- 1Department of Orthopedics, Beijing Shijitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Rehabilitation, The First Medical Center of Chinese People's Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing, China
Objective: To investigate the relationship between TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ serum levels and the severity of infection and prognosis in patients with diabetic foot infection (DFI).
Methods: A total of 144 patients diagnosed with diabetic foot at our hospital from January 2020 to December 2023 were enrolled in the study. Patients were divided into an infection group (70 cases) and a non-infection group (74 cases) based on the presence of infection. The infection group was further categorized into mild (29 cases), moderate (18 cases), and severe infection (23 cases) subgroups according to infection severity. Serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ in DFI patients were analyzed, and their predictive value for treatment outcomes was evaluated
Results: Serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ were significantly higher in the infection group than in the non-infection group (P<0.05). Moreover, there were significant differences in TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels among patients with mild, moderate, and severe infections (P<0.05). ROC curve analysis demonstrated that the area under the curve (AUC) for the combined detection of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ in assessing DFI severity was 0.855, which was significantly higher than that of TNF-α (0.811), IL-6 (0.793), and IFN-γ (0.764) (P<0.05). Furthermore, serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ were significantly higher in the poor prognosis group than in the good prognosis group (P<0.05). ROC curve analysis showed that the AUC for predicting poor prognosis in DFI patients was 0.926 when TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ were combined, which was significantly higher than that of TNF-α (0.849), IL-6 (0.834), and IFN-γ (0.809) (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ are elevated in DFI patients and are closely associated with infection severity and prognosis. The combined detection of these three inflammatory factors can serve as a predictive indicator for infection severity and poor prognosis in DFI patients.
1 Introduction
Diabetic foot is one of the most common complications of diabetes, primarily caused by neuropathy and vascular lesions induced by prolonged hyperglycemia (Jeffcoate et al., 2018). Clinical data indicate that the incidence of diabetic foot is rising annually, likely due to the increasing number of diabetic patients and the trend of population aging (Lavery et al., 2019). Chronic hyperglycemia damages the nervous and vascular systems, leading to reduced sensation in the feet and impaired blood circulation, which significantly increases the risk of foot ulcers and infections. In severe cases, this can result in gangrene and necessitate amputation (Castiglioni et al., 2017; Lauri et al., 2020; Lavery et al., 2020). Currently, the amputation rate among diabetic foot patients is approximately 1.1%, with infection playing a crucial role in the onset and progression of diabetic foot. It is also a major cause of disability and mortality in these patients (Lipsky et al., 2004; Pitocco et al., 2019). More than 50% of diabetic foot wounds exhibit infection at an early stage. Therefore, clinical efforts should focus on preventing and controlling DFI and identifying convenient and sensitive biomarkers for assessing infection severity and prognosis to guide clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) is a potent pro-inflammatory cytokine produced by monocytes, T lymphocytes, and macrophages, playing a crucial role in inflammatory responses and cellular immunity (Wang et al., 2021). Studies have shown that TNF-α expression is significantly upregulated and prolonged during the chronic wound healing process of infected diabetic foot ulcers (Dhamodharan et al., 2019). Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a key inflammatory mediator involved in inflammatory responses and immune regulation (Pena-Duran et al., 2025). Research has indicated that IL-6 levels are positively correlated with disease severity in patients with type 2 diabetes, and excessive IL-6 may impair tissue repair capacity (Nicchio et al., 2025). Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), primarily secreted by T helper 1 (Th1) cells, is a key inflammatory cytokine involved in the pathogenesis of diabetes and is closely associated with secondary infections in diabetic foot ulcers (Umapathy et al., 2018; Amin et al., 2020).
TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ play crucial roles in DFI and may reflect different pathophysiological mechanisms and clinical significance. Investigating the changes in these three biomarkers in DFI patients and their association with disease progression can enhance the understanding of DFI pathophysiology and provide valuable insights for early diagnosis and individualized treatment strategies. This study aims to examine the peripheral blood levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ in DFI patients and analyze their relationship with infection severity and prognosis, thereby offering diagnostic evidence for the early identification and personalized treatment of DFI.
