- 1Lanzhou Institute of Husbandry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
- 2College of Veterinary Medicine, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
- 3Key Laboratory of New Animal Drug Project of Gansu Province, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
- 4Key Laboratory of Veterinary Pharmaceutical Development, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
Introduction: The co-existence phenomenon of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), particularly of last-resort antibiotics in multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria, is of particular concern in the least studied bacterial species.
Methods: In 2023, strain M2 was isolated from the sludge sample at a commercial bovine farm in Hebei province, China, using a MacConkey plate containing meropenem. PCR amplification and Sanger sequencing verified it co-carrying blaNDM and tet(X) genes. It was classified within the Acinetobacter genus by MALDI-TOF-MS and 16S rDNA analyses. Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) was performed on the Oxford Nanopore platform, with species-level identification via ANI and dDDH. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed against 20 antibiotics. Conjugation assays employed the filter-mating method using E. coli J53 and Salmonella LGJ2 as recipients.
Results: This strain was confirmed as a novel species of Acinetobacter genus, showing resistance to meropenem, ampicillin, ceftazidime, cefepime, gentamicin, kanamycin, fosfomycin, imipenem, ertapenem, and tetracycline. Despite carrying tet(X3), it remained susceptible to tigecycline, omadacycline, and doxycycline. The genome carried 11 ARG types, multiple metal resistance genes (MRGs), and virulence factor (VF) genes. The blaNDM-1 was located in a skeleton, ISAba125-blaNDM-1-bleMBL-trpF, which was carried by an ISAba14-mediated rolling-circle-like structure in pM2-2-NDM-1 (rep_cluster_481). Integrative and conjugative element (ICE) and multiple pdif modules (driven by the XerCD site-specific recombination (XerCD SSR) system), which were associated with the mobilization of resistance determinants, were identified in this plasmid. Chromosomal tet(X3) was mediated by ISVsa3, forming a skeleton, ISVsa3-XerD-tet (X3)-res-ISVsa3.
Discussion: The co-occurrence of blaNDM and tet(X) in a novel species of the Acinetobacter genus hints that substantial undiscovered bacteria co-carrying high-risk ARGs are concealing in the agroecological system, which should cause particular concern.
Introduction
Acinetobacter, an organism known for its natural resistance and remarkable ability to acquire additional resistance factors, is clinically significant (Peleg et al., 2008). It can survive on the surfaces of medical devices or host tissues in hospital environments via biofilms (Dijkshoorn et al., 2007; Shi et al., 2024). Its spread among patients can occur through the hands of healthcare personnel and the cross-contamination of medical devices, making it a significant contributor to nosocomial infections (Ching et al., 2024; Shi et al., 2024). In recent years, there has been a significant increase in reports of Acinetobacter genus from medical or agricultural systems carrying ARGs, even the genes conferring resistance to last-resort antibiotics (Poirel and Nordmann, 2006; He et al., 2019; Cheng et al., 2021; Cheng et al., 2023). Notably, after 2018, reports regarding the co-occurrence of the genes conferring resistance to last-resort antibiotics in Acinetobacter (Liu et al., 2021; Tang et al., 2021; Cheng et al., 2023; Opazo-Capurro et al., 2024; Long et al., 2025; Mallonga et al., 2025), Klebsiella (Seiffert et al., 2014), and Escherichia (Delgado-Blas et al., 2016; Lu et al., 2022) genera have become more frequent. Studies have revealed that the co-occurrence phenomenon in the Acinetobacter genus primarily involves blaOXA-58, tet(X3), tet(X5), tet(X6), tet(X7), blaNDM-1, blaNDM-3 and blaNDM-5 genes (Tang et al., 2021; Gutiérrez et al., 2024; Opazo-Capurro et al., 2024; Jia et al., 2025; Long et al., 2025; Mallonga et al., 2025; Mmatli et al., 2025). Among these genes, blaNDM and tet(X) are the most prevalent in clinical and agricultural settings as a co-existence unit. This co-existence was mainly found in A. baumannii, A. indicus, A. towneri, and A. bereziniae (Opazo-Capurro et al., 2024; Jia et al., 2025; Long et al., 2025; Mallonga et al., 2025), with A. baumannii being the dominant host. Notably, the increasing species in the Acinetobacter genus co-carry the genes conferring resistance to last-resort antibiotics, particularly scarce species. In addition, current research suggests that the co-occurrence is predominantly found in Asia, primarily within meat production systems such as poultry farms, pig farms, and slaughterhouses (Tang et al., 2021; Long et al., 2025), with a secondary presence in healthcare systems (Mallonga et al., 2025).
A prominent manifestation of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) involves the global distribution of carbapenem-resistant bacteria (CRB), such as the blaNDM gene. This gene encodes New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase (NDM) with the capability of hydrolyzing nearly all β-lactam antibiotics, including carbapenems, the last-resort therapeutic agents for multidrug-resistant bacterial infections. The blaNDM gene has been detected in at least 11 bacterial genera. Although blaNDM has been observed in the bacterial chromosome, it predominantly resides on plasmids (Toleman and Walsh, 2012). This gene has been associated with over 20 distinct plasmid types, including major types such as IncFIB, IncFII, IncA/C (IncC), IncX3, IncH, and IncL/M, as well as untyped plasmids (Wang et al., 2017; Acman et al., 2022; Kikuchi et al., 2022). The tet(X) can degrade all tetracyclines, particularly tigecycline, one of the last options for treating carbapenem-resistant bacteria (CRB). Similarly, the tet(X) exhibits the distribution characteristic of cross-bacteria genera and cross-plasmid types (He et al., 2019; Sun et al., 2019). Its co-existence with blaNDM compromises the efficacy of last-resort antibiotics, posing a significant challenge to antimicrobial stewardship and infection control strategies.
Here, we exhibit Acinetobacter sp. M2 co-carrying blaNDM-1 and tet(X3). Furthermore, the ICEs and pdif-ARG modules related to the horizontal transfer of ARGs have been identified in the pM2-2-NDM-1 of this strain. ICE is an important member of the bacterial mobile genetic elements (MGEs), which is integrative to the bacterial chromosome and encodes fully functional conjugation machinery and is thus self-transmissible between bacterial cells (Bi et al., 2012; Li et al., 2018; Lin et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2024). The pdif-ARG module is flanked by XerCD site-specific recombination sites (Lin et al., 2020; Shao et al., 2023). These modules have been found in plasmids of multiple bacterial genera, regarded as MGEs driven by the XerCD SSR to facilitate horizontal gene transfer (Lin et al., 2020; Shao et al., 2023). XerC and XerD are encoded by numerous bacteria, usually in pairs, and are homologous recombinases (tyrosine recombinase family) that catalyze the cleavage of two consecutive pairs of DNA strands and exchange with a restriction site, dif, located in the terminus region of the chromosome (Mindlin et al., 2019; Lin et al., 2020; Shao et al., 2023). Typically, the dif site is a 28 bp site consisting of two inverted repeat 11 bp Xer binding motifs (the left and the right regions of C/D and D/C) separated by a six bp interval called the central region (Mindlin et al., 2019; Lin et al., 2020; Shao et al., 2023). A monomer of XerC and XerD each binds to an 11 bp semi-binding site (Mindlin et al., 2019; Lin et al., 2020; Shao et al., 2023). The dif sites in plasmids are called pdif sites and appear multiple times in a plasmid (Shao et al., 2023).
Results
Source
In August 2023, we isolated a meropenem-unsusceptible strain M2 from a sludge sample at a commercial cattle farm in Hebei, China.
