- Department of Urology, Institute of Urology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Purpose: We aimed to compare the efficacy of radical prostatectomy (RP) + extended pelvic lymph node dissection (ePLND) and radiotherapy (RT) in localized prostate cancer (PCa) patients with a risk of lymph node invasion (LNI) over 5%.
Methods: The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) databases were used to identify patients with PCa from 2010 to 2014. Propensity score matching (PSM) was performed to balance baseline characteristics between patients in different treatment groups. Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox regression were used to assess the effects of treatments on cancer-specific survival (CSS) and overall survival (OS).
Results: Overall 20584 patients were included in this study, with 4,057 and 16,527 patients receiving RP + ePLND and RT, respectively. After PSM, patients with RP + ePLND had similar CSS (5-year CSS rate: 97.8% vs. 97.2%, P=0.310) but longer OS (5-year OS rate: 96.0% vs. 90.8%, P<0.001) compared to those receiving RT. When separating RT cohort into external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) group and EBRT+ brachytherapy (BT) group, treatments with RP + ePLND and EBRT+ BT achieved equivalent OS and were both superior to EBRT alone (5-year OS rate: 96.0% vs. 94.4% vs. 90.0%, P<0.001). Subgroup analyses and multivariate analyses further confirmed the superiority of RP + ePLND and EBRT+ BT.
Conclusion: RP + ePLND and EBRT + BT were associated with better survival outcomes compared to EBRT alone in PCa patients with a probability of LNI over 5%. However, no survival difference was observed between RP + ePLND and EBRT + BT.
Introduction
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common malignancy in men in the United States, with 191,930 estimated new cases and 33,330 estimated deaths in 2020 (1). Although an increasing number of patients are diagnosed as PCa at early stages with the introduction of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening, approximately 12% of patients still have lymph node invasion (LNI) at initial presentation (1). It has been widely reported that the presence of positive lymph nodes represents an adverse pathologic finding associated with poor survival outcomes in patients with PCa (2–4). At present, extended pelvic lymph node dissection (ePLND) represents the most accurate procedure for nodal staging and several pre-operative tools have been established to predict the individual risk of LNI in patients with PCa and select candidates for ePLND (5–7). Given the essential role of ePLND in tumor staging and its potential therapeutic effect, the current European Association of Urology (EAU) guidelines recommend performing radical prostatectomy (RP) and ePLND for patients with a risk of LNI greater than 5% according to Briganti nomogram (8). Meanwhile, radiotherapy (RT) with prophylactic nodal radiation is also the standard of care for clinically localized PCa, especially in unfavorable intermediate-risk and high-risk patients (8, 9). However, there is uncertainty regarding the efficacy of RP plus ePLND compared to RT in localized PCa patients with a relatively high risk of LNI.
Against this backdrop, this study aimed to use the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database to examine the effectiveness of RP plus ePLND versus RT in treating localized PCa patients with a probability of LNI over 5%.
Patients and Methods
Study Population and Data
This study was approval by institutional ethics committee and informed consents were waived due to the de-identified nature of SEER database. Data were extracted from the SEER database using SEER*Stat, version 8.3.6. Patients with histologically confirmed adenocarcinoma of the prostate [International Classification of Disease for Oncology (61.9); histological code: 8140] diagnosed from 2010 to 2014 were identified. Inclusion criteria were: 1) patients with complete baseline clinicopathologic data; 2) patients with a probability of LNI>5% based on 2012-Briganti nomogram; 3) patients received RP plus ePLND or RT as primary treatment. Patients with a tumor stage>T3, clinically positive nodes, distant metastasis, neoadjuvant therapies, other malignancies, or missing follow-up data were excluded from this study.
Data regarding the age of diagnosis, race, clinical T (cT) stage, PSA value, Gleason score (GS) at biopsy, number of positive or negative cores, number of lymph nodes positive, number of lymph nodes examined, survival time and cause of death were collected for each patient. EPLND was defined as dissected lymph nodes ≥10 according to previous reports (5–7).
Endpoints and Statistical Analysis
Primary endpoints were cancer-specific survival (CSS) and overall survival (OS), defined by the SEER database. The probability of LNI was calculated based on the 2012-Briganti nomogram. Continuous variables were presented using the median and interquartile range (IQR). Frequency and proportion were reported for categorical variables. Chi-square test and Student’s t test were used to compare categorical and continuous variables of baseline characteristics, respectively. To balance the baseline clinicopathologic characteristics of two treatment groups, 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) was conducted with a caliper of 0.001. Survival estimates were generated and compared using the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test, respectively. To further assess the survival differences between treatment modalities, patients with RT were subdivided into external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) group and EBRT+ brachytherapy (BT) group. Besides, subgroup analyses were conducted according to baseline features and presented with forest plots. At last, univariate and multivariate analyses were performed using Cox proportional hazards regressions to determine independent predictors of survival. SPSS, version 25.0 was used for all statistical analyses. A two-sided P value<0.05 indicated statistical significance.
Results
Patients Characteristics
Overall, 20,584 patients with a risk of LNI>5% were identified from the SEER database between 2010 and 2014. Among them, 4,057 and 16,527 patients received RP + ePLND and RT, respectively. In the RT group, 14,134 and 2,393 patients were treated with EBRT and EBRT + BT, respectively. In the RP + ePLND group, a median of 14 lymph nodes (IQR 12–19) were removed and 714 patients (17.6%) harbored LNI. A total of 549 (13.5%) patients received adjuvant or salvage RT after surgery. As shown in Table 1, compared to patients treated with RT, patients receiving RP + ePLND were younger and had significantly lower PSA value, lower probability of LNI but higher cT stage. After PSM, the baseline clinicopathologic characteristics were well balanced between the RP + ePLND group and RT group.
