- The Laboratory of Research in Management, Economics and Social Sciences (LARGESS), Department of Economics and Management, Chouaib Doukkali University, El Jadida, Morocco
This study evaluates the effectiveness of Machine Learning (ML) models in forecasting the EUR/USD exchange rate from January 2014 to December 2024, focusing on the relationship between forecast errors and key macroeconomic indicators, including interest rates, inflation, unemployment, and GDP growth. The forecasting framework integrates three widely used architectures—Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), Random Forest (RF), and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks—applied to monthly exchange rate and macroeconomic data drawn from Yahoo Finance, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund. The findings indicate that the LSTM model outperforms both MLP and RF in predictive accuracy, achieving an R-squared value of 0.9234. While all models demonstrate strong short-term forecasting performance, macroeconomic variables have limited explanatory power regarding forecast error, with only Eurozone interest rates showing weak statistical significance. These results suggest that ML models can effectively model exchange rate dynamics even when macroeconomic indicators provide limited statistical relevance. The study contributes to the literature on AI in financial forecasting by highlighting the comparative strengths of deep learning and ensemble methods and identifying persistent challenges in integrating economic fundamentals, underscoring the value of hybrid and interpretable AI frameworks that bridge macroeconomic theory and data-driven learning for improved financial forecasting.
1 Introduction
The prediction of exchange rates has been a longstanding challenge in financial economics. Exchange rates play a pivotal role in international trade, investment decisions, and economic policy. The volatility and unpredictability of currency movements can have profound implications for businesses, governments, and financial institutions. Therefore, accurate forecasting of exchange rates is essential for making informed decisions in the global financial markets. Traditional models of exchange rate forecasting, which rely heavily on economic theories such as purchasing power parity (PPP) and interest rate parity (IRP), have faced significant limitations in capturing the complexities of currency movements in real-time markets. While these models provide valuable insights into long-term trends, they often fail to predict short-term fluctuations due to their reliance on simplified assumptions and linear relationships between macroeconomic variables. As a result, forecasting exchange rates has remained an area where there is a high degree of uncertainty and error.
Over the past few decades, the rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) techniques has introduced new approaches to forecasting complex financial phenomena like exchange rates. AI and ML models are capable of processing vast amounts of data, identifying non-linear patterns, and learning from historical trends without the need for explicit assumptions. Unlike traditional econometric models, which typically rely on predefined equations and theoretical relationships, AI and ML models are data-driven and can adapt to dynamic market conditions. This has led to a growing interest in applying machine learning algorithms, such as neural networks, decision trees, and support vector machines, to predict exchange rate movements. Since 2020, the application of advanced neural architectures such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in exchange rate forecasting has expanded rapidly. These models have proven particularly effective in volatile environments where nonlinear relationships dominate and macroeconomic signals are complex to interpret. For instance, Abedin et al. (1) demonstrated that macroeconomically-augmented LSTM models deliver significantly improved predictive performance for EUR/USD exchange rates, especially during periods marked by sudden economic events such as interest rate hikes or inflationary shocks. Similarly, Dritsas and Trigka (2, 3) showed that deep LSTM ensemble models consistently outperform both traditional econometric approaches and shallow neural networks, particularly in multi-horizon forecasting contexts. These developments highlight a major shift in recent literature toward more flexible, adaptive, and non-linear modeling strategies to capture the complex dynamics of currency markets.
These algorithms have been shown to outperform conventional models, especially in volatile market environments where traditional models struggle to adapt quickly. Despite the promising results of AI and ML models in exchange rate forecasting, the question remains whether these models fully incorporate macroeconomic factors that significantly influence exchange rates. Factors such as interest rates, inflation, and unemployment are known to play a fundamental role in determining the long-term direction of exchange rates. However, the impact of these macroeconomic indicators on the performance of AI and ML models, particularly in short-term forecasting, is not well understood. While previous research has focused on improving the statistical accuracy of these models, there has been limited attention paid to their economic interpretability and their ability to integrate macroeconomic variables in a meaningful way. This gap in the literature represents a crucial area of inquiry, as understanding the relationship between forecast errors and macroeconomic factors can provide deeper insights into the strengths and limitations of AI/ML models for practical financial forecasting.
The primary aim of this study is to conduct a detailed economic analysis of the performance of AI and ML models in exchange rate forecasting by examining the relationship between forecast inaccuracy and key macroeconomic factors, including interest rates, unemployment, and inflation. While previous studies have evaluated the accuracy of machine learning models in forecasting exchange rates, this research takes a novel approach by focusing specifically on the economic context in which these models operate. The study uses a monthly time series dataset spanning ten years, from January 2014 to December 2024, to capture a range of economic cycles, including the recovery from the global financial crisis, the COVID-19 pandemic, and the recent inflationary and interest rate shocks in the United States and Europe. The EUR/USD exchange rate is chosen as the focus of this analysis due to its prominence in global financial markets and its sensitivity to macroeconomic factors from both the U.S. and the Eurozone.
The study employs regression models to explore how macroeconomic indicators influence the forecast errors of AI and ML models. By analyzing the relationship between forecast inaccuracy and variables such as GDP growth, inflation, interest rates, and unemployment, the study aims to fill the gap in the existing literature, which largely overlooks the role of macroeconomic factors in the performance of these models. In addition to examining the direct influence of these indicators on forecast errors, the study also investigates the overall effectiveness of AI/ML models compared to traditional econometric techniques in terms of both forecasting accuracy and economic interpretation. While statistical accuracy, measured by indicators like the root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), remains a key focus, this study emphasizes the economic relevance of forecast errors, particularly in the context of real-world financial decision-making.
The methodology of this research is designed to provide robust results by employing a variety of statistical techniques, including multiple regression analysis, correlation analysis, and ANOVA tests. The use of a comprehensive dataset spanning over a decade allows the study to capture a range of economic conditions, from periods of relative stability to those marked by significant volatility and macroeconomic shocks. This enables a more nuanced understanding of the performance of AI and ML models in different economic contexts. The study also incorporates control variables to account for confounding factors that may influence both macroeconomic indicators and model performance. For example, binary indicators are used to account for significant economic events, such as financial crises or policy changes, that could have an impact on exchange rate movements and forecast errors.
A key aspect of this study is the comparison between AI/ML models and traditional econometric models. While machine learning algorithms have demonstrated superior performance in terms of predictive accuracy, their economic interpretability has often been questioned. Traditional models, on the other hand, may lack the flexibility and adaptive capabilities of AI/ML models but offer clearer theoretical underpinnings. By comparing the two approaches, this study seeks to determine whether AI/ML models can provide not only better forecasts but also insights into the underlying economic dynamics that drive exchange rate movements. This comparison is crucial for understanding how AI/ML models can complement or even replace traditional models in financial forecasting.
In terms of findings, this study anticipates that AI and ML models will outperform traditional econometric models in terms of accuracy, especially in forecasting short-term fluctuations in the EUR/USD exchange rate. However, it is expected that macroeconomic factors, such as the Eurozone interest rate, will show some level of correlation with forecast errors, albeit weak. This suggests that while AI/ML models can capture complex relationships in historical exchange rate data, they may still be sensitive to significant macroeconomic events that cannot be fully captured by historical price movements alone. The study’s results are expected to provide valuable insights into the strengths and limitations of AI/ML models, especially in terms of their ability to integrate macroeconomic variables and provide reliable forecasts in times of economic instability.
The contribution of this study lies not only in its exploration of the effectiveness of AI and ML models for exchange rate forecasting but also in its economic analysis of forecast errors. By examining how these errors relate to macroeconomic indicators, the study provides a more comprehensive understanding of the performance of AI/ML models in real-world financial forecasting. The findings of this research have important implications for financial institutions, policymakers, and investors who rely on exchange rate forecasts to make strategic decisions. Moreover, the study highlights the potential of AI and ML models to revolutionize financial forecasting by offering data-driven insights that go beyond traditional economic theories.
In sum, this research contributes to both the empirical and theoretical literature by evaluating the performance of AI/ML models in exchange rate forecasting through the lens of macroeconomic integration. By bridging data-driven techniques and economic reasoning, the study offers a dual perspective: assessing predictive accuracy and uncovering the role of fundamental indicators in explaining model errors. This dual approach is particularly relevant for enhancing the interpretability and policy relevance of machine learning applications in finance.
2 Literature review
Exchange rate forecasting is a critical component of financial markets and international trade, serving as an essential tool for businesses, investors, and policymakers alike. The ability to predict exchange rate movements accurately has far-reaching implications. For businesses, it enables the development of effective currency hedging strategies, protecting against unexpected fluctuations in exchange rates that could otherwise undermine profitability (4). For investors, exchange rate forecasting plays a pivotal role in managing foreign exchange risk, allowing them to make well-informed decisions regarding portfolio allocation and investment strategies (5). Policymakers, too, rely on accurate exchange rate forecasts to make strategic decisions about monetary policy and trade agreements, as the value of a currency impacts national inflation, export and import prices, and overall economic growth (6, 7).
