Willingness to pay for social health insurance in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- 1Department of Pharmacy, College of Medicine and Health Sciences (CMHS), Wollo University, Dessie, Ethiopia
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Woldia Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Woldia, Ethiopia
- 3Department of Pharmaceutics and Social Pharmacy, School of Pharmacy, College of Health Sciences, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
A corrigendum on
Willingness to pay for social health insurance in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
by Bayked, E. M., Toleha, H. N., Chekole, B. B., Workneh, B. D., and Kahissay, M. H. (2023). Front. Public Health 11: 1089019.doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1089019
In the published article, there was an error in the Results section of the Abstract. This error occurred when we compared the willingness of teachers and health professionals to pay for social health insurance, without considering the proportions (3.22:0.42) of the odds ratios of the two groups' willingness to pay.
A correction has been made to the Abstract, Results. This sentence previously stated:
“Professionally, teachers were 3.22 times more likely to pay for the scheme (OR = 3.22; 95% CI: 1.80–5.76) than health professionals.”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“Professionally, teachers were 7.67 times more likely to pay for the scheme (OR = 3.22; 95% CI: 1.80–5.76) than health professionals (OR = 0.42; 95% CI: 0.19–0.93).”
In the published article, there was an error in the Results section, “Results of Quantitative Synthesis”, paragraph 3. The error occurred for the same reason stated above in the previous correction.
A correction has been made to Results, “Results of Quantitative Synthesis”, paragraph 3. This sentence previously stated:
“Thus, as shown in Figure 5, regarding the sub-group analysis by profession, teachers were 3.22 times more likely to pay for SHI (OR = 3.22; 95% CI: 1.80–5.76) than health professionals.”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“Thus, as shown in Figure 5, regarding the sub-group analysis by profession, teachers were 7.67 times more likely to pay for SHI (OR = 3.22; 95% CI: 1.80–5.76) than health professionals (OR = 0.42; 95% CI: 0.19–0.93).”
For clarity, the sentence: “However, the WTP of health professionals to the scheme was 58% less likely (OR = 0.42; 95% CI: 0.19–0.93) than that of teachers”, which is the last sentence in paragraph 3 of the Results section, subsection “Results of Quantitative Synthesis”, has been removed.
In the published article, there was an error in the Discussion section, subsection “Limitations”. This was a typographical error.
A correction has been made to Discussion, “Limitations”. The sentence previously stated:
“The direction of association between the dependent variable (WTP for SHI) and the dependent variables was not estimated due to the variability of the reports of the included studies.”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“The direction of association between the dependent variable (WTP for SHI) and the independent variables was not estimated due to the variability of the reports of the included studies.”
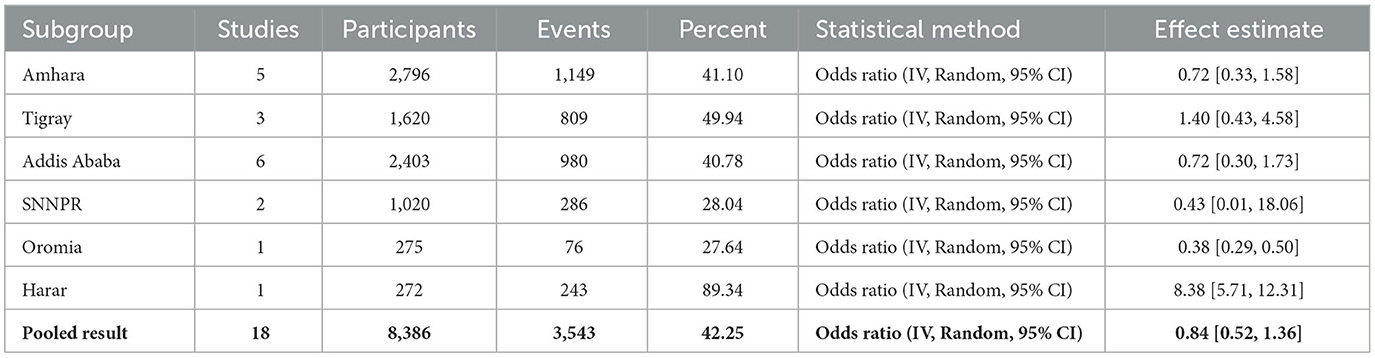
In the published article, there was an error in Table 2 as published. Under the column “Statistical Method”, the abbreviations “M-H” in each row should be corrected as “IV” as they appear in the pooled result.
The corrected Table 2 and its caption appear below:
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: willingness to pay, social health insurance, associated factors, systematic review, meta-analysis, Ethiopia
Citation: Bayked EM, Toleha HN, Chekole BB, Workneh BD and Kahissay MH (2023) Corrigendum: Willingness to pay for social health insurance in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 11:1252289. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1252289
Received: 03 July 2023; Accepted: 18 September 2023;
Published: 27 September 2023.
Approved by:
Ayan Jha, The Palladium Group, United StatesCopyright © 2023 Bayked, Toleha, Chekole, Workneh and Kahissay. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ewunetie Mekashaw Bayked, emebirhan7@gmail.com
 Ewunetie Mekashaw Bayked
Ewunetie Mekashaw Bayked Husien Nurahmed Toleha
Husien Nurahmed Toleha Beletu Berihun Chekole2
Beletu Berihun Chekole2