- 1College of Veterinary Medicine, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment Techniques for Animal Disease, Ministry of Agriculture, Hohhot, China
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of compound yeast culture on production performance, antioxidant function, and inflammatory factors in Hu sheep.
Methods: A total of 180 45-day-old healthy Hu sheep were randomly divided into two groups. The control group was fed a basal diet, and the experimental group was supplemented with 50 g/kg compound yeast culture during the conservation period (1–30 days) and 60 g/kg during the fattening period (31–117 days). The experiment lasted 124 days, with a pre-feeding period of 7 days and a formal period of 117 days. Daily feed intake was recorded, and the animals were weighed before morning feeding on days 1, 36, 67, 97, and 117 of the experiment and slaughtered on the 117th day. At the same time, non-anticoagulant blood was collected before morning feeding on days 1, 30, 60, and 90, and serum antioxidant indices and serum inflammatory factors were measured.
Results: The results showed that the average daily gain of Hu sheep in the experimental group increased by 38 g compared to that in the control group, which increased by 13.4% (p < 0.05). The average daily feed intake of the experimental group increased by 80 g, an increase of 5% (p < 0.05). The feed-to-weight ratio in the experimental group decreased by 8.3% (p < 0.05). Compared with the control group, the economic profit of the experimental group increased by 130.27 yuan, an increase of 34.6% (p < 0.01). The serum total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) content and superoxide dismutase activity (SOD) activity of Hu sheep in the experimental group significantly increased (p < 0.05). The malondialdehyde (MDA) content decreased significantly (p < 0.01). The contents of inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-6, IL-4 and IL-10 in the serum of Hu sheep in the experimental group were significantly increased (p < 0.05).
Discussion: The above results showed that compound yeast culture significantly increased Hu sheep’s feed intake, daily gain, and economic benefit, and significantly reduced the feed-to-weight ratio, improved the antioxidant capacity, improved the immune function, and alleviated the effect of stress on Hu sheep.
Highlights
• Improved productivity: yeast culture boosted feed intake, daily gain, and feed efficiency.
• Higher profitability: economic returns increased by over 30%.
• Better health outcomes: antioxidant capacity and immune resilience were enhanced.
• Wider potential: yeast culture shows promise for other ruminant production systems.
Introduction
In the breeding process, free radicals are often increased due to long-distance transportation, environmental changes, and poor diet (1–3). A large number of free radicals are produced, leading to the accumulation of free radicals, causing damage to the animal body, destroying the body’s proteins, nucleic acids, and biofilm system, and causing oxidative stress and various inflammatory reactions (4–6). Recent studies have shown that yeast culture has positive effects on animal production performance and antioxidant capacity (7–10). Studies have shown that the addition of yeast culture to diet improves the growth and slaughter performance of mutton sheep (11), increases animal milk production (12), reduces somatic cell count (13), and improves rumen microflora (14, 15). Feeding the yeast culture to Simmental cattle not only enhanced the growth performance but also increased the activity of glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) in serum, reduced the content of malondialdehyde (MDA), and enhanced the antioxidant function of the body. Adding yeast culture to the diet of dairy cows can increase the (SOD) and total antioxidant capacity of lactating cows (16).
