- Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang, China
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a globally prevalent metabolic disorder characterized by impaired immune function due to poor glycaemia control, significantly increasing the risk of osteomyelitis. The occurrence of bone infection not only compromises patients’ quality of life but also poses substantial challenges in clinical management. Recent studies have identified immunometabolic reprogramming as a pivotal player in the pathogenesis and progression of diabetic osteomyelitis. This reprogramming not only disrupts immune cell functionality but also modulates the local microenvironment, thereby impairing bone repair processes. Although preliminary research has explored the underlying mechanisms, a comprehensive understanding of the precise role of immunometabolic reprogramming and its potential therapeutic targeting in diabetic osteomyelitis remains elusive. This review synthesizes current advances in immunometabolic reprogramming within diabetic osteomyelitis, elucidates its biological mechanisms, and proposes novel intervention strategies to inform clinical practice and inspire future therapeutic development.
1 Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder affecting hundreds of millions of people worldwide. Its prevalence continues to rise, making it a major global public health challenge. Diabetic patients often develop various complications, among which bone infections, such as osteomyelitis, are one of the most common and serious. Diabetic osteomyelitis is a severe complication frequently encountered in diabetic patients. Its pathogenesis is closely associated with immune dysfunction under hyperglycemic conditions. Hyperglycemia not only impairs the function of immune cells but also leads to persistent activation of inflammatory responses, thereby hindering the effective resolution of inflammation and resulting in bone destruction and refractory infection (Frazee, 2024). The occurrence of osteomyelitis in diabetic patients significantly impairs quality of life and may lead to serious outcomes such as amputation. Therefore, a deeper understanding of its underlying mechanisms and corresponding treatment strategies is of great importance.
In recent years, increasing attention has been paid to the role of immunometabolic reprogramming in diabetic osteomyelitis. The metabolic state of immune cells directly influences their function, thereby affecting anti-infective mechanisms and bone healing processes. For example, under chronic hyperglycemia, immune cells in diabetic patients often exhibit metabolic dysfunction, leading to impaired immune responses and increased susceptibility to infection (Favoino et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021; Osório et al., 2023). Studies have shown that deep bone ulcers and inflammatory wounds in diabetic patients are significant risk factors for osteomyelitis, highlighting the crucial role of the local immunometabolic microenvironment in the pathogenesis of infection.
Furthermore, research has revealed that diabetic patients exhibit distinct immunometabolic reprogramming features during infection. For instance, macrophages in diabetic patients may adapt to the inflammatory environment by enhancing glycolysis and fatty acid oxidation. This metabolic shift not only alters immune cell behavior but may also promote chronic inflammation and bone tissue damage (Roverato et al., 2021). Thus, investigating the mechanisms of immunometabolic reprogramming in diabetic osteomyelitis may provide new avenues for treatment.
Conventional management of diabetic osteomyelitis primarily includes antibiotic therapy and surgical intervention (Fountas et al., 2024). However, with growing insights into immunometabolic reprogramming, novel therapeutic strategies are emerging. These advances underscore the importance of personalized treatment and multidisciplinary collaboration in clinical practice.
2 Diabetic osteomyelitis
Foot infections in diabetic patients often present as chronic ulcers and osteomyelitis, particularly in cases with restricted blood flow. Studies indicate that the incidence of foot osteomyelitis in diabetic patients can be as high as 30% (Zhan et al., 2023). Up to 25% of individuals with diabetes will develop a foot ulcer in their lifetime, and untreated ulcers may progress to bone infection, ultimately leading to amputation (Jaroenarpornwatana et al., 2023). The pathogenesis of diabetic osteomyelitis is complex, involving multiple physiological and pathological factors—including a diabetes-related low-grade inflammatory state, abnormal bone metabolism, and bacterial infection—as illustrated in Figure 1.
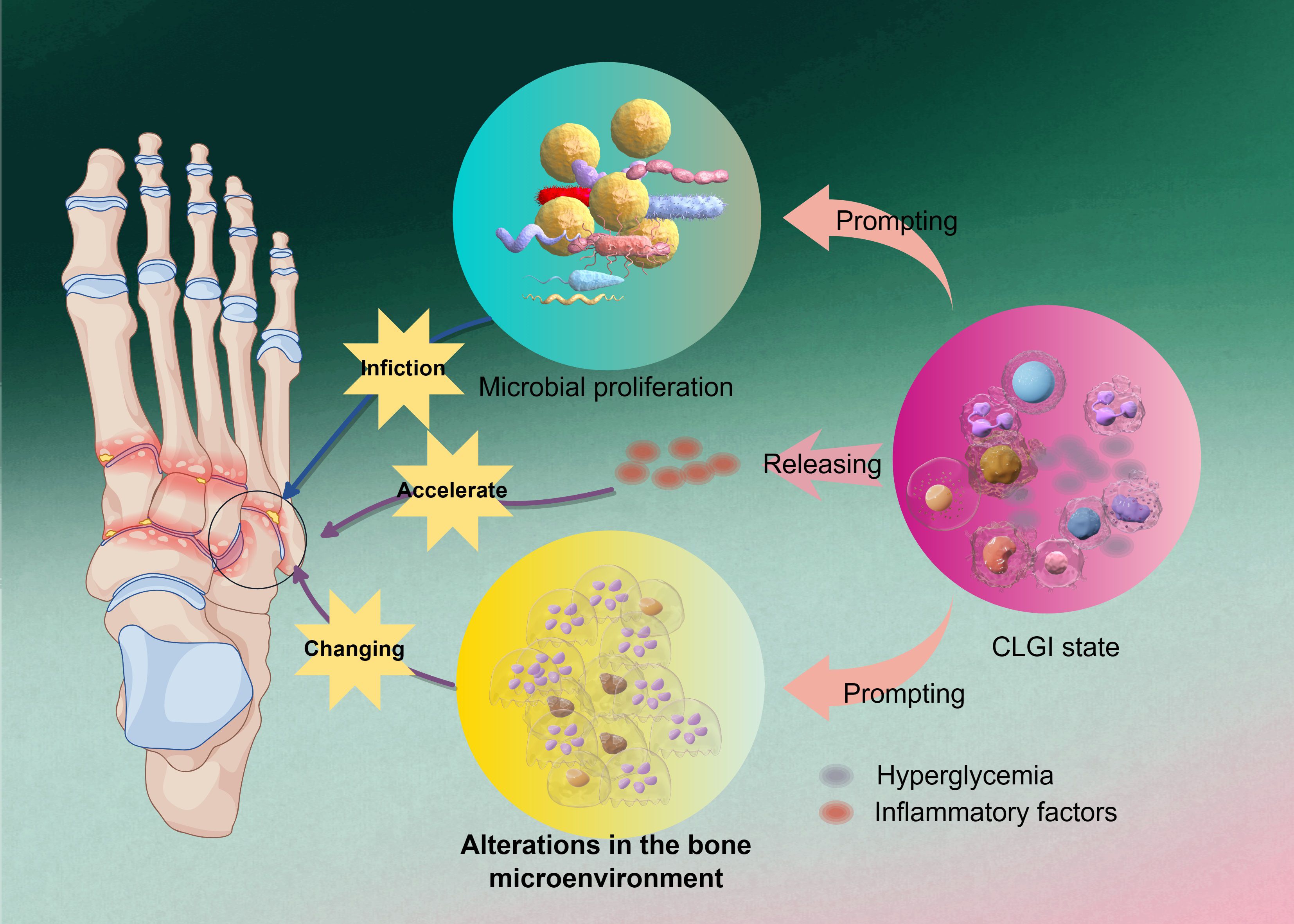
Figure 1. The initiating factor in the pathogenesis of DO. Hyperglycemia exacerbates osteomyelitic progression by inducing a chronic low-grade inflammatory state and releasing inflammatory factors, which alter the bone microenvironment to accelerate microbial proliferation and further amplify pathological alterations in bone tissue, ultimately establishing a self-perpetuating vicious cycle.
2.1 Chronic low-grade inflammation
A hyperglycemic environment impairs immune cell function, particularly diminishing chemotaxis, oxidative burst, and complement activation in neutrophils, thereby increasing susceptibility to various infections in diabetic patients (Kim and Choi, 2025). Under such conditions, immune cells are unable to effectively recognize and eliminate invading pathogens, leading to persistent bacterial infection in bone tissues. Diabetes is fundamentally a metabolic disorder characterized by the accumulation of excess sugars, lipids, and amino acids in the blood and organs, placing patients in a chronic low-grade inflammatory (CLGI) state. This condition resembles “inflammaging” observed in aging and directly compromises immune cell function (Urszula et al., 2024; Uthaya Kumar et al., 2024). CLGI not only affects glycemic control and induces immune dysfunction, increasing the risk of infection, but also exacerbates diabetes-related complications such as diabetic foot and diabetic nephropathy. Clinically, diabetic foot infection (DFI) is one of the most common complications among diabetic patients, and severe infections including DFI-related osteomyelitis are major causes of hospitalization and limb amputation (Frazee, 2024).
Immune cells in diabetic patients exhibit significant impairments in proliferation and cytokine secretion, particularly in macrophage and T-cell function. Under CLGI conditions, T cells and B cells display features of cellular senescence (Wei et al., 2021; Saadh et al., 2025). Macrophages show reduced ability to recognize and clear pathogens, manifested by weakened phagocytosis and dysregulated cytokine secretion (Pan et al., 2024; Saadh et al., 2025). Consequently, diabetic patients are notably more susceptible to infections, especially those caused by certain bacteria and viruses (Alexander et al., 2024; Uthaya Kumar et al., 2024). Thus, CLGI can be regarded as both the pathological basis and initiating factor in the development of diabetic osteomyelitis.
2.2 Alterations in the bone tissue microenvironment
In hyperglycemic mice infected with Staphylococcus aureus, the bacterial load within the bone is significantly increased, and the extent of bone destruction is more severe compared to normoglycemic mice, indicating exacerbated osteomyelitis symptoms (Butrico et al., 2023). This suggests that hyperglycemia not only promotes bacterial proliferation but also aggravates infection-induced bone damage. Within the context of chronic low-grade inflammation (CLGI), an imbalance in inflammatory mediators and cytokines disrupts the dynamic equilibrium between bone resorption and bone formation. For instance, infiltrating inflammatory cells such as macrophages secrete large quantities of pro-inflammatory factors within the bone marrow. These factors promote osteoclastogenesis, enhance bone resorption, and inhibit osteoblast function, thereby exacerbating osteoporosis and increasing the risk of fracture (Heng et al., 2023; Chen J. et al., 2025). Furthermore, such inflammatory cytokines may also induce osteoblast apoptosis, impairing the bone’s regenerative capacity (Zhang F. et al., 2024; Hu et al., 2025). For example, macrophages in the bone marrow of diabetic patients often exhibit a pro-inflammatory phenotype, secreting substantial amounts of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). The release of these cytokines promotes osteoclast activation, accelerating bone resorption and impairing bone repair and regeneration (Yu et al., 2020; Hu et al., 2025).
Thus, within the setting of diabetic osteomyelitis, alterations in the bone microenvironment constitute a complex and multifactorial process. Firstly, imbalanced bone metabolism—a common pathological feature in diabetes—is characterized by enhanced bone resorption and impaired bone formation (Bakhtiyari et al., 2023; Perera Molligoda Arachchige and Verma, 2024). This ultimately leads to aggravated bone destruction and reduced bone density, compromising bone structural integrity (Heng et al., 2023). Additionally, diabetic patients often exhibit microangiopathy in bone tissue, resulting in local ischemia that exacerbates tissue damage and increases infection risk. Impaired blood supply due to microvascular complications places bone tissue at a disadvantage during repair and regeneration, making infections more likely to occur and worsen (Perera Molligoda Arachchige and Verma, 2024). Therefore, from a pathological perspective, changes in the bone microenvironment can be viewed as an extension of CLGI, representing its structural impact on bone. The destruction of bone structure allows pathogenic microorganisms to directly enter the bone marrow through damaged sites, triggering the onset of diabetic osteomyelitis.
2.3 Characteristics of pathogenic microorganism infection
Common pathogenic microorganisms responsible for osteomyelitis include Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Escherichia coli. Among these, Staphylococcus aureus is considered the most prevalent and virulent pathogen. The persistence of its infection is closely linked to its metabolic characteristics. S. aureus facilitates its survival and proliferation through the production of various toxins and enzymes. For instance, it can secrete β-lactamase, which confers resistance to penicillin-based antibiotics, thereby contributing to persistent infection (Urish and Cassat, 2020). Polymicrobial infections are highly common in osteomyelitis, especially in patients with prolonged antibiotic use or compromised immune function. For example, the proportion of Gram-negative bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli in mixed infections is gradually increasing, and the drug resistance of these bacteria is continuously strengthening, posing significant challenges to conventional treatment strategies (Ruiz Holgado et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2023).
Moreover, the formation of microbial biofilms is a critical factor contributing to the persistence of osteomyelitis infections. Biofilms are structures formed by bacterial self-produced polymers on surfaces, which confer strong drug resistance and immune evasion capabilities. Bacteria within biofilms can adapt their metabolic patterns to evade host immune responses and antibiotic treatments, thereby enhancing their survival (Yu et al., 2025). For instance, S. aureus in a biofilm environment can modulate its metabolic pathways to establish a persistent infectious niche within bone and surrounding tissues, protecting itself from host immune attacks while increasing tolerance to antibiotics, leading to reduced efficacy of conventional therapies. Furthermore, biofilm formation not only influences pathogen resistance but also significantly exacerbates bone destruction. Bacteria within biofilms secrete various enzymes and toxins that directly contribute to bone degradation and intensify inflammatory responses, thereby worsening the condition of osteomyelitis (Unsworth et al., 2024; Al Ghaithi et al., 2025).
