- 1Guangdong Laboratory for Lingnan Modern Agriculture, Genome Analysis Laboratory of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Agricultural Genomics Institute at Shenzhen, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Shenzhen, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Biology in Arid Areas, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Plant Nutrition and Agri-Environment in Northwest China, Ministry of Agriculture, College of Natural Resources and Environment, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China
An effective solution to global human zinc (Zn) deficiency is Zn biofortification of staple food crops, which has been hindered by the low available Zn in calcareous soils worldwide. Many culturable soil microbes have been reported to increase Zn availability in the laboratory, while the status of these microbes in fields and whether there are unculturable Zn-mobilizing microbes remain unexplored. Here, we use the culture-independent metagenomic sequencing to investigate the rhizosphere microbiome of three high-Zn (HZn) and three low-Zn (LZn) wheat cultivars in a field experiment with calcareous soils. The average grain Zn concentration of HZn was higher than the Zn biofortification target 40 mg kg–1, while that of LZn was lower than 40 mg kg–1. Metagenomic sequencing and analysis showed large microbiome difference between wheat rhizosphere and bulk soil but small difference between HZn and LZn. Most of the rhizosphere-enriched microbes in HZn and LZn were in common, including many of the previously reported soil Zn-mobilizing microbes. Notably, 30 of the 32 rhizosphere-enriched species exhibiting different abundances between HZn and LZn possess the functional genes involved in soil Zn mobilization, especially the synthesis and exudation of organic acids and siderophores. Most of the abundant potential Zn-mobilizing species were positively correlated with grain Zn concentration and formed a module with strong interspecies relations in the co-occurrence network of abundant rhizosphere-enriched microbes. The potential Zn-mobilizing species, especially Massilia and Pseudomonas, may contribute to the cultivars’ variation in grain Zn concentration, and they deserve further investigation in future studies on Zn biofortification.
Introduction
Around 20% of the world population are suffering from zinc (Zn) deficiency, and the situation will become worse with the increase of atmosphere carbon dioxide (Myers et al., 2014; Smith and Myers, 2018). An effective solution to address human Zn deficiency is to increase the grain Zn concentration of staple food crops like wheat, namely, Zn biofortification. The target of wheat Zn biofortification is to increase the current grain Zn concentration of 20 ∼ 30 to above 40 mg kg–1 that is sufficient for human Zn nutrition (Liu et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2017). Achieving the target of wheat grain Zn biofortification has been hindered by the low soil Zn availability because over 50% of the global wheat growing soils are poor in available Zn (Cakmak and Kutman, 2018). Therefore, it is of great significance to increase the Zn availability in agricultural soils.
Due to the poor mobility of Zn in soil, the absorption of Zn by plant roots mainly occurs in the rhizosphere, where the activities of roots and microorganisms can somewhat increase the amount of available Zn (Rehman et al., 2018). In the calcareous soils distributed worldwide, Zn availability is restricted by alkaline environment and high carbonate content; and various root exudates like carboxylic acids, amino acids, and low-molecular-weight polypeptides can acidify the rhizosphere and solubilize the Zn immobilized in minerals (Rengel, 2015). Besides, the microbes living on root exudates can also produce organic acids, siderophores, and exopolysaccharides that can mobilize micronutrients in rhizosphere soil (Sathya et al., 2016). Inoculation of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) like Bacillus, Arthrobacter, and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) has been reported to increase soil available Zn and crop grain Zn concentration, especially in soils with low available Zn (Singh et al., 2018; Coccina et al., 2019). Despite many reports on the isolation and functional verification of soil Zn-mobilizing bacteria, the roles of soil microbes in improving soil Zn availability and promoting crop Zn biofortification remain to be extensively explored.
Previous studies on soil Zn-mobilizing microbes are mainly conducted in the laboratory and focus on the culturable soil Zn-mobilizing microbes, while the natural status of these microbes in fields and whether there are more unculturable Zn-mobilizing microbes are unknown. Recently, the culture-independent metagenomics approach has been used to study the whole rhizosphere microbiome of many plants like wheat (Ofek-Lalzar et al., 2014), barley (Bulgarelli et al., 2015), rice (Zhang et al., 2019), and potato (Shi et al., 2019). It has been widely recognized that rhizosphere microbiome contributes substantially to nutrient uptake (Oldroyd and Leyser, 2020), drought resistance (de Vries et al., 2020), and plant health (Trivedi et al., 2020). Here, we use metagenomic sequencing to investigate the rhizosphere microbiome of six wheat cultivars that exhibit different grain Zn concentrations in a field experiment to (1) characterize the rhizosphere microbiome of high-Zn (HZn) and low-Zn (LZn) wheat; (2) identify the potential soil Zn-mobilizing microbes; and (3) determine the natural abundance of Zn-mobilizing microbes and their contributions to the variation of grain Zn concentration among cultivars. The results show large difference of microbial communities and functions between wheat rhizosphere and bulk soil but small difference between HZn and LZn wheat cultivars. Of the rhizosphere-enriched microbes exhibiting different abundances among cultivars, we identify 30 potential soil Zn-mobilizing bacteria that may contribute to the variation of grain Zn concentration among wheat cultivars.
Materials and Methods
Field Experiment
The field experiment was located at the Agriculture Research Station of Northwest A&F University in Yangling, Shaanxi, China (34°18′N, 108°05′E). This site is in the temperate continental monsoon climate zone and located on the southern edge of the Loess Plateau, with elevation of 520 m, annual atmosphere temperature of 12.9°C, annual precipitation of 579 mm, and annual potential evaporation of 1,400 mm. The soil type of the experimental filed is Eum-Orthic Anthrosol according to the soil taxonomy system of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), and the soil texture is silt clay loam. Basic soil chemical properties are as follows: pH (water:soil = 2.5:1) 8.23, cation exchange capacity (CEC; 1 M of NaAc) 16.3 cmol kg–1, organic matter (0.8 M of K2Cr2O7) 16.3 g kg–1, total nitrogen (N) (Kjeldahl) 1.01 g kg–1, nitrate-N (1 M of KCl) 15.3 mg kg–1, ammonium-N (1 M of KCl) 0.1 mg kg–1, total phosphorus (P) (HClO4 + H2SO4) 0.78 g kg–1, available P (0.5 M of NaHCO3) 11.7 mg kg–1, total potassium (K) (NaOH) 14.2 g kg–1, available K (1 M of NH4Ac) 122 mg kg–1, total Zn (HF + HNO3 + HClO4) 74 mg kg–1, and available Zn (0.005 M of DTPA) 0.46 mg kg–1.
Based on our previous studies on screening hundreds of wheat cultivars by yield and grain Zn concentration (Wang et al., 2018), six cultivars with similar yields and different grain Zn concentrations were selected for investigation in the present study (Figure 1A). A randomized complete block design was used for the field experiment. Each cultivar had four replicates and was grown with the uniform nutrient application of 150 kg N ha–1 as urea (46% N), 100 kg P2O5 ha–1 as calcium superphosphate (16% P2O5), and 74 kg K2O ha–1 as potassium sulfate (51% K2O). Each plot consisted of five 2-m-long rows with the seed spacing of 2.5 cm and the row spacing of 20 cm. All cultivars were sown on October 3, 2018, and harvested on June 18, 2019. All the fertilizers were applied before sowing, no irrigation was applied during wheat growth period, and only pesticides were used when necessary.
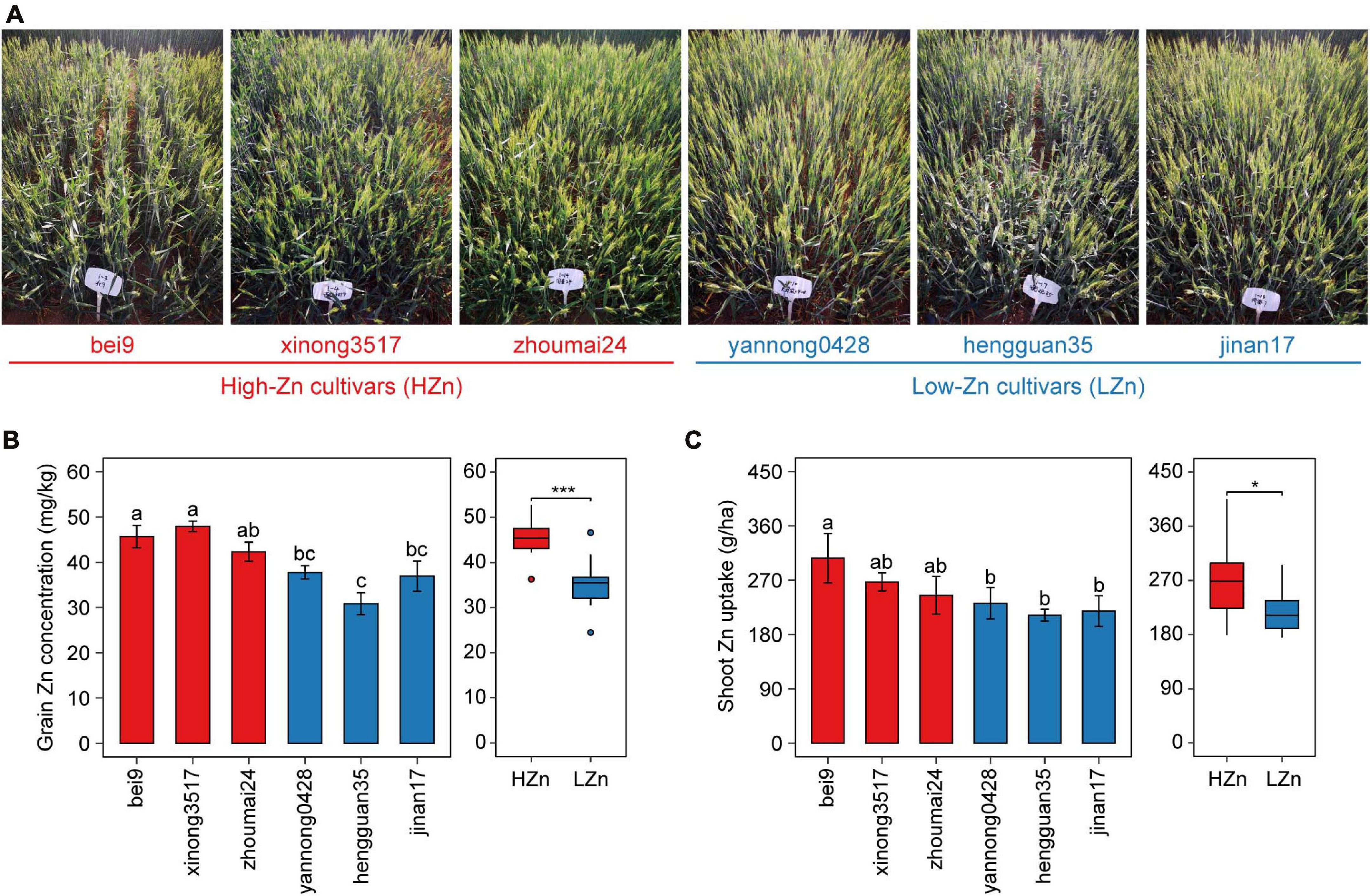
Figure 1. Phenotypic data of the six wheat cultivars grown in calcareous soil. Photographs taken at anthesis (A), grain Zn concentration (B), and shoot Zn uptake (C) at maturity of three high-Zn (HZn) and three low-Zn (LZn) cultivars with average grain Zn concentrations higher or lower than the Zn biofortification target 40 mg kg– 1. In the left panel of (B,C), the error bars stand for mean ± standard error (n = 4), and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among cultivars (ANOVA, Duncan, P < 0.05). In the right panel of (B,C), the inner horizontal lines, and bottom and top of boxes indicate the medians, and 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively; the lower and upper whiskers extend to the minimum and maximum of the data excluding the outliers denoted by dots, respectively; and asterisks indicate significant differences between HZn (n = 12) and LZn (n = 12) (t-test, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001).
