- Star and Planet Formation Laboratory, RIKEN Pioneering Research Institute (PRI), Saitama, Japan
Collisional excitation in reactive systems plays a central role in astrochemistry. Accurate state-to-state rate coefficients are key parameter for the determination of excitation conditions of interstellar molecules with the most abundant species in space (H, He and H2) through collisions. Unfortunately, reliable data for collisions involving interstellar reactive radicals and ions are scarce. Despite the molecular simplicity of these systems, considering the competition between nonreactive and reactive processes on equal footing remains a true theoretical and computational challenge in particular for bimolecular reactions, in addition to excitation processes in open-shell species. This minireview emphasizes recent progress in theoretical approaches for state-to-state scattering in reactive systems of astrochemical interest. We discuss the strengths and limitations of state-of-the-art quantum methods on collisions involving direct and indirect reactions; and the encouraging alternatives proposed by statistical frameworks. We highlight the impact of the computed state-to-state rate coefficients in astrophysical modeling.
1 Introduction
Molecular collisions constitute fundamental processes governing the chemical transformation of matter. Although inherently quantum by nature, they participate in the understanding of structures on astronomical scales. The astrochemical community aims to understand both the molecular composition and the physical conditions lying in the Interstellar Medium (ISM). Since the advent of radio astronomy in the 1960s, the resolution and sensitivity of ground-based and space telescopes have reached unprecedented levels of accuracy, enabling not only the detection of a large number of interstellar molecules, but also probing the chemical diversity in the gas-phase at small scale structures of interstellar sources, notably thanks to the ALMA interferometer (McGuire, 2022). More recently, JWST observations probed a rich chemistry on icy grain mantles, providing key insights into formation of molecules in star-forming regions (McClure et al., 2023).
Molecular spectra offer a window into the physical conditions of interstellar sources. On one hand, the chemical composition is inferred from the line assignment supported by computational and laboratory spectroscopy. On the other hand, line intensity is directly related to the population of molecular energy levels and hence the excitation conditions of interstellar environments. However, the microscopic mechanisms driving the molecular excitation in the ISM are complex due to its extreme density conditions (
Two main cases occur during a collision between two molecules A and B in the gas-phase:
In Equation 1,
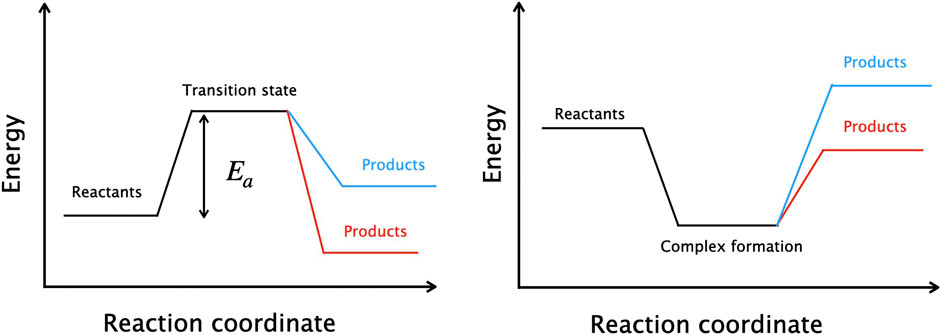
Figure 1. Schematic diagrams of direct (left) and indirect (right) reactions. Red pathways denote exothermic reactions and blue correspond to endothermic reactions.
