- INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Magnetic turbulence plays a crucial role in confining charged particles near the shock front of Supernova Remnants, enabling them to reach energies up to hundreds of TeV through a process known as Diffusive Shock Acceleration (DSA). These high-energy electrons spiral along magnetic field lines, emitting X-ray synchrotron radiation. The launch of the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) has opened a new window into the study of magnetic fields in SNRs through X-ray polarization measurements. For the first time, IXPE allows us to resolve the polarization degree (PD) and angle (PA) in the X-ray band across different areas of SNRs, offering direct insight into the geometry and coherence of magnetic fields on different scales. In this mini-review, I summarize the key observational results on SNRs obtained with IXPE over the past 4 years and discuss their implications for our understanding of magnetic turbulence in synchrotron-emitting regions. I also show how we can combine polarization parameters and standard X-ray spectral/imaging analysis to better constrain the structure and scale of magnetic turbulence immediately downstream of the shock and understand the particle acceleration occurring in SNRs.
1 Introduction
Shocks in supernova remnants (SNRs) are widely recognized as prime candidates for the acceleration of Galactic cosmic rays (CRs), primarily through the mechanism of Diffusive Shock Acceleration (DSA, Fermi, 1949; Blandford and Eichler, 1987). Within this framework, magnetic turbulence plays a crucial role as it confines charged particles near the shock front, enabling them to repeatedly cross it and gain energy up to PeV energies. The key parameter quantifying this degree of turbulence and the efficiency of particle acceleration is the Bohm factor
where
It is often useful to rewrite Equation 1 and Equation 2 as functions of the characteristic synchrotron energy
When the acceleration time scale
where I have used the relation (Zirakashvili and Aharonian, 2007; Tsuji et al., 2021; Sapienza et al., 2024) for the second part of the equation.
From Equation 5, one can see that magnetic turbulence, expressed in the form of
Observations with high-resolution X-ray instruments such as Chandra and XMM-Newton (see Helder et al., 2012 for a review) have revealed the presence of narrow synchrotron filaments immediately downstream of the shock. By measuring the thickness of these structures from the images, several studies (e.g., Vink and Laming, 2003) reported values
Particle-in-cell (PIC) simulations by Caprioli and Spitkovsky (2014a), Caprioli and Spitkovsky (2014b) have shown that self-consistent acceleration of ions can excite magnetic turbulence both upstream and downstream of strong shocks, leading to
1.1 Diagnostic on turbulence through X-ray polarization
The recent launch, in December 2021, of the Imaging X-ray Polarimetric Explorer (IXPE; Weisskopf et al., 2022) has opened a new channel to probe turbulence in SNRs: IXPE allows direct, spatially resolved measurements of the X-ray polarization degree (PD) and angle (PA), thus mapping the magnetic-field configuration across different SNRs regions. Since synchrotron radiation is intrinsically linearly polarized - up to
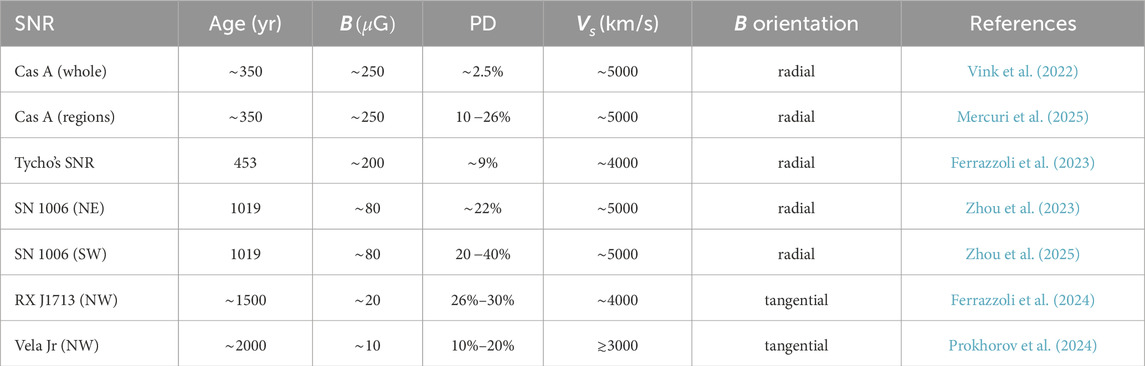
Table 1 highlights the main features of the sample of SNRs observed, completely or partially, by IXPE so far: Cas A, Tycho, the two limbs of SN1006, the north western region of RX J1713.7-3946 (Vela Jr) and a filament of Vela Jr.