Plant and Soil Sampling
The top 0- to 20-cm soil of the experimental field was sampled before sowing for the determination of basic soil physicochemical properties. At anthesis, the plant, rhizosphere, and bulk soil samples used for chemical analyses and metagenomic sequencing were collected. For each cultivar, 10 wheat plants were randomly selected and dug out from each plot, cut-off at the stem-root jointing part, and separated into ears, leaves, stems, and roots with adhered rhizosphere soils by sterile stainless tools and shaking. For bulk soil sampling, 10 points were randomly selected from the unplanted areas over 50 cm away from wheat plots in each block and sampled at 0- to 10-cm soil layer and then mixed into one sample using sterile stainless tools. At maturity, the plant samples used for chemical analyses and estimation of yield and biomass were collected. For each cultivar, the wheat plants of 30 ears without roots and soil were sampled by the same procedures used in plant sampling at anthesis, and all the remaining plants were harvested to estimate grain yield.
One third of the samples of root with rhizosphere soil and bulk soil were transported to the laboratory in a dry ice box and stored in an ultra-low-temperature refrigerator at −80°C before metagenomic sequencing, and the other soil and plant samples were transported to the laboratory under air temperature for further processing. Firstly, the rhizosphere soils were separated from roots using a nylon brush; then, the separated rhizosphere soil and bulk soil samples were air-dried and ground to pass through a 1-mm sieve for chemical analysis; finally, the plant samples of separated root, stem, leaf, ear, glume, and grain were successively washed by tap water and distilled water, oven-dried at 65°C and weighed, and ground to powder using a ball miller (Retsch MM400, Haan, Germany) for chemical analysis.
Physicochemical Analyses
The chemical analyses of soil and plant samples were conducted according to the methods described by Wang et al. (2018). In short, soil pH was measured using CO2–free water extraction (water:soil = 2.5:1) and a pH meter, and soil available Zn was extracted by 0.005 M of DTPA-TEA-CaCl2 solution and determined by an atomic absorption spectrometer (AAS). Grain yield and biomasses were expressed in oven-dried weight, and plant Zn concentration was determined by microwave digestion with HNO3 and H2O2 and an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), and then shoot Zn uptake was calculated.
Metagenomic Sequencing
Rhizosphere soil samples used for metagenomic sequencing were separated from roots according to the methods described by Lundberg et al. (2012) and Donn et al. (2015). Briefly, 2∼3 g of roots with adhered rhizosphere soil were cut into 1- to 2-cm-long pieces and then washed in 30 ml of phosphate-buffered solution (PBS) in a 50-ml sterile tube by continuous shaking at 180 rpm and 4°C for 20 min. Then, the turbid suspension was poured into a new 50-ml tube and centrifuged at 10,000 g and 4°C for 20 min to get the rhizosphere soil pellet, which was firstly frozen in liquid nitrogen and then stored at −80°C for DNA extraction. All the above operations were done using sterile tools under sterile conditions. Soil DNA was extracted using the DNeasy PowerSoil DNA Isolation Kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) according to the provided protocol with minor modifications. In short, 0.4 g of soil was weighed, added into the PowerBead Tube and mixed on a vortex, and incubated at 65°C in a water bath for 10 min before being subjected to the same procedures as described in the protocol. The extracted DNA was quantified by Invitrogen Qubit 4.0 and Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States) and quality checked by NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States) and agarose gel electrophoresis (Beijing LiuYi Biotechnology, Beijing, China). The DNA concentration was diluted or concentrated to ∼ 25 ng μl–1 for the preparation of sequencing library.
The prepared DNA sample was fragmented into 350-bp fragments in 60-μl volume in a microTUBE by Covaris S220 ultrasonicator (Covaris, Woburn, MA, United States). Then, the fragmented DNA was transformed into sequencing library using the Truseq DNA PCR-Free Library Prep Kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, United States) according to the provided protocol. Finally, the prepared library was sequenced by the Illumina Hiseq X ten (Illumina, United States) in the mode of paired-end 150 bp.
Bioinformatic Analyses
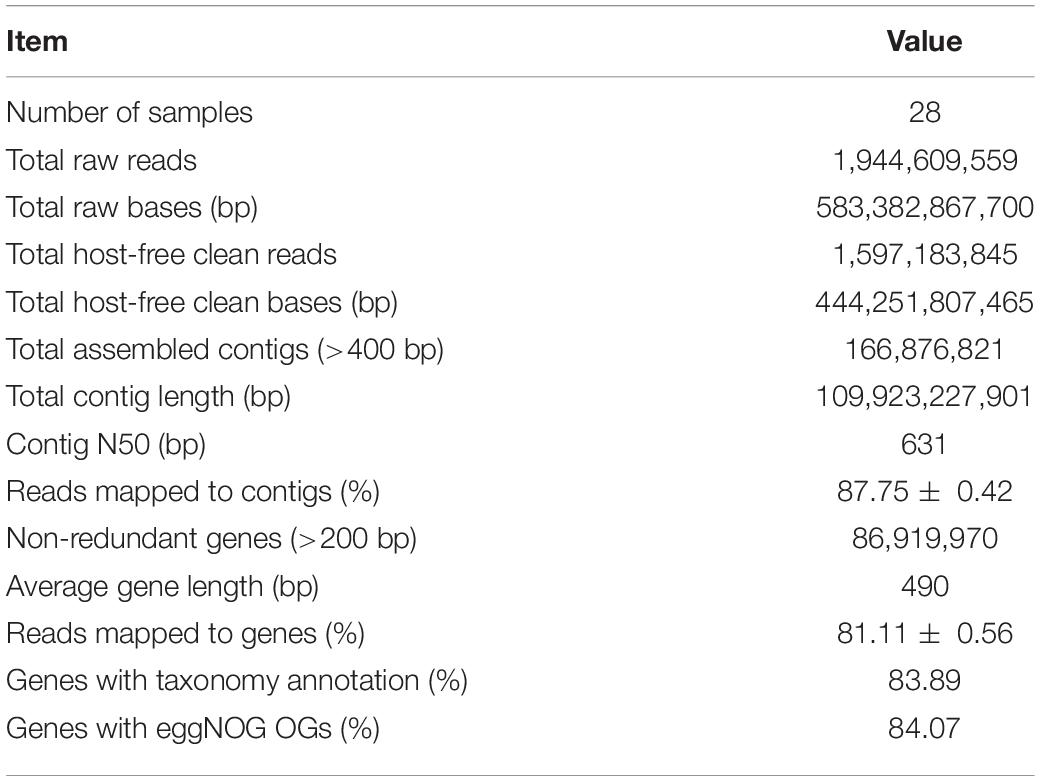
The raw reads were firstly checked for sequencing quality; and the ambiguous bases, low-quality bases, and adapter contamination were removed using fastp v0.20.0 (Chen et al., 2018). Then the reads were mapped to wheat genome sequence IWGSC RefSeq v1.0 (IWGSC, 2018) using Bowtie 2 v2.2.7 (Langmead and Salzberg, 2012) to remove host contamination and get the clean reads derived from microbes. Afterward, the clean reads were assembled into contigs by MEGAHIT v1.1.3 (Li et al., 2016) with the parameter “–presets meta-large” through three steps: (1) the clean reads of each sample were assembled separately; (2) for each sample, the clean reads were mapped to the assembled contigs by Bowtie 2, and the unmapped clean reads of all samples were pooled and assembled into contigs; and (3) all the contigs of separate and pooled assemblies with length >400 bp were combined to get the final assembly. The genes in assembled contigs were predicted using Prodigal v2.6.3 (Hyatt et al., 2012) with the parameter “-p meta,” and the genes with length >200 bp were clustered by MMseqs2 Linclust (Steinegger and Söding, 2017, 2018) to remove redundant genes with sequence identity >95% and coverage >90%. Then, the non-redundant genes were taxonomically annotated using kaiju v1.7.3 (Menzel et al., 2016) with the parameter “-a greedy” and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) NR and Taxonomy as reference databases and functionally annotated using eggNOG-Mapper v2.0.1 (Huerta-Cepas et al., 2017) by diamond v0.9.24 (Buchfink et al., 2015) searching against eggNOG 5.0 (Huerta-Cepas et al., 2018) database. The clean reads of each sample were mapped back to the annotated non-redundant gene set by Bowtie 2 to calculate the relative abundances of genes, different taxonomic ranks like phylum and species, and different functional orthologous groups like eggNOG Orthologous Groups (OGs) and categories. The scripts used for bioinformatic analyses are available on https://github.com/kingforest93/Ta6_rhizo_meta_scripts.
