- 1College of Physics, Hebei Normal University, Shijiazhuang, China
- 2College of Sciences, Hebei University of Science and Technology, Shijiazhuang, China
Introduction: The chemical abundances of metal poor (MP) stars in globular clusters provide valuable information for constraining their evolutionary scenarios.
Methods: Using both main
Results and discussion: The coefficients of the main and weak r-process components are nearly constant for the sample stars, including
1 Introduction
Metal poor (MP) stars are typically old and are often regarded as cosmic fossils due to their abundance patterns, which preserve valuable information about the early stages of galactic evolution. The analysis of elemental abundance patterns is fundamental for understanding the chemical evolution of galaxies and refining nucleosynthesis theory, which describes the formation of elements in stars and other astrophysical environments. Elements with atomic numbers
The synthesis of heavy elements in the cosmos is governed by two distinct mechanisms: the slow neutron-capture process (
Observations of the ultra metal poor halo stars CS 22892-052 (Sneden et al., 2003; Cowan et al., 2005) and CS 31082-001 (Hill et al., 2002; Honda et al., 2004) have revealed that their heavier elements
For many years, globular clusters have played an important role in testing many aspects of stellar evolution and stellar nucleosynthesis. In this context, the abundance patterns of neutron-capture elements offer valuable insights into stellar nucleosynthesis and the chemical evolution of globular clusters. Marino et al. (2009) performed a chemical abundance analysis of the globular cluster M22, and reported that it exhibits an intrinsic Fe abundance spread based on optical spectroscopic analyses. However, more recent work using high-resolution, homogeneously analyzed near-infrared spectra from the APOGEE survey Mészáros et al. (2020) did not confirm such a spread, concluding instead that M22 is chemically homogeneous in Fe. A key consideration is that the stellar samples analyzed in these two studies are not identical, which may partially account for the contrasting results. Differences in evolutionary stage, spatial distribution, or membership probability of the selected stars can significantly influence the derived abundance patterns. It remains possible that distinct sub-populations exist within M22, and that Fe variations, if present, are confined to a subset of stars not captured in the APOGEE sample. This highlights the importance of sample selection and motivates further targeted studies to resolve the presence or absence of Fe variations in M22. In particular, based on the abundance analysis of 35 stars, Marino et al. (2011) found that M22 exhibits a complex chemical pattern. They reported the presence of two distinct stellar groups in this cluster, characterized by significant differences in the neutron-capture elements Y, Zr, Ba, and La, namely,
In this paper, we fit the abundances of 30 stars in M22 with a parametric model and calculate the relative contributions from individual neutron-capture processes to the elemental abundances in these stars. To analyze the origins of neutron-capture elements in M22, the parametric model used for the abundance decomposition of 30 stars in M22 is described in Section 2. The calculations and best-fit results are presented in Section 3. Our conclusions are summarized in Section 4.
2 The origins of the neutron-capture elements in M22
Since the main
Li et al. (2013) derived the main
2.1 Parametric model and calculations
The chemical elements in stars usually come from the molecular clouds where they were born, and they can be produced through multiple mechanisms. In general, the formation of elements with
where
where
3 Results and discussions
We performed our calculations based on Equations 1,2 using the observed abundances of
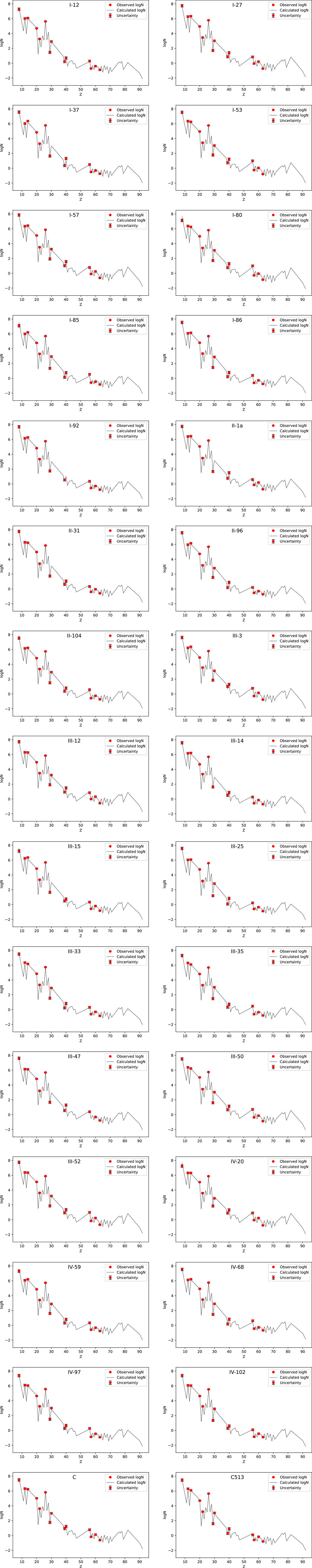
Figure 1. The calculated best-fit results. The observed elemental abundances are marked by red filled circles. The solid lines represent the best-fit results.