3 Immunometabolic reprogramming
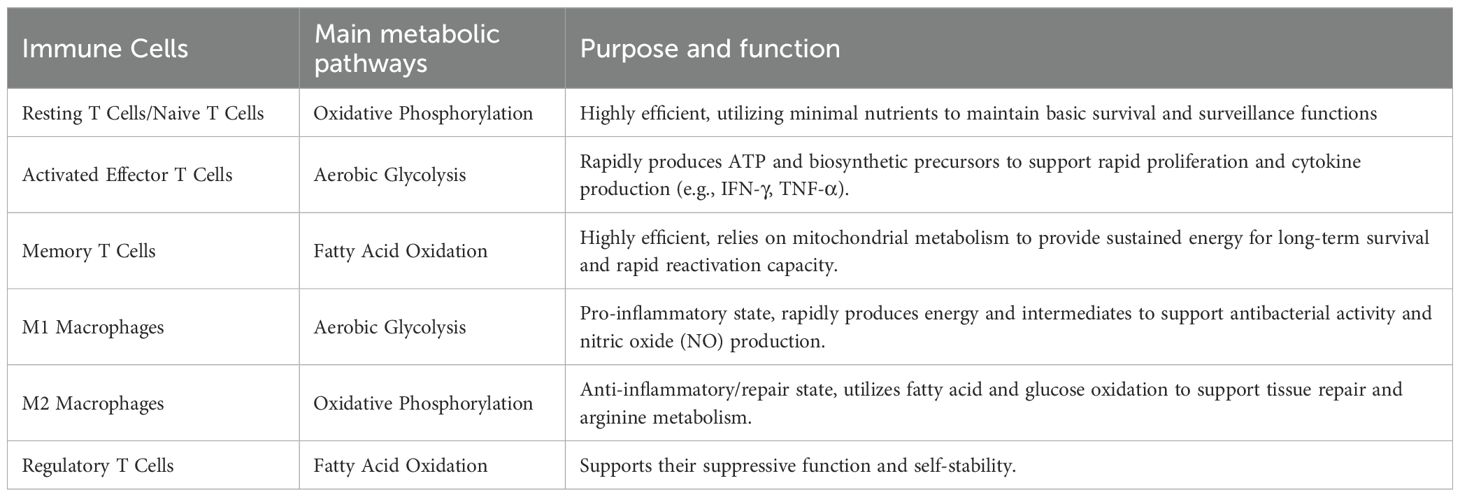
The immune system comprises various cell populations, including lymphocytes (T cells and B cells), monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils, each playing distinct roles in host defense. T cells mediate cellular immunity, while B cells contribute to humoral immunity through antibody production. Macrophages and monocytes act as professional phagocytic cells, and neutrophils form the primary defense against bacterial infections (Alexander et al., 2024). The metabolic state of immune cells is closely linked to their functions, as summarized in Table 1 (Pearce and Pearce, 2013), which lists the metabolic profiles of major immune cells and their corresponding purposes and functions. In a resting state, immune cells primarily rely on oxidative phosphorylation for energy production. However, upon activation, they rapidly shift to glycolysis to meet the energy and biosynthetic demands required for proliferation and effector functions (Hu et al., 2022). This metabolic reprogramming is a critical mechanism by which immune cells adapt to environmental changes and regulate their biological functions.
In infection and tumor microenvironments, activated T cells upregulate glycolysis to rapidly acquire ATP and precursor molecules necessary for biosynthesis, thereby enhancing their effector functions (Bittman, 2022). This metabolic reprogramming not only affects the energy metabolism of immune cells but also directly regulates their cytokine secretion. For instance, the glycolytic byproduct lactate has been found to modulate immune cell functions, influencing T cell differentiation and activity (Fortuny and Sebastián, 2021). In the tumor microenvironment, the acidic and nutrient-deprived conditions resulting from tumor cell metabolism suppress oxidative phosphorylation in immune cells, further promoting glycolysis and leading to an immunosuppressive state (Talty and Olino, 2021). In addition to glucose metabolism dysregulation, patients with diabetes often exhibit alterations in lipid metabolism (Talty and Olino, 2021) and amino acid metabolism pathways (Mark and Tansey, 2025). For example, M1 macrophages in inflammatory environments enhance fatty acid synthesis and oxidation, which promotes the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Shanley et al., 2022). In adipose tissue, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18) are abnormally activated and excessively released (Alghamdi et al., 2023; Yan, 2024), thereby exacerbating inflammatory responses.
In fact, beyond directly mediating inflammatory responses, metabolic dysregulation is itself a key trigger of immune cell metabolic reprogramming, with the two processes often being mutually causal. Inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), can regulate the metabolic state of immune cells by activating specific signaling pathways (Khandelwal et al., 2022). Conversely, inflammation-induced insulin resistance impairs cellular glucose utilization and exacerbates metabolic dysregulation. Under inflammatory conditions, cells typically upregulate glycolytic flux to meet increased energy demands—a phenomenon known as the “Warburg effect.” For instance, activated macrophages significantly enhance glucose uptake and glycolytic activity during inflammatory responses to support rapid proliferation and effector functions (Balic et al., 2020). However, this metabolic reprogramming not only disrupts energy homeostasis but also leads to the accumulation of potentially harmful metabolites, such as lactate, forming a pathological positive feedback loop that perpetuates cellular dysfunction (Deng et al., 2025).
4 Immunometabolic reprogramming in diabetic osteomyelitis
4.1 Cytokines involved in the formation of diabetic osteomyelitis
As previously described, the formation of diabetic osteomyelitis is a complex process involving vascular endothelial dysfunction, abnormal bone metabolism, and bacterial infections. However, its core mechanism can be summarized as the excessive activation of the immune system under a chronic low-grade inflammatory state. In this chronic low-grade inflammatory state, the cytokines that induce diabetic osteomyelitis can be categorized as follows:
4.1.1 Pro-inflammatory cytokines
Pro-inflammatory cytokines are the most critical cytokines in inducing diabetic osteomyelitis, with their upregulation being a hallmark of its pathological process. In a persistent inflammatory state, bone cell energy metabolism shifts from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis to meet cellular energy demands. This metabolic reprogramming alters the energy supply pathways of bone cells, subsequently affecting their downstream functions, such as increased bone resorption and decreased bone formation. Consequently, metabolic reprogramming in bone cells increases the risk of osteoporosis and bone infections. For instance, IL-1β and TNF-α influence bone cell energy metabolism by regulating glucose uptake and utilization. TNF-α directly activates NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways (e.g., p38, JNK) through TNFR, driving osteoclast differentiation even under low RANKL conditions. IL-1β activates NF-κB and MAPK via IL-1R1, synergizing with TNF-α to promote osteoclastogenesis. IL-1β also mediates TNF-α-induced osteoclast formation (Baud’Huin et al., 2010; O’Brien et al., 2016). IL-6 induces IFN-γ-dependent endothelial cell damage and subsequent IgG loss, ultimately exacerbating bone infections following bone marrow transplantation. Furthermore, IL-6 may aggravate the pathological progression of bone infections by affecting bone metabolism (Li et al., 2022; Luo et al., 2024). In summary, these cytokines can alter the activity and differentiation state of bone cells by influencing glucose and lipid metabolism (Figure 2).
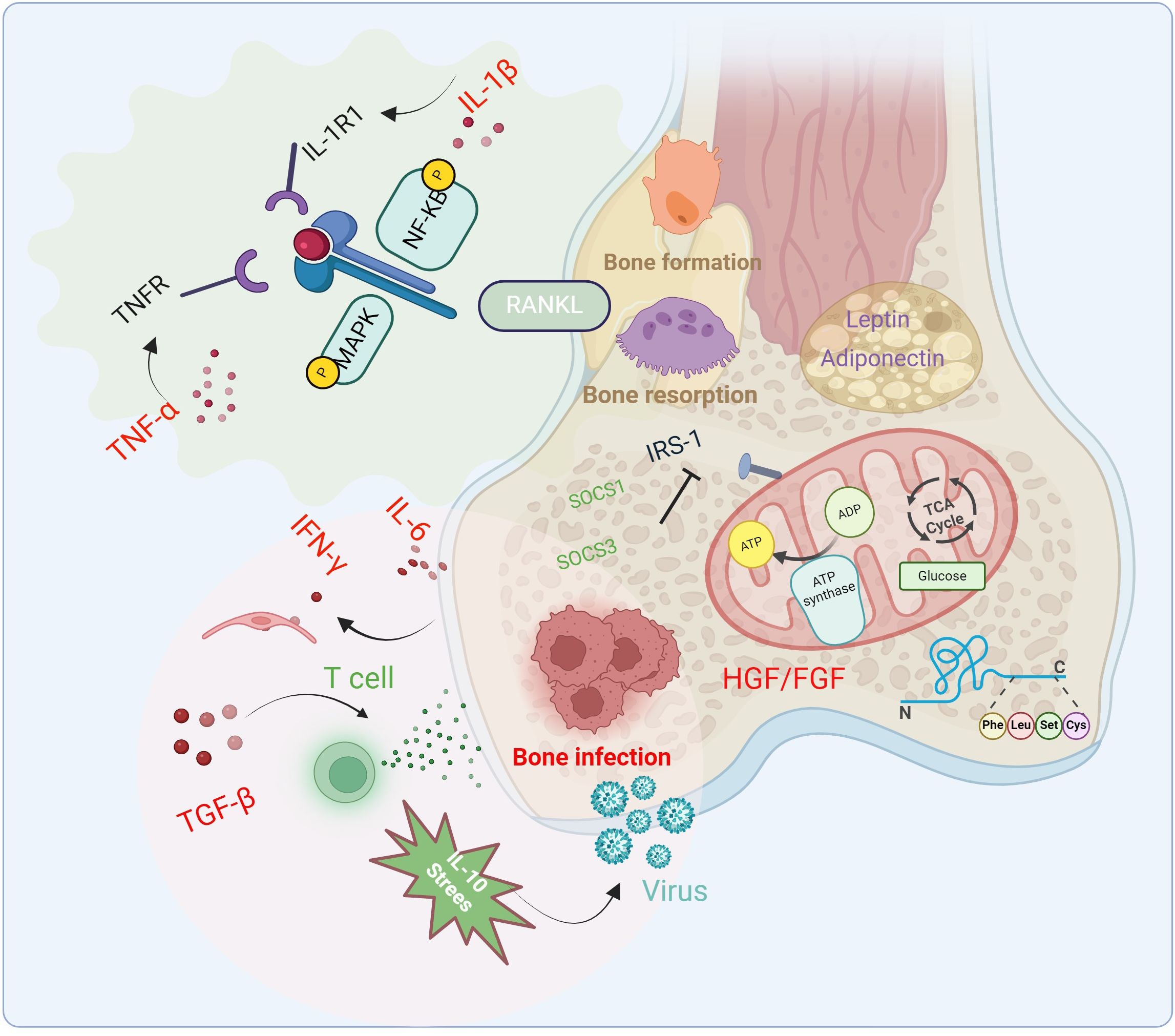
Figure 2. Changes of cytokines, signaling pathways and related immune factors in the pathophysiology of diabetic osteomyelitis. Cytokines and inflammatory factors inhibit bone formation, promote bone resorption and bone infection through glycolysis and fat metabolism, and aggravate the occurrence of diabetic osteomyelitis.
4.1.2 Anti-inflammatory cytokines
Compared to pro-inflammatory cytokines, anti-inflammatory cytokines play a more significant important role in diabetic osteomyelitis. In a hyperglycemic state, the accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) promotes the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines while inhibiting the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10, thereby exacerbating the inflammatory response (Zhao et al., 2024). In a chronic low-grade inflammatory (CLGI) state, the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines gradually increases, while that of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10 and TIPE2, decreases. These anti-inflammatory cytokines are critical for alleviating the progression of diabetic osteomyelitis and accelerating disease recovery. For example, significant downregulation of TIPE2 is closely associated with the progression of diabetic retinopathy (Suo et al., 2021).
As a key anti-inflammatory cytokine in diabetic osteomyelitis, IL-10 inhibits the activity of T cells and macrophages, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and thereby mitigating tissue inflammation. In diabetic patients, IL-10 levels are typically low, which may lead to more severe inflammatory and infectious responses, thus impairing the healing process of osteomyelitis (Bui et al., 2022). TGF-β is another critical anti-inflammatory cytokine, widely involved in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and immune responses. Studies show that TGF-β promotes fibroblast activation and proliferation, facilitating wound healing, and reduces inflammatory cell infiltration to restore the function of damaged tissues. In diabetic patients, TGF-β regulates the local microenvironment, reducing inflammatory cell infiltration and destructive responses in osteomyelitis (Dormer and Gkotsoulias, 2022). Anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10 and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), can directly induce macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype, thereby altering the immune microenvironment. In chronic inflammatory conditions like diabetic osteomyelitis, the generation and function of M2 macrophages are considered important factors in improving disease outcomes. Notably, the functions of anti-inflammatory cytokines extend beyond suppressing inflammation to include participation in tissue remodeling and healing processes (Xie et al., 2020). Insufficient anti-inflammatory cytokines lead to persistent chronic inflammation, impairing wound healing and increasing the risk of osteomyelitis.
4.1.3 Pro-resolving mediators
Specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) are important bioactive lipids, including resolvins, maresins, and lipoxins, primarily derived from the metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), particularly ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids. Unlike anti-inflammatory cytokines, which directly suppress inflammatory cytokines to regulate the immune microenvironment, SPMs promote inflammation resolution in a more systematic and multi-level manner. In addition to regulating inflammatory responses, SPMs also facilitate tissue repair and suppress excessive immune responses (Rasquel-Oliveira et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2024). Resolvins are divided into E-series and D-series, with E-series resolvins primarily derived from eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and D-series resolvins from docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). The synthesis of resolvins requires regulation by specific enzymes, with lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase being key enzymes in their production (Cebrián-Prats et al., 2022). Additionally, maresins, another important SPM derived from DHA, play a significant role in regulating inflammation and promoting tissue repair. Studies have shown that maresins not only suppress inflammatory responses but also enhance macrophage functions, improving their pathogen clearance capabilities (Rasquel-Oliveira et al., 2023). Furthermore, SPMs reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibit the activity of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways such as NF-κB, which is crucial for maintaining immune homeostasis and reducing chronic inflammation (Peh and Chen, 2025).
In the context of diabetic osteomyelitis, the lack of effective inflammation resolution mechanisms leads to persistent chronic inflammation, exacerbating disease progression. Thus, promoting inflammation resolution is of significant importance in diabetic osteomyelitis (Zhao et al., 2023; Leuti et al., 2024). For example, SPMs significantly enhance the clearance rate of inflammatory cells and improve tissue healing in diabetic mouse models (Albuquerque-Souza and Dalli, 2025). Diabetic osteomyelitis often involves tissue damage, and SPMs enhance tissue regeneration by promoting cell proliferation and migration, thereby accelerating wound healing and tissue repair (Serhan et al., 2024).
One of the mechanisms by which SPMs ameliorate diabetic osteomyelitis is through modulation of the immune landscape. Resolvins and protectins, as key regulators of macrophage polarization, effectively promote the shift to the M2 phenotype. These M2 macrophages not only secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines but also contribute to repair processes by clearing cellular debris and promoting tissue regeneration (Videla et al., 2023). SPMs also enhance macrophage efferocytosis (the clearance of apoptotic cells), facilitating inflammation resolution and tissue regeneration (Vetter and Saas, 2024). By inducing neutrophil apoptosis, SPMs effectively reduce the release of inflammatory mediators, thereby alleviating inflammation. This process not only aids in tissue repair and reconstruction but also restores normal immune function (Baker and Cantley, 2025). Pro-resolving mediators promote the transition of neutrophils to an anti-inflammatory phenotype, enhancing their clearance functions and suppressing inflammatory responses by altering their metabolic pathways (Psarras and Clarke, 2023). Additionally, certain SPMs reduce tissue damage by inhibiting neutrophil activation, thereby decreasing the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory cytokines (Albiero and Baragetti, 2025). This multi-level regulation of neutrophils effectively ameliorates the inflammatory state in diabetic osteomyelitis, accelerating the recovery of damaged tissues.
