- 1Department of Pathophysiology, College of Basic Medical Science, China Medical University, Shenyang, China
- 2Department of Urology, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
- 3Department of Nephrology, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
- 4Liaoning Branch of China Telecom, Shenyang, China
Background: Immune microenvironment within tumors affects initiation, progression and clinical outcome of human cancers. Here we explored an immune-related gene signature associated with prognosis of patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma.
Method: The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database was interrogated for expressions of immune-related genes in bladder urothelial carcinomas. Integrated bioinformatics analyses were performed to identify prognostic factors.
Results: Twenty-seven immune-related genes were revealed significantly associated with patient's overall survival (OS) by univariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis. Nine-core immune-related genes including MMP9, PDGFRA, AHNAK, OLR1, RAC3, IGF1, PGF, OAS1, and SH3BP2 were selected to construct a risk score model by multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis. Bioinformatics analyses further validated that risk score could be used as an important independent factor in evaluating prognosis.
Conclusion: We established a prognostic immune signature for patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma, which may provide novel targets for prediction and therapy of these patients.
Introduction
Bladder cancer incidence ranks first in men among malignant cancers of the urinary system in China and second only to prostate cancer in Western countries (1). In the USA, according to the latest data, there will be 80,470 new cases and 17,670 deaths in 2019 (2). The incidence of bladder cancer in men is three to four times higher than that in women (2). Bladder cancer consists of two major types, non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) and muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). NMIBC is associated with a longer survival compared with MIBC, although NMIBC is prone to local recurrence and can develop invasive disease. In contrast, MIBC is usually accompanied by metastasis and unfavorable prognosis. There are no advances in the treatment of metastatic bladder cancer for decades (3, 4). Until recent years, immune checkpoint blockade has been demonstrated to be a promising method and approved for clinical treatment for metastatic bladder cancer (4, 5) (KEYNOTE 045, KEYNOTE 052, IMVIGOR211, IMVIGOR 210).
Bladder cancer is one of the most immunogenic cancers (6, 7). However, bladder cancer can still establish an immunosuppressive microenvironment thereby evading immune surveillance. Bladder cancer is infiltrated by FOXP3+ T-cells (Tregs) with production of TH1 inhibitory cytokines (8). Moreover, high FOXP3/CD8 ratio is associated with poor prognosis of patients with bladder cancer (9, 10). Bladder cancer is also characterized by infiltration of innate immune cells (11–13). Interaction between tumor cells and immune cells on one hand suppresses immune response, on the other hand promotes tumor progression.
As immune microenvironment affects tumor progression, in the present study, we intended to explore an immune-related gene signature associated with prognosis of patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma, the most common type of bladder cancer. We identified a panel of 9-core differentially expressed genes (DEG) including MMP9, PDGFRA, AHNAK, OLR1, RAC3, IGF1, PGF, OAS1, and SH3BP2. Using these 9-core DEG, we set up a model to evaluate prognosis of patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma.
Materials and Methods
Data Acquisition
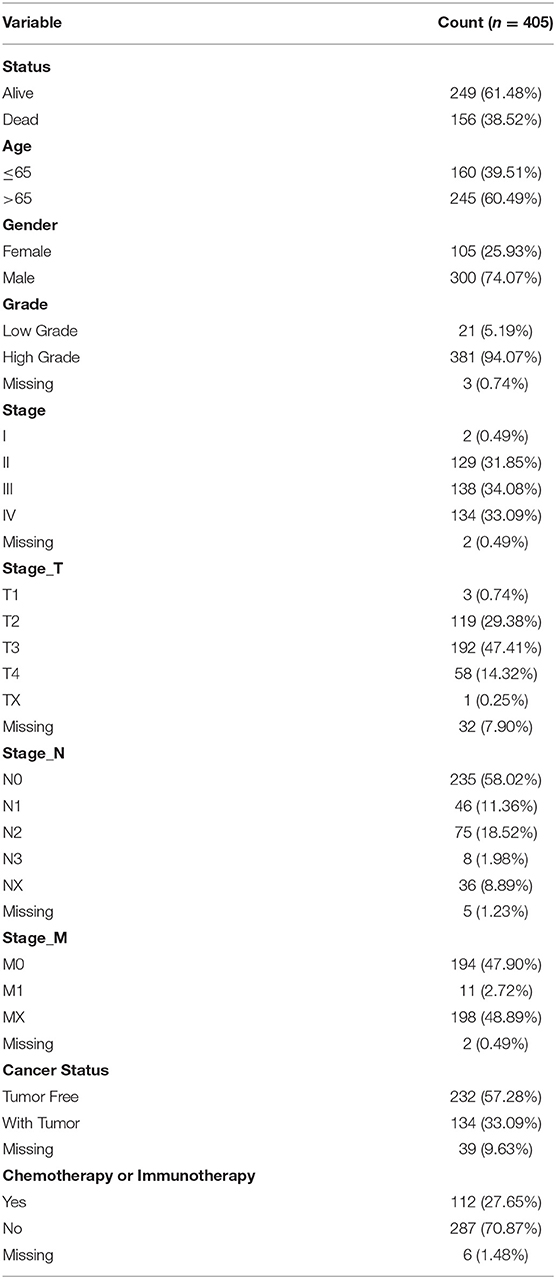
A total of 411 urothelial carcinoma samples and 19 matched cancer-adjacent normal samples from TCGA database were included in this study. The transcriptome profiling of RNA expression was corrected by FPKM in TCGA. All data were integrated into one matrix file using a script of Perl language. Ensembl database was used to transform gene IDs into gene symbols. Clinical information was also extract from TCGA (Table 1). Two thousand four hundred ninety-eight immune-related genes listed in the immunology Database and Analysis Portal (ImmPort) were investigated. Moreover, 318 transcription factor-related genes in Critrome were analyzed.
