- Hunan Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Druggability and Preparation, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
Antimicrobial resistance has emerged as a critical global health challenge requiring urgent multidisciplinary interventions. Pathogenic bacteria utilize six principal resistance mechanisms: (1) Enzymatic degradation of antibiotics via the production of inactivating enzymes; (2) Inactivation of antibiotics by changing the drug targets; (3) Reduction of antibiotics entry by decreasing bacterial permeability; (4) Enhanced antibiotics efflux through overexpression of efflux pumps; (5) Acquisition of antibiotics resistance via genetic mutations; (6) Development of antibiotics resistance through formation of microbial biofilms. Notably, these resistance determinants demonstrate close coordination through quorum sensing, collectively establishing recalcitrant infections that defy conventional therapies. Emerging evidence confirms the therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine in combating antimicrobial resistance. Traditional Chinese medicine can be used as quorum sensing inhibitors to interfere with the quorum sensing of bacteria, thereby achieving antibacterial effects. Moreover, traditional Chinese medicine has the characteristics of rich components, long history, mild action and no drug resistance, which makes it stand out in the research against drug-resistant bacterial infections. This paper systematically describes six mechanisms of bacterial resistance and reviews the antagonistic effects of traditional Chinese medicine against these mechanisms based on quorum sensing. It highlights that the active ingredients, extracts and compound formulations of traditional Chinese medicine have good reversal effects on bacterial antibiotic resistance, which can effectively treat drug-resistant bacterial infections. When combined with antibiotics, traditional Chinese medicine not only reduces antibiotics dosage but also adverse reactions, holding promise for improving and addressing clinical challenges posed by bacterial resistance. This article further discusses the impact of different delivery methods on the anti-bacterial biofilms efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine. It introduces the main delivery methods of traditional Chinese medicine at present and the new delivery methods under research, pointing out the huge development potential in the research of traditional Chinese medicine dosage forms. Additionally, the deficiencies and improvement methods of the current research were pointed out, and prospects for future related research were put forward.
Introduction
The misuse of antibiotics has intensified the global crisis of bacterial antibiotic resistance, with superbugs posing a significant threat to public health (Liu et al., 2022c). Antimicrobial resistance has become the leading cause of death worldwide, with the largest increase in deaths due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections. For all abbreviations used in this article, please refer to Supplementary File 1. Among Gram negative bacteria, the increase in resistance to carbapenem antibiotics is the highest, and antimicrobial resistance is heaviest in resource-limited areas (Christopher et al., 2022; Larsson and Flach, 2022; Sheila et al., 2023), Therefore, deciphering the mechanisms of bacterial resistance and developing strategies to reverse antibiotic resistance are critical imperatives for addressing infections caused by drug-resistant pathogens. As scientific research progresses, the mechanisms underlying bacterial resistance are being progressively elucidated, while strategies to reverse this resistance are undergoing continuous exploration. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics typically arises from antibiotic destruction or modification, target alterations (target substitution, target mutation, target enzymatic alteration, target protection, target overproduction or target bypass), and reduced intracellular antibiotic accumulation due to decreased permeability or increased efflux (Christaki et al., 2020; Denk-Lobnig and Wood, 2023; Smith et al., 2023). Genetic mutation or biofilm formation also represent critical mechanisms of antibiotic resistance (Asenjo et al., 2021; Darby et al., 2023; Grooters et al., 2024). These resistance mechanisms rarely act in isolation; instead, they often involve systemic interactions mediated by quorum sensing among bacteria. As a cellular signal transmission system, quorum sensing generates diverse signal molecules to facilitate intercellular communication, just like weaving a dense network, manipulating the close relationship and interaction between bacterial populations (Liu et al., 2022b; Smith and Schuster, 2022; Su et al., 2023). It is these interwoven relationships that contribute to bacterial resistance. Antibiotics have been hailed as one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century, but now hygiene concerns are forcing people to find new ways to fight them (Behling et al., 2023; Lessa and Sievert, 2023). As a treasure of Chinese cultural heritage, traditional Chinese medicine offers distinct advantages, including diverse botanical resources, high therapeutic value, minimal toxicity, and broad clinical applicability. Traditional Chinese medicine contains rich natural compounds and has great potential for development. In recent years, traditional Chinese medicine has seen extensive applications across industries, including cosmetics, food and healthcare. Popular products such as essential oils, skincare products, functional drinks and milk tea, added with traditional Chinese medicine ingredients, exemplify its versatility. Studies have confirmed that many traditional Chinese medicines have strong antibacterial effect and reverse the bacterial antibiotic resistance. When combined with antibiotics, it can restore the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics, offering an effective strategy to mitigate antibiotics resistance. This review summarizes the mechanisms of bacterial drug resistance and discusses the resistance-reversing effects of traditional Chinese medicine through quorum sensing modulation.
Study on drug resistance mechanism of bacteria
At present, typical multidrug-resistant bacteria include Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa), Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii), MRSA, Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), etc. The commonalities of these multidrug-resistant bacteria are strong resistance, high virulence, and strong pathogenicity. Their resistance mechanisms are roughly shown in Figure 1 (Chakraborty et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022; Qin et al., 2022; Darby et al., 2023).
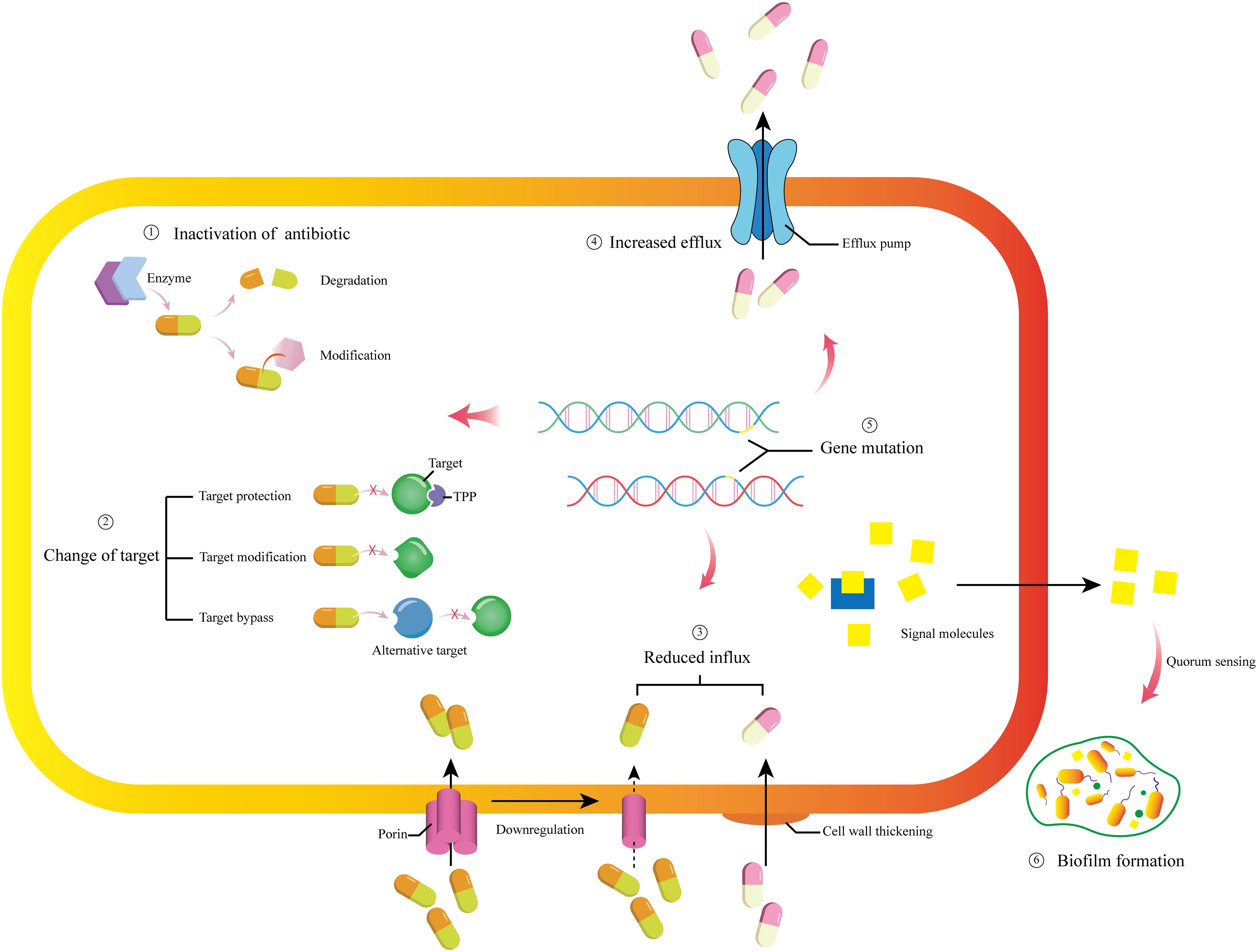
Figure 1. Brief depictions of the molecular mechanism of bacterial resistance. ① Under the enzymatic action of relevant enzymes, antibiotics are degraded and inactivated, or their structures are modified to lose their activity. ② Changing drug targets through three pathways: target protection, target modification, and target bypass. ③ Downregulating the number of porins and thickening the cell wall to reduce the intake of drug molecules. ④ Regulating the efflux pumps to increase the efflux of drug molecules. ⑤ Mutations occur in resistance related gene, and the mutations can regulate other resistance mechanisms. ⑥ Generate signal molecules for quorum sensing, mediating biofilm formation.