Compound yeast culture is a microecological preparation developed in our laboratory based on the physiological characteristics of ruminants. In a previous study, it was found that compound yeast culture can significantly improve the immunity of small-tailed Han sheep and significantly improve the weight gain, slaughter rate, and carcass weight of mutton sheep (17). A study on pigs, revealed that feeding compound yeast culture could improve production performance and reduce the number of stillbirths and constipation in sows (18). In a study on beef cattle, a compound yeast culture was found to improve immunity and provide economic benefits in animals (16). This study further explored the effects of compound yeast culture on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and inflammatory factors in Hu sheep and provided a theoretical basis for the application of compound yeast culture in Hu sheep breeding.
Materials and methods
Preparation of yeast culture
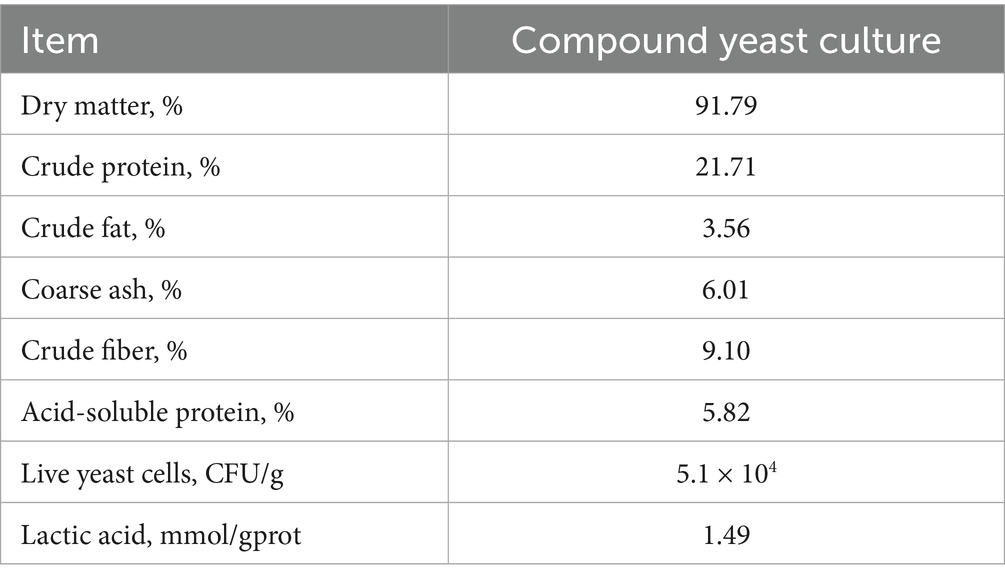
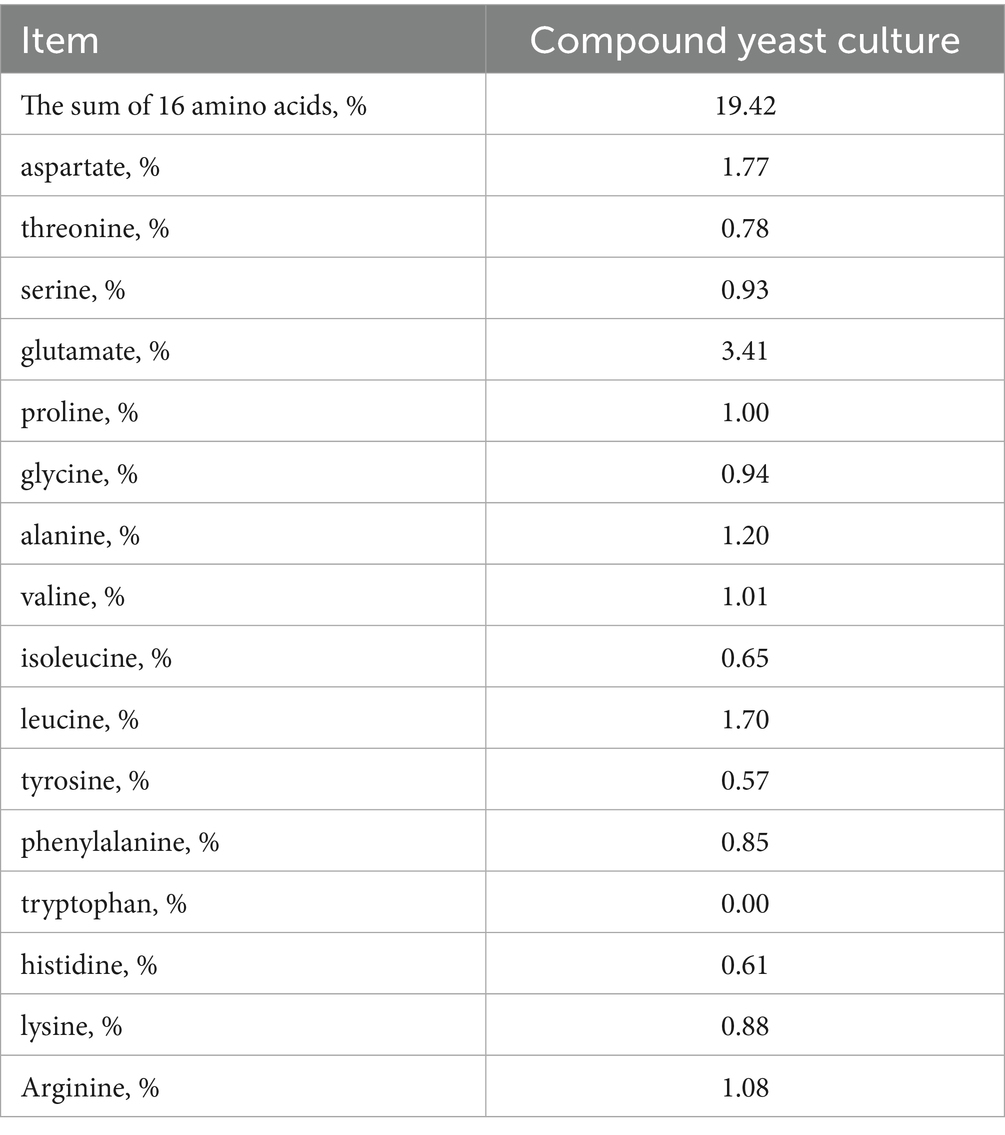
The compound yeast culture was fermented with 15% wheat bran, 12% corn bran, 16% corn meal, 10% rice bran meal, 8% DDGS, 27% corn germ meal, and 12% soybean meal. The fermentation strains, Saccharomyces cerevisiae XR4 and Kluyveromyces marxianus BC, were isolated by our research group with independent intellectual property rights. The two strains were mixed in a ratio of 1:1 to make a fermentation broth (1.5 × 108 cfu/g). Inoculation was performed at a dose of 10% of the solid substrate mass, and a certain amount of water was added to make the initial water content of the fermentation substrate 38–40%. Solid-state stacking fermentation was performed in a fermentation workshop with a stacking height of 60–65 cm. The temperature of the material was recorded every 3 h during fermentation. When the fermentation time reached 24 h and the temperature reached more than 40°C, the material was turned over once. After the material was turned over, stacking fermentation continued. The entire fermentation process lasted for 72 h. After fermentation, low-temperature drying and crushing bagging were performed, and the preparation of the composite yeast culture was completed. Nutritional indicators and amino acid compositions are shown in Tables 1, 2, respectively.
Animals and diet
The experiment was conducted at the Hu sheep breeding base in Qingyang City, Gansu Province, China. A total of 180, 45-day-old weaned healthy lambs were randomly divided into two groups (n = 90 per group). The trial period was 124 days, including 7 days of prefeeding and 117 days of the trial period. During the prefeeding period, the lambs were disinfected, epidemic prevention, earmarked, and dewormed, according to the routine procedures of the sheep farm. Feed at 08:00 and 18:00 every day, with free access to water.
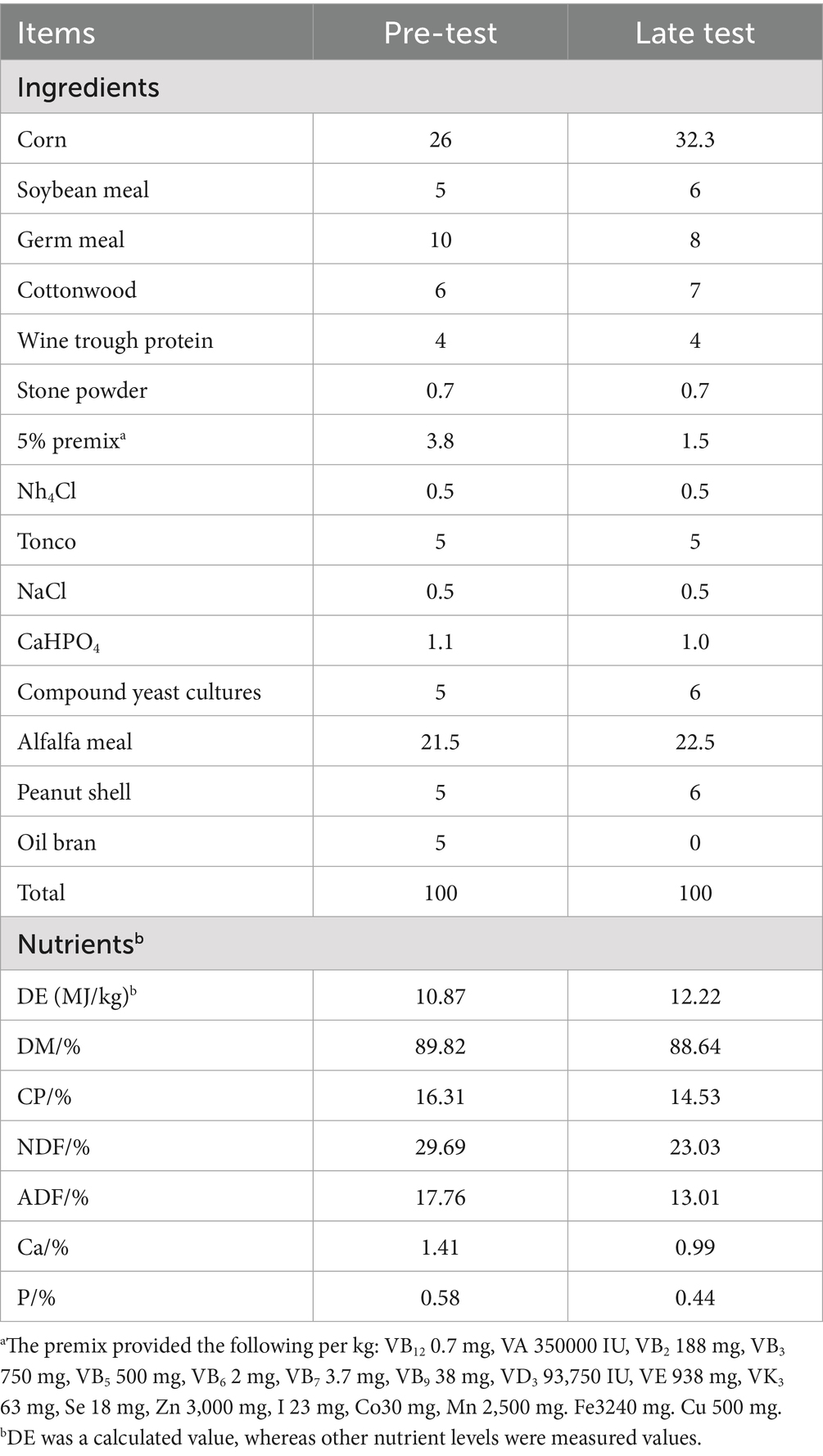
The nutritional requirements for different growth stages vary. The fattening process was divided into a conservation period (1–30 days of age) and a fattening period (31–117 days of age). The control group was fed the basic diet of the sheep farm, and the experimental group was fed the basic diet. Compound yeast culture was added at 50 g/kg during the conservation period and at 60 g/kg during the fattening period. The basal diet was formulated according to mutton sheep feeding standards’ (NY/T 816-2004). The energy and protein levels in each group were the same, and the feed composition is shown in Table 3.