The identification of bacterial species
PCR amplification and Sanger sequencing verified that this strain co-carried blaNDM and tet(X) genes. This strain was classified as Acinetobacter genus using MALDI-TOF-MS and 16S rDNA. Subsequently, this strain was sequenced using whole-genome sequencing (WGS) on the Oxford Nanopore platform (long-read sequencing technology). The analysis confirmed 99.03% completeness and 0.89% contamination in this genome assembly (Acinetobacter sp. A2 genome assembly ASM4853755v1 - NCBI - NLM). To confirm the species of this genome, the Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI) match was performed using the NCBI annotation service. The result found that no genome showed >95% ANI with this genome (Acinetobacter sp. A2 genome assembly ASM4853755v1 - NCBI - NLM). The search on the DSMZ (Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulture) platform using the type strain genome server (TYGS) identified this genome as a potential new species, with the best match A. seohaensis DSM 16313 (34.1% dDDH), A. towneri DSM 14962 (33%), and A. indicus CIP 110367 (24%). This genome best matched A. towneri DSM 14962 = CIP 107472 (0.98559 Z-Score, 87.32% ANI), A. towneri DSM 14962 = CIP 107472 DSM 14962(0.98498, 87.27%), and A. tibetensis Y-23 (0.94622, 77.69%) on the JSpeciesWS platform using the tetra correlation search (TCS). Subsequently, we employed Mash (a k-mer-based rapid sequence alignment tool) on the Pathogenwatch platform. The analysis revealed that this genome best matched NZ_JAAZQX010000010.1, with a mash distance of 0.0147665, a p-value of 0, and matching hashes of 579/1000. We found that the NZ_JAAZQX010000010.1 was one of the contigs in the genome, GCA_012371325.1 (this is the only genome identified as Acinetobacter sp. A2 in the NCBI genome database). Thus, the ANI calculation on the EZBioCloud platform was executed for GCA_012371325.1 and genome M2. We found that these genomes exhibited 98.35% ANI. Furthermore, the digital DNA-DNA hybridization (dDDH) calculation of these genomes was performed on the DSMZ platform using the genome-to-genome distance calculator (GGDC). The analysis revealed that these genomes exhibited 85.5% dDDH. The thresholds of ANI and dDDH are usually applied to define genomic species (95–96 and 70 % for ANI and dDDH, respectively) (Meier-Kolthoff et al., 2013). However, 98.35% ANI and 85.5% dDDH are beyond defined thresholds, suggesting genome M2 and GCA_012371325.1 are very close but may belong to different species (Riesco and Trujillo, 2024). Furthermore, Acinetobacter sp. A2 belongs to an unclassified species of the Acinetobacter genus in the family Moraxellaceae (NCBI taxonomy database). Thus, it is classified only at the genus level, not at the species level. As a result, although strain M2 is closest related to Acinetobacter sp. A2 (Taxonomy ID: 362457, Acinetobacter sp. A2 - NCBI - NLM), it should be defined as a novel species under the Acinetobacter genus.
Antibiotic resistance phenotype
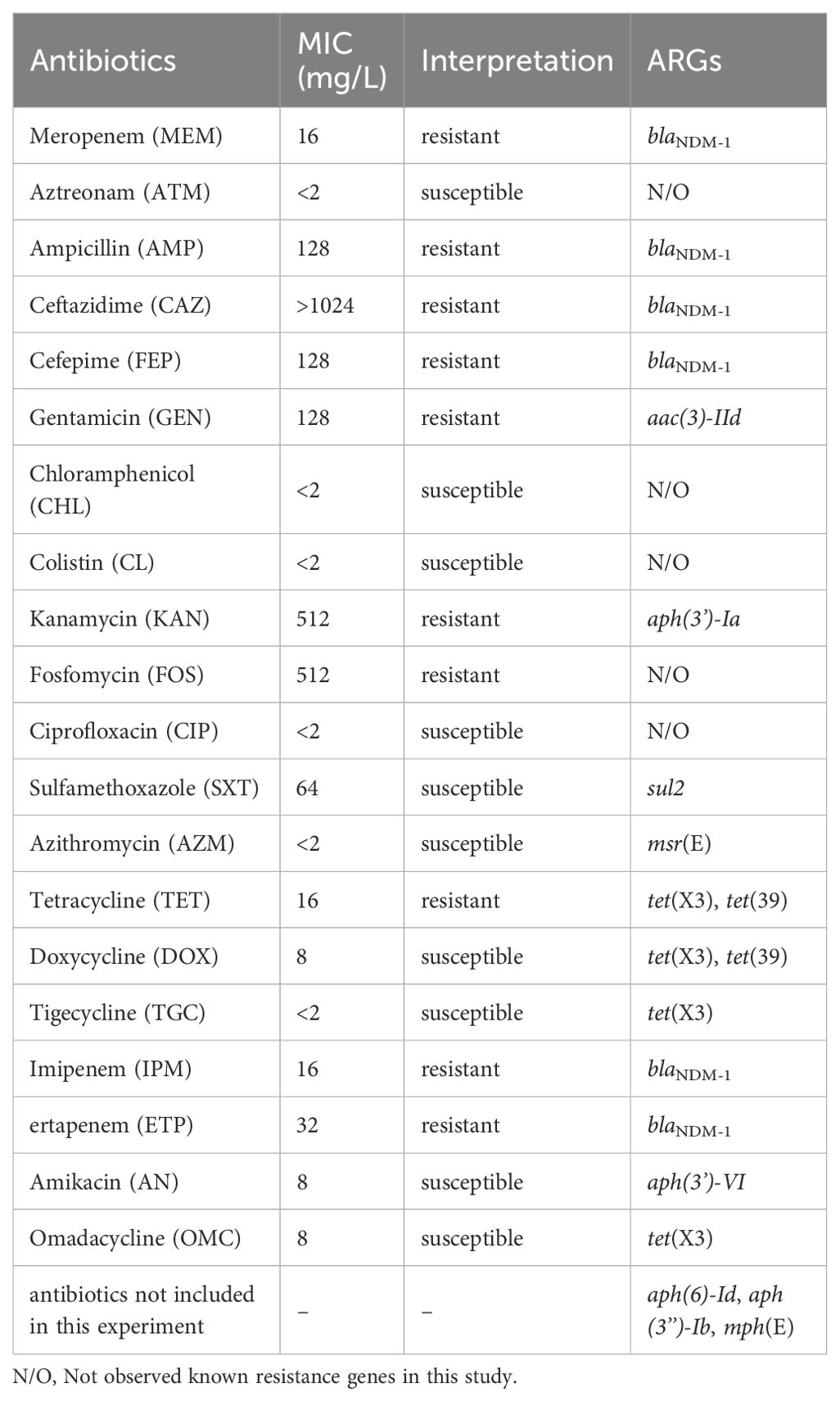
The antimicrobial susceptibility testing showed that the strain M2 was resistant to meropenem (16 mg/L), ampicillin (128 mg/L), ceftazidime (>1024 mg/L), cefepime (128 mg/L), gentamicin (128 mg/L), kanamycin (512 mg/L), fosfomycin (512 mg/L), imipenem (16 mg/L), ertapenem (32 mg/L) and tetracycline (16 mg/L) (Table 1). However, it was susceptible to aztreonam, chloramphenicol, colistin, ciprofloxacin, sulfamethoxazole, azithromycin, doxycycline, tigecycline, amikacin and omadacycline (Table 1).
The horizontal transferability of plasmid
The previous report regarding successful conjugation in the Acinetobacter plasmid remains rare. However, successful conjugation in the A. indicus plasmid was observed in our laboratory. In this study, we used the same parameters and tried new ones. However, the horizontal transfer of the plasmid carrying blaNDM was not observed.
Genetic diversity analysis
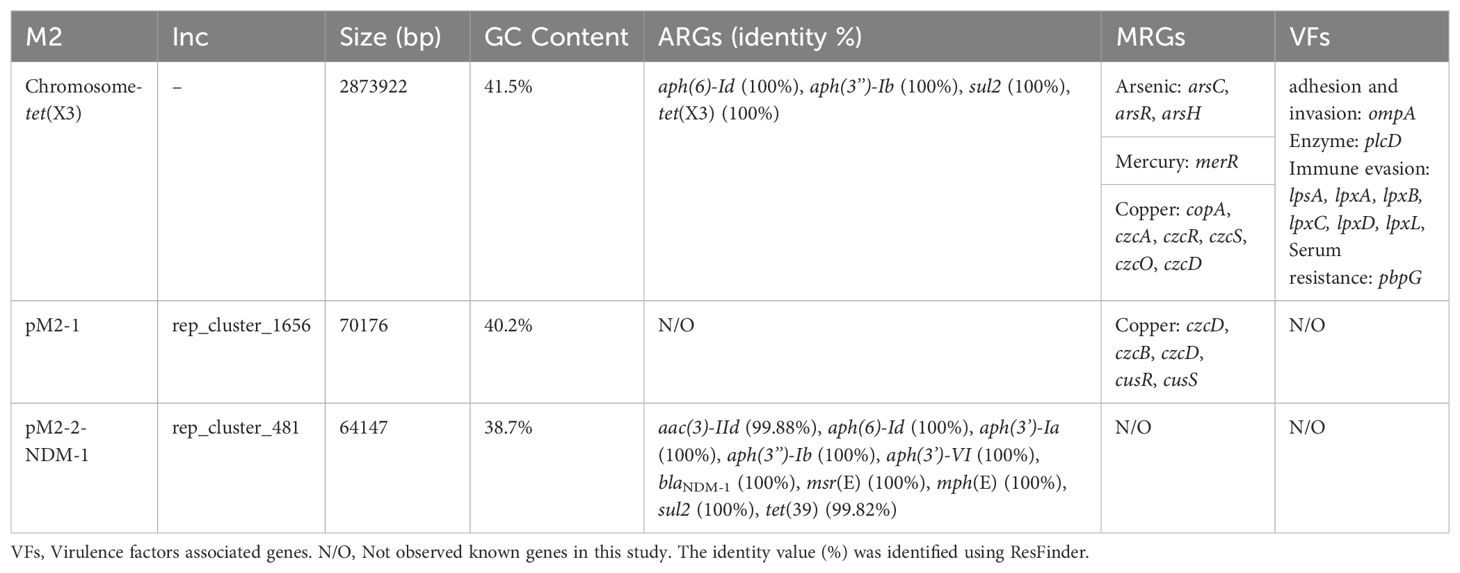
The WGS revealed that strain M2 contained one circular chromosome genome (2873922 bp, 41.5% GC content) and two circular plasmid genomes (pM2-1: 70176 bp, 40.2%; pM2-2-NDM-1: 64147 bp, 38.7%) (Table 2; Figure 1). The GC content of pM2-2-NDM-1 was lower than chromosome, hinting that they originated from different hosts. The GC content can serve as a marker to measure the origin of plasmids, indicating the potential horizontal transfer of plasmids (Tang et al., 2021; Long et al., 2025). The chromosome of the strain M2 carried multiple ARGs, including tet(X3), aph(6)-Id, aph(3’’)-Ib, and sul2 (Figure 1). In addition to ARGs, this chromosome carried MRGs against arsenic, mercury, and copper, as well as genes encoding VFs related to bacterial adhesion, invasion, enzyme, immune evasion, and serum resistance (Table 2: Figure 1). The pM2–1 did not carry ARGs but harbored the genes related to copper resistance and the CusS-CusR two-component regulatory system (TCS) (Table 2: Figure 1). The pM2-2-NDM-1 carried various ARGs, such as blaNDM-1, aac(3)-IId, aph(6)-Id, aph(3’)-Ia, aph(3’’)-Ib, aph(3’)-VI, msr(E), mph(E), sul2, and tet(39) (Table 2: Figure 1).
