- Department of Pharmacy, Medical Security Center Stationed in the 5th Medical Center Pharmacy Room, People’s Liberation Army of China General Hospital, Beijing, China
Background: Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of azvudine in alleviating clinical symptoms among patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, evidence regarding its real-world effectiveness and safety profile remains limited.
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of azvudine in COVID-19 patients.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included 192 COVID-19 patients hospitalized in Fengtai District, Beijing, from November 1 to December 31, 2022. Patients were divided into azvudine (n=118) and non-azvudine (n=74) groups. Propensity score matching (PSM) was applied to balance baseline characteristics (age, sex, vaccination status, etc.), yielding 48 matched pairs. Outcomes included time to SARS-CoV-2 RNA negativity, hospitalization duration, and symptom resolution (fever, cough). Adverse events were recorded.
Results: After PSM, 48 pairs of COVID-19 patients were identified. The azvudine group exhibited significantly shorter hospitalization than the non-azvudine group (median: 8 vs. 10 days, P ≤ 0.05). No significant differences were observed in time to RNA negativity (4.23 vs. 4.52 days, P>0.05), fever duration (2 vs. 2 days, P>0.05), or cough duration (4.5 vs. 5 days, P>0.05). One case of mild gastrointestinal discomfort was reported in the azvudine group.
Conclusion: Azvudine significantly reduced hospitalization duration in mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients with a favorable safety profile.
1 Introduction
From the start of COVID-19 until November 10, 2024, over 776.8 million confirmed COVID-19 cases and over 7 million confirmed deaths were notified to WHO across 234 countries. To date, more than 1,000 variants of SARS-CoV-2 have been identified, and the virus epidemic continues to pose a significant threat to global health (Yu and Chang, 2022). Currently, Antiviral agents against COVID-19 reported mainly include polymerase inhibitors, protease inhibitors, inhibitors of nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase, entry and uncoating inhibitors, and other antivirals (Yuan et al., 2023).
Azvudine is the world’s first dual-target anti-HIV drug (Zhang et al., 2021), which also exhibits certain activity against HCV (Smith et al., 2009), EV71 (Xu et al., 2020), and HBV (Zhou et al., 2012). It’s also the first small molecule anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapeutic drug, which was independently developed in China (Ma and Chen, 2023). It is a nucleoside analogue of the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), a well-known conserved protein without a corresponding human protein, making it an ideal target for treating SARS-CoV-2 (Maio et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021). RdRp is metabolized intracellularly into an active 5 ′-triphosphate metabolite. This activator acts exclusively on RdRp to embed viral RNA during SARS-CoV-2 RNA synthesis. Thus, inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 replication achieves a therapeutic effect for COVID-19 (Chen and Tian, 2023). During 2020-2022, four phase III clinical trials were carried out to evaluate the efficacy and safety of azvudine in treating COVID-19. The results demonstrated that azvudine reduced the nucleic acid negative conversion time, viral load, and the time to improvement of clinical symptoms in patients with moderate COVID-19. Moreover, azvudine has a favorable safety and tolerability profile (Zhu, 2023). In 2022, It was conditionally approved in China for COVID-19 treatment; and on August 9, 2022, it was included in the 2019 Coronary Virus Disease Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines (Ninth Edition) issued by the National Health and Health Commission and the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. In the same year, it was approved by the National Healthcare Security Administration on 12 August for inclusion in the medical reimbursement list.
