- 1School of Information Engineering, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China
- 2School of Advanced Energy, Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen, China
- 3Department of Radiological Sciences, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States
- 4Department of Radiation Oncology, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University & Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
Background: The retina plays a critical role in visual perception, yet lesions affecting it can lead to severe and irreversible visual impairment. Consequently, early diagnosis and precise identification of these retinal lesions are essential for slowing disease progression. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) stands out as a pivotal imaging modality in ophthalmology due to its exceptional performance, while the inherent complexity of retinal structures and significant noise interference present substantial challenges for both manual interpretation and AI-assisted diagnosis.
Methods: We propose MSLI-Net, a novel framework built upon the ResNet50 backbone, which enhances the global receptive field via a multi-scale dilation fusion module (MDF) to better capture long-range dependencies. Additionally, a multi-segmented lesion localization module (LLM) is integrated within each branch of a modified feature pyramid network (FPN) to effectively extract critical features while suppressing background noise through parallel branch refinement, and a wavelet subband spatial attention module (WSSA) is designed to significantly improve the model’s overall performance in noise suppression by collaboratively processing and exchanging information between the low- and high-frequency subbands extracted through wavelet decomposition.
Results: Experimental evaluation on the OCT-C8 dataset demonstrates that MSLI-Net achieves 96.72% accuracy in retinopathy classification, underscoring its strong discriminative performance and promising potential for clinical application.
Conclusion: This model provides new research ideas for the early diagnosis of retinal diseases and helps drive the development of future high-precision medical imaging-assisted diagnostic systems.
1 Introduction
The eye plays an indispensable role in how we perceive the world. Its retina, which primarily receives, adjusts, and relays visual stimuli from the environment, supplies the brain with essential visual information, serving as the core structure for our visual perception (Grossniklaus et al., 2015; Kermany et al., 2018). Consequently, retinal diseases are predisposed to causing severe visual impairment and even permanent blindness. At the same time, retinal diseases typically lack pronounced early clinical symptoms, and patients often fail to notice changes in their condition in time, missing the optimal window for intervention. Therefore, early diagnosis combined with high-precision detection is vital in slowing disease progression and minimizing visual impairment (Pennington and DeAngelis, 2016; Robinson, 2003). Figure 1 shows the OCT images of normal retina and seven common retinal diseases.
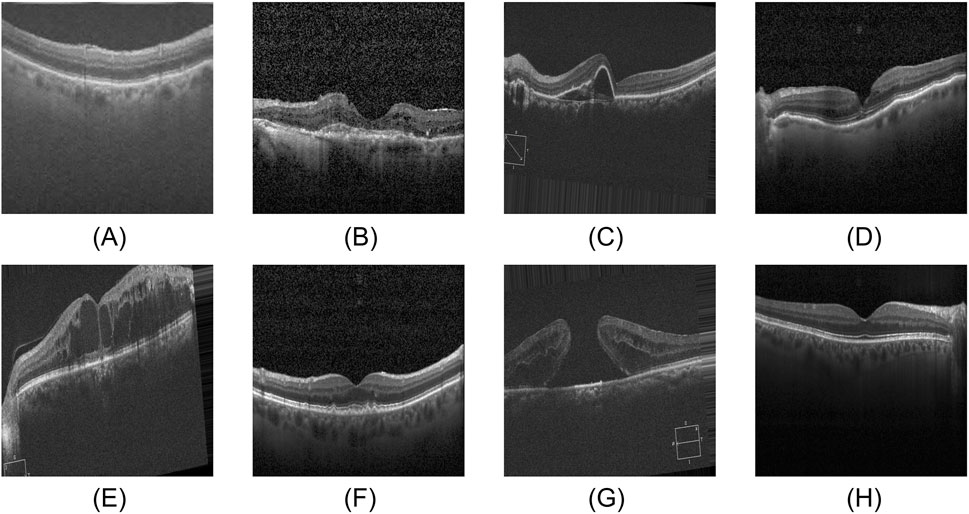
Figure 1. Eight categories of OCT images. (A) AMD, (B) CNV, (C) CSR, (D) DME, (E) DR, (F) DRUSEN, (G) MH, (H) NORMAL.
As a non-contact, non-invasive imaging technique, optical coherence tomography (OCT) utilizes low-coherence interferometry to obtain high-resolution cross-sectional images of biological tissues. With its excellent imaging performance, OCT has become an indispensable diagnostic tool in ophthalmology, playing an increasingly important role in early screening, clinical diagnosis, and efficacy assessment of retinal diseases (Huang et al., 1991). Although this technology has significantly improved the diagnostic efficiency and accuracy of doctors in detecting related conditions, manual interpretation of retinal OCT images still faces considerable challenges in clinical settings. On one hand, as the incidence of retinal diseases continues to rise, the relative scarcity of specialized healthcare resources makes it challenging to meet the ever-growing demand for diagnosis and treatment. On the other hand, the identification of lesion features in OCT images relies heavily on the doctor’s professional knowledge and clinical experience, rendering the diagnostic process highly subjective and potentially compromising diagnostic accuracy (Tsuji et al., 2020; He et al., 2023). In this context, the precise classification of OCT images to distinguish various types of retinal lesions has emerged as an indispensable component in the diagnosis of retinal diseases (Khalil et al., 2024). Therefore, the development of automated retinal image diagnosis systems is essential to assist clinicians in accurately detecting retinal pathologies.
In recent years, deep learning technology has made significant progress in both natural language processing and computer vision, which has promoted the development of various AI-driven diagnostic techniques. Among these, convolutional neural networks (CNN) have increasingly been applied in medical image analysis owing to their excellent feature extraction and pattern recognition capabilities (Zhang et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2025; Gong et al., 2024; Ji et al., 2022; Simonyan and Zisserman, 2014). Numerous CNN-based models have been developed to address complex tasks such as disease detection (Hong et al., 2019b; Simonyan and Zisserman, 2014), image segmentation (Hong et al., 2022a; Li et al., 2024; Hong et al., 2022b), and classification (Hong et al., 2020a; Hong et al., 2020b; Zhu et al., 2022; Wan et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2022), substantially enhancing both the automation and diagnostic efficiency in medical image processing. In the realm of ophthalmic image analysis, CNN have been extensively employed for OCT image classification and lesion detection, yielding noteworthy results (Qian et al., 2025; Subramanian et al., 2022; Laouarem et al., 2024; Song et al., 2025). For instance, Qian et al. enhanced the model’s feature representation by fusing the outputs of multiple DenseBlocks based on DenseNet121 and replaced the positive and negative sample pairs in the conventional triplet loss with the class proxy concept. This modification enabled more efficient and accurate classification of retinal OCT images (Qian et al., 2025).
However, the inherent characteristics of OCT retinal images pose a significant challenge to the discriminative performance of existing models. On the one hand, because OCT is a grayscale imaging technique, subtle lesion features are not clear enough to be accurately identified. Moreover, there is a certain diversity in the shape, size and spatial distribution of lesion regions, which also increases the difficulty of lesion localization (Cheng et al., 2025; Simonyan and Zisserman, 2014; Lo et al., 2019). On the other hand, limited by the performance of imaging equipment and hardware conditions, OCT images are often accompanied by unavoidable noise interference during the acquisition process, resulting in many CNN-based models capturing a large amount of speckle noise information while learning lesion features, which makes the model unable to accurately distinguish between important and unimportant features, thus affecting the model’s discriminative ability. In addition, the process of performing downsampling operations to extract high-level semantic features in CNN-based models often inevitably leads to the reduction of the spatial resolution of the image, resulting in the loss of some of the critical lesion information, which together with the residual noise interference weakens the model’s discriminative ability for the lesion region (Zhang et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2022; Alaba and Ball, 2024).
To address these challenges, this study proposes a retinal disease detection network (MSLI-Net) built upon multi-stage localization and multi-scale interaction. Initially, the network utilizes the residual blocks of ResNet50 for preliminary feature extraction from retinal images. It then employs a Multiscale Dilation Fusion Module (MDF) to enhance the feature representation across scales and expand the model’s receptive field. Subsequently, a Multi-segmented Lesion Localization Fusion Module (LLM) is adopted to emphasize the lesion regions and suppress background noise. Finally, we introduce an MSA module (Xiao et al., 2023) and design a Wavelet Subband Spatial Attention Module (WSSA) to further refine the feature representations in the lesion regions, thereby achieving more precise disease detection. The contributions of this paper are as follows:
1) Our MSLI-Net is based on the ResNet50 network framework, which effectively integrates the MDF, LLM and WSSA, realizing the complementary advantages between shallow high-resolution features and deep semantic information. This enables the model to significantly enhance the representation of lesion regions in retinal OCT images, and effectively improves classification performance.
2) We design a multiscale dilation fusion module (MDF), which effectively extracts multiscale feature information by introducing convolutional branches with different dilation factors and deeply fuses it with original image features. It effectively enhances the global receptive field and improves the model’s ability to model long-range dependencies.
3) We propose a multi-segmented lesion localization fusion module (LLM). By constructing multiple parallel branches, the LLM realizes the hierarchical extraction of local features as well as the enhancement of key channel features of a lesion. This design effectively mitigates the limitations of the traditional channel attention mechanism that is susceptible to interference in the context of complex noise while enhancing the accurate localization of the lesion region.
4) We develop the wavelet subband spatial attention module (WSSA) based on the introduction of the MSA module. This module decomposes the input features into four subbands of different frequencies by discrete wavelet transform, and realizes feature interaction and information fusion across subbands. The module is capable of extracting lesion-related features in greater detail while effectively suppressing noise interference.
