- Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Fujian Maternity and Child Health Hospital, College of Clinical Medicine for Obstetrics & Gynecology and Pediatrics, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
Disruptions in vaginal microbiota and metabolites during pregnancy may be the most important risk factor for preterm delivery, thus the difference in vaginal microbiota and metabolites between women who subsequently delivered at term and who eventually experienced preterm birth. In this study, 63 participants were enrolled before the cervical cerclage surgery (namely pre-cerclage), comprising women who subsequently delivered at term and who eventually experienced preterm birth. The cervical-vaginal fluid (CVF) was collected two days prior to the cervical cerclage surgery. Compared with the term birth groups (PrTG), the proportion of beneficial bacteria (Lactobacillus, Prevotella, Trichococcus, Neisseria and Gemella) in the preterm birth group (PrPG) were significantly reduced (p < 0.05), while the proportion of harmful bacteria (Thauera, Ochrobactrum, Gardnerella, Massilia, Phyllobacteriaceae and Atopobium) were significantly increased (p < 0.05). In addition, vaginal metabolomics-based LC-Orbitrap-MS/MS revealed that the contents of 2-Piperidone, Melphalan, N-acetylputrescine, Obatoclax, Eurostoside, Pregnanediol 3-O-glucuronide, O-Phospho-L-serine, 1-Kestose and N-arachidonylglycine were significantly decreased in the PrPG group compared with the PrTG group, while Acenocoumarol, Isopyrazam, Pentosidine, hexose, 7-Hydroxymitragynine, PE, Tamoxifen and 1-Deoxynojirimycin contents were significantly increased. These results suggest that specific bacterial species and metabolites may serve as potential biomarkers for preterm birth prediction, and approve the theoretical basis for the intervention of preterm birth.
1 Introduction
Preterm delivery is described as birth occurring before 37 weeks of gestation (or less than 259 days from the first day of a woman’s last menstrual period), which includes spontaneous and iatrogenic preterm births. Preterm delivery is the major cause of infant morbidity and mortality worldwide and is related to long-time adverse outcomes in children (Xie et al., 2022). The high incidence of preterm deliveries not only imposes a significant annual economic burden on society, but also undermines family well-being and social harmony. According to the Global Disease Burden Study from 2022, over 15 million babies are born preterm annually, and the prevalence of preterm birth is on the rise globally (Adane et al., 2024). Among these preterm births, approximately 45% are diagnosed with spontaneous preterm labor with intact membranes, and approximately 30% of premature infants are diagnosed with spontaneous preterm labor with ruptured membranes in the world (Beernink et al., 2023). According a previous report, the occurrence of preterm delivery is associated with factors, such as a short cervix, extremes of maternal age (< 25 years and > 35 years) and body mass index (BMI, from 18 to 28), low socio-economic status, smoking, and genetic polymorphisms (Wei et al., 2024). There is obvious difference in the incidence rate of preterm delivery among different regions. For example, it is reported that the rates of preterm delivery accounted for more than 80% of global cases in low-income and middle-income countries, such as Southern Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa (Ohuma et al., 2023). At present, cervical cerclage and vaginal progesterone are widely used in the preventive treatment of preterm delivery and preterm premature rupture of membranes. Cervical cerclage mechanically maintains a long and closed cervix, which is one of the universal methods applied to decrease preterm birth in pregnant women with older age or high risk (Seyama et al., 2022). However, there is an obvious difference in the intervention effect of cervical cerclage among the different people.
As is well known, the vaginal microbiota is an essential regulator of reproductive tract pathophysiology, but the diversity of vaginal microbiome was obviously lower than that of other mucosal surfaces (Golob et al., 2024). A previous study indicated that pregnant women diagnosed with bacterial vaginosis-associated vaginal dysbiosis before 20 weeks of gestation face a five-fold increased risk of late miscarriage or preterm birth before 34 weeks, with the risk rising to sevenfold when bacterial vaginosis is detected before 16 weeks (Peelen et al., 2019). Lactobacillus species are the major bacterium in the vagina, and are generally regarded as a hallmark of health, especially during reproductive years. A high proportion of Lactobacillus in the vagina is beneficial for elevating the level of short-chain fatty acids that provide energy for the growth of vaginal epithelial cells and suppress the growth of harmful bacteria (Hong et al., 2021). Another study displayed that elevating the abundance of Lactobacillus effectively suppressed the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, relieves oxidative stress, and regulated the composition of vaginal microbiota (Chee et al., 2020). On the contrary, the reduction of Lactobacillus species and increases in microbial diversity elevate the risk of bacterial vaginosis, which may be associated with the high rate of preterm delivery (Fettweis et al., 2019). The changes in vaginal microbiota induce the alterations in vaginal metabolite contents. Microbial metabolites are reported to have prominence and various influences on human health and are detectable in a series of biological tissues, including the colon, liver, brain and vagina (Guo et al., 2023a, 2023). At present, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) are extensively applied to detect the metabolites because of their relatively high sensitivity, which is beneficial for distinguishing different vaginal metabolites between the pregnant woman who later experienced preterm delivery and term birth.
The association between the vaginal microbiota and the occurrence of preterm delivery is widely investigated, which may not accurately predict premature birth. In the present study, the vagina microbiota and vaginal metabolites between pregnant women (years: 21–38 and BMI: 19.57-28.00) who later experienced preterm delivery and term birth from Fujian maternity and child health hospital (Fuzhou, China) before the cervical cerclage surgery (namely pre-cerclage) were measured by 16S rRNA gene sequencing and untargeted metabolomics, respectively. Then, the key microbial phylotypes and marked metabolites in the vagina of pregnant women who eventually experienced preterm delivery were screened using statistical analysis, which offers useful information to predict preterm delivery or the development of new therapeutics for pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Participant recruitment
In this study, participants were recruited from Fujian maternity and child health hospital (Fuzhou, China) between 2021 and 2023, and were supported by the Ethics Committee of Fujian Maternity and Child Health Hospital (Approval No. 2021KLR601). A total of 132 participants, who had not used antibiotics, engaged in sexual activity, or used tobacco in the 12 weeks prior, provided written informed consent before enrollment in accordance with the approved institutional guidelines. However, only 63 participants met the experimental requirements (excluding 46 cases of multiple pregnancies, 20 cases of lost contact, 2 cases of uterine malformations, and 1 case of severe fetal malformations).
2.2 Data collection
The current and historical pregnancy outcomes of participants were collected and recorded, including maternal age, body mass index (BMI), abortion frequency and fertility frequency). Before the cervical cerclage surgery (namely pre-cerclage), all participants were divided into 2 groups according to the outcome of pregnancy, namely the preterm delivery group (PrPG) and the term birth groups (PrTG).
2.3 Sample collection
A single-use sterile endoscope was used to expose the vagina, and then a cotton swab was gently rotated across the vaginal wall for 20 s. The sampling loop was taken out from the cannula to fully exposed in the uterine, then rotate the handle of the sampler ten times to collect the endometrial sample, and hen rotate the handle of the sampler ten times to collect the endometrial sample. In the passage of the sampler through the vagina, the sampling loop remains retracted within the cannula to avoid contact with microorganisms from these two body parts, thus eliminating cross-contamination between intrauterine and vaginal samples. All samples were immediately frozen using liquid nitrogen for 3–4 min, and then placed in -80 °C until further use. To avoid potential interference from the cervical cerclage surgery on vaginal microbiota and their metabolites, the cervical-vaginal fluid (CVF) was collected two days prior to surgery. In addition, the clinical patients enrolled in this study subsequently underwent surgical treatment following sample collection. The specific surgical steps and preoperative management of cervical cerclage surgery were carried out according to our previous study (Fang et al., 2020).
2.4 16S rRNA gene sequencing
The sequencing analysis of vaginal microbiota was implemented by the MiSeq platform based on the methodology outlined in a previous report with slight modifications (Guo et al., 2025a). In brief, total bacterial DNA from CVF sample was extracted using a FastDNA™ Fecal Kit (MoBio, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and then the V3-V4 regions of bacterial 16S rRNA genes were amplified by broad-range bacterial primers, namely 338F primers (5′-CCTAYGGGRBGCASCAG-3′) and 806R primers (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′). These products were purified using 2.0% agarose gel electrophoresis, target fragment was collected and recovered by a QIAquick Gel Extraction kit (BeckmanA63880, Hangzhou, China). Sequencing libraries consisted of equal concentrations of each sample, and their quality was evaluated on the Qubit@ 2.0 Fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, CA, USA), and then was implemented on Illumina Miseq platform (San Diego, CA, USA) at Shanghai Biotree Biotech. Co., Ltd.
