- 1 College of Earth, Ocean and the Environment, University of Delaware, Lewes, DE, USA
- 2 Department of Biological Sciences, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA
- 3 Department of Biology, East Carolina University, Greenville, NC, USA
- 4 Biology Department, Western Washington University, Bellingham, WA, USA
Since the days of Darwin, scientists have used the framework of the theory of evolution to explore the interconnectedness of life on Earth and adaptation of organisms to the ever-changing environment. The advent of molecular biology has advanced and accelerated the study of evolution by allowing direct examination of the genetic material that ultimately determines the phenotypes upon which selection acts. The study of evolution has been furthered through examination of microbial evolution, with large population numbers, short generation times, and easily extractable DNA. Such work has spawned the study of microbial biogeography, with the realization that concepts developed in population genetics may be applicable to microbial genomes (Martiny et al., 2006; Manhes and Velicer, 2011). Microbial biogeography and adaptation has been examined in many different environments. Here we argue that the deep biosphere is a unique environment for the study of evolution and list specific factors that can be considered and where the studies may be performed. This publication is the result of the NSF-funded Center for Dark Energy Biosphere Investigations (C-DEBI) theme team on Evolution (www.darkenergybiosphere.org).
What is the Deep Biosphere?
The deep biosphere is often operationally defined as described in Teske and Sørensen (2008). For this paper, we consider the marine deep biosphere, starting on average at 1 mbsf (meters below seafloor). Sediments above 10 cm have an average cell density of 109 cells/ml, versus sediments below 10 m averaging 107 cells/ml (Whitman et al., 1998). Studies suggest that despite the low apparent biomass in this environment, the large total volume of the deep biosphere could allow it to harbor the majority of biomass on the planet (Gold, 1992; Whitman et al., 1998). Using this definition of deep biosphere, we also include all potential reserviors in the igneous crust. Recent projects have begun to delineate the abundance and diversity of organisms present in the subseafloor biosphere and their global geochemical importance (D’Hondt et al., 2004, 2009). Genetic studies tracking the locations of microorganisms (Inagaki et al., 2006) and observations of their genomes (Biddle et al., 2008, 2011) have shown that subsurface habitats, even those with low biomass, are tractable for genomic studies.
What Makes the Deep Biosphere a Unique Place to Study Evolution?
It is our opinion that the deep biosphere offers a unique opportunity to examine microbial evolution in action. Often, microbial evolution is studied in an environment where numerous factors are controlling the rate of diversification and adaptation, in areas of abundant resources, undetermined connectedness and unknown species interactions. In contrast, the deep biosphere offers an environment where many of the standard forces in ecology are either not in play or much reduced. As examples, we will focus on dispersal, activity, metabolic flexibility, and thermodynamic extremes.
Dispersal
The deep biosphere in the marine realm is an environment existing in a physical matrix of sediments or igneous basalt. Unlike pelagic environments, where transport is influenced by many factors including temperature, currents, wind, and attachment to larger surfaces, dispersal is constrained in the deep biosphere. The study of subsurface hydrology in igneous crustal habitats has shown us that fluid exchange between crustal and oceanic reservoirs spans the range between advection and diffusion, and may be quite dynamic. In contrast, fluid exchange in deep sedimentary biomes is dictated almost entirely by diffusion. This range of constraints on the exchange between reservoirs of microbial diversity can facilitate the study of the evolution of individual populations by specifically addressing how adaptation in isolation influences evolution. For example as seen in the study of Sulfolobus species in hot spring environments in the continental realm (Whitaker et al., 2003). The study of local adaptation as an evolutionary force has been widespread throughout isolated populations (Kawecki and Ebert, 2004) however, the extreme time scales over which populations in the subsurface are isolated from the rest of the planet are likely to have profound evolutionary consequences, perhaps the drastic slowing or speeding of molecular clocks, that should be experimentally testable, and provide a unique place to study local adaptation.
Activity
The deep biosphere, where it has been examined so far (i.e., principally in sedimentary habitats) is generally considered to be a nutrient poor environment, despite some “hot spots” of high nutrients, such as those seen below active upwelling regions on continental margins (D’Hondt et al., 2004). Consequently, subsurface microbes are considered to have low activity and extremely long doubling times, potentially as long as 200–2,000 years (Biddle et al., 2006). This decrease in activity may result in mostly isolated cells, whose individual cellular responses may have more control over metabolism than signals given through ecological interactions among the community. Additionally, the role of viruses is relatively unknown in the deep biosphere (see Anderson et al., 2011, for a theoretical examination of their role and Engelhardt et al., 2011 for empirical discussion). The deep biosphere is therefore a unique place to study the evolution of organisms living at the lower limits of metabolic activity.
Metabolic Flexibility/Invention
Due to nutrient limitation and interaction with geologic features within the deep biosphere, novel metabolisms may exist in its microbial inhabitants that are not seen elsewhere. Already geochemical evidence points to the microbial production of ethane and propane, although a defined pathway has not been determined (Hinrichs et al., 2006). Many physiological processes may behave in surprising ways under the pressure and temperature extremes encountered in deep life, such as the formation of isotopically heavy methane (Takai et al., 2008). A comparison between metagenomes from the marine water column and subsurface sediments reveals that subsurface metagenomes exist in their own genetic “space,” as seen by the subsurface sample’s separation from the other samples, based on PCA plots of KEGG categories (Figure 1; Biddle et al., 2006, 2011), indicating unique genomic innovation may have evolved in this biome.
