- 1Faculty of Applied Sciences and Technology, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Muar, Malaysia
- 2Centre of Research for Sustainable Uses of Natural Resources, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Parit Raja, Malaysia
- 3Faculty of Medicine, YARSI University, Jakarta, Indonesia
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes painful inflammation in one or more joints. In gout, elevation of uric acid in the blood triggers the formation of crystals, causing joint pain. Malaysia is a mega-biodiversity country that is rich in medicinal plants species. Therefore, its flora might offer promising therapies for gout. This article aims to systematically review the anti-gout potential of Malaysian medicinal plants. Articles on gout published from 2000 to 2017 were identified using PubMed, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar with the following keyword search terms: “gout,” “medicinal plants,” “Malaysia,” “epidemiology,” “in vitro,” and “in vivo.” In this study, 85 plants were identified as possessing anti-gout activity. These plants had higher percentages of xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity (>85%); specifically, the Momordica charantia, Chrysanthemum indicum, Cinnamomum cassia, Kaempferia galanga, Artemisia vulgaris, and Morinda elliptica had the highest values, due to their diverse natural bioactive compounds, which include flavonoids, phenolics, tannin, coumarins, luteolin, and apigenin. This review summarizes the anti-gout potential of Malaysian medicinal plants but the mechanisms, active compounds, pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and safety of the plants still remain to be elucidated.
Background
Gout incidence has increased over the past 50 years, especially in developing countries (Kuo et al., 2015). Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis triggered by interactions between monosodium urate (MSU) crystals and tissue (Dalbeth et al., 2014) during purine catabolism by the enzyme of xanthine oxidase (Nile et al., 2013). Xanthine oxidase catalyzes the oxidative hydroxylation of hypoxanthine to xanthine to uric acid, leading to painful inflammation (Nile and Khobragade, 2011). Uricase is an enzyme that further catalyzes the conversion of uric acid to the highly soluble allantoin that is excreted in the urine (Figure 1). Unfortunately, uricase is not a functional human enzyme and, as a result, humans can develop hyperuricemia (Gliozzi et al., 2016). Gout has also been reported to cause tophi, joint deformities, and kidney stones (Teh et al., 2014).
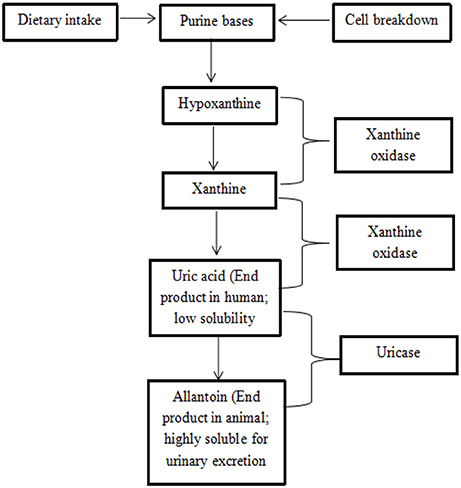
Figure 1. Mechanism of purine catabolism (Offermanns and Rosenthal, 2008; Bustanji et al., 2011).
Hyperuricemia, a major etiological factor of gout, develops either due to overproduction caused by a metabolic disorder or due to under excretion of blood uric acid due to abnormal renal urate transport activity (Ichida et al., 2012). Kidney is the main regulator of serum uric acid levels where renal urate excretion is determined by the balance of the reabsorption and secretion of urate. Renal urate reabsorption is mainly mediated by two urate transporters—urate transporter 1 (URAT1) and glucose transporter 9 (GLUT9) (Enomoto et al., 2002; Matsuo et al., 2008). One of the mechanisms involved in reducing the plasma uric acid concentration is an inhibition of the reabsorption of urate in renal tissue via renal mRNA and protein levels of urate transporter 1 (URAT1), glucose transporter 9 (GLUT9), organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1) and organic cation/carnitine transporters (OCT1/2, OCTN1/2) (Sungthong et al., 2016). Hyperuricemia occurs when serum uric acid levels are >0.42 mmol/L (Stamp et al., 2007). Therefore, reducing uric acid is the main approach for the treatment of gout, with target levels of serum uric acid of less than 0.36 mmol/L (Falasca, 2006; Pillinger et al., 2007).
Several risk factors for the development of gout have been established, including hyperuricemia, age, genetic factors, dietary factors, alcohol consumption, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, obesity, diuretic use, cholesterol level, and chronic renal disease (Roddy and Doherty, 2010). Men are believed to have four- to nine-fold increased the risk of developing gout compared to women; however, once women reach menopause, they tend to develop gout, as the uricosuric action of estrogen is lost (Tausche et al., 2009). Genetics and race may also be important factors that contribute to the incidence of gout (Mohd et al., 2011).
Several drugs are approved for the treatment of gout, including colchicine, steroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin, and aspirin), cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) inhibitors (etoricoxib), and allopurinol. Although these agents are effective, they also cause side effects, such as skin allergies, fever, rash, renal dysfunction, aseptic meningitis, and hepatic dysfunction (Nguyen et al., 2004; Strazzullo and Puig, 2007). For example, allopurinol, which is the most commonly used xanthine oxidase inhibitor for gout (Pacher et al., 2006), causes nephrolithiasis, hypersensitivity reaction, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, renal toxicity, allergic reactions, and fatal liver necrosis, and increases the toxicity of 6-mercaptopurin (Kong et al., 2004; Wang et al., 2004).
Recently, treating disease using medicinal plants is gaining new interest (Unno et al., 2004) and research on medicinal plants has increased worldwide (Tapsell et al., 2006; Triggiani et al., 2006) due to fewer side effects and lower costs (Srivastava et al., 2012). Malaysia is a country that has more than 8,000 species of flowering plants and ~7,411 plant species have been identified in Sabah, Malaysia Borneo; in addition, 1,300 medicinal plant species have been documented in Peninsular, Malaysia (Kulip, 2003; Abd Aziz et al., 2011). The aim of the present review is to provide comprehensive information on the potential of anti-gout Malaysian medicinal plants and review the scientific data, including the experimental methodologies, active compounds, and mechanisms of action against gout.
Methods
PubMed, Scopus, ScienceDirect and Google Scholar databases were searched for publications from 2000 to 2017 with in vitro and in vivo data on Malaysian medicinal plants for gout. The search terms included the following: “gout,” “medicinal plants,” “in vivo,” “in vitro,” “epidemiology,” “Malaysia,” and “mechanisms.” Publications with available abstracts were also reviewed and ~99 publications, including journal articles and proceedings, were reviewed. Data from these studies were then were summarized (Table 1: in vitro data; Table 2: in vivo data).