Current guidelines prioritize the use of direct antiviral drugs in COVID-19 patients, and several real-world studies have demonstrated that early antiviral treatment reduces the risk of serious illness. A real-life cohort study confirmed that Remdesivir has a good safety profile and significantly reduces the risk of disease progression and COVID-19 sequelae compared to untreated controls, in the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and Omicron era, in patients at high risk of developing severe disease (Mazzitelli et al., 2023). A Single-Center, Prospective, Comparative, Real-Life Study proved that Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and Remdesivir show equivalent efficacy in preventing hospitalization and death (Basoulis et al., 2023). A Chinese real-world retrospective cohort study conducted a head-to-head comparison between azvudine and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir. Azvudine demonstrated comparable safety and potential clinical advantages in specific outcomes (Wei et al., 2023). However, the current evidence regarding the effectiveness and safety of antiviral agents remains inadequate. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the real-world clinical effectiveness and safety of azvudine in hospitalized COVID-19 patients at the Medical Security Center Stationed in the 5th Medical Center, PLA General Hospital.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design and patient selection
A retrospective cohort study included 192 COVID-19 patients(confirmed via RT-PCR or antigen testing)hospitalized in Fengtai District, Beijing between November 1 and December 31, 2022. Inclusion criteria (Department of Medical Emergency Response and National Health Commission of the PRC, 2023): (1)age≧18 years; (2)All patients diagnosed with COVID-19 were confirmed by testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 real-time polymerase chain reaction, SARS-CoV-2 antigen, or both; (3) taking only one type of antiviral drug, azvudine, or not taking any antiviral drug; (4) hospitalization days≧3 days. Exclusion criteria: (1) receiving other antiviral agents such as Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir, Remdesivir or Lopinavir/Ritonavir; (2) pregnancy/lactation; (3) patients concurrently enrolled in other interventional clinical studies; (4) cases presenting incomplete or missing critical baseline parameters; (5) individuals with documented hypersensitivity to azvudine or excipients contained in the pharmaceutical formulation; (6) subjects exhibiting moderate-to-severe hepatic insufficiency (Child-Pugh class B/C) or renal dysfunction.
Patients were stratified into azvudine (n=118) and non-azvudine (n=74) groups.
2.2 Interventions
Patients in both groups received standard symptomatic care. The control group received standard care primarily aimed at alleviating clinical symptoms. Specifically: (1) Patients with high fever underwent physical cooling measures with antipyretic medication administration; (2) Those manifesting severe cough and sputum production were administered antitussive and expectorant agents. Meanwhile, the azvudine group received antiviral treatment with azvudine tablets: swallowed whole on an empty stomach, 5mg each time, once a day, until two nucleic acid conversions 24 hours apart, for a maximum of 14 days.
2.3 Data collection
The following patient data were systematically collected: (1) age and gender; (2) vaccination status; (3) preexisting comorbidities; (4) clinical typing of COVID-19; (5) symptomatic treatment regimens; (6) duration of febrile symptoms and cough(days); (7) viral clearance time-defined as the interval between initial positive RT-PCR result and first consecutive negative test; (8) length of hospital stay (admission to discharge interval); (9) azvudine-related adverse events(AEs).
The primary endpoints included virological clearance time and hospitalization duration (Gao et al., 2023). Viral shedding cessation was confirmed according to the Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for COVID-19 (Trial Version 9.0), requiring either: a) Two consecutive negative SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR tests (cycle threshold [CT] value≥35 for both ORF1ab and N genes, with≥24-hour sampling interval); b) CT values>35 for O and N genes. Secondary endpoints focused on the resolution of clinical symptoms, particularly the duration of pyrexia and persistent cough.