Determination method of dietary nutrient levels
The dry matter (DM) content was determined according to the method of GB/T 6435-2014, crude protein (CP) content was determined according to the method of GB/T 6432-2018, crude fat (EE) content was determined according to the method of GB/T 6433-2006, crude ash (Ash) content was determined according to the GB/T 6438-2007 method, and crude fiber (CF) content was determined according to the method of GB/T 6434-2006. The neutral detergent fiber (NDF) content was determined according to GB/T 20806-2022 method, content of acid detergent fiber (ADF) content was determined according to the NY/T 1459-2007 method, acid soluble protein (ASCP) content was determined according to the NY/T 3801-2020 method, number of live yeast was determined according to the GB method 7300.501-2021, and amino acid content was determined according to the GB/T 18246-2019 method. Calcium (Ca) content was determined according to the GB/T 6436-2018 method, phosphorus (P) content was determined according to the GB/T 6437-2018 method, and lactic acid was determined using a lactic acid detection kit (no. G4308, Wuhan Sevier Biotechnology Co. Ltd., Wuhan, China). Digestible energy (DE) was calculated using the Refs3000 software.
Sample collection and detection
Determination of growth performance indexes
After the start of the experiment, leftovers were accurately weighed daily and the daily feed intake of the animals was calculated. The average daily gain and feed-to-weight ratio were calculated by weighing the sheep on days 1, 36, 67, 97, and 117, weighed on an empty stomach on the last day of the trial period and slaughtered every other day. Carcass weight was measured on the day of slaughter, and the slaughter rate and economic benefits were calculated. The relevant formulae are as follows:
Serum sample collection
Fifteen sheep were randomly selected from each group, and blood was collected from the jugular vein before morning feeding on days 1, 30, 60, and 90. The serum was placed at 4°C for 24 h, and the isolated serum was stored in a sterile non-enzymatic cryopreservation tube. It was stored at −20°C for the detection of antioxidant serum indices and inflammatory factors.
Analysis of serum indexes of immune function
The levels of cytokines interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in serum were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit. All ELISA kits were purchased from Quanzhou Ruixin Biotechnology Co. Ltd. Detection was performed in strict accordance with manufacturer’s instructions. The microplate reader used in this experiment was an Agilent Technologies 800TS-SN microplate reader (United States). Information on the kit is shown in Supplementary Table 1.
Analysis of serum indexes of antioxidant capacity
MDA content was detected using the thiobarbituric acid method, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was detected by the xanthine oxidase method, catalase (CAT) activity was detected by the ammonium molybdate method, glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activity was detected by colorimetry, and total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) was detected by the Fe3+ reduction method. Information on the kit is shown in Supplementary Table 2.
Data analysis
Excel 2020 was used to process and calculate experimental data for each group. Statistical software (SAS 9.0) was used to analyze the data using one-way analysis of variance. Multiple comparisons were made using the least significant difference method (p < 0.05, significant p < 0.01, extremely significant; p > 0.05, not significant).
Results
Effects of compound yeast culture on production performance of Hu sheep
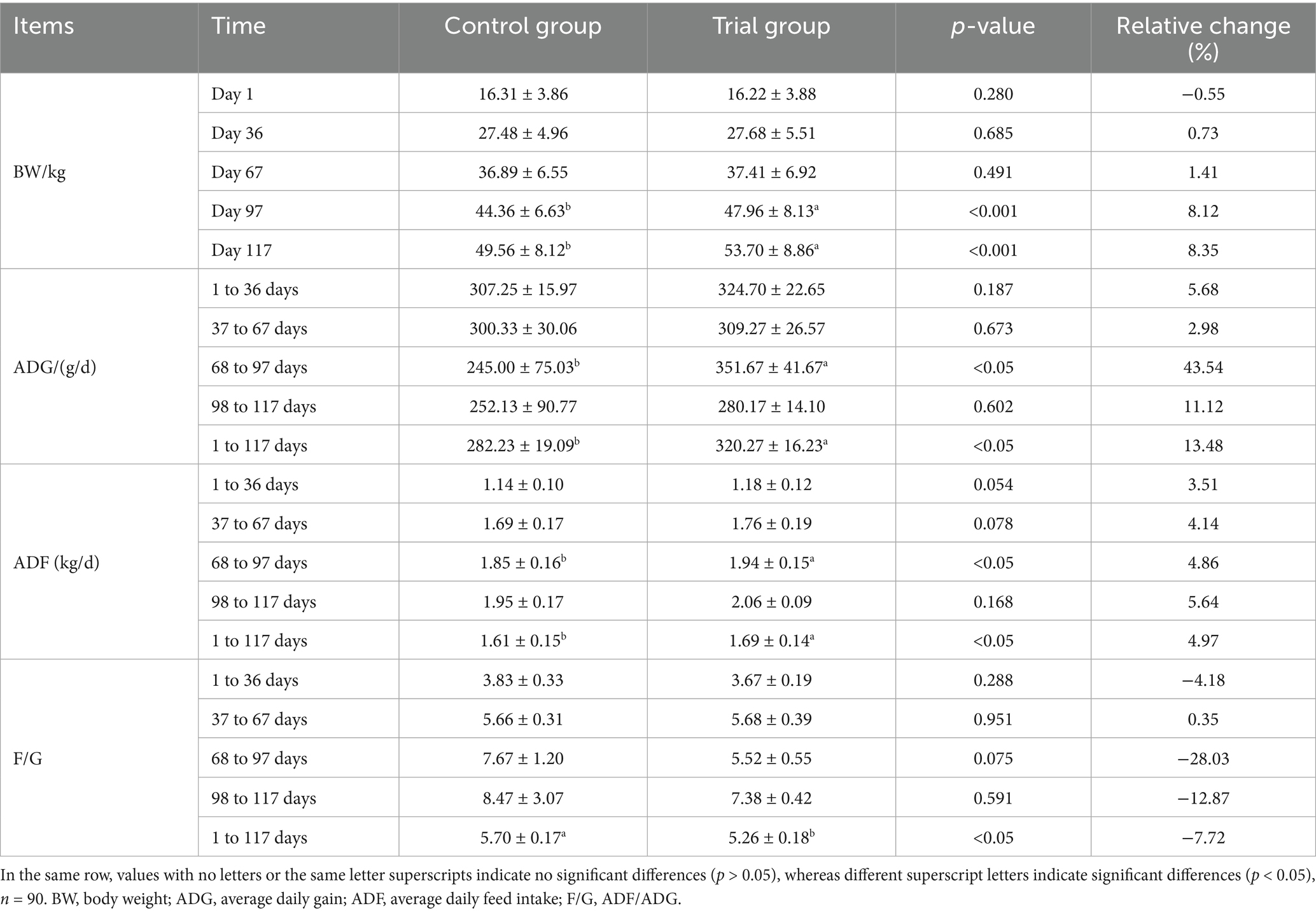
As shown in Table 4, on the 67th day of the experiment, the body weight, average daily feed intake, daily gain, and feed-to-weight ratio of the experimental group were not significantly different from those of the control group (p > 0.05). During the period of 68–97 days, the average daily gain of Hu sheep in the experimental group increased by 106.7 g compared to that in the control group, which increased by 43.5% (p < 0.05). The average daily feed intake of the experimental group was 90 g higher than that of the control group, an increase of 4.8% (p < 0.05). On day 97 of the experiment, the weight gain of Hu sheep in the experimental group was 3.6 kg, which was 8.1% higher than that in the control group (p < 0.01). On experiment day 117, the average weight of the experimental group was 53.70 kg, which was 4.14 kg higher than that of the control group, an increase of 8.3% (p < 0.01); the average daily gain of the experimental group was 320.27 g, which was 38.04 g higher than that of the control group and increased by 13.4% (p < 0.05). Feed intake of the experimental group was 80 g higher than that of the control group, an increase of 5% (p < 0.05). The feed-to-weight ratio in the experimental group decreased by 8.3% (p < 0.05). The above results show that the growth performance of Hu sheep could be improved by feeding them a compound yeast culture.
