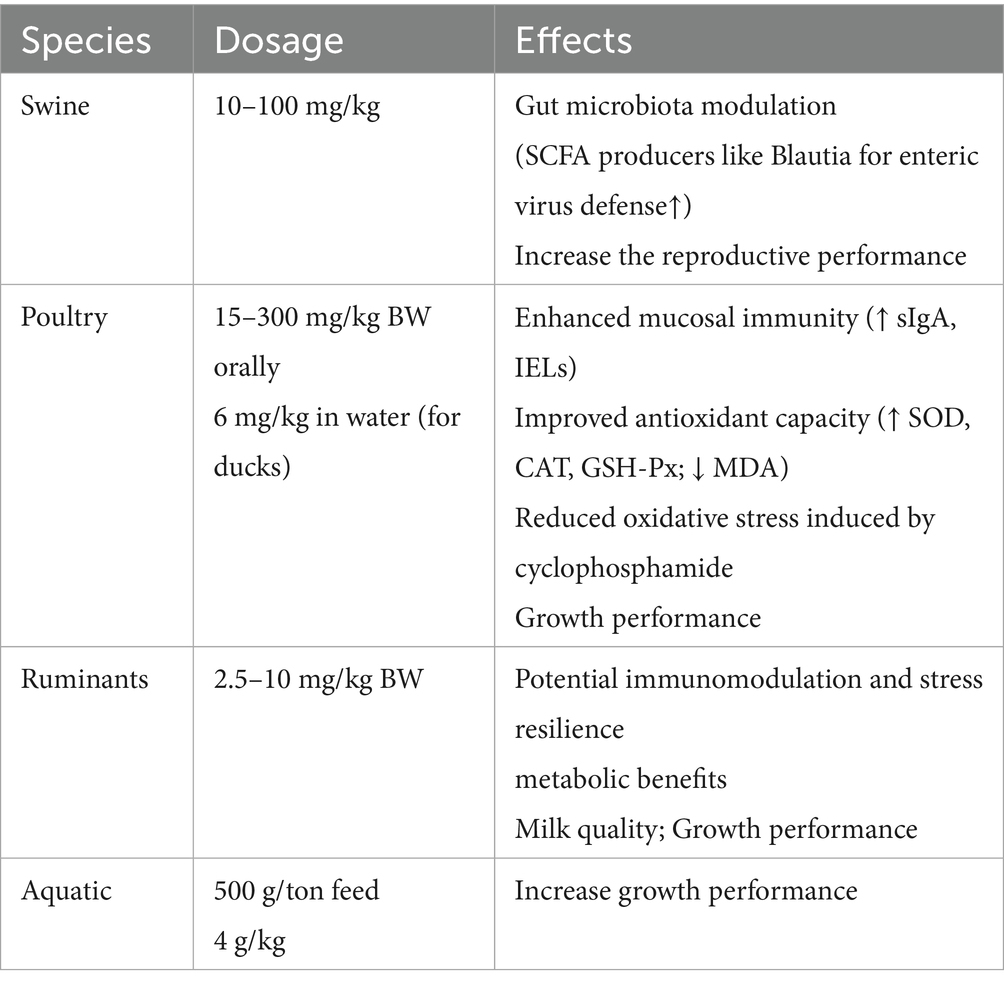
Ginsenosides, primarily administered as feed additives or oral supplements, demonstrate species-specific benefits across livestock: in poultry, doses of 15 mg/kg body weight enhance mucosal immunity, boost antioxidant capacity and improve vaccine efficacy against pathogens (52). In aquatic species such as large yellow croaker, inclusion at 500 mg/kg feed reduces winter mortality by 80%, accelerates post-cold weight gain, and strengthens disease resilience (53). While ruminant applications remain emerging, early evidence suggests potential for metabolic modulation and stress mitigation (54). Conversely, swine research is sparse but proposes roles in gut microbiota optimization and inflammation control (55). Critically, core effects such as immune regulation, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, underpin these benefits across all species, though ruminant and swine models urgently require targeted validation. The summary of ginsenosides were used in animals was shown in Table 1.