5) We evaluate our model on the publicly available OCT-C8 dataset, achieving 96.72% accuracy in retinal OCT classification, demonstrating that this model has a strong discriminative capability in this domain.
2 Related work
In recent years, the advancement of deep learning technology and its extensive application in medical image analysis have propelled research and produced significant results in fundus image analysis (Zheng et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2022a; Xu et al., 2022b). Early studies mainly focused on transfer learning and architecture optimization for classical convolutional neural networks (CNN). Wang et al. employed a transfer learning strategy by fine-tuning various classical CNN models (including VGG16, ResNet18, ResNet50, and InceptionV3) that were pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset, thereby achieving higher precision in retinal OCT image classification (Wang et al., 2019). Meanwhile, steady progress has been made in refining the model architecture itself, such as Karthik et al., who proposed Edgen blocks to replace the residual connection method in the traditional ResNet50 and designed a novel activation function to further enhance the network’s ability to capture image boundary features and effectively highlight key lesion information (Karthik and Mahadevappa, 2023). Sunija et al. also designed OCTnet based on the ResNet50 architecture, achieving excellent classification performance while significantly reducing the number of model parameters (Sunija et al., 2021).
In addition to optimizing traditional CNN architectures, recent research has also focused on fusing CNN and Transformer architectures to further enhance the model’s feature representation and global modeling capabilities. Laouarem et al. proposed a hybrid model, HTC-Retina, that combines the advantages of CNN in local feature extraction with the capability of a visual Transformer for global dependency modeling, effectively overcoming the limitations of a single architecture in image analysis (Laouarem et al., 2024). Similarly, the CRAT network mitigates the common attention collapse problem in deep Transformers by introducing the Re-Attention module to dynamically adjust the multi-head self-attention mechanism (Yang et al., 2025). Moreover, the introduction of the Swin Poly transformer network further broadens the research boundaries of fusion modeling, and its mechanism of establishing flexible connectivity between image regions significantly improves the model’s ability to facilitate information exchange among multi-scale features (He et al., 2023).
In addition to integrating different model architectures, task-level co-design has emerged as a prominent research topic. Diao et al. proposed an innovative method that tightly integrates segmentation and classification tasks (Diao et al., 2023). This approach employs an auxiliary segmentation branch within the classification network (CM-CNN) to generate a complementary mask for the input image, which is subsequently used to enhance the original features and effectively guide the classification network to focus on the features of the lesion region, thereby improving classification performance. Moreover, the application of the Grad-CAM algorithm enables CM-CNN to generate a class activation map (CAM) that further assists the segmentation network (CAM-UNet) in refining its segmentation accuracy, ultimately achieving more precise feature extraction and segmentation of the lesion regions. This model exhibits excellent performance on both classification and segmentation tasks, demonstrating the potential of explicit information interaction between tasks in enhancing diagnostic performance.
2.1 Image cropping and local feature extraction
It has been shown that the classification performance of deep learning models can be effectively improved by an appropriate cropping strategy for retinal OCT images (Awais et al., 2017). Some researchers have manually cropped out rectangular boxes containing lesion regions at the image preprocessing stage to help neural networks capture key lesion features more effectively (Kaothanthong et al., 2023). However, this cropping method is not only cumbersome and time-consuming, but also poses the risk of degrading the model performance by mistakenly deleting important lesion features. To address these issues, some studies have proposed dividing the OCT images into fixed-size patches and extracting features from each patch individually, thereby improving the model’s ability to extract features from local lesion regions while preserving the overall spatial structure of the image (Dutta et al., 2023).
In other related studies, Sharma et al. proposed a network structure called AELGNet, which successfully achieved efficient capture of both subtle and global features of plant leaf images by partitioning the image feature map into four fixed patches and extracting local features using independent RSA and RCA mechanisms, respectively (Sharma and Vardhan, 2025). However, since most retinal lesions tend to be concentrated in a few localized regions of the image, dividing the patches in a fixed manner and indiscriminately extracting features not only wastes computational resources but also amplifies irrelevant background noise, thereby reducing the model’s classification accuracy.
Unlike existing methods, our proposed LLM employs parallel cropping branches based on the characteristics of retinal OCT images, allowing the model to automatically locate the lesion region and extract key features, effectively mitigating interference from background noise and thereby improving the model’s discriminative capacity and robustness.
2.2 Discrete wavelet transform
As a common method for image denoising, the discrete wavelet transform can decompose the signal into low-frequency subbands and high-frequency subbands (Gao and Yan, 2010). Specifically, the low-frequency subbands mainly retain the color and structural information of the image, while the high-frequency subbands preserve detailed features such as edges, textures, and high-frequency noise. This property renders the wavelet transform particularly advantageous in image processing (Yu et al., 2025; Burrus et al., 1998; Xu et al., 2020). Some researchers have attempted to eliminate the HH subband, where the noise is most concentrated, and have introduced an attention mechanism solely for the remaining three subbands, employing the wavelet transform as a downsampling operation to mitigate noise interference (Zhao et al., 2022). Alaba et al. strengthened the information of the LL subband by efficiently fusing the important features in the LH and HL subbands and passing them to the LL subband (Alaba and Ball, 2024). Finder et al. enhanced the model’s receptive field by implementing multi-level wavelet decomposition and independently processing the LL subband (Finder et al., 2024). Although these methods have improved the performance of the wavelet transform in image analysis to some degree, most studies have focused only on low-frequency information or have achieved feature extraction and denoising at the expense of discarding high-frequency information, thereby limiting the comprehensive utilization of the potential information contained in all subbands.
To this end, we propose the WSSA, which synergistically processes all subbands while fully preserving all subband features, adaptively suppressing background noise and highlighting key edge and structural information. Unlike previous approaches that focus solely on information from a single subband, WSSA enables synergistic processing and information interaction between the low-frequency and high-frequency subbands, thereby more comprehensively enhancing the model’s performance in noise suppression and lesion perception.
2.3 Dilated convolution
The convolutional kernel is a core component of convolutional neural networks (CNN), but when expanding the receptive field, traditional methods often require stacking multiple convolutional layers into a deep network, which significantly increases the number of parameters. To address this issue, Yu et al. proposed achieving an exponential expansion of the receptive field by introducing different dilation factors, so that the receptive field expands exponentially while parameters grow only linearly (Yu and Koltun, 2015). Based on this design concept, some researchers proposed parallel dilated convolution modules for more efficient image processing tasks (Feng et al., 2020; Li et al., 2019; Bui et al., 2024). For example, Kamran et al. replaced the traditional 3 × 3 convolution with two parallel dilated convolutions with a dilation factor of 2 in the residual block to enhance the network’s ability to model contextual information (Kamran et al., 2019), and Li et al. extracted spatial features from the feature map using a parallel dilated convolution module (Li et al., 2019). Although these designs expanded the receptive field, they did not fully consider the fusion mechanism with the original feature map, which resulted in the loss of local details. In contrast, the MDF designed in our work further strengthens fusion with the original feature map while employing dilated convolution to capture multi-scale features and enlarge the receptive field, thereby preserving local details and enhancing the model’s ability to capture long-range dependencies. Experimental results show that the network using the MDF outperforms the traditional design employing a single dilated convolution module in terms of accuracy.
3 Methods
3.1 Overall framework
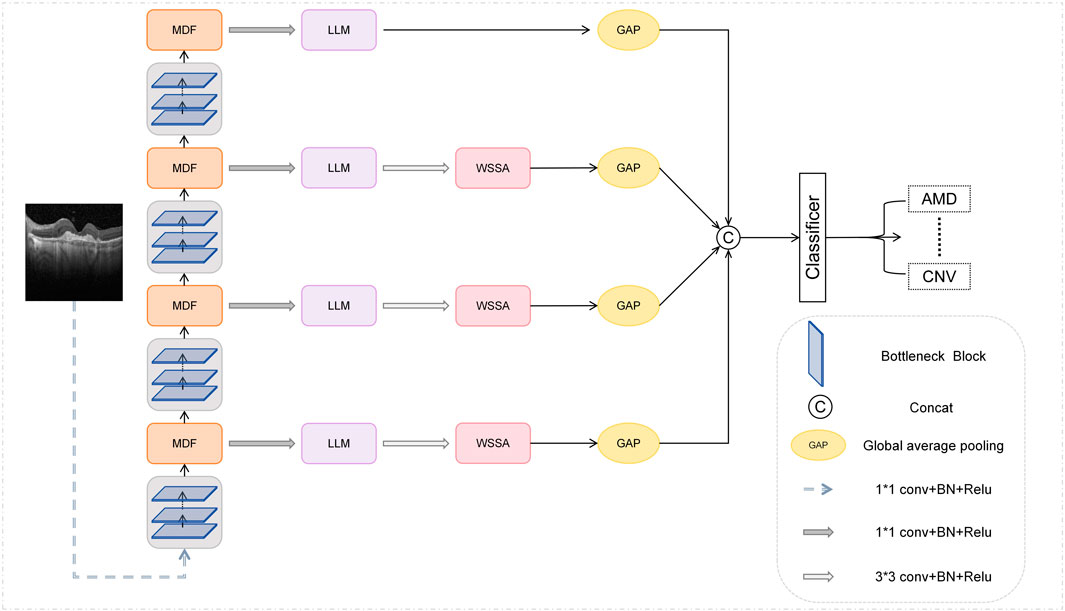
We propose a new network structure MSLI-Net as shown in Figure 2, the overall architecture of MSLI-Net is composed of three core modules, namely, the multi-scale dilation fusion module (MDF), the multi-segmented lesion localization fusion module (LLM), and the wavelet subband spatial attention module (WSSA). MSLI-Net comprehensively extracts lesion features, effectively enhances focus on key pathological regions, and improves classification accuracy and discriminative performance for retinal OCT images.