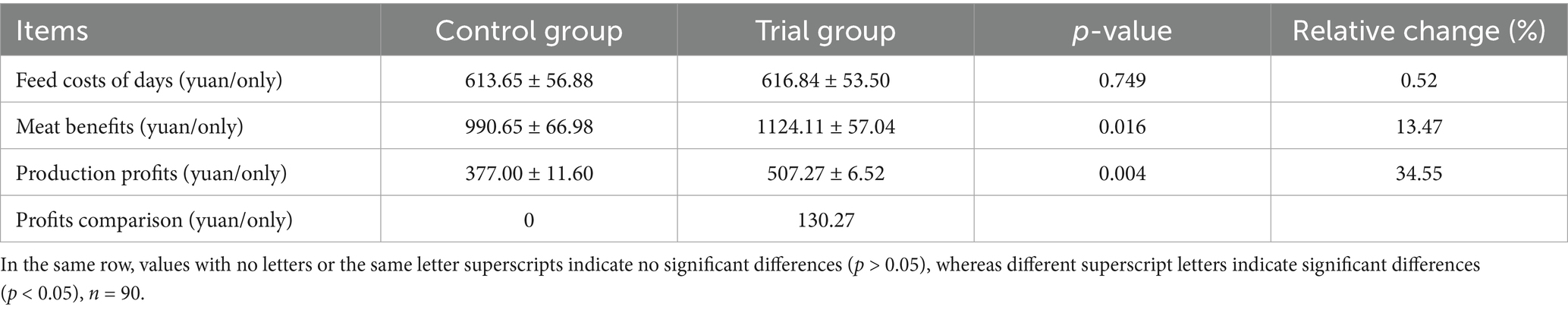
Effect of compound yeast culture on economic benefit of Hu sheep
In this experiment, the conservation period (1–30 d) based diet was 3,800 yuan/ton, containing a compound bacterial culture feed of 3,600 yuan/ton. The fattening period (31 to 117 d) included a basal diet of 3,200 yuan/ton, compound bacterial culture feed of 3,000 yuan/ton, corn of 3,000 yuan/ton, and Hu wool weight price of 30 yuan/kg. The experimental group invested 2,216 yuan more than the control group. Cycle additional investment of 50 yuan (water, electricity, and labor costs). As shown in Table 5, the production profit of the experimental group increased by 130.27 yuan, which is an increase of 34.6% (p < 0.01).
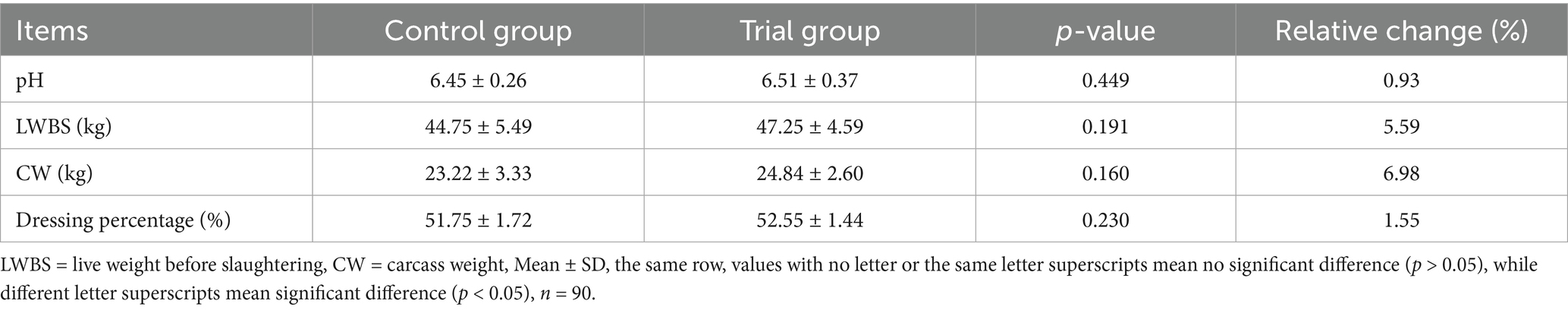
Effects of compound yeast culture on slaughter performance of Hu sheep
As shown in Table 6, the slaughter indexes of the experimental group were higher than those of the control group; however, the difference was not significant.
Effect of compound yeast culture on antioxidant capacity index of Hu sheep
As shown in Figure 1, there were no significant differences in the five indicators between the experimental and control groups during the first month of the experiment. When the experiment was performed for 60 d, SOD activity in the serum of Hu sheep in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group (p < 0.05), and serum T-AOC in the experimental group was significantly increased (p < 0.01). On day 90, the SOD activity and T-AOC in the serum of Hu sheep in the experimental group were significantly higher than those in the control group (p < 0.05), and the MDA content in the experimental group was significantly lower than that in the control group (p < 0.01). Throughout the experiment, the serum SOD activity and T-AOC of the experimental group increased significantly, whereas the MDA content decreased significantly. There was no significant change in serum CAT and GSH-Px activity in the experimental group compared to the control group. These results showed that feeding compound yeast culture could improve the antioxidant capacity of Hu sheep.
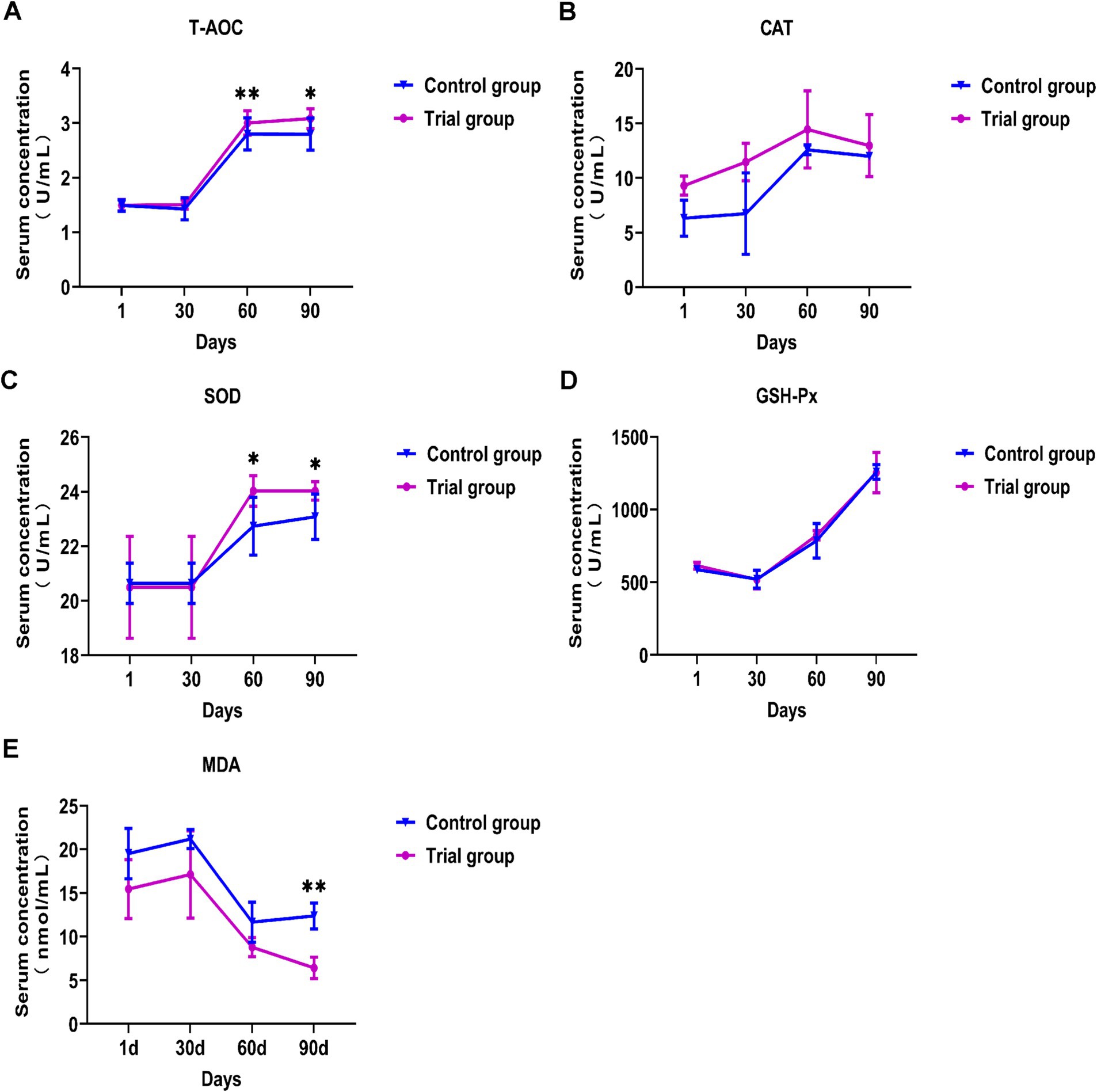
Figure 1. Effects of compound bacteria culture on serum antioxidant indexes of Hu sheep. (A) Effects on the serum T-AOC activity. (B) Effects on the serum CAT activity. (C) Effects on the serum SOD activity. (D) Effects on the serum GSH-Px activity. (E) Effects on the serum MDA concentration. SOD = Superoxide dismutase, T-AOC = Total antioxidant capacity, GSH-Px = Glutathione peroxidase, CAT = Catalase, MDA = Malondialdehyde. Mean ± SD; * (p < 0.05) vs. control; ** (p < 0.01) vs. control. T-test, n = 5.