4.1 The application of ginsenosides in swine industry
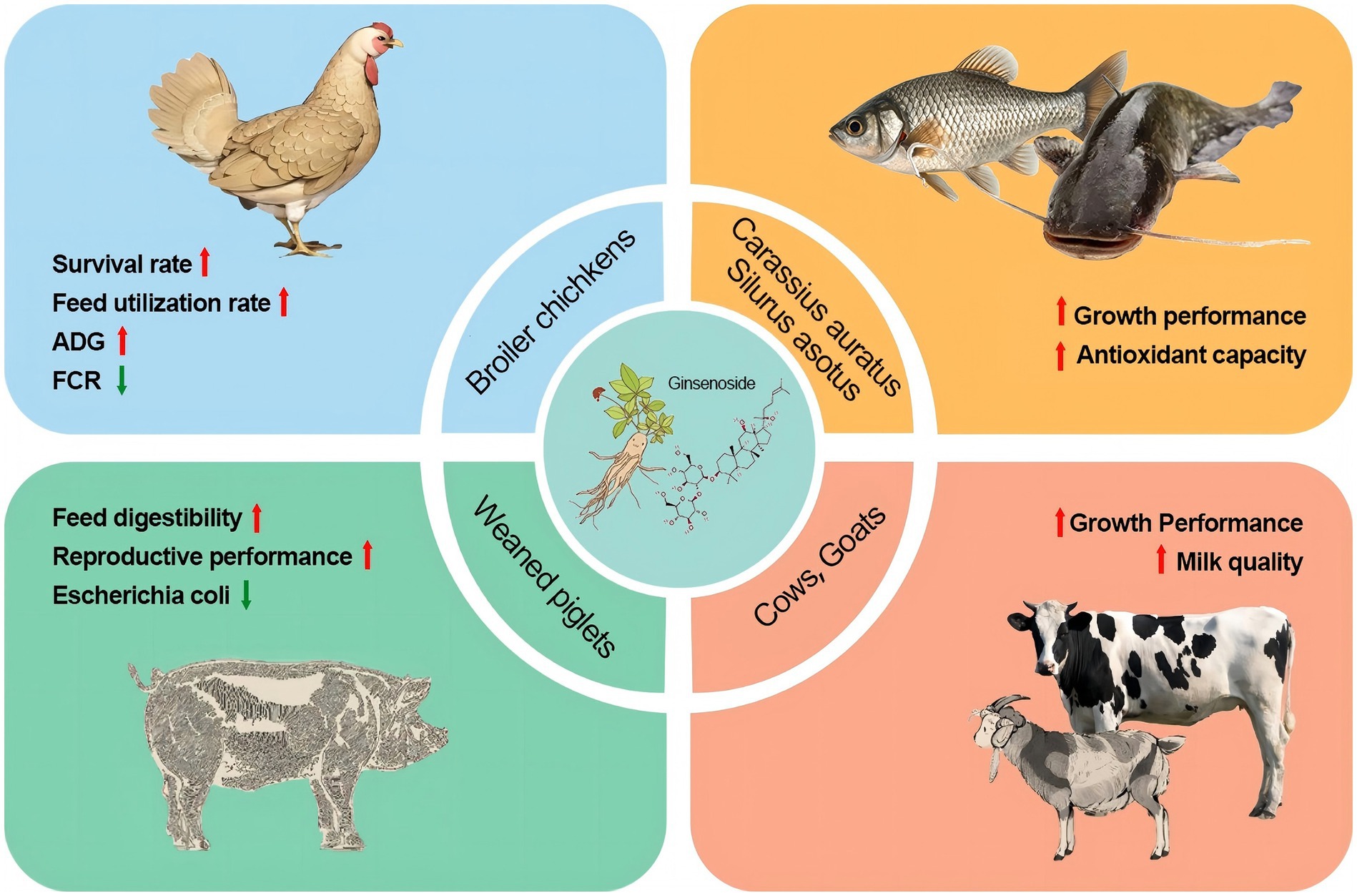
Ginsenosides, mainly administered as oral supplements or feed additives, demonstrate emerging potential in swine production through multifaceted biological actions, they enhance gut health by modulating microbiota composition (56), strengthen intestinal barrier integrity via up-regulation of tight junction proteins such as ZO-1 and occludin (57), and boost systemic and mucosal immunity by elevating serum IgG/IgA levels and activating TLR4/NF-κB pathways (58), thereby improving vaccine efficacy against pathogens like PRRSV (59) and PEDV (60). Concurrently, they mitigate oxidative stress by elevating antioxidant enzymes (SOD, GSH-Px) via Nrf2 activation while suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines and preliminary evidence suggests roles in improving growth performance by optimizing nutrient metabolism (61). The intestinal microbiota of early-weaned piglets is easily disturbed, resulting in reduce the abilities of digestion and absorption. Yin et al. (62) added ginsenoside extract to the diet of weaned piglets, they found that the feed digestibility of weaned piglets was significantly improved compared with the control group, and the number of Escherichia coli in feces was significantly reduced. Ginsenoside Rb1 can inhibit porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) and exert its antiviral effect by interfering with RNA replication. This indicates that ginsenoside Rb1 can protect the health of sows through antiviral effects to increase the reproductive performance because PRRSV was mainly have negative effect on fertility. Kim et al. (63) found that 20 μg/mL ginsenosides Rg1 treatment improved embryo quality by culturing porcine embryo cells in vitro. The main mechanism is to promote the increase of glucose uptake by blastocysts through ginsenosides Rg1, and reduces the apoptosis of embryonic cells under oxidative stress conditions. This indicates that ginsenoside Rg1 can improve the survival rate of pig embryonic cells by stimulating metabolic pathways and thus indirectly improve the reproductive performance of sows. Therefore, ginsenosides can be used as a potential feed additive to improve the reproductive performance of sows.
