Abstract
Prostate cancer, ranking among the most prevalent malignancies in males worldwide, is undergoing a significant evolution in therapeutic paradigms from conventional approaches to precision medicine, with recent advances in targeted therapies offering novel strategic insights. This review delineates the molecular foundations of prostate carcinogenesis, elucidating pivotal domains including genetic mutations, hormonal regulation, tumor microenvironment dynamics, cell cycle dysregulation, epigenetic modifications, and tumor heterogeneity. Furthermore, we evaluate the clinical translation of targeted strategies such as AR signaling axis inhibition, PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway modulation, DNA damage repair machinery exploitation, prostate-specific membrane antigen -directed interventions, and combinatorial immunotherapy. Concurrent challenges—AR-driven heterogeneity, adaptive drug resistance mechanisms, spliceosomal vulnerabilities, and scarcity of selective molecular targets—are critically analyzed. Notwithstanding these obstacles, targeted therapies exhibit considerable potential to enhance therapeutic efficacy while mitigating systemic toxicities, paving the way for more personalized and precision-oriented oncologic care. By underscoring the imperative to decode prostate cancer’s molecular architecture, this work outlines future research priorities and advances a robust scientific framework for innovation in therapeutic development.
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
PROTACs degrade resistant AR variants–Novel AR degraders (e.g., ARV-110) overcome castration resistance in clinical trials.
PSMA theranostics redefine mCRPC management–225Ac-J591 achieves 46.9% PSA50 response with targeted alpha therapy.
PARP-ICI synergy exploits DDR defects–Olaparib/durvalumab combinations induce immunogenic death in HRR-deficient tumors.
Molecular stratification guides precision therapy–BRCA2 (56.6%), MSI-H, and AR-V7 serve as actionable biomarkers.
TME reprogramming reverses immunosuppression–AR inhibition synergizes with ICIs by downregulating PD-L1/Tregs.
1 Introduction
Prostate cancer (PCa), one of the most prevalent solid malignancies among men worldwide, represents a leading cause of male cancer-related mortality (Sung et al., 2021; Bergengren et al., 2023). For localized early-stage PCa, therapeutic options include radical prostatectomy, external beam radiotherapy, and androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), while advanced or metastatic disease typically necessitates multimodal approaches combining ADT with chemotherapy and radiation (Li et al., 2024). ADT has remained the cornerstone of PCa management for over seven decades, demonstrating unparalleled efficacy in disease control (Nabavi et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023). However, both surgical and pharmacological castration inevitably culminate in therapeutic resistance (Vigneswaran et al., 2021). Castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) emerges as the terminal trajectory for most patients, characterized by dismal clinical outcomes, with metastatic CRPC (mCRPC) exhibiting a median overall survival (OS) of less than 2 years (Lowrance et al., 2018). A significant proportion of patients with CRPC develop resistance to prior ADT or chemotherapy and experience systemic toxicities, accompanied by rising prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, AR mutations, and aberrant RNA transcription. Consequently, their survival benefit is typically less than six months—a stark imperative for novel therapeutic interventions (Jones et al., 2020; Kour et al., 2023; Carranza-Aranda et al., 2024; Lv et al., 2024).
Targeted therapy, an innovative oncologic strategy, operates through precise identification and engagement of tumor-specific molecular targets, diverging from conventional therapies that indiscriminately affect rapidly dividing cells. This approach offers superior selectivity, minimized off-target toxicity, and enhanced therapeutic precision (Qian et al., 2020; Pham et al., 2021; Viktorsson et al., 2023). The advent of targeted therapies has contributed to a shift in oncology—from traditional histology-driven chemoradiotherapy paradigms to molecularly informed personalized approaches. Building on this framework, this review synthesizes recent advancements in PCa-targeted therapeutics, encompassing molecular pathogenesis, contemporary pharmacologic agents, and innovative strategies, while providing a critical appraisal of persistent challenges and emerging countermeasures in this rapidly evolving field.
2 Molecular pathogenesis of prostate cancer
PCa represents a multifactorial disorder driven by intricate genetic and molecular alterations, as illustrated in Figure 1. A comprehensive understanding of its molecular underpinnings is pivotal for advancing targeted therapeutic strategies.
FIGURE 1
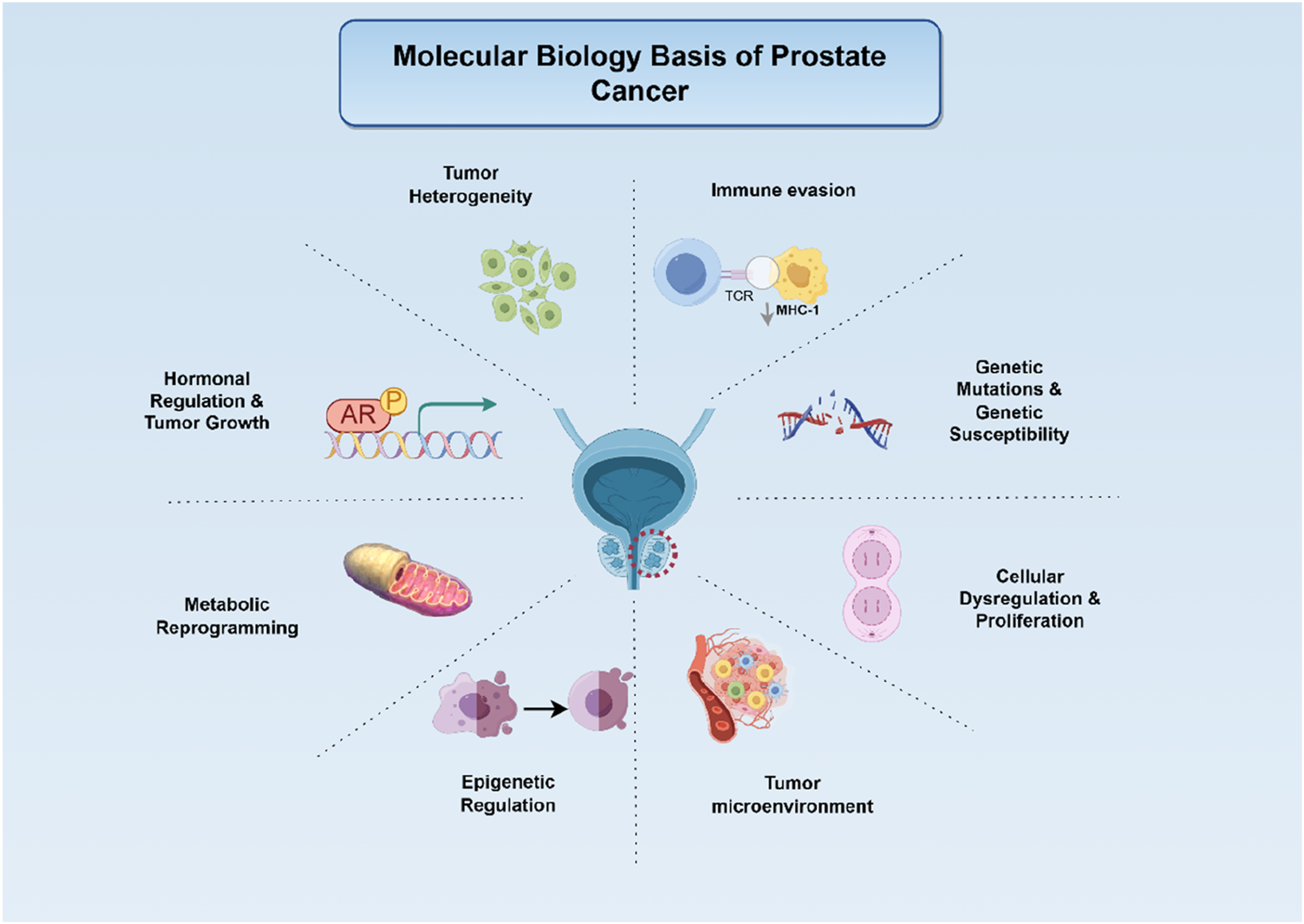
Biological mechanisms underlying prostate carcinogenesis and progression (Legend: Red circular dashed line: The location of PCa. Arrows: Activating or promoting effects. From top to bottom: (1) Tumour heterogeneity arises through clonal selection, generating sub-populations with distinct genomic/epigenomic profiles. (2) Immune evasion mechanisms allow tumour cells to escape immune surveillance. (3) Hormonal regulation centred on AR signalling supports tumour cell survival and proliferation. (4) Inherited genetic susceptibility and sporadic mutations destabilise the genome. (5) Metabolic reprogramming (aerobic glycolysis, lipid synthesis) fuels biomass production and redox balance. (6) Cellular Dysregulation and Proliferation is driven by cell-cycle checkpoint loss that trigger unchecked prostate-cancer cell division. (7) Epigenetic alterations (DNA methylation, histone modifications) silence tumour-suppressor genes and activate oncogenes. (8) The altered tumour microenvironment further promotes growth and metastasis).
2.1 Genetic mutations and hereditary predisposition
Genetic mutations and hereditary susceptibility serve as critical determinants in PCa pathogenesis. Table 1 summarizes the frequency of gene mutations closely associated with PCa. Among these, BRCA1/2 mutations—originally linked to breast and ovarian cancers—have emerged as significant risk amplifiers for PCa (Abida et al., 2020; Boussios et al., 2022; Fettke et al., 2023). These genes encode proteins essential for homologous recombination repair (HRR) of DNA double-strand breaks; their dysfunction leads to genomic instability and carcinogenesis. Chen et al. characterized BRCA germline mutations in Chinese PCa cohorts, analyzing 172 patients with BRCA1/2 alterations (Chen et al., 2022). The cohort exhibited a median diagnosis age of 67 (range: 34—89), with 54.65% (94/172) presenting metastatic castration-resistant disease, indicative of aggressive biology. Frameshift, missense, and splice variants predominated, with BRCA2 mutations surpassing BRCA1 in frequency. Notably, HOXB13, MSH2, and MSH6 mutations further contribute to PCa susceptibility.
TABLE 1
| BRCA1+ | BRCA2+ | AR+ | TP53+ | FOXA1+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17.46% (11–63) | 56.55% (82/145) | 15% (9/59) | 15% (9/59) | 34% (20/59) |
The proportion of important gene mutations related to prostate cancer.
