- Indian Institute of Geomagnetism, Navi Mumbai, India
This paper introduces a method and an innovative graphical user interface (GUI) tool to identify bipolar solitary wave structures in the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) mission dataset. As input to this tool, we utilized medium-frequency burst mode calibrated electric field data obtained from the Langmuir Probe and Waves (LPW) instrument aboard MAVEN. To detect solitary waves, we first discuss the typical theoretical solitary wave structure and its key features. Based on these features, we developed a series of mathematical conditions that are applied to the LPW electric field dataset. After rigorous testing, a MATLAB executable GUI application named SWIT (Solitary Wave Identifying Tool) was developed. The output of SWIT provides the amplitude, width, and time of occurrence of the solitary waves. Furthermore, we evaluate the accuracy and limitations of SWIT. It is found that SWIT demonstrates high efficiency. It is a dedicated identifier for analyzing medium-frequency electric field measurements from the MAVEN spacecraft to search for solitary wave structures in the Martian plasma environment. It is suggested that this novel method can be applied to datasets from different spacecraft in other planetary plasma environments with minor modifications.
1 Introduction
Electrostatic solitary waves (ESWs) are nonlinear, isolated electric field pulses observed in space plasmas. These waves typically propagate along the direction of the magnetic field and exhibit negligible fluctuations in the perpendicular component of the magnetic field. They were first detected in auroral plasma by the S3-3 polar-orbiting satellite (Temerin et al., 1982). Later, high-resolution electric field measurements from the Geotail spacecraft revealed that broadband electrostatic noise (BEN) consists of isolated bipolar solitary structures (Matsumoto et al., 1994). Since then, ESWs have been observed in various regions of the Earth’s magnetosphere, such as the auroral zone (Ergun et al., 1998; Pickett et al., 2004), magnetopause (Cattell et al., 2002; Graham et al., 2015; Graham et al., 2016), magnetosheath (Pickett et al., 2003; Holmes et al., 2018; Shaikh et al., 2024), bow shock (Hobara et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2014; Vasko et al., 2018; Vasko et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2022; Kamaletdinov et al., 2022), plasma sheet (Ergun et al., 2009; Tong et al., 2018; Mozer et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2022), magnetotail (Norgren et al., 2015), inner magnetosphere (Vasko et al., 2017a), dusk flank region (Arya and Kakad, 2025), and so on. As new observations continue to emerge, theoretical (Singh and Lakhina, 2001; Pickett et al., 2005; Kakad et al., 2007; Lakhina et al., 2008a; Lakhina et al., 2008b, 2009; Kakad et al., 2009; Lakhina et al., 2011a; Lakhina et al., 2011b; Olivier et al., 2015; Maharaj et al., 2015; Kakad et al., 2016; Singh et al., 2024) and simulation (Omura et al., 1996; Umeda et al., 2002; Kakad et al., 2013; Kakad et al., 2014; Lotekar et al., 2016; Kakad A. et al., 2017; Lotekar et al., 2017; Vasko et al., 2017b; Dillard et al., 2018; Lotekar et al., 2019; Kakad and Kakad, 2019) studies have been conducted to investigate their generation mechanisms. In general, monopolar (double layer), bipolar, and occasionally observed tripolar structures fall under the ESW category. In this paper, the term solitary waves refers specifically to bipolar solitary structures.
In fluid models, ESWs can be classified as ion or electron acoustic solitary waves (IASWs/EASWs), depending on the dominant driving species. EASWs exhibit phase velocities of a few thousand kilometers per second, whereas IASWs typically have phase velocities of a few hundred kilometers per second. A review article on ESWs as acoustic soliton models is provided by Lakhina et al. (2021). In kinetic models, ESWs are interpreted as ion or electron holes in phase space, depending on the polarity of the associated potential structures (Eliasson and Shukla, 2006; Aravindakshan et al., 2018a; Aravindakshan et al., 2018b, Aravindakshan et al., 2020; Aravindakshan et al., 2021; Aravindakshan et al., 2023). In space plasmas, they play a role in the acceleration, heating, energy dissipation, and trapping of charged particles (Ergun et al., 2004; Andersson and Ergun, 2012; Mozer et al., 2013; Kakad et al., 2017a; Kakad et al., 2017b; Wang et al., 2023).
ESWs are not confined to Earth’s plasma environment; they have also been observed in the Martian magnetosheath (Kakad et al., 2022; Thaller et al., 2022; Pandey et al., 2025a; Pandey et al., 2025c), the Venusian plasma environment (Malaspina et al., 2020), and Saturn’s magnetosphere (Williams et al., 2006). By studying the ambient plasma parameters, various generation mechanisms have been proposed for the ESWs (Singh et al., 2022; Rubia et al., 2023; Varghese et al., 2024a; Varghese et al., 2024b). In case of Mars, in recent studies the ESWs have been reported using the electric field data from Langmuir Probe and Waves (LPW) instrument aboard the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission. However, ESWs on Mars have not been studied as extensively as those on Earth. The LPW instrument measures the y-component of the electric field in the spacecraft’s coordinate system (Andersson et al., 2015). Therefore, limited information is available about the propagation of ESWs. A statistical study of ESWs would provide valuable insights into their occurrence in the plasma environment of an unmagnetized planet like Mars, helping to understand their role in particle dynamics. However, manual detection of solitary waves from such a large dataset is a real challenge.
In this paper, we present a tool for identifying bipolar solitary waves from the MAVEN dataset. Previously, Kojima et al. (2000) developed a method to identify ESWs from the Geotail spacecraft dataset. They employed a bit-pattern comparison technique using two sample waveforms of ESWs with opposite polarity. They defined an ESW index that quantifies the deviation from or similarity to the sample waveforms. This process is carried out by shifting the sample waveforms in time to match the observed signals. However, since the width of ESWs in the time domain can vary, different sample waveforms with varying pulse widths are required. Hansel et al. (2021) used the Solitary Wave Detector (SWD) on NASA’s Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission to map solitary waves in the Earth’s magnetosphere, identifying 60% of all bipolar solitary waves. It is based on a pseudo-standard deviation technique. In the present paper, we use a cumulative-integration-based approach to identify solitary waves. The developed tool is rigorously tested using LPW medium-frequency electric field data from the MAVEN spacecraft, and its efficiency in detecting solitary waves is examined. The paper is organized as follows: the methodology and module sequence in the program are detailed in Sections 2, 3, respectively. The usage and requirements of the Solitary Wave Identifying Tool (SWIT) are elaborated in Section 4. The results are discussed in Section 5. Finally, the study is summarized and concluded in Section 6.