2 Study subjects and methods
2.1 Study subjects
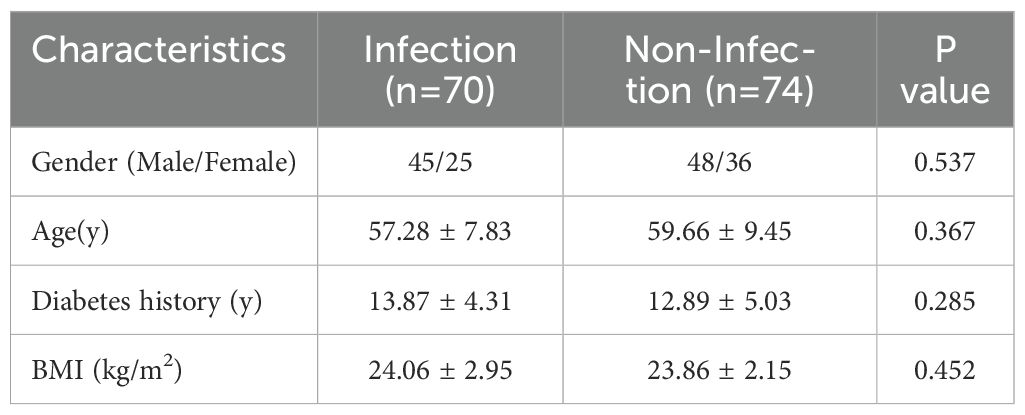
This study enrolled 144 patients diagnosed with diabetic foot who were treated at Beijing Shijitan Hospital from January 2020 to December 2023. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) meeting the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes; (2) meeting the diagnostic criteria for diabetic foot; (3) actively cooperating with treatment and demonstrating good adherence; (4) age between 18 and 80 years; and (5) providing informed consent and signing the consent form. The exclusion criteria included: (1) type 1 diabetes; (2) coexisting diabetes-related complications; (3) presence of other infectious diseases; (4) severe cardiac, hepatic, or renal dysfunction; (5) malignancies; (6) long-term use of corticosteroids or immunosuppressants; and (7) psychiatric disorders. Based on the presence of infection, the patients were categorized into an infection group (n=70) and a non-infection group (n=74). This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Beijing Shijitan Hospital, Capital Medical University (IIT2025-002-002).
2.2 Data collection
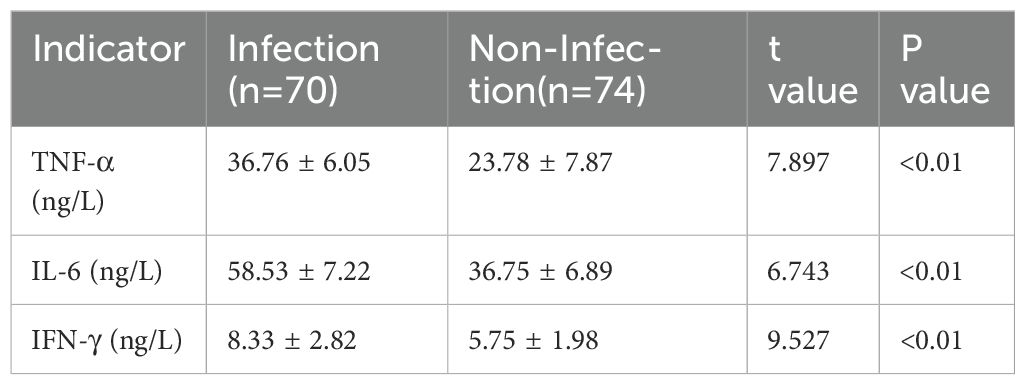
Upon hospital admission, demographic and clinical data, including gender, age, diabetes history, and body mass index (BMI). The determination of infection severity was based on the Wagner classification (Lipsky et al., 2020), categorized as mild (grades 0-2), moderate (grade 3), and severe (grades 4-5). According to the 4-week follow-up outcomes of DFI patients, those who achieved wound healing were classified into the good prognosis group, whereas patients with unhealed wounds, amputations, or death were classified into the poor prognosis group. For all patients, 3 mL of venous blood was collected in the early morning under fasting conditions and centrifuged at 3,000 r/min for 5 minutes. The supernatant was then stored at -80°C for subsequent analysis. The levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ were measured using a sandwich ELISA assay (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA). The intra- and inter-assay coefficient of variation (CV) was <10%, with concentrations expressed in ng/L. All procedures were performed strictly according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.3 Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using SPSS 23.0 statistical software. Normally distributed quantitative data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation ( ± s), and comparisons between groups were conducted using the t-test. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for comparisons among multiple groups, followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls (SNK-q) test for pairwise comparisons. Categorical data were presented as counts (n) or percentages (%) and analyzed using the chi-square (χ²) test. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the predictive value of serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels in assessing infection severity and prognosis in DFI patients. For the analysis of ROC curves, we compared the diagnostic performance of three biomarkers. To account for multiple comparisons, Bonferroni correction was applied, adjusting the significance level to α/m, where m is the number of comparisons (m = 3). Thus, the corrected significance threshold was set to α = 0.05/3 = 0.0167. A p-value below this threshold was considered statistically significant, indicating that the biomarker’s diagnostic performance was significantly different from the null hypothesis. The area under the curve (AUC) comparisons were conducted using the Z-test, with statistical significance set at P<0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Comparison of general characteristics and serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels between infection and non-infection groups
The general clinical characteristics, including gender, age, diabetes history, and BMI, were compared between the infection and non-infection groups. No significant differences were observed between the two groups (P>0.05), indicating comparability (Table 1). However, serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ were significantly higher in the infection group than in the non-infection group, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05) (Table 2).
