- 1Department of Veterinary Medicine, College of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine, United Arab Emirates University, Al Ain, United Arab Emirates
- 2United Arab Emirates University (UAEU) Center for Public Policy and Leadership, United Arab Emirates University, Al Ain, United Arab Emirates
- 3Department of Animal Medicine, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Kafrelsheikh University, Kafrelsheikh, Egypt
- 4Biology Department, Faculty of Education and Arts, Sohar University, Sohar, Oman
- 5Department of Biotechnology and Bioinformatics, Korea University, Sejong, Republic of Korea
- 6Department of Botany and Microbiology, College of Science, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- 7Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Sohag University, Sohag, Egypt
- 8Division of Internal Medicine, Department of Animal Medicine, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, South Valley University, Qena, Egypt
The escalating prevalence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria presents a critical global health challenge, necessitating the urgent development of alternative antimicrobial strategies. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have emerged as promising antimicrobial agents due to their broad-spectrum activity, unique physicochemical properties, and multiple mechanisms of bacterial inhibition. Their nanoscale size, high surface area-to-volume ratio, and ability to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) make them highly effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. AgNPs exert their antimicrobial effects through diverse mechanisms, including membrane disruption, protein and DNA interactions, enzymatic inhibition, and interference with bacterial metabolic pathways. Despite their potent antibacterial activity, concerns regarding bacterial adaptation, cytotoxicity, and non-specific interactions have prompted extensive research into innovative delivery systems to enhance AgNP efficacy while minimizing adverse effects. This review comprehensively explores the synthesis methods and physical properties of AgNPs, emphasizing their antimicrobial mechanisms and emerging resistance patterns. Additionally, we discuss advanced targeted delivery approaches, including surface functionalization, biopolymer encapsulation, liposomal carriers, and stimuli-responsive nanoplatforms, which enhance the stability, selectivity, and controlled release of AgNPs. These strategies not only improve AgNP bioavailability but also reduce host toxicity and prevent bacterial resistance development. Furthermore, we highlight future directions in AgNP-based antimicrobial therapy, such as combinatorial treatments with antibiotics, advanced nanostructure modifications, and the integration of AgNPs into wound dressings, coatings, and biomedical devices. By synthesizing recent advancements, this review underscores the transformative potential of AgNPs as next-generation antimicrobial agents to combat MDR bacterial infections. Addressing the current limitations and optimizing AgNP formulations will be crucial for their successful clinical translation and for mitigating the global antibiotic resistance crisis.
1 Introduction
Antibiotics, which are substances effective against bacteria, were first discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928 (Fleming, 1929). These drugs have since become indispensable in modern medicine, as well as in various other sectors, including agriculture and the food industry (Capita and Alonso-Calleja, 2013). Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) refers to the process by which microorganisms—such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites—develop resistance to the drugs designed to combat them. The primary driver of AMR is the excessive and improper use of antibiotics in humans, animals, and the environment (Ahmed et al., 2015; Khalifa et al., 2022a). This growing problem is largely attributed to the overuse of antibiotics in human and veterinary fields, which has become a critical global public health concern (Khalifa et al., 2021a; Oreiby et al., 2019). AMR makes infections harder to treat, increasing the risk of disease transmission, severe illness, and death (Khalifa et al., 2025; Khalifa et al., 2024b). According to a recent comprehensive study, bacterial AMR was linked to approximately 4.95 million deaths in 2019, with an estimated 1.27 million of those deaths directly caused by bacterial AMR (95% uncertainty interval: 0.911–1.71 million) (Murray et al., 2022). Therefore, several international organizations, including the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), have begun publishing country-specific guidelines for antimicrobial use and raising awareness about this issue (Hegazy and Oreiby, 2024).
The demand for unconventional antibiotics has become an essential focus for modern antibiotic researchers, who are working to navigate the evolving challenges of bacterial pathogenesis, particularly in relation to Gram-negative bacteria (Khalifa et al., 2022b; Al-Hakkani et al., 2023). This approach aims to tackle problems that initially seem insurmountable. Encouragingly, a recent review of the global preclinical antibacterial pipeline reveals a significant surge in activity related to unconventional treatments (Theuretzbacher et al., 2019). Although nontraditional therapies show promise for the future, demonstrating their clinical effectiveness will require substantial funding. This is especially true given that many of the translational demands for small, direct-acting molecules are unlikely to align with the alternative development pathways. Moreover, unconventional treatments are more likely to be used alongside antibiotics than as stand-alone therapies. This can complicate clinical trials by making it difficult to attribute outcomes to the new agent, potentially affecting efficacy assessments and regulatory approval (Theuretzbacher and Piddock, 2019).
Currently, there is widespread evidence that nanoparticles could serve as a promising alternative to antibiotics, potentially offering significant help in tackling the issue of bacterial multi-drug resistance (Rai et al., 2012). In particular, AgNPs have attracted considerable attention within the scientific community (Baveloni et al., 2025; Aljowaie and Aziz, 2025; Al-Asbahi et al., 2024). In recent years, AgNPs have been viewed as particularly promising for the development of a new class of antibiotics, offering a novel approach to combat a variety of bacterial infections (Caniglia et al., 2024; Ibraheem et al., 2024; Iwuji et al., 2024; Tunç, 2024; Soltani et al., 2024; Yiğit et al., 2024). This review aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the potential of AgNPs as antimicrobial agents against multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. It will explore the synthesis methods, physical properties, and antimicrobial activities of AgNPs. Furthermore, we will discuss the mechanisms by which AgNPs exert their bactericidal effects and address emerging concerns related to bacterial resistance to AgNPs. We will also review advanced strategies for targeted delivery, which aim to improve the selectivity and effectiveness of AgNPs while reducing cytotoxicity. Finally, we will highlight future directions for enhancing AgNP-based antimicrobial therapies, focusing on innovative methods to optimize their clinical use. Through this detailed review, we hope to offer valuable insights into the potential of AgNPs as a novel and effective solution for treating MDR bacterial infections.
2 Synthesis of AgNPs
The synthesis of AgNPs can be achieved through various approaches, including physical, chemical, and green synthesis methods.
2.1 Physical and chemical synthesis
Physical methods, such as evaporation-condensation, spark discharge, and pyrolysis, offer rapid synthesis without hazardous chemicals but suffer from high energy consumption, low yield, and inconsistent particle distribution (Kruis et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2016; Elsupikhe et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2020).
Chemical synthesis, which involves metal precursors, reducing agents, and stabilizers, follows either a “top-down” (mechanical grinding) or “bottom-up” (chemical reduction, electrochemical methods) approach (Figure 1) (Amulyavichus et al., 1998; Mallick et al., 2004; Xu et al., 2020). While this method provides high yield, it is costly, involves toxic reagents (e.g., citrate, borohydride), and requires additional purification steps to prevent contamination and aggregation (Malik et al., 2002; Mallick et al., 2004). Chemical methods include laser ablation, lithography, electrochemical reduction, thermal decomposition, and sono-decomposition (Zhang et al., 2016). Despite their efficiency, chemical synthesis poses environmental and biological risks due to toxic byproducts (Gurunathan et al., 2015).
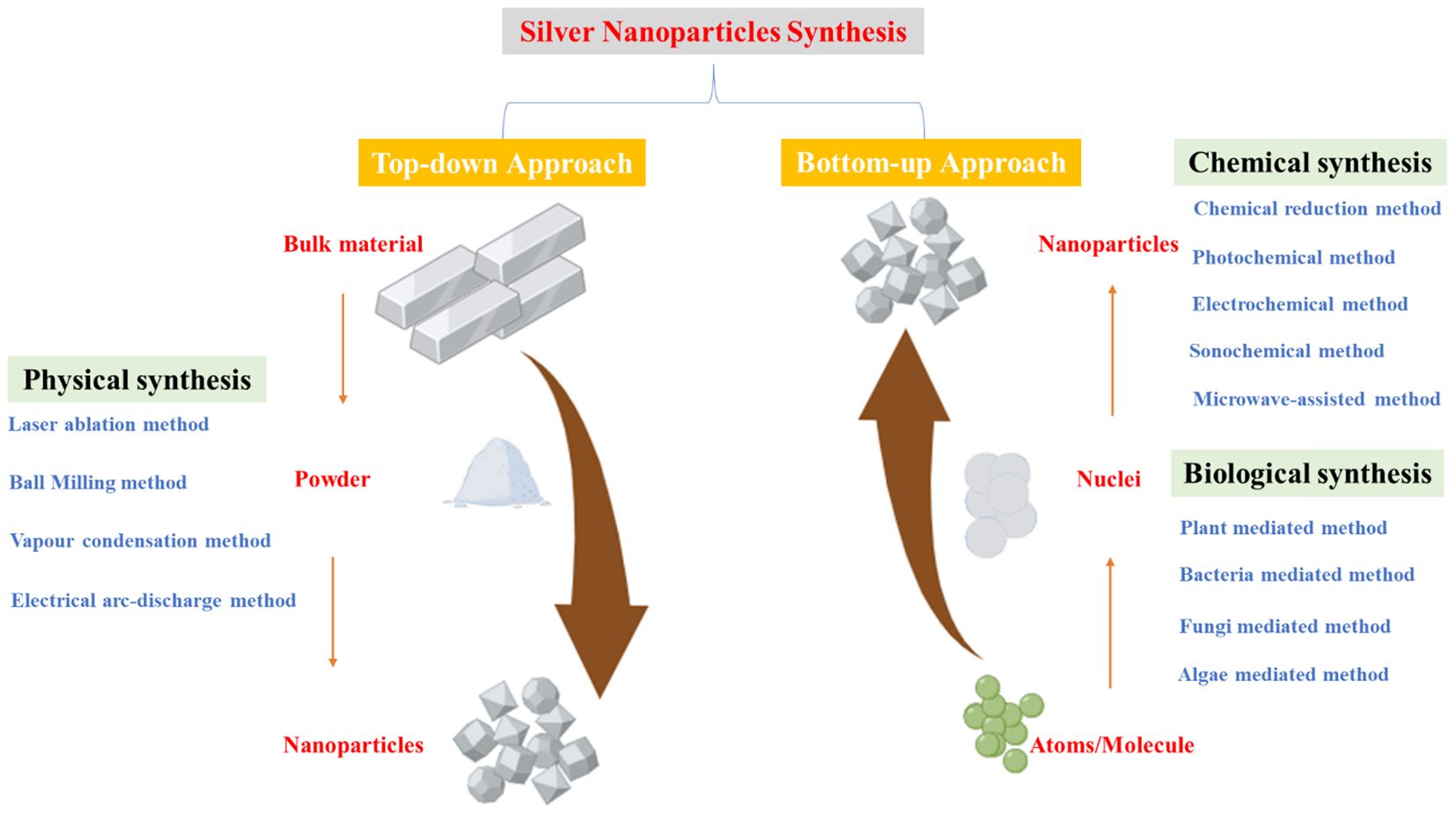
Figure 1. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles can be categorized into two main approaches: the top-down and bottom-up methods. The top-down approach involves breaking down bulk metal materials into nanoparticles, whereas the bottom-up approach focuses on assembling nanoparticles from molecular components, leading to the formation of complex clusters. These approaches encompass various synthesis techniques, including physical, chemical, and biological methods, each employed separately. Adapted with modifications from (Xu et al., 2020).
2.2 Green synthesis
To address the limitations of chemical methods, biological synthesis has emerged as an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative. This method utilizes bacteria, fungi, plant extracts, and biomolecules like amino acids and vitamins to produce AgNPs in a controlled manner (Gurunathan et al., 2013, 2014; Zhang et al., 2016). Early studies on bacterial bio-sorption of metals indicated the potential for nanoparticle synthesis, though initial results were aggregates rather than discrete nanoparticles (Mullen et al., 1989). Various microorganisms, including Pseudomonas stutzeri AG259, Lactobacillus species, Bacillus licheniformis, and Escherichia coli, as well as fungi like Fusarium oxysporum and Ganoderma neo-japonicum Imazeki, have been used for AgNP production (Zhang et al., 2016). Plant-based synthesis has been demonstrated with Allophylus cobbe, Artemisia princeps, and Typha angustifolia (Gurunathan et al., 2014; Gurunathan, 2015; Gurunathan et al., 2015). Additionally, biopolymers, starch, enzymes, and amino acids serve as reducing agents (Leung et al., 2010; Deepak et al., 2011; Kumar et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2016).
Biological synthesis methods provide improved control over nanoparticle size and shape due to the presence of natural reducing and capping agents—such as polyphenols, proteins, and flavonoids—in plant extracts, which guide uniform nucleation and growth while eliminating the need for toxic chemicals or synthetic stabilizers (Gurunathan et al., 2014; Restrepo and Villa, 2021). The use of natural reducing agents allows for monodisperse, stable, and water-soluble nanoparticles (Thakkar et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2016). Particle morphology influences bioactivity, with smaller, triangular nanoparticles exhibiting enhanced effects (Morones et al., 2005). Unlike chemical methods, biological synthesis allows optimization of reaction conditions to achieve desired nanoparticle characteristics (Zhang et al., 2016).
Green synthesis of AgNPs has emerged as an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional physical and chemical methods. However, several challenges hinder its large-scale application and industrial adoption. One major limitation is the dependence on plant materials that are often geographically restricted or seasonally available. For instance, Lithodora hispidula, used for Pd NP synthesis, is only found in limited regions such as Cyrenaica and southern Turkey (Turunc et al., 2017). Similarly, plants like coconut, Acacia, and Andean blackberry, which have been employed in synthesizing Ag or Cu nanoparticles, are region-specific and not easily accessible worldwide (Ying et al., 2022). Seasonal constraints further complicate sourcing; materials like cotton leaves, peach blossoms, and Trigonella trifoliata seeds must be harvested during narrow windows, which limits continuous production (Ying et al., 2022). Moreover, some raw materials require additional processing or extraction steps, such as the case with carboxymethyl cellulose and tea polyphenols, which increases complexity and cost (Wang et al., 2017). These factors challenge the feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and scalability of green synthesis in industrial contexts.
In addition to raw material constraints, the synthesis process itself presents technical and environmental limitations. Many green synthesis protocols require excessive energy input, long reaction durations, or strict environmental controls, such as high-temperature treatments or inert atmospheres. For example, AgNPs have been synthesized using Ferula persica root extract at 600°C for 3 hours (Nasiri et al., 2018), and Cystoseira baccata extract was stored at −24°C to retain its reactivity (González-Ballesteros et al., 2017). These conditions contradict the principle of sustainability and elevate production costs. Furthermore, the resulting nanoparticles often exhibit high variability in size, morphology, and crystallinity. AgNPs synthesized using Nigella arvensis leaf extract, for example, ranged from 5 to 100 nm, while NZVI particles from grape seeds varied between 63 and 381 nm (Gao et al., 2016; Chahardoli et al., 2018). This inconsistency limits reproducibility and standardization required for commercial and biomedical applications. In many cases, yields and metal ion conversion rates remain low—often below 50%—which diminishes economic viability (Ying et al., 2022). The limited understanding of the underlying biosynthetic mechanisms further complicates optimization, as many studies only infer the roles of plant extracts (e.g., reducing, capping, or chelating agents) without detailing specific chemical pathways (Ying et al., 2022). Collectively, these limitations highlight the need for more systematic research to improve the reliability, efficiency, and industrial compatibility of green synthesis methods.