2 Methodology
First, we present the mathematical formulation of a solitary wave and outline its key properties using cumulative integration and first-order differentiation. We examined discrepancies between the ideal and observed solitary wave structures and used this information to ensure accurate identification of solitary waves in the real data. Below, in different subsections, we describe the specific criteria employed in the program to identify solitary waves. We assume the following form for the electric potential linked to the solitary wave structure, as outlined by Kojima et al. (2000) and Krasovsky et al. (1997),
where
where
To reduce parametric dependency and focus on the behavior of the electric field as a function of time, we take
An electric field profile of the type-1 solitary waves in the time domain is shown in Figure 1A. Its cumulative integration (CI), defined as
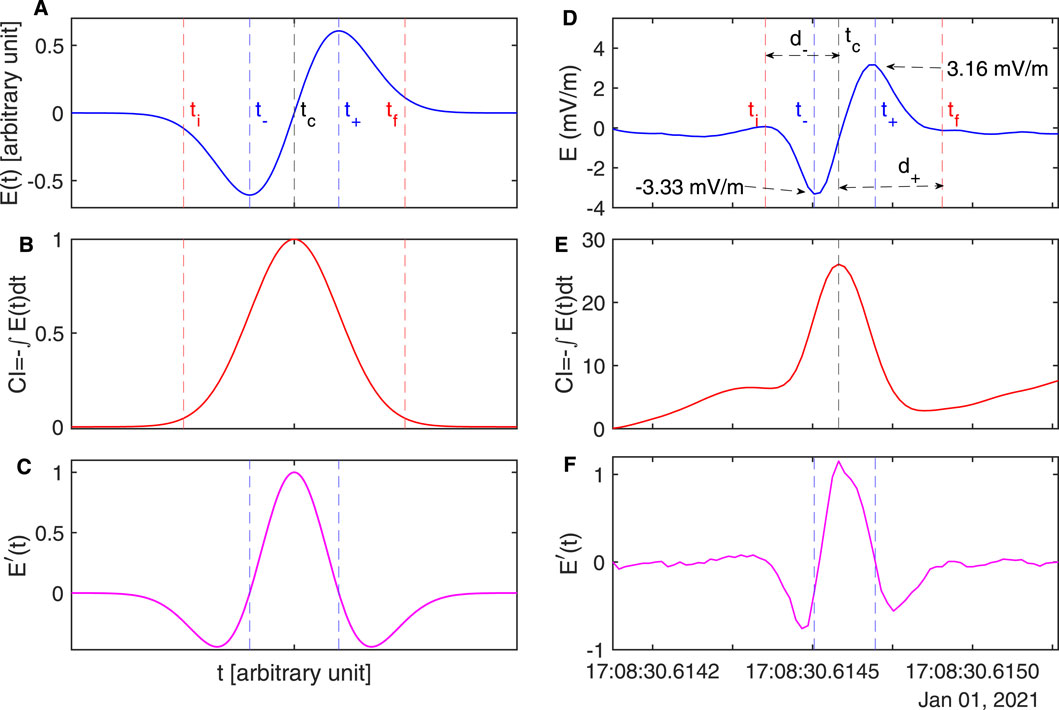
Figure 1. The ideal form of the solitary wave: (A) electric field profile of the solitary wave waveform, (B) cumulative integration (CI) of the solitary wave waveform, and (C) the first-order derivative of the solitary wave waveform are shown as functions of time. Similarly, observation of a solitary wave from the LPW instrument on 1 January 2021: (D) electric field profile, (E) cumulative integration, and (F) first-order derivative are shown as functions of time in UT. In panel (D)
As an example, the type-1 solitary wave structure seen in LPW electric field data is displayed in Figure 1D with its CI in panel (E) and first-order derivative in panel (F). We mark the instances
Next, let us discuss the solitary wave properties (iii)-(v). The solitary waves are typically observed in high-resolution electric field data. Between
3 Module sequence in SWIT
This subsection describes the logical workflow of different modules in the computer program, emphasizing the significance of each step in the process. For clarity, the explanation focuses solely on type-1 solitary wave, as the logic used to detect the type-2 solitary wave is identical, differing only in sign at specific points. A flowchart illustrating the main structure of the SWIT program is presented in Figure 2. It may be noted that SWIT is developed using MATLAB software.
3.1 Data loading and filtering
In this study, we use the medium-frequency (100 Hz–32 kHz) burst-mode calibrated electric field data obtained from the LPW instrument onboard MAVEN (Andersson, 2024). The sampling frequency
A Butterworth bandpass filter is applied to the electric field signal based on the input sampling frequency, with appropriate lower cut-off
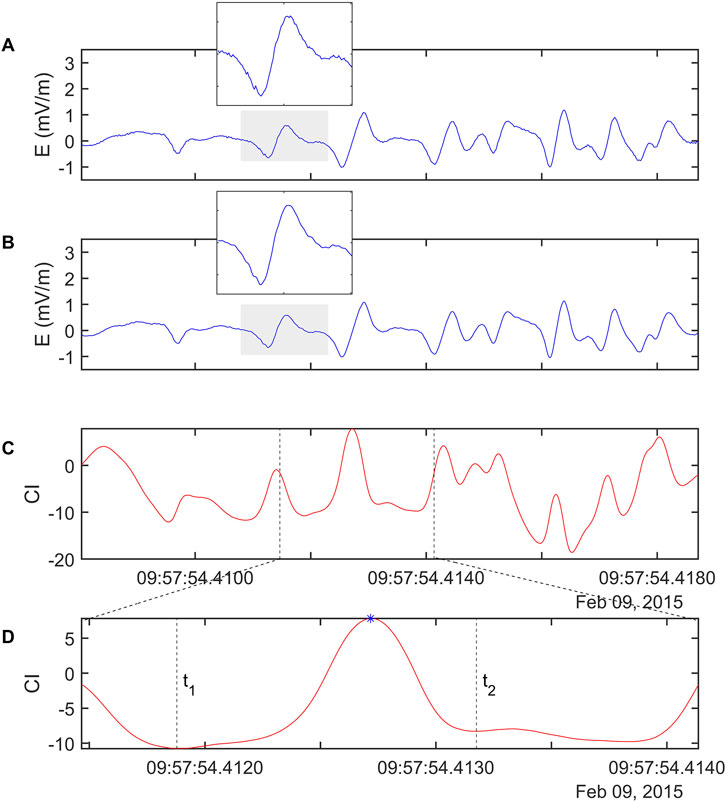
Figure 3. An electric field signal illustrating solitary waves: (A) original data showing solitary waves with small kinks, visible in the zoomed-in view of the grey-shaded region; (B) data after filtering, demonstrating the removal of kinks in the same region; (C) cumulative integration (CI) of the filtered data; (D) a zoomed-in view of the CI peak (marked by an asterisk), highlighting turning points
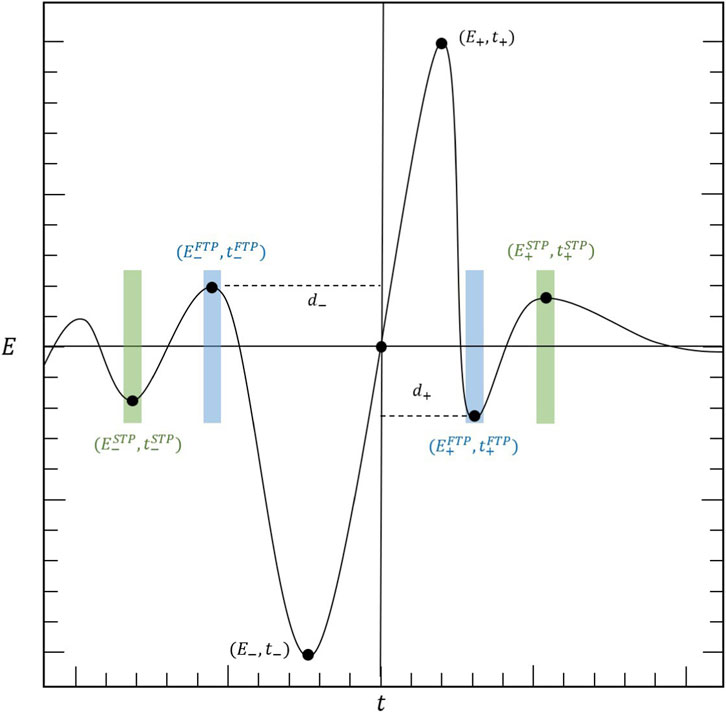
Figure 4. A schematic of the solitary wave waveform, illustrating the allowed ranges for the first and second turning points before
3.2 Cumulative integration and peak identification