Differential Analysis and Risk-Score Model Construction
The package “limma” in R with the statistical method of Wilcox Test was used to make the differential analysis of all mRNA expression between tumor group and normal group, and DEG (|log2FC| > 1, P < 0.05) was acquired. The volcano and heat maps were plotted by R. Overlaps between immune-related gene and DEG were immune-related DEG. Subsequently, immune-related DEG and clinical information data were merged, data of OS <90 days were deleted, and the univariate Cox proportional hazard regression analysis was performed. Thereafter, 27 immune-related DEG significantly associated with prognosis were obtained, with the package “survival” in R (P < 0.01). Overlaps between transcription factor-related genes and DEG were transcription factor-related DEG. The correlation of 27 immune-related DEG with transcription factor (TF) -related DEG was analyzed (|r| > 0.4, P < 0.001). The interaction network of TF-related DEG and 27 immune-related DEG was made with the Cytoscape. The “survival” package in R was used to make the multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression based on 27 immune-related DEG. After a number of similar and relevant genes were streamlined, 9-core immune-related DEG were obtained and then Cox regression model was constructed to calculate their respective coefficient (βi). An individual's risk score model for each patient was built for predicting prognosis of patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma by including expression level of each optimal prognostic core genes (Expi), which was weighted by their estimated regression coefficients(βi) of multivariate Cox regression model. The risk score of each patient was calculate as follows:
Verification of Prognosis Evaluation by Risk Score
By using the median risk score, all patients with urothelial carcinoma were sorted into high-risk group and low-risk group. Kaplan-Meier analysis was utilized to compare the survival between two groups. The survival difference between the low-risk and high-risk group was assessed by the log-rank test. The time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was performed to identify the exactitude of the Cox regression model by packages “survival” and “survival ROC” in R. According to the risk score and clinical data of each patient, Risk curve, survival state map and heatmap of 9-core immune-related DEG were plotted. Cases with incomplete data were deleted. The “risk score” together with age, gender, grade, stage, “T-stage,” “M-stage,” and “N-stage” was made for univariate and multivariate independent prognosis analysis and the forest map was plotted.