HOXB13, a homeobox transcription factor critical in embryogenesis and tissue homeostasis, harbors pathogenic variants strongly associated with hereditary PCa (Nyberg et al., 2019). Mechanistically, Lu et al. demonstrated that HOXB13 recruits HDAC3 to suppress de novo lipogenesis and metastasis, while its loss or mutation drives lipid accumulation, enhancing tumor cell motility and metastatic potential (Lu et al., 2022). These findings suggest therapeutic utility of lipogenic pathway inhibitors in HOXB13-deficient PCa. MSH2 and MSH6, core components of DNA mismatch repair (MMR), safeguard replication fidelity. Their inactivation induces microsatellite instability (MSI), a biomarker of immunotherapy responsiveness. Wyvekens et al. evaluated 19 MMR-deficient PCa cases, identifying MSH2/MSH6 loss as the predominant defect, with distinct histopathological features aiding diagnostic recognition (Wyvekens et al., 2022).
2.2 Hormonal regulation and neoplastic progression
Androgen signaling, mediated via the androgen receptor (AR), remains central to PCa biology (Figure 2). Testosterone and its potent metabolite dihydrotestosterone (DHT) bind AR, a steroid receptor comprising four domains: N-terminal transcriptional regulation, DNA-binding, hinge, and ligand-binding. In unliganded states, AR resides in the cytoplasm, chaperoned by HSP90/70 complexes (Likos et al., 2022; Knerr et al., 2023). Ligand binding triggers conformational changes, nuclear translocation, dimerization, and DNA binding to androgen response elements, driving transcription of genes that promote proliferation, survival, and metastasis (Xie et al., 2022; Özturan et al., 2022; Sun et al., 2023).
FIGURE 2
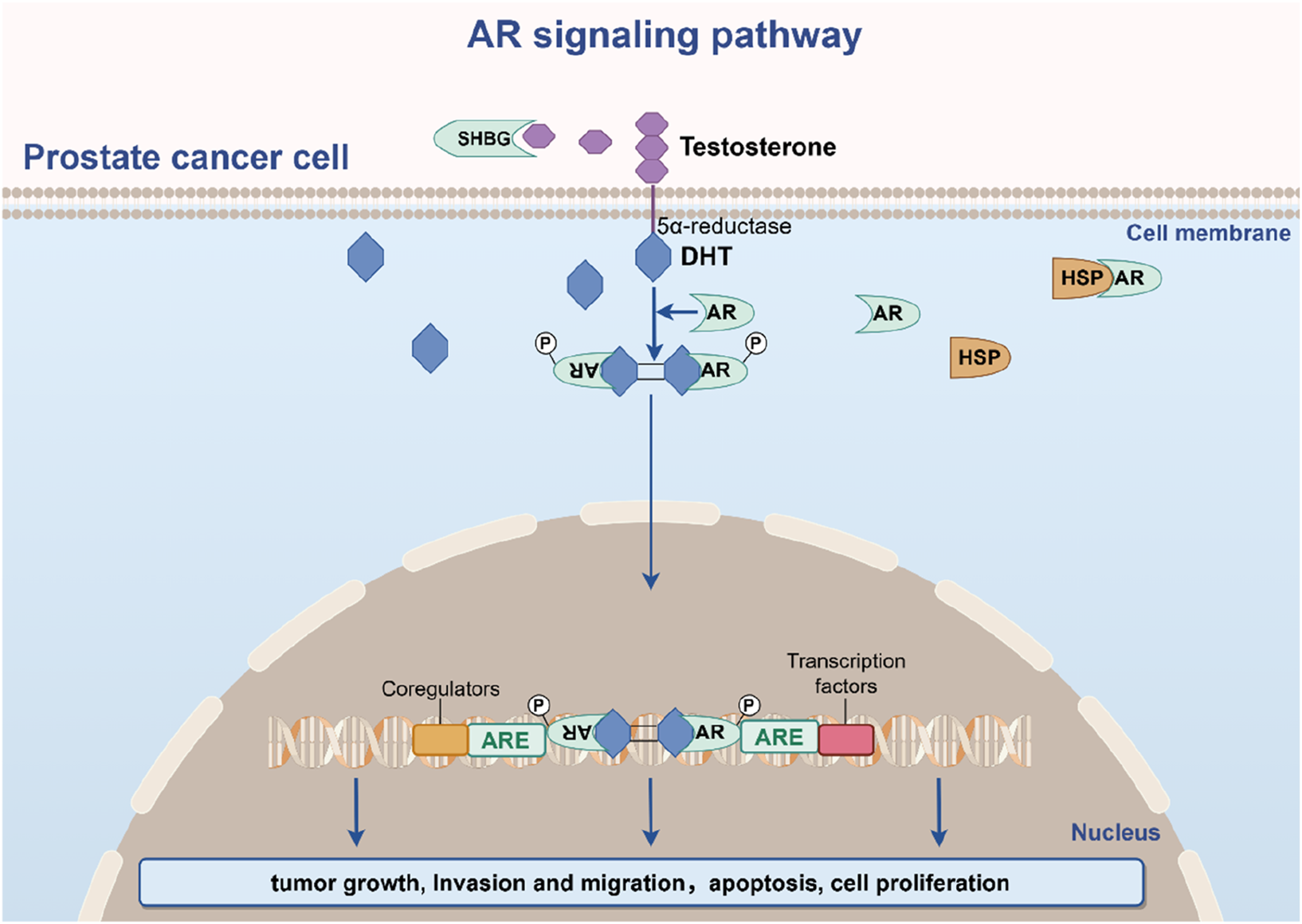
The AR signaling pathway in prostate cancer pathogenesis.
Early-stage PCa exhibits androgen dependence, making AR pathway inhibition a cornerstone of therapy for locally advanced or metastatic disease. However, adaptive mechanisms—AR amplification, gain-of-function mutations, splice variant generation (e.g., AR-V7), and downstream signaling rewiring—culminate in CRPC (Formaggio et al., 2021; Isebia et al., 2023). Beyond intrinsic tumor cell effects, androgens modulate the tumor microenvironment (TME) by polarizing tumor-associated macrophages, activating cancer-associated fibroblasts, suppressing immune surveillance, and stimulating angiogenesis (Hahn et al., 2023). Deciphering these multidimensional interactions is critical for identifying novel therapeutic vulnerabilities in PCa’s evolving landscape.
2.3 Tumor microenvironment and immune evasion
The TME and immune evasion mechanisms play pivotal roles in PCa progression. The TME constitutes a dynamic ecosystem comprising cancer cells, immune cells (e.g., tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), regulatory T cells (Tregs), natural killer (NK) cells), stromal fibroblasts, vascular networks, and extracellular matrix components. This milieu not only sustains tumor survival but also orchestrates immune evasion through multifaceted interactions (Kwon et al., 2021; Wong et al., 2022; Hirz et al., 2023). TAMs, particularly lipid-laden subsets, drive PCa invasiveness via IL-1β-mediated upregulation of MARCO, which reciprocally triggers CCL6 secretion to enhance cancer cell migration (Masetti et al., 2022). Tregs amplify immunosuppression by releasing TGF-β and IL-10, establishing an immune-tolerant niche linked to elevated recurrence risk (Karpisheh et al., 2021). Paradoxically, NK cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) exhibit dual roles—suppressing tumor growth or being co-opted to facilitate immune escape (Pasero et al., 2016; Ocana et al., 2017).
PCa cells employ multifaceted immune-editing mechanisms to evade immune surveillance, fostering clonal selection of immunoresistant subpopulations. Key immunosuppressive strategies involve the secretion of specific ligands and cytokines—such as PD-L1, TGF-β, and IL-10—which inhibit T-cell activation and promote Tregs expansion (Zhu et al., 2023). Additionally, PCa cells recruit inhibitory immune cells including myeloid-derived suppressor cells and M2-polarized TAMs via chemokine signaling (Wu et al., 2022). These cells further amplify immunosuppression through arginase-1, iNOS, and reactive oxygen species production, effectively dampening cytotoxic T-cell responses. Concurrently, downregulation of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules impairs antigen presentation, enabling tumor cells to evade CD8+ T-cell recognition. These processes collectively establish an immunosuppressive TME that shields tumors from cytotoxic immune responses, posing formidable therapeutic challenges.
2.4 Cell cycle dysregulation and proliferative signaling
Dysregulated cell cycle control is a hallmark of PCa pathogenesis. Normally governed by stringent checkpoints to ensure genomic fidelity, the cell cycle becomes hijacked in PCa through aberrant activation of proliferative pathways and inactivation of tumor suppressors. PTEN, a critical phosphatase, constrains PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling to inhibit uncontrolled growth. Its frequent loss in PCa leads to constitutive AKT activation, NF-κB-driven stemness, and evasion of growth suppression (Dubrovska et al., 2009; Kim et al., 2014). Concurrently, p53 dysfunction—via mutation or epigenetic silencing—compromises DNA damage response, enabling survival of genomically unstable clones (Macedo-Silva et al., 2023).
MYC proto-oncogene overexpression further disrupts cell cycle governance by antagonizing AR-mediated transcriptional programs and bypassing AR-dependent transcriptional pausing. This drives S-phase entry through upregulation of ribosome biogenesis genes and cyclin-dependent kinases, accelerating proliferation while fostering genomic instability (Qiu et al., 2022). The interplay between PTEN/PI3K/AKT, p53, and MYC pathways creates a complex regulatory nexus, complicating therapeutic targeting and underscoring the need for combinatorial strategies to address convergent oncogenic networks.
2.5 Epigenetic regulation and metabolic reprogramming
Epigenetic mechanisms—including DNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNA-mediated regulation—orchestrate PCa pathogenesis by modulating gene expression patterns without altering genomic sequences. These processes drive tumor progression, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance through transcriptional silencing or activation of critical pathways. Hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes, exemplified by GSTP1 inactivation in PCa, disrupts detoxification mechanisms and potentiates carcinogen-induced DNA damage, as evidenced by a meta-analysis of 15 studies (Zhou et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2020). Concurrently, histone acetylation/methylation dynamically remodels chromatin architecture to either enhance oncogenic transcription or repress tumor-suppressive programs (Metzger et al., 2019; Topchu et al., 2022; Nguyen et al., 2023).
Metabolic reprogramming represents an adaptive strategy for PCa cells to meet biosynthetic and energetic demands. Unlike normal prostate epithelium, PCa exhibits heightened lipogenesis and a pronounced Warburg effect—preferential glycolysis despite oxygen availability—to fuel rapid proliferation and therapy resistance (Lai et al., 2023). This metabolic shift is bidirectionally linked to epigenetic regulation: epigenetic modifiers directly control metabolic enzyme expression, while metabolites such as α-ketoglutarate and S-adenosylmethionine serve as cofactors for histone/DNA-modifying enzymes. Such crosstalk enables dynamic adaptation to microenvironmental stressors, fostering tumor survival and dissemination.