To identify the potential soil Zn-mobilizing species, we summarized the functional characteristics of the reported soil Zn-mobilizing microbes in published literature (Supplementary Table 3), selected the OGs relevant to soil Zn mobilization by the functional description, and classified them into three groups as the transmembrane transport of Zn (transporter, export, efflux, etc.), the metabolism of Zn ligands (siderophore, citric acid, etc.), and the promotion of root Zn uptake (growth promotion, auxin, N fixation, etc.) (Supplementary Table 4). Then, the genome sequences of potential soil Zn-mobilizing species were downloaded from NCBI Genome database and subjected to the same functional annotation procedures as described in the annotation of non-redundant genes. The microbes possessing the above functional genes relevant to soil Zn mobilization were regarded as potential soil Zn-mobilizing microorganisms.
Statistical Analyses
The comparisons of soil pH, soil DTPA-Zn, plant Zn concentration, and Zn uptake among cultivars and bulk soil were conducted by ANOVA and Duncan’s multiple comparison in R 4.0.2 (R Core Team, 2020). The differences of grain Zn concentration and shoot Zn uptake between HZn and LZn group were tested by t-test. The within-sample microbial alpha diversity (the Shannon–Wiener index) of species and OGs were analyzed using vegan v2.5-6 package (Oksanen et al., 2019), and its difference between HZn and LZn was tested by t-test. The between-sample microbial beta diversity was analyzed by the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity of species and eggNOG OGs, and different samples were ordinated by principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) and non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) using vegan and ggplot2 v3.3.2 package (Wickham, 2016). The relative abundance differences of microbial phyla, species, and OGs between rhizosphere (Rhizo) and bulk soil (Soil) and between HZn and LZn were tested by Wilcoxon’s rank-sum test, and P-values were adjusted by the Benjamini–Hochberg (BH) method (Benjamini and Hochberg, 1995). Spearman’s correlations between plant Zn concentration and Zn uptake and the relative abundances of soil Zn-mobilizing microbial species were analyzed using psych package (Revelle, 2013). The co-occurrence network of rhizosphere-enriched microbes soil Zn-mobilizing microbes based on their Spearman’s correlations were constructed using igraph package (Csardi and Nepusz, 2005). All figures were drawn in R 4.0.2 and Adobe Illustrator CC 2017. The scripts used for statistical analyses and graphing are available on https://github.com/kingforest93/Ta6_rhizo_meta_scripts.
Results
Rhizosphere Metagenome Assembly and Annotation of Wheat Cultivars With Various Grain Zn Concentrations
The six wheat cultivars exhibited significant differences in grain Zn concentration and shoot Zn uptake when grown on calcareous soils (ANOVA, P < 0.05, Figures 1B,C), consistent with the previous studies on these cultivars (Wang et al., 2018). Based on the average grain Zn concentration higher or lower than the wheat Zn biofortification target 40 mg kg–1, the six cultivars were classified into HZn and LZn groups, and the grain Zn concentration and shoot Zn uptake of HZn wheat were significantly higher than those of LZn wheat (t-test, P < 0.05, Figures 1B,C). Metagenomic sequencing of the 24 rhizosphere soil samples of six cultivars and four bulk soil samples generated a total of 583.4-Gb raw reads and 444.3-Gb clean reads without low-quality bases and adapter and host contamination (Table 1 and Supplementary Table 1). The clean reads were assembled into 166,876,821 contigs with N50 of 631 bp, and the average read mapping rate to assembly was 87.75% (Table 1 and Supplementary Table 1), higher than the previously reported rhizosphere metagenome of wheat (49.2%) and cucumber (70.8%) (Ofek-Lalzar et al., 2014) and citrus (48.3%) (Xu et al., 2018).
To get the taxonomic and functional information of wheat rhizosphere microbiome, the genes in the assembled contigs were predicted and clustered to generate a total of 86,919,970 non-redundant genes with the average length of 490 bp and the average read mapping rate of 81.11% (Table 1 and Supplementary Table 1). Of the non-redundant genes, 83.89% had taxonomy annotation, and 79.21, 48.59, and 20.71% were taxonomically classified to 84 phyla, 1,023 families, and 13,254 species (Supplementary Table 2), respectively. Besides, 84.07% of the non-redundant genes had functional annotation, and 84.07 and 53.37% were functionally annotated with 1,572,349 eggNOG OGs and 15,180 KEGG KOs (Table 1 and Supplementary Table 2), respectively. Therefore, the constructed gene set here provides the foundation for analyzing the rhizosphere microbial communities and functions of winter wheat grown in calcareous soils.
Wheat Rhizosphere and Bulk Soil Exhibit Large Difference in Microbial Taxonomic and Functional Profiles
The plant rhizosphere microbiome has been regarded as a subset of the bulk soil microbiome, and we compared the microbial taxonomic and functional diversity between wheat rhizosphere and bulk soil. The microbial taxonomic alpha diversity (species Shannon index) of wheat rhizosphere was 4.3% lower than that of bulk soil (t-test, P < 0.05, Figure 2A). Of the major phyla in both wheat rhizosphere and bulk soil, Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes showed significantly higher relative abundances in wheat rhizosphere, while Acidobacteria showed significantly higher abundances in bulk soil (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, BH adjusted P < 0.05, Supplementary Figure 2E), consistent with the recent studies on wheat rhizosphere microbiome (Illescas et al., 2020; Rossmann et al., 2020). The microbial functional alpha diversity (eggNOG OG Shannon index) showed no significant difference between rhizosphere and bulk soil (Figure 2B), and the relative abundances of most eggNOG functional categories were also similar between rhizosphere and bulk soil (Supplementary Figure 2F). Due to the high functional redundancy in soil microbial communities (Banerjee et al., 2016), possibly less diverse microbial communities in rhizosphere can carry out the similar diverse functions to that in bulk soil.
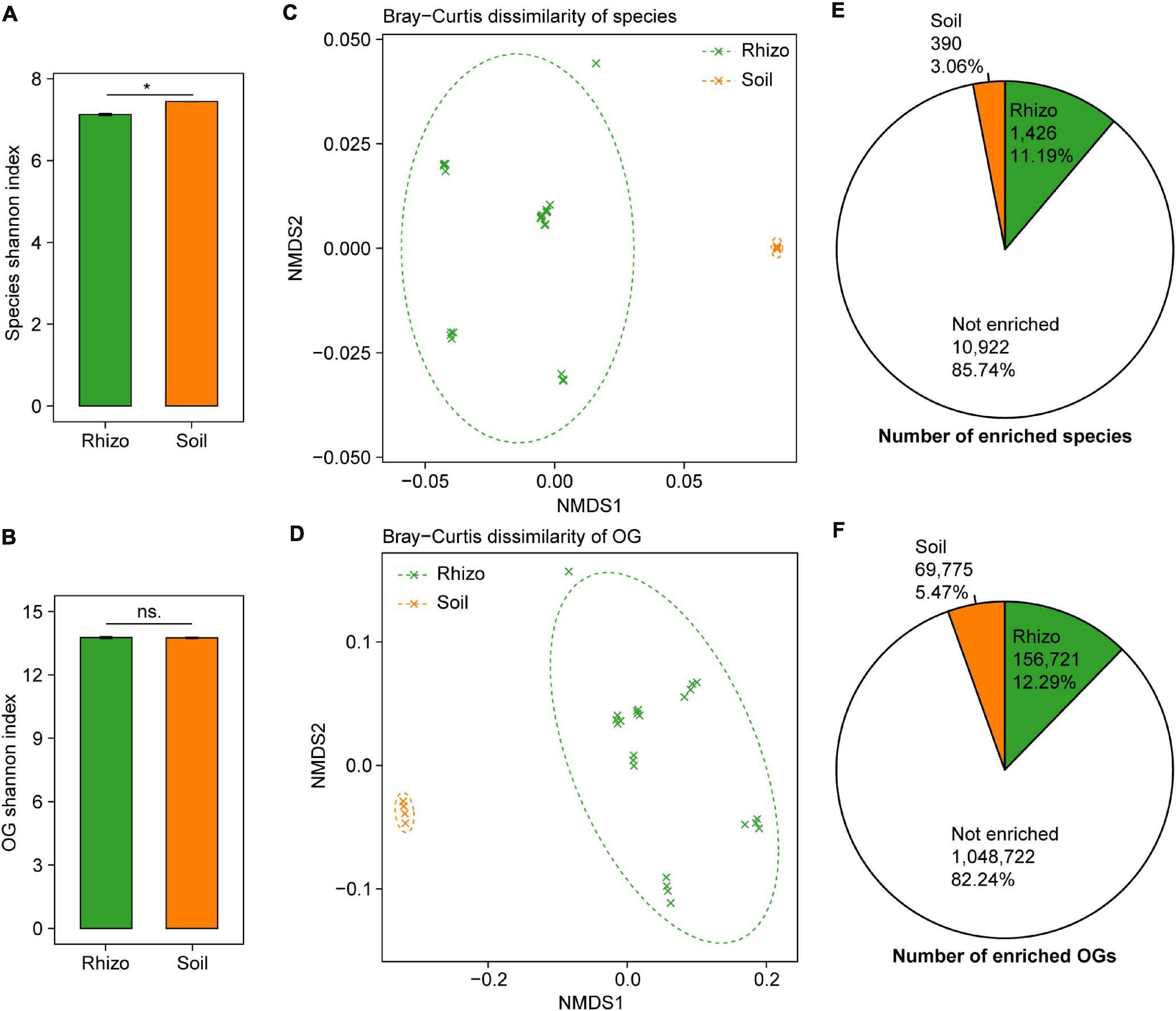
Figure 2. Comparisons of microbial taxonomic and functional diversity between wheat rhizosphere (Rhizo) and bulk soil (Soil). Within-sample alpha diversity (the Shannon–Wiener index) of microbial species (A) and eggNOG Orthologous Groups (OGs) (B) between Rhizo and Soil. The error bars stand for mean ± standard error (Rhizo, n = 24; Soil, n = 4), and asterisks indicate significant differences between Rhizo and Soil (t-test, *P < 0.05; ns, not significant). Between-sample beta diversity of species (C) and OGs (D) among Rhizo and Soil samples are analyzed by non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) of the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity. Green and orange crosses refer to Rhizo and Soil samples, respectively; and the corresponding ellipses cover 90% of the data range. The number of species (E) and OGs (F) enriched in Rhizo (green pie, relative abundance ratio of Rhizo/Soil >1.5), Soil (orange pie, Rhizo/Soil <0.5) [Wilcoxon rank sum test, the Benjamini–Hochberg (BH) adjusted P < 0.05], and neither enriched.