Correlation Analysis of Clinical Parameters and 9-Core Immune-Related DEG Together With Risk Score
In order to verify the correlation of 9-core immune-related DEG with clinical parameters, cases with incomplete clinical data were deleted, and T-test between Risk score, 9-core immune-related DEG and clinical parameters was analyzed (P < 0.05).
Results
Identification of Prognostic Immune-Related DEG
By analyzing the differences between tumor group and normal group, we obtained 4,880 DEG. Based on the differential analysis, the volcanic and heat maps were made (Figures 1A,B). We thereafter crossed these DEG with 2,498 immune-related genes from ImmPort database, and acquired 259 immune-related DEG. The volcanic and heat maps were made similarly (Figures 1C,D). A total of 27 immune-related DEG were found to be significantly associated with the overall survival (OS) of patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma (adjusted P < 0.01), and were entered into the candidate pool for further selection (Figure 1E).
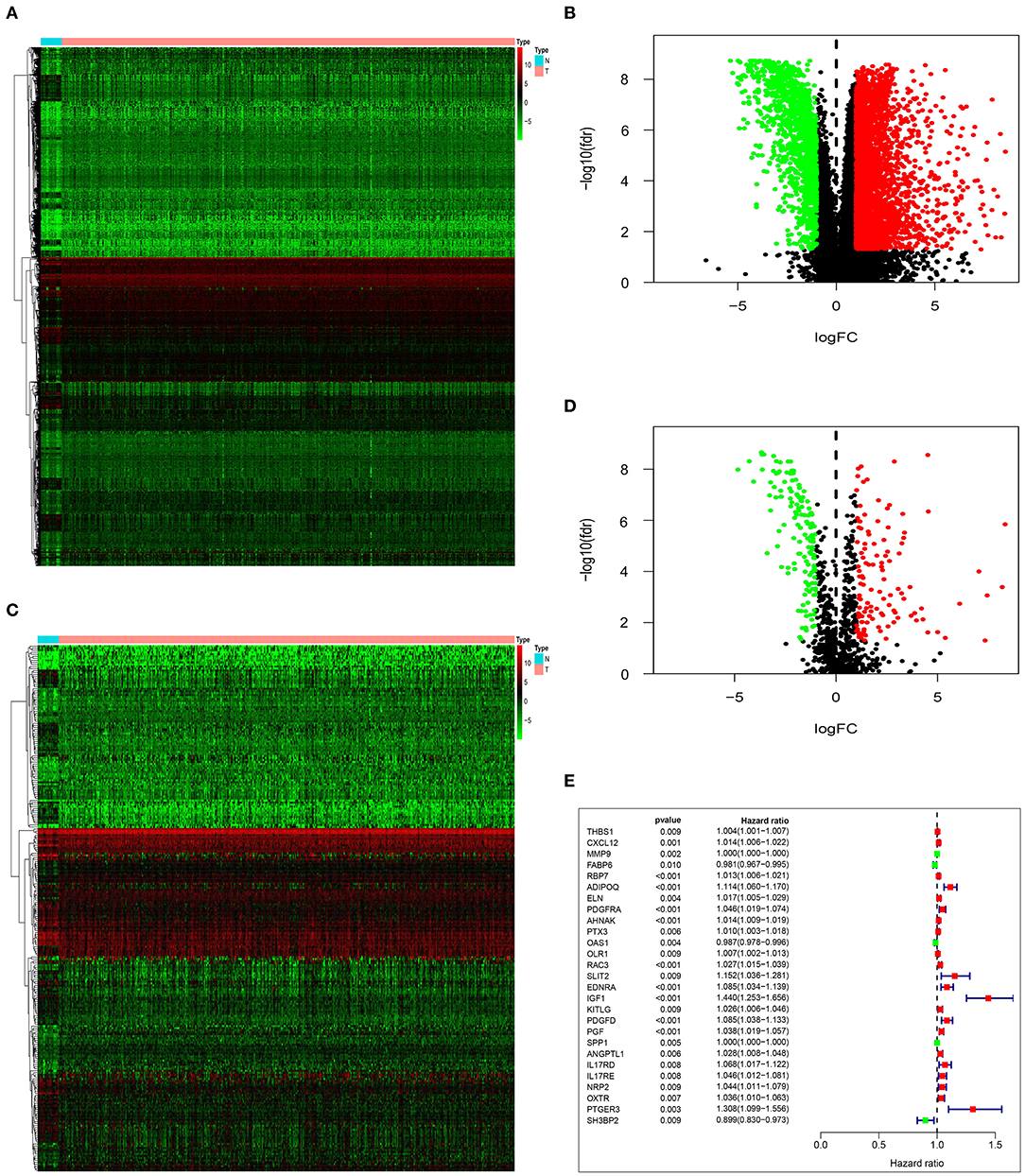
Figure 1. Identification of prognostic immune-related DEG. Heatmap (A) and volcano plot (B) demonstrating DEG between normal bladder tissues and urothelial carcinoma tissues. Heatmap (C) and volcano plot (D) indicating immune-related DEG. (E) Forest plot of hazard ratios and P-value showing the prognostic values of 27 immune-related DEG in univariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis.
TF-Related Genes Regulating Prognostic Immune-Related DEG
Three hundred eighteen TF-related genes were downloaded from Critrome. After crossing these TF-related genes with 4,880 DEG, we obtained 77 TF-related DEG (Figures 2A,B). Correlation analysis between 27 immune-related DEG and 77 TF-related DEG was made. There was a correlation between 10 TF-related DEG and 16 immune-related DEG. All of the 16 immune-related DEG were high risk genes. A gene regulatory network by cytoscape was built (Figure 2C).
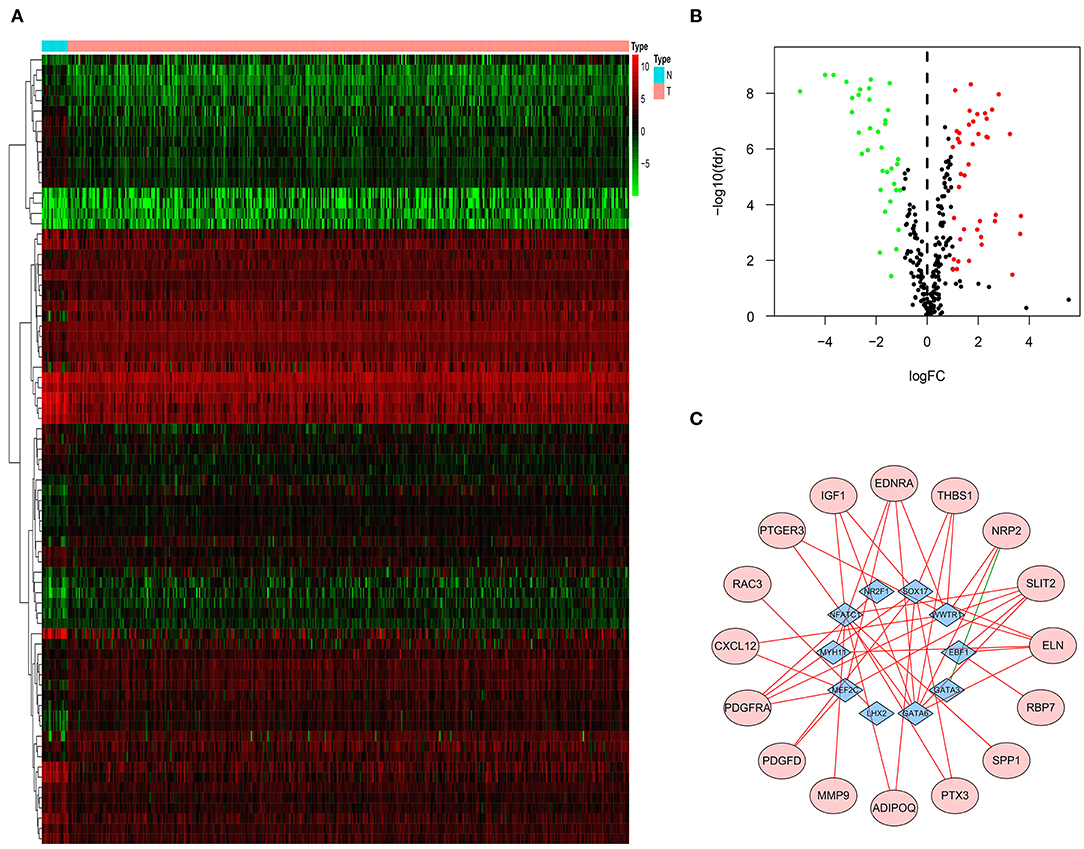
Figure 2. TF-related genes regulating prognostic immune-related DEG. Heatmap (A) and volcano plot (B) indicating TF-related DEG. (C) A gene regulatory network between TF-related DEG and immune-related DEG. The purple ellipses represent the immune-related DEG. The blue diamonds represent TF-related DEG. The red and green solid lines represent positive and negative correlation, respectively.