2.6 Tumor heterogeneity and evolutionary dynamics
PCa progression is defined by multidimensional heterogeneity—interpatient (intertumoral), intratumoral, and cellular—arising from clonal evolution under selective pressures. This diversity, driven by stochastic mutations, epigenetic plasticity, metabolic adaptations, and microenvironmental gradients, underpins therapeutic failure and relapse (Haffner et al., 2021; Chakraborty et al., 2023). Exome sequencing of 37 samples from 16 PCa patients revealed recurrent alterations in DNA damage repair (DDR) genes, RTK/RAS pathway components, and autophagy regulators, with copy number variation burden correlating with metastatic potential (Wu et al., 2020). Spatial heterogeneity in oxygen tension and nutrient availability further selects for clones optimized for survival in hypoxic or nutrient-deprived niches (Peitzsch et al., 2022).
The TME acts as both a driver and consequence of heterogeneity, fostering competitive interactions between clones with divergent genetic, epigenetic, and metabolic profiles. This evolutionary arms race necessitates polytherapeutic strategies targeting core vulnerabilities across heterogeneous subpopulations to mitigate adaptive resistance.
3 Current targeted therapeutics and clinical strategies
Targeted therapies have revolutionized the management of PCa, offering patients more precise and effective treatment options. By specifically targeting key molecules and pathways driving tumor growth and dissemination, these therapies minimize damage to normal cells, achieving superior therapeutic efficacy and reduced systemic toxicity compared to conventional approaches. In PCa, therapeutic focus centers on critical biomarkers such as the AR, proliferative signaling cascades, and DNA repair mechanisms. Advances in basic research and clinical trials continue to expand the pipeline of targeted agents and combination strategies, heralding a new era of innovation in PCa therapeutics. Current investigational agents under clinical evaluation are summarized in Table 2.
TABLE 2
| Trial identification | Drug name | Target | Trial phase | No. of patients | Target disease (prior therapy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTR20150501 | GT0918 | AR | phase I | 16 | CRPC (Chemotherapy failure) |
| NCT02861573 | Pembrolizumab | PD-1 | phase Ib/II | 102 | CRPC (ADT failure) |
| NCT02361086 | ODM-204 | CYP17A1/AR | phase I | 23 | CRPC (ADT failure) |
| NCT02709889 | Rovalpituzumab tesirine (SC16LD6.5) | AR | phase II | 99 | CRPC (ADT failure) |
| NCT03888612 | Bavdegalutamide | AR | phase I/II | 195 | mCRPC (ADT failure) |
| NCT02121639 | Capivasertib | AKT | phase II | 150 | CRPC (Chemotherapy failure) |
| NCT04087174 | Capivasertib | PI3K/AKT/mTOR | phase Ib | 27 | nmCRPC (ADT failure) |
| NCT02407054 | Samotolisib | PI3K and mTOR | phase Ib/II | 13/129 | mCRPC (ADT failure) |
| NCT03017833 | Sapanisertib (CB-228/TAK-228) | mTORC1/2 | phase I | 30 | PCa (ADT failure) |
| NCT02215096 | GSK2636771 | PI3Kβ | phase I | 37 | CRPC (ADT failure) |
| NCT03317392 | Olaparib | PARP | phase I | 12 | mCRPC (ADT failure) |
| NCT04169841 | Olaparib | PARP | phase II | 213 | PCa (ADT failure) |
| NCT03431350 | Niraparib | PARP | phase II | 24 | mCRPC (ADT failure) |
| NCT02924766 | Niraparib | PARP1/2 | phase Ib | 33 | mCRPC (ADT failure) |
| NCT02854436 | Niraparib | PARP1/2 | phase II | 289 | mCRPC (ADT failure) |
| NCT03276572 | 225Ac-J591 | PSMA | phase II | 32 | mCRPC (Chemotherapy or ADT failure) |
| NCT03999749 | JNJ-63898081 | PSMA | phase I | 39 | mCRPC (Chemotherapy or ADT failure) |
| NCT02484404 | Olaparib + durvalumab | PARP + PD-L1 | phase II | 17 | mCRPC (Chemotherapy or ADT failure) |
| NCT03016312 | Enzalutamide + Atezolizumab | AR + PD-L1 | phase Ⅲ | 759 | mCRPC (ADT failure) |
| NCT03805594 | 177Lu-PSMA-617+pembrolizumab | PSMA + PD-1 | phase I | 43 | mCRPC (ADT failure) |
List of drug information during clinical trials.
3.1 Targeting the androgen receptor signaling pathway
3.1.1 Clinical applications of second-generation antiandrogens and emerging agents
The AR signaling axis plays a central role in PCa initiation and progression. While ADT remains a mainstay by suppressing AR activity, long-term treatment inevitably leads to resistance (Obinata et al., 2024). Recent discoveries of novel AR-associated targets have spurred the development of next-generation antiandrogens. Second-generation agents such as enzalutamide and abiraterone inhibit AR signaling through distinct mechanisms, demonstrating robust antitumor activity and improved clinical outcomes in mCRPC (Mitsogianni et al., 2023; Obinata et al., 2024). Nevertheless, resistance persists in a subset of patients, driving exploration of novel AR-targeted strategies.
A phase I trial evaluated GT0918, a novel AR antagonist, in 16 patients with mCRPC across five escalating dose cohorts (Zhou et al., 2020). Ten and two patients completed three and six treatment cycles, respectively. Six patients achieved ≥30% PSA decline, with two attaining ≥50% reduction. Stable disease was observed in all 12 patients with metastatic soft tissue lesions. GT0918 demonstrated high AR binding affinity, downregulation of AR protein expression, and favorable tolerability, suggesting promising antitumor activity in the CRPC population.
Combination strategies leveraging multi-target inhibition are gaining momentum. ODM-204, a dual CYP17A1/AR inhibitor, was tested in a clinical trial where 13% of patients achieved ≥50% PSA reduction by week 12, with 60.9% experiencing mild treatment-related adverse events (Peltola et al., 2020). ODM-204 was well-tolerated, with preliminary antitumor activity observed in mCRPC. In a preclinical study, Baker et al. developed a combinatorial nanotherapeutic platform—abiraterone-enzalutamide bio-conjugated survivin-encapsulated gold nanoparticles (AbEzSvGNPs)—for targeted PCa therapy (Baker et al., 2023). Compared to free abiraterone and enzalutamide, AbEzSvGNPs exhibited enhanced cytotoxicity against DU145(IC50 = 4.21 μM) and PC-3(IC50 = 5.58 μM) cells while showing no significant toxicity in normal rat kidney cells.
3.1.2 Advances in PROTAC-Based targeted therapies
Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) represent a novel therapeutic modality in PCa, leveraging the ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade pathogenic proteins—a mechanism distinct from traditional small-molecule inhibition (Wang et al., 2025). PROTACs are heterobifunctional molecules comprising three components: a target protein ligand, an E3 ubiquitin ligase recruiter, and a linker. By bridging the target protein with an E3 ligase, PROTACs induce ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of the target (Zeng et al., 2021). This approach has garnered significant attention in oncology, particularly for addressing resistant AR variants and castration-resistant AR signaling in PCa.
ARV-110 (bavdegalutamide), the first PROTAC to enter clinical trials, is currently in phase II evaluation for mCRPC. ARV-110, an orally bioavailable, CRBN-based AR degrader developed by Arvinas, Inc., demonstrated promising efficacy in a phase I/II trial. It reduced PSA levels by ≥ 50% in 40% of patients with mCRPC harboring specific genetic alterations. Furthermore, in initial clinical studies, biopsy data from one patient showed a 70%–90% reduction in AR levels (Liu et al., 2022). Malarvannan et al. highlighted the potential of PROTACs to overcome drug resistance and target “undruggable” proteins, citing ARV-110 and ARV-766 (another AR-directed PROTAC in phase II trials for CRPC) as exemplars (Malarvannan et al., 2025). Omar et al. reviewed advancements in PROTAC design, proposing the use of heterocyclic compounds as warheads to optimize binding affinity, selectivity, and pharmacokinetic properties (Omar et al., 2025). This structural refinement enhances PROTAC efficacy, positioning them as promising tools for addressing persistent challenges in PCa therapy.
3.2 Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling axis
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, a critical oncogenic cascade, drives PCa progression by promoting tumor cell proliferation, migration, and therapeutic resistance through aberrant activation (Pungsrinont et al., 2021; Wylaź et al., 2023; Yi et al., 2023). Multiple PI3K, AKT, and mTOR inhibitors have entered clinical trials, demonstrating variable antitumor efficacy. Emerging next-generation inhibitors aim to enhance therapeutic precision while minimizing adverse effects.
Capivasertib, a pan-AKT inhibitor, exhibits synergistic activity with docetaxel in mCRPC. In a randomized phase II trial involving 150 mCRPC patients receiving up to 10 cycles of docetaxel (21-day cycles), capivasertib combined with chemotherapy prolonged OS, though these findings require prospective validation to address potential biases (Crabb et al., 2021). A phase Ib study further evaluated capivasertib (400 mg twice daily, 4 days on/3 days off) combined with abiraterone acetate (1,000 mg daily) and prednisone (5 mg twice daily) in mCRPC. Nine patients (33%) achieved ≥20% PSA decline, with no dose-limiting toxicities observed, supporting further investigation of this regimen (Shore et al., 2023).
Samotolisib, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor employing intermittent target suppression, demonstrated enhanced tolerability and delayed resistance in a blinded, placebo-controlled Ib/II trial (Sweeney et al., 2022). Phase Ib (n = 13) revealed no dose-limiting toxicities, while phase II (n = 129) showed significantly prolonged median progression-free survival (PFS) and radiographic PFS(rPFS) in the samotolisib/enzalutamide arm versus placebo. This underscores the feasibility of combining PI3K/mTOR inhibition with AR-targeted therapy.