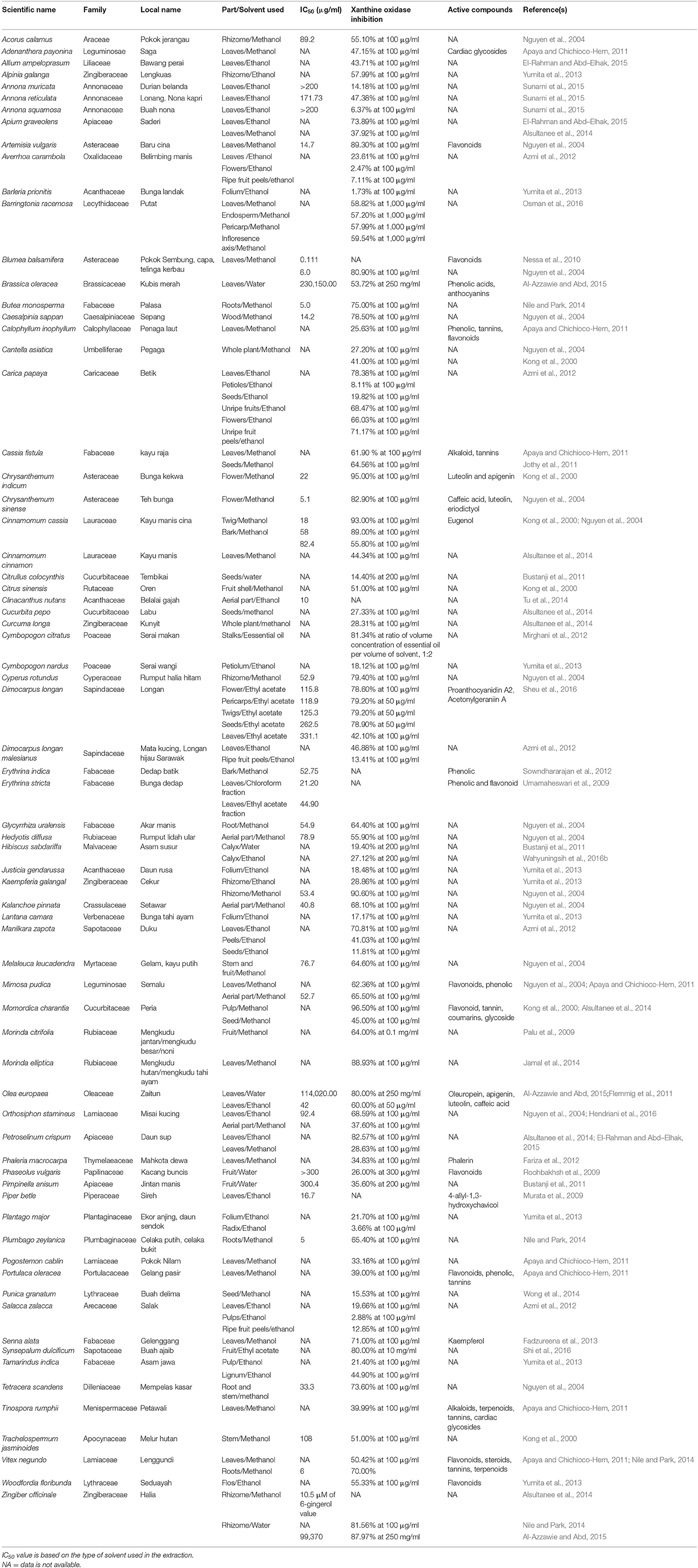
Table 1. The medicinal plants which are considered to possess anti-gout activity based on in vitro studies.
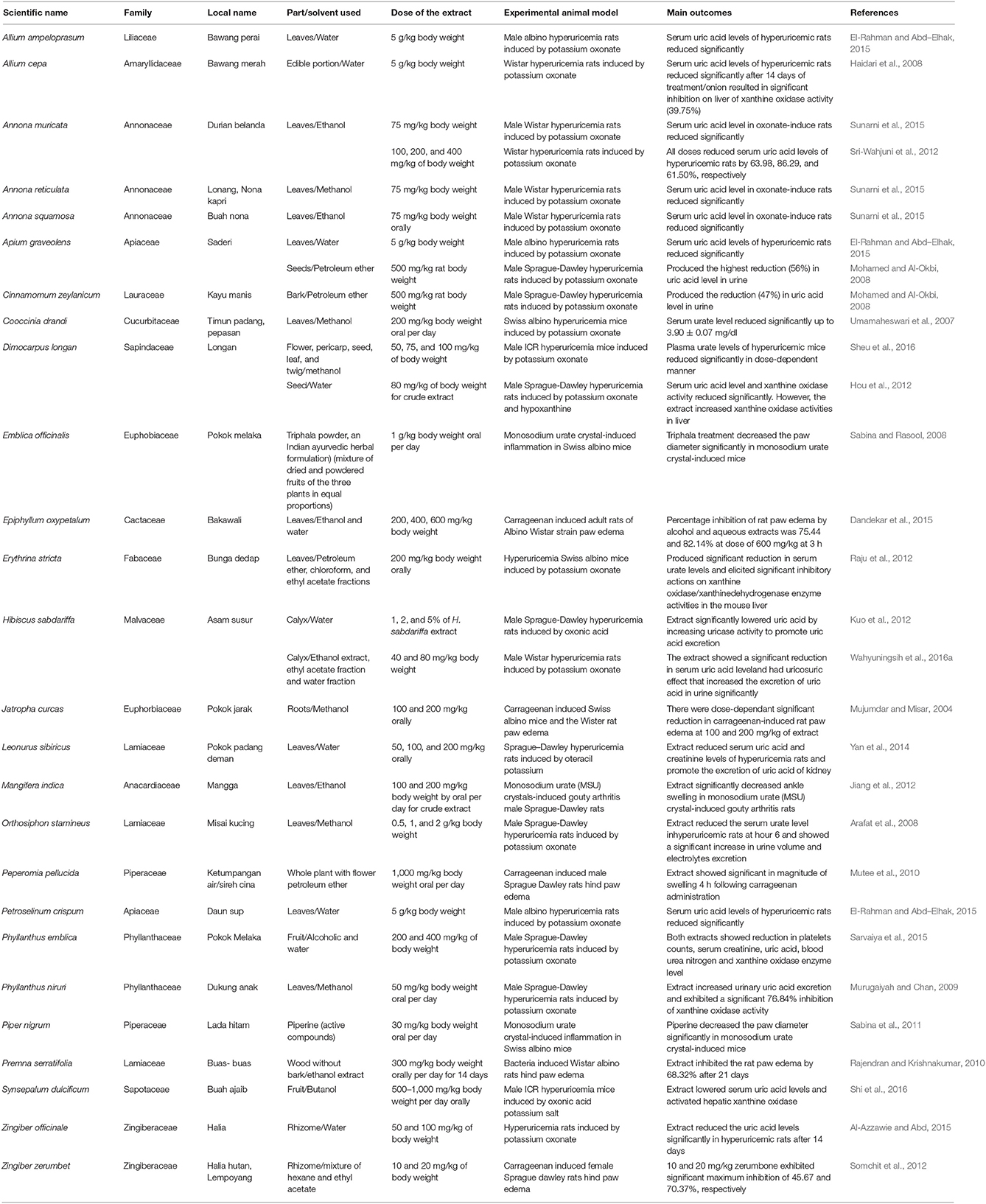
Table 2. The medicinal plants which are considered to possess anti-gout activity based on in vivo studies.
Discussion
Medicinal plants contain many bioactive compounds and antioxidants that can be used as complementary or alternative medicines to treat gout. In fact, ~65–80% of people in developing countries use medicinal plants as remedies (World Health Organization, 2011). Plants are also important sources of medicines in the United States, where at least one plant-based ingredient is used in 25% of pharmaceutical prescriptions (Kumar and Azmi, 2014).
The xanthine oxidase inhibition assay is considered a gold standard to study the anti-gout potential of medicinal plants. Some plants and their phytochemicals are worthy of exploration as they can act as xanthine oxidase inhibitors. These compounds are also safe if an appropriate amount is taken and have few side effects (Rates, 2001; Abd Aziz et al., 2011). Previous studies have reported that five vegetables contain possible agents that can cause acute or chronic toxicities when consumed in large quantities or over a long period of time (Orech et al., 2005). Thus, it is very important for researchers to evaluate the toxicity of plants in in vitro and in vivo studies and clinical trials.