Construction of Risk Score Model Using Prognostic Immune-Related DEG
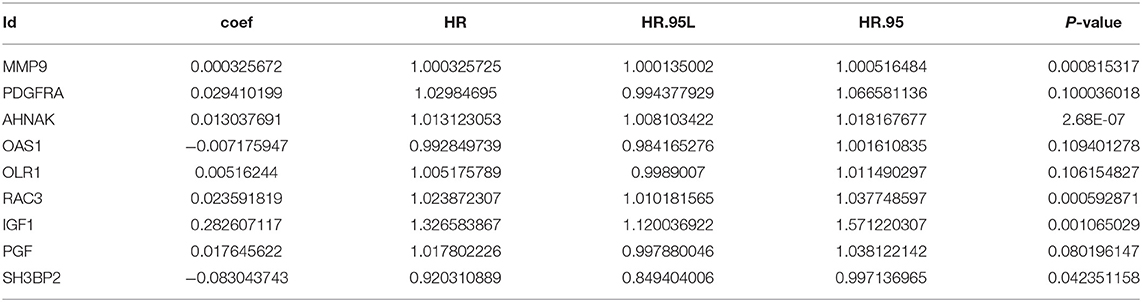
To determine the optimal prognostic immune-related DEG, we adopted multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression using 9-core genes from the pool of 27 candidate prognostic immune-related DEG to evaluate independent prognostic values. In these 9-core DEG, 7 core genes (MMP9, PDGFRA, AHNAK, OLR1, RAC3, IGF1, and PGF) with positive coefficient of multivariate regression analysis may be risk factors owing to the close association between their high expression and shorter patients' survival, whereas the remaining two core DEG (OAS1 and SH3BP2) tended to be prognostic protective factors and their high expressions were associated with longer survival (Table 2). An individual's risk score model was developed using the regression coefficients of multivariate Cox regression model to weight the expression level of each core DEG. Through this risk score model, we could get the risk score of every case in TCGA database.
Validation of the Risk Score Model
After getting the risk score of every case, we divided all cases into high-risk group and low-risk group based on median of Risk score. OS was significantly different between two groups (P = 6.977e-10). In addition, the 3- and 5-year survival rates of the high-risk group were 35% (95% CI: 26.9–45.5%) and 28.2% (95% CI: 20.1–39.6%), respectively, whereas the corresponding rates in the low-risk group were 70.4% (95% CI: 62.7–79.1%) and 64.4% (95% CI: 55.7–74.5%) (Figure 3A). In order to measure the predictive performance of 9-core immune-related DEG prognostic risk model, we used time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for 1-year survival. The area under the ROC (AUC) for the 9-core immune-related DEG prognostic model was 0.725 at 1-year of OS (Figure 3B). In the risk curve, we ranked patients by risk score from low to high and found the median. Each patient's OS and survival status were marked in the survival state map. The heatmap revealed expression patterns of prognostic 9-core immune-related DEG (Figure 3C). For patients with high-risk scores, expression of seven risky immune-related DEG was up-regulated while expression of two protective DEG was down-regulated. On the contrary, expression of prognostic immune-related DEG in patients with low-risk scores displayed an opposite pattern to that with high-risk scores. Taking risk score as an independent risk factor, we made univariate and multivariate independent prognosis together with age, gender, grade, stage, “T-stage,” “M-stage,” and “N-stage.” It was found that risk score was the most potential independent factor in both univariate (Figure 3D) and multivariate (Figure 3E) independent prognosis analysis. It was shown that risk score could be used as an important independent factor in evaluating prognosis (P < 0.001).