Subbiah et al. explored sapanisertib, an ATP-competitive mTORC1/2 inhibitor, combined with metformin in patients with mTOR/AKT/PI3K pathway-altered advanced malignancies (Subbiah et al., 2024). The combination exhibited tolerable safety and antitumor activity, particularly in PTEN-mutated cohorts. Metformin’s AMPK-mediated mTOR suppression may potentiate sapanisertib’s efficacy, offering a rationale for dual metabolic-oncogenic targeting in PCa. A phase I dose-escalation study of GSK2636771(PI3Kβ inhibitor) with enzalutamide in PTEN-deficient mCRPC(n = 37) reported a 50% non-progression rate at 12 weeks with the recommended 200 mg dose, though objective responses remained limited (1 patient with 36-week partial response) (Sarker et al., 2021). These data highlight modest activity despite acceptable safety, emphasizing the need for biomarker-driven patient selection. In addition, bioactive phytochemicals, including flavonoids, terpenoids, alkaloids, lignans, phenolic acids, and polysaccharides, exhibit preclinical efficacy in PCa through selective modulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. These natural agents regulate downstream effectors to suppress tumor proliferation, induce apoptosis, and reverse therapeutic resistance, positioning them as promising candidates for adjunctive therapeutic modalities or complementary strategies in PCa management (Lu et al., 2020; León-González et al., 2021; Jeong et al., 2023; Elsayed and Fahim, 2025; Filippi et al., 2025).
3.3 Targeting DNA damage repair pathways
Dysregulation of DDR mechanisms is a hallmark of prostate carcinogenesis. Therapeutic strategies targeting these pathways have demonstrated clinical promise, particularly in genetically defined subsets of PCa. PARP inhibitors, such as olaparib and rucaparib, exploit synthetic lethality by impairing base excision repair in tumors with homologous recombination deficiency, notably those harboring BRCA1/2 mutations (Teyssonneau et al., 2021; Stracker et al., 2023).
A phase I dose-escalation study evaluated olaparib combined with radium-223 in mCRPC patients with bone metastases, establishing a recommended phase II dose (RP2D) of 200 mg twice daily for olaparib when administered with radium-223 (Pan et al., 2023). Niraparib (NIRA), a selective PARP1/2 inhibitor, was investigated in a phase II trial combining it with abiraterone acetate and prednisone in mCRPC patients progressing on androgen receptor signaling inhibitors (ARSIs) and taxanes (Chi et al., 2023). The regimen showed measurable antitumor activity and manageable toxicity, supporting further exploration. A phase Ib trial further assessed NIRA paired with apalutamide or abiraterone acetate/prednisone (AAP) in mCRPC, confirming tolerability and identifying NIRA 200 mg as the RP2D for combination with AAP (Saad et al., 2021). In a multicenter phase II study (n = 289), niraparib exhibited clinical activity in heavily pretreated mCRPC patients with DDR defects, particularly BRCA-mutated cohorts, reinforcing its therapeutic potential in biomarker-selected populations (Smith et al., 2022).
3.4 PSMA-targeted therapeutic innovations
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), a transmembrane glycoprotein overexpressed in PCa with expression levels correlating to tumor aggressiveness, has emerged as a cornerstone for precision theranostics. Current PSMA-directed strategies encompass radioligand therapies (e.g., 177Lu-PSMA-617, 225Ac-PSMA-RLT), antibody-drug conjugates (MLN2704, PSMA-MMAE), cellular immunotherapies (PSMA-CAR-T, BiTEs), and experimental modalities such as photodynamic therapy and ultrasound-mediated nanobubble ablation. Radioligand therapies, characterized by high tumor specificity and reduced off-target toxicity, are increasingly prioritized for their ability to overcome tumor heterogeneity (Parghane and Basu, 2023; Desai et al., 2024; Ling et al., 2024; Nakajima, 2024; Ye et al., 2024; Belabaci et al., 2025). A phase I dose-escalation trial of 225Ac-J591, an α-emitting anti-PSMA monoclonal antibody, demonstrated preliminary efficacy in 32 patients with progressive mCRPC, with 46.9% achieving ≥50% PSA decline (34.4% confirmed) and 59.1% exhibiting circulating tumor cell control, alongside a manageable safety profile (Tagawa et al., 2024). At the final follow-up, disease progression and/or death had occurred in nearly all patients (29 out of 32). The median PFS was 5.6 months (95% CI, 3.7–7.9), and the median OS was 10.7 months. Similarly, a phase I study of JNJ-63898081 (JNJ-081), a PSMA-targeted agent, explored intravenous (0.3–3.0 µg/kg) and subcutaneous (3.0–60 µg/kg) administration in 39 mCRPC patients. While dose-limiting toxicities occurred in four cases, transient PSA reductions were observed at subcutaneous doses ≥30 µg/kg, suggesting therapeutic potential despite challenges such as cytokine release syndrome at higher doses (Lim et al., 2023). The integration of PSMA-PET/CT into clinical workflows has revolutionized diagnostic staging and restaging, enabling precise patient stratification for PSMA-directed therapies. However, the synergistic potential of combining PSMA-targeted approaches with standard treatments remains underexplored, necessitating further investigation to optimize combinatorial efficacy and safety. Advances in radiopharmaceutical engineering and imaging technologies are poised to refine therapeutic precision, offering renewed hope for metastatic PCa management through tumor-selective targeting and minimized systemic toxicity.
3.5 Combinatorial targeted and immunotherapeutic strategies in prostate cancer
The integration of targeted therapies with immunomodulatory agents represents an important strategy in PCa management. Targeted therapies disrupt oncogenic signaling by selectively inhibiting molecular drivers of tumorigenesis, while immunotherapies harness the host immune system to eradicate residual disease. This synergy is amplified by the ability of targeted agents to remodel the TME, enhance tumor antigen presentation, and potentiate immune effector cell activity, thereby overcoming limitations of monotherapy and improving therapeutic efficacy and tolerability (Zhu et al., 2021).
3.5.1 PARP inhibitors and immune checkpoint blockade
The combination of PARP inhibitors with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) exploits dual mechanisms of synthetic lethality and immune activation. PARP inhibitors impair DNA repair via PARP enzyme blockade, inducing lethal DNA damage in homologous recombination repair (HRR)-deficient tumors (e.g., BRCA1/2-mutated PCa) (Wu et al., 2021). Concurrently, ICIs such as anti-PD-1/PD-L1 or anti-CTLA-4 agents reinvigorate T-cell-mediated antitumor responses, which are often suppressed in PCa(Catalano et al., 2022).
Crucially, the efficacy of this combinatorial strategy is highly dependent on the specific underlying DDR defect. A growing body of clinical evidence indicates that tumors harboring “BRCA1/2” mutations derive the greatest benefit. For instance, in the phase I/II Study study (n = 17), the combination of olaparib and durvalumab in mCRPC demonstrated a higher objective response rate (ORR) in patients with “BRCA1/2” alterations compared to those with other HRR gene mutations (Karzai et al., 2018).
A phase II trial evaluating durvalumab (anti-PD-L1) and tremelimumab (anti-CTLA-4) with olaparib in HRR-deficient solid tumors demonstrated synergistic immunogenic cell death and disease stabilization, supporting further exploration in PCa cohorts (Fumet et al., 2020). Meta-analyses of clinical trials reveal superior ORR, prolonged median progression-free survival, and significant PSA reductions with PARP-ICI combinations compared to monotherapy, alongside acceptable toxicity profiles (Mateo et al., 2015; Karzai et al., 2018; Antonarakis et al., 2020). However, increased risks of hematologic abnormalities, gastrointestinal toxicity, and immune-related adverse events necessitate vigilant monitoring and refined, biomarker-guided patient selection, prioritizing those with “BRCA1/2” mutations for the most robust clinical benefit (Hunia et al., 2022).
3.5.2 AR pathway inhibition and immunotherapy synergy
AR inhibitors modulate the immunosuppressive TME by downregulating PD-L1 expression, reducing Tregs infiltration, and enhancing CD8+ T-cell functionality (Cordes et al., 2018; Dib et al., 2019). Preclinical studies demonstrate that AR blockade mitigates T-cell exhaustion and augments interferon-γ signaling, sensitizing tumors to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition (Guan et al., 2022). Clinical trials, however, yield mixed outcomes. The KEYNOTE-365 Cohort C trial (Ib/II phase) reported limited antitumor activity for enzalutamide combined with pembrolizumab in chemotherapy-naïve mCRPC patients post-abiraterone failure, though safety profiles aligned with individual agent characteristics (Yu et al., 2024). Conversely, a phase III trial (n = 759) showed improved PFS in mCRPC patients with high PD-L1(IC2/3) and CD8+ gene expression treated with enzalutamide plus atezolizumab, though OS benefits were not observed (Powles et al., 2022). These findings underscore the need for biomarker-driven stratification and optimized dosing to address heterogeneous responses and mitigate immune-related toxicities.
3.5.3 PSMA-targeted and immunotherapeutic convergence
PSMA-directed therapies synergize with immunotherapies through multimodal mechanisms: 1. Radioligand-induced immunogenic cell death: 177Lu-PSMA-617 and 225Ac-PSMA-RLT trigger tumor apoptosis and neoantigen release, enhancing immune recognition and dendritic cell activation (Pouget et al., 2023). 2. TME reprogramming: Radiation-induced DNA damage stimulates STING pathway activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion, augmenting ICI efficacy (Bellavia et al., 2022; Pouget et al., 2023). 3. Antibody-drug conjugate precision: PSMA-MMAE and similar agents deliver cytotoxic payloads directly to tumor cells while sparing normal tissues, concurrently promoting immune cell infiltration and activation (Lanka et al., 2023).
Early-phase trials demonstrate enhanced ORR and manageable toxicity with 177Lu-PSMA-617 plus PD-1 inhibitors in mCRPC, including a phase I study where pembrolizumab combination therapy achieved superior activity and reduced adverse events compared to monotherapy (Prasad et al., 2021; Aggarwal et al., 2023). These data highlight the potential of PSMA-immune combinatorial strategies to redefine metastatic PCa treatment paradigms.