Specifically, we feed the image into the multi-scale dilation fusion module after initial feature extraction at various stages of the ResNet50 network. This module extracts multi-scale feature representations with enlarged receptive fields through dilated convolutions with different dilation factors and effectively fuses them with the original feature maps, thereby better incorporating both global semantic context and local detailed features present in the image.
On this basis, we introduced a feature pyramid network (FPN) structure removing the upsampling branches, used the MDF outputs as inputs for each FPN branch, and designed a Multi-segmented Lesion Localization Fusion Module to realize the refinement of the feature maps output from the MDF. In view of the inherent characteristics of retinal OCT images, we innovatively introduced the strategy of parallel cropping in this module to retain and extract feature information segment by segment, which effectively enhanced the localization ability of the lesion region.
Meanwhile, we introduce the MSA module and design the wavelet subband spatial attention module. Considering that when the feature map size is odd, the structural distortion may be caused by the wavelet transform and its inverse transform, the WSSA only process the feature maps produced by the LLM in the first three branches of the FPN. This module effectively enhances key edge information through inter-subband feature interaction and fusion, while suppressing irrelevant noise interference.
Finally, we perform global average pooling on the feature maps output from each of the four branches of the FPN to reduce the spatial dimensionality, and subsequently perform stacked fusion on them in terms of channel dimensions to achieve deep interaction and complementary information between features at different scales. We then feed the fused feature maps into a classifier for retinal image classification. Through this strategy, our network fully fuses the local detail information carried by the high-resolution shallow feature maps with the global semantic information expressed by the deep feature maps, thereby strengthening multi-scale contextual relevance and improving classification accuracy and model robustness.
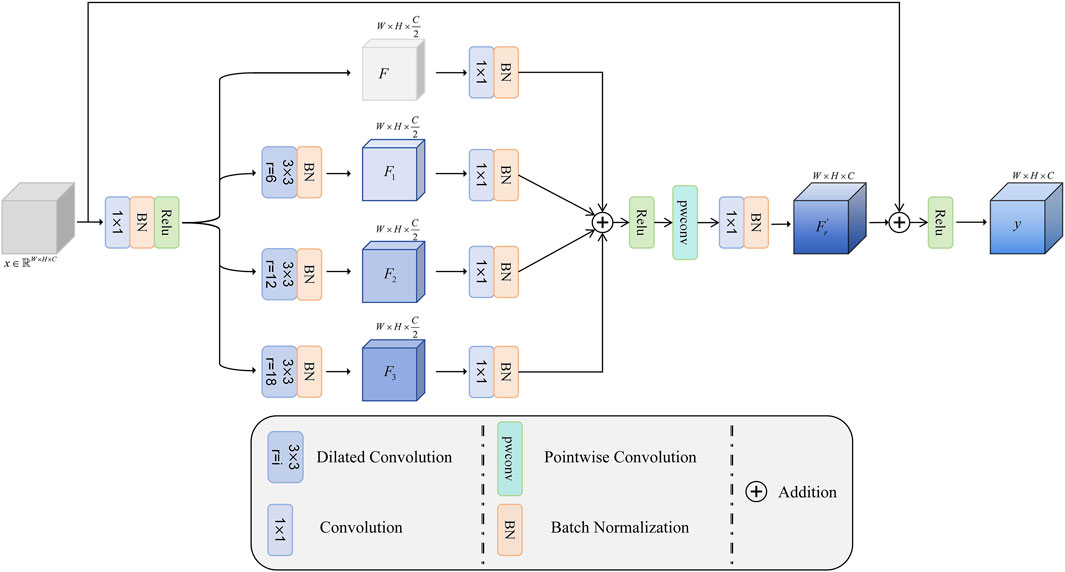
3.2 Multi-scale dilation fusion module (MDF)
To obtain a larger receptive field without reducing the spatial resolution of the feature maps, Yu et al. proposed achieving this by introducing different dilation factors—that is, by effectively increasing the spacing between values in the convolution kernel (Yu and Koltun, 2015; Song et al., 2024). However, due to its sparse sampling pattern resembling a checkerboard, it is prone to triggering the grid effect, which leads to the loss of local information and affects the completeness of feature expression (Mehta et al., 2018). In order to fuse global and local features more effectively, this paper proposes a multi-scale dilation fusion module (MDF). This module effectively improves the overall performance of the model by fully fusing the features extracted by the convolution with different dilation factors with the original features.
The structure of the MDF is shown in Figure 3. Let the input feature map be
Subsequently, different dilation factors (6, 12, and 18) are used to perform convolution operations on
where
Next, the fused features are linearly combined between channels by pointwise convolution, so as to further mine the feature relationships between channels and enrich the feature representation. Finally, the number of channels is reduced to the original dimension
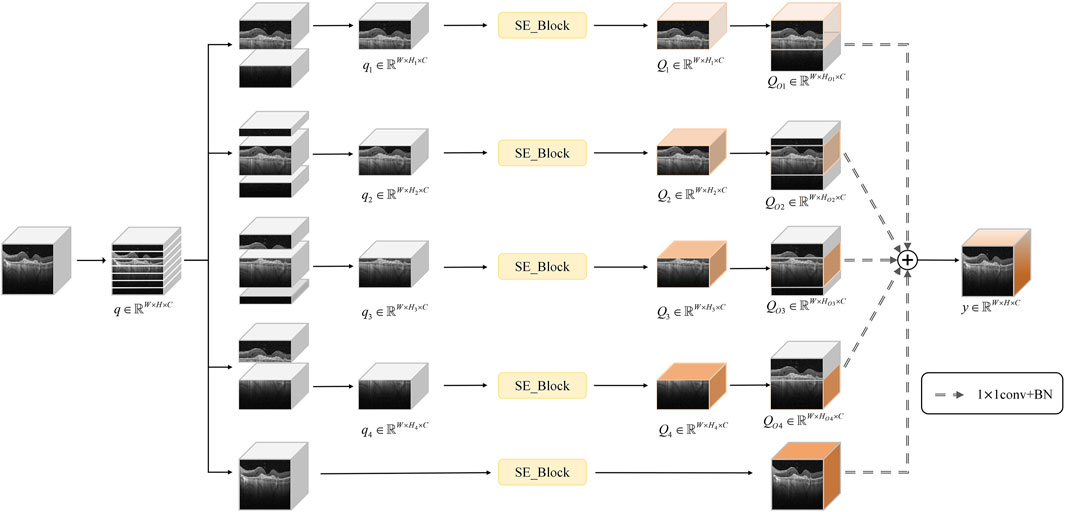
3.3 Multi-segmented lesion localization fusion module (LLM)
Considering that, in OCT images, the retina typically appears as a horizontally elongated structure while lesions usually occupy only localized regions, we divided the feature map uniformly along the vertical axis into seven subregions and observed that the retinal region is primarily contained within four contiguous segments. To achieve accurate lesion localization, effective extraction of key features, and suppression of irrelevant background noise, this paper proposes a multi-segmented lesion localization fusion module (LLM), as illustrated in Figure 4.
We assume that the original feature map is
where
Subsequently, the SE channel attention mechanism is introduced to process the sub-feature maps of the above four parallel branches with channel-level features, which further enhances the key channel features in each branch, and yields
With this fusion approach, lesion localization is further enhanced, effectively reducing the susceptibility of the traditional channel-attention mechanism to complex background noise interference.
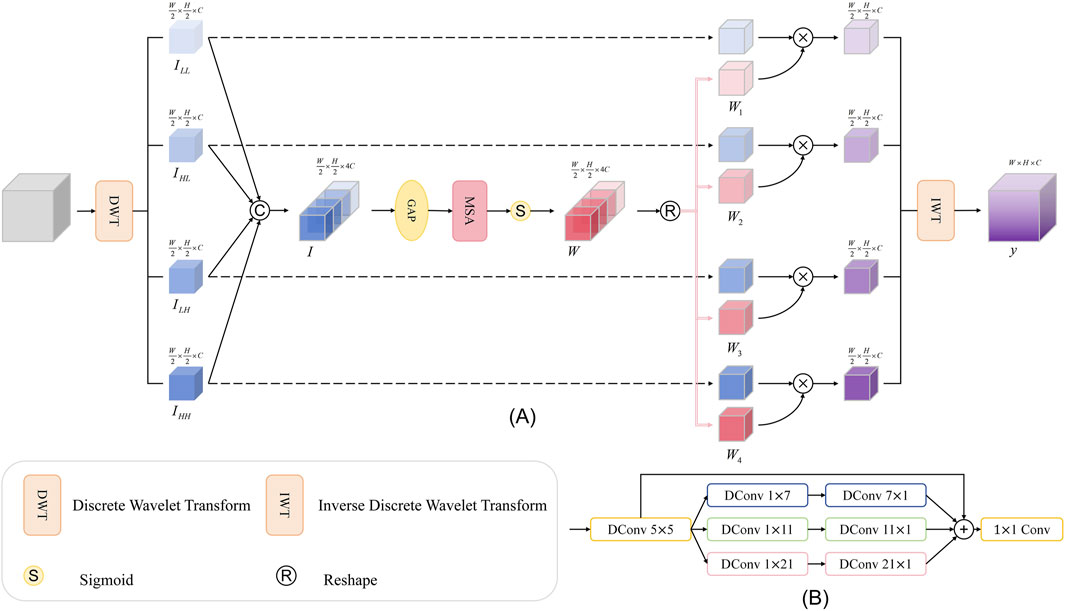
3.4 Wavelet subband spatial attention module (WSSA)
As an effective mathematical approach for addressing nonstationary signal decomposition, the wavelet transform can capture information at various frequencies and time positions by adjusting its scale and translation parameters, thereby reflecting the local variation characteristics of a signal. In the context of the commonly used two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform, the Haar wavelet decomposes the input feature map into four subbands via low-pass and high-pass filters, which correspond to the low-frequency subband (LL), horizontal high-frequency subband (LH), vertical high-frequency subband (HL), and diagonal high-frequency subband (HH). Among these, the low-frequency subband encapsulates the image’s color and structural information, while the high-frequency subbands contain abundant detail and texture information. Subsequently, the signal is then reconstructed through the inverse wavelet transform. During reconstruction, wavelet-based edge detection is first applied to enhance edge features in each subband, then thresholding is performed to eliminate noise.