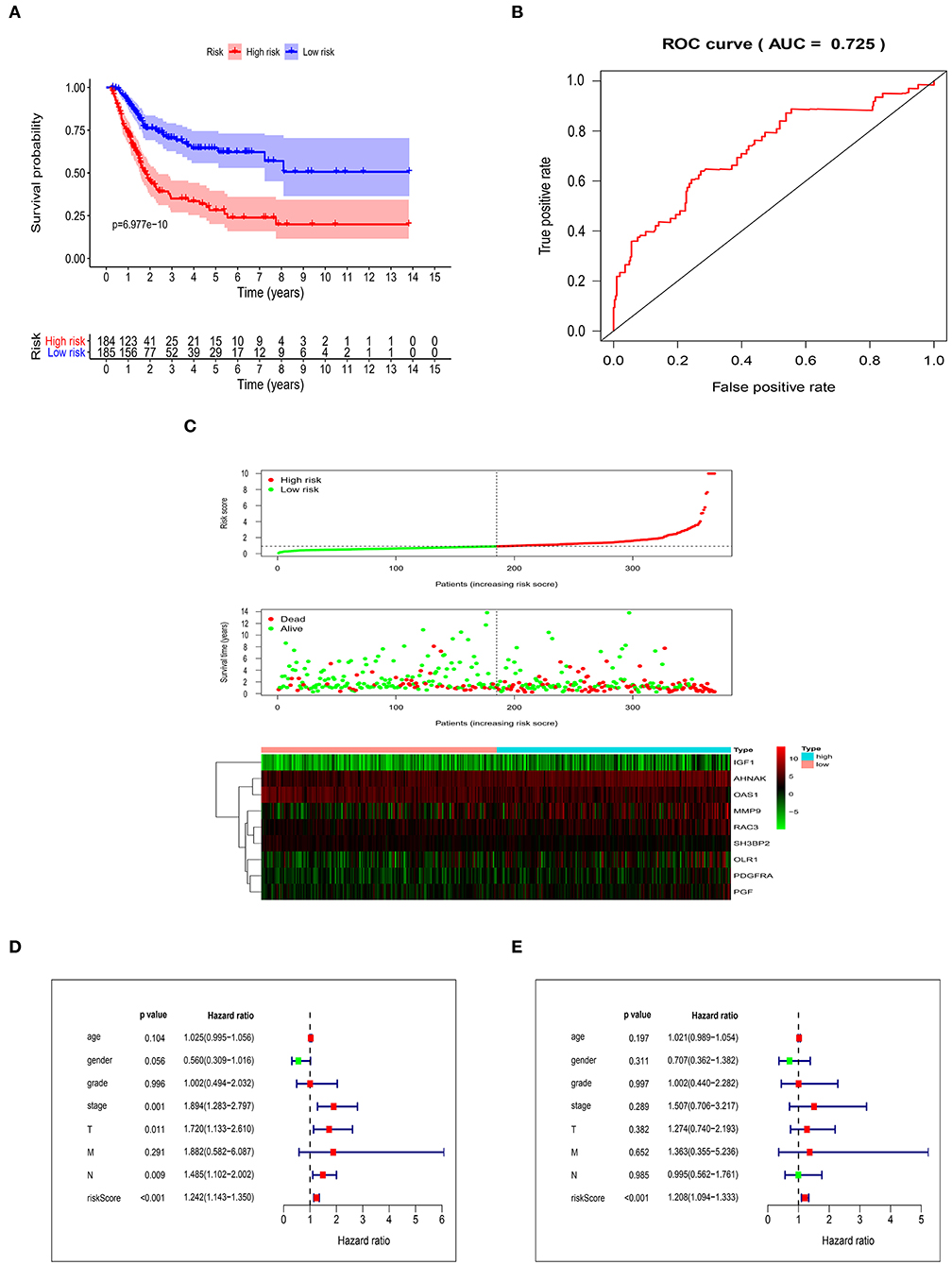
Figure 3. Validation of the risk score model. (A) Kaplan-Meier curve showing overall survival of urothelial carcinoma patients with high- and low-risk. (B) Analysis of time-dependent ROC curves. (C) Risk score distribution, survival status, and prognostic 9-core immune-related DEG patterns of urothelial carcinoma patients with high- and low-risk. Univariate (D) and multivariate (E) independent prognosis analysis of clinical parameters and risk score.
Correlation of 9-Core Immune-Related DEG as Well as Risk Score With Clinical Data
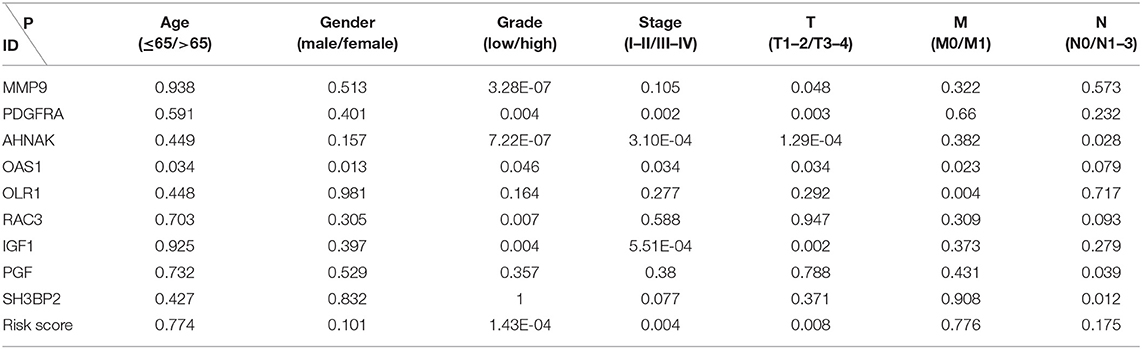
After merging 9-core immune-related DEG expression and clinical data and excluding the patients with incomplete information, we made T-test between 9-core immune-related DEG expression as well as risk score and age (≤65/>65), gender (male/female), grade (low/high grade), stage (stage I-II/III-IV), “T-stage (T1-2/T3-4),” “N-stage (N0/N1-3),” “M-stage (M0/M1).” Several core genes were related to clinical parameters (Figure 4) (Table 3). MMP9 and RAC3 were highly expressed in high grade. PDGFRA, IGF1, and AHNAK were highly expressed in high grade, stage III-IV and T3-4 stage. On the contrary, OAS1 was highly expressed in ≤ 65 years old group, male, low grade, stage I-II, T1-2 stage and M0, and SH3BP2 was highly expressed in N0. Finally, risk score was significantly high in high grade, stage I-II and T3-4 stage. These data indicated that risk score together with MMP9, PDGFRA, AHNAK, RAC3, IGF1 were risk factors while OAS1 and SH3BP2 were protective factors.