4 Challenges and strategic countermeasures in targeted therapy
While targeted therapies have revolutionized PCa management, inherent challenges—including clonal heterogeneity, adaptive resistance, and tumor evolution—persist, necessitating innovative solutions to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
4.1 AR heterogeneity and therapeutic resistance
The AR, a master regulator of male reproductive physiology, exhibits profound heterogeneity across patients and tumor subclones, driven by genetic mutations (e.g., AR-V7 splice variants), post-translational modifications (phosphorylation, acetylation), and epigenetic rewiring (Zamagni et al., 2019; Jaiswal et al., 2022; Kim et al., 2022; Wasim et al., 2022). This variability underpins divergent responses to ADT, with subsets of patients developing resistance through mechanisms such as AR amplification, ligand-independent activation, or glucocorticoid receptor crosstalk (Germain et al., 2020). Paradoxically, AR remains the dominant oncogenic driver in CRPC, yet ARSIs—clinically deployed for over seven decades—yield transient benefits, as most patients progress to CRPC within 12–18 months (Germain et al., 2020). Emerging strategies to circumvent resistance include: 1. Next-generation PROTACs: Advancing beyond first-generation AR degraders, novel dual-target PROTACs are being engineered to simultaneously degrade AR and other key resistance-driving proteins, such as epigenetic regulators (e.g., BRD4) or kinases (e.g., CDK9). This polypharmacological approach can more comprehensively dismantle the oncogenic network and overcome compensatory pathways that lead to single-agent resistance. 2. AR splice variant-specific inhibitors: The AR-V7 variant, which lacks the ligand-binding domain, is a major driver of resistance to conventional antiandrogens. New therapeutic modalities, including small-molecule inhibitors specifically designed to target the unique constitutive activation domain of AR-V7, and monoclonal antibodies that selectively recognize and neutralize AR-V7, are under active investigation to address this critical vulnerability. 3. Subtype-selective AR targeting: Beyond splice variants, development of agents targeting other AR isoforms or specific post-translationally modified AR states. 4. Multimodal combination regimens: Integrating ADT with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or immune checkpoint inhibitors to exploit synthetic lethality and delay resistance. 5. Epigenetic modulation: Targeting AR co-regulators (e.g., FOXA1, HOXB13) to dismantle compensatory signaling networks. Prospective research must prioritize longitudinal genomic profiling to map AR evolutionary trajectories and identify predictive biomarkers for stratified therapeutic interventions.
4.2 Vulnerabilities in alternative splicing and hereditary predisposition
Hereditary predisposition accounts for 10%–20% of PCa cases, with germline mutations in genes such as BRCA2, HOXB13, and MMR pathways contributing to familial clustering (Brandão et al., 2020; Rosellini et al., 2021). Multigene panel testing has identified conserved signaling pathways across hereditary cancers, providing insights into pan-cancer susceptibility mechanisms and enabling molecular stratification to reduce patient heterogeneity (Rosellini et al., 2021). Alternative splicing, a process frequently dysregulated in tumors, disrupts critical pathways involved in drug metabolism, nuclear receptor activation, apoptosis regulation, and immunotherapy response, thereby promoting therapeutic resistance (Ku et al., 2019; Sciarrillo et al., 2020; Li et al., 2023; Seltzer et al., 2023). Clinically, genetic counseling, germline testing, and systematic PSA screening are recommended for high-risk individuals and families to guide early intervention and personalized management (Çelik et al., 2021; Tímár and Uhlyarik, 2022). Addressing splicing-related vulnerabilities and hereditary risk stratification may enhance precision oncology strategies in PCa.
4.3 Challenges in selective therapeutic target identification
The development of effective targeted therapies relies on identifying selective molecular targets—proteins or enzymes with which drugs can interact to exert therapeutic effects. However, the complexity and redundancy of biological systems complicate the discovery of such targets, often leading to off-target interactions, unintended systemic effects, and reduced therapeutic efficacy (Dong et al., 2021). Non-selective drug activity not only diminishes clinical outcomes but also poses safety risks, prolongs drug development timelines, and escalates costs. Recent advances have uncovered potential targets through mechanistic studies of prostate carcinogenesis. For instance, circTENM3 suppresses PCa progression by upregulating RUNX3 expression (Janik et al., 2020), while the circSMARCA5/miR-432/PDCD10 axis emerges as a promising therapeutic node via modulation of apoptotic pathways (Lu et al., 2023). Computational approaches, including molecular docking and AI-driven database mining, now accelerate target prediction and drug candidate screening, optimizing preclinical workflows (Ling et al., 2020; Vietri et al., 2021). Additionally, polypharmacological strategies—designing agents that engage multiple targets—may address pathway redundancy while balancing efficacy and toxicity (Chang et al., 2025). These innovations underscore ongoing efforts to overcome target identification barriers and expand precision therapeutic options.
4.4 Management of targeted therapy-related adverse effects
The management of adverse effects remains a critical challenge in PCa targeted therapy. While these therapies demonstrate precision in suppressing tumor growth, they often induce systemic toxicities such as gastrointestinal disturbances, immune-related complications, fatigue, hypertension, and hepatotoxicity, which can significantly compromise patient quality of life (Sandhu et al., 2021; Vietri et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2023). PSMA-targeted radioligand therapies, now established for mCRPC, are under evaluation in earlier disease states, necessitating vigilant monitoring of hematologic and renal parameters (Germain et al., 2020). Similarly, novel ARSIs improve survival in non-castration-resistant metastatic and non-metastatic CRPC but are associated with metabolic and cardiovascular side effects. Optimizing treatment regimens through dose adjustment, preemptive management of predictable toxicities, and enhanced real-time surveillance can mitigate adverse event incidence. Future advancements will rely on prospective clinical trials to refine therapeutic sequencing and combinatorial strategies, aiming to delay resistance while minimizing toxicity. Continued research into molecular mechanisms of drug-related toxicity will further enable the development of safer, more selective agents, ultimately improving the therapeutic index in PCa management.
5 Conclusion
Targeted therapies have emerged as a cornerstone of precision oncology in PCa, marked by significant advancements in modulating the AR signaling axis, PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, DNA damage repair machinery, and PSMA-directed theranostics. However, the clinical translation of these strategies faces formidable challenges, including AR heterogeneity, spliceosome-driven adaptive resistance, limited target selectivity, and the management of treatment-related adverse events. Addressing these obstacles will require interdisciplinary collaboration, leveraging technologies such as CRISPR-based gene editing, polypharmacological agent design, and artificial intelligence-driven drug discovery to refine therapeutic precision and overcome biological complexity.
Future progress in PCa treatment will depend on integrating mechanistic insights with technological innovation. Future progress will depend on elucidating tumor heterogeneity, optimizing multi-targeted therapeutic regimens, and integrating computational approaches for accelerated drug development. As scientific understanding deepens and translational pipelines mature, the goal of highly personalized, durable PCa management becomes increasingly attainable, potentially enabling metastatic progression to be managed as a chronic condition rather than a terminal diagnosis.
Statements
Author contributions
LW: Writing – original draft. JQ: Writing – original draft. ZH: Writing – original draft. QW: Writing – review and editing. QL: Writing – review and editing. WZ: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We appreciated the Figdraw (www.figdraw.com) for their assistance in drawing.
Conflict of interest
Author QL was employed by Shenzhen Bao’an Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Group.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AAP, Abiraterone acetate/prednisone; AbEzSvGNPs, Abiraterone-enzalutamide bioconjugated survivin-encapsulated gold nanoparticles; ADT, Androgen Deprivation Therapy; ARSIs, Androgen receptor signaling inhibitors; CRPC, Castration-resistant prostate cancer; DDR, DNA damage repair; DHT, Dihydrotestosterone; HRR, Homologous recombination repair; ICIs, Immune checkpoint inhibitors; MMR, Mismatch repair; MSI, Microsatellite instability; NIRA, Niraparib; NK, Natural killer; ORR, Objective response rates; OS, Overall survival; PCa, Prostate cancer; PROTACs, Proteolysis-targeting chimeras; PSA, Prostate-specific antigen; PSMA, Prostate-specific membrane antigen; RP2D, Recommended phase II dose; TAMs, Tumor-associated macrophages; TILs, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes; TME, Tumor microenvironment; Tregs, Regulatory T cells.
References
1
Abida W. Patnaik A. Campbell D. Shapiro J. Bryce A. H. McDermott R. et al (2020). Rucaparib in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer harboring a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene alteration. J. Clin. Oncol.38 (32), 3763–3772. 10.1200/JCO.20.01035
2
Aggarwal R. Starzinski S. de Kouchkovsky I. Koshkin V. Bose R. Chou J. et al (2023). Single-dose (177)Lu-PSMA-617 followed by maintenance pembrolizumab in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: an open-label, dose-expansion, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol.24 (11), 1266–1276. 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00451-5
3
Antonarakis E. S. Piulats J. M. Gross-Goupil M. Goh J. Ojamaa K. Hoimes C. J. et al (2020). Pembrolizumab for treatment-refractory metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: multicohort, open-label phase II KEYNOTE-199 study. J. Clin. Oncol.38 (5), 395–405. 10.1200/JCO.19.01638
4