Production of inactivation enzymes by bacteria
Bacteria develop antibiotic resistance by producing inactivating enzymes or through enzymatic action. Enzymes play a crucial role in the formation of drug resistance via various enzymatic reactions, including hydrolysis, group transfer and oxidation-reduction. For example, β-lactamases hydrolyze β-lactam antibiotics (e.g., penicillin and cephalosporin) by disrupting their four-membered lactam ring, thereby abolishing their biological activity. Similarly, erythromycin esterase inactivates macrolide antibiotics like erythromycin through hydrolysis of their ester bonds (Lima et al., 2020; Mohanty et al., 2021; Michał et al., 2023). Histone acetyltransferase, a member of the N-acetyltransferase family, can transfer acetyl groups to amine groups in a variety of substrates. It can acetylate histones, nuclear high-mobility group proteins, and polyamine isomers, and also exhibits acetylation activity toward kanamycin and streptomycin, two common aminoglycoside antibiotics, resulting in associated resistance (Tomar et al., 2019). Pyruvate kinase, a glycolytic enzyme regulating bacterial metabolism, can be acetylated under the action of non-enzymatic acetyl phosphatase, and its acetylated form is highly expressed in the drug-resistant strains. Studies have demonstrated that acetylation reduces pyruvate kinase activity, enhancing bacterial resistance to antibiotics. Deacetylation can change the conformation of its ATP-binding site, restoring enzyme activity and increasing energy production, thus enhancing the sensitivity of drug-resistant strains to antibiotics (Fang et al., 2022). Tetracycline can be oxidized and inactivated by TetX enzymes (Rudra et al., 2018; Cheng et al., 2021), in which purified monooxygenase MabTetX can rapidly monooxidize tetracycline and doxycycline, which endows Mycobacterium abscessus with high resistance to these two tetracycline. In addition, the monooxygenase Tet (X4) endows a variety of bacteria with resistance to tigecycline, and amino acid changes in the Tet (X4) structure trigger several alpha helical and beta folds to refold in the second-order structure of the Tet (X4) substrate binding domain, thus forming more rings in the structure, making it more flexible and efficient at trapping substrate molecules. The oxidative destruction effect of antibiotics is better, and the resistance is stronger.
Alteration of drug targets by bacteria
Altering drug targets represents a prevalent mechanism of antibiotic resistance (Hunashal et al., 2023; Aleksandrova et al., 2024). For example, polymyxin resistance arises from the morphological changes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Mutations in genes encoding the two-component regulatory system—such as those driving pmrC overexpression—lead to lipid A modification. When phosphoethanolamine was added to lipid A, the negative charge on LPS and the binding with polymyxin were reduced. The resistance of bacteria to daptomycin was also associated with changes in membrane charge and phospholipid content, the mechanism of drug resistance was due to the redistribution of the cardiophospholipid domain of the main binding site of daptomycin and cocci. Ribosome is an important drug target, and methyltransferase can make bacteria resistant to aminoglycoside antibiotics by modifying the target ribosome with methylylation. After methyltransferase Cfr, which is expressed in thermophilic bacteria, methylates adenine residues 2503 in the ribosome center, nucleotide A2062 is also allosteric rearrangement, which likely prevents catalytic peptidyl transferase-targeting antibiotics from binding to the ribosome. This mechanism underscores the drug resistance caused by methyltransferase Cfr. Tetracycline drugs inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 30S subunit of ribosomes, and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) circumvents tetracycline activity through targets protection mechanisms, primarily involving Tet(M) and Tet(S) proteins that dissociate tetracycline molecules from the 30S subunit of the ribosome (Mlynarczyk-Bonikowska et al., 2022). Target protection plays a key role in clinical antibiotic resistance (Wilson et al., 2020), and Target protective proteins (TPPs) can mediate antibiotic resistance in three ways: remove drugs sterically from the targets (class I), separate the drugs from the targets allosterically by inducing a structural change within the target (class II), or restore the function of the targets in the presence of binding antibiotics by inducing a conformational change within the target (Class III),as shown in Figure 2 (Darby et al., 2023; Xiao et al., 2023).
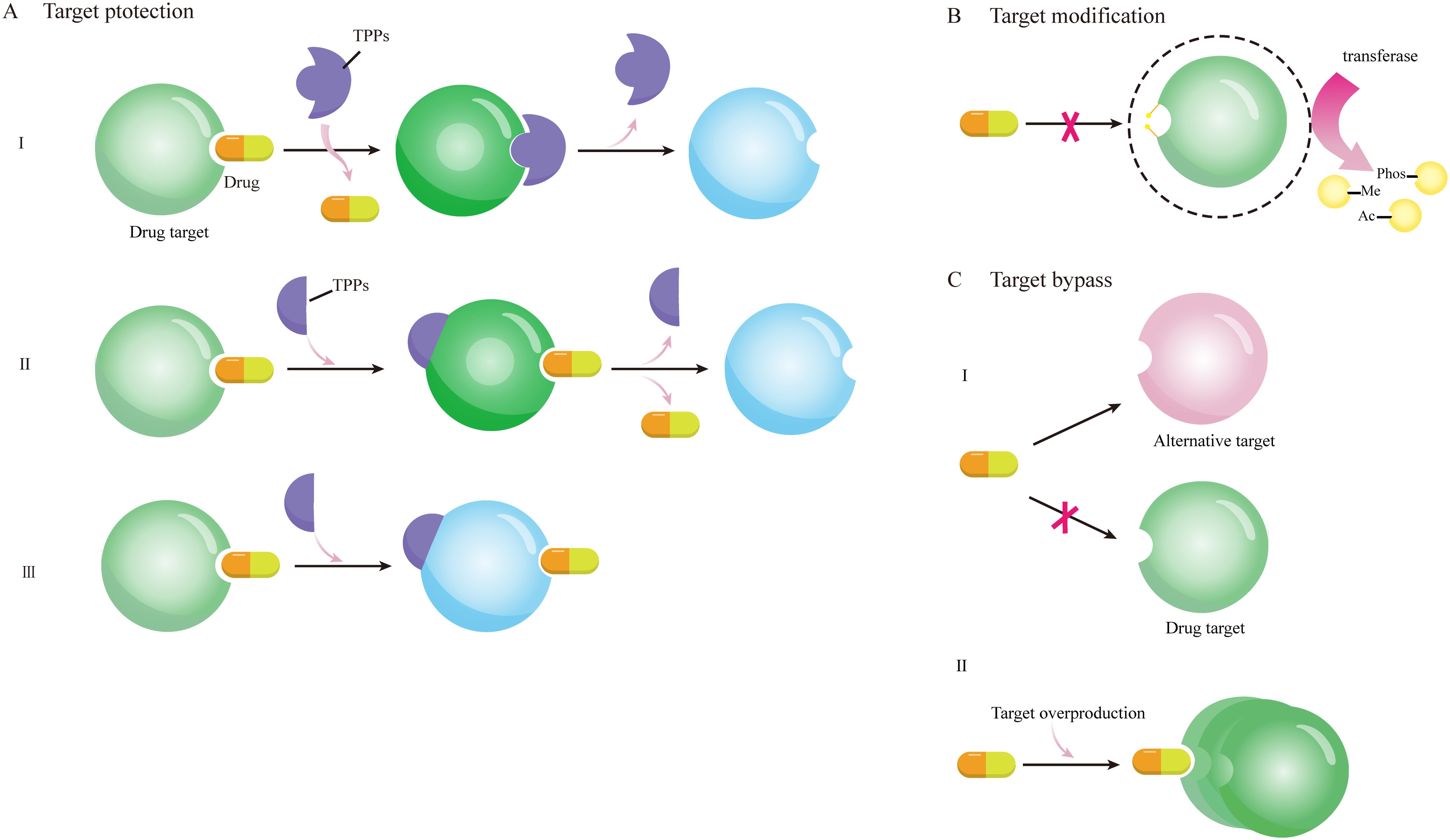
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of drug resistance mechanisms mediated by target protection, target modification, and target bypass. (A) shows three ways of target protection: (I) TPPs bind to drug targets and remove drugs stereoscopically from the target; (II) TPPs bind to drug targets, causing conformational dissociation between drugs and targets; (III) TPPs bind to drug targets to cause conformational changes, allowing target proteins to function even in the presence of drugs; (B) After the target is modified by various functional groups such as methyl, acetyl and phosphate under the action of transferase, the drug cannot bind to the target to exert its effect; (C) alternative targets combine with drugs to resume the function of drug targets, or the overproduction of drug targets make the excess drug targets still function.
Reduction of cellular permeability in bacteria
Gram negative bacteria can synthesize various specific Outer membrane porins (Omps). Hydrophilic antibiotics (such as lactams, fluoroquinolones, and tetracyclines) are difficult to pass through the lipid bilayer, rely on Omps for cellular entry to exert antibacterial effects. Therefore, loss or impairment of Omps, or reduced bacterial membrane permeability via changes in the properties and quantity of porins can lead to bacterial resistance (Zhang and Cheng, 2022; Gauba and Rahman, 2023). For example, P. aeruginosa expresses specific porins, including OprD (an alkaline amino acid-specific porin with a carbapenem-binding site critical for antibiotic uptake). The absence of OprD in P. aeruginosa is a key driver of its resistance phenotype (Pang et al., 2019). In Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae), point mutations or insertions in the coding sequences or promoter regions of the major general diffusion porins OmpK35 and OmpK36 lead to their loss, conferring resistance to beta lactams and fluoroquinolones (Khalid et al., 2020). Gram positive bacteria can alter gene expression levels by coordinating the action of tyrosine kinase WalK and response regulatory factor WalR. For example, overexpression of glmU and murG involved in cell wall metabolism regulation enhances peptidoglycan synthesis in Staphylococcus species, thickening the cell wall and impeding antibiotic penetration, thereby increasing the resistance (Baran et al., 2023).
Enhanced drug efflux in bacteria
A well-known mechanism of drug resistance is the overexpression of AcrAB-TolC pumps caused by mutations in the regulatory gene coding region. AcrAB-TolC efflux pumps belong to resistant nodule differentiation (RND) family efflux pumps. They can mediates antibiotic efflux across the bacterial inner membrane, periplasmic space, and outer membrane into the extracellular environment (Plé et al., 2022; Vieira Da Cruz et al., 2024). Previous studies have shown (Hornsey et al., 2010) that efflux pumps such as mexXY, AcrAB, and OqxAB are often associated with bacterial multidrug resistance. The decreased sensitivity of Enterococcus cloacae to tigecycline is the result of ramA mediated overexpression of AcrAB efflux pumps; The reduced sensitivity of K. pneumoniae to tigecycline is also related to the structural overexpression of mexXY and AcrAB. In a tracking study of clinical strains of K. pneumoniae (Ye et al., 2017), it was found that the inhibition of the ribosome binding site sequence led to the abolition of RamR translation and the disruption of RamR’s inhibitory effect on RamA, resulting in an increase in the levels of ramA and AcrAB, which contributes to the development of bacterial resistance. When the concentration of antibiotics in Escherichia coli (E. coli) increases, the outer membrane protein TolC can transiently bind to AcrAB, MacAB, and EmrAB proteins, forming a tripartite efflux pump component that spans the entire cytoplasmic space and can expel harmful substances from the cytoplasm to the extracellular region (Kantarcioglu et al., 2024). Research has also revealed that RNA can regulate drug efflux to develop drug resistance. Under reatment with the antituberculosis drug rifampicin, the number of small RNA MTS1438 in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis) is significantly upregulated. MTS1438 upregulates the efflux protein CydC, causing rifampicin to flow out of cells, resulting in higher abundance of MTS1438 in cells, less drug accumulation, and stronger drug resistance (Singh and Dutta, 2024).