However, the synthesis of SPMs in diabetic patients is suppressed by hyperglycemia (Brennan et al., 2021). Impaired pro-resolving signaling pathways are also a significant cause of defective inflammation resolution in diabetic environments. For instance, macrophages lacking PRMT2 exhibit enhanced inflammatory responses, further exacerbating atherosclerosis development (Vurusaner et al., 2022). Similarly, SIRT6 deficiency has been found to impair macrophage efferocytosis, thereby aggravating persistent inflammation (Ontoria-Oviedo et al., 2022). These findings indicate that the combined effects of impaired SPM synthesis and defective signaling pathways in diabetic environments hinder effective inflammation resolution, ultimately affecting bone tissue health and healing capacity.
4.2 Immunometabolic reprogramming of immune cells in diabetic osteomyelitis
As mentioned above, diabetic osteomyelitis is often a more severe form of diabetic bone infection, accompanied by immune cell metabolic reprogramming, immune system dysfunction, and impaired pathogen clearance, leading to abnormal proliferation of external bacteria at the infection site (Bermejo Olano et al., 2024). Therefore, aside from the microbial infection factors inherent to osteomyelitis, the core factor contributing to the disease is immune system dysfunction, which involves changes in the phenotypes of multiple immune cells (see Figure 3).
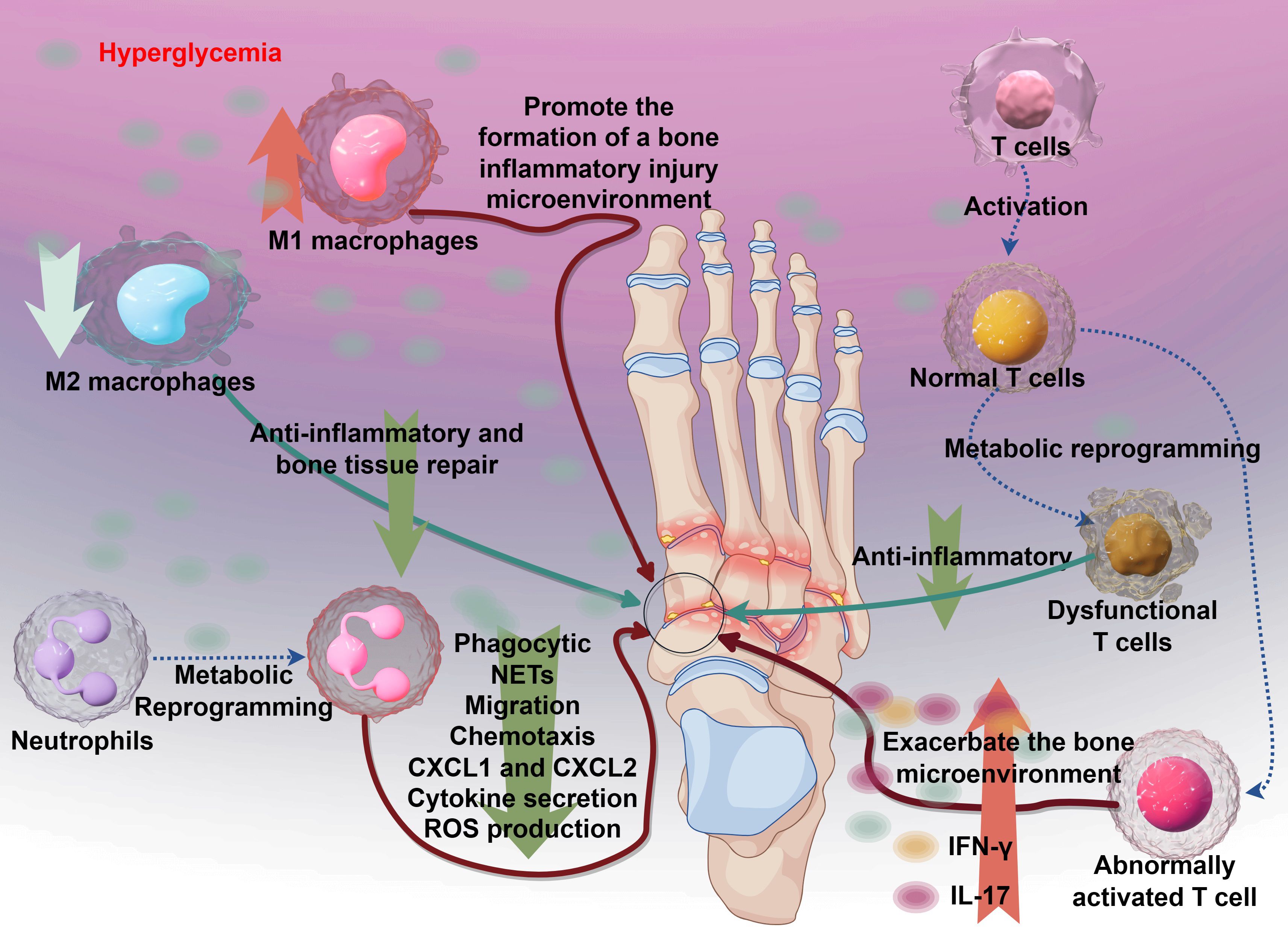
Figure 3. The immune mechanisms underlying diabetic osteomyelitis and the dysregulation of key immune cells. Hyperglycemia initiates the process by promoting the formation of a bone inflammatory injury microenvironment. This leads to aberrant T cell activation, resulting in dysfunctional T cells that exacerbate the bone microenvironment instead of resolving inflammation. Concurrently, metabolic reprogramming alters immune responses: M1 macrophages drive pro-inflammatory reactions, while M2 macrophages contribute to anti-inflammatory and bone tissue repair. Neutrophils exhibit impaired function, with reduced phagocytic activity, aberrant NETS formation, and disrupted migration and chemotaxis (mediated by CXCL1 and CXCL2), alongside enhanced cytokine secretion and ROS production. Collectively, these immune perturbations amplify tissue damage and hinder resolution of infection in diabetic osteomyelitis.
4.2.1 M1/M2 polarization of macrophages
Macrophages in the immune system exhibit high plasticity, differentiating into pro-inflammatory M1 or anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages under the mediation of various cytokines in the immune microenvironment (Davis et al., 2013). Glycolysis is critical for M1 activation and serves as the core pathway for the antibacterial and antitumor functions of M1 macrophages (Corrado et al., 2020). Under hyperglycemic conditions, bone marrow-derived macrophages and monocytes exhibit enhanced glycolysis and oxidative responses, with altered oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) and modified hexokinase II (HK2) activity in M1 macrophages. Although M1 polarization contributes to microbial killing, excessive M1 activation exacerbates bone destruction in diabetic osteomyelitis. Additionally, bacterial infections in diabetic osteomyelitis may further stimulate these pathways by activating nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) in B cells. Persistent inflammation at the infection site recruits more macrophages and promotes M1 polarization (Case et al., 2021; Liu H. et al., 2023), forming a vicious cycle. Given that the primary feature of M1 polarization is the upregulation of glycolytic enzymes, including phosphofructokinase (PFK1 and PFK2) isoforms, PFK-catalyzed reactions are irreversible key steps in glycolysis. Inhibiting PFK2 can reduce the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2), ultimately suppressing M1 macrophage polarization. Phosphofructokinase-2/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3) is also an important regulatory target, and its inhibition significantly suppresses downstream glycolytic reactions and M1 macrophage activation (Cui et al., 2015; De Rosa et al., 2015).
In contrast, M2 macrophages preferentially utilize oxidative phosphorylation to maintain their anti-inflammatory and reparative functions (Li et al., 2021). Studies indicate that M2 polarization enhances collagen deposition, angiogenesis, and wound healing. For example, M2 macrophage-derived exosomes (M2D-Exos) promote osteogenic differentiation both in vitro and in vivo. M2D-Exos containing miR-5106 may inhibit salt-inducible kinase 2 (SIK2) expression via the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) signaling pathway to stimulate angiogenesis (Chen et al., 2023). It has also been reported that M2D-Exos reduce adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) via the miR-690/IRS-1/TAZ axis (Li et al., 2021), suggesting that M2D-Exos promote bone repair through metabolic reprogramming pathways (MacKenna et al., 2022). However, in diabetic osteomyelitis, M2 macrophages are not predominant, leading to a significant reduction in their ability to clear apoptotic cells and suppress inflammatory damage induced by IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, and TGF-β. This manifests in the body as T lymphocyte recruitment and granuloma formation in bone marrow tissue (Lawrence and Gilroy, 2007; Murray et al., 2014), further activating downstream chronic innate immune activation and low-grade inflammation (Hotamisligil, 2006; Alghamdi et al., 2023), accelerating the progression of diabetic osteomyelitis.
4.2.2 Neutrophil chemotaxis
Neutrophils are the most abundant white blood cells in the immune system and possess multiple critical immune functions. During infection and inflammation, neutrophils participate in host defense through mechanisms such as chemotaxis, phagocytosis (Liu J. et al., 2023), oxidative bursts (Guo et al., 2024), and neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation (Abuaita et al., 2021). The multifaceted roles of neutrophils in infection defense and their importance in maintaining immune homeostasis make them key targets for studying immune-related diseases. Studies indicate that neutrophil dysfunction may contribute to the development of various diseases, such as autoimmune disorders and chronic inflammation (Simmons et al., 2025). Chemotaxis is a critical mechanism by which neutrophils respond to infections, as they are attracted to infection sites by chemical signals (e.g., bacterial compounds or inflammatory mediators), enabling rapid aggregation and function (Trivedi et al., 2021). During this process, neutrophil surface receptors recognize pathogens and their products, initiating intracellular signaling pathways that enhance antibacterial capabilities.
As the first line of defense in the immune system, neutrophils rely heavily on metabolic pathways during immune responses. Regarding glycolysis, studies show that activated neutrophils primarily depend on glycolysis to generate energy to meet the demands of rapid responses. Activated neutrophils increase glucose uptake and metabolism, promoting energy production and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, thereby enhancing their bactericidal capacity (Toller-Kawahisa and O’Neill, 2022). Additionally, glycolysis not only provides energy but also enhances antibacterial effects by promoting NET formation (Calo et al., 2025). In terms of oxidative phosphorylation, although neutrophils are traditionally considered reliant on glycolysis, recent studies have found that they can also utilize oxidative phosphorylation under specific conditions. This shift plays a critical role in neutrophil differentiation and functional regulation. For example, mature neutrophils switch to oxidative phosphorylation-dominated metabolism under hypoxic conditions to adapt to the tumor microenvironment (Huang et al., 2025). This metabolic adaptability affects not only neutrophil energy metabolism but also their role in tumor progression. Fatty acid oxidation is another critical component of neutrophil metabolism, particularly in chronic inflammation and tumor microenvironments. Neutrophils can rely on fatty acid oxidation to support energy supply, especially in nutrient-limited conditions (Calo et al., 2025). Moreover, fatty acid oxidation is closely associated with neutrophil antibacterial activity, chemotaxis, and NET formation, and these functions may be altered in different pathological states.
Neutrophil function is largely regulated by their metabolic state. Metabolic reprogramming enables these cells to adjust energy production and functional performance in response to microenvironmental changes, addressing various physiological and pathological challenges. For instance, during acute infections, neutrophils rapidly generate ATP and ROS through glycolysis to enhance pathogen clearance (Jiang et al., 2022). These metabolic changes affect not only energy supply but also cellular signaling and function execution. In chronic inflammation or tumor microenvironments, neutrophil metabolism undergoes significant changes. For example, tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) often exhibit metabolic reprogramming, relying primarily on enhanced glycolysis and fatty acid oxidation, leading to immunosuppressive functions (Lee et al., 2024). This reprogramming enables neutrophils to protect tumor cells and suppress anti-tumor immune responses, promoting tumor growth and metastasis.
Additionally, metabolic state is closely linked to neutrophil survival and death. Different metabolic pathways regulate neutrophil lifespan through mechanisms such as apoptosis and autophagy. For example, studies suggest that enhanced glycolysis can prolong neutrophil lifespan by delaying apoptosis, a regulation particularly significant in infection and inflammation contexts (Leblanc et al., 2024). In hyperglycemic conditions, neutrophil metabolism undergoes significant changes, primarily characterized by enhanced glycolysis and increased oxidative stress. Elevated intracellular glucose concentrations in hyperglycemia stimulate neutrophils to enhance energy production via glycolysis, a process closely linked to NADPH oxidase activation (Joshi et al., 2020). Studies indicate that hyperglycemia-induced glucose metabolism alterations lead to excessive ROS production by neutrophils, triggering oxidative stress responses that impair neutrophil survival and function (Cázares-Preciado et al., 2024).
Metabolic abnormalities extend beyond enhanced glycolysis to include changes in fatty acid metabolism. In hyperglycemia, neutrophil energy metabolism shifts from primarily glycolysis to fatty acid oxidation, which sustains cellular activity to some extent but may also lead to functional dysregulation. For example, in diabetic patients, metabolic reprogramming significantly weakens neutrophil antibacterial capacity, manifesting as reduced phagocytosis and NET formation (Li et al., 2023; Jolibois et al., 2024). This metabolic reprogramming increases the persistence and severity of inflammatory responses in diabetic patients, making them more susceptible to infections (Sun et al., 2025).
Metabolic abnormalities may also lead to neutrophil dysfunction, characterized by reduced migration, chemotaxis, and cytokine secretion, accelerating the progression of diabetic osteomyelitis. For instance, in hyperglycemia, the expression of chemokines CXCL1 and CXCL2 is suppressed, impairing neutrophil recruitment and the effectiveness of inflammatory responses (Thimmappa et al., 2023). Additionally, reduced ROS production capacity in diabetic neutrophils further weakens their bacterial clearance ability, a phenomenon termed “diabetes-associated immunosuppression” (Darwitz et al., 2024).
4.2.3 T lymphocyte activation
In the resting state, T cells primarily rely on oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) for energy production, a process occurring in mitochondria to support basic physiological functions and maintain metabolic homeostasis. However, upon activation, T cells undergo significant metabolic reprogramming. Studies show that activated T cells enhance glycolysis to meet the energy demands of rapid proliferation and effector functions, favoring glycolysis even under aerobic conditions, a phenomenon known as the Warburg effect (Romero-Carramiñana et al., 2024). This metabolic shift not only supports cell activation but also provides the energy and biosynthetic precursors necessary for cytokine synthesis and proliferation. Through glycolysis, T cells rapidly produce ATP and lactate, with lactate accumulation further influencing the microenvironment and immune responses (Liu et al., 2022). Additionally, the balance between oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis is critical for T cell function, and its disruption may lead to T cell exhaustion and dysfunction, particularly pronounced in metabolic diseases like diabetes (Cao et al., 2024).
In the diabetic state, hyperglycemia and metabolic dysregulation cause T cell metabolic abnormalities, significantly impairing their activation and effector functions. Studies indicate that T cells in diabetic patients exhibit defective metabolic reprogramming, leading to suppressed functions and reduced anti-infection capabilities (Cao et al., 2024; Romero-Carramiñana et al., 2024). Metabolic abnormalities may cause T cell exhaustion and dysfunction, closely linked to chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases. Notably, lactate accumulation can modulate the immune microenvironment, suppressing effector T cell functions while promoting regulatory T cell activity, thus influencing inflammation progression (Moraly et al., 2024).