The raw data were filtered, denoised, merged and chimera removed using Microbial Ecology software (v 2.0), and the high-quality sequences were collected, and then grouped into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) with similarities more than 97%. Taxonomy annotation process was carried out on the OTU sequences by the Mothur approach and the SSU rRNA database of SILVA138.1. Alpha and beta diversity of vaginal microbiota were analyzed by X shell (v 7.0). The overall differences of vaginal microbiota were assessed based on the principal coordinates analysis (PCoA, based on Bray method) by R software (v 4.4.2), the key microbial phylotypes were screened using Microbial Ecology software.
2.5 Untargeted metabolomics analysis
Untargeted metabolomics analysis was implemented by liquid chromatography-Orbitrap-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (LC-Orbitrap-MS/MS, Thermo Fisher Scientific, CA, USA) based on a previous report with minor modifications (Guo et al., 2025). Briefly, the vaginal contents were freeze-dried, weighted, and extracted using the organic solution (methanol: acetonitrile = 1:1). The mixture solution was sufficiently vibrated using a high-throughput oscillator, and placed at 0-4°C environment. After 2 h of stillness, the supernatant of each sample was collected by centrifugation (12000 g, 10 min, 2°C), and then dried at 25°C under a vacuum environment. The sediment of each sample was resuspended using the organic solution (methanol: acetonitrile = 1:1), the supernatant was collected by centrifugation (12000 g, 15 min, 2°C), and then filtrated by 0.22-μm aqueous membrane. Quality control samples consist of an equal volume of each sample, so as to assess the stability of instruments during the experiment.
The vagina metabolic profiling was analyzed using LC-Orbitrap-MS/MS with an ACQUITY UPLC BEH Amide column (50 × 2.1 mm, 1.7 µm; Waters, Milford, USA). Among these, MS detection of metabolites was carried out on Orbitrap Exploris 120 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, CA, USA) with an ESI ion source in positive and negative modes. Mobile phase A contained 0.1% formic acid and 5 mM ammonium acetate, and the mobile phase B was acetonitrile. The raw data were preliminarily treated using ProteoWizard software and R software (v 4.2.2), including peak alignment, peak identification, and deconvolution. Principal components analysis (PCA, based on Z-score normalization method), partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA, based on Kernelpls method), and orthogonal partial least-squares discrimination analysis (OPLS-DA) of vaginal metabolomics were carried out by MetaboAnalyst (v 6.0). Differential vaginal metabolites between the PrPG and PrTG groups were screened by S-loading plot based on OPLS-DA. The proportion of obviously different vaginal metabolites (VIP > 1.0, and p < 0.05) between the PrPG and PrTG groups was analyzed by R software (v 4.4.2).
2.6 Statistical analysis
All data of the present study were presented as the mean ± SD using GraphPad Prism 9.0 (GraphPad Software, Santiago, USA). The significant differences between the two groups were assessed based on Unpaired Student’s t test or Mann-Whitney U test using SPSS 24.0 statistical package (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
3 Results
3.1 Clinical characteristics and pregnancy outcome of participants
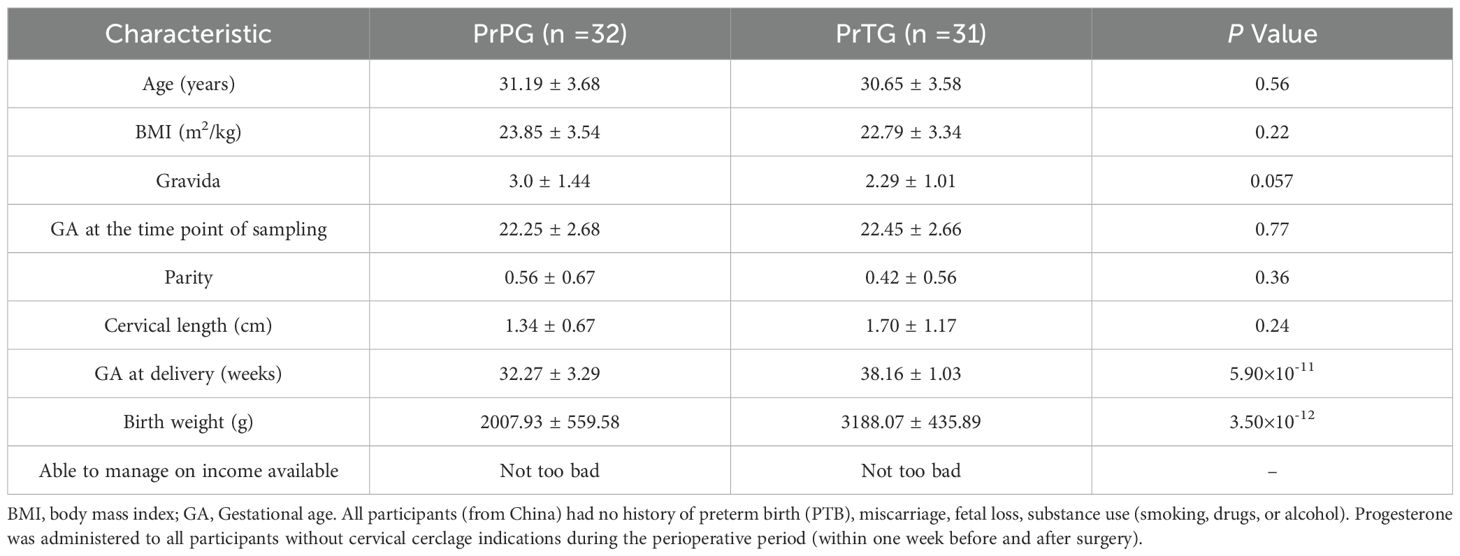
As shown in Table 1, a total of 63 participants were recruited in this study, including 32 women (50.79%) who delivered at term birth and 31 women (49.21%) who later experienced preterm delivery. No significant difference was observed between the PrPG and PrTG groups in maternal age, BMI, gravida, parity and cervical length (p > 0.05), but gestational age at delivery and birth weight in the PrTG group were higher than that in the PrPG group (p < 0.05).
3.2 Change of vaginal microbiota in pregnant women who eventually experienced preterm delivery
The vaginal microbiome diversity and composition were analyzed by 16S rDNA sequencing. As indicated in Figure 1A, the observed (180.53 ± 75.71 vs 178.10 ± 100.50, p = 0.91), Shannon (1.93 ± 1.19 vs 1.86 ± 1.87, p = 0.86), Simpson (0.45 ± 0.26 vs 0.38 ± 0.27, p = 0.31) and Chao1 (183.19 ± 76.81 vs 180.59 ± 101.12, p = 0.91) indexes of vaginal microbiota in the PrPG group were slightly higher than that in the PrTG group (p > 0.05). Among these, Shannon, Simpson, and Chao1 indexes are widely used to evaluate overall community complexity, emphasize dominant species, and address rare taxa to avoid underestimation of diversity, respectively. The Venn diagram showed that the quantity of operational taxonomic units (OTUs) shared by the two groups was 839, with the number of unique OTUs in the PrPG and PrTG groups being 1470 and 1301 respectively (Supplementary Figure S1). In addition, principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) was used to investigate the association between preterm delivery and vaginal microbiota composition (Figure 1B). The first principal components (PC1), second principal components (PC2) and third principal components (PC3) contributed 61%, 15% and 11% of the total variance in the PCoA score plot, respectively. Samples from the PrTG group were predominantly distributed along the negative of PC1, whereas those from the PrPG group exhibited a more dispersed distribution, suggesting that the disorder of vaginal microbiota was presented in pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery.