However, for retinal OCT images, due to their inherent speckle noise characteristics, it is difficult to effectively denoise them by simply using traditional wavelet transform methods. Therefore, to further suppress noise interference and highlight edge features, we propose the wavelet subband spatial attention module (WSSA) on the basis of the multiscale attention (MSA) module, which is structured as shown in Figure 5A.
In this module, we first use the wavelet transform to decompose the original feature map at multiple scales, and obtain four subbands containing low-frequency and high-frequency information,
Next, we apply an average pooling operation (AvgPool) to the fused feature map
Where
This module enables the global structural information embedded in the low-frequency subbands to effectively guide the recognition of edge details in the high-frequency subbands, effectively suppressing noise interference. At the same time, the fine-grained edge features captured by the high-frequency subbands feed back to the low-frequency subbands, enhancing their ability to perceive the edge region.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Datasets
We use the publicly available OCT-C8 dataset (Obuli, 2021) to evaluate the performance of the model proposed in this paper. The dataset contains a total of 24,000 optical coherence tomography (OCT) images of seven types of retinal diseases as well as normal retina: Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD), Choroidal Neovascularization (CNV), Central Serous Retinopathy (CSR), Diabetic Macular Edema (DME), Diabetic Retinopathy (DR), Yellow deposits under the retina (Drusen), Macular Hole (MH), and Healthy eyes with no abnormalities (NORMAL). Each category contains 3,000 images. The official data split is 2,300 images for training, 350 for validation, and 350 for testing. Considering that increasing the training sample size can improve the model generalization ability, in this paper, the original training set and the validation set are combined as the training set (2,650 images) for model training, and the test set (350 images) remains unchanged.
4.2 Evaluation metrics
To evaluate the effectiveness of the model, we use Accuracy (ACC), Precision, Sensitivity, and F1-score as the classification metrics. The formulas for these metrics are as follows.
where
4.3 Implementation details
The training and testing of this experiment were done on a single NVIDIA RTX 4090 GPU. In the data preprocessing stage, we uniformly resize the input feature map to 224 × 224 pixels and normalize the image using pre-calculated mean and standard deviation. During the training process, the loss function was chosen to be cross-entropy loss and the model was optimized using the Adam optimizer, where the optimizer parameters were set to
4.4 Performance of our proposed method
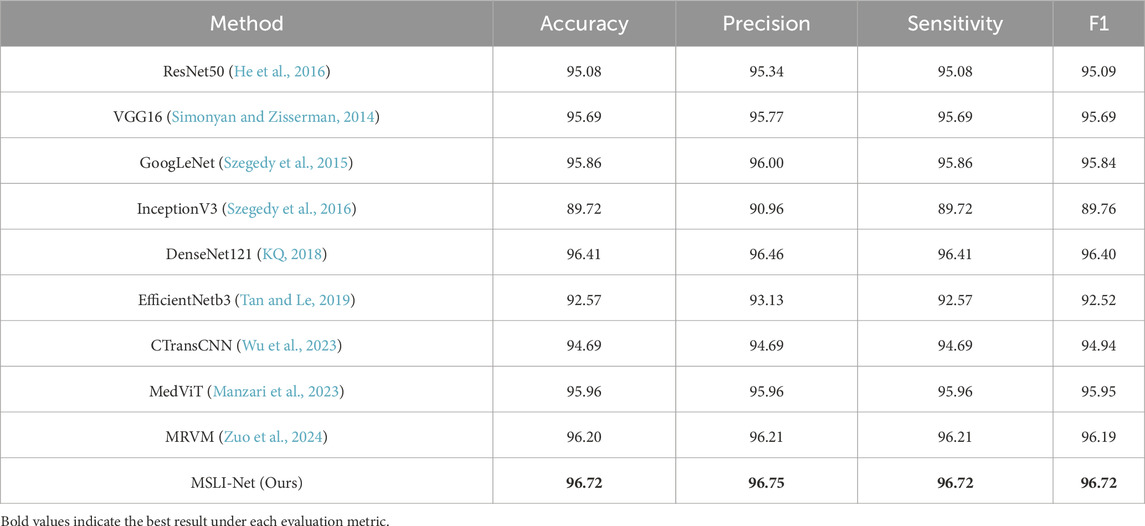
In this section, we evaluate the classification performance of the proposed MSLI-Net model on the OCT-C8 retinal image dataset and analyze it in comparison with several representative convolutional neural network architectures, including ResNet50 (He et al., 2016), VGG16 (Simonyan and Zisserman, 2014), GoogLeNet (Szegedy et al., 2015), InceptionV3 (Szegedy et al., 2016), DenseNet121 (KQ, 2018) and EfficientNetB3 (Tan and Le, 2019), among others. In addition to the classical architectures, we also compare them with some of the models that have performed well in the retinal OCT image analysis task in recent years, including CTransCNN (Wu et al., 2023), MedViT (Manzari et al., 2023) and MRVM (Zuo et al., 2024). According to the experimental results shown in Table 1, DenseNet121 has the highest accuracy of 96.41% on the OCT-C8 dataset among the compared baseline models, followed by the MRVM model with an accuracy of 96.20%. Our MSLI-Net achieves a classification accuracy of 96.72% and outperformed the other compared models in all metrics. This demonstrates clear superiority in performance.
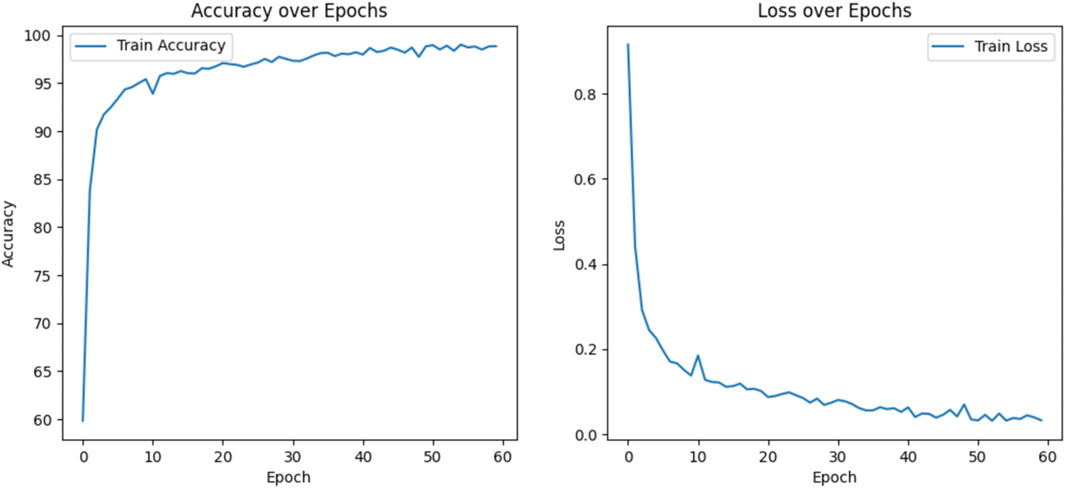
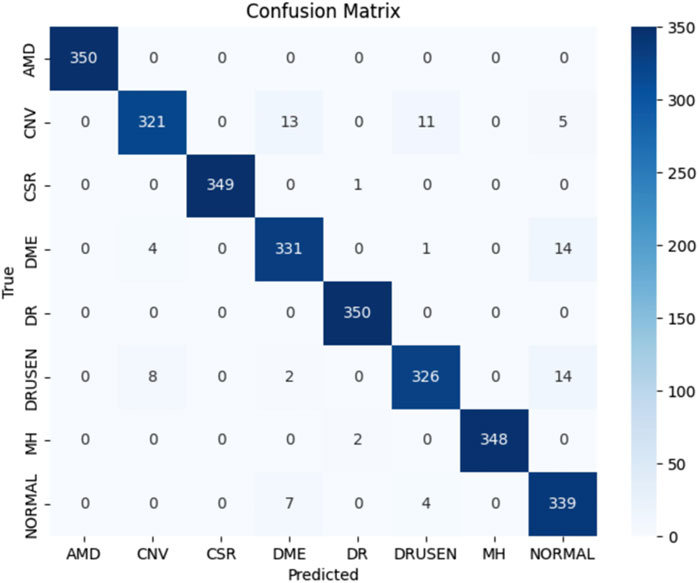
Figure 6 shows the training metrics for MSLI-Net, where the left graph shows the training-accuracy curve and the right graph shows the training-loss curve. It can be observed that both curves eventually stabilize without significant overfitting. Figure 7 further shows the confusion matrix obtained from one representative experiment. As can be seen, our model achieves 100% classification accuracy on AMD and DR categories, and relatively lower classification accuracy on CNV, DME and DRUSEN, but still maintains a high overall level. These results fully demonstrate the strong generalization capability of MSLI-Net in the task of automatic classification of multi-category retinal OCT images, further validating the effectiveness of the proposed method.