4.2 The application in poultry
Adding 10, 15, and 20 mg/kg ginsenosides to the basal diet of broiler chickens aged 0–7 weeks, respectively. The results showed that ginsenosides can significantly improve the survival rate and feed utilization rate, and the best effect was achieved when 15 mg/kg ginsenosides was added (52). Another study showed that adding 300 mg/kg ginsenoside Rg1 to the diet can significantly increase the average daily gain (ADG) of yellow-feathered broilers in the late growth period and significantly reduce the feed conversion ratio (FCR) (64, 65). Adding Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) to laying hen diets can improve egg quality. As the amount of PNS added increases, the egg white weight increases and the eggshell hardness improved. Song et al. (65) found that adding 300 mg/kg ginsenoside Rg1 to the diet could significantly increase the final body weight of broilers, reduce feed conversion rate, and improve the growth performance of broilers in the later stages. Tajudeen et al. (66) reported that adding 0.5% ginsenosides to the diet can increase the yolk content of laying hens, reduce feed conversion rate (FCR) and improve egg production performance. The reason may be that ginsenosides have a stimulating effect on oocyte meiosis and proliferation. In summary, ginsenosides can be used in poultry feed formula to improve their productive performance.
4.3 The application in ruminant
Studies that provide comprehensive insights into the interplay between host metabolism, gut microbiota, and feed efficiency are highly relevant to the potential applications of ginsenosides in improving livestock performance (67), especially in ruminants. There were very few literature reported the application of ginsenosides in cattle. When 1% ginsenosides were added to cattle diets, it was found that the growth performance and meat quality were improved, and there was no negative effect on other tissues or organs. The possible reason is that ginsenosides have a wide range of pharmacological activities, which can significantly improve the function of rumen fermentation, increase protein utilization and thus promote cattle growth (54). Ginsenosides Rg1 and Rg3 can inhibit bacterial reproduction by enhancing immune response and inhibiting bacterial protein signal transduction pathways, ultimately alleviating cow mastitis caused by bacterial infection (68). Ginsenosides can increase the relative abundance of beneficial bacteria in the rumen microorganisms, thereby improving the utilization of nutrients and thus increasing body weight (69). In the study on goats, intravenous injection of ginsenoside Rg1 at a dose of 1.9–2.5 mg/kg body weight into the breast can treat LPS induced mastitis. The possible mechanism is that ginsenoside Rg1 promotes binding to TLR4 and inhibits the activation of TLR4 signaling pathway by LPS, thereby exerting anti-inflammatory effects and protective effects on the mammary gland (70). Therefore, the application of ginsenosides in ruminants can enhance growth performance and also improve the quality of dairy products.