In this study, ~46 families of plants were identified and studied, both in vitro (n = 30) and in vivo (n = 24), for anti-gout activity (Tables 1, 2). Plants from the Asteraceae, Cucurbitaceae, Fabaceae, Lamiaceae, and Zingiberaceae families have been studied extensively. Momordica charantia, from the Cucurbitaceae, had the highest in percentage of xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of 96.5% at 100 μg/mL using 70% methanol extract (Alsultanee et al., 2014); the total phenolic content of this plant was 80.83 ± 0.30 mg gallic acid equivalent/100 g. Further phenolic compound analysis revealed the presence of phenolic compounds, including tannin, coumarin, flavonoid, and glycoside; among these, coumarine had the strongest inhibitory activity (97.29 %) against xanthine oxidase (Alsultanee et al., 2014). Other studies have suggested that this activity is due to the presence of bioactive phenolic compounds, such as polyphenols, tocopherols, and alkaloids, in the pulp of the plant (Tan et al., 2008). However, other plants in this family, such as Cucurbita pepo and Citrullus colocynthis, have lower xanthine oxidase inhibition values of 27.33% at 100 μg/mL and 14.40% at 200 μg/mL, respectively (Bustanji et al., 2011; Alsultanee et al., 2014).
In the Zingiberaceae family, Kaempferia galanga had the highest xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity at 100 μg/mL (90.6%), followed by Zingiber officinale (81.56%), Alpinia galanga (57.99%), and Curcuma longa (28.31%) (Nguyen et al., 2004; Yumita et al., 2013; Alsultanee et al., 2014). Yumita et al. (2013) also studied K. galanga but the results were in contrast to other studies (28.86%). These contrary results could be due to the different localities (Vietnam and Indonesia), although both studies employed similar drying methods. Moderate total phenolic content was found in Z. officinale, with a value of 62.18 ± 0.65 mg gallic acid equivalent/100 g (Alsultanee et al., 2014).
Plants from the Asteraceae family include Artemisia vulgaris, Blumea balsamifera, Chrysanthemum indicum, and Chrysanthemum sinense, of which C. indicum exhibited 95% xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity at 100 μg/mL. The isolated flavonoid compounds from the flower of C. indicum, namely luteolin and apigenin, may act as xanthine oxidase inhibitors (Kong et al., 2000). Moreover, C. sinense also had higher xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity (82.90%) at 100 μg/mL with an IC50 value of 5.1 μg/mL (Nguyen et al., 2004). Further isolation of the active compounds from the flower of C. sinense led to the identification of caffeic acid, luteolin, eriodictyol, and 1,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid, which, among them, luteolin displayed more potent inhibitory activity compared to the positive control allopurinol, with IC50 values of 1.3 and 2.5 μM, respectively (Nguyen et al., 2004). A. vulgaris also exhibited higher xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of 89.30% at 100 μg/mL (Nguyen et al., 2004).
Method of extraction is considered an important factor that affects xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity. The type of solvents used also contributes to differences in compounds extracted from the plants. El-Rahman and Abd–Elhak (2015) and Alsultanee et al. (2014) reported similar results on the ethanol and methanol extracts of Petroselinum crispum, with inhibition values of 82.57 and 28.63%, respectively. In contrast, Alsultanee et al. (2014) and Al-Azzawie and Abd (2015) reported that both the methanol and aqueous extracts of Z. officinale had similar xanthine oxidase inhibition percentages, with values of 81.56% and 87.97%, respectively. In addition, Azmi et al. (2012) reported that both methanol and ethanol had a higher capacity to extract xanthine oxidase inhibitors from all parts of plants; 25% of all plant extracts showed more than 50% inhibition using these two solvents compared to distilled water with only 20% of all plant extracts showing more than 50% xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity. In another study, methanol extract was found to be more active than hydroalcoholic and aqueous extracts (Nguyen et al., 2004; Umamaheswari et al., 2007). Even though methanol and ethanol extracts have higher rates of xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity, safety is the main concern of the pharmaceutical industry. Alcohol is a nervous system depressant that impairs the transmission of nerve signals, ultimately leading to respiratory suppression (Bailey and Bailey, 2000). Methanol is a highly poisonous solvent that can upset the acid-base balance of body (Azmi et al., 2012). Therefore, identifying a less toxic solvent is important.
Based on results of xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity analysis, the following plants showed more than 85% activity at 100 μg/mL: M. charantia (96.50%), C. indicum (95.00%), Cinnamomum cassia (93.00%), K. galanga (90.60%), A. vulgaris (89.30%), and Morinda elliptica (88.93%) (Kong et al., 2000; Nguyen et al., 2004; Alsultanee et al., 2014; Jamal et al., 2014). Of the other studied plants, three exhibited at least 80% activity, including C. sinense (82.90%), Z. officinale (81.56%), and B. balsamifera (80.90%) (Nguyen et al., 2004; Alsultanee et al., 2014; Jamal et al., 2014) at 100 μg/mL, while Olea europaea and Synsepalum dulcificum exhibited 80.00% activity at 250 mg/mL and 10 mg/mL, respectively (Al-Azzawie and Abd, 2015; Shi et al., 2016). IC50 values, the concentration at which half the xanthine oxidase activity is inhibited, were determined in a few studies. In this study, the lowest IC50 value was 0.111 μg/mL, indicating that B. balsamifera extract inhibited 50% of xanthine oxidase activity (Nessa et al., 2010).
A few studies further analyzed and isolated the bioactive compounds present in plants that exerted the highest xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity, allowing them to act as xanthine oxidase inhibitors by blocking the biosynthesis of uric acid from purine in the body (Unno et al., 2004). Please see the following examples: cardiac glycosides (Apaya and Chichioco-Hern, 2011), flavonoids (Nguyen et al., 2004; Roohbakhsh et al., 2009; Umamaheswari et al., 2009; Nessa et al., 2010; Apaya and Chichioco-Hern, 2011; Yumita et al., 2013), phenolics (Umamaheswari et al., 2009; Apaya and Chichioco-Hern, 2011; Sowndhararajan et al., 2012; Alsultanee et al., 2014; Al-Azzawie and Abd, 2015), anthocyanins (Al-Azzawie and Abd, 2015), tannins (Apaya and Chichioco-Hern, 2011), alkaloids (Apaya and Chichioco-Hern, 2011), proanthocyanidin A2 (Sheu et al., 2016), acetonylgeraniin A (Sheu et al., 2016), phalerin (Fariza et al., 2012), 4-allyl-1,3- hydroxychavicol (Murata et al., 2009), kaempferol (Fadzureena et al., 2013), terpenoids Apaya and Chichioco-Hern, 2011, luteolin (Kong et al., 2000; Nguyen et al., 2004; Flemmig et al., 2011), apigenin (Kong et al., 2000; Flemmig et al., 2011), caffeic acid (Nguyen et al., 2004; Flemmig et al., 2011), eriodictyol (Nguyen et al., 2004), oleuropein (Flemmig et al., 2011), luteolin-7-O–d-glucoside (Flemmig et al., 2011), and scopoletin (Ding et al., 2005). Until now, these bioactive compounds have not been further analyzed or developed into anti-gout medications.