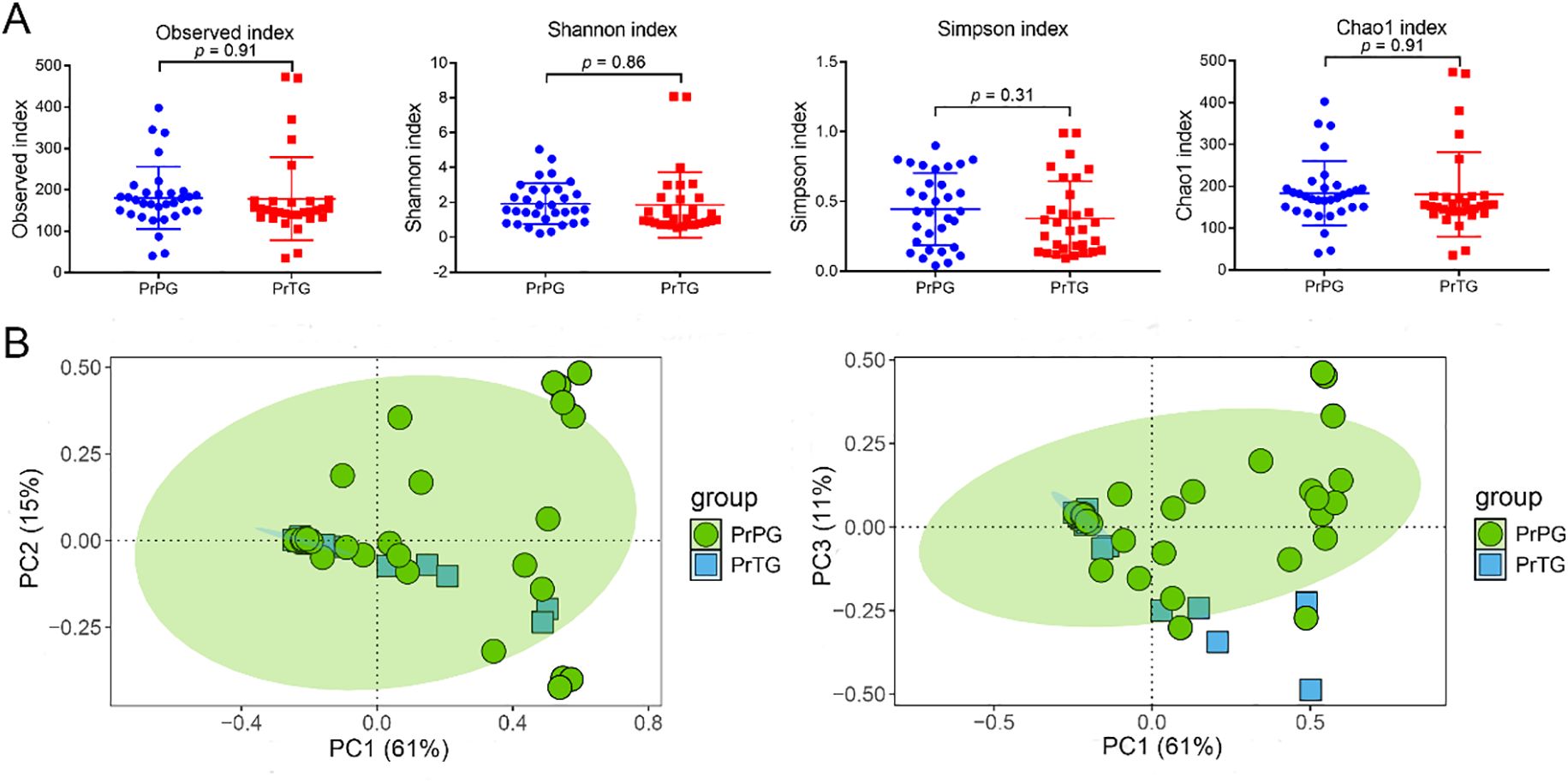
Figure 1. The diversity of between pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery and term birth. (A) Observed, Shannon, Simpson and Chao1 indexes, and (B) PCoA analysis based on Bray-Curtis distance.
3.3 Screening for key microbial phylotypes
The changes in microbiota composition in the vagina from pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery and term birth were revealed at differing levels. Firmicutes, Actinobacteriota, Proteobacteria, Bacteroidota, Fusobacteriota, Verrucomicrobiota and Acidobacteriota were mainly microorganisms in the PrPG and PrTG groups at the phylum level (Figure 2A). Notably, compared with the PrTG group, the proportion of Firmicutes (from 83.68% to 57.42%), Verrucomicrobiota (from 0.39% to 0.20%) and Acidobacteriota (from 1.35% to 0.31%) in the PrPG group was obviously reduced (p < 0.05), but the proportion of Actinobacteriota (from 6.23% to 27.92%), Proteobacteria (from 6.24% to 7.78%), Bacteroidota (from 1.69% to 3.70%) and Fusobacteriota (from 0.11% to 2.67%) was remarkably increased (p < 0.05). At the genus level, the proportion of Prevotella, Trichococcus, Actinomyces, Neisseria, Lactobacillus, Rothia, Gemella, Haemophilus and Porphyromonas was remarkably reduced in the PrPG group compared with that in the PrTG group (p < 0.05), but the relative abundance of Pseudoxanthomonas, Thauera, Ochrobactrum, Olivibacter, Gardnerella, Massilia, Phyllobacteriaceae_unclassified, Buchnera, Staphylococcus and Atopobium was significantly increased (p < 0.05) (Figure 2B).
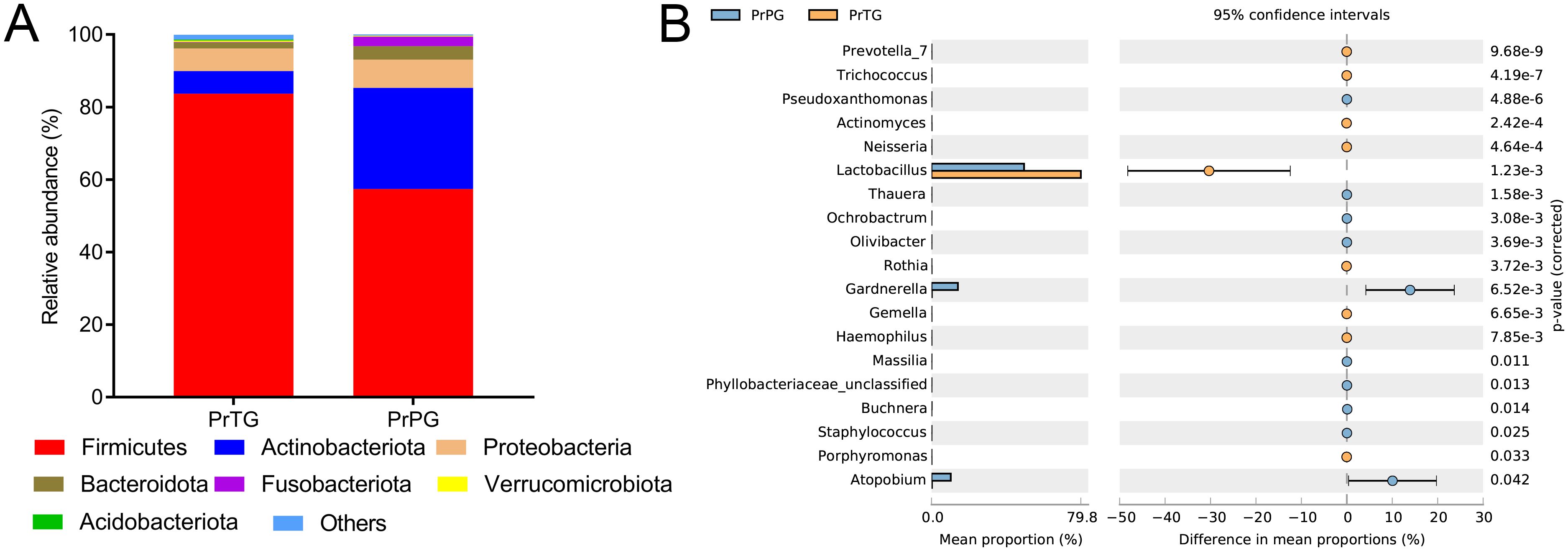
Figure 2. The relative abundance of vaginal microbiota between pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery and term birth before cervical cerclage. (A) phylum and (B) genus.
3.4 Change of vagina metabolic profiling in pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery
In the present study, vaginal metabolites between the PrTG and PrPG groups were detected by untargeted metabolomics based on LC-Orbitrap-MS/MS. PCA was used to reveal metabolic profile clustering between pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery and term birth. The result of PCA analysis displayed that PC1 and PC2 contributed for 26.6% and 12.7% of the total variation in the positive ion modes (Figure 3A), while PC1 and PC2 accounted for 36.0% and 8.4% of the total variation in the negative ion modes (Figure 4A). A clear separation was observed between the PrTG and PrPG groups, suggesting that alteration of vagina metabolic profiling may be one of the essential causes for preterm delivery. Subsequently, PLS-DA and OPLS-DA were applied to further revealed the changes in vagina metabolites (Figures 3B, C, 4B, C). Partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) and orthogonal partial least-squares discrimination analysis (OPLS-DA) scores plot showed an obvious distinction between the PrTG and PrPG groups in both the positive and negative ion modes. Furthermore, the S-plots of OPLS-DA confirmed differences in the vaginal metabolites between the PrTG and PrPG groups (Figures 3D, 4D).