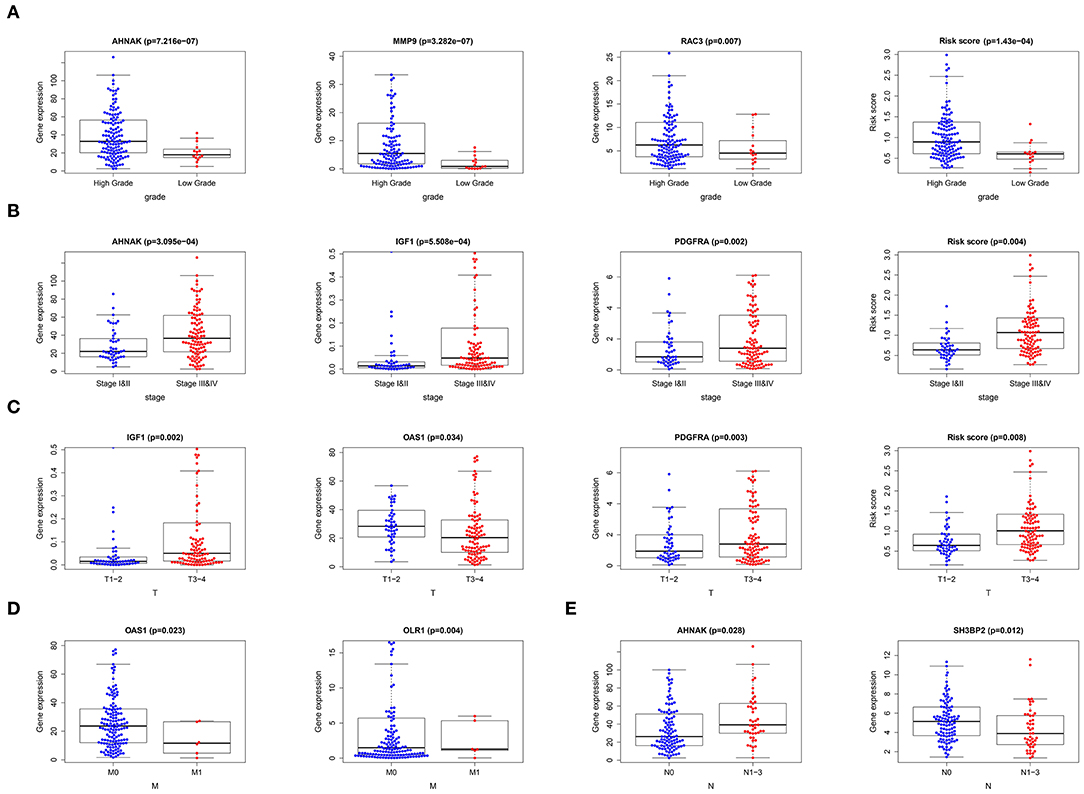
Figure 4. Correlation of 9-core immune-related DEG as well as risk score with clinical data. (A) Correlation of gene expression and risk score with tumor grade. (B) Correlation of gene expression and risk score with tumor stage. (C) Correlation of gene expression and risk score with tumor “T-stage.” (D) Correlation of gene expression with tumor “M-stage.” (E) Correlation of gene expression with tumor “N-stage”.
Discussion
Human tumors are characterized by infiltration of immune cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells (DC), granulocytes and mast cells. These cells are located in different areas of a tumor. However, density and location of immune cells vary greatly in different tumors with the same cancer type, indicating that the distinct immune pattern may affect clinical outcome. A large body of research has revealed that levels of lymphocyte infiltration was associated with prognosis in a series of human cancers (14). Although the effect of CD4+ T cells on clinical outcome was debatable, high infiltration of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells and memory T cells were clearly shown with a longer survival, and these patients demonstrated an increased expression of T-helper 1 and cytotoxicity-related genes (15). Moreover, an immune scoring was proposed based on the type, density and location of lymphocyte infiltrates as a novel prognostic factor (16–18).
In urothelial carcinoma, it was shown that patients with advanced disease (pT2, pT3, or pT4) who have higher numbers of CD8+ T cells within the tumor had longer survival than did patients with similar stage and fewer CD8+ T cells (19). However, study by Wang et al. observed that high stromal CD8+ T cells were associated with poorer OS, and PD-L1+ immune cells were an independent prognostic factor for OS and recurrence-free survival in patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma (20). Intriguingly, this study showed that PD-L1+ tumor cells were also associated with unfavorable survival. Recently, an 18-gene signature that molecularly defines urothelial cellular differentiation was identified with prognostic value (21).
In the present study, we identified 27 immune-related DEG significantly associated with OS of patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma. Moreover, we constructed a TF-mediated network to uncover TFs that could regulate expression of 27 immune-related DEG. We further developed a 9-core DEG signature which could be adopted to classify patients into the high-risk group and low-risk group with significantly different OS. The 9-core DEG included protective OAS1 and SH3BP2 and risky MMP9, PDGFRA, AHNAK, OLR1, RAC3, IGF1, and PGF. We verified the prognostic value of the 9-core DEG signature. Results suggested that the 9-core DEG signature had good repeatability and stability in predicting prognosis of patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma. The 9-core DEG signature was independent on traditional clinical risk factors and molecular features.