Baker A. Syed A. Mohany M. Elgorban A. M. Sajid Khan M. Al-Rejaie S. S. (2023). Survivin-targeted nanomedicine for increased potency of abiraterone and enzalutamide against prostate cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm.192, 88–111. 10.1016/j.ejpb.2023.10.005
5
Belabaci Z. Schmidt L. Sleiay M. Couñago F. Campos F. L. Tolba M. et al (2025). Efficacy and safety of rechallenge therapy with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 10.1007/s00259-025-07438-1
6
Bellavia M. C. Patel R. B. Anderson C. J. (2022). Combined targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy and immune checkpoint blockade: from preclinical advances to the clinic. J. Nucl. Med.63 (11), 1636–1641. 10.2967/jnumed.122.264373
7
Bergengren O. Pekala K. R. Matsoukas K. Fainberg J. Mungovan S. F. Bratt O. et al (2023). 2022 update on prostate cancer epidemiology and risk Factors-A systematic review. Eur. Urol.84 (2), 191–206. 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.04.021
8
Boussios S. Rassy E. Moschetta M. Ghose A. Adeleke S. Sanchez E. et al (2022). BRCA mutations in ovarian and prostate cancer: bench to bedside. Cancers (Basel)14 (16), 3888. 10.3390/cancers14163888
9
Brandão A. Paulo P. Teixeira M. R. (2020). Hereditary predisposition to prostate cancer: from genetics to clinical implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci.21 (14), 5036. 10.3390/ijms21145036
10
Carranza-Aranda A. S. Santerre A. Segura-Cabrera A. Cárdenas-Vargas A. Martínez-Velázquez M. Hernández-Gutiérrez R. et al (2024). Chrysin: a potential antiandrogen ligand to mutated androgen receptors in prostate cancer. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol.17, e18761429350210. 10.2174/0118761429350210250102131611
11
Catalano M. Francesco Iannone L. Cosso F. Generali D. Mini E. Roviello G. (2022). Combining inhibition of immune checkpoints and PARP: rationale and perspectives in cancer treatment. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets26 (11), 923–936. 10.1080/14728222.2022.2158813
12
Çelik U. Aydemir E. H. Engin B. Oba M. Ç. Yılmaz M. Meşe Ş. G. (2021). Dermatological side effects of immunotherapy drugs and targeted cancer therapies: importance of dermatology and oncology collaboration. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract.27 (8), 1853–1860. 10.1177/1078155220970621
13
Chakraborty G. Gupta K. Kyprianou N. (2023). Epigenetic mechanisms underlying subtype heterogeneity and tumor recurrence in prostate cancer. Nat. Commun.14 (1), 567. 10.1038/s41467-023-36253-1
14
Chang Y. Zhou H. Ren Y. Zhang J. Sun L. Du M. et al (2025). Identifying multi-target drugs for prostate cancer using machine learning-assisted transcriptomic analysis. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.43 (4), 2109–2119. 10.1080/07391102.2023.2294168
15
Chen W. Xia W. Xue S. Huang H. Lin Q. Liu Y. et al (2022). Analysis of BRCA germline mutations in Chinese prostate cancer patients. Front. Oncol.12, 746102. 10.3389/fonc.2022.746102
16
Chi K. N. Fleshner N. Chiuri V. E. Van Bruwaene S. Hafron J. McNeel D. G. et al (2023). Niraparib with abiraterone acetate and prednisone for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: phase II QUEST study results. Oncologist28 (5), e309–e312. 10.1093/oncolo/oyad008
17
Cordes L. M. Gulley J. L. Madan R. A. (2018). Perspectives on the clinical development of immunotherapy in prostate cancer. Asian J. Androl.20 (3), 253–259. 10.4103/aja.aja_9_18
18
Crabb S. J. Griffiths G. Marwood E. Dunkley D. Downs N. Martin K. et al (2021). Pan-AKT inhibitor capivasertib with docetaxel and prednisolone in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a randomized, placebo-controlled phase II trial (ProCAID). J. Clin. Oncol.39 (3), 190–201. 10.1200/JCO.20.01576
19
Desai V. M. Choudhary M. Chowdhury R. Singhvi G. (2024). Photodynamic therapy induced mitochondrial targeting strategies for cancer treatment: emerging trends and insights. Mol. Pharm.21 (4), 1591–1608. 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c01185
20
Dib E. G. Antonarakis E. S. Wasco M. J. Powell S. F. (2019). Favorable response to pembrolizumab in a patient with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer progressing while receiving enzalutamide. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer17 (2), e365–e368. 10.1016/j.clgc.2018.11.021
21
Dong C. Fan B. Ren Z. Liu B. Wang Y. (2021). CircSMARCA5 facilitates the progression of prostate cancer through miR-432/PDCD10 axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm.36 (1), 70–83. 10.1089/cbr.2019.3490
22
Dubrovska A. Kim S. Salamone R. J. Walker J. R. Maira S. M. García-Echeverría C. et al (2009). The role of PTEN/Akt/PI3K signaling in the maintenance and viability of prostate cancer stem-like cell populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.106 (1), 268–273. 10.1073/pnas.0810956106
23
Elsayed G. H. Fahim A. M. (2025). Studying the impact of chitosan salicylaldehyde/schiff base/CuFe(2)O(4) in PC3 cells via theoretical studies and inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling. Sci. Rep.15 (1), 4129. 10.1038/s41598-025-86096-7
24
Fettke H. Dai C. Kwan E. M. Zheng T. Du P. Ng N. et al (2023). BRCA-Deficient metastatic prostate cancer has an adverse prognosis and distinct genomic phenotype. EBioMedicine95, 104738. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104738
25
Filippi A. Deculescu-Ioniță T. Hudiță A. Baldasici O. Gălățeanu B. Mocanu M. M. (2025). Molecular mechanisms of dietary compounds in cancer stem cells from solid tumors: insights into colorectal, breast, and prostate cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci.26 (2), 631. 10.3390/ijms26020631
26
Formaggio N. Rubin M. A. Theurillat J. P. (2021). Loss and revival of androgen receptor signaling in advanced prostate cancer. Oncogene40 (7), 1205–1216. 10.1038/s41388-020-01598-0
27
Fumet J. D. Limagne E. Thibaudin M. Truntzer C. Bertaut A. Rederstorff E. et al (2020). Precision medicine phase II study evaluating the efficacy of a double immunotherapy by durvalumab and tremelimumab combined with olaparib in patients with solid cancers and carriers of homologous recombination repair genes mutation in response or stable after olaparib treatment. BMC Cancer20 (1), 748. 10.1186/s12885-020-07253-x
28
Germain L. Lafront C. Beaudette J. Karthik Poluri R. T. Weidmann C. Audet-Walsh É. (2020). Alternative splicing regulation by the androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.202, 105710. 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105710
29
Guan X. Polesso F. Wang C. Sehrawat A. Hawkins R. M. Murray S. E. et al (2022). Androgen receptor activity in T cells limits checkpoint blockade efficacy. Nature606 (7915), 791–796. 10.1038/s41586-022-04522-6
30
Haffner M. C. Zwart W. Roudier M. P. True L. D. Nelson W. G. Epstein J. I. et al (2021). Genomic and phenotypic heterogeneity in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol.18 (2), 79–92. 10.1038/s41585-020-00400-w
31
Hahn A. W. Siddiqui B. A. Leo J. Dondossola E. Basham K. J. Miranti C. K. et al (2023). Cancer cell-extrinsic roles for the androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Endocrinology164 (6), bqad078. 10.1210/endocr/bqad078
32
Hirz T. Mei S. Sarkar H. Kfoury Y. Wu S. Verhoeven B. M. et al (2023). Dissecting the immune suppressive human prostate tumor microenvironment via integrated single-cell and spatial transcriptomic analyses. Nat. Commun.14 (1), 663. 10.1038/s41467-023-36325-2
33
Hunia J. Gawalski K. Szredzka A. Suskiewicz M. J. Nowis D. (2022). The potential of PARP inhibitors in targeted cancer therapy and immunotherapy. Front. Mol. Biosci.9, 1073797. 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1073797
34
Isebia K. T. Lolkema M. P. Jenster G. de Wit R. Martens J. van Riet J. (2023). A compendium of AR splice variants in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24 (6), 6009. 10.3390/ijms24066009
35
Jaiswal B. Agarwal A. Gupta A. (2022). Lysine acetyltransferases and their role in AR signaling and prostate cancer. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne)13, 886594. 10.3389/fendo.2022.886594
36
Janik E. Niemcewicz M. Ceremuga M. Krzowski L. Saluk-Bijak J. Bijak M. (2020). Various aspects of a gene editing System-CRISPR-Cas9. Int. J. Mol. Sci.21 (24), 9604. 10.3390/ijms21249604
37
Jeong S. H. Kim H. H. Park M. Y. Bhosale P. B. Abusaliya A. Won C. K. et al (2023). Flavones: the apoptosis in prostate cancer of three flavones selected as therapeutic candidate models. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24 (11), 9240. 10.3390/ijms24119240
38
Jones W. Griffiths K. Barata P. C. Paller C. J. (2020). PSMA theranostics: review of the current status of PSMA-targeted imaging and radioligand therapy. Cancers (Basel)12 (6), 1367. 10.3390/cancers12061367
39
Karpisheh V. Mousavi S. M. Naghavi Sheykholeslami P. Fathi M. Mohammadpour Saray M. Aghebati-Maleki L. et al (2021). The role of regulatory T cells in the pathogenesis and treatment of prostate cancer. Life Sci.284, 119132. 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119132
40
Karzai F. VanderWeele D. Madan R. A. Owens H. Cordes L. M. Hankin A. et al (2018). Activity of durvalumab plus olaparib in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in men with and without DNA damage repair mutations. J. Immunother. Cancer6 (1), 141. 10.1186/s40425-018-0463-2
41
Kim R. J. Bae E. Hong Y. K. Hong J. Y. Kim N. K. Ahn H. J. et al (2014). PTEN loss-mediated akt activation increases the properties of cancer stem-like cell populations in prostate cancer. Oncology87 (5), 270–279. 10.1159/000363186
42
Kim S. Au C. C. Jamalruddin M. Abou-Ghali N. E. Mukhtar E. Portella L. et al (2022). AR-V7 exhibits non-canonical mechanisms of nuclear import and chromatin engagement in castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Elife11, e73396. 10.7554/eLife.73396
43
Knerr J. Werner R. Schwan C. Wang H. Gebhardt P. Grötsch H. et al (2023). Formin-mediated nuclear actin at androgen receptors promotes transcription. Nature617 (7961), 616–622. 10.1038/s41586-023-05981-1
44
Kour B. Shukla N. Bhargava H. Sharma D. Sharma A. Singh A. et al (2023). Identification of plausible candidates in prostate cancer using integrated machine learning approaches. Curr. Genomics24 (5), 287–306. 10.2174/0113892029240239231109082805
45
Ku S. Y. Gleave M. E. Beltran H. (2019). Towards precision oncology in advanced prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol.16 (11), 645–654. 10.1038/s41585-019-0237-8
46
Kwon J. Bryant R. J. Parkes E. E. (2021). The tumor microenvironment and immune responses in prostate cancer patients. Endocr. Relat. Cancer28 (8), T95–T107. 10.1530/ERC-21-0149
47
