- 1Department of Pharmacy, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Effective Components of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun, China
Coptis, a traditional medicinal plant, has been used widely in the field of traditional Chinese medicine for many years. More recently, the chemical composition and bioactivity of Coptis have been studied worldwide. Berberine is a main component of Rhizoma Coptidis. Modern medicine has confirmed that berberine has pharmacological activities, such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antimicrobial, hypolipidemic, and blood pressure-lowering effects. Importantly, the active ingredient of berberine has clear inhibitory effects on various cancers, including colorectal cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, liver cancer, and cervical cancer. Cancer, ranked as one of the world’s five major incurable diseases by WHO, is a serious threat to the quality of human life. Here, we try to outline how berberine exerts antitumor effects through the regulation of different molecular pathways. In addition, the berberine-mediated regulation of epigenetic mechanisms that may be associated with the prevention of malignant tumors is described. Thus, this review provides a theoretical basis for the biological functions of berberine and its further use in the clinical treatment of cancer.
Introduction
Natural medicine plays a very important role in novel drug discovery (Zhang et al., 2013; Zhang L. et al., 2017). In recent years, many natural products have been confirmed to play an important role in cancer prevention and therapy (Tao et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2015, 2016; Meng et al., 2018). Coptis chinensis is a valuable Chinese medicine used commonly in China. The medicinal parts are the dried rhizome of Coptis chinensis Franch., Coptis deltoidea C.Y.Cheng, and P.K.Hsiao, or Coptis teeta Wall (Wang et al., 2015b). It has been reported that Coptis exerts antibacterial, immune-enhancing, anti-ulcer, hypoglycemic, detoxifying, antitumor, and other pharmacological effects (Imenshahidi and Hosseinzadeh, 2016). Coptis is mainly used for the adjuvant treatment of depression, coronary heart disease, diabetes, liver cancer, and other malignant tumors. There are several active ingredients of Coptis chinensis, such as berberine (BBR), palmatine, coptisine, jatrorrhizine, worenine, columbamine, cedarone, obakunone, obakulactone, magnoflorine, and ferulic acid; berberine is the main bioactive component of Coptis chinensis and is present at a content of 5.20–7.69%. Consequently, it has become one of the natural small-molecule drugs used commonly in the clinical setting treatment for chronic disease such like diabetes (Cicero and Baggioni, 2016; Tabeshpour et al., 2017).
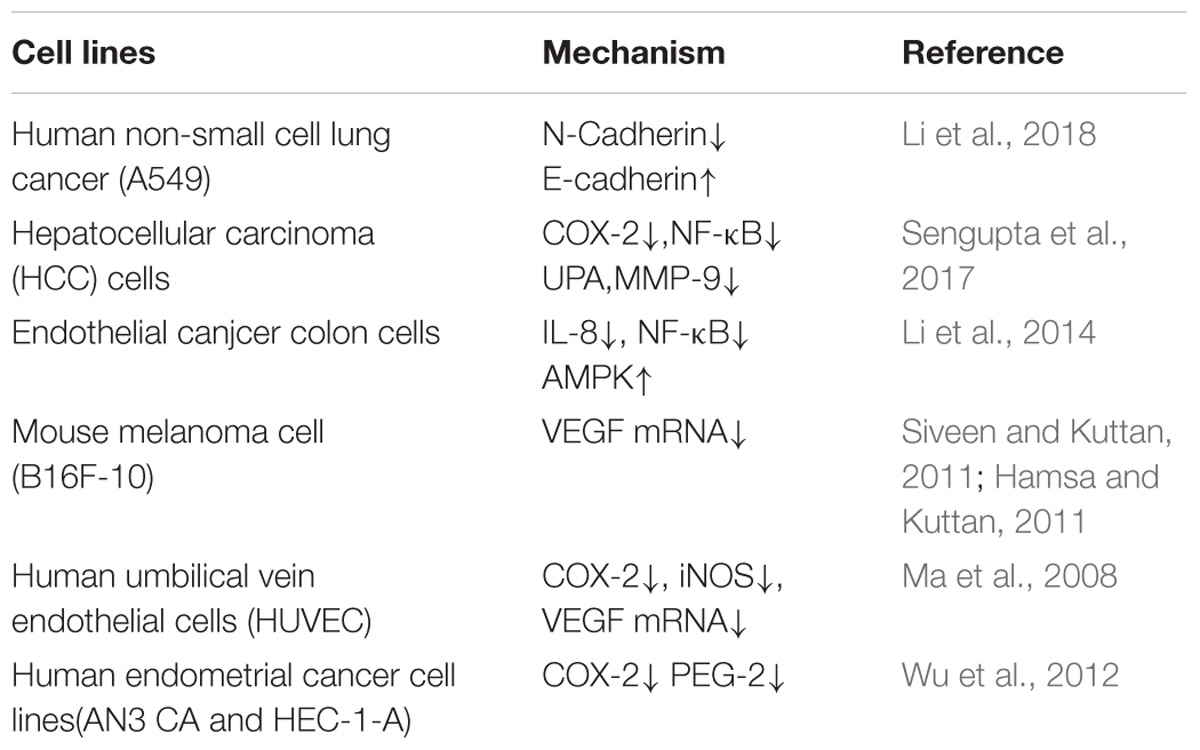
Berberine hydrochloride, the more commonly available salt form of berberine, is a quaternary ammonium isoquinoline alkaloid with the chemical formula C20H18ClNO4 (Figure 1) that forms yellow needle-like crystals (Neag et al., 2018). Berberine was originally used as a broad-spectrum antibacterial drug. Extensive research revealed a wide range of pharmacological activities, including antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antihypertensive, hypolipidemic, and antidiarrheal effects. In addition, berberine exhibits inhibitory effects on a variety of tumors (Xu et al., 2017), such as esophageal cancer. Many studies (Kumar et al., 2015; Foroutan F. et al., 2018; Foroutan T. et al., 2018; Mirhadi et al., 2018) have confirmed that berberine affects the development of tumor cells through the inhibition of tumor cell growth and the induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest (Iizuka et al., 2000; Kong et al., 2004; Tang and Feng, 2009; Xue et al., 2013; Signorelli et al., 2017).
It is reported that 8.2 million people die of cancer every year globally and that this number is continuously rising; according to the American Cancer Society, cancer is the cause of more than 600,000 deaths every year in the United States, a mortality rate second only to heart disease (Khalil et al., 2016; Walker et al., 2017). Owing to the seriousness of this situation, scientific approaches to the prevention and control of cancer have become a major public health issue (Gu et al., 2015; Viegas et al., 2017).
It has long been believed that the occurrence and development of tumors are attributable to only genetic abnormalities, which include gene mutations, translocations, and chromatin insertions (Dupont et al., 2009; Li et al., 2018). However, in recent years, the emergence and progress of genome sequencing technology have led to the rapid development of epigenetics and many researchers have determined that epigenetics plays an important role in the regulation of tumors. Epigenetic changes are reversible, heritable changes in gene expression and protein function in which the genomic DNA sequence remains unchanged (Biswas and Rao, 2018). Epigenetic changes can regulate gene expression at multiple levels, for example, at the DNA level through DNA methylation, at the RNA level through non-coding RNA regulation, at the protein level through histone modification, and at the chromatin level through chromatin remodeling. The continuous presence of these mechanisms in cell division allows cells to retain their respective characteristics, respond to intrinsic cellular signals, and participate in cell evolution and adaptation to environmental changes. Many research studies have confirmed that epigenetic mechanisms are implicated in tumorigenesis through the regulation of oncogene activation and tumor suppressor gene inactivation. For example, DNA methylation can inactivate tumor suppressor genes, abnormal histone acetylation can change tumor-associated gene expression, and non-coding microRNAs can result in dysregulation of tumor suppressor genes (Blandino et al., 2014; Wong and Chim, 2015). It is of note that different epigenetic modifications in cells often interact with each other in a synergistic manner to maintain body’s homeostasis through the regulation of the expression of key genes, and that when abnormal changes occur, they may cause a variety of diseases, including tumors (Vijayaraghavalu et al., 2013). Recent evidence has suggested that epigenetic modifications may be involved in the processes tumor cells use to shape a microenvironment suitable for their own growth (Honda et al., 2006). There are a large number of active substances, such as growth factors, inflammatory factors, and proteases, in the tumor microenvironment and these participate in the various processes of tumorigenesis through their own functional properties or mediated signaling pathways (Booth and Gutierrez-Hartmann, 2015). Epigenetic modifications are involved in the regulation of the secretory processes of these biomolecules or their mediated signaling pathways (Li et al., 2018). From the perspective of the tumor development process, the regulation of epigenetic modification in the tumor microenvironment occurs at various stages of tumorigenesis, progression, and metastasis, and is one of the important tools for diversifying between tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment. That is to say, tumors may have specific epigenetic modification characteristics that may lead to changes in cell biological characteristics and malignant transformation. Therefore, an exploration the mechanism of tumor biology from the perspective of epigenetics is of great significance.