There were high microbial taxonomic and functional beta diversity between wheat rhizosphere and bulk soil, as shown by the clearly separated rhizosphere and bulk soil samples in both PCoA and NMDS ordination plots based on the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity of species and eggNOG OG (Figures 2C,D and Supplementary Figures 2A,B). Comparisons of the relative abundances of species and OG between rhizosphere and bulk soil showed that 1,426 species and 156,721 OGs were significantly enriched in rhizosphere with the abundance ratio of rhizosphere to bulk soil >1.5 (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, BH adjusted P < 0.05, Figures 2E,F and Supplementary Figures 2C,D). In contrast, 390 species and 69,775 OGs were significantly enriched in bulk soil with the abundance ratio of rhizosphere to bulk soil <0.5 (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, BH adjusted P < 0.05, Figures 2E,F and Supplementary Figures 2C,D). Many of the rhizosphere-enriched species are widely reported plant growth-promoting microorganisms, such as the species of Bacillus, Burkholderia, Glomus, Pseudomonas, Rhizobium, Rhizophagus, and Trichoderma (de Souza et al., 2015; Rosier et al., 2018). Besides, 17 of 38 previously reported soil Zn-mobilizing microbial genera or species were also among the rhizosphere-enriched microbes (Supplementary Table 3). Therefore, wheat roots may recruit a subset of soil microbes in the rhizosphere to promote plant growth and nutrient uptake.
Small Difference of Rhizosphere Microbiome Exists Between High-Zn and Low-Zn Wheat
Compared with the large difference of microbial diversity between rhizosphere and bulk soil, small difference of rhizosphere microbiome was observed between HZn and LZn wheat. The microbial alpha diversity (Shannon index) of rhizosphere-enriched species and eggNOG OGs showed no significant difference between HZn and LZn (Figures 3A,B). Possibly, many of the rhizosphere-enriched microbes provides beneficial functions necessary for both HZn and LZn wheat cultivars. Although the microbial beta diversity of rhizosphere-enriched species and OGs between HZn and LZn were also small, there were still some differences among HZn and LZn cultivars as shown by the non-overlapping sample points in both PCoA and NMDS ordination plots based on the Bray–Curtis distance (Figures 3C,D and Supplementary Figures 3A,B). Thus, it is necessary to further analyze the difference of each species and OG between HZn and LZn rhizosphere.
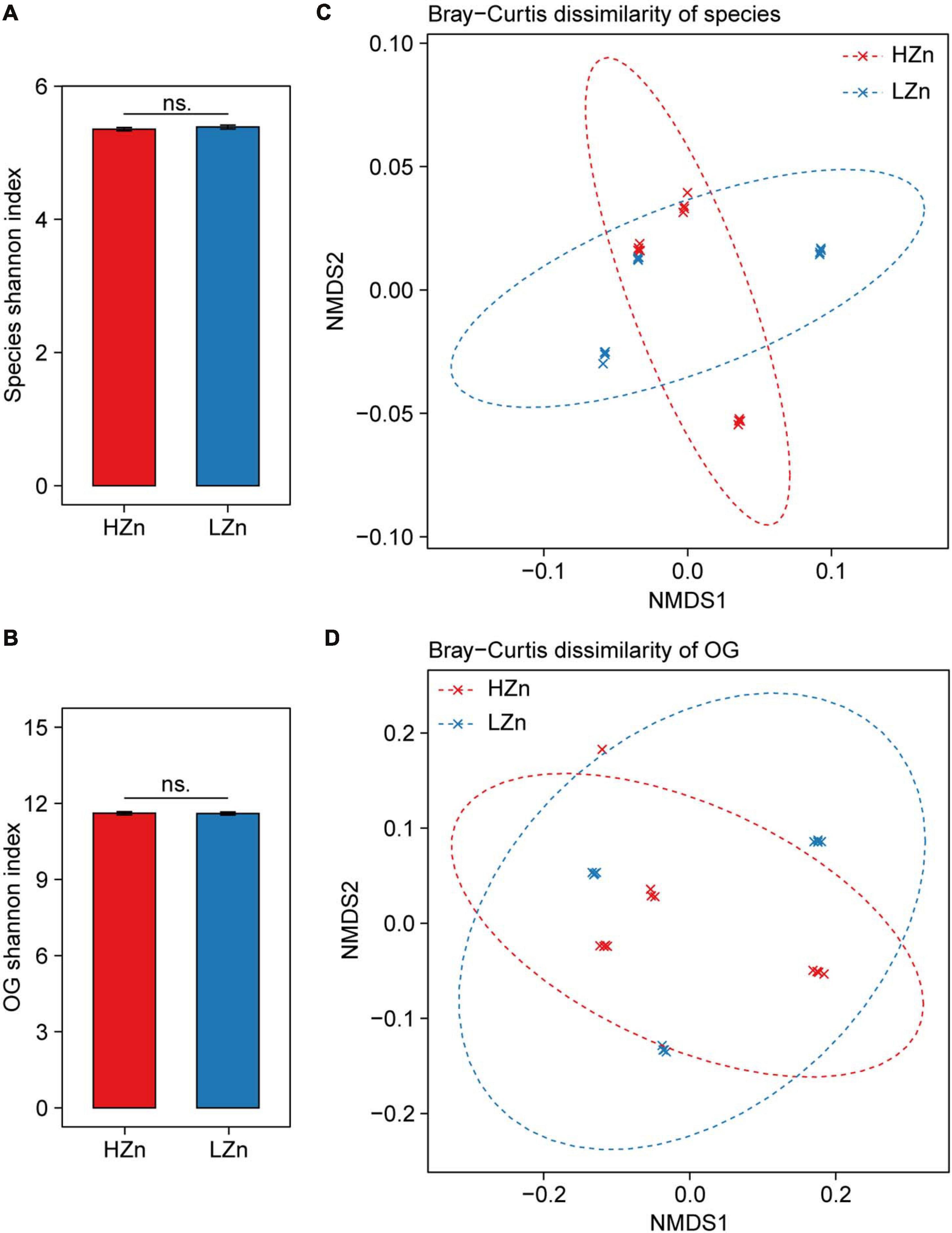
Figure 3. Comparisons of rhizosphere microbiome diversity between high-Zn (HZn) and low-Zn (LZn) wheat. Within-sample alpha diversity (the Shannon–Wiener index) of rhizosphere-enriched species (A) and eggNOG Orthologous Groups (OGs) (B) between HZn and LZn. The error bars stand for mean ± standard error (HZn, n = 12; LZn, n = 12); and ns indicates no significant difference between HZn and LZn (t-test, P < 0.05). Between-sample beta diversity of rhizosphere-enriched species (C) and OGs (D) among HZn and LZn samples are analyzed by non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) of the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity. Red and blue crosses refer to HZn and LZn samples, respectively; and the corresponding ellipses cover 90% of the data range.
High-Zn Wheat Recruit More Bacteria Relevant to Soil Zn Mobilization in the Rhizosphere
Comparisons of the relative abundances of rhizosphere-enriched eggNOG OGs between HZn and LZn wheat showed that 368 OGs were significantly enriched in HZn with the abundance ratio of HZn to LZn >1.5 and 86 OGs were enriched in LZn with the abundance ratio of HZn to LZn <0.5 (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, BH adjusted P < 0.05, Figure 4B). Of these OGs, 16 HZn-enriched and 16 LZn-enriched OGs are relevant to soil Zn mobilization by comparing their functional descriptions with the functional characteristics of previously reported soil Zn-mobilizing microbes (Supplementary Tables 3, 5). The 16 HZn-enriched OGs are mainly involved in the synthesis of Zn ligands like malate (ENOG502NTY5), siderophore (ENOG502VIDA), and auxin export (ENOG501RMV0) that can promote soil Zn mobilization, while the 16 LZn-enriched OGs are mainly involved in the lysis of Zn ligands like citrate (ENOG504EY0V and ENOG504EY25) that are unfavorable to soil Zn mobilization (Figure 4D and Supplementary Table 5). Hence, HZn wheat cultivars may recruit more functional genes relevant to Zn mobilization to help increase the Zn availability in rhizosphere soil.