Usually, the extreme low temperatures of interstellar objects such as molecular clouds (
Recent achievements in experiments like crossed-beam laser techniques or cryogenic ion traps has enabled precise measurements of rate coefficients for reactive processes (Toscano et al., 2020). Supported by theoretical investigations, these data are reported in KIDA (Wakelam et al., 2024) and UMIST (Millar et al., 2023), which are the most important reaction databases for chemical modeling. However, although experimental data take into account all processes occuring during a collision, state-to-state resolved rate coefficients tracking both, excitation and reaction, are still hardly achievable, however necessary in radiative transfer. Scattering calculations remain currently the most reliable approach to provide such collisional data. Typical study of a molecular system lies in the Born-Openheimer approximation (Born and Oppenheimer, 1927). Ab initio methods such as Configurational Interaction type (Knowles and Werner, 1988) or Coupled Clusters (Knowles et al., 1993) are currently the methods of choice for treating high dimensional reactive potential energy surface (PES), as the scattering is highly sensitive to its accuracy (Tonolo and Alessandrini, 2024; Bowman et al., 2011; Jiang et al., 2020). Collisional cross sections and rate coefficients are then derived from the
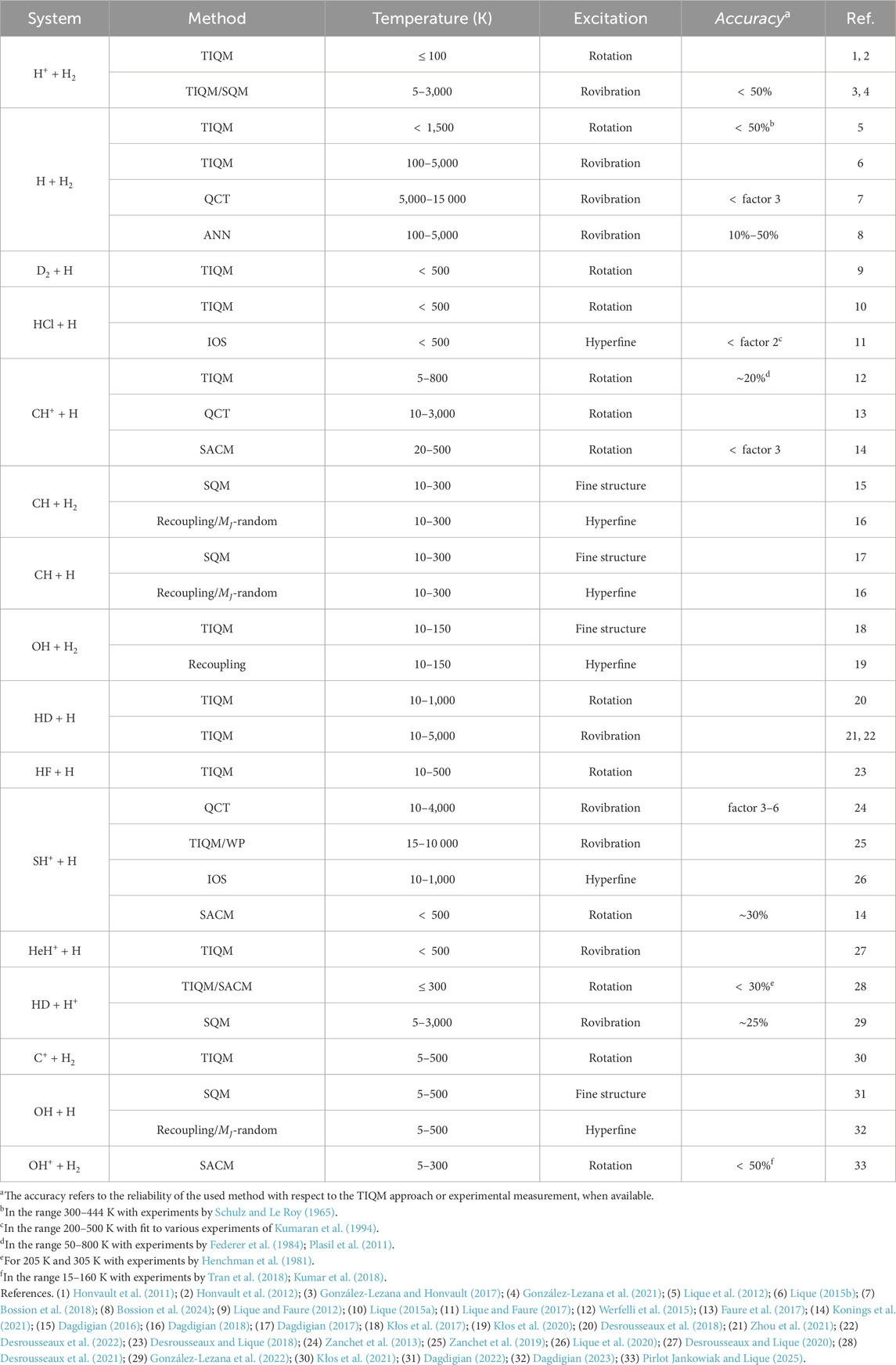
In this minireview, we restrict the discussion to collisional excitation in reactive systems relevant to astrochemical applications over the past decade; and available in the molecular databases EMAA (Faure et al., 2025), BASECOL (Dubernet et al., 2023) and LAMDA (Van der Tak et al., 2020). The manuscript is organized as follows: Section 2 presents the state-of-the-art methods for providing state-to-state collisional data, section 3 discusses recent work on collisions involving direct reactions, while section 4 highlights recent achievements for indirect reactions. Finally, section 5 will discuss excitation processes in open-shell molecules and the impact of the data sets in astrophysical applications.