Gene mutations in bacteria
M. tuberculosis can acquire drug resistance through mutations in the gyrA and gyrB genes, which affect DNA replication. Among them, gyrA is a hotspot region for mutations, termed the quinolone resistance determining region (QRDR). Mutations in this region often lead to resistance to quinolone drugs. The rpoB gene mutation can prevent rifampicin from binding to the RNA polymerase beta subunit, thereby blocking drug-mediated inhibition of bacterial transcription and conferring drug resistance. Aminoglycoside drugs exert bactericidal effects mainly by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis by combining with ribosome. The codon 43 mutation in rpsL (encoding ribosomal protein S12), which converts lysine to arginine, disrupts the structure of 16S rRNA, interrupt the interaction between 16S rRNA and streptomycin, and make M. tuberculosis resistant to streptomycin. Similarly, rpsL substitution mutations are also responsible for high-level streptomycin resistance in Yersinia pestis. In addition, mutations in the rrs gene (encoding 16S rRNA) have been implicated in streptomycin resistance in M. tuberculosis, while rrs mutations can also confer kanamycin resistance. The tlyA gene mutation render M. tuberculosis resistant to polypeptide antibiotics that inhibit the protein synthesis of them, thereby complicating tuberculosis treatment (Dai et al., 2021; Shafipour et al., 2022; Hou et al., 2024). What’s more, mutations in genes related to central carbon and energy metabolism can reduce bacterial basal respiration, thereby preventing antibiotics-mediated induction of tricarboxylic acid cycle activity and evading metabolic toxicity (Lopatkin et al., 2021). In addition, reduced tricarboxylic acid cycle activity promotes lipid anabolic metabolism, leading to increased lipid anabolic metabolism, and thickened cell wall, thus reducing drug sensitivity (Goossens et al., 2020).
Biofilm formation by bacteria
Biofilm is a protective membrane composed of Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), such as polysaccharides and proteins, constantly secreted by bacterial clusters. Its growth is regulated by quorum sensing, and bacteria are enveloped in it to withstand environmental pressure and drug attacks. Biofilm (Karygianni et al., 2020; Buzzo et al., 2021; Du Toit, 2024; Li et al., 2024) form a protective barrier that antibiotics cannot penetrate. The EPS produced by bacteria can create a unique microenvironment for cells within the biofilm by inducing potential oxygen gradients or signaling nutrient limitations. Cellulose and curli pili act synergistically in the biofilm as scaffolds, mediating surface adhesion and tightly stacking cells within hydrophobic networks, which endows cells with resistance to the antibiotic by restricting antibiotics penetration. For example, extracellular DNA in the matrix imposes cationic restrictions on cells within the biofilm, increasing antibiotic resistance in the biofilm. Therefore, the drug resistance of biofilms can be partially attributed to both the physical barrier formed by matrix polymers and the microenvironment stress induced by high-density cell proliferation within the matrix (MacKenzie et al., 2017; Aleksandrowicz et al., 2023).
Edeer et al. (Montoya-Hinojosa et al., 2024) reported that planktonic bacteria exhibit moderate resistance to trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole but low resistance to chloramphenicol, minocycline, levofloxacin cefotaxime, and meropenem. In contrast, bacterial biofilms formed by these bacteria display high resistance to the same antibiotics, requiring higher concentrations of antibiotics for eradication. When the populations of planktonic E. Coli and biofilm E. Coli were exposed to the antibiotic amikacin for several weeks, biofilm-forming E. coli rapidly acquired mutations in genes encoding transporters and elongation factors. This elevated mutation rate drove the enhancement of drug resistance, a phenomenon not observed in planktonic cells. These findings highlight that the biofilm microenvironment facilitates rapid antibiotic resistance evolution (Usui et al., 2023). (Rahmoun et al., 2021) compared the biofilm-forming capabilities across Clostridium difficile strains and identified a positive correlation between reduction of antibiotic sensitivity and enhancement of biofilm production capacity. Specifically, stronger biofilm-forming capacity was associated with greater bacterial resistance.
Quorum sensing in bacteria
Quorum sensing is a chemical communication process used by bacteria to coordinate group behavior, involving the production, release, and population-wide detection of signaling molecules termed autoinducer. It will be replaced by QS in the following text. QS enables bacterial communities to synchronously modulate behaviors in response to fluctuations in population density and species composition of neighboring communities (Eickhoff and Bassler, 2018; Mukherjee and Bassler, 2019). Its coordinated behaviors in cellular populations includes bioluminescence, production of virulence factors, secondary metabolism, biofilm formation, etc. The mechanism of bacterial QS signaling molecules mediating biofilm formation can be referred to Figure 3 (Sahli et al., 2022; Sahreen et al., 2022). In the flow experiment of S. aureus, the pathogen can leverages flow-induced silencing of peripheral cell QS to form a robust biofilm, while allowing cells at the bottom of the biofilm to escape and establish new colonies elsewhere, thereby safeguarding the bacterial community (Hofer, 2016). The genes encoding extracellular product generation are upregulated under QS regulation, and P. aeruginosa can produce a series of tissue-damaging extracellular products, including proteases that facilitate its dissemination within host tissues. Notably, many of these extracellular products are generated by QS regulation (Azimi et al., 2020). Collectively, QS systems contribute to the expression of bacterial virulence factors and facilitate the development of bacterial resistance. Therefore, targeting QS to suppress bacterial resistance represents a promising strategy for treating bacterial infections (Fan et al., 2022; Su and Ding, 2023; Vashistha et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024b). For example, the signaling molecule autoinducers-2 (AI2) in QS plays an important role in interspecies bacterial communication and resistance development, coordinating bacterial biofilm formation and virulence factors production (Zhang et al., 2020; Ramić et al., 2022). The AI-2 inhibitory compound Str7410 can inhibit bacterial QS activity, not only significantly impeding mixed-species biofilm formation but also enhancing the susceptibility of bacterial consortia to antibiotics when used in combination. This synergistic effect is attributed to Str7410’s ability to reduce the production of virulence factors (e.g., pyocyanin, elastase) and downregulate the expression of QS-related genes (Jiang et al., 2022). In addition, molecularly imprinted polymers can be developed to capture prototype QS autoinducer, thereby interrupting QS and inhibiting biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa. Molecularly imprinted polymers hold promise as biofilm-intervening agents for clinical environments and the surfaces of food-processing equipment (Ma et al., 2018). Both signal molecule inhibitors and biofilm-intervening strategies offer innovative ideas for treating multidrug-resistant bacterial infections: Inhibiting the QS system represents a critical breakthrough in addressing bacterial resistance. Research has demonstrated (Zhang et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2024) that the combination of quorum sensing inhibitors (QSIs) and antibiotics can improve bactericidal efficiency and avoid antibiotic resistance caused by excessive use of antibiotics.
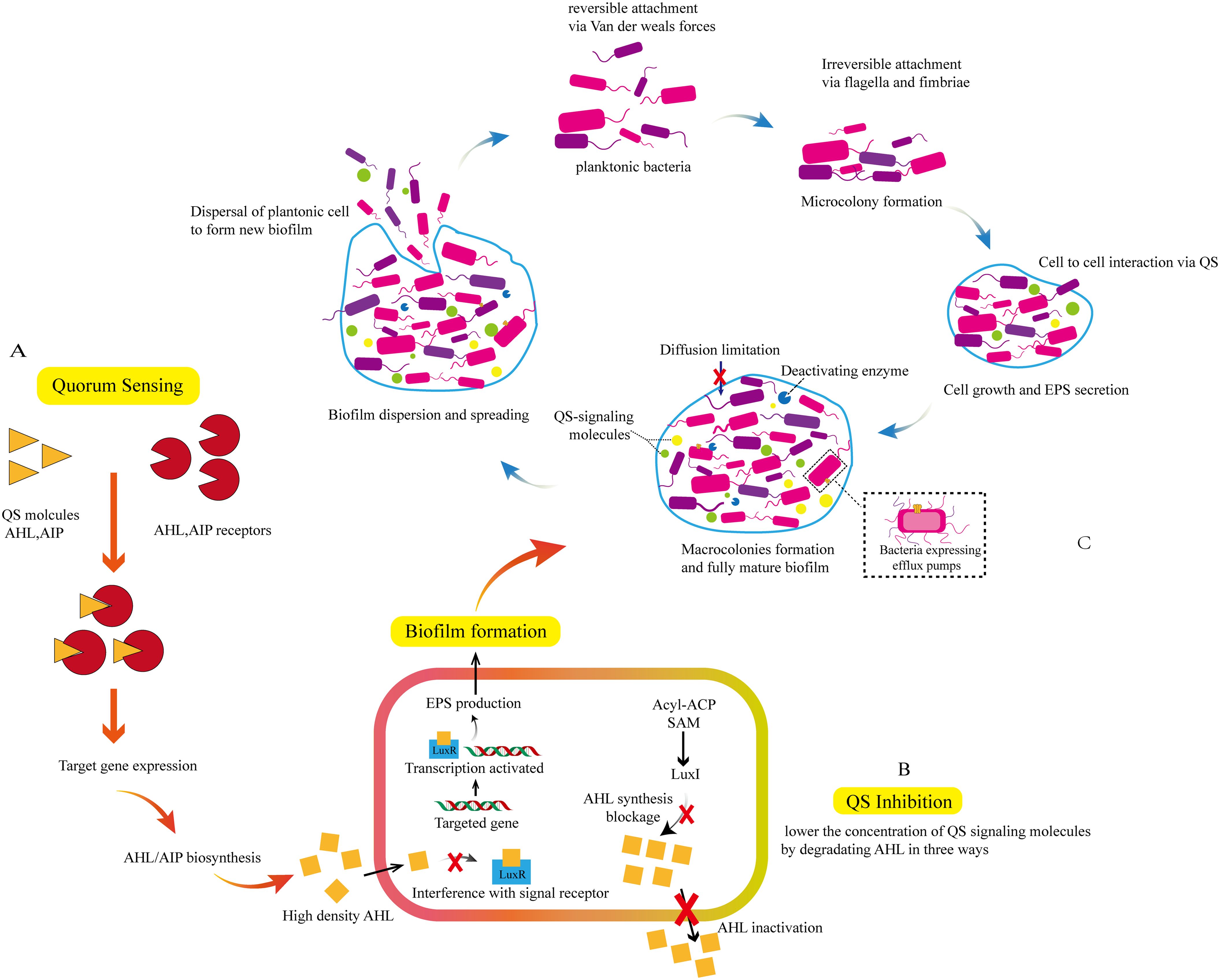
Figure 3. The mechanism by which QS signaling molecules mediate the generation of bacterial biofilms. Signal molecules such as Acyl - homoserine lactones (AHL) and Autoinducing Peptides (AIP) bind to corresponding receptors to induce targeted gene expression and promote the generation of signal molecules, as shown in (A); Signal molecules are transmitted between cells to assist bacteria in QS. Reducing the concentration of signal molecule AHL can inhibit QS. The degradation of AHL includes: (1) interfering with AHL signal receptors (2) blocking AHL biosynthesis(3) inactivating AHL; as shown in (B) Signal molecules induce target gene expression, transcription, and generation of EPS, promoting the formation of biofilms. The formation of biofilms includes: (1) reversible binding of planktonic bacteria via van der Weals forces (2) irreversible binding of bacteria via flagella and fimbriae and forming microcolonies (3) transmission of signal molecules between bacterial microcolonies, and interaction between cells via QS. During this stage, bacteria continue to grow and secrete EPS, and the biofilm begins to take shape (4) formation of macrocolonies and fully mature biofilms (5) dispersal of mature biofilms and the spread of planktonic bacteria to generate new biofilms, as shown in (B, C).