4.4 The application in aquaculture
There are few reports on the application of ginsenosides in aquaculture. Sun et al. (71) found that the addition of ginsenosides to the diet significantly improved the growth performance and feed utilization of fish, including weight gain rate (WGR), feed efficiency ratio (FER), protein efficiency ratio (PER) and protein deposition rate (PDR). Microbial fermentation can transform ginsenosides in ginseng stems and leaves into rare saponins through deglycosylation, making them more pharmacologically active. The extract obtained by fermenting ginseng stems and leaves with Lactobacillus casei was added to Carassius auratus feed to increase the activity of GSH-Px, SOD and CAT, reduce the MDA content, and increase the gene expression levels of serum anti-inflammatory factors such as IL-10 and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) in various tissues (72). This indicated that ginsenosides can enhance the antioxidant capacity and immune-related gene expression of Carassius auratus. Gao et al. (73) added ginsenosides to the diet of Silurus asotus to explore the effect of ginseng on lipid metabolism in Silurus asotus. The results showed that adding 4 g/kg ginsenosides to the feed could effectively promote the growth and significantly reduce the total cholesterol and triglyceride levels in serum. The reason may be that ginsenosides can regulate the transcription level of the gene encoding iodothyronine deiodinase 2 (DIO2), reduce the synthesis of triglycerides and thyroxine, finally reduce liver fat deposition in catfish by regulating lipid metabolism (74). The above studies show that adding ginsenosides to fish diet can improve growth performance, therefore ginsenosides be used as a potential feed additive in aquaculture. The application of ginsenosides in animals was shown in Figure 3.
5 Conclusions and perspectives
Ginsenosides have multiple biological activities including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immune regulation and anti-stress. Therefore, it can be used as feed additives to improve animal growth performance and address urgent issues in the animal husbandry such as cow mastitis and piglet weaning stress. However, there are significant differences in the effects of ginsenosides on different animals, and the appropriate dosage for addition has not yet been clearly explored. The extraction process of ginsenosides is still very complicated, thus its manufacturing cost is very high. Therefore, it is very important to optimize the extraction process of ginsenosides, in order to provide theoretical support for exploring the most suitable dosage of ginsenosides in different animals and its application in aquaculture as a feed additive.
Author contributions
YoL: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft. GZ: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Supervision. JW: Writing – original draft, Software, Methodology. JL: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Investigation. YuL: Writing – original draft, Software, Investigation. SP: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation. SC: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YG: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The research review was supported by the funding of Baicheng Normal University Doctoral Research Initiation Fund Project (90024169041).
Conflict of interest
YoL was employed by Changchun Borui Science & Technology Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Mancuso, C, and Santangelo, R. Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius: from pharmacology to toxicology. Food Chem Toxicol. (2017) 107:362–72. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.07.019
2. Nag, SA, Qin, J-J, Wang, W, Wang, M-H, Wang, H, and Zhang, R. Ginsenosides as anticancer agents: in vitro and in vivo activities, structure–activity relationships, and molecular mechanisms of action. Front Pharmacol. (2012) 3:25. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00025
3. Chen, W, Balan, P, and Popovich, DG. Review of ginseng anti-diabetic studies. Molecules. (2019) 24:4501. doi: 10.3390/molecules24244501
4. Assinewe, VA, Baum, BR, Gagnon, D, and Arnason, JT. Phytochemistry of wild populations of Panax quinquefolius L. (north American ginseng). J Agric Food Chem. (2003) 51:4549–53. doi: 10.1021/jf030042h
5. Li, W, Gu, C, Zhang, H, Awang, DV, Fitzloff, JF, Fong, HH, et al. Use of high-performance liquid chromatography− tandem mass spectrometry to distinguish Panax ginseng CA Meyer (Asian ginseng) and Panax quinquefolius L. (north American ginseng). Anal Chem. (2000) 72:5417–22. doi: 10.1021/ac000650l
6. Yang, C, Qu, L, Wang, R, Wang, F, Yang, Z, and Xiao, F. Multi-layered effects of Panax notoginseng on immune system. Pharmacol Res. (2024) 204:107203. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107203