Lai H. W. Kasai M. Yamamoto S. Fukuhara H. Karashima T. Kurabayashi A. et al (2023). Metabolic shift towards oxidative phosphorylation reduces cell-density-induced cancer-stem-cell-like characteristics in prostate cancer in vitro. Biol. Open12 (4), bio059615. 10.1242/bio.059615
48
Lanka S. M. Zorko N. A. Antonarakis E. S. Barata P. C. (2023). Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and beyond. Curr. Oncol.30 (4), 4246–4256. 10.3390/curroncol30040323
49
León-González A. J. Sáez-Martínez P. Jiménez-Vacas J. M. Herrero-Aguayo V. Montero-Hidalgo A. J. Gómez-Gómez E. et al (2021). Comparative cytotoxic activity of hydroxytyrosol and its semisynthetic lipophilic derivatives in prostate cancer cells. Antioxidants (Basel)10 (9), 1348. 10.3390/antiox10091348
50
Li F. Ling X. Chakraborty S. Fountzilas C. Wang J. Jamroze A. et al (2023). Role of the DEAD-box RNA helicase DDX5 (p68) in cancer DNA repair, immune suppression, cancer metabolic control, virus infection promotion, and human microbiome (microbiota) negative influence. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res.42 (1), 213. 10.1186/s13046-023-02787-x
51
Li S. Kang Y. Zeng Y. (2024). Targeting tumor and bone microenvironment: novel therapeutic opportunities for castration-resistant prostate cancer patients with bone metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer1879 (1), 189033. 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.189033
52
Likos E. Bhattarai A. Weyman C. M. Shukla G. C. (2022). The androgen receptor messenger RNA: what do we know. RNA Biol.19 (1), 819–828. 10.1080/15476286.2022.2084839
53
Lim E. A. Schweizer M. T. Chi K. N. Aggarwal R. Agarwal N. Gulley J. et al (2023). Phase 1 study of safety and preliminary clinical activity of JNJ-63898081, a PSMA and CD3 bispecific antibody, for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer21 (3), 366–375. 10.1016/j.clgc.2023.02.010
54
Ling Y. Liu J. Qian J. Meng C. Guo J. Gao W. et al (2020). Recent advances in multi-target drugs targeting protein kinases and histone deacetylases in cancer therapy. Curr. Med. Chem.27 (42), 7264–7288. 10.2174/0929867327666200102115720
55
Ling S. W. van der Veldt A. Konijnenberg M. Segbers M. Hooijman E. Bruchertseifer F. et al (2024). Evaluation of the tolerability and safety of [(225)Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T in patients with metastatic prostate cancer: a phase I dose escalation study. BMC Cancer24 (1), 146. 10.1186/s12885-024-11900-y
56
Liu Z. Hu M. Yang Y. Du C. Zhou H. Liu C. et al (2022). An overview of PROTACs: a promising drug discovery paradigm. Mol. Biomed.3 (1), 46. 10.1186/s43556-022-00112-0
57
Lowrance W. T. Murad M. H. Oh W. K. Jarrard D. F. Resnick M. J. Cookson M. S. (2018). Castration-resistant prostate cancer: AUA guideline amendment 2018. J. Urol.200 (6), 1264–1272. 10.1016/j.juro.2018.07.090
58
Lu X. Yang F. Chen D. Zhao Q. Chen D. Ping H. et al (2020). Quercetin reverses docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer via androgen receptor and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int. J. Biol. Sci.16 (7), 1121–1134. 10.7150/ijbs.41686
59
Lu X. Fong K. W. Gritsina G. Wang F. Baca S. C. Brea L. T. et al (2022). HOXB13 suppresses de novo lipogenesis through HDAC3-mediated epigenetic reprogramming in prostate cancer. Nat. Genet.54 (5), 670–683. 10.1038/s41588-022-01045-8
60
Lu L. Wang F. Chen J. Zhao C. Guo S. Dong D. et al (2023). CircTENM3 inhibites tumor progression via the miR-558/RUNX3 axis in prostate cancer. J. Transl. Med.21 (1), 850. 10.1186/s12967-023-04708-0
61
Lv Z. Shi Y. Wu H. Cao K. Liu X. Wang C. (2024). Novel circular RNA CircUBAP2 drives tumor progression by regulating the miR-143/TFAP2B axis in prostate cancer. Protein Pept. Lett.31 (1), 61–73. 10.2174/0109298665268943231103114654
62
Macedo-Silva C. Miranda-Gonçalves V. Tavares N. T. Barros-Silva D. Lencart J. Lobo J. et al (2023). Epigenetic regulation of TP53 is involved in prostate cancer radioresistance and DNA damage response signaling. Signal Transduct. Target Ther.8 (1), 395. 10.1038/s41392-023-01639-6
63
Malarvannan M. Unnikrishnan S. Monohar S. Ravichandiran V. Paul D. (2025). Design and optimization strategies of PROTACs and its application, comparisons to other targeted protein degradation for multiple oncology therapies. Bioorg Chem.154, 107984. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107984
64
Masetti M. Carriero R. Portale F. Marelli G. Morina N. Pandini M. et al (2022). Lipid-loaded tumor-associated macrophages sustain tumor growth and invasiveness in prostate cancer. J. Exp. Med.219 (2), e20210564. 10.1084/jem.20210564
65
Mateo J. Carreira S. Sandhu S. Miranda S. Mossop H. Perez-Lopez R. et al (2015). DNA-repair defects and olaparib in metastatic prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med.373 (18), 1697–1708. 10.1056/NEJMoa1506859
66
Metzger E. Wang S. Urban S. Willmann D. Schmidt A. Offermann A. et al (2019). KMT9 monomethylates histone H4 lysine 12 and controls proliferation of prostate cancer cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.26 (5), 361–371. 10.1038/s41594-019-0219-9
67
Mitsogianni M. Papatsoris A. Bala V. M. Issa H. Moussa M. Mitsogiannis I. (2023). An overview of hormonal directed pharmacotherapy for the treatment of prostate cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother.24 (16), 1765–1774. 10.1080/14656566.2023.2244415
68
Nabavi N. Mahdavi S. R. Ardalan M. A. Chamanara M. Mosaed R. Lara A. et al (2023). Bipolar androgen therapy: when excess fuel extinguishes the fire. Biomedicines11 (7), 2084. 10.3390/biomedicines11072084
69
Nakajima R. (2024). Targeted therapy for prostate cancer by prostate-specific membrane antigen-targeted small-molecule drug conjugates. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo)72 (2), 136–142. 10.1248/cpb.c23-00535
70
Nguyen T. Sridaran D. Chouhan S. Weimholt C. Wilson A. Luo J. et al (2023). Histone H2A Lys130 acetylation epigenetically regulates androgen production in prostate cancer. Nat. Commun.14 (1), 3357. 10.1038/s41467-023-38887-7
71
Nyberg T. Govindasami K. Leslie G. Dadaev T. Bancroft E. Ni Raghallaigh H. et al (2019). Homeobox B13 G84E mutation and prostate cancer risk. Eur. Urol.75 (5), 834–845. 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.11.015
72
Obinata D. Takayama K. Inoue S. Takahashi S. (2024). Exploring androgen receptor signaling pathway in prostate cancer: a path to new discoveries. Int. J. Urol.31 (6), 590–597. 10.1111/iju.15424
73
Ocana A. Nieto-Jiménez C. Pandiella A. Templeton A. J. (2017). Neutrophils in cancer: prognostic role and therapeutic strategies. Mol. Cancer16 (1), 137. 10.1186/s12943-017-0707-7
74
Omar E. A. R. R. Das P. K. Pal R. Purawarga Matada G. S. Maji L. (2025). Next-generation cancer therapeutics: PROTACs and the role of heterocyclic warheads in targeting resistance. Eur. J. Med. Chem.281, 117034. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.117034
75
Özturan D. Morova T. Lack N. A. (2022). Androgen receptor-mediated transcription in prostate cancer. Cells11 (5), 898. 10.3390/cells11050898
76
Pan E. Xie W. Ajmera A. Araneta A. Jamieson C. Folefac E. et al (2023). A phase I study of combination olaparib and Radium-223 in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) with bone metastases (COMRADE). Mol. Cancer Ther.22 (4), 511–518. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-22-0583
77
Parghane R. V. Basu S. (2023). PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy in prostate cancer: current status and future prospects. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther.23 (9), 959–975. 10.1080/14737140.2023.2247562
78
Pasero C. Gravis G. Guerin M. Granjeaud S. Thomassin-Piana J. Rocchi P. et al (2016). Inherent and tumor-driven immune tolerance in the prostate microenvironment impairs natural killer cell antitumor activity. Cancer Res.76 (8), 2153–2165. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1965
79
Peitzsch C. Gorodetska I. Klusa D. Shi Q. Alves T. C. Pantel K. et al (2022). Metabolic regulation of prostate cancer heterogeneity and plasticity. Semin. Cancer Biol.82, 94–119. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.12.002
80
Peltola K. J. Bono P. Jones R. H. Vjaters E. Nykänen P. Vuorela A. et al (2020). ODM-204, a novel dual inhibitor of CYP17A1 and androgen receptor: early results from phase I dose escalation in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus6 (1), 63–70. 10.1016/j.euf.2018.08.022
81
Pham T. C. Jayasinghe M. K. Pham T. T. Yang Y. Wei L. Usman W. M. et al (2021). Covalent conjugation of extracellular vesicles with peptides and nanobodies for targeted therapeutic delivery. J. Extracell. Vesicles10 (4), e12057. 10.1002/jev2.12057
82
Pouget J. P. Chan T. A. Galluzzi L. Constanzo J. (2023). Radiopharmaceuticals as combinatorial partners for immune checkpoint inhibitors. Trends Cancer9 (11), 968–981. 10.1016/j.trecan.2023.07.014
83
Powles T. Yuen K. C. Gillessen S. Kadel E. E. 3rd Rathkopf D. Matsubara N. et al (2022). Atezolizumab with enzalutamide versus enzalutamide alone in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a randomized phase 3 trial. Nat. Med.28 (1), 144–153. 10.1038/s41591-021-01600-6
84
Prasad V. Zengerling F. Steinacker J. P. Bolenz C. Beer M. Wiegel T. et al (2021). First experiences with (177)Lu-PSMA therapy in combination with pembrolizumab or after pretreatment with olaparib in single patients. J. Nucl. Med.62 (7), 975–978. 10.2967/jnumed.120.249029
85
Pungsrinont T. Kallenbach J. Baniahmad A. (2021). Role of PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway as a pro-survival signaling and resistance-mediating mechanism to therapy of prostate cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci.22 (20), 11088. 10.3390/ijms222011088
86
Qian Y. Gong Y. Fan Z. Luo G. Huang Q. Deng S. et al (2020). Molecular alterations and targeted therapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol.13 (1), 130. 10.1186/s13045-020-00958-3
87
Qiu X. Boufaied N. Hallal T. Feit A. de Polo A. Luoma A. M. et al (2022). MYC drives aggressive prostate cancer by disrupting transcriptional pause release at androgen receptor targets. Nat. Commun.13 (1), 2559. 10.1038/s41467-022-30257-z
88
Rosellini M. Santoni M. Mollica V. Rizzo A. Cimadamore A. Scarpelli M. et al (2021). Treating prostate cancer by antibody-drug conjugates. Int. J. Mol. Sci.22 (4), 1551. 10.3390/ijms22041551
89
Saad F. Chi K. N. Shore N. D. Graff J. N. Posadas E. M. Lattouf J. B. et al (2021). Niraparib with androgen receptor-axis-targeted therapy in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: safety and pharmacokinetic results from a phase 1b study (BEDIVERE). Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol.88 (1), 25–37. 10.1007/s00280-021-04249-7
90