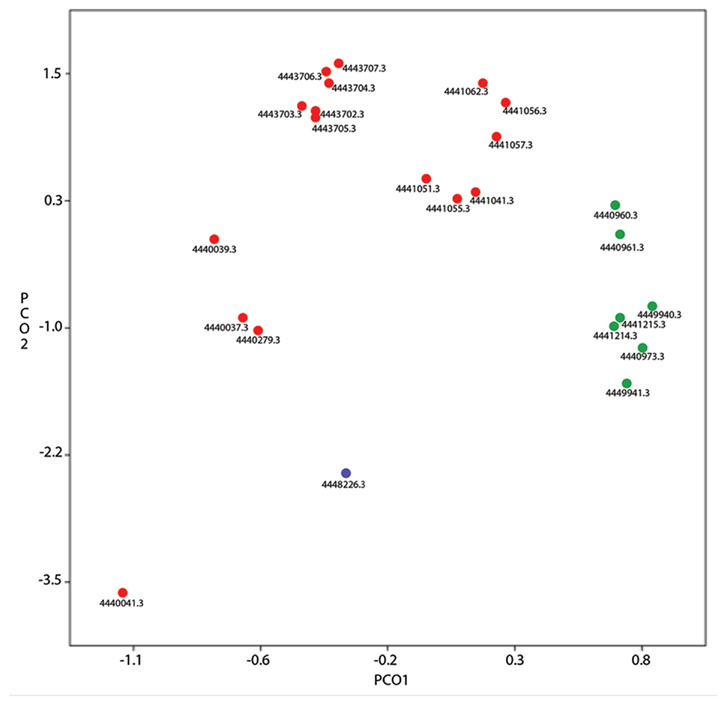
Figure 1. Principle component analysis of KEGG categories from pyrosequenced marine metagenomes available in MG-RAST. A filter for alignments over 25 bp was used. Metagenome IDs in MG-RAST are listed. Green symbols are from sediment metagenomes [ODP (Ocean Drilling Program) Site 1229, IODP (Integrated Ocean Drilling Program) Site 1320], blue symbols are from hydrothermal vent fluid (Mariana Trough Hydrothermal Fluid), red symbols are other marine water pyrosequenced metagenomes (Northern Line Islands, HOT/ALOHA series, Coastal Plymouth Marine). PCO1 explains 59% of the data, PCO2 explains 10%. The blue symbol groups toward the subsurface samples, an example of how hydrothermal systems are viewed as windows to the deep biosphere. The separation between the red and green symbols indicates the distinctiveness between the sediment and pelagic biomes.
Extreme Habitats
The deep biosphere is one of the few places on Earth where a similar physical environment, for example: sediment, is in contact with multiple geochemical and geothermal regimes. For example, sediments within one drilled hole can range in temperatures from 2 to 50°C (Parkes et al., 2000). Sediments cored during the expedition to the Newfoundland Margin ranged from seafloor temperature of 4°C up to 100°C, where microbial signatures were still detected (Roussel et al., 2008). The ability to analyze taxonomically similar microbial populations across multiple temperatures, as detected in this environment, is a unique opportunity, considering that in most environments with hydrothermal activity (Yellowstone hot springs, hydrothermal vents) microbial communities rapidly change across the heat gradient (Rothschild and Mancinelli, 2001). Thermal gradients are often more gradual in the subsurface biome, compared to vent environments, where extreme gradients exist across a mere few centimeters. This allows for more careful experimentation with the effects of thermal gradients on evolution within microbial populations that may take place slowly over millennia.
What are Ways to Study Evolution in the Deep Biosphere?
Many major questions can affect the ability to study evolution in the deep biosphere. Factors governing dispersal need to be constrained in order to assess the amount of gene flow and isolation that may occur in the subsurface. As suggested above, there may be limited dispersal of microorganisms in this mostly solid environment, but areas of high fluid exchange through subsurface basalt where fast advective flow may allow gene flow among microbes (e.g., Wheat and Fisher, 2008). The doubling times of subsurface organisms is not well constrained, and may need to be examined in detail in order to estimate a proper sampling distance for evolutionary studies. Additionally, habitat size and quality will influence local adaptation, so geochemical and geophysical parameters should also be considered during sampling schemes (Kawecki and Ebert, 2004). Due to the difficulty of sampling and detection in the deep biosphere, coupled with the prediction that the majority of its inhabitants are microbial, we anticipate the evolutionary studies will predominantly be genome-based, observed by the genomes of model organisms, metagenomic, and PCR-generated sequences.