Activated T cells play a critical role in the pathogenesis of diabetic osteomyelitis. Studies show that these cells secrete various pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and interleukin-17 (IL-17), which promote local inflammatory responses in osteomyelitis, leading to bone tissue destruction. For example, IFN-γ enhances macrophage activity, exacerbating local inflammation, while IL-17 stimulates fibroblast and osteoclast proliferation and activation, accelerating bone resorption (Leney-Greene et al., 2020; Schwager et al., 2021). As pro-inflammatory cytokines increase, osteoclast activity is significantly enhanced, leading to further bone destruction and lesion expansion. Meanwhile, interactions between immune cells and bone cells exacerbate this pathological progression, forming a vicious cycle that aggravates diabetic osteomyelitis (Waugh et al., 2023; Szabó et al., 2024).
Additionally, metabolic abnormalities in diabetic patients may impair T cell function, reducing their response to infections. The hyperglycemic environment induces T cell metabolic reprogramming, affecting proliferation and effector functions, thereby weakening immune responses and increasing the risk of osteomyelitis recurrence (Yang et al., 2023; Reed et al., 2025). This chronic inflammatory state not only sustains T cell activation but also forms a self-reinforcing cycle, further aggravating the pathological state of osteomyelitis.
4.3 Role of immune cell metabolic reprogramming in bacterial infections of diabetic osteomyelitis
The occurrence and progression of diabetic osteomyelitis extend beyond simple bacterial infections, fundamentally representing a complex interaction between pathogens and the host immune system in a unique environment of metabolic dysregulation. The diabetic metabolic microenvironment, characterized by hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and chronic inflammation, profoundly reprograms the metabolic homeostasis and functional states of various immune cells. This intrinsic cellular metabolic dysregulation, combined with bacterial strategies to actively manipulate host metabolism for survival, collectively leads to immune response failure and the onset of infections.
4.3.1 Bacterial immune adaptation features
As previously described, diabetic osteomyelitis is accompanied by immune cell metabolic reprogramming, which limits their function in responding to infections and inflammation. On the other hand, bacteria, as a factor in osteomyelitis infections, influence host immune cell function and alter immune responses by releasing metabolic products. For instance, bacterial exogenous metabolites (e.g., the bacterial “exometabolome”) have been found to suppress host immune responses to some extent, thereby promoting bacterial survival and pathogenicity (Chugh et al., 2025). For example, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and other metabolites can promote immune tolerance and anti-inflammatory responses by activating specific host immune pathways (Fang et al., 2025). Bacteria manipulate host cell metabolism to enhance their adaptability and survival in the host immune environment, such as by promoting glycolysis and inhibiting oxidative phosphorylation to regulate macrophage metabolism (Quan et al., 2023), thereby favoring bacterial growth rather than eliciting effective immune responses (Ahator et al., 2024). These findings suggest that bacterial metabolites are critical signaling molecules in regulating host immune metabolism. This immune adaptation mechanism not only enhances bacterial survival but also enables their long-term persistence in the host, leading to chronic infections.
4.3.2 Macrophage metabolic reprogramming and bacterial clearance
M1 macrophages generate energy and metabolic intermediates through enhanced glycolysis to support rapid proliferation, inflammatory responses, and bacterial killing, a hallmark feature of their role as innate immune cells (Malla et al., 2025). For instance, enhanced glycolysis is closely associated with bacterial phagocytosis and subsequent killing, particularly in managing infections like Escherichia coli, where glycolytic metabolites are critical for macrophage antibacterial activity (Yang et al., 2021). In contrast, M2 macrophages primarily promote tissue healing and reduce excessive inflammation through anti-inflammatory cytokine secretion post-infection (Zhang Z. et al., 2024). Additionally, M2 macrophage metabolic activity is linked to bacterial clearance efficiency, particularly in chronic infection scenarios, where their metabolic reprogramming influences responses to pathogens (Lane et al., 2023). However, in diabetic patients, hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and inflammation disrupt the balance between M1 and M2 macrophage functions. Macrophages exhibit enhanced M1 characteristics while M2 functions are suppressed, leading to reduced anti-infection capacity (Hegde et al., 2024). This metabolic imbalance impairs macrophage antibacterial activity, increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications (Xu et al., 2025).
4.3.3 T cell metabolic reprogramming and immune response
Unlike macrophages, T cells do not directly participate in bacterial killing but clear virus- or bacteria-infected cells through cellular immunity, with their activation and function heavily dependent on their metabolic state. Upon antigen stimulation, T cell metabolic pathways shift from glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation. Specifically, effector T cells typically rely on glycolysis to meet the energy demands of rapid proliferation, while memory T cells preferentially utilize oxidative phosphorylation to maintain longevity and functionality (Levine et al., 2021).
In the pathological environment of diabetes, T cell metabolic abnormalities significantly impair their immune response capacity. Factors such as hyperglycemia, chronic inflammation, and metabolic syndrome may lead to T cell dysfunction, manifesting as reduced proliferation and cytokine production (Gao et al., 2024; Qiu et al., 2025). For instance, in diabetic mouse models, T cell metabolic reprogramming is inhibited, significantly weakening their anti-infection capacity, likely due to imbalanced metabolic competition and insufficient energy supply (Ricci, 2025). Additionally, metabolic regulation impacts the balance between regulatory T cells (Tregs) and effector T cells (Teffs). Tregs primarily rely on oxidative phosphorylation and fatty acid oxidation to maintain their suppressive functions, while Teffs enhance activity through activated glycolytic pathways (He et al., 2021; Noble et al., 2024). For example, Treg function and proliferation are influenced by their metabolic state, and excessive glycolysis may suppress Treg function, promoting autoimmune disease development (Röring et al., 2024). Diabetic osteomyelitis involves immune dysregulation, and changes in T cell metabolic reprogramming further exacerbate inflammatory responses and bone tissue damage.
4.3.4 Neutrophil metabolic reprogramming and inflammatory response
Neutrophils, a critical component of the innate immune system, play key roles in combating infections and inflammatory responses. Their metabolic state directly affects chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and bactericidal capacity. Recent studies indicate that neutrophils exhibit diverse metabolic adaptability beyond traditional glycolysis. In inflammatory microenvironments, where oxygen and nutrients are limited, neutrophils must adjust their metabolic pathways to maintain function. Studies have found that neutrophils at inflammatory sites reprogram their metabolic pathways to generate energy and support antibacterial functions (Morrison et al., 2023). For instance, mitochondrial metabolism plays a significant role in supporting neutrophil migration, neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation, and bacterial killing (Maldarelli and Noto, 2024). Upon activation, neutrophils rapidly reprogram their metabolic pathways to enhance pathogen responses. This metabolic reprogramming not only affects energy production but also alters the nature of their inflammatory responses, enabling task execution in diverse microenvironments. In chronic disease states like diabetes, neutrophil glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation are impaired, suppressing their metabolic functions, reducing antibacterial capacity, and inducing infections (Holder et al., 2025). Concurrently, neutrophil metabolic abnormalities not only weaken their function but also exacerbate chronic inflammation, forming a vicious cycle.
4.3.4 Potential significance of the microbiome–metabolism–immunity axis in the treatment of DO
In recent years, studies have gradually revealed the relationship between the gut microbiota and bone metabolism, referred to as the “gut–bone axis.” Evidence indicates that microorganisms and their metabolites not only affect the local intestinal environment but also regulate immune responses and metabolic balance in bone tissue through immune, endocrine, and metabolic pathways, thereby influencing bone health and disease progression (Grüner et al., 2023; Chen Y. et al., 2025). For example, postmenopausal osteoporosis (PMOP), which is closely associated with estrogen deficiency, is also characterized by dysbiosis of the gut microbiota and imbalance in Th17/Treg ratios. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) regulate T-cell differentiation through specific receptors, suggesting that modulation of the microbiota and its metabolites may provide novel strategies for PMOP therapy (Chen Y. et al., 2025). Moreover, gut microbial diversity and functional status directly affect bone mineral density and remodeling, and in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), dysbiosis is strongly associated with bone-related complications such as osteoporosis and arthritis (Grüner et al., 2023).
Microbial metabolites such as SCFAs, bile acids, and tryptophan derivatives can reshape immune cell metabolism and regulate their functions (Michaudel and Sokol, 2020; Wang et al., 2023). Specifically, SCFAs promote Treg differentiation while suppressing pro-inflammatory cells; bile acid metabolites (e.g., GLCA) enhance Treg proliferation via nuclear receptors and induce osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (Cai et al., 2024); tryptophan derivatives act through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) to improve gut barrier function and modulate immune responses (Fu et al., 2023). In addition, both gut and oral microbiota can regulate the local bone immune environment via the “gut–bone axis.” Their metabolites may translocate to bone tissue, leading to aberrant immune cell activation, bone resorption, and inflammation (Jia et al., 2021; Han et al., 2023).
More recently, increasing attention has been paid to the presence and characteristics of local bone microbiota. Although bone was traditionally considered a sterile environment, accumulating evidence suggests otherwise. The bone microbiota displays considerable diversity, including major bacterial phyla such as Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Firmicutes, and Bacteroidetes (Emmons et al., 2020). These microbes may contribute to the maintenance of the local bone environment and, through their metabolites, regulate the bone immune microenvironment. Metabolic activities within bone generate bioactive molecules—such as SCFAs, bile acid derivatives, and tryptophan metabolites—that influence local immune cell function and bone metabolic processes (Hansdah and Lui, 2024; Qiao et al., 2025).
Bone microbial metabolites modulate the activity of immune cells such as T cells, macrophages, and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs), thereby shaping the bone immune microenvironment. For example, butyrate promotes Treg expansion and suppresses inflammation, protecting bone tissue from excessive inflammatory damage (Kermgard et al., 2021; He et al., 2025). Certain microbial metabolites, such as deoxycholic acid, regulate hematopoietic progenitors in the bone marrow, enhancing monocyte numbers and function to support immune homeostasis (Burgess et al., 2020). Conversely, dysbiosis of the local bone microbiota may create a pro-inflammatory milieu, promoting bone resorption and contributing to bone metabolic disorders and inflammatory bone diseases (Han et al., 2023; Dmytrenko et al., 2024).
The interactions between the bone microbiota, metabolism, and inflammation underscore the complexity of the microbiota–immune–bone metabolism axis. Microorganisms and their metabolites within bone tissue regulate local immune responses, thereby influencing the balance between bone formation and resorption. For instance, gut microbiota-derived metabolites can indirectly affect bone mineral density and strength (Castaneda et al., 2020; Luna et al., 2021). Meanwhile, bone-resident microbiota may activate immune cells to release pro- or anti-inflammatory factors, modulating bone matrix remodeling (Pianko and Golob, 2022). In pathological states such as osteoporosis, bone metastases, and bone marrow disorders, changes in the composition and function of the bone microbiota are closely linked to immune dysregulation, suggesting a potential regulatory role in the pathogenesis of bone diseases (Lian et al., 2022; Sevcikova et al., 2024).
In summary, gut and bone microbiota, together with their metabolites, regulate immune cell metabolic reprogramming through complex signaling and metabolic networks. They are critical for maintaining immune homeostasis, modulating inflammation, and controlling bone metabolism. Elucidating these mechanisms not only highlights the role of the “gut–bone axis” in health and disease but also provides a theoretical basis for developing therapeutic strategies targeting microbiota and their metabolites (Grüner et al., 2023; Chen Y. et al., 2025).
5 Immunomodulatory perspective on the treatment and outlook for diabetic osteomyelitis
5.1 Current treatment strategies and their limitations
Given that the core pathogenesis of diabetic foot osteomyelitis (DFO) involves immunosuppression and bacterial infections induced by hyperglycemia, clinical management of DFO primarily focuses on glycemic control, antibiotic therapy, and surgical debridement, with antibiotic therapy being the most critical. DFO is typically caused by mixed infections involving multiple pathogens, commonly including Staphylococcus aureus and other Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, making the antimicrobial spectrum of antibiotics a cornerstone of treatment (Aicale et al., 2020). Beyond traditional antibiotic combinations, the use of anti-biofilm antibiotics, such as rifampin, significantly improves healing outcomes and reduces the risk of infection recurrence (Senneville et al., 2023). Antibiotic-impregnated bone cement can also be used during tissue reconstruction, effectively shortening healing time, hospital stays, and infection recurrence rates (Mendame Ehya et al., 2021). Some clinical cases demonstrate that combining these novel therapies with traditional antibiotics can effectively reduce hospitalization time and amputation rates (Hassanin et al., 2025). The widespread use of novel drugs like dalbavancin effectively controls multidrug-resistant bacterial infections and reduces hospitalization duration (Loupa et al., 2020). Additionally, studies have found that rifampin, as an adjuvant therapy, significantly improves healing rates in diabetic foot osteomyelitis and offers better efficacy than traditional treatments (Bessesen et al., 2020). However, drug interactions and patient comorbidities limit its clinical application, necessitating further research to explore safer alternatives, such as rifabutin (Mallarino-Haeger et al., 2024). Notably, the lack of high-quality clinical trial data for medical and surgical treatments of diabetic foot osteomyelitis poses challenges in selecting optimal treatment strategies (Tardáguila-García et al., 2021).
The pathogenesis of DO is rooted in hyperglycemia, and the chronic low-grade inflammatory (CLGI) state in patients continuously increases infection risk and delays wound healing. Therefore, glycemic control is essential during DO treatment to prevent complications (Gramberg et al., 2024). Poor glycemic control exacerbates DO clinical symptoms (Nilesh et al., 2022). Interventions targeting the metabolic state of diabetic patients can reduce inflammation in osteomyelitis, thereby promoting healing (Pakkiyaretnam and Chong, 2023). Compared to general infections, DO often accelerates gangrene development, necessitating surgical debridement in severe cases to remove infected bone tissue, prevent infection spread, and promote healing (Jing et al., 2025). Early surgical intervention significantly improves DO prognosis (Venkatesan and Rangasamy, 2023). Among patients undergoing surgical debridement, approximately 93.6% achieve complete healing, with only a minority requiring amputation (Moosa et al., 2023).
Overall, traditional antibiotic therapy and surgical debridement remain the primary methods for DO management, but immunomodulatory and metabolic regulation approaches offer new perspectives and possibilities for improving patient outcomes. These approaches demonstrate potential to enhance efficacy when combined with traditional treatments (Meyer-Schwickerath et al., 2023), representing a critical entry point for future DO therapies.