The Biological Efficacy of Berberine
Berberine Inhibits the Migration and Invasion of Tumor Cells
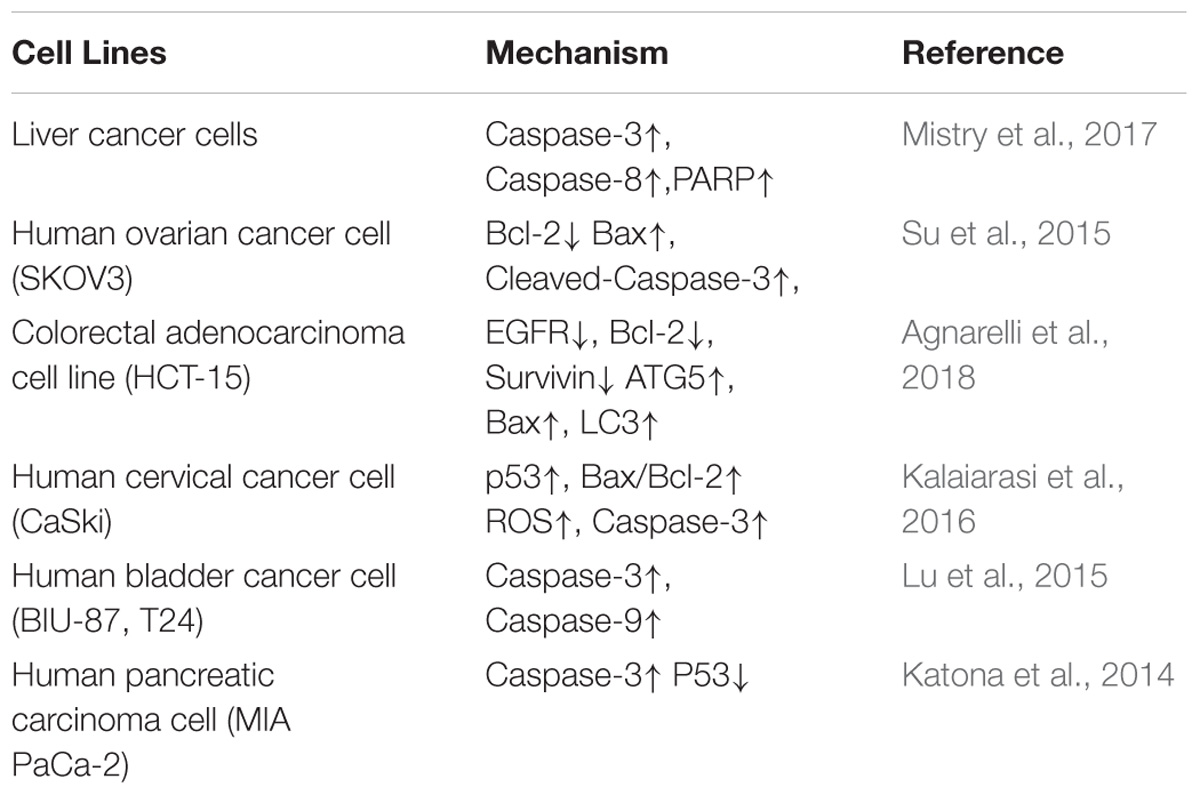
Migration and invasion are the basic characteristics of tumor cells. Therefore, it is valuable to study whether berberine can affect the migration and invasion ability of tumor cells. It is well known that E-cadherin and N-Cadherin proteins are closely related to cell migration and invasion. Moreover, E-cadherin is not only an important mediator that regulates cell-cell adhesion, but also an important molecule in the maintenance of the morphology and structural integrity of epithelial cells (Qi et al., 2014; Shi et al., 2017). There is a large amount of experimental evidence suggesting that berberine can inhibit the migration and invasion of tumor cells. In human lung cancer A549 cells, berberine increased the expression of E-cadherin protein in a concentration- and time-dependent manner (Li et al., 2018), and significantly downregulated the expression of N-cadherin; these changes inhibited invasion and metastasis. MMPs are a class of important proteins that are involved in that the degradation of the extracellular matrix barrier, which is the first step in tumor cell metastasis (Hao et al., 2017). Studies have shown that berberine inhibits the expression of MMP2 and MMP9 in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. Simultaneously, berberine also regulates the expression of MMPs through the inhibition of the transfer of p-STAT3 to the nucleus, which affects its activity. Wang X et al. found that berberine was an effective inhibitor of the invasion and migration of HCC cells. Berberine treatment of HCC cells downregulated the expression of cox-2, NF-κB, uPA, and MMP9 in a dose-dependent manner (Sengupta et al., 2017). In summary, the data strongly suggest that berberine has an important role in the regulation of cadherin- and MMP-mediated pathways, which leads to inhibitory effects on cancer migration and invasion (Table 1).
Furthermore, Jin Y. et al. (2017) showed that the effect of berberine on the metastatic potential of cancer cells may be mediated by the activation of the AMPK signaling pathway, which reduces the activity of ERK and the expression of COX-2, thereby inhibiting the adhesion, migration, and invasion of tumor cells. Moreover, berberine inhibited tumor cells through signaling pathways, including the NF-κB and AMPK pathways. Studies have demonstrated that berberine prevents tumor cells from producing IL-8 and blocks NF-κb signaling pathway, ultimately inhibiting endometrial cancer metastasis, and that colon cancer cell migration was inhibited by targeting AMPK signaling (Li et al., 2014).
Vascular endothelial growth factor, the most important angiogenic factor secreted from tumor cells, stimulates tumor neovascularization through an increase in the mitogenic and survival properties of vascular endothelial cells. Berberine not only reduces the expression of SC-M1 cells with normal oxygen content and low oxygen content. VEGF also directly inhibits the proliferation and migration of umbilical vein epithelial cells. Berberine treatment in B16F-10 melanoma cells reduced the expression of VEGF mRNA and inhibited angiogenesis. Inflammation plays an important role in tumor angiogenesis, which is mainly manifested through the activation of NF-κB to regulate VEGF, and results have shown that berberine treatment of tumor cells significantly inhibited NF-κB and ultimately decreased the expression of VEGF and IL-8 in tumor cells (Hamsa and Kuttan, 2011; Siveen and Kuttan, 2011). In addition, berberine significantly inhibited the VEGF-induced migration and invasion of human umbilical vein endothelial cells HUVEC in a dose-dependent manner, and significantly reduced the expression of COX-2, Inos, and VEGF mRNA and downregulated pro-angiogenic factors to inhibit angiogenesis (Naveen et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2018). These results indicated the critical effects of berberine on the HIF1α/VEGF pathway.
Angiogenesis plays an important role in tumor growth, as progression and metastasis are prerequisites for solid tumor growth. The angiogenic process is therefore a target for the inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis (Ma et al., 2008) Studies have shown that berberine can reduce the levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF, and GMCSF in the serum of tumor-inoculated animals and inhibit the elevation of NO and TNF-α, inflammatory mediators involved in angiogenesis. Wang Y et al. inferred that berberine suppressed the growth and metastasis of endometrial cancer cells via miR-101/COX2, and berberine is also known to inhibit tumors via the COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathway. The transcription of miR-101 is up-regulated by berberine through AP-1 to regulate the transcription of COX-2 in EC cells (Wu et al., 2012). The high expression of p-STAT3 in malignant tumor cells and the expression level of p-STAT3 in tumor tissues, the more obvious the proliferation and metastasis of tumor cells (Munir et al., 2000).
Berberine Inhibits Tumor Cell Proliferation (Autophagy, Apoptosis)
Apoptosis is an ideal form of cell death in cancer therapy because it generally does not cause an inflammatory response. Thus, the induction of apoptosis is one of the various mechanisms that inhibit the growth of tumor cells (Yakata et al., 2007). It has also been reported that berberine significantly inhibited the proliferation of human prostate cancer PC3 cells (Huang et al., 2015). In recent years, studies have shown that the proliferation of renal cell cancer cells can be effectively inhibited by berberine; when a certain concentration of berberine is treated to renal cell cancer cells, the effects continue for some time. The inhibitory effect of berberine on the tumor cells gradually increased, and it was found that the effect of inhibitory effect was greatest for treatment times of up to 48 h. In addition, the total apoptotic rate of renal tumor cells detected by a double staining method showed that after treatment of renal cell cancer cell lines A498 and 786-0 with different concentrations of berberine, the rate of total apoptosis in cells gradually increased as the concentration of the drug increased (Wang et al., 2015a; Liu et al., 2017a,b, 2018).