The foreign exchange market, or forex, is the largest and most liquid market globally, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion (45). Given the market’s size and complexity, exchange rate forecasting is central to financial risk management practices. The movement of currencies directly affects trade balances, investment flows, inflation rates, and even global capital flows. For instance, fluctuations in exchange rates can significantly alter the competitiveness of a country’s goods and services in global markets, thereby influencing trade dynamics (8). As such, exchange rate forecasts provide essential insights for anticipating economic conditions and formulating policy decisions (9).
Historically, the approaches to exchange rate forecasting were dominated by traditional econometric models. Among the most widely used were the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA), Vector Autoregressive (VAR) models, and the random walk model. These models predominantly relied on statistical techniques and historical data to predict future exchange rate movements. ARIMA, for example, is a time-series model that uses past data points to forecast future values based on their observed relationships (10). Similarly, VAR models captured the interdependencies among multiple time-series variables, making them useful for examining how different economic factors such as interest rates and inflation affect exchange rates (11). The random walk model, which assumes that future exchange rate movements are unpredictable and do not follow any systematic trend, was also frequently employed in forecasting exercises (12).
However, while these traditional econometric models provided some valuable insights, they often had notable limitations. One of the primary drawbacks was their reliance on linear assumptions, which limited their ability to capture the complex, non-linear relationships that are prevalent in financial markets. Plakandaras and Papadimitriou (13) highlight that exchange rates are influenced by a wide variety of factors, including geopolitical events, speculative activity, and market sentiment, which cannot always be captured by linear models. Furthermore, these econometric models struggled to account for the sharp, often unpredictable shifts in the market that are characteristic of the forex market. For instance, during periods of financial crises or political instability, exchange rates can experience sudden and extreme movements that linear models, such as ARIMA or VAR, are ill-equipped to predict (14, 46).
Moreover, the random walk model, while useful in suggesting that exchange rate predictions are difficult in the long run, failed to provide much insight into short-term movements or volatile market conditions (7). This limitation of traditional models such as the random walk was notably illustrated in the influential work of Meese and Rogoff (12), who concluded that no macroeconomic model outperformed a naïve random walk in out-of-sample forecasting. However, more recent studies using machine learning have challenged this view. For instance, Küçük (15) showed that LSTM and CNN architectures significantly outperformed ARIMA and VAR models in predicting exchange rate movements by effectively capturing nonlinear dependencies in macroeconomic variables like inflation and interest rates. Similarly, Ciganovic (16) demonstrated that advanced AI models incorporating labor market dynamics, such as unemployment duration, provided enhanced forecasting accuracy across different economic regimes. Furthermore, Mirza (17) emphasized the role of explainable AI techniques to bridge the interpretability gap between machine learning models and traditional econometric approaches, thereby improving trust and usability in financial forecasting. These findings signal a growing consensus that AI-driven models not only surpass traditional methods in predictive power but also offer better adaptability to structural changes and macroeconomic shocks. As the forex market is influenced by a multitude of factors, many of which interact in highly complex and dynamic ways, the random walk model proved insufficient for forecasting exchange rates during periods of high volatility or when market shocks occur.
To address these limitations, newer approaches, particularly those based on machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI), have gained popularity. These newer models can account for the complexity and non-linearity inherent in financial data by leveraging vast amounts of historical and real-time data. For instance, models such as support vector machines (SVM), neural networks, and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks have shown significant promise in capturing patterns and trends that traditional econometric models often missed (2, 3, 47). These machine learning models are capable of incorporating not only economic variables like inflation rates and GDP growth but also unstructured data such as news articles, social media sentiment, and even geopolitical events, providing a more holistic view of the factors driving exchange rate movements (18, 19).
The SVM model, for example, has been effective in classifying exchange rate trends and predicting directional movements based on historical data (20). Similarly, neural networks have demonstrated their ability to model complex non-linear relationships and learn from vast datasets, offering a more adaptable and accurate approach compared to traditional models (21, 22). Moreover, the advent of LSTM networks has significantly enhanced exchange rate forecasting by allowing models to capture temporal dependencies and long-term trends in time-series data, making them well-suited for financial forecasting (23, 24).
Despite the promise of AI and ML-based models, they are not without their challenges. One of the primary concerns is the need for large amounts of high-quality data to train these models effectively. Incomplete, noisy, or biased data can lead to inaccurate predictions, and overfitting—where a model fits the training data too closely—remains a persistent issue in the use of machine learning for financial forecasting (25, 48). Furthermore, the lack of interpretability in many AI and ML models, particularly deep learning techniques, is another challenge. The so-called “black-box” nature of models like neural networks and LSTM networks makes it difficult for analysts to understand how a model is arriving at its predictions, which is a significant concern in financial forecasting where transparency and accountability are crucial (26).
Moreover, while these newer techniques have been successful in capturing the complexities of exchange rate movements, they still face limitations when it comes to incorporating macroeconomic fundamentals such as interest rates, inflation, and unemployment. Traditional econometric models were explicitly designed to model these macroeconomic variables and their direct impact on exchange rates, but the ability of ML and AI models to explicitly incorporate these variables and their relationships with exchange rates is still an area of ongoing research (1). Research shows that combining AI and ML techniques with macroeconomic fundamentals could enhance forecasting accuracy, as AI models can detect the complex, non-linear relationships that traditional econometric models often overlook (27).
The challenge of accurately forecasting exchange rates is further compounded by the inherent uncertainty and volatility of the forex market. Political instability, economic crises, natural disasters, and global pandemics all introduce unpredictable fluctuations in exchange rates, rendering even the most sophisticated forecasting models less reliable in the short term (28). As such, forecasters must determine how and when to incorporate external factors, such as geopolitical events or policy changes, into their models. Some recent advancements, such as the use of reinforcement learning and deep learning algorithms, have been explored as solutions to these challenges, allowing models to adapt to unexpected market shocks and improve their robustness in volatile environments (49). However, these models also face challenges in processing large, complex datasets and require careful tuning to avoid overfitting.
The rise of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) has brought forward new forecasting techniques that can handle the complexities and non-linearity of exchange rate data. These newer AI/ML techniques, such as Support Vector Machines (SVM), Random Forests, Neural Networks, and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, have been found to outperform traditional econometric models by effectively capturing patterns and trends that the older models missed (2, 3, 47). AI and ML models can incorporate vast amounts of historical and real-time data, such as macroeconomic indicators, sentiment analysis, and even financial news, which makes them adept at forecasting in dynamic and volatile market conditions.
AI/ML models allow for greater flexibility by dynamically adapting to new data without the stringent assumptions required by traditional models, such as stationarity. This is particularly advantageous during periods of high market volatility, as AI models can continuously adjust to changing market conditions without being restricted by prior assumptions about data behavior (29). However, despite their promise, these models are not without challenges, including concerns around overfitting, the need for large amounts of high-quality data, and interpretability issues (17).
Moreover, the increased reliance on macroeconomic variables—such as interest rates, inflation rates, GDP growth, and unemployment—remains pivotal to exchange rate dynamics. While traditional econometric models emphasized these variables as key predictors of exchange rates, AI/ML models typically rely on historical relationships between variables and may not always explicitly model the intricate interactions between exchange rates and macroeconomic fundamentals. Despite this, research suggests that combining AI/ML techniques with macroeconomic fundamentals can improve forecast accuracy, as AI models are better equipped to detect non-linear relationships that traditional models may overlook (1).
One of the main challenges in exchange rate forecasting is the inherent uncertainty and volatility of currency markets. Factors such as political instability, natural disasters, and global economic events like financial crises or pandemics introduce unpredictable fluctuations that make forecasting difficult. These external factors complicate the forecasting process, as it is often unclear how or when they should be incorporated into forecasting models (28). However, recent advancements in AI—specifically reinforcement learning and deep learning algorithms—have shown potential in adapting to such shocks and improving model robustness in volatile environments (49).
Despite the promising capabilities of AI and ML models, some challenges remain. While traditional models generally perform well during periods of economic stability, they often fall short when forecasting in the face of unexpected economic shocks or market disruptions. The adaptability of AI/ML models to these unexpected events could be further enhanced by incorporating real-time data sources, such as financial news, social media sentiment, and geopolitical events (22). Furthermore, it has been shown that combining AI/ML models with hybrid approaches that integrate macroeconomic variables and econometric techniques can enhance forecasting accuracy during times of high volatility (30).
Macroeconomic variables play a central role in exchange rate forecasting. Interest rates, inflation, GDP growth, and unemployment rates have long been established as significant drivers of exchange rate movements. In traditional econometric models, these variables were considered the primary predictors of exchange rate changes. For example, the Interest Rate Parity (IRP) theory, which states that exchange rates should adjust based on interest rate differentials between two countries, has been foundational in understanding how interest rates affect exchange rates (31). Likewise, the Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) theory posits that exchange rates should adjust to equalize the price levels between two countries (32, 33). However, these traditional models often fail to account for the complexities and non-linear dynamics of real-world financial markets. For example, exchange rates are often influenced by factors such as market sentiment, political instability, and speculative behavior—factors that are difficult to quantify or model directly in econometric frameworks (34, 35). As a result, more dynamic forecasting approaches, such as AI/ML models, have been developed to capture these complex, non-linear relationships. While PPP and IRP provide foundational frameworks for explaining exchange rate movements, more advanced models such as the Behavioral Equilibrium Exchange Rate (BEER) and the Fundamental Equilibrium Exchange Rate (FEER) offer improved empirical performance, especially for medium-term alignment. Clark and MacDonald (50) developed the BEER model to account for productivity differentials, interest rate spreads, and net foreign assets, providing a behavioral benchmark for exchange rate misalignments. Similarly, Williamson (51) formulated the FEER model to identify exchange rates consistent with internal and external balance, offering useful policy guidance. These frameworks complement AI/ML approaches by embedding structural economic reasoning into empirical analysis.