Use of Model Organisms/Genomes
Considering the challenges in the assessment of biogeography and evolution of microbial populations, a focus on a particular group of microorganisms may be warranted in order to detect evolutionary events of local adaptation. Microbial groups such as the Zetaproteobacteria, Epsilonproteobacteria, Chloroflexi, and Miscellaneous Crenarchaeotal Group (MCG; Figure 2) serve as a few of the interesting candidates for the study of evolution due to the following reasons:
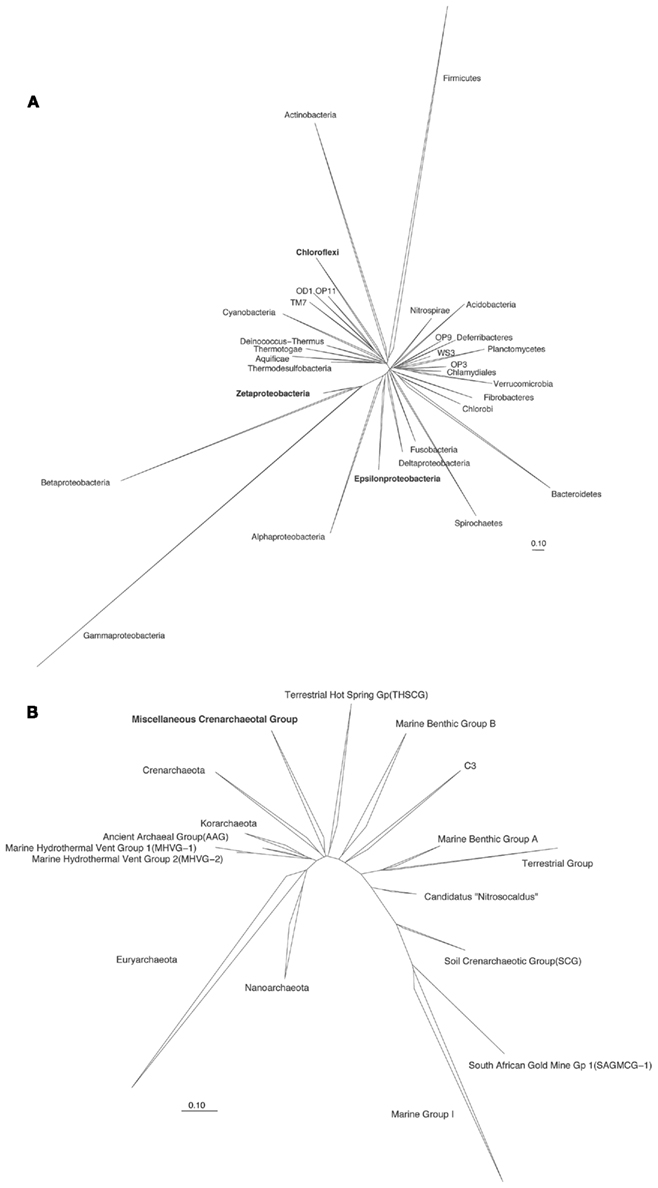
Figure 2. Overview of the phylogenetic relationship of 16S rRNA genes sequences for (A) Bacteria and (B) Archaea. For the Archaea phylogenetic tree, the groups of the phylum Thaumarchaeota are shown in detail to highlight the relationship of the Miscellaneous Crenarchaeotal Group (MCG) within the phylum. Trees were exported (pre-aligned) from the SILVA comprehensive ribosomal RNA database (SSU database, Release 108) and visualized in ARB. Bar, 10 nucleotide substitutions per 100 nucleotides.
Zetaproteobacteria
The Zetaproteobacteria contain iron-oxidizing bacteria, or FeOB, including the cultured isolate Mariprofundus ferrooxydans (Emerson et al., 2007). Recently the Zetaproteobacteria, now recognized as ubiquitous microorganisms that often dominate specific deep-sea habitats such as seamounts and borehole fluid, were shown to exhibit biogeographic separation based on habitat (McAllister et al., 2011). Some groups of Zetaproteobacteria appear ubiquitous throughout the Pacific Ocean, while others show more endemism toward their local habitats. Due to the widespread distribution and unique biogeochemistry of the Zetaproteobacteria, this group is an intriguing one to examine, particularly since analysis of the Zetaproteobacterial sequences originating from borehole fluids of the Southern Mariana Trough suggests that there may be a unique group of these organisms endemic to the deep subsurface (McAllister et al., 2011). In addition, Zetaproteobacteria have been detected (IODP Expedition 331) using enrichment culture and by qPCR from distinct subsurface habitats (Moyer and McAllister, 2011). A genome sequence is available for M. ferrooxydans, allowing for more intricate examination of FeOB endemism, beyond the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene (Singer et al., 2011).
Epsilonproteobacteria
The Epsilonproteobacteria (Figure 2A) are abundant and ubiquitous inhabitants of many hydrothermal vent environments including chimneys, fluids, sediments, and animal hosts (Campbell et al., 2006). Most species are supported by hydrogen or sulfur oxidation, but the group is extraordinarily diverse. One hydrothermal chimney can harbor many different metabolic guilds of Epsilonproteobacteria in distinct ecological niches (Campbell et al., 2006), and a single fluid sample can contain thousands of Epsilonproteobacterial 16S rRNA sequence clusters (Huber et al., 2007). Furthermore, there are indications of biogeographic patterns in the Epsilonproteobacterial populations within and among vent fields (Huber et al., 2010). Because the fluid samples collected from the chimneys are exiting from the subsurface, these results indicate local and global dispersal limitations in the subsurface biosphere. The Epsilonproteobacteria are amenable to laboratory cultivation (Takai et al., 2005; Campbell et al., 2006), making them ideal representatives of the subsurface for experimental research.