4.5 Ablation study
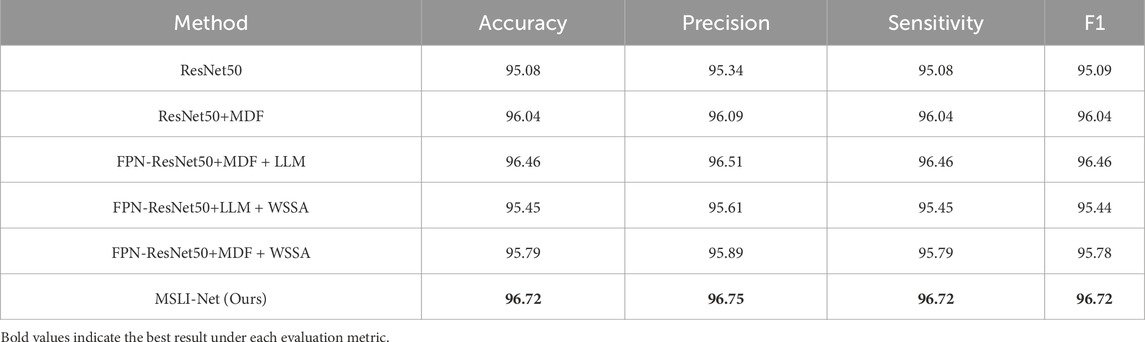
To evaluate the contribution of each module in the proposed model to the overall performance, we conducted systematic ablation experiments on the OCT-C8 dataset, the results of which were shown in Table 2. The accuracy was 95.08% when using ResNet50 alone, which we adopted as our baseline. We first built the ResNet50+MDF architecture by adding the multi-scale dilation fusion module (MDF) to each stage of ResNet50, at which point the model accuracy was improved to 96.04%, an improvement of about 1% from the baseline. Next, we introduced the feature pyramid network (FPN) that removes the up-sampling branches, and added the multi-segmented lesion localization fusion module (LLM) on top of it to form the FPN-ResNet50+MDF + LLM architecture. The results showed that this combination further improves the model accuracy to 96.46%. Finally, we incorporated the Wavelet Subband Spatial Attention module (WSSA) into the first three FPN branches to form the full MSLI-Net; this achieved 96.72% accuracy. These results confirm that each module synergistically enhances overall performance.
To further verify the impact of each module on the overall performance, we removed MDF (FPN-ResNet50+LLM + WSSA) and LLM (FPN-ResNet50+MDF + WSSA) from the full model, respectively, and analyzed their performance in comparison with the complete MSLI-Net model. The experimental results show that after removing MDF and LLM, the classification accuracy of the model is 95.45% and 95.79%, respectively, both of which show a decrease compared with the complete structure. This verifies the key role of each module in the performance improvement. The result further demonstrate that there is a close synergistic dependency between the modules, and the absence of any sub-module will weaken the discriminative ability of the model, thus affecting the overall performance.
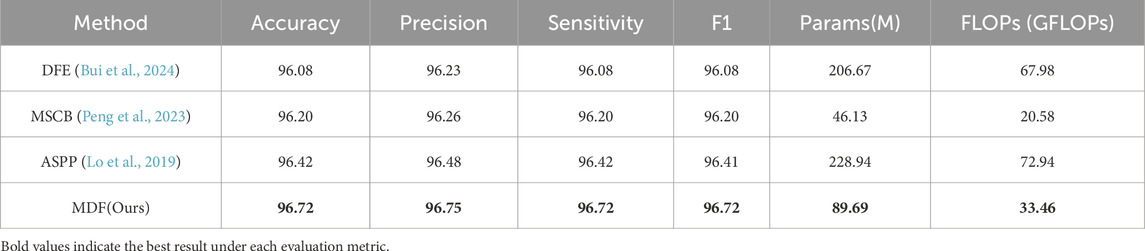
In order to verify the effectiveness of the multi-scale dilation fusion module (MDF) proposed in this paper, we reproduced three representative dilated convolution modules and individually replaced the MDF with each of them for comparative experiments. Specifically, we reproduced the proposed dilated feature enhancement module (DFE) designed by Bui et al. (2024); the Multi-scale Context Block (MSCB) proposed by Peng et al. (2023); and the ASPP module (Lo et al., 2019) used by Lo et al. in their work. The experimental results are shown in Table 3, where the model accuracy reached 96.42% when the ASPP was used instead of MDF, 96.20% when MSCB was used, and only 96.08% when MDF was replaced by the DFE module. In contrast, using our proposed MDF within the same network architecture, the model achieved an accuracy of 96.72%. Moreover, our model contained 89.69 million parameters and 33.46 GFLOPs—an increase relative to the MSCB model (46.13 million, 20.58 GFLOPs) but still far smaller than both the DFE (206.67 million, 67.98 GFLOPs) and the ASPP (228.94 million, 72.94 GFLOPs) counterparts. These results demonstrate that our MDF effectively enhances feature extraction and semantic understanding performance while maintaining a lightweight architecture.
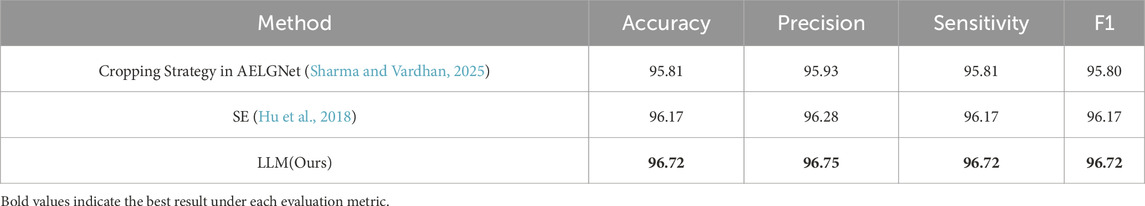
In addition, to evaluate the multi-segmented lesion localization fusion module (LLM), we devised two comparison schemes: one did not introduce a cropping strategy at all and only used the SE channel attention mechanism (Hu et al., 2018) for feature processing; the other used the cropping strategy proposed by Sharma and Vardhan (2025) in the AELGNet model, i.e., to divided the feature map into four patches using a four-quadrant partitioning strategy, and then applied the SE channel attention mechanism to each patch. The comparison results were shown in Table 4, when only the SE channel attention mechanism was used, the model achieved an accuracy of 96.17%. The accuracy dropped to 95.81% when the AELGNet cropping strategy was used, which may have been due to the fact that retinal structures in OCT images are usually distributed in long horizontal strips, and some patches may contain only background information when dividing the feature map with this cropping strategy. Meanwhile, the four patches were processed indiscriminately during the feature extraction process, which led to the amplification of the interference of irrelevant noise in the background region, and ultimately reduced the effectiveness of the model feature extraction. In contrast, our proposed LLM enabled the model to pay more attention to the features in the retinal region, and as shown in the experimental results in Table 4, the classification accuracy and various indexes of the model when using the LLM were significantly better than those of the comparative methods using the SE module and adopting the cropping strategy in AELGNet, thus verifying the effectiveness of the LLM in the retinal OCT image classification task.
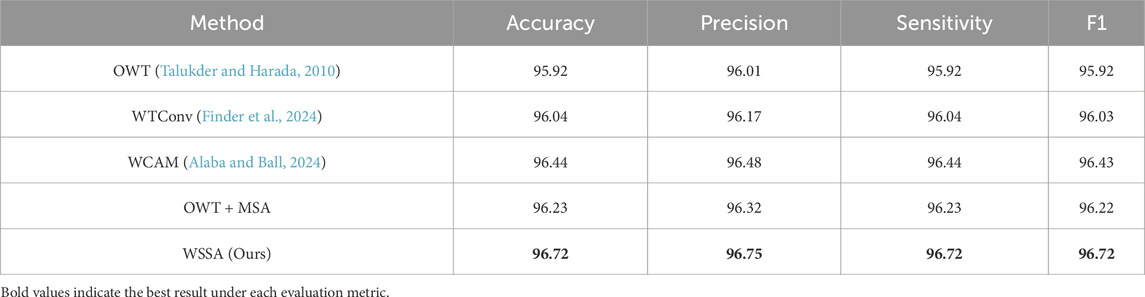
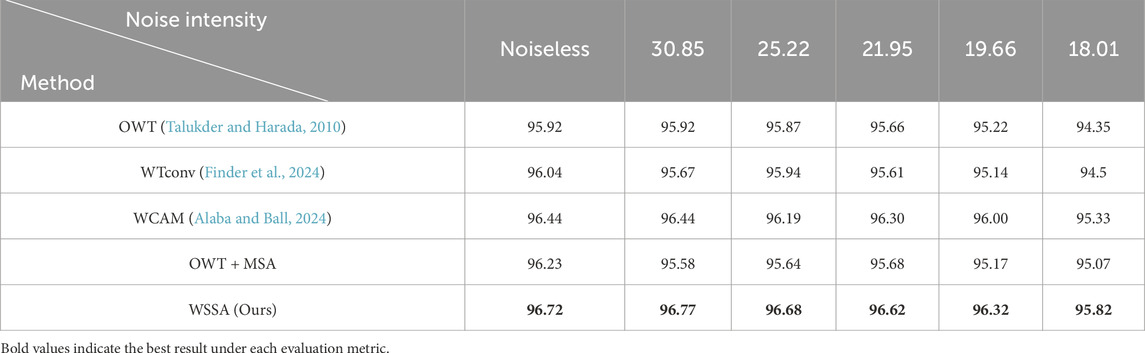
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed wavelet subband spatial attention module (WSSA), we designed two sets of comparison experiments. In the first set of experiments, we replaced the WSSA module, in turn, with the following four methods: (1) using the wavelet transform and its inverse transform (OWT) (Talukder and Harada, 2010) without any processing; (2) adopting the WTConv (Finder et al., 2024) proposed by Finder et al. which involves a convolutional operation for each wavelet subband individually; (3) replicating the WCAM proposed by Alaba and Ball (2024), which is processed by fusing the features of the LH and HL subbands to the LL subband; (4) the MSA (Xiao et al., 2023) applying independently to each wavelet subband, constituting the OWT + MSA.