Hyperuricemia has been modeled in pre-clinical studies by blocking uricase enzyme with potassium oxonate (Umamaheswari et al., 2007; Haidari et al., 2008). Administration of potassium oxonate (250 mg/kg) results in marked increases in serum uric acid level in rats (Shi et al., 2016). Several in vivo studies have demonstrated a reduction of serum uric acid levels in hyperuricemic rats. For example, administration of aqueous and alcoholic extracts of Phyllanthus emblica (200 and 400 mg/kg) reduced serum uric acid and xanthine oxidase enzyme levels in hyperuricemic rats while allopurinol was more potent in inhibiting xanthine oxidase enzyme (Sarvaiya et al., 2015). Similar results have also been reported by El-Rahman and Abd–Elhak (2015) for Allium ampeloprasum, Apium graveolens, and P. crispum using albino rats, where both extracts significantly reduced serum uric acid and lipid peroxidation and increased antioxidant enzyme activity levels at a dose of 5 g/kg. Phytochemical screening of the extracts also revealed their major constituents, which include phenolic (polyphenols, tocopherols, and alkaloids), flavonoids, and saponins that may act as xanthine oxidase inhibitors (Fejes et al., 2000; Zhou and Yu, 2006; Sreeramulu and Raghunath, 2010).
Some of the active compounds were isolated from the medicinal plants for investigating the underlying mechanisms of hypouricemic actions in rat model. Zeng et al. (2017) studied the bioavailability of scopoletin or 6-methoxy-7-hydroxycoumarin, a major active coumarin isolated from the stems of Erycibe obtusifolia and its hypouricemic effects in vivo. In this study, they encapsulated scopoletin into Soluplus micelles (Soluplus-based scopoletin micelles, Sco-Ms) in order to improve its oral bioavailability. To study the pharmacokinetics and biodistribution in vivo, the rats were orally administered with scopoletin suspension, physical mixtures of scopoletin and Soluplus (Sco-PM) and Sco-Ms at dose of 100 mg/kg scopoletin. At predetermined time intervals (2, 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 45, 60, 90, and 120 min), the blood samples were collected for determining the plasma concentrations of scopoletin. Sco-Ms showed significantly higher maximum plasma concentration, Cmax of 14,674.796 ± 2,997.147 μg/L than scopoletin and Sco-PM at 10 min. Orally administered Sco-Ms was rapidly absorbed than Sco-PM and scopoletin, with a time to reach maximum plasma concentration, tmax of 0.167 h while the time taken for plasma concentration of Sco-Ms to reduce by 50% of its initial value, t1/2 was 0.468 h. Sco-Ms showed CL value (ability to clear drug from the bloodstream which usually by hepatic metabolism or renal excretion) of 28.703 ± 3.482 L.h−1.kg−1. Interestingly, Sco-Ms was found to have higher scopoletin concentration in liver than the scopoletin suspension which would be importance for the inhibition of hepatic xanthine oxidase activity. The hepatic and serum xanthine oxidase activity of hyperuricemic rats were investigated in order to determine the possible mechanism of the anti-hyperuricemic effect of Sco-MS. Based on the result obtained, the oral administration of Sco-Ms at dose of 300 mg/kg reduced the serum uric acid concentration to the normal level. In addition, Zhang et al. (2016) studied the biodistribution and hypouricemic efficacy of morin (3,5,7,2′,4′-pentahydroxyflavone), a yellow pigment present in the plants from the Moraceae family. In this study, they tested a novel self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system based on morin-phospholipid complex (MPC-SNEDDS) in vivo which improved the oral bioavailability of morin. After the administration of morin suspension, the concentration of morin in liver was markedly higher than other tissues (e.g., heart, spleen, lung, and kidney) at 0.5, 1, and 4 h. Moreover, the morin concentration in the liver at 0.5 h after orally administered with MPC-SNEDDS (1,096 μg/mg) was three-fold higher than morin suspension (252 μg/mg) and thus, MPC-SNEDDS possessed more potent inhibitory effect on hepatic xanthine oxidase activity than morin. As expected, MPC-SNEDDS reduced serum uric acid level of hyperuricemic rats (145 μmol/l) to normal (45 μmol/l) at 6 h after oral administration. Hence, the hypouricemic effect of the active compounds (e.g., morin and scopoletin) may therefore be explained, at least in part, by a lowering of xanthine oxidase activity in rat liver.
Another possible mechanism to reduce plasma uric acid concentration is to inhibit the reabsorption of urate in renal tissue. In some studies, the mRNA and protein expression levels of the transporters responsible for urate reabsorption are examined in order to explore the underlying molecular mechanisms of uricosuric effects of active compounds or medicinal plants. For instance, mangiferin, an isolated compound from the leaves of Mangifera indica significantly decreased the mRNA and protein levels of URAT1 and GLUT9 in kidney of hyperuricemic rats, suggesting that it possessed the uricosuric action, which was associated to inhibiting reabsorption of urate (Yang et al., 2015). In other study, Dimocarpus longan Lour seed decreased GLUT9 protein level from the liver of the rat model (Hou et al., 2012). The ethanol extract of Ramulus mori, the branch of Morus alba possessed the uricosuric effects in hyperuricemic mice by down-regulating renal mURAT1 and mGLUT9 expression and up-regulating renal mOAT1 expression, which contributed to the enhancement of urate excretion and reduction of serum urate level as well as improved renal dysfunction in hyperuricemic rats by up-regulating renal expression of mOCT1, mOCT2, mOCTN1, and mOCTN2 (Shi et al., 2012). In cell culture model, stably hURAT1 transfected human epithelial kidney cell line was used by Zhang et al. (2017) to evaluate the ability of tigogenin (active metabolites of dioscin) in inhibiting 14C-uric acid uptake via hURAT1 and the result showed that this compound possessed significant inhibitory effect from 10 to 100 μM with a concentration-dependent manner and the uric acid permeability was significantly reduced to 60% at 100 μM.
The results of standard in vitro screening assays provided useful information to guide the next stage of investigation such as testing the plant extract in rodents. Administration of ethyl acetate fraction from a butanol extract of S. dulcificum resulted in 80% of xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity at 10 mg/mL; the effects of butanol extract from this fruit was similar to the results of an in vivo study using allopurinol (Shi et al., 2016). Al-Azzawie and Abd (2015) showed that the Z. officinale extract had the highest xanthine oxidase inhibition in vitro (87.97%) at 250 mg/mL; at both doses (100 and 250 mg/kg), ginger extract significantly reduced mean serum uric acid levels and inhibited xanthine oxidase activity in hyperuricemia rats.
Some studies have shown that different parts of the same plants can contribute differently to effects on uric acid levels. For example, methanol extracted from the D. longan flowers had a greater effect on lowering uric acid compared to the seeds due to the 10 phytochemicals in the flowers. Further analysis revealed that proanthocyanidin A2 and acetonylgeraniin have higher inhibitory activity against xanthine oxidase compared to allopurinol (Sheu et al., 2016). In addition, the ethanol extract from Hibiscus sabdariffa calyx, as well as ethyl acetate and water fractions, reduced uric acid levels in male Sprague-Dawley rats and Wistar rats, where the ethyl acetate fraction at a dose of 6.25 mg/kg demonstrated the best effect on uricosuric compared to water fraction and ethanol. Phytochemical screening of the ethanol extract of this plant also revealed the presence of flavonoid, saponin, polyphenol, and quinone (Wahyuningsih et al., 2016b). Monosodium urate crystal-induced inflammation in mice or rats is commonly used to study the anti-gout effect of plant extracts (Sabina and Rasool, 2008). Oral administration of triphala significantly reduced paw diameter at a dose of 1 g/kg body weight (Sabina and Rasool, 2008). Extracts from the M. indica leaf also significantly reduced ankle swelling in monosodium urate crystal-induced gout arthritis at a dose of 200 mg/kg across 8 h (Jiang et al., 2012).