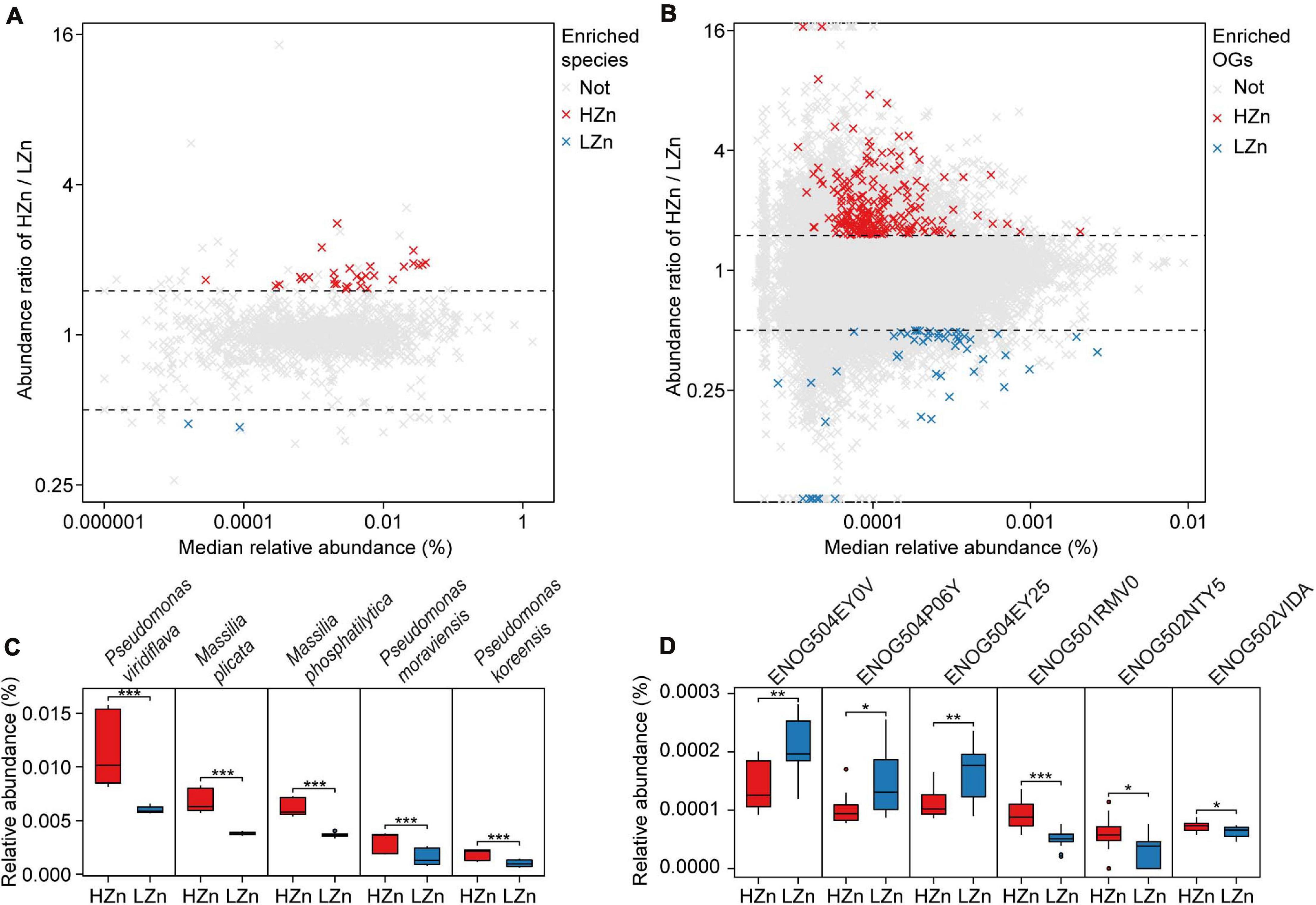
Figure 4. Comparisons of the rhizosphere microbes and functions relevant to soil Zn mobilization between high-Zn (HZn) and low-Zn (LZn) wheat. The median relative abundance and abundance ratio (HZn/LZn) of microbial species (A) and eggNOG Orthologous Groups (OGs) (B) enriched in the rhizosphere of HZn (ratio >1.5, red crosses) or LZn (ratio <0.5, blue crosses) [Wilcoxon rank sum test, the Benjamini–Hochberg (BH) adjusted P < 0.05] and neither enriched (light gray crosses). Comparisons of the relative abundances of representative HZn or LZn-enriched species (C) and OGs (D) relevant to soil Zn mobilization between HZn and LZn. The inner horizontal lines, and bottom and top of boxes indicate the medians, and 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively; the lower and upper whiskers extend to the minimum and maximum of the data excluding the outliers denoted by dots, respectively; and asterisks indicate significant differences between HZn (n = 12) and LZn (n = 12) [Wilcoxon rank sum test, the Benjamini–Hochberg (BH) adjusted, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001].
Comparisons of the relative abundances of rhizosphere-enriched species between HZn and LZn wheat found that 30 species were significantly enriched in HZn with the abundance ratio of HZn to LZn >1.5 and two species were enriched in LZn with the abundance ratio of HZn to LZn <0.5 (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, BH adjusted P < 0.05, Figure 4A and Supplementary Table 6). Of the 32 species, three HZn-enriched species belong to the reported soil Zn-mobilizing genus Pseudomonas, which is one of the 38 previously published Zn-mobilizing microbial species or genera (Supplementary Table 3). Nearly half of the previously reported Zn-mobilizing microbes were enriched in wheat rhizosphere, but most of them showed no significant difference between HZn and LZn (Supplementary Figures 4A,B and Supplementary Table 3). Differently, the 32 HZn- or LZn-enriched species were also enriched in wheat rhizosphere, and they exhibited significant differences between HZn and LZn, such as the much higher abundances of Pseudomonas and Massilia species in HZn than those in LZn (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, BH adjusted P < 0.05, Figure 4C and Supplementary Table 6). Besides, genome functional annotation of the 32 species showed that 28 HZn-enriched and two LZn-enriched species possess the functional genes involved in soil Zn mobilization (Table 2). Therefore, the previously reported Zn-mobilizing microbes can promote the Zn uptake of all wheat plants, while the identified 30 HZn- or LZn-enriched species may be the potential soil Zn-mobilizing microbes contributing to the variations of shoot Zn uptake and grain Zn concentration among cultivars.
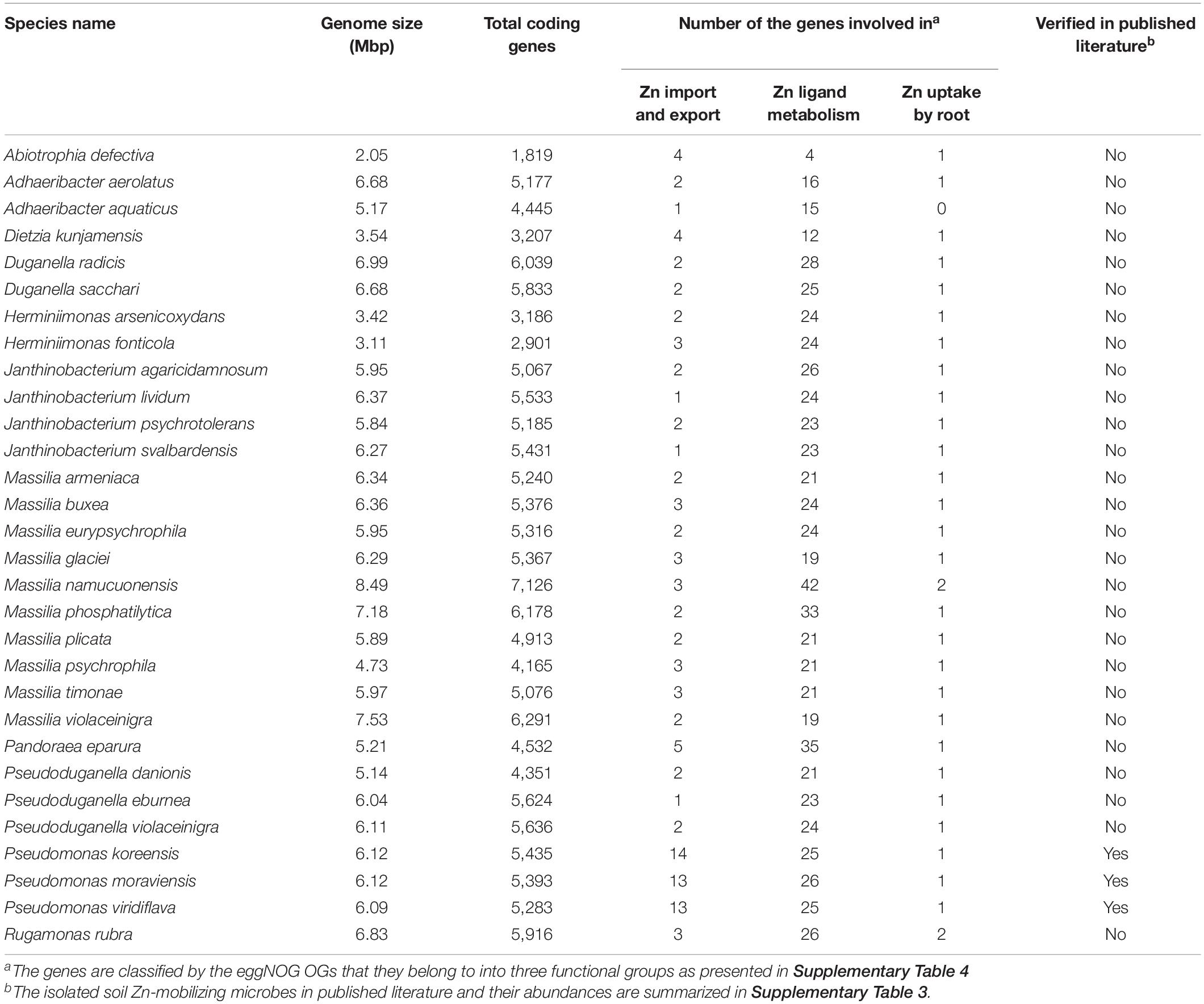
Table 2. Functional statistics of the potential soil Zn-mobilizing microbes enriched in wheat rhizosphere.