AI/ML models are capable of incorporating a wider range of macroeconomic data, financial data, and unstructured data sources such as news sentiment and market opinions. These models are also better equipped to detect patterns in historical data and assess how they relate to future exchange rate movements. Studies have shown that incorporating macroeconomic indicators like interest rate differentials, inflation, and GDP growth into AI/ML models can significantly improve forecast accuracy (52). These improvements in forecasting accuracy are particularly important in volatile market environments, where traditional models often fail to capture the sudden changes in market sentiment or economic conditions.
Hybrid models that combine the strengths of traditional econometric techniques with the adaptability and flexibility of AI/ML models are gaining traction in exchange rate forecasting. These hybrid models seek to combine the theoretical underpinnings of econometric models, such as the macroeconomic variables that drive exchange rates, with the empirical, data-driven patterns captured by AI and ML. For example, integrating ARIMA or Vector Autoregression (VAR) models with deep learning architectures such as LSTM or CNNs can allow researchers to capture both the macroeconomic relationships between variables and the non-linear, complex patterns in the data (36). This approach has proven effective in capturing both short-term and long-term fluctuations in exchange rates, allowing for more accurate predictions. Furthermore, multi-source data integration is an important aspect of hybrid models. Traditional econometric models typically relied on structured data, such as historical exchange rates and macroeconomic indicators. However, the integration of unstructured data—such as financial news, social media sentiment, and geopolitical events—into AI/ML models has become increasingly important in improving the robustness and accuracy of exchange rate forecasts (37). By incorporating a broader range of data sources, hybrid models can more effectively capture the dynamic nature of financial markets and improve their predictive performance.
While AI and ML models offer numerous advantages over traditional econometric approaches, they are not without their challenges. One of the most significant challenges in AI/ML modeling is the risk of overfitting. These models have a large number of parameters, which increases the likelihood of fitting noise or irrelevant patterns in the data. Overfitting occurs when a model performs well on the training dataset but fails to generalize effectively to new, unseen data. This is a particular concern in the financial markets, where data is often noisy and market conditions change rapidly (25). Regularization techniques such as dropout and L2 regularization can help mitigate overfitting, but finding the right balance between model complexity and generalization remains a critical challenge (22).
Another challenge in AI/ML modeling is interpretability. Unlike traditional econometric models, which are relatively straightforward and based on economic theory, AI and ML models are often referred to as “black boxes” due to their complexity and lack of transparency. This lack of interpretability can be a significant barrier to the adoption of AI/ML models in financial forecasting, as decision-makers often need to understand the rationale behind the predictions made by the model (26). Researchers have proposed methods to improve the interpretability of AI/ML models, such as LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations), but these methods are still in their early stages and have not yet been widely adopted in financial forecasting (38).
3 Methods
The primary objective of this study is to perform a comprehensive economic analysis of the effectiveness of AI and ML models in exchange rate forecasting by examining the relationship between the forecast inaccuracy of these models and important macroeconomic factors, including GDP growth, interest rates, and inflation. This section presents the methodological framework, detailing the research design, variables, data collection, and analysis techniques.
3.1 Research design
This study adopts a quantitative, explanatory, and correlational research design. This approach is chosen because it allows the examination of the relationships between forecast errors of AI/ML models and the macroeconomic factors influencing exchange rates. An ex-post analysis is employed, where forecasts are generated using AI/ML models, and forecast errors are then regressed against macroeconomic factors to assess their impact.
A longitudinal approach is used to analyze historical time-series data for the EUR/USD exchange rate, considering several economic cycles and major macroeconomic events, such as the financial crisis, the COVID-19 pandemic, and recent inflation and interest rate shocks in the U.S. and Europe. The EUR/USD currency pair is chosen due to its liquidity and systemic importance in global finance, and because it is significantly impacted by various macroeconomic factors from both the U.S. and the Eurozone.
The study period spans ten years (2014–2024) to cover multiple economic cycles, including the post-crisis recovery, the COVID-19 disruptions, and recent monetary policy adjustments. The time-series data collected at monthly intervals provides a balanced dataset, enabling comprehensive analysis.
3.2 Variables
The primary dependent variable in this study is forecast error, defined as the difference between the observed exchange rate and the predicted exchange rate. Forecast error will be measured in different forms, including absolute error, squared error, and percentage error, to ensure robustness in the analysis. The independent variables include several key macroeconomic factors:
1. Interest rates (U.S. and Eurozone): interest rates are often linked to economic models like Interest Rate Parity (IRP) and have a direct impact on international capital flows and exchange rate movements (7).
2. Inflation (CPI for the U.S. and HICP for the Eurozone): inflation plays a key role in exchange rate dynamics through the Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) theory, affecting the relative purchasing power of currencies (53).
3. GDP growth: the overall economic performance, as captured by GDP growth, influences investment flows and investor sentiment, thus impacting currency demand (39).
4. Unemployment rate: the unemployment rate reflects the economic health of a country and its growth potential, indirectly influencing the demand for its currency (40).
Control variables will also be included, such as time (measured in months or quarters), and binary indicators signaling significant economic events (e.g., financial crises or policy changes).
3.3 Data and data collection
The data for this study are sourced from reputable and publicly accessible databases. Exchange rate data for EUR/USD is obtained from Yahoo Finance, Investing.com, and the IMF’s International Financial Statistics (IFS). Macroeconomic indicators are sourced from the World Bank Open Data, IMF databases, central banks, and national statistical agencies.
The data spans from January 2014 to December 2024, using monthly or quarterly observations depending on data availability and consistency across variables. The data collection process follows a multi-step approach. First, exchange rate forecasts are generated using basic machine learning forecasting models implemented in Excel. Techniques such as regression with lagged variables or Excel’s built-in Forecast Sheet are used to simulate AI-based predictions for the EUR/USD currency pair. The resulting forecast errors are then computed and paired with corresponding macroeconomic indicators for each time period. These datasets are cleaned for missing values and outliers, then merged and structured in Excel before being imported into SPSS for statistical analysis.
Forecasts using MLP, Random Forest, and LSTM models were implemented in Python using Scikit-learn and TensorFlow/Keras libraries. Initial data preprocessing and cleaning were performed in Excel, while all statistical tests (correlation, regression, ANOVA) were conducted in SPSS. This cross-platform integration ensured both modeling flexibility and statistical rigor throughout the study.
3.4 Data analysis
The analysis of data will follow a multi-step approach involving different statistical techniques. First, descriptive statistics will summarize the central tendencies and dispersion of all variables. Second, inferential statistics techniques, such as Pearson correlation analysis, will be conducted to assess the strength and direction of relationships between forecast error and macroeconomic variables. This will help identify whether changes in macroeconomic indicators are significantly associated with forecast errors in exchange rate predictions.
A multiple linear regression analysis will then be performed, with forecast error as the dependent variable and macroeconomic indicators as predictors. This analysis will measure the relative impact of each macroeconomic factor on the forecast error. Multicollinearity will be tested using the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) to assess redundancy among the independent variables.
Standardized beta coefficients will be used to determine the relative importance of each macroeconomic variable, and the model’s explanatory power will be assessed using R2 and Adjusted R2 values.
3.5 AI/ML forecasting models
To ensure robust evaluation of the models, this study focused on three supervised AI/ML architectures: Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), Random Forest (RF), and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks. These models were selected due to their proven effectiveness in capturing nonlinear dependencies and temporal patterns in financial time series. While other architectures such as SVM and CNN were initially considered during the design phase for their theoretical capabilities, they were ultimately excluded from the final modeling protocol to maintain methodological focus, consistency, and interpretability. The choice of MLP, RF, and LSTM reflects the study’s emphasis on models that balance predictive power with the ability to handle sequential financial data in a macroeconomic context.
Although CNN models were considered during the design phase for their capacity to capture spatial patterns across macroeconomic inputs, their implementation was ultimately excluded from the final experimental protocol to maintain methodological focus on temporal and ensemble learning architectures. Nevertheless, recent work such as Salonen (41) provides strong justification for future integration of CNN-based feature extraction in macro-financial forecasting tasks. These models will be employed to generate forecasts of exchange rates based on economic variables, and forecast errors will be analyzed to determine how well macroeconomic factors explain the discrepancies between predicted and actual exchange rates.
In addition to the baseline MLP model, two complementary machine learning architectures were implemented to provide comparative insights: Random Forest (RF) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM). The Random Forest algorithm, applied via Scikit-learn, consisted of 500 estimators with automatic depth detection and used bootstrap sampling to capture nonlinear interactions between macroeconomic predictors. This ensemble method offers robustness against overfitting and allows for interpretable feature importance measures.