2 Theoretical methods
State-to-state collisional cross sections characterize the probability for the reactants to transit from an initial energy state to a final one, or to react and form products (see Equation 1). Computing this observable requires the solution of the Close-Coupling equations within the Time-Independent Quantum Mechanical (TIQM) framework. This approach provides the
Both TIQM and TDQM methods are efficient for direct reactions contrary to indirect ones, which often involve a deep potential well. In the latter, calculations require large basis functions to reach convergence, especially at high angular momentum. Statistical methods are proposed as an alternative to overcome this challenge. The main assumption is that the collision proceed through a long-lived enough intermediate complex so that its formation and decay are treated as independent events. Among various approaches, the Statistical Adiabatic Channel Model (SACM; Quack and Troe (1975)) have shown satisfactory agreement with TIQM methods at low temperatures for nonreactive (Loreau et al., 2018) systems and collisions involving heavy colliders (Godard Palluet et al., 2025; Tonolo et al., 2025). For reactive systems, both SACM and Statistical Quantum Methods (SQM; Rackham et al. (2003)) were employed for indirect reactions. Comparisons with TIQM benchmarks show that statistical methods reproduce cross sections within a factor of
3 Direct reactions
Unimolecular reactions are by far the most studied due to the molecular simplicity of the colliders. In case of collisional excitation in direct reactions, TIQM and TDQM can be easily applied. It is intuitive to think that activation energy should a priori inhibit reactive processes, depending on the temperature regime. For instance, in the HF + H
Because reactive rate coefficients are often small at low temperatures, it might be tempting to facilitate scattering studies and reduce the dimensionality of the problem by omiting reactive channels. However, severe discrepancies can appear compared to full calculation especially when vibrational excitation is not negligible. Indeed, vibration has been established to strongly enhance reactivity, explained, for example, by Polanyi (1987) to the location of the barrier for atom-diatom reactions. Also, Barg et al. (1981) emphasized the decreasing of the threshold reaction energy with increasing vibration mode. For the H–H2 (Lique, 2015b) and HD–H (Desrousseaux et al., 2022) systems, comparisons with previous studies which considered pure inelastic calculations revealed discrepancies by several orders of magnitude (Wrathmall et al., 2007; Flower and Roueff, 1999). Moreover, exchange processes were found to facilitate vibrational relaxation. Properly accounting for these effects permitted Lique (2015b) to be in good agreement with the experimental measurements of the H2 (
Reactive systems involve sometimes radicals which are open-shell molecules, i.e., their nonzero electronic spin leads to a splitting of the energy levels into a fine structure when coupling to the rotation. Accounting simultaneously for both excitation in a complex energetic structure and reactive processes is difficult in scattering calculations. When the spin-rotation coupling is weak, one idea is closing fine structure and only consider the competition between rovibrational excitation and reactivity. This was applied to the SH+–H system by Zanchet et al. (2019) for the direct reaction. However, when the coupling of the electronic spin is strong, fine structure cannot be avoided. In this framework, Dagdigian (2017), Dagdigian (2022) investigated pure fine structure excitation of (
4 Indirect reactions
For indirect reactions, calculations become more complicated due to the presence of deep potential well, requiring large basis functions in scattering calculations. Despite this challenge, TIQM approach have been successfully applied in atom-diatom reactions like H+–H2 (González-Lezana and Honvault, 2017; González-Lezana et al., 2021), HD–H+ (Desrousseaux et al., 2021), HeH+–H (Desrousseaux and Lique, 2020) and CH+–H (Werfelli et al., 2015); however for a restricted range of temperature or basis level (see Table 1).