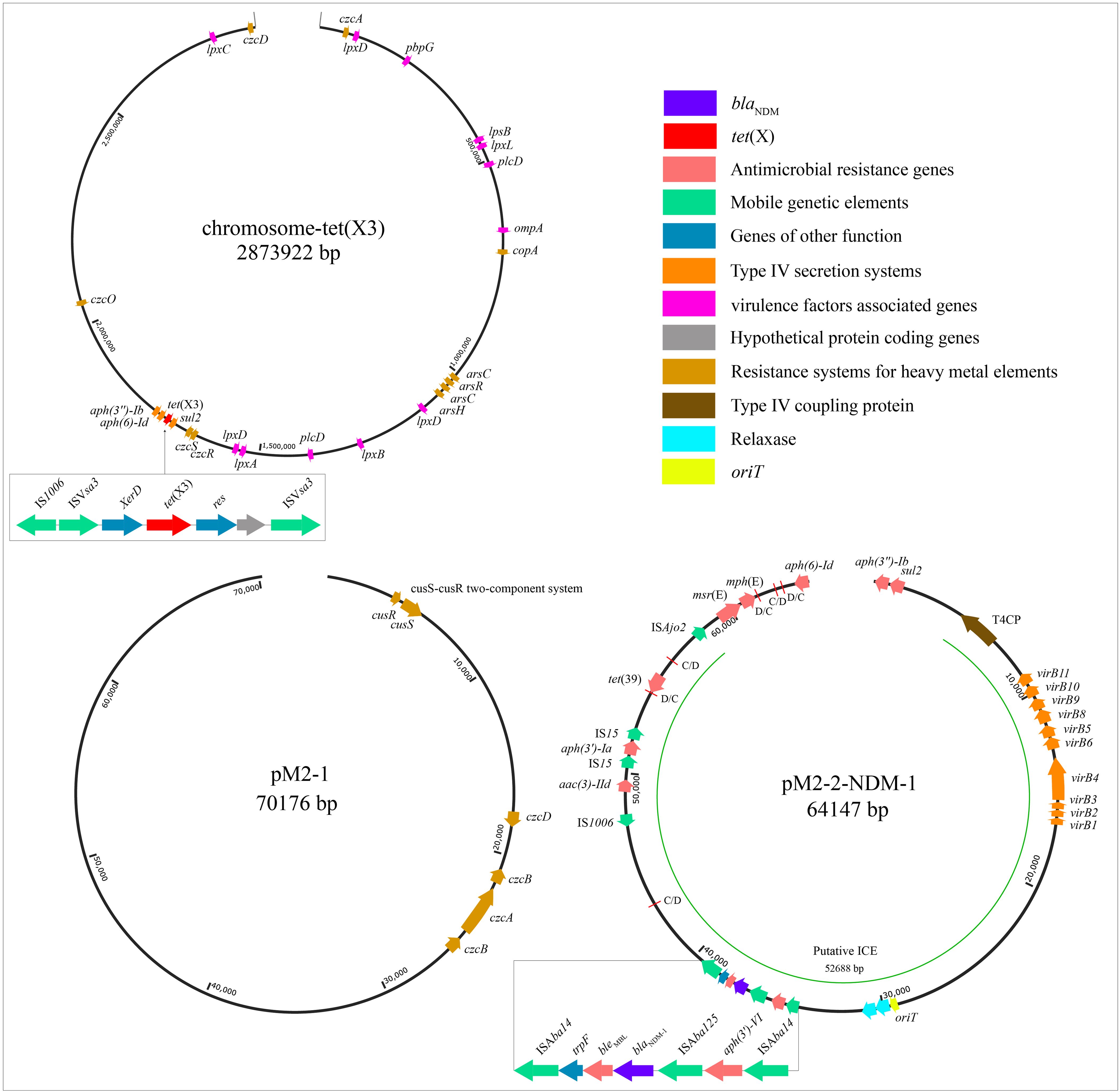
Figure 1. Structural features of the elements in the chromosome and plasmids. This figure shows the backgrounds of blaNDM and tet(X), ARGs, MRGs, genes encoding VFs, putative ICE region (oriT, T4SS, T4CP, relaxase), and pdif modules. In pM2-2-NDM-1, the red lines mark the C/D and D/C of the pdif modules.
Plasmid typing
The analysis of the pM2–1 and pM2-2-NDM-1 on the Pathogenwatch platform (homology-based alignment) revealed that they could not be identified as any known replicon type. Subsequently, the analysis of these plasmids on the Galaxy platform using MOB-typer revealed that pM2-2-NDM-1 was typed to rep_cluster_481 and predicted as conjugative, and pM2–1 was typed to rep_cluster_1656 and predicted as mobilizable. Furthermore, these plasmids were searched on the PLSDB database. The result revealed that pM2-2-NDM-1 exhibited the highest identity (>99.3%) with five plasmids. Among these, the sizes of three plasmids <5000 bp could not be identified as any known replicon type. The remaining two plasmids (NZ_CP051870.1 and NZ_CP051876.1) with the same size of 48239 bp were sourced from A. baumannii, typed to rep_cluster_481 and predicted as conjugative. However, these plasmids did not carry blaNDM or tet(X). In addition, the search of pM2–1 found that no plasmid exhibited identity.
Mobile genetic elements
The analysis of the pM2-2-NDM-1 on the ICEfinder platform identified a putative ICE region of 52688 bp (4758–57445 bp) containing the origin site of DNA transfer (oriT, 29162–29538 bp), T4SS (virB11, virB10, virB9, virB8, virB5, virB6, virB4, virB3, virB2, and virB1), T4CP (Type IV Coupling Proteins), relaxase (mobC and MOBP), integrase, and ARGs (blaNDM-1, aac(3)-IId, aph(3’)-Ia and tet(39)) (Figure 1). Furthermore, six pdif sites were identified in the pM2-2-NDM-1, and they formed five pdif modules including three pdif-ARGs modules (pdif-aac(3)-IId-aph(3’)-Ia, pdif-tet(39) and pdif-msr(E)-mph(E)), pdif-ser (a serine recombinase) module and pdif-hp (hypothetical protein) module (Figures 1, 2). These modules collectively build a pdif module island. This inevitably leads to sharing the internal C/D or D/C sites to form two types of pdif modules (Blackwell and Hall, 2017), one flanked by a C/D and a D/C site, and the other type flanked by a D/C and a C/D site. We searched the pdif-aac(3)-IId-aph(3’)-Ia module in the NCBI database and found that only one plasmid (pRp428) was highly similar (coverage 99% and identity 100%) to this module. The pdif-tet(39), pdif-msr(E)-mph(E) and pdif-ser modules were reported in pS30-1 (Blackwell and Hall, 2017). Thus, we used these plasmids and pM2-2-NDM-1 to construct the linear comparison (Figure 2) and identified pdif sites (Table 3). The pdif-aac(3)-IId-aph(3’)-Ia, pdif-tet(39), pdif-msr(E)-mph(E), pdif-ser and pdif-hp modules were identified in pRp428. Among these, the pdif-tet(39), pdif-ser, and pdif-hp modules were identical (100% coverage and identity) to those in pM2-2-NDM-1. The pdif-aac(3)-IId-aph(3’)-Ia module exhibited 98.64% identity to that in pM2-2-NDM-1. A gap of 178 bp existed in the non-coding region between left-hand IS15 and aph(3’)-Ia. The pdif-tet(39) and pdif-ser modules in pS30–1 were identical (100% coverage and identity) to those in pM2-2-NDM-1. Interestingly, the pdif-msr(E)-mph(E) module in pRp428 and pS30–1 only carried msr(E)-mph(E) gene pair. This structure was commonly seen in previous reports (Blackwell and Hall, 2017; Shao et al., 2023). However, the pdif-msr(E)-mph(E) module in pM2-2-NDM-1 additionally carried ISAjo2 and higA-higB. The pdif-higA-higB and pdif-ISAjo2 modules were independently present in pS30-1. However, the C/D and D/C sites flanking higA-higB and ISAjo2 were not found in pM2-2-NDM-1. In addition, the D/C site is located upstream of msr(E) in the pdif-msr(E)-mph(E) modules of pRp428 and pS30-1. However, the C/D site is located upstream of ISAjo2 in the pdif-msr(E)-mph(E) module of pM2-2-NDM-1. The analysis of pdif sites (Table 3) found that the base variant appeared in the D/C sites of the pdif-ser module of pS30-1. The C/D and D/C sites of the remaining pdif modules of pRp428 and pS30–1 were identical to those in pM2-2-NDM-1.