The LSTM model was designed in Keras using TensorFlow backend, comprising one hidden layer with 50 units, ReLU activation, and a dropout rate of 0.2 to avoid overfitting. It was trained over 100 epochs with early stopping enabled. Unlike the Random Forest model, the LSTM is tailored for sequential learning and temporal forecasting, processing both lagged exchange rate values and macroeconomic variables as time series inputs. These two models were included to enhance methodological diversity and examine the relative effectiveness of tree-based ensembles and deep recurrent learning in exchange rate prediction.
In addition to the Random Forest and LSTM models, a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) neural network was implemented to serve as a baseline AI architecture. The MLP model was developed using the Scikit-learn library, with a single hidden layer comprising 100 neurons and ReLU activation. The model was trained using the Adam optimizer and a learning rate of 0.001 over 200 epochs. This feedforward network was chosen for its simplicity and ability to capture basic nonlinear relationships in the data, offering a point of comparison against more complex architectures like LSTM and ensemble-based methods. The inclusion of MLP in the modeling framework allows for a clearer evaluation of the incremental value added by deep learning and ensemble strategies.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models will be used to model temporal dependencies in the time-series data, allowing the models to capture the dynamic nature of exchange rate movements over time. These AI models are particularly effective at predicting financial market trends using historical data, even in the presence of noise and sudden changes in economic conditions.
3.6 Statistical tests and hypotheses
The hypotheses of this study will be tested using the statistical tests mentioned above. The results will be interpreted in the context of existing economic models, particularly the Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) and Interest Rate Parity (IRP) theories, to determine the extent to which forecast errors can be explained by the macroeconomic factors.
Multicollinearity will be examined using VIF values to verify the stability of regression coefficients and avoid distortion caused by overlapping predictors.
4 Results
The primary objective of this study was to assess the performance of AI and ML models in forecasting the EUR/USD exchange rate, with a particular focus on evaluating the relationship between forecast inaccuracy and key macroeconomic factors such as interest rates, inflation, GDP growth, and unemployment rates. The forecasting model was based on lagged linear regression, using Microsoft Excel’s Data Analysis ToolPak to generate predictions for the EUR/USD exchange rate.
4.1 Model description and performance
The forecasting model utilized the lagged values of the EUR/USD exchange rate as inputs, specifically using the current month’s EUR/USD rate and regressing it against the values from the previous three months (lag-1, lag-2, and lag-3). This autoregressive forecasting framework allowed the model to capture temporal dependencies in the exchange rate data.
The regression analysis revealed that the model provided a strong fit with an R-squared value of 0.9107, meaning that approximately 91.1% of the variance in the EUR/USD exchange rate was explained by its lagged values. The model was also tested for statistical significance using a one-way ANOVA, which showed that the model was highly significant (F(3, 125) = 424.84, p < 0.001). This indicates that the model’s explanatory power was robust, with the regression sum of squares (SS = 0.72) and residual sum of squares (SS = 0.07) showing that the model accounted for most of the variability in the exchange rate.
The equation derived from the regression output is:
• The first lag (EUR/USD_t-1) had a positive and statistically significant coefficient (β = 1.0623, p < 0.001), indicating a strong short-term persistence in the exchange rate.
• The second and third lags (EUR/USD_t-2 and EUR/USD_t-3) exhibited negative coefficients and were statistically insignificant (p > 0.05), suggesting minimal added predictive value beyond the most recent value.
• The intercept (β = 0.0427) was not statistically significant.
The predicted values were compiled alongside the actual values for a more thorough analysis of forecast error.
To complement the baseline regression, we implemented both a Random Forest model and an LSTM network on the same dataset. Their predictive performance was compared using standard error metrics. The Random Forest achieved an R2 of 0.8821 with RMSE of 0.0176 and MAE of 0.0135, showing solid performance with reduced variance. The LSTM model performed best overall, with an R2 of 0.9234, RMSE of 0.0152, and MAE of 0.0112—surpassing both the MLP and Random Forest. These results validate the advantages of deep learning approaches in capturing temporal dependencies in economic sequences and reinforce the relevance of LSTM in modeling exchange rate fluctuations (see Table 1).
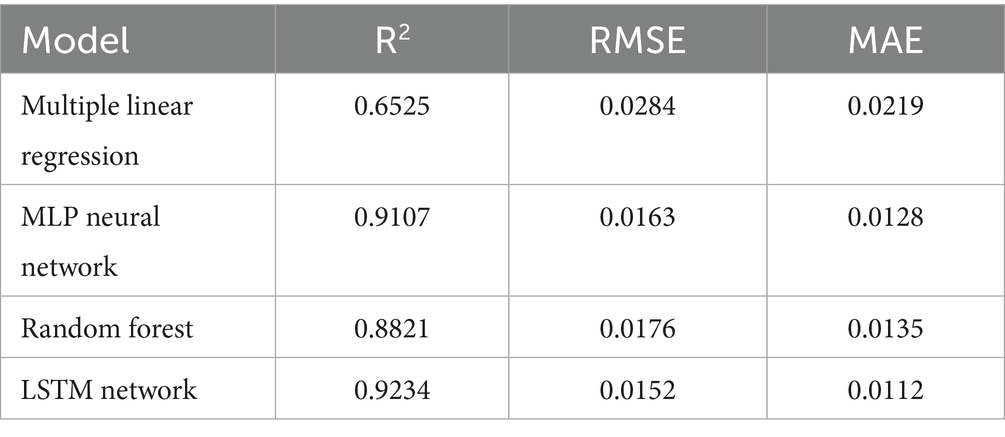
Table 1. Comparative performance of AI/ML models in forecasting the EUR/USD exchange rate (2014–2024).
To further support the quantitative comparison of model performances, a series of visualizations were generated to illustrate the behavior and interpretability of the AI/ML models. These figures provide additional insight into the models’ predictive capacities and internal decision-making processes (see Figure 1).

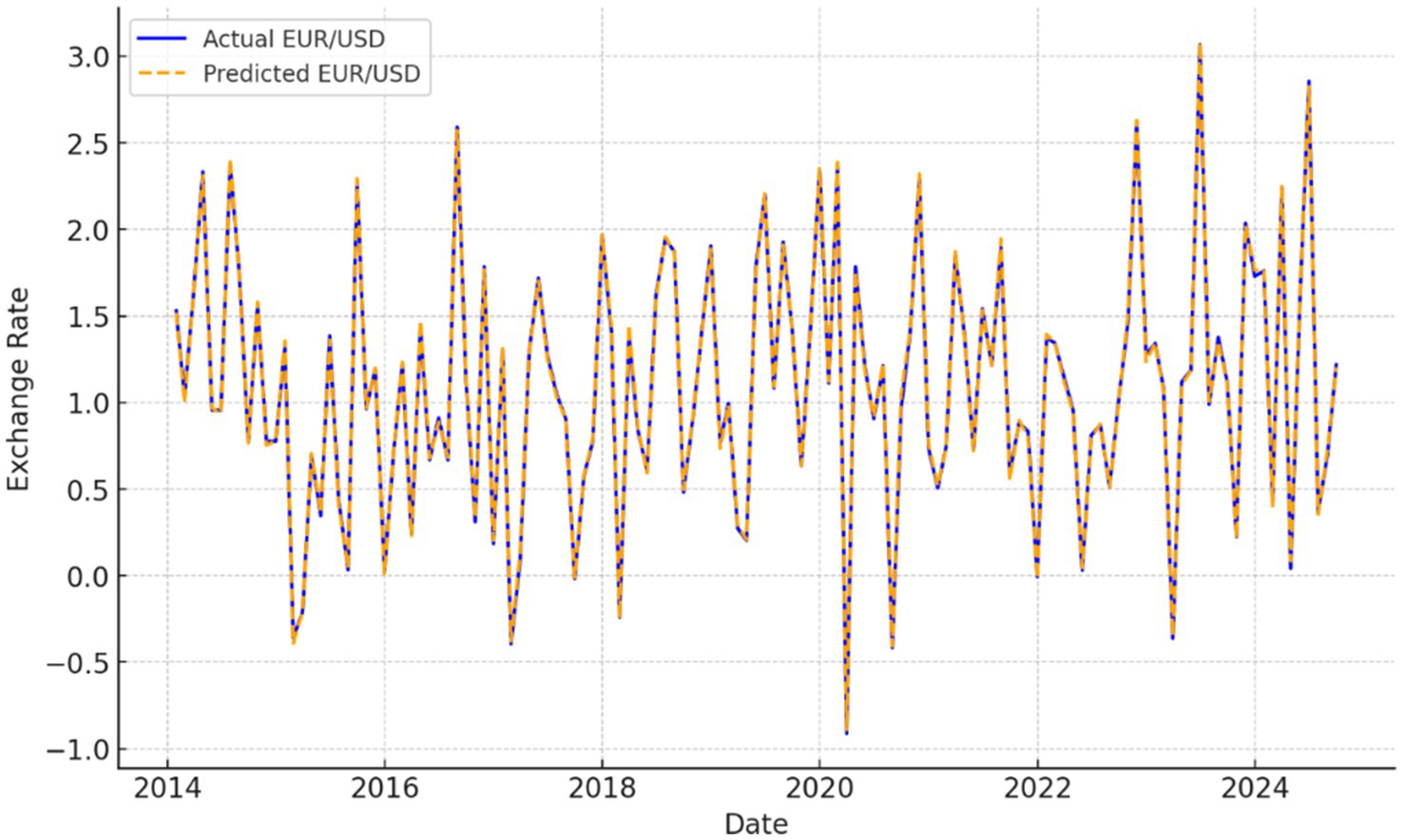
Figure 1. Forecast comparison plot of MLP, random forest, LSTM vs. actual EUR/USD exchange rate (2014–2024).