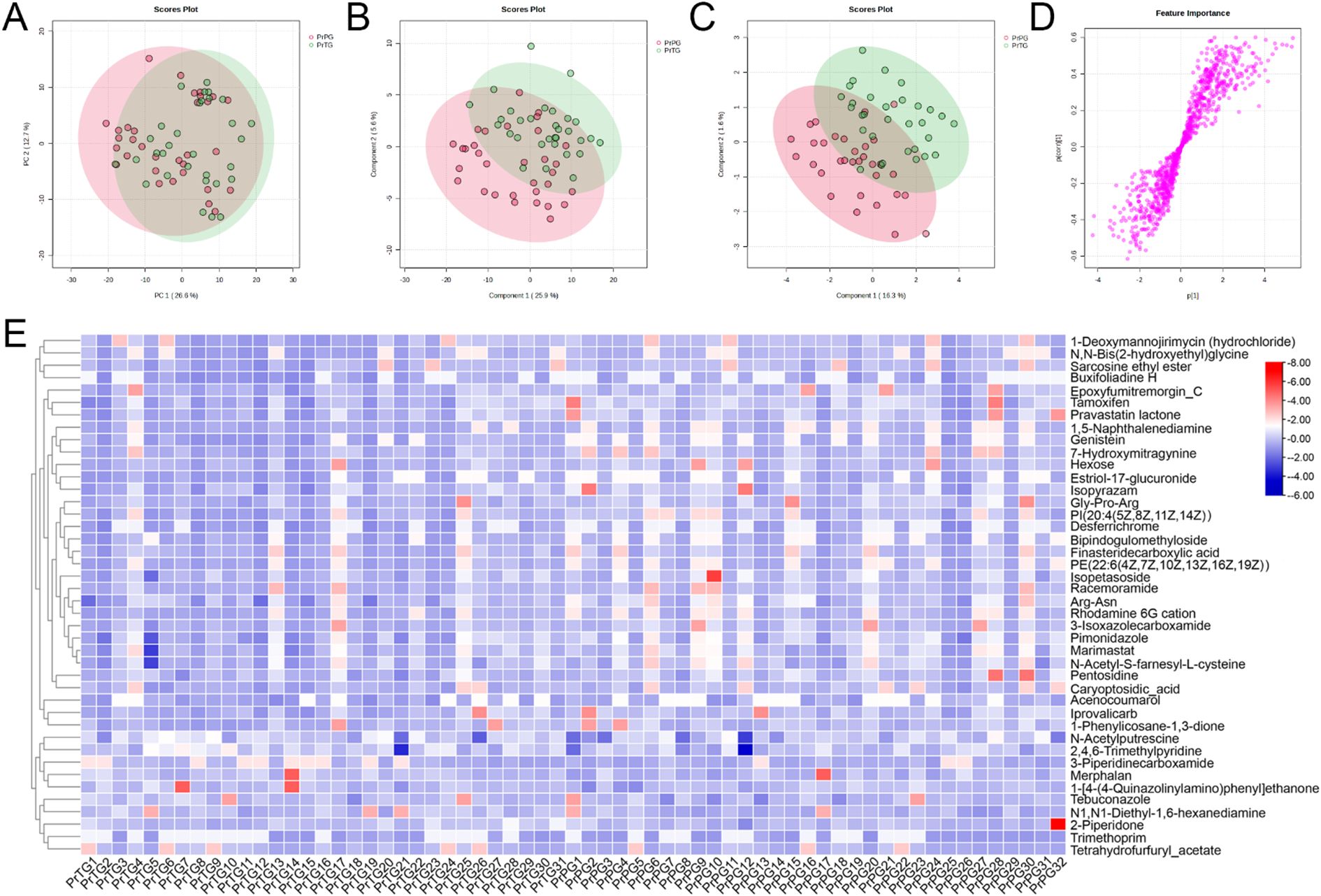
Figure 3. The alteration in vaginal metabolites in pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery in the positive ion modes. (A) PCA, (B) PLS-DA, (C) OPLS-DA, (D) S-plots of OPLS-DA, and (E) Heatmap exhibited the differential metabolites between the PrPG and PrTG groups.
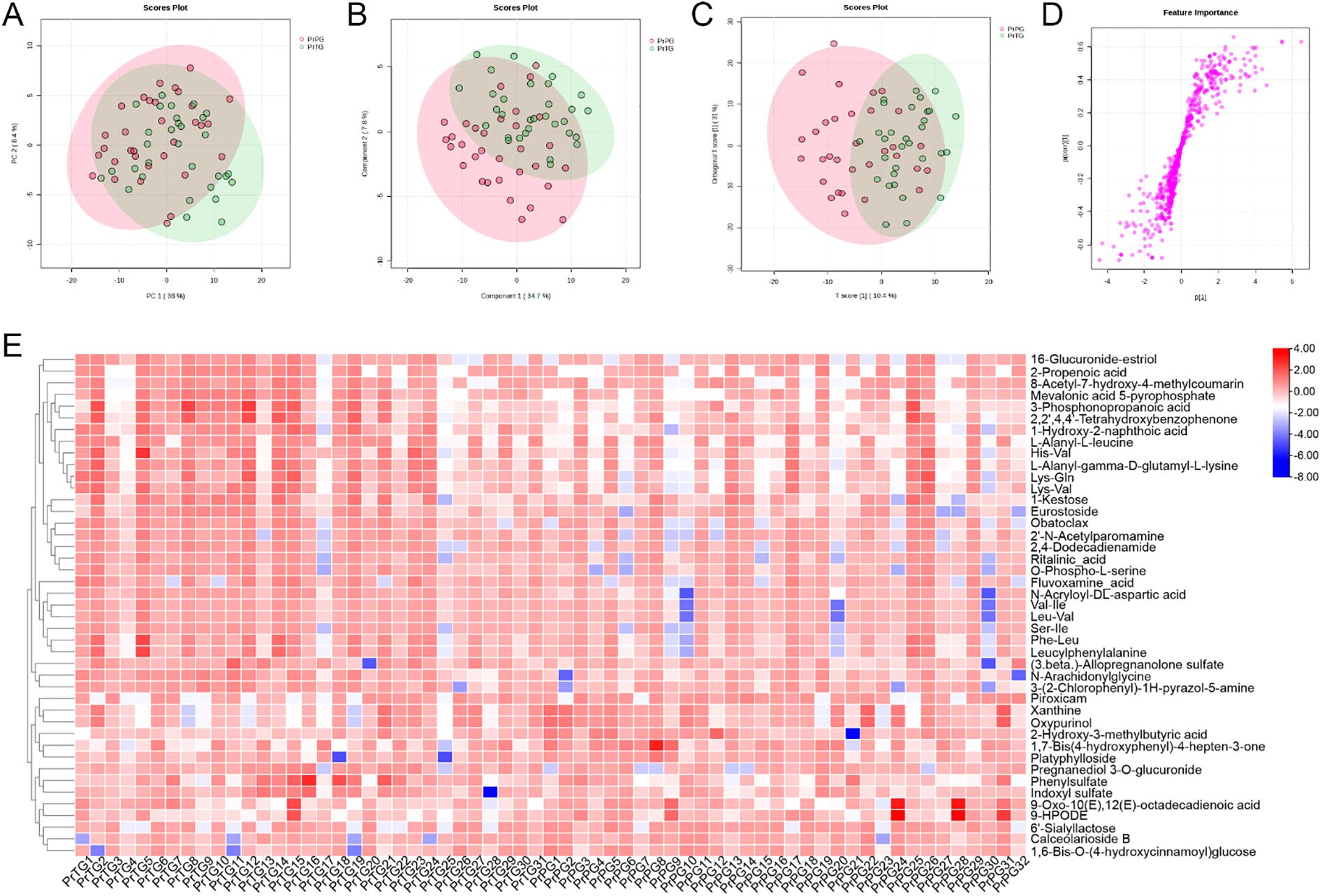
Figure 4. The alteration in vaginal metabolites in pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery in the negative ion modes. (A) PCA, (B) PLS-DA, (C) OPLS-DA, (D) S-plots of OPLS-DA, and (E) Heatmap exhibited the differential metabolites between the PrPG and PrTG groups.
3.5 Screening for differential vagina metabolites
Based on S-plot analysis of the OPLS-DA model, a total of 42 differential metabolites were identified between the PrTG and PrPG groups in positive ion mode (VIP value > 1 and p < 0.05) (Figure 3E). Among them, the levels of 2,4,6-Trimethylpyridine, N1,N1-Diethyl-1,6-hexanediamine, Tebuconazole, 1-[4-(4-Quinazolinylamino)phenyl]ethenone, Trimethoprim, Merphalan, 3-Piperidinecarboxamide, Tetrahydrofurfuryl_acetate, 2-Piperidone and N-Acetylputrescine in the PrPG group were significantly reduced compared with that in the PrTG group, while the levels of Pimonidazole, 1,5-Naphthalenediamine, Racemoramide, Acenocoumarol, Caryoptosidic_acid, Finasteridecarboxylic acid, Iprovalicarb, Gly-Pro-Arg, Isopyrazam, Pravastatin lactone, Pentosidine, 1-Phenylicosane-1,3-dione, Epoxyfumitremorgin_C, 3-Isoxazolecarboxamide, Bipindogulomethyloside, Marimastat, Hexose, Arg-Asn, Buxifoliadine H, 7-Hydroxymitragynine, Estriol-17-glucuronide, PE(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)), Isopetasoside, Rhodamine 6G cation, Desferrichrome, Tamoxifen, 1-Deoxymannojirimycin (hydrochloride), N-Acetyl-S-farnesyl-L-cysteine, N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine, PI(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)), Genistein and Sarcosine ethyl ester were significantly increased.