3 Physical properties of AgNPs in relation to antimicrobial effect
AgNPs possess unique physicochemical properties that make them highly effective as antimicrobial agents against MDR bacteria. Their physical characteristics—including size, shape, surface charge, electrical conductivity, melting point, thermal conductivity, and optical properties—strongly influence their biological interactions and antimicrobial efficacy.
3.1 Size and surface area
The size of AgNPs is a critical determinant of their antimicrobial activity, as it directly affects their surface-area-to-volume ratio and interaction with bacterial cells. Smaller nanoparticles exhibit enhanced bioactivity due to their increased surface area, facilitating greater silver ion release and direct interaction with microbial membranes (Khan et al., 2021). Studies have shown that AgNPs attach to bacterial cell membranes, disrupting the lipid bilayer and increasing permeability, leading to cell death—an effect more pronounced with smaller nanoparticles (Li et al., 2013). The size of AgNPs also influences their toxicity; for instance, nanoparticles below 10 nm have been shown to induce more significant cytotoxic effects in mammalian cells than larger particles. For example, AgNPs exhibit strong potency, possess small average diameters of approximately 10 nm, and demonstrate cytotoxicity in human lung cells (Gliga et al., 2014). Furthermore, Fernández et al., 2019 examined the cytotoxic effects of 10 nm and 60 nm silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in hepatic (HepG2) cells, a model chosen due to the liver’s known tendency to accumulate AgNPs. Their findings showed that 10 nm AgNPs could enter the nucleus, whereas 60 nm particles remained aggregated in the cytoplasm. Proteomic analysis revealed that nearly 50 proteins were altered by each nanoparticle size, but only four showed similar regulation patterns, suggesting that distinct cellular pathways were triggered depending on particle size (Fernández et al., 2019). Complementing this, Wu et al., 2019 studied AgNPs of various diameters (3.2, 20.7, 54.7, and 93.6 nm) in B16 mouse melanoma cells and found that nanoparticle size not only affected uptake efficiency but also dictated the endocytic pathways involved. These findings highlight the importance of nanoparticle size in determining both cellular entry routes and biological responses.
3.2 Shape and antimicrobial efficacy
The morphology of AgNPs significantly affects their interaction with bacterial membranes and their overall antimicrobial properties. AgNPs can be synthesized in various shapes, including spherical, triangular, cubic, rod-shaped, and star-like structures (Khodashenas and Ghorbani, 2019). Studies have demonstrated that the shape of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) plays a critical role in determining their antimicrobial efficacy. For instance, Alshareef et al. (2017) reported strong antibacterial activity of both rod- and spherical-shaped AgNPs. Similarly, Cheon et al. (2019) synthesized AgNPs in three shapes—spherical, disc-shaped, and triangular—and observed the highest bactericidal activity in spherical forms, followed by disc-shaped and then triangular nanoparticles. In contrast, other studies have highlighted the superior antibacterial properties of triangular nanoparticles due to their sharp edges, which enhance interactions with bacterial membranes and lead to mechanical disruption (Liao et al., 2019). These variations suggest that the antibacterial effectiveness of AgNPs may depend on multiple factors, including bacterial type, environment, and application. Additionally, comparative studies have shown that rod-shaped AgNPs penetrate bacterial biofilms more effectively than spherical particles, making them particularly useful for combating biofilm-associated MDR infections (Wang et al., 2021). Other studies have compared the antimicrobial activities of spherical, rod-shaped, and truncated triangular silver nanoplates against planktonic E. coli cells, revealing that truncated triangular AgNPs exhibit the strongest bactericidal effect. This enhanced activity is attributed to the greater number of facets on triangular nanoparticles, which allows for increased interaction with bacterial surfaces, leading to more extensive membrane damage (Pal et al., 2007). This difference is likely due to the higher aspect ratio of rod-shaped nanoparticles, which enhances their interaction with biofilms (Slomberg et al., 2013). This variation in antimicrobial activity is likely due to differences in silver ion release, which is influenced by the surface area of the nanoparticles. Consequently, they concluded that modifying the morphology of AgNPs can effectively regulate their antimicrobial efficacy.
3.3 Surface charge and stability
Surface charge plays a crucial role in the stability and biological interactions of AgNPs. The zeta potential of AgNPs determines their colloidal stability, with highly positive or negative values preventing aggregation (Bélteky et al., 2019). Positively charged AgNPs exhibit stronger interactions with bacterial cell membranes, which are typically negatively charged due to the presence of lipopolysaccharides and teichoic acids (Franco et al., 2022). This electrostatic attraction enhances bacterial membrane penetration and increases antimicrobial activity. For example, Abbaszadegan et al. investigated the impact of AgNP surface charge on antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive (S. aureus, S. mutans, and S. pyogenes) and Gram-negative (E. coli and P. vulgaris) bacteria (Abbaszadegan et al., 2015). Their findings revealed that positively charged AgNPs exhibited the strongest bactericidal effect against all tested strains, while negatively charged AgNPs demonstrated the weakest activity. Neutral AgNPs displayed an intermediate level of antibacterial effectiveness. Functionalization of AgNPs with biocompatible polymers such as chitosan or polyethyleneimine further improves stability and bioavailability while reducing cytotoxicity to human cells (Liao et al., 2019).
3.4 Electrical conductivity and melting point
To date, numerous nanomaterials have been developed with the potential to serve as transducing elements, owing to their superior electrical conductivity, as well as enhanced thermal and optical properties (Ventura-Aguilar et al., 2023). AgNPs exhibit a reduced melting point compared to bulk silver due to their high surface energy and increased atom mobility (Asoro et al., 2009). This property is particularly beneficial in antimicrobial coatings for medical devices, as it enables the formation of conductive and biocidal nanocomposites at lower processing temperatures (Abbas et al., 2024). The high electrical conductivity of AgNPs also facilitates their integration into biosensors for rapid detection of bacterial infections (Ventura-Aguilar et al., 2023).
3.5 Thermal conductivity
AgNPs exhibit remarkable thermal conductivity, making them highly suitable for heat-based antimicrobial applications. In previous studies, the researchers explored their potential as multifunctional agents to enhance hyperthermia, directly eliminate cancer and bacterial cells, or function as photothermal therapy agents (Liu S. et al., 2023). The findings demonstrated the effectiveness of AgNPs in eradicating both breast cancer cells and bacteria within the breast tumor microenvironment. Recent studies also have highlighted the role of AgNP-based nanocomposites in improving heat transfer efficiency in antimicrobial surface coatings, and reducing bacterial colonization on biomedical implants (Sahoo et al., 2022).
3.6 Optical properties and plasmon resonance
AgNPs exhibit unique optical properties due to localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR), where conduction electrons oscillate in response to incident light (Loiseau et al., 2019). This property makes AgNPs highly effective in biosensing and antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (Gabudean et al., 2011). This phenomenon enhances the generation of ROS, which contribute to bacterial cell membrane disruption and oxidative stress-induced cell death (Canaparo et al., 2020). Additionally, LSPR facilitates photothermal and photodynamic effects, where AgNPs absorb light energy and convert it into localized heat, further aiding in bacterial eradication (Liu H. et al., 2023). The plasmonic properties of AgNPs can also be tuned by modifying their size, shape, and surrounding environment, allowing for optimized antimicrobial effects (Vasil’kov et al., 2018). These optical characteristics make AgNPs promising candidates for developing light-activated antimicrobial therapies against multidrug-resistant bacteria.
4 Antimicrobial activities of AgNPs
AgNPs have demonstrated potent antimicrobial effects against a wide range of pathogenic microorganisms, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, as well as fungi (Table 1). Their effectiveness varies based on their synthesis method, particle size, and microbial target. Most studies report spherical nanoparticles with sizes typically between 5–100 nm. While antimicrobial effects were consistently observed across different concentrations and testing methods, detailed investigations into their mechanisms of action remain limited (Table 1).
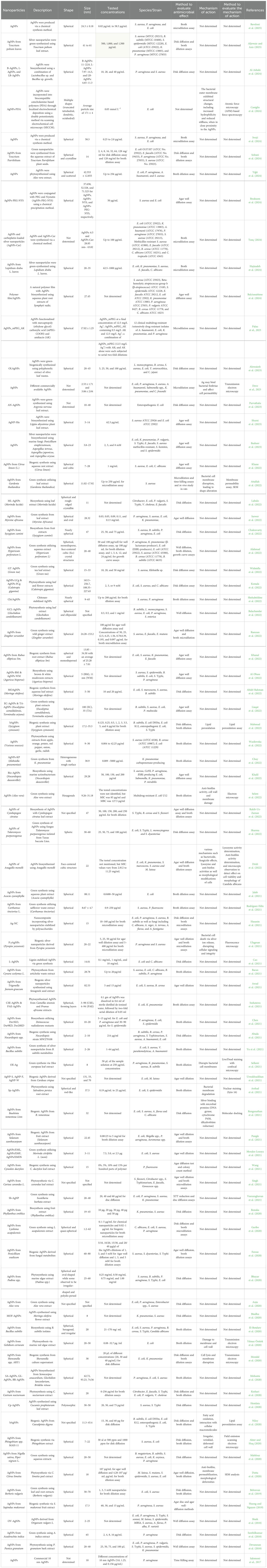
Table 1. Characteristics, antimicrobial activities, and mechanism of action of silver nanoparticles.
4.1 Synthesis and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity
AgNPs have been widely studied for their antibacterial properties. Green-synthesized AgNPs using Teucrium polium leaf extract exhibited strong antimicrobial effects against multiple bacterial strains, including Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The antimicrobial activity was evaluated using both disk diffusion and broth dilution assays, showing significant inhibition of bacterial growth (Aljowaie and Aziz, 2025). Similarly, AgNPs synthesized from Teucrium Parvifolium seeds demonstrated high efficacy against E. coli O157:H7, Enterococcus faecalis, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus using similar evaluation methods (Soltani et al., 2024).
Plant extracts have been widely documented for their diverse therapeutic applications (Abd El-Hafeez et al., 2018, 2022). Green-synthesized AgNPs using various plant extracts have shown significant antibacterial properties (Table 1). AgNPs derived from Olive leaf wastes exhibited notable activity against Listeria monocytogenes, Bacillus cereus, S. aureus, E. coli, Yersinia enterocolitica, and Campylobacter jejuni (Alowaiesh et al., 2023). Similarly, AgNPs synthesized from Argyreia nervosa leaf extract effectively inhibited enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) (Parvathalu et al., 2023). AgNPs derived from Citrus limon zest extract demonstrated inhibitory effects against S. aureus, E. coli, and C. albicans via disk diffusion assays (Khane et al., 2022). Furthermore, Gardenia thailandica-synthesized AgNPs exhibited strong antibacterial activity against S. aureus, as confirmed by both disk diffusion and in vivo antibacterial studies in rats (Attallah et al., 2022). The efficacy of phytosynthesized AgNPs was further highlighted in a study by Hajizadeh et al. (2024), where AgNPs synthesized from Lepidium draba leaves exhibited potent antimicrobial activity against E. coli, K. pneumoniae, S. aureus, E. faecalis, and Candida albicans.
Biosynthesized AgNPs using bacterial strains have also shown effective antimicrobial action. AgNPs derived from Lactobacillus and Bacillus species demonstrated strong inhibition against P. aeruginosa and S. aureus, as confirmed by disk diffusion assays at concentrations of 10, 20, and 40 μg/mL (Al-Asbahi et al., 2024). Furthermore, Basheer et al. (2023) reported the biosynthesis of AgNPs using marine fungi (Penicillium simplicissimum, Aspergillus terreus, A. japonicus, and A. oryzae), which displayed significant antimicrobial effects against E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. vulgaris, S. Typhi, E. faecalis, S. aureus (methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA)), S. hominis, and S. epidermidis using the agar well diffusion assay at 2, 5, and 8 mM concentrations. Similarly, Shumi et al. (2023) synthesized AgNPs from Lippia abyssinica plant extract, which exhibited antimicrobial activity against S. aureus and E. coli at a concentration of 62.5 μg/mL using the agar well diffusion method.
AgNPs produced via chemical synthesis have also been assessed for their antibacterial potency (Table 1). For instance, Baveloni et al. (2025) synthesized spherical AgNPs (~24.3 nm) that exhibited significant antimicrobial activity against S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, and E. coli using the broth microdilution assay at concentrations ranging from 6.74 to 117 μg/mL. Similarly, Iwuji et al. (2024) reported chemically synthesized AgNPs (~58.3 nm) demonstrating potent inhibition against the same bacterial species, further confirming their broad-spectrum efficacy.
4.2 Enhanced antibacterial efficacy through nanoparticle modifications
Nanoparticle modifications have been explored to enhance antimicrobial properties. AgNPs conjugated with polyethylene glycol (PEG) and nystatin (AgNPs-PEG-NYS) exhibited superior antibacterial activity against S. aureus and E. coli compared to non-functionalized AgNPs, as evidenced by agar well diffusion assays (Ibraheem et al., 2024). Furthermore, AgNPs integrated with catecholamine-based polymers (PDA) displayed notable antibacterial activity against E. coli (Caniglia et al., 2024). Caniglia et al. (2024) synthesized AgNPs incorporated into catecholamine-based polymers (AgNPs-PDA) using a double potentiostatic method, which exhibited significant structural modifications in E. coli membranes, leading to bacterial inhibition. Additionally, Balciunaitiene et al. (2024) developed a polymer film embedded with biosynthesized AgNPs using Symphyti radix root extracts, demonstrating strong antibacterial activity against S. aureus, β-hemolytic streptococcus, S. epidermidis, E. faecalis, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, P. vulgaris, B. cereus, and C. albicans.
4.3 Fungal inhibition
Apart from their efficacy against bacteria, AgNPs have exhibited antifungal activity (Table 1). AgNPs synthesized using Lepidium draba L. leaves demonstrated strong inhibitory effects against C. albicans (Hajizadeh et al., 2024). Furthermore, Tunç (2024) reported significant antifungal activity of chemically synthesized AgNPs and carboplatin-loaded AgNPs (AgNPs-Car) against C. albicans and C. tropicalis using broth microdilution assays. Similarly, Balciunaitiene et al. (2024) showed inhibition of C. albicans by AgNPs incorporated into a natural polymer film biosynthesized with Symphyti radix extract. In another green synthesis approach, Cao et al. (2021) evaluated lignin-stabilized AgNPs (L-AgNPs) and observed inhibition of C. albicans growth via disk diffusion. Broader antifungal activity was noted by Hasanin et al. (2021), who reported activity of AgNP-based nanocomposites (Ag-NC) against multiple fungal strains including C. albicans, A. niger, A. terreus, A. flavus, and A. fumigatus. Additionally, Renganathan et al. (2021) identified antifungal activity of AgNPs from Bauhinia tomentosa against C. albicans via molecular docking, indicating potential interactions with fungal protein targets. This may be indicated as an efficient approach develop new therapies to combat the emerging antifungal resistance (Khalifa et al., 2024a; Khalifa et al., 2024c).