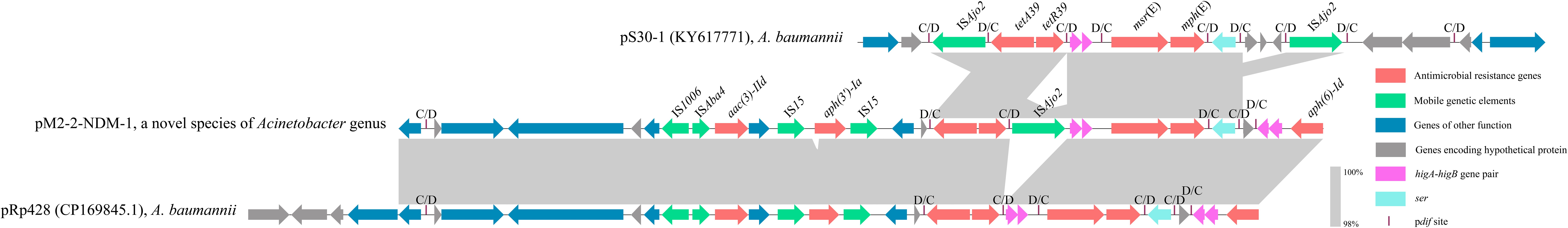
Figure 2. Comparison analysis of the pdif module island. The C/D and D/C sites of each pdif module are shown in Table 3.
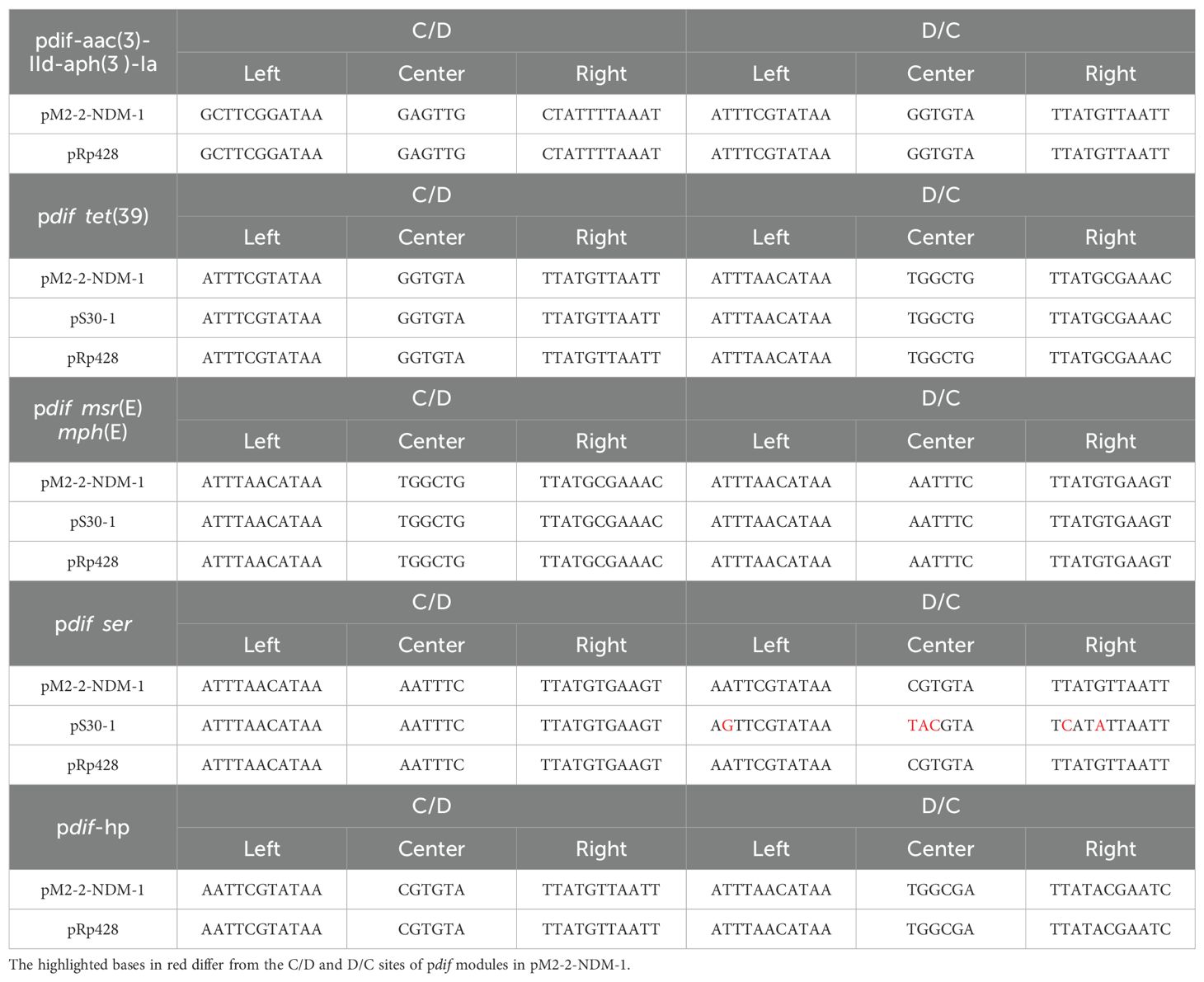
Table 3. The C/D and D/C sites of pdif modules in Figure 2.
Plasmid analysis
BLASTn analysis in the GenBank database found that pM2-2-NDM-1 was similar to pRp428 (100% identity and 90% coverage), pAb-D10a-a (99.91% identity and 68% coverage), pDT01139C (99.07% identity and 67% coverage), pFk2-7 (98.5% identity and 68% coverage), and pAR3 (99.21% identity and 66% coverage) (Figure 3A). Among these, three plasmids (pRp428, pAb-D10a-a, and pDT01139C) were sourced from A. baumannii, pAR3 from A. radioresistens, and pFk2–7 from an unidentified strain. These plasmids and pM2-2-NDM-1 were used to build an alignment analysis (Figure 3A). The analysis found that the conserved region contained oriT and the genes encoding T4SS, T4CP, and relaxase. The non-conserved regions included ARGs, pdif-ARG modules, and IS elements. Only pDT01139C carried blaNDM in the genomes from the public database. Thus, pM2-2-NDM-1 and pDT01139C genomes were used to build a comparison analysis of the blaNDM skeleton (Figure 3B). The analysis found that the trpF in the blaNDM-1 framework of pDT01139C consisted of 636 bp. The trpF in the blaNDM-1 framework of pM2-2-NDM-1 consisted of 114 bp. Furthermore, no IS element could be identified downstream of the blaNDM-1 framework in pDT01139C.
