- 1Intensive Care Unit, The Central Hospital Wuhan, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong of University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
- 2Key Laboratory for Molecular Diagnosis of Hubei Province, The Central Hospital of Wuhan, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
- 3Hubei Provincial Engineering Research Center of Intestinal Microecological Diagnostics, Therapeutics, and Clinical Translation, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Introduction: Sepsis remains a critical challenge in intensive care medicine, necessitating novel therapeutic approaches.
Methods: In this study, healthy 8-week-old male C57BL/6J mice were treated with cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) to induce a sepsis model. After successful model establishment, mice in the sham and CLP groups were injected with 200 μL of normal saline, while mice in the SFI group were injected with 200 μL of SFI. Changes in intestinal mucosal barrier function, inflammation, and intestinal microbiota were assessed in septic mice after SFI treatment.
Results: SFI treatment significantly ameliorated intestinal inflammation and reduced serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6) and renal injury markers (SCr, BUN). 16S rRNA sequencing revealed SFI-mediated gut microbial remodeling, characterized by a marked reduction in pathogenic Escherichia-Shigella abundance and concurrent enrichment of beneficial probiotics, including Akkermansia and Lactobacillus. Mechanistically, SFI exhibited dual regulatory effects on both systemic inflammation and gut microbiota homeostasis.
Discussion: These findings not only validate SFI's efficacy in sepsis treatment but also propose a novel mechanism involving gut microbiome modulation. This study provides critical experimental evidence for repurposing traditional Chinese medicine in sepsis therapy and establishes a foundation for future research on microbiota-targeted interventions in critical care.
1 Introduction
Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) caused by infection with a complex pathogenesis, and it is one of the main causes of death in critically ill patients (Meyer and Prescott, 2024; Klingensmith and Coopersmith, 2023). According to the international consensus (Sepsis-3 definition), sepsis is defined as a dysregulated host response to infection, accompanied by a Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score ≥2 (Seymour et al., 2016). The core pathological mechanism of sepsis is that after the invasion of pathogens, the body excessively releases inflammatory mediators and cytokines, triggering an imbalance between systemic inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses, causing vascular endothelial damage, microcirculation disorders, and abnormal cell metabolism, ultimately leading to multiple organ failure (Dobson et al., 2024; Hotchkiss and Karl, 2003; Hunt, 2019; Shankar-Hari et al., 2016). In addition, patients with sepsis often have reduced intestinal microbiota diversity, an increased proportion of pathogenic bacteria (such as Escherichia coli and Fusobacterium nucleatum), and a decrease in beneficial bacteria (such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus) (Haak and Wiersinga, 2017). Many studies have reported that the intestinal immunity plays an important role in the development of many diseases like systemic inflammatory response syndrome, and sepsis, and (multiple organ dysfunction) MODS (Brandt et al., 2022; Oami et al., 2024; Ge et al., 2020). Moreover, it was reported that Claudin-2 upregulation enhanced the intestinal permeability, immune activation, dysbiosis, and mortality in sepsis (Oami et al., 2024). Therefore, it is increasingly urgent to study the effects of sepsis on the intestinal immunity.
Intestinal microbiota is an important factor affecting intestinal immunity, imbalance of microbiota causes pathogen-associated molecular patterns (such as LPS) to enter the blood circulation through the damaged intestinal barrier, activate the Toll-like receptor (TLR4/2) signaling pathway, trigger excessive inflammatory response (such as TNF-α, IL - 6 release), and then cause systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and MODS (Adelman et al., 2020; Kullberg et al., 2021). In addition, intestinal flora imbalance can lead to reduced expression of tight junction proteins and increased intestinal permeability, allowing bacteria and endotoxins to translocate to extraintestinal organs (Gai et al., 2021). For example, LPS released by Gram-negative bacteria enters the liver through the portal vein, activates Kupffer cells to release inflammatory factors, and aggravates sepsis-related liver damage and systemic inflammatory responses (Liu et al., 2023; Luan et al., 2024). Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs, such as butyrate) produced by intestinal metabolism have anti-inflammatory effects, inhibit the NF-κB pathway and promote the differentiation of regulatory T cells. The level of SCFAs in the intestine of patients with sepsis is reduced, leading to imbalanced immune regulation and uncontrolled inflammatory response (Lou et al., 2023). And it was reported that the composition of the intestinal microbiome is affected by sepsis, and might contribute to the development of organ failure (Haak and Wiersinga, 2017). Therefore, restoring the balance of the microbiota is a key target for the treatment of sepsis.
Shenfu injection (SFI) is a traditional Chinese medicine containing extracts of red ginseng (Panax), aconite root (Radix aconiti lateralis preparata) and black monkshood (Aconitum) (Yang et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2024). It has been reported that SFI has a variety of anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptosis, anti-oxidation and regulation of innate immunity (Hong et al., 2015; Zhao et al., 2022). When administered clinically, it has been reported to inhibit excessive inflammatory responses (such as reducing TNF-α and IL - 6 levels) and alleviate the “inflammatory storm” in sepsis (Yang et al., 2014; Luo et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2022). Traditionally, SFI is used to enhance myocardial contractility, dilate peripheral blood vessels, and increase blood pressure, and has the effects of improving circulation and resisting shock (Xu et al., 2024). It is reported that the mechanism of action of SFI includes restoring hemodynamic stability, increasing tissue oxygen partial pressure and oxygen content, and improving microcirculation and tissue metabolism. Therefore, SFI can promote shock resuscitation (Liu et al., 2015; Hua et al., 2024). SFI has also been shown to improve tissue function and hemodynamic status in heart failure and exert potent anti-endotoxin, anti-inflammatory effects and act as a potent oxygen free radical scavenger (Li et al., 2014; Zhao et al., 2025). In addition, studies have shown that SFI can alleviate the “inflammatory storm” in sepsis by inhibiting excessive inflammatory responses (such as reducing TNF-α and IL - 6 levels) (Jin et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2015; Xing et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2025). However, the effects of SFI on the gut microbiota remain largely unknown.
In this study, SFI was administered to septic mice to investigate its effects on gut microbiota alterations. A severe sepsis model was established via cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), followed by intravenous SFI administration. We systematically assessed intestinal epithelial integrity, inflammatory cytokine levels (e.g., IL - 1β, IL - 6) to evaluate SFI’s potential intestinal protective effects. High-throughput sequencing was employed to characterize gut microbiome dynamics, with particular attention to changes in dominant taxa. Our multimodal approach combining histopathological analysis, cytokine profiling, and 16S rDNA sequencing collectively contributes to a deeper understanding of SFI’s therapeutic mechanisms in sepsis management, particularly its role in microbiota-host crosstalk. This study provides valuable insights for developing microbiota-targeted adjuvant therapies for septic patients.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Animals
All experiments were conducted with the consent of the hospital’s animal ethics committee with the approval number BSMS 2025 - 04-25A. Healthy 8-week-old male C57BL/6J mice (25.0g ± 5.0g) were housed in our hospital’s experimental animal center, with a temperature of 20°C ± 1°C, humidity of 50% to 60%, under a 12:12 light/dark cycle, and a ventilation rate of 8 to 15 times per hour. Using a randomized complete block design, mice were divided randomly into 3 groups of 15: sham operation group (Sham), severe sepsis group (CLP), and Shenfu injection group (SFI).
2.2 Animal model establishment and intervention
Severe sepsis model was induced by CLP, as previously described (Rittirsch et al., 2009). Briefly, on the day before CLP surgery, the mice were fasted for 12 hours. After weighing, they were anesthetized with 40mg/kg pentobarbital sodium. Under sterile conditions, a small amount of feces was extruded. Immediately after surgery, the animals were subcutaneously injected with 50 mL/kg body weight of physiological saline to counteract shock, and then returned to their cages. Fifteen minutes later, mice in the sham group and CLP group received 200 μL of normal saline, whereas SFI-treated animals were administered 200 μL SFI. The mice were treated through tail vein injections. After the procedure, the mice were kept in an environment at 22°C with unlimited access to food and water. They were observed until they recovered from anesthesia, then every 2 hours until 8 hours after surgery. Disease severity was assessed using the Mouse Clinical Assessment Score (M-CASS) method as reported previously (Mai et al., 2018). Briefly, the most severe sepsis is manifested by the coat being shaggy and erect, the posture being hunched, there being little or no movement, breathing being labored, eyelid and chest movements being mostly or completely closed, there being a strong fishy odor from the abdominal cavity, the intestine being obviously congested and edematous, and the ligated cecum being dark purple. Moderate sepsis is manifested by shaggy fur, an arched back, tense or stiff when disturbed or stimulated, and moderate dyspnea. Mild sepsis is manifested by normal behavior and normal appetite. The coat is slightly shaggy, activity is reduced, the back is arched, and behavior and movements are slowed, with mild dyspnea.