5 Antimicrobial mechanisms of AgNPs
The capacity of AgNPs to inhibit microbial growth has been thoroughly investigated, with ongoing efforts to elucidate the underlying processes. Research indicates that several mechanisms are associated with AgNPs. It can attach to and subsequently breach bacterial cell walls, leading to cell membrane damage and the release of internal components (Dakal et al., 2016). Moreover, AgNPs can disrupt vital internal cellular functions, such as interfering with the respiratory pathway, disrupting DNA duplication, and halting cell proliferation (Wang et al., 2016). The processes by which AgNPs combat bacteria are depicted in Figure 2. In this section, we will discuss the major mechanisms associated with the antimicrobial effects of AgNPs.
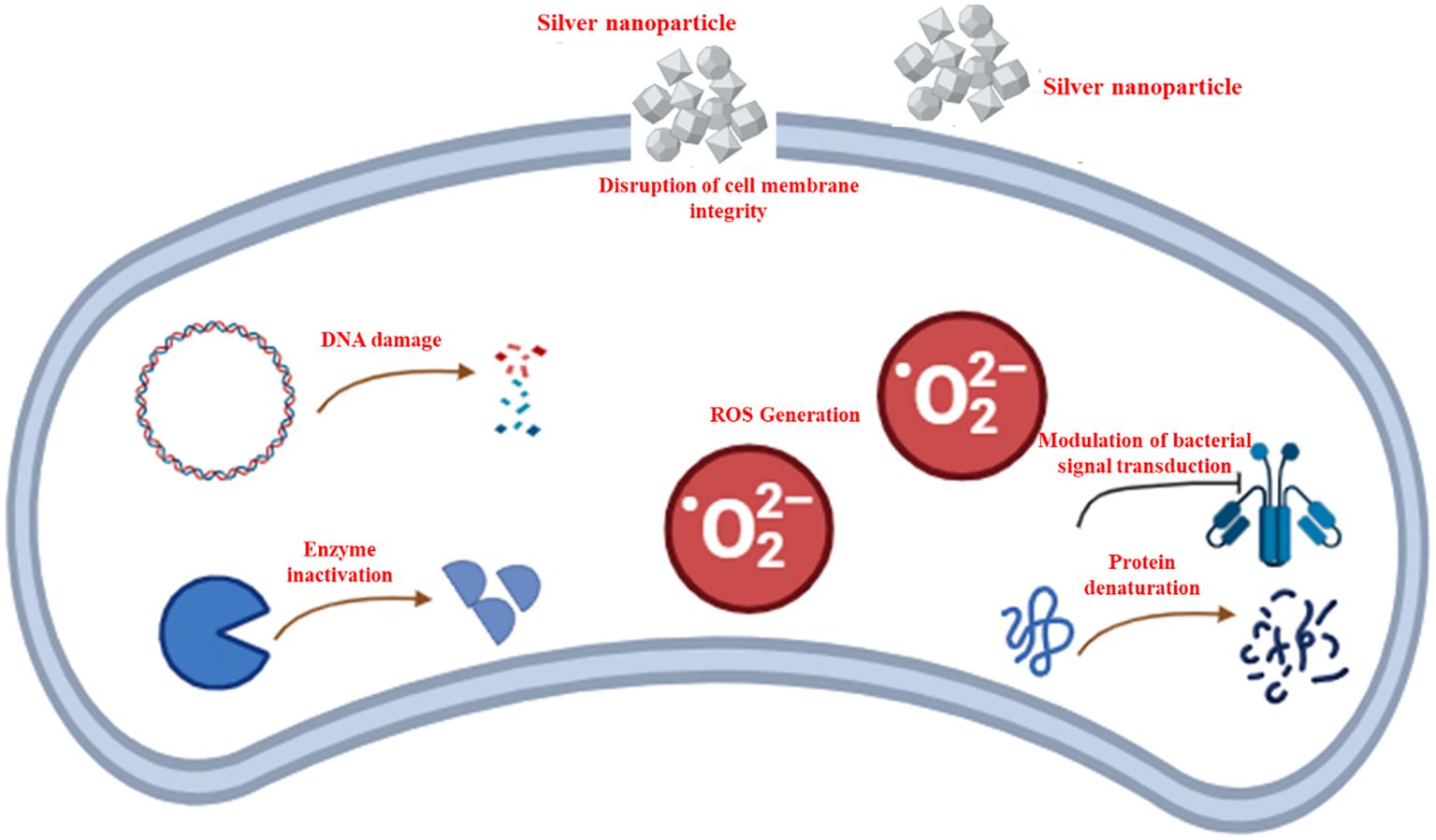
Figure 2. A schematic representation illustrating the antibacterial mechanisms of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), highlighting the disruption of cell membrane integrity, reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent pathway, DNA damage, protein denaturation, enzyme inactivation, and modulation of bacterial signal transduction.
5.1 Disruption of bacterial cell membrane integrity
One of the primary antimicrobial mechanisms of AgNPs involves their interaction with bacterial cell walls and membranes. AgNPs exhibit strong affinities for bacterial membranes due to their positive charge, which facilitates electrostatic interactions with negatively charged bacterial surfaces (Mikhailova, 2024). Upon attachment, AgNPs can cause structural disintegration of the cell membrane, leading to increased permeability and leakage of cytoplasmic contents. This process ultimately compromises bacterial viability and initiates cell death (Dakal et al., 2016). The antimicrobial efficacy of AgNPs is significantly influenced by the structural differences in bacterial cell walls. Gram-negative bacteria, such as E. coli, tend to be more vulnerable to AgNPs than Gram-positive bacteria like S. aureus. This is primarily due to variations in peptidoglycan composition and thickness. Gram-positive bacteria possess a substantially thicker peptidoglycan layer (~30 nm), which serves as a protective barrier, whereas Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner peptidoglycan layer (~3–4 nm) (Rai et al., 2012). The negatively charged peptidoglycan in Gram-positive bacteria can also bind silver ions, limiting their penetration and reducing their antimicrobial effectiveness (Feng et al., 2000). Conversely, Gram-negative bacteria are more susceptible to AgNPs due to their thinner cell wall and the presence of lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which not only contribute to membrane stability but also facilitate AgNP adhesion through electrostatic interactions. This enhanced attachment leads to greater bacterial inhibition, even at lower AgNP concentrations (Pal et al., 2007). Several studies confirm that AgNPs preferentially accumulate on the surface of Gram-negative bacteria due to LPS, increasing their antimicrobial susceptibility (Pal et al., 2007). These structural and compositional differences explain why S. aureus exhibits greater resistance, while E. coli is significantly inhibited by AgNPs, establishing a clear relationship between AgNP concentration and bacterial cell wall properties (Dakal et al., 2016).
5.2 Generation of ROS
AgNPs have been shown to induce oxidative stress in bacterial cells by generating ROS, including hydroxyl radicals (•OH), superoxide anions (O2•−), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (He et al., 2011). These ROS are highly reactive and can cause significant cellular damage by oxidizing lipids, proteins, and DNA. Silver ions (Ag+) interfere with the function of the respiratory electron transport chain by inhibiting key respiratory enzymes, leading to its uncoupling from oxidative phosphorylation. This disruption affects the efficiency of cellular respiration, ultimately impairing energy production (Holt and Bard, 2005; Dakal et al., 2016). The excessive accumulation of free radicals resulting from this process causes direct oxidative damage to the mitochondrial membrane, inducing necrosis and ultimately leading to cell death. Additionally, increased ROS levels contribute to the oxidation of essential biomolecules, including lipids, proteins, and DNA, further exacerbating cellular damage (Juan et al., 2021). Free radicals also interact with lipid molecules, which are abundant in cellular membranes, triggering lipid peroxidation. This process generates lipid hydroperoxides as an initial step in ROS formation, particularly affecting polyunsaturated fatty acids (Chandimali et al., 2025). AgNP-mediated ROS production also affects the activity of various antioxidant enzymes, including NADPH-dependent flavoenzyme, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase, disrupting the balance between ROS generation and detoxification (Dakal et al., 2016).
5.3 Interaction with intracellular components and processes
Following penetration of the bacterial cell, AgNPs interfere with various intracellular processes. They can bind to essential enzymes and proteins, leading to the inhibition of critical metabolic pathways (More et al., 2023). Additionally, AgNPs can displace essential metal ions, such as zinc and iron, from bacterial proteins, thereby disrupting enzyme functions and cellular homeostasis (Girma, 2023).
Another critical antimicrobial mechanism of AgNPs is their ability to interact with bacterial nucleic acids. AgNPs can directly bind to bacterial DNA, causing structural distortions that hinder replication and transcription. Ag+ ions intercalate between purine and pyrimidine base pairs, disrupting the hydrogen bonds between the complementary DNA strands and thereby destabilizing the double-helix structure (Klueh et al., 2000). Additionally, AgNPs induce structural changes in DNA, causing it to transition from a relaxed to a condensed state, which ultimately inhibits its ability to replicate (Feng et al., 2000).
Furthermore, Ag+ has been shown to interact with functional groups in proteins, leading to their deactivation. Specifically, Ag+ ions bind to thiol (-SH) groups in membrane-associated proteins, forming stable Ag–S bonds that disrupt protein function (Fahim et al., 2024). These proteins play essential roles in transmembrane ATP production and ion transport across the cell membrane (Klueh et al., 2000). Both AgNPs and Ag+ ions can alter the three-dimensional structure of proteins, disrupt disulfide bonds, and block active binding sites, ultimately impairing bacterial proliferation and contribute to AgNP-mediated cytotoxicity (Lok et al., 2006).
5.4 Modulation of bacterial signaling transduction pathways
Recent studies suggest that AgNPs can interfere with bacterial quorum sensing (QS) and signal transduction pathways (Aflakian and Hashemitabar, 2025). Quorum sensing is a critical communication mechanism that bacteria use to regulate gene expression and coordinate collective behaviors, including biofilm formation and virulence. AgNPs have been shown to inhibit quorum sensing by disrupting signaling molecules, thereby preventing the establishment of biofilms and reducing bacterial pathogenicity (Awadelkareem et al., 2023). Studies have demonstrated that AgNPs serve as effective anti-QS agents, inhibiting biofilm formation and reducing violacein production in Chromobacterium violaceum (Jagtap and Priolkar, 2013). Additionally, green-synthesized AgNPs have shown significant potential in managing microbial infections. Research indicates that AgNPs can interfere with the synthesis of QS signaling molecules by inhibiting the LasI and RhlI synthases, thereby disrupting bacterial communication and virulence regulation (Lahiri et al., 2021). Furthermore, AgNPs have been shown to downregulate quorum sensing-related genes. In P. aeruginosa, green-synthesized AgNPs exhibited a dose-dependent inhibition of pyocyanin production, a key virulence factor (Selem et al., 2022). Pyocyanin, a blue redox-active secondary metabolite, plays a crucial role in biofilm development and significantly contributes to bacterial evasion of the host immune system. By suppressing pyocyanin synthesis, AgNPs can weaken bacterial pathogenicity and enhance susceptibility to antimicrobial treatments (Awadelkareem et al., 2023). Beyond quorum sensing inhibition, AgNPs can also modulate bacterial signal transduction pathways by interfering with phosphorylation-based signaling cascades (More et al., 2023). Many bacterial regulatory systems rely on histidine kinases and response regulators to sense environmental changes and control adaptation (Capra and Laub, 2012). Furthermore, analyzing the phosphotyrosine profile of bacterial proteins in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria provides valuable insight into how AgNPs influence bacterial signal transduction pathways. These pathways regulate essential cellular functions, including growth and metabolism. The reversible phosphorylation of tyrosine residues in key protein substrates, such as RNA polymerase sigma factor (RNA pol σ factor), single-stranded DNA binding proteins (ssDBPs), and UDP-glucose dehydrogenase, is crucial for their activation (Mijakovic et al., 2006). Once phosphorylated, these proteins play significant roles in DNA replication, recombination, metabolism, and cell cycle regulation. Consequently, AgNP-mediated inhibition of protein phosphorylation disrupts enzymatic activity, ultimately hindering bacterial growth and survival (Dakal et al., 2016).
5.5 Induction of apoptotic-like cell death
In addition to oxidative stress and metabolic disruption, AgNPs can trigger apoptosis-like responses in bacteria. Some studies have demonstrated that AgNPs activate bacterial self-destruction pathways, akin to programmed cell death in eukaryotic cells. Research has demonstrated that AgNPs can inhibit the growth of E. coli and trigger apoptosis-like cell death (Kim and Lee, 2021). However, the exact mechanism underlying AgNP-induced apoptosis-like death, as well as its potential link to DNA damage-inducible protein F (DinF), a key component of the SOS response, remains unclear (Kim and Lee, 2021).
6 Antimicrobial resistance to AgNPs
Microbial resistance to nanoparticles develops through various adaptive mechanisms, including efflux pumps, biofilm formation, exopolysaccharide overproduction, genetic mutations, and metabolic alterations as shown in Table 2, Figure 3 (Kamat and Kumari, 2023). AgNPs are among the most widely used nanomaterials in commercial products, particularly in personal care items. Consequently, it is not surprising that bacteria have developed resistance to them. Studies have demonstrated that chronic exposure to AgNPs leads to the emergence of bacterial resistance. For example, E. coli K-12 MG1655 exhibited resistance to citrate-coated AgNPs after 225 generations, linked to mutations in cusS, purI, rpoB, and ompR (Graves et al., 2015). Similarly, E. coli BW25113 ΔyhaK developed resistance through the overproduction of exopolysaccharides, which likely hinder nanoparticle penetration (Joshi et al., 2012). Another notable adaptation is the production of flagellin, observed in E. coli O13 and P. aeruginosa CCM 3955, which promotes nanoparticle aggregation and reduces their antimicrobial effectiveness (Panáček et al., 2018). Additionally, prolonged exposure to silver sulfide-coated nanoparticles in E. coli resulted in the upregulation of MDR genes and copper efflux transporters, further enhancing bacterial survival under nanoparticle stress (Li et al., 2019). Furthermore, McNeilly et al. (2021) reported that the prolonged use of AgNO3 and AgNPs against E. coli led to the development of resistance to Ag+, driven by the induction of endogenous mutations.