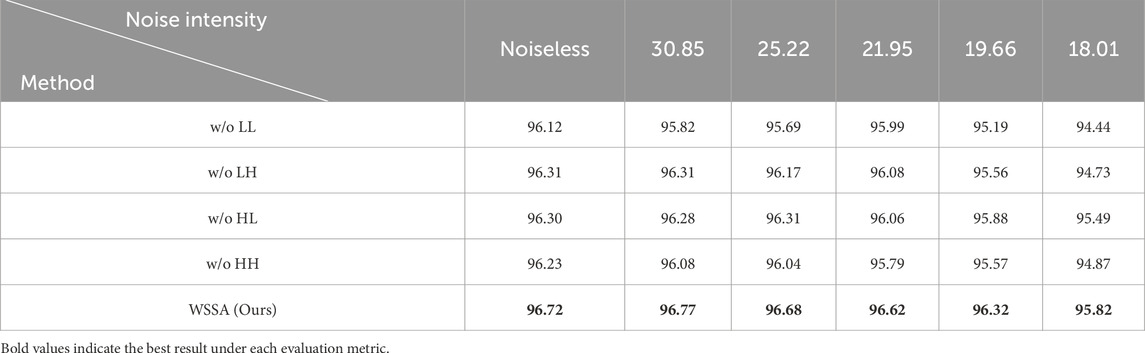
In addition, our WSSA module stacks all wavelet subbands, extracts subband weights via global average pooling, and then refines these weights using the MSA module. These weights are then multiplied with the original subband features to facilitate inter-subband information interaction. Finally, we perform the inverse wavelet transform to restore the image size. Therefore, we further designed a second set of comparative experiments to comprehensively evaluate the advantages of the WSSA. Specifically, without altering the remaining process, we independently excluded each of the LL, LH, HL, and HH subbands—resulting in four modules referred to as w/o LL, w/o LH, w/o HL, and w/o HH—in which only the remaining three subbands are stacked and processed. This setup allows us to analyze the role of each subband in the process of information fusion.
Table 5 shows the performance comparison results of models using different modules in the first set of experiments for the retinal OCT image classification task. The results show that the classification accuracy of the model using OWT is only 95.92%, indicating that although the wavelet transform possesses some image processing capability, the lack of subsequent feature extraction may lead to the disruption of intrinsic structure, which affects the classification performance. Further, the models using WTconv and OWT + MSA obtain classification accuracies of 96.04% and 96.23%, respectively, indicating that there is a close intrinsic correlation between the wavelet subbands, and it is difficult to effectively tap the potential complementary information of each subband by only performing independent feature extraction, thus restricting the enhancement of the model’s discriminative ability. In contrast, the classification accuracy of the model using WCAM that fuses the LH and HL with the LL subband features is 96.44%, which verifies that the information interaction between the subbands helps to fully mine the feature information.
Table 6 displays the results of the second set of comparative experiments. It can be seen that the model accuracy using the second set of comparison methods (w/o LL, w/o LH, w/o HL, and w/o HH) is distributed between 96.12% and 96.31%, highlighting that the synergistic effect of each wavelet subband in feature extraction is indispensable. The model accuracy reaches 96.72% when using our proposed WSSA. This suggests that omitting any sub-band may degrade feature representation, thereby impairing the model’s overall discriminative performance. The effectiveness of WSSA in the retinal OCT image classification task is also demonstrated.
4.6 Robustness of the noise processing module
OCT image quality varies significantly because acquisition is affected by external factors such as imaging-equipment performance and ambient-light interference. Some images even contain severe speckle noise. These issues pose major challenges for subsequent image processing and analysis. In order to verify the effectiveness of our WSSA model for the denoising of retinal OCT images, we added a multiplicative scattering noise model (Huang et al., 2019) to the test dataset and used the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) to measure the noise level. It can be expressed by the following Equation:
where, in Equation 18,
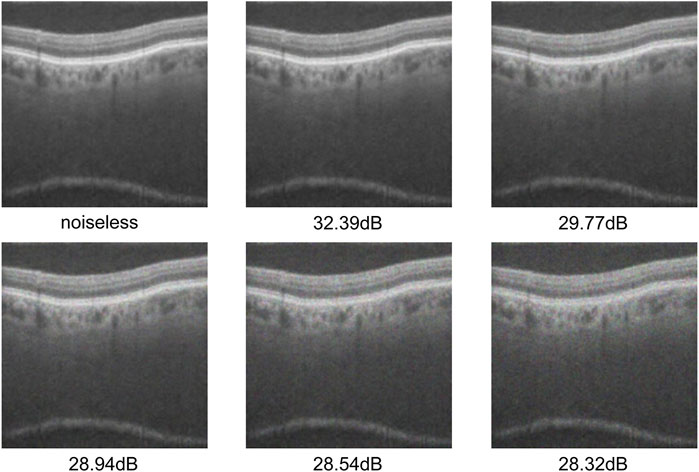
We trained the model using the original training dataset, and added multiplicative scattering noise of five variance levels (
As shown in Tables 7, 8, the overall performance of all modules decreases with the increase of noise intensity. Among them, except for the MSLI-Net model proposed in this study and its variant without the HL subband—which both exhibit a performance degradation within 1%—all other models experience a degradation exceeding 1%, specifically ranging from 1.11% to 1.68%. In addition, our model shows significant performance degradation only when the noise intensity decreases to 19.66 dB, and its fluctuation of no more than 0.1% between no noise and a noise intensity of 21.95 dB, demonstrating good stability. Moreover, across all noise levels, the overall performance of our model is always better than that of other comparative methods, indicating that the method in this paper has good robustness under high-intensity noise interference.
In order to verify the robustness of the proposed LLM in noisy environments, we conducted systematic tests on each module listed in Table 4 under different noise intensities, and the test results are shown in Table 9. From the results, it can be seen that the classification accuracy of the model with the AELGNet cropping strategy decreases by 0.55% when noise is first added, which is the largest decrease among the three modules, indicating that the strategy is more sensitive to noise, and further proving that this cropping approach may amplify the interference of extraneous noise in the background region. As noise intensity increases, the performance of the model using only the SE module is more significantly impaired under high-intensity noise. It is worth noting that the model (MSLI-Net) using LLM shows better classification accuracy than the other two strategies across all noise levels, which fully verifies that the LLM method has stronger noise robustness in complex noise environments.
4.7 Visualization and analysis
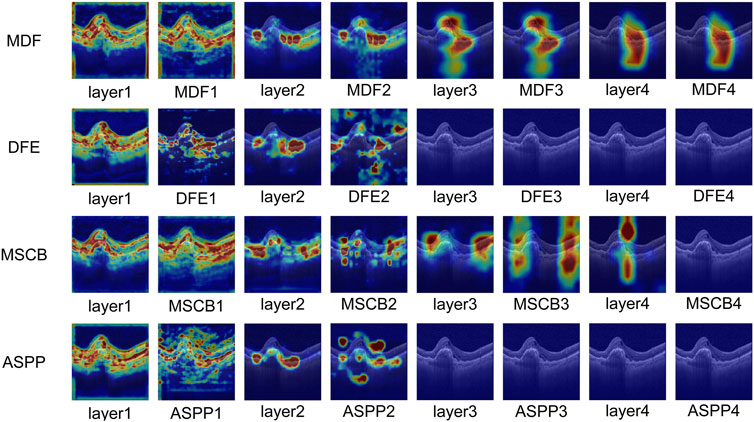
In order to visually assess the effectiveness of the MDF proposed in this paper in multi-scale feature extraction and its ability to deeply integrate with the original image features, this paper introduces the Grad-CAM method to visualize and analyze the image regions that each of the comparative modules pays attention to in the classification decision-making process. The method effectively reveals the ability of each module to pay attention to the key regions of the input image through the generation of heat maps.
In this paper, based on each module in Table 3, its corresponding heat map is generated at different network stages of ResNet50 and visualized for comparison. As shown in Figure 9, in the layer1 stage of ResNet50, each module shows high consistency in focusing on the lesion region. As the network deepens, the MDF consistently maintains high consistency with the backbone network at all stages and further enhances its ability to focus on lesion regions. In contrast, during the first two stages, the MSCB consistently aligns its focus on the lesion regions with that of the backbone network and remains relatively stable; however, the region of focus deviates significantly in the third stage. Conversely, DFE and ASPP show a tendency of divergence of the total attention region after the first stage, and although they briefly enhance the ability of layer2 of ResNet50 to focus on the lesion, by the third and fourth stages, their ability to focus on the lesion decreases significantly, and neither of them is able to focus on the lesion portion well.