To enable a rigorous comparison between the predicted nucleosynthetic yields and the observed stellar abundances, we plot the observed data as filled circles, while the solid black lines denote the best-fit model abundances derived from our component decomposition analysis. A visual inspection reveals that the theoretical predictions align remarkably well with the observed elemental abundances across all sample stars, with discrepancies generally falling within the bounds of observational uncertainty.
To quantitatively assess the quality of the fit, we present in the top panel of Figure 2 the relative offsets, defined as
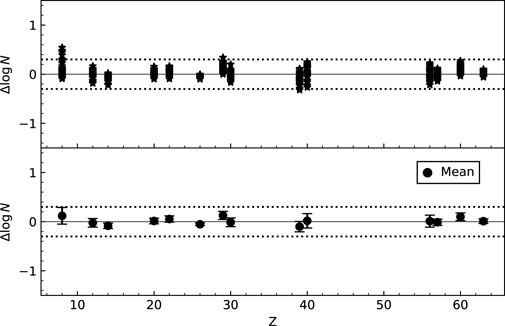
Figure 2. Top panel: Individual relative offsets
The bottom panel of Figure 2 shows the root-mean-square (RMS) deviations of the offsets for each element. These RMS values remain below
From Figure 1, we also observe good agreement between the predicted and observed abundances of
The component coefficients as a function of metallicity, illustrated in Figure 3, provide important insights into the pollution history of M22. As shown in Figure 3, the sample stars are clearly divided into two groups based on
![Scatter plot showing C values versus [Fe/H] ranging from -1.95 to -1.65. Data points include blue squares for \(C_{r,m}\) (s-rich), open blue squares for (s-poor), green circles for \(C_{r,w}\) (s-rich), open green circles for (s-poor), red stars for \(C_s\) both (s-rich) and (s-poor). Logarithmic scale on the vertical axis from 0.01 to 10.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1663125/fspas-12-1663125-HTML/image_m/fspas-12-1663125-g003.jpg)
Figure 3. The component coefficients as a function of metallicity. Symbols: open squares, open circles, and open stars represent the component coefficients for the main
Marino et al. (2011) found that most
Moreover, Marino et al. (2011) observed that stars in M22 are distinctly separated into
4 Conclusion
In globular clusters, the vast majority of chemical evolution and nucleosynthetic information is encoded in the elemental abundances of stars exhibiting a range of metallicities. In this context, the chemical abundances of metal poor stars in M22 serve as invaluable data for constraining theoretical models of both the
1. The abundances of most
2. For
i. The
ii. The trends of component coefficients for the
Clearly, it is crucial for future studies to determine the specific evolutionary scenario of M22. Further theoretical and observational investigations will enhance our understanding of the r-process at low metallicity and provide insight into the history of neutron-capture element enrichment in globular clusters.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
MA: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. WC: Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. HL: Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study is supported by the National Key Basic R&D Program of China No. 2024YFA1611903, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant No. 12173013, the project of Hebei provincial department of science and technology under the grant number 226Z7604G.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbott, B., Abbott, R., Abbott, T., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., et al. (2017). Gw170817: observation of gravitational waves from a binary neutron star inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 161101. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.119.161101