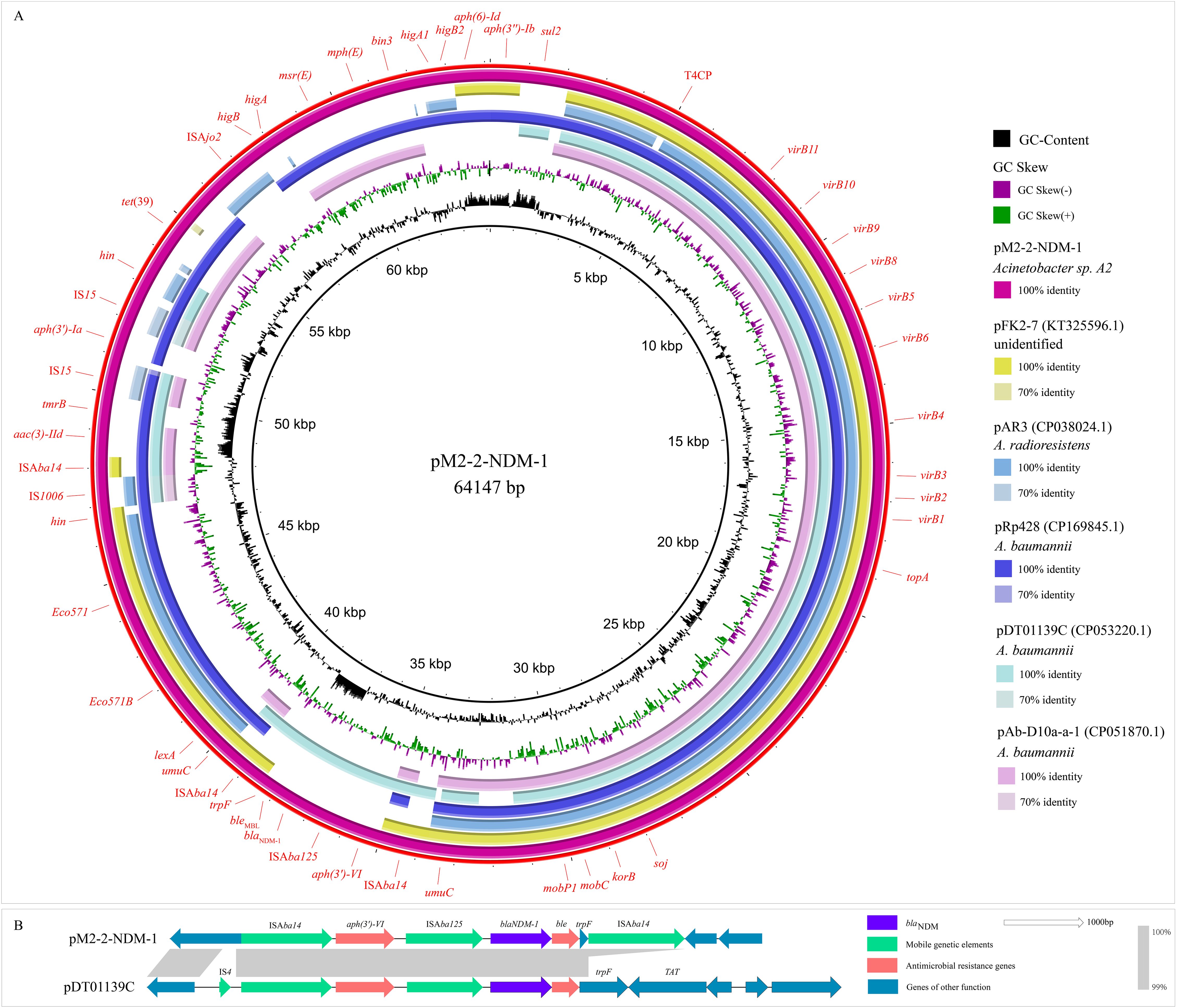
Figure 3. Plasmid analysis. (A): Circular comparison between pM2-2-NDM-1 and the similar plasmids from the NCBI database. (B): Comparison analysis of the blaNDM-1 skeletons from pM2-2-NDM-1 and pDT01139C.
Phylogenetic analysis
Three genomes were classified as Acinetobacter sp. A1 (GCA_012371315.1), A2 (GCA_012371325.1), and A3 (GCA_012371415.1) in the NCBI genome database. A total of 51 genomes closely related to genome M2 were retrieved from the JSpesiesWS platform (TCS) and DSMZ platform (TYGS). Subsequently, the above genomes and genome M2 were used to build a phylogenetic tree (Figure 4). Phylogenetic analysis revealed that this tree was diverged into three branches, highlighting three different ancestors. In the branch one, Acinetobacter sp. A1-A3 (A1-A3), A. towneri (DSM 14962 and DSM 14962 CIP 107472), and A. seohaensis (DSM 16313) were diverged from a clade, indicating their high homology. Among this, genomes M2 and A2 were diverged from a leaf node, suggesting they originated from a most recent common ancestor. Branch length quantifies accumulated genetic divergence from the most recent common ancestor. Genome M2 has higher genetic variability than A2 (branch length, 0.025 (M2) > 0.00707 (A2)), hinting that it undergoes prolonged independent evolution and accelerated evolution derived by selective pressure. Like the Acinetobacter sp. A2, the Acinetobacter sp. A1 (Taxonomy ID: 401467) and Acinetobacter sp. A3 (Taxonomy ID: 2725492) belong to unclassified species of the Acinetobacter genus in the family Moraxellaceae.

Figure 4. Phylogenetic tree. Bootstrap values were shown on the branch of this tree as circles. Branch lengths were displayed as numbers on each branch of this tree.
The genetic context of blaNDM-1
The blaNDM-1 framework consisted of ISAba125-blaNDM-1-bleMBL-trpF with a size of 2426 bp, located in the pM2-2-NDM-1 (Figure 1). We found that an aph-(3’)-VI was located upstream of blaNDM-1 framework. Two intact ISAba14 (1282 bp, orienting the same direction) flanking the structure of aph-(3’)-VI-ISAba125-blaNDM-1-bleMBL-trpF formed a rolling-circle-like structure of 5966 bp, ISAba14-aph-(3’)-VI-ISAba125-blaNDM-1-bleMBL-trpF-ISAba14 (Figure 1). ISFinder analysis revealed that this ISAba14 (the group IS150 of family IS3) had 99% identity with the reference sequence (1280/1282 bp) from A. baumannii. The BLASTn analysis of this rolling-circle-like structure in the NCBI database found that the plasmids of multiple bacterial species were high similar (>99% identity and coverage), including Acinetobacter genus (A. baumannii, A. nosocomialis, A. baylyi, A. johnsonii, A. junnii, A. lwoffii, A. pittii, A. schindleri, A. soli, and A. towneri), Citrobacter genus (Citrobacter freundii and Citrobacter werkmanii), Providencia genus (Providencia rettgeri and Providencia stuartii), E. coli, Enterobacter hormaechei, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. These plasmids (one plasmid genome selected from each bacterial species) and the pM2-2-NDM-1 were used to construct a comparison analysis (Figure 5A-1). Meanwhile, ISFinder was used to search downstream of the blaNDM skeleton. The analysis found that ISAba14 frequently emerged upstream of the blaNDM skeleton in the plasmids from the public database but rarely downstream of the blaNDM skeleton. Furthermore, the BLASTn analysis on the UniProt database found that an intact trpF consisted of 639 bp, which could be identified in the plasmids from the public database. However, the trpF in the blaNDM framework of pM2-2-NDM-1 was truncated by ISAba14 with a size of 114 bp. Tn7382 is derived from Tn125 and encompasses seven open reading frames (aph-(3’)-VI, ISAba125, blaNDM-1, ble, iso, TAT, cutA) enclosed by two direct copies of ISAba14 (Hamed et al., 2022). It was found in multiple chromosomes (TP2, TP3, AbBAS-1, and CI300) from A. baumannii and exhibited structural similarity to the rolling-circle-like structure in pM2-2-NDM-1. Thus, a linear comparison was built (Figure 5A-2). The analysis found three genes (iso, TAT, cutA) between ble and downstream ISAba14 in Tn7382. However, only one gene (fragmentary trpF) was located in the same site of pM2-2-NDM-1. Furthermore, an IS4 or ISAba33 was located upstream of the left-hand ISAba14. A similar location was not observed in pM2-2-NDM-1.

Figure 5. Comparison analysis. (A-1): The comparison analysis between the rolling-circle-like structure and the similar segments of plasmids from the NCBI database. (A-2): The comparison analysis between the rolling-circle-like structure and Tn7382. (B): The comparison analysis of the tet(X3) skeleton.
The genetic context of tet(X3)
The tet(X3) framework, ISVsa3-XerD-tet(X3)-res-ISVsa3, with a size of 5819 bp, was located in the chromosome of strain M2. Two ISVsa3 flanked the structure of XerD-tet(X3)-res. The upstream ISVsa3 was a fragmentary element of 715 bp, and the downstream ISVsa3 was an intact element of 1494 bp. ISFinder analysis revealed that ISVsa3, belonging to the ISCR family, originated from Vibrio salmonicida. The BLASTn analysis of this tet(X3) framework in the NCBI database found that the similar frameworks were mainly identified in the Acinetobacter genus and E. coli. The plasmid genomes with >99% identity and coverage to this framework were selected to construct the alignment analysis (Figure 5B). The analysis found that in addition to tet(X3), the ISVsa3 also mediated the formation of tet(X4) and tet(X5) frameworks. Most ISVsa3-mediated tet(X3) frameworks were sourced from the Acinetobacter genus. An intact ISVsa3 was commonly located downstream of tet(X). However, either a fragmentary or intact ISVsa3 was located upstream of tet(X). In addition to ISVsa3, an IS26 frequently appeared upstream of tet(X). An IS element, IS1006, that is rarely reported to be associated with the tet(X) family emerged upstream of the left-hand ISVsa3. Furthermore, ISVsa3 mediated the rolling-circle-like structures carrying tet(X3) (p34AB) or tet(X4) (p47EC).