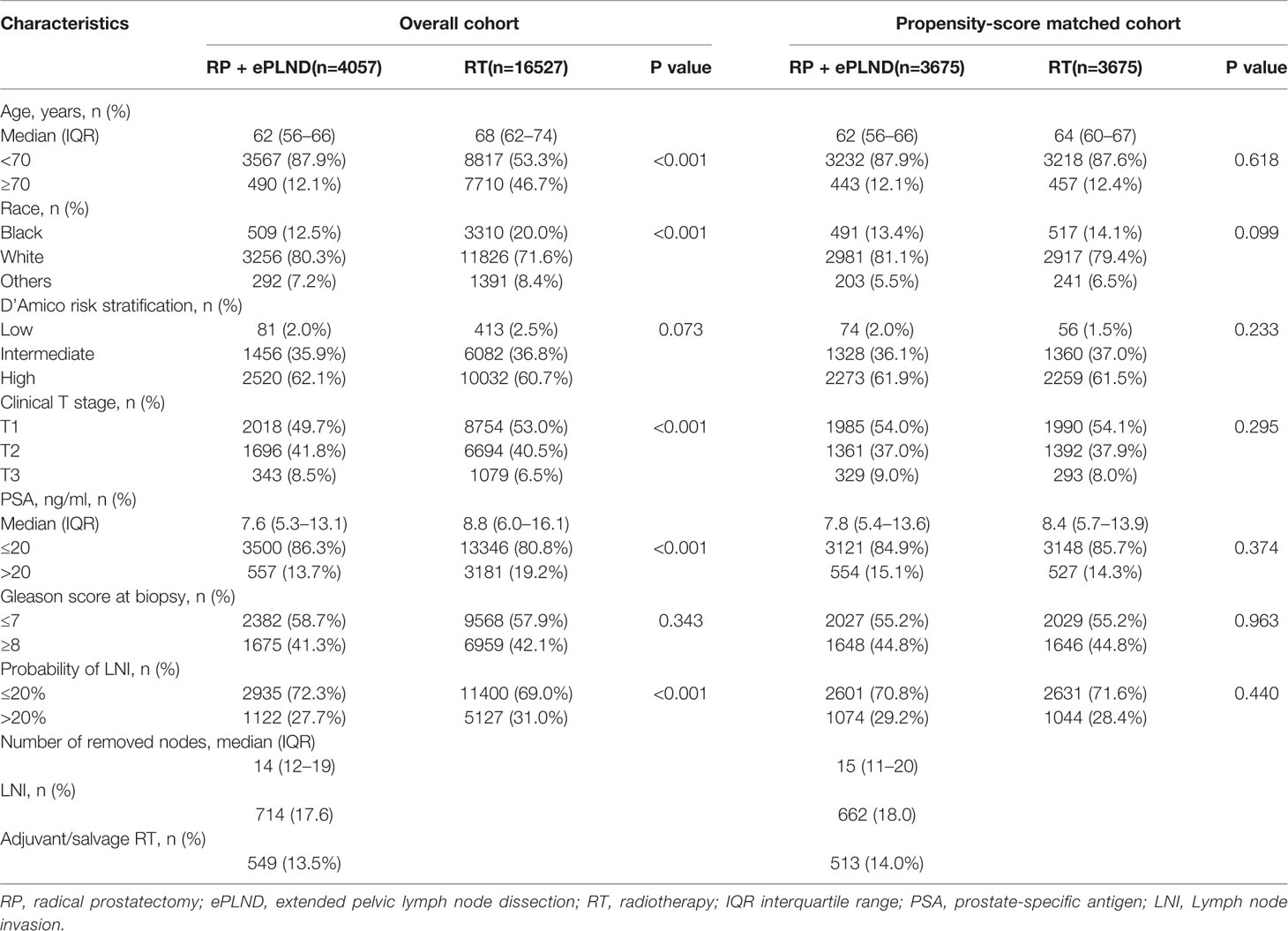
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of patients treated with RP + ePLND and RT in overall cohort and propensity-score matched cohort.
Treatment Effect of RP + ePLND Versus RT
The median follow-up was 50 months for overall patients, 48 and 52 months for patients with RP + ePLND and RT, respectively. As shown in Figures 1A, B, compare to patients with RT, those receiving RP + ePLND were associated with significantly improved CSS (5-year CSS rate: 98.0% vs. 96.6%, P<0.001) and OS (5-year OS rate: 96.1% vs. 88.7%, P<0.001) before PSM. After PSM, the CSS was comparable between two treatment groups (5-year CSS rate: 97.8% vs. 97.2%, P=0.310), while patients treated with RP + ePLND had longer OS (5-year OS rate: 96.0% vs. 90.8%, P<0.001) than patients with RT (Figures 1C, D).