These systems are ideal test cases for statistical treatments. For most of the cited reactions, comparisons between TIQM and SQM methods show satisfactory statistical behavior for indirect reactions with deep well of
Collisional excitation at a state-to-state level in bimolecular reactions remains a true issue due to the coordinate problem mentioned in section 1. As discussed in section 3, a possibility is reducing the dimension and treat the problem as a pure nonreactive system in the case of direct reactions. For exothermic and barrierless reactions, this aspect cannot be ignored. Pirlot Jankowiak and Lique (2025) proposed the use of SACM to investigate the rotational excitation of OH+(3
5 Discussion
The inclusion of the reactive channel in the reported studies was done at the expense of interactions arising from the presence of the nuclear spin. However, the sensitivity of telescopes enables observations of hyperfine lines. Properly accounting for hyperfine excitation in scattering calculations is crucial for providing complete data set for radiative transfer modeling. Direct treatment with TIQM and TDQM approaches is computationally prohibitive, as the number of energy levels increases rapidly with the energy. Several approximations can overcome this limitation, the most accurate being recoupling techniques based on the assumption that the nuclear spin to be spectator during collision, allowing hyperfine-resolved cross sections to be reconstructed from rotational/fine-structure data (Alexander and Dagdigian, 1985). This method has been applied to the CH–H, CH–H2 (Dagdigian, 2018), OH–H (Dagdigian, 2023) and OH–H2 (Kłos et al., 2020) for the direct reaction. Excitation driven by a formation and decay of an intermediate complex still remains computationally excessive for recoupling approaches. Then, the
It is interesting to look at the impact of the collisional data in the excitation of these molecules in the ISM. When the collisional data are absent, one common practice is to use data set involving He or H as a proxy for H2 as a collision partner (Roueff and Lique, 2013). While this substitution can be somehow relevant for nonreactive systems at low temperature, fundamental differences arise for reactive systems from the nature of their interactions. As an example, Lique and Faure (2017) reported large differences in trend and magnitude between HCl collisions with H, He (Lanza and Lique, 2012) and H2 (Lanza and Lique, 2014). Lique and Faure (2017) also found a substantial difference of a factor 1.5–2 in brightness temperatures for the hyperfine components of the HCl(
Finally, the collisional data for the HD–H+ collisional system (González-Lezana et al., 2022) have been notably implemented in chemical network simulations for primordial chemistry of H2 and HD in the ISM (Faure et al., 2024). Although the refine of the abundance of H2 and HD was modest, they also checked the impact of the data for the HD–H system (Desrousseaux et al., 2022) and noticed a decreasing of the HD abundance by a factor of 3 for redshifts of
In this minireview, we emphasized the importance of inelastic and reactive pathways in interstellar collisions through recent advancements about collisional excitation in reactive systems of astrochemical interest. For reactions presenting a large barrier or endothermicity, reactive processes can be safely neglected up to about one-tenth of the activation barrier. However, neglecting reactive channels in case of vibrational excitation can result in large overestimations of the collisional data. In general, state-of-the-art methods can be easily applied to atom-diatom collisions especially for direct reactions. Statistical methods have proven to be efficient and reliable for treating indirect reactions. The increasing dimensionality of the systems and the complexity of open-shell molecules remain difficult for describing collisional processes at a state-to-state level, but encouraged by the use of statistical methods. Explorations based on artificial neural networks (ANN) algorithms can also offer promising perspectives to cover a more range of complex systems involving polyatomic molecules (Bossion et al., 2024).
Author contributions
PP: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This manuscript received the support by RIKEN Special Post Doctoral Reaserchers Program.
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges Pr. François Lique, Dr. Francesca Tonolo and Dr. Duncan Bossion for fruitful discussions and comments on the present manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alexander, M. H., and Dagdigian, P. J. (1985). Collision-induced transitions between molecular hyperfine levels: Quantum formalism, propensity rules, and experimental study of CaBr(X2Σ+) + Ar. J. Chem. Phys. 83, 2191–2200. doi:10.1063/1.449311
Arthurs, A., and Dalgarno, A. (1960). The theory of scattering by a rigid rotator. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 256, 540–551. doi:10.1098/rspa.1960.0125