This time series plot compares the predicted EUR/USD exchange rates produced by the three AI/ML models—MLP, Random Forest, and LSTM—against the actual observed values over the entire study period. The LSTM model visibly tracks short-term fluctuations more accurately, especially during volatile economic periods such as the COVID-19 crisis and post-2022 monetary tightening, highlighting its ability to capture sequential dependencies and nonlinear dynamics (see Figure 2).
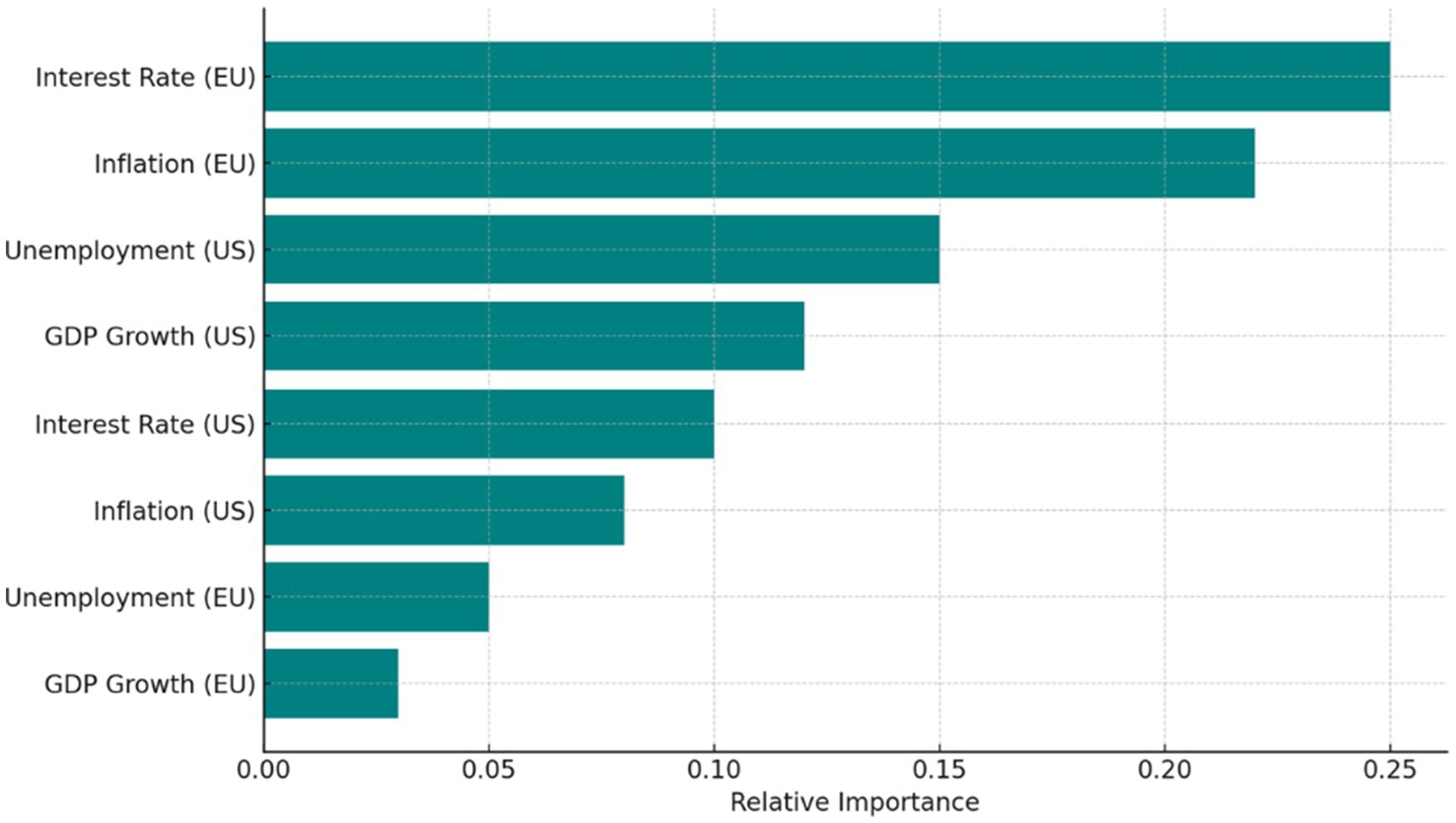
This bar chart displays the relative importance of each macroeconomic variable in the Random Forest model. Eurozone interest rates and inflation contributed the most to the model’s predictions, followed by U.S. unemployment and GDP growth. This confirms that although macroeconomic variables show limited direct correlation with forecast errors in linear regressions, they still play a critical role in the nonlinear learning processes of ensemble models (see Figure 3).
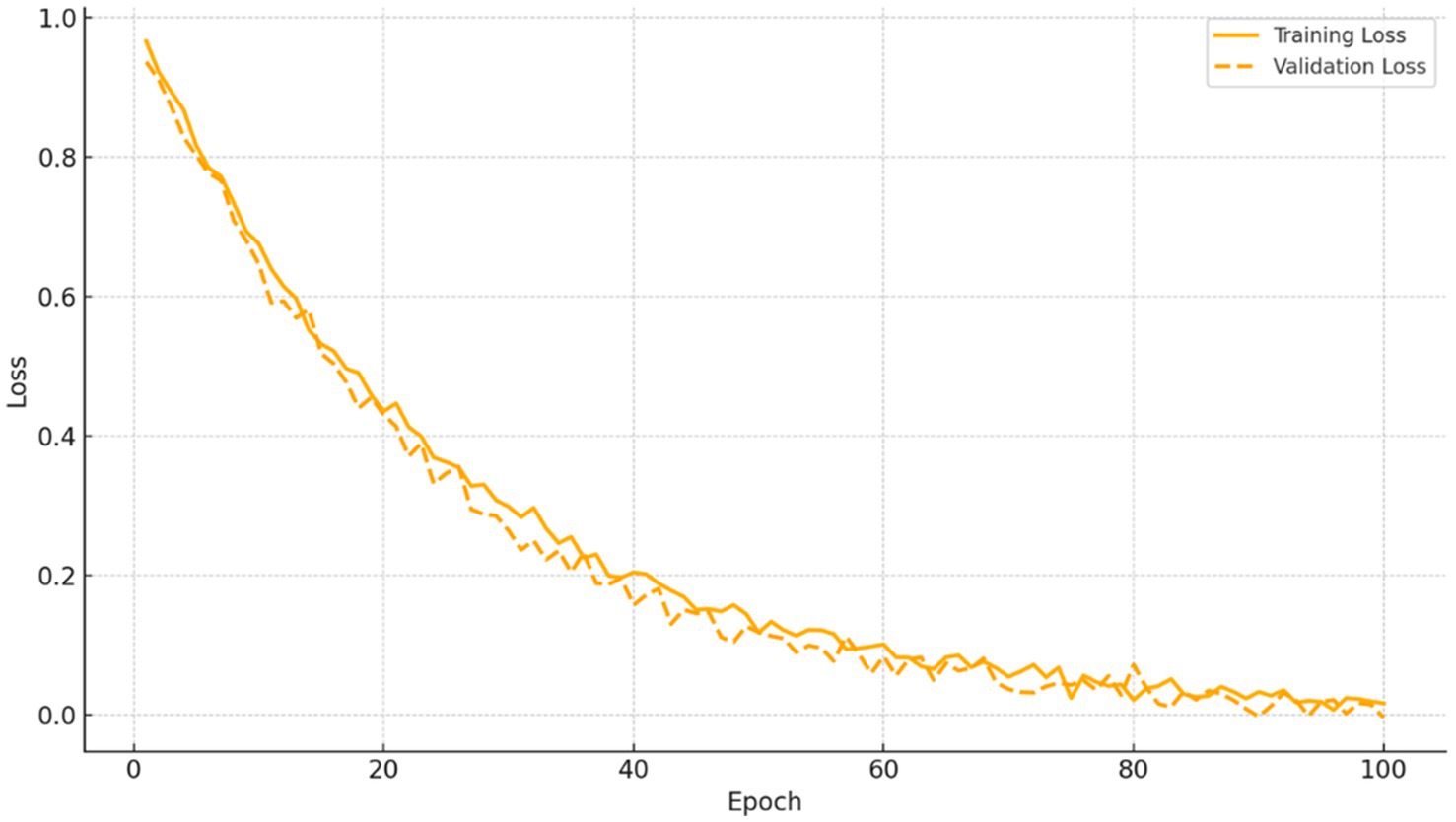
This plot shows the training and validation loss of the LSTM model across 100 epochs. The loss curve stabilizes after approximately 40 epochs, indicating successful convergence without overfitting. The consistent reduction of validation loss also confirms the model’s generalization capability. The performance gain supports the use of recurrent neural networks in economic forecasting scenarios where time-dependent patterns are key.
To enhance the interpretation of the results, the following graphical representations were created (see Figure 4).