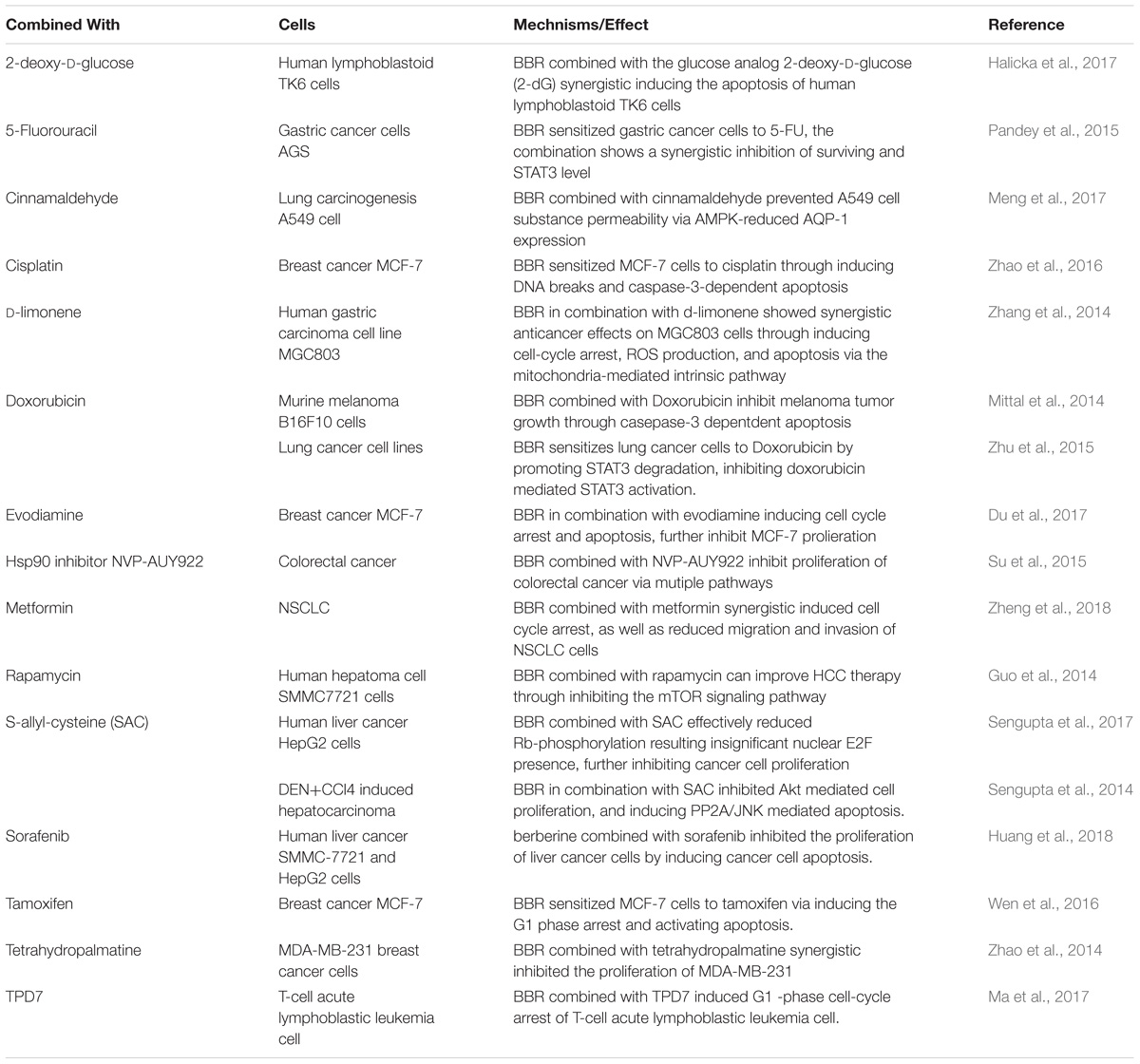
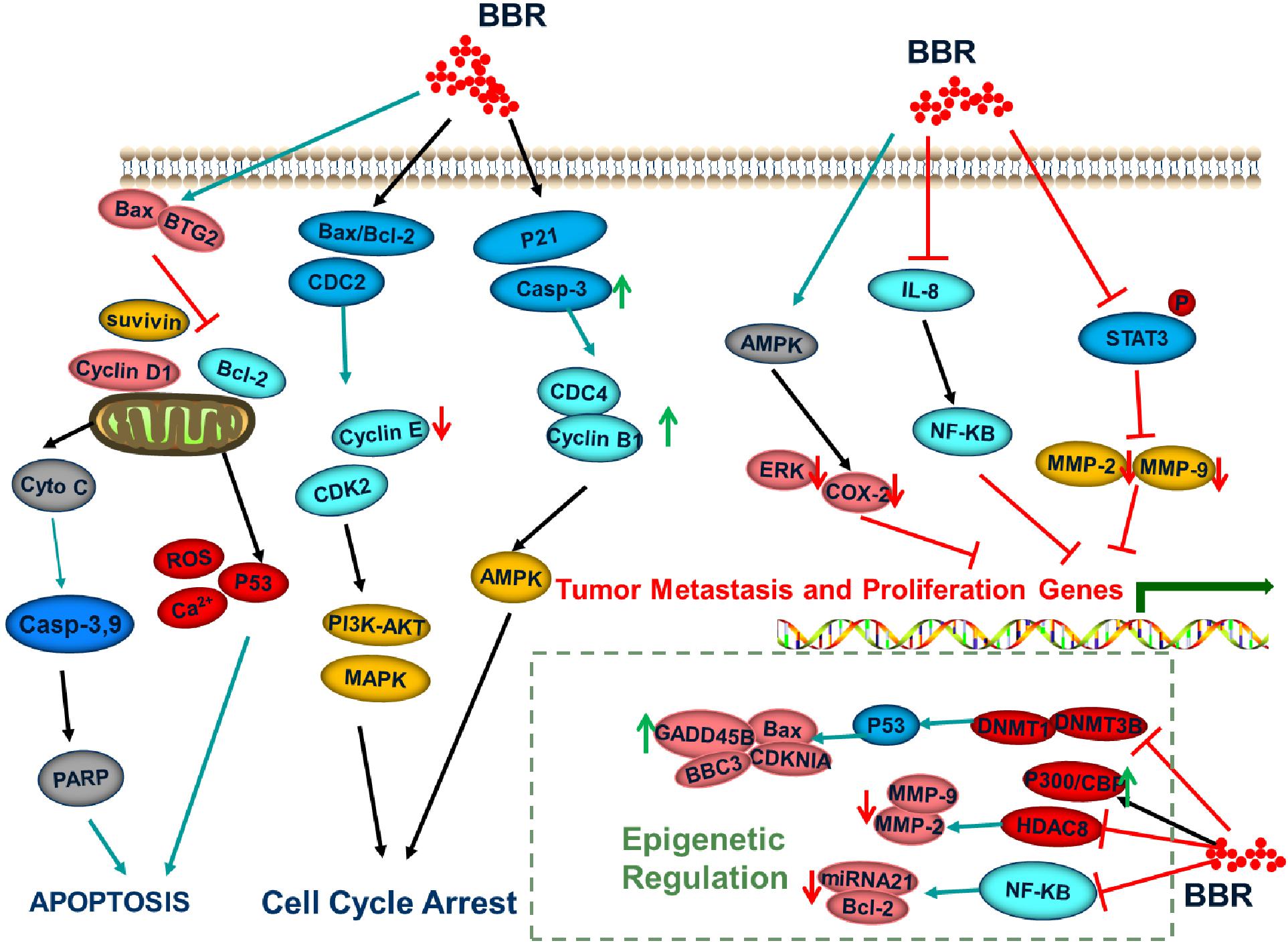
Berberine induces apoptosis in tumor cells, mainly through upregulation of pro-apoptotic genes and downregulation of apoptosis-inhibiting genes. For example, berberine can upregulate the expression of the pro-apoptotic protein BAD in HL-60 cells and downregulate the expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 to achieve regulation of tumor cell apoptosis. In addition, apoptosis can be induced by the mitochondrial/caspase pathway, DNA cleavage induces tumor cell apoptosis, tumor cell apoptosis is induced by inflammatory factors, and tumor cell apoptosis is induced by cyclooxygenase. For example, berberine treatment of liver cancer cells revealed that DNA fragments, caspase-3, and caspase-8 were activated, which was followed by the activation of PARP, and the release of cytochrome c to inhibit tumor metastasis (Mistry et al., 2017).
Studies have showed that berberine can regulate apoptosis-associated proteins. Caspase cleavage is a typical phenomenon in apoptosis cells. Thus, numerous reports have used the detection of this cleavage to clarify the role of berberine in the induction of apoptosis. For example, berberine decreased the expression of Bcl-2 and survivin and, conversely, increased the expression of the pro-apoptotic genes Bax and cleaved caspase-3 in a dose-dependent manner in human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells (Su et al., 2015). Moreover, the treatment of berberine to treat human colorectal adenocarcinoma (HCT-15) cells significantly increased the expression of spliced caspase-3 and the mitochondrial apoptosis-related protein Bax, and significantly decreased the expression of Bcl-2 and survivin, finally inducing apoptosis (Agnarelli et al., 2018). Berberine inhibited the proliferation of human cervical cancer Ca Ski cells through alteration of the ratio of p53 and Bax/Bcl-2 proteins, upregulation of ROS, and enhancement of caspase-3 activity to induce apoptosis (Kalaiarasi et al., 2016). In addition, berberine induced the proliferation of BIU-87 and T24 cells through the inhibition of protein expression, the induction of G1 cell cycle arrest, and the induction of apoptosis via the caspase-3 and caspase-9 pathways (Lu et al., 2015). Agnarelli A et al. treated U343 cells and MIA PaCa-2 cells with 50 μM berberine for 48 h, and found that the activity of caspase-3 was decreased in U343 cells and increased in MIA PaCa-2 cells. Therefore, they concluded that berberine promoted the apoptosis of tumor cells (Katona et al., 2014). It has been reported that berberine induces Bax activation in human lung cancer A549 cells, enables p53 pathway-mediated cytochrome c release, and leads to the activation of caspase signaling ultimately causing apoptosis (Shi et al., 2013). The reported data also showed that berberine induced cancer cell apoptosis mainly through the regulation of the expression of caspases and Bcl-2; this results in the release of cytochrome c and the activation of the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway to promote apoptosis in PC3 cells (Wang et al., 2017).
Autophagy is one type of cellular self-protection mechanism, consisting mainly of the degradation of macromolecular material and damaged organelles in cytoplasm after autophagosome formation with lysosomes. The products of degradation are used to restore cell homeostasis. There are three forms of cell autophagy: macro-autophagy, micro-autophagy, and autophagy, which are mediated by different molecular chaperones. Autophagy is involved in many of the physiological and pathological processes of cells, and there is a close relationship between autophagy and tumorigenesis. The effects of autophagy vary in different cell lines and maybe inhibitory or stimulatory. In addition, the occurrence of autophagy is regulated by various signal pathways. Recent experimental studies have shown that berberine inhibits the proliferation of colon cancer cells through the downregulation of the expression of EGFR and that it activates autophagy and apoptosis through the p38 signaling pathway to inhibit the proliferation of HCT-15 cells. Similarly, in berberine-treated HCT-15 cells, the autophagy marker proteins ATG5 and LC3 were upregulated in a time-dependent manner (Zhang L. et al., 2017), indicating that berberine induced autophagy in HCT-15 cells. These data demostrate a role of Berberin in regulating cancer cell proliferation (Tables 1, 2).
Berberine Arrests Tumor Cell Cycle
Many studies have shown that low concentrations of berberine arrest human osteosarcoma U20S cells in the G1 phase through the induction of DNA double-strand breaks that activate the p53-p21 pathway. In contrast to low concentrations of berberine, high concentrations induce arrest in the G2/M phase, but do not depend on the p53-p21 pathway (Yang et al., 2015; Li et al., 2017). Other studies demonstrated that berberine significantly inhibited human ovarian cancer cells (HEY and SKOV3 cells) in a time- and dose-dependent manner. It is demonstrated that that berberine exerts a significant inhibitory effect on human gastric cancer MGC 80 3 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Using laser confocal microscopy, the nucleus condenses, and apoptotic bodies are seen, which indicate that berberine can inhibit the proliferation of MGC 80 3 cells and arrest cells in the G0/G1 phase to inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells in vitro.