Bai, M., Lu, D., and Li, J. (2017). Quasi-classical trajectory studies on the full-dimensional accurate potential energy surface for the OH + H2O = H2O + OH reaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 17718–17725. doi:10.1039/C7CP02656K
Barg, G.-D., Mayne, H. R., and Toennies, J. P. (1981). Quasiclassical trajectory studies of the H + H2 reaction on an accurate potential energy surface. II. Effect of initial vibration and rotation on reactivity. J. Chem. Phys. 74, 1017–1025. doi:10.1063/1.441234
Born, M., and Oppenheimer, R. (1927). Zur Quantentheorie Der Molekeln. Ann. Phys. 389, 457–484. doi:10.1002/andp.19273892002
Bossion, D., Scribano, Y., Lique, F., and Parlant, G. (2018). Ro-vibrational excitation of H2 by H extended to high temperatures. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 480, 3718–3724. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2089
Bossion, D., Nyman, G., and Scribano, Y. (2024). Machine learning prediction of state-to-state rate constants for astrochemistry. AIC 2, 100052. doi:10.1016/j.aichem.2024.100052
Bowman, J. M., Czakó, G., and Fu, B. (2011). High-dimensional ab initio potential energy surfaces for reaction dynamics calculations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13, 8094–8111. doi:10.1039/C0CP02722G
Caselli, P., and Ceccarelli, C. (2012). Our astrochemical heritage. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 20, 56. doi:10.1007/s00159-012-0056-x
Codella, C., Ceccarelli, C., Bottinelli, S., Salez, M., Viti, S., Lefloch, B., et al. (2011). First detection of hydrogen chloride toward protostellar shocks. ApJ 744, 164. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/744/2/164
Dagdigian, P. J. (2016). Theoretical investigation of rotationally inelastic collisions of CH(X2Π) with molecular hydrogen. J. Chem. Phys. 145, 234305. doi:10.1063/1.4972142
Dagdigian, P. J. (2017). Theoretical investigation of rotationally inelastic collisions of CH(X2Π) with hydrogen atoms. J. Chem. Phys. 146, 224308. doi:10.1063/1.4984940
Dagdigian, P. J. (2018). Hyperfine excitation of CH in collisions with atomic and molecular hydrogen. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 475, 5480–5486. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty193
Dagdigian, P. J. (2022). Theoretical investigation of rotationally inelastic collisions of OH(X2Π) with hydrogen atoms. J. Chem. Phys. 157, 104305. doi:10.1063/5.0110724
Dagdigian, P. J. (2023). Collisional excitation of hyperfine levels of OH by hydrogen atoms. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 518, 5976–5981. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac3458
Desrousseaux, B., and Lique, F. (2018). The rotational excitation of HF by H. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 476, 4719–4724. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty605
Desrousseaux, B., and Lique, F. (2020). Collisional energy transfer in the HeH+–H reactive system. J. Chem. Phys. 152, 074303. doi:10.1063/1.5142655
Desrousseaux, B., Coppola, C. M., Kazandjian, M. V., and Lique, F. (2018). Rotational excitation of HD by hydrogen revisited. J. Phys. Chem. A 122, 8390–8396. doi:10.1021/acs.jpca.8b08618
Desrousseaux, B., Konings, M., Loreau, J., and Lique, F. (2021). HD–H+ collisions: statistical and quantum state-to-state studies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 23, 19202–19208. doi:10.1039/D1CP02564C
Desrousseaux, B., Coppola, C. M., and Lique, F. (2022). Collisional excitation of HD by H. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 513, 900–905. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac911
Dubernet, , Boursier, C., Denis-Alpizar, O., Ba, Y. A., Moreau, N., Zwölf, C. M., et al. (2023). BASECOL2023 scientific content. A&A 683, A40. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202348233
Faure, A., and Lique, F. (2012). The impact of collisional rate coefficients on molecular hyperfine selective excitation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 425, 740–748. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21601.x
Faure, A., Halvick, P., Stoecklin, T., Honvault, P., Epée Epée, M. D., Mezei, J.Zs., et al. (2017). State-to-state chemistry and rotational excitation of CH+ in photon-dominated regions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 469, 612–620. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx892
Faure, A., Hily-Blant, P., Pineau des Forêts, G., and Flower, D. R. (2024). The chemistry and excitation of H2 and HD in the early universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 531, 340–354. doi:10.1093/mnras/stae994
Faure, A., Bacmann, A., and Jacquot, R. (2025). Excitation of molecules and atoms for astrophysics (EMAA): a spectroscopic and collisional database. A&A 700, A266. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202554403
Federer, W., Villinger, H., Howorka, F., Lindinger, W., Tosi, P., Bassi, D., et al. (1984). Reaction of O+, CO+, and CH+ ions with atomic hydrogen. Phys. Rev. Lett. 52, 2084–2086. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.52.2084
Flower, D. R. (2007). Molecular collisions in the interstellar medium (cambridge astrophysics series). Second edn.