2.3 Specimen collection
Sixteen hours after surgery, all live mice were anesthetized with 0.3% pentobarbital sodium. The eye blood sample was collected as follows: the mice was fixed on the experimental table, the head and body were kept stable, the eyes were disinfected, the blood vessels were cut at the base of the eyeball with ophthalmic scissors, and then the blood was gently squeezed out. The collected blood sample was placed in a test tube containing heparin anticoagulant and gently shaken to prevent blood coagulation, then the abdominal cavity was opened. The whole intestine was removed and rinsed with PBS and then divided into two parts. One part was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for histological observation, and the other was used for subsequent biochemical analysis. The flushed contents of large intestine were collected in Eppendorf tubes for subsequent intestinal flora analysis. All operations were performed in a sterile environment.
2.4 Histological observation
Intestine tissues fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde were maintained in 10% neutral formalin buffer solution for 24h at room temperature, dehydrated in wax, and embedded in paraffin wax (JB-P5, Wuhan Junjie Electronics Co., Ltd, China). Sections were cut at a thickness of 4 μm with a paraffin sectioning machine (RM2016, Shanghai Leica Instrument, China) and stained with H&E. Observations were made with a microscope camera Nikon Eclipse E10 (Nikon, Japan).
2.5 Biochemical analysis
The blood samples were collected and centrifuged at 3,500 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C and the serum was harvested. Serum interleukin (IL)-1β, IL - 6, serum creatinine (SCr), and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Wuhan Beiyinlai Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.6 DNA extraction, PCR amplification, and sequencing
Genomic DNA from the gut contents was extracted using the TIANamp Stool DNA Kit (Beijing Tiangen Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Extracted DNA were assessed using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer. Genomic DNA was used as a template to amplify the V3-V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene using the barcode universal primer 341F (5’-CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3’) and 806R (5’-GACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC-3’). The amplification products were sequenced by a commercial company using Illumina NovaSeq PE250.
2.7 Bioinformatics and data analysis
Raw data from the Illumina platform were filtered using FASTP (v0.18.0), and all obtained sequences were classified according to the corresponding unique barcode. Reads from each sample were spliced using FLASH (v1.2.7), and the spliced sequences were processed by Fastp software (Bokulich et al., 2013) to obtain high-quality reads. High-quality sequences were aligned with the Species Annotation Database (https://github.com/torognes/vsearch/) to detect chimeric sequences, and chimeric sequences were finally removed using the UCHIME algorithm (Edgar et al., 2011). Sequences were clustered into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) using UPARSE software (v7.0.1001) with 97% identity as a threshold (Edgar, 2013). Alpha diversity indices were calculated using QIIME (v1.9.1) (Caporaso et al., 2010). For the beta diversity index, the principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) was performed using the UniFrac web tool (Lozupone et al., 2006). To assess overall differences in microbial community structure, principal coordinate analysis (PCoA)and cluster analysis using Bray- Curtis distances were conducted, and microbial community functional profiles were inferred with PICRUSt version 1.0.0 (Langille et al., 2013). Bacterial community profile data were statistically analyzed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a Tukey’s test in SPSS 19.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
Data presented are pooled from three independent experiments. Values of the results are presented with mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad Prism (v 10.0). Comparisons between two independent groups employed either the independent samples t-test (for homogeneous variances) or the Satterthwaite t-test (for heterogeneous variances). When comparing three or more independent groups, a one-way ANOVA was executed, with subsequent pairwise comparisons made using Tukey’s method. Repeated measures data were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA. The differences were considered statistically significant at P<0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Establishment of a mice model of sepsis
During the 16-hour postoperative observation period, no mice died. Mice in the sham group exhibited typical behavior, were responsive, had shiny fur, regular bowel movements, and displayed no signs of intestinal hyperemia or edema. Mice in the CLP group displayed altered behavior, manifested as unkempt and upright fur, slow reactions, difficulty breathing, decreased appetite, loose stools, dark fur, and bloody ascites. The abdominal cavity emitted a strong fishy odor, the intestinal congestion and edema were obvious, and the ligated cecum was dark purple. Furthermore, mice in the SFI groups showed minimal differences in sham group. They exhibited typical behavior and maintained a normal appetite. However, they had formless stools, dull hair, and ascites.
3.2 The beneficial impact of Shenfu injection on the intestinal mucosal barrier in septic mice
In the sham group mice, it was observed that the intestinal villi were abundant in number and uniform in length on the surface of the intestinal tissue, with a single layer of columnar epithelium and normal morphology and structure (Figure 1A). However, in mice in the CLP group, mucosal epithelial cells were necrotic and sloughed off, and a large amount of necrotic cell debris was seen in the intestinal lumen (Figure 1B). In addition, after treatment with ginseng and aconite injection, the intestinal tissue returned to normal levels, with abundant and uniform intestinal villi on the surface, a single layer of columnar epithelium, and occasional necrosis and shedding of mucosal epithelial cells (Figure 1C).
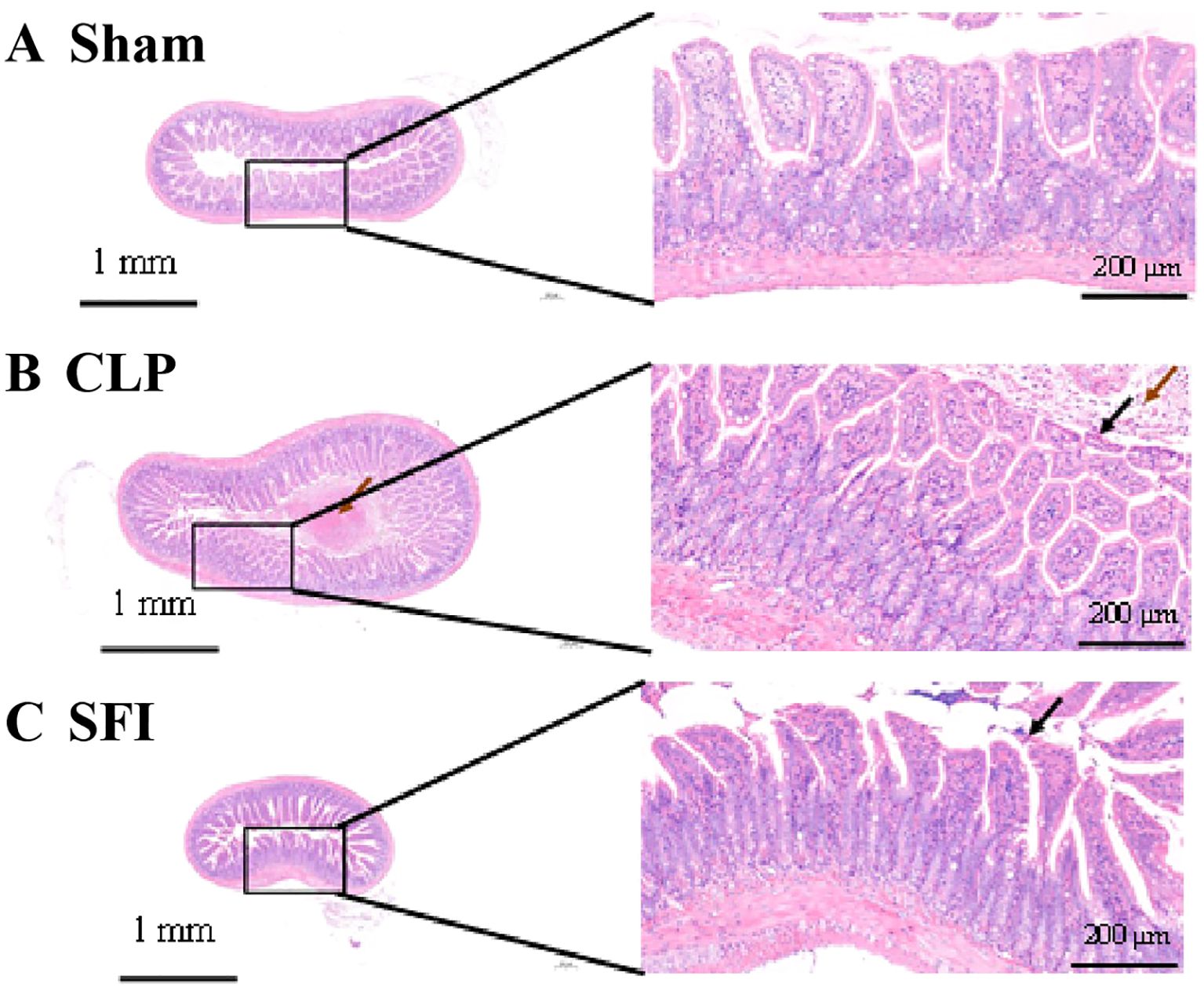
Figure 1. Histological comparison of intestinal tissue in three conditions: (A) Sham with normal tissue structure, (B) CLP showing tissue damage and inflammation, (C) SFI exhibiting reduced damage. Each condition features a small-scale image with a detailed magnified section highlighting tissue morphology. Scale bars indicate 1 millimeter and 200 micrometers.