Aoki, W., Honda, S., Beers, T., Kajino, T., Ando, H., Norris, J., et al. (2005). Spectroscopic studies of very metal-poor stars with the subaru high dispersion spectrograph. Iii. Light neutron-capture elements. Astrophysical J. 632, 611–637. doi:10.1086/432862
Bisterzo, S., Gallino, R., Straniero, O., Cristallo, S., and Käppeler, F. (2010). s-process in low-metallicity Stars–i. theoretical predictions. Mon. Notices R. Astronomical Soc. 404, 1529–1544. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16369.x
Burbidge, E., Burbidge, G., Fowler, W., and Hoyle, F. (1957). Synthesis of the elements in stars. Rev. Mod. Phys. 29, 547–650. doi:10.1103/revmodphys.29.547
Busso, M., Gallino, R., and Wasserburg, G. (1999). Nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars: relevance for galactic enrichment and solar system formation. Annu. Rev. Astronomy Astrophysics 37, 239–309. doi:10.1146/annurev.astro.37.1.239
Cowan, J., Sneden, C., Beers, T., Lawler, J., Simmerer, J., Truran, J., et al. (2005). Hubble space telescope observations of heavy elements in metal-poor galactic halo stars. Astrophysical J. 627, 238–250. doi:10.1086/429952
Farouqi, K., Thielemann, F., Rosswog, S., and Kratz, K. (2022). Correlations of r-process elements in very metal-poor stars as clues to their nucleosynthesis sites. Astron. Astrophys. 663, A70. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202141038
Gallino, R., Arlandini, C., Busso, M., Lugaro, M., Travaglio, C., Straniero, O., et al. (1998). Evolution and nucleosynthesis in low-mass asymptotic giant branch stars. ii. neutron capture and the s-process. Astrophysical J. 497, 388–403. doi:10.1086/305437
Hill, V., Plez, B., Cayrel, R., Beers, T., Nordström, B., Andersen, J., et al. (2002). First stars. i. the extreme r-element rich, iron-poor halo giant cs 31082-001-implications for the r-process site (s) and radioactive cosmochronology. Astron. Astrophys. 387, 560–579. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020434
Honda, S., Aoki, W., Kajino, T., Ando, H., Beers, T., Izumiura, H., et al. (2004). Spectroscopic studies of extremely metal-poor stars with the subaru high dispersion spectrograph. ii. the r-process elements, including thorium. Astrophysical J. 607, 474–498. doi:10.1086/383406
Honda, S., Aoki, W., Ishimaru, Y., and Wanajo, S. (2007). Neutron-capture elements in the very metal-poor star hd 88609: another star with excesses of light neutron-capture elements. Astrophysical J. 666, 1189–1197. doi:10.1086/520034
Ishimaru, Y., Wanajo, S., Aoki, W., Ryan, S., and Prantzos, N. (2005). First enrichment of r-process elements in our galaxy. Nucl. Phys. A 758, 603–606. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2005.05.109
Izutani, N., Umeda, H., and Tominaga, N. (2009). Explosive nucleosynthesis of weak r-process elements in extremely metal-poor core-collapse supernovae. Astrophysical J. 692, 1517–1531. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/692/2/1517
Johnson, J. (2002). Abundances of 30 elements in 23 metal-poor stars. Astrophysical J. Suppl. Ser. 139, 219–247. doi:10.1086/338117
Li, H., Shen, X., Liang, S., Cui, W., and Zhang, B. (2013). Study of neutron-capture element abundances in metal-poor stars, 125. Bristol: IOP publishing, 143.
Liang, S., Li, H., Shen, X., Cui, W., and Zhang, B. (2012). Abundance analysis of r + s stars: r-process abundance comparison between r+ s stars and r-rich stars, 124. Bristol: IOP publishing, 304.