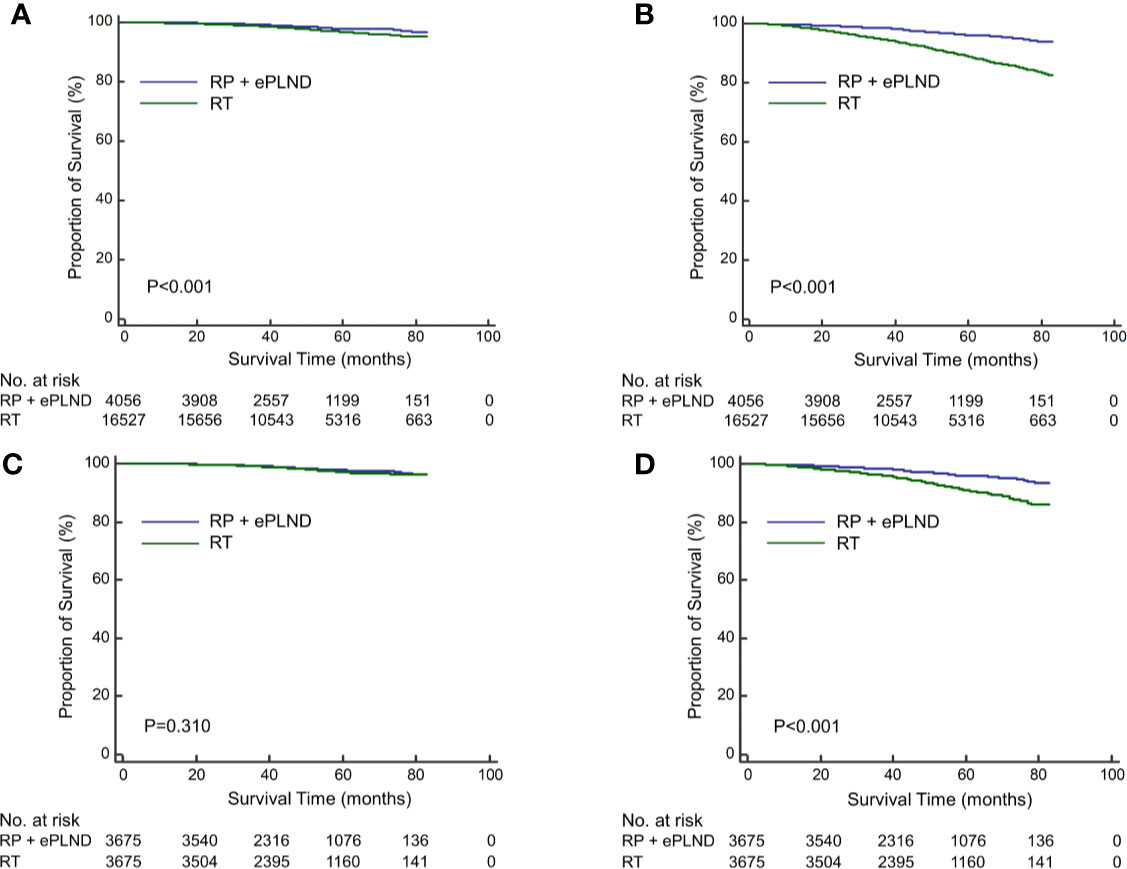
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier curves of cancer-specific survival (A) and overall survival (B) for patients receiving RP + ePLND and RT in the entire cohort before PSM; Kaplan-Meier curves of cancer-specific survival (C) and overall survival (D) for patients receiving RP + ePLND and RT after PSM.
Treatment Effect of RP + ePLND Versus EBRT Versus EBRT + BT
To further investigate the efficacy of different radiation modalities, the RT cohort was subdivided into EBRT group and EBRT + BT group. Before PSM, patients underwent RP + ePLND had similar CSS (5-year CSS rate: 98.0% vs. 98.0%, P=0.569) with those receiving EBRT + BT but longer CSS (5-year CSS rate: 98.0% vs. 96.3%, P<0.001) compared to men with EBRT alone (Figure 2A). In terms of OS, RP + ePLND had obvious superiority to EBRT + BT or EBRT alone (5-year OS rate: 96.1% vs. 93.1% vs. 87.9%, P<0.001, Figure 2B). After PSM, as shown in Figure 2C, CSS was comparable among three treatment groups with a 5-year CSS was 97.8%, 98.0%, and 97.0% (P=0.136) for patients with RP + ePLND, EBRT + BT and EBRT alone, respectively. However, patients receiving RP + ePLND or EBRT + BT had significantly longer OS than those receiving EBRT alone (5-year OS rate: 96.0% vs. 94.4% vs. 90.0%, P<0.001, Figure 2D). When comparing the efficacy of RP + ePLND versus EBRT + BT, no statistical difference was observed for OS(P=0.167).