Flower, D. R., and Roueff, E. (1999). Rovibrational excitation of HD in collisions with atomic and molecular hydrogen. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 309, 833–835. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1999.02888.x
Gerin, M., Neufeld, D. A., and Goicoechea, J. R. (2016). Interstellar hydrides. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 54, 181–225. doi:10.1146/annurev-astro-081915-023409
Godard Palluet, A., Dawes, R., Quintas-Sánchez, E., Batista-Planas, A., and Lique, F. (2025). A promising statistical approach for studying the collisional excitation induced by CO: application to the CS–CO system. J. Chem. Phys. 162, 241101. doi:10.1063/5.0273126
Gomez-Carrasco, S., Godard, B., Lique, F., Bulut, N., Kłos, J., Roncero, O., et al. (2014). OH+ in astrophysical media: state-to-state formation rates, einstein coefficients and inelastic collision rates with He. ApJ 794, 33. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/794/1/33
González-Lezana, T. (2007). Statistical quantum studies on insertion atom–diatom reactions. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 26, 29–91. doi:10.1080/03081070600933476
González-Lezana, T., and Honvault, P. (2017). Rovibrational transitions of H2 by collision with H+ at high temperature. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 467, 1294–1299. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx192
González-Lezana, T., Hily-Blant, P., and Faure, A. (2021). Rate constants for the H+ + H2 reaction from 5 K to 3000 K with a statistical quantum method. J. Chem. Phys. 154, 054310. doi:10.1063/5.0039629
González-Lezana, T., Hily-Blant, P., and Faure, A. (2022). A statistical investigation of the rate constants for the H+ + HD reaction at temperatures of astrophysical interest. J. Chem. Phys. 157, 214302. doi:10.1063/5.0128598
Heidner, R., and Kasper, J. V. (1972). An experimental rate constant for H + H2 (ν″ = 1) → H + H2 (ν″ = 0). Chem. Phys. Lett. 15, 179–184. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(72)80144-1
Henchman, M. J., Adams, N. G., and Smith, D. (1981). The isotope exchange reactions H+ + D2 → HD + D+ and D+ + H2 → HD + H+ in the temperature range 200–300 K. J. Chem. Phys. 75, 1201–1206. doi:10.1063/1.442168
Honvault, P., Jorfi, M., González-Lezana, T., Faure, A., and Pagani, L. (2011). Ortho-para H2 conversion by proton exchange at low temperature: an accurate quantum mechanical study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 023201. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.023201
Honvault, P., Jorfi, M., González-Lezana, T., Faure, A., and Pagani, L. (2012). Erratum: ortho-para H2 conversion by proton exchange at low temperature: an accurate quantum mechanical study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 109903. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.109903
Hu, W., and Schatz, G. C. (2006). Theories of reactive scattering. J. Chem. Phys. 125, 132301. doi:10.1063/1.2213961
Jiang, B., Li, J., and Guo, H. (2020). High-fidelity potential energy surfaces for gas-phase and gas–surface scattering processes from machine learning. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11, 5120–5131. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c00989
Kłos, J., Ma, Q., Dagdigian, P. J., Alexander, M. H., Faure, A., and Lique, F. (2017). The excitation of OH by H2 revisited – I: fine-structure resolved rate coefficients. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 471, 4249–4255. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx1968
Kłos, J., Dagdigian, P. J., Alexander, M. H., Faure, A., and Lique, F. (2020). The excitation of OH by H2 revisited – II. Hyperfine resolved rate coefficients. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 493, 3491–3495. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa530
Kłos, J., Dagdigian, P. J., and Lique, F. (2021). Collisional excitation of C+(2P) spin-orbit levels by molecular hydrogen revisited. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 501, L38–L42. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slaa192
Knowles, P. J., and Werner, H.-J. (1988). An efficient method for the evaluation of coupling coefficients in configuration interaction calculations. Chem. Phys. Lett. 145, 514–522. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(88)87412-8
Knowles, P. J., Hampel, C., and Werner, H. J. (1993). Coupled cluster theory for high spin, open shell reference wave functions. J. Chem. Phys. 99, 5219–5227. doi:10.1063/1.465990
Konings, M., Desrousseaux, B., Lique, F., and Loreau, J. (2021). Benchmarking an improved statistical adiabatic channel model for competing inelastic and reactive processes. J. Chem. Phys. 155, 104302. doi:10.1063/5.0062388
Kumar, S. S., Grussie, F., Suleimanov, Y. V., Guo, H., and Kreckel, H. (2018). Low temperature rates for key steps of interstellar gas-phase water Formation. Sci. Adv. 4, eaar3417. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aar3417