In this study, we evaluated whether the doses used in in vitro and in vivo studies are physiologically relevant. In one study, administration of 250 mg/mL of Z. officinale extract resulted in high levels of xanthine oxidase inhibiton (87.97%) in vitro, while 250 mg/kg exhibited 57.14% of xanthine oxidase inhibition and significantly reduced serum uric acid levels (Al-Azzawie and Abd, 2015). In another study, S. dulcificum extract administration suppressed xanthine oxidase activity in MSU-treated RAW264.7 macrophages at 500 μg/mL, while a 1000 mg/kg dose in vivo reduced uric acid levels in rats (Shi et al., 2016). Methanol extracts from Phyllanthus niruri resulted in 67.66% inhibition at 100 μg/mL in an in vitro study and caused significant inhibition (76.84%) of xanthine oxidase activity at a 50 mg/kg dose in vivo (Murugaiyah and Chan, 2009). The results from these studies were very similar results in inhibiting xanthine oxidase activity, suggesting that the doses used were physiologically relevant.
Allopurinol, common drug used for gout patients, is approved by the US FDA for doses up to 800 mg/day for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout (Chao and Terkeltaub, 2009). One study reported that gout patients attained target serum uric acid levels of <360 mmol/L at 300 mg/day of allopurinol, and that this dose was increased up to 600 mg/day in some patients; favorable results were observed as the dose increased and it was well tolerated, such that the therapeutic goal was achieved in 92.5% of patients. These doses are therefore well tolerated in those with well-preserved renal function (RadakPerović and ZlatkovićŠvenda, 2013). However, febuxostat, a non-purine selective xanthine oxidase inhibitor, at a daily dose of 80 mg or 120 mg was reported to be more effective than allopurinol (300 mg) in lowering serum urate levels (Becker et al., 2005).
Many plants used in in vivo studies, including Peperomia pellucida, Mangifera indica, Jatropha curcas, Epiphyllum oxypetalum, Zingiber zerumbet, Emblica officinalis, and Piper nigrum, have exhibited anti-inflammatory activities (Mujumdar and Misar, 2004; Mutee et al., 2010; Sabina et al., 2011; Somchit et al., 2012; Dandekar et al., 2015). In addition, zerombone, which is found in the rhizome of Zingiber zerumbet, may act as an anti-inflammatory agent similar to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Somchit et al., 2012). It has been proposed that phenolic compounds, such as anthocyanins and quercetin, which are found abundantly in certain plants, can inhibit xanthine oxidase activity, as they are structurally related to xanthine (Mo et al., 2007). Additional studies must be conducted on the possible mechanisms of the anti-gout activity of these medicinal plants.
In addition, there are also human clinical trials performed in gout using plant based drugs. For instance, Prasongwatana et al. (2008) investigated the effects of roselle (H. sabdariffa) on urinary excretions of uric acid in human models with and without renal-stone history where they found the mean levels of uric acid clearance, uric acid excretion and fractional excretion of uric acid increased significantly after consuming H. sabdariffa tea and then decreased to baseline level (control) at the end of the washout period in both groups, suggesting its uricosuric effect provides a long-term benefit of hyperuricemia in gouty subjects. However, the chemical constituents responsible for the anti-gout effects in this plant yet to be fully elucidated. Furthermore, the same trend of results were observed in Orthosiphon stamineus tea where the consumption of this tea caused an increasing of uric acid excretion (Premgamone et al., 2001). It is well understood that the increase of uric acid excretion may result in urolithiasis (development of stones in the kidney due to supersaturation of the urine with stone-forming salts). As reviewed by Butterweck and Khan (2009), they gathered the information of few plants that have been studied for the management of urolithiasis such as H. sabdariffa, P. niruri, O. stamineus, Andrographis paniculata, Sambucus nigra, Solidago virgaurea, and Dolichos biflores. For instance, Nishiura et al. (2004) demonstrated that P. niruri extract reduced the uric acid level as well as normalized the urinary calcium levels in calcium stone forming patients. As mentioned above, many plants had been studied for the anti-urolithiasis rather than anti-gout activities. Furthermore, there is also a very limited number of clinical studies for the anti-gout activity as compared to in vitro and in vivo studies. To the best of our knowledge, there are no human studies on the anti-gout activity specifically to xanthine oxidase inhibitor mechanism. It is further suggested that pharmacologist and clinical investigators to conduct larger randomized clinical trials of longer duration in order to determine the efficacy of plant based drugs in the treatment of gout. The doses of the plant extract, method of extract preparation, and extraction solvent must also be taken into consideration.
Conclusion
This review summarized the potential of Malaysian medicinal plants treat gout based on research conducted over the last 17 years. Taking all results into consideration, M. charantia, C. indicum, C. cassia, K. galanga, A. vulgaris, and M. elliptica were found to have the highest xanthine oxidase inhibitory potential in vitro. This review suggests further research on the natural xanthine oxidase inhibitors, especially in in vivo studies, clinical studies, investigation of active compounds, safety of the plants as well as the pharmacokinetic and bioavailability studies, which remain to be elucidated.
Author Contributions
FA: preparing and writing the manuscript; MA: initiate the process of the review paper; AR, NA, SS, SE: check and comment the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The reviewer MK and handling Editor declared their shared affiliation.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia (UTHM) for providing internal research grant (Vot No. U758; E15501; U673; U908) to fund this research.
References
Abd Aziz, S. M., Low, C. N., Chai, L. C., Abd Razak, S. S. N., Selamat, J., Son, R., et al. (2011). Screening of selected Malaysian plants against several food borne pathogen bacteria. Int. Food Res. J. 18, 1141–1147.
Al-Azzawie, H. F., and Abd, S. A. (2015). Effect of some plant extracts on serum uric acid levels and xanthine oxidase activity in vitro and in oxonate-induced hyperuricemic rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Med. Res. 2, 55–61.
Alsultanee, I. R., Ewadh, M. J., and Mohammed, M. F. (2014). Novel natural anti gout medication extract from Momordica charantia. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 4, 16–23.
Apaya, K. L., and Chichioco-Hern, C. L. (2011). Xanthine oxidase inhibition of selected Philippine medicinal plants. J. Med. Plant Res. 5, 289–292.
Arafat, O. M., Tham, S. Y., Sadikun, A., Zhari, I., Haughton, P. J., and Asmawi, M. Z. (2008). Studies on diuretic and hypouricemic effects of Orthosiphon stamineus methanol extracts in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 118, 354–360. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2008.04.015
Azmi, S. M. N., Jamal, P., and Amid, A. (2012). Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity from potential Malaysian medicinal plant as remedies for gout. Int. Food Res. J. 19, 159-165.
Bailey, P. S. Jr., and Bailey, C. A. (2000). Organic Chemistry: A Brief Survey of Concepts and Applications. New Jersey, NJ: Pearson Education International; Prentice-Hall Inc
Becker, M. A., Schumacher, H. R. Jr., Wortmann, R. L., MacDonald, P. A., Eustace, D., Palo, W. A., et al. (2005). Febuxostat compared with allopurinol in patients with hyperuricemia and gout. N. Engl. J. Med. 353, 2450–2461. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050373
Bustanji, Y., Hudaib, M., Tawaha, K., Mohammad, M. K., Almasri, I., Hamed, S., et al. (2011). In vitro xanthine oxidase inhibition by selected Jordanian medicinal plants. Jordan J. Pharm. Sci. 4, 49–56.