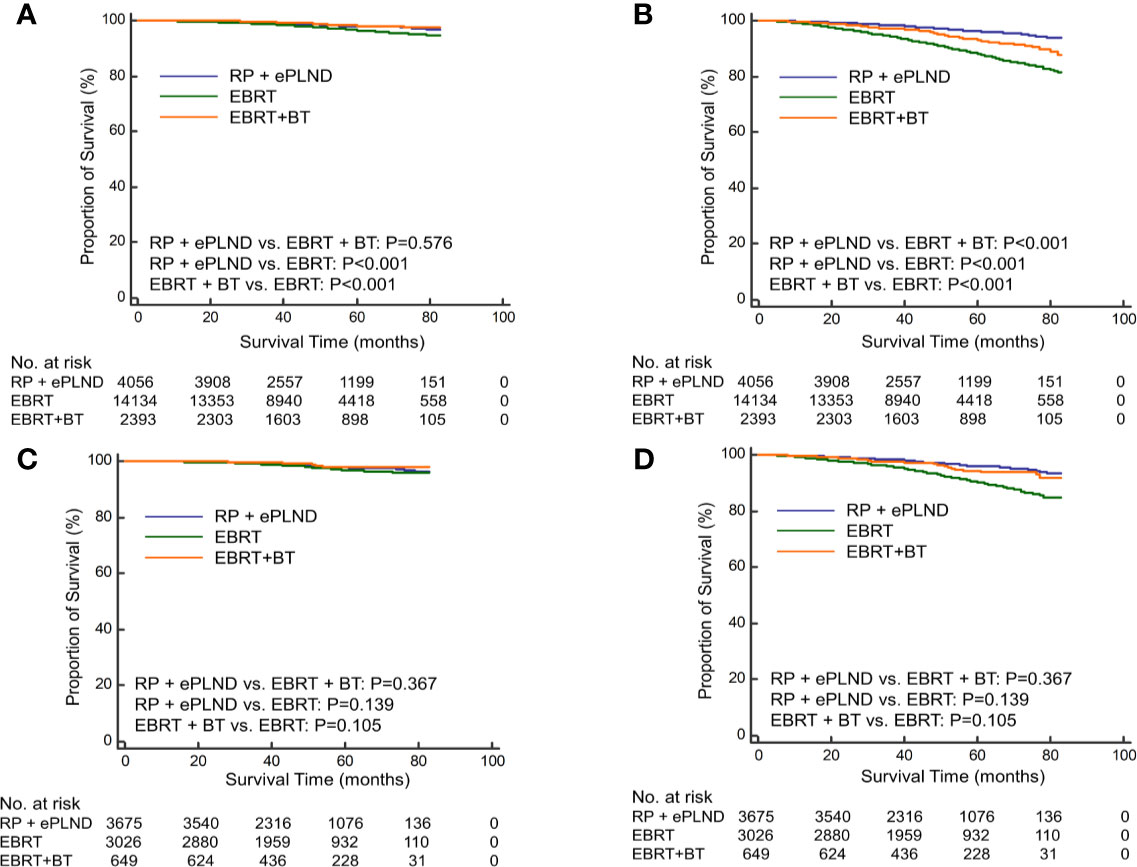
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier curves of cancer-specific survival (A) and overall survival (B) for patients receiving RP + ePLND, EBRT alone and EBRT + BT in the entire cohort before PSM; Kaplan-Meier curves of cancer-specific survival (C) and overall survival (D) for patients receiving RP + ePLND, EBRT alone and EBRT + BT in after PSM.
Subgroup Analyses and Multivariate Cox Regression
To select the optimal treatment for patients with distinct features, subgroup analyses were conducted based on baseline clinicopathologic characteristics in post-PSM cohorts. As shown in Figure 3, the results were basically consistent with prior analyses that patients in different treatment groups had similar CSS, while men receiving RP + ePLND or EBRT + BT could gain more OS benefits than those with EBRT alone. To note, patients with a higher risk of LNI (>20%) or a GS 9-10 might have not only longer CSS but also improved OS when treated with RP + ePLND.
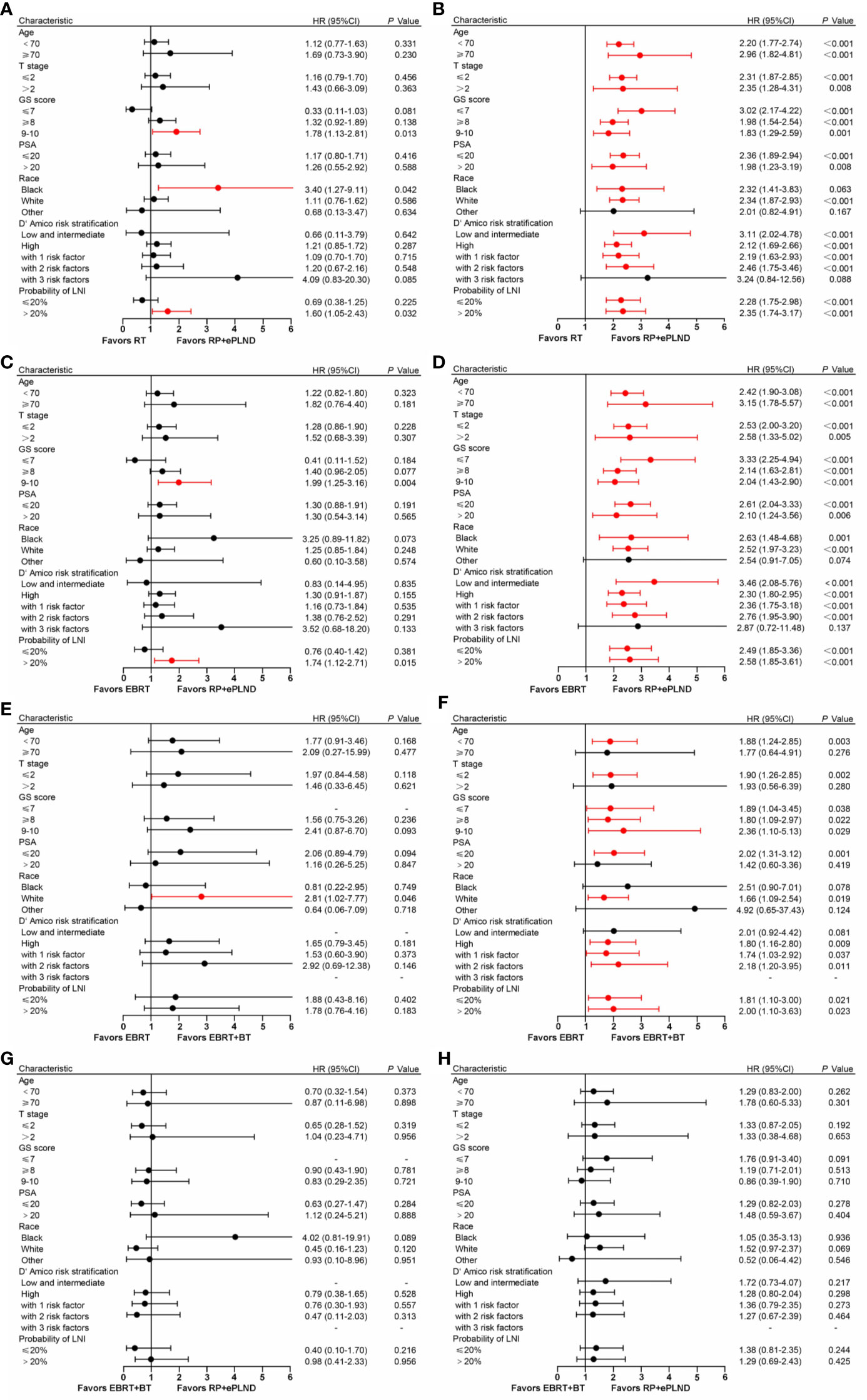