2.4 PSM
To address potential confounding factors and mitigate baseline imbalances between comparative cohorts in real-world study settings, PSM was systematically implemented using SPSS Statistics software(version 25.0; IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). The propensity score model incorporated clinically relevant baseline covariates including chronological age, biological sex, comorbidity burden, vaccination status, COVID-19 clinical staging, administration of symptomatic treatment, presence of febrile symptoms, occurrence of cough, and cycle threshold (Ct) values of admission nucleic acid testing. Ct values upon admission constituted predictor covariates. The azvudine-treated and control cohorts underwent 1:1 nearest-neighbor matching; caliper width was set at 0.05 propensity score standard deviations.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses (Yu et al., 2023) were performed using SPSS 25.0 (IBM Corp., USA), with two-tailed P values ≤ 0.05 considered statistically significant. Normally distributed continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation ( ± s) and compared using independent Student’s t-tests. Non-normally distributed continuous variables were reported as median (interquartile range) [M(P25, P75)] and compared through Mann-Whitney U tests. Categorical variables were presented as frequencies (percentages), with between-group differences assessed using χ2 tests or Fisher’s exact tests when appropriate.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics
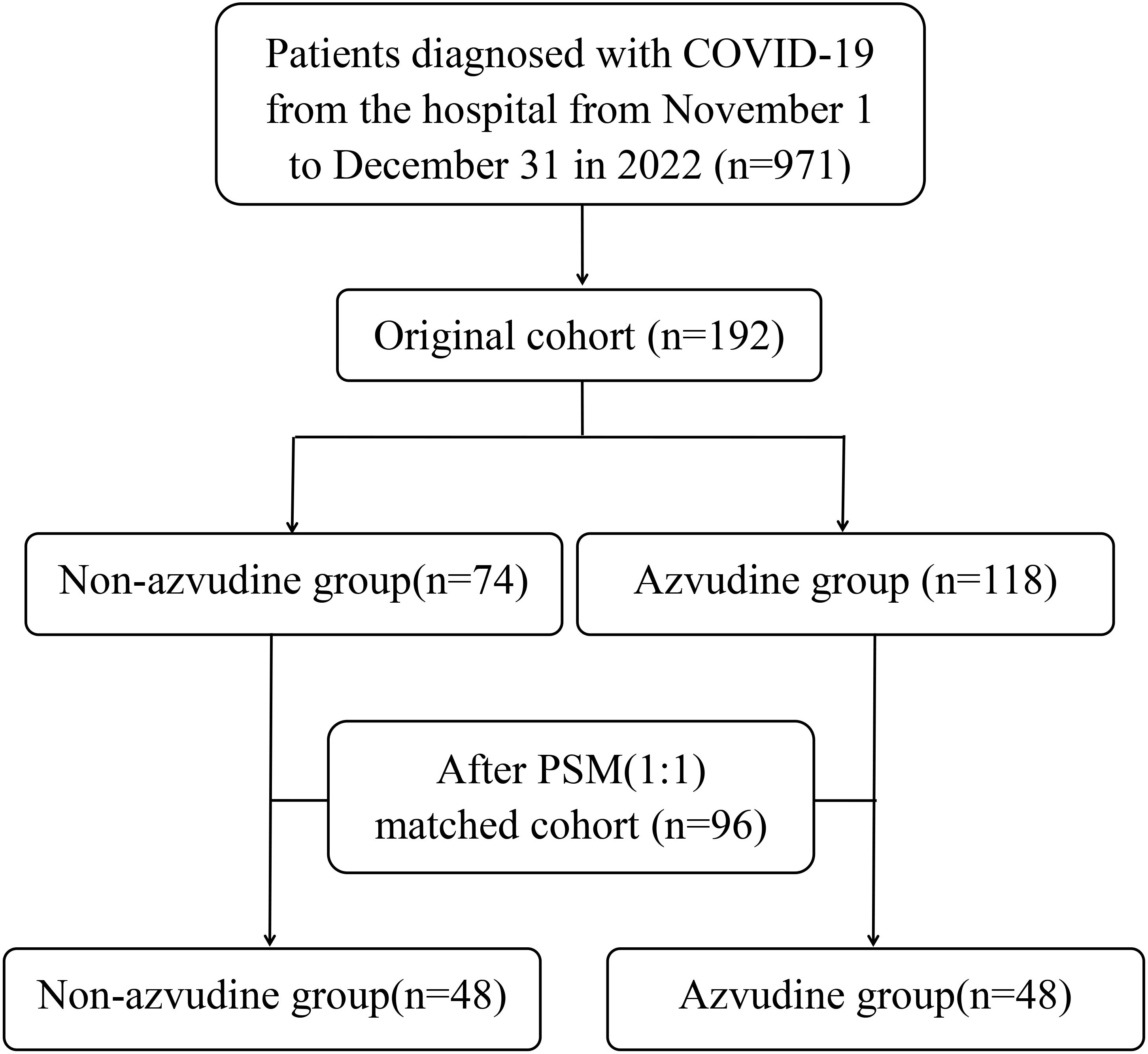
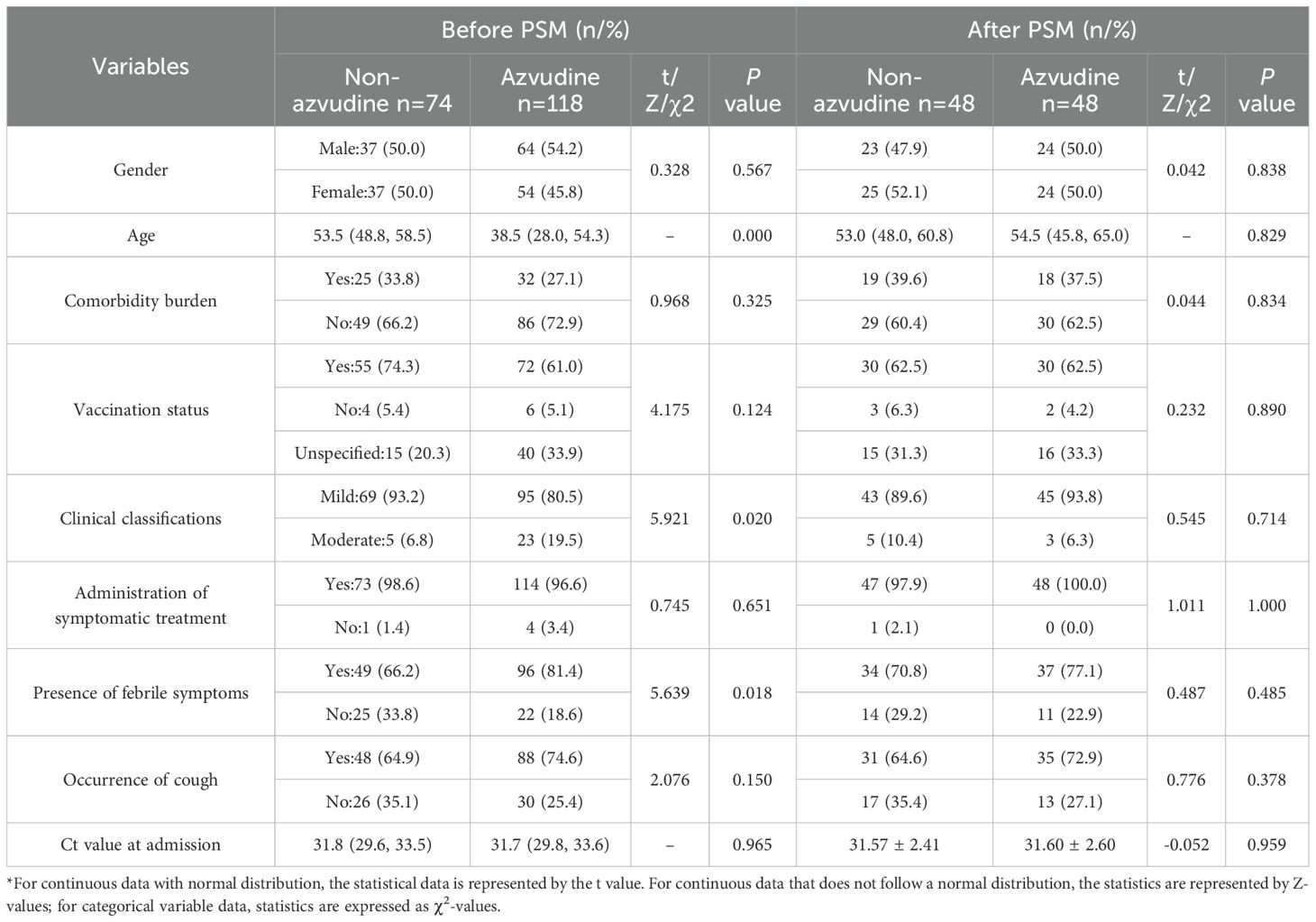
The real-world cohort initially comprised 192 eligible patients, including 118 recipients of azvudine therapy and 74 controls receiving standard symptomatic treatment only before PSM. Significant intergroup disparities were observed in baseline characteristics including age distribution, COVID-19 clinical classification, and febrile status (all P<0.05). Following 1:1 PSM implementation, balanced cohorts of 48 matched pairs were successfully generated (Figure 1). Comprehensive pre- and post-matching demographic and clinical characteristics are systematically presented in Table 1 for both groups.