3.3 The effects of Shenfu injection on the of mice inflammation with sepsis
In order to assessment of sepsis and organ dysfunction, we studied the inflammatory factors in the blood of mice. The concentration of blood inflammatory factors after successful model establishment are shown in Figure 2. The results showed that compared with the sham group, the CLP group significantly increased the concentrations of IL - 1β (8.9-fold), IL - 6 (344.6-fold), SCr (5.5-fold) and BUN (4.4-fold) (P<0.05). However, compared with the untreated group (CLP group), shenfu administration group (SFI group) significantly reduced the concentrations of IL - 1β (10.3-fold), IL - 6 (3.8-fold), SCr (4.5-fold) and BUN (3.3-fold) (P<0.05). In addition, the concentrations of IL - 1β, IL - 6, SCr and BUN in the CLP group were significantly higher than those in the sham group (P<0.05), while there were no significant differences in the concentrations of IL - 1β, SCr and BUN between the SFI group and the sham group.
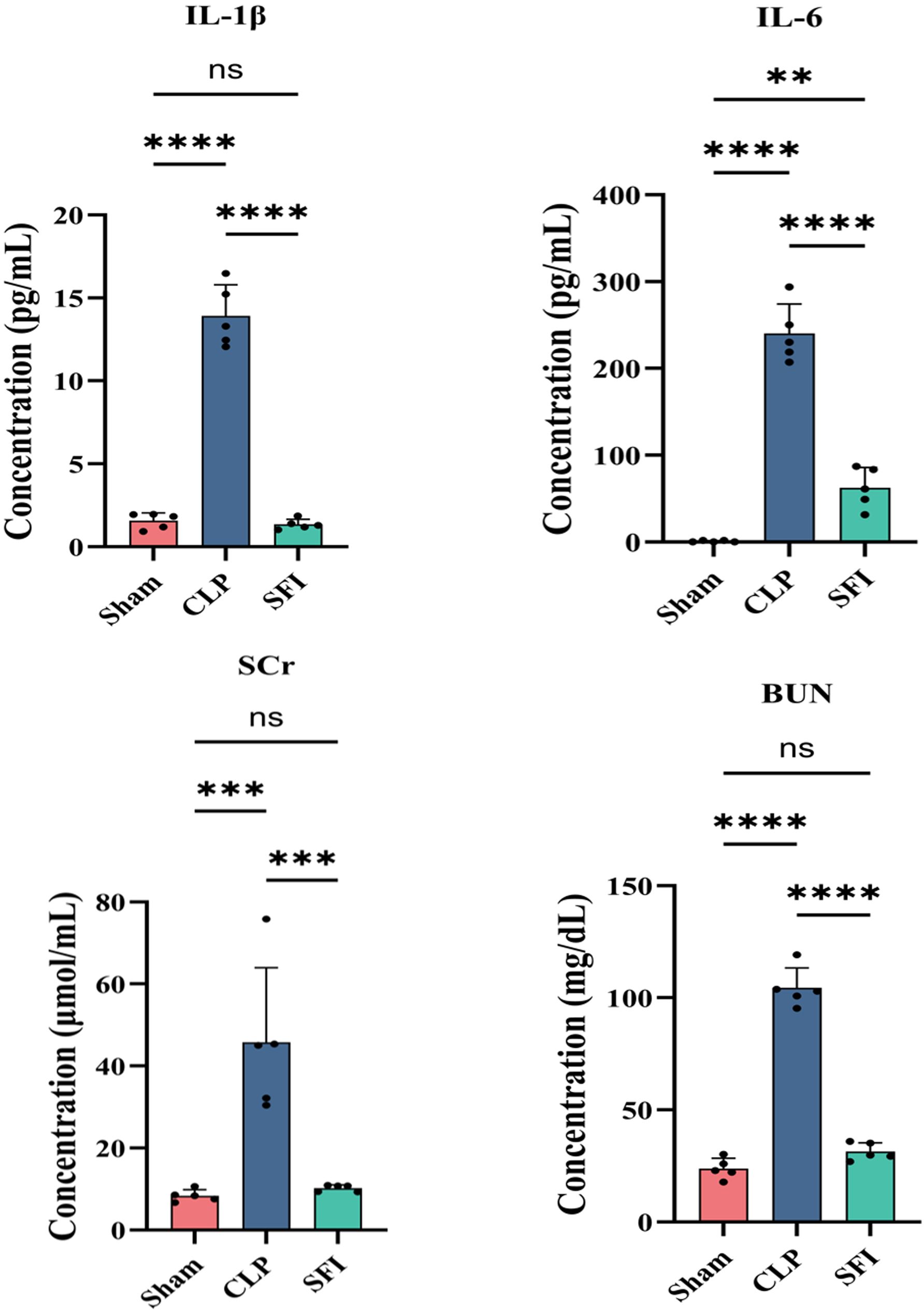
Figure 2. Comparison of biochemical indices in mice 16 hours after surgery. Levels of interleukin-1β (A), interleukin-6 (B), blood urea nitrogen (C) and serum creatinine (D) in the serum. The all data are shown as the mean±S.D. of least five independent replicates and analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. P<0.01, P<0.001, ***P<0.0001 and and “ns” means “P>0.05”.
3.4 Microbial diversity
The microbial complexity in the three groups was estimated using alpha diversity index, including richness estimators (Observed ASV) and diversity indexes (Shannon and Simpson index). The result of Observed ASV showed there were significantly differences between the sham and SFI or CLP (P <0.05) (Figure 3A), and significant differences of Shannon and Simpson Index were found between Sham and SFI (Figures 3B, C). Using Tukey and Wilcoxon tests, beta diversity index showed a significant difference between sham and CLP (P = 0.00 and 0.00, respectively), but no significant difference between SFI and sham (P >0.05). According to A principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) result (based on weighted UniFrac distance matrixes), the similarity among the microbial community composition of the samples were estimated (Figure 3D). Based on PCoA results, it was found that there were obvious differences in the bacterial community composition between the sham group compared to the CLP group, which indicated that the mice injected with CLP significantly changed the composition of intestinal microbiome, while when treated with Shenfu, more similarity was found in that composition between the sham and SFI groups, which showed that Shenfu injection could effectively regulate the disturbance of intestinal microbiome.

Figure 3. Alpha diversity estimators and bacterial community composition of gut microbiota in mice 16 hours after surgery. (A–C) Alpha diversity estimators: Observed ASV (A), Shannon (B), and Simpson (C). Differences are determined by one-way ANOVA analysis (with P < 0.05). A non-significant difference is indicated with “ns.”. (D) Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) (PCoA1: 33.2% and CoA2: 23.6% of the explained variance). Each dot shows a single sample (Sham, CLP, and SFI indicate the samples from sham operation group, severe sepsis group, and Shenfu injection group, respectively).
3.5 Microbial composition
To further investigate the effect of SFI treatment on sepsis, the differences in phylum and genus levels were analyzed. At the phylum level, Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Bacteroidota, Verrucomicrobiota, and Actinobacteriota were predominant (together accounting for 95.6, 94.9, and 93.7% of the microbiota in the sham, CLP, and SFI, respectively). The relative abundance of dominant phyla changed 16 hours after CLP surgery. Compared with the sham group, the CLP group significantly increased the levels of Proteobacteria and Desulfobacterota and significantly decreased the levels of Firmicutes, Actinobacteriota, and Nitrospirota (P< 0.05). In the SFI-treated group, the most significant change was a significant increase in the level of Firmicutes and a significant decrease in the level of Proteobacteria compared with the CLP group (P< 0.05). In addition, the SFI-treated group significantly increased the levels of Verrucomicrobiota and Proteobacteria and significantly decreased the level of Actinobacteriota compared with the sham group (P< 0.05) (Figure 4A).