In the negative ion modes, a total of 43 differential metabolites between the PrTG and PrPG groups were screened (VIP value > 1 and p < 0.05) (Figure 4E). Among these, the proportion of 2-Hydroxy-3-methylbutyric acid, 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-hepten-3-one, Platyphylloside, Piroxicam, Oxypurinol, Xanthine, 1,6-Bis-O-(4-hydroxycinnamoyl)glucose, 6’-Sialyllactose, 9-Oxo-10(E),12(E)-octadecadienoic acid, Calceolarioside B and 9-HPODE in the PrPG group was significantly elevated compared with the PrPG group, but the proportion of Lys-Val, Obatoclax, L-Alanyl-gamma-D-glutamyl-L-lysine, Ser-Ile, L-Alanyl-L-leucine, Val-Ile, Leu-Val, Lys-Gln, Eurostoside, 2’-N-Acetylparomamine, Pregnanediol 3-O-glucuronide, Ritalinic_acid, 1-Hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, Leucylphenylalanine, Phe-Leu, N-Acryloyl-DL-aspartic acid, O-Phospho-L-serine, 3-(2-Chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-amine, 16-Glucuronide-estriol, 2,2’,4,4’-Tetrahydroxybenzophenone, Fluvoxamine_acid, 1-Kestose, Indoxyl sulfate, 2-Propenoic acid, His-Val, 2,4-Dodecadienamide, N-Arachidonylglycine, (3.beta.)-Allopregnanolone sulfate, Phenylsulfate, 3-Phosphonopropanoic acid, 8-Acetyl-7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin and Mevalonic acid 5-pyrophosphate was significantly decreased.
3.6 Metabolic pathway analysis
Untargeted metabolomic profiling revealed significant differences in vaginal metabolites between PrTG and PrPG groups. These differential metabolites were analyzed using MetaboAnalyst 6.0 to identify associated metabolic pathways through the KEGG database. In the metabolic pathway, each circle expresses one metabolic pathway, and the size and color of the circles depend on the importance and p-values of the pathway. In the positive ion modes, galactose metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism, and drug metabolism-cytochrome P450 were significantly disturbed in pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery (p < 0.05, Figure 5A). In the negative ion modes, ascorbate and aldarate metabolism, terpenoid backbone biosynthesis, pentose and glucuronate interconversions, cysteine and methionine metabolism, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, purine metabolism and steroid hormone biosynthesis were significantly disturbed in the pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery (p < 0.05, Figure 5B). These results revealed that the mentioned metabolic pathways were associated with preterm delivery in pregnant women.
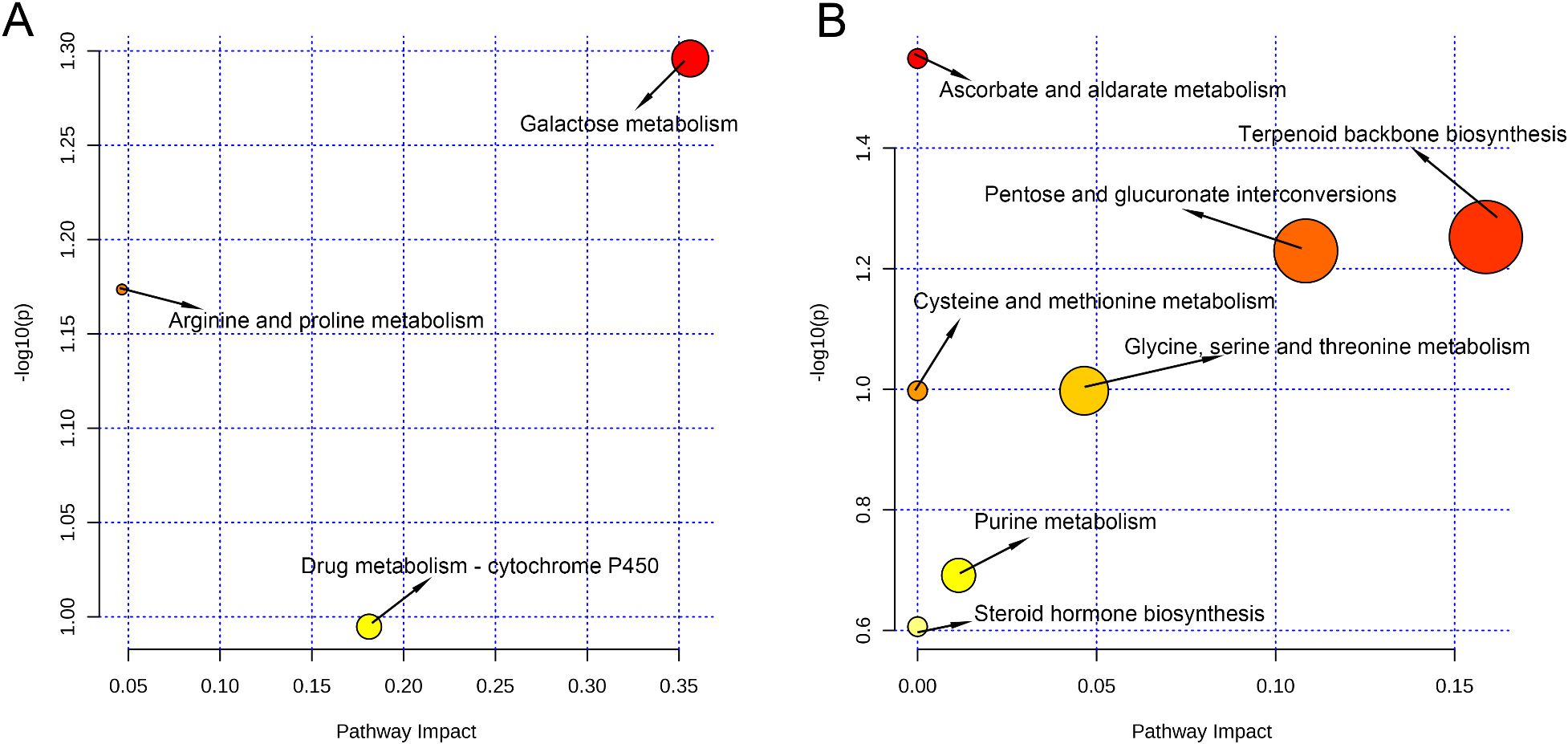
Figure 5. Analysis of key metabolic pathways (each point represents a metabolic pathway). (A) Pathway analysis in the positive ion modes and (B) in the negative ion modes. The p values calculated from the enrichment analysis are indicated by a color gradient: from white (highest p value) to red (lowest p value), while the pathway impact value calculated from pathway topology analysis is indicated by dot size.
4 Discussion
Preterm delivery has become an alarming public health concern due to the relatively higher mortality rate presented in preterm infants. According to the previous report, approximately three-quarters of preterm delivery cases are diagnosed as spontaneous preterm delivery, which includes previous spontaneous preterm delivery or preterm pre-labor rupture of the membranes (Humberg et al., 2020). Although the great progress made in cervical cerclage, there are substantial differences in treatment effectiveness among different populations (Park et al., 2022). Gut microbiota and its metabolites play a vital role in enhancing the host’s health, such as exhibiting hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic, antidiabetic, and antidepressant effects. Therefore, we hypothesized that preterm delivery is related to the alterations in vaginal microbiota and its metabolites. In the present study, 16S rRNA gene sequencing and untargeted metabolomics were used to detect and identify the vaginal microbiota and its metabolites, with the aim of screening the key microbial phylotypes and differential vagina metabolites.
The risk of preterm delivery is strongly related to the BMI of pregnant women. Specifically, a BMI above 28.0 or below 18.0 increases the risk of preterm delivery (Cnattingius et al., 2013). A high BMI in pregnant women elevates the likelihood of gestational diabetes, hypertensive disorders and fetal malformations, which are among the most significant factors contributing to medically indicated preterm delivery (Robinson et al., 2021). In addition, advanced maternal age (more than 35 years) and young maternal age (less than 25 years) also elevate the risk of preterm delivery (Wu et al., 2024). Therefore, participants were collected based on a BMI within the range of 18 to 28 and a maternal age within the range of 25 to 35, which is beneficial for eliminating the influence of BMI and year of pregnant woman on preterm delivery. In addition, the body weight of preterm infants was significantly lower than that of term infants, because of the infant development is not yet complete, which is in agreement with the result of this study (Kozuki et al., 2015).