Theoretically, each bipolar electric field pulse of type-1 will give rise to one positive peak in CI. We used this approach to identify the location of likely solitary waves in the observed electric field signal. The CI of the filtered signal is calculated, and the location of several peaks apparent in CI is identified. Each peak in CI corresponds to the center of the respective solitary wave structure (see Figure 3C). A peak in CI is identified if the amplitudes of the five preceding and five following points are smaller and decrease continuously on both sides of the peak. Next, the occurrence of turning points in CI preceding and following such peaks are identified and marked as
It may be noted that a major part of the solitary wave identification is covered by different steps elaborated so far. However, electric field data often possess small amplitude oscillations close to the solitary wave structure. Therefore, solitary waves identified within the turning points obtained in the previous step undergo further refinement to minimize error in the identification of solitary wave. A previously discussed issue involves the presence of multiple turning points in
4 Solitary wave identifying tool
By integrating all the conditions mentioned above, we developed a stand-alone desktop GUI application, SWIT, using MATLAB software. The requirements and instructions for the use of SWIT are given below.
4.1 Hardware and software requirements
This stand-alone desktop application SWIT is developed using MATLAB 2024b. It is freely available at https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.15174978 for download (Pandey et al., 2025b). The package includes an installer (.exe) that contains the MATLAB Runtime R2024b, which provides the necessary shared libraries for the execution of the program. To install the application, users must download the ZIP file, extract its contents, and run the installer on a Windows 10 or later version (64-bit). The installation requires a system with at least an Intel or AMD x86-64 processor (2 GHz or faster), a minimum of 4 GB RAM (8 GB or more is recommended), and at least 8–10 GB of free disk space for the MATLAB Runtime and application files. Detailed installation and usage instructions can be found in the included ReadMe file.
4.2 Instructions for SWIT
Upon executing the file, a window appears at the center of the screen, as shown in Figure 5. There are three load buttons for input parameters: electric field, time series data, and number density data. Users are required to load these data files in
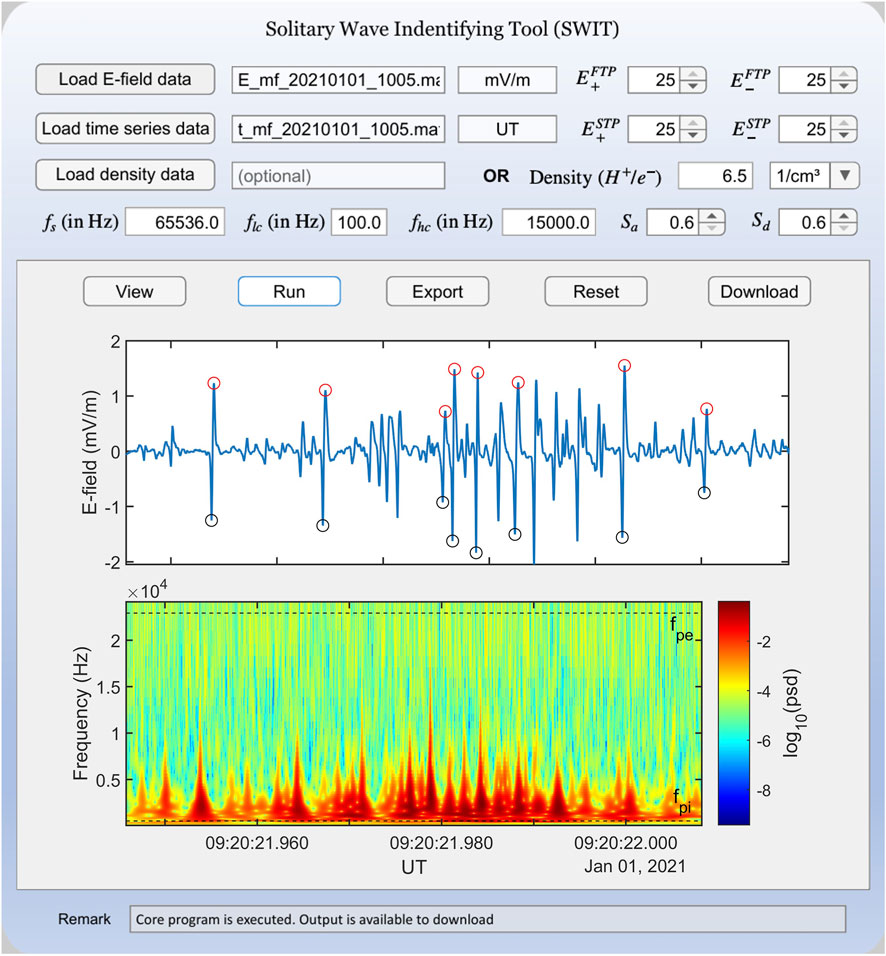
Figure 5. GUI of SWIT, featuring multiple buttons, input fields, and two subplots for waveform visualization. In the waveform panel, the red and blue circles indicate the
Other parameters like
Once the electric field data is loaded, the user can click on the “View” button to plot the electric field in the upper panel and its spectrogram in the lower panel. There will be two horizontal black dashed lines in the lower panel corresponding to the electron plasma frequency
To evaluate SWIT’s baseline performance, we used a Dell G15 5,330 system with Windows 11, powered by 13th-generation Intel Core i5-13450HX CPU (2.4 GHz), and 16 GB RAM. The start-up time of SWIT is approximately 6–9 s after launch. Its RAM usage, measured as the active private working set, ranges from 100 to 300 MB. The total memory footprint (working set) is approximately 900 MB, including around 200 MB of shared memory. We evaluated the CPU time required for data loading and visualization. For example, loading a 62.5 ms signal sampled at 65,536 Hz takes approximately 0.6 ms. On average, loading a 1-s burst signal takes around 8 ms. Similarly, the time required to plot the signal and its spectrogram also varies with signal length. For a 1-s signal, rendering both panels takes about 3 s of CPU time.