Chloroflexi
Chloroflexi (Figure 2A) are highly abundant in deeply buried marine sediments, but unlike their representatives in surface environments, they have resisted classic cultivation techniques (Figure 2A; Blazejak and Schippers, 2010). The phylum Chloroflexi is frequently divided into at least six classes: Chloroflexi, Thermomicrobia, Anaerolineae, Caldilineae, Dehalococcoidetes, and subphylum IV (SAR202 cluster; Rappe and Giovannoni, 2003; Hugenholtz and Stackebrandt, 2004; Morris et al., 2004). The most common Chloroflexi sequences in marine margin sediments fall within the classes Anaerolineae, Caldilineae, and Dehalococcoidetes (Parkes et al., 2005; Biddle et al., 2006; Inagaki et al., 2006). Members of Dehalococcoidetes derive energy through the reduction of organohalide compounds and the oxidation of H2 (Seshadri et al., 2005). The wide distribution of Dehalococcoidetes sequences in deep anoxic sediments may indicate a common niche for organisms that grow on organohalides that is globally exploited, and the presence of reductive dehalogenase homologous (rdhA) genes globally distributed in subsurface sediments (Futagami et al., 2009) supports this hypothesis. Members of the Dehalococcoidetes have also shown a high potential for horizontal gene transfer, moving ecologically relevant, content-variable genomic islands between members of the same species (McMurdie et al., 2011), further increasing their potential as a model group of interest allowing for the study of horizontal gene transfer within the deep marine sediment environment.
MCG Archaea
The MCG was first labeled in 2003 and since then the group’s molecular signatures have been found in a wide array of subsurface habitats (Figure 2B; Inagaki et al., 2003). This archaeal group remains uncultivated and its metabolism is currently unknown. The group’s wide distribution in sediments indicates that it may be a useful group to examine for the transition into a “deep” lifestyle, since phylogenetically similar clones are seen in shallow estuaries and deep ocean sediments (Biddle et al., 2006; Meng et al., 2009). This group could also be used for biogeography studies in the deep biosphere since it appears to have a global distribution in anoxic sediments (Inagaki et al., 2003; Biddle et al., 2006).
Where to Study Evolution in the Deep Biosphere?
The ability to compare different physical conditions, geographically distinct settings, or settings that are geographically distinct but have similar physical conditions would benefit the study of deep biosphere evolution greatly. Proposals for future drilling expeditions can be submitted and those that are planned can be viewed through the IODP web resources (www.iodp.org/expeditions). Here we make the case for the study of evolution in model systems that have been suggested for future exploration based on prior research:
Areas of Similar Geochemistry
Expeditions have often focused on areas of sediment that contain high concentrations of methane, including methane hydrates, to investigate the biological and physical formations of this gas. Those cruises include: Cascadia Margin (IODP Expeditions 311, 328, and ODP Leg 146), Costa Rica (IODP expeditions 344, 334, and ODP Legs 137, 140, 148), Peru Margin (ODP Legs 112, 201, 202), and other margin areas. The examination of similarly aged sediments with similar geochemical regimes (for example, the sulfate/methane transition zone) would allow for the specific investigation of how geographic separation may affect microorganisms undergoing potential divergent evolutionary processes. If possible, finding areas of similar sediment composition (typically seen on margin sites), sediment age, and similar geochemistry (such as an SMTZ), it may be possible to limit variables to interpret the effect of geographic location. Similar surface studies have yielded interesting results (Whitaker et al., 2003), suggesting that geographic separation alone can yield evolutionary shifts in microbes when populations are subjected to similar chemical forces. A potential similar experiment focusing on subsurface rocks could ask similar questions in a massive sulfide setting. This ubiquitous subseafloor substrate was drilled during ODP Legs 158 (Humphris et al., 1995) and 169 (Zierenberg et al., 1998).
Reactivation after Stasis
The idea that some microbial groups may be dormant in deep sediments due to a lack of nutrient and energy fluxes may play a role in the evolution of subsurface microbes. A microbial response to an increase in nutrients made available by geothermal activity was examined on the Newfoundland Margin on ODP Leg 210 (Roussel et al., 2008). This type of investigation is in its infancy, but due to the success of the initial experiments, this type of system could be investigated more thoroughly in the future. The evolution occurring in these “reactivated” microbes may parallel the models of bursts in positive selection seen after stasis in influenza A viral populations (Wolf et al., 2006). Additionally, it may provide insight into microbial succession.