1.1.1 Cas A
Cas A, a
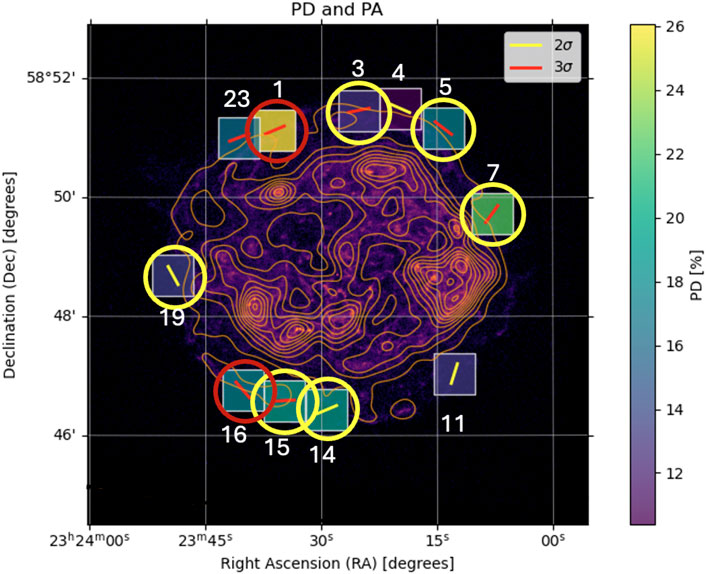
Figure 1. Map of PD reported for Cas A from Mercuri et al. (2025), overlaid with X-ray polarization vectors. Red and yellow vectors indicate the direction of the X-ray polarization vectors at the 3- and 2-
1.1.2 Tycho
The historical Tycho’s SNR, exploded in 1572 is a Type Ia SNR, characterized by shock velocities of around 4,000 km/s (Williams et al., 2016). Significant radio polarization was found only in the outer rim at the
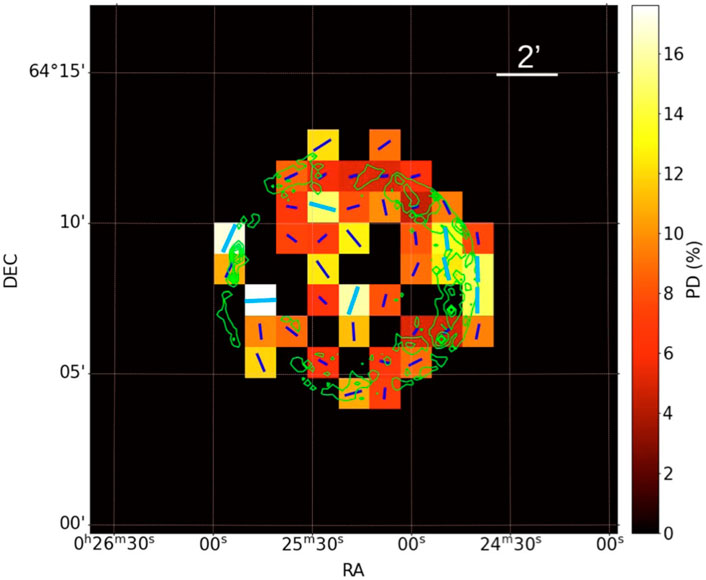
Figure 2. Map of PD reported for Tycho’s SNR from Ferrazzoli et al. (2023). Blue vectors represent the direction of the polarization and their length is proportional to the degree of polarization. The thicker cyan bars mark the pixels with significance higher than 2
1.1.3 SN 1006
The remnant of the historical SN 1006 is popular for being the first one for which X-ray synchrotron radiation was observed in its limbs (Koyama et al., 1995). IXPE observed both the NorthEastern (NE, Zhou et al., 2023) and SouthWestern (SW, Zhou et al., 2025) limbs finding for both the limbs a radially-oriented magnetic field and an X-ray PD of
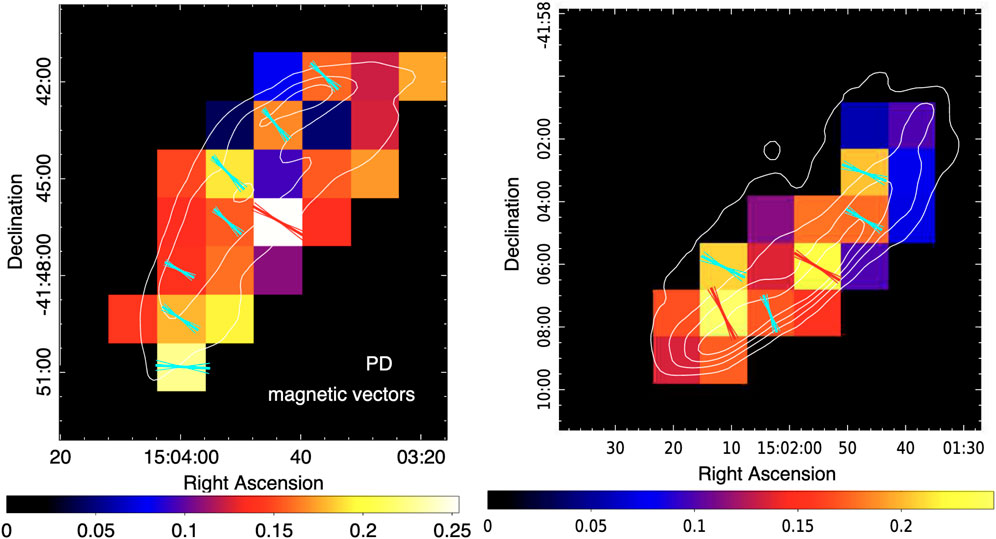
Figure 3. Map of PD reported for the NE and SW limbs of SN 1006 from Zhou et al. (2023) and Zhou et al. (2025), in the left and right panels respectively. Vectors represent the direction of the magnetic field and their
1.1.4 RX J1713.7-3946
RX J1713.7-3946 (hereafter RX J1713) is a close (
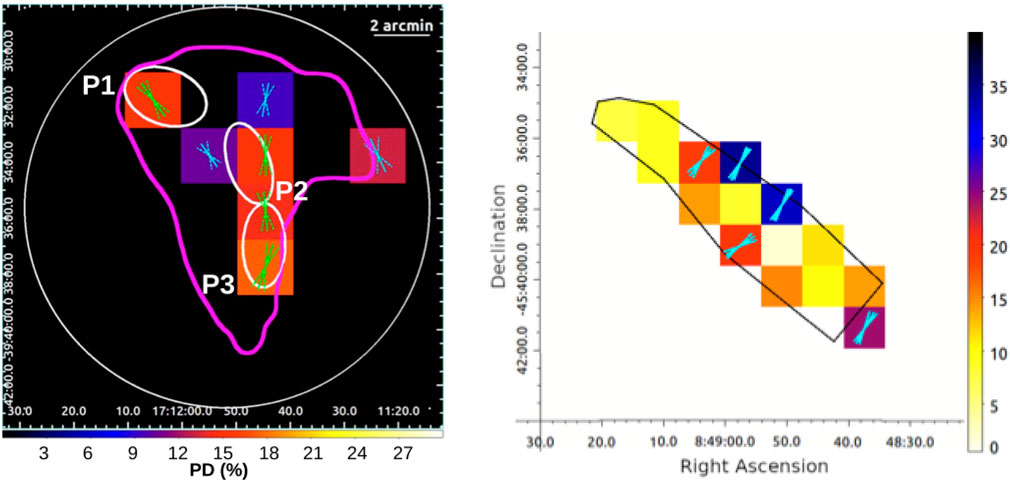
Figure 4. Left panel. PD and PA values reported for the NW area of RX J1713 from Ferrazzoli et al. (2024). Cyan and green vectors mark the magnetic field direction at the 2- and 3-
1.1.5 Vela Jr
Vela Jr shares several features with RX J1713, being dominated by X-ray nonthermal emission, having an angular size of roughly 2° and being roughly 2000 years old (Katsuda et al., 2008). IXPE targeted the NW rim of Vela Jr (Prokhorov et al., 2024), which is the brightest in the X-rays, providing similar results to those obtained for RX J1713, with a tangential magnetic field and a PD
1.2 Diagnostic on turbulence through X-ray spectra