Effects of compound yeast culture on the content of inflammatory factors in Hu sheep
As shown in Figure 2, there was no significant difference in serum inflammatory factors between the experimental and control groups at the beginning of the experiment. The serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 were significantly increased at 1 month (p < 0.05). On day 60, the serum levels of IL-4 and IL-10 in the experimental group were significantly higher than those in the control group (p < 0.05). On day 90, the serum IL-4 level in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group (p < 0.05). Throughout the test period, the serum TNF-α, IL-6, IL-4, and IL-10 contents of the experimental group were significantly increased, and the differences of IL-1β and IL-2 were not significant. These results suggest that supplementation with compound yeast culture supplementation modulates immune-related cytokines in Hu sheep.
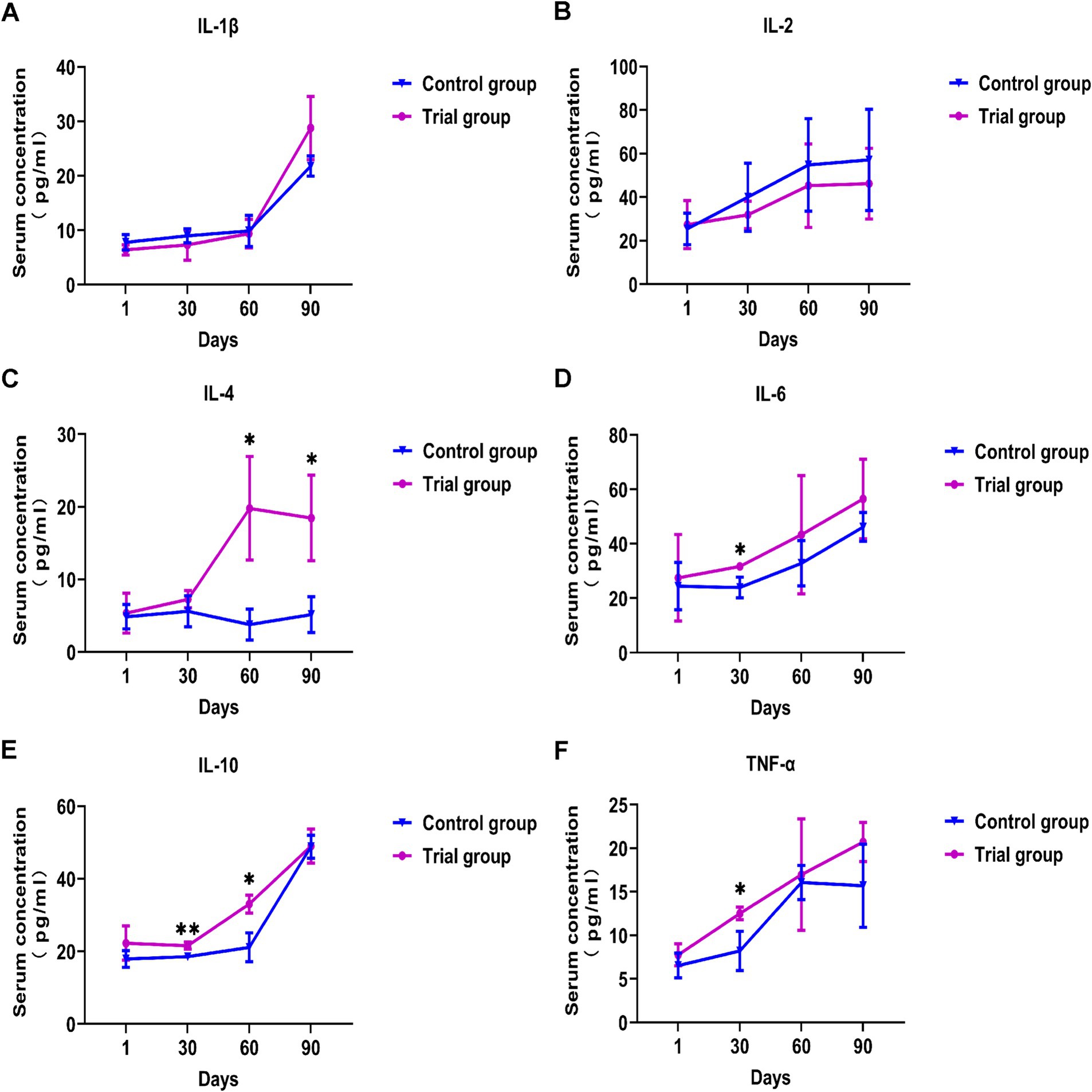
Figure 2. Effects of compound yeast culture on the content of inflammatory factors in Hu sheep. (A) Effects on the serum IL-1β concentration. (B) Effects on the serum IL-2 concentration. (C) Effects on the serum IL-4 concentration. (D) Effects on the serum IL-6 concentration. (E) Effects on the serum IL-10 concentration. (F) Effects on the serum TNF-α concentration. IL-1β = Interleukin-1β, IL-2 = Interleukin-2, IL-4 = Interleukin-4, IL-6 = Interleukin-6, IL-10 = Interleukin-10, TNF-α = Tumor necrosis factor-α. Mean ± SD; * (p < 0.05) vs. control; ** (p < 0.01) vs. control. T-test, n = 5.