Ridge Flanks
The Juan de Fuca ridge flank in the Pacific Ocean has recently become a site of intense scientific focus for understanding the deep biosphere in igneous ocean crust. Pioneering work using observatories has enabled scientists for the first time to study microbial populations in situ within the crust (see Edwards et al., 2012). The first long-term observatory study conducted at Juan de Fuca revealed succession of microbial communities over time which correlated with geochemical and mineralogical conditions within the borehole (Orcutt et al., 2011). Current work at a contrasting geochemical/geological setting in the Atlantic (North Pond, IODP Expedition 336) will allow for important comparisons to be made about ridge flank microbial communities as a function of these conditions (Edwards et al., 2012). The porous and permeable upper oceanic aquifer system at Juan de Fuca, North Pond, and other ridge flank settings allow for questions regarding the interconnectedness and evolutionary forces that shape these subseafloor microbial communities.
Future Potential Subsurface Experiments, all of Which Requiring the Use of Drilling Platforms, Which Have not been Previously Investigated by Drilling: Lost City
A major uncertainty in subsurface ecosystems is the availability of energy and carbon to drive microbial activity. Hydration of the ultramafic rocks of the Atlantis Massif underlying the Lost City hydrothermal field (Kelley et al., 2005) results in a set of geochemical reactions known as serpentinization, which is highly exothermic and can release large quantities of hydrogen gas and variable levels of methane and other low molecular weight organic compounds. These chemicals support dense microbial communities in the carbonate chimneys of the Lost City hydrothermal field, but the extent and activity of organisms in the underlying subsurface awaits exploration and initial examination of unroofed gabbros has begun (Mason et al., 2011). The apparent longevity of serpentinization-associated processes (Fruh-Green et al., 2003) indicates that the microbial denizens of the Atlantis Massif subsurface have had access to copious energy and organic carbon for possibly millions of years. The nature of fluid circulation between the massif and adjacent regions of the seafloor is currently unknown, but would have profound consequences on the dispersal of microorganisms within the subsurface biosphere. It is possible that some organisms could be reactivated during their transit through the massif and then return to a dormant state after they have been transported out of it. Clearly, this habitat provides exciting opportunities for studying the evolution of potentially isolated but energy-rich ecosystems and their influence on other regions of the subsurface biosphere.
Marine and Freshwater Hydrothermal Systems
One of the great surprises in subsurface microbiology is that some of the dominant organisms detected in terrestrial subsurface habitats, such as gold mines, are very similar to those detected in the marine subsurface basement (Takai et al., 2001; Moser et al., 2005). With this in mind, much can be learned by studying similar environments in terrestrial and marine settings, with the specific goal of determining degrees of connectedness between these biomes and testing hypotheses about convergent evolution. Freshwater hydrothermal systems are common in rift lakes such as Lake Baikal in Russia (Crane et al., 1991) and Lake Tanganyika in Africa (Tiercelin et al., 1993), and these systems harbor microbial fauna similar to those in deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Similarly, freshwater alkaline springs harbor microbial communities that bear resemblances to those in seafloor alkaline springs (Brazelton et al., 2011). Subsurface studies of a series of hydrothermal systems from freshwater and marine systems are likely fertile areas for exciting discoveries in biogeography and geographical isolation, and may also have similarities to well studied thermal systems such as Yellowstone National Park. Additionally, the study of several systems for one project would require international cooperation and many researchers, thereby fostering collaboration within the international research community.
Summary and Outlook
Although the deep subsurface biosphere is difficult to access and most often can be studied as only a snapshot of an environment, many experiments to assess the unique forces acting on evolution in this vast habitat are possible. Through the study of specific groups of microorganisms that are common inhabitants of the subseafloor, biogeography, and local adaptation questions may be posed. Understanding of hydrogeology and geophysical parameters are needed, making any evolutionary questions posed in this environment inherently multidisciplinary in nature, even if they are approached with a genomics-oriented investigation. Past expeditions have allowed the generation of hypotheses or situational investigations and future expeditions, including long-term CORK observatories, will allow for further investigation into this unique biosphere on our planet.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This paper is a product of the Center for Dark Energy Biosphere Investigations (C-DEBI) Science and Technology Center Evolution theme team, which met on Catalina Island in 2011. Team member Jonathan Eisen contributed to discussions that led to this paper. Funding for the meeting was provided by the Center for Dark Energy Biosphere Investigations, NSF OCE-0939564. This is C-DEBI publication 112.
References
Anderson, R. E., Brazelton, W. J., and Baross, J. A. (2011). Is the genetic landscape of the deep subsurface biosphere affected by viruses? Front. Microbio. 2:219. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00219
Biddle, J. F., Fitz-Gibbon, S., Schuster, S. C., Brenchley, J. E., and House, C. H. (2008). Metagenomic signatures of the Peru Margin subseafloor biopshere show a genetically distinct environment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 10583–10588.
Biddle, J. F., Lipp, J. S., Lever, M. A., Lloyd, K. G., Sørensen, K. B., Anderson, R., Fredricks, H. F., Elvert, M., Kelly, T. J., Schrag, D. P., Sogin, M. L., Brenchley, J. E., Teske, A., House, C. H., and Hinrichs, K. U. (2006). Heterotrophic archaea dominate sedimentary subsurface ecosystems off Peru. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 3846–3851.