5.2 Immunomodulatory therapies for diabetic osteomyelitis
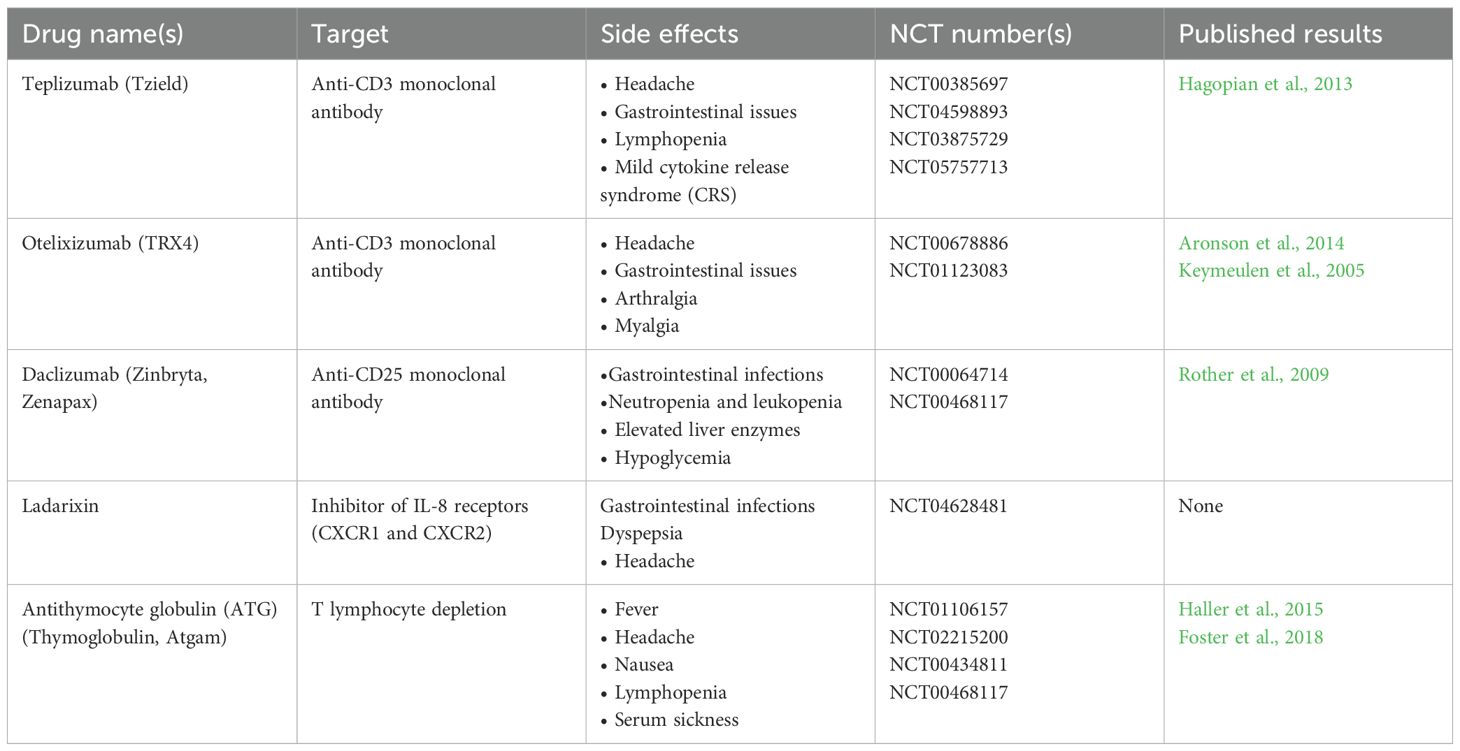
As previously described, although DFO manifests as bacterial infections, its core pathology stems from immune system dysfunction caused by the CLGI state. From an immunomodulatory perspective, suppressing chronic inflammatory damage and enhancing immune responses can potentially improve DFO prognosis. Existing studies show that glucocorticoids reduce inflammation by suppressing immune cell activity, thereby lowering infection susceptibility (Lipsky et al., 2012). Biologics achieve immunomodulation by neutralizing specific pro-inflammatory cytokines (Mens et al., 2023). A retrospective study reported that diabetic foot osteomyelitis patients treated with bioactive glass (S53P4) achieved significantly higher healing rates than those receiving conventional treatment (90% vs. 61.9%) (De Giglio et al., 2021). Patients treated with small-molecule immunomodulatory agents exhibited better infection control and faster healing compared to controls (Zhang et al., 2021), highlighting their value in managing refractory infections. Notably, current immunomodulatory agents for diabetes primarily target type 1 diabetes (T1D) [summarized in Table 2 (Ajmal et al., 2024)]. Few immunomodulatory agents are available for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), significantly limiting their application in DFO treatment. This is because T1D is an autoimmune disease characterized by T-cell-mediated specific attacks on pancreatic β-cells, allowing precise interventions like anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies or antigen vaccines to delay or prevent onset (Mauvais and van Endert, 2025). In contrast, T2DM is driven by metabolic syndrome, with insulin resistance and β-cell failure, where inflammation is a chronic, low-grade, multi-cytokine “background noise” without a single immune target or clear biomarkers like autoantibodies. As described earlier, the CLGI state in T2DM creates a complex interplay of excessive inflammation and immunosuppression, which cannot be simply managed with immune agonists or suppressors. Moreover, immunomodulation carries risks of increased infections, tumors, and cardiovascular events, particularly in chronic conditions like DFO requiring long-term intervention, further limiting the clinical application and development of immunomodulatory therapies. Nevertheless, their potential therapeutic benefits have prompted numerous research efforts.
For instance, N-acetylcysteine (NAC), an immunometabolic regulator, significantly reduces inflammation in DFO patients and accelerates antibiotic treatment responses (Hooshmand Gharabagh et al., 2025). Other metabolism-related biomarkers, such as serum lipids and amino acids, can serve as monitoring indicators to guide clinical decision-making and improve DFO management (Boucher et al., 2024; Roh et al., 2024). Clinical trials have also explored personalized immunomodulatory therapies for DFO. For example, a diabetic cohort study showed that patients receiving small-molecule immunomodulatory agents had superior infection control and healing rates compared to controls (Osório et al., 2023). However, the complex immune characteristics of T2DM significantly increase the difficulty of DFO immunotherapy, making “risk-benefit” assessments critical for clinical decision-making.
Notably, leveraging the immune characteristics of DFO, potential treatment approaches are being explored and optimized. Nanodrug delivery systems enhance targeting and biocompatibility, with nanoparticle carriers enabling localized delivery of immunomodulatory agents to infection sites while minimizing systemic exposure. Gene-editing tools like CRISPR show promise in correcting diabetes-related immune defects, with preclinical studies indicating improved antibacterial responses and reduced osteomyelitis incidence (Tubin et al., 2023). Cell therapies also hold translational potential. Transplantation of umbilical cord blood or bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) reshapes the immune microenvironment and enhances anti-infection capacity by secreting trophic factors, thereby improving osteogenesis in diabetic patients (Yan, 2024; Freitas et al., 2025). However, these approaches require extensive preclinical validation before clinical use, and systemic immunotherapies for DFO remain largely conceptual. In contrast, interventions targeting metabolic reprogramming are relatively simple and controllable. Modulating the metabolic characteristics of the DFO environment to influence downstream immune cell functions represents a promising approach to address the complex immune background of DFO.
5.3 Metabolic interventions for diabetic osteomyelitis
The core pathogenesis of DFO is the CLGI state under a hyperglycemic background, making glycemic stability a primary goal in treating diabetic patients, particularly those with osteomyelitis. Studies indicate that good glycemic control reduces bone infection risk and promotes healing in diabetic patients (Khandelwal et al., 2022; Jaroenarpornwatana et al., 2023). Additionally, maintaining glycemic stability reduces postoperative complications, enhances recovery, and lowers infection rates. Beyond direct pharmacological interventions, auxiliary metabolic regulation therapies, such as diet, exercise, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy, are critical for alleviating DFO clinical symptoms.
Balanced diets improve the metabolic state of diabetic patients, reducing bone infection risk. High-fiber, low-sugar, low-fat dietary patterns are foundational for maintaining healthy blood glucose levels. For instance, the Mediterranean diet, characterized by abundant fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, has been shown to improve metabolic markers in diabetic patients, reducing cardiovascular disease and bone infection risks (Szymczak et al., 2023). Nutritional interventions, such as vitamin D and calcium supplementation, effectively promote bone healing—vitamin D not only aids calcium absorption but also enhances osteoblast function. Thus, personalized dietary plans tailored to the specific needs of diabetic patients are critical strategies for preventing bone infections (Iles et al., 2021). Additionally, moderate exercise effectively improves metabolic markers in diabetic patients (Silva et al., 2024), enhances blood circulation, and boosts immune function (Seidu et al., 2021). Exercise also stimulates bone cell proliferation and differentiation, increasing bone mechanical strength (Chang et al., 2022), which is beneficial for accelerating DFO healing. Furthermore, exercise reduces chronic inflammation levels, mitigating diabetes-related osteoporosis and bone infection risks. For example, studies show that diabetic patients engaging in regular weight-bearing exercise exhibit significantly higher bone density and strength than non-exercisers, highlighting exercise’s critical role in bone health (Kawanishi et al., 2022; D’Haese et al., 2024). Blood oxygen metabolism is another key approach for improving DO. Diabetic patients often experience microvascular complications, leading to poor blood circulation and impaired bone tissue blood supply and nutrient delivery. Local treatments using bioactive materials like bioactive glass enhance local blood circulation, improve oxygenation, and accelerate bone healing (De Giglio et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021). The classic oxygen metabolism regulation method is hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), where high-concentration oxygen improves tissue oxygenation and promotes angiogenesis. In diabetic patients, HBOT effectively increases local oxygen partial pressure, improves microcirculation, and reduces infection occurrence and progression. Despite its lower applicability, higher costs, and significant individual variability, HBOT remains an important method for regulating blood oxygen metabolism (Huang et al., 2021).
6 Conclusion
As our understanding of the mechanisms behind immunometabolic reprogramming deepens, researchers have increasingly recognized that immune cells in diabetic patients often exhibit metabolic dysfunction when confronted with infections. This dysfunction not only impairs the immune system’s ability to combat pathogens but also hinders the regeneration of bone tissue. This understanding is crucial in diabetic osteomyelitis, as the metabolic state of immune cells directly influences the inflammatory response, infection resolution, and bone healing. Current research has highlighted the involvement of multiple signaling pathways and metabolic routes in this process. Key factors such as inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress, and nutritional status influence immunometabolic reprogramming, leading to chronic inflammation and impaired immune cell function. In clinical practice, these factors must be considered to develop more effective treatment strategies. While traditional therapies, such as antibiotics and surgical debridement, continue to play a pivotal role, they often fall short in addressing the underlying immune and metabolic dysfunctions that exacerbate diabetic osteomyelitis. Emerging treatments that target specific immunometabolic pathways offer significant promise. For example, immunomodulatory therapies that regulate immune responses and metabolic interventions aimed at restoring normal immune cell function may complement traditional therapies. These strategies represent a promising direction for future clinical approaches, which could improve patient outcomes by addressing both the infection and the underlying immune-metabolic disturbances. However, the complexity of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and its associated chronic low-grade inflammation pose challenges in developing and implementing these novel therapies. The immunosuppressive environment in diabetic patients complicates the identification of specific therapeutic targets and increases the difficulty of achieving long-term efficacy. Thus, future clinical research should focus on personalized treatment strategies that integrate both metabolic and immunomodulatory approaches. Multidisciplinary collaboration and large-scale, randomized clinical trials will be critical in validating these new treatments and translating laboratory findings into effective clinical practices. By bridging the gap between basic research and clinical applications, we can enhance our ability to manage and treat diabetic osteomyelitis, improving both the quality of life and clinical outcomes for patients.