In the original cohort, participants in the non-azvudine group exhibited a significantly higher mean age than those in the azvudine group (mean age 53.5 vs. 38.5, P<0.001). Additionally, significant intergroup disparities were observed in COVID-19 clinical severity classifications and febrile symptoms. However, after PSM, no statistically significant differences in baseline characteristics, including subgroup distributions, were identified between the non-azvudine and azvudine cohorts.
3.2 Comparison of the viral nucleic acid conversion time and hospitalization duration
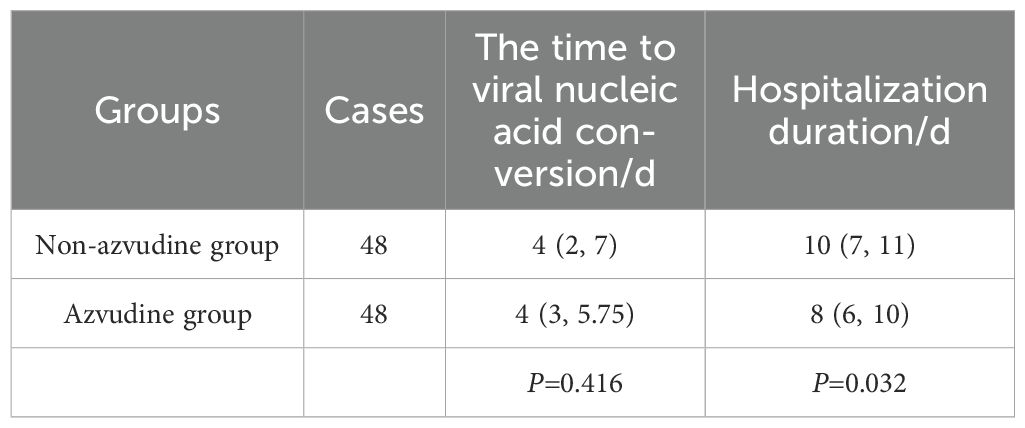
The primary endpoints were Viral nucleic acid conversion time and hospitalization duration. The mean time to conversion in the azvudine group was 4.23 days (vs. 4.52 days in the non-azvudine group). The median time to conversion in the azvudine group was 4 (3, 5.75) days and 4 (2, 7) days in the non-azvudine group, with no statistically significant intergroup difference (P>0.05) (Table 2). However, the hospitalization duration in the azvudine group was significantly shorter than that in the non-azvudine group(median: 8 vs. 10; P ≤ 0.05), indicating that azvudine may reduce hospital stays for COVID-19 patients (Table 2).
3.3 Comparison of fever and cough duration
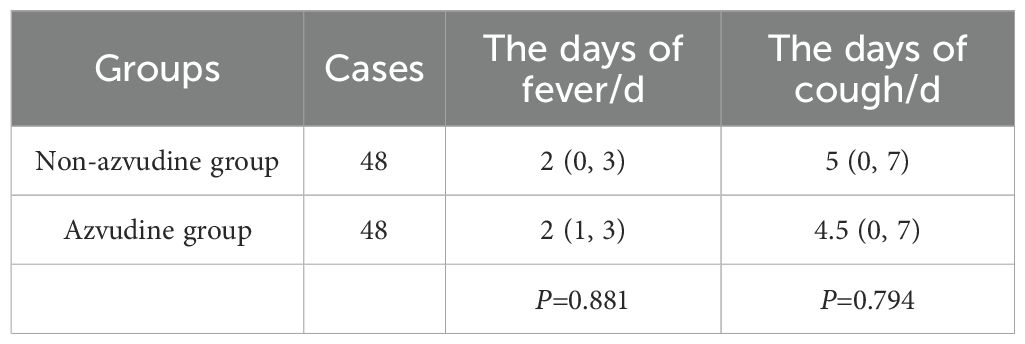
Secondary endpoints included the duration of fever and cough. The azvudine group exhibited a trend toward shorter cough duration compared to the non-azvudine group post-treatment, though the difference lacked statistical significance (P > 0.05). Similarly, no significant advantage in fever duration was observed between the groups (Table 3).