Kumaran, S. S., Lim, K. P., and Michael, J. V. (1994). Thermal rate constants for the Cl + H2 and Cl + D2 reactions between 296 and 3000 K. J. Chem. Phys. 101, 9487–9498. doi:10.1063/1.468486
Lanza, M., and Lique, F. (2012). Collisional excitation of interstellar HCl by He. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 424, 1261–1267. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21304.x
Lanza, M., and Lique, F. (2014). Hyperfine excitation of linear molecules by Para- and Ortho-H2: application to the HCl–H2 system. J. Chem. Phys. 141, 164321. doi:10.1063/1.4898855
Light, J. C., and Carrington, Jr., T. (2000). Discrete-variable representations and their utilization. Adv. Chem. Phys., 263–310. doi:10.1002/9780470141731.ch4
Lique, F. (2015a). Communication: rotational excitation of HCl by H: rigid rotor vs. reactive approaches. J. Chem. Phys. 142, 241102. doi:10.1063/1.4922987
Lique, F. (2015b). Revisited study of the ro-vibrational excitation of H2 by H: towards a revision of the cooling of astrophysical media. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 453, 810–818. doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1683
Lique, F., and Faure, A. (2012). Communication: the rotational excitation of D2 by H: on the importance of the reactive channels. J. Chem. Phys. 136, 031101. doi:10.1063/1.3678310
Lique, F., and Faure, A. (2017). Collisional excitation and dissociation of HCl by H. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 472, 738–743. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx2025
Lique, F., and Faure, A. (2019). Gas-phase chemistry in space: from elementary particles to complex organic molecules. London: The Institute of Physics. doi:10.1088/2514-3433/aae1b5
Lique, F., Honvault, P., and Faure, A. (2012). Ortho–Para-H2 conversion by hydrogen exchange: Comparison of theory and experiment. J. Chem. Phys. 137, 154303. doi:10.1063/1.4758791
Lique, F., Zanchet, A., Bulut, N., Goicoechea, J. R., and Roncero, O. (2020). Hyperfine excitation of SH+ by H. A&A 638. Astron. Astrophys. 638, A72. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202038041
Loreau, J., Lique, F., and Faure, A. (2018). An efficient statistical method to compute molecular collisional rate coefficients. ApJL 853, 5. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aaa5fe
McClure, M. K., Rocha, W. R. M., Pontoppidan, K. M., Crouzet, N., Chu, L. E. U., Dartois, E., et al. (2023). An ice age JWST inventory of dense molecular cloud ices. Nat. Astron 7, 431–443. doi:10.1038/s41550-022-01875-w
McGuire, B. A. (2022). 2021 census of interstellar, circumstellar, extragalactic, protoplanetary disk, and exoplanetary molecules. ApJS 259, 30. doi:10.3847/1538-4365/ac2a48
Millar, T. J., Walsh, C., Van de Sande, M., and Markwick, A. J. (2023). The UMIST database for astrochemistry 2022. A&A 682, A109. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202346908
Neufeld, D. A., and Green, S. (1994). Excitation of interstellar hydrogen chloride. ApJ 432, 158–166. doi:10.1086/174557
Pirlot Jankowiak, P. (2024). Collisional excitation of radicals of astrophysical interest. France: Université de Rennes. Thesis. Available online at: https://theses.hal.science/tel-05039944v1.
Pirlot Jankowiak, P., and Lique, F. (2025). Collisional energy transfer in the highly reactive OH+–H2 system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 134, 253002. doi:10.1103/hpcb-q7wh
Plasil, R., Mehner, T., Dohnal, P., Kotrik, T., Glosik, J., and Gerlich, D. (2011). Reactions of cold trapped CH+ ions with slow H atoms. ApJ 737, 60. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/737/2/60
Polanyi, J. C. (1987). Some concepts in reaction dynamics. Science 236, 680–690. doi:10.1126/science.236.4802.680
Quack, M., and Troe, J. (1975). Complex formation in reactive and inelastic scattering: statistical adiabatic channel model of unimolecular processes III. Berichte Bunsenges. für Phys. Chem. 79, 170–183. doi:10.1002/bbpc.19750790211
Rackham, E. J., Gonzalez-Lezana, T., and Manolopoulos, D. E. (2003). A rigorous test of the statistical model for atom–diatom insertion reactions. J. Chem. Phys. 119, 12895–12907. doi:10.1063/1.1628218
Roueff, E., and Lique, F. (2013). Molecular excitation in the interstellar medium: recent advances in collisional, radiative, and chemical processes. Chem. Rev. 113, 8906–8938. doi:10.1021/cr400145a
Schreiner, P. R. (2020). Quantum mechanical tunneling is essential to understanding chemical reactivity. Trends Chem. 2, 980–989. doi:10.1016/j.trechm.2020.08.006
Schulz, W. R., and Le Roy, D. J. (1965). Kinetics of the reaction H + p-H2=o-H2 + H. J. Chem. Phys. 42, 3869–3873. doi:10.1063/1.1695853
Skouteris, D., Castillo, J. F., and Manolopoulos, D. E. (2000). ABC: a quantum reactive scattering program. Comput. Phys. Comm. 133, 128–135. doi:10.1016/S0010-4655(00)00167-3
Song, H., and Guo, H. (2023). Theoretical insights into the dynamics of gas-phase bimolecular reactions with submerged barriers. ACS Phys. Chem. Au 3, 406–418. doi:10.1021/acsphyschemau.3c00009
Tonolo, F., and Alessandrini, S. (2024). Ab initio calculations for astrochemistry. Mem. S. A. It. 95, 77.