X-ray spectral analysis by itself is a powerful diagnostic tool to estimate the degree of turbulence in the plasma emitting X-ray synchrotron radiation, mainly through the estimate of the Bohm factor
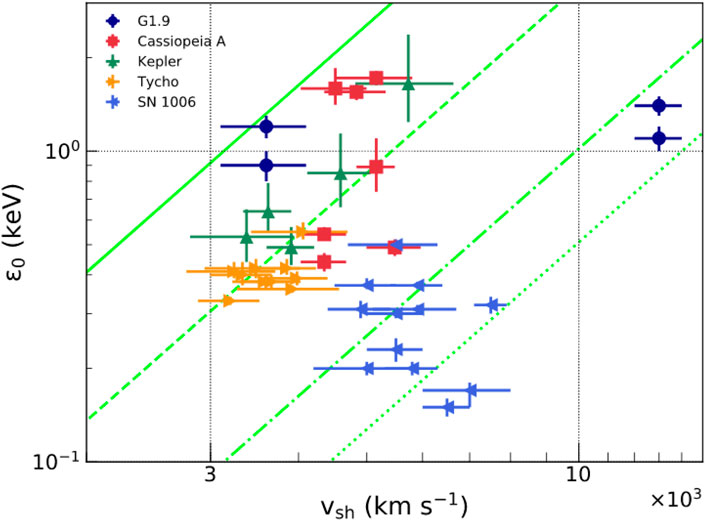
Figure 5. Shock velocity
They found that the Tycho’s and Kepler’s SNR nicely match the theoretical prediction, indicating a constant
Despite its crucial role in the DSA paradigm and the low PD observed, prevailing models used to fit X-ray nonthermal spectra of SNRs (e.g., SRcut by Reynolds and Keohane (1999), the loss-limited model by Zirakashvili and Aharonian (2007), or a simple phenomenological power-law) are calculated assuming an homogeneous magnetic field. The resulting analytical expressions are typically power-law with a cutoff, with the shape of the cutoff depending mainly on whether the maximum energy of the electrons is time-limited or loss-limited. Therefore, it is natural to ask what the emitted spectrum would look like by considering a turbulent magnetic field. This has been explored theoretically by Toptygin and Fleishman (1987) and Kelner et al. (2013), who labeled “jitter radiation” this emission process in which the electrons are sensitive also to the magnetic field’s turbulent component. The resulting jitter radiation photon spectrum emitted from a power-law distribution of electrons can be described as a broken power-law having a smooth break between the regime dominated by standard synchrotron radiation (at lower energy) and that dominated by the jitter component (at higher energy). Interestingly, despite using different approximation and assumptions, both Toptygin and Fleishman (1987) and Kelner et al. (2013) agree on two striking features of jitter radiation: i) the slope of the spectrum at high energies is directly linked to the turbulence spectrum; ii) the maximum energy to which the spectrum extends is proportional to minimum scale of the turbulence. Jitter radiation is therefore a powerful tool that could provide direct diagnostics on turbulence parameters otherwise inaccessible for astrophysical sources. Greco et al. (2023) applied the jitter paradigm to the SNR Cas A, finding that it describes the X-ray broadband nonthermal spectra better than any standard cutoff model. They inferred an index in the turbulence spectrum