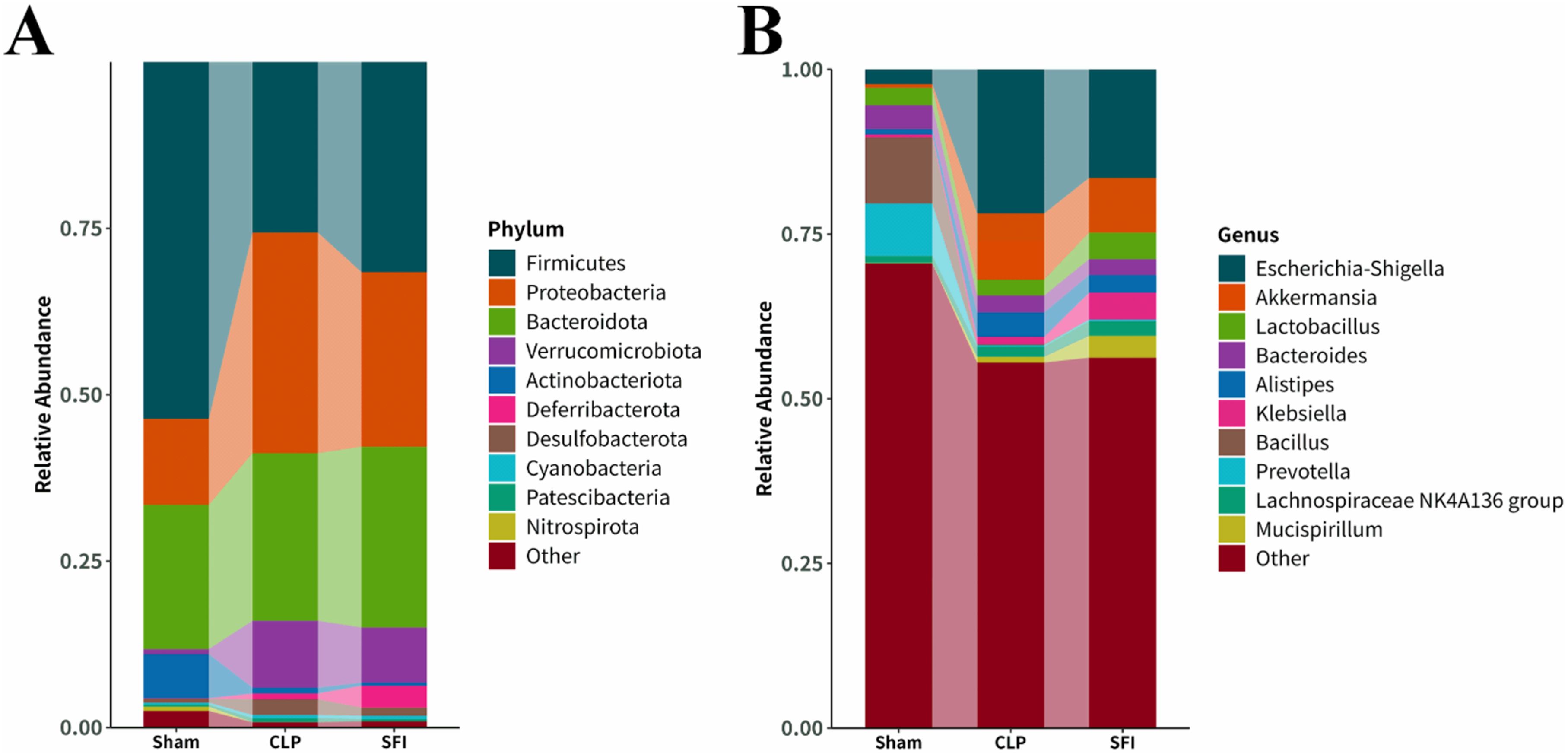
Figure 4. Composition of gut microbiota in mice 16 hours after surgery of CLP and SFI, as well as in the Sham group. (A) Phylum level. (B) Genus level.
At the genus level, the dominant genera were classified as Escherichia-Shigell, Akkermansia, Lactobacillus, Bacteroides, Alistipes, Klebsiella, Bacillus, Prevotella, Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group and Mucispirillum (together accounting for 29.45%, 44.50%, and 43.76% of the microbiota in the sham, CLP, and SFI groups, respectively). Sixteen hours after CLP surgery, the CLP group significantly increased the levels of Klebsiella and Alistipes, and significantly decreased the levels of Bacillus, Lactobacillus, Bacteroides, and Prevotella compared with the sham group (P< 0.05). In the SFI-treated groups, the SFI group significantly increased the levels of Lactobacillus, Mucispirillum, and Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group, and significantly decreased the level of Escherichia-Shigella compared with the CLP group (P< 0.05). In addition, the abundance of Akkermansia and Lactobacillus was significantly increased, while the abundance of Bacteroides and Bacillus was significantly decreased in the SFI group compared with the sham group (P< 0.05) (Figure 4B).
Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) effect size (LEfSe) analysis (LDA score > 2.0) was performed to identify specific taxa that contributed to the differences between the three populations (Figure 4). A total of 60 bacterial taxa (49 in the sham group; 1 in the CLP group; and 10 in the SFI group) showed differences between the three populations (Figure 5A). Firmicutes and Bacillales were enriched in the control group, while Staphylococcus were enriched in the CLP group, and Muribaculaceae and Bacteria were enriched in the SFI group. Specifically, Muribaculaceae and Erysipelatoclostridium were enriched in the SFI, while Staphylococcus were enriched in the CLP. Cladogram analysis also revealed differences in bacterial taxa between the experimental groups (Figure 5B).
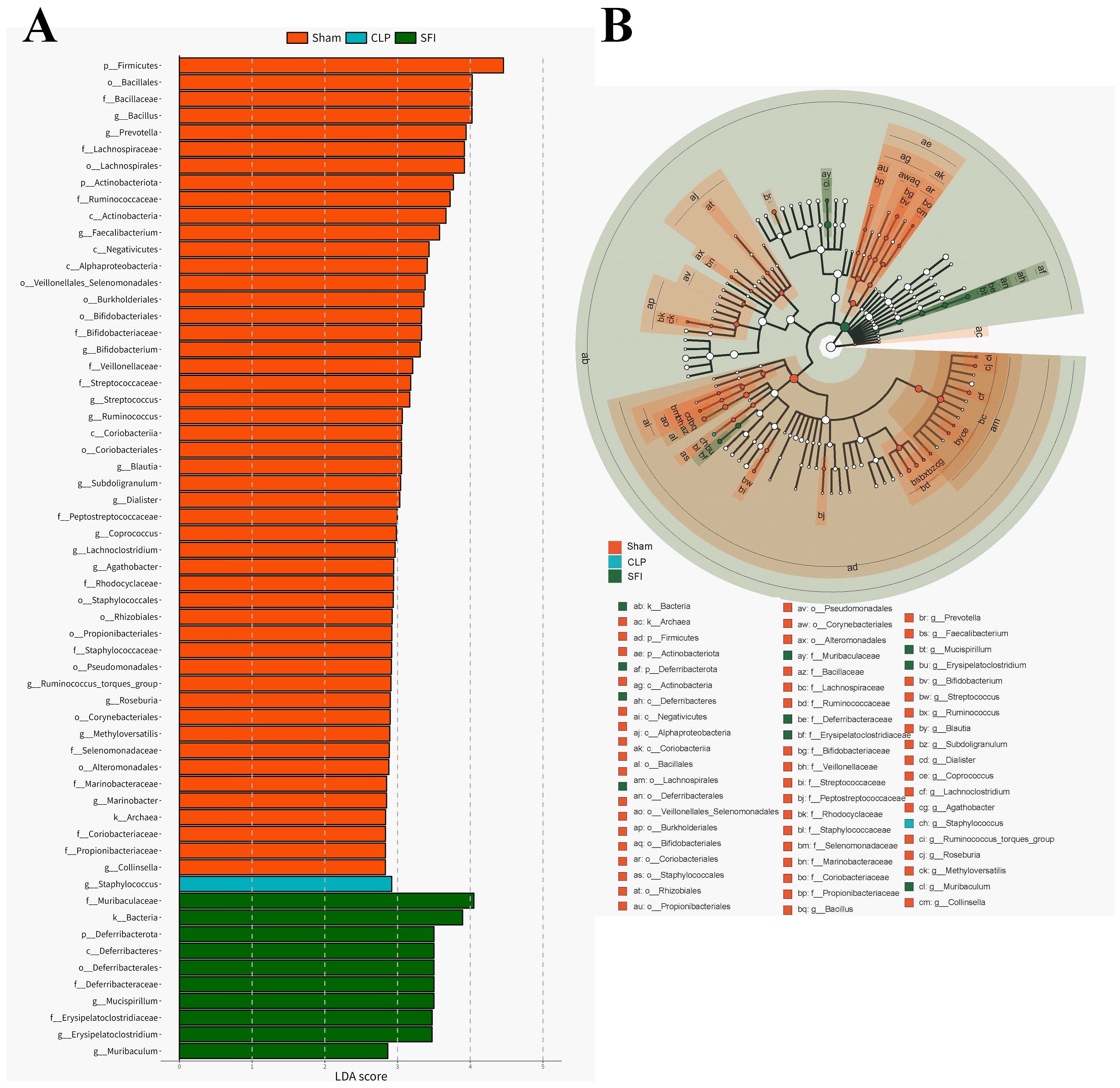
Figure 5. Characterization of gut microbiota in mice 16 hours after surgery of CLP and SFI, as well as in the Sham by LDA and LEfSe analysis. (A) Histogram of the LDA scores (log10) calculated for features differentially abundant in control, GOS, and RS samples (with LDA scores> 2.0). (B) Bacterial taxa differentially represented among groups identified by LEfSe.