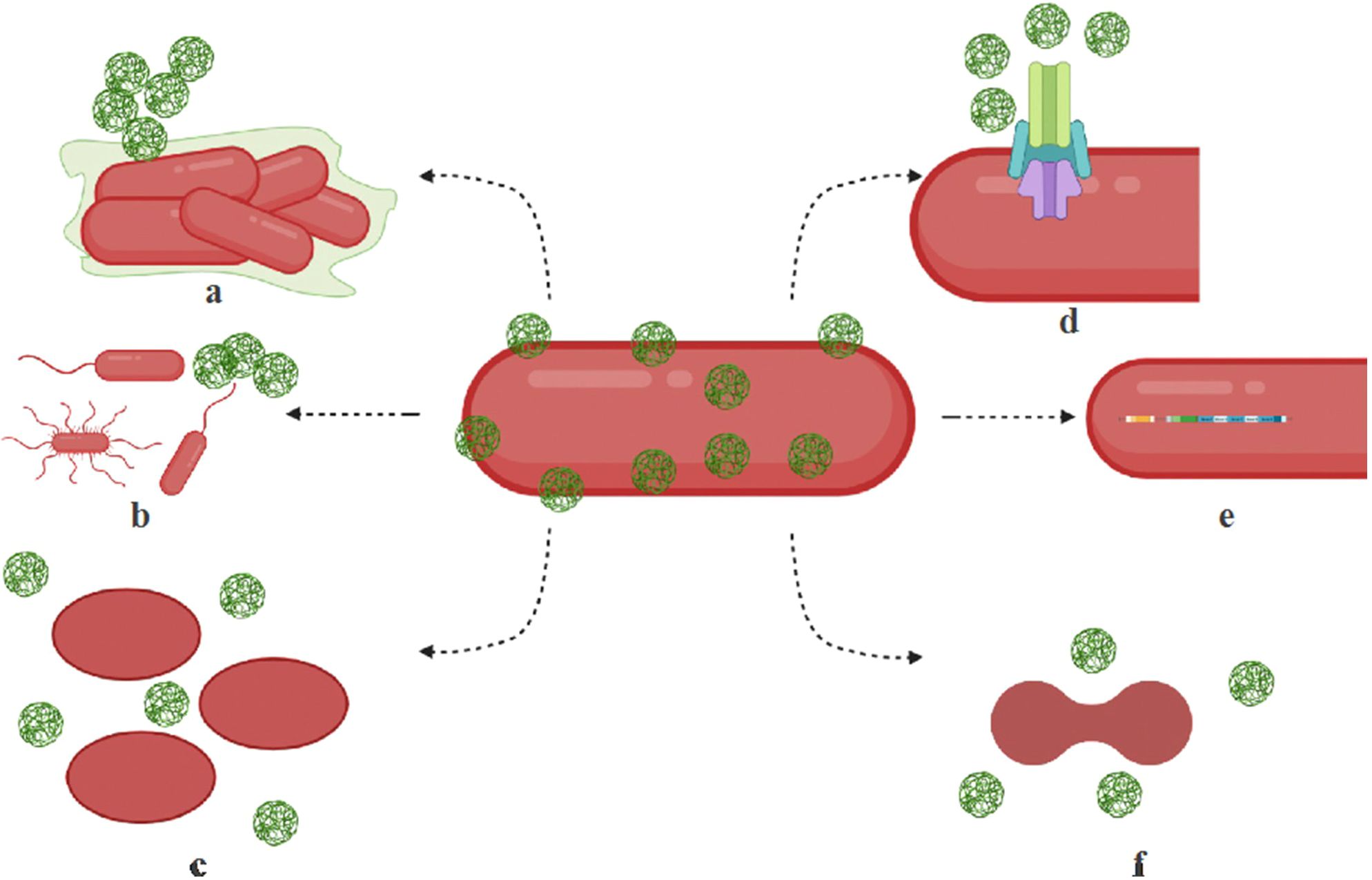
Figure 3. Mechanisms of microbial resistance to nanoparticles. Microorganisms employ various strategies to resist the effects of nanoparticles. (a) Biofilm formation occurs when bacteria produce exopolysaccharides that create a protective biofilm or facilitate nanoparticle aggregation. (b) Motility adaptations enable hypermotile bacteria to evade nanoparticles and optimize nutrient uptake. (c) Morphological alterations allow bacteria to change their shape, such as transitioning from rod-shaped to oval forms, through modifications in fatty acids, membrane lipids, and proteins, helping them filter out nanoparticles. (d) Efflux systems contribute to resistance by overexpressing efflux pump complexes that actively expel nanoparticles from bacterial cells. (e) Operon activation plays a role in resistance by triggering cytoprotective mechanisms through specialized operons and resistance genes. (f) Cell division interference occurs when nanoparticle-induced stress disrupts cell cycle regulation, further enhancing microbial resistance. These mechanisms collectively allow bacteria to withstand nanoparticle exposure, posing challenges for antimicrobial treatments. Reproduced with permission from (Kamat and Kumari, 2023), under License CC BY 4.0.
The environmental persistence of AgNPs also contributes to resistance development. In mixed microbiota models including E. coli and Bacillus species, exposure to AgNPs led to significant genetic and phenotypic changes, such as modifications in cell division machinery and upregulation of cytoprotective genes, permease components, and efflux proteins (Gunawan et al., 2013). Long-term presence of AgNPs in natural ecosystems raises concerns about their role in promoting co-selection of antibiotic resistance genes. Studies have reported that bacteria exposed to AgNPs can develop cross-resistance to multiple antibiotics, including penicillin, kanamycin, ciprofloxacin, and gentamicin (Li et al., 2019). This phenomenon is linked to oxidative stress responses that drive the overexpression of efflux pump genes such as marA and acrAB-tolC, enabling bacteria to expel both silver ions and antibiotics effectively. Additionally, silver-resistant E. coli strains have been found to carry resistance genes for multiple antibiotics, including beta-lactams (blaCTX-M), quinolones (oqxAB), and aminoglycosides (aac-Ib-cr) (Fang et al., 2016). Furthermore, environmental studies highlight the impact of AgNPs on microbial communities in soil and water. The release of nanosilver into these environments may lead to co-selection for antibiotic resistance determinants, increasing the persistence of resistant pathogens in nature (Pal et al., 2017). This underscores the importance of evaluating nanoparticle waste disposal and the long-term effects of nanosilver on microbial ecosystems.
7 Targeted delivery systems to enhance the antimicrobial efficacy of AgNPs
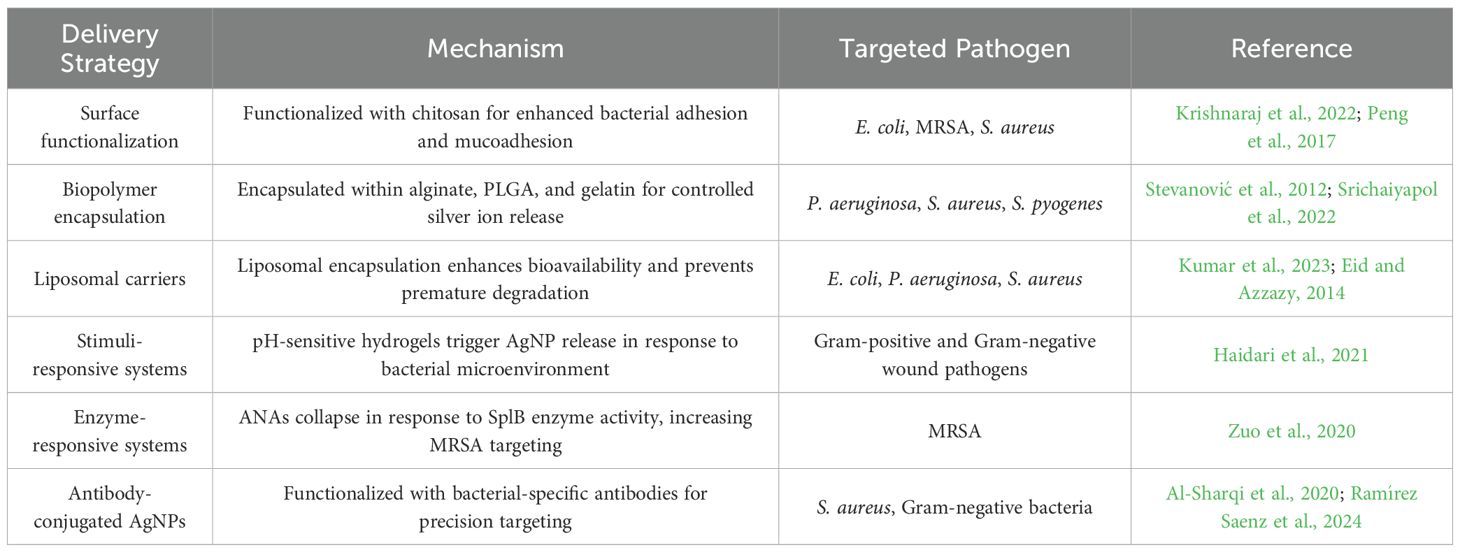
The application of targeted delivery systems has significantly enhanced the antimicrobial activity of AgNPs, particularly against MDR bacteria. Despite their well-established bactericidal properties, conventional AgNPs suffer from limitations such as non-specific interactions, rapid aggregation, and toxicity to mammalian cells (Liao et al., 2019; Ipe et al., 2020). These challenges necessitate the development of targeted strategies that can improve AgNP selectivity, stability, and controlled release while minimizing adverse effects. Advanced approaches, including surface functionalization, biopolymer encapsulation, liposomal carriers, stimuli-responsive systems, and antibody-conjugated AgNPs, have been extensively explored to optimize AgNP delivery and enhance their therapeutic potential (Table 3).
7.1 Surface functionalization for enhanced targeting
One of the most effective methods for improving AgNP targeting is surface functionalization with biocompatible ligands, which facilitates selective bacterial adhesion and penetration (Fu et al., 2024). Among the various functionalization approaches, chitosan-coated AgNPs have demonstrated superior mucoadhesive properties, allowing for stronger electrostatic interactions with negatively charged bacterial membranes (Krishnaraj et al., 2022). For instance, Wang et al. developed a chitosan/oxidized konjac glucomannan hydrogel incorporating AgNPs for the treatment of irregular wounds. The hydrogel exhibited self-healing properties, strong tissue adhesion, and potent antibacterial activity (Wang et al., 2020). Another example is chitosan-coated AgNPs, which have proven effective in treating wounds infected with MRSA (Peng et al., 2017). Furthermore, research by Mostafa et al. (2022) demonstrated that chitosan-silver conjugates exhibit promising broad-spectrum anti-biofilm activity against B. subtilis, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and E. coli (Mostafa et al., 2022). Similarly, AgNPs conjugated with antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), such as LL-37, help overcome their inherent limitations. This combination shows promise as a potential therapeutic agent against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, particularly MRSA (Masimen et al., 2022). Additionally, functionalizing AgNPs with folic acid has demonstrated promising antibacterial activity against both Gram-negative (E. coli) and Gram-positive (S. aureus) bacteria (Chowdhuri et al., 2015). These modifications enable AgNPs to achieve higher bacterial selectivity while reducing unintended cytotoxicity to human cells.
7.2 Biopolymer encapsulation for controlled release
Encapsulation within biodegradable polymeric matrices represents another promising approach for controlled AgNP release and prolonged antimicrobial effects. Natural and synthetic biopolymers, including alginate, poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), and gelatin, have been utilized as nanocarriers to enhance AgNP stability and mitigate toxicity. For example, a hydrogel incorporating tannic acid-stabilized AgNPs (TA-AgNPs/alginate) exhibited strong antibacterial activity against S. pyogenes, S. aureus, and P. aeruginosa. Additionally, it showed promising potential for treating complex wound biofilms (Srichaiyapol et al., 2022). Rugaie et al. (2022) developed a straightforward, single-step method to coat AgNPs using polymeric stabilizers, specifically polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and ethyl cellulose (EC) (Rugaie et al., 2022). Their investigation demonstrated that these coated AgNPs effectively inhibited biofilm formation by clinical isolates of E. coli on urinary catheters. Notably, AgNPs coated with PVP exhibited significantly greater biofilm inhibition compared to those stabilized with EC. Furthermore, PLGA-encapsulated AgNPs ensure a controlled and sustained release of silver ions, offering prolonged and enhanced antimicrobial activity while reducing host toxicity (Stevanović et al., 2012). Moreover, gelatin-PVA-AgNPs hydrogel has been explored for wound healing applications, demonstrating accelerated tissue regeneration while maintaining potent antimicrobial activity (Bag et al., 2022). The incorporation of AgNPs into polymeric matrices not only enhances their therapeutic efficacy but also facilitates localized drug delivery, thereby reducing systemic toxicity.
7.3 Liposomal carriers for improved bioavailability
Liposomal carriers have emerged as effective nanocarriers for improving AgNP bioavailability and stability. Liposomal encapsulation shields AgNPs from premature degradation and enhances their circulation time in the biological environment. Liposomes are spherical vesicles with a phospholipid bilayer capable of encapsulating various chemical compounds (Kumar et al., 2023). Their unique bilayer structure enables the efficient entrapment of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs, making them a versatile and promising platform for drug delivery applications (Kumar et al., 2023). Previous research has shown nanoliposomes loaded with AgNPs exhibit potent broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against various pathogens, including E. coli, S. enterica, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus (Eid and Azzazy, 2014). Additionally, these formulations have shown potential in promoting wound healing. This finding is reinforced by studies indicating that encapsulating antimicrobial agents, such as AgNPs, within nanoliposomes enhances their stability and targeted delivery. Additionally, nanoliposomes have demonstrated the ability to transport encapsulated agents directly to target bacteria in both in vitro and in vivo settings (Mozafari et al., 2021). The use of liposomal nanocarriers not only enhances AgNP stability but also reduces toxicity by preventing direct interaction with mammalian cells.
7.4 Stimuli-responsive AgNP delivery systems
In addition to passive targeting mechanisms, stimuli-responsive AgNP delivery systems offer an advanced strategy for spatiotemporal control over silver ion release. These systems are designed to respond to specific bacterial microenvironmental cues, such as pH variations, enzymatic activity, or oxidative stress levels. For example, a pH-responsive hydrogel has been developed to enable the controlled, pH-triggered release of AgNPs. This system is designed to detect changes in environmental pH and release AgNPs when the pH shifts from acidic to alkaline, a condition associated with pathogenic bacterial presence in wounds (Haidari et al., 2021). This innovative hydrogel shows promise as an effective material for treating infected wounds, demonstrating the ability to eliminate both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria without causing toxicity to mammalian skin cells. Additionally, enzyme-responsive silver nanoparticle assemblies (ANAs) have been developed to selectively target MRSA (Zuo et al., 2020). These assemblies undergo a stable-to-collapsed transition upon encountering MRSA due to the decomposition of branched copolymers—used as macrotemplates in ANA synthesis—triggered by serine protease-like B (SplB) enzyme proteins. This structural transition significantly enhances the targeting affinity and efficiency of ANAs against MRSA. These smart nanoplatforms allow for on-demand silver release, minimizing toxicity while maximizing antibacterial efficacy.