Biddle, J. F., White, J. R., Teske, A. P., and House, C. H. (2011). Metagenomics of the subsurface Brazos-Trinity Basin (IODP site 1320): comparison with other sediment and pyrosequenced metagenomes. ISME J. 5, 1038–1047.
Blazejak, A., and Schippers, A. (2010). High abundance of JS-1 and Chloroflexi-related bacteria in deeply buried marine sediments revealed by quantitative, real-time PCR. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 72, 198–207.
Brazelton, W. J., Nelson, B., and Schrenk, M. O. (2011). Metagenomic evidence for H2 oxidation and H2 production by serpentinite-hosted subsurface microbial communities. Front. Microbio. 2:268. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00268
Campbell, B. J., Engel, A. S., Porter, M. L., and Takai, K. (2006). The versatile Epsilonproteobacteria: key players in sulphidic habitats. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4, 458–468.
D’Hondt, S., Jørgensen, B. B., Miller, D. J., Batzke, A., Blake, R., Cragg, B. A., Cypionka, H., Dickens, G. R., Ferdelman, T., Hinrichs, K. U., Holm, N. G., Mitterer, R., Spivack, A., Wang, G., Bekins, B., Engelen, B., Ford, K., Gettemy, G., Rutherford, S. D., Sass, H., Skilbeck, C. G., Aiello, I. W., Guèrin, G., House, C. H., Inagaki, F., Meister, P., Naehr, T., Niitsuma, S., Parkes, R. J., Schippers, A., Smith, D. C., Teske, A., Wiegel, J., Padilla, C. N., and Acosta, J. L. (2004). Distributions of microbial activities in deep subseafloor sediments. Science 306, 2216–2221.
D’Hondt, S., Spivack, A. J., Pockalny, R., Ferdelman, T. G., Fischer, J. P., Kallmeyer, J., Abrams, L. J., Smith, D. C., Graham, D., Hasiuk, F., Schrum, H., and Stancin, A. M. (2009). Subseafloor sedimentary life in the South Pacific Gyre. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 11651–11656.
Edwards, K., Fisher, A., and Wheat, C. (2012). The deep subsurface biosphere in igneous ocean crust: frontier habitats for microbiological exploration. Front. Microbio. 3:8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00008
Emerson, D., Rentz, J. A., Lilburn, T. G., Davis, R. E., Aldrich, H., Chan, C., and Moyer, C. L. (2007). A novel lineage of proteobacteria involved in formation of marine Fe oxidizing microbial mat communities. PLoS ONE 2, e667. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000667
Engelhardt, T., Sahlberg, M., Cypionka, H., and Engelen, B. (2011). Induction of prophages from deep-subseafloor bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 4, 459–465.
Fruh-Green, G. L., Kelley, D. S., Bernasconi, S. M., Karson, J. A., Ludwig, K. A., Butterfield, D. A., Boschi, C., and Proskurowski, G. (2003). 30,000 years of hydrothermal activity at the lost city vent field. Science 301, 495–498.
Futagami, T., Morono, Y., Terada, T., Kaksonen, A. H., and Inagaki, F. (2009). Dehalogenation activities and distribution of reductive dehalogenase homologous genes in marine subsurface sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 6905–6909.
Hinrichs, K.-U., Hayes, J. M., Bach, W., Spivack, A. J., Hmelo, L. R., Holm, N. G., Johnson, C. G., and Sylva, S. P. (2006). Biological formation of ethane and propane in the deep marine subsurface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 14684–14689.
Huber, J. A., Cantin, H. V., Huse, S. M., Mark Welch, D. B., Sogin, M. L., and Butterfield, D. A. (2010). Isolated communities of epsilonproteobacteria in hydrothermal vent fluids of the Mariana Arc seamounts. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 73, 538–549.
Huber, J. A., Welch, D. B., Morrison, H. M., Huse, S. M., Neal, P. R., Butterfield, D. A., and Sogin, M. L. (2007). Microbial population structures in the deep marine biosphere. Science 318, 97–100.
Hugenholtz, P., and Stackebrandt, E. (2004). Reclassification of Sphaerobacter thermophilus from the subclass Sphaerobacteridae in the phylum Actinobacteria to the class Thermomicrobia (emended description) in the phylum Chloroflexi (emended description). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 54, 2049–2051.
Humphris, S. E., Herzig, P. M., Miller, D. J., Alt, J. C., Becker, K., Brown, D., Brugmann, G., Chiba, H., Fouquet, Y., Gemmell, J. B., Guerin, G., Hannington, M. D., Holm, N. G., Honnorez, J. J., Iturrino, G. J., Knott, R., Ludwig, R., Nakamura, K., Petersen, S., Reysenbach, A. L., Rona, P. A., Smith, S., Sturz, A. A., Tivey, M. K., and Zhao, X. (1995). The internal structure of an active sea-floor massive sulfide deposit. Nature 377, 713–716.