B-cell translocation gene 2 is a transient early-response gene induced by p53. It is a member of the gene family that regulates cell proliferation and is an important bridge molecule that links p53, pRB, the cell cycle, cell proliferation, and differentiation. The current body of evidence indicates that berberine can promote the cell cycle arrest of human hepatoma HEPG2 cells in the G1 phase through the upregulation of BTG2 and the downregulation of cyclin D1, consequently inhibiting the proliferation of hepatoma cells and inducing apoptosis.
Cyclin is one of the target proteins that regulate the G1 phase. As a proto-oncogene, it is involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, and its overexpression is closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors. Berberine has a variety of effects on the cell cycle; for example, it can arrest the G2/M phase in the cell growth cycle through a reduction in the expression of cyclin B1 and increase in the expression of Wee1, which stops the tumor cells in the early stage of DNA synthesis (G1) and late DNA synthesis (G2). The induction of tumor cell apoptosis through the downregulation of cyclin E expression and upregulation of p21 expression, which causes G1 arrest in HEY and SKOV3 cells and downregulates Bcl-2 protein expression and upregulates Bax protein expression. Berberine treatment of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 human breast cancer cells dose-dependently caused G0/G1 arrest, which was possibly associated with a decrease in the cell cycle regulation protein cyclin B1. Furthermore, it increased the expression of CDC4 and cyclin B1 through an increase in the expression of CDC2 and caspase-3 in human hepatoma HepG2 cells, causing arrest in the S and G2/M phases, and activating the AMPK signaling pathway to induce the apoptosis of HepG2 cells (Chidambaram et al., 2012; Murthy et al., 2012; Balestrieri et al., 2018). Li et al. demonstrated that berberine regulates the PI3K-AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in PTC (the most common subtype) and ATC (the most malignant and aggressive subtype), leading to mitochondrial apoptosis, G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, increased Bax/Bcl-2, cleaved caspase-3, p21, and decreased cyclin E1, CDK2, and vimentin were verified by western blotting (Waterbeemd et al., 2013). The combination of drugs upregulated the expression of the cell cycle-dependent kinase inhibitory proteins p27 and p21, and downregulated the expression of cyclin D1, CDK2, and CDK4-cyclin.
In addition, studies have reported that berberine can bind to topoisomerase (TOP1), which hinders the synthesis of S phase cells and prevents cell proliferation.
Effects of Berberine in Compatibility
With the identification of numerous anti-tumor drugs, research of cancer therapy has gradually shifted from a focus on monotherapy to combined therapy. More and more reports have demonstrated that berberine combined with radio-therapy or chemotherapy drugs can achieve better anti-tumor effect. For instance, berberine combined with gamma-radiation enhance the anti-cancer effects, including inducing apoptosis and ROS generation (Jung-Mu et al., 2009). Also, berberine sensitizes lung cancer cells to radiation via autophagy both in vitro and in vivo (Peng et al., 2008). Indicated an adjuvant role in radio-therapy of cancer. Another major anti-cancer therapy is chemotherapy, several novel chemotherapy drugs such like doxorubicin, rapamycin were texted combined with berberine, and showed a more effective result. It is reported that berberine sensitizes mutliple human cancer cells to the anticancer effects of doxorubicin (Tong et al., 2012). More details and drugs were summarized in Table 3, which clarified that berberine synergistic work with chemotherapy drugs in anti-tumor proliferation through inducing cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, as well as autophagy. These data have laid theoretical foundation for the combined therapy in clinic trial.
Epigenetic Effects of Berberine on Tumors
For many years, researchers have been studying and developing drugs for cancer prevention and treatment. Chinese medicines, such as berberine, are commonly used as drugs. As an active ingredient of Coptis, berberine is inevitably closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors (Wang-Johanning et al., 2008; Coward et al., 2014; Delgado-Cruzata et al., 2015; Dkhil et al., 2015). Extensive research has led scholars to conclude that, ultimately, the antitumor effect of berberine may be related to epigenetic effects. The following is a brief description of the methods through which berberine regulates tumor cells, including migration, proliferation, and apoptosis, through epigenetic mechanisms.
DNA Methylation
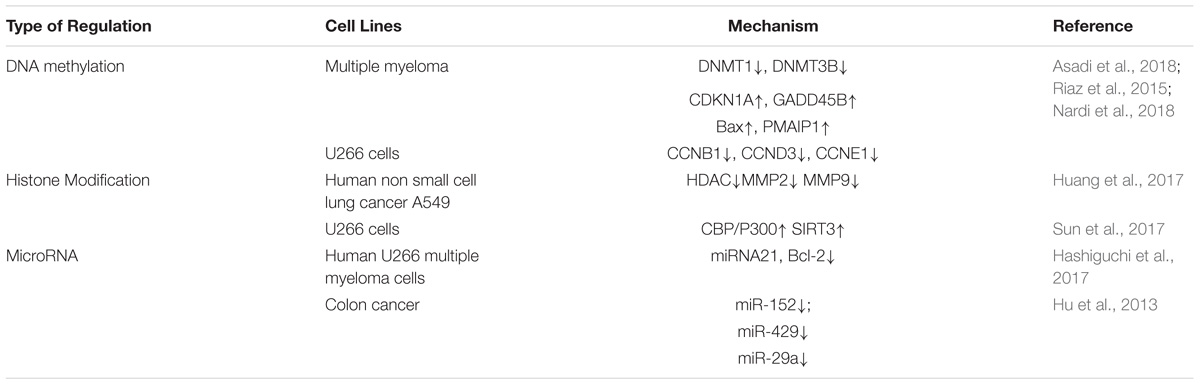
DNA methylation refers to the covalent attachment of the fifth carbon atom of cytosine on the CpG dinucleotide to the methyl group through the action of DNMT, which is modified to 5-methylcytosine. DNA methylation is a potential epigenetic mechanism involving a variety of biological processes. The DNMT family consists of three main members: DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B. DNMT1 mainly maintains DNA methylation status and DNMT3A and DNMT3B catalyze new DNA methylations (Kalinkova et al., 2018; Li et al., 2018; Puneet et al., 2018). Human CpG exists mainly in two forms: one is dispersed in genomic DNA; the other is highly aggregated to form CpG islands, which are present in the promoter region or the first exon region of various genes. In the human genome, the CpG site is usually in an unmethylated state in the CpG islands, but in a methylated outside the CpG islands. When tumors occur, the degree of unmethylation of CpG sites outside CpG islands increases, whereas the CpG sites in CpG islands are highly methylated, causing a decrease in the overall methylation level of the genome, as well as certain gene CpG islands. Local methylation levels are abnormally elevated, leading to genomic instabilities, such as chromosomal instability, the activation of proto-oncogenes, and the silencing of tumor suppressor genes (Qing et al., 2014; Crawford et al., 2018; Lee and Gang, 2018; Sanna et al., 2018). DNA methylation abnormalities are mainly divided into the hypomethylation state of proto-oncogenes and the hypermethylation state of tumor suppressor genes. The most studied of these is the hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes. It is of interest that berberine has been found to inhibit the expression of human DNA methyltransferases DNMT1 and DNMT3B in multiple myeloma U266 cells. For example, berberine can alter the CpG methylation of p53 DNA, affect the mRNA expression of key apoptosis-related proteins, and increases apoptosis in U266 cells, and thereby leads to cell cycle arrest. Although the hypomethylation of the p53 promoter can regulate apoptosis-related genes, such as GADD45, Bax, PMAIP1, BBC3, CCNB1, CCND3, and CCNE1. Specifically, in the p53 pathway, CDKN1A, GADD45B, Bax, PMAIP1, and BBC3 were upregulated, and CCNB1, CCND3, and CCNE1 were downregulated, which suggested that berberine activated the p53 signaling pathway through the impairment of U266 cells. In addition, results have shown that treatment of colorectal cancer cells with berberine results in a significant increase in the expression of DNMT1 and DNMT3A in the presence of TGF-β1; this hypermethylation in the promoter CpG island leads to further silencing of TSG, which results in tumor cell proliferation (Riaz et al., 2015; Asadi et al., 2018; Nardi et al., 2018).
Histone Modification
Histones play an important role in gene expression and tumorigenesis and development. The nucleosome is the basic constituent unit of chromatin. A nucleosome is an octamer composed of histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 and DNA entangled on the outside of the 147 base pairs. Histones not only protect the DNA structure and genetic information, but also participate in the regulation of gene expression. The extracellular amino terminus of histones can be modified by a variety of enzymes to form specific “histone codes” that alter the “open” or “closed” state of the local chromatin structure, or determine which proteins bind to specific DNA regions. Consequently, they regulate the various functions of DNA, including transcription and damage repair. Histone acetylation is highly dynamic and is coordinated by HATs and HDACs, and occurs at the amino-specific lysine residues of histones (Stevens et al., 1984; Yan et al., 2001; Bhat et al., 2018; Georgoff et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2018; Rahnamoun et al., 2018). Histone modification is a major determinant of the epigenetic silencing of genes and the regulation of cellular processes. Histone modifications often occur at the amino terminus of histones, and modifications of various chemical groups are acceptable due to exposure to chromatin (Oliver et al., 2013; Bennetzen and Wang, 2014; Hoen and Bureau, 2015; Yamada et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2015; Li and Zhao, 2016; Rayan et al., 2016; Jiang et al., 2018; Salimian et al., 2018; Shang et al., 2018; Yan et al., 2018; Sahebi et al., 2018; Zhang L. et al., 2018; Zhang S. et al., 2018). The most widely studied are the acetylation and methylation of lysine K on histone H3 and H4. Histone acetylation plays an important role in the epigenetic theory proposed in recent years. Histone acetylation can affect the chromatin structure in cells, and thus participate in the transcriptional regulation of genes at specific sites, playing an important role in cell growth and differentiation. With a deeper understanding of the mechanism of histone acetylation in gene transcriptional regulation, the role of HDAC inhibitors in tumor therapy has received increasing attention (Sun et al., 2017).