Traditional Chinese medicine inhibits quorum sensing to combat bacterial resistance mechanisms
QS plays a crucial role in bacterial drug resistance. With the escalating crisis of antimicrobial resistance, the therapeutic efficacy of conventional antibiotics alone has gradually diminished. Most traditional Chinese medicines can function as QSI targeting the QS system, reversing bacterial drug resistance, enhancing the efficacy of antibiotics, and helping to alleviate the clinical drug resistance predicament. Traditional Chinese medicine as QSI has the following advantages: 1. Chinese medicinal materials are rich in components and contain various active ingredients. Their extracts can act on multiple links of the QS system, interfere with QS through multiple pathways to combat bacterial resistance, and also provide resources for the development of new QSI. Traditional Chinese medicine compound prescriptions have a long history and rich experience in medication, and can provide guidance for the screening and development of potential QSI. 2. Compared with chemical drugs, most traditional Chinese medicines have milder effects on the human body, fewer toxic and side effects, higher safety. They are more accessible than chemical drugs, and less likely to develop drug resistance. Their development as QSI has obvious advantages. At present, screening QSI from traditional Chinese medicine resources has become a new strategy for developing natural antibacterial drugs (Yang et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2021; Farha et al., 2023; Fu et al., 2024).
Active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine
The licorice flavonoids in traditional Chinese medicine Glycyrrhiza uralensis can effectively inhibit the QS system and reduce the virulence of A. baumannii by downregulating the expression of the autoinducer synthase gene abaI. Among them, Glabridin exhibits dose-dependent inhibition of the motility and biofilm formation ability of multidrug-resistant A. baumannii. Its mechanism involves downregulating the autoinducer synthase genes abaI and abaR, inhibiting the generation of AHL in the QS system, and consequently disrupting the formation of abaR-AHL complexes (Lin et al., 2023). Chlorogenic acid demonstrates analogous effects on multidrug-resistant A. baumannii. Under the treatment of chlorogenic acid, the expression of QS-related genes in bacteria was also downregulated (Xu et al., 2022). Chlorogenic acid eliminates multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa by inhibiting bacterial movement, reducing pyocyanin production, suppressing elastase activity, and inhibiting biofilm formation. Nine monomers of traditional Chinese medicine, including caffeic acid, cinnamic acid, and myricetin, can also combat A. baumannii infections by downregulating QS genes, inhibiting bacterial QS, and inhibiting the expression of bacterial virulence factors (Zeng et al., 2023). Among them, chlorogenic acid is widely present in traditional Chinese medicinal materials of the genus Lonicera in the family Caprifoliaceae and the genus Artemisia in the family Asteraceae. Traditional Chinese medicinal materials with relatively high chlorogenic acid content include Eucommia ulmoides, Lonicera japonica, Chrysanthemum morifolium, and Houttuynia cordata, all of which are commonly used. The QS system can regulate the formation of bacterial biofilm, and the ability of bacterial biofilm formation is positively correlated with bacterial resistance. Studies have shown that berberine and matrine can inhibit biofilm formation and weaken bacterial resistance by suppressing the QS system of E. coli, and berberine is more effective than matrine (Sun et al., 2019). Berberine mainly comes from the traditional Chinese medicines Coptis chinensis and Phellodendron amurense, while matrine mainly exists in the traditional Chinese medicine Sophora flavescens. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (APDT) can effectively eradicates biofilms,and Curcumin (Abdulrahman et al., 2020; Xia et al., 2023) mediated APDT can inhibit the expression of QS pathway related genes, and the inhibition intensity varies under different light conditions. Upon increasing the light dose to 10J/cm2, QS gene expression levels decline sharply, resulting in a significant decrease in the thickness of P. aeruginosa biofilm and the production of EPS. Therefore, curcumin mediated APDT may be a potential therapeutic method for controlling biofilm mediated infections. Curcumin is the primary active component of the traditional Chinese medicine Curcuma longa. Besides, the traditional Chinese medicines Curcuma wenyujin and Curcuma zedoaria are also important sources of curcumin. The non cyclic monophenolic compound geraniol is widely present in various Chinese medicinal materials such as Citrus reticulata, Rosa rugosa, and Cymbopogon citratus. Studies have found that geraniol (Li et al., 2023a) can inhibit the expression of key genes in the QS system of P. aeruginosa PAO1, including the signal synthase-coding genes lasI, rhlI, and pqsABCDEH, the corresponding signal receptor coding genes lasR, rhlR,pqsR, as well as virulence genes including rhlABC, lasAB, lecAB, phzABMS, and pelABG, which weaken virulence factors such as rhamnolipids, proteases, and biofilms, helping to reduce the resistance of P. aeruginosa PAO1. The natural furan coumarin compound psoralen (Wen et al., 2024) can inhibit most QS activated genes and virulence factors, with the strongest inhibition observed in the Rhl system. When combined with levofloxacin, kanamycin, etc., psoralen exhibits synergistic antibacterial activity and enhances the sensitivity of P. aeruginosa to antibiotics. Psoralen is mainly derived from Psoralea corylifolia, a leguminous plant.
The common QS pathways involved in some of the mentioned active ingredients are shown in Figure 4 (Liu et al., 2022a).
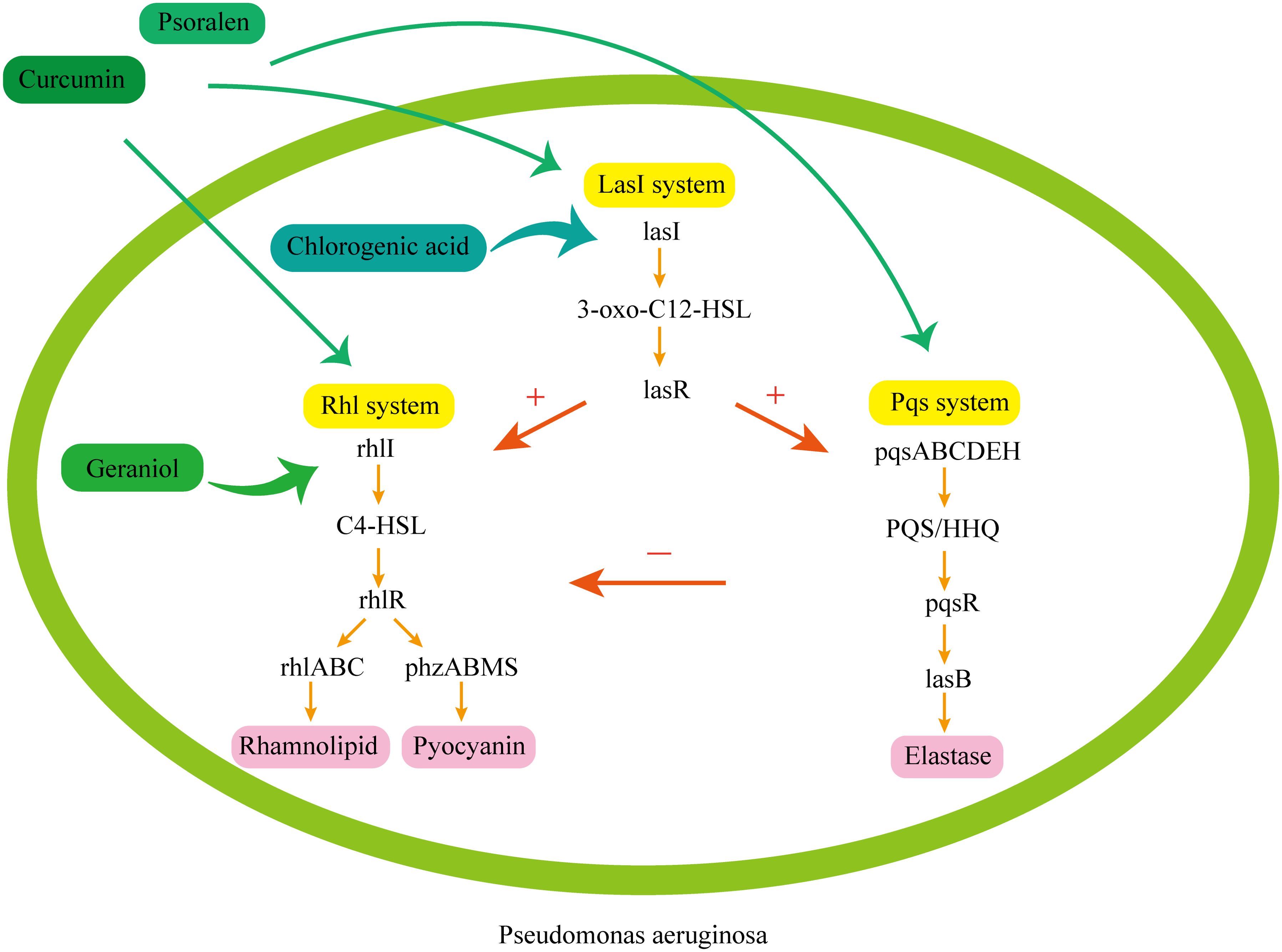
Figure 4. Common QS pathways in P. aeruginosa. 1. Las system: The lasI gene encodes autoinducer synthase generation, generating the signal molecule 3-oxo-C12-HSL and lasR binds to the signal molecule, activating the target gene. The Las system can activate the Rhl system and the Pqs system. 2. Rhl system: The rhlI gene encodes related enzymes to produce the signal molecule C4-HSL and rhlR binds to the signal molecule, activating the target gene which regulates the generation of virulence factors such as rhamnolipid and pyocyanin. 3. Pqs system: The pqsABCDEH gene encodes the synthesis of the signal molecules PQS and HHQ. pqsR binds to the signal molecules, activating the virulence gene, which regulates the generation of the virulence factor elastase. Chlorogenic acid mainly acts on the Las system. It inhibits LasI synthase to reduce the generation of the signal molecule 3-oxo-C12-HSL, and affects the generation of subsequent virulence factors. Curcumin and psoralen can act widely on three systems. Curcumin mainly affects the expression of virulence factors by inhibiting the synthase of signal molecules, reducing the production of signal molecules and the expression of receptor genes, while psoralen can simultaneously inhibit the expression and transcription of receptor genes lasR, rhlR, and pqsR in the three systems. Geranol mainly acts on the Rhl system. It inhibits RhlI synthase, reduces the synthesis of the signal molecule C4-HSL, and blocks the generation of virulence factors.