3.6 Associations between gut microbiota and inflammation
Spearman’s correlation analysis was used to determine the relationships between differentially abundant taxa (at the genus levels) and inflammation (Figure 6). The result showed that the expression level of IL - 1β was negatively correlated with the relative abundance of Enterococcus (Spearman’s ρ [rs] = -0.40, P = 0.04). IL - 6 had a significant positive correlation with the relative abundance of Ruminococcus (rs = 0.42, P = 0.04) and Odoribacter (rs = 0.40, P = 0.04), while negatively correlated with Enterococcus and Staphylococcus. Furthermore, a strong positive correlation was observed between SCR and Enterococcus (rs = -0.49, P = 0.01).
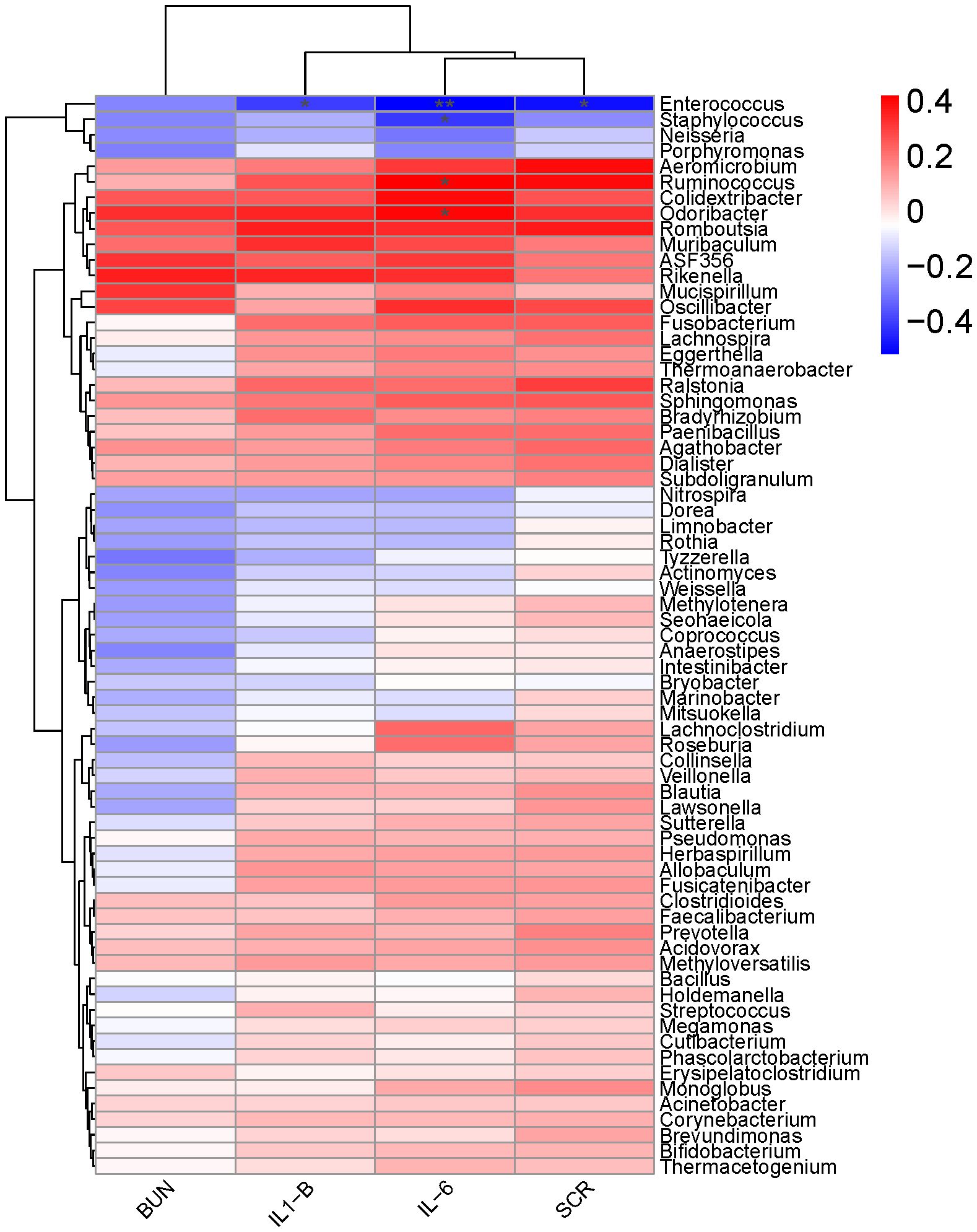
Figure 6. A heat map of Spearman’s correlation coefficients. Correlation between the abundance of key microbial taxa (at the genus levels) and the levels of inflammatory factors (IL-1β, IL-6, SCr and BUN) in mice 16 hours after surgery. Red and blue colors indicate positive and negative correlation coefficients, respectively. Significant correlations (P< 0.05) are indicated with an asterisk.
4 Discussion
In this study, a model of severe sepsis was established in mice using CLP (Rittirsch et al., 2009), and the effects of drug administration on intestinal epithelial cells and inflammation to assess whether SFI can restore the balance of the microbiota. Cecal ligation and puncture resulted in elevated heart rate, body temperature, and white blood cell, indicating systemic inflammation, which was not detected in the sham surgery. It also significantly increased serum levels of IL - 1β and IL - 6, liver and kidney function markers BUN and SCr levels. This model meets the criteria of the Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines for Sepsis: 2012 (Dellinger et al., 2013), indicating that a severe sepsis mice model was successfully established.
Severe trauma or sepsis can induce accelerated apoptosis of intestinal mucosal epithelial cells, lamina propria lymphocytes, and eosinophils, thereby destroying the integrity of the intestinal barrier, leading to abnormally increased mucosal permeability and translocation of intestinal microbiota (Hotchkiss et al., 2016; Tao et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024a; Yan et al., 2025). In the severe sepsis model that we established, the intestinal morphology changed significantly 16 hours after CLP surgery, with a large amount of necrotic cell fragments, necrotic and detached epithelial cells, and a small amount of capillary congestion observed in the intestinal cavity. These observations may be attributed to sepsis-induced systemic blood flow redistribution, which can lead to intestinal microcirculatory hypoperfusion, followed by hypoxic injury of intestinal mucosal epithelial cells (Duess et al., 2023). This pathological process further leads to increased mucosal endothelial permeability, enhanced leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion, and degradation of tight junction proteins, ultimately resulting in dual dysfunction of the intestinal mechanical barrier and immune barrier (King et al., 2014).