5 Results
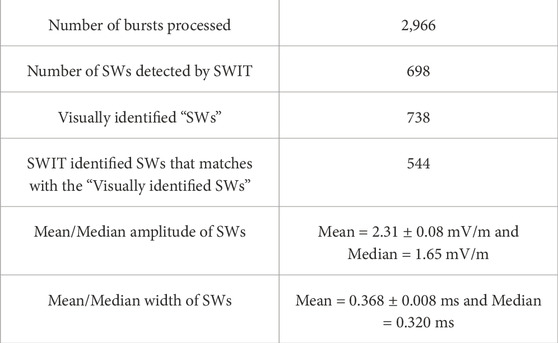
In this section, we discuss the efficiency of SWIT and some results based on the analysis of medium-frequency calibrated burst mode electric field data from MAVEN for February 2015. In the development of SWIT, we ensure high efficiency, which is needed for the automatic identifier. However, in spite of all these measures, the automatic program may detect some solitary waves, which may be either false positive or false negative. Therefore, the number of solitary waves identified by visual inspection and through automatic programs can differ. In such a scenario, one needs to check the efficiency of SWIT by comparing the number of solitary waves identified visually and through SWIT. For this purpose, we took the electric field data from 1 January 2021 as an example. It contains 2,966 individual burst datasets having durations between 62.5 and 375 ms. Each individual burst is loaded in SWIT GUI with recommended input criteria (i.e.,
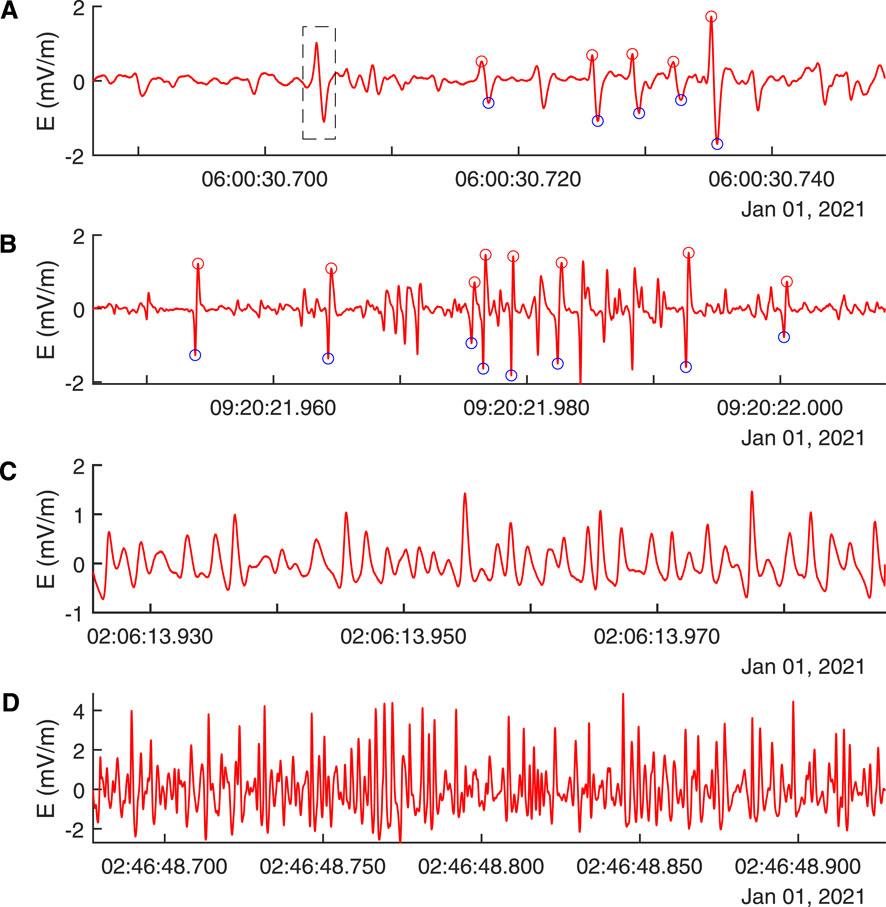
Figure 6. Four examples of electric field burst datasets: (A) A good case where solitary waves have been identified with one false negative solitary wave waveform (see solitary wave marked with a dashed rectangle). (B) Shows another case where all solitary waves have correctly identified. (C,D) Depict cases with no solitary waves, and SWIT GUI does not detect solitary waves for these two cases.