Inagaki, F., Nunoura, T., Nakagawa, S., Teske, A., Lever, M., Lauer, A., Suzuki, M., Takai, K., Delwiche, M., Colwell, F. S., Nealson, K. H., Horikoshi, K., D’Hondt, S., and Jørgensen, B. B. (2006). Biogeographical distribution and diversity of microbes in methane hydrate-bearing deep marine sediments on the Pacific Ocean Margin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 2815–2820.
Inagaki, F., Suzuki, M., Takai, K., Oida, H., Sakamoto, T., Aoki, K., Nealson, K. H., and Horikoshi, K. (2003). Microbial communities associated with geological horizons in coastal subseafloor sediments from the sea of Okhotsk. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 7224–7235.
Kawecki, T. J., and Ebert, D. (2004). Conceptual issues in local adaptation. Ecol. Lett. 7, 1225–1241.
Kelley, D. S., Karson, J. A., Fruh-Green, G. L., Yoerger, D. R., Shank, T. M., Butterfield, D. A., Hayes, J. M., Schrenk, M. O., Olson, E. J., Proskurowski, G., Jakuba, M., Bradley, A., Larson, B., Ludwig, K., Glickson, D., Buckman, K., Bradley, A. S., Brazelton, W. J., Roe, K., Elend, M. J., Delacour, A., Bernasconi, S. M., Lilley, M. D., Baross, J. A., Summons, R. E., and Sylva, S. P. (2005). Aserpentinite-hosted ecosystem: the Lost City hydrothermal field. Science 307, 1428–1434.
Manhes, P., and Velicer, G. J. (2011). Experimental evolution of selfish policing in social bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 8357–8362.
Martiny, J. B., Bohannan, B. J., Brown, J. H., Colwell, R. K., Furhman, J. A., Green, J. L., Horner-Devine, M. C., Kane, M., Krumins, J. A., Kuske, C. R., Morin, P. J., Naeem, S., Ovreås, L., Reysenbach, A. L., Smith, V. H., and Staley, J. T. (2006). Microbial biogeography: putting microorganisms on the map. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4, 102–112.
Mason, O. U., Nakagawa, T., Rosner, M., Van Nostrand, J. D., Zhou, J., Maruyama, A., Fisk, M., and Giovannoni, S. J. (2011). First investigation of the microbiology of the deepest layer of ocean crust. PLoS ONE 5, e15399. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015399
McAllister, S. M., Davis, R. E., McBeth, J. M., Tebo, B. M., Emerson, D., and Moyer, C. L. (2011). Biodiversity and emerging biogeography of the neutrophilic iron-oxidizing Zetaproteobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 5445–5457.
McMurdie, P. J., Hug, L. A., Edwards, E. A., Holmes, S., and Spormann, A. M. (2011). Site-specific mobilization of vinyl chloride respiration islands by a mechanism common in dehalococcoides. BMC Genomics 12, 287. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-287
Meng, J., Wang, F., Wang, F., Zheng, Y., Peng, X., Zhou, H., and Xiao, X. (2009). An uncultivated 478 crenarchaeota contains functional bacteriochlorophyll a synthase. ISME J. 3, 106–116.
Morris, R. M., Rappe, M. S., Urbach, E., Connon, S. A., and Giovannoni, S. J. (2004). Prevalence of the Chloroflexi-related SAR202 bacterioplankton cluster throughout the mesopelagic zone and deep ocean. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 2836–2842.
Moser, D. P., Gihring, T. M., Brockman, F. J., Fredrickson, J. K., Balkwill, D. L., Dollhopf, M. E., Lollar, B. S., Pratt, L. M., Boice, E., Southam, G., Wanger, G., Baker, B. J., Pfiffner, S. M., Lin, L. H., and Onstott, T. C. (2005). Desulfotomaculum and Methanobacterium spp. dominate a 4-to 5-kilometer-deep fault. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 8773–8783.
Moyer, C. L., and McAllister, S. M. (2011). IODP Exp 331: Iron-oxidizing bacteria from the Okinawa trough deep subsurface biosphere. AGU Fall Meeting. abstr. B51K-0556.
Orcutt, B. N., Sylvan, J. B., Knab, N. J., and Edwards, K. J. (2011). Microbial ecology of the dark ocean above, at, and below the seafloor. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 75, 361–422.
Parkes, R. J., Cragg, B. A., and Wellsbury, P. (2000). Recent studies on bacterial populations and processes in subseafloor sediments: a review. Hydrogeol. J. 8, 11–28.
Parkes, R. J., Webster, G., Cragg, B. A., Weightman, A. J., Newberry, C. J., Ferdelman, T. G., Kallmeyer, J., Jørgensen, B. B., Aiello, I. W., and Fry, J. C. (2005). Deep sub-seafloor prokaryotes stimulated at interfaces over geological time. Nature 436, 390–394.
Rappe, M. S., and Giovannoni, S. J. (2003). The uncultured microbial majority. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57, 369–394.
Roussel, E. G., Bonavita, M. C., Querellou, J., Cragg, B. A., Webster, G., Prieur, D., and Parkes, R. J. (2008). Extending the sub-seafloor biosphere. Science 320, 1046.