7. Kwok, H-H, Guo, G-L, Lau, JK-C, Cheng, Y-K, Wang, J-R, Jiang, Z-H, et al. Stereoisomers ginsenosides-20 (S)-Rg3 and-20 (R)-Rg3 differentially induce angiogenesis through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Biochem Pharmacol. (2012) 83:893–902. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.12.039
8. Liu, D, Zhang, H, Gu, W, Liu, Y, and Zhang, M. Ginsenoside Rb1 protects hippocampal neurons from high glucose-induced neurotoxicity by inhibiting GSK3β-mediated CHOP induction. Mol Med Rep. (2014) 9:1434–8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.1958
9. Im, D-S. Pro-resolving effect of ginsenosides as an anti-inflammatory mechanism of Panax ginseng. Biomolecules. (2020) 10:444. doi: 10.3390/biom10030444
10. Im Chung, S, Kang, MY, and Lee, SC. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant activity of aged ginseng (Panax ginseng). Prev Nutr Food Sci. (2016) 21:24–30. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2016.21.1.24
11. Chen, X-J, Zhang, X-J, Shui, Y-M, Wan, J-B, and Gao, J-L. Anticancer activities of protopanaxadiol-and protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides and their metabolites. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2016) 2016:5738694. doi: 10.1155/2016/5738694
12. Piao, X, Zhang, H, Kang, JP, Yang, DU, Li, Y, Pang, S, et al. Advances in saponin diversity of Panax ginseng. Molecules. (2020) 25:3452. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153452
13. Sun, Y, Liu, X, Fu, X, Xu, W, Guo, Q, and Zhang, Y. Discrepancy study of the chemical constituents of Panax Ginseng from different growth environments with UPLC-MS-based metabolomics strategy. Molecules. (2023) 28:2928. doi: 10.3390/molecules28072928
14. Ashrafizadeh, M, Ahmadi, Z, Yaribeygi, H, Sathyapalan, T, Jamialahmadi, T, and Sahebkar, A. The effects of Ginsenosides on the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2021) 1328:307–22. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-73234-9_20
15. Jang, WY, Hwang, JY, and Cho, JY. Ginsenosides from Panax ginseng as key modulators of NF-κB signaling are powerful anti-inflammatory and anticancer agents. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:6119. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076119
16. Li, ZY, Dai, YX, Wu, ZM, Li, G, Pu, PM, Hu, CW, et al. Network pharmacology analysis and animal experiment validation of neuroinflammation inhibition by total ginsenoside in treating CSM. Phytomedicine. (2024) 126:155073. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155073
17. Zeng, JJ, Shi, HQ, Ren, FF, Zhao, XS, Chen, QY, Wang, DJ, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice via suppressing TAK1-JNK/p38 signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2023) 44:1366–79. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01057-y
18. Li, H, Zhu, J, Xu, YW, Mou, FF, Shan, XL, Wang, QL, et al. Notoginsenoside R1-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles targeting the site of injury through inflammatory cells improves heart repair after myocardial infarction. Redox Biol. (2022) 54:102384. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102384
19. Arafa, EA, Refaey, MS, Abd El-Ghafar, OAM, Hassanein, EHM, and Sayed, AM. The promising therapeutic potentials of ginsenosides mediated through p38 MAPK signaling inhibition. Heliyon. (2021) 7:e08354. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08354
20. Ashrafizadeh, M, Tavakol, S, Mohammadinejad, R, Ahmadi, Z, Yaribeygi, H, Jamialahmadi, T, et al. Paving the road toward exploiting the therapeutic effects of Ginsenosides: an emphasis on autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2021) 1308:137–60. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-64872-5_12
21. Cheung, EC, and Vousden, KH. The role of ROS in tumour development and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. (2022) 22:280–97. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00435-0
22. Zorov, DB, Juhaszova, M, and Sollott, SJ. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol Rev. (2014) 94:909–50. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00026.2013
23. Kim, HM, Song, Y, Hyun, GH, Long, NP, Park, JH, Hsieh, YS, et al. Characterization and antioxidant activity determination of neutral and acidic polysaccharides from Panax ginseng CA Meyer. Molecules. (2020) 25:791. doi: 10.3390/molecules25040791
24. Rani, V, Deep, G, Singh, RK, Palle, K, and Yadav, UC. Oxidative stress and metabolic disorders: pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Life Sci. (2016) 148:183–93. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.02.002
25. Zhao, B, Wang, X, Liu, H, Lv, C, and Lu, J. Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of oligosaccharides from Panax ginseng CA Meyer. Int J Biol Macromol. (2020) 150:737–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.016