7.5 Antibody-conjugated AgNPs for bacteria-specific targeting
A highly specific approach to AgNP targeting involves antibody-conjugated AgNPs, which are engineered to selectively bind to bacterial surface markers. This strategy enables highly targeted antimicrobial action while reducing off-target toxicity. For example, AgNPs functionalized with a specific antibody can be combined with laser radiation as an innovative treatment to selectively target resistant bacteria, particularly S. aureus, while minimizing effects on the normal microflora (Al-Sharqi et al., 2020). Similarly, AgNPs conjugated with BK510Lys endolysin at a concentration of 0.01 mg/mL, in a 2:1 ratio, at 40°C, and pH 5, exhibited a stronger inhibitory effect than AgNPs alone (0.5 µg/mL) against over 65% of the Gram-negative bacteria tested, indicating it highly specific alternative drugs for super-resistant Gram-negative bacteria (Ramírez Saenz et al., 2024). By harnessing the high specificity of monoclonal antibodies, antibody-functionalized AgNPs hold great potential for precision antimicrobial therapy against MDR pathogens.
8 Future directions
AgNPs have emerged as promising antimicrobial agents MDR bacteria. However, to maximize their therapeutic potential and overcome current limitations, several future directions should be considered. These approaches focus on enhancing efficacy, reducing toxicity, improving stability, and preventing bacterial resistance development.
8.1 Surface functionalization and conjugation
Enhancing the antimicrobial activity of AgNPs can be achieved by functionalizing their surface with bioactive molecules, polymers, or targeting ligands. For instance, conjugating AgNPs with antimicrobial peptides, antibodies, or small molecules can improve specificity and reduce non-specific interactions (Al-Sharqi et al., 2020; Ramírez Saenz et al., 2024). Additionally, coating AgNPs with biocompatible polymers such as PEG can enhance stability and bioavailability while reducing toxicity (Srichaiyapol et al., 2022; Ibraheem et al., 2024).
8.2 Synergistic combinations with antibiotics and natural compounds
Combining AgNPs with conventional antibiotics or natural antimicrobial agents may enhance their efficacy and prevent resistance development. Studies have shown that AgNPs can potentiate the effects of antibiotics by disrupting bacterial membranes and increasing drug uptake (Dove et al., 2023; More et al., 2023; Palau et al., 2023). For instance, recent studies have demonstrated that AgNPs conjugated with antibiotics such as amikacin (e.g., AgNPs_mPEG_AK) displayed enhanced antibacterial activity against MDR strains, including E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, and A. baumannii (Palau et al., 2023). These hybrid nanomaterials achieved notable activity at lower antibiotic concentrations, suggesting a dose-sparing effect. Moreover, integrating AgNPs with plant-derived bioactive compounds, such as flavonoids and essential oils, could provide a dual mechanism of action, improving antimicrobial potency and reducing cytotoxicity (Xu et al., 2020). Additionally, AgNPs synthesized using plant extracts—such as those from Teucrium polium, Teucrium parvifolium, Lepidium draba L., and Moringa oleifera—have shown synergistic antimicrobial activity when paired with natural compounds like flavonoids, polyphenols, and essential oils. These green-synthesized AgNPs offer dual mechanisms: physical disruption of bacterial membranes and bioactive-mediated interference in bacterial metabolism, while also exhibiting reduced cytotoxicity compared to chemically synthesized counterparts (Aljowaie and Aziz, 2025; Soltani et al., 2024; Alowaiesh et al., 2023; Abdel-Rahman et al., 2022).
8.3 Controlled and targeted release systems
Developing advanced delivery systems, such as pH-responsive, enzyme-triggered, or temperature-sensitive nanocarriers, can help achieve controlled and targeted release of AgNPs. This approach can enhance antibacterial efficacy while minimizing exposure to healthy cells. For example, hydrogels or liposomes loaded with AgNPs have shown promising results in wound infections and biofilm-associated bacterial resistance (Mozafari et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2020). Additionally, nanocarriers designed for site-specific release can reduce the required dosage and mitigate potential cytotoxic effects.
8.4 Modulation of size, shape, and surface charge
The physicochemical properties of AgNPs, including size, shape, and surface charge, play a crucial role in their antimicrobial efficacy. Smaller nanoparticles exhibit greater surface area and enhanced bacterial interaction, while specific shapes, such as triangular or rod-shaped nanoparticles, have demonstrated improved antimicrobial effects compared to spherical ones (Liao et al., 2019; Rodrigues et al., 2024). Moreover, tuning the surface charge of AgNPs can influence their interaction with bacterial membranes, optimizing their antibacterial activity while reducing toxicity to mammalian cells (Bélteky et al., 2019).
8.5 Biosynthesis and green nanotechnology approaches
To improve the biocompatibility and environmental sustainability of AgNPs, green synthesis methods utilizing plant extracts, fungi, or bacteria have been explored. These eco-friendly approaches reduce the use of toxic chemical agents and enhance the biological properties of AgNPs (Zhang et al., 2016; Xu et al., 2020). Future research should focus on optimizing these biosynthetic techniques to ensure reproducibility, scalability, and clinical applicability.
8.6 Combating bacterial resistance to AgNPs
Although AgNPs exhibit broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, there is a growing concern about bacterial adaptation and resistance. To mitigate this risk, researchers should investigate combination strategies, adaptive dosing regimens, and mechanisms to prevent bacterial efflux of silver ions. Additionally, integrating AgNPs with nanomaterials that disrupt bacterial communication systems, such as quorum sensing inhibitors, could reduce the likelihood of resistance development (Awadelkareem et al., 2023).
8.7 In vivo studies and clinical trials
Despite extensive in vitro research, the clinical translation of AgNP-based antimicrobials remains limited. Future studies should focus on in vivo models to evaluate pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and long-term safety. Clinical trials are necessary to validate their effectiveness against MDR bacterial infections while assessing potential side effects (Zhang et al., 2016; Xu et al., 2020). Regulatory guidelines must also be established to ensure the safe application of AgNPs in medical and pharmaceutical settings.
9 Conclusion
In the era of emerging threats such as AMR, antifungal resistance, and global pandemics like COVID-19 (Khalifa and Al Ramahi, 2024), the search for effective infection therapies remains a critical challenge. Therefore, the development of alternative antimicrobial agents has become a priority in modern medicine (Khalifa et al., 2021b). AgNPs have demonstrated significant potential as next-generation antimicrobial agents due to their broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, unique physicochemical properties, and multiple mechanisms of bacterial inhibition. Their ability to disrupt bacterial membranes, interfere with essential biomolecules, and induce ROS production positions them as promising candidates for combating MDR bacterial infections.
Despite their advantages, concerns regarding bacterial adaptation, cytotoxicity, and environmental impact necessitate further optimization of AgNP formulations. Advanced delivery strategies, including surface functionalization, biopolymer encapsulation, and stimuli-responsive nanoplatforms, have shown promise in enhancing AgNP stability, selectivity, and controlled release. Additionally, integrating AgNPs with conventional antibiotics or incorporating them into biomedical applications, such as wound dressings and medical coatings, may provide innovative solutions to counteract bacterial resistance while minimizing adverse effects.
Future research should focus on optimizing AgNP synthesis methods, improving their biocompatibility, and conducting rigorous clinical trials to validate their safety and efficacy. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for translating AgNP-based therapies into clinical practice and mitigating the global antibiotic resistance crisis. By harnessing the potential of nanotechnology, AgNPs could play a transformative role in the development of novel antimicrobial strategies, offering a sustainable and effective approach to combat MDR bacterial infections.
Author contributions
HK: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Software, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Data curation, Visualization, Formal Analysis, Resources, Validation, Project administration. AO: Methodology, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Software. TM: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation. MA: Investigation, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. ES: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Data curation. HH: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Data curation. RF: Methodology, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the United Arab Emirates University (UAEU) Strategic Research Program 2024 grant (proposal number 3702; fund code 12R310) and UAEU Start-Up grant, (proposal number 3219; fund code 12FO58) for HK.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abada, E., Galal, T., and Ismail, I. (2021). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Nocardiopsis sp.-MW279108 and its antimicrobial activity. J. Basic Microbiol. 61, 993–1001. doi: 10.1002/jobm.202100248
Abbas, R., Luo, J., Qi, X., Naz, A., Khan, I. A., Liu, H., et al. (2024). Silver nanoparticles: synthesis, structure, properties and applications. Nanomaterials 14, 1425. doi: 10.3390/nano14171425
Abbaszadegan, A., Ghahramani, Y., Gholami, A., Hemmateenejad, B., Dorostkar, S., Nabavizadeh, M., et al. (2015). The effect of charge at the surface of silver nanoparticles on antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria: a preliminary study. J. Nanomater. 2015, 720654. doi: 10.1155/2015/720654
Abd El-Hafeez, A. A., Khalifa, H. O., Elgawish, R. A., Shouman, S. A., Abd El-Twab, M. H., and Kawamoto, S. (2018). Melilotus indicus extract induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via a mechanism involving mitochondria-mediated pathways. Cytotechnology 70, 831–842. doi: 10.1007/s10616-018-0195-7
Abd El-Hafeez, A. A., Marzouk, H. M., Abdelhamid, M. A., Khalifa, H. O., Hasanin, T. H., Habib, A. G., et al. (2022). Anti-cancer effect of Hyoscyamus muticus extract via its activation of Fas/FasL-ASK1-p38 pathway. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 27, 833–845. doi: 10.1007/s12257-022-0085-x
Abdel-Rahman, L. H., Al-Farhan, B. S., El-ezz, D. A., Sayed, M., Zikry, M. M., and Abu-Dief, A. M. (2022). Green biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Moringa oleifera: access to a powerful antimicrobial, anticancer, pesticide and catalytic agents. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 32, 1422–1435. doi: 10.1007/s10904-021-02186-9
Aflakian, F. and Hashemitabar, G. (2025). Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles at subinhibitory concentrations as inhibitors of quorum sensing, pathogenicity, and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Heliyon. 11, e42899. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42899
Ahmed, A. M., Maruyama, A., Khalifa, H. O., and Shimamoto, T. (2015). Seafood as a reservoir of Gram-negative bacteria carrying integrons and antimicrobial resistance genes in Japan. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 28, 924–926. doi: 10.3967/bes2015.128
Akter, S. and Huq, M. A. (2020). Biologically rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Sphingobium sp. MAH-11T and their antibacterial activity and mechanisms investigation against drug-resistant pathogenic microbes. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 48, 672–682. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2020.1730390
Alahmad, A., Al-Zereini, W. A., Hijazin, T. J., Al-Madanat, O. Y., Alghoraibi, I., Al-Qaralleh, O., et al. (2022). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Hypericum perforatum L. aqueous extract with the evaluation of its antibacterial activity against clinical and food pathogens. Pharmaceutics 14, 1104. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14051104
Al-Asbahi, M. G. S. S., Al-Ofiry, B. A., Saad, F. A. A., Alnehia, A., and Al-Gunaid, M. Q. A. (2024). Silver nanoparticles biosynthesis using mixture of Lactobacillus sp. and Bacillus sp. growth and their antibacterial activity. Sci. Rep. 14, 10224. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59936-1
Al-Dbass, A. M., Daihan, S. A., Al-Nasser, A. A., Al-Suhaibani, L. S., Almusallam, J., Alnwisser, B. I., et al. (2022). Biogenic silver nanoparticles from two varieties of Agaricus bisporus and their antibacterial activity. Molecules 27, 21. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217656
Al-Hakkani, M. F., Ahmed, N., Abbas, A. A., Hassan, M. H. A., Aziz, H. A., Elshamsy, A. M., et al. (2023). Synthesis, physicochemical characterization using a facile validated HPLC quantitation analysis method of 4-Chloro-phenylcarbamoylmethyl ciprofloxacin and its biological investigations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 14818. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914818
Aljowaie, R. M. and Aziz, I. M. (2025). Anticancer and antimicrobial effects of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles using Teucrium polium leaves extract. Green Process. Synth. 14, 20240227. doi: 10.1515/gps-2024-0227
Alowaiesh, B. F., Alhaithloul, H. A. S., Saad, A. M., and Hassanin, A. A. (2023). Green biogenic of silver nanoparticles using polyphenolic extract of olive leaf wastes with focus on their anticancer and antimicrobial activities. Plants 12, 6. doi: 10.3390/plants12061410
Alshareef, A., Laird, K., and Cross, R. B. M. (2017). Shape-dependent antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecium bacterium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 424, 310–315. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.176
Al-Sharqi, A., Apun, K., Vincent, M., Kanakaraju, D., Bilung, L. M., and Sum, M. S. (2020). Investigation of the antibacterial activity of Ag-NPs conjugated with a specific antibody against Staphylococcus aureus after photoactivation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 128, 102–115. doi: 10.1111/jam.14471
Amulyavichus, A., Daugvila, A., Davidonis, R., and Sipavichus, C. (1998). Study of chemical composition of nanostructural materials prepared by laser cutting of metals. Fiz. Met. Metalloved. 85, 111–117.