Butterweck, V., and Khan, S. R. (2009). Herbal medicines in the management of urolithiasis: alternative or complementary? Planta Med. 75, 1095–1103. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1185719
Chao, J., and Terkeltaub, R. (2009). A critical reappraisal of allopurinol dosing, safety, and efficacy for hyperuricemia in gout. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 11, 135–140. doi: 10.1007/s11926-009-0019-z
Dalbeth, N., Lauterio, T. J., and Wolfe, H. R. (2014). Mechanism of action of colchicine in the treatment of gout. Clin. Ther. 36, 1465–1479. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.07.017
Dandekar, R., Fegade, B., and Naik, A. (2015). Evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity of alcohol and aqueous extract of Epiphyllum oxypetalum leaves. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 4, 851–858.
Ding, Z., Dai, Y., and Wang, Z. (2005). Hypouricemic action of scopoletin arising from xanthineoxidase inhibition and uricosuric activity. Planta Med. 71, 183–185. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-837789
El-Rahman, H. S., and Abd–Elhak, N. A. (2015). Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity and antigout of celery leek parsley and molokhia. Adv. Biochem. 3, 40–50. doi: 10.11648/j.ab.20150304.11
Enomoto, A., Kimura, H., Chairoungdua, A., Shigeta, Y., Jutabha, P., Cha, S. H., et al. (2002). Molecular identification of a renal urate–anion exchanger that regulates blood urate levels. Nature 417, 447–452. doi: 10.1038/nature742
Fadzureena, J., Mazura, M. P., Adiana, M. A., and Hani, I. B. (2013). “An investigation into the inhibitory effect of Senna alata L. leaf extract as well as its isolated compound on xanthine oxidase assay,” in Proceedings of the Conference on Forestry and Forest Products Research (Kuala Lumpur), 262.
Falasca, G. F. (2006). Metabolic diseases: gout. Clin. Dermatol. 24, 498–508. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2006.07.015
Fariza, I., Fadzureena, J., Zunoliza, A., Chuah, A. L., Pin, K. Y., and Adawiah, I. (2012). Anti-inflammatory activity of the major compound from methanol extract of Phaleria macrocarpa leaves. J. Appl. Sci. 12, 1195–1198. doi: 10.3923/jas.2012.1195.1198
Fejes, S. Z., Blazovics, A., Lemberkovics, E., Petri, G., Szöke, E., and Kery, A. (2000). Free radical scavenging and membrane protective effects of methanol extracts from Anthriscus cerefolium L.(Hoffm.) and Petroselinum crispum (Mill.) Nym. ex AW Hill. Phytother. Res. 14, 362–365. doi: 10.1002/1099-1573(200008)14:5<362::AID-PTR554>3.0.CO;2-G
Flemmig, J., Kuchta, K., Arnhold, J., and Rauwald, H. W. (2011). Olea europaea leaf (Ph. Eur.) extract as well as several of its isolated phenolics inhibit the gout-related enzyme xanthine oxidase. Phytomedicine 18, 561–566. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2010.10.021
Gliozzi, M., Malara, N., Muscoli, S., and Mollace, V. (2016). The treatment of hyperuricemia. Int. J. Cardiol. 213, 23–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.08.087
Haidari, F., Rashidi, M. R., Eshraghian, M. R., Mahboob, S. A., Shahi, M. M., and Keshavarz, S. A. (2008). Hypouricemic and antioxidant activities of Allium cepa Lilliaceae and quercetin in normal and hyperuricemic rats. Saudi Med. J. 29, 1573–1579.
Hendriani, R., Sukandar, E. Y., Anggadiredja, K., and Sukrasno (2016). In vitro evaluation of xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of selected medicinal plants. Int. J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 8, 235–238.
Hou, C. W., Lee, Y. C., Hung, H. F., Fu, H. W., and Jeng, K. C. (2012). Longan seed extract reduces hyperuricemia via modulating urate transporters and suppressing xanthine oxidase activity. Am. J.Chin. Med. 40, 979–991. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X12500723
Ichida, K., Matsuo, H., Takada, T., Nakayama, A., Murakami, K., Shimizu, T., et al. (2012). Decreased extra-renal urate excretion is a common cause of hyperuricemia, Nat. Commun. 3:764. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1756
Jamal, P., Azmi, S. M., Amid, A., Salleh, H. M., and Hashim, Y. Z. (2014). Development and improvement of anti-gout property from aqueous-methanol extract of Morinda elliptica using central composite design. Adv. Environ. Biol. 8, 734–743.
Jiang, Y., You, X. Y., Fu, K. L., and Yin, W. L. (2012). Effects of extract from Mangifera indica leaf on monosodium urate crystal-induced gouty arthritis in rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012:967573. doi: 10.1155/2012/967573.
Jothy, S. L., Zuraini, Z., and Sasidharan, S. (2011). Phytochemicals screening, DPPH free radical scavenging and xanthine oxidase inhibitiory activities of Cassia fistula seeds extract. J. Med. Plants Res. 5, 1941–1947.
Kong, L. D., Cai, Y., Huang, W. W., Cheng, C. H., and Tan, R. X. (2000). Inhibition of xanthine oxidase by some Chinese medicinal plants used to treat gout. J. Ethnopharmacol. 73, 199–207. doi: 10.1016/S0378-8741(00)00305-6
Kong, L. D., Yang, C., Ge, F., Wang, H. D., and Guo, Y. S. (2004). A Chinese herbal medicine Ermiao wan reduces serum uric acid level and inhibits liver xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 93, 325–330. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.04.008
Kulip, J. (2003). An ethnobotanical survey of medicinal and other useful plants of Muruts in Sabah, Malaysia. Telopea 10, 81–98. doi: 10.7751/telopea20035608
Kumar, A., and Azmi, W. (2014). Phytomedicine: a novel alternative for treatment of gout. Ann. Phys. Med. 3, 80–88.
Kuo, C. F., Grainge, M. J., Zhang, W., and Doherty, M. (2015). Global epidemiology of gout: prevalence, incidence and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 11, 649–662. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.91
Kuo, C. Y., Kao, E. S., Chan, K. C., Lee, H. J., Huang, T. F., and Wang, C. J. (2012). Hibiscus sabdariffa L. extracts reduce serum uric acid levels in oxonate-induced rats. J. Funct. Foods. 4, 375–381. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2012.01.007
Matsuo, H., Chiba, T., Nagamori, S., Nakayama, A., Domoto, H., Phetdee, K., et al. (2008). Mutations in glucose transporter 9 gene SLC2A9 cause renal hypouricemia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 83, 744–751. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.11.001
Mirghani, M. E. S., Liyana, Y., and Parveen, J. (2012). Bioactivity analysis of lemongrass (Cymbopogan citratus) essential oil. Int. Food. Res. J. 19, 569–575.
Mo, S. F., Zhou, F., Lv, Y. Z., Hu, Q. H., Zhang, D. M., and Kong, L. D. (2007). Hypouricemic action of selected flavonoids in mice: structure–activity relationships. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 30, 1551–1556. doi: 10.1248/bpb.30.1551
Mohamed, D. A., and Al-Okbi, S. Y. (2008). Evaluation of anti-gout activity of some plant food extracts. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 58, 389–395.
Mohd, A., Das Gupta, E., Loh, Y. L., Gandhi, C., D'Souza, B., and Gun, S. C. (2011). Clinical characteristics of gout: a hospital case series. Malaysian Fam. Phys. 6, 72–73.