Figure 3 Forest plot showing the effect of RP + ePLND versus RT on cancer-specific survival (A) and overall survival (B) in patients with different baseline characteristics; Forest plot showing the effect of RP + ePLND versus EBRT alone on cancer-specific survival (C) and overall survival (D) in patients with different baseline characteristics; Forest plot showing the effect of EBRT + BT versus EBRT alone on cancer-specific survival (E) and overall survival (F) in patients with different baseline characteristics; Forest plot showing the effect of RP + ePLND versus EBRT + BT on cancer-specific survival (G) and overall survival (H) in patients with different baseline characteristics.
After adjusting for clinicopathologic covariates, multivariate Cox regression analyses indicated that neither RP + ePLND nor RT was an independent predictor of CSS. However, RP + ePLND/EBRT + BT along with the lower probability of LNI, lower GS, younger age, and low/intermediate-risk disease independently predicted better OS. No survival difference was observed between RP + ePLND group and EBRT + BT group in multivariate analyses (Table 2).
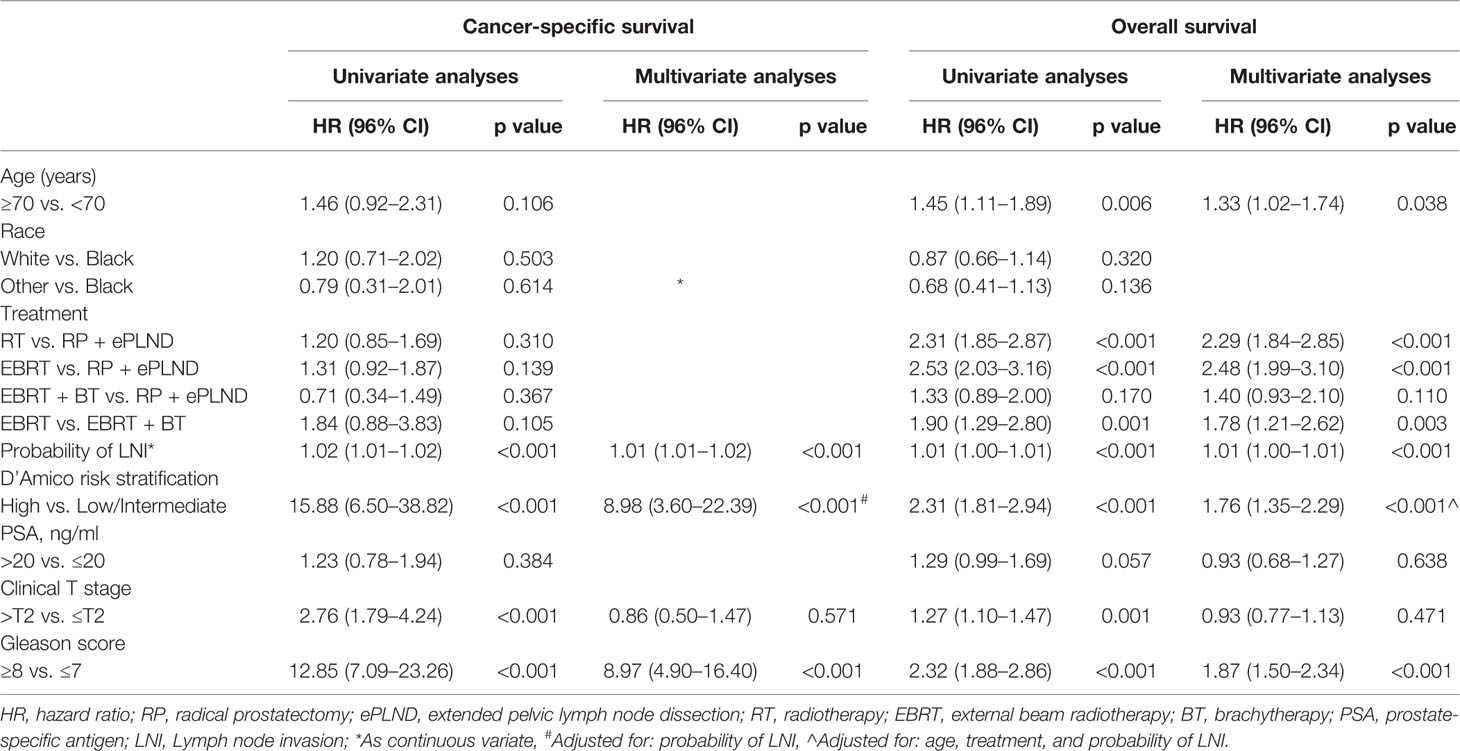
Table 2 Univariate and Multivariate analyses of cancer-specific survival and overall survival for patients in post-propensity score matching cohort.