Traditional Chinese herbal extracts
Herbal extracts made from Artemisia argyi, Dictamni cortex, and the root of Solanum melongena can target and inhibit the Pqs system in the QS system of P. aeruginosa. This herbal extract can act as a competitive agent to inhibit the binding of MvfR to the corresponding pqsA promoter region, thereby suppressing bacterial virulence and quenching QS function in P. aeruginosa. Its effect on the Las and Rhl systems is relatively small (Wei et al., 2020). Essential oils extracted from traditional Chinese medicinal materials of the family citrus (e.g., Citrus limon, Citrus paradisi) are rich in terpenes such as limonene, which can reduce the synthesis of QS signals, proteases, and pyocyanins in P. aeruginosa, inhibiting bacterial movement and biofilm formation (María Constanza et al., 2016; Luciardi et al., 2021). The antibacterial mechanism of Cinnamomum cassia leaf ethanol extract (Alva et al., 2021) against P. aeruginosa is similar. Multiple extract components, including aniline, Cyclohexyl-15-crown-5, 2-Acrylic acid, etc., exhibit anti-QS activity, which can serve as potential QSIs for the treatment of drug-resistant bacterial infections. Extracts of Cassia fistula (Peerzada et al., 2022) and Artemisia annua leaves (Khan et al., 2024) are also potential QSIs, which can significantly inhibit the production of virulence factors (e.g., anthocyanins, pyocyanins, proteases, chitinase, rhamnolipids) and biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa PAO1, thereby combating bacterial resistance. Scutellaria baicalensis contains abundant flavonoids such as baicalin and baicalein (Wang et al., 2021b; Zhang et al., 2021), which can interfere with the synthesis of Pqs molecules by regulating pqsA and pqsR, downregulate the expression of QS-related genes, reduce many important virulence factors in P. aeruginosa, including the type III secretion system, diminish cytotoxicity, and accelerate bacterial clearance. Studies have found that Ginkgo biloba peel extracts (Wang et al., 2021a, Wang et al., 2022) can inhibit the biofilms formation in S. aureus and Staphylococcus haemolyticus by regulating relevant genes, and it demonstrates broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against both Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. Panax ginseng (Wang et al., 2020), rich in active substances such as ginsenosides, polysaccharides, proteins, and panaxatriols, exerts antibacterial effects against multidrug-resistant bacteria (e.g., H. pylori, S. aureus, E. coli) by inhibiting microbial motility and QS ability, affecting biofilm formation and destroying mature biofilm, thereby reducing the infection of microorganisms. Extracts of Coptis chinensis and Schisandra chinensis have inhibitory effects on biofilm formation, motility, and expression of virulence factors in Vibrio alginolyticus (Yi et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2024), with mechanisms potentially involving downregulation of QS-related genes.
Traditional Chinese medicine compound
The traditional Chinese medicine compound Tanreqing (TRQ) can inhibit the expression of upstream regulatory factors in the QS system of P. aeruginosa, including the two-component systems GacS/GacA and Ppra/PprB, as well as the production of virulence factors such as pyocyanin, rhamnolipids, elastase, and alkaline protease (Yang et al., 2020). Notably, TRQ demonstrates potent reversal effects on the resistance of multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa. S. aureus utilizes diffusible autoinducers for intercellular communication and generates biofilms triggered by AI-2 (Sedlmayer et al., 2021), contributing to its robust multidrug resistance. TRQ can resist S. aureus infections by modulating QS-related genes and downregulating the expression of virulence factors such as hemolysin and autolysin (Yang et al., 2022b). When combined with vancomycin or linezolid, TRQ can significantly enhance the anti biofilm efficacy against MRSA, increase bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics, and reduce required antibiotic dosage (Yang et al., 2018). In H. pylori (Yang et al., 2022a), the QS signaling molecule AI-2 induces expression of urease structural proteins UreA and UreB, enabling the pathogen to produce large amounts of urease for acidic environment adaptation and gastric survival. Orphan response regulator HP1021 can directly bind to UreAB to inhibit urease expression, while HP1021 can be downregulated by AI-2 to restore urease expression. As bacterial density increases, AI-2 mediated QS enhances acid tolerance and facilitates bacterial dissemination following gastric acid exposure. Therefore, inhibiting the QS system to reduce biofilm formation and urease production (Gopalakrishnan et al., 2020) may effectively combat multidrug-resistant H. pylori infections. For example, Chinese patent medicine Jinghua Weikang capsule can reverse the resistance of H. pylori to metronidazole by reducing the adsorption of H. pylori to gastric mucosal epithelial cells and inhibiting the formation of biofilm (Jia et al., 2022). Banxia Xiexin Tang contains multiple ingredients inhibiting H. pylori, such as berberine, emodin, and luteolin, which can activate immune function, reduce virulence factors like urease of H. pylori, and enhance bactericidal effects. Its mechanism may involve inhibiting AI-2 activity in the QS system, with superior therapeutic efficacy and safety compared to triple therapy for H. pylori infections (Mei et al., 2019; Li et al., 2023b). When combined with triple therapy, it can reduce antibiotic dosage, enhance efficacy, and mitigate resistance development. Xuebijing can inhibit biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa, downregulate the expression of QS-related genes, involving Las, Rhl, Pqs systems, and the virulence factors, to combat pathogenic bacterial infections. The combination of Qiguiyin compound (Chen et al., 2022) and antibiotics can treat multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa infections, enhancing antibiotic efficacy. Serum proteomics revealed 76 differentially expressed proteins in rats before/after Qiguiyin compound treatment. Proteins including PhzA, PhzB, PhzM, MetQ1 can promote QS and biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa and were downregulated after treatment. Qiguiyin compound affects the drug resistance of P. aeruginosa by modulating protein expression, with these proteins individually or synergistically participate in regulating QS, secretion system, and biofilm formation.
Effect of different delivery methods of traditional Chinese medicines on their anti-biofilm ability
QS is intricately linked to the formation of biofilms, and the eradication of biofilms remains a thorny issue in clinical treatment. Different delivery methods of drugs have different eradication effects on bacterial biofilms. Currently, the delivery method of most traditional Chinese medicines rely on oral delivery, with common dosage forms including pills, granules, capsules, decoctions, etc (Wu et al., 2023). However, oral delivery often suffers from low bioavailability and limited efficacy. Therefore, the development of traditional Chinese medicine dosage forms has broad prospects. The traditional Chinese medicine compound TRQ comes in various dosage forms such as capsules, granules, injections, and gels. Currently, the most commonly used method in clinical practice is intravenous injection of TRQ. Compared with oral delivery and local delivery, injection delivery enables the active drug to enter the bloodstream more rapidly. It can exert the efficacy of TRQ in inhibiting the biofilm of K. pneumoniae more fully (Zhang et al., 2024a). Nanotechnology has emerged as a promising delivery method. The advantages of nanoparticles, such as small volume and large surface area, facilitate their penetration into the biofilm matrix. Surface-modified ligands enable receptor-targeted binding, facilitating localized drug release and superior anti-biofilm activity (To et al., 2023). Nanodelivery systems not only improve drug stability but also overcome physiological barriers through altering surface modification, expanding therapeutic applications, which make them excellent delivery methods for enhancing drug efficacy. The shiborin extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine Radix lithospermi has poor water solubility (Sun et al., 2022) and low bioavailability for oral delivery. Making it into shiborin nanoemulsion and shiborin-Fe nanoparticles can address the problems of poor water solubility and light stability, enhancing shikonin’s eradication efficacy against biofilms of drug-resistant bacteria such as Candida albicans, P. aeruginosa, and MRSA (Hu et al., 2022; Kaur et al., 2023). At present, the research on traditional Chinese medicine dosage forms is at a critical stage of vigorous development. Although there are numerous varieties and complex components of traditional Chinese medicine, which bring considerable challenges to the research and development work, its huge development potential is indeed worth looking forward to.