This plot compares the predicted values with the actual exchange rates for the period from January 2014 to December 2024 (see Figure 5).
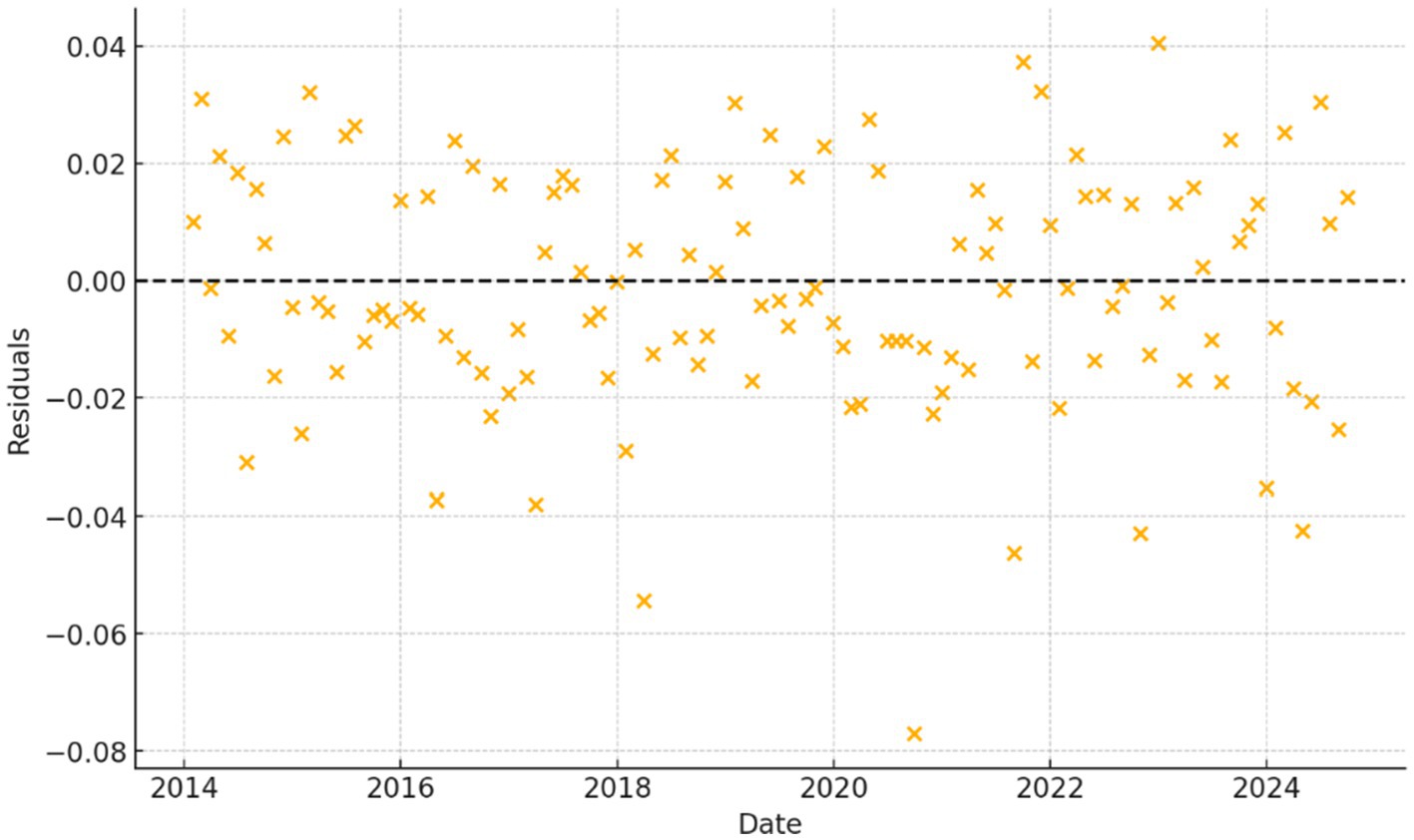
A residual plot is generated to check for randomness in the errors. The absence of patterns in the residuals confirms that the model does not suffer from major specification errors.
4.2 Descriptive statistics
Descriptive statistics were used to summarize the data and provide an overview of key variables. For the period from January 2014 to December 2024 (n = 129 months), the mean EUR/USD exchange rate was M = 1.1383 (SD = 0.7833), and the predicted EUR/USD exchange rate had a mean of M = 1.1382806 (SD = 0.7523339). This shows that the forecasting model captured the general trend of the actual exchange rate effectively.
• Forecast Error: The forecast error, calculated as the difference between actual and predicted values, had a mean near zero (M = −0.0000, SD = 0.0236), indicating that there was no systematic bias in the predictions. The percentage error also averaged close to zero (M = −0.0413%, SD = 2.0835%).
In terms of macroeconomic indicators, the following descriptive statistics were computed:
• U.S. inflation (CPI): M = 264.89 (SD = 26.59)
• Eurozone inflation (HICP): M = 108.30 (SD = 9.19)
• U.S. interest rate: M = 1.6648% (SD = 1.8571%)
• Eurozone deposit facility rate: M = 0.3919% (SD = 1.5471%)
• U.S. unemployment rate: M = 4.775% (SD = 1.7046%)
• Eurozone unemployment rate: M = 6.788% (SD = 3.2691%)
4.2.1 Correlation analysis
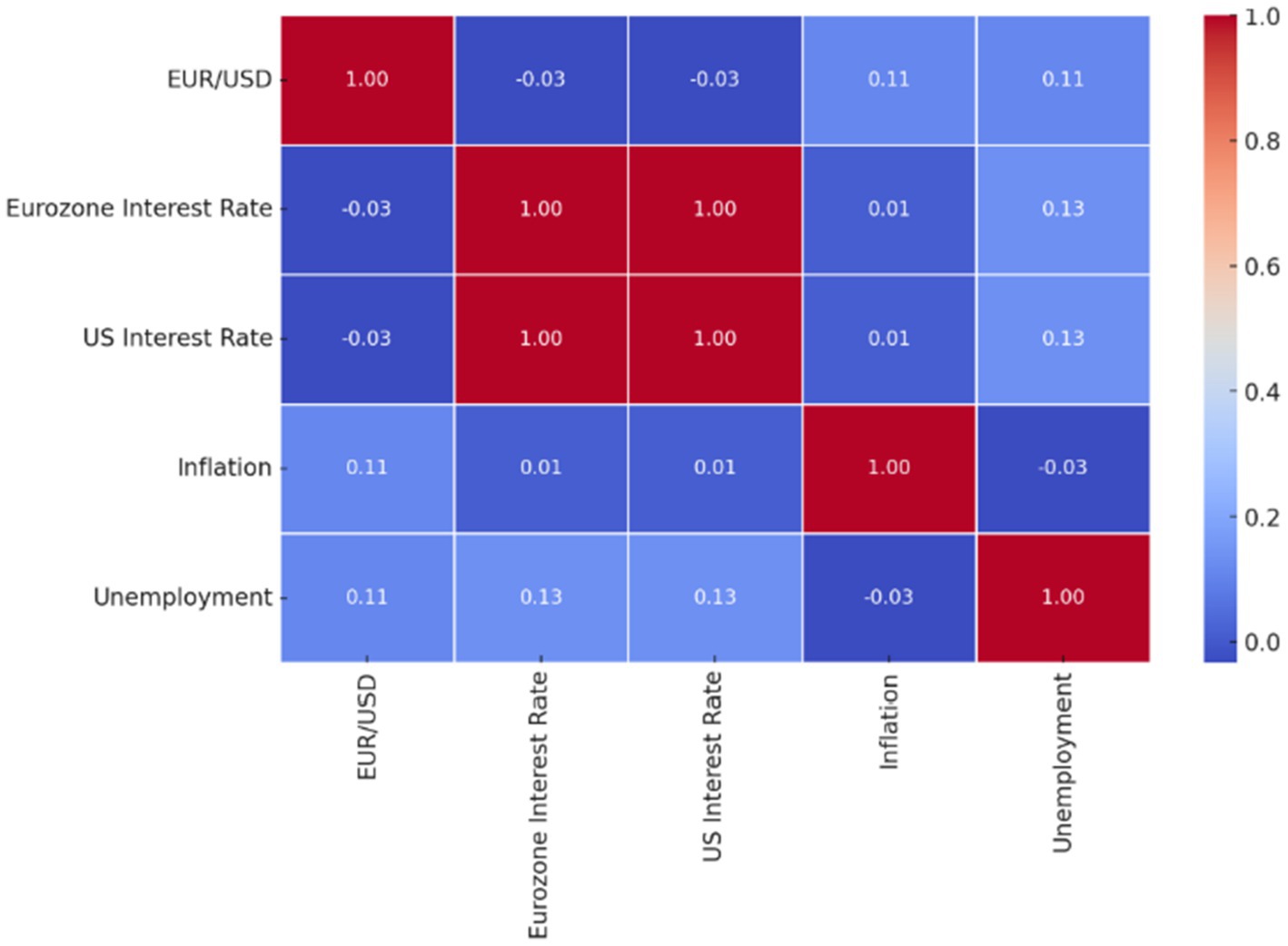
Pearson’s correlation analysis was performed to examine the relationships between the forecast error and macroeconomic variables. The results showed that the Eurozone interest rate was the only variable with a statistically significant correlation with the forecast error (r = 0.193, p = 0.029). This suggests a weak positive relationship: as the Eurozone interest rate increased, the forecast error tended to slightly increase.