The comparative results heat map visualization further validates the advantages of the MDF module in feature fusion and semantic modeling. Especially In deeper layers, MDF is still able to maintain a stable and precise attention region, reflecting stronger discriminative and semantic retention abilities.
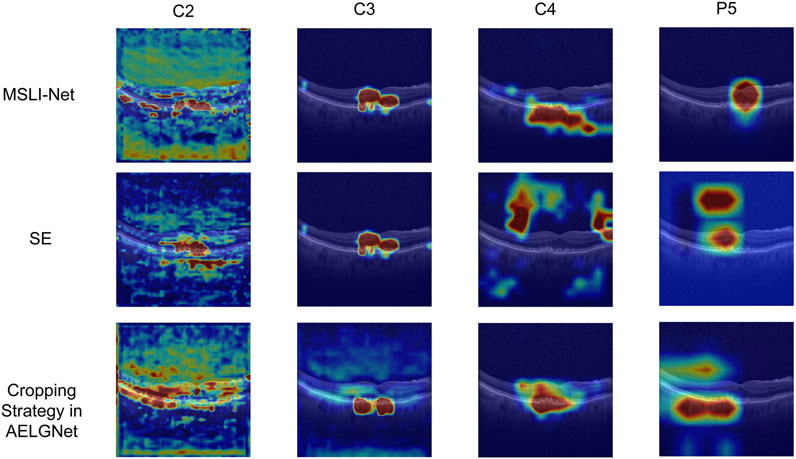
Meanwhile, we also visualize and compare the mentioned models in Table 4. As shown in Figure 10, in the shallow stage (c2 and c3), the models using SE, the cropping strategy in AELGNet, and the LLM proposed in this paper are able to locate the lesion region more accurately, which reflects a good initial discriminative ability. However, in the deeper network stages (c4 and p5), SE and cropping strategy in AELGNet gradually demonstrate increased background attention, compared to LLM which still maintains a stable focus on the lesion region in the deeper stages. This result fully demonstrates the effectiveness of our LLM’s performance for lesion localization.
5 Conclusion
In this study, we propose a novel network architecture called MSLI-Net for the classification task of retinal optical coherence tomography (OCT) images. The model effectively enhances the feature extraction capability of the model for the lesion region and significantly improves the overall classification performance through three core modules, namely, the multi-scale dilation fusion module (MDF), the multi-segmented lesion localization fusion module (LLM), and the wavelet subband spatial attention module (WSSA). On the publicly available OCT-C8 dataset, this method achieves a classification accuracy of 96.72%. We further confirm the critical role of each of the three modules, MDF, LLM and WSSA, in network performance improvement through comprehensive ablation experiments. Meanwhile, MSLI-Net still exhibits robust performance under stronger noise interference environment. MSLI-Net architecture not only has practical value for OCT image classification, but also provides new research ideas and effective technical references for future network design for similar tasks.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://doi.org/10.34740/KAGGLE/DSV/2736749.
Author contributions
ZQ: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. JC: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. GL: Conceptualization, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. HW: Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. SL: Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. SC: Formal Analysis, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62466033), in part by the Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (20242BAB20070).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alaba, S. Y., and Ball, J. E. (2024). WCAM: wavelet convolutional attention module SoutheastCon 2024. SoutheastCon 2024, Atlanta, GA, United States, 15-24 March 2024 (IEEE), 854–859.
Awais, M., Muller, H., and Meriaudeau, F. (2017). Classification of sd-OCT images using a deep learning approach. IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications, 8120661–492. doi:10.1109/ICSIPA.2017.8120661
Bui, P.-N., Le, D.-T., Bum, J., and Choo, H. (2024). Multi-scale feature enhancement in multi-task learning for medical image analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.00351. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2412.00351
Burrus, C. S., Gopinath, R. A., and Guo, H. (1998). Wavelets and wavelet transforms. houston edition. Houston, TX: rice university, 98.
Cheng, J., Long, G., Zhang, Z., Qi, Z., Wang, H., Lu, L., et al. (2025). WaveNet-SF: a hybrid network for retinal disease detection based on wavelet transform in the spatial-frequency domain. arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.11854. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2501.11854
Diao, S., Su, J., Yang, C., Zhu, W., Xiang, D., Chen, X., et al. (2023). Classification and segmentation of OCT images for age-related macular degeneration based on dual guidance networks. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 84, 104810. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2023.104810
Dutta, P., Sathi, K. A., Hossain, M. A., and Dewan, M. A. A. (2023). Conv-ViT: a convolution and vision transformer-based hybrid feature extraction method for retinal disease detection. J. Imaging 9 (7), 140. doi:10.3390/jimaging9070140
Feng, S., Zhao, H., Shi, F., Cheng, X., Wang, M., Ma, Y., et al. (2020). CPFNet: context pyramid fusion network for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. imaging 39 (10), 3008–3018. doi:10.1109/TMI.2020.2983721
Finder, S. E., Amoyal, R., Treister, E., and Freifeld, O. (2024). Wavelet convolutions for large receptive fields European Conference on Computer Vision (Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland), 363–380. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-72949-2_21
Gao, R. X., and Yan, R. (2010). In Wavelets: theory and applications for manufacturing, From fourier transform to wavelet transform: a historical perspective. 17–32. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-1545-0_2
Gong, D., Li, W. T., Li, X. M., Wan, C., Zhou, Y. J., Wang, S. J., et al. (2024). Development and research status of intelligent ophthalmology in China. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 17 (12), 2308–2315. doi:10.18240/ijo.2024.12.20
Grossniklaus, H. E., Geisert, E. E., and Nickerson, J. M. (2015). Introduction to the retina. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 134, 383–396. doi:10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.06.001
He, J., Wang, J., Han, Z., Ma, J., Wang, C., and Qi, M. (2023). An interpretable transformer network for the retinal disease classification using optical coherence tomography. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 3637. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-30853-z
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 770–778. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Hong, J., Cheng, H., Wang, S. H., and Liu, J. (2019b). Improvement of cerebral microbleeds detection based on discriminative feature learning. Fundam. Inf. 168 (2-4), 231–248. doi:10.3233/fi-2019-1830
Hong, J., Cheng, H., Zhang, Y. D., and Liu, J. (2019a). Detecting cerebral microbleeds with transfer learning. Mach. Vis. Appl. 30 (7), 1123–1133. doi:10.1007/s00138-019-01029-5
Hong, J., Feng, Z., Wang, S. H., Peet, A., Zhang, Y. D., Sun, Y., et al. (2020a). Brain age prediction of children using routine brain MR images via deep learning. Front. Neurology 11, 584682. doi:10.3389/fneur.2020.584682
Hong, J., Wang, S. H., Cheng, H., and Liu, J. (2020b). Classification of cerebral microbleeds based on fully-optimized convolutional neural network. Multimedia Tools Appl. 79 (21), 15151–15169. doi:10.1007/s11042-018-6862-z
Hong, J., Yu, S. C. H., and Chen, W. (2022a). Unsupervised domain adaptation for cross-modality liver segmentation via joint adversarial learning and self-learning. Appl. Soft Comput. 121, 108729. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2022.108729
Hong, J., Zhang, Y. D., and Chen, W. (2022b). Source-free unsupervised domain adaptation for cross-modality abdominal multi-organ segmentation. Knowledge-Based Syst. 250, 109155. doi:10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109155
Hu, J., Shen, L., and Sun, G. (2018). Squeeze-and-excitation networks. Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. pattern Recognit., 7132–7141.