Mujumdar, A. M., and Misar, A. V. (2004). Anti-inflammatory activity of Jatropha curcas roots in mice and rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 90, 11–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2003.09.019
Murata, K., Nakao, K., Hirata, N., Namba, K., Nomi, T., Kitamura, Y., et al. (2009). Hydroxychavicol: a potent xanthine oxidase inhibitor obtained from the leaves of betel, Piper betle. J. Nat. Med. 63, 355–359. doi: 10.1007/s11418-009-0331-y
Murugaiyah, V., and Chan, K. L. (2009). Mechanisms of antihyperuricemic effect of Phyllanthus niruri and its lignan constituents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 124, 233–239. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.04.026
Mutee, A. F., Salhimi, S. M., Yam, M. F., Lim, C. P., Abdullah, G. Z., Ameer, O. Z., et al. (2010). In vivo anti-inflammatory and in vitro antioxidant activities of Peperomia pellucida. Int. J. Pharmacol. 6, 686–690. doi: 10.3923/ijp.2010.686.690
Nessa, F., Ismail, Z., and Mohamed, N. (2010). Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities of extracts and flavonoids of the leaves of Blumea balsamifera. Pharm. Biol. 48, 1405–1412. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2010.487281
Nguyen, M. T. T., Awale, S., Tezuka, Y., Le Tran, Q., Watanabe, H., and Kadota, S. (2004). Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of Vietnamese medicinal plants. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 27, 1414–1421. doi: 10.1248/bpb.27.1414
Nile, S. H., and Khobragade, C. N. (2011). In vitro anti-inflammatory and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of Tephrosia purpurea shoot extract. Nat. Prod. Commun. 6, 1437–1440.
Nile, S. H., Kumar, B., and Park, S. W. (2013). In vitro evaluation of selected benzimidazole derivatives as an antioxidant and xanthine oxidase inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 82, 290–295. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12141
Nile, S. H., and Park, S. W. (2014). HPTLC analysis, antioxidant and antigout activity of Indian plants. Iran, J. Pharm. Res. 13, 531.
Nishiura, J. L., Campos, A. H., Boim, M. A., Heilberg, I. P., and Schor, N. (2004). Phyllanthus niruri normalizes elevated urinary calcium levels in calcium stone forming (CSF) patients. Urol. Res. 32, 362–366. doi: 10.1007/s00240-004-0432-8
Offermanns, S., and Rosenthal, W. (2008). Encyclopedia of Molecular Pharmacology. New York, NY: Springer.
Orech, F. O., Akenga, T., Ochora, J., Friis, H., and Aagaard-Hansen, J. (2005). Potential toxicity of some traditional leafy vegetables consumed in Nyang'oma Division, Western Kenya. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 5, 1–13.
Osman, N. I., Sidik, N. J., Awal, A., Adam, N. A. M., and Rezali, N. I. (2016). In vitro xanthine oxidase and albumin denaturation inhibition assay of Barringtonia racemosa L. and total phenolic content analysis for potential anti-inflammatory use in gouty arthritis. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 5, 343–349. doi: 10.5455/jice.20160731025522
Pacher, P., Nivorozhkin, A., and Szabó, C. (2006). Therapeutic effects of xanthine oxidase inhibitors: renaissance half a century after the discovery of allopurinol. Pharmacol. Rev. 58, 87–114. doi: 10.1124/pr.58.1.6
Palu, A., Deng, S., West, B., and Jensen, J. (2009). Xanthine oxidase inhibiting effects of noni (Morinda citrifolia) fruit juice. Phytother. Res. 23, 1790–1791. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2842
Pillinger, M. H., Rosenthal, P., and Abeles, A. M. (2007). Hyperuricemia and gout: new insights into pathogenesis and treatment. Bull. NYU Hosp. Jt. Dis. 65, 215–215.
Prasongwatana, V., Woottisin, S., Sriboonlue, P., and Kukongviriyapan, V. (2008). Uricosuric effect of Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa) in normal and renal-stone former subjects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 117, 491–495. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2008.02.036
Premgamone, A., Sriboonlue, P., Disatapornjaroen, W., Maskasem, S., Sinsupan, N., and Apinives, C. (2001). A long-term study on the efficacy of a herbal plant, Orthosiphon grandiflorus, and sodium potassium citrate in renal calculi treatment. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health. 32, 654–660.
Sri-Wahjuni Putra-Manuaba, I. B., Rahayu-Artini, N. P., and Wahyu-Dwijani, S. (2012). Uric acid inhibition activity of Annona muricata L. leave extract in hyperuricemia induced wistar rat. Adv. Pure and Appl. Chem. 2, 86–90.
RadakPerović, M., and ZlatkovićŠvenda, M. (2013). The efficacy and tolerability of allopurinol dose escalation in patients with gout. Srpski arhiv za celokupno lekarstvo, 141, 333–336. doi: 10.2298/SARH1306333R
Rajendran, R., and Krishnakumar, E. (2010). Anti-arthritic activity of Premna serratifolia Linn., wood against adjuvant induced arthritis. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2, 101–106.
Raju, R., Joseph, S., Scria, S., Mathews, S. M., and Umamheshwari, M. (2012). Effect of the fractions of Erythrina stricta leaf extract on serum urate levels and Xo/Xdh activities in oxonate-induced hyperuricaemic mice. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2, 89–94.
Rates, S. M. K. (2001). Plants as source of drugs. Toxicon 39, 603–613. doi: 10.1016/S0041-0101(00)00154-9
Roddy, E., and Doherty, M. (2010). Gout. Epidemiology of gout. Arthritis Res. Ther. 12:223. doi: 10.1186/ar3199
Roohbakhsh, A., Shamsara, J., Khayyat, M. H., and Karimi, G. (2009). Inhibition of xanthine oxidase by some Iranian plant remedies used for gout. Pharmacologyonline. 3, 1031–1036.
Sabina, E. P., Nagar, S., and Rasool, M. (2011). A role of piperine on monosodium urate crystal-induced inflammation—an experimental model of gouty arthritis. Inflammation 34, 184–192. doi: 10.1007/s10753-010-9222-3
Sabina, E. P., and Rasool, M. (2008). An in vivo and in vitro potential of Indian ayurvedic herbal formulation Triphala on experimental gouty arthritis in mice. Vasc. Pharmacol. 48, 14–20. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2007.11.001
Sarvaiya, V. N., Sadariya, K. A., Pancha, P. G., Thaker, A. M., Patel, A. C., and Prajapati, A. S. (2015). Evaluation of antigout activity of Phyllanthus emblica fruit extracts on potassium oxonate-induced gout rat model. Vet. World 8, 1230–1236. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2015.1230-1236
Sheu, S. Y., Fu, Y. T., Huang, W. D., Chen, Y. A., Lei, Y. C., Yao, C. H., et al. (2016). Evaluation of xanthine oxidase inhibitory potential and in vivo hypouricemic activity of Dimocarpus longan lour. extracts. Pharmacogn. Mag. 12, 206–212. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.182176
Shi, Y. C., Lin, K. S., Jhai, Y. F., Lee, B. H., Han, Y., Cui, Z., et al. (2016). Miracle fruit (Synsepalum dulcificum) exhibits as a novel anti-hyperuricaemia agent. Molecules 21:140. doi: 10.3390/molecules21020140
Shi, Y. W., Wang, C. P., Wang, X., Zhang, Y. L., Liu, L., Wang, R. W., et al. (2012). Uricosuric and nephroprotective properties of Ramulus Mori ethanol extract in hyperuricemic mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 143, 896–904. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.08.023
Somchit, M. N., Mak, J. H., Bustamam, A. A., Zuraini, A., Arifah, A. K., Adam, Y., et al. (2012). Zerumbone isolated from Zingiber zerumbet inhibits inflammation and pain in rats. J. Med. Plants Res. 6, 177–180. doi: 10.5897/JMPR10.492
Sowndhararajan, K., Joseph, J. M., and Rajendrakumaran, D. (2012). In vitro xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of methanol extracts of Erythrina indica Lam. leaves and stem bark. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2, 1415–S1417. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(12)60428-6
Sreeramulu, D., and Raghunath, M. (2010). Antioxidant activity and phenolic content of roots, tubers and vegetables commonly consumed in India. Food Res. Int. 43, 1017–1020. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2010.01.009
Srivastava, S., Lal, V. K., and Pant, K. K. (2012). Polyherbal formulations based on Indian medicinal plants as antidiabetic phytotherapeutics. Phytopharmacology 2, 1–5.