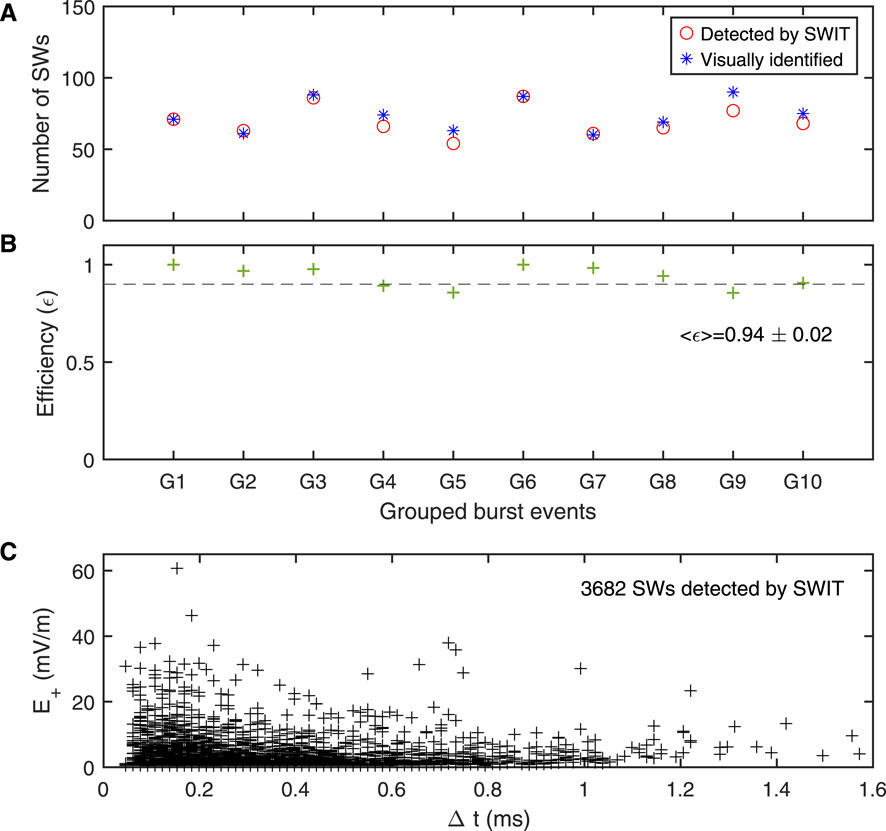
Figure 7. (A) Represents the number of solitary waves detected visually and by SWIT for 2,966 burst events on 1 January 2021. These events are grouped in 10 bins, and the total number of solitary waves in each bin is plotted. Solitary waves identified by SWIT are marked with red circles, while those identified visually are shown with blue asterisks. The corresponding efficiency of SWIT is shown in (B). The dashed line in (B) indicates the 90% efficiency. The mass plot of the peak electric field amplitude as a function of the width of solitary wave identified by SWIT by processing 50,835 burst events recorded on 19 days in February 2015 is shown in (C).
To justify the choice of parameters
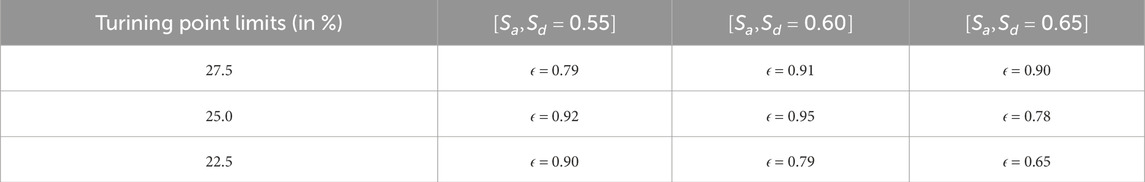
Table 1. The efficiency
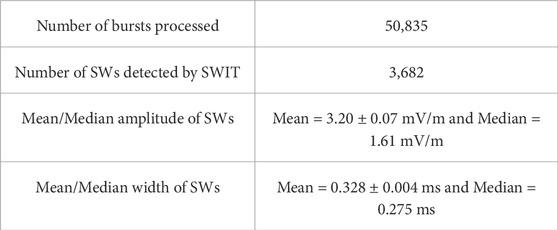
Further, to test SWIT, we analyzed the electric field burst datasets for 19 days in February 2015. A total of 50,835 bursts were recorded during February 2015. SWIT identified a total of 3,682 solitary waves. The mean amplitude and width of these waves are approximately 3.2 mV/m and 0.328 ms, respectively (see Table A3). The amplitude as a function of width is shown in Figure 7C for these identified solitary waves. It may be noted that, in general, the amplitude varies between
6 Summary and conclusion
The paper presents a new automatic tool to identify bipolar solitary waves from high-resolution electric field measurements by a spacecraft. It is named as SWIT and is well tested for the medium-frequency (100 Hz–32 kHz) calibrated burst mode electric field data recorded by MAVEN spacecraft. We began by discussing features of the ideal form of the solitary waves and then compared them with the observed electric field bipolar pulse. Accordingly, the criteria to identify solitary waves in the electric field data were built. The series of implemented criteria and their significance in the logical development of the computer program are elaborated. Fundamentally, SWIT is based on the cumulative integration of filtered electric field signals to identify the locations of the bipolar structures present in the data. In the output, SWIT provide
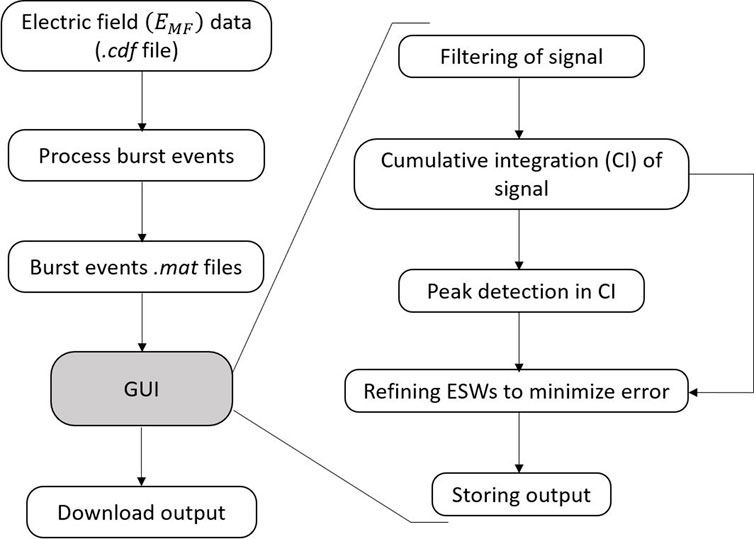
The SWIT GUI is developed using MATLAB 2024b as a stand-alone desktop application for Windows. In order to run this application, users need the MATLAB Runtime, which is included in the installer. The instructions for the installation and usage of SWIT can be found in the accompanying ReadMe file. Initially, using “process_burst_events.m” program file for MATLAB, the user can convert electric field raw data into individual “.mat” files that contain the electric field and time information separately for each burst files that occurred on a given day. These individual burst files (time and electric field) serve as input to the SWIT module. The recommended parameters for
SWIT serves as an important resource for conducting detailed statistical analyses, enabling users to explore the characteristics of solitary waves and their relationships with altitude, local time, and space weather conditions, particularly for the Martian plasma environment. The insights gained from this analysis help in understanding the generation of solitary waves in the plasma environment of unmagnetized planets like Mars. This automatic tool will reduce analysis time and aid in processing large-scale, high-resolution data acquired by spacecraft. SWIT is a versatile package that allows modifications in its code to make it applicable for high-resolution electric field datasets from other spacecraft, enabling comparative studies of solitary waves across different planetary plasma environments. In a nutshell, SWIT will be useful to explore the dynamics of bipolar solitary wave structures with good accuracy and efficiency in planetary plasma environments.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
SP: Methodology, Validation, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Software. AK: Methodology, Conceptualization, Supervision, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Visualization, Software. BK: Visualization, Validation, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Methodology, Software.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Authors acknowledge support from the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG) India for research funding under the project IIG/MI-PEARL/2024–2025.