Discussion
Effects of compound yeast culture on growth performance of Hu sheep
This study was conducted at the Hu sheep breeding base in Qingyang City, Gansu Province. Hu sheep have the advantages of requiring little exercise and growing rapidly, but they also have poor disease resistance and slow digestion (19, 20). In this study, the average daily feed intake, average daily gain, and feed-to-weight ratio of Hu sheep in the experimental group significantly increased after feeding with the compound yeast culture. The digestive and absorptive capacities of the gastrointestinal tract determine the feed intake of Hu sheep. The key to fattening Hu sheep is the nutritional content, palatability, and digestibility of the feed itself (21–23). In this study, the feed intake of Hu sheep in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group. Compound yeast cultures are rich in various nutritionally active substances and probiotics (24, 25). Under the synergistic effect of nutritionally active substances and probiotics, the digestibility of crude protein and dry matter improved (26), and the decomposition, digestion, and absorption of nutrients in Hu sheep feed were enhanced. It promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract of Hu sheep, strengthens the digestive and absorptive functions of the intestinal tract, and improves the growth performance of Hu sheep (27). In contrast, compound yeast cultures have a unique fermented acid aroma (28), which can stimulate the appetite of animals and increase feed intake in Hu sheep. Compound yeast culture also increased the feed conversion rate and feed intake of Hu sheep. This study also found that the economic benefit of Hu sheep after feeding with a compound yeast culture was 34.6% higher than that of the control group, which also proved that adding a compound bacterial culture to feed could reduce the feeding cost of the farm and help shorten the growth cycle of Hu sheep. Various studies have shown differences in whether yeast culture can significantly improve slaughter performance. Studies have shown that adding yeast culture to sheep diets has been found to significantly increase the slaughter rate of animals (29–31). Some studies have indicated that yeast culture has no effect on the slaughter performance of mutton sheep (32). Additionally, this demonstrates the results of this experiment. In this experiment, the slaughter data were higher than those of the control group; however, the difference was not significant. This shows that the slaughter performance of Hu sheep fed a compound bacterial culture can be improved.
Effects of compound yeast culture on serum antioxidant indexes of Hu sheep
Under normal circumstances, the production and scavenging of free radicals in the body are in a state of dynamic balance (33, 34). This experiment has been conducted over 117 days in the Hu sheep feeding test. In this process, Hu sheep often encounter the situation of the Hu sheep turning circle, sudden change in sheep circle temperature, excessive noise from cleaning vehicles, scattering vehicles, etc., which will lead to a strong stress response in Hu sheep. A study by Chen et al. showed that feeding polysaccharides could increase the T-AOC and SOD activity in the serum of mutton sheep (35) and enhance the antioxidant capacity of animals. T-AOC is an overall evaluation index of antioxidant levels in the body (36, 37). SOD represents the ability of the animal body to scavenge oxygen free radicals (38–40). Functional additives reduce oxidative stress by reducing the formation of free radicals. In this study, the serum T-AOC and SOD activity of the experimental group significantly increased, indicating that feeding the compound yeast culture can improve the antioxidant capacity of Hu sheep and reduce damage caused by oxidative stress. In this experiment, Hu sheep experienced a sudden change in temperature and continuous light rain for many days. The results showed that the Hu sheep in the experimental group did not show an obvious stress response, and their feed intake was normal. The control group not only showed a significant decrease in feed intake, but also death, which further confirmed that the compound yeast culture could improve the anti-oxidative stress ability of Hu sheep. MDA is the best index of oxidative stress and can be used to measure the degree of oxidative damage (41–43). On the 90th day of the experiment, the serum MDA content of the experimental group was significantly reduced, which proved that the addition of compound yeast culture to the diet improved the antioxidant capacity of Hu sheep. Previous studies have shown that supplementation with yeast cultures can improve the antioxidant capacity of animals (44). These findings correspond with the results of our experiment. After feeding the compound yeast culture, it was beneficial for Hu sheep to scavenge free radicals produced during the metabolic process, reduce the damage caused by oxygen free radicals to the body, and improve the antioxidant capacity of Hu sheep. Lu et al. reported that yeast culture can improve the antioxidant capacity of Sheep Livers and reached a similar conclusion to this experiment (45). There was no significant change in serum GSH-Px activity, which differs from the results of previous studies (36). This may be due to the excessive consumption of concentrate, resulting in nutritional metabolic oxidative stress in Hu sheep.
Effect of compound yeast culture on the content of serum inflammatory factors in Hu sheep
Although the cytokine content in animal serum is low, it plays an important role in the body’s defense against diseases (46). It mediates the interactions between cells, participates in inflammatory responses, and regulates immune responses. Therefore, the health status of Hu sheep can be determined using cytokine detection. Under normal circumstances, the body’s pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors are in dynamic balance (47). When the body has a disease or changes in the external environment, it will lead to an increase in pro-inflammatory factors in the body. An appropriate amount of pro-inflammatory factors activates the body’s immune function, while excessive pro-inflammatory cytokines lead to an inflammatory response in the body. TNF-α can enhance infection resistance by activating neutrophils and platelets, enhancing the killing ability of macrophages/NK cells, and stimulating the immune system. IL-6 promotes the proliferation and differentiation of B-lymphocytes to produce antibodies (48). TNF-α and IL-6 are involved in the regulation of immune activity, thereby enhancing animal immunity (49). Both IL-1β and IL-2 are pro-inflammatory factors, and the level of IL-2 cytokines will increase after stress (50). IL-1β has a strong pro-inflammatory ability in neutrophil infiltration and is a strong pro-inflammatory factor (51). During the experiment, the serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-4, and IL-10 in the experimental group were significantly increased. On the one hand, an appropriate increase in cytokine content can help the body promote the immune response (52); on the other hand, the content of IL-4 and IL-10 increases significantly in harsh environments, which can inhibit the occurrence of inflammation and tissue damage and alleviate the damage caused by stress in animals (53–55). The serum IL-1β and IL-2 in the experimental group did not change significantly compared with the control group. It may be because the increase of IL-4 and IL-10 inhibited pro-inflammatory factors such as IL-1β. IL-4 can inhibit the activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines and IL-10 can inhibit lymphocytes to reduce inflammation (56, 57). In this experiment, the content of serum IL-4 and IL-10 increased, combined with the determination of antioxidant indices, which proved that the immune ability of Hu sheep was enhanced by feeding with the compound yeast culture.