Stamp, L. K., O'Donnell, J. L., and Chapman, P. T. (2007). Emerging therapies in the long-termmanagement of hyperuricaemia and gout. Intern. Med. J. 37, 258–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.2007.01315.x
Strazzullo, P., and Puig, J. G. (2007). Uric acid and oxidative stress: relative impact on cardiovascular risk. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 17, 409–414. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2007.02.011
Sunarni, T., Leviana, F., Fidrianny, I., Iwo, M. I., and Wirasutisna, K. R. (2015). Antihyperuricemic activity of four plants Annonaceae using hyperuricemic rats model and enzyme assay. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 8, 250–253.
Sungthong, B., Manok, S., Sato, H., and Sato, V. H. (2016). Effects of Aquilaria Crassna on xanthine oxidase activity in vitro and hyperuricemic mice. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 78, 547–552. doi: 10.4172/pharmaceutical-sciences.1000151
Tan, M. J., Ye, J. M., Turner, N., Hohnen-Behrens, C., Ke, C. Q., Tang, C. P., et al. (2008). Antidiabetic activities of triterpenoids isolated from bitter melon associated with activation of the AMPK pathway. Chem. Biol. 15, 263–273. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.01.013
Tapsell, L. C., Hemphill, I., Cobiac, L., Sullivan, D. R., Fenech, M., Patch, C. S., et al. (2006). Supplement-health benefits of herbs and spices: the past, the present, the future. Med. J. Aust. 185, 4–24.
Tausche, A. K., Jansen, T. L., Schröder, H. E., Bornstein, S. R., Aringer, M., and Müller-Ladner, U. (2009). Gout—current diagnosis and treatment. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 106, 549–555. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2009.0549
Teh, C. L., Chew, K. F., and Ling, G. R. (2014). Acute gout in hospitalized patients in Sarawak general hospital. Med. J. Malaysia 69, 126–128.
Triggiani, V., Resta, F., Guastamacchia, E., Sabbà, C., Licchelli, B., Ghiyasaldin, S., et al. (2006). Role of antioxidants, essential fatty acids, carnitine, vitamins, phytochemicals and trace elements in the treatment of diabetes mellitus and its chronic complications. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 6, 77–93. doi: 10.2174/187153006776056611
Tu, S. F., Liu, R. H., Cheng, Y. B., Hsu, Y. M., Du, Y. C., El-Shazly, M., et al. (2014). Chemical constituents and bioactivities of Clinacanthus nutans aerial parts. Molecules 19, 20382–20390. doi: 10.3390/molecules191220382
Umamaheswari, M., Asokkumar, K., Sivashanmugam, A. T., Remyaraju, A., Subhadradevi, V., and Ravi, T. K. (2009). In vitro xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of the fractions of Erythrina stricta Roxb. J. Ethnopharmacol. 124, 646–648. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.05.018
Umamaheswari, M., AsokKumar, K., Somasundaram, A., Sivashanmugam, T., Subhadradevi, V., and Ravi, T. K. (2007). Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of some Indian medical plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 109, 547–551. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.08.020
Unno, T., Sugimoto, A., and Kakuda, T. (2004). Xanthine oxidase inhibitors from the leaves of Lagerstroemia speciosa (L.) Pers. J. Ethnopharmacol. 93, 391–395. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.04.012
Wahyuningsih, S., Sukandar, E. Y., and Sukrasno (2016a). Antihyperuricemia activity of the ethanol extract of Roselle calyx and its fraction (Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn) on male wistar rats. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 8, 278–280.
World Health Organization (2011). The World Traditional Medicines Situation, in Traditional Medicines: Global Situation, Issues and Challenges. Geneva 3, 1–14.
Wahyuningsih, S., Sukandar, E. Y., and Sukrasno (2016b). In vitro xanthine oxidase inhibitor activity of ethanol extract and fraction roselle calyx (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.). Int. J. Pharma. Clin. Res. 94, 5–35.
Wang, Y., Zhu, J. X., Kong, L. D., Yang, C., Cheng, C. H. K., and Zhang, X. (2004). Administration of procyanidins from grape seeds reduces serum uric acid levels and decreases hepatic xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase activities in oxonate-treated mice. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 94, 232–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2004.pto940506.x
Wong, Y. P., Ng, R. C., Chuah, S. P., Koh, R. Y., and Ling, A. P. K. (2014). “Antioxidant and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities of Swietenia macrophylla and Punica granatum,” in International Conference on Biological, Environment and Food Engineering (Bali).
Yang, H., Gao, L., Niu, Y., Zhou, Y., Lin, H., Jiang, J., et al. (2015). Mangiferin inhibits renal urate reabsorption by modulating urate transporters in experimental hyperuricemia. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38, 1591–1598. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b15-00402
Yan, M., An, Y. T., Li, J., Wu, Z. Z., and Wang, T. (2014). Regulatory effect of leonurus extracts on hyperuricemia in rats. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 39, 4856–4859.
Yumita, A., Suganda, A. G., and Sukandar, E. Y. (2013). Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of some Indonesian medicinal plants and active fraction of selected plants. Int. J. Pharmacy Pharm. Sci. 5, 293–296.
Zeng, Y. C., Li, S., Liu, C., Gong, T., Sun, X., Fu, Y., et al. (2017). Soluplus micelles forimproving the oral bioavailability of scopoletin and their hypouricemic effect in vivo. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 38, 424–433. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.126
Zhang, J., Shuai, X., Li, J., Xiang, N., Gong, T., and Zhang, Z. (2016). Biodistribution, hypouricemic efficacy and therapeutic mechanism of morin phospholipid complex loaded self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems in an experimental hyperuricemic model in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 68, 14–25. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12492
Zhang, Y., Jin, L., Liu, J., Wang, W., Yu, H., Li, J., et al. (2017). Regulation mechanism of Dioscin on uric acid excretion. J. Ethnopharmacol. 214, 29–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.12.004
Keywords: xanthine oxidase inhibition, anti-gout, phytochemical, Malaysian medicinal plants, in vitro, in vivo
Citation: Abu Bakar FI, Abu Bakar MF, Rahmat A, Abdullah N, Sabran SF and Endrini S (2018) Anti-gout Potential of Malaysian Medicinal Plants. Front. Pharmacol. 9:261. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00261
Received: 28 September 2017; Accepted: 08 March 2018;
Published: 23 March 2018.
Edited by:
Per-Johan Jakobsson, Karolinska Institute (KI), SwedenReviewed by:
Marina Korotkova, Karolinska Institute (KI), SwedenSoon Yew Tang, University of Pennsylvania, United States
Copyright © 2018 Abu Bakar, Abu Bakar, Rahmat, Abdullah, Sabran and Endrini. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mohd F. Abu Bakar, ZmFkemVsbHlAdXRobS5lZHUubXk=
Asmah Rahmat, YXNtYWhyQHV0aG0uZWR1Lm15
 Fazleen I. Abu Bakar
Fazleen I. Abu Bakar Mohd F. Abu Bakar
Mohd F. Abu Bakar Asmah Rahmat1*
Asmah Rahmat1* Siti F. Sabran
Siti F. Sabran