Acknowledgments
We thank the MAVEN team for making this valuable data available to the scientific community. This work is supported by the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism under the program MI-PEARL/2024-2025.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Andersson, L. (2024). MAVEN LPW medium frequency burst mode calibrated electric-field data collection. doi:10.17189/8DBB-Y985
Andersson, L., and Ergun, R. E. (2012). “The search for double layers in space plasmas,”, 197. Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union, 241–250. doi:10.1029/2011GM001170
Andersson, L., Ergun, R., Delory, G., Eriksson, A., Westfall, J., Reed, H., et al. (2015). The langmuir probe and waves (LPW) instrument for MAVEN. Space Sci. Rev. 195, 173–198. doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0194-3
Aravindakshan, H., Kakad, A., and Kakad, B. (2018a). Bernstein-greene-kruskal theory of electron holes in superthermal space plasma. Phys. Plasmas 25, 052901. doi:10.1063/1.5025234
Aravindakshan, H., Kakad, A., and Kakad, B. (2018b). Effects of wave potential on electron holes in thermal and superthermal space plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 25, 122901. doi:10.1063/1.5046721
Aravindakshan, H., Yoon, P. H., Kakad, A., and Kakad, B. (2020). Theory of ion holes in space and astrophysical plasmas. Mon. Notices R. Astronomical Soc. Lett. 497, L69–L75. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slaa114
Aravindakshan, H., Kakad, A., Kakad, B., and Yoon, P. H. (2021). Structural characteristics of ion holes in plasma. Plasma 4, 435–449. doi:10.3390/plasma4030032
Aravindakshan, H., Vasko, I. Y., Kakad, A., Kakad, B., and Wang, R. (2023). Theory of ion holes in plasmas with flat-topped electron distributions. Phys. Plasmas 30, 022903. doi:10.1063/5.0086613
Arya, N., and Kakad, A. (2025). Lower hybrid and solitary waves in dusk flank region of the earth’s magnetosphere. Adv. Space Res. 75, 876–885. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2024.08.065
Cattell, C., Crumley, J., Dombeck, J., Wygant, J., and Mozer, F. (2002). Polar observations of solitary waves at the Earth’s magnetopause. Geophys. Res. Lett. 29, 1065. doi:10.1029/2001GL014046
Dillard, C., Vasko, I., Mozer, F., Agapitov, O., and Bonnell, J. (2018). Electron-acoustic solitary waves in the Earth’s inner magnetosphere. Phys. Plasmas 25, 022905. doi:10.1063/1.5007907
Eliasson, B., and Shukla, P. K. (2006). Formation and dynamics of coherent structures involving phase-space vortices in plasmas. Phys. Rep. 422, 225–290. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2005.10.003
Ergun, R., Carlson, C., McFadden, J., Mozer, F., Muschietti, L., Roth, I., et al. (1998). Debye-scale plasma structures associated with magnetic-field-aligned electric fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 826–829. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.826
Ergun, R., Andersson, L., Main, D., Su, Y.-J., Newman, D., Goldman, M., et al. (2004). Auroral particle acceleration by strong double layers: the upward current region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 109, A12220. doi:10.1029/2004JA010545
Ergun, R., Andersson, L., Tao, J., Angelopoulos, V., Bonnell, J., McFadden, J., et al. (2009). Observations of double layers in Earth’s plasma sheet. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 155002. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.155002
Graham, D. B., Khotyaintsev, Y. V., Vaivads, A., and André, M. (2015). Electrostatic solitary waves with distinct speeds associated with asymmetric reconnection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 215–224. doi:10.1002/2014GL062538
Graham, D. B., Khotyaintsev, Y. V., Vaivads, A., and Andre, M. (2016). Electrostatic solitary waves and electrostatic waves at the magnetopause. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 121, 3069–3092. doi:10.1002/2015JA021527
Hansel, P. J., Wilder, F., Malaspina, D. M., Ergun, R. E., Ahmadi, N., Holmes, J. C., et al. (2021). Mapping MMS observations of solitary waves in Earth’s magnetic field. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 126, e2021JA029389. doi:10.1029/2021JA029389
Hobara, Y., Walker, S., Balikhin, M., Pokhotelov, O., Gedalin, M., Krasnoselskikh, V., et al. (2008). Cluster observations of electrostatic solitary waves near the earth’s bow shock. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113, A05211. doi:10.1029/2007JA012789
Holmes, J., Ergun, R., Newman, D., Wilder, F., Sturner, A., Goodrich, K., et al. (2018). Negative potential solitary structures in the magnetosheath with large parallel width. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 123, 132–145. doi:10.1002/2017JA024890
Kakad, A., and Kakad, B. (2019). Generation of series of electron Acoustic solitary wave pulses in plasma. Phys. Plasmas 26, 102105. doi:10.1063/1.5113743
Kakad, A., Singh, S., Reddy, R., Lakhina, G., Tagare, S., and Verheest, F. (2007). Generation mechanism for electron acoustic solitary waves. Phys. plasmas 14, 052305. doi:10.1063/1.2732176
Kakad, A., Singh, S., Reddy, R., Lakhina, G., and Tagare, S. (2009). Electron acoustic solitary waves in the Earth’s magnetotail region. Adv. Space Res. 43, 1945–1949. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2009.03.005
Kakad, A., Omura, Y., and Kakad, B. (2013). Experimental evidence of ion acoustic soliton chain formation and validation of nonlinear fluid theory. Phys. Plasmas 20, 062103. doi:10.1063/1.4810794
Kakad, B., Kakad, A., and Omura, Y. (2014). Nonlinear evolution of ion acoustic solitary waves in space plasmas: fluid and particle-in-cell simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119, 5589–5599. doi:10.1002/2014JA019798
Kakad, A., Kakad, B., Anekallu, C., Lakhina, G., Omura, Y., and Fazakerley, A. (2016). Slow electrostatic solitary waves in Earth’s plasma sheet boundary layer. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 121, 4452–4465. doi:10.1002/2016JA022365
Kakad, A., Kakad, B., and Omura, Y. (2017a). Formation and interaction of multiple coherent phase space structures in plasma. Phys. Plasmas 24, 060704. doi:10.1063/1.4986109
Kakad, B., Kakad, A., and Omura, Y. (2017b). Particle trapping and ponderomotive processes during breaking of ion acoustic waves in plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 24, 102122. doi:10.1063/1.4986030