Author contributions
HZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Visualization, Investigation, Validation, Software, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. Z-SF: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Resources, Visualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. S-NW: Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Investigation. S-YY: Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Validation, Visualization, Methodology. A-NW: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Data curation, Project administration, Validation. J-TL: Methodology, Supervision, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Data curation, Resources, Software, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Project administration, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Integrative Medicine Research on Diabetes in Liaoning Province. Liaoning Province Science and Technology Plan: Applied Basic Research Program No. 2023010033-JH2/1013: Research on the Optimized Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Protocol for Prediabetes Based on the Therapeutic Methods of Strengthening the Spleen to Resolve Dampness and Activating Blood Circulation to Disperse Stasis. Liaoning Province Science and Technology Plan Project 2024 Joint Fund Project Doctoral Research Start-up Project No. 2023-BSBA-216: Research and Development of a Remote Pulse Reproduction Device Based on Traditional Chinese Medicine Pulse Diagnosis and Objective Study of Pulse Patterns in Different Syndromes of Metabolic Syndrome.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abuaita, B. H., Sule, G. J., Schultz, T. L., Gao, F., Knight, J. S., and O’Riordan, M. X. (2021). The IRE1α Stress signaling axis is a key regulator of neutrophil antimicrobial effector function. J. Immunol. 207, 210–220. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2001321
Ahator, S. D., Hegstad, K., Lentz, C. S., and Johannessen, M. (2024). Deciphering Staphylococcus aureus-host dynamics using dual activity-based protein profiling of ATP-interacting proteins. mSystems 9, e0017924. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00179-24
Aicale, R., Cipollaro, L., Esposito, S., and Maffulli, N. (2020). An evidence based narrative review on treatment of diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Surgeon 18, 311–320. doi: 10.1016/j.surge.2020.01.007
Ajmal, N., Bogart, M. C., Khan, P., Max-Harry, I. M., Healy, A. M., and Nunemaker, C. S. (2024). Identifying promising immunomodulators for type 1 diabetes (T1D) and islet transplantation. J. Diabetes Res. 2024, 5151171. doi: 10.1155/jdr/5151171
Albiero, M. and Baragetti, A. (2025). Exploring neutrophils as therapeutic targets in cardiometabolic diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 46, 102–116. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2024.12.003
Albuquerque-Souza, E. and Dalli, J. (2025). Specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators in gut immunophysiology: from dietary precursors to inflammation resolution. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 28, 96–103. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000001103
Alexander, M., Cho, E., Gliozheni, E., Salem, Y., Cheung, J., and Ichii, H. (2024). Pathology of diabetes-induced immune dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 7105. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137105
Al Ghaithi, A., Husband, J., Al Bimani, A., Al Kindi, M., and Al Maskari, S. (2025). Biofilm-Induced Bone Degradation in Osteomyelitis: Insights from a comprehensive ex vivo pathogen interaction study. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 25, 98–104. doi: 10.18295/squmj.10.2024.053
Alghamdi, M., Gutierrez, J., and Komarnytsky, S. (2023). Essential minerals and metabolic adaptation of immune cells. Nutrients 15, 123. doi: 10.3390/nu15010123
Aronson, R., Gottlieb, P. A., Christiansen, J. S., Donner, T. W., Bosi, E., Bode, B. W., et al. (2014). Low-dose otelixizumab anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody DEFEND-1 study: results of the randomized phase III study in recent-onset human type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 37, 2746–2754. doi: 10.2337/dc13-0327
Baker, M. L. and Cantley, L. G. (2025). Adding insult to injury: the spectrum of tubulointerstitial responses in acute kidney injury. J. Clin. Invest. 135, e188358. doi: 10.1172/JCI188358
Bakhtiyari, M., Liaghat, M., Aziziyan, F., Shapourian, H., Yahyazadeh, S., Alipour, M., et al. (2023). The role of bone marrow microenvironment (BMM) cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) progression: immune checkpoints, metabolic checkpoints, and signaling pathways. Cell communication signaling: CCS 21, 252. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01282-2
Balic, J. J., Albargy, H., Luu, K., Kirby, F. J., Jayasekara, W. S. N., Mansell, F., et al. (2020). STAT3 serine phosphorylation is required for TLR4 metabolic reprogramming and IL-1β expression. Nat. Commun. 11, 3816. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17669-5
Baud’Huin, M., Renault, R., Charrier, C., Riet, A., Moreau, A., Brion, R., et al. (2010). Interleukin-34 is expressed by giant cell tumours of bone and plays a key role in RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. J. Pathol. 221, 77–86. doi: 10.1002/path.2684
Bermejo Olano, M. D. M., Campelo Gutierrez, C., Hervas Gómez, R., Alfayate García, J. M., Sánchez Ríos, J. P., and Moreno Núñez, L. (2024). Risk factors associated with osteomyelitis due to Corynebacterium striatum in patients with diabetic foot. Med. Clin. (Barc) 162, 15–18. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2023.09.015
Bessesen, M. T., Doros, G., Henrie, A. M., Harrington, K. M., Hermos, J. A., Bonomo, R. A., et al. (2020). A multicenter randomized placebo controlled trial of rifampin to reduce pedal amputations for osteomyelitis in veterans with diabetes (VA INTREPID). BMC Infect. Dis. 20, 23. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4751-3
Bittman, K. S. (2022). Immune cell metabolic fitness for life. Antibodies (Basel) 11, 32. doi: 10.3390/antib11020032
Boucher, A., Pradier, M., Lafondesmurs, B., Thill, P., Patoz, P., Blondiaux, N., et al. (2024). Dalbavancin as salvage therapy in difficult-to-treat patients for diabetes-related foot osteomyelitis. Infect. Dis. Now 54, 104835. doi: 10.1016/j.idnow.2023.104835
Brennan, E., Kantharidis, P., Cooper, M. E., and Godson, C. (2021). Pro-resolving lipid mediators: regulators of inflammation, metabolism and kidney function. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 17, 725–739. doi: 10.1038/s41581-021-00454-y
Bui, T. I., Gill, A. L., Mooney, R. A., and Gill, S. R. (2022). Modulation of gut microbiota metabolism in obesity-related type 2 diabetes reduces osteomyelitis severity. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e0017022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00170-22
Burgess, S. L., Leslie, J. L., Uddin, J., Oakland, D. N., Gilchrist, C., Moreau, G. B., et al. (2020). Gut microbiome communication with bone marrow regulates susceptibility to amebiasis. J. Clin. Invest. 130, 4019–4024. doi: 10.1172/JCI133605
Butrico, C. E., Klopfenstein, N., Green, E. R., Johnson, J. R., Peck, S. H., Ibberson, C. B., et al. (2023). Hyperglycemia increases severity of staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis and influences bacterial genes required for survival in bone. Infect. Immun. 91, e0052922. doi: 10.1128/iai.00529-22
Cai, X., Li, Z., Yao, Y., Zheng, Y., Zhang, M., and Ye, Y. (2024). Glycolithocholic acid increases the frequency of circulating Tregs through constitutive androstane receptor to alleviate postmenopausal osteoporosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 219, 115951. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115951
Calo, G., Merech, F., Sabbione, F., Hauk, V., Lara, B., Doga, L., et al. (2025). Pregnancy entails a metabolic rewiring of maternal circulating neutrophils. J. Cell. Physiol. 240, e31502. doi: 10.1002/jcp.31502
Cao, H., Xiao, J., Baylink, D. J., Nguyen, V., Shim, N., Lee, J., et al. (2024). Development of a competitive nutrient-based T-cell immunotherapy designed to block the adaptive warburg effect in acute myeloid leukemia. Biomed. 12, 2250. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102250
Case, N. T., Duah, K., Larsen, B., Wong, C. J., Gingras, A. C., O’Meara, T. R., et al. (2021). The macrophage-derived protein PTMA induces filamentation of the human fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Cell Rep. 36, 109584. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109584
Castaneda, M., Strong, J. M., Alabi, D. A., and Hernandez, C. J. (2020). The gut microbiome and bone strength. Curr. osteoporosis Rep. 18, 677–683. doi: 10.1007/s11914-020-00627-x
Cázares-Preciado, J. A., López-Arredondo, A., Cruz-Cardenas, J. A., Luévano-Martínez, L. A., García-Rivas, G., Prado-Garcia, H., et al. (2024). Metabolic features of neutrophilic differentiation of HL-60 cells in hyperglycemic environments. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 12, e004181. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2024-004181
Cebrián-Prats, A., Pinto, A., González-Lafont, À., Fernandes, P. A., and Lluch, J. M. (2022). The role of acetylated cyclooxygenase-2 in the biosynthesis of resolvin precursors derived from eicosapentaenoic acid. Org Biomol Chem. 20, 1260–1274. doi: 10.1039/D1OB01932E
Chang, X., Xu, S., and Zhang, H. (2022). Regulation of bone health through physical exercise: Mechanisms and types. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 1029475. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1029475
Chen, J., Cui, N., He, S. H., Xia, C. Y., and Li, W. Q. (2025). Single-cell transcriptomics reveals metabolic remodeling and functional specialization in the immune microenvironment of bone tumors. J. Trans. Med. 23, 554. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06346-0
Chen, Y., Xie, Y., and Yu, X. (2025). Progress of research on the gut microbiome and its metabolite short-chain fatty acids in postmenopausal osteoporosis: a literature review. Front. Med. 19, 474–492. doi: 10.1007/s11684-025-1129-3
Chen, L., Yu, C., Xiong, Y., Chen, K., Liu, P., Panayi, A. C., et al. (2023). Multifunctional hydrogel enhances bone regeneration through sustained release of Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1α and exosomes. Bioact Mater 25, 460–471. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.07.030
Chugh, S., Létisse, F., and Neyrolles, O. (2025). The exometabolome as a hidden driver of bacterial virulence and pathogenesis. Trends Microbiol. 33, 546–557. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2024.11.009
Corrado, M., Edwards-Hicks, J., Villa, M., Flachsmann, L. J., Sanin, D. E., Jacobs, M., et al. (2020). Dynamic cardiolipin synthesis is required for CD8(+) T cell immunity. Cell Metab. 32, 981–995.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.003
Cui, G., Staron, M. M., Gray, S. M., Ho, P. C., Amezquita, R. A., Wu, J., et al. (2015). IL-7-induced glycerol transport and TAG synthesis promotes memory CD8+ T cell longevity. Cell 161, 750–761. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.021
D’Haese, S., Claes, L., de Laat, I., Van Campenhout, S., Deluyker, D., Heeren, E., et al. (2024). Moderate-intensity and high-intensity interval exercise training offer equal cardioprotection, with different mechanisms, during the development of type 2 diabetes in rats. Nutrients 16, 431. doi: 10.3390/nu16030431
Darwitz, B. P., Genito, C. J., and Thurlow, L. R. (2024). Triple threat: how diabetes results in worsened bacterial infections. Infect. Immun. 92, e0050923. doi: 10.1128/iai.00509-23
Davis, M. J., Tsang, T. M., Qiu, Y., Dayrit, J. K., Freij, J. B., Huffnagle, G. B., et al. (2013). Macrophage M1/M2 polarization dynamically adapts to changes in cytokine microenvironments in Cryptococcus neoformans infection. mBio 4, e00264-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00264-13
De Giglio, R., Di Vieste, G., Mondello, T., Balduzzi, G., Masserini, B., Formenti, I., et al. (2021). Efficacy and safety of bioactive glass S53P4 as a treatment for diabetic foot osteomyelitis. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 60, 292–296. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2020.06.029
Deng, C., Xiao, Y., Zhao, X., Li, H., Chen, Y., Ai, K., et al. (2025). Sequential targeting chondroitin sulfate-bilirubin nanomedicine attenuates osteoarthritis via reprogramming lipid metabolism in M1 macrophages. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 12, e2411911. doi: 10.1002/advs.202411911
De Rosa, V., Galgani, M., Porcellini, A., Colamatteo, A., Santopaolo, M., Zuchegna, C., et al. (2015). Glycolysis controls the induction of human regulatory T cells by modulating the expression of FOXP3 exon 2 splicing variants. Nat. Immunol. 16, 1174–1184. doi: 10.1038/ni.3269
Dmytrenko, G., Fernández-Solari, J., Correa, F., and De Laurentiis, A. (2024). Oxytocin alleviates periodontitis in adult rats. J. periodontal Res. 59, 280–288. doi: 10.1111/jre.13212
Dormer, K. J. and Gkotsoulias, E. (2022). The role of hemodynamic shear stress in healing chronic wounds. Wounds 34, 254–262. doi: 10.25270/wnds/21101
Emmons, A. L., Mundorff, A. Z., Keenan, S. W., Davoren, J., Andronowski, J., Carter, D. O., et al. (2020). Characterizing the postmortem human bone microbiome from surface-decomposed remains. PloS One 15, e0218636. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218636
Fang, H., Rodrigues, E. L. R., Barra, N. G., Kukje Zada, D., Robin, N., Mehra, A., et al. (2025). Postbiotic impact on host metabolism and immunity provides therapeutic potential in metabolic disease. Endocr. Rev. 46, 60–79. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnae025
Favoino, E., Urso, L., Serafino, A., Misceo, F., Catacchio, G., Prete, M., et al. (2021). HLA allele prevalence in disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs-responsive enthesitis and/or arthritis not fulfilling ASAS criteria: comparison with psoriatic and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis. J. Clin. Med. 10, 3006. doi: 10.3390/jcm10143006
Fortuny, L. and Sebastián, C. (2021). Sirtuins as metabolic regulators of immune cells phenotype and function. Genes (Basel) 12, 1698. doi: 10.3390/genes12111698
Foster, E. D., Bridges, N. D., Feurer, I. D., Eggerman, T. L., Hunsicker, L. G., and Alejandro, R. (2018). Improved health-related quality of life in a phase 3 islet transplantation trial in type 1 diabetes complicated by severe hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 41, 1001–1008. doi: 10.2337/dc17-1779
Fountas, A., Coulden, A., Fernández-García, S., Tsermoulas, G., Allotey, J., and Karavitaki, N. (2024). Central diabetes insipidus (vasopressin deficiency) after surgery for pituitary tumours: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 191, S1–s13. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvae084
Frazee, B. W. (2024). Diabetic foot infections in the emergency department. Emergency Med. Clinics North America 42, 267–285. doi: 10.1016/j.emc.2024.01.003
Freitas, B. F. A., Verchere, C. B., and Levings, M. K. (2025). Advances in engineering myeloid cells for cell therapy applications. ACS Synth Biol. 14, 10–20. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.4c00589
Fu, Y., Lyu, J., and Wang, S. (2023). The role of intestinal microbes on intestinal barrier function and host immunity from a metabolite perspective. Front. Immunol. 14, 1277102. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1277102
Gao, Y., Kennelly, J. P., Xiao, X., Whang, E., Ferrari, A., Bedard, A. H., et al. (2024). T cell cholesterol transport is a metabolic checkpoint that links intestinal immune responses to dietary lipid absorption. bioRxiv. 390, eadt4169. doi: 10.1126/science.adt4169
Gramberg, M., Torensma, B., van Asten, S., Sieswerda, E., Sabelis, L. W. E., den Heijer, M., et al. (2024). Duration of antibiotic treatment for foot osteomyelitis in people with diabetes. Antibiotics (Basel) 13, 1173. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13121173
Grüner, N., Ortlepp, A. L., and Mattner, J. (2023). Pivotal role of intestinal microbiota and intraluminal metabolites for the maintenance of gut-bone physiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 5161. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065161
Guo, G., Liu, Z., Yu, J., You, Y., Li, M., Wang, B., et al. (2024). Neutrophil function conversion driven by immune switchpoint regulator against diabetes-related biofilm infections. Advanced materials (Deerfield Beach Fla.) 36, e2310320. doi: 10.1002/adma.202310320
Hagopian, W., Ferry, R. J., Jr., Sherry, N., Carlin, D., Bonvini, E., Johnson, S., et al. (2013). Teplizumab preserves C-peptide in recent-onset type 1 diabetes: two-year results from the randomized, placebo-controlled Protégé trial. Diabetes 62, 3901–3908. doi: 10.2337/db13-0236
Haller, M. J., Gitelman, S. E., Gottlieb, P. A., Michels, A. W., Rosenthal, S. M., Shuster, J. J., et al. (2015). Anti-thymocyte globulin/G-CSF treatment preserves β cell function in patients with established type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 125, 448–455. doi: 10.1172/JCI78492
Han, N., Li, X., Du, J., Xu, J., Guo, L., and Liu, Y. (2023). The impacts of oral and gut microbiota on alveolar bone loss in periodontitis. J. periodontal Res. 58, 1139–1147. doi: 10.1111/jre.13168
Hansdah, K. and Lui, J. C. (2024). Emerging insights into the endocrine regulation of bone homeostasis by gut microbiome. J. Endocrine Soc. 8, bvae117. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvae117
Hassanin, A., Feeney, E., Varman, R., Kellegher, E., Gahan, T., O’Donoghue, A., et al. (2025). Predictors of successful antibiotic treatment of osteomyelitis in diabetic forefoot infection. Acta Diabetol. 62, 661–670. doi: 10.1007/s00592-024-02386-y
He, S., Cai, T., Yuan, J., Zheng, X., and Yang, W. (2021). Lipid metabolism in tumor-infiltrating T cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1316, 149–167. doi: 10.1007/978-981-33-6785-2_10
He, S., Chen, H., Xi, H., Sun, G., Du, B., and Liu, X. (2025). Gut microbiota-derived butyric acid alleviates glucocorticoid-associated osteonecrosis of the femoral head via modulating inflammatory cytokines in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mediators Inflammation 2025, 8742817. doi: 10.1155/mi/8742817