Discussion
Considering the poor prognosis associated with LNI, much effort has been invested into predicting the risk of LNI in patients with PCa and seeking subsequent therapies for men with LNI (5–7). Among various prediction tools, the 2012-Briganti nomogram has been validated in North American patients and was reported to have high accuracy and best performance characteristics in the decision curve analysis (10). Despite that the 2012-Briganti nomogram has been updated recently with inclusion of MRI features and improved predictive power, the new nomograms have not been widely externally validated (11, 12). Thus, current international guidelines still recommend to select patients for RP + ePLND with a cut-off point of 5% based on 2012-Briganti nomogram (8). At the same time, RT is also the standard treatment for localized PCa regardless of the risk of LNI (8, 9). Although a large number of studies have investigated the optimal therapy for overall patients with localized PCa, men with a relatively high risk of LNI stills represent a grey zone as no comparison has been made of currently available treatments in this setting (13–20). To the best of our knowledge, this was the first study to compare the efficacy of RP + ePLND and RT in localized PCa patients with a relatively high risk of LNI.
In this study, we observed that patients receiving RP + ePLND were younger and associated with lower PSA value, lower risk of LNI. Consistently, previous population-based studies also reported that compared to men with RT, those who underwent RP had more favorable clinicopathologic characteristics (15, 18). Thus, it was not surprising that RP + ePLND achieved improved survival outcomes than RT in overall patients. Interestingly, after adjusting clinicopathologic features, patients with RP + ePLND still had longer survival than those with RT. When comparing men who underwent different types of RT versus RP + ePLND, RP + ePLND, and EBRT + BT showed significant superiority to EBRT alone. However, no survival difference was observed between patients with RP + ePLND and EBRT + BT.
In line with our results, several previous studies demonstrated that RP provided more survival benefits than RT in patients with high-risk PCa who were more likely to harbor positive nodes (14, 16, 17, 20). In theory, RP + ePLND could remove the primary prostate lesion as well as potential micro-metastases in pelvic lymph nodes, resulting in long-term disease control. Meanwhile, RT with concomitant prophylactic nodal radiation could also achieve satisfied survival outcomes by eliminating local cancer cells. Nevertheless, the therapeutic role of ePLND in addition to RP remained controversial, it provided important nodal information and aided adjuvant treatments in selected patients (21–23). On the contrary, the efficacy of RT might be highly limited by the absence of accurate pathological nodal staging and corresponding adjuvant therapies, which finally led to undertreatment in patients in our study who were at a relatively higher risk of LNI. This point might partly explain the better survival benefit of RP + ePLND than RT in this setting.
Currently, RT options for PCa include EBRT alone and EBRT + BT, with the latter constituting extreme dose escalation. Several randomized trials suggested a biochemical recurrence-free survival benefit to EBRT+BT over EBRT but failed to show significant improvements in long-term survival outcomes (24–26). Therefore, the question arises simultaneously whether RP + ePLND and different RT modalities offer varied survival benefits in PCa patients with a probability of LNI over 5%. In this study, we found that RP + ePLND and EBRT + BT achieved similar OS, and both of them outperformed EBRT alone. This finding was consistent with the study by Ennis and colleagues, which indicated that, after adjusting lymph node status, there was no statistical difference in survival between RP and EBRT + BT (15). However, EBRT plus androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) was associated with higher mortality than RP. The superior results observed in our study with the combination of EBRT and BT might be due to an increased dose of radiation to the prostate and periprostatic area as well as radiobiological factors associated with shorter duration (26). Thus, our findings further confirmed the perspective that dose escalation in a short delivery time should be the key to improve the effectiveness of RT in PCa (27, 28).
To further select patients for preferred treatment, we conducted subgroup analyses based on baseline characteristics. We found that men with a higher risk of LNI or a GS≥9 could gain more CSS and OS benefit form RP + ePLND and EBRT + BT, which suggested that more intense treatments were needed in this setting. In line with our results, another recent study has also indicated the treatment with Max RP (RP with adjuvant therapies) or MaxRT (EBRT + BT + ADT) for PCa patients with a GS≥9 could lead to equivalent and favorable CSS and OS outcomes (19). Intriguingly, it seemed that race may also play a role in the response to different therapies as no survival difference was seen between treatment groups in men of other races such as American Indians and Asians. Further studies are warranted to verify our results and novel stratification tools are needed to select candidates for optimal therapies.