26. Jomová, K, Hudecova, L, Lauro, P, Simunkova, M, Alwasel, SH, Alhazza, IM, et al. A switch between antioxidant and prooxidant properties of the phenolic compounds myricetin, morin, 3′, 4′-dihydroxyflavone, taxifolin and 4-hydroxy-coumarin in the presence of copper (II) ions: a spectroscopic, absorption titration and DNA damage study. Molecules. (2019) 24:4335. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234335
27. Chang, MS, Lee, SG, and Rho, HM. Transcriptional activation of cu/Zn superoxide dismutase and catalase genes by panaxadiol ginsenosides extracted from Panax ginseng. Phytother Res. (1999) 13:641–4. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-1573(199912)13:8<>3.0.co;2-z
28. Ong, W-Y, Farooqui, T, Koh, H-L, Farooqui, AA, and Ling, E-A. Protective effects of ginseng on neurological disorders. Front Aging Neurosci. (2015) 7:129. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00129
29. Loboda, A, Damulewicz, M, Pyza, E, Jozkowicz, A, and Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2016) 73:3221–47. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2223-0
30. Cui, G, Luk, SCW, Li, RA, Chan, KKK, Lei, SW, Wang, L, et al. Cytoprotection of baicalein against oxidative stress-induced cardiomyocytes injury through the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2015) 65:39–46. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000161
31. Liu, M, Bai, X, Yu, S, Zhao, W, Qiao, J, Liu, Y, et al. Ginsenoside re inhibits ROS/ASK-1 dependent mitochondrial apoptosis pathway and activation of Nrf2-antioxidant response in beta-amyloid-challenged SH-SY5Y cells. Molecules. (2019) 24:2687. doi: 10.3390/molecules24152687
32. Kim, JH, Yi, Y-S, Kim, M-Y, and Cho, JY. Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J Ginseng Res. (2017) 41:435–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2016.08.004
33. Liu, H, Lu, X, Hu, Y, and Fan, X. Chemical constituents of Panax ginseng and Panax notoginseng explain why they differ in therapeutic efficacy. Pharmacol Res. (2020) 161:105263. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105263
34. Liu, Y, Liu, N, Liu, Y, He, H, Luo, Z, Liu, W, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 reduces D-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver injury by regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome. J Clin Transl Hepatol. (2021) 10:474–85. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2021.00072
35. Luo, M, Yan, D, Sun, Q, Tao, J, Xu, L, Sun, H, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammation via the TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 pathway. J Cell Biochem. (2020) 121:2994–3004. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29556
36. Li, H, Huang, N, Zhu, W, Wu, J, Yang, X, Teng, W, et al. Modulation the crosstalk between tumor-associated macrophages and non-small cell lung cancer to inhibit tumor migration and invasion by ginsenoside Rh2. BMC Cancer. (2018) 18:579. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4299-4
37. Wen, S, Zou, ZR, Cheng, S, Guo, H, Hu, HS, Zeng, FZ, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 improves energy metabolism after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. (2023) 18:1332–8. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.357915
38. Qian, Y, Ke-Wu, Z, Xiao-Li, M, Peng-Fei, T, and Xue-Mei, W. Ginsenoside Rk1 suppresses pro-inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells by inhibiting the Jak 2/Stat3 pathway. Chin J Nat Med. (2017) 15:751–7. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(17)30106-1
39. Ahmed, SMU, Luo, L, Namani, A, Wang, XJ, and Tang, X. Nrf2 signaling pathway: pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2017) 1863:585–97. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.11.005
40. Hu, S, Liu, T, Wu, Y, Yang, W, Hu, S, Sun, Z, et al. Panax notoginseng saponins suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced barrier disruption and monocyte adhesion on bEnd. 3 cells via the opposite modulation of Nrf2 antioxidant and NF-κB inflammatory pathways. Phytother Res. (2019) 33:3163–76. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6488
41. Kim, S, Oh, M-H, Kim, B-S, Kim, W-I, Cho, H-S, Park, B-Y, et al. Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 by ginsenoside Ro attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in macrophage cells. J Ginseng Res. (2015) 39:365–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.03.008
42. Wan, C, Lu, R, Zhu, C, Wu, H, Shen, G, Yang, Y, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 enhanced immunity and altered the gut microflora in mice immunized by H1N1 influenza vaccine. PeerJ. (2023) 11:e16226. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16226
43. Wang, D, Li, X, Xu, L, Hu, Y, Zhang, B, and Liu, J. Immunologic synergism with IL-2 and effects of cCHMIs on mRNA expression of IL-2 and IFN-gamma in chicken peripheral T lymphocyte. Vaccine. (2006) 24:7109–14. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.07.005