Conclusion
This experiment was conducted to study the effects of a compound yeast culture on the growth performance, immune function, and antioxidant capacity of Hu sheep. The results showed that the addition of the compound yeast culture to the diet improved their growth performance, immune function, and antioxidant capacity. Therefore, compound yeast culture is considered a potential antibiotic substitute that can be used as an animal feed additive. These data provide theoretical support for the development of mutton sheep breeding programs.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available at: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/dx_doi_org_10_6084_m9_figshare_6025748/6025748.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by all animal experiments were carried out in compliance with the experimental practices and standards approved by the animal welfare and research ethics committee of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (no: NND2022104). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
SL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JM: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. LY: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. HC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. XL: Software, Writing – review & editing. RD: Writing – review & editing. CX: Writing – review & editing. DL: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program (2023YFE0100400), First-class Disciplines of Inner Mongolia Scientific Research Special Program (YLXKZX-NND-012), Basic Scientific Research Projects of Colleges and Universities directly under the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (BR22-11-17), and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Graduate Research and Innovation Project (KC2024044B).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2025.1674231/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Tozlu Çelik, H, Aslan, FA, Us Altay, D, Kahveci, ME, Konanç, K, Noyan, T, et al. Effects of transport and altitude on hormones and oxidative stress parameters in sheep. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0244911. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244911
2. Danyer, E, Bilal, T, Altiner, A, Aytekin, İ, and Atalay, H. The effect of vitamin E treatment on selected immune and oxidative parameters in Kivircik ewes suffering from transport stress. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). (2021) 105:34–41. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13560
3. Guo, H, Zhou, G, Tian, G, Liu, Y, Dong, N, Li, L, et al. Changes in rumen microbiota affect metabolites, immune responses and antioxidant enzyme activities of sheep under cold stimulation. Animals (Basel). (2021) 11:712. doi: 10.3390/ani11030712
4. Hassan, HA, Ahmed, HS, and Hassan, DF. Free radicals and oxidative stress: mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Hum Antibodies. (2024) 32:151–67. doi: 10.3233/HAB-240011
5. Gökçe, E, Cihan, P, Atakişi, O, Kirmizigül, AH, and Erdoğan, HM. Oxidative stress in neonatal lambs and its relation to health status and passive colostral immunity. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. (2022) 251:110470. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2022.110470
6. Sahoo, DK, Heilmann, RM, Paital, B, Patel, A, Yadav, VK, Wong, D, et al. Oxidative stress, hormones, and effects of natural antioxidants on intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1217165. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1217165
7. Song, B, Wu, T, You, P, Wang, H, Burke, JL, Kang, K, et al. Dietary supplementation of yeast culture into pelleted Total mixed rations improves the growth performance of fattening lambs. Front Vet Sci. (2021) 8:657816. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.657816
8. Xu, J, Li, X, Fan, Q, Zhao, S, and Jiao, T. Effects of yeast culture on lamb growth performance, rumen microbiota, and metabolites. Animals (Basel). (2025) 15:738. doi: 10.3390/ani15050738
9. Sun, Z, Aschalew, ND, Cheng, L, Xia, Y, Zhang, L, Yin, G, et al. Dietary 5-hydroxytryptophan improves sheep growth performance by enhancing ruminal functions, antioxidant capacity, and tryptophan metabolism: in vitro and in vivo studies. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1398310. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1398310
10. Mavrommatis, A, Mitsiopoulou, C, Christodoulou, C, Karabinas, D, Nenov, V, Zervas, G, et al. Dietary supplementation of a live yeast product on dairy sheep Milk performance, oxidative and immune status in peripartum period. J Fungi (Basel). (2020) 6:334. doi: 10.3390/jof6040334
11. Liu, YZ, Lang, M, Zhen, YG, Chen, X, Sun, Z, Zhao, W, et al. Effects of yeast culture supplementation and the ratio of non-structural carbohydrate to fat on growth performance, carcass traits and the fatty acid profile of the longissimus dorsi muscle in lambs. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). (2019) 103:1274–82. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13128
12. Lim, DH, Han, MH, Ki, KS, Kim, TI, Park, SM, Kim, DH, et al. Changes in milk production and blood metabolism of lactating dairy cows fed Saccharomyces cerevisiae culture fluid under heat stress. J Anim Sci Technol. (2021) 63:1433–42. doi: 10.5187/jast.2021.e114
13. Du, D, Feng, L, Chen, P, Jiang, W, Zhang, Y, Liu, W, et al. Effects of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae cultures on performance and immune performance of dairy cows during heat stress. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:851184. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.851184
14. Li, Z, Hu, Y, Li, H, Lin, Y, Cheng, M, Zhu, F, et al. Effects of yeast culture supplementation on milk yield, rumen fermentation, metabolism, and bacterial composition in dairy goats. Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1447238. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1447238
15. Jiao, P, Wei, C, Sun, Y, Xie, X, Zhang, Y, Wang, S, et al. Screening of live yeast and yeast derivatives for their impact of strain and dose on in vitro ruminal fermentation and microbial profiles with varying media pH levels in high-forage beef cattle diet. J Sci Food Agric. (2019) 99:6751–60. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9957
16. Li, X, An, N, Chen, H, and Liu, D. Effects of yeast culture on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, immune function, and intestinal microbiota structure in Simmental beef cattle. Front Vet Sci. (2025) 11:1533081. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1533081
17. Xu, Z, Yang, L, Chen, H, Liu, S, Li, X, Li, S, et al. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Kluyveromyces marxianus yeast co-cultures modulate the ruminal microbiome and metabolite availability to enhance rumen barrier function and growth performance in weaned lambs. Anim Nutr. (2024) 19:139–52. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.06.005
18. Ma, Z, Wu, Z, Wang, Y, Meng, Q, Chen, P, Li, J, et al. Effect of yeast culture on reproductive performance, gut microbiota, and Milk composition in primiparous sows. Animals (Basel). (2023) 13:2954. doi: 10.3390/ani13182954
19. Wang, Q, Wang, Y, Hussain, T, Dai, C, Li, J, Huang, P, et al. Effects of dietary energy level on growth performance, blood parameters and meat quality in fattening male Hu lambs. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). (2020) 104:418–30. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13278
20. Li, Y, Chen, Z, Fang, Y, Cao, C, Zhang, Z, Pan, Y, et al. Runs of homozygosity revealed reproductive traits of Hu sheep. Genes (Basel). (2022) 13:1848. doi: 10.3390/genes13101848
21. Zhang, Z, Shahzad, K, Shen, S, Dai, R, Lu, Y, Lu, Z, et al. Altering dietary soluble protein levels with decreasing crude protein may be a potential strategy to improve nitrogen efficiency in Hu sheep based on rumen microbiome and metabolomics. Front Nutr. (2022) 8:815358. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.815358
22. Cheng, Y, Zhang, H, Zhang, J, Duan, H, Yin, Y, Li, Y, et al. Effects of fermented rice husk powder on growth performance, rumen fermentation, and rumen microbial communities in fattening Hu sheep. Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1503172. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1503172
23. Luo, J, Jiang, J, Duan, H, Zhang, H, Sun, M, Mao, S, et al. Comparative effects of nisin and monensin supplementation on growth performance, rumen fermentation, nutrient digestion, and plasma metabolites of fattening Hu sheep. Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1441431. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1441431
24. Tao, Z, Yuan, H, Liu, M, Liu, Q, Zhang, S, Liu, H, et al. Yeast extract: characteristics, production, applications and future perspectives. J Microbiol Biotechnol. (2023) 33:151–66. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2207.07057
25. Cao, Y, Xu, M, Chen, Q, Wu, D, Lu, J, and Cai, G. Potential nutritional and functional matters in yeast culture prepared by soybean meal fermentation. J Sci Food Agric. (2024) 104:8869–78. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13713
26. Razzaghi, A, Malekkhahi, M, and Brito, AF. Lactation performance, milk fat output, and nutrient digestibility responses to the addition of liquid molasses or yeast culture in dairy cows fed super-conditioned corn. J Dairy Sci. (2023) 106:6080–93. doi: 10.3168/jds.2022-22768
27. Zhou, S, Huang, J, Zhang, H, Song, X, Jiang, Y, Zhao, X, et al. Live yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) improves growth performance and liver metabolic status of lactating Hu sheep. J Dairy Sci. (2025) 108:3700–15. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-25829
28. Ge, Y, Wu, Y, Aihaiti, A, Wang, L, Wang, Y, Xing, J, et al. The metabolic pathways of yeast and acetic acid Bacteria during fruit vinegar fermentation and their influence on flavor development. Microorganisms. (2025) 13:477. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13030477
29. Liu, S, Shah, AM, Yuan, M, Kang, K, Wang, Z, Wang, L, et al. Effects of dry yeast supplementation on growth performance, rumen fermentation characteristics, slaughter performance and microbial communities in beef cattle. Anim Biotechnol. (2022) 33:1150–60. doi: 10.1080/10495398.2021.1878204
30. Li, X, Wang, Y, Xu, J, Yang, Q, Sha, Y, Jiao, T, et al. Effects of yeast cultures on meat quality, flavor composition and rumen microbiota in lambs. Curr Res Food Sci. (2024) 9:100845. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100845
31. Lin, Y, Yu, C, Ma, Z, Che, L, Feng, B, Fang, Z, et al. Effects of yeast culture supplementation in wheat-Rice-based diet on growth performance, meat quality, and gut microbiota of growing-finishing pigs. Animals (Basel). (2022) 12:2177. doi: 10.3390/ani12172177
32. Bai, X, Wang, L, Sun, H, Sun, L, An, J, Fu, S, et al. Yeast culture supplementation improves meat quality by enhancing immune response and purine metabolism of small-tail Han sheep (Ovis aries). Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26:4512. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104512
33. Chandimali, N, Bak, SG, Park, EH, Lim, HJ, Won, YS, Kim, EK, et al. Free radicals and their impact on health and antioxidant defenses: a review. Cell Death Discov. (2025) 11:19. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02278-8
34. Jakubczyk, K, Dec, K, Kałduńska, J, Kawczuga, D, Kochman, J, and Janda, K. Reactive oxygen species - sources, functions, oxidative damage. Pol Merkur Lekarski. (2020) 48:124–127.