Anju, T. R., Parvathy, S., Valiya Veettil, M., Rosemary, J., Ansalna, T. H., Shahzabanu, M. M., et al. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Aloe vera leaf extract and its antimicrobial activity. Mater. Today Proc. 43, 3956–3960. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.665
Arshad, H., Sami, M. A., Sadaf, S., and Hassan, U. (2021). Salvadora persica-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial efficacy. Sci. Rep. 11, 5996. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85584-w
Asoro, M. A., Damiano, J., and Ferreira, P. J. (2009). Size effects on the melting temperature of silver nanoparticles: in-situ TEM observations. Microsc. Microanal. 15, 706–707. doi: 10.1017/S1431927609097013
Attallah, N. G. M., Elekhnawy, E., Negm, W. A., Hussein, I. A., Mokhtar, F. A., and Al-Fakhrany, O. M. (2022). In vivo and in vitro antimicrobial activity of biogenic silver nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates. Pharmaceuticals 15, 194. doi: 10.3390/ph15020194
Awad, M. A., Hendi, A., Ortashi, K. M., Alzahrani, B., Soliman, D., Alanazi, A., et al. (2021). Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Trigonella foenum-graecum seed extract: characterization, photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 323, 112670. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2021.112670
Awadelkareem, A. M., Siddiqui, A. J., Noumi, E., Ashraf, S. A., Hadi, S., Snoussi, M., et al. (2023). Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles derived from probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus (AgNPs-LR) targeting biofilm formation and quorum sensing-mediated virulence factors. Antibiotics 12, 986. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12060986
Bag, S. S., Bora, A., Golder, A., Raina, K., Haridhasapavalan, K. K., and Thummer, R. P. (2022). Gelatin-Pva-AgNPs triad composite as wound healing hydrogel with wounded skin surface protective efficiency. SSRN Electron. J. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4219683
Balachandar, R., Navaneethan, R., Biruntha, M., Ashok Kumar, K. K., Govarthanan, M., and Karmegam, N. (2022). Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles phytosynthesized from Glochidion candolleanum leaves. Mater. Lett. 311, 131572. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.131572
Balciunaitiene, A., Januskevice, V., Saunoriute, S., Raubyte, U., Viskelis, J., Memvanga, P. B., et al. (2024). Antimicrobial antioxidant polymer films with green silver nanoparticles from Symphyti radix. Polymers 16, 317. doi: 10.3390/polym16030317
Baran, A., Baran, M. F., Keskin, C., Kandemir, S. I., Valiyeva, M., Mehraliyeva, S., et al. (2021). Ecofriendly/rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles using extract of waste parts of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and evaluation of their cytotoxic and antibacterial activities. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2270472. doi: 10.1155/2021/2270472
Basheer, M. A., Abutaleb, K., Abed, N. N., and Mekawey, A. A. I. (2023). Mycosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using marine fungi and their antimicrobial activity against pathogenic microorganisms. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 21, 127. doi: 10.1186/s43141-023-00572-z
Baveloni, F. G., Meneguin, A. B., Sábio, R. M., de Camargo, B. A., Trevisan, D. P., Duarte, J. L., et al. (2025). Antimicrobial effect of silver nanoparticles as a potential healing treatment for wounds contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus in Wistar rats. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 103, 106445. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2024.106445
Behravan, M., Panahi, A. H., Naghizadeh, A., Ziaee, M., Mahdavi, R., and Mirzapour, A. (2019). Facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Berberis vulgaris leaf and root aqueous extract and its antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 124, 148–154. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.101
Bélteky, P., Rónavári, A., Igaz, N., Szerencsés, B., Tóth, I. Y., Pfeiffer, I., et al. (2019). Silver nanoparticles: aggregation behavior in biorelevant conditions and its impact on biological activity. Int. J. Nanomedicine 14, 667–687. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S189099
Bhuyar, P., Rahim, M. H. A., Sundararaju, S., Ramaraj, R., Maniam, G. P., and Govindan, N. (2020). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using marine macroalgae Padina sp. and its antibacterial activity towards pathogenic bacteria. Beni Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 9, 3. doi: 10.1186/s43088-019-0031-y
Bindhu, M. R., Umadevi, M., Esmail, G. A., Al-Dhabi, N. A., and Arasu, M. V. (2020). Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Moringa oleifera flower and assessment of antimicrobial and sensing properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 205, 111836. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2020.111836
Canaparo, R., Foglietta, F., Limongi, T., and Serpe, L. (2020). Biomedical applications of reactive oxygen species generation by metal nanoparticles. Materials 14, 53. doi: 10.3390/ma14010053
Caniglia, G., Valavanis, D., Tezcan, G., Magiera, J., Barth, H., Bansmann, J., et al. (2024). Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticle-microspots on the mechanical properties of single bacteria. Analyst 149, 2637–2646. doi: 10.1039/D4AN00123A
Cao, X., Zhu, L., Bai, Y., Li, F., and Yu, X. (2021). Green one-step synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biosafety and antibacterial properties. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 15, 28–34. doi: 10.1080/17518253.2021.2018506
Capita, R. and Alonso-Calleja, C. (2013). Antibiotic-resistant bacteria: a challenge for the food industry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 53, 11–48. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2010.519837
Capra, E. J. and Laub, M. T. (2012). Evolution of two-component signal transduction systems. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 66, 325–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150039
Chahardoli, A., Karimi, N., and Fattahi, A. (2018). Nigella arvensis leaf extract mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Their characteristic properties and biological efficacy. Adv. Powder Technol. 29, 202–210. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2017.11.003
Chakravarty, A., Ahmad, I., Singh, P., Ud Din Sheikh, M., Aalam, G., Sagadevan, S., et al. (2022). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using fruits extracts of Syzygium cumini and their bioactivity. Chem. Phys. Lett. 795, 139493. doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2022.139493
Chandimali, N., Bak, S. G., Park, E. H., Lim, H. J., Won, Y. S., Kim, E. K., et al. (2025). Free radicals and their impact on health and antioxidant defenses: a review. Cell Death Discov. 11, 19. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-00345-9
Chen, A., Hernandez-Vargas, J., Han, R., Cortazar-Martínez, O., Gonzalez, N., Patel, S., et al. (2021). Small RNAs as a new platform for tuning the biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles for enhanced material and functional properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 36769–36783. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c07400
Cheon, J. Y., Kim, S. J., Rhee, Y. H., Kwon, O. H., and Park, W. H. (2019). Shape-dependent antimicrobial activities of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 14, 2773–2780. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S196472
Chowdhuri, A. R., Tripathy, S., Haldar, C., Chandra, S., Das, B., Roy, S., et al. (2015). Theoretical and experimental study of folic acid conjugated silver nanoparticles through electrostatic interaction for enhanced antibacterial activity. RSC Adv. 5, 21515–21524. doi: 10.1039/C4RA16785F
Chuy, G. P., Muraro, P. C. L., Viana, A. R., Pavoski, G., Espinosa, D. C. R., Vizzotto, B. S., et al. (2022). Green nanoarchitectonics of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial activity against resistant pathogens. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 32, 1213–1222. doi: 10.1007/s10904-021-02162-3
Dakal, T. C., Kumar, A., Majumdar, R. S., and Yadav, V. (2016). Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 7, 1831. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01831
Deepak, V., Umamaheshwaran, P. S., Guhan, K., Nanthini, R. A., Krithiga, B., Jaithoon, N. M., et al. (2011). Synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using purified URAK. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces. 86, 353–358. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.04.019
Devanesan, S., AlSalhi, M. S., Balaji, R. V., Ranjitsingh, A. J. A., Ahamed, A., Alfuraydi, A. A., et al. (2018). Antimicrobial and cytotoxicity effects of synthesized silver nanoparticles from Punica granatum peel extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 13, 315. doi: 10.1186/s11671-018-2731-y
Dove, A. S., Dzurny, D. I., Dees, W. R., Qin, N., Nunez Rodriguez, C. C., Alt, L. A., et al. (2023). Silver nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of aminoglycosides against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 13, 1064095. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1064095
Dridi, R., Essghaier, B., Hannachi, H., Khedher, G. B., Chaffei, C., and Zid, M. F. (2022). Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Anagallis monelli: evaluation of antioxidant activity, antibacterial and antifungal effects. J. Mol. Struct. 1251, 132076. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.132076
Dutta, T., Ghosh, N. N., Das, M., Adhikary, R., Mandal, V., and Chattopadhyay, A. P. (2020). Green synthesis of antibacterial and antifungal silver nanoparticles using Citrus limetta peel extract: experimental and theoretical studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 104019. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104019
Eid, K. A. and Azzazy, H. M. (2014). Sustained broad-spectrum antibacterial effects of nanoliposomes loaded with silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 9, 1301–1310. doi: 10.2217/nnm.13.89
El-Bendary, M. A., Afifi, S. S., Moharam, M. E., Abo El-Ola, S. M., Salama, A., Omara, E. A., et al. (2020). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using isolated Bacillus subtilis: characterization, antimicrobial activity, cytotoxicity, and their performance as antimicrobial agents for textile materials. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 51, 54–68. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2020.1789992
Elsupikhe, R. F., Shameli, K., Ahmad, M. B., Ibrahim, N. A., and Zainudin, N. (2015). Green sonochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles at varying concentrations of κ-carrageenan. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10, 302. doi: 10.1186/s11671-015-0916-1
Fahim, M., Shahzaib, A., Nishat, N., Jahan, A., Bhat, T. A., and Inam, A. (2024). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: A comprehensive review of methods, influencing factors, and applications. JCIS Open. 16, 100125. doi: 10.1016/j.jciso.2024.100125
Fang, L., Li, X., Li, L., Li, S., Liao, X., Sun, J., et al. (2016). Co-spread of metal and antibiotic resistance within ST3-IncHI2 plasmids from E. coli isolates of food-producing animals. Sci. Rep. 6, 25312. doi: 10.1038/srep25312
Feng, Q. L., Wu, J., Chen, G. Q., Cui, F. Z., Kim, T. N., and Kim, J. O. (2000). A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 52, 662–668. doi: 10.1002/1097-4636(20001215)52:4<662::AID-JBM10>3.0.CO;2-3
Fernández, M. N., Munoz-Olivas, R., and Luque-Garcia, J. L. (2019). SILAC-based quantitative proteomics identifies size-dependent molecular mechanisms involved in silver nanoparticles-induced toxicity. Nanotoxicology 13, 812–826. doi: 10.1080/17435390.2019.1579374
Feroze, N., Arshad, B., Younas, M., Afridi, M. I., Saqib, S., and Ayaz, A. (2020). Fungal mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of antibacterial activity. Microsc. Res. Tech. 83, 72–80. doi: 10.1002/jemt.23390
Fleming, A. (1929). On the antibacterial action of cultures of a Penicillium, with special reference to their use in the isolation of B. influenzae. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 10, 226–236.
Franco, D., Calabrese, G., Guglielmino, S. P., and Conoci, S. (2022). Metal-based nanoparticles: Antibacterial mechanisms and biomedical applications. Microorganisms 10, 1778. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10091778
Fu, Y., Liu, T., Wang, H., Wang, Z., Hou, L., Jiang, J., et al. (2024). Applications of nanomaterial technology in biosensing. J. Sci.: Adv. Mater. Devices. 9, 100694. doi: 10.1016/j.jsamd.2024.100694
Gabudean, A. M., Biro, D., and Astilean, S. (2011). Localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) and surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) studies of 4-aminothiophenol adsorption on gold nanorods. J. Mol. Struct. 993(9), 420–424. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2010.11.045
Gao, J. F., Li, H. Y., Pan, K. L., and Si, C. Y. (2016). Green synthesis of nanoscale zero-valent iron using a grape seed extract as a stabilizing agent and the application for quick decolorization of azo and anthraquinone dyes. RSC Adv. 6, 22526–22537. doi: 10.1039/C5RA26668H
Garibo, D., Borbón-Nuñez, H. A., de León, J. N. D., García Mendoza, E., Estrada, I., Toledano-Magaña, Y., et al. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Lysiloma acapulcensis exhibit high-antimicrobial activity. Sci. Rep. 10, 12805. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69606-7
Girma, A. (2023). Alternative mechanisms of action of metallic nanoparticles to mitigate the global spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Cell Surface. 10, 100112. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsur.2023.100112
Gliga, A. R., Skoglund, S., Wallinder, I. O., Fadeel, B., and Karlsson, H. L. (2014). Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: the role of cellular uptake, agglomeration, and Ag release. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 11, 11. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-11-11
González-Ballesteros, N., Prado-López, S., Rodríguez-González, J. B., Lastra, M., and Rodríguez-Argüelles, M. (2017). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using brown algae Cystoseira baccata: Its activity in colon cancer cells. Colloids Surfac. B: Biointerfaces 153, 190–198. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.02.020
Graves, J. L., Tajkarimi, M., Cunningham, Q., Campbell, A., Nonga, H., Harrison, S. H., et al. (2015). Rapid evolution of silver nanoparticle resistance in Escherichia coli. Front. Genet. 5. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00042
Gunawan, C., Teoh, W. Y., Marquis, C. P., and Amal, R. (2013). Induced adaptation of Bacillus sp. to antimicrobial nanosilver. Small 9, 3554–3560. doi: 10.1002/smll.201300761
Gurunathan, S. (2015). Biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles enhance antibiotic activity against Gram-negative bacteria. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 29, 217–226. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2015.04.005
Gurunathan, S., Han, J. W., and Kim, J. H. (2013). Green chemistry approach for the synthesis of biocompatible graphene. Int. J. Nanomed. 8, 2719–2732. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S45174
Gurunathan, S., Han, J. W., Kim, E. S., Park, J. H., and Kim, J. H. (2015). Reduction of graphene oxide by resveratrol: A novel and simple biological method for the synthesis of an effective anticancer nanotherapeutic molecule. Int. J. Nanomed. 10, 2951–2969. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S79879
Gurunathan, S., Han, J., Park, J. H., and Kim, J. H. (2014). A green chemistry approach for synthesizing biocompatible gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9, 248. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-248
Haidari, H., Kopecki, Z., Sutton, A. T., Garg, S., Cowin, A. J., and Vasilev, K. (2021). pH-responsive “smart” hydrogel for controlled delivery of silver nanoparticles to infected wounds. Antibiotics 10, 49. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10010049
Hajizadeh, M., Sarayan, M. S., Taleghani, A., Shafaei, E., Sahebkar, A., Eghbali, S., et al. (2024). Evaluation of antimicrobial and antioxidant effects of silver nanoparticles synthesized with leaves of Lepidium draba L. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 17, 101004. doi: 10.1016/j.jrras.2024.101004
Hasanin, M., Elbahnasawy, M. A., Shehabeldine, A. M., and Hashem, A. H. (2021). Ecofriendly preparation of silver nanoparticles-based nanocomposite stabilized by polysaccharides with antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral activities. Biometals 34, 1313–1328. doi: 10.1007/s10534-021-00344-7
He, D., Jones, A. M., Garg, S., Pham, A. N., and Waite, T. D. (2011). Silver nanoparticle– reactive oxygen species interactions: application of a charging– discharging model. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 5461–5468. doi: 10.1021/jp110832y
Hegazy, Y. M. and Oreiby, A. F. (2024). Guidelines for antimicrobial use in poultry and livestock sectors in Egypt. Available online at: https://openknowledge.fao.org/items/68fb6ce4-6d40-48fa-9b8d-0f5ffcfabfa5 (Accessed March 24, 2025).