MacFadyen, A., and Woosley, S. (1999). Collapsars: gamma-ray bursts and explosions in “Failed Supernovae”. Astrophysical J. 524, 262–289. doi:10.1086/307790
Marino, A., Milone, A., Piotto, G., Villanova, S., Bedin, L., Bellini, A., et al. (2009). A double stellar generation in the globular cluster ngc 6656 (m 22)—two stellar groups with different iron and s-process element abundances. Astron. Astrophys. 505, 1099–1113. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200911827
Marino, A., Sneden, C., Kraft, R., Wallerstein, G., Norris, J., Da Costa, G., et al. (2011). The two metallicity groups of the globular cluster m 22: a chemical perspective. Astron. Astrophys. 532, A8. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201116546
Mészáros, S., Masseron, T., García-Hernández, D. A., Allende Prieto, C., Beers, T. C., Bizyaev, D., et al. (2020). Homogeneous analysis of globular clusters from the apogee survey with the bacchus code–ii. the southern clusters and overview. Mon. Notices R. Astronomical Soc. 492, 1641–1670. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz3496
Montes, F., Beers, T., Cowan, J., Elliot, T., Farouqi, K., Gallino, R., et al. (2007). Nucleosynthesis in the early galaxy. Astrophysical J. 671, 1685–1695. doi:10.1086/523084
Qian, Y., and Wasserburg, G. (2007). Where, oh where has the r-process gone? Phys. Rep. 442, 237–268. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2007.02.006
Roederer, I. U., Sneden, C., Lawler, J. E., and Cowan, J. J. (2010). New abundance determinations of cadmium, lutetium, and osmium in the r-process enriched star bd+ 17 3248. Astrophysical J. Lett. 714, L123–L127. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/714/1/l123
Sneden, C., Cowan, J., Ivans, I., Fuller, G., Burles, S., Beers, T., et al. (2000). Evidence of multiple [CLC] [ITAL]r[/ITAL] [/CLC]-Process sites in the early galaxy: new observations of CS 22892−052. Astrophysical J. 533, L139–L142. doi:10.1086/312631
Sneden, C., Cowan, J., Lawler, J., Ivans, I., Burles, S., Beers, T., et al. (2003). The extremely metal-poor, neutron capture-rich star cs 22892-052: a comprehensive abundance analysis. Astrophysical J. 591, 936–953. doi:10.1086/375491
Sneden, C., Cowan, J., and Gallino, R. (2008). Neutron-capture elements in the early galaxy. Annu. Rev. Astronomy Astrophysics 46, 241–288. doi:10.1146/annurev.astro.46.060407.145207
Thielemann, F., Farouqi, K., Rosswog, S., and Kratz, K. (2023). Sources of r-process abundances. Mem. della Soc. Astron. Ital. 94, 105. doi:10.36116/MEMSAIT_94N2.2023.105
Travaglio, C., Gallino, R., Arnone, E., Cowan, J., Jordan, F., and Sneden, C. (2004). Galactic evolution of sr, y, and zr: a multiplicity of nucleosynthetic processes. Astrophysical J. 601, 864–884. doi:10.1086/380507
Truran, J., Cowan, J., Pilachowski, C., and Sneden, C. (2002). Probing the neutron-capture nucleosynthesis history of galactic matter, 114. Bristol: IOP publishing, 1293.
Wanajo, S., and Ishimaru, Y. (2006). r-process calculations and galactic chemical evolution. Nucl. Phys. A 777, 676–699. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2005.10.012
Westin, J., Sneden, C., Gustafsson, B., and Cowan, J. (2000). The r-process-enriched low-metallicity giant hd 115444. Astrophysical J. 530, 783–799. doi:10.1086/308407
Winteler, C., Kaeppeli, R., Perego, A., Arcones, A., Vasset, N., Nishimura, N., et al. (2012). Magnetorotationally driven supernovae as the origin of early galaxy r-process elements? Astrophysical J. Lett. 750, L22. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/750/1/L22
Woosley, S., and Weaver, T. (1995). “The evolution and explosion of massive stars II: explosive hydrodynamics and nucleosynthesis,”, 101. Livermore, CA (United States): Lawrence Livermore National Lab. LLNL, 181. doi:10.1086/192237
Keywords: nucleosynthesis, metal poor stars, main s-process, main r-process, weak r-process
Citation: Ashraf MZ, Cui W and Li H (2025) The origins of neutron-capture elements in globular cluster M22. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 12:1663125. doi: 10.3389/fspas.2025.1663125
Received: 10 July 2025; Accepted: 06 August 2025;
Published: 26 August 2025.
Edited by:
Xiaohu Li, Chinese Academy of Sciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Beatriz Barbuy, University of São Paulo, BrazilJose Fernandez, Catholic University of the North, Chile
Copyright © 2025 Ashraf, Cui and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenyuan Cui, Y3Vpd2VueXVhbkBoZWJ0dS5lZHUuY24=
 Muhammad Zeshan Ashraf
Muhammad Zeshan Ashraf Wenyuan Cui
Wenyuan Cui Hongjie Li
Hongjie Li