MMP9 is a member of matrix metalloproteinase family, promoting cancer invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Its expression was correlated with tumor grade, invasiveness and unfavorable prognosis of patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma (22, 23). AHNAK is a giant protein which exerts diverse functions in different human cancers. It was shown that AHNAK was preferentially expressed in the nucleus of urothelial carcinoma cell (24). The insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1) pathway is associated with growth, metastasis and clinical outcome of various cancers. Urothelial overexpression of IGF1 increases susceptibility to p-cresidine-induced mouse bladder cancer, especially transitional cell carcinoma (25). Furthermore, patients with bladder cancer had higher plasma levels of IGF-1, which were associated with an increased risk of bladder cancer (26). Until now, the roles of PDGFRA, OLR1, RAC3, PDF, OAS1, and SH3BP2 in bladder urothelial carcinoma remain largely unexplored.
Some recent investigations based on databases such as TCGA and GEO are related to our findings. Qiu et al. identified seven prognostic immune-related genes in patients with bladder cancer, including RBP7, PDGFRA, AHNAK, RAC3, EDNRA, OAS1, and SH3BP2 (27). Consistent with our study, PDGFRA, AHNAK and RAC3 were risk factors, whereas OAS1 and SH3BP2 were protective factors. Another study revealed that DEG between bladder cancers and normal tissues were enriched in PDGF signaling and immune-related signalings (28). Moreover, PDGF signaling contributed to immune microenvironment and unfavorable prognosis in an analysis of multiple tumors (29). Kudryavtseva et al. reported that RAC3 was associated with poor prognosis of patients with prostate cancer (30). High AHNAK in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) was associated with short survival (31); however, in melanoma low AHNAK was associated with poor prognosis, suggesting a tumor-specific role of AHNAK in prognosis (32).
In conclusion, we for the first time identified and validated a 9-core immune-related genes signature with independent prognostic significance for patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma. These 9-core immune-related genes can be adopted alone or maybe better in combination, to predict clinical outcome of urothelial carcinoma. However, our study is limited because it is retrospective. For better clinical application, the capacity of our signature for prognostic evaluation should be tested. Meanwhile, functional and mechanistical investigations on the 9-core genes in urothelial carcinoma should be further performed.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study, these can be found in The Cancer Genome Atlas (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/).
Author Contributions
LN and CZ proposed the study concept, design, and drafted the manuscript. YB and YS collected, analyzed, and interpreted the data. WW, ZW, and LY participated in revising the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
LY was employed by the company Liaoning Branch of China Telecom.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S, He J. Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2011. Chin J Cancer Res. (2015) 27:2–12. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2015.01.06
2. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. (2019) 69:7–34. doi: 10.3322/caac.21551
3. Knowles MA, Hurst CD. Molecular biology of bladder cancer: new insights into pathogenesis and clinical diversity. Nat Rev Cancer. (2015) 15:25–41. doi: 10.1038/nrc3817
4. Zibelman M, Ramamurthy C, Plimack ER. Emerging role of immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma-Advanced disease. Urol Oncol. (2016) 34:538–47. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.10.017
5. Powles T, Eder JP, Fine GD, Braiteh FS, Loriot Y, Cruz C, et al. MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in metastatic bladder cancer. Nature. (2014) 515:558–62. doi: 10.1038/nature13904
6. Smith SG, Zaharoff DA. Future directions in bladder cancer immunotherapy: towards adaptive immunity. Immunotherapy. (2016) 8:351–65. doi: 10.2217/imt.15.122
7. Kandoth C, McLellan MD, Vandin F, Ye K, Niu B, Lu C, et al. Mutational landscape and significance across 12 major cancer types. Nature. (2013) 502:333–9. doi: 10.1038/nature12634
8. Loskog A, Ninalga C, Paul-Wetterberg G, de la Torre M, Malmstrom PU, Totterman TH. Human bladder carcinoma is dominated by T-regulatory cells and Th1 inhibitory cytokines. J Urol. (2007) 177:353–8. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2006.08.078
9. Horn T, Laus J, Seitz AK, Maurer T, Schmid SC, Wolf P, et al. The prognostic effect of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytic subpopulations in bladder cancer. World J Urol. (2016) 34:181–7. doi: 10.1007/s00345-015-1615-3
10. Le Goux C, Vacher S, Pignot G, Sibony M, Barry Delongchamps N, Terris B, et al. mRNA Expression levels of genes involved in antitumor immunity: identification of a 3-gene signature associated with prognosis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Oncoimmunology. (2017) 6:e1358330. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1358330
11. Rubio C, Munera-Maravilla E, Lodewijk I, Suarez-Cabrera C, Karaivanova V, Ruiz-Palomares R, et al. Macrophage polarization as a novel weapon in conditioning tumor microenvironment for bladder cancer: can we turn demons into gods? Clin Transl Oncol. (2019) 21:391–403. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1952-y
12. Brincks EL, Risk MC, Griffith TS. PMN and anti-tumor immunity–the case of bladder cancer immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol. (2013) 23:183–9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.02.002