The vaginal microbiota accounts for approximately 9% of the total human microbiota, which plays an essential role in improving vaginal health (Saraf et al., 2021). As a dynamic ecosystem composed of various microorganisms in different quantities and ratios, it helps preserve the integrity of the vaginal barrier and inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria (Shen et al., 2016). Recently, it has been reported that the composition of the vaginal microbiota often determines pregnancy outcomes (Salinas et al., 2020). In reproductive-age women, the proportion of Lactobacillus was obviously higher than that in others (Hayashida et al., 2022). Feehily et al. found vaginal Lactobacillus is consisted of L. crispatus, L. delbruecki, L. gasseri, L. gasseriA, L. H fermentum, L. H gastricus, L. helveticus, L. jensenii, L. kefiranofaciens and L. taiwanensis (Feehily et al., 2020). Lactobacillus is regarded as a probiotic that is beneficial for the host’s health when given in adequate amounts. Lactobacillus processes a series of physiological effects, such as suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory responses (Qin et al., 2024). Lactobacillus also prevents the growth of harmful bacteria in the vagina by elevating the levels of short-chain fatty acids (Tachedjian et al., 2017). However, Gardnerella is a keystone genus in the vaginal microbiome, which has been confirmed to negative health outcomes including preterm birth (Berman et al., 2024). Gardnerella could destroy the vagina barrier and stimulate inflammatory response by degrading the protective mucins and up-regulating the NF-κB pathway, respectively (Schellenberg et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2024). Therefore, the lower abundance of Lactobacillus and high abundance of Gardnerella may be related to preterm delivery.
Prevotella could regulate mucin metabolism by stimulating both its production and degradation, which maintain the integrity of the vaginal barrier (Tett et al., 2021). Trichococcus functions as a short-chain fatty acid-producing bacteria, providing energy for the proliferation of vaginal epithelial cells (Xiang et al., 2022). Gemella is an essential member of the human microbiome in healthy individuals, and rarely causes systemic illness (Zaidi et al., 2018). In this study, the proportion of Prevotella, Trichococcus, Neisseria and Gemella was remarkably reduced in the PrPG group, while Thauera, Ochrobactrum, Gardnerella, Massilia, Phyllobacteriaceae and Atopobium were significantly increased. Among them, Thauera has the capacity to break down androgen under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions (Hsiao et al., 2023). Ochrobactrum is a non-enteric and Gram-negative organism, and its abundance is strongly related to inflammatory responses (Gigi et al., 2017). Gardnerella is widely distributed in women of childbearing age, and the high proportion of Gardnerella cause various diseases, which is extensively used to establish the bacterial vaginitis in animal (Wong et al., 2022; Jothi et al., 2024). Massilia belongs to the family Oxalobacteraceae and is associated with bacteremia, central nervous system infections, wound infections, lymphadenitis, and osteomyelitis (Ali et al., 2022). Phyllobacteriaceae has been confirmed to destroy carbohydrate and/or fat metabolism, as well as stimulate inflammatory responses by producing lipopolysaccharide (Chen et al., 2021). A high abundance of Staphylococcus can cause severe infectious diseases, such as impetigo, folliculitis, and cutaneous abscesses (Tabiś et al., 2022). The presence of Staphylococcus can promote the occurrence of inflammatory responses, which elevates the risk of preterm birth (Astley et al., 2019; Cappelletti et al., 2016). In addition, a previous study found that high abundance of Atopobium was positively associated with the incidence rate of infertility, endometritis, and pelvic inflammatory disease (Ravel et al., 2021). These results suggested that vaginal microbiota plays a vital role in altering the gestational age.
Apart from vaginal microbiota, vaginal metabolites play the most important role in pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery (Kindschuh et al., 2023). 2-Piperidone could suppress the accumulation of reactive oxygen species and lipid peroxidation by regulating the activity of cytochrome P450 2E1 (Cheng et al., 2013). Obatoclax, a synthetic derivative of bacterial prodiginines, promotes the apoptosis of human colorectal carcinoma cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Eurostoside acts as a useful organic compound that has been proven to inhibit the inflammatory responses by regulating the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) (Le et al., 2023). Pregnanediol 3-O-glucuronide is a natural metabolite, and its levels are negatively associated with the risk of preterm delivery (Zhang et al., 2020). O-Phospho-L-serine acts as an inhibitor of serine racemase that can elevate the regulatory cytokine [(transforming growth factor-β (TGF‐β)] level and reduce the pro-inflammatory cytokines [tumor necrosis factor (TNF‐α) and interleukin-12p70 (IL-12p70)] in bone‐marrow‐derived dendritic cells (Fathallah et al., 2014). 1-Kestose is the smallest fructooligosaccharide component that modulates the composition of vaginal microbiota, particularly by up-regulating the abundance of Bifidobacteria, which protect the vaginal barrier (Tochio et al., 2018). Oral administration of 1-Kestose improves the symptoms of type 2 diabetes by elevating the short-chain fatty acids levels, such as acetate, butyrate and lactate (Watanabe et al., 2020). Short-chain fatty acids provide energy for vaginal epithelial cells, which is beneficial for the integrity of vaginal barrier. N-arachidonylglycine, an amino acid derivative of arachidonic acid, reduces CD4T cell responsiveness by reducing Th1 and Th17 cytokine levels, and regulating GPR18 MTORC1 signaling (Meadows et al., 2023). In this study, the relative contents of 2-Piperidone, Melphalan, N-acetylputrescine, Obatoclax, Eurostoside, Pregnanediol 3-O-glucuronide, O-Phospho-L-serine, 1-Kestose and N-arachidonylglycine in the PrPG group were obviously lower than that in the PrTG group. Acenocoumarol, a major organic compound in 4-hydroxycoumarins, is widely regarded as a potentially toxic compound (Valdivielso et al., 2004). Isopyrazam is a broad-spectrum succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor fungicide and has been confirmed to destroy the heart function by stimulating oxidative stress (Yan et al., 2023). Pentosidine is one of the best-characterized advanced glycation end-products that plays a pathological role in several aging-related disorders and can promote the development of diabetes (Li and Yu, 2018). Long-term consumption of hexose disrupt glucose metabolism, thereby elevating the risk of hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia (Ai et al., 2023). 7-Hydroxymitragynine is widely used as an anesthetic, but its excessive use can result in a series of adverse reactions (Vento et al., 2021). A previous study found that high-fat diet accelerates the accumulation of phosphoethanolamine (PE) in the liver, which promotes liver function injury (Guo et al., 2020). Tamoxifen is considered a path-breaking medication in tumor treatment, but it has also been reported to give rise to thrombosis, epigastric discomfort and nausea (Wibowo et al., 2016). 1-Deoxynojirimycin destroys endoplasmic reticulum function, leading to the accumulation of unfolded or misfolded proteins (Lu et al., 2006). In the present study, Acenocoumarol, Isopyrazam, Pentosidine, hexose, 7-Hydroxymitragynine, PE, Tamoxifen and 1-Deoxynojirimycin concentrations in the PrPG group were higher than that in the PrTG group. Therefore, we deduce that the alterations in vaginal metabolites may be one of the important causes for preterm delivery.
5 Conclusion
In this study, we found a significant difference in vaginal microbiota between the PrPG and PrTG groups, characterized by reduced Lactobacillus and increased Gardnerella. Vaginal metabolomics analysis also revealed specific metabolites in pregnant women who later experienced preterm delivery, such as pregnanediol 3-O-glucuronide. These results offer useful information to enhance the accuracy of the model of premature birth prediction by integrating vaginal microbiomics and metabolomics.