Potential Soil Zn-Mobilizing Bacteria Are Highly Related With the Variation of Wheat Grain Zn Concentration
The relationships of the 30 potential soil Zn-mobilizing species and 25 published Zn-mobilizing species with the variation of Zn uptake and concentration among wheat cultivars were analyzed by Spearman’s correlation. Results showed that 23 potential Zn-mobilizing species were positively correlated with wheat grain Zn concentration, while only two of the 30 species were negatively correlated with grain Zn concentration (Table 3). Differently, most of the previously published Zn-mobilizing species showed weak correlations with wheat Zn uptake and grain Zn concentration (Table 3). Thus, the identified potential Zn-mobilizing bacteria, especially the species of genera Adhaeribacter, Janthinobacterium, Massilia, and Pseudomonas, may contribute to the variation of wheat grain Zn concentration among different cultivars.
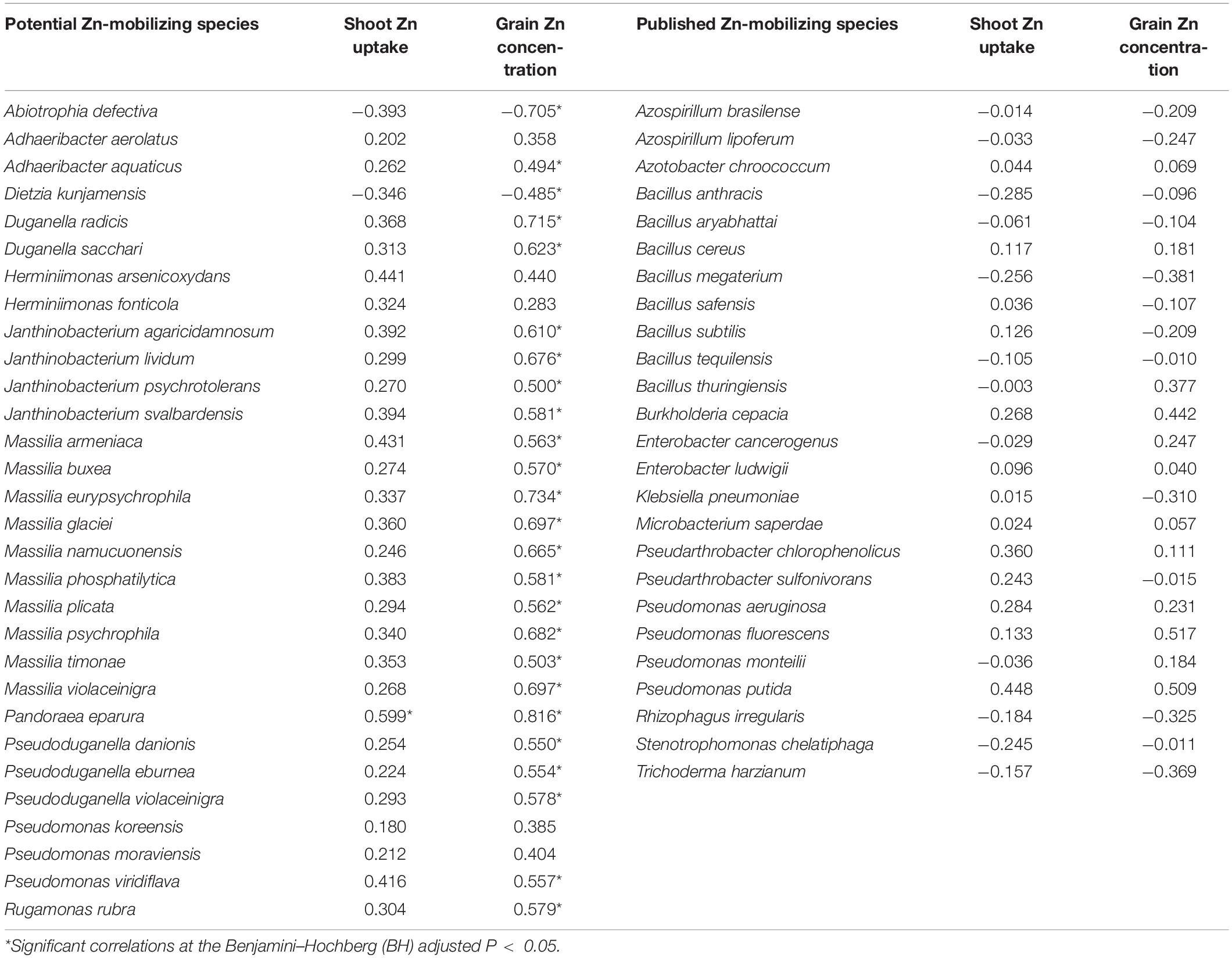
Table 3. Spearman’s correlations between the relative abundances of soil Zn-mobilizing microbes and wheat grain Zn concentration and shoot Zn uptake at maturity.
Furthermore, the interspecies relationships of soil Zn-mobilizing species with other abundant rhizosphere-enriched microbes (abundance >0.001%) in wheat rhizosphere were analyzed by Spearman’s correlation of their relative abundances and illustrated in a co-occurrence network (Figure 5). Considering the strong correlations (| r| > 0.8) among species, most of the relatively abundant potential Zn-mobilizing species closely related with each other and formed a module in the network, while the published Zn-mobilizing species scattered in the network (Figure 5). Besides, both the potential and published Zn-mobilizing species had many links with other rhizosphere-enriched microbes in the network (Figure 5). Therefore, the relatively abundant potential Zn-mobilizing species like Adhaeribacter, Janthinobacterium, Massilia, and Pseudomonas could cooperate with many rhizosphere-enriched microbes and form a local community to mobilize nutrients and promote the plant growth of wheat.
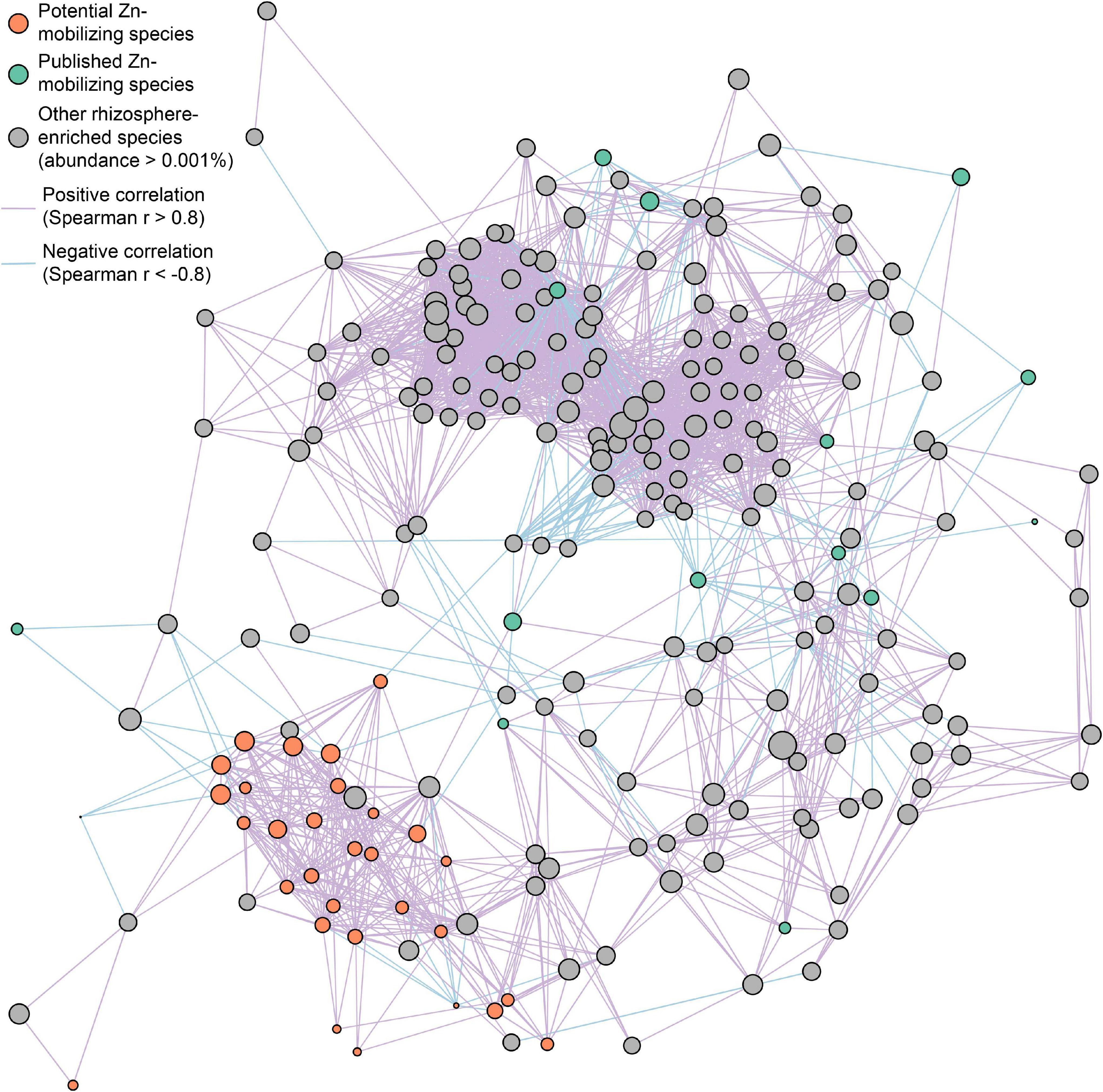
Figure 5. Co-occurrence network of potential (orange circles) and published (green circles) soil Zn-mobilizing microbial species and other rhizosphere-enriched species (gray circles) with median relative abundances above 0.001% in high-Zn and low-Zn wheat cultivars. The size of each circle is proportional to the median relative abundance of the corresponding microbial species in wheat rhizosphere. The purple and blue lines linking circles refer to highly positive (r > 0.8) and negative (r < –0.8) Spearman’s correlations, respectively, between the relative abundances of the corresponding species.