35. Chen, H, Liu, S, Li, S, Li, D, Li, X, Xu, Z, et al. Effects of yeast culture on growth performance, immune function, antioxidant capacity and hormonal profile in Mongolian ram lambs. Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1424073. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1424073
36. Yi, S, Tian, X, Qin, X, Zhang, Y, Guan, S, Chen, Z, et al. Effects of yeast cultures on growth performance, Fiber digestibility, ruminal dissolved gases, antioxidant capacity and immune activity of beef cattle. Animals (Basel). (2025) 15:1452. doi: 10.3390/ani15101452
37. Sun, Y, Zhang, Y, Liu, M, Li, J, Lai, W, Geng, S, et al. Effects of dietary Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CECT 5940 supplementation on growth performance, antioxidant status, immunity, and digestive enzyme activity of broilers fed corn-wheat-soybean meal diets. Poult Sci. (2022) 101:101585. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101585
38. Zhang, X, Zhang, Z, Sun, Y, Liu, Y, Zhong, X, Zhu, J, et al. Antioxidant capacity, inflammatory response, carcass characteristics and meat quality of Hu sheep in response to dietary soluble protein levels with decreased crude protein content. Antioxidants (Basel). (2023) 12:2098. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122098
39. Yang, X, Zhang, H, Pang, F, Zhang, L, Fu, T, Wang, L, et al. Effects of α-lipoic acid on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and immune function in sheep. J Anim Sci. (2023) 101:skad 092. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad092
40. Wang, X, Hu, C, Ding, L, Tang, Y, Wei, H, Jiang, C, et al. Astragalus membranaceus alters rumen Bacteria to enhance Fiber digestion, improves antioxidant capacity and immunity indices of small intestinal mucosa, and enhances liver metabolites for energy synthesis in Tibetan sheep. Animals (Basel). (2021) 11:3236. doi: 10.3390/ani11113236
41. Liu, X, Zhao, J, Zhang, L, Lu, J, Lv, X, Liu, C, et al. Effects of different doses of excessive Iron in diets on oxidative stress in immune organs of sheep. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2020) 197:475–86. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-02006-9
42. Ramadan, G, Fouda, WA, Ellamie, AM, and Ibrahim, WM. Dietary supplementation of Sargassum latifolium modulates thermo-respiratory response, inflammation, and oxidative stress in bacterial endotoxin-challenged male Barki sheep. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2020) 27:33863–71. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09568-5
43. Cao, QQ, Lin, LX, Xu, TT, Lu, Y, Zhang, CD, Yue, K, et al. Aflatoxin B1 alters meat quality associated with oxidative stress, inflammation, and gut-microbiota in sheep. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2021) 225:112754. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112754
44. Qiu, Q, Zhan, Z, Zhou, Y, Zhang, W, Gu, L, Wang, Q, et al. Effects of yeast culture on laying performance, antioxidant properties, intestinal morphology, and intestinal Flora of laying hens. Antioxidants (Basel). (2024) 13:779. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070779
45. Lu, X, Ma, H, Liu, Y, Chen, M, Dang, J, Su, X, et al. Rhodotorula yeast culture improved the antioxidant capacity, lipid metabolism, and immunity of sheep livers. Vet Sci. (2025) 12:314. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12040314
46. De Baat, A, Trinh, B, Ellingsgaard, H, and Donath, MY. Physiological role of cytokines in the regulation of mammalian metabolism. Trends Immunol. (2023) 44:613–27. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2023.06.002
47. Bhol, NK, Bhanjadeo, MM, Singh, AK, Dash, UC, Ojha, RR, Majhi, S, et al. The interplay between cytokines, inflammation, and antioxidants: mechanistic insights and therapeutic potentials of various antioxidants and anti-cytokine compounds. Biomed Pharmacother. (2024) 178:117177. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117177
48. Mata, R, Yao, Y, Cao, W, Ding, J, Zhou, T, Zhai, Z, et al. The dynamic inflammatory tissue microenvironment: Signality and disease therapy by biomaterials. Research (Wash D C). (2021) 2021:4189516. doi: 10.34133/2021/4189516
49. Zheng, D, Liwinski, T, and Elinav, E. Inflammasome activation and regulation: toward a better understanding of complex mechanisms. Cell Discov. (2020) 6:36. doi: 10.1038/s41421-020-0167-x
50. Zhang, H, and Dhalla, NS. The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:1082. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021082
51. Chen, X, OuYang, L, Qian, B, Qiu, Y, Liu, L, Chen, F, et al. IL-1β mediated fibroblast-neutrophil crosstalk promotes inflammatory environment in skin lesions of SLE. Clin Immunol. (2024) 269:110396. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2024.110396
52. Silva, RCMC, Travassos, LH, and Dutra, FF. The dichotomic role of single cytokines: fine-tuning immune responses. Cytokine. (2024) 173:156408. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156408
53. Mitchell, RE, Hassan, M, Burton, BR, Britton, G, Hill, EV, Verhagen, J, et al. IL-4 enhances IL-10 production in Th1 cells: implications for Th1 and Th2 regulation. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:11315. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11803-y
54. Nikovics, K, Favier, AL, Rocher, M, Mayinga, C, Gomez, J, Dufour-Gaume, F, et al. In situ identification of both IL-4 and IL-10 cytokine-receptor interactions during tissue regeneration. Cells. (2023) 12:1522. doi: 10.3390/cells12111522
55. Chatterjee, P, Chiasson, VL, Bounds, KR, and Mitchell, BM. Regulation of the anti-inflammatory cytokines Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-10 during pregnancy. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:253. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00253
56. Woodward, EA, Prêle, CM, Nicholson, SE, Kolesnik, TB, and Hart, PH. The anti-inflammatory effects of interleukin-4 are not mediated by suppressor of cytokine signalling-1 (SOCS1). Immunology. (2010) 131:118–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03281.x
Keywords: antioxidant function, compound yeast culture, Hu sheep, inflammatory factors, production performance
Citation: Liu S, Ma J, Yang L, Chen H, Li X, Du R, Xue C and Liu D (2025) Effects of compound yeast culture on growth performance, antioxidant function and inflammatory factors of Hu sheep. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1674231. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1674231
Edited by:
Zhicheng Peng, University of Pennsylvania, United StatesReviewed by:
Jing Zhang, Stanford University, United StatesYu Zhou, City of Hope National Medical Center, United States
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Ma, Yang, Chen, Li, Du, Xue and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dacheng Liu, bm1nbGRjQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Shixiong Liu
Shixiong Liu Jiabin Ma
Jiabin Ma Lan Yang1,2
Lan Yang1,2 Dacheng Liu
Dacheng Liu