Discussion
Most Acinetobacter plasmids are considered non-conjugative due to the rarely observed transfer of plasmids. Although this study did not observe the horizontal transfer of plasmid carrying blaNDM (pM2-2-NDM-1), it was predicted as conjugative. This may be attributed to laboratory systems omitting key microbial ecologic drivers, such as nutrient gradients, multispecies competitive dynamics, stress-induced epigenetic regulatory pathways, etc. These drivers are hard to replicate in the laboratory. This may be why the horizontal transfer of Acinetobacter plasmids is rarely observed. In addition to plasmid conjugation, the MGEs related to horizontal transfer of ARGs, including ICEs, pdif modules, and a rolling-circle-like structure, were identified in the pM2-2-NDM-1. A putative ICE region containing oriT, T4SS, T4CP, relaxase, integrase, and ARGs was identified. The genes ICEs carry common encoding antibiotic resistance determinants and virulence factors (Bellanger et al., 2014; Delavat et al., 2017) can confer the host with selective advantages, suggesting that ICE is a vital element for bacterial adaptation and evolution (Burrus et al., 2002; Bellanger et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2024). In ICEs, the T4SS and T4CP serve distinct yet complementary core functions (Bellanger et al., 2014; Delavat et al., 2017). The T4SS mediates the assembly of transport channels, and the T4CP orchestrates adaptor-mediated DNA delivery (Bellanger et al., 2014; Delavat et al., 2017). Their synergistic interaction critically governs the efficiency and specificity of conjugative transfer (Bi et al., 2012; Bellanger et al., 2014; Delavat et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2024). Typically, these elements carrying an integrase gene, a relaxase gene, and T4SS gene clusters are considered ICEs (Bi et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2024). The putative ICE region in pM2-2-NDM-1 carries the above elements. Thus, we consider that this ICE region is a fully functional ICE with the potential to transfer ARGs (blaNDM-1, aac(3)-IId, aph(3’)-Ia, and tet(39)) horizontally. Furthermore, six pdif sites and associated pdif-ARG modules have been detected in the pM2-2-NDM-1. The widespread distribution of the pdif-ARG module copes in the plasmid genomes of the Acinetobacter genus (Blackwell and Hall, 2017; Mindlin et al., 2019; Lin et al., 2020; Shao et al., 2023) indicates that pdif-ARG modules are associated with the horizontal transfer of resistance genes. In this study, the copies of pdif-aac(3)-IId-aph(3’)-Ia and pdif-tet(39) modules were identified in the plasmid genomes of the public database, suggesting the horizontal mobilization of these modules. The rare structure of the pdif-msr(E)-mph(E) module in the pM2-2-NDM-1 suggests that pdif modules are variable. This module carrying the higA-higB gene pair is critical for bacterial survival, stress adaptation, and pathogenicity. The common role of all types of pdif modules is to increase the fitness of their respective bacterial hosts in their habitats (Mindlin et al., 2019).
The blaNDM-positive strains were first retrospectively identified in 2005 from A. baumannii in an Indian hospital (Toleman and Walsh, 2012). In early isolates, blaNDM is located within the intact Tn125 transposon, leading to the hypothesis that Tn125 is the ancestral transposon for blaNDM (Kikuchi et al., 2022). The upstream region of Tn125 carries ISs from families such as IS5/IS30, and frequent recombination of these IS elements has generated diverse genetic backgrounds (Toleman and Walsh, 2012; Acman et al., 2022). Studies (Kikuchi et al., 2022) found that multiple MGEs played critical roles in blaNDM dissemination, including IS3000, IS26, IS5, ISCR1, Tn3, Tn125, and Tn3000. ISAba125, a member of the IS30 family, is typically located upstream of blaNDM and forms a structure, ISAba125-blaNDM-bleMBL-trpF-dsbC. It has been widely accepted that blaNDM-1 is regulated by a hybrid promoter containing the sequence from blaNDM-1 and ISAba125 (Kikuchi et al., 2022), and ISAba125 is commonly present in some form within blaNDM-positive isolates (Acman et al., 2022). In this study, two intact ISAba14 flank the blaNDM skeleton to form a rolling-circle-like structure. Similar segments can be found in the plasmids of multiple bacterial genera, particularly in the Acinetobacter genus. However, these segments cannot be confirmed as rolling-circle-like structures due to the absence of downstream ISAba14. The discrepancy between the rolling-circle-like structure and Tn7382 focuses on the downstream region of ble in the blaNDM skeleton, suggesting that this region is variable and unassociated with the blaNDM expression. However, the upstream region of ble keeps a high similarity, suggesting that this region is potentially associated with the effective expression of aph(3’)-VI and blaNDM. The abundance of ISAba14 is present in the Acinetobacter genus (Hamed et al., 2022), and the Tn7382 shows structural similarity to the rolling-circle-like structure mediated by ISAba14, hinting that this rolling-circle-like structure has the potential for transmission.
ISVsa3 plays a pivotal role in the formation of the tet(X) framework, such as tet(X3), tet(X4), and tet(X5). Typically, full-length ISVsa3 is positioned downstream of tet(X), while the upstream region may observe intact/truncated ISVsa3 or other ISs. ISVsa3 participates in forming rolling-circle replication structures to mediate the horizontal mobilization of tet(X3) or tet(X4) (He et al., 2019). ISVsa3 also mediated tet(X) skeleton and other ARGs, such as aph, to form composite transposon. In addition to the tet(X) family, ISVsa3 is associated with multiple ARGs, such as floR, tet(A), aph(6)-Id, aph(3″)-Ib, and sul2 (Lewis et al., 2023). Thus, monitoring ISVsa3 is critical for understanding the distribution and spread of ARGs, particularly tet(X). Additionally, we found that an IS element, IS1006, that is rarely seen in the tet(X) skeleton closely links with ISVsa3. This link was also observed in the p80-1–2 of A. indicus (Figure 5B). In this work, the strain M2 was susceptible to tetracycline antibiotics (doxycycline, tigecycline, and omadacycline). The BLASTn analysis between the tet(X3) sequence of strain M2 and the reference sequence (NG_048307, 1361 bp) from the NCBI nucleotide database found that these sequences were identical (100% identity and coverage). This silent phenotype was also observed in most Acinetobacter isolates carrying tet(X) (including tet(X3) and tet(X5)) in our laboratory. These strains have a common characteristic that a fragmented ISVsa3 or an IS element previously unreported to associate with the tet(X) family, IS1008, was located upstream of the tet(X) skeleton. This change in structure is attributed to frequent recombination events upstream of tet(X), which may lead to the downregulation of the expression level of tet(X3). The expression of the resistance gene is regulated by a hybrid promoter, which has been observed in blaNDM (Kikuchi et al., 2022). The subsequent evolutionary trajectory may fix the gap. Furthermore, in light of strict antibiotic restrictions in bovine production, plasmids may downregulate tet(X) expression to reduce fitness costs and facilitate host survival until environmental triggers activate resistance mechanisms. This strategy conforms to the “stealth-to-threat” model of plasmid evolution, in which genetic cargo is closed until environmental pressure demands its activation.
Livestock is recognized as a critical reservoir for carbapenem-resistant bacteria (CRB) (Wang et al., 2017), yet investigations into bovine production remain limited. This is the first report of the co-occurrence of blaNDM-1 and tet(X3) genes in a strain belonging to a novel species of the Acinetobacter genus from bovine production. This co-occurrence reflected the functional convergence of carbapenem and tetracycline resistance mechanisms. This convergence may be caused by dual selection pressures mediated by antimicrobial usage patterns. Although carbapenems and tigecycline undergo strict usage controls, the extensive application of tetracyclines and β-lactams in bovine production leads to the co-occurrence of blaNDM and tet(X), such as amoxicillin and tetracycline as the major veterinary antibiotics (Ma et al., 2024). Thus, we consider that the frequently observed co-occurrence of these genes represents an established dissemination network rather than sporadic acquisition events. This co-occurrence may be more frequently observed in the future. Furthermore, the co-occurrence of blaNDM and tet(X) in a novel species of the Acinetobacter genus should cause public concern because this co-occurrence highlights the presence of substantial undiscovered co-occurrence of high-risk ARGs in the agroecological system. This will inevitably lead to an elevated risk of disseminating high-risk ARGs into human populations.
Methods
Sampling and microbial identification
The sludge was collected from a commercial beef cattle farm in Hebei province, China. The strain was isolated from MacConkey (Huan Kai Microbial, China) agar plates supplemented with 2 μg/mL meropenem and cultured at 37°C for 16 hours. PCR amplification and Sanger sequencing verification were performed for blaNDM and tet(X) genes (Wang et al., 2017; He et al., 2019).
Whole-genome sequencing
The long-read sequencing was executed on the Oxford Nanopore platform. Briefly, the genome was sequenced using Oxford Nanopore and the DNBSEQ platform. The resulting corrected reads were carried out by hybrid assembly in combination with DNBSEQ short reads. The assembled genome was checked for completeness and contamination using the CheckM (v1.2.3) of the NCBI annotation service.