CBP and p300 proteins with acetylase activity are transcriptional coactivators and hematopoietic tumor suppressors. Studies have shown that berberine can upregulate the expression of CBP/P300 and SIRT3 in U266 cells, and downregulate the expression of HDAC8; however, in HL-60/ADR and KG1-α cells, CBP/P300 and SIRT3 were also upregulated, but HDAC8 did not change significantly. Histone acetylation maintains its balance through HAT and HDAC. Berberine downregulated HDAC in human lung cancer A549 cells, which resulted in decreased expression of the metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNA and protein, inhibiting cell migration and invasion (Huang et al., 2017). Simultaneously, another study has shown that berberine treatment of A549 cells significantly reduced the expression of class I, II-a, II-b, and IV mRNA, histone H3, and H4 hyperacetylation.
MicroRNA
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short-chain non-coding RNAs of 19–22 nucleotides in length that bind to the 3′UTR in target mRNAs, thereby degrading or blocking the translation of target mRNAs. It plays an important role in the growth, differentiation, apoptosis, and tumor cell development. miRNAs can regulate the expression of multiple tumor-associated genes. In accordance with the function of miRNAs, they can be divided into two types: oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes (Hu et al., 2013). Not only can it act directly as a proto-oncogene or a tumor suppressor gene, but also regulate the expression of other proto-oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes. miRNAs play a central role in many cellular biology processes, and their dysregulation is a ubiquitous feature in tumors. Epigenetic effects have been shown to be a major cause of miRNA dysregulation in tumors (Hashiguchi et al., 2017). In the TGF-β1-induced colorectal cancer model, berberine significantly decreased the expression of miR-152 (targeting DNMT1), miR-429 (targeting DNMT3A), and miR-29a (targeting DNMT3A/3B), which suggested that berberine inactivates some tumor suppressor factors, including DNMT1 and DNMT3A/3B, through the regulation of the expression of the above miRNAs during colon cancer development. Furthermore, other evidence has suggested that berberine treatment of human U266 multiple myeloma cells led to the inhibition of NF-κB nuclear translocation via Set9-mediated lysine methylation, which resulted in decreased miRNA21 and Bcl-2 expression, inducing the cells to produce ROS and promoting cell apoptosis. Berberine treatment of colorectal cancer cells increased the expression of miR-200a-5p and decreased the expression of miR-429. These epigenetic regulation affected by Berberine was briefly summarized in Table 4.
Summary and Future Perspectives
The importance of epigenetic regulation in the occurrence and development of tumors is now an established fact. An increasing body of research has been devoted to the exploration of epigenetic molecular markers for the early diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of tumors. Simultaneously, epigenetic drugs provide a new direction for the treatment of tumors owing to the reversibility and ease of regulation of epigenetics. At present, the anticancer drugs that inhibit the proliferation of malignant tumor cells via induction of apoptosis or that regulate signal transduction are mostly multi-targeted (He et al., 2010). Berberine is a natural isoquinoline alkaloid that significantly contributed to the development of anticancer drugs (Figure 2). Given the continuous development in the field of medicine and the extension of research and development in the field of medicine, berberine has gained attention of researchers owing to the combination of multiple effects. Berberine is not irreplaceable with respect to its traditional pharmacological activities, such as antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral effects (Huang S.X. et al., 2018). Moreover, the efficacy of the antihypertensive, antitumor, and hypolipidemic effects has also become a “hot topic” in contemporary research. Berberine regulates the molecular mechanisms that cause tumor cells through a variety of signaling pathways, confirming the potential therapeutic effects in a variety of tumor cells. However, there are few reports on the effects of berberine on the epigenetic functions of tumors. Epigenetics is also the main controlling factor of oncogenes in the development of cancer. Therefore, the application of epigenetic properties of berberine in the treatment of malignant tumors offers broad prospects for drug development. At the same time, extended research into epigenetics has provided a new strategy to understand the various characteristics of tumors, optimize the early diagnosis of tumors, and improve the prognosis of patients. In future, basic research and clinical transformations in the epigenetics of cancer will provide new strategies for the precise diagnosis and treatment of cancer.
Author Contributions
DL contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation. XM contributed significantly to manuscript preparation. DW helped to writing the manuscript. ZQ and HL contributed to the conception of the study.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81803680). Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Project in China (Grant Nos. 20170307031 and YY20180520050JH).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
AP-1, activating protein 1; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; BTG2, B-cell translocation gene 2; Bax, BCL2 associated X; BBC3, BCL2-binding component 3; CCNB, cyclin B; CCND, cyclin D; CCNE, cyclin E; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinases; CDKN1A/p21, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor; COX2, cyclooxygenase-2; DNMT, DNA methyltransferase; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; GMCSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; GADD45, growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 45; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma cells; HAT, histone acetyltransferase; HDAC, histone deacetylase; HIF1α, hypoxia-induced factor α; INOS, inducible NO synthase; IL-8, interleukin-8; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer cells; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; PARP, poly-ADP ribose polymerase; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; SIRT, sirtuins; Bcl-2, the B cell lymphoma-2; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; uPA, urokinase-type plasminogen activator; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
References
Agnarelli, A., Natali, M., Garciagil, M., Pesi, R., Tozzi, M. G., Ippolito, C., et al. (2018). Cell-specific pattern of berberine pleiotropic effects on different human cell lines. Sci. Rep. 8:10599. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28952-3
Asadi, R., Omrani, M. D., Ghaedi, H., Mirfakhraie, R., Azargashb, E., Habibi, M., et al. (2018). Premutations of fmr1 cgg repeats are not related to idiopathic premature ovarian failure in iranian patients: a case control study. Gene 676, 189–194. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.07.034
Balestrieri, E., Argaw-Denboba, A., Gambacurta, A., Cipriani, C., Bei, R., Serafino, A., et al. (2018). Human endogenous retrovirus k in the crosstalk between cancer cells microenvironment and plasticity: a new perspective for combination therapy. Front. Microbiol. 9:1448. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01448
Bennetzen, J. L., and Wang, H. (2014). The contributions of transposable elements to the structure, function, and evolution of plant genomes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 65:505. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-035811
Bhat, A. V., Hora, S., Pal, A., Jha, S., and Taneja, R. (2018). Stressing the (epi) genome: dealing with reactive oxygen species in cancer. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 29, 1273–1292. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7158
Biswas, S., and Rao, C. M. (2018). Epigenetic tools (The Writers, the readers and the erasers) and their implications in cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 837, 8–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.08.021
Blandino, G., Fazi, F., Donzelli, S., Kedmi, M., Saschen, A., Muti, P., et al. (2014). Tumor suppressor micrornas: a novel non-coding alliance against cancer. FEBS Lett. 588, 2639–2652. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.03.033
Booth, A. K., and Gutierrez-Hartmann, A. (2015). Signaling pathways regulating pituitary lactotrope homeostasis and tumorigenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 846, 37–59. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-12114-7_2
Chidambaram, A., Fillmore, H. L., Van Meter, T. E., Dumur, C. I., Band roaddus, W. C., (2012). Novel report of expression and function of CD97 in malignant gliomas: correlation with Wilms tumor 1 expression and glioma cell invasiveness. J. Neurosurg. 116, 843–853. doi: 10.3171/2011.11.JNS111455
Cicero, A. F., and Baggioni, A. (2016). Berberine and its role in chronic disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 928:27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41334-1_2
Coward, W. R., Feghalibostwick, C. A., Jenkins, G., Knox, A. J., and Pang, L. (2014). A central role for g9a and ezh2 in the epigenetic silencing of cyclooxygenase-2 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. FASEB J. 28, 3183–3196. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-241760
Crawford, B., Craig, Z., Mansell, G., White, I., Spaull, S., Imm, J., et al. (2018). DNA methylation and inflammation marker profiles associated with a history of depression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 27, 2840–2850. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy199
Delga-docruzata, L., Zhang, W., Mcdonald, J. A., Tsai, W. Y., Valdovinos, C., Falci, L., et al. (2015). Dietary modifications, weight loss, and changes in metabolic markers affect global dna methylation in hispanic, african american, and afro-caribbean breast cancer survivors. J. Nutr. 145:783. doi: 10.3945/jn.114.202853
Dkhil, M. A., Metwaly, M. S., Saleh, A. Q., Sherif, N. E., Denis, D., Omar, S. Y. A., et al. (2015). Anti-eimeria activity of berberine and identification of associated gene expression changes in the mouse jejunum infected with eimeria papillata. Parasitol. Res. 114, 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4344-z
Du, J., Sun, Y., Lu, Y. Y., Lau, E., Zhao, M., Zhou, Q. M., et al. (2017). Berberine and evodiamine act synergistically against human breast cancer mcf-7 cells by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 37, 6141–6151.
Dupont, C., Armant, D. R., and Brenner, C. A. (2009). Epigenetics: definition, mechanisms and clinical perspective. Semin. Reprod. Med. 27, 351–357. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1237423
Foroutan, F., Alba, A. C., Stein, M., Krakovsky, J., Chien, K. G. W., Chih, S., et al., (2018). Validation of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation primary graft dysfunction instrument in heart transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2018.12.007 [Epub ahead of print].