Discussion
Host plant genetic factors are thought to have much weaker influences on shaping rhizosphere microbiome than compartment niches do (Xiong et al., 2020). We provide more evidence to this by showing the large difference of microbial communities and functions between wheat rhizosphere and bulk soil but small difference among wheat cultivars (Figures 2, 3), similar to the previous studies on the rhizosphere microbiome of wheat, maize, barley, oat, bean, tomato, and cucumber (Turner et al., 2013; Ofek et al., 2014). Many of the rhizosphere microbes can help host plants fight against plant pathogens (Trivedi et al., 2020), cope with abiotic stresses like drought (de Vries et al., 2020), and absorb nutrients from soil (Oldroyd and Leyser, 2020); and these benefits are necessary for all plants regardless of cultivar or genotype. As observed in this study, many of the rhizosphere-enriched previously reported soil Zn-mobilizing microbes can promote the Zn mobilization and uptake in both HZn and LZn wheat cultivars.
Inoculation of soil microorganisms has been widely reported to improve plant Zn uptake by solubilizing unavailable Zn in soil or promoting the Zn absorption by roots (Rehman et al., 2018). The mechanisms of improving soil Zn availability by microorganisms mainly include three ways: (1) exudate organic acids or protons to acidify soil to solubilize unavailable Zn-containing minerals; (2) release siderophores, nicotinamides, etc., to chelate with Zn ions fixed in soil minerals and metal oxides and make this part of Zn mobile; and (3) produce auxins or fix nitrogen to promote the growth of plant roots and the absorption of Zn from soil (Supplementary Table 3; Sathya et al., 2016; Rehman et al., 2018). In the present study, all the 30 newfound potential soil Zn-mobilizing bacteria possess the genes involved in soil Zn mobilization, in particular the synthesis and exudation of Zn ligands like organic acids and chelates, and may contribute to the cultivars’ variation in grain Zn concentration (Figure 4 and Tables 2, 3). Among the 30 potential soil Zn-mobilizing bacteria, Pseudomonas has been reported to produce citric acids (Saleh et al., 2019) and siderophores (Bultreys and Gheysen, 2000) that can solubilize unavailable Zn in soil (Duffner et al., 2012; Oburger et al., 2014), and Massilia has been reported to fix N (Feng et al., 2015) and produce organic acids (Zheng et al., 2017) that can promote the growth and Zn uptake by roots. Therefore, the various abundance of newfound potential Zn-mobilizing bacteria, especially Massilia and Pseudomonas species, may partly contribute to the different grain Zn concentrations among wheat cultivars.
Due to the enormous complex microbial community in soil and plant rhizosphere, a single microbe usually performs a small part of complex functions like nutrient mobilization. In plant rhizosphere, a group of microbes are often necessary to generate effective and stable plant growth promotion effects in agricultural system (Vorholt et al., 2017; Toju et al., 2018). Here, we find that most of the potential soil Zn-mobilizing microbes form a local community with strong positive interspecies relationships, and they may cooperate with other plant growth-promoting species in wheat rhizosphere (Figure 5). In other words, the newfound potential Zn-mobilizing species, in particular Massilia and Pseudomonas species, may constitute a small functional module to promote soil Zn mobilization and contribute to the various grain Zn concentrations among wheat cultivars. In the future, the 30 newfound potential soil Zn-mobilizing bacteria deserve to be isolated and cultured with the development of high-throughput targeted culturomics technology. Furthermore, the isolates with strong abilities to increase soil Zn availability can be used as a synthetic community to promote the nutrient uptake and growth performance of cereal crops.
Conclusion
In conclusion, analyses of the rhizosphere metagenome of six wheat cultivars that exhibit different grain Zn concentrations in calcareous soils reveal large difference in the microbial communities and functions between wheat rhizosphere and bulk soil but small difference between HZn and LZn cultivars. The rhizosphere-enriched microbes include many PGPR and previously reported soil Zn-mobilizing microbes, which may promote the growth and nutrient uptake of both HZn and LZn wheat cultivars. Thirty rhizosphere-enriched bacteria are identified as newfound potential soil Zn-mobilizing microbes, which exhibit different relative abundances between HZn and LZn and possess the functional genes involved in soil Zn mobilization or promoting root Zn uptake, especially the synthesis and exudation of organic acids and siderophores. Most of the potential Zn-mobilizing microbes are positively correlated with grain Zn concentration and may constitute a local community to promote soil Zn mobilization. The variation of potential Zn-mobilizing species, especially Massilia and Pseudomonas, may be the source of variation in grain Zn concentration among wheat cultivars, and they deserve further isolation and verification in future studies on Zn biofortification of cereal crops.
Data Availability Statement
The generated reads in the present study have been deposited in NCBI SRA under BioProject accession PRJNA688820 (SRR3336283 to SRR3336319) and National Genomics Data Center and BIG Data Center (NGDC BIG) under BioProject accession PRJCA003344 (CRR196125 to CRR196152).
Author Contributions
SW: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, visualization, and writing (draft and revision). ZG and LW: data curation, investigation, methodology, resources, visualization, and writing (revision). YZ: formal analysis, methodology, resources, and visualization. FJ: formal analysis, methodology, software, and visualization. XW: data curation, investigation, methodology, and resources. LY: formal analysis, methodology, resources, and visualization. BL, HL, HW, and AW: formal analysis, resources, software, and visualization. YR and CL: methodology, investigation, and resources. WF: conceptualization, funding acquisition, methodology, project administration, supervision, visualization, and writing (revision). ZW: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, resources, supervision, and writing (revision). All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
The authors thank for the financial support by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M650919), China Agricultural Research System (CARS-3), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0200408), Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (JCYJ20190814163805604), the research program of Urban Management Bureau of Shenzhen Municipality (No. 201914), the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program and The Elite Young Scientists Program of CAAS, the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program Cooperation and Innovation Mission (CAAS-XTCX2016), and the Fund of Key Laboratory of Shenzhen (ZDSYS20141118170111640).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.689855/full#supplementary-material
References
Banerjee, S., Kirkby, C. A., Schmutter, D., Bissett, A., Kirkegaard, J. A., and Richardson, A. E. (2016). Network analysis reveals functional redundancy and keystone taxa amongst bacterial and fungal communities during organic matter decomposition in an arable soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 97, 188–198. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.03.017
Benjamini, Y., and Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 57, 289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x
Buchfink, B., Xie, C., and Huson, D. H. (2015). Fast and sensitive protein alignment using diamond. Nat. Methods 12:59. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3176
Bulgarelli, D., Garrido-Oter, R., Muench, P. C., Weiman, A., Droege, J., Pan, Y., et al. (2015). Structure and function of the bacterial root microbiota in wild and domesticated barley. Cell Host Microbe 17, 392–403. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.01.011
Bultreys, A., and Gheysen, I. (2000). Production and comparison of peptide siderophores from strains of distantly related pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae and Pseudomonas viridiflava LMG 2352. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 325–331. doi: 10.1128/aem.66.1.325-331.2000
Cakmak, I., and Kutman, U. B. (2018). Agronomic biofortification of cereals with zinc: a review. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 69, 172–180. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12437
Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y., and Gu, J. (2018). fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, i884–i890. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Chen, X. P., Zhang, Y. Q., Tong, Y. P., Xue, Y. F., Liu, D. Y., Zhang, W., et al. (2017). Harvesting more grain zinc of wheat for human health. Sci. Rep. 7:7016. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07484-2
Coccina, A., Cavagnaro, T. R., Pellegrino, E., Ercoli, L., McLaughlin, M. J., and Watts-Williams, S. J. (2019). The mycorrhizal pathway of zinc uptake contributes to zinc accumulation in barley and wheat grain. BMC Plant Biol. 19:133. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1741-y
Csardi, G., and Nepusz, T. (2005). The igraph software package for complex network research. Inter J. Complex Syst. 1695, 1–9.
de Souza, R., Ambrosini, A., and Passaglia, L. M. P. (2015). Plant growth-promoting bacteria as inoculants in agricultural soils. Genet. Mol. Biol. 38, 401–419. doi: 10.1590/s1415-475738420150053
de Vries, F. T., Griffiths, R. I., Knight, C. G., Nicolitch, O., and Williams, A. (2020). Harnessing rhizosphere microbiomes for drought-resilient crop production. Science 368, 270–274. doi: 10.1126/science.aaz5192
Donn, S., Kirkegaard, J. A., Perera, G., Richardson, A. E., and Watt, M. (2015). Evolution of bacterial communities in the wheat crop rhizosphere. Environ. Microbiol. 17, 610–621. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12452
Duffner, A., Hoffland, E., and Temminghoff, E. J. M. (2012). Bioavailability of zinc and phosphorus in calcareous soils as affected by citrate exudation. Plant Soil 361, 165–175. doi: 10.1007/s11104-012-1273-9
Feng, W., Qin, S., Shao, C., Wu, B., and Zhang, Y. (2015). New Massilia Plicata MBC9 Strain With Nitrogen Fixation Activity Useful in Improving Soil. Patent numbers: CN105400716-A and CN105400716-B.