Sandhu S. Moore C. M. Chiong E. Beltran H. Bristow R. G. Williams S. G. (2021). Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer. Lancet.398 (10305), 1075–1090. 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00950-8
91
Sarker D. Dawson N. A. Aparicio A. M. Dorff T. B. Pantuck A. J. Vaishampayan U. N. et al (2021). A phase I, open-label, dose-finding study of GSK2636771, a PI3Kβ inhibitor, administered with enzalutamide in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res.27 (19), 5248–5257. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1115
92
Sciarrillo R. Wojtuszkiewicz A. Assaraf Y. G. Jansen G. Kaspers G. J. L. Giovannetti E. et al (2020). The role of alternative splicing in cancer: from oncogenesis to drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat53, 100728. 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100728
93
Seltzer S. Giannopoulos P. N. Bismar T. A. Trifiro M. Paliouras M. (2023). Investigation of androgen receptor-dependent alternative splicing has identified a unique subtype of lethal prostate cancer. Asian J. Androl.25 (3), 296–308. 10.4103/aja202263
94
Shore N. Mellado B. Shah S. Hauke R. Costin D. Adra N. et al (2023). A phase I study of capivasertib in combination with abiraterone acetate in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer21 (2), 278–285. 10.1016/j.clgc.2022.11.017
95
Smith M. R. Scher H. I. Sandhu S. Efstathiou E. Lara P. N. Jr Yu E. Y. et al (2022). Niraparib in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer and DNA repair gene defects (GALAHAD): a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol.23 (3), 362–373. 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00757-9
96
Stracker T. H. Osagie O. I. Escorcia F. E. Citrin D. E. (2023). Exploiting the DNA damage response for prostate cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel)16 (1), 83. 10.3390/cancers16010083
97
Subbiah V. Coleman N. Piha-Paul S. A. Tsimberidou A. M. Janku F. Rodon J. et al (2024). Phase I study of mTORC1/2 inhibitor sapanisertib (CB-228/TAK-228) in combination with metformin in patients with mTOR/AKT/PI3K pathway alterations and advanced solid malignancies. Cancer Res. Commun.4 (2), 378–387. 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-22-0260
98
Sun R. Yan B. Li H. Ding D. Wang L. Pang J. et al (2023). Androgen receptor variants confer castration resistance in prostate cancer by counteracting antiandrogen-induced ferroptosis. Cancer Res.83 (19), 3192–3204. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0285
99
Sung H. Ferlay J. Siegel R. L. Laversanne M. Soerjomataram I. Jemal A. et al (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.71 (3), 209–249. 10.3322/caac.21660
100
Sweeney C. J. Percent I. J. Babu S. Cultrera J. L. Mehlhaff B. A. Goodman O. B. et al (2022). Phase Ib/II study of enzalutamide with samotolisib (LY3023414) or placebo in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res.28 (11), 2237–2247. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-2326
101
Tagawa S. T. Thomas C. Sartor A. O. Sun M. Stangl-Kremser J. Bissassar M. et al (2024). Prostate-specific membrane antigen-targeting alpha emitter via antibody delivery for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a phase I dose-escalation study of (225)Ac-J591. J. Clin. Oncol.42 (7), 842–851. 10.1200/JCO.23.00573
102
Teyssonneau D. Margot H. Cabart M. Anonnay M. Sargos P. Vuong N. S. et al (2021). Prostate cancer and PARP inhibitors: progress and challenges. J. Hematol. Oncol.14 (1), 51. 10.1186/s13045-021-01061-x
103
Tímár J. Uhlyarik A. (2022). On-Target side effects of targeted therapeutics of cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res.28, 1610694. 10.3389/pore.2022.1610694
104
Topchu I. Pangeni R. P. Bychkov I. Miller S. A. Izumchenko E. Yu J. et al (2022). The role of NSD1, NSD2, and NSD3 histone methyltransferases in solid tumors. Cell Mol. Life Sci.79 (6), 285. 10.1007/s00018-022-04321-2
105
Vietri M. T. D'Elia G. Caliendo G. Resse M. Casamassimi A. Passariello L. et al (2021). Hereditary prostate cancer: genes related, target therapy and prevention. Int. J. Mol. Sci.22 (7), 3753. 10.3390/ijms22073753
106
Vigneswaran H. T. Warnqvist A. Andersson T. Leval A. Eklund M. Nordström T. et al (2021). Real world treatment utilization patterns in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Scand. J. Urol.55 (4), 299–306. 10.1080/21681805.2021.1936626
107
Viktorsson K. Rieckmann T. Fleischmann M. Diefenhardt M. Hehlgans S. Rödel F. (2023). Advances in molecular targeted therapies to increase efficacy of (chemo)radiation therapy. Strahlenther Onkol.199 (12), 1091–1109. 10.1007/s00066-023-02064-y
108
Wang E. C. Lee W. R. Armstrong A. J. (2023). Second generation anti-androgens and androgen deprivation therapy with radiation therapy in the definitive management of high-risk prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.26 (1), 30–40. 10.1038/s41391-022-00598-3
109
Wang L. Y. Hung C. L. Wang T. C. Hsu H. C. Kung H. J. Lin K. H. (2025). PROTACs as therapeutic modalities for drug discovery in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol.65 (1), 375–396. 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-030624-110238
110
Wasim S. Lee S. Y. Kim J. (2022). Complexities of prostate cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23 (22), 14257. 10.3390/ijms232214257
111
Wong H. Y. Sheng Q. Hesterberg A. B. Croessmann S. Rios B. L. Giri K. et al (2022). Single cell analysis of cribriform prostate cancer reveals cell intrinsic and tumor microenvironmental pathways of aggressive disease. Nat. Commun.13 (1), 6036. 10.1038/s41467-022-33780-1
112
Wu B. Lu X. Shen H. Yuan X. Wang X. Yin N. et al (2020). Intratumoral heterogeneity and genetic characteristics of prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer146 (12), 3369–3378. 10.1002/ijc.32961
113
Wu Z. Cui P. Tao H. Zhang S. Ma J. Liu Z. et al (2021). The synergistic effect of PARP inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol.15, 1179554921996288. 10.1177/1179554921996288
114
Wu W. Wang X. Le W. Lu C. Li H. Zhu Y. et al (2022). Immune microenvironment infiltration landscape and immune-related subtypes in prostate cancer. Front. Immunol.13, 1001297. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1001297
115
Wylaź M. Kaczmarska A. Pajor D. Hryniewicki M. Gil D. Dulińska-Litewka J. (2023). Exploring the role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors in hormone-related cancers: a focus on breast and prostate cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother.168, 115676. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115676
116
Wyvekens N. Tsai H. K. Sholl L. M. Tucci J. Giannico G. A. Gordetsky J. B. et al (2022). Histopathological and genetic features of mismatch repair-deficient high-grade prostate cancer. Histopathology.80 (7), 1050–1060. 10.1111/his.14645
117
Xie J. He H. Kong W. Li Z. Gao Z. Xie D. et al (2022). Targeting androgen receptor phase separation to overcome antiandrogen resistance. Nat. Chem. Biol.18 (12), 1341–1350. 10.1038/s41589-022-01151-y
118
Ye J. Wu Q. Ji Q. You S. Gao S. Zhao G. et al (2024). Au/Doc/Quer@PDA/A10-3.2 nanoparticles for targeted treatment of docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed.35 (11), 1631–1655. 10.1080/09205063.2024.2346395
119
Yi X. Zhang C. Liu B. Gao G. Tang Y. Lu Y. et al (2023). Ribosomal protein L22-like1 promotes prostate cancer progression by activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med.27 (3), 403–411. 10.1111/jcmm.17663
120
Yu E. Y. Berry W. R. Gurney H. Retz M. Conter H. J. Laguerre B. et al (2024). Pembrolizumab and enzalutamide in patients with abiraterone acetate-pretreated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: cohort C of the phase 1b/2 KEYNOTE-365 study. Eur. Urol. Oncol.7 (3), 509–518. 10.1016/j.euo.2023.10.008
121
Zamagni A. Cortesi M. Zanoni M. Tesei A. (2019). Non-nuclear AR signaling in prostate cancer. Front. Chem.7, 651. 10.3389/fchem.2019.00651
122
Zeng S. Huang W. Zheng X. Liyan Cheng Zhang Z. Wang J. et al (2021). Proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) in drug discovery paradigm: recent progress and future challenges. Eur. J. Med. Chem.210, 112981. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112981
123
Zhang J. Lu T. Lu S. Ma S. Han D. Zhang K. et al (2023). Single-cell analysis of multiple cancer types reveals differences in endothelial cells between tumors and normal tissues. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J.21, 665–676. 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.12.049
124
Zhao S. G. Chen W. S. Li H. Foye A. Zhang M. Sjöström M. et al (2020). The DNA methylation landscape of advanced prostate cancer. Nat. Genet.52 (8), 778–789. 10.1038/s41588-020-0648-8
125
Zhou X. Jiao D. Dou M. Chen J. Li Z. Li Y. et al (2019). Association of glutathione-S-transferase p1 gene promoter methylation and the incidence of prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol.145 (8), 1939–1948. 10.1007/s00432-019-02962-8
126
Zhou T. Xu W. Zhang W. Sun Y. Yan H. Gao X. et al (2020). Preclinical profile and phase I clinical trial of a novel androgen receptor antagonist GT0918 in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. J. Cancer134, 29–40. 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.04.013
127
Zhu S. Zhang T. Zheng L. Liu H. Song W. Liu D. et al (2021). Combination strategies to maximize the benefits of cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol.14 (1), 156. 10.1186/s13045-021-01164-5
128
Zhu Y. Duong L. Lu X. Lu X. (2023). Cancer-cell-intrinsic mechanisms shaping the immunosuppressive landscape of prostate cancer. Asian J. Androl.25, 171–178. 10.4103/aja202283
Summary
Keywords
prostate cancer, targeted therapy, PROTACs, androgen receptor, tumor microenvironment, molecular mechanisms
Citation
Wu L, Qiu J, Hong Z, Wang Q, Li Q and Zhou W (2025) Unravelling targeted therapy in prostate cancer: from molecular mechanisms to translational opportunities. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:1685857. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1685857
Received
14 August 2025
Revised
25 October 2025
Accepted
27 October 2025
Published
14 November 2025
Volume
13 - 2025
Edited by
Jingrui Huang, Central South University, China
Reviewed by
Chen Xue, Zhejiang University, China
Adrian Mansini, Rush University, United States
Mohammed AL Zobaidy, University of Baghdad, Iraq
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Wu, Qiu, Hong, Wang, Li and Zhou.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenbin Zhou, zwb1054@126.com; Qixin Li, 1423440039@qq.com; Quan Wang, wang3169332@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.