Our findings should be interpreted with caution as this study is not devoid of limitations. First, the present results were derived from retrospective analyses with inherent bias, whereas we used the PSM method to balance the differential clinicopathologic features between groups, which helped minimize the impact of potential bias. Second, the definition of ePLND was based on the number of dissected nodes due to the lack of anatomic nodal information. However, a median number of 14 removed nodes was achieved in our study, which was equivalent to that in previous reports based on anatomical ePLND (5–7). Third, due to the limitation of SEER databases, the protocols of RT and data regarding the use of ADT were not available. As such, the effectiveness of RT might be underestimated. At last, with a median follow-up of 50 months, the data concerning CSS might not be mature enough to address significant differences between treatments. Large prospective trials with complete treatment details are needed to validate our findings.
Conclusion
Our study is the first to compare the efficacy of RP + ePLND and RT in PCa patients with a relatively high risk of LNI. We demonstrated that RP + ePLND and EBRT + BT were associated with better survival outcomes compared to EBRT alone in men with a probability of LNI over 5%. However, no significant survival difference was observed between RP + ePLND and EBRT + BT.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database (https://seer.cancer.gov/).
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by The ethics committee of West China Hospital, Sichuan University. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author Contributions
JC: Conceptualization, software, data curation, formal analysis, data interpretation, manuscript drafting, and manuscript editing. YN: Conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, data interpretation, manuscript drafting, and manuscript editing. GS, SZ, JZ, ZW, HRZ, XDZ, XMZ, and JD: Data curation, data interpretation, and manuscript editing. PS, and HZ: Conceptualization, formal analysis, data curation, data interpretation, and manuscript editing. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 81672547 and 81974398); The 1.3.5 project for disciplines of excellence, West China Hospital, Sichuan University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin (2020) 70(1):7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590
2. Boorjian SA, Thompson RH, Siddiqui S, Bagniewski S, Bergstralh EJ, Karnes RJ, et al. Long-term outcome after radical prostatectomy for patients with lymph node positive prostate cancer in the prostate specific antigen era. J Urol (2007) 178(3 Pt 1):864–70; discussion 70-1. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.05.048
3. Cheng L, Zincke H, Blute ML, Bergstralh EJ, Scherer B, Bostwick DG. Risk of prostate carcinoma death in patients with lymph node metastasis. Cancer (2001) 91(1):66–73. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(20010101)91:1<66::AID-CNCR9>3.0.CO;2-P
4. Da Pozzo LF, Cozzarini C, Briganti A, Suardi N, Salonia A, Bertini R, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with prostate cancer and nodal metastases treated by pelvic lymphadenectomy and radical prostatectomy: the positive impact of adjuvant radiotherapy. Eur Urol (2009) 55(5):1003–11. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.01.046
5. Briganti A, Larcher A, Abdollah F, Capitanio U, Gallina A, Suardi N, et al. Updated nomogram predicting lymph node invasion in patients with prostate cancer undergoing extended pelvic lymph node dissection: the essential importance of percentage of positive cores. Eur Urol (2012) 61(3):480–7. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.10.044
6. Cagiannos I, Karakiewicz P, Eastham JA, Ohori M, Rabbani F, Gerigk C, et al. A preoperative nomogram identifying decreased risk of positive pelvic lymph nodes in patients with prostate cancer. J Urol (2003) 170(5):1798–803. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000091805.98960.13
7. Godoy G, Chong KT, Cronin A, Vickers A, Laudone V, Touijer K, et al. Extent of pelvic lymph node dissection and the impact of standard template dissection on nomogram prediction of lymph node involvement. Eur Urol (2011) 60(2):195–201. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.01.016
8. Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E, Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur Urol (2017) 71(4):618–29. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.003
9. Sanda MG, Cadeddu JA, Kirkby E, Chen RC, Crispino T, Fontanarosa J, et al. Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: AUA/ASTRO/SUO Guideline. Part II: Recommended Approaches and Details of Specific Care Options. J Urol (2018) 199(4):990–7. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2018.01.002
10. Bandini M, Marchioni M, Pompe RS, Tian Z, Gandaglia G, Fossati N, et al. First North American validation and head-to-head comparison of four preoperative nomograms for prediction of lymph node invasion before radical prostatectomy. BJU Int (2018) 121(4):592–9. doi: 10.1111/bju.14074
11. Gandaglia G, Fossati N, Zaffuto E, Bandini M, Dell’Oglio P, Bravi CA, et al. Development and Internal Validation of a Novel Model to Identify the Candidates for Extended Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection in Prostate Cancer. Eur Urol (2017) 72(4):632–40. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.03.049
12. Gandaglia G, Ploussard G, Valerio M, Mattei A, Fiori C, Fossati N, et al. A Novel Nomogram to Identify Candidates for Extended Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection Among Patients with Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer Diagnosed with Magnetic Resonance Imaging-targeted and Systematic Biopsies. Eur Urol (2019) 75(3):506–14. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.10.012
