There was a mistake in Figure 7 as published. Figure 7 was inadvertently overwritten by an incorrect image. The corrected Figure 7 appears below.
Figure 7
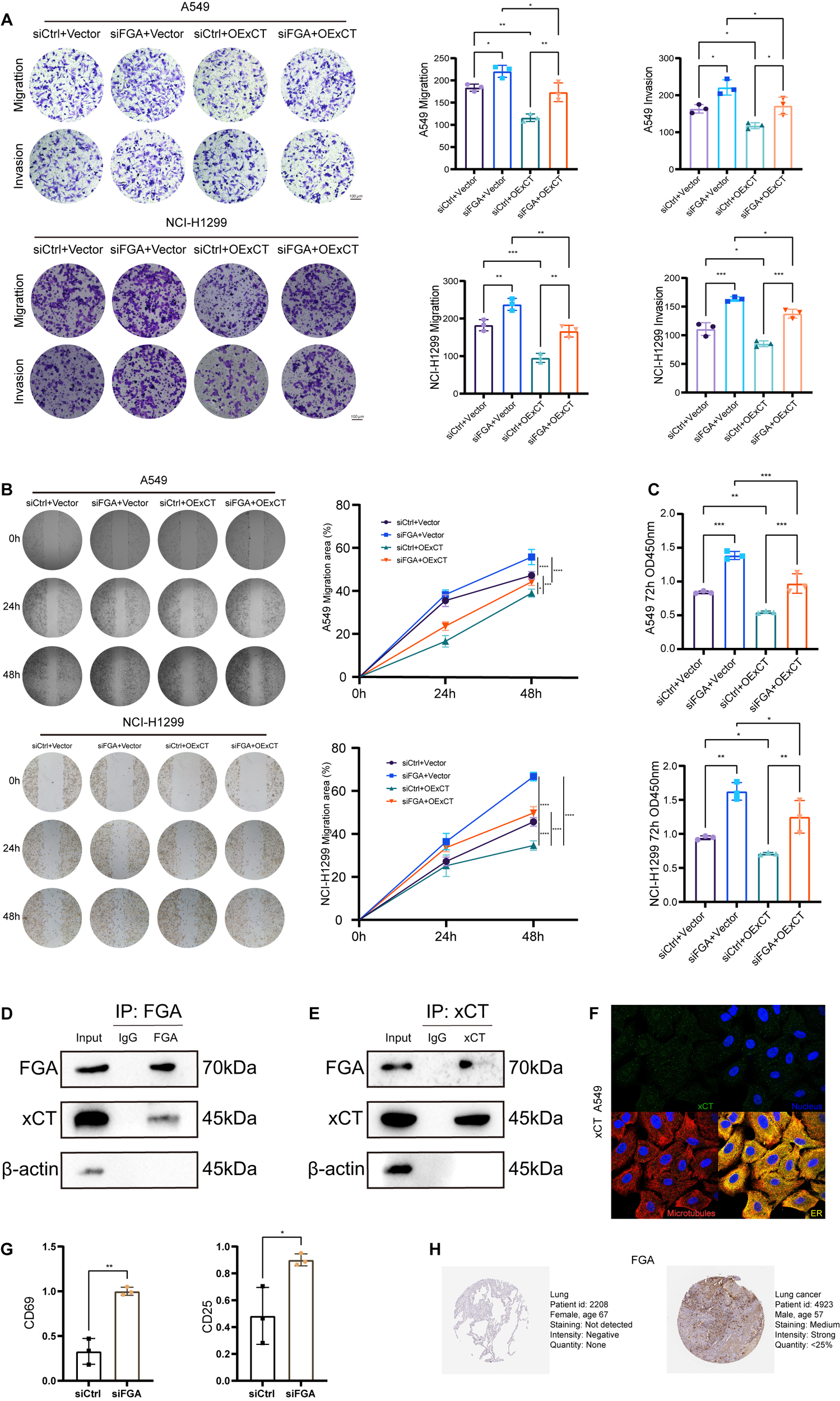
Protein-protein interaction between FGA and xCT modulates progression and immune evasion in lung cancer. (A) Transwell migration and invasion assays were performed in a rescue experiment. (B) Wound healing assays were performed to detect cell migration in the rescue experiment. (C) Cell proliferation in the rescue experiment after 72h was detected by CCK8. (D) Endogenous FGA co-immunoprecipitates xCT in A549 cells. (E) Endogenous xCT co-immunoprecipitates FGA in A549 cells. (F) Immunostaining for xCT in A549 cell from the Human Protein Atlas. (G) Tumor cell FGA deficiency potentiates CD8+ T-cell activation via soluble factors in a non-contact Transwell co-culture system. (H) Immunohistochemical staining of FGA proteins in normal tissues and lung cancer from the Human Protein Atlas. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
The original version of this article has been updated.
Statements
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Summary
Keywords
immune infiltration, disulfidptosis, tumor microenvironment, non-small-cell lung cancer, lung adenocarcinoma
Citation
Li G, Li Q, Yang S, Guo D, Tao Y and Jia Y (2026) Correction: FGA modulates immune infiltration and tumor progression via SLC7A11/xCT-mediated disulfidptosis in the tumor microenvironment of lung adenocarcinoma. Front. Immunol. 17:1789896. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2026.1789896
Received
17 January 2026
Revised
17 January 2026
Accepted
10 February 2026
Published
17 February 2026
Volume
17 - 2026
Edited and reviewed by
Nahum Puebla-Osorio, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2026 Li, Li, Yang, Guo, Tao and Jia.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yan Jia, 202036106@mail.sdu.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.