2 Discussion
In section 1 of this mini-review I briefly recalled the main recent results strictly related to the degree of turbulence and acceleration efficiency in the X-ray nonthermal emission of SNRs. The first clear takeaway is that acceleration efficiency - and, therefore, magnetic turbulence - is very high in most X-ray synchrotron-emitting SNR, with the case of Vela Jr and RX J1713 showcasing the lowest values of Bohm factor
It is important to notice that there is not necessarily a 1-to-1 relationship between the bohm factor
Turbulence does not always imply depolarization, especially in case in which there is a strong anisotropy, as has been shown for Tycho’s SNR by Bykov et al. (2024). Anisotropic turbulence can also easily lead to ordered magnetic field structures that can increase the polarization level locally. For example, anisotropic turbulence may locally enhance/decrease the acceleration efficiency, inducing lower/higher values of
In Sect. 1 I also described a new potential spectroscopic diagnostic tool on turbulence, based on the jitter radiation paradigm. The only application on SNR was performed by Greco et al. (2023) on Cas A. They found a turbulence spectrum steeper than the typical Kolmogorov value of
3 Conclusion
In this mini-review I summarized some of the most relevant recent results inferred from X-ray polarimetric and spectral analysis relative to magnetic turbulence in SNRs. The current picture clearly shows that turbulence is a key ingredient in the acceleration and X-ray emission mechanism in SNRs. Thanks to the IXPE telescope it is now possible to measure the PD and PA in several SNRs. These unprecedented information coupled with the results obtained on the curvature of the X-ray nonthermal spectra show that every synchrotron-emitting SNR is characterized by turbulence, mainly self-generated by the expanding shock. However, also the configuration of the pre-existing medium seems to play a significant role. Additional observations and numerical simulations are needed to better understand to what extent the preexisting medium affects the acceleration and emission processes.