Hegde, S., Akbar, H., Wellendorf, A. M., Nestheide, S., Johnson, J. F., Zhao, X., et al. (2024). Inhibition of RHOA activity preserves the survival and hemostasis function of long-term cold-stored platelets. Blood 144, 1732–1746. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023021453
Heng, B. C., Bai, Y., Li, X., Lim, L. W., Li, W., Ge, Z., et al. (2023). Electroactive biomaterials for facilitating bone defect repair under pathological conditions. Advanced Sci. (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany) 10, e2204502. doi: 10.1002/advs.202204502
Holder, B. E., Reber, C. P., and Monteith, A. J. (2025). Live fast, die young: neutrophils streamline their metabolism to maximize inflammation. Infect. Immun. 93, e0049824. doi: 10.1128/iai.00498-24
Hooshmand Gharabagh, L., Heydaroghli, M., and Esmaeili, A. (2025). Efficacy of N-acetyl-cysteine as adjuvant therapy for diabetic foot osteomyelitis: an open-label randomized controlled trial. Arch. Iran Med. 28, 257–263. doi: 10.34172/aim.33355
Hotamisligil, G. S. (2006). Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 444, 860–867. doi: 10.1038/nature05485
Hu, K., Song, M., Song, T., Jia, X., and Song, Y. (2025). Osteoimmunology in osteoarthritis: unraveling the interplay of immunity, inflammation, and joint degeneration. J. Inflammation Res. 18, 4121–4142. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S514002
Hu, C., Xuan, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, Y., Yang, S., and Yang, K. (2022). Immune cell metabolism and metabolic reprogramming. Mol. Biol. Rep. 49, 9783–9795. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07474-2
Huang, D., Li, K., Zheng, X., and Liu, L. (2021). Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: an effective auxiliary treatment method for large jaw cysts. Int. J. Med. Sci. 18, 3692–3696. doi: 10.7150/ijms.57360
Huang, S., Shi, J., Shen, J., and Fan, X. (2025). Metabolic reprogramming of neutrophils in the tumor microenvironment: Emerging therapeutic targets. Cancer Lett. 612, 217466. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217466
Iles, K. A., Heisler, S., Chrisco, L., King, B., Williams, F. N., and Nizamani, R. (2021). In patients with lower extremity burns and osteomyelitis, diabetes mellitus increases amputation rate. J. Burn Care Res. 31:irab093. doi: 10.1093/jbcr/irab093
Jaroenarpornwatana, A., Koonalinthip, N., Chawaltanpipat, S., and Janchai, S. (2023). Is the duration of diabetic foot ulcers an independent risk factor for developing diabetic foot osteomyelitis? Foot (Edinb) 56, 102000. doi: 10.1016/j.foot.2023.102000
Jia, X., Yang, R., Li, J., Zhao, L., Zhou, X., and Xu, X. (2021). Gut-bone axis: A non-negligible contributor to periodontitis. Front. Cell. infection Microbiol. 11, 752708. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.752708
Jiang, J., Tu, H., and Li, P. (2022). Lipid metabolism and neutrophil function. Cell. Immunol. 377, 104546. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2022.104546
Jing, C., Ralph, J. E., Lim, J., Cathey, J. M., O’Neill, C. N., and Anastasio, A. T. (2025). Novel treatments for diabetic foot osteomyelitis: A narrative review. Microorganisms 13, 1639. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13071639
Jolibois, J., Domingues, A., El Hamaoui, D., Awaida, R., Berger-de-Gaillardo, M., Guérin, D., et al. (2024). Targeting TXNIP in endothelial progenitors mitigates IL-8-induced neutrophil recruitment under metabolic stress. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 15, 225. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03850-w
Joshi, M. B., Ahamed, R., Hegde, M., Nair, A. S., Ramachandra, L., and Satyamoorthy, K. (2020). Glucose induces metabolic reprogramming in neutrophils during type 2 diabetes to form constitutive extracellular traps and decreased responsiveness to lipopolysaccharides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. basis Dis. 1866, 165940. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165940
Kawanishi, M., Kami, K., Nishimura, Y., Minami, K., Senba, E., Umemoto, Y., et al. (2022). Exercise-induced increase in M2 macrophages accelerates wound healing in young mice. Physiol. Rep. 10, e15447. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15447
Kermgard, E., Chawla, N. K., and Wesseling-Perry, K. (2021). Gut microbiome, parathyroid hormone, and bone. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. hypertension 30, 418–423. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000714
Keymeulen, B., Vandemeulebroucke, E., Ziegler, A. G., Mathieu, C., Kaufman, L., Hale, G., et al. (2005). Insulin needs after CD3-antibody therapy in new-onset type 1 diabetes. N Engl. J. Med. 352, 2598–2608. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043980
Khandelwal, P., Saluja, H., Shah, S., Dadhich, A., and Hajira, N. (2022). Diabetic maxillary osteomyelitis: A worrisome vulnerability-our experience. J. Maxillofac. Oral. Surg. 21, 590–598. doi: 10.1007/s12663-020-01371-6
Kim, T. and Choi, S. H. (2025). Diabetes mellitus and infectious diseases: current evidence and clinical implications. Diabetes Metab. J. 49, 915–933. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2025.0508
Lane, S., White, T. L. A., Walsh, E. E., Cattley, R. T., Cumberland, R., Hawse, W. F., et al. (2023). Antiviral epithelial-macrophage crosstalk permits secondary bacterial infections. mBio 14, e0086323. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00863-23
Lawrence, T. and Gilroy, D. W. (2007). Chronic inflammation: a failure of resolution? Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 88, 85–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2006.00507.x
Leblanc, P. O., Bourgoin, S. G., Poubelle, P. E., Tessier, P. A., and Pelletier, M. (2024). Metabolic regulation of neutrophil functions in homeostasis and diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 116, 456–468. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae025
Lee, H. T., Lin, C. S., Liu, C. Y., Chen, P., Tsai, C. Y., and Wei, Y. H. (2024). Mitochondrial plasticity and glucose metabolic alterations in human cancer under oxidative stress-from viewpoints of chronic inflammation and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 9458. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179458
Leney-Greene, M. A., Boddapati, A. K., Su, H. C., Cantor, J. R., and Lenardo, M. J. (2020). Human plasma-like medium improves T lymphocyte activation. iScience 23, 100759. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.100759
Leuti, A., Fava, M., Forte, G., Pellegrini, N., Oddi, S., Scipioni, L., et al. (2024). The endocannabinoid anandamide activates pro-resolving pathways in human primary macrophages by engaging both CB(2) and GPR18 receptors. FASEB J. 38, e23675. doi: 10.1096/fj.202301325R
Levine, L. S., Hiam-Galvez, K. J., Marquez, D. M., Tenvooren, I., Madden, M. Z., Contreras, D. C., et al. (2021). Single-cell analysis by mass cytometry reveals metabolic states of early-activated CD8(+) T cells during the primary immune response. Immunity 54, 829–844.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.02.018
Li, S., Huang, C., Xiao, J., Wu, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhou, Y., et al. (2022). The potential role of cytokines in diabetic intervertebral disc degeneration. Aging Dis. 13, 1323–1335. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0129
Li, Z., Wang, Y., Li, S., and Li, Y. (2021). Exosomes derived from M2 macrophages facilitate osteogenesis and reduce adipogenesis of BMSCs. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 12, 680328. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.680328
Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Deng, Q., Mao, J., Jia, Z., Tang, M., et al. (2023). Resveratrol reverses Palmitic Acid-induced cow neutrophils apoptosis through shifting glucose metabolism into lipid metabolism via Cav-1/CPT 1-mediated FAO enhancement. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 233, 106363. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2023.106363
Lian, W. S., Wang, F. S., Chen, Y. S., Tsai, M. H., Chao, H. R., Jahr, H., et al. (2022). Gut microbiota ecosystem governance of host inflammation, mitochondrial respiration and skeletal homeostasis. Biomedicines 10, 860. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040860
Lipsky, B. A., Berendt, A. R., Cornia, P. B., Pile, J. C., Peters, E. J., Armstrong, D. G., et al. (2012). 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 54, e132–e173. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis346
Liu, J., Chen, X., Xu, L., Tu, F., Rui, X., Zhang, L., et al. (2023). Neutrophil membrane-coated nanoparticles exhibit increased antimicrobial activities in an anti-microbial resistant K. pneumonia infection model. Nanomedicine: nanotechnology biology Med. 48, 102640. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2022.102640
Liu, X., Hoft, D. F., and Peng, G. (2022). Tumor microenvironment metabolites directing T cell differentiation and function. Trends Immunol. 43, 132–147. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.12.004
Liu, X., Tang, Y., Luo, Y., Gao, Y., and He, L. (2024). Role and mechanism of specialized pro-resolving mediators in obesity-associated insulin resistance. Lipids Health Dis. 23, 234. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02207-9
Liu, H., Zhang, Q., He, X., Jiang, M., Wang, S., Yan, X., et al. (2023). Structural insights into ligand recognition and activation of the medium-chain fatty acid-sensing receptor GPR84. Nat. Commun. 14, 3271. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38985-6
Loupa, C. V., Lykoudi, E., Meimeti, E., Moisoglou, I., Voyatzoglou, E. D., Kalantzi, S., et al. (2020). Successful treatment of diabetic foot osteomyelitis with dalbavancin. Med. Arch. 74, 243–245. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2020.74.243-245
Luna, M., Guss, J. D., Vasquez-Bolanos, L. S., Castaneda, M., Rojas, M. V., Strong, J. M., et al. (2021). Components of the gut microbiome that influence bone tissue-level strength. J. Bone mineral research: Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Mineral Res. 36, 1823–1834. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4341
Luo, J., Ning, T., Li, X., Jiang, T., Tan, S., and Ma, D. (2024). Targeting IL-12 family cytokines: A potential strategy for type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. BioMed. Pharmacother. 170, 115958. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115958
MacKenna, B., Kennedy, N. A., Mehrkar, A., Rowan, A., Galloway, J., Matthewman, J., et al. (2022). Risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes associated with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases and immune-modifying therapies: a nationwide cohort study in the OpenSAFELY platform. Lancet Rheumatol 4, e490–e506. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(22)00098-4
Maldarelli, M. E. and Noto, M. J. (2024). The emerging role for neutrophil mitochondrial metabolism in lung inflammation. Immunometabolism (Cobham) 6, e00036. doi: 10.1097/IN9.0000000000000036
Malla, S., Shahreen, N., and Saha, R. (2025). Immunometabolism at the crossroads of infection: mechanistic and systems-level perspectives from host and pathogen. ArXiv. 2:arXiv:2506.02236v1.
Mallarino-Haeger, C., Watson, A., Mahgoub, U., Francis, L., Heydari, M., Choudhary, M., et al. (2024). High prescription rate of medications with rifampin drug-drug interactions in patients with diabetic foot osteomyelitis: should rifabutin be included in clinical trials for adjunctive therapy? Open Forum Infect. Dis. 11, ofae582. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae582
Mark, J. R. and Tansey, M. G. (2025). Immune cell metabolic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 20, 36. doi: 10.1186/s13024-025-00827-y
Mauvais, F. X. and van Endert, P. M. (2025). Type 1 diabetes: A guide to autoimmune mechanisms for clinicians. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 27 Suppl 6, 40–56. doi: 10.1111/dom.16460
Mendame Ehya, E., Zhang, H., Qi, B., and Yu, A. (2021). Application and clinical effectiveness of antibiotic-loaded bone cement to promote soft tissue granulation in the treatment of neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers complicated by osteomyelitis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 9911072. doi: 10.1155/2021/9911072
Mens, M. A., de Geus, A., Wellenberg, R. H. H., Streekstra, G. J., Weil, N. L., Bus, S. A., et al. (2023). Preliminary evaluation of dual-energy CT to quantitatively assess bone marrow edema in patients with diabetic foot ulcers and suspected osteomyelitis. Eur. Radiol. 33, 5645–5652. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09479-2
Meyer-Schwickerath, C., Jochimsen, D., and Jung, N. (2023). Update bone infections. Dtsch Med. Wochenschr 148, 313–317. doi: 10.1055/a-1853-4777
Michaudel, C. and Sokol, H. (2020). The gut microbiota at the service of immunometabolism. Cell Metab. 32, 514–523. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.09.004
Moosa, S. R., Allan, A. H., Younes, A. N., Bakri, F. G., and Younes, N. A. (2023). Percutaneous partial bone excision in the management of diabetic toe osteomyelitis. Foot Ankle Int. 44, 836–844. doi: 10.1177/10711007231178530
Moraly, J., Kondo, T., Benzaoui, M., DuSold, J., Talluri, S., Pouzolles, M. C., et al. (2024). Metabolic dialogues: regulators of chimeric antigen receptor T cell function in the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Oncol. 18, 1695–1718. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13691
Morrison, T., Watts, E. R., Sadiku, P., and Walmsley, S. R. (2023). The emerging role for metabolism in fueling neutrophilic inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 314, 427–441. doi: 10.1111/imr.13157
Murray, P. J., Allen, J. E., Biswas, S. K., Fisher, E. A., Gilroy, D. W., Goerdt, S., et al. (2014). Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 41, 14–20. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.008
Nilesh, K., Patil, P., Patil, D., and Patil, M. (2022). Non-radiation and non-drug-induced maxillary osteomyelitis: Study of underlying risk factors, presentation, management and treatment outcomes. Med. J. Armed Forces India 78, S145–s151. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2020.06.008
Noble, J., Macek Jilkova, Z., Aspord, C., Malvezzi, P., Fribourg, M., Riella, L. V., et al. (2024). Harnessing immune cell metabolism to modulate alloresponse in transplantation. Transpl Int. 37, 12330. doi: 10.3389/ti.2024.12330
O’Brien, W., Fissel, B. M., Maeda, Y., Yan, J., Ge, X., Gravallese, E. M., et al. (2016). RANK-independent osteoclast formation and bone erosion in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 68, 2889–2900. doi: 10.1002/art.39837
Ontoria-Oviedo, I., Amaro-Prellezo, E., Castellano, D., Venegas-Venegas, E., González-Santos, F., Ruiz-Saurí, A., et al. (2022). Topical Administration of a Marine Oil Rich in Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators Accelerates Wound Healing in Diabetic db/db Mice through Angiogenesis and Macrophage Polarization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 9918. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179918
Osório, J. H., Amrani, F., Delahaye, F., Dhaybi, A., Vasko, K., Melli, F., et al. (2023). Hollow-core fibers with reduced surface roughness and ultralow loss in the short-wavelength range. Nat. Commun. 14, 1146. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36785-6
Pakkiyaretnam, M. and Chong, J. (2023). Study of diabetic foot problems among patients attending the diabetic foot clinic at royal hampshire county hospital, United Kingdom: A single-centre experience. Cureus 15, e41454. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41454
Pan, S., Yang, L., Zhong, W., Wang, H., Lan, Y., Chen, Q., et al. (2024). Integrated analyses revealed the potential role and immune link of mitochondrial dysfunction between periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. Immunopharmacol. 130, 111796. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111796
Pearce, E. L. and Pearce, E. J. (2013). Metabolic pathways in immune cell activation and quiescence. Immunity 38, 633–643. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.04.005
Peh, H. Y. and Chen, J. (2025). Pro-resolving lipid mediators and therapeutic innovations in resolution of inflammation. Pharmacol. Ther. 265, 108753. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108753
Perera Molligoda Arachchige, A. S. and Verma, Y. (2024). State of the art in the diagnostic evaluation of osteomyelitis: exploring the role of advanced MRI sequences-a narrative review. Quantitative Imaging Med. Surg. 14, 1070–1085. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-1138
Pianko, M. J. and Golob, J. L. (2022). Host-microbe interactions and outcomes in multiple myeloma and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cancer metastasis Rev. 41, 367–382. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10033-7
Psarras, A. and Clarke, A. (2023). A cellular overview of immunometabolism in systemic lupus erythematosus. Oxf Open Immunol. 4, iqad005. doi: 10.1093/oxfimm/iqad005
Qiao, Y., Zheng, H., Cheng, R., Rong, L., Guo, J., Li, G., et al. (2025). A review of the relationship between gut microbiota and osteoporosis in high altitude environments. J. health population Nutr. 44, 241. doi: 10.1186/s41043-025-00994-0
Qiu, Y., Su, Y., Xie, E., Cheng, H., Du, J., Xu, Y., et al. (2025). Mannose metabolism reshapes T cell differentiation to enhance anti-tumor immunity. Cancer Cell 43, 103–121.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2024.11.003
Quan, H., Chung, H., Je, S., Hong, J. J., Kim, B. J., Na, Y. R., et al. (2023). Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase inhibitor dichloroacetate augments autophagy mediated constraining the replication of Mycobacteroides massiliense in macrophages. Microbes Infect. 25, 105139. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2023.105139
Rasquel-Oliveira, F. S., Silva, M., Martelossi-Cebinelli, G., Fattori, V., Casagrande, R., and Verri, W. A., Jr (2023). Specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators: endogenous roles and pharmacological activities in infections. Molecules 28, 5032. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135032
Reed, E. C., Lauten, T. H., Natour, T., Pitts, L. J., Jojo, C. N., Griffin, B. L., et al. (2025). Hemoglobin alpha regulates T-lymphocyte activation and mitochondrial function. bioRxiv. 24:2025.08.01.668160.