Foroutan, T., Farhadi, A., Abroun, S., and Mohammad Soltani, B. (2018). Adipose derived stem cells affect miR-145 and p53 expressions of co-cultured hematopoietic stem cells. Cell J. 19, 654–659. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2018.4393
Georgoff, P. E., Nikolian, V. C., Higgins, G., Chtraklin, K., Eidy, H., Ghandour, M. H., et al. (2018). Valproic acid induces pro-survival transcriptomic changes in swine subjected to traumatic injury and hemorrhagic shock. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 84:1. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001763
Gu, L., Frommel, S. C., Oakes, C. C., Simon, R., Grupp, K., Gerig, C. Y., et al. (2015). Baz2a (tip5) is involved in epigenetic alterations in prostate cancer and its overexpression predicts disease recurrence. Nat. Genet. 47:22. doi: 10.1038/ng.3165
Guo, N., Yan, A., Gao, X., Chen, Y., He, X., Hu, Z., et al. (2014). Berberine sensitizes rapamycin-mediated human hepatoma cell death in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 10, 3132–3138. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2608
Halicka, H. D., Garcia, J., Li, J., Zhao, H., and Darzynkiewicz, Z. (2017). Synergy of 2-deoxy-d-glucose combined with berberine in inducing the lysosome/autophagy and transglutaminase activation-facilitated apoptosis. Apoptosis 22, 229–238. doi: 10.1007/s10495-016-1315-5
Hamsa, T. P., and Kuttan, G. (2011). Studies on anti-metastatic and anti-invasive effects of harmine using highly metastatic murine b16f-10 melanoma cells. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 30:123. doi: 10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.v30.i2.40
Hao, D. C., He, C. N., and Shen, J. (2017). Anticancer chemodiversity of ranunculaceae medicinal plants molecular mechanisms and functions. Curr. Genomics 18, 39–59. doi: 10.2174/1389202917666160803151752
Hashiguchi, Y., Kawano, S., Goto, Y., Yasuda, K., Kaneko, N., Sakamoto, T., et al. (2017). Tumor-suppressive roles of Δnp63β-mir-205 axis in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oral squamous cell carcinoma via targeting zeb1 and zeb2. J. Cell. Physiol. 233, 6565–6577. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26267
He, X. Y., Chen, J. X., Zhang, Z., Li, C. L., Peng, Q. L., and Peng, H. M. (2010). The let-7a microrna protects from growth of lung carcinoma by suppression of k-ras and c-myc in nude mice. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 136, 1023–1028. doi: 10.1007/s00432-009-0747-5
Hoen, D. R., and Bureau, T. E. (2015). Discovery of novel genes derived from transposable elements using integrative genomic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 32, 1487–1506. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv042
Honda, H., Pazin, M. J., Ji, H., Wernyj, R. P., and Morin, P. J. (2006). Crucial roles of sp1 and epigenetic modifications in the regulation of the cldn4 promoter in ovarian cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 281:21433. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603767200
Liu, H. C., Lämke, J., Lin, S. Y., Hung, M. J., Liu, K. M., Charng, Y. Y., et al. (2018). Distinct heat shock factors and chromatin modifications mediate the organ-autonomous transcriptional memory of heat stress. Plant J. 95, 401–413. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13958
Hu, H., Li, K., Wang, X., Liu, Y., Lu, Z. G., Dong, R. H., et al. (2013). Set9, NF-κB, and microRNA-21 mediate berberine-induced apoptosis of human multiple myeloma cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 34:157. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.161
Huang, C., Liu, H., Gong, X. L., Wu, L. Y., and Wen, B. (2017). Effect of evodiamine and berberine on the interaction between dnmts and target micrornas during malignant transformation of the colon by tgf-β1. Oncol. Rep. 37, 1637–1645. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5379
Huang, S. X., Qiu, G., Cheng, F. R., Pei, Z., Yang, Z., Deng, X. H., et al. (2018). Berberine protects secondary injury in mice with traumatic brain injury through anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory modulation. Neurochem. Res. 43, 1–12. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2597-5
Huang, Y., Wang, K., Gu, C., Yu, G., Zhao, D., Mai, W., et al. (2018). Berberine, a natural plant alkaloid, synergistically sensitizes human liver cancer cells to sorafenib. Oncol. Rep. 40, 1525–1532. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6552
Huang, Z. H., Zheng, H. F., Wang, W. L., Wang, Y., Zhong, L. F., Wu, J. L., et al. (2015). Berberine targets epidermal growth factor receptor signaling to suppress prostate cancer proliferation in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 11:2125. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2929
Iizuka, N., Miyamoto, K., Okita, K., Tangoku, A., Hayashi, H., Yosino, S., et al. (2000). Inhibitory effect of coptidis rhizoma and berberine on the proliferation of human esophageal cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett. 148, 19–25. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3835(99)00264-5
Imenshahidi, M., and Hosseinzadeh, H. (2016). Berberis vulgaris and berberine. Phytother. Res. 30, 1745–1764. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5693
Jiang, L., Xue, W., and Wang, Y. (2018). Inhibition of miR-31a-5p decreases inflammation by down-regulating IL-25 expression in human dermal fibroblast cells (CC-2511 cells) under hyperthermic stress via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 107, 24–33. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.142
Jin, Y., Liu, S., Ma, Q., Xiao, D., and Chen, L. (2017). Berberine enhances the ampk activation and autophagy and mitigates high glucose-induced apoptosis of mouse podocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol 794, 106–114. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.11.037
Jung-Mu, H., Mee-Sun, H., Sang-Yong, L., Woo-Yiel, L., and Dongho, K. (2009). The combination of berberine and irradiation enhances anti-cancer effects via activation of p38 mapk pathway and ros generation in human hepatoma cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 107, 955–964. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22198
Kalaiarasi, A., Anusha, C., Sankar, R., Rajasekaran, S., John, M. J., Muthusamy, K., et al. (2016). Plant isoquinoline alkaloid berberine exhibits chromatin remodeling by modulation of histone deacetylase to induce growth arrest and apoptosis in the a549 cell line. J. Agric. Food Chem. 64:9542. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b04453
Kalinkova, L., Zmetakova, I., Smolkova, B., Minarik, G., Sedlackova, T., Kajabova, V. H., et al. (2018). Decreased methylation in the SNAI2 and ADAM23 genes associated with de-differentiation and haematogenous dissemination in breast cancers. BMC Cancer 18:875. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4783-x
Katona, B. W., Liu, Y., Ma, A., Jin, J., and Hua, X. (2014). Ezh2 inhibition enhances the efficacy of an egfr inhibitor in suppressing colon cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 15:11. doi: 10.4161/15384047.2014.972776
Khalil, I., Colombara, D. V., Forouzanfar, M. H., Troeger, C., Daoud, F., Moradi-Lakeh, M., et al. (2016). Burden of diarrhea in the eastern mediterranean region, 1990–2013: findings from the global burden of disease study 2013. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 95, 1319–1329. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0339
Kong, W., Wei, J., Abidi, P., Lin, M., Inaba, S., Li, C., et al. (2004). Berberine is a novel cholesterol-lowering drug working through a unique mechanism distinct from statins. Nat. Med. 7, 464–464. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5688(06)81865-9
Kumar, A., Ekavali, Chopra, K., Mukherjee, M., Pottabathini, R., and Dhull, D. K. (2015). Current knowledge and pharmacological profile of berberine: an update. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 761, 288–297. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.05.068
Lee, C., and Gang, J. (2018). A label-free detection of ndei endonuclease activity by using dna-templated silver nanoclusters. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 18:6339. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2018.15657
Li, B., Wang, Z., Wu, H., Xue, M., Lin, P., Wang, S., et al. (2018). Epigenetic regulation of cxcl12 plays a critical role in mediating tumor progression and the immune response in osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 78:3938. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-17-3801
Li, C. H., Wu, D. F., Ding, H., Zhao, Y., Zhou, K. Y., and Xu, D. F. (2014). Berberine hydrochloride impact on physiological processes and modulation of twist levels in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cne-1 cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 15, 1851–1857. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.4.1851
Li, J., Liu, F., Jiang, S., Liu, J., Chen, X., Zhang, S., et al. (2018). Berberine hydrochloride inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer via the suppression of the mmp2 and bcl-2/bax signaling pathways. Oncol. Lett. 15:7409. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8249
Li, L., Wang, X., Sharvan, R., Gao, J., Qu, S., Li, L., et al. (2017). Berberine could inhibit thyroid carcinoma cells by inducing mitochondrial apoptosis, g0/g1 cell cycle arrest and suppressing migration via pi3k-akt and mapk signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 95, 1225–1231. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.010
Li, L., and Zhao, G. (2016). Downregulation of microrna-218 relieves neuropathic pain by regulating suppressor of cytokine signaling 3. Int. J. Mol. Med. 37:851. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2455
Li, N., Xu, F., Cheng, J., Zhang, Y., Huang, G., Zhu, J., et al. (2018). Perfluorocarbon nanocapsules improve hypoxic microenvironment for the tumor ultrasound diagnosis and photodynamic therapy. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 14, 2162–2171. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2018.2656
Li, W., Li, Q., Kang, S., Same, M., Zhou, Y., Sun, C., et al. (2018). Cancerdetector: ultrasensitive and non-invasive cancer detection at the resolution of individual reads using cell-free dna methylation sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:e89.
Liu, L., Chen, L., Jiang, C., Guo, J., Xie, Y., Kang, L., et al. (2017a). Berberine inhibits the lps-induced proliferation and inflammatory response of stromal cells of adenomyosis tissues mediated by the lps/tlr4 signaling pathway. Exp. Therap. Med. 14:6125. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5316
Liu, L., Luo, N., Guo, J., Xie, Y., Chen, L., and Cheng, Z. (2017b). Berberine inhibits growth and inflammatory invasive phenotypes of ectopic stromal cells: imply the possible treatment of adenomyosis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 137, 5–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2017.12.001
Lu, W., Du, S., and Wang, J. (2015). Berberine inhibits the proliferation of prostate cancer cells and induces g0/g1 or g2/m phase arrest at different concentrations. Mol. Med. Rep. 11, 3920–3924. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.3139
Ma, C. Y., Shen, S. C., Huang, D. W., Chang, H. M., and Wu, J. S. B. (2008). Growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in u937 cells by coptis chinensis extract. J. Food Sci. 73, H127–H133. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.00837.x
Ma, W., Zhu, M., Yang, L., Yang, T., and Zhang, Y., (2017). Synergistic effect of TPD7 and berberine against leukemia jurkat cell growth through regulating ephrin-B2 signaling. Phytother. Res. 31, 1392–1399.