In addition, in the early stage of sepsis, the NF-κB signaling cascade, triggers the positive feedback release of pro-inflammatory factors such as IL - 1β, IL - 6, and PAF, and upregulates the secondary infiltration of neutrophils mediated by IL - 8, forming an “inflammation-coagulation vicious cycle”, which ultimately leads to intestinal barrier collapse and multiple organ dysfunction (Kurt et al., 2007; Sun et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021). As observed in our model, injury and bleeding may accelerate the inflammatory response of intestinal epithelial cells. At 8 h after CLP surgery, the levels of IL - 1β and IL - 6 in intestinal epithelial cells in the CLP group were significantly higher than those in the control group. SFI has previously been reported to alleviate inflammatory responses by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway (Liu et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2024b). In our model, SFI improved CLP-induced inflammatory responses by reducing IL - 1β and IL - 6 levels.
In patients with sepsis, serum creatinine (SCr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) are important indicators of renal function damage and are closely related to the severity and prognosis of the disease. Studies have shown that the BUN level of patients with sepsis is significantly higher than that of patients without sepsis (Gao et al., 2012; Min et al., 2022). Although there is no statistical difference in SCr between the two groups, it is positively correlated with oxidative stress factors such as malondialdehyde (MDA) and nitric oxide (NO), indicating that oxidative stress may aggravate renal function damage. The systemic inflammatory response and microcirculatory disorders caused by sepsis can lead to acute kidney injury (AKI), which in turn increases SCr and BUN, reflecting decreased glomerular filtration rate and azotemia (Costa et al., 2016; Qiu et al., 2019). In addition, the increase in BUN may also be related to a high metabolic state, increased protein breakdown, and insufficient renal perfusion. In our model, SCr and BUN levels in the blood were significantly increased by 5.5-fold and 4.4-fold at 16 h after CLP surgery. SFI significantly reduced SCr and BUN levels. These results suggest that SFI can prevent renal injury by regulating SCr and BUN levels, an observation previously reported in a rat model of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion (Hua et al., 2024) and heart failure (Zhao et al., 2020) after SFI into intestinal and cardiac tissues.
The intestine has long been considered a key factor in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) (Klingensmith and Coopersmith, 2016; Mittal and Coopersmith, 2014; Van Coillie et al., 2022). Maintaining intestinal and systemic immune homeostasis depends on a balanced microbiota, and an imbalance in the intestinal microbiota may increase an individual’s risk of sepsis (Haak and Wiersinga, 2017). Regulating the intestinal flora may become a new direction for the treatment of sepsis (Haak et al., 2018). In critically ill patients, dysbiosis is common, manifested by a decrease in the number of “beneficial” commensal bacteria (such as Firmicutes or Bacteroidetes) and an enrichment of potentially pathogenic intestinal bacteria (such as Proteobacteria) (Sun et al., 2022; Wozniak et al., 2022). The abundance of Proteobacteria may become a potential indicator for disease diagnosis (Rizzatti et al., 2017; Shin et al., 2015). In addition, the intestinal microbiota is able to prevent foreign microorganisms from colonizing the gastrointestinal tract, a phenomenon known as “colonization resistance” (Kim et al., 2017). Studies have shown that Escherichia coli, Proteobacterium, and Enterobacter may cause bacteremia in frail patients because these intestinal bacteria are more prone to translocation, especially obligate anaerobes (Girard and Ely, 2007; Hyernard et al., 2019). Our study showed that there were significant differences in the intestinal microbial composition between the sham and CLP groups. As expected, Shenfu could regulate the abundance of Muribaculaceae, Lachnospirales, Escherichia-Shigella, and other bacteria, restoring them to levels similar to those in healthy mice. Escherichia-Shigella may cause sepsis-associated inflammation due to its ability to invade and damage the human colonic epithelium (Azimirad et al., 2020). Lachnospirales are butyrate-producing bacteria, anaerobes with probiotic properties, and play specific roles in metabolic diseases, inflammatory environments, and biotransformations (Xia et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2024). Muribaculaceae was significantly reduced in abundance in colitis mice and has an important role in microbiota homeostasis (Niu et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2024). In addition, Interleukins can also interact with the microbiota in certain circumstances. For example, gut microbiota can influence the concentration of bile acid and the level of interleukin-22 to orchestrate polycystic ovary syndrome (Qi et al., 2019), Akkermansia muciniphila can improves cognitive function in aged mice by reducing the proinflammatory cytokine IL - 6 (Zhu et al., 2023). In this study, Enterococcus were significantly positive correlated with IL - 1β, IL - 6, SCR. A previous study has reported that antimicrobial overproduction sustains intestinal inflammation by inhibiting Enterococcus colonization (Jang et al., 2023), which demonstrate the relationship between Enterococcus and inflammation. In addition, the relative abundance changes of Staphvlococcus, Ruminococcus, Odoribacten were also significantly correlated with the expression of IL - 6, indicating that IL6 might be able to regulate the diversity changes of the bacterial community. As mentioned above, Shenfu can regulate the intestinal microbiota of septic mice by increasing beneficial bacteria and reducing pathogenic bacteria. However, although this article has to some extent expounded on the role of SFI in regulating the intestinal flora, the 16-hour observation window can only capture the acute-phase response and cannot reflect the long-term results. Therefore, in subsequent research and applications, if SFI is to be used clinically, further in-depth studies on its mechanism of action are still necessary.
5 Conclusions
In conclusion, this study established a cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) model to evaluate the therapeutic effects of Shenfu Injection (SFI) in sepsis management. The experimental results demonstrated that SFI administration significantly attenuated intestinal inflammation and reduced serum levels of pro-inflammatory mediators, including IL - 1β, IL - 6, SCr, and BUN. Furthermore, microbial analysis revealed that SFI treatment effectively modulated gut microbiota composition by decreasing the relative abundance of pathogenic bacteria (particularly Escherichia-Shigella) while enhancing probiotic populations, notably Akkermansia and Lactobacillus species. These findings collectively indicate the therapeutic potential of SFI in sepsis treatment through dual mechanisms of inflammatory response mitigation and gut microbiota regulation. Notably, this investigation provides a valuable foundation for future mechanistic studies exploring SFI-mediated sepsis management via intestinal microbiome modulation, potentially informing the development of novel therapeutic strategies for critical care medicine.
Data availability statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to YThsZzExQDE2My5jb20=.
Ethics statement
The animal studies were approved by Intensive Care Unit, The Central Hospital Wuhan, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong of University of Science and Technology. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the owners for the participation of their animals in this study.