Hemlata, M., Meena, P. R., Singh, A. P., and Tejavath, K. K. (2020). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Cucumis prophetarum aqueous leaf extract and their antibacterial and antiproliferative activity against cancer cell lines. ACS Omega 5, 5520–5528. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00155
Holt, K. B. and Bard, A. J. (2005). Interaction of silver (I) ions with the respiratory chain of Escherichia coli: an electrochemical and scanning electrochemical microscopy study of the antimicrobial mechanism of micromolar Ag+. Biochemistry 44, 13214–13223. doi: 10.1021/bi0509566
Huong, T. L. and Nguyen, N. T. (2019). Green synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles using Sapindus mukorossi fruit pericarp extract. Mater. Today: Proc. 42, 88–93. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.015
Ibraheem, D. R., Alwas, N. G., Dawood, R. A., Nasser, S. M., Abbood, S. H., Sulaiman, G. M., et al. (2024). Inhibitory effect of silver nanoparticles–conjugated PEG-nystatin against some resistance pathogenic bacteria. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 168, 112952. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2024.112952
Ipe, D. S., Kumar, P. S., Love, R. M., and Hamlet, S. M. (2020). Silver nanoparticles at biocompatible dosage synergistically increases bacterial susceptibility to antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 11, 1074. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01074
Iwuji, C., Saha, H., Ghann, W., Dotson, D., Bhuiya, M. A., Parvez, M. S., et al. (2024). Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles and their promising antimicrobial effects. Chem. Phys. 9, 100758. doi: 10.1016/j.cphic.2024.100758
Jagtap, S. and Priolkar, K. R. (2013). Evaluation of ZnO nanoparticles and study of ZnO-TiO2 composites for lead-free humidity sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 183, 411–418. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2013.04.010
Jalab, J., Abdelwahed, W., Kitaz, A., and Al-Kayali, R. (2021). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Acacia cyanophylla and its antibacterial activity. Heliyon 7, e08033. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08033
Joshi, N., Ngwenya, B. T., and French, C. E. (2012). Enhanced resistance to nanoparticle toxicity is conferred by overproduction of extracellular polymeric substances. J. Hazard. Mater. 241, 363–370. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.09.057
Juan, C. A., Pérez de la Lastra, J. M., Plou, F. J., and Pérez-Lebeña, E. (2021). The chemistry of reactive oxygen species (ROS) revisited: outlining their role in biological macromolecules (DNA, lipids, and proteins) and induced pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4642. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094642
Kamat, S. and Kumari, M. (2023). Emergence of microbial resistance against nanoparticles: Mechanisms and strategies. Front. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1102615
Kemala, P., Idroes, R., Khairan, K., Ramli, M., Jalil, Z., Idroes, G. M., et al. (2022). Green synthesis and antimicrobial activities of silver nanoparticles using Calotropis gigantea from Ie Seu-um geothermal area, Aceh Province, Indonesia. Molecules 27, 5310. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165310
Keshari, A. K., Srivastava, R., Singh, P., Yadav, V. B., and Nath, G. (2020). Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Cestrum nocturnum. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 11, 37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2017.11.003
Khalifa, H. O. and Al Ramahi, Y. M. (2024). After the hurricane: Anti-COVID-19 drugs development, molecular mechanisms of action and future perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 739. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020739
Khalifa, H. O., Hubka, V., Watanabe, A., Nagi, M., Miyazaki, Y., Yaguchi, T., et al. (2022a). Prevalence of antifungal resistance, genetic basis of acquired azole and echinocandin resistance, and genotyping of Candida krusei recovered from an international collection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 66, e01856–e01821. doi: 10.1128/aac.01856-21
Khalifa, H. O., Kayama, S., Elbediwi, M., Yu, L., Hayashi, W., Sugawara, Y., et al. (2025). Genetic basis of carbapenem-resistant clinical Serratia marcescens in Japan. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 9, 141. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2024.11.003
Khalifa, H. O., Oreiby, A., Abd El-Hafeez, A. A., Abd El Latif, A., Okanda, T., Kato, Y., et al. (2021a). High β-lactam and quinolone resistance of Enterobacteriaceae from the respiratory tract of sheep and goat with respiratory disease. Animals 11, 2258. doi: 10.3390/ani11082258
Khalifa, H. O., Oreiby, A., Abdelhamid, M. A., Ki, M. R., and Pack, S. P. (2024a). Biomimetic antifungal materials: Countering the challenge of multidrug-resistant fungi. Biomimetics 9, 425. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9070425
Khalifa, H. O., Oreiby, A. F., Okanda, T., Kato, Y., and Matsumoto, T. (2021b). High β-lactam resistance in Gram-negative bacteria associated with kennel cough and cat flu in Egypt. Sci. Rep. 11, 3347. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-79872-5
Khalifa, H. O., Shikoray, L., Mohamed, M. Y., Habib, I., and Matsumoto, T. (2024b). Veterinary drug residues in the food chain as an emerging public health threat: Sources, analytical methods, health impacts, and preventive measures. Foods 13, 1629. doi: 10.3390/foods13091629
Khalifa, H. O., Watanabe, A., and Kamei, K. (2022b). Azole and echinocandin resistance mechanisms and genotyping of Candida tropicalis in Japan: Cross-boundary dissemination and animal–human transmission of C. tropicalis infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 28, 302–3e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.08.023
Khalifa, H. O., Watanabe, A., and Kamei, K. (2024c). Genetic mutations in FKS1 gene associated with acquired echinocandin resistance in Candida parapsilosis complex. Mycopathologia 189, 40. doi: 10.1007/s11046-024-00493-3
Khalil, M. A., El-Shanshoury, A. E.-R. R., Alghamdi, M. A., Alsalmi, F. A., Mohamed, S. F., Sun, J., et al. (2022). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by marine actinobacterium Nocardiopsis dassonvillei and exploring their therapeutic potentials. Front. Microbiol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.705673
Khan, B., Nawaz, M., Hussain, R., Price, G. J., Warsi, M. F., and Waseem, M. (2021). Enhanced antibacterial activity of size-controlled silver and polyethylene glycol functionalized silver nanoparticles. Chem. Pap. 75, 743–752. doi: 10.1007/s11696-020-01335-7
Khanal, L. N., Sharma, K. R., Paudyal, H., Parajuli, K., Dahal, B., Ganga, G. C., et al. (2022). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from root extracts of Rubus ellipticus Sm. and comparison of antioxidant and antibacterial activity. J. Nanomater. 2022, 1–11. doi: 10.1155/2022/1832587
Khane, Y., Benouis, K., Albukhaty, S., Sulaiman, G. M., Abomughaid, M. M., Al Ali, A., et al. (2022). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous Citrus limon zest extract: characterization and evaluation of their antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Nanomaterials 12, 2013. doi: 10.3390/nano12122013
Khodashenas, B. and Ghorbani, H. R. (2019). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles with different shapes. Arabian J. Chem. 12, 1823–1838. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.12.014
Kim, S. and Lee, D. G. (2021). Silver nanoparticles-induced H2O2 triggers apoptosis-like death and is associated with dinF in Escherichia coli. Free Radic. Res. 55, 107–118. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2020.1866178
Klueh, U., Wagner, V., Kelly, S., Johnson, A., and Bryers, J. D. (2000). Efficacy of silver-coated fabric to prevent bacterial colonization and subsequent device-based biofilm formation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 53, 621–631. doi: 10.1002/1097-4636(2000)53:6<621::AID-JBM2>3.0.CO;2-Q
Krishnaraj, C., Radhakrishnan, S., Ramachandran, R., Ramesh, T., Kim, B. S., and Yun, S. I. (2022). In vitro toxicological assessment and biosensing potential of bioinspired chitosan nanoparticles, selenium nanoparticles, chitosan/selenium nanocomposites, silver nanoparticles, and chitosan/silver nanocomposites. Chemosphere 301, 134790. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134790
Kruis, F. E., Fissan, H., and Rellinghaus, B. (2000). Sintering and evaporation characteristics of gas-phase synthesis of size-selected PbS nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 69, 329–334. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5107(99)00298-6
Kumar, L., Bisen, M., Harjai, K., Chhibber, S., Azizov, S., Lalhlenmawia, H., et al. (2023). Advances in nanotechnology for biofilm inhibition. ACS Omega 8, 21391–21409. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02239
Kumar, B., Smita, K., Cumbal, L., Debut, A., and Pathak, R. N. (2014). Sonochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles using starch: A comparison. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2014, 784268. doi: 10.1155/2014/784268
Labulo, A. H., David, O. A., and Terna, A. D. (2022). Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Morinda lucida leaf extract and evaluation of its antioxidant and antimicrobial activity. Chem. Pap. 76, 7313–7325. doi: 10.1007/s11696-022-02392-w
Lahiri, D., Nag, M., Sheikh, H. I., Sarkar, T., Edinur, H. A., Pati, S., et al. (2021). Microbiologically-synthesized nanoparticles and their role in silencing the biofilm signaling cascade. Front. Microbiol. 12, 636588. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.636588
Leung, T. C., Wong, C. K., and Xie, Y. (2010). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using biopolymers, carboxymethylated-curdlan and fucoidan. Mater. Chem. Phys. 121, 402–405. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.02.026
Li, M., Li, J., Sun, J., He, Y., Chen, P., and Zhang, C. (2019). Is sulfidation a true detoxification process for silver nanoparticles?: from the perspective of chronic exposure. Environ. Sci. Nano 6, 3611–3624. doi: 10.1039/C9EN00989B
Li, J., Rong, K., Zhao, H., Li, F., Lu, Z., and Chen, R. (2013). Highly selective antibacterial activities of silver nanoparticles against Bacillus subtilis. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 13, 6806–6813. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2013.7781
Liao, C., Li, Y., and Tjong, S. C. (2019). Bactericidal and cytotoxic properties of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 449. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020449
Liaqat, N., Jahan, N., Khalil-ur-Rahman, A., and Qureshi, H. (2022). Green synthesized silver nanoparticles: optimization, characterization, antimicrobial activity, and cytotoxicity study by hemolysis assay. Front. Chem. 10. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.952006
Liu, S., Phillips, S., Northrup, S., and Levi, N. (2023). The impact of silver nanoparticle-induced photothermal therapy and its augmentation of hyperthermia on breast cancer cells harboring intracellular bacteria. Pharmaceutics 15, 2466. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102466
Liu, H., Xing, F., Zhou, Y., Yu, P., Xu, J., Luo, R., et al. (2023). Nanomaterials-based photothermal therapies for antibacterial applications. Mater. Des. 233, 112231. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2023.112231
Loiseau, A., Asila, V., Boitel-Aullen, G., Lam, M., Salmain, M., and Boujday, S. (2019). Silver-based plasmonic nanoparticles for and their use in biosensing. Biosensors 9, 78. doi: 10.3390/bios9020078
Lok, C. N., Ho, C. M., Chen, R., He, Q. Y., Yu, W. Y., Sun, H., et al. (2006). Proteomic analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles. J. Proteome. Res. 5, 916–924. doi: 10.1021/pr0504079
Mahfouz, A. Y., Daigham, G. E., Radwan, A. M., and Mohamed, A. A. (2020). Eco-friendly and superficial approach for synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Nigella sativa and Piper nigrum L. seeds for evaluation of their antibacterial, antiviral, and anticancer activities: a focus study on its impact on seed germination and seedling growth of Vicia faba and Zea mays. Majallah al-saydaliyah al-Misriyah 19, 401. doi: 10.4103/epj.epj_48_20
Mahmud, K. M., Hossain, M. M., Polash, S. A., Takikawa, M., Shakil, M. S., Uddin, M. F., et al. (2022). Investigation of antimicrobial activity and biocompatibility of biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesized using Syzigyum cymosum extract. ACS Omega 7, 27216–27229. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01922
Malik, M. A., O'Brien, P., and Revaprasadu, N. (2002). A simple route to the synthesis of core/shell nanoparticles of chalcogenides. Chem. Mater. 14, 2004–2010. doi: 10.1021/cm011154w
Mallick, K., Witcomb, M. J., and Scurrell, M. S. (2004). Polymer stabilized silver nanoparticles: A photochemical synthesis route. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 4459–4463. doi: 10.1023/B:JMSC.0000034138.80116.50
Masimen, M. A., Harun, N. A., Maulidiani, M., and Ismail, W. I. (2022). Overcoming methicillin-resistance Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) using antimicrobial peptides-silver nanoparticles. Antibiotics 11, 951. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11070951
McNeilly, O., Mann, R., Hamidian, M., and Gunawan, C. (2021). Emerging concern for silver nanoparticle resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and other bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.652863
Mijakovic, I., Petranovic, D., Macek, B., Cepo, T., Mann, M., Davies, J., et al. (2006). Bacterial single-stranded DNA-binding proteins are phosphorylated on tyrosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, 1588–1596. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj514
Mikhailova, E. O. (2024). Green silver nanoparticles: an antibacterial mechanism. Antibiotics 14, 5. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14010005
Mohanta, Y. K., Biswas, K., Jena, S. K., Hashem, A., Abd_Allah, E. F., and Mohanta, T. K. (2020). Anti-biofilm and antibacterial activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized by the reducing activity of phytoconstituents present in the Indian medicinal plants. Front. Microbiol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01143
Mondal, A. H., Yadav, D., Mitra, S., and Mukhopadhyay, K. (2020). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using culture supernatant of Shewanella sp. ARY1 and their antibacterial activity. Int. J. Nanomedicine 15, 8295–8310. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S274535
Morales-Lozoya, V., Espinoza-Gómez, H., Flores-López, L., Sotelo-Barrera, E. L., Núñez-Rivera, A., Cadena-Nava, R. D., et al. (2021). Study of the effect of the different parts of Morinda citrifolia L. (noni) on the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 537, 147855. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147855
More, P. R., Pandit, S., Filippis, A. D., Franci, G., Mijakovic, I., and Galdiero, M. (2023). Silver nanoparticles: Bactericidal and mechanistic approach against drug-resistant pathogens. Microorganisms 11, 369. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020369
Morones, J. R., Elechiguerra, J. L., Camacho, A., Holt, K., Kouri, J. B., Ramírez, J. T., et al. (2005). The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 16, 2346–2353. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/16/10/059
Mostafa, E. M., Abdelgawad, M. A., Musa, A., Alotaibi, N. H., Elkomy, M. H., Ghoneim, M. M., et al. (2022). Chitosan silver and gold nanoparticle formation using endophytic fungi as powerful antimicrobial and anti-biofilm potentialities. Antibiotics 11, 668. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11050668
Mozafari, M. R., Torkaman, S., Karamouzian, F. M., Rasti, B., and Baral, B. (2021). Antimicrobial applications of nanoliposome encapsulated silver nanoparticles: A potential strategy to overcome bacterial resistance. Curr. Nanoscience 17, 26–40. doi: 10.2174/18756786MTA4iMTAi3
Mullen, M. D., Wolf, D. C., Ferris, F. G., Beveridge, T. J., Flemming, C. A., and Bailey, G. W. (1989). Bacterial sorption of heavy metals. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55, 3143–3149. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3143-3149.1989
Murray, C. J., Ikuta, K. S., Sharara, F., Swetschinski, L., Aguilar, G. R., Gray, A., et al. (2022). Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 399, 629–655. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0
Nasiri, J., Rahimi, M., Hamezadeh, Z., Motamedi, E., and Naghavi, M. R. (2018). Fulfillment of green chemistry for synthesis of silver nanoparticles using root and leaf extracts of Ferula persica: Solid-state route vs. solution-phase method. J. Cleaner Prod. 192, 514–530. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.218
Niloy, M. S., Hossain, M. M., Takikawa, M., Shakil, M. S., Polash, S. A., Mahmud, K. M., et al. (2020). Synthesis of biogenic silver nanoparticles using Caesalpinia digyna and investigation of their antimicrobial activity and in vivo biocompatibility. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 3, 7722–7733. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c00926