Kakad, B., Kakad, A., Aravindakshan, H., and Kourakis, I. (2022). Debye-scale solitary structures in the Martian magnetosheath. Astrophysical J. 934, 126. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac7b8b
Kamaletdinov, S., Vasko, I., Wang, R., Artemyev, A., Yushkov, E., and Mozer, F. (2022). Slow electron holes in the Earth’s bow shock. Phys. Plasmas 29, 092303. doi:10.1063/5.0102289
Kojima, H., Omura, Y., Matsumoto, H., Miyaguti, K., and Mukai, T. (2000). Automatic waveform selection method for electrostatic solitary waves. Earth, planets space 52, 495–502. doi:10.1186/BF03351653
Krasovsky, V., Matsumoto, H., and Omura, Y. (1997). Bernstein-greene-kruskal analysis of electrostatic solitary waves observed with geotail. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 102, 22131–22139. doi:10.1029/97JA02033
Lakhina, G., Kakad, A., Singh, S., and Verheest, F. (2008a). Ion-and electron-acoustic solitons in two-electron temperature space plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 15, 062903. doi:10.1063/1.2930469
Lakhina, G., Singh, S., Kakad, A., Verheest, F., and Bharuthram, R. (2008b). Study of nonlinear ion-and electron-acoustic waves in multi-component space plasmas. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 15, 903–913. doi:10.5194/npg-15-903-2008
Lakhina, G., Singh, S., Kakad, A., Goldstein, M., Vinas, A., and Pickett, J. (2009). A mechanism for electrostatic solitary structures in the Earth’s magnetosheath. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 114, A09212. doi:10.1029/2009JA014306
Lakhina, G., Singh, S., Kakad, A., and Pickett, J. (2011a). Generation of electrostatic solitary waves in the plasma sheet boundary layer. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 116. doi:10.1029/2011JA016700
Lakhina, G. S., Singh, S., and Kakad, A. (2011b). Ion-and electron-acoustic solitons and double layers in multi-component space plasmas. Adv. Space Res. 47, 1558–1567. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2010.12.013
Lakhina, G. S., Singh, S., Rubia, R., and Devanandhan, S. (2021). Electrostatic solitary structures in space plasmas: Soliton perspective. Plasma 4, 681–731. doi:10.3390/plasma4040035
Lotekar, A., Kakad, A., and Kakad, B. (2016). Fluid simulation of dispersive and nondispersive ion acoustic waves in the presence of superthermal electrons. Phys. Plasmas 23, 102108. doi:10.1063/1.4964478
Lotekar, A., Kakad, A., and Kakad, B. (2017). Generation of ion acoustic solitary waves through wave breaking in superthermal plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 24, 102127. doi:10.1063/1.4991467
Lotekar, A., Kakad, A., and Kakad, B. (2019). Formation of asymmetric electron acoustic double layers in the Earth’s inner magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 124, 6896–6905. doi:10.1029/2018JA026303
Maharaj, S., Bharuthram, R., Singh, S., and Lakhina, G. (2015). Existence domains of slow and fast ion-acoustic solitons in two-ion space plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 22, 032313. doi:10.1063/1.4916319
Malaspina, D. M., Goodrich, K., Livi, R., Halekas, J., McManus, M., Curry, S., et al. (2020). Plasma double layers at the boundary between Venus and the solar wind. Geophys. Res. Lett. 47, e2020GL090115. doi:10.1029/2020GL090115
Matsumoto, H., Kojima, H., Miyatake, T., Omura, Y., Okada, M., Nagano, I., et al. (1994). Electrostatic solitary waves (ESW) in the magnetotail: BEN wave forms observed by GEOTAIL. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21, 2915–2918. doi:10.1029/94gl01284
Mozer, F., Bale, S., Bonnell, J., Chaston, C., Roth, I., and Wygant, J. (2013). Megavolt parallel potentials arising from double-layer streams in the earth’s outer radiation belt. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 235002. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.235002
Mozer, F., Agapitov, O., Giles, B., and Vasko, I. (2018). Direct observation of electron distributions inside millisecond duration electron holes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 135102. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.135102
Norgren, C., André, M., Vaivads, A., and Khotyaintsev, Y. V. (2015). Slow electron phase space holes: Magnetotail observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 1654–1661. doi:10.1002/2015GL063218
Olivier, C., Maharaj, S., and Bharuthram, R. (2015). Ion-acoustic solitons, double layers and supersolitons in a plasma with two ion-and two electron species. Phys. Plasmas 22, 082312. doi:10.1063/1.4928884
Omura, Y., Matsumoto, H., Miyake, T., and Kojima, H. (1996). Electron beam instabilities as generation mechanism of electrostatic solitary waves in the magnetotail. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 101, 2685–2697. doi:10.1029/95JA03145
Pandey, S., Kakad, A., and Kakad, B. (2025a). First observational evidence of plasma waves in the Martian magnetosheath jet. Mon. Notices R. Astronomical Soc. Lett. 537, L7–L13. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slae105
Pandey, S., Kakad, A., and Kakad, B. (2025b). Solitary wave identifying tool (SWIT) for electric field dataset from MAVEN spacecraft. doi:10.5281/zenodo.15174978
Pandey, S., Kakad, A., Kakad, B., Singh, K., and Kourakis, I. (2025c). Double layers in the Martian magnetosheath. Astrophysical J. 981, 44. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/adad6f
Pickett, J., Menietti, J., Gurnett, D., Tsurutani, B., Kintner, P., Klatt, E., et al. (2003). Solitary potential structures observed in the magnetosheath by the cluster spacecraft. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 10, 3–11. doi:10.5194/npg-10-3-2003
Pickett, J., Kahler, S., Chen, L.-J., Huff, R., Santolik, O., Khotyaintsev, Y., et al. (2004). Solitary waves observed in the auroral zone: the cluster multi-spacecraft perspective. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 11, 183–196. doi:10.5194/npg-11-183-2004
Pickett, J., Chen, L.-J., Kahler, S., Santolik, O., Goldstein, M., Lavraud, B., et al. (2005). On the generation of solitary waves observed by cluster in the near-Earth magnetosheath. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 12, 181–193. doi:10.5194/npg-12-181-2005
Rubia, R., Singh, S., Lakhina, G., Devanandhan, S., Dhanya, M., and Kamalam, T. (2023). Electrostatic solitary waves in the venusian ionosphere pervaded by the solar wind: a theoretical perspective. Astrophysical J. 950, 111. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acd2d7