Identification of bacterial species
The identification of bacterial genus was performed by MALDI-TOF-MS and 16s rRNA (Kim et al., 2010; Singhal et al., 2015). The identification of bacterial species was executed on the NCBI database using ANI match of the NCBI annotation service, on the DSMZ platform (Leibniz Institute DSMZ: Welcome to the Leibniz Institute DSMZ) using the type strain genome server (TYGS), and on the JSpeciesWS platform (JSpeciesWS - Taxonomic Thresholds) using tetra correlation search (TCS). Furthermore, we used the mash match tool to identify bacterial species on the Pathogenwatch platform (Pathogenwatch | A Global Platform for Genomic Surveillance) (Argimón et al., 2021). The ANI calculation was executed on the EZBioCloud platform (ANI Calculator | Ezbiocloud.net) using the OrthoANIu algorithm (Yoon et al., 2017). The GGDC platform (ggdc.dsmz.de/ggdc.php#) was used to calculate the dDDH value.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 20 antibiotics (meropenem, aztreonam, ampicillin, ceftazidime, cefepime, gentamicin, chloramphenicol, colistin, kanamycin, fosfomycin, ciprofloxacin, sulfamethoxazole, azithromycin, tetracycline, doxycycline, tigecycline, imipenem, ertapenem, amikacin and omadacycline) was performed using microdilution of Mueller-Hinton broth (Huan Kai Microbial, China). The testing concentration range is 2 mg/L to 1024 mg/L. Results were determined according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) documents M100-S34 (2024). Since there is no established breakpoint for tigecycline and omadacycline resistance in Acinetobacter spp., their breakpoint was determined by FDA-defined interpretive criteria for Enterobacteriaceae (R≥ 8 μg/mL for tigecycline and R≥ 16 μg/mL for omadacycline).
Conjugation assay
Conjugation assays were conducted based on the filter mating method using E. coli J53 (sodium azide-resistant) and Salmonella LGJ2 (rifampicin-resistant) as recipients. A donor-recipient mixture of 10:1 (the ratio 10:1 of the donor (M2) to the recipient (J53 or LGJ2)) was incubated on a 0.22-μm filter membrane at 35°C for 16h, then moved to MacConkey plates supplemented with donor resistance (0.5 mg/L meropenem) and recipient resistance (100 mg/L sodium azide or 200 mg/L rifampicin). The ratio 5:1 and 15:1 of the donor to the recipient were supplementarily tested. At least three attempts were made for each parameter, and three parallel experiments were made for each attempt.
Phylogenetic construction
Core genomes were extracted using Roary (GitHub - sanger-pathogens/Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis). Recombination was filtered using Gubbins (GitHub - nickjcroucher/gubbins: Rapid phylogenetic analysis of large samples of recombinant bacterial whole genome sequences using Gubbins). Filtered polymorphic sites were employed to build a tree on the PhyML platform (GitHub - stephaneguindon/phyml: PhyML – Phylogenetic estimation using (Maximum) Likelihood). The iTOL (iTOL: Interactive Tree Of Life) visualized this tree with the corresponding features of each genome.
Bioinformatics analysis
ResFinder (v4.6.0) was used to screen all known acquired AMRs (Bortolaia et al., 2020). The threshold of ARG identification was set to 90%, and the minimum length was set to 80%. Plasmid typing was carried out on the Pathogenwatch platform using homology-based alignment and on the Galaxy (Galaxy | China) platform using MOB-typer. The PLSDB database (PLSDB) was used to analyze the plasmid characterization further. The VFDB was used to search for the genes encoding VFs (VFDB: Virulence Factors of Bacterial Pathogens) (Liu et al., 2022). Genome annotation was performed using the RAST genome annotation service (RAST Server - RAST Annotation Server) (Overbeek et al., 2014), with manual refinement using ORFfinder (ORFfinder Home-NCBI), UniPort (UniProt), and ISFinder (ISfinder) (Siguier et al., 2006). The pdif module was identified using PdifFinder (Home) (Shao et al., 2023). ICEfinder (ICEfinder) was employed to detect the oriT, integrase, relaxase, T4CP, T4SS, and the other associated components (28). The circular and linear comparisons were created using BRIG (ver. 0.95) and Easyfig (ver. 2.2.5).
Data availability statement
Genome assemblies of the strain M2 have been deposited in the NCBI database under BioProject accession no. PRJNA1228993.
Ethics statement
All animal studies were performed according to the US National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Lanzhou Institute of Husbandry and Pharmaceutical Science of CAAS.
Author contributions
JZ: Formal analysis, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. QW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Software, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Visualization, Data curation. YW: Supervision, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Resources. MS: Writing – review & editing. YQ: Writing – review & editing, Software, Investigation. CZ: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Methodology. GD: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. HL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. WW: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 32273068), the earmarked fund for the China Agriculture Research System (CARS) (grant No. CARS-37), and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant No. 2022YFD1602201).
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Jian Sun and Hao Ren, South China Agricultural University, for providing Salmonella LGJ2.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Acman, M., Wang, R., van Dorp, L., Shaw, L. P., Wang, Q., Luhmann, N., et al. (2022). Role of mobile genetic elements in the global dissemination of the carbapenem resistance gene bla NDM. Nat. Commun. 13, 1131. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28819-2
Argimón, S., Yeats, C. A., Goater, R. J., Abudahab, K., Taylor, B., Underwood, A., et al. (2021). A global resource for genomic predictions of antimicrobial resistance and surveillance of salmonella typhi at pathogenwatch. Nat. Commun. 12, 2879. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23091-2
Bellanger, X., Payot, S., Leblond-Bourget, N., and Guédon, G. (2014). Conjugative and mobilizable genomic islands in bacteria: evolution and diversity. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 38, 720–760. doi: 10.1111/1574-6976.12058
Bi, D., Xu, Z., Harrison, E. M., Tai, C., Wei, Y., He, X., et al. (2012). ICEberg: A web-based resource for integrative and conjugative elements found in bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, D621–D626. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr846
Blackwell, G. A. and Hall, R. M. (2017). The tet39 determinant and the msrE-mphE genes in acinetobacter plasmids are each part of discrete modules flanked by inversely oriented pdif (XerC-xerD) sites. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 61, e00780-17 doi: 10.1128/AAC.00780-17
Bortolaia, V., Kaas, R. S., Ruppe, E., Roberts, M. C., Schwarz, S., Cattoir, V., et al. (2020). ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 75, 3491–3500. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa345
Burrus, V., Pavlovic, G., Decaris, B., and Guédon, G. (2002). Conjugative transposons: the tip of the iceberg. Mol. Microbiol. 46, 601–610. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03191.x
Cheng, Y., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Song, J., Chen, Y., Shan, T., et al. (2021). Detection of a new tet(X6)-encoding plasmid in acinetobacter towneri. J. Glob Antimicrob. Resist. 25, 132–136. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2021.03.004
Cheng, Y., Li, Y., Yang, M., He, Y., Shi, X., Zhang, Z., et al. (2023). Emergence of novel tigecycline resistance gene tet(X5) variant in multidrug-resistant acinetobacter indicus of swine farming environments. Vet. Microbiol. 284, 109837. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2023.109837
Ching, C., Brychcy, M., Nguyen, B., Muller, P., Pearson, A. R., Downs, M., et al. (2024). RecA levels modulate biofilm development in acinetobacter baumannii. Mol. Microbiol. 121, 196–212. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15188
Delavat, F., Miyazaki, R., Carraro, N., Pradervand, N., and van der Meer, J. R. (2017). The hidden life of integrative and conjugative elements. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 41, 512–537. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fux008
Delgado-Blas, J. F., Ovejero, C. M., Abadia-Patiño, L., and Gonzalez-Zorn, B. (2016). Coexistence of mcr-1 and blaNDM-1 in escherichia coli from Venezuela. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60, 6356–6358. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01319-16
Dijkshoorn, L., Nemec, A., and Seifert, H. (2007). An increasing threat in hospitals: multidrug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 5, 939–951. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1789
Gutiérrez, K., Vásquez-Mendoza, A., and Rodríguez, C. (2024). An outbreak of severe or lethal infections by a multidrug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii ST126 strain carrying a plasmid with blaNDM-1 and blaOXA-58 carbapenemases. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 110, 116428. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2024.116428
Hamed, S. M., Hussein, A. F. A., Al-Agamy, M. H., Radwan, H. H., and Zafer, M. M. (2022). Tn7382, a novel composite transposon harboring blaNDM-1 and aphA6 in acinetobacter baumannii. J. Glob Antimicrob. Resist. 30, 414–417. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2022.08.001