3.4 Safety assessment
Among azvudine-treated patients, one case of epigastric discomfort and loose yellow stools was reported. This patient concurrently received Ibuprofen sustained-release capsules, Lanqin oral liquid, human interferon α2a for injection, and Watermelon Cream Runlaryngeal tablet. As per the azvudine tablet prescribing information, gastrointestinal adverse reactions (e.g., diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain) have been documented in clinical trials. Although causality could not be definitively excluded, symptoms resolved following symptomatic treatment with berberine hydrochloride tablets and montmorillonite powder.
4 Discussion
Few real-world studies have evaluated azvudine’s effectiveness and safety. This retrospective propensity score-matched analysis of COVID-19 patients (November–December 2022) demonstrated that azvudine significantly reduced hospitalization duration compared to the non-azvudine group, despite no significant differences in viral conversion time, fever duration, and cough duration. These findings align with a prior retrospective study by Zhang et al. (2023) which reported shorter hospital stays in 170 azvudine-treated patients. Notably, no severe adverse reactions were observed in our cohort; only one mild gastrointestinal event occurred, resolving post-treatment. A 2022 Phase III trial in China further supports azvudine’s safety profile. Among 341 participants, azvudine and placebo groups exhibited comparable rates and severity of adverse events (AEs), with most graded as mild to moderate (CTCAE v4.03). Grade 3 AEs occurred in one azvudine recipient versus three placebo recipients, and no Grade 4 or serious AEs were reported in the azvudine group.
This study further validates that mild and moderate COVID-19 patients can benefit clinically from taking azvudine. Anyway, this study has several limitations: (1) exclusion of severe/critical cases, precluding effectiveness assessment in high-risk subgroups (9); (2) lack of laboratory or lung CT data to evaluate additional prognostic variables; (3) the study is inherently limited by its retrospective design, which precluded analysis of vaccination status impacts on treatment efficacy; (4) a relatively small sample size. Larger prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. Despite these constraints, this analysis provides valuable insights into azvudine’s role in COVID-19 management.
5 Conclusion
The results of our study indicated that azvudine significantly shortened the patients hospitalization duration. There were no significant differences in nucleic acid conversion time, fever duration, and cough duration.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Medical Ethics Committee, General Hospital of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because Informed consent was waived by the ethics committee as this retrospective study analyzed anonymized clinical data without patient intervention, adhering to national guidelines for non-invasive observational research.
Author contributions
JZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. YX: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Methodology. QL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. ZZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. YD: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China(No.23SWAQ40) and the Biosafety Special Fund Project ( BWS20J006).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Basoulis, D., Tsakanikas, A., Gkoufa, A., Bitsani, A., Karamanakos, G., Mastrogianni, E., et al. (2023). Effectiveness of oral nirmatrelvir/ritonavir vs. Intravenous three-day remdesivir in preventing progression to severe COVID-19: A single-center, prospective, comparative, real-life study. Viruses. 15, 1515. doi: 10.3390/v15071515
Chen, Z. and Tian, F. (2023). Efficacy and safety of azvudine in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon 9, e20153. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20153
Department of Medical Emergency Response and National Health Commission of the PRC (2023). Circular on the issuance of a protocol for the diagnosis and treatment of novel coronavirus infections (Trial 10th edition). Available online at: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/ylyjs/pqt/202301/32de5b2ff9bf4eaa88e75bdf7223a65a.shtml (Accessed May 4, 2023).