Oreiby, A., Khalifa, H., Eid, A., Ahmed, A., and Shimamoto, T. (2019). Staphylococcus aureus and bovine mastitis: molecular typing of methicillin-resistance and clinical description of infected quarters. J. Hellenic Vet. Med. Soc 70, 1511–1516. doi: 10.12681/jhvms.20826
Pal, C., Asiani, K., Arya, S., Rensing, C., Stekel, D. J., Larsson, D. G. J., et al. (2017). Metal resistance and its association with antibiotic resistance. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 70, 261–313. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2017.02.001
Pal, S., Tak, Y. K., and Song, J. M. (2007). Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 1712–1720. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02218-06
Palau, M., Muñoz, E., Gusta, M. F., Larrosa, N., Gomis, X., Gilabert, J., et al. (2023). In vitro antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles conjugated with amikacin and combined with hyperthermia against drug-resistant and biofilm-producing strains. Microbiol. Spectr. 11, e00280–e00223. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00280-23
Panáček, A., Kvítek, L., Smékalová, M., Večerová, R., Kolár, M., Röderová, M., et al. (2018). Bacterial resistance to silver nanoparticles and how to overcome it. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 65–71. doi: 10.1038/s41565-017-0013-y
Parvathalu, K., Chinmayee, S., Preethi, B., Swetha, A., Maruthi, G., Pritam, M., et al. (2023). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Argyreia nervosa leaf extract and their antimicrobial activity. Plasmonics 18, 1075–1081. doi: 10.1007/s11468-023-01835-8
Peng, Y., Song, C., Yang, C., Guo, Q., and Yao, M. (2017). Low molecular weight chitosan-coated silver nanoparticles are effective for the treatment of MRSA-infected wounds. Int. J. Nanomedicine 12, 295–304. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S122357
Pungle, R., Nile, S. H., and Kharat, A. S. (2021). Green synthesis and characterization of Solanum xanthocarpum capped silver nanoparticles and its antimicrobial effect on multidrug-resistant bacterial (MDR) isolates. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 101, 469–478. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13945
Rai, M. K., Deshmukh, S. D., Ingle, A. P., and Gade, A. K. (2012). Silver nanoparticles: The powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 112, 841–852. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05253.x
Rakib-Uz-Zaman, S. M., Hoque Apu, E., Muntasir, M. N., Mowna, S. A., Khanom, M. G., Jahan, S. S., et al. (2022). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Cymbopogon citratus leaf extract and evaluation of their antimicrobial properties. Challenges 13, 18. doi: 10.3390/challe13010018
Ramírez Saenz, D., Martínez Espinosa, J. C., Mancillas, A. G., Lechuga Arana, A. A., Silva Contreras, R. A., and Gutiérrez Chávez, A. J. (2024). Silver nanoparticles conjugated with BK510Lys endolysin for Gram-negative bacteria inhibition. Appl. Sci. 14, 6493. doi: 10.3390/app14156493
Ramzan, M., Karobari, M. I., Heboyan, A., Mohamed, R. N., Mustafa, M., Basheer, S. N., et al. (2022). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles from extracts of wild ginger (Zingiber zerumbet) with antibacterial activity against selective multidrug-resistant oral bacteria. Molecules 27, 2007. doi: 10.3390/molecules27062007
Renganathan, S., Subramaniyan, S., Karunanithi, N., Vasanthakumar, P., Kutzner, A., Kim, P. S., et al. (2021). Antibacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant activities of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized from Bauhinia tomentosa Linn. Antioxidants 10, 1959. doi: 10.3390/antiox10121959
Renuka, R., Devi, K. R., Sivakami, M., Thilagavathi, T., Uthrakumar, R., and Kaviyarasu, K. (2020). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Phyllanthus emblica fruit extract for antimicrobial application. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 24, 101567. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101567
Restrepo, C. V. and Villa, C. C. (2021). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles, influence of capping agents, and dependence on size and shape: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manage. 15, 100428. doi: 10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100428
Rodrigues, A. S., Batista, J. G., Rodrigues, M. A., Thipe, V. C., Minarini, L. A., Lopes, P. S., et al. (2024). Advances in silver nanoparticles: a comprehensive review on their potential as antimicrobial agents and their mechanisms of action elucidated by proteomics. Front. Microbiol. 15, 1440065. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1440065
Rodríguez-Félix, F., López-Cota, A. G., Moreno-Vásquez, M. J., Graciano-Verdugo, A. Z., Quintero-Reyes, I. E., Del-Toro-Sánchez, C. L., et al. (2021). Sustainable-green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) waste extract and its antibacterial activity. Heliyon 7, e06923. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06923
Rugaie, O. A., Abdellatif, A. A., El-Mokhtar, M. A., Sabet, M. A., Abdelfattah, A., Alsharidah, M., et al. (2022). Retardation of bacterial biofilm formation by coating urinary catheters with metal nanoparticle-stabilized polymers. Microorganisms 10, 1297. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071297
Sahoo, J., Sarkhel, S., Mukherjee, N., and Jaiswal, A. (2022). Nanomaterial-based antimicrobial coating for biomedical implants: new age solution for biofilm-associated infections. ACS Omega 7, 45962–45980. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c06211
Salomoni, R., Léo, P., Montemor, A. F., Rinaldi, B. G., and Rodrigues, M. F. A. (2017). Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nanotechnol Sci. Appl. 10, 115–121. doi: 10.2147/NSA.S133415
Sarwer, Q., Amjad, M. S., Mehmood, A., Binish, Z., Mustafa, G., Farooq, A., et al. (2022). Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Myrsine africana leaf extract for their antibacterial, antioxidant and phytotoxic activities. Molecules 27, 2186. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217612
Selem, E., Mekky, A. F., Hassanein, W. A., Reda, F. M., and Selim, Y. A. (2022). Antibacterial and antibiofilm effects of silver nanoparticles against the uropathogen Escherichia coli U12. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 29, 103457. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103457
Sellami, H., Khan, S. A., Ahmad, I., Alarfaj, A. A., Hirad, A. H., and Al-Sabri, A. E. (2021). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Olea europaea leaf extract for their enhanced antibacterial, antioxidant, cytotoxic and biocompatibility applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 12562. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212562
Senthilkumar, P., Rashmitha, S., Veera, P., Vijay Ignatious, C., SaiPriya, C., and Samrot, A. V. (2018). Antibacterial activity of neem extract and its green synthesized silver nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 12, 969–974. doi: 10.22207/JPaM.12.2.60
Shaik, M. R., Khan, M., Kuniyil, M., Al-Warthan, A., Alkhathlan, H. Z., Siddiqui, M. R. H., et al. (2018). Plant-extract-assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Origanum vulgare L. extract and their microbicidal activities. Sustainability 10, 913. doi: 10.3390/su10040913
Sharma, A., Sagar, A., Rana, J., and Rani, R. (2022). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity using fungus Talaromyces purpureogenus isolated from Taxus baccata Linn. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 10, 2. doi: 10.1186/s40486-022-00144-9
Shehabeldine, A. M., Salem, S. S., Ali, O. M., Abd-Elsalam, K. A., Elkady, F. M., and Hashem, A. H. (2022). Multifunctional silver nanoparticles based on chitosan: antibacterial, antibiofilm, antifungal, antioxidant, and wound-healing activities. J. Fungi 8, 612. doi: 10.3390/jof8060612
Shumi, G., Demissie, T. B., Eswaramoorthy, R., Bogale, R. F., Kenasa, G., and Desalegn, T. (2023). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles functionalized with histidine and phenylalanine amino acids for potential antioxidant and antibacterial activities. ACS Omega 8, 24371–24386. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01910
Singh, R., Hano, C., Nath, G., and Sharma, B. (2021). Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Carissa carandas L. and their antioxidant and antimicrobial activity against human pathogenic bacteria. Biomol. Ther. 11, 299. doi: 10.3390/biom11020299
Slomberg, D. L., Lu, Y., Broadnax, A. D., Hunter, R. A., Carpenter, A. W., and Schoenfisch, M. H. (2013). Role of size and shape on biofilm eradication for nitric oxide-releasing silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 9322–9329. doi: 10.1021/am402618w
Soltani, M., Shirvani, H., Veisi, H., Hemmati, S., Mohammadi, P., and Jafard, O. (2024). Antimicrobial effect of green nano-silver synthesized using aqueous extract of Teucrium Parvifolium seed and investigation of structural and morphological characteristics. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 159, 111847. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2023.111847
Srichaiyapol, O., Maddocks, S. E., Thammawithan, S., Daduang, S., Klaynongsruang, S., and Patramanon, R. (2022). TA-AgNPs/Alginate Hydrogel and its potential application as a promising antibiofilm material against polymicrobial wound biofilms using a unique biofilm flow model. Microorganisms 10, 2279. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10112279
Ssekatawa, K., Byarugaba, D. K., Kato, C. D., Wampande, E. M., Ejobi, F., Nakavuma, J. L., et al. (2021). Green strategy–based synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. Front. Nanotec. 3. doi: 10.3389/fnano.2021.697303
Stevanović, M. M., Škapin, S. D., Bračko, I., Milenković, M., Petković, J., Filipič, M., et al. (2012). Poly (lactide-co-glycolide)/silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial activity, cytotoxicity assessment and ROS-inducing potential. Polymer 53, 2818–2828. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2012.04.057
Thakkar, K. N., Mhatre, S. S., and Parikh, R. Y. (2010). Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 6, 257–262. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2009.07.002
Theuretzbacher, U., Outterson, K., Engel, A., and Karlén, A. (2019). The global preclinical antibacterial pipeline. Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0288-0
Theuretzbacher, U. and Piddock, L. J. V. (2019). Non-traditional antibacterial therapeutic options and challenges. Cell Host Microbe 26, 61–72. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.06.004
Tunç, T. (2024). Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles loaded with carboplatin as a potential antimicrobial and cancer therapy. Cancer Nanotechnology 15, 2. doi: 10.1186/s12645-023-00243-1
Turunc, E., Binzet, R., Gumus, I., Binzet, G., and Arslan, H. (2017). Green synthesis of silver and palladium nanoparticles using Lithodora hispidula (Sm.) Griseb.(Boraginaceae) and application to the electrocatalytic reduction of hydrogen peroxide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 202, 310–319. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.09.032
Ulagesan, S., Nam, T.-J., and Choi, Y.-H. (2021). Biogenic preparation and characterization of Pyropia yezoensis silver nanoparticles (P.Y AgNPs) and their antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 44, 443–452. doi: 10.1007/s00449-020-02454-x
Urnukhsaikhan, E., Bold, B. E., Gunbileg, A., Sukhbaatar, N., and Mishig-Ochir, T. (2021). Antibacterial activity and characteristics of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized from Carduus crispus. Sci. Rep. 11, 21047. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00520-2
Vasil’kov, A. Y., Dovnar, R. I., Smotryn, S. M., Iaskevich, N. N., and Naumkin, A. V. (2018). Plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles as a method of increasing their antibacterial action. Antibiotics 7, 80. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics7030080
Veeraraghavan, V. P., Periadurai, N. D., Karunakaran, T., Hussain, S., Surapaneni, K. M., and Jiao, X. (2021). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Scutellaria barbata and coating on the cotton fabric for antimicrobial applications and wound healing activity. Fibers 8, 28. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.05.007
Ventura-Aguilar, R. I., Bautista-Baños, S., Mendoza-Acevedo, S., and Bosquez-Molina, E. (2023). Nanomaterials for designing biosensors to detect fungi and bacteria related to food safety of agricultural products. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 195, 112116. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2022.112116
Wang, L., Periyasami, G., Aldalbahi, A., and Fogliano, V. (2021). The antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles biocomposite films depends on the silver ions release behaviour. Food Chem. 359, 129859. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129859
Wang, X., Wang, A., Ma, J., and Fu, M. (2017). Facile green synthesis of functional nanoscale zero-valent iron and studies of its activity toward ultrasound-enhanced decolorization of cationic dyes. Chemosphere 166, 80–88. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.056
Wang, Y., Xie, R., Li, Q., Dai, F., Lan, G., Shang, S., et al. (2020). A self-adapting hydrogel based on chitosan/oxidized konjac glucomannan/AgNPs for repairing irregular wounds. Biomater. Sci. 8, 1910–1922. doi: 10.1039/C9BM01635J
Wang, L., Xu, H., Gu, L., Han, T., Wang, S., and Meng, F. (2016). Bioinspired synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using purple sweet potato root extract. Mater. Technol. 31, 437–442. doi: 10.1080/10667857.2015.1105575
Wasilewska, A., Klekotka, U., Zambrzycka, M., Zambrowski, G., Święcicka, I., and Kalska-Szostko, B. (2022). Physico-chemical properties and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles fabricated by green synthesis. Food Chem. 400, 133960. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133960
Widatalla, H. A., Yassin, L. F., Alrasheid, A. A., Rahman Ahmed, S. A., Widdatallah, M. O., Eltilib, S. H., et al. (2022). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using green tea leaf extract, characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial activity. Nanoscale Adv. 4, 911–915. doi: 10.1039/d1na00509j
Wu, M., Guo, H., Liu, L., Liu, Y., and Xie, L. (2019). Size-dependent cellular uptake and localization profiles of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 14, 4247–4259. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S201107
Xu, L., Wang, Y. Y., Huang, J., Chen, C. Y., Wang, Z. X., and Xie, H. (2020). Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, medical applications and biosafety. Theranostics 10, 8996. doi: 10.7150/thno.45413
Yiğit, A., Tunç, A. K., and Sarıtaş, B. M. (2024). Investigation of the antimicrobial and antibiofilm effects of silver nanoparticles obtained from Aloe Vera plant by green synthesis. Osmaniye Korkut Ata Univ. Fen Bilim. Enstitüsü Derg. 7, 166–176. doi: 10.47495/okufbed.1279010
Ying, S., Guan, Z., Ofoegbu, P. C., Clubb, P., Rico, C., He, F., et al. (2022). Green synthesis of nanoparticles: Current developments and limitations. Environ. Technol. Innov. 26, 102336. doi: 10.1016/j.eti.2022.102336
Yılmaz Öztürk, B., Yenice Gürsu, B., and Dağ, İ. (2020). Antibiofilm and antimicrobial activities of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using marine red algae Gelidium corneum. Process Biochem. 89, 208–219. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2019.10.027
Yu, X., Li, J., Mu, D., Zhang, H., Liu, Q., and Chen, G. (2021). Green synthesis and characterizations of silver nanoparticles with enhanced antibacterial properties by secondary metabolites of Bacillus subtilis (SDUM301120). Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 14, 190–203. doi: 10.1080/17518253.2021.1894244
Zhang, X. F., Liu, Z. G., Shen, W., and Gurunathan, S. (2016). Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, properties, applications, and therapeutic approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17, 1534. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091534
Keywords: silver nanoparticles, antimicrobial mechanisms, antibiotic resistance, multidrug resistance, targeted delivery, nanomedicine, controlled release
Citation: Khalifa HO, Oreiby A, Mohammed T, Abdelhamid MAA, Sholkamy EN, Hashem H and Fereig RM (2025) Silver nanoparticles as next-generation antimicrobial agents: mechanisms, challenges, and innovations against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1599113. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1599113
Received: 24 March 2025; Accepted: 14 July 2025;
Published: 14 August 2025.
Edited by:
Irena Maliszewska, Wrocław University of Science and Technology, PolandReviewed by:
Daniel Czyz, University of Florida, United StatesDeepak Samuel Ipe, Phoenix Power Recyclers, Australia
Copyright © 2025 Khalifa, Oreiby, Mohammed, Abdelhamid, Sholkamy, Hashem and Fereig. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hazim O. Khalifa, aGF6aW1raGFsaWZhQHVhZXUuYWMuYWU=
 Hazim O. Khalifa
Hazim O. Khalifa Atef Oreiby1,3
Atef Oreiby1,3 Temesgen Mohammed
Temesgen Mohammed Mohamed A. A. Abdelhamid
Mohamed A. A. Abdelhamid Essam Nageh Sholkamy
Essam Nageh Sholkamy Hamada Hashem
Hamada Hashem