Conclusion and prospect
The escalating problem of bacterial resistance, driven by the overuse of antibiotics, poses a significant threat to public health. This review systematically summarizes the mechanisms underlying antibiotic resistance in common bacteria across six key aspects: production of inactivating enzymes, alteration of drug targets, reduction in bacterial membrane permeability, enhanced drug efflux, induction of gene mutations, and formation of biofilms. From the QS perspective, this article elucidates the effects of active compounds, extracts, and compound formulas derived from traditional Chinese medicine against multidrug-resistant bacteria such as P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, and H. pylori. This provides a strong basis for traditional Chinese medicine in reversing bacterial resistance and offers innovative strategies to address this global challenge. This article further discusses diverse delivery methods of traditional Chinese medicine and studies the differential impacts of these delivery methods on biofilms elimination. It highlights that nanotechnology may play an important role in the research and development of traditional Chinese medicine dosage forms, in the future. The research prospects of traditional Chinese medicine dosage forms are broad. However, current research perspective on QS-mediated reversal of bacterial resistance remains relatively narrow, mainly focusing on several bacteria led by P. aeruginosa. In the future, research on the relationship between QS and antibiotic resistance should be appropriately expanded to explore new breakthroughs in the mechanism of bacterial antibiotic resistance. Additionally, while existing literature has delineated certain mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine in reversing resistance, the molecular mechanisms of most traditional Chinese medicine interventions remain poorly characterized. Moreover, The complex interactions among components in TCM formulas and their individual contributions to modulating bacterial resistance require further research to elucidate. In the future, research should focus on the development and utilization of traditional Chinese medicine resources and formulas, and standardize the combination of antibiotics and traditional Chinese medicine. Important attention should be paid to the following points: 1. Improve the standards for the cultivation and processing of medicinal materials, which strengthens the quality management of Chinese medicinal materials to reduce counterfeit and inferior products, and to ensure the safety and efficacy of medicinal materials. 2. Optimize the preparation process of traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions and traditional Chinese patent medicines and simple preparations, which reduces the loss of active ingredients to ensure the efficacy. Additionally, develop new traditional Chinese medicine formulations using nanotechnology, microencapsulation technology, etc., to improve the stability and targeting of traditional Chinese medicine, enhance its therapeutic efficacy, and prepare traditional Chinese medicine products with higher bioavailability and better compliance. 3. Improve toxicology research related to the combination of antibiotics and traditional Chinese medicine ingredients, which facilitates clarifying medication compatibility and avoiding serious adverse reactions. Additionally, strengthen the clinical application of combining Chinese and Western medicine to explore the best combination of antibiotics and traditional Chinese medicine, and reduce the dosage, toxic side effects, and risk of bacterial resistance of antibiotics.
We believe that with the continuous scientific advancement, the problem of bacterial resistance will be effectively addressed or alleviated.
Author contributions
NQ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81874344), the Hunan Provincial Key R&D Program (2023SK2046), the Hunan Health Commission High-Level Talent Research Project (R2023139), the Hunan Natural Science Foundation Joint Fund for Chinese Medicine Research (2023JJ60474), the Changsha Natural Science Foundation (kq2208148, kq2208191), and the Hunan Innovative Province Construction Project (2024RC8110).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1582003/full#supplementary-material
References
Abdulrahman, H., Misba, L., Ahmad, S., and Khan, A. U. (2020). Curcumin induced photodynamic therapy mediated suppression of quorum sensing pathway of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An approach to inhibit biofilm in vitro. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 30, 101645. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2019.101645
Aleksandrova, E. V., Wu, K. J. Y., Tresco, B. I. C., Syroegin, E. A., Killeavy, E. E., Balasanyants, S. M., et al. (2024). Structural basis of Cfr-mediated antimicrobial resistance and mechanisms to evade it. Nat. Chem. Biol. 20, 867–876. doi: 10.1038/s41589-023-01525-w
Aleksandrowicz, A., Carolak, E., Dutkiewicz, A., Błachut, A., Waszczuk, W., and Grzymajlo, K. (2023). Better together-Salmonella biofilm-associated antibiotic resistance. Gut Microbes 15, 2229937. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2229937
Alva, P. P., Suresh, S., Nanjappa, D. P., James, J. P., Kaverikana, R., Chakraborty, A., et al. (2021). Isolation and identification of quorum sensing antagonist from Cinnamomum verum leaves against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Life Sci. 267, 118878. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118878
Asenjo, A., Oteo-Iglesias, J., and Alós, J. I. (2021). What’s new in mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria of clinical origin? Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. (Engl Ed) 39, 291–299. doi: 10.1016/j.eimce.2020.02.017
Azimi, S., Klementiev, A. D., Whiteley, M., and Diggle, S. P. (2020). Bacterial quorum sensing during infection. Annu. Rev. Microbiol 74, 201–219. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-032020-093845
Baran, A., Kwiatkowska, A., and Potocki, L. (2023). Antibiotics and bacterial resistance-A short story of an endless arms race. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 5777. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065777
Behling, A. H., Wilson, B. C., Ho, D., Virta, M., O’Sullivan, J. M., and Vatanen, T. (2023). Addressing antibiotic resistance: computational answers to a biological problem? Curr. Opin. Microbiol 74, 102305. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2023.102305
Buzzo, J. R., Devaraj, A., Gloag, E. S., Jurcisek, J. A., Robledo-Avila, F., Kesler, T., et al. (2021). Z-form extracellular DNA is a structural component of the bacterial biofilm matrix. Cell 184, 5740–5758.e5717. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.10.010
Chakraborty, N., Jha, D., Roy, I., Kumar, P., Gaurav, S. S., Marimuthu, K., et al. (2022). Nanobiotics against antimicrobial resistance: harnessing the power of nanoscale materials and technologies. J. Nanobiotechnology 20, 375. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01573-9
Chen, G., Zhang, W., Kong, L., Wang, C., Lai, X., Yu, X., et al. (2022). Qiguiyin decoction improves multidrug-resistant pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in rats by regulating inflammatory cytokines and the TLR4/myD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. BioMed. Res. Int. 2022, 5066434. doi: 10.1155/2022/5066434
Cheng, Q., Cheung, Y., Liu, C., Xiao, Q., Sun, B., Zhou, J., et al. (2021). Structural and mechanistic basis of the high catalytic activity of monooxygenase Tet(X4) on tigecycline. BMC Biol. 19, 262. doi: 10.1186/s12915-021-01199-7
Christaki, E., Marcou, M., and Tofarides, A. (2020). Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: mechanisms, evolution, and persistence. J. Mol. Evol. 88, 26–40. doi: 10.1007/s00239-019-09914-3
Christopher, J. L. M., Kevin, S. I., Fablina, S., Lucien, R. S., Gisela Robles, A., Authia, P. G., et al. (2022). Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 399, 629–655. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(21)02724-0
Dai, R., He, J., Zha, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Gao, H., et al. (2021). A novel mechanism of streptomycin resistance in Yersinia pestis: Mutation in the rpsL gene. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 15, e0009324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009324
Darby, E. M., Trampari, E., Siasat, P., Gaya, M. S., Alav, I., Webber, M. A., et al. (2023). Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance revisited. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 21, 280–295. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00820-y
Denk-Lobnig, M. and Wood, K. B. (2023). Antibiotic resistance in bacterial communities. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 74, 102306. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2023.102306
Du Toit, A. (2024). Bacterial architects build the biofilm structures. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 22, 187. doi: 10.1038/s41579-024-01020-6
Eickhoff, M. J. and Bassler, B. L. (2018). SnapShot: bacterial quorum sensing. Cell 174, 1328–1328.e1321. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.003
Fan, Q., Zuo, J., Wang, H., Grenier, D., Yi, L., and Wang, Y. (2022). Contribution of quorum sensing to virulence and antibiotic resistance in zoonotic bacteria. Biotechnol. Adv. 59, 107965. doi: 10.1016/j.bioteChadv.2022.107965
Fang, Z., Lai, F., Cao, K., Zhang, Z., Cao, L., Liu, S., et al. (2022). Potential role of lysine acetylation in antibiotic resistance of escherichia coli. mSystems 7, e0064922. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00649-22
Farha, A. K., Li, Z., Xu, Y., Bordiga, M., Sui, Z., and Corke, H. (2023). Anti-quorum sensing effects of batatasin III: in vitro and in silico studies. J. Biomol Struct. Dyn 41, 11341–11352. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2187226
Fu, S., Song, W., Han, X., Chen, L., and Shen, L. (2024). Veratryl Alcohol Attenuates the Virulence and Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Mainly via Targeting las Quorum-Sensing System. Microorganisms 12, 985. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12050985
Gauba, A. and Rahman, K. M. (2023). Evaluation of antibiotic resistance mechanisms in gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics (Basel) 12, 1590. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12111590
Goossens, S. N., Sampson, S. L., and Van Rie, A. (2020). Mechanisms of drug-induced tolerance in mycobacterium tuberculosis. Clin. Microbiol Rev. 34, e00141–e00120. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00141-20
Gopalakrishnan, V., Masanam, E., Ramkumar, V. S., Baskaraligam, V., and Selvaraj, G. (2020). Influence of N-acylhomoserine lactonase silver nanoparticles on the quorum sensing system of Helicobacter pylori: A potential strategy to combat biofilm formation. J. Basic Microbiol 60, 207–215. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201900537
Grooters, K. E., Ku, J. C., Richter, D. M., Krinock, M. J., Minor, A., Li, P., et al. (2024). Strategies for combating antibiotic resistance in bacterial biofilms. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol 14. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1352273
Hofer, U. (2016). Biofilms: Turning tides for quorum sensing. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 14, 64. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2015.26
Hornsey, M., Ellington, M. J., Doumith, M., Scott, G., Livermore, D. M., and Woodford, N. (2010). Emergence of AcrAB-mediated tigecycline resistance in a clinical isolate of Enterobacter cloacae during ciprofloxacin treatment. Int. J. Antimicrob Agents 35, 478–481. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.01.011