Gao, Y., Luo, Z., Ren, S., Duan, Z., Han, Y., Liu, H., et al. (2023). Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J. Infect. 86, e158–e160. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.023
Ma, R. Z. and Chen, Z. H. (2023). The latest progress of small molecule anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs. Chin. J. Pharmacovigilance 20, 961–966. doi: 10.19803/j.1672-8629.20230357
Maio, N., Lafont, B. A. P., Sil, D., Li, Y., Bollinger, J. M., Jr, Krebs, C., et al. (2021). Fe-S cofactors in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase are potential antiviral targets. Science. 373, 236–241. doi: 10.1126/science.abi5224
Mazzitelli, M., Trunfio, M., Sasset, L., Scaglione, V., Ferrari, A., Mengato, D., et al. (2023). Risk of hospitalization and sequelae in patients with COVID-19 treated with 3-day early remdesivir vs. controls in the vaccine and Omicron era: A real-life cohort study. J. Med. Virol. 95, e28660. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28660
Smith, D. B., Kalayanov, G., Sund, C., Winqvist, A., Maltseva, T., Leveque, V. J., et al. (2009). The design, synthesis, and antiviral activity of monofluoro and difluoro analogues of 4’-azidocytidine against hepatitis C virus replication: the discovery of 4’-azido-2’-deoxy-2’-fluorocytidine and 4’-azido-2’-dideoxy-2’,2’-difluorocytidine. J. Med. Chem. 52, 2971–2978. doi: 10.1021/jm801595c
Wang, Y., Anirudhan, V., Du, R., Cui, Q., and Rong, L. (2021). RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 as a therapeutic target. J. Med. Virol. 93, 300–310. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26264
Wei, A. H., Zeng, L., Wang, L., Gui, L., Zhang, W. T., Gong, X. P., et al. (2023). Head-to-head comparison of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for the hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a real-world retrospective cohort study with propensity score matching. Front. Pharmacol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1274294
Xu, N., Yang, J., Zheng, B., Zhang, Y., Cao, Y., Huan, C., et al. (2020). The pyrimidine analog FNC potently inhibits the replication of multiple enteroviruses. J. Virol. 94, e00204–e00220. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00204-20
Yu, B. and Chang, J. (2022). The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug Azvudine launched. Innovation (Camb). 3, 100321. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100321
Yu, H. Y., Qi, X. X., Fang, Y. N., Zhang, D. L., Chen, Q., Liu, D., et al. (2023). Efficacy of jinyebaidu granule and lianhuaqingwen capsule in the treatment of severe COVID-19 patients:A retrospective cohort study adjusted with propensity score matching. Pharmacol. Clinics Chin. Materia Med. 39, 66–70. doi: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.20220608.004
Yuan, Y., Jiao, B., Qu, L., Yang, D., and Liu, R. (2023). The development of COVID-19 treatment. Front. Immunol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1125246
Zhang, W., Li, M. Z., Qian, X. J., and Xu, P. (2023). Clinical effectiveness evaluation of Azvudine in mild and moderate high-risk patients with COVID-19 infection. Chin. J. Hosp. Pharm. 43(23):2672–2674+2700.1–5. Available at: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1204.R.20230911.1652.004.html (Accessed May 4, 2023).
Zhang, J. L., Li, Y. H., Wang, L. L., Liu, H. Q., Lu, S. Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2021). Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6, 414. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
Zhou, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, X., Zhao, J., Zheng, L., Sun, C., et al. (2012). Novel nucleoside analogue FNC is effective against both wild-type and lamivudine-resistant HBV clinical isolates. Antivir Ther. 17, 1593–1599. doi: 10.3851/IMP2292
Keywords: azvudine, COVID-19, propensity score matching, hospitalization duration, retrospective study
Citation: Zhang J, Wang F, Xie Y, Li Q, Zhu Z and Dong Y (2025) Effectiveness and safety of azvudine in the treatment of COVID-19 patients: a retrospective cohort study using propensity score matching. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1584261. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1584261
Received: 27 February 2025; Accepted: 22 May 2025;
Published: 18 June 2025.
Edited by:
Ming Yue, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, China, ChinaReviewed by:
Daniele Mengato, University Hospital of Padua, ItalyJincui Gu, The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Wang, Xie, Li, Zhu and Dong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuan Dong, Y25kb25neUAxNjMuY29t
 Jing Zhang
Jing Zhang Fang Wang
Fang Wang