Author contributions
EG: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. E.G., acknowledge support from the INAF Minigrant RSN4 “Investigating magnetic turbulence in young Supernova Remnants through X-ray observations”.
Acknowledgments
E.G., acknowledge discussion and collaboration with colleagues M. Miceli, S. Orlando, J. Vink, A. Mercuri, S. Perri, D. Caprioli.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Anderson, M. C., Keohane, J. W., and Rudnick, L. (1995). The polarization and depolarization of radio emission from supernova remnant cassiopeia A. ApJ 441, 300. doi:10.1086/175356
Bell, A. R. (2004). Turbulent amplification of magnetic field and diffusive shock acceleration of cosmic rays. MNRAS 353, 550–558. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08097.x
Blandford, R., and Eichler, D. (1987). Particle acceleration at astrophysical shocks - a theory of cosmic-ray origin. PhR 154, 1–+75. doi:10.1016/0370-1573(87)90134-7
Bykov, A. M., Uvarov, Y. A., Slane, P., and Ellison, D. C. (2020). Uncovering magnetic turbulence in young supernova remnants with polarized X-Ray imaging. ApJ 899, 142. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aba960
Bykov, A. M., Osipov, S. M., Uvarov, Y. A., Ellison, D. C., and Slane, P. (2024). X-ray polarization: a view deep inside cosmic ray driven turbulence and particle acceleration in supernova remnants. PhysRevD 110, 023041. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.110.023041
Caprioli, D., and Spitkovsky, A. (2014a). Simulations of ion acceleration at non-relativistic shocks. I. Acceleration efficiency. ApJ 783, 91. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/783/2/91
Caprioli, D., and Spitkovsky, A. (2014b). Simulations of ion acceleration at non-relativistic shocks. II. Magnetic field amplification. ApJ 794, 46. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/794/1/46
DeLaney, T., Koralesky, B., Rudnick, L., and Dickel, J. R. (2002). Radio spectral index variations and physical conditions in Kepler’s Supernova remnant. ApJ 580, 914–927. doi:10.1086/343787
Dickel, J. R., van Breugel, W. J. M., and Strom, R. G. (1991). Radio structure of the remnant of tycho’s Supernova (SN 1572). AJ 101, 2151. doi:10.1086/115837
Eriksen, K. A., Hughes, J. P., Badenes, C., Fesen, R., Ghavamian, P., Moffett, D., et al. (2011). Evidence for particle acceleration to the knee of the cosmic ray spectrum in Tycho’s Supernova remnant. ApJL 728, L28. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/728/2/L28
Fermi, E. (1949). On the origin of the cosmic radiation. Phys. Rev. 75, 1169–1174. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.75.1169
Ferrazzoli, R., Slane, P., Prokhorov, D., Zhou, P., Vink, J., Bucciantini, N., et al. (2023). X-Ray polarimetry reveals the magnetic-field topology on sub-parsec scales in Tycho’s Supernova remnant. ApJ 945, 52. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acb496
Ferrazzoli, R., Prokhorov, D., Bucciantini, N., Slane, P., Vink, J., Cardillo, M., et al. (2024). Discovery of a shock-compressed magnetic field in the Northwestern rim of the young Supernova remnant RX J1713.7–3946 with X-Ray polarimetry. ApJL 967, L38. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ad4a68
Ginzburg, V. L., and Syrovatskii, S. I. (1965). Cosmic Magnetobremsstrahlung (synchrotron Radiation). ARA&A 3, 297–350. doi:10.1146/annurev.aa.03.090165.001501
Greco, E., Vink, J., Ellien, A., and Ferrigno, C. (2023). Jitter radiation as an alternative mechanism for the Nonthermal X-Ray emission of cassiopeia A. ApJ 956, 116. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acf567
Helder, E. A., Vink, J., Bykov, A. M., Ohira, Y., Raymond, J. C., and Terrier, R. (2012). Observational signatures of particle acceleration in Supernova remnants. SSR 173, 369–431. doi:10.1007/s11214-012-9919-8