Meng, F. C., Wu, Z. F., Yin, Z. Q., Lin, L. G., Wang, R., and Zhang, Q. W. (2018). Coptidis rhizoma and its main bioactive components: recent advances in chemical investigation, quality evaluation and pharmacological activity. Chinese Med. 13:13. doi: 10.1186/s13020-018-0171-3
Meng, M., Geng, S., Du, Z., Yao, J., Zheng, Y., Li, Z., et al. (2017). Berberine and cinnamaldehyde together prevent lung carcinogenesis. Oncotarget 8:76385. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20059
Mirhadi, E., Rezaee, M., and Malaekehnikouei, B. (2018). Nano strategies for berberine delivery, a natural alkaloid of berberis. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 1060:e4279. doi: 10.1002/bmc.4279
Mistry, B. M., Keum, Y. S., Pandurangan, M., Kim, D. H., Moon, S. H., Kadam, A. A., et al. (2017). Synthesis and evaluation of antioxidant and cytotoxicity of the n-mannich base of berberine bearing benzothiazole moieties. Anti-cancer Agents Med. Chem. 17, 1652–1660. doi: 10.2174/1871520617666170710180549
Mittal, A., Tabasum, S., and Singh, R. P. (2014). Berberine in combination with doxorubicin suppresses growth of murine melanoma b16f10 cells in culture and xenograft. Phytomedicine 21, 340–347. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.09.002
Munir, I., Fukunaga, K., Kanasaki, H., Miyazaki, K., Ohba, T., Okamura, H., et al. (2000). Expression of cyclooxygenase 2 by prostaglandin e2 in human endometrial adenocarcinoma cell line hec-1b1. Biol. Reprod. 63, 933–941. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod63.3.933
Murthy, K. N. C., Kim, J., Vikram, A., and Patil, B. S. (2012). Differential inhibition of human colon cancer cells by structurally similar flavonoids of citrus. Food Chem. 132, 27–34. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.10.014
Nardi, I., Reno, T., Yun, X., Sztain, T., Wang, J., Dai, H., et al. (2018). Triptolide inhibits Wnt signaling in NSCLC through upregulation of multiple Wnt inhibitory factors via epigenetic modifications to Histone H3. Int. J. Cancer 143, 2470–2478. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31756
Naveen, C. R., Gaikwad, S., and Agrawalrajput, R. (2016). Berberine induces neuronal differentiation through inhibition of cancer stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in neuroblastoma cells. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharmacol. 23, 736–744. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.03.013
Neag, M. A., Mocan, A., Echeverría, J., Pop, R. M., Bocsan, C. I., Crişan, G., et al. (2018). Berberine: botanical occurrence, traditional uses, extraction methods, and relevance in cardiovascular, metabolic, hepatic, and renal disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 9:557. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00557
Oliver, K. R., Mccomb, J. A., and Greene, W. K. (2013). Transposable elements: powerful contributors to angiosperm evolution and diversity. Genome Biol. Evol. 5, 1886–1901. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evt141
Pandey, A., Vishnoi, K., Mahata, S., Tripathi, S. C., Misra, S. P., Misra, V., et al. (2015). Berberine and curcumin target survivin and stat3 in gastric cancer cells and synergize actions of standard chemotherapeutic 5-fluorouracil. Nutr. Cancer Int. J. 67, 1293–1304. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2015.1085581
Peng, P. L., Kuo, W. H., Tseng, H. C., and Chou, F. P., (2008). Synergistic tumor-killing effect of radiation and berberine combined treatment in lung cancer: the contribution of autophagic cell death. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 70, 529–542. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.08.034
Puneet, Kazmi, H. R., Kumari, S., Tiwari, S., Khanna, A., and Narayan, G. (2018). Epigenetic mechanisms and events in gastric cancer-emerging novel biomarkers. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2, 1–14. doi: 10.1007/s12253-018-0410-z
Qi, H. W., Xin, L. Y., Xu, X., Ji, X. X., and Fan, L. H. (2014). Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers to predict response of berberine in suppressing lung cancer invasion and metastasis. J. Trans. Med. 12:22. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-22
Qing, Y., Hu, H., Liu, Y., Feng, T., Meng, W., Jiang, L., et al. (2014). Berberine induces apoptosis in human multiple myeloma cell line u266 through hypomethylation of p53 promoter. Cell Biol. Int. 38, 563–570. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10206
Rahnamoun, H., Lee, J., Sun, Z., Lu, H., Ramsey, K. M., Komives, E. A., et al. (2018). RNAs interact with BRD4 to promote enhanced chromatin engagement and transcription activation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 25:687. doi: 10.1038/s41594-018-0102-0
Rayan, N. A., Rosario, R. C. H. D., and Prabhakar, S. (2016). Massive contribution of transposable elements to mammalian regulatory sequences. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 57, 51–56. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.05.004
Riaz, S. K., Saeed, M., and Malik, M. F. (2015). Clinical and therapeutic implications of histone acetylation in breast cancer. West Indian Med. J. 65, 337–344. doi: 10.7727/wimj.2014.297
Sahebi, M., Hanafi, M. M., van Wijnen, A. J., Rice, D., Rafii, M. Y., Azizi, P., et al. (2018). Contribution of transposable elements in the plant’s genome. Gene 665, 155–166. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.04.050
Salimian, N., Peymani, M., Ghaedi, K., and Esfahani, M. (2018). Modulation in mir-200a/sirt1axis is associated with apoptosis in mpp+-induced sh-sy5y cells. Gene 674, 24–30. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.06.061
Sanna, L., Marchesi, I., Melone, M. A. B., and Bagella, L. (2018). The role of enhancer of zeste homolog 2: from viral epigenetics to the carcinogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 233, 6508–6517. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26545
Sengupta, D., Chowdhury, K. D., Chatterjee, S., Sarkar, A., Paul, S., Sur, P. K., et al. (2017). Modulation of adenylate cyclase signaling in association with mkk3/6 stabilization under combination of sac and berberine to reduce hepg2 cell survivability. Apoptosis 22, 1–18. doi: 10.1007/s10495-017-1407-x
Sengupta, D., Chowdhury, K. D., Sarkar, A., Paul, S., and Sadhukhan, G. C., (2014). Berberine and S allyl cysteine mediated amelioration of DEN+ CCl4 induced hepatocarcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subjects 1840, 219–244. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.08.020
Shang, A., Bylipudi, S., and Bieszczad, K. M. (2018). Inhibition of histone deacetylase 3 via rgfp966 facilitates cortical plasticity underlying unusually accurate auditory associative cue memory for excitatory and inhibitory cue-reward associations. Behav. Brain Res. 356, 453–469. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.05.036
Shi, H. L., Wu, X. J., Liu, Y., and Xie, J. Q. (2013). Berberine counteracts enhanced il-8 expression of ags cells induced by evodiamine. Life Sci. 93, 830–839. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2013.09.010
Shi, Y., Zhao, Y., Shao, N., Ye, R., Lin, Y., Zhang, N., et al. (2017). Overexpression of microrna-96-5p inhibits autophagy and apoptosis and enhances the proliferation, migration and invasiveness of human breast cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 13, 4402–4412. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6025
Signorelli, C., Odone, A., Ciorba, V., Cella, P., Audisio, R. A., Lombardi, A., et al. (2017). Human papillomavirus 9-valent vaccine for cancer prevention: a systematic review of the available evidence. Epidemiol. Infect. 145:21. doi: 10.1017/s0950268817000747
Siveen, K. S., and Kuttan, G. (2011). Thujone inhibits lung metastasis induced by b16f-10 melanoma cells in c57bl/6 mice. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 89:691. doi: 10.1139/y11-067
Stevens, M. S., Aliabadi, Z., and Moore, M. R. (1984). Associated effects of sodium butyrate on histone acetylation and estrogen receptor in the human breast cancer cell line mcf-7. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 119, 132–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(84)91628-0
Su, Y. H., Tang, W. C., Cheng, Y. W., Sia, P., Huang, C. C., Lee, Y. C., et al. (2015). Targeting of multiple oncogenic signaling pathways by hsp90 inhibitor alone or in combination with berberine for treatment of colorectal cancer. BBA – Mol. Cell Res. 1853, 2261–2272. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.05.012
Sun, W., Zhang, L., and Li, R. (2017). Overexpression of miR-206 ameliorates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats via the MEK/ERK pathway by targeting brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neurosci. Lett. 646, 68–74. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.12.047
Tabeshpour, J., Imenshahidi, M., and Hosseinzadeh, H. (2017). A review of the effects ofberberis vulgarisand its major component, berberine, in metabolic syndrome. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 20, 557–568. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2017.8682
Tang, J., and Feng, Y. S. (2009). Berberine and coptidis rhizoma as novel antineoplastic agents: a review of traditional use and biomedical investigations. J. Ethnopharmacol. 126, 5–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.08.009
Tao, Y., Lin, Y., She, Z., Lin, M., Chen, P., and Zhang, J. (2015). Anticancer activity and mechanism investigation of beauvericin isolated from secondary metabolites of the mangrove endophytic fungi. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 15, 258–266. doi: 10.2174/1871520614666140825112255