Author contributions
NL: Visualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. FY: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Software, Formal Analysis. YW: Validation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. FG: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Software. YL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Software, Validation. QL: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. YG: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Project administration, Conceptualization. DL: Supervision, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from Hubei Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Project (ZY2023F059) and Wuhan Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Project (WZ22Q45).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Maintainbiotech. Ltd. (Wuhan) for the technical support and assistance provided in the analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adelman, M. W., Woodworth, M. H., Langelier, C., Busch, L. M., Kempker, J. A., Kraft, C. S., et al. (2020). The gut microbiome’s role in the development, maintenance, and outcomes of sepsis. Crit. Care 24, 1–10. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02989-1
Azimirad, M., Krutova, M., Balaii, H., Kodori, M., Shahrokh, S., Azizi, O., et al. (2020). Coexistence of Clostridioides difficile and Staphylococcus aureus in gut of Iranian outpatients with underlying inflammatory bowel disease. Anaerobe 61, 102113. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2019.102113
Bokulich, N. A., Subramanian, S., Faith, J. J., Gevers, D., Gordon, J. I., Knight, R., et al. (2013). Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 10, 57–59. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2276
Brandt, A., Baumann, A., Hernández-Arriaga, A., Jung, F., Nier, A., Staltner, R., et al. (2022). Impairments of intestinal arginine and NO metabolisms trigger aging-associated intestinal barrier dysfunction and ‘inflammaging’. Redox Biol. 58, 102528. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102528
Caporaso, J. G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F. D., Costello, E. K., et al. (2010). QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 7, 335–336. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Costa, N. A., Gut, A. L., Azevedo, P. S., Tanni, S. E., Cunha, N. B., Magalhães, E. S., et al. (2016). Erythrocyte superoxide dismutase as a biomarker of septic acute kidney injury. Ann. Intensive Care 6, 1–8. doi: 10.1186/s13613-016-0198-5
Dellinger, R. P., Levy, M. M., Rhodes, A., Annane, D., Gerlach, H., Opal, S. M., et al. (2013). Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit. Care Med. 41, 580–637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af
Dobson, G. P., Letson, H. L., and Morris, J. L. (2024). Revolution in sepsis: a symptoms-based to a systems-based approach? J. Biomed. Sci. 31, 57. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01043-4
Duess, J. W., Sampah, M. E., Lopez, C. M., Tsuboi, K., Scheese, D. J., and Sodhi, C. P. (2023). Necrotizing enterocolitis, gut microbes, and sepsis? Gut Microbes 15, 2221470. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01043-4
Edgar, R. C. (2013). UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 10, 996–998. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2604
Edgar, R. C., Haas, B. J., Clemente, J. C., Quince, C., and Knight, R. (2011). UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27, 2194–2200. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381
Gai, X., Wang, H., Li, Y., Zhao, H., He, C., Wang, Z., et al. (2021). Fecal microbiota transplantation protects the intestinal mucosal barrier by reconstructing the gut microbiota in a murine model of sepsis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 11, 736204. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.736204
Gao, M., Zhang, L., Liu, Y., Yang, M., Wang, N., Wang, K., et al. (2012). Use of blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, interleukin-6, granulocyte–macrophage colony stimulating factor in combination to predict the severity and outcome of abdominal sepsis in rats. Inflammation Res. 61, 889–897. doi: 10.1007/s00011-012-0481-3
Ge, P., Luo, Y., Okoye, C. S., Chen, H., Liu, J., Zhang, G., et al. (2020). Intestinal barrier damage, systemic inflammatory response syndrome, and acute lung injury: A troublesome trio for acute pancreatitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. = Biomed. Pharmacother. 132, 110770. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110770
Girard, T. D. and Ely, E. W. (2007). Bacteremia and sepsis in older adults. Clinics Geriatric. Med. 23, 633–647. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2007.05.003
Haak, B. W., Prescott, H. C., and Wiersinga, W. J. (2018). Therapeutic potential of the gut microbiota in the prevention and treatment of sepsis. Front. Immunol. 9, 2042. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02042
Haak, B. W. and Wiersinga, W. J. (2017). The role of the gut microbiota in sepsis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2, 135–143. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30119-4
Hong, F. F., Guo, F. X., Ying, Z., Min, Q. H., Zhang, D. L., Bei, Y., et al. (2015). Shenfu injection protects human ECV304 cells from hydrogen peroxide via its anti-apoptosis way. J. Ethnopharmacol. 163, 203–209. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.032
Hotchkiss, R. S. and Karl, I. E. (2003). The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. New Engl. J. Med. 348, 138–150. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra021333
Hotchkiss, R. S., Moldawer, L. L., Opal, S. M., Reinhart, K., Turnbull, I. R., and Vincent, J.-L. (2016). Sepsis and septic shock. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2, 1–21. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.45
Hua, T., Lu, Z., Wang, M., Zhang, Y., Chu, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2024). Shenfu injection alleviate gut ischemia/reperfusion injury after severe hemorrhagic shock through improving intestinal microcirculation in rats. Heliyon 10, e31377. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31377
Hunt, A. (2019). Sepsis: an overview of the signs, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. Emergency Nurse. 27, 32–41. doi: 10.7748/en.2019.e1926
Hyernard, C., Breining, A., Duc, S., Kobeh, D., Dubos, M., Prevel, R., et al. (2019). Atypical presentation of bacteremia in older patients is a risk factor for death. Am. J. Med. 132, 1344–1352. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.04.049
Jang, K. K., Heaney, T., London, M., Ding, Y., Putzel, G., Yeung, F., et al. (2023). Antimicrobial overproduction sustains intestinal inflammation by inhibiting Enterococcus colonization. Cell Host Microbe 31, 1450–1468.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2023.08.002
Jin, S., Jiang, R., Lei, S., Jin, L., Zhu, C., Feng, W., et al. (2018). Shenfu injection prolongs survival and protects the intestinal mucosa in rats with sepsis by modulating immune response. Turkish. J. Gastroenterol. 30, 364. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2019.18418
Kim, S., Covington, A., and Pamer, E. G. (2017). The intestinal microbiota: antibiotics, colonization resistance, and enteric pathogens. Immunol. Rev. 279, 90–105. doi: 10.1111/imr.12563
King, E. G., Bauzá, G. J., Mella, J. R., and Remick, D. G. (2014). Pathophysiologic mechanisms in septic shock. Lab. Invest. 94, 4–12. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2013.110
Klingensmith, N. J. and Coopersmith, C. M. (2016). The gut as the motor of multiple organ dysfunction in critical illness. Crit. Care Clinics 32, 203–212. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2015.11.004
Klingensmith, N. J. and Coopersmith, C. M. (2023). Gut microbiome in sepsis. Surg. Infect. 24, 250–257. doi: 10.1089/sur.2022.420
Kullberg, R. F., Wiersinga, W. J., and Haak, B. W. (2021). Gut microbiota and sepsis: from pathogenesis to novel treatments. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 37, 578–585. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000781
Kurt, A. N. C., Aygun, A. D., Godekmerdan, A., Kurt, A., Dogan, Y., and Yilmaz, E. (2007). Serum IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α levels in early diagnosis and management of neonatal sepsis. Mediators Inflammation 2007, 031397. doi: 10.1155/2007/31397
Langille, M. G., Zaneveld, J., Caporaso, J. G., McDonald, D., Knights, D., Reyes, J. A., et al. (2013). Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 31, 814–821. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2676
Li, X., Huang, F., Zhu, L., Luo, T., Zhang, Y., Gu, H., et al. (2022). Effects of combination therapy with Shenfu Injection in critically ill patients with septic shock receiving mechanical ventilation: a multicentric, real-world study. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1041326. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1041326
Li, Y. H., Yu, B., Duan, Z. Z., Akinyi, O. M., Yu, J. H., Zhou, K., et al. (2014). The coronary dilation effect of shen fu injection was mediated through NO. PloS One 9, e92415. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092415
Liu, X., Ai, F., Li, H., Xu, Q., Mei, L., Miao, J., et al. (2019). Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Shenfu Injection against Acute Lung Injury through Inhibiting HMGB1-NF-κB Pathway in a Rat Model of Endotoxin Shock. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 9857683. doi: 10.1155/2019/9857683
Liu, Y., Guo, Y., Hu, S., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Yu, L., et al. (2023). Analysis of the dynamic changes in gut microbiota in patients with different severity in sepsis. BMC Infect. Dis. 23, 614. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08608-y
Liu, C., Hou, Y., Wang, X., Zhao, Z., Liu, Z., Zhai, J., et al. (2015). Clinical assessment of Shenfu injection loading in the treatment of patients with exacerbation of chronic heart failure due to coronary heart disease: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 16, 1–8. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-0729-7
Lou, X., Xue, J., Shao, R., Yang, Y., Ning, D., Mo, C., et al. (2023). Fecal microbiota transplantation and short-chain fatty acids reduce sepsis mortality by remodeling antibiotic-induced gut microbiota disturbances. Front. Immunol. 13, 1063543. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1063543
Lozupone, C., Hamady, M., and Knight, R. (2006). UniFrac–an online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context. BMC Bioinf. 7, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-371