13. Marchioni M, Primiceri G, Ingrosso M, Filograna R, Castellan P, De Francesco P, et al. The clinical use of the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in urothelial cancer: a systematic review. Clin Genitourin Cancer. (2016) 14:473–84. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2016.04.008
14. Fridman WH, Pages F, Sautes-Fridman C, Galon J. The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat Rev Cancer. (2012) 12:298–306. doi: 10.1038/nrc3245
15. Pages F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Asslaber M, Tosolini M, Bindea G, et al. In situ cytotoxic and memory T cells predict outcome in patients with early-stage colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2009) 27:5944–51. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.6147
16. Galon J, Pages F, Marincola FM, Thurin M, Trinchieri G, Fox BA, et al. The immune score as a new possible approach for the classification of cancer. J Transl Med. (2012) 10:1. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-1
17. Galon J, Pages F, Marincola FM, Angell HK, Thurin M, Lugli A, et al. Cancer classification using the immunoscore: a worldwide task force. J Transl Med. (2012) 10:205. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-205
18. Pages F, Galon J, Dieu-Nosjean MC, Tartour E, Sautes-Fridman C, Fridman WH. Immune infiltration in human tumors: a prognostic factor that should not be ignored. Oncogene. (2010) 29:1093–102. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.416
19. Sharma P, Shen Y, Wen S, Yamada S, Jungbluth AA, Gnjatic S, et al. CD8 tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are predictive of survival in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2007) 104:3967–72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611618104
20. Wang B, Pan W, Yang M, Yang W, He W, Chen X, et al. Programmed death ligand-1 is associated with tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and poorer survival in urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Sci. (2019) 110:489–98. doi: 10.1111/cas.13887
21. Mo Q, Nikolos F, Chen F, Tramel Z, Lee YC, Hayashi K, et al. Prognostic power of a tumor differentiation gene signature for bladder urothelial carcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2018) 110:448–59. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djx243
22. Papathoma AS, Petraki C, Grigorakis A, Papakonstantinou H, Karavana V, Stefanakis S, et al. Prognostic significance of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in bladder cancer. Anticancer Res. (2000) 20:2009–13.
23. Reis ST, Leite KR, Piovesan LF, Pontes-Junior J, Viana NI, Abe DK, et al. Increased expression of MMP-9 and IL-8 are correlated with poor prognosis of Bladder Cancer. BMC Urol. (2012) 12:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2490-12-18
24. Lee H, Kim K, Woo J, Park J, Kim H, Lee KE, et al. Quantitative proteomic analysis identifies AHNAK (neuroblast differentiation-associated protein AHNAK) as a novel candidate biomarker for bladder urothelial carcinoma diagnosis by liquid-based cytology. Mol Cell Proteomics. (2018) 17:1788–802. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.000562
25. Hursting SD, Perkins SN, Lavigne JA, Beltran L, Haines DC, Hill HL, et al. Urothelial overexpression of insulin-like growth factor-1 increases susceptibility to p-cresidine-induced bladder carcinogenesis in transgenic mice. Mol Carcinog. (2009) 48:671–7. doi: 10.1002/mc.20548
26. Zhao H, Grossman HB, Spitz MR, Lerner SP, Zhang K, Wu X. Plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 and binding protein-3, and their association with bladder cancer risk. J Urol. (2003) 169:714–7. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)63999-7
27. Qiu H, Hu X, He C, Yu B, Li Y, Li J. Identification and validation of an individualized prognostic signature of bladder cancer based on seven immune related genes. Front Genet. (2020) 11:12. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00012
28. Xu Y, Wu G, Li J, Li J, Ruan N, Ma L, et al. Screening and identification of key biomarkers for bladder cancer: a study based on TCGA and GEO Data. Biomed Res Int. (2020) 2020:8283401. doi: 10.1155/2020/8283401
29. Bartoschek M, Pietras K. PDGF family function and prognostic value in tumor biology. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2018) 503:984–90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.106
30. Kudryavtseva AV, Lukyanova EN, Kharitonov SL, Nyushko KM, Krasheninnikov AA, Pudova EA, et al. Bioinformatic identification of differentially expressed genes associated with prognosis of locally advanced lymph node-positive prostate cancer. J Bioinform Comput Biol. (2019) 17:1950003. doi: 10.1142/S0219720019500033
31. Zhang Z, Liu X, Huang R, Liu X, Liang Z, Liu T. Upregulation of nucleoprotein AHNAK is associated with poor outcome of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma prognosis via mediating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cancer. (2019) 10:3860–70. doi: 10.7150/jca.31291
Keywords: immune, bladder urothelial carcinoma (bladder cancer), prognosis, overall survival, TCGA
Citation: Na L, Bai Y, Sun Y, Wang Z, Wang W, Yuan L and Zhao C (2020) Identification of 9-Core Immune-Related Genes in Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Prognosis. Front. Oncol. 10:1142. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01142
Received: 22 February 2020; Accepted: 05 June 2020;
Published: 08 July 2020.
Edited by:
Fabio Grizzi, Humanitas Research Hospital, ItalyCopyright © 2020 Na, Bai, Sun, Wang, Wang, Yuan and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lin Yuan, MTg5NDAwMDA3NjFAMTg5LmNu; Chenghai Zhao, Y2h6aGFvQGNtdS5lZHUuY24=
 Lei Na
Lei Na Yu Bai1,3
Yu Bai1,3