Data availability statement
The data presented in the study are deposited in the NCBI database, accession number PRJNA1122359.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Ethics Committee of Fujian Maternity and Child Health Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
MZ: Formal Analysis, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. JZ: Resources, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. LW: Writing – original draft, Project administration. BL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – original draft. MP: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZX: Resources, Writing – review & editing, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Fujian Provincial Technology Innovation Project (No.2021Y9175 and 2020Y9148), Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No.2022J011034 and 2021J01406).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1580801/full#supplementary-material
References
Adane, H. A., Iles, R., Boyle, J. A., Gelaw, A., and Collie, A. (2024). Effects of psychosocial work factors on preterm birth: systematic review and meta-analysis. Public Health 228, 65–72. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2023.12.002
Ai, Y. L., Wang, W. J., Liu, F. J., Fang, W., Chen, H. Z., Wu, L. Z., et al. (2023). Mannose antagonizes GSDME-mediated pyroptosis through AMPK activated by metabolite GlcNAc-6P. Cell Res. 33, 904–922. doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00848-6
Ali, G. A., Ibrahim, E. B., Doiphode, S. H., and Goravey, W. (2022). Massilia timonae bacteremia: An unusual pathogen of septic abortion. IDCases 29, e01592. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2022.e01592
Astley, R., Miller, F. C., Mursalin, M. H., Coburn, P. S., and Callegan, M. C. (2019). An eye on staphylococcus aureus toxins: Roles in ocular damage and inflammation. Toxins (Basel) 11, 356. doi: 10.3390/toxins11060356
Beernink, R. H. J., Schuitemaker, J. H. N., Zwertbroek, E. F., Scherjon, S. A., and Cremers, T. I. F. H. (2023). Early pregnancy biomarker discovery study for spontaneous preterm birth. Placenta 139, 112–119. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2023.06.011
Berman, H. L., Goltsman, D. S. A., Relman, D. A., and Callahan, B. J. (2024). Gardnerella diversity and ecology in pregnancy and preterm birth. mSystems 9 (16), 1–24. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01339-23
Cappelletti, M., Della Bella, S., Ferrazzi, E., Mavilio, D., and Divanovic, S. (2016). Inflammation and preterm birth. J. Leukoc. Biol. 99, 67–78. doi: 10.1189/jlb.3MR0615-272RR
Chee, W. J. Y., Chew, S. Y., and Than, L. T. L. (2020). Vaginal microbiota and the potential of Lactobacillus derivatives in maintaining vaginal health. Microb. Cell Fact. 19, 203. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01464-4
Chen, P., Chen, P., Guo, Y., Fang, C., and Li, T. (2021). Interaction between chronic endometritis caused endometrial microbiota disorder and endometrial immune environment change in recurrent implantation failure. Front. Immunol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.748447
Cheng, J., Chen, C., Kristopher, K. W., Manna, S. K., Scerba, M., Friedman, F. K., et al. (2013). Identification of 2-piperidone as a biomarker of CYP2E1 activity through metabolomic phenotyping. Toxicol. Sci. 135, 37–47. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft143
Cnattingius, S., Villamor, E., Johansson, S., Edstedt Bonamy, A. K., Persson, M., Wikström, A. K., et al. (2013). Maternal obesity and risk of preterm delivery. JAMA 309, 2362–2370. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.6295
Fang, J., Chen, L., Chen, Z., Jiang, X., and Pan, M. (2020). Association of the vaginal microbiota with pregnancy outcomes in Chinese women after cervical cerclage. Reprod. Biomed. Online. 41, 698–706. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2020.06.016
Fathallah, A. M., Ramakrishnan, R., and Balu-Iyer, S. V. (2014). O-Phospho-l-Serine mediates hyporesponsiveness toward FVIII in hemophilia a-murine model by inducing tolerogenic properties in dendritic cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 103, 3457–3463. doi: 10.1002/jps.24173
Feehily, C., Crosby, D., Walsh, C. J., Lawton, E. M., Higgins, S., McAuliffe, F. M., et al. (2020). Shotgun sequencing of the vaginal microbiome reveals both a species and functional potential signature of preterm birth. NPJ Biofilms. Microbi. 6, 50. doi: 10.1038/s41522-020-00162-8
Fettweis, J. M., Serrano, M. G., Brooks, J. P., Edwards, D. J., Girerd, P. H., Parikh, H. I., et al. (2019). The vaginal microbiome and preterm birth. Nat. Med. 25, 1012–1021. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0450-2
Gigi, R., Flusser, G., Kadar, A., Salai, M., and Elias, S. (2017). Ochrobactrum anthropi-caused osteomyelitis in the foot mimicking a bone tumor: case report and review of the literature. J. Foot. Ankle Surg. 56, 851–853. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2017.02.008
Golob, J. L., Oskotsky, T. T., Tang, A. S., Roldan, A., Chung, V., Ha, C. W. Y., et al. (2024). Microbiome preterm birth DREAM challenge: crowdsourcing machine learning approaches to advance preterm birth research. Cell Rep. Med. 5, 101350. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101350
Guo, W., Cui, S., Tang, X., Yan, Y., Xiong, F., Zhang, Q., et al. (2023a). Intestinal microbiomics and hepatic metabolomics insights into the potential mechanisms of probiotic Bifidobacterium pseudolongum CCFM1253 preventing acute liver injury in mice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 103, 5958–5969. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12665
Guo, W., Cui, S., Tang, X., Zhang, Q., Zhao, J., Mao, B., et al. (2023b). Intestinal microbiomics and metabolomics insights into the hepatoprotective effects of Lactobacillus paracasei CCFM1222 against the acute liver injury in mice. Probiotics Antimicro. 15, 1063–1077. doi: 10.1007/s12602-022-09986-6
Guo, W. L., Guo, J. B., Liu, B. Y., Lu, J. Q., Chen, M., Liu, B., et al. (2020). Ganoderic acid A from Ganoderma lucidum ameliorates lipid metabolism and alters gut microbiota composition in hyperlipidemic mice fed a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 11, 6818–6833. doi: 10.1039/d0fo00436g
Guo, W., Liu, W., Liang, P., Ni, L., Lv, X., Fan, J., et al. (2025a). High molecular weight polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum attenuates inflammatory responses, gut microbiota, and liver metabolomic in lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 287, 138400. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.138400
Guo, W., Mao, B., Tang, X., Zhang, Q., Zhao, J., Zhang, H., et al. (2025). Improvement of inflammatory bowel disease by lactic acid bacteria-derived metabolites: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 65, 1261–1278. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2291188
Hayashida, S., Takada, K., Melnikov, V. G., Komine-Aizawa, S., Tsuji, N. M., and Hayakawa, S. (2022). How were Lactobacillus species selected as single dominant species in the human vaginal microbiota? Coevolution of humans and Lactobacillus. Med. Hypotheses 163, 110858. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2022.110858
Hong, X., Surkan, P. J., Zhang, B., Keiser, A., Ji, Y., Ji, H., et al. (2021). Genome-wide association study identifies a novel maternal gene × stress interaction associated with spontaneous preterm birth. Pediatr. Res. 89, 1549–1556. doi: 10.1038/s41390-020-1093-1
Hsiao, T. H., Chou, C. H., Chen, Y. L., Wang, P. H., Brandon-Mong, G. J., Lee, T. H., et al. (2023). Circulating androgen regulation by androgen-catabolizing gut bacteria in male mouse gut. Gut Microbes 15, 2183685. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2183685
Humberg, A., Fortmann, I., Siller, B., Kopp, M. V., Herting, E., Göpel, W., et al. (2020). Preterm birth and sustained inflammation: consequences for the neonate. Semin. Immunopathol. 42, 451–468. doi: 10.1007/s00281-020-00803-2
Jothi, R., Kamaladevi, A., Muthuramalingam, P., Malligarjunan, N., Karutha Pandian, S., and Gowrishankar, S. (2024). Untargeted metabolomics uncovers prime pathways linked to antibacterial action of citral against bacterial vaginosis-causing Gardnerella vaginalis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Heliyon 10, e27983. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27983
Kindschuh, W. F., Baldini, F., Liu, M. C., Liao, J., Meydan, Y., Lee, H. H., et al. (2023). Preterm birth is associated with xenobiotics and predicted by the vaginal metabolome. Nat. Microbiol. 8, 246–259. doi: 10.1038/s41564-022-01293-8
Kozuki, N., Katz, J., Lee, A. C. C., Vogel, J. P., Silveira, M. F., Sania, A., et al. (2015). Short maternal stature increases risk of small-for-gestational-age and preterm births in low- and middle-income countries: individual participant data meta-analysis and population attributable fraction1, 2, 3. J. Nutr. 145, 2542–2550. doi: 10.3945/jn.115.216374
Le, D. D., Han, S., Yu, J., Ahn, J., Kim, C. K., and Lee, M. (2023). Iridoid derivatives from Vitex rotundifolia L.f. with their anti-inflammatory activity. Phytochemistry 210, 113649. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2023.113649