44. Su, X, Pei, Z, and Hu, S. Ginsenoside re as an adjuvant to enhance the immune response to the inactivated rabies virus vaccine in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. (2014) 20:283–9. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.03.008
45. Yuan, D, Yuan, Q, Cui, Q, Liu, C, Zhou, Z, Zhao, H, et al. Vaccine adjuvant ginsenoside Rg1 enhances immune responses against hepatitis B surface antigen in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. (2016) 94:676–81. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2015-0528
46. Liu, X, Hussain, R, Mehmood, K, Tang, Z, Zhang, H, and Li, Y. Mitochondrial-endoplasmic reticulum communication-mediated oxidative stress and autophagy. Biomed Res Int. (2022) 2022:6459585. doi: 10.1155/2022/6459585
47. Li, Q, Xiang, Y, Chen, Y, Tang, Y, and Zhang, Y. Ginsenoside Rg1 protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling and inhibition of JNK. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2018) 44:21–37. doi: 10.1159/000484578
48. Jin, SH, Sun, JJ, Liu, G, Shen, LJ, Weng, Y, Li, JY, et al. Nrf2/PHB2 alleviates mitochondrial damage and protects against Staphylococcus aureus-induced acute lung injury. MedComm. (2023) 4:e448. doi: 10.1002/mco2.448
49. Niu, X, Ding, Y, Chen, S, Gooneratne, R, and Ju, X. Effect of immune stress on growth performance and immune functions of livestock: mechanisms and prevention. Animals (Basel). (2022) 12:909. doi: 10.3390/ani12070909
50. Fischer, TW, Bergmann, A, Kruse, N, Kleszczynski, K, Skobowiat, C, Slominski, AT, et al. New effects of caffeine on corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)-induced stress along the intrafollicular classical hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis (CRH-R1/2, IP(3) -R, ACTH, MC-R2) and the neurogenic non-HPA axis (substance P, p75 (NTR) and TrkA) in ex vivo human male androgenetic scalp hair follicles. Br J Dermatol. (2021) 184:96–110. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19115
51. Wan, Y, Zhang, Z, Lin, D, Wang, X, Huang, T, Su, J, et al. Characterization of CRH-binding protein (CRHBP) in chickens: molecular cloning, tissue distribution and investigation of its role as a negative feedback regulator within the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal Axis. Genes (Basel). (2022) 13:1680. doi: 10.3390/genes13101680
52. Zhu, H, Kulyar, MF, Ding, Y, Yao, W, Mo, Q, and Li, J. Ginsenoside Rg1 regulates thiram-induced chondrocytes' apoptosis and angiogenesis in broiler chickens. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2023) 30:34188–202. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-24598-x
53. Chen, B, Wei, Y, Wang, D, and Jia, X. Metabolism of ginsenosides Rk₃ and Rh₄ from steamed notoginseng in zebrafish by ultraperformance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Arch Pharm Res. (2015) 38:1468–76. doi: 10.1007/s12272-014-0538-7
54. Wang, M, Zhang, L, Jiang, X, Song, Y, Wang, D, Liu, H, et al. Multiomics analysis revealed that the metabolite profile of raw milk is associated with the lactation stage of dairy cows and could be affected by variations in the ruminal microbiota. J Dairy Sci. (2024) 107:8709–21. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-24753
55. Zheng, X, Zhu, D, Xiang, Q, Guo, D, Kuang, Q, Zeng, Y, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication through suppressing S1 protein mediated the MAPK/ERK pathway and reducing apoptosis. Int J Biol Macromol. (2025) 304:140937. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140937
56. Jia, F, Chen, Y, Xin, G, Li, L, Liu, Z, Xu, S, et al. Shuangshen Ningxin capsule alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in miniature pigs by modulating mitophagy: network pharmacology and experiments in vivo. Chin Med. (2023) 18:120. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00810-z
57. Zhou, Y, Xiong, X, Cheng, Z, Chen, Z, Wu, S, Yu, Y, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by protecting the intestinal barrier through the signal network of VDR, PPARγ and NF-κB. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2024) 18:4825–38. doi: 10.2147/dddt.S481769
58. Xu, A, Deng, F, Chen, Y, Kong, Y, Pan, L, Liao, Q, et al. NF-κB pathway activation during endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in a rat model of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 130:110525. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110525
59. Yuan, F, Sharma, J, Nanjappa, SG, Gaulke, CA, and Fang, Y. Effect of killed PRRSV vaccine on gut microbiota diversity in pigs. Viruses. (2022) 14:1081. doi: 10.3390/v14051081
60. Xing, JH, Niu, TM, Zou, BS, Yang, GL, Shi, CW, Yan, QS, et al. Gut microbiota-derived LCA mediates the protective effect of PEDV infection in piglets. Microbiome. (2024) 12:20. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01734-4