He, T., Wang, R., Liu, D., Walsh, T. R., Zhang, R., Lv, Y., et al. (2019). Emergence of plasmid-mediated high-level tigecycline resistance genes in animals and humans. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 1450–1456. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0445-2
Jia, H., Tong, Q., Wang, L., Wu, Y., Li, X., Li, S., et al. (2025). Silent circulation of plasmid-borne tet(X6) and blaOXA-58 genes in a community-acquired acinetobacter baumannii strain. Drug Resistance Updates 79, 101194. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2024.101194
Kikuchi, Y., Matsui, H., Asami, Y., Kuwae, A., Inahashi, Y., Hanaki, H., et al. (2022). Landscape of bla NDM genes in enterobacteriaceae. J. Antibiotics 75, 559–566. doi: 10.1038/s41429-022-00553-3
Kim, T. W., Kim, Y. H., Kim, S. E., Lee, J. H., Park, C. S., and Kim, H. Y. (2010). Identification and distribution of bacillus species in doenjang by whole-cell protein patterns and 16s RRNA gene sequence analysis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20, 1210–1214. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1002.02008
Lewis, G. L., Fenton, R. J., Moriyama, E. N., Loy, J. D., and Moxley, R. A. (2023). Association of ISVsa3 with multidrug resistance in salmonella enterica isolates from cattle (Bos taurus). Microorganisms 11, 631. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030631
Li, J., Tai, C., Deng, Z., Zhong, W., He, Y., and Ou, H. Y. (2018). VRprofile: gene-cluster-detection-based profiling of virulence and antibiotic resistance traits encoded within genome sequences of pathogenic bacteria. Brief Bioinform. 19, 566–574. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbw141
Lin, D. L., Traglia, G. M., Baker, R., Sherratt, D. J., Ramirez, M. S., and Tolmasky, M. E. (2020). Functional analysis of the acinetobacter baumannii xerc and xerd site-specific recombinases: potential role in dissemination of resistance genes. Antibiotics 9, 1–14. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9070405
Liu, H., Moran, R. A., Chen, Y., Doughty, E. L., Hua, X., Jiang, Y., et al. (2021). Transferable acinetobacter baumannii plasmid PDETAB2 encodes OXA-58 and NDM-1 and represents a new class of antibiotic resistance plasmids. J. Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 76, 1130–1134. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab005
Liu, B., Zheng, D., Zhou, S., Chen, L., and Yang, J. (2022). VFDB 2022: A general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 50, D912–D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1107
Long, X., Lin, F., Tang, B., Miao, F., Li, Z., Shen, Y., et al. (2025). Acinetobacter indicus coharboring tet(X6) and blaNDM-1 isolated from slaughterhouse waste. J. Glob Antimicrob. Resist. 41, 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2024.12.004
Lu, X., Du, Y., Peng, K., Zhang, W., Li, J., Wang, Z., et al. (2022). Coexistence of tet (X4), mcr-1, and bla NDM-5 in ST6775 escherichia coli isolates of animal origin in China. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e0019622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00196-22
Ma, T., Xie, N., Gao, Y., Fu, J., Tan, C. E., Yang, Q. E., et al. (2024). VirBR, a transcription regulator, promotes incX3 plasmid transmission, and persistence of blaNDM-5 in zoonotic bacteria. Nat. Commun. 15, 5498. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49800-1
Mallonga, Z., Tokuda, M., Yamazaki, R., Tsuruga, S., Nogami, I., Sato, Y., et al. (2025). Emergence of acinetobacter towneri harbouring a novel plasmid with blaNDM-1 and tet(X7) from hospital wastewater in the Philippines. J. Glob Antimicrob. Resist. 41, 287–289. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2025.01.017
Meier-Kolthoff, J. P., Auch, A. F., Klenk, H.-P., and Oker, M. G. (2013). Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinformatics 14, 60. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Mindlin, S., Beletsky, A., Mardanov, A., and Petrova, M. (2019). Adaptive dif modules in permafrost strains of acinetobacter lwoffiiand their distribution and abundance among present day acinetobacter strains. Front. Microbiol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00632
Mmatli, M., Mbelle, N. M., and Osei Sekyere, J. (2025). Plasmid-borne mcr-1 and replicative transposition of episomal and chromosomal blaNDM-1, blaOXA-69, and blaOXA-23 carbapenemases in a clinical acinetobacter baumannii isolate. mSystems 10, e0168324. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01683-24
Opazo-Capurro, A., Xanthopoulou, K., Arazo del Pino, R., González-Muñoz, P., Matus-Köhler, M., Amsteins-Romero, L., et al. (2024). Co-occurrence of two plasmids encoding transferable blaNDM-1 and tet(Y) genes in carbapenem-resistant acinetobacter bereziniae. Genes (Basel) 15, 1213. doi: 10.3390/genes15091213
Overbeek, R., Olson, R., Pusch, G. D., Olsen, G. J., Davis, J. J., Disz, T., et al. (2014). The SEED and the rapid annotation of microbial genomes using subsystems technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D206–D214. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1226
Peleg, A. Y., Seifert, H., and Paterson, D. L. (2008). Acinetobacter baumannii: emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 21, 538–582. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00058-07
Poirel, L. and Nordmann, P. (2006). Carbapenem resistance in acinetobacter baumannii: mechanisms and epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Infection 12, 826–836. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01456.x
Riesco, R. and Trujillo, M. E. (2024). Update on the proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 74, 006300. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006300
Seiffert, S. N., Marschall, J., Perreten, V., Carattoli, A., Furrer, H., and Endimiani, A. (2014). Emergence of klebsiella pneumoniae co-producing NDM-1, OXA-48, CTX-M-15, CMY-16, qnrA and armA in Switzerland. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 44, 260–262. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.05.008
Shao, M., Ying, N., Liang, Q., Ma, N., Leptihn, S., Yu, Y., et al. (2023). Pdif-mediated antibiotic resistance genes transfer in bacteria identified by pdifFinder. Brief Bioinform. 24, bbac521. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac521
Shi, J., Cheng, J., Liu, S., Zhu, Y., and Zhu, M. (2024). Acinetobacter baumannii: an evolving and cunning opponent. Front. Microbiol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1332108
Siguier, P., Perochon, J., Lestrade, L., Mahillon, J., and Chandler, M. (2006). ISfinder: the reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, D32–D36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj014
Singhal, N., Kumar, M., Kanaujia, P. K., and Virdi, J. S. (2015). MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: an emerging technology for microbial identification and diagnosis. Front. Microbiol. 6. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00791
Sun, J., Chen, C., Cui, C. Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, X., Cui, Z. H., et al. (2019). Plasmid-encoded tet(X) genes that confer high-level tigecycline resistance in escherichia coli. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 1457–1464. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0496-4
Tang, B., Yang, H., Jia, X., and Feng, Y. (2021). Coexistence and characterization of tet(X5) and NDM-3 in the MDR-acinetobacter indicus of duck origin. Microb. Pathog. 150, 104697. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104697
Toleman, M. A. and Walsh, T. R. (2012). Reply to “Genetic contexts of bla NDM-1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56, 6071. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01128-12
Wang, M., Liu, G., Liu, M., Tai, C., Deng, Z., Song, J., et al. (2024). ICEberg 3.0: functional categorization and analysis of the integrative and conjugative elements in bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 52, D732–D737. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad935
Wang, Y., Zhang, R., Li, J., Wu, Z., Yin, W., Schwarz, S., et al. (2017). Comprehensive resistome analysis reveals the prevalence of NDM and MCR-1 in chinese poultry production. Nat. Microbiol. 2, 16260. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.260
Keywords: antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), tet(X), blaNDM, Acinetobacter, multi-drug resistance, pdif module
Citation: Wang Q, Wei Y, Shoaib M, Qiu Y, Zhang C, Dai G, Lin H, Wang W and Zhang J (2025) A strain defined as a novel species in the Acinetobacter genus co-harboring chromosomal associated tet(X3) and plasmid associated blaNDM-1 from a beef cattle farm in Hebei, China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1594982. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1594982
Received: 17 March 2025; Accepted: 10 June 2025;
Published: 02 July 2025.
Edited by:
Jinxin Zhao, Monash University, AustraliaReviewed by:
German Matias Traglia, Universidad de La Republica, Salto, UruguaySamira M. Hamed, October University for Modern Sciences and Arts, Egypt
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wei, Shoaib, Qiu, Zhang, Dai, Lin, Wang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiyu Zhang, aW5memp5QHNpbmEuY29t; Weiwei Wang, d2Vpd2Vpd2FuZzE5OTBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
‡ORCID: Qing Wang, orcid.org/0009-0007-7459-1228
Muhammad Shoaib, orcid.org/0000-0001-8695-1840
Guonian Dai, orcid.org/0009-0009-6219-3358
 Qing Wang1,2,3,4†
Qing Wang1,2,3,4† Muhammad Shoaib
Muhammad Shoaib Yanhua Qiu
Yanhua Qiu Weiwei Wang
Weiwei Wang Jiyu Zhang
Jiyu Zhang