Inoue, T., Shimoda, J., Ohira, Y., and Yamazaki, R. (2013). The origin of radially aligned magnetic fields in young Supernova remnants. ApJL 772, L20. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/772/2/L20
Katsuda, S., Tsunemi, H., and Mori, K. (2008). The slow X-Ray expansion of the Northwestern rim of the Supernova remnant RX J0852.0-4622. ApJL 678, L35–L38. doi:10.1086/588499
Katsuda, S., Acero, F., Tominaga, N., Fukui, Y., Hiraga, J. S., Koyama, K., et al. (2015). Evidence for thermal X-Ray line emission from the synchrotron-dominated Supernova remnant RX J1713.7-3946. ApJ 814, 29. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/814/1/29
Kelner, S. R., Aharonian, F. A., and Khangulyan, D. (2013). On the jitter radiation. ApJ 774, 61. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/774/1/61
Kothes, R., Sun, X., Gaensler, B., and Reich, W. (2018). A radio continuum and polarization Study of SNR G57.2+0.8 associated with magnetar SGR 1935+2154. ApJ 852, 54. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa9e89
Koyama, K., Petre, R., Gotthelf, E. V., Hwang, U., Matsura, M., Ozaki, M., et al. (1995). Evidence for shock acceleration of high-energy electrons in the supernova remnant sn:1006. Nature 378, 255–258. doi:10.1038/378255a0
Malkov, M. A., and O’C Drury, L. (2001). Nonlinear theory of diffusive acceleration of particles by shock waves. Rep. Prog. Phys. 64, 429–481. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/64/4/201
Matsuda, M., Tanaka, T., Uchida, H., Amano, Y., and Tsuru, T. G. (2020). Temporal and spatial variation of synchrotron X-ray stripes in Tycho’s supernova remnant. PASJ 72, 85. doi:10.1093/pasj/psaa075
Mercuri, A., Greco, E., Vink, J., Ferrazzoli, R., and Perri, S. (2025). Revisiting the X-Ray polarization of the shell of cassiopeia A using spectropolarimetric analysis. ApJ 986, 6. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/adcedb
Meshkov, E. E. (1969). Instability of the interface of two gases accelerated by a shock wave. Fluid Dyn. 4, 101–104. doi:10.1007/BF01015969
Miceli, M., Acero, F., Dubner, G., Decourchelle, A., Orlando, S., and Bocchino, F. (2014). Shock-Cloud interaction and particle acceleration in the Southwestern limb of SN 1006. ApJL 782, L33. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/782/2/L33
Parizot, E., Marcowith, A., Ballet, J., and Gallant, Y. A. (2006). Observational constraints on energetic particle diffusion in young supernovae remnants: amplified magnetic field and maximum energy. A&A 453, 387–395. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20064985
Prokhorov, D. A., Yang, Y.-J., Ferrazzoli, R., Vink, J., Slane, P., Costa, E., et al. (2024). Evidence for a shock-compressed magnetic field in the northwestern rim of vela jr. from X-ray polarimetry. A&A 692, A59. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202452062
Reynolds, S. P., and Keohane, J. W. (1999). Maximum energies of shock-accelerated electrons in young shell supernova remnants. ApJ 525, 368–374. doi:10.1086/307880
Reynolds, S. P., Borkowski, K. J., Hwang, U., Hughes, J. P., Badenes, C., Laming, J. M., et al. (2007). A deep chandra observation of Kepler’s Supernova remnant: a type Ia event with circumstellar interaction. ApJL 668, L135–L138. doi:10.1086/522830
Reynoso, E. M., Hughes, J. P., and Moffett, D. A. (2013). On the radio polarization signature of efficient and inefficient particle acceleration in Supernova remnant SN 1006. AJ 145, 104. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/145/4/104
Richmyer, R. D. (1960). Taylor instability in shock acceleration of compressible fluids. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. XIII, 297–319. doi:10.1002/cpa.3160130207
Rosenberg, I. (1970). Distribution of brightness and polarization in Cassiopeia A at 5.0 GHz. MNRAS 151, 109–122. doi:10.1093/mnras/151.1.109