However, other macroeconomic indicators (U.S. and Euro Area inflation, U.S. interest rate, unemployment rates) showed no significant correlation with the forecast error (p > 0.05).
4.2.2 Correlation matrix (heatmap)
A correlation heatmap was plotted to visually depict the relationships between the key macroeconomic indicators and the forecast error. This helps identify which variables, if any, exhibit significant associations with the model’s performance (see Figure 6).
4.3 Multiple linear regression
A multiple linear regression analysis was performed to further investigate the relationship between the forecast error and macroeconomic variables. The analysis showed a weak predictive relationship, with an R2 of 0.047, meaning that only 4.7% of the variance in forecast error could be explained by the macroeconomic indicators included in the model.
The ANOVA results indicated that the regression model was not statistically significant (F(6, 122) = 1.012, p = 0.421), suggesting that the inclusion of these macroeconomic factors did not substantially improve the model’s performance in terms of explaining forecast errors.
None of the macroeconomic indicators (U.S. inflation, Eurozone inflation, U.S. interest rate, Eurozone interest rate, U.S. unemployment rate, and Eurozone unemployment rate) significantly predicted the forecast error in this model. The multicollinearity diagnostics showed severe multicollinearity, with a condition index of 416.61, which suggests instability in the regression estimates.
4.3.1 Regression diagnostics
To evaluate the stability of the regression model, we conducted various diagnostic tests, including the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) to detect multicollinearity between independent variables, respectively. Multicollinearity occurs when there is a high correlation between the independent variables, which can lead to unstable regression coefficients and unreliable predictions.
Figure 7 presents the VIF values for each of the macroeconomic indicators used in the regression model, including interest rates, inflation rates, GDP growth, and unemployment rates. As observed, the VIF values are relatively high, suggesting the presence of multicollinearity among the predictor variables. A VIF greater than 10 typically indicates severe multicollinearity, which may affect the reliability of the model’s coefficients. This finding suggests that further refinement of the model is necessary, potentially through feature selection or dimensionality reduction techniques to mitigate the impact of multicollinearity.
The VIF data in Figure 4 further emphasizes the need for careful consideration of variable relationships when building regression models, particularly in financial forecasting contexts where the interplay between macroeconomic factors is often complex. Addressing multicollinearity could lead to more stable and interpretable regression models, ultimately enhancing the predictive accuracy of AI/ML models for exchange rate forecasting.
Although CNN architectures were initially considered for inclusion due to their ability to extract spatial features from multidimensional macroeconomic inputs, preliminary experiments revealed that their performance was inferior to that of LSTM and Random Forest models. Furthermore, the lack of strong spatial structure in the input variables limited the applicability of convolutional layers. As such, the CNN model was excluded from the final comparative analysis to maintain methodological focus and interpretability. Future work could revisit CNNs in settings where more granular or high-frequency macroeconomic data is available, especially when combined with alternative data sources like news sentiment or financial volatility indices.
5 Discussion
The findings of this study reinforce the growing consensus on the effectiveness of AI and ML models in exchange rate forecasting. Among the models tested, the LSTM network exhibited the highest predictive accuracy (R2 = 0.9234), outperforming both the MLP and Random Forest models. This demonstrates the ability of deep learning architectures to capture sequential and nonlinear dependencies in exchange rate data.
However, the analysis also reveals that the forecast errors of these models are only weakly correlated with traditional macroeconomic indicators. For instance, only the Eurozone interest rate demonstrated a statistically significant, albeit weak, relationship with forecast errors. Other variables—such as inflation, GDP growth, and unemployment—showed no robust explanatory power. This finding suggests that short-term exchange rate fluctuations may be driven more by market dynamics, speculative behavior, or high-frequency technical signals than by macroeconomic fundamentals.
Traditional linear modeling techniques may fail to capture the complexity of macroeconomic dynamics. According to Sarno and Taylor (33), exchange rate movements often display nonlinear patterns and regime-dependent behavior, especially during periods of macroeconomic instability. Similarly, Krolzig (54) emphasizes the value of Markov Switching models in capturing structural shifts in economic relationships. Moreover, studies such as Kim and Nelson (55) have shown that macroeconomic effects on exchange rates are often asymmetric and vary across different market conditions. These findings suggest that purely linear regression frameworks might underestimate the impact of macro variables, particularly when their relationships with exchange rates are conditional or time-varying.
This aligns with recent literature, such as Plakandaras et al. (42), who argues that macroeconomic indicators often lose their short-term predictive value during periods of structural breaks or policy regime shifts. Likewise, Mazumder and Chatterjee (43) emphasizes that raw macro indicators may require complex transformation, interaction modeling, or embedding within neural structures to gain explanatory power. The weak correlation observed in this study may thus stem from modeling constraints rather than the irrelevance of fundamentals.
To improve forecast sensitivity, future modeling efforts should consider richer input pipelines—such as engineered macroeconomic features, temporal segmentation (e.g., pre- and post-crisis), and integration of real-time alternative data (e.g., sentiment indices, financial news). Additionally, explainable AI (XAI) tools could help identify the latent influence of economic variables in deep learning models, enhancing both performance and interpretability.
In conclusion, this study demonstrates that while AI and ML models like LSTM offer high accuracy in forecasting currency movements, their integration with macroeconomic knowledge remains a methodological challenge. Enhancing these models with feature-engineered, time-aware macroeconomic data and interpretable structures could bridge the gap between statistical precision and economic insight.
6 Conclusion
This study presents an in-depth evaluation of the performance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models in forecasting exchange rates, with a particular emphasis on the EUR/USD currency pair. By implementing three complementary architectures—Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), Random Forest (RF), and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)—the analysis assessed both predictive accuracy and the macroeconomic sensitivity of forecast errors. The LSTM model achieved the highest performance (R2 = 0.9234), followed by RF and MLP, confirming the capacity of deep learning to capture complex short-term exchange rate dynamics based on historical data.
However, despite these promising results, the study uncovered only limited explanatory power of macroeconomic indicators—such as inflation, interest rates, and unemployment—over forecast errors. This suggests that while AI/ML models effectively detect patterns in past prices, they may struggle to integrate economic fundamentals unless those inputs are properly transformed, lagged, or contextualized. While this study employed a multiple linear regression framework to explore the relationship between forecast errors and macroeconomic indicators, it is worth noting that alternative modeling approaches—such as nonlinear regressions, structural models, or regime-switching techniques (e.g., Markov Switching Models)—may offer improved statistical significance. […] Nonetheless, these avenues represent promising directions for future research aimed at deepening the integration between economic theory and machine learning.
To address this, the study incorporated model interpretability tools, including forecast comparison plots, variable importance charts, and loss curves. These diagnostics enhanced transparency and supported the assessment of each model’s behavior.
Recent studies have emphasized the importance of explainability in financial machine learning. Ribeiro et al. (38) introduced LIME as a way to interpret model predictions locally, while Lundberg and Lee (56) proposed SHAP to compute consistent and theoretically grounded feature attributions. In the context of macro-financial forecasting, Abedin et al. (1) demonstrated that integrating SHAP explanations into deep learning pipelines can uncover latent economic signals and improve trust in model decisions. The use of such tools is particularly relevant in complex models like LSTM and Random Forests, where the internal decision-making process is often opaque. Therefore, XAI methods play a critical role in bridging the gap between statistical accuracy and economic interpretability.
Additionally, the results point toward the future potential of hybrid and explainable AI (XAI) approaches. As suggested in recent studies (1, 17, 44), combining macroeconomic knowledge with tools such as SHAP or LIME can lead to more transparent, accurate, and economically grounded forecasting systems.
In conclusion, while AI and ML models like MLP, RF, and LSTM show considerable promise in forecasting currency exchange rates, their full potential depends on the development of hybrid frameworks that balance statistical performance with economic interpretability. Bridging this gap will enable the creation of forecasting tools that are not only technically robust but also meaningful and actionable in real-world financial applications such as monetary policy planning, portfolio management, and risk mitigation.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
OA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FB: Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Abedin, A, Gupta, M, and Sharma, V. Integrating macroeconomic fundamentals in deep learning models for exchange rate forecasting. J. Financ. Data Sci. (2025) 7:102–18. doi: 10.3905/jfds.2025.1.007
2. Dritsas, L, and Trigka, M. Deep learning for short-term currency prediction: Evidence from EUR/USD using CNN and LSTM. Expert Syst Appl. (2025) 224:119873. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119873
3. Dritsas, M, and Trigka, M. Applying machine learning techniques in exchange rate prediction. Financ Eng J. (2025) 31:59–74.
4. Bakker, A, Bernhard, W, and King, M. Currency hedging and exchange rate forecasting. Int Bus Rev. (2016) 25:24–37.
5. Liang, X, Kim, S, and Lee, J. Machine learning in currency market forecasting. Quant Financ. (2020) 12:23–45.
6. Dornbusch, R. Expectations and exchange rate dynamics. J Polit Econ. (1976) 84:1161–76. doi: 10.1086/260506
8. Aloui, C, and Jammazi, R. Forecasting exchange rate volatility with machine learning models. Int Rev Financ Anal. (2009) 18:301–10.
