In the published article, there was an error in Figure 2 as published. We mistakenly used Figure 1 as Figure 2. The Figure 1 describes us CD163 in urine and SLEDAI-2K in SLE patients while the Figure 2 describes usCD163/creatinine in urine and SLEDAI-2K in SLE patients. The corrected Figure 2 and its caption appear below.
Figure 2
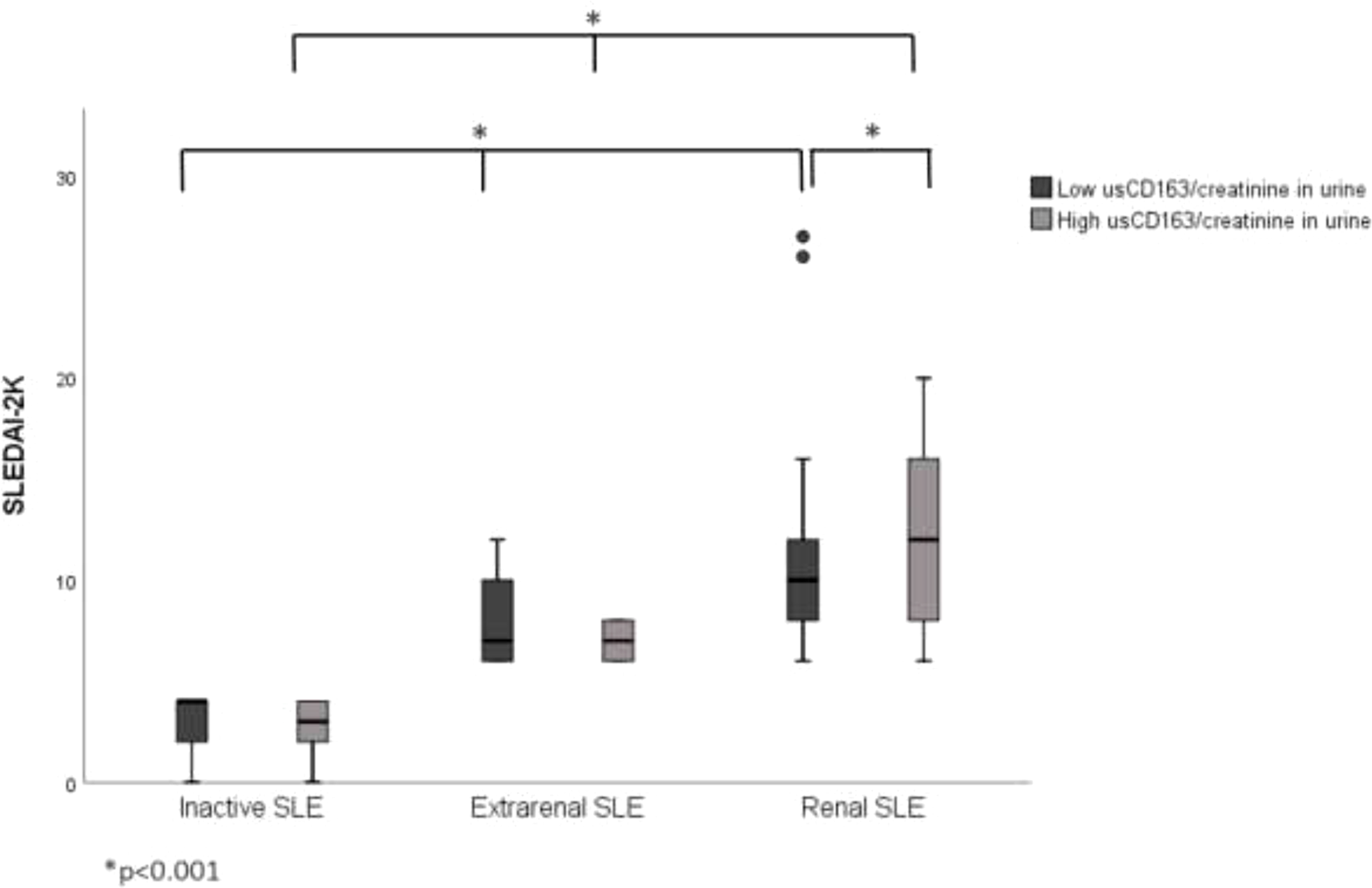
Correlation between usCD163/creatinine in urine and SLEDAI-2K in SLE patients. The renal SLE patients with high usCD163/creatinine ratios had higher SLEDAI-2K scores compared with those with low usCD163 levels. However, no difference in SLEDAI-2K score was seen between the inactive and extrarenal SLE patients. SLEDAI-2k, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000.
In the published article, there was an error in the Funding statement. Funding from Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Research Program (CMRPG3J0031) was omitted. The correct Funding statement appears below.
Funding
This study received funding from Key Development Project of Department of Science and Technology (2015C03Bd051) and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Research Program (CMRPG3J0031).
The authors apologize for these errors and state that they do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Summary
Keywords
Systemic lupus erythematosus, lupus nephritis, urine soluble CD163, urine biomarker, chronic kidney disease, macrophage, SLEDA
Citation
Huang Y-J, Lin C-H, Yang H-Y, Luo S-F and Kuo C-F (2022) Corrigendum: Urine soluble CD163 is a promising biomarker for the diagnosis and evaluation of lupus nephritis. Front. Immunol. 13:1003761. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1003761
Received
26 July 2022
Accepted
08 August 2022
Published
29 August 2022
Volume
13 - 2022
Edited and reviewed by
Margaret Hibbs, Monash University, Australia
Updates
Copyright
© 2022 Huang, Lin, Yang, Luo and Kuo.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chang-Fu Kuo, zandis@gmail.com
This article was submitted to Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Disorders : Autoimmune Disorders, a section of the journal Frontiers in Immunology
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.