Ricci, J. E. (2025). Tumor-induced metabolic immunosuppression: Mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Cell Rep. 44, 115206. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.115206
Roh, S., Hashimoto, K., Kiriishi, R., Matsubara, K., Isozaki, Y., Tanaka, H., et al. (2024). Piperacillin/tazobactam-induced sudden severe thrombocytopenia in a patient with a pressure ulcer: a case report. J. Wound Care 33, S25–s30. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2021.0074
Romero-Carramiñana, I., Dominguez-Zorita, S., Esparza-Moltó, P. B., and Cuezva, J. M. (2024). Ablation of Atp5if1 impairs metabolic reprogramming and proliferation of T lymphocytes and compromises mouse survival. iScience 27, 109863. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109863
Röring, R. J., Debisarun, P. A., Botey-Bataller, J., Suen, T. K., Bulut, Ö., Kilic, G., et al. (2024). MMR vaccination induces trained immunity via functional and metabolic reprogramming of γδ T cells. J. Clin. Invest. 134, e170848. doi: 10.1172/JCI170848
Rother, K. I., Spain, L. M., Wesley, R. A., Digon, B. J., 3rd, Baron, A., Chen, K., et al. (2009). Effects of exenatide alone and in combination with daclizumab on beta-cell function in long-standing type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 32, 2251–2257. doi: 10.2337/dc09-0773
Roverato, N. D., Sailer, C., Catone, N., Aichem, A., Stengel, F., and Groettrup, M. (2021). Parkin is an E3 ligase for the ubiquitin-like modifier FAT10, which inhibits Parkin activation and mitophagy. Cell Rep. 34, 108857. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108857
Ruiz Holgado, M. C., Depasupil, J. I., Stracher, M., Fakioglu, E., and Lew, L. Q. (2023). Staphylococcus schleiferi: an uncommon pathogen in an immunocompetent adolescent with chronic osteomyelitis. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2023, 9597582. doi: 10.1155/2023/9597582
Saadh, M. J., Allela, O. Q. B., Kareem, R. A., Kyada, A., Malathi, H., Nathiya, D., et al. (2025). Immune cell dysfunction: A critical player in development of diabetes complications. Curr. Res. Trans. Med. 73, 103510. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2025.103510
Schwager, J., Seifert, N., Bompard, A., Raederstorff, D., and Bendik, I. (2021). Resveratrol, EGCG and vitamins modulate activated T lymphocytes. Molecules (Basel Switzerland) 26, 5600. doi: 10.3390/molecules26185600
Seidu, S., Khunti, K., Yates, T., Almaqhawi, A., Davies, M. J., and Sargeant, J. (2021). The importance of physical activity in management of type 2 diabetes and COVID-19. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 12, 20420188211054686. doi: 10.1177/20420188211054686
Senneville, E., Gachet, B., Blondiaux, N., and Robineau, O. (2023). Do anti-biofilm antibiotics have a place in the treatment of diabetic foot osteomyelitis? Antibiotics (Basel) 12, 317. doi: 10.20944/preprints202301.0333.v1
Serhan, C. N., Chiang, N., and Nshimiyimana, R. (2024). Low-dose pro-resolving mediators temporally reset the resolution response to microbial inflammation. Mol. Med. 30, 153. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00877-w
Sevcikova, A., Martiniakova, M., Omelka, R., Stevurkova, V., and Ciernikova, S. (2024). The link between the gut microbiome and bone metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 12086. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212086
Shanley, L. C., Fitzgerald, H. K., O’Rourke, S. A., and Dunne, A. (2022). Endogenous drivers of altered immune cell metabolism. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 247, 2192–2200. doi: 10.1177/15353702221134093
Silva, F. M., Duarte-Mendes, P., Teixeira, A. M., Soares, C. M., and Ferreira, J. P. (2024). The effects of combined exercise training on glucose metabolism and inflammatory markers in sedentary adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 14, 1936. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51832-y
Simmons, S. R., Rivera, A., and Ghanem, E. N. B. (2025). Basal activation of ERK1/2 blunts the antimicrobial activity of neutrophils from aged hosts against antibody opsonized Streptococcus pneumoniae. bioRxiv. 30, 2025.05.27.656427. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.27.656427
Sun, W., Xu, J., Li, S., Zhao, Y., Fu, J., Di, L., et al. (2025). GLUT1-mediated HMGB1 O-GlcNAcylation drives hyperglycemia-Induced neutrophil extracellular trap networks formation via TLR4 signaling and exacerbates fibroblast inflammation. Sci. Rep. 15, 18853. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03642-z
Suo, L. G., Qin, R. X., Cui, Y. Y., and Qin, X. J. (2021). Decreased expression of TIPE2 in the eye under high-glucose conditions tested in vivo and in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol 95, 107517. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107517
Szabó, K., Makkai, G., Konkoly, J., Kormos, V., Gaszner, B., Berki, T., et al. (2024). TRPA1 covalent ligand JT010 modifies T lymphocyte activation. Biomolecules 14, 632. doi: 10.3390/biom14060632
Szymczak, K., Pelletier, M. G. H., Mackay, J. M., Reid, D., and Gaines, P. C. W. (2023). CXCR2 antagonist RIST4721 acts as a potent chemotaxis inhibitor of mature neutrophils derived from ex vivo-cultured mouse bone marrow. Biomedicines 11, 479. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020479
Talty, R. and Olino, K. (2021). Metabolism of innate immune cells in cancer. Cancers (Basel) 13, 904. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040904
Tardáguila-García, A., Sanz-Corbalán, I., García-Alamino, J. M., Ahluwalia, R., Uccioli, L., and Lázaro-Martínez, J. L. (2021). Medical versus surgical treatment for the management of diabetic foot osteomyelitis: A systematic review. J. Clin. Med. 10, 1237. doi: 10.3390/jcm10061237
Thimmappa, P. Y., Vasishta, S., Ganesh, K., Nair, A. S., and Joshi, M. B. (2023). Neutrophil (dys)function due to altered immuno-metabolic axis in type 2 diabetes: implications in combating infections. Hum. Cell 36, 1265–1282. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-00905-7
Toller-Kawahisa, J. E. and O’Neill, L. A. J. (2022). How neutrophil metabolism affects bacterial killing. Open Biol. 12, 220248. doi: 10.1098/rsob.220248
Trivedi, A., Khan, M. A., Bade, G., and Talwar, A. (2021). Orchestration of neutrophil extracellular traps (Nets), a unique innate immune function during chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) development. Biomedicines 9, 53. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9010053
Tubin, S., Vozenin, M. C., Prezado, Y., Durante, M., Prise, K. M., Lara, P. C., et al. (2023). Novel unconventional radiotherapy techniques: Current status and future perspectives - Report from the 2nd international radiation oncology online seminar. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 40, 100605. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2023.100605
Unsworth, A., Young, B., Scarborough, M., and McNally, M. (2024). A comparison of causative pathogens in bone and prosthetic joint infections: implications for antimicrobial therapy. Antibiotics (Basel Switzerland) 13, 1125. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13121125
Urish, K. L. and Cassat, J. E. (2020). Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis: bone, bugs, and surgery. Infect. Immun. 88, e00932–19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00932-19
Urszula, Ł., Ulana, J., Bartosz, S., Maja, O., Małgorzata, M., and Monika, R. S. (2024). Exploring CCR5 + T regulatory cell subset dysfunction in type 1 diabetes patients: implications for immune regulation. Immunologic Res. 72, 1061–1070. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09508-2
Uthaya Kumar, A., Ahmad Zan, M., Ng, C. L., Chieng, S., and Nathan, S. (2024). Diabetes and infectious diseases with a focus on melioidosis. Curr. Microbiol. 81, 208. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03748-z
Venkatesan, V. and Rangasamy, J. (2023). Diabetic pedal osteomyelitis and its treatment. Chonnam. Med. J. 59, 109–114. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2023.59.2.109
Vetter, M. and Saas, P. (2024). Strong as death or how efferocytotic macrophages promote the resolution of inflammation. Med. Sci. (Paris) 40, 428–436. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2024050
Videla, L. A., Valenzuela, R., Del Campo, A., and Zúñiga-Hernández, J. (2023). Omega-3 lipid mediators: modulation of the M1/M2 macrophage phenotype and its protective role in chronic liver diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 15528. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115528
Vurusaner, B., Thevkar-Nages, P., Kaur, R., Giannarelli, C., Garabedian, M. J., and Fisher, E. A. (2022). Loss of PRMT2 in myeloid cells in normoglycemic mice phenocopies impaired regression of atherosclerosis in diabetic mice. Sci. Rep. 12, 12031. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15349-6
Wang, J., Zhu, N., Su, X., Gao, Y., and Yang, R. (2023). Gut-microbiota-derived metabolites maintain gut and systemic immune homeostasis. Cells 12, 793. doi: 10.3390/cells12050793
Waugh, R. E., Lomakina, E., Amitrano, A., and Kim, M. (2023). Activation effects on the physical characteristics of T lymphocytes. Front. bioengineering Biotechnol. 11, 1175570. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1175570
Wei, C., Sun, M., Liang, X., Che, B., Wang, N., Shi, L., et al. (2021). Spermine regulates immune and signal transduction dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 12, 740493. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.740493
Xie, Q., Li, F., Fang, L., Liu, W., and Gu, C. (2020). The antitumor efficacy of β-elemene by changing tumor inflammatory environment and tumor microenvironment. BioMed. Res. Int. 2020, 6892961. doi: 10.1155/2020/6892961
Xu, W., Bradstreet, T. R., Zou, Z., Hickerson, S., Zhou, Y., He, H., et al. (2025). Reprogramming aerobic metabolism mitigates Streptococcus pyogenes tissue damage in a mouse necrotizing skin infection model. Nat. Commun. 16, 2559. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57348-x
Yan, K. (2024). Recent advances in the effect of adipose tissue inflammation on insulin resistance. Cell Signal 120, 111229. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111229
Yang, Y., Liu, K., Zhou, W., and Dai, S. (2023). Exosomes from Ub−HBcAg−overexpressing dendritic cells induce T−lymphocyte differentiation and enhance cytotoxic T−lymphocyte activity. Exp. Ther. Med. 25, 167. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11866
Yang, S., Yang, Y., Wang, F., Luo, Q., Zhang, Y., Zheng, F., et al. (2021). TREM2 dictates antibacterial defense and viability of bone marrow-derived macrophages during bacterial infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 65, 176–188. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0521OC
Yu, K. E., Alder, K. D., Morris, M. T., Munger, A. M., Lee, I., Cahill, S. V., et al. (2020). Re-appraising the potential of naringin for natural, novel orthopedic biotherapies. Ther. Adv. musculoskeletal Dis. 12, 1759720X20966135. doi: 10.1177/1759720X20966135
Yu, Z., Su, S., Xiong, X., Huang, W., Tong, T., and Peng, Z. (2025). A rare case of osteomyelitis caused by scedosporium apiospermum in the right foot of an immunocompetent patient. Infection Drug resistance 18, 3343–3350. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S525682
Zhan, Q. Y., Xie, L. X., and Wang, C. (2023). Promoting critical care system and capacity building in pulmonary and critical care medicine subspecialties. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 103, 3149–3151. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20230602-00919
Zhang, K., Bai, Y. Z., Liu, C., Liu, S. S., Lu, X. X., and Yang, R. G. (2023). Composition of pathogenic microorganism in chronic osteomyelitis based on metagenomic sequencing and its application value in etiological diagnosis. BMC Microbiol. 23, 313. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-03046-x
Zhang, F., Lv, M., Wang, S., Li, M., Wang, Y., Hu, C., et al. (2024). Ultrasound-triggered biomimetic ultrashort peptide nanofiber hydrogels promote bone regeneration by modulating macrophage and the osteogenic immune microenvironment. Bioactive materials 31, 231–246. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.08.008
Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., Xia, L., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Roles of critical amino acids metabolism in the interactions between intracellular bacterial infection and macrophage function. Curr. Microbiol. 81, 280. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03801-x
Zhang, L. X., Wang, Y. T., Zhao, J., Li, Y., and Chen, H. L. (2021). Sex differences in osteomyelitis of the foot in persons with diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Wound Manag Prev. 67, 19–25. doi: 10.25270/wmp.2021.5.1925
Zhao, Y. Z., Du, C. C., Xuan, Y., Huang, D., Qi, B., Shi, Y., et al. (2024). Bilirubin/morin self-assembled nanoparticle-engulfed collagen/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel accelerates chronic diabetic wound healing by modulating inflammation and ameliorating oxidative stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 261, 129704. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129704
Keywords: diabetes mellitus, osteomyelitis, immunometabolic reprogramming, mechanisms, therapeutics
Citation: Zhang H, Fu Z-S, Zhou Y, Wang S-N, Ye S-Y, Wang A-N and Liu J-T (2025) Immunometabolic reprogramming in diabetic osteomyelitis: from mechanisms to therapeutics. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1606317. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1606317
Received: 05 April 2025; Accepted: 30 September 2025;
Published: 24 October 2025.
Edited by:
Beatrice Dufrusine, University of Teramo, ItalyReviewed by:
Andy Ruiz, National Institute of Respiratory Diseases-Mexico (INER), MexicoLian Chun Tang, Wuchang Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Fu, Zhou, Wang, Ye, Wang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hui Zhang, emgxODAwNDAxODQzNkAxNjMuY29t; An-Na Wang, NDcyMDM4NTY0QHFxLmNvbQ==; Jun-Tong Liu, d29qaWFvbGl1anVudG9uZ0AxNjMuY29t
†These authors share first authorship
 Hui Zhang
Hui Zhang Zi-Shan Fu
Zi-Shan Fu Ying Zhou
Ying Zhou Song-Nan Wang
Song-Nan Wang Si-Ying Ye
Si-Ying Ye An-Na Wang
An-Na Wang Jun-Tong Liu
Jun-Tong Liu