Huang, D., Swanson, E. A., Lin, C. P., Schuman, J. S., Stinson, W. G., Chang, W., et al. (1991). Optical coherence tomography. science 254 (5035), 1178–1181. doi:10.1126/science.1957169
Huang, L., He, X., Fang, L., Rabbani, H., and Chen, X. (2019). Automatic classification of retinal optical coherence tomography images with layer guided convolutional neural network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 26 (7), 1026–1030. doi:10.1109/lsp.2019.2917779
Ji, Y., Chen, N., Liu, S., Yan, Z., Qian, H., Zhu, S., et al. (2022). Research progress of artificial intelligence image analysis in systemic disease-related ophthalmopathy. Dis. Markers 2022 (1), 3406890. doi:10.1155/2022/3406890
Kamran, S. A., Saha, S., Sabbir, A. S., and Tavakkoli, A. (2019). Optic-net: a novel convolutional neural network for diagnosis of retinal diseases from optical tomography images, 2019 18th IEEE international conference on machine learning and applications (ICMLA), (IEEE), 964–971. doi:10.1109/ICMLA.2019.00165
Kaothanthong, N., Limwattanayingyong, J., Silpa-Archa, S., Tadarati, M., Amphornphruet, A., Singhanetr, P., et al. (2023). The classification of common macular diseases using deep learning on optical coherence tomography images with and without prior automated segmentation. Diagnostics 13 (2), 189. doi:10.3390/diagnostics13020189
Karthik, K., and Mahadevappa, M. (2023). Convolution neural networks for optical coherence tomography (OCT) image classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 79, 104176. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2022.104176
Kermany, D. S., Goldbaum, M., Cai, W., Valentim, C. C. S., Liang, H., Baxter, S. L., et al. (2018). Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell 172 (5), 1122–1131. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.010
Khalil, I., Mehmood, A., Kim, H., and Kim, J. (2024). OCTNet: a modified multi-scale attention feature fusion network with InceptionV3 for retinal OCT image classification. Mathematics 12 (19), 3003. doi:10.3390/math12193003
Laouarem, A., Kara-Mohamed, C., Bourennane, E. B., and Hamdi-Cherif, A. (2024). Htc-retina: a hybrid retinal diseases classification model using transformer-convolutional neural network from optical coherence tomography images. Comput. Biol. Med. 178, 108726. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108726
Li, F., Chen, H., Liu, Z., Zhang, X. D., Jiang, M. S., Wu, Z. Z., et al. (2019). Deep learning-based automated detection of retinal diseases using optical coherence tomography images. Biomed. Opt. express 10 (12), 6204–6226. doi:10.1364/BOE.10.006204
Li, S., Zhao, S., Zhang, Y., Hong, J., and Chen, W. (2024). Source-free unsupervised adaptive segmentation for knee joint MRI. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 92, 106028. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2024.106028
Lo, S.-Y., Hang, H.-M., Chan, S.-W., and Lin, J.-J. (2019). Efficient dense modules of asymmetric convolution for real-time semantic segmentation, Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Conference on Multimedia in Asia, 1–6. doi:10.1145/3338533.3366558
Manzari, O. N., Ahmadabadi, H., Kashiani, H., Shokouhi, S. B., and Ayatollahi, A. (2023). MedViT: a robust vision transformer for generalized medical image classification. Comput. Biol. Med. 157, 106791. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106791
Mehta, S., Rastegari, M., Caspi, A., Shapiro, L., and Hajishirzi, H. (2018). Espnet: efficient spatial pyramid of dilated convolutions for semantic segmentation, Proceedings of the european conference on computer vision (ECCV). 552–568. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-01249-6_34
Obuli, S. N. (2021). “Retinal OCT image classification - C8,”. San Francisco, CA: Kaggle. doi:10.34740/KAGGLE/DSV/2736749
Peng, J., Lu, J., Zhuo, J., and Li, P. (2023). Multi-scale-denoising residual convolutional network for retinal disease classification using OCT. Sensors 24 (1), 150. doi:10.3390/s24010150
Pennington, K. L., and DeAngelis, M. M. (2016). Epidemiology of age-related macular degeneration (AMD): associations with cardiovascular disease phenotypes and lipid factors. Eye Vis. 3, 34–20. doi:10.1186/s40662-016-0063-5
Qian, Z., Li, K., Kong, M., Qin, T., Yan, W., Xi, Z., et al. (2025). Enhanced diagnosis of thyroid-associated eye diseases based on deep learning: a novel triplet loss design strategy. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 100, 107161. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2024.107161
Robinson, B. E. (2003). Prevalence of Asymptomatic Eye Disease Prévalence des maladies oculaires asymptomatiques. Rev. Can. D'Optométrie 65 (5), 175.
Sharma, S., and Vardhan, M. (2025). AELGNet: attention-based enhanced local and global features network for medicinal leaf and plant classification. Comput. Biol. Med. 184, 109447. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.109447
Simonyan, K., and Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556.
Song, T., Zang, B., Kong, C., Zhang, X., Luo, H., Wei, W., et al. (2025). Construction of a predictive model for the efficacy of anti-VEGF therapy in macular edema patients based on OCT imaging: a retrospective study. Front. Med. 12, 1505530. doi:10.3389/fmed.2025.1505530
Song, X., Fang, X., Meng, X., Lv, M., and Zhuo, Y. (2024). Real-time semantic segmentation network with an enhanced backbone based on Atrous spatial pyramid pooling module. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 133, 107988. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2024.107988
Subramanian, M., Shanmugavadivel, K., Naren, O. S., Premkumar, K., and Rankish, K. (2022). Classification of retinal oct images using deep learning, 2022 international conference on computer communication and informatics (ICCCI) (IEEE), 1–7. doi:10.1109/ICCCI54379.2022.9740985
Sunija, A. P., Kar, S., Gayathri, S., Gopi, V. P., and Palanisamy, P. (2021). OCTnet: a lightweight cnn for retinal disease classification from optical coherence tomography images. Comput. methods programs Biomed. 200, 105877. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105877
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov, D., et al. (2015). Going deeper with convolutions, Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1–9. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., and Wojna, Z. (2016). Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision, Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern rRecognition, 2818–2826. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2016.308
Talukder, K. H., and Harada, K. (2010). Haar wavelet based approach for image compression and quality assessment of compressed image. arXiv preprint arXiv:1010.4084.
Tan, M., and Le, Q. (2019). “Efficientnet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks,” in International conference on machine learning. Long Beach, CA: PMLR, 6105–6114.
Tsuji, T., Hirose, Y., Fujimori, K., Hirose, T., Oyama, A., Saikawa, Y., et al. (2020). Classification of optical coherence tomography images using a capsule network. BMC Ophthalmol. 20, 1–9. doi:10.1186/s12886-020-01382-4
Wan, C., Mao, Y., Xi, W., Zhang, Z., Wang, J., and Yang, W. (2024). DBPF-net: dual-branch structural feature extraction reinforcement network for ocular surface disease image classification. Front. Med. 10, 1309097. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1309097
Wang, J., Deng, G., Li, W., Chen, Y., Gao, F., Liu, H., et al. (2019). Deep learning for quality assessment of retinal OCT images. Biomed. Opt. express 10 (12), 6057–6072. doi:10.1364/BOE.10.006057
Wu, X., Feng, Y., Xu, H., Lin, Z., Chen, T., Li, S., et al. (2023). CTransCNN: combining transformer and CNN in multilabel medical image classification. Knowledge-Based Syst. 281, 111030. doi:10.1016/j.knosys.2023.111030
Xiao, L., Li, X., Yang, S., and Yang, W. (2023). ADNet: lane shape prediction via anchor decomposition. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 6404–6413. doi:10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00589
Xu, J., Shen, J., Wan, C., Jiang, Q., Yan, Z., and Yang, W. (2022a). A few-shot learning-based retinal vessel segmentation method for assisting in the central serous chorioretinopathy laser surgery. Front. Med. 9, 821565. doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.821565
Xu, J., Shen, J., Yan, Z., Zhou, F., Wan, C., and Yang, W. (2022b). An intelligent location method of key boundary points for assisting the diameter measurement of central serous chorioretinopathy lesion area. Comput. Biol. Med. 147, 105730. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105730
Xu, J., Yang, W., Wan, C., and Shen, J. (2020). Weakly supervised detection of central serous chorioretinopathy based on local binary patterns and discrete wavelet transform. Comput. Biol. Med. 127, 104056. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.104056
Yang, M., Du, J., and Lv, R. (2025). CRAT: advanced transformer-based deep learning algorithms in OCT image classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 104, 107544. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2025.107544
Yu, F., and Koltun, V. (2015). Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:1511.07122.
Yu, S., Pang, S., Ning, J., Wang, M., and Song, L. (2025). ANC-Net: a novel multi-scale active noise cancellation network for rotating machinery fault diagnosis based on discrete wavelet transform. Expert Syst. Appl. 265, 125937. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2024.125937
Zhang, G., Sun, B., Zhang, Z., Wu, S., Zhuo, G., Rong, H., et al. (2022). Hypermixed convolutional neural network for retinal vein occlusion classification. Dis. Markers 2022 (1), 1730501. doi:10.1155/2022/1730501
Zhang, H., Dai, Y., Li, H., and Koniusz, P. (2019). Deep stacked hierarchical multi-patch network for image deblurring, Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 5978–5986. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2019.00613
Zhang, J., Tian, B., Tian, M., Si, X., Li, J., and Fan, T. (2025). A scoping review of advancements in machine learning for glaucoma: current trends and future direction. Front. Med. 12, 1573329. doi:10.3389/fmed.2025.1573329
Zhang, Z., Gao, Q., Fang, D., Mijit, A., Chen, L., Li, W., et al. (2024). Effective automatic classification methods via deep learning for myopic maculopathy. Front. Med. 11, 1492808. doi:10.3389/fmed.2024.1492808
Zhao, X., Huang, P., and Shu, X. (2022). Wavelet-Attention CNN for image classification. Multimed. Syst. 28 (3), 915–924. doi:10.1007/s00530-022-00889-8
Zheng, B., Zhang, M., Zhu, S., Wu, M., Chen, L., Zhang, S., et al. (2024). Research on an artificial intelligence-based myopic maculopathy grading method using EfficientNet. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 72 (Suppl. 1), S53–S59. doi:10.4103/IJO.IJO_48_23
Zhu, S., Lu, B., Wang, C., Wu, M., Zheng, B., Jiang, Q., et al. (2022). Screening of common retinal diseases using six-category models based on EfficientNet. Front. Med. 9, 808402. doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.808402
Keywords: retinal disease detection, multi-scale feature fusion, lesion localization, wavelet transform, noise suppression
Citation: Qi Z, Hong J, Cheng J, Long G, Wang H, Li S and Cao S (2025) MSLI-Net: retinal disease detection network based on multi-segment localization and multi-scale interaction. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1608325. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1608325
Received: 08 April 2025; Accepted: 12 May 2025;
Published: 06 June 2025.
Edited by:
Yanwu Xu, Baidu, ChinaReviewed by:
Shumao Pang, Guangzhou Medical University, ChinaJiaojiao Yu, Hubei University of Economics, China
Copyright © 2025 Qi, Hong, Cheng, Long, Wang, Li and Cao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jin Hong, aG9uZ2ppbkBuY3UuZWR1LmNu; Shuangliang Cao, Y3NsaWFuZ3VwQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Zhenjia Qi
Zhenjia Qi Jin Hong
Jin Hong Jilan Cheng1
Jilan Cheng1 Siyue Li
Siyue Li Shuangliang Cao
Shuangliang Cao