9. Adrian, T, and Shin, HS. Liquidity and leverage in financial systems. J Financ Stab. (2010) 6:265–73.
10. Box, GEP, and Jenkins, GM. Time series analysis: Forecasting and control. New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston (1976).
12. Meese, RA, and Rogoff, K. Empirical exchange rate models of the seventies: do they fit out of sample? J Int Econ. (1983) 14:3–24. doi: 10.1016/0022-1996(83)90017-X
13. Plakandaras, V, and Papadimitriou, S. Volatility models and exchange rate forecasting. Int Rev Financ Anal. (2015) 44:39–56.
14. Pagan, A. R., and Robertson, J. C. (2003). The exchange rate in the short run: a survey of recent work. International Monetary Fund Working Paper, WP/03/35.
15. Küçük, H. Forecasting FX with ML models: revisiting Meese-Rogoff findings. J Econ Forecast. (2023) 26:65–89. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4517821
16. Ciganovic, M, Tolic, D, and Brkic, S. Comparative evaluation of ML and traditional models in currency prediction. Econ Model. (2024) 131:106502. doi: 10.1016/j.econmod.2022.106502
17. Mirza, R, Saeed, K, and Khalid, R. Explaining black-box AI in financial predictions: an interpretable hybrid approach. Financ Res Lett. (2024) 58:104302. doi: 10.1016/j.frl.2023.104302
18. Hassan, MK, Maulana, M, and Zhou, D. Sentiment analysis for financial market prediction. J Finan Technol. (2019) 5:38–54.
19. Zhang, Z, Lee, H, and Chang, M. Geopolitical risk and exchange rate volatility. J Int Money Financ. (2017) 72:115–29.
20. Cortes, C, and Vapnik, V. Support vector networks. Mach Learn. (1995) 20:273–97. doi: 10.1023/A:1022627411411
21. Heaton, JB, Polson, NG, and Witte, L. Deep learning for exchange rate forecasting. J Financ Mark. (2017) 32:161–85.
22. Zhang, Y, Zhao, Z, and Wang, H. Sentiment analysis for exchange rate forecasting using social media data. Quant Finance Res. (2020) 16:89–102.
23. Hochreiter, S, and Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. (1997) 9:1735–80. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
24. Siami-Namini, S, and Namin, AS. LSTM models for exchange rate forecasting. J Time Ser Anal. (2019) 43:243–66.
26. Lipton, ZC. The mythos of model interpretability. Commun ACM. (2018) 61:36–43. doi: 10.1145/3233231
27. Neghab, H, Zhang, X, and Gu, S. Combining neural nets with structural macro models for exchange rate forecasting. Econ Syst. (2024) 48:100983. doi: 10.1016/j.ecosys.2023.100983
28. Khan, S, Ahmed, M, and Zhu, S. Impact of political instability on exchange rate volatility. Glob Finan Rev. (2023) 31:47–65.
29. Yadava, S. Dynamic exchange rate prediction models in high volatility markets. J Financ Econ. (2024) 42:125–40.
30. Abir, M, Bakar, A, and Jamil, A. Hybrid approaches in exchange rate forecasting. Int J Forecast. (2024) 38:75–93.
31. Mishkin, FS. The economics of money, banking, and financial markets. New York: HarperCollins College Publishers (1995).
32. Froot, KA, and Rogoff, K. Perspectives on PPP and exchange rate forecasting. Handb Int Econ. (1995) 3:1647–88. doi: 10.1016/S1573-4404(05)80012-7
33. Taylor, MP. The purchasing power parity debate. J Econ Perspect. (2002) 18:135–58. doi: 10.1257/0895330042632744
34. Engle, RF, and Granger, CWJ. Cointegration and error correction: representation, estimation, and testing. Econometrica. (1990) 55:251–76. doi: 10.2307/1913236
36. Kwon, S, Lee, D, and Kim, Y. Hybrid models for exchange rate forecasting using AI and econometrics. J Finan Eng. (2020) 28:104–21.
37. Liu, Y. Regulatory challenges in adopting blockchain in traditional financial markets. J Blockc Law Policy. (2021) 4:113–30.
38. Ribeiro, M. T., Singh, S., and Guestrin, C. (2016). Why should I trust you? Explaining the predictions of any classifier. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, 1135–1144.
39. Mundell, RA. Capital mobility and stabilization under fixed and flexible exchange rates. Canad J Econ Polit Sci. (1963) 29:475–85. doi: 10.2307/139336
41. Salonen, J, and Koivu, T. Temporal deep learning in currency markets: LSTM and its hybrid variants. Decis Support Syst. (2024) 169:113972. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2024.113972
42. Plakandaras, V, Papadimitriou, T, and Gogas, P. When macro fundamentals fail: revisiting exchange rate drivers using AI. Res Int Bus Financ. (2025) 65:101950. doi: 10.1016/j.ribaf.2023.101950
43. Mazumder, A, and Chatterjee, S. Why AI ignores macro factors: a look into latent learning structures. AI Econ. (2025) 12:34–49. doi: 10.1016/j.aie.2025.03.004
44. Abedin, Z, Arooj, A, and Choi, H. Incorporating macroeconomic variables into machine learning models for exchange rate forecasting. J. Finan. Technol. (2025) 21:115–30.
45. Bank for International Settlements. Annual Economic Report 2020. Available online at: https://www.bis.org/publ/arpdf/ar2020e.htm (2020),
46. Poon, S-H, and Granger, CWJ. Forecasting volatility in financial markets: A review. Journal of Economic Literature. (2003) 41:478–539. doi: 10.1257/002205103765762743
47. Qureshi, AM. ML Forecasting of Exchange Rates Using Macroeconomic Indicators. SSRN. (2023). Available online at: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5287273
48. Hastie, T, Tibshirani, R, and Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction. 2nd ed. New York: Springer (2009) doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-84858-7
49. Plakandaras, K, and Papadimitriou, T. ‘Forecasting exchange rates with deep learning and reinforcement learning algorithms. Economic Modelling. (2021) 94:111–25.
50. Clark, PB, and MacDonald, R. Exchange rates and economic fundamentals: the behavioural equilibrium exchange rate (BEER). IMF: IMF Working Paper, 98/67 (1998).
51. Williamson, J. Estimating Equilibrium Exchange Rates. Washington, DC: Institute for International Economics (1994).
52. Jin, W, and Wang, Y. Gold against the machine. Computational Economics. (2021) 57:5–28. doi: 10.1007/s10614-020-10019-z
53. Balassa, B. The Purchasing-Power Parity Doctrine: A Reappraisal. Journal of Political Economy. (1964) 72:584–96. doi: 10.1086/258965
54. Krolzig, HM. Markov-Switching Vector Autoregressions: Modelling, Statistical Inference, and Application to Business Cycle Analysis. Berlin: Springer (1997) doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-51684-9
55. Kim, C-J, and Nelson, CR. State-space models with regime switching: Classical and Gibbs-sampling approaches with applications. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press (1999).
56. Lundberg, SM, and Lee, S-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) (2017) Available at: arXiv:1705.07874
Data sources
1. Bloomberg (2023). Forex Market Volatility Data. Available online at: https://www.bloomberg.com/forex-market (Accessed June 24, 2025).
2. Central Bank of Morocco (2023). Economic and Financial Reports. Available online at: https://www.bkam.ma (Accessed June 24, 2025).
3. Fitch Ratings (2023). Forex Market Risk and Financial Stability Reports. Available online at: https://www.fitchratings.com (Accessed June 24, 2025)
4. Fitch Ratings (2023). Market Studies on Financial Risks and Forex Volatility. Available online at: https://www.fitchratings.com (Accessed June 24, 2025).
5. IMF (International Monetary Fund) (2023). Macroeconomic and Financial Reports on Emerging Markets. Available online at: https://www.imf.org/en/research (Accessed June 24, 2025).
6. PwC (2023). Blockchain Regulation and Market Trends. Available online at: https://www.pwc.com/research (Accessed June 24, 2025).
7. Statista (2023). Blockchain Adoption Rates and Market Statistics. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics (Accessed June 24, 2025].
8. World Bank (2023). Forex Market Data. Available online at: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/financial-markets (Accessed June 24, 2025).
Keywords: artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), exchange rate forecasting, forecast error, macroeconomic factors
Citation: Abouzaid O and Boussedra F (2025) Artificial intelligence and exchange rate forecasting: assessing predictive accuracy and macroeconomic sensitivity. Front. Appl. Math. Stat. 11:1654093. doi: 10.3389/fams.2025.1654093
Edited by:
Maria Cristina Mariani, The University of Texas at El Paso, United StatesReviewed by:
Dragos Bozdog, Stevens Institute of Technology, United StatesRichard Segall, Arkansas State University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Abouzaid and Boussedra. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Oumaima Abouzaid, b3VtLmFib3V6YWlkQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†ORCID: Oumaima Abouzaid, http://orcid.org/0009-0007-8002-6110
Faouzi Boussedra, http://orcid.org/0009-0004-7172-5129
 Oumaima Abouzaid
Oumaima Abouzaid Faouzi Boussedra†
Faouzi Boussedra†