Li, H. and Yu, S. J. (2018). Review of pentosidine and pyrraline in food and chemical models: formation, potential risks and determination. J. Sci. Food Agric. 98, 3225–3233. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8853
Liu, Y., He, L., Hu, Y., Liao, X., Wang, H., and Yang, L. (2024). Synthetic bacterial consortia transplantation attenuates vaginal inflammation and modulates the immune response in a mouse model of Gardnerella vaginalis-induced bacterial vaginosis. Heliyon 10, e38218. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38218
Lu, Y., Xu, Y. Y., Fan, K. Y., and Shen, Z. H. (2006). 1-Deoxymannojirimycin, the alpha1,2-mannosidase inhibitor, induced cellular endoplasmic reticulum stress in human hepatocarcinoma cell 7721. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 344, 221–225. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.111
Meadows, A. M., Han, K., Singh, K., Murgia, A., McNally, B. D., West, J. A., et al. (2023). N-arachidonylglycine is a caloric state-dependent circulating metabolite which regulates human CD4+T cell responsiveness. iScience 26, 106578. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106578
Ohuma, E. O., Moller, A.-B., Bradley, E., Chakwera, S., Hussain-Alkhateeb, L., Lewin, A., et al. (2023). National, regional, and global estimates of preterm birth in 2020, with trends from 2010: a systematic analysis. Lancet 402, 1261–1271. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00878-4
Park, S., Moon, J., Kang, N., Kim, Y. H., You, Y. A., Kwon, E., et al. (2022). Predicting preterm birth through vaginal microbiota, cervical length, and WBC using a machine learning model. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.912853
Peelen, M. J., Luef, B. M., Lamont, R. F., de Milliano, I., Jensen, J. S., Limpens, J., et al. (2019). The influence of the vaginal microbiota on preterm birth: A systematic review and recommendations for a minimum dataset for future research. Placenta 79, 30–39. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2019.03.011
Qin, J., Ma, Y., Wang, C., Li, H., Zou, Z., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024). Effects of carnosine combined with Lactobacillus on the antioxidant capacity of liver and kidney in normal or stressed mice. Food Biosci. 59, 103904. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2024.103904
Ravel, J., Moreno, I., and Simón, C. (2021). Bacterial vaginosis and its association with infertility, endometritis, and pelvic inflammatory disease. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 224, 251–257. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.10.019
Robinson, D. T., Van Horn, L., Balmert, L., Silver, R. M., Parry, S., Haas, D. M., et al. (2021). Dietary fat and fatty acid intake in nulliparous women: Associations with preterm birth and distinctions by maternal BMI. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 5, nzab074. doi: 10.1093/cdn/nzab074
Salinas, A. M., Osorio, V. G., Pacha-Herrera, D., Vivanco, J. S., Trueba, A. F., and MaChado, A. (2020). Vaginal microbiota evaluation and prevalence of key pathogens in Ecuadorian women: an epidemiologic analysis. Sci. Rep. 10, 18358. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74655-z
Saraf, V. S., Sheikh, S. A., Ahmad, A., Gillevet, P. M., Bokhari, H., and Javed, S. (2021). Vaginal microbiome: normalcy vs dysbiosis. Arch. Microbiol. 203, 3793–3802. doi: 10.1007/s00203-021-02414-3
Schellenberg, J. J., Jayaprakash, P. T., Gamage, N. W., Patterson, M. H., Vaneechoutte, M., and Hill, J. E. (2016). Gardnerella vaginalis subgroups defined by cpn60 sequencing and sialidase activity in isolates from Canada, Belgium and Kenya. PloS One 11, e0146510. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146510
Seyama, R., Makino, S., Takeda, J., Takeda, S., and Itakura, A. (2022). The retrospective study for effectiveness of cervical cerclage in preventing recurrent preterm birth. Taiwanese J. Obstet. Gynecolo. 61, 63–69. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2021.11.012
Shen, J., Song, N., Williams, C. J., Brown, C. J., Yan, Z., Xu, C., et al. (2016). Effects of low dose estrogen therapy on the vaginal microbiomes of women with atrophic vaginitis. Sci. Rep. 6, 24380. doi: 10.1038/srep24380
Tabiś, A., Gonet, M., Schubert, J., Miazek, A., Nowak, M., Tomaszek, A., et al. (2022). Analysis of enterotoxigenic effect of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis enterotoxins C and L on mice. Microbiol. Res. 258, 126979. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.126979
Tachedjian, G., Aldunate, M., Bradshaw, C. S., and Cone, R. A. (2017). The role of lactic acid production by probiotic Lactobacillus species in vaginal health. Res. Microbiol. 168, 782–792. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2017.04.001
Tett, A., Pasolli, E., Masetti, G., Ercolini, D., and Segata, N. (2021). Prevotella diversity, niches and interactions with the human host. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 19, 585–599. doi: 10.1038/s41579-021-00559-y
Tochio, T., Kadota, Y., Tanaka, T., and Koga, Y. (2018). 1-Kestose, the smallest fructooligosaccharide component, which efficiently stimulates faecalibacterium prausnitzii as well as Bifidobacteria in humans. Foods 7, 140. doi: 10.3390/foods7090140
Valdivielso, M., Longo, I., Lecona, M., and Lázaro, P. (2004). Cutaneous necrosis induced by acenocoumarol. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 18, 211–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2004.00735.x
Vento, A. E., de Persis, S., De Filippis, S., Schifano, F., Napoletano, F., Corkery, J. M., et al. (2021). Case report: treatment of kratom use disorder with a classical tricyclic antidepressant. Front. Psychiatry 12. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.640218
Watanabe, A., Kadota, Y., Kamio, R., Tochio, T., Endo, A., Shimomura, Y., et al. (2020). 1-Kestose supplementation mitigates the progressive deterioration of glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes OLETF rats. Sci. Rep. 10, 15674. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72773-2
Wei, J., Zhang, L., Xu, H., and Luo, Q. (2024). Preterm birth, a consequence of immune deviation mediated hyperinflammation. Heliyon 10, e28483. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28483
Wibowo, E., Pollock, P. A., Hollis, N., and Wassersug, R. J. (2016). Tamoxifen in men: a review of adverse events. Andrology 4, 776–788. doi: 10.1111/andr.12197
Wong, Y. P., Cheah, F. C., Wong, K. K., Shah, S. A., Phon, S. E., Ng, B. K., et al. (2022). Gardnerella vaginalis infection in pregnancy: Effects on placental development and neonatal outcomes. Placenta 120, 79–87. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2022.02.018
Wu, S. T., Lin, C. H., Lin, Y. H., Hsu, Y. C., Hsu, C. T., and Lin, M. C. (2024). Maternal risk factors for preterm birth in Taiwan, a nationwide population-based cohort study. Pediatr. Neonatol. 65, 38–47. doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2023.03.014
Xiang, J. Y., Chi, Y. Y., Han, J. X., Kong, P., Liang, Z., Wang, D., et al. (2022). Litchi chinensis seed prevents obesity and modulates the gut microbiota and mycobiota compositions in high-fat diet-induced obese zebrafish. Food Funct. 13, 2832–2845. doi: 10.1039/d1fo03991a
Xie, Y., Mu, Y., Chen, P., Liu, Z., Wang, Y., Li, Q., et al. (2022). Interrupted-time-series analysis of the immediate impact of COVID-19 mitigation measures on preterm birth in China. Nat. Commun. 13, 5190. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32814-y
Yan, Y., Liang, S., Zhang, T., Deng, C., Li, H., Zhang, D., et al. (2023). Acute exposure of Isopyrazam damages the developed cardiovascular system of zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Environ. Sci. Health B 58, 367–377. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2023.2197655
Zaidi, S. J., Husayni, T., and Collins, M. A. (2018). Gemella bergeri infective endocarditis: a case report and brief review of literature. Cardiol. Young 28, 762–764. doi: 10.1017/s1047951118000070
Zhang, Y., Li, W., Chen, T. T., Yang, Y., Wu, M. Y., Luo, J. Y., et al. (2020). Chemical fingerprint analysis and ultra-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry-based metabolomics study of the protective effect of buxue yimu granule in medical-induced incomplete abortion rats. Front. Pharmacol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.578217
Keywords: preterm birth, vaginal microbiome, vaginal metabolomics, microbial-marker, metabolic pathway
Citation: Wang L, Zhang J, Zhang M, Xu Z, Zheng Y, Lv B and Pan M (2025) Insights into the alteration of vaginal microbiota and metabolites in pregnant woman with preterm delivery: prospective cohort study. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1580801. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1580801
Received: 31 March 2025; Accepted: 21 July 2025;
Published: 18 September 2025.
Edited by:
Martin Mueller, University Hospital Bern, SwitzerlandReviewed by:
Martin Mueller, University Hospital Bern, SwitzerlandKeiji Nagano, Health Sciences University of Hokkaido, Japan
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Zhang, Zhang, Xu, Zheng, Lv and Pan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mian Pan, cGFubWlhbjE5NzNAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Lihua Wang
Lihua Wang Mian Pan
Mian Pan