Huerta-Cepas, J., Forslund, K., Coelho, L. P., Szklarczyk, D., Jensen, L. J., von Mering, C., et al. (2017). Fast genome-wide functional annotation through orthology assignment by eggNOG-mapper. Mol. Biol. Evol. 34, 2115–2122. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx148
Huerta-Cepas, J., Szklarczyk, D., Heller, D., Hernández-Plaza, A., Forslund, S. K., Cook, H., et al. (2018). eggNOG 5.0: a hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically annotated orthology resource based on 5090 organisms and 2502 viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, D309–D314. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1085
Hyatt, D., LoCascio, P. F., Hauser, L. J., and Uberbacher, E. C. (2012). Gene and translation initiation site prediction in metagenomic sequences. Bioinformatics 28, 2223–2230. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts429
Illescas, M., Rubio, M. B., Hernández-Ruiz, V., Moran-Diez, M. E., de Alba, M., and Emilio, Á, et al. (2020). Effect of inorganic N top dressing and Trichoderma harzianum seed-inoculation on crop yield and the shaping of root microbial communities of wheat plants cultivated under high basal N fertilization. Front. Plant Sci. 11:1658. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.575861
IWGSC (2018). Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science 361:eaar7191. doi: 10.1126/science.aar7191
Langmead, B., and Salzberg, S. L. (2012). Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 9, 357–359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923
Li, D. H., Luo, R. B., Liu, C. M., Leung, C. M., Ting, H. F., Sadakane, K., et al. (2016). MEGAHIT v1.0: a fast and scalable metagenome assembler driven by advanced methodologies and community practices. Methods 102, 3–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.02.020
Liu, H., Wang, Z. H. H., Li, F. C., Li, K. Y., Yang, N., Yang, Y. E., et al. (2014). Grain iron and zinc concentrations of wheat and their relationships to yield in major wheat production areas in China. Field Crops Res. 156, 151–160. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2013.11.011
Lundberg, D. S., Lebeis, S. L., Paredes, S. H., Yourstone, S., Gehring, J., Malfatti, S., et al. (2012). Defining the core Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome. Nature 488, 86–90. doi: 10.1038/nature11237
Menzel, P., Ng, K. L., and Krogh, A. (2016). Fast and sensitive taxonomic classification for metagenomics with Kaiju. Nat. Commun. 7:11257. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11257
Myers, S. S., Zanobetti, A., Kloog, I., Huybers, P., Leakey, A. D., Bloom, A. J., et al. (2014). Increasing CO2 threatens human nutrition. Nature 510, 139–142. doi: 10.1038/nature13179
Oburger, E., Gruber, B., Schindlegger, Y., Schenkeveld, W. D., Hann, S., Kraemer, S. M., et al. (2014). Root exudation of phytosiderophores from soil-grown wheat. New Phytol. 203, 1161–1174. doi: 10.1111/nph.12868
Ofek, M., Voronov-Goldman, M., Hadar, Y., and Minz, D. (2014). Host signature effect on plant root-associated microbiomes revealed through analyses of resident vs. active communities. Environ. Microbiol. 16, 2157–2167. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12228
Ofek-Lalzar, M., Sela, N., Goldman-Voronov, M., Green, S. J., Hadar, Y., and Minz, D. (2014). Niche and host-associated functional signatures of the root surface microbiome. Nat. Commun. 5:4950. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5950
Oksanen, J., Blanchet, F. G., Friendly, M., Kindt, R., Legendre, P., McGlinn, D., et al. (2019). vegan: Community Ecology Package [Online]. R Package Version 2.5-6. Available online at: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed January 1, 2021).
Oldroyd, G. E. D., and Leyser, O. (2020). A plant’s diet, surviving in a variable nutrient environment. Science 368:eaba0196. doi: 10.1126/science.aba0196
R Core Team (2020). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing [Online]. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Rehman, A., Farooq, M., Ozturk, L., Asif, M., and Siddique, K. H. M. (2018). Zinc nutrition in wheat-based cropping systems. Plant Soil 422, 283–315. doi: 10.1007/s11104-017-3507-3
Rengel, Z. (2015). Availability of Mn, Zn and Fe in the rhizosphere. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 15, 397–409.
Revelle, W. (2013). psych: Procedures for Psychological, Psychometric, and Personality Research. R Package Version 1.0–95. Evanston, IL. Available online at: https://www.scholars.northwestern.edu/en/publications/psych-procedures-for-personality-and-psychological-research
Rosier, A., Medeiros, F. H. V., and Bais, H. P. (2018). Defining plant growth promoting rhizobacteria molecular and biochemical networks in beneficial plant-microbe interactions. Plant Soil 428, 35–55. doi: 10.1007/s11104-018-3679-5
Rossmann, M., Pérez-Jaramillo, J. E., Kavamura, V. N., Chiaramonte, J. B., Dumack, K., Fiore-Donno, A. M., et al. (2020). Multitrophic interactions in the rhizosphere microbiome of wheat: from bacteria and fungi to protists. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 96:fiaa032. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiaa032
Saleh, D. K., Abdollahi, H., Noaparast, M., Nosratabad, A. F., and Tuovinen, O. H. (2019). Dissolution of Al from metakaolin with carboxylic acids produced by Aspergillus niger, Penicillium bilaji, Pseudomonas putida, and Pseudomonas koreensis. Hydrometallurgy 186, 235–243. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.03.014
Sathya, A., Vijayabharathi, R., and Gopalakrishnan, S. (2016). “Exploration of plant growth-promoting actinomycetes for biofortification of mineral nutrients,” in Plant Growth Promoting Actinobacteria: A New Avenue for Enhancing the Productivity and Soil Fertility of Grain Legumes, eds G. Subramaniam, S. Arumugam, and V. Rajendran (Singapore: Springer), 263–274.
Shi, W., Li, M., Wei, G., Tian, R., Li, C., Wang, B., et al. (2019). The occurrence of potato common scab correlates with the community composition and function of the geocaulosphere soil microbiome. Microbiome 7:14. doi: 10.1186/s40168-019-0629-2
Singh, D., Geat, N., Rajawat, M. V. S., Prasanna, R., Kar, A., Singh, A. M., et al. (2018). Prospecting endophytes from different Fe or Zn accumulating wheat genotypes for their influence as inoculants on plant growth, yield, and micronutrient content. Ann. Microbiol. 68, 815–833. doi: 10.1007/s13213-018-1388-1
Smith, M. R., and Myers, S. S. (2018). Impact of anthropogenic CO2 emissions on global human nutrition. Nat. Clim. Change 8, 834–839. doi: 10.1038/s41558-018-0253-3
Steinegger, M., and Söding, J. (2017). MMseqs2 enables sensitive protein sequence searching for the analysis of massive data sets. Nat. Biotechnol. 35:1026. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3988
Steinegger, M., and Söding, J. (2018). Clustering huge protein sequence sets in linear time. Nat. Commun. 9:2542. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04964-5
Toju, H., Peay, K. G., Yamamichi, M., Narisawa, K., Hiruma, K., Naito, K., et al. (2018). Core microbiomes for sustainable agroecosystems. Nat. Plants 4, 247–257. doi: 10.1038/s41477-018-0139-4
Trivedi, P., Leach, J. E., Tringe, S. G., Sa, T., and Singh, B. K. (2020). Plant–microbiome interactions: from community assembly to plant health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 18, 607–621. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-0412-1
Turner, T. R., Ramakrishnan, K., Walshaw, J., Heavens, D., Alston, M., Swarbreck, D., et al. (2013). Comparative metatranscriptomics reveals kingdom level changes in the rhizosphere microbiome of plants. ISME J. 7, 2248–2258. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.119
Vorholt, J. A., Vogel, C., Carlström, C. I., and Müller, D. B. (2017). Establishing causality: opportunities of synthetic communities for plant microbiome research. Cell Host Microbe 22, 142–155. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.07.004
Wang, S., Wang, Z. H., Li, S. S., Diao, C. P., Liu, L., Hui, X. L., et al. (2018). Identification of high-yield and high-Zn wheat cultivars for overcoming “yield dilution” in dryland cultivation. Eur. J. Agron. 101, 57–62. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2018.08.008
Wickham, H. (2016). ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis [Online]. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag.
Xiong, C., Zhu, Y. G., Wang, J. T., Singh, B., Han, L. L., Shen, J. P., et al. (2020). Host selection shapes crop microbiome assembly and network complexity. New Phytol. 229, 1091–1104. doi: 10.1111/nph.16890
Xu, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, P., Trivedi, P., Riera, N., Wang, Y., et al. (2018). The structure and function of the global citrus rhizosphere microbiome. Nat. Commun. 9:4894. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07343-2
Zhang, J., Liu, Y. X., Zhang, N., Hu, B., Jin, T., Xu, H., et al. (2019). NRT1.1B is associated with root microbiota composition and nitrogen use in field-grown rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 676–684. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0104-4
Keywords: wheat cultivar, rhizosphere, microbiome, soil Zn mobilization, bacteria, Zn biofortification
Citation: Wang S, Guo Z, Wang L, Zhang Y, Jiang F, Wang X, Yin L, Liu B, Liu H, Wang H, Wang A, Ren Y, Liu C, Fan W and Wang Z (2021) Wheat Rhizosphere Metagenome Reveals Newfound Potential Soil Zn-Mobilizing Bacteria Contributing to Cultivars’ Variation in Grain Zn Concentration. Front. Microbiol. 12:689855. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.689855
Received: 01 April 2021; Accepted: 24 May 2021;
Published: 23 June 2021.
Edited by:
Mark Radosevich, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, United StatesReviewed by:
Digvijay Verma, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University, IndiaGustavo Santoyo, Universidad Michoacana de San Nicolás de Hidalgo, Mexico
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Guo, Wang, Zhang, Jiang, Wang, Yin, Liu, Liu, Wang, Wang, Ren, Liu, Fan and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Fan, ZmFud2VpQGNhYXMuY24=; Zhaohui Wang, dy16aGFvaHVpQDI2My5uZXQ=
 Sen Wang
Sen Wang Zikang Guo
Zikang Guo Li Wang
Li Wang Yan Zhang
Yan Zhang Fan Jiang
Fan Jiang Xingshu Wang
Xingshu Wang Lijuan Yin
Lijuan Yin Bo Liu
Bo Liu Hangwei Liu
Hangwei Liu Hengchao Wang
Hengchao Wang Anqi Wang
Anqi Wang Yuwei Ren
Yuwei Ren Conghui Liu
Conghui Liu Wei Fan
Wei Fan Zhaohui Wang
Zhaohui Wang