61. Wang, TT, Hu, J, Jiao, HH, Liu, Y, Zhou, JH, Zhao, YY, et al. Effect of BBM gene on callus growth and ginsenoside content in Panax quinquefolius. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. (2023) 48:3156–61. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230313.101
62. Yin, J, Kim, HS, Kim, YM, and Kim, IH. Effects of dietary fermented red ginseng marc and red ginseng extract on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, blood profile, fecal microbial, and noxious gas emission in weanling pigs. J Appl Anim Res. (2018) 46:1084–9. doi: 10.1080/09712119.2018.1466708
63. Kim, S-H, Choi, K-H, Lee, D-K, Oh, J-N, Hwang, JY, Park, C-H, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 improves in vitro-produced embryo quality by increasing glucose uptake in porcine blastocysts. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2015) 29:1095–101. doi: 10.5713/ajas.15.0678
64. Bi, S, Shao, J, Qu, Y, Xu, W, Li, J, Zhang, L, et al. Serum metabolomics reveal pathways associated with protective effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on immune stress. Poult Sci. (2022) 101:102187. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102187
65. Song, Z, Xie, K, Zhang, Y, Xie, Q, He, X, and Zhang, H. Effects of dietary ginse-noside Rg1 supplementation on growth performance, gut health, and serum immunity in broiler chickens. Front Nutr. (2021) 8:705279. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.705279
66. Tajudeen, H, Mun, J, Ha, S, Hosseindoust, A, Lee, S, and Kim, J. Effect of wild ginseng on the laying performance, egg quality, cytokine expression, ginsenoside concentration, and microflora quantity of laying hens. J Anim Sci Technol. (2023) 65:351–64. doi: 10.5187/jast.2022.e108
67. Zhang, Y, Zhang, X, Cao, D, Yang, J, Mao, H, Sun, L, et al. Integrated multi-omics reveals the relationship between growth performance, rumen microbes and metabolic status of Hu sheep with different residual feed intakes. Anim Nutr. (2024) 18:284–95. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.04.021
68. Hu, S, Concha, C, Lin, F, and Persson Waller, K. Adjuvant effect of ginseng extracts on the immune responses to immunisation against Staphylococcus aureus in dairy cattle. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. (2003) 91:29–37. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(02)00264-7
69. Bagath, M, Krishnan, G, Devaraj, C, Rashamol, VP, Pragna, P, Lees, AM, et al. The impact of heat stress on the immune system in dairy cattle: a review. Res Vet Sci. (2019) 126:94–102. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2019.08.011
70. Su, F, Xue, Y, Wang, Y, Zhang, L, Chen, W, and Hu, S. Protective effect of ginsenosides Rg1 and re on lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis by competitive binding to toll-like receptor 4. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2015) 59:5654–63. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01381-15
71. Sun, Z, Tan, X, Ye, H, Zou, C, Ye, C, and Wang, A. Effects of dietary Panax notoginseng extract on growth performance, fish composition, immune responses, intestinal histology and immune related genes expression of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂× Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀) fed high lipid diets. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2018) 73:234–44. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.11.007
72. Ramya, EM, Kumar, GP, Chandrasekhar, Y, and Anilakumar, KR. Adaptogenic potential of ginsenosides against domoic acid-induced toxicity by regulating neuronal stress and kinate receptors: ex vivo and in silico studies. J Food Biochem. (2022) 46:e14089. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14089
73. Gao, C-L, Zhu, C, Zhao, Y-P, Chen, X-H, Ji, C-B, Zhang, C-M, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction is induced by high levels of glucose and free fatty acids in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2010) 320:25–33. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.01.039
Keywords: ginsenoside, biological function, animal production, feed additives, application
Citation: Li Y, Zhang G, Wang J, Li J, Liu Y, Pan S, Chang S and Gao Y (2025) The biological functions of ginsenoside and its applications in animal husbandry. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1648629. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1648629
Edited by:
Awad A. Shehata, Helmholtz Association of German Research Centers (HZ), GermanyReviewed by:
Sameh A. Abdelnour, Zagazig University, EgyptShahid Ali Rajput, Muhammad Nawaz Shareef University of Agriculture, Pakistan
Copyright © 2025 Li, Zhang, Wang, Li, Liu, Pan, Chang and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yang Gao, MTc5NjkyMDU4QHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yongqiang Li
Yongqiang Li Guohui Zhang3†
Guohui Zhang3† Yang Gao
Yang Gao