3.2 Comparison of serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels among patients with different infection severity and prognosis
Patients were classified into mild infection (n=29), moderate infection (n=18), and severe infection (n=23) groups based on infection severity. According to our p retrospective power analysis, the study achieved a statistical power of 82.5% at the α = 0.05 significance level, indicating a statistically reliable result within the context of the observed effect size. Serological analysis revealed a progressive increase in TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels with increasing infection severity, with statistically significant differences among the groups (P<0.05) (Table 3). Additionally, patients were categorized into a good prognosis group (n=37) and a poor prognosis group (n=107) based on clinical outcomes. Serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ were significantly lower in the good prognosis group compared to the poor prognosis group, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05) (Table 4).
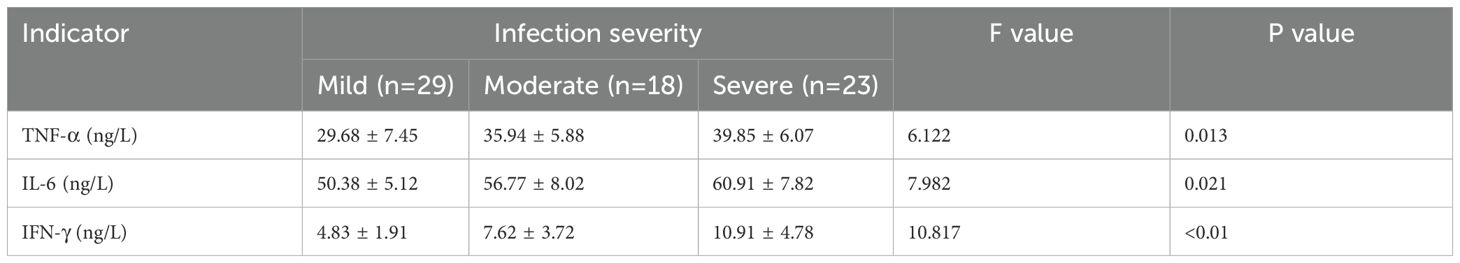
Table 3. Comparison of serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ among patients with different severities of infection.
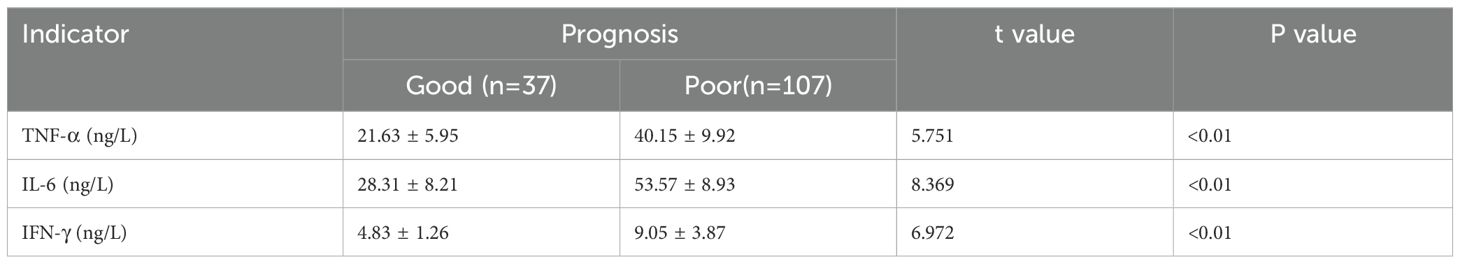
Table 4. Comparison of serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels between the good and poor prognosis groups.
3.3 Diagnostic value of serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels in assessing infection severity and prognosis in DFI patients
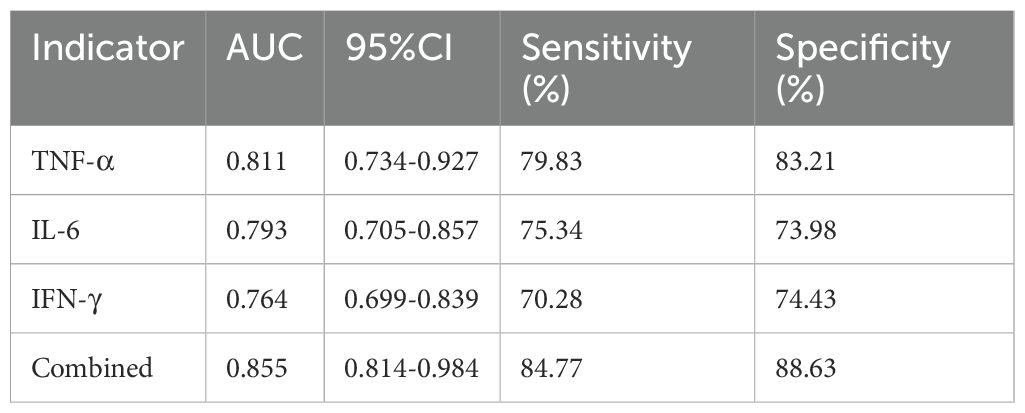
For infection severity diagnosis, ROC curve analysis demonstrated that serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels had diagnostic value in assessing DFI infection severity, with AUC