Luan, F., Zhou, Y., Ma, X., Li, Y., Peng, Y., Jia, X., et al. (2024). Gut microbiota composition and changes in patients with sepsis: potential markers for predicting survival. BMC Microbiol. 24, 45. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03188-6
Luo, S., Gou, L., Liu, S., and Cao, X. (2021). Efficacy and safety of Shenfu injection in the treatment of sepsis: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Baltim. 100, e27196. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027196
Mai, S. H. C., Sharma, N., Kwong, A. C., Dwivedi, D. J., Khan, M., Grin, P. M., et al. (2018). Body temperature and mouse scoring systems as surrogate markers of death in cecal ligation and puncture sepsis. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 6, 20. doi: 10.1186/s40635-018-0184-3
Meyer, N. J. and Prescott, H. C. (2024). Sepsis and septic shock. New Engl. J. Med. 391, 2133–2146. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra2403213
Min, J., Lu, J., Zhong, L., Yuan, M., and Xu, Y. (2022). The correlation study between blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio and prognosis of patients with sepsis during hospitalization. BMC Anesthesiol. 22, 404. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01947-4
Mittal, R. and Coopersmith, C. M. (2014). Redefining the gut as the motor of critical illness. Trends Mol. Med. 20, 214–223. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2013.08.004
Niu, M.-M., Guo, H.-X., Cai, J.-W., and Meng, X.-C. (2022). Bifidobacterium breve alleviates DSS-induced colitis in mice by maintaining the mucosal and epithelial barriers and modulating gut microbes. Nutrients 14, 3671. doi: 10.3390/nu14183671
Oami, T., Abtahi, S., Shimazui, T., Chen, C. W., Sweat, Y. Y., Liang, Z., et al. (2024). Claudin-2 upregulation enhances intestinal permeability, immune activation, dysbiosis, and mortality in sepsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United. States America 121, e2217877121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2217877121
Qi, X., Yun, C., Sun, L., Xia, J., Wu, Q., Wang, Y., et al. (2019). Gut microbiota-bile acid-interleukin-22 axis orchestrates polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat. Med. 25, 1225–1233. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0509-0
Qiu, C., Wu, J., Pei, F., Wang, L., Mei, M., Guan, X., et al. (2019). Correlation between oxidative stress factors and prognosis of patients with sepsis. Zhonghua. Wei. Zhong. Bing. Ji. Jiu. Yi. Xue. 31, 847–851. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.07.010
Rittirsch, D., Huber-Lang, M. S., Flierl, M. A., and Ward, P. A. (2009). Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and puncture. Nat. Protoc. 4, 31–36. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.214
Rizzatti, G., Lopetuso, L., Gibiino, G., Binda, C., and Gasbarrini, A. (2017). Proteobacteria: a common factor in human diseases. BioMed. Res. Int. 2017, 9351507. doi: 10.1155/2017/9351507
Seymour, C. W., Liu, V. X., Iwashyna, T. J., Brunkhorst, F. M., Rea, T. D., Scherag, A., et al. (2016). Assessment of clinical criteria for sepsis: for the third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). Jama 315, 762–774. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0288
Shankar-Hari, M., Phillips, G. S., Levy, M. L., Seymour, C. W., Liu, V. X., Deutschman, C. S., et al. (2016). Developing a new definition and assessing new clinical criteria for septic shock: for the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). Jama 315, 775–787. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0289
Shin, N.-R., Whon, T. W., and Bae, J.-W. (2015). Proteobacteria: microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 33, 496–503. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.06.011
Sun, J., Sun, X., Chen, J., Liao, X., He, Y., Wang, J., et al. (2021). microRNA-27b shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes prevents sepsis by targeting JMJD3 and downregulating NF-κB signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 12, 14. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-02068-w
Sun, T., Wang, L., and Zhang, H. (2022). Intestinal microbiota in sepsis. Intensive Care Res. 2, 1–7. doi: 10.1007/s44231-022-00001-8
Tao, Y. L., Wang, J. R., Liu, M., Liu, Y. N., Zhang, J. Q., Zhou, Y. J., et al. (2024). Progress in the study of the correlation between sepsis and intestinal microecology. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 14, 1357178. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1357178
Van Coillie, S., Van San, E., Goetschalckx, I., Wiernicki, B., Mukhopadhyay, B., Tonnus, W., et al. (2022). Targeting ferroptosis protects against experimental (multi)organ dysfunction and death. Nat. Commun. 13, 1046. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28718-6
Wang, Z., Chen, W., Li, Y., Zhang, S., Lou, H., Lu, X., et al. (2021). Reduning injection and its effective constituent luteoloside protect against sepsis partly via inhibition of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-кB/MAPKs signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 270, 113783. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113783
Wang, Y., Kang, K., Lin, Y., Lai, Q., Tang, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2024b). Shenfu injection alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced septic acute kidney injury by regulating the nrf2/NF-κ B axis. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 20, 920–927. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2024.383
Wang, G., Ma, F., Xie, K., Li, X., Tan, X., Xia, Y., et al. (2024a). Liensinine alleviates mouse intestinal injury induced by sepsis through inhibition of oxidative stress, inflammation, and cell apoptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 127, 111335. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111335
Wozniak, H., Beckmann, T. S., Fröhlich, L., Soccorsi, T., Le Terrier, C., de Watteville, A., et al. (2022). The central and biodynamic role of gut microbiota in critically ill patients. Crit. Care 26, 250. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-04127-5
Wu, W., Jiang, R. L., Wang, L. C., Lei, S., Xing, X., Zhi, Y. H., et al. (2015). Effect of Shenfu injection on intestinal mucosal barrier in a rat model of sepsis. Am. J. Emergency Med. 33, 1237–1243. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2015.01.056
Xia, H., Guo, J., Shen, J., Jiang, S., Han, S., and Li, L. (2023). Butyrate ameliorated the intestinal barrier dysfunction and attenuated acute pancreatitis in mice fed with ketogenic diet. Life Sci. 334, 122188. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122188
Xing, X., Jiang, R., Wang, L., Lei, S., Zhi, Y., Wu, Y., et al. (2015). Shenfu injection alleviates intestine epithelial damage in septic rats. Am. J. Emergency Med. 33, 1665–1670. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2015.08.001
Xu, C., Xia, Y., Jia, Z., Wang, S., Zhao, T., and Wu, L. (2022). The curative effect of Shenfu-injection in the treatment of burn sepsis and its effect on the patient’s immune function, HMGB, and vWF. Am. J. Trans. Res. 14, 2428–2435.
Xu, F.-F., Xie, X.-F., Hu, H.-Y., Tong, R.-S., and Peng, C. (2024). Shenfu injection: a review of pharmacological effects on cardiovascular diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1279584. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1279584
Yan, Y., Li, B., Gao, Q., Wu, M., Ma, H., Bai, J., et al. (2025). Intestine-decipher engineered capsules protect against sepsis-induced intestinal injury via broad-spectrum anti-inflammation and parthanatos inhibition. Adv. Sci. (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany). 12, e2412799. doi: 10.1002/advs.202412799
Yang, C. J., Chang, H. C., Sung, P. C., Ge, M. C., Tang, H. Y., Cheng, M. L., et al. (2024). Oral fecal transplantation enriches Lachnospiraceae and butyrate to mitigate acute liver injury. Cell Rep. 43, 113591. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113591
Yang, H., Liu, L., Gao, W., Liu, K., Qi, L.-W., and Li, P. (2014). Direct and comprehensive analysis of ginsenosides and diterpene alkaloids in Shenfu injection by combinatory liquid chromatography–mass spectrometric techniques. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 92, 13–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.12.041
Yang, B., Wang, S., Yang, Y., and Wang, Y. (2025). Toxicity and safety profile evaluation of Shenfu injection in a murine sepsis model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 337, 118903. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118903
Zhao, Z., Hu, Z., and Li, L. (2025). Cardiac energy metabolic disorder and gut microbiota imbalance: a study on the therapeutic potential of Shenfu Injection in rats with heart failure. Front. Microbiol. 16, 1509548. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1509548
Zhao, L., Jin, L., Luo, Y., Wang, L., Li, Y., Xian, S., et al. (2022). Shenfu injection attenuates cardiac dysfunction and inhibits apoptosis in septic mice. Ann. Trans. Med. 10, 597. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-836
Zhao, S., Tang, Z., Cui, H., Yang, Z., Shao, F., Wang, S., et al. (2020). Effect of Shenfu injection on porcine renal function after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 3789268. doi: 10.1155/2020/3789268
Zhu, Y., Chen, B., Zhang, X., Akbar, M. T., Wu, T., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024). Exploration of the muribaculaceae family in the gut microbiota: diversity, metabolism, and function. Nutrients 16, 2660. doi: 10.3390/nu16162660
Zhu, X., Shen, J., Feng, S., Huang, C., Wang, H., Huo, F., et al. (2023). Akkermansia muciniphila, which is enriched in the gut microbiota by metformin, improves cognitive function in aged mice by reducing the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6. Microbiome 11, 120. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01567-1
Keywords: sepsis, Shenfu injection, intestinal microbiota, inflammation, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)
Citation: Li N, Yi F, Wang Y, Geng F, Liu Y, Liu Q, Guo Y and Long D (2025) Effects of Shenfu injection on intestinal microbiota and inflammation in sepsis mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1599903. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1599903
Received: 25 March 2025; Accepted: 19 August 2025;
Published: 15 September 2025.
Edited by:
Veeranoot Nissapatorn, Walailak University, ThailandCopyright © 2025 Li, Yi, Wang, Geng, Liu, Liu, Guo and Long. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanan Guo, Z3VveWFuYW4xMTA0QHNpbmEuY29t; Ding Long, YThsZzExQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Ning Li1,2,3†
Ning Li1,2,3† Yujun Wang
Yujun Wang Yanli Liu
Yanli Liu Ding Long
Ding Long