Seshadri, R., Adrian, L., Fouts, D. E., Eisen, J. A., Phillippy, A. M., Methe, B. A., Ward, N. L., Nelson, W. C., Deboy, R. T., Khouri, H. M., Kolonay, J. F., Dodson, R. J., Daugherty, S. C., Brinkac, L. M., Sullivan, S. A., Madupu, R., Nelson, K. E., Kang, K. H., Impraim, M., Tran, K., Robinson, J. M., Forberger, H. A., Fraser, C. M., Zinder, S. H., and Heidelberg, J. F. (2005). Genome sequence of the PCE-dechlorinating bacterium Dehalococcoides ethenogenes. Science 307, 105–108.
Singer, E., Emerson, D., Webb, E. A., Barco, R. A., Kuenen, J. G., Nelson, W. C., Chan, C. S., Comolli, L. R., Ferriera, S., Johnson, J., Heidelberg, J. F., and Edwards, K. J. (2011). Mariprofundus ferroosydans PV-1 the first genome of a marine Fe(II) oxidizing Zetaproteobacterium. PLoS ONE 6, e25386. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025386
Takai, K., Campbell, B. J., Cary, S. C., Suzuki, M., Oida, H., Nunoura, T., Hirayama, H., Nakagawa, S., Suzuki, Y., Inagaki, F., and Horikoshi, K. (2005). Enzymatic and genetic characterization of carbon and energy metabolisms by deep-sea hydrothermal chemolithoautotrophic isolates of Epsilonproteobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 7310–7320.
Takai, K., Moser, D. P., Deflaun, M., Onstott, T. C., and Fredrickson, J. K. (2001). Archaeal diversity in waters from deep South African gold mines. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 5750–5760.
Takai, K., Nakamur, K., Toki, T., Tsunogai, U., Miyazaki, M., Miyazaki, J., Hirayama, H., Nakagawa, S., Nunoura, T., and Horikoshi, K. (2008). Cell proliferation at 122C and isotopically heavy CH4 production by a hyperthermophilic methanogen under high-pressure cultivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 10949–10954.
Teske, A., and Sørensen, K. (2008). Uncultured archaea in deep marine sediments: have we caught them all? ISME J. 2, 3–18.
Tiercelin, J. J., Pflumio, C., Castrec, M., Boulegue, J., Gente, P., Rolet, J., Coussement, C., Stetter, K. O., Huber, R., Buku, S., and Mifundu, W. (1993). Hydrothermal vents in Lake Tanganyika, East African rift system. Geology 21, 499–502.
Wheat, C. G., and Fisher, A. T. (2008). Massive, low-temperature hydrothermal flow from a basaltic outcrop on 23 Ma seafloor of the Cocos Plate: chemical constraints and implications. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 9, Q12O14.
Whitaker, R. J., Grogan, D. W., and Taylor, J. W. (2003). Geographic barriers isolate endemic populations of hyperthermophilic archaea. Science 301, 976–978.
Whitman, W. B., Coleman, D. C., and Wiebe, W. J. (1998). Prokaryotes: the unseen majority. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95, 6578–6583.
Wolf, Y. I., Viboud, C., Holmes, E. C., Koonin, E. V., and Lipman, D. J. (2006). Long intervals of stasis punctuated by bursts of positive selection in the seasonal evolution of influenza A virus. Biol. Direct 1. doi:10.1186/1745-6150-1-34
Zierenberg, R. A., Fouquet, Y., Miller, D. J., Bahr, J. M., Baker, P. A., Bjerkgard, T., Brunner, C. A., Duckworth, R. C., Gable, R., Gieskes, J., Goodfellow, W. D., Groschel-Becker, H. M., Guerin, G., Ishibashi, J., Iturrino, G., James, R. H., Lackschewitz, K. S., Marquez, L. L., Nehlig, P., Peter, J. M., Rigsby, C. A., Schultheiss, P., Shanks, W. C., Simoneit, B. R. T., Summit, M., Teagle, D. A. H., Urbat, M., and Zuffa, G. G. (1998). The deep structure of a sea-floor hydrothermal deposit. Nature 392, 485–488.
Keywords: deep biosphere, subsurface, evolution, C-DEBI, adaptation
Citation: Biddle JF, Sylvan JB, Brazelton WJ, Tully BJ, Edwards KJ, Moyer CL, Heidelberg JF and Nelson WC (2012) Prospects for the study of evolution in the deep biosphere. Front. Microbio. 2:285. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00285
Received: 14 October 2011;
Accepted: 31 December 2011;
Published online: 24 January 2012.
Edited by:
Andreas Teske, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, USAReviewed by:
Patricia Lynne Siering, Humboldt State University, USACasey R. J. Hubert, Newcastle University, UK
Copyright: © 2012 Biddle, Sylvan, Brazelton, Tully, Edwards, Moyer, Heidelberg and Nelson. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial License, which permits non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in other forums, provided the original authors and source are credited.
*Correspondence: Jennifer F. Biddle, College of Earth, Ocean and the Environment, University of Delaware, Lewes, DE 19958, USA. e-mail:amZiaWRkbGVAdWRlbC5lZHU=


 William J. Brazelton3
William J. Brazelton3