Tong, N., Zhang, J., Chen, Y., Zhubo, L. I., Luo, Y., Zuo, H., et al. (2012). Berberine sensitizes mutliple human cancer cells to the anticancer effects of doxorubicin in vitro. Oncol. Lett. 3, 1263–1267. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.644
Viegas, S., Ladeira, C., Costaveiga, A., Perelman, J., and Gajski, G. (2017). Forgotten public health impacts of cancer – An overview. Arh. Hig. Rada. Toksikol. 68:287. doi: 10.1515/aiht-2017-68-3005
Vijayaraghavalu, S., Dermawan, J. K., and Cheriyath, V. (2013). Highly synergistic effect of sequential treatment with epigenetic and;anticancer drugs to overcome drug resistance in breast cancer cells is;mediated via activation of p21 gene expression leading to g2/m cycle;arrest. Mol. Pharm. 10, 337–352. doi: 10.1021/mp3004622
Walker, D. K., Edwards, R. L., Bagcivan, G., and Bakitas, M. A. (2017). Cancer and palliative care in the united states, turkey, and malawi: developing global collaborations. Asia-Pacific J. Oncol. Nurs. 4, 209–219. doi: 10.4103/apjon.apjon_31_17
Wang, J., Kang, M., Wen, Q., Qin, Y. T., Wei, Z. X., Xiao, J. J., et al. (2017). Berberine sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to radiation through inhibition of sp1 and emt. Oncol. Rep. 37, 2425–2432. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5499
Wang, N., Feng, Y., Cheung, F., Wang, X., Zhang, Z., and Feng, Y. (2015a). A chinese medicine formula gegen qinlian decoction suppresses expansion of human renal carcinoma with inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2. Integr. Cancer Ther. 14:75. doi: 10.1177/1534735414550036
Wang, N., Tan, H. Y., Li, L., Yuen, M. F., and Feng, Y. (2015b). Berberine and coptidis rhizoma as potential anticancer agents: recent updates and future perspectives. J. Ethnopharmacol. 176, 35–48. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.028
Wang, S., Xiao, Z., Hong, Z., Jiao, H., Zhu, S., Zhao, Y., et al. (2018). FOXF1 promotes angiogenesis and accelerates bevacizumab resistance in colorectal cancer by transcriptionally activating VEGFA. Cancer Lett. 439, 78–90. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.09.026
Wang-Johanning, F., Radvanyi, L., Rycaj, K., Plummer, J. B., Yan, P., Sastry, K. J., et al. (2008). Human endogenous retrovirus k triggers an antigen-specific immune response in breast cancer patients. Cancer Res. 68, 5869–5877. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6838
Waterbeemd, B. V. D., Mommen, G. P. M., Pennings, J. L. A., Eppink, M. H., Wijffels, R. H., Pol, L. A. V. D., et al. (2013). Quantitative proteomics reveals distinct differences in the protein content of outer membrane vesicle vaccines. J. Proteome Res. 12, 1898–1908. doi: 10.1021/pr301208g
Wen, C., Wu, L., Fu, L., Zhang, X., and Zhou, H. (2016). Berberine enhances the anti-tumor activity of tamoxifen in drug-sensitive MCF-7 and drug-resistant MCF-7/TAM cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 14, 2250–2256. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5490
Wong, K. Y., and Chim, C. S. (2015). DNA methylation of tumor suppressor protein-coding and non-coding genes in multiple myeloma. Epigenomics 7, 985–1001. doi: 10.2217/epi.15.57
Wu, Y. Q., Chen, X. S., and Chai, J. B. (2012). The involvement of the cd40-cd40l pathway in activated platelet-induced changes in huvec cox-2 and pparα expression. Inflammation 35, 1184–1190. doi: 10.1007/s10753-011-9427-0
Xu, Z., Feng, W., Shen, Q., Yu, N., Yu, K., Wang, S., et al. (2017). Rhizoma coptidis and berberine as a natural drug to combat aging and aging-related diseases via anti-oxidation and ampk activation. Aging Dis. 8, 760–777. doi: 10.14336/AD.2016.0620
Xue, M., Yang, M. X., Zhang, W., Li, X. M., Gao, D. H., Ou, Z. M., et al. (2013). Characterization, pharmacokinetics, and hypoglycemic effect of berberine loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 8(Issue 1), 4677–4687. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S51262
Yakata, Y., Nakayama, T., Yoshizaki, A., Kusaba, T., and Sekine, I. (2007). Expression of p-stat3 in human gastric carcinoma: significant correlation in tumour invasion and prognosis. Int. J. Oncol. 30, 437–442. doi: 10.3892/ijo.30.2.437
Yamada, K., Mizukoshi, E., Sunagozaka, H., Arai, K., Yamashita, T., Takeshita, Y., et al. (2015). Response to importance of confounding factors in assessing fatty acid compositions in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 35, 1773–1773. doi: 10.1111/liv.12755
Yan, L., Yang, X., and Davidson, N. E. (2001). Role of dna methylation and histone acetylation in steroid receptor expression in breast cancer. J. Mamm. Gland Biol. Neoplasia 6, 183–192. doi: 10.1023/a:1011308707512
Yan, X. T., Zhao, Y., and Cheng, X. L. (2018). Inhibition of mir-200b/mir-429 contributes to neuropathic pain development through targeting zinc finger e box binding protein-1. J. Cell Physiol. 233, 4815–4824. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26284
Yang, M., Yang, Y., Cui, H., Guan, Z., Yang, Y., Zhang, H., et al. (2015). The natural compound gambogic acid radiosensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells under hypoxic conditions. Tumori 102:135. doi: 10.5301/tj.5000411
Zhang, J., Lai, Z., Huang, W., Ling, H., Lin, M., Tang, S., et al. (2017). Apicidin inhibited proliferation and invasion and induced apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway in non-small cell lung cancer glc-82 cells. Anti-cancer Agents Med. Chem. 17, 1374–1382. doi: 10.2174/1871520617666170419120044
Zhang, J., Yi, T., Liu, J., Zhao, Z., and Chen, H. (2013). Quercetin induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in kb and kbv200 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 61, 2188–2195. doi: 10.1021/jf305263r
Zhang, J., Zhang, H., and Zi, T. (2015). Overexpression of microrna-141 relieves chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain via targeting high-mobility group box 1. Int. J. Mol. Med. 36:1433. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2342
Zhang, J. Y., Huang, W. J., Sun, H. M., Liu, Y., Zhao, X. Q., Tang, S. L., et al. (2017). Structure identification and in vitro anticancer activity of lathyrol-3-phenylacetate-5,15-diacetate. Molecules 22:1412. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091412
Zhang, J. Y., Lin, M. T., Tung, H. Y., Tang, S. L., Yi, T., Zhang, Y. Z., et al. (2016). Bruceine d induces apoptosis in human chronic myeloid leukemia k562 cells via mitochondrial pathway. Am. J. Cancer Res. 6:819.
Zhang, J. Y., Lin, M. T., Zhou, M. J., Yi, T., Tang, Y. N., Tang, S. L., et al. (2015). Combinational treatment of curcumin and quercetin against gastric cancer mgc-803 cells in vitro. Molecules 20, 11524–11534. doi: 10.3390/molecules200611524
Zhang, L., Fang, Y., Xu, X. F., and Jin, D. Y. (2017). Moscatilin induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells via reactive oxygen species and the jnk/sapk pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 15, 1195–1203. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6144
Zhang, L., Wang, Y., Wang, L., Yin, G., Li, W., Xian, Y., et al. (2018). miR-23c suppresses tumor growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma by attenuating ERBB2IP. Biomed. Pharmacother. 107, 424–432. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.155
Zhang, S., Chang, M., Zhou, Z., Dai, X., and Xu, Z. (2018). Pdhs-elm: computational predictor for plant dnase i hypersensitive sites based on extreme learning machines. Mol. Genet. Genomics 293, 1035–1049. doi: 10.1007/s00438-018-1436-3
Zhang, X. Z., Wang, L., Liu, D. W., Tang, G. Y., Zhang, H. Y., et al. (2014). Synergistic inhibitory effect of berberine and d-limonene on human gastric carcinoma cell line MGC803. J. Med. Food 17, 955–962. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2013.2967
Zhao, Y., Gao, J. L., Ji, J. W., Gao, M., Yin, Q. S., Qiu, Q. L., et al. (2014). Cytotoxicity enhancement in MDA-MB-231 cells by the combination treatment of tetrahydropalmatine and berberine derived from Corydalis yanhusuo WT Wang. J. Int. Ethnopharmacol. 3:68. doi: 10.5455/jice.20140123040224
Zhao, Y., Jing, Z., Li, Y., and Mao, W., (2016). Berberine in combination with cisplatin suppresses breast cancer cell growth through induction of dna breaks and caspase-3-dependent apoptosis. Oncol. Rep. 36, 567–572. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4785
Zheng, F., Wu, J., Tang, Q., Xiao, Q., Wu, W., Hann, S. S., et al. (2018). The enhancement of combination of berberine and metformin in inhibition of DNMT1 gene expression through interplay of SP1 and PDPK1. J. Cell Mol. Med. 22, 600–612. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13347
Keywords: berberine, biological activities, antitumor, autophagy, epigenetic effects
Citation: Liu D, Meng X, Wu D, Qiu Z and Luo H (2019) A Natural Isoquinoline Alkaloid With Antitumor Activity: Studies of the Biological Activities of Berberine. Front. Pharmacol. 10:9. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00009
Received: 21 November 2018; Accepted: 07 January 2019;
Published: 14 February 2019.
Edited by:
Zhe-Sheng Chen, St. John’s University, United StatesCopyright © 2019 Liu, Meng, Wu, Qiu and Luo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhidong Qiu, UWl1emRAY2N1Y20uZWR1LmNu Haoming Luo, bHVvLmhhb21pbmdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Da Liu1,2
Da Liu1,2 Xue Meng
Xue Meng Haoming Luo
Haoming Luo