Hou, K., Jabeen, R., Sun, L., and Wei, J. (2024). How do mutations of mycobacterium genes cause drug resistance in tuberculosis? Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 25, 724–736. doi: 10.2174/0113892010257816230920053547
Hu, J., Feng, K., Cong, Y., Li, X., Jiang, Y., Jiao, X., et al. (2022). Nanosized shikonin-fe(III) coordination material for synergistic wound treatment: an initial explorative study. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 14, 56510–56524. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c16011
Hunashal, Y., Kumar, G. S., Choy, M. S., D’Andréa É, D., Da Silva Santiago, A., Schoenle, M. V., et al. (2023). Molecular basis of β-lactam antibiotic resistance of ESKAPE bacterium E. faecium Penicillin Binding Protein PBP5. Nat. Commun. 14, 4268. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39966-5
Jia, X., Huang, Q., Lin, M., Chu, Y., Shi, Z., Zhang, X., et al. (2022). Revealing the novel effect of Jinghua Weikang capsule against the antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori. Front. Microbiol 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.962354
Jiang, K., Xu, Y., Yuan, B., Yue, Y., Zhao, M., Luo, R., et al. (2022). Effect of autoinducer-2 quorum sensing inhibitor on interspecies quorum sensing. Front. Microbiol 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.791802
Kantarcioglu, I., Gaszek, I. K., Guclu, T. F., Yildiz, M. S., Atilgan, A. R., Toprak, E., et al. (2024). Structural shifts in TolC facilitate Efflux-Mediated β-lactam resistance. Commun. Biol. 7, 1051. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06750-0
Karygianni, L., Ren, Z., Koo, H., and Thurnheer, T. (2020). Biofilm matrixome: extracellular components in structured microbial communities. Trends Microbiol 28, 668–681. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.03.016
Kaur, K., Singh, A., Monga, A., Mohana, P., Khosla, N., and Bedi, N. (2023). Antimicrobial and antibiofilm effects of shikonin with tea tree oil nanoemulsion against Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus. Biofouling 39, 962–979. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2023.2281511
Khalid, A., Lubián, A. F., Ma, L., Lin, R. C. Y., and Iredell, J. R. (2020). Characterizing the role of porin mutations in susceptibility of beta lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates to ceftaroline and ceftaroline-avibactam. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 93, 252–257. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.02.005
Khan, M. A., Shahid, M., Celik, I., Khan, H. M., Shahzad, A., Husain, F. M., et al. (2024). Attenuation of quorum sensing regulated virulence functions and biofilm of pathogenic bacteria by medicinal plant Artemisia annua and its phytoconstituent 1, 8-cineole. Microsc Res. Tech 87, 133–148. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24418
Larsson, D. G. J. and Flach, C. F. (2022). Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 20, 257–269. doi: 10.1038/s41579-021-00649-x
Lessa, F. C. and Sievert, D. M. (2023). Antibiotic resistance: A global problem and the need to do more. Clin. Infect. Dis. 77, S1–s3. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciad226
Li, Y., Feng, T., and Wang, Y. (2022). The role of bacterial signaling networks in antibiotics response and resistance regulation. Mar Life Sci. Technol. 4, 163–178. doi: 10.1007/s42995-022-00126-1
Li, P., Pan, J., Dong, Y., Sun, Y., Wang, Y., Liao, K., et al. (2024). Microenvironment responsive charge-switchable nanoparticles act on biofilm eradication and virulence inhibition for chronic lung infection treatment. J. Control Release 365, 219–235. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.11.032
Li, X. H., Xu, J. Y., Wang, X., Liao, L. J., Huang, L., Huang, Y. Q., et al. (2023b). BanXiaXieXin decoction treating gastritis mice with drug-resistant Helicobacter pylori and its mechanism. World J. Gastroenterol. 29, 2818–2835. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i18.2818
Li, W. R., Zeng, T. H., Zhang, Z. Q., Shi, Q. S., and Xie, X. B. (2023a). Geraniol attenuates virulence factors by inhibiting quorum sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1190619
Lima, L. M., Silva, B., Barbosa, G., and Barreiro, E. J. (2020). β-lactam antibiotics: An overview from a medicinal chemistry perspective. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 208, 112829. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112829
Lin, H., Zhou, C., Yu, K. H., Lin, Y. S., Wang, L. B., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Glabridin functions as a quorum sensing inhibitor to inhibit biofilm formation and swarming motility of multidrug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii. Infect. Drug Resist. 16, 5697–5705. doi: 10.2147/idr.S417751
Liu, J., Hou, J. S., Chang, Y. Q., Peng, L. J., Zhang, X. Y., Miao, Z. Y., et al. (2022a). New Pqs Quorum Sensing System Inhibitor as an Antibacterial Synergist against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Med. Chem. 65, 688–709. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01781
Liu, X., Liu, Q., Sun, S., Sun, H., Wang, Y., Shen, X., et al. (2022b). Exploring AI-2-mediated interspecies communications within rumen microbial communities. Microbiome 10, 167. doi: 10.1186/s40168-022-01367-z
Liu, X., Xiao, J., Wang, S., Zhou, J., Qin, J., Jia, Z., et al. (2022c). Research progress on bacterial membrane vesicles and antibiotic resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 11553. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911553
Lopatkin, A. J., Bening, S. C., Manson, A. L., Stokes, J. M., Kohanski, M. A., Badran, A. H., et al. (2021). Clinically relevant mutations in core metabolic genes confer antibiotic resistance. Science 371, eaba0862. doi: 10.1126/science.aba0862
Luciardi, M. C., Blázquez, M. A., Alberto, M. R., Cartagena, E., and Arena, M. E. (2021). Lemon oils attenuate the pathogenicity of pseudomonas aeruginosa by quorum sensing inhibition. Molecules 26, 2863. doi: 10.3390/molecules26102863
Ma, L., Feng, S., Fuente-Núñez, C., Hancock, R. E. W., and Lu, X. (2018). Development of molecularly imprinted polymers to block quorum sensing and inhibit bacterial biofilm formation. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 10, 18450–18457. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b01584
MacKenzie, K. D., Palmer, M. B., Köster, W. L., and White, A. P. (2017). Examining the link between biofilm formation and the ability of pathogenic salmonella strains to colonize multiple host species. Front. Vet Sci. 4. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2017.00138
María Constanza, L., María Amparo, B., Elena, C., Alicia, B., and María Rosa, A. (2016). Mandarin essential oils inhibit quorum sensing and virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 68, 373–380. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.12.056
Mei, H., Amanda, C., Jianping, L., Xuemei, L., Jie, Z., Ce, D., et al. (2019). Banxia Xiexin Decoction for patients with peptic ulcer or chronic gastritis infected with Helicobacter pylori. J. Traditional Chin. Med. Sci. 6, 9. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcms.2019.04.001
Michał, Z., Justyna, F., Kenji, O., Monika, S., Martyna, N., Renata, J., et al. (2023). Complexes of β-lactam antibiotics and their Schiff-base derivatives as a weapon in the fight against bacterial resistance. Coordination Chem. Rev. 493, 215326. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215326
Mlynarczyk-Bonikowska, B., Kowalewski, C., Krolak-Ulinska, A., and Marusza, W. (2022). Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance in staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 8088. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158088
Mohanty, H., Pachpute, S., and Yadav, R. P. (2021). Mechanism of drug resistance in bacteria: efflux pump modulation for designing of new antibiotic enhancers. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 66, 727–739. doi: 10.1007/s12223-021-00910-z
Montoya-Hinojosa, E. I., Villarreal-Treviño, L., Bocanegra-Ibarias, P., Camacho-Ortiz, A., and Flores-Treviño, S. (2024). Drug Resistance in Biofilm and Planktonic Cells of Achromobacter spp., Burkholderia spp., and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Clinical Isolates. Microb Drug Resist. 30, 354–362. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2023.0301
Mukherjee, S. and Bassler, B. L. (2019). Bacterial quorum sensing in complex and dynamically changing environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 17, 371–382. doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0186-5
Pang, Z., Raudonis, R., Glick, B. R., Lin, T. J., and Cheng, Z. (2019). Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 37, 177–192. doi: 10.1016/j.bioteChadv.2018.11.013
Peerzada, Z., Kanhed, A. M., and Desai, K. B. (2022). Effects of active compounds from Cassia fistula on quorum sensing mediated virulence and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. RSC Adv. 12, 15196–15214. doi: 10.1039/d1ra08351a
Plé, C., Tam, H. K., Vieira Da Cruz, A., Compagne, N., Jiménez-Castellanos, J. C., Müller, R. T., et al. (2022). Pyridylpiperazine-based allosteric inhibitors of RND-type multidrug efflux pumps. Nat. Commun. 13, 115. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27726-2
Qin, S., Xiao, W., Zhou, C., Pu, Q., Deng, X., Lan, L., et al. (2022). Pseudomonas aeruginosa: pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7, 199. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01056-1
Rahmoun, L. A., Azrad, M., and Peretz, A. (2021). Antibiotic resistance and biofilm production capacity in clostridioides difficile. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol 11. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.683464
Ramić, D., Klančnik, A., Možina, S. S., and Dogsa, I. (2022). Elucidation of the AI-2 communication system in the food-borne pathogen Campylobacter jejuni by whole-cell-based biosensor quantification. Biosens Bioelectron 212, 114439. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114439
Rudra, P., Hurst-Hess, K., Lappierre, P., and Ghosh, P. (2018). High levels of intrinsic tetracycline resistance in mycobacterium abscessus are conferred by a tetracycline-modifying monooxygenase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 62, e00119–e00118. doi: 10.1128/aac.00119-18
Sahli, C., Moya, S. E., Lomas, J. S., Gravier-Pelletier, C., Briandet, R., and Hémadi, M. (2022). Recent advances in nanotechnology for eradicating bacterial biofilm. Theranostics 12, 2383–2405. doi: 10.7150/thno.67296
Sahreen, S., Mukhtar, H., Imre, K., Morar, A., Herman, V., and Sharif, S. (2022). Exploring the function of quorum sensing regulated biofilms in biological wastewater treatment: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 9751. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179751
Sedlmayer, F., Woischnig, A. K., Unterreiner, V., Fuchs, F., Baeschlin, D., Khanna, N., et al. (2021). 5-Fluorouracil blocks quorum-sensing of biofilm-embedded methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, e73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab251
Shafipour, M., Shirzad-Aski, H., Mohammadzadeh, A., Ghazvini, K., Zamani, S., Koohi, P. M., et al. (2022). Evaluation of mutations related to streptomycin resistance in mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates. Curr. Microbiol 79, 343. doi: 10.1007/s00284-022-03043-9