13. Berg S, Cole AP, Krimphove MJ, Nabi J, Marchese M, Lipsitz SR, et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Radical Prostatectomy Versus External Beam Radiation Therapy Plus Brachytherapy in Patients with High-risk Localized Prostate Cancer. Eur Urol (2019) 75(4):552–5. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.10.032
14. Boorjian SA, Karnes RJ, Viterbo R, Rangel LJ, Bergstralh EJ, Horwitz EM, et al. Long-term survival after radical prostatectomy versus external-beam radiotherapy for patients with high-risk prostate cancer. Cancer (2011) 117(13):2883–91. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25900
15. Ennis RD, Hu L, Ryemon SN, Lin J, Mazumdar M. Brachytherapy-Based Radiotherapy and Radical Prostatectomy Are Associated With Similar Survival in High-Risk Localized Prostate Cancer. J Clin Oncol (2018) 36(12):1192–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.75.9134
16. Feldman AS, Meyer CP, Sanchez A, Krasnova A, Reznor G, Menon M, et al. Morbidity and Mortality of Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer: A Population Based Analysis Comparing Radical Prostatectomy versus External Beam Radiation. J Urol (2017) 198(5):1061–8. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.05.073
17. Kibel AS, Ciezki JP, Klein EA, Reddy CA, Lubahn JD, Haslag-Minoff J, et al. Survival among men with clinically localized prostate cancer treated with radical prostatectomy or radiation therapy in the prostate specific antigen era. J Urol (2012) 187(4):1259–65. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.11.084
18. Kishan AU, Cook RR, Ciezki JP, Ross AE, Pomerantz MM, Nguyen PL, et al. Radical Prostatectomy, External Beam Radiotherapy, or External Beam Radiotherapy With Brachytherapy Boost and Disease Progression and Mortality in Patients With Gleason Score 9-10 Prostate Cancer. JAMA (2018) 319(9):896–905. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.0587
19. Tilki D, Chen MH, Wu J, Huland H, Graefen M, Braccioforte M, et al. Surgery vs Radiotherapy in the Management of Biopsy Gleason Score 9-10 Prostate Cancer and the Risk of Mortality. JAMA Oncol (2019) 5(2):213–20. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.4836
20. Wang Z, Ni Y, Chen J, Sun G, Zhang X, Zhao J, et al. The efficacy and safety of radical prostatectomy and radiotherapy in high-risk prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol (2020) 18(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-01824-9
21. Fossati N, Willemse PM, Van den Broeck T, van den Bergh RCN, Yuan CY, Briers E, et al. The Benefits and Harms of Different Extents of Lymph Node Dissection During Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. Eur Urol (2017) 72(1):84–109. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.12.003
22. Messing EM, Manola J, Yao J, Kiernan M, Crawford D, Wilding G, et al. Immediate versus deferred androgen deprivation treatment in patients with node-positive prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy. Lancet Oncol (2006) 7(6):472–9. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70700-8
23. Touijer KA, Karnes RJ, Passoni N, Sjoberg DD, Assel M, Fossati N, et al. Survival Outcomes of Men with Lymph Node-positive Prostate Cancer After Radical Prostatectomy: A Comparative Analysis of Different Postoperative Management Strategies. Eur Urol (2018) 73(6):890–6. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.09.027
24. Hoskin PJ, Rojas AM, Bownes PJ, Lowe GJ, Ostler PJ, Bryant L. Randomised trial of external beam radiotherapy alone or combined with high-dose-rate brachytherapy boost for localised prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol (2012) 103(2):217–22. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2012.01.007
25. Morris WJ, Tyldesley S, Rodda S, Halperin R, Pai H, McKenzie M, et al. Androgen Suppression Combined with Elective Nodal and Dose Escalated Radiation Therapy (the ASCENDE-RT Trial): An Analysis of Survival Endpoints for a Randomized Trial Comparing a Low-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy Boost to a Dose-Escalated External Beam Boost for High- and Intermediate-risk Prostate Cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2017) 98(2):275–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.11.026
26. Sathya JR, Davis IR, Julian JA, Guo Q, Daya D, Dayes IS, et al. Randomized trial comparing iridium implant plus external-beam radiation therapy with external-beam radiation therapy alone in node-negative locally advanced cancer of the prostate. J Clin Oncol (2005) 23(6):1192–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.06.154
27. Lyons JA, Kupelian PA, Mohan DS, Reddy CA, Klein EA. Importance of high radiation doses (72 Gy or greater) in the treatment of stage T1-T3 adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Urology (2000) 55(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(99)00380-5
Keywords: clinical management, prostate cancer, radiotherapy, surgery, SEER
Citation: Chen J, Ni Y, Sun G, Zhu S, Zhao J, Wang Z, Zhang H, Zhu X, Zhang X, Dai J, Shen P and Zeng H (2020) Survival Outcomes of Radical Prostatectomy + Extended Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection and Radiotherapy in Prostate Cancer Patients With a Risk of Lymph Node Invasion Over 5%: A Population-Based Analysis. Front. Oncol. 10:607576. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.607576
Received: 17 September 2020; Accepted: 29 October 2020;
Published: 26 November 2020.
Edited by:
Jonas Busch, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin, GermanyReviewed by:
Alessandro Nini, Saarland University Hospital, GermanyCarmine D’Aniello, Colli Monaldi Hospital, Italy
Copyright © 2020 Chen, Ni, Sun, Zhu, Zhao, Wang, Zhang, Zhu, Zhang, Dai, Shen and Zeng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hao Zeng, a3VjYWl6ZW5nQDE2My5jb20=; Pengfei Shen, Y2RoeDUxMEAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Junru Chen
Junru Chen Yuchao Ni†
Yuchao Ni† Hao Zeng
Hao Zeng