Tonolo, F., Quintas-Sánchez, E., Batista-Planas, A., Dawes, R., and Lique, F. (2025). Collisional excitation of HCN by CO to refine the modeling of cometary comae. J. Phys. Chem. A 129, 9583–9590. doi:10.1021/acs.jpca.5c05448
Toscano, J., Lewandowski, H. J., and Heazlewood, B. R. (2020). Cold and controlled chemical reaction dynamics. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22, 9180–9194. doi:10.1039/D0CP00931H
Tran, T. D., Rednyk, S., Kovalenko, A., Roučka, Š., Dohnal, P., Plašil, R., et al. (2018). Formation of H2O+ and H3O+ cations in reactions of OH+ and H2O+ with H2: experimental studies of the reaction rate coefficients from T = 15 to 300K. ApJ 854, 25. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aaa0d8
Van der Tak, F. F. S., Lique, F., Faure, A., Black, J. H., and van Dishoeck, E. F. (2020). The leiden atomic and molecular database (LAMDA): current status, recent updates, and future plans. Atoms 8, 15. doi:10.3390/atoms8020015
Wakelam, V., Gratier, P., Loison, J.-C., Hickson, K. M., Penguen, J., and Mechineau, A. (2024). The 2024 KIDA network for interstellar chemistry. A&A 689, A63. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202450606
Werfelli, G., Halvick, P., Honvault, P., Kerkeni, B., and Stoecklin, T. (2015). Low temperature rate coefficients of the H + CH+ → C+ + H2 reaction: new potential energy surface and time-independent quantum scattering. J. Chem. Phys. 143, 114304. doi:10.1063/1.4931103
Wrathmall, S. A., Gusdorf, A., and Flower, D. R. (2007). The excitation of molecular hydrogen by atomic hydrogen in astrophysical media. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 382, 133–138. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12420.x
Zanchet, A., Agúndez, M., Herrero, V. J., Aguado, A., and Roncero, O. (2013). Sulfur chemistry in the interstellar medium: the effect of vibrational excitation of H2 in the reaction S+ + H2 → SH+ + H. AJ 146, 125. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/146/5/125
Zanchet, A., Lique, F., Roncero, O., Goicoechea, J. R., and Bulut, N. (2019). Formation of interstellar SH+ from vibrationally excited H2: Quantum study of S+ + H2 → SH+ + H reaction and inelastic collision. A&A 626, A103. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935471
Zhang, H., and Guo, H. (2016). Recent advances in quantum dynamics of bimolecular reactions. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 67, 135–158. doi:10.1146/annurev-physchem-040215-112016
Zhao, B., and Guo, H. (2017). State-to-state quantum reactive scattering in four-atom systems. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 7, e1301. doi:10.1002/wcms.1301
Keywords: molecular data, quantum dynamics, astrochemistry, reactive systems, rate coefficients
Citation: Pirlot Jankowiak P (2025) Collisional excitation in reactive systems: recent advances in modeling molecular processes for astrochemistry. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 12:1710248. doi: 10.3389/fspas.2025.1710248
Received: 22 September 2025; Accepted: 16 October 2025;
Published: 10 November 2025.
Edited by:
German Molpeceres De Diego, Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), SpainReviewed by:
Tomás González-Lezana, Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), SpainLisan David Cabera Gonzalez, The University of Manchester, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2025 Pirlot Jankowiak. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Paul Pirlot Jankowiak, cGF1bC5waXJsb3RqYW5rb3dpYWtAcmlrZW4uanA=
 Paul Pirlot Jankowiak
Paul Pirlot Jankowiak