Sheila, V., Clare, C., Kym, W., Syed Masud, A., Caesar, A., Deepshikha, B., et al. (2023). A just transition for antimicrobial resistance: planning for an equitable and sustainable future with antimicrobial resistance. Lancet 403, 2766–2767. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(23)01687-2
Singh, S. and Dutta, T. (2024). A virulence-associated small RNA MTS1338 activates an ABC transporter CydC for rifampicin efflux in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Front. Microbiol 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1469280
Smith, P. and Schuster, M. (2022). Antiactivators prevent self-sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 119, e2201242119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2201242119
Smith, W. P. J., Wucher, B. R., Nadell, C. D., and Foster, K. R. (2023). Bacterial defences: mechanisms, evolution and antimicrobial resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 21, 519–534. doi: 10.1038/s41579-023-00877-3
Su, Y. and Ding, T. (2023). Targeting microbial quorum sensing: the next frontier to hinder bacterial driven gastrointestinal infections. Gut Microbes 15, 2252780. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2252780
Su, Y., Xu, M. Y., Cui, Y., Chen, R. Z., Xie, L. X., Zhang, J. X., et al. (2023). Bacterial quorum sensing orchestrates longitudinal interactions to shape microbiota assembly. Microbiome 11, 241. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01699-4
Sun, Q., Gong, T., Liu, M., Ren, S., Yang, H., Zeng, S., et al. (2022). Shikonin, a naphthalene ingredient: Therapeutic actions, pharmacokinetics, toxicology, clinical trials and pharmaceutical researches. Phytomedicine 94, 153805. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153805
Sun, T., Li, X. D., Hong, J., Liu, C., Zhang, X. L., Zheng, J. P., et al. (2019). Inhibitory effect of two traditional chinese medicine monomers, berberine and matrine, on the quorum sensing system of antimicrobial-resistant escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol 10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02584
To, D., Kakar, A., Kali, G., Wibel, R., Knoll, P., Marx, F., et al. (2023). Iminated aminoglycosides in self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: Dual approach to break down the microbial defense. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 630, 164–178. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.10.077
Tomar, J. S., Peddinti, R. K., and Hosur, R. V. (2019). Aminoglycoside antibiotic resistance conferred by Hpa2 of MDR Acinetobacter baumannii: an unusual adaptation of a common histone acetyltransferase. Biochem. J. 476, 795–808. doi: 10.1042/bcj20180791
Usui, M., Yoshii, Y., Thiriet-Rupert, S., Ghigo, J. M., and Beloin, C. (2023). Intermittent antibiotic treatment of bacterial biofilms favors the rapid evolution of resistance. Commun. Biol. 6, 275. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04601-y
Vashistha, A., Sharma, N., Nanaji, Y., Kumar, D., Singh, G., Barnwal, R. P., et al. (2023). Quorum sensing inhibitors as Therapeutics: Bacterial biofilm inhibition. Bioorg Chem. 136, 106551. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106551
Vieira Da Cruz, A., Jiménez-Castellanos, J. C., Börnsen, C., Van Maele, L., Compagne, N., Pradel, E., et al. (2024). Pyridylpiperazine efflux pump inhibitor boosts in vivo antibiotic efficacy against K. pneumoniae. EMBO Mol. Med. 16, 93–111. doi: 10.1038/s44321-023-00007-9
Wang, S., Feng, Y., Han, X., Cai, X., Yang, L., Liu, C., et al. (2021b). Inhibition of Virulence Factors and Biofilm Formation by Wogonin Attenuates Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 via Targeting pqs Quorum-Sensing System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 12699. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312699
Wang, L., Huang, Y., Yin, G., Wang, J., Wang, P., Chen, Z. Y., et al. (2020). Antimicrobial activities of Asian ginseng, American ginseng, and notoginseng. Phytother. Res. 34, 1226–1236. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6605
Wang, J., Lu, X., Wang, C., Yue, Y., Wei, B., Zhang, H., et al. (2024). Research progress on the combination of quorum-sensing inhibitors and antibiotics against bacterial resistance. Molecules 29, 1674. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071674
Wang, C., Wei, P. W., Song, C. R., Wang, X., Zhu, G. F., Yang, Y. X., et al. (2022). Evaluation of the antimicrobial function of Ginkgo biloba exocarp extract against clinical bacteria and its effect on Staphylococcus haemolyticus by disrupting biofilms. J. Ethnopharmacol 298, 115602. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115602
Wang, B., Wei, P. W., Wan, S., Yao, Y., Song, C. R., Song, P. P., et al. (2021a). Ginkgo biloba exocarp extracts inhibit S. aureus and MRSA by disrupting biofilms and affecting gene expression. J. Ethnopharmacol 271, 113895. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113895
Wei, Q., Bhasme, P., Wang, Z., Wang, L., Wang, S., Zeng, Y., et al. (2020). Chinese medicinal herb extract inhibits PQS-mediated quorum sensing system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Ethnopharmacol 248, 112272. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112272
Wen, F., Wu, Y., Yuan, Y., Yang, X., Ran, Q., Gan, X., et al. (2024). Discovery of psoralen as a quorum sensing inhibitor suppresses Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Appl. Microbiol Biotechnol. 108, 222. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13067-9
Wilson, D. N., Hauryliuk, V., Atkinson, G. C., and O’Neill, A. J. (2020). Target protection as a key antibiotic resistance mechanism. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 18, 637–648. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-0386-z
Wu, S., Wang, C., Bai, D., Chen, N., Hu, J., and Zhang, J. (2023). Perspectives of international multi-center clinical trials on traditional Chinese herbal medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1195364
Xia, F. W., Guo, B. W., Zhao, Y., Wang, J. L., Chen, Y., Pan, X., et al. (2023). Type I photosensitizer targeting glycans: overcoming biofilm resistance by inhibiting the two-component system, quorum sensing, and multidrug efflux. Adv. Mater 35, e2309797. doi: 10.1002/adma.202309797
Xiao, G., Li, J., and Sun, Z. (2023). The combination of antibiotic and non-antibiotic compounds improves antibiotic efficacy against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 15493. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015493
Xu, W., Zhang, X., Wang, L., Zeng, W., Sun, Y., Zhou, C., et al. (2022). Effect of chlorogenic acid on the quorum-sensing system of clinically isolated multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol 132, 1008–1017. doi: 10.1111/jam.15275
Yang, W., Cui, K., Tong, Q., Ma, S., Sun, Y., He, G., et al. (2022b). Traditional chinese medicine tanreqing targets both cell division and virulence in staphylococcus aureus. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol 12. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.884045
Yang, D., Hao, S., Zhao, L., Shi, F., Ye, G., Zou, Y., et al. (2021). Paeonol attenuates quorum-sensing regulated virulence and biofilm formation in pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol 12. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.692474
Yang, H., Huang, X., Zhang, X., Zhang, X., Xu, X., She, F., et al. (2022a). AI-2 induces urease expression through downregulation of orphan response regulator HP1021 in helicobacter pylori. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 9. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.790994
Yang, W., Liu, J., Blažeković, B., Sun, Y., Ma, S., Ren, C., et al. (2018). In vitro antibacterial effects of Tanreqing injection combined with vancomycin or linezolid against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 18, 169. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2231-8
Yang, W., Wei, Q., Tong, Q., Cui, K., He, G., Lin, L., et al. (2020). Traditional chinese medicine tanreqing inhibits quorum sensing systems in pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol 11. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.517462
Ye, M., Ding, B., Qian, H., Xu, Q., Jiang, J., Huang, J., et al. (2017). In vivo development of tigecycline resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae owing to deletion of the ramR ribosomal binding site. Int. J. Antimicrob Agents 50, 523–528. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.04.024
Yi, X., Xu, X., Chen, Y., Xu, G., Zhu, Z., Li, H., et al. (2023). Genetic analysis of Vibrio alginolyticus challenged by Fructus schisandrae reveals the mechanism of virulence genes. Gene 870, 147421. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147421
Zeng, L., Lin, F., and Ling, B. (2023). Effect of traditional Chinese medicine monomers interfering with quorum-sensing on virulence factors of extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Pharmacol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1135180
Zhang, P., Chen, W., Ma, Y. C., Bai, B., Sun, G., Zhang, S., et al. (2023). Design and synthesis of 4-fluorophenyl-5-methylene-2(5H)-furanone derivatives as potent quorum sensing inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 66, 8441–8463. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01866
Zhang, F. and Cheng, W. (2022). The mechanism of bacterial resistance and potential bacteriostatic strategies. Antibiotics (Basel) 11, 1215. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11091215
Zhang, P., Guo, Q., Wei, Z., Yang, Q., Guo, Z., Shen, L., et al. (2021). Baicalin Represses Type Three Secretion System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa through PQS System. Molecules 26, 1497. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061497
Zhang, W., He, M., Kong, N., Niu, Y., Li, A., and Yan, Y. (2024a). Study on the inhibition activity and mechanism of Tanreqing against Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilm formation in vitro and in vivo. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol 14. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1368450
Zhang, L., Li, S., Liu, X., Wang, Z., Jiang, M., Wang, R., et al. (2020). Sensing of autoinducer-2 by functionally distinct receptors in prokaryotes. Nat. Commun. 11, 5371. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19243-5
Zhang, Y., Ma, N., Tan, P., and Ma, X. (2024b). Quorum sensing mediates gut bacterial communication and host-microbiota interaction. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 3751–3763. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2134981
Zhao, C., Zheng, H., Zhou, L., Ji, H., Zhao, L., Yu, W., et al. (2021). Falcarindiol Isolated from Notopterygium incisum Inhibits the Quorum Sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules 26, 5896. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195896
Keywords: bacterial resistance mechanism, quorum sensing, reversal of antibiotic resistance, research progress, Traditional Chinese Medicine
Citation: Qiu N, Liu W and Zhang X (2025) Based on quorum sensing: reverse effect of traditional Chinese medicine on bacterial drug resistance mechanism. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1582003. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1582003
Received: 23 February 2025; Accepted: 15 May 2025;
Published: 03 June 2025.
Edited by:
Emanuela Roscetto, Federico II University Hospital, ItalyReviewed by:
Javier Alberto Garza Cervantes, Autonomous University of Nuevo León, MexicoBasem Battah, Syrian Private University (SPU), Syria
Copyright © 2025 Qiu, Liu and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenlong Liu, ZHJhZ29uNTI0MEAxMjYuY29t
‡ORCID: Xili Zhang, orcid.org/0009-0005-6967-127X
 Ningning Qiu
Ningning Qiu Wenlong Liu
Wenlong Liu Xili Zhang‡
Xili Zhang‡