Shaikh, Z., Vasko, I., Hutchinson, I., Kamaletdinov, S., Holmes, J., Newman, D., et al. (2024). Slow electron holes in the Earth’s magnetosheath. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 129, e2023JA032059. doi:10.1029/2023JA032059
Singh, S., and Lakhina, G. (2001). Generation of electron-acoustic waves in the magnetosphere. Planet. Space Sci. 49, 107–114. doi:10.1016/S0032-0633(00)00126-4
Singh, K., Kakad, A., Kakad, B., and Kourakis, I. (2022). Fluid simulation of dust-acoustic solitary waves in the presence of suprathermal particles: application to the magnetosphere of Saturn. Astronomy and Astrophysics 666, A37. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202244136
Singh, K., Varghese, S. S., Saini, N. S., and Kourakis, I. (2024). Oblique electrostatic solitary and supersolitary waves in earth’s magnetosheath. Astrophysical J. 971, 25. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ad5c6b
Sun, J., Vasko, I. Y., Bale, S. D., Wang, R., and Mozer, F. S. (2022). Double layers in the Earth’s bow shock. Geophys. Res. Lett. 49, e2022GL101348. doi:10.1029/2022GL101348
Temerin, M., Cerny, K., Lotko, W., and Mozer, F. (1982). Observations of double layers and solitary waves in the auroral plasma. Phys. Rev. Lett. 48, 1175–1179. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.48.1175
Thaller, S. A., Andersson, L., Schwartz, S. J., Mazelle, C., Fowler, C., Goodrich, K., et al. (2022). Bipolar electric field pulses in the Martian magnetosheath and solar wind; their implication and impact accessed by system scale size. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 127, e2022JA030374. doi:10.1029/2022JA030374
Tong, Y., Vasko, I., Mozer, F., Bale, S. D., Roth, I., Artemyev, A., et al. (2018). Simultaneous multispacecraft probing of electron phase space holes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 45, 11–513. doi:10.1029/2018GL079044
Umeda, T., Omura, Y., Matsumoto, H., and Usui, H. (2002). Formation of electrostatic solitary waves in space plasmas: particle simulations with open boundary conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 107, 1449. doi:10.1029/2001JA000286
Varghese, S. S., Singh, K., and Kourakis, I. (2024a). Electrostatic solitary waves in a bi-ion plasma with two suprathermal electron populations–application to Saturn’s magnetosphere. Mon. Notices R. Astronomical Soc. 527, 8337–8354. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad3763
Varghese, S. S., Singh, K., Verheest, F., and Kourakis, I. (2024b). Electrostatic solitary waves in electronegative Martian plasma. Astrophysical J. 977, 100. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ad8b49
Vasko, I., Agapitov, O., Mozer, F., Bonnell, J., Artemyev, A., Krasnoselskikh, V., et al. (2017a). Electron-acoustic solitons and double layers in the inner magnetosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 44, 4575–4583. doi:10.1002/2017gl074026
Vasko, I., Kuzichev, I., Agapitov, O., Mozer, F., Artemyev, A., and Roth, I. (2017b). Evolution of electron phase space holes in inhomogeneous plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 24, 062311. doi:10.1063/1.4989717
Vasko, I., Mozer, F., Krasnoselskikh, V., Artemyev, A., Agapitov, O., Bale, S., et al. (2018). Solitary waves across supercritical quasi-perpendicular shocks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 45, 5809–5817. doi:10.1029/2018GL077835
Vasko, I. Y., Wang, R., Mozer, F. S., Bale, S. D., and Artemyev, A. V. (2020). On the nature and origin of bipolar electrostatic structures in the Earth’s bow shock. Front. Phys. 8, 156. doi:10.3389/fphy.2020.00156
Wang, R., Lu, Q., Khotyaintsev, Y. V., Volwerk, M., Du, A., Nakamura, R., et al. (2014). Observation of double layer in the separatrix region during magnetic reconnection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41, 4851–4858. doi:10.1002/2014GL061157
Wang, R., Vasko, I., Artemyev, A., Holley, L., Kamaletdinov, S., Lotekar, A., et al. (2022). Multisatellite observations of ion holes in the Earth’s plasma sheet. Geophys. Res. Lett. 49, e2022GL097919. doi:10.1029/2022GL097919
Wang, C., Huang, S., Yuan, Z., Jiang, K., Zhang, J., Dong, Y., et al. (2023). In situ observation of electron acceleration by a double layer in the bow shock. Astrophysical J. 952, 78. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acdacb
Williams, J., Chen, L.-J., Kurth, W., Gurnett, D., and Dougherty, M. (2006). Electrostatic solitary structures observed at Saturn. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L06103. doi:10.1029/2005GL024532
Appendix A
A1 SWIT output summary: 1 January 2021 datasets
A2 confusion matrix: 1 January 2021 datasets
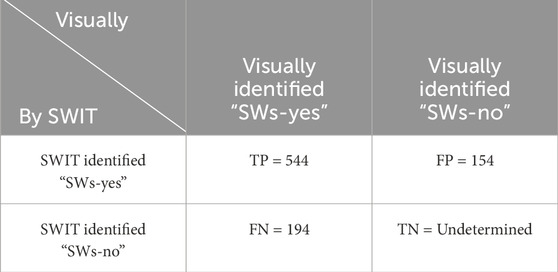
TABLE A2. Confusion matrix based on SWIT’s predictions for the presence of SWs on 1 January 2021. Columns indicate the visually identified presence or absence of SWs, while rows show the SWs detected by SWIT. The False negative rate is estimated to be 0.26.
Our dataset consists of continuous electric field measurements over time, which may include solitary waves (SWs) with varying characteristics (e.g., amplitude and width). Moreover, there is no defined criterion for how many SWs should appear in a given burst signal. The signal segments that exclude visually identified SWs can be considered as true negatives; however, they remain unquantified. Therefore, it is not possible to estimate the number of true negatives.
A3 SWIT output summary: February 2015 datasets
Keywords: planetary magnetosphere, martian upper atmosphere, electrostatic solitary waves, phase space holes, graphical user interface
Citation: Pandey S, Kakad A and Kakad B (2025) Novel method and tool to identify solitary waves in the Martian plasma environment. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 12:1644464. doi: 10.3389/fspas.2025.1644464
Received: 10 June 2025; Accepted: 13 August 2025;
Published: 11 September 2025.
Edited by:
Ankush Bhaskar, Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre, IndiaReviewed by:
Manpreet Singh, Southwest Jiaotong University, ChinaSteffy Sara Varghese, Khalifa University, United Arab Emirates
Copyright © 2025 Pandey, Kakad and Kakad. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sahil Pandey, cHNhaGlsMTc3QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Sahil Pandey
Sahil Pandey Amar Kakad
Amar Kakad Bharati Kakad
Bharati Kakad