Sapienza, V., Miceli, M., Bamba, A., Katsuda, S., Nagayoshi, T., Terada, Y., et al. (2022). A spatially resolved Study of hard X-Ray emission in Kepler’s Supernova remnant: indications of different regimes of particle acceleration. ApJ 935, 152. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac8160
Sapienza, V., Miceli, M., Petruk, O., Bamba, A., Katsuda, S., Orlando, S., et al. (2024). Time evolution of the synchrotron X-Ray emission in Kepler’s Supernova remnant: the effects of turbulence and shock velocity. ApJ 973, 105. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ad6566
Toptygin, I. N., and Fleishman, G. D. (1987). A role of cosmic-rays in generation of radio and optical radiation by plasma mechanisms. Ap&SS 132, 213–248. doi:10.1007/BF00641755
Tsuji, N., Uchiyama, Y., Khangulyan, D., and Aharonian, F. (2021). Systematic Study of acceleration efficiency in young Supernova remnants with nonthermal X-Ray observations. ApJ 907, 117. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abce65
Uchiyama, Y., Aharonian, F. A., Tanaka, T., Takahashi, T., and Maeda, Y. (2007). Extremely fast acceleration of cosmic rays in a supernova remnant. Nature 449, 576–578. doi:10.1038/nature06210
Vink, J. (2006). “X-ray high resolution and imaging spectroscopy of Supernova remnants”. Proceedings of the X-ray Universe 2005 (Esa Special Publication), 319.
Vink, J. (2020). Physics and evolution of Supernova remnants. Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-55231-2
Vink, J., and Laming, J. M. (2003). On the magnetic fields and particle acceleration in cassiopeia A. ApJ 584, 758–769. doi:10.1086/345832
Vink, J., Prokhorov, D., Ferrazzoli, R., Slane, P., Zhou, P., Asakura, K., et al. (2022). X-ray polarization detection of cassiopeia A with IXPE. arXiv e-prints 938, 40. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac8b7b
Weisskopf, M. C., Soffitta, P., Baldini, L., Ramsey, B. D., O’Dell, S. L., Romani, R. W., et al. (2022). Imaging X-ray polarimetry explorer: prelaunch. J. Astronomical Telesc. Instrum. Syst. 8, 026002. doi:10.1117/1.JATIS.8.2.026002
Williams, B. J., Chomiuk, L., Hewitt, J. W., Blondin, J. M., Borkowski, K. J., Ghavamian, P., et al. (2016). An X-Ray and radio Study of the varying expansion velocities in Tycho’s Supernova remnant. ApJL 823, L32. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/823/2/L32
Xu, J. W., Han, J. L., Sun, X. H., Reich, W., Xiao, L., Reich, P., et al. (2007). Polarization observations of SNR G156.2+5.7 at λ6 Cm. A&A 470, 969–975. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20077549
Zhou, P., Prokhorov, D., Ferrazzoli, R., Yang, Y.-J., Slane, P., Vink, J., et al. (2023). Magnetic structures and turbulence in SN 1006 revealed with imaging X-Ray polarimetry. ApJ 957, 55. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acf3e6
Zhou, P., Slane, P., Prokhorov, D., Vink, J., Ferrazzoli, R., Cotton, W., et al. (2025). X-Ray polarization in SN 1006 Southwest shows spatial variations and differences in the radio band. ApJ 986, 210. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/add532
Keywords: supernova remnants, particle acceleration, synchrotron radiation, magnetic turbulence, X-ray polarization, X-rayobservations
Citation: Greco E (2025) From shock to synchrotron: a mini-review on magnetic turbulence in supernova remnants. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 12:1717808. doi: 10.3389/fspas.2025.1717808
Received: 02 October 2025; Accepted: 29 October 2025;
Published: 11 November 2025.
Edited by:
Alexandre Marcowith, UMR5299 Laboratoire Univers et Particules de Montpellier (LUPM), FranceReviewed by:
Andrei Bykov, Ioffe Institute (RAS), RussiaCopyright © 2025 Greco. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Emanuele Greco, ZW1hbnVlbGUuZ3JlY29AaW5hZi5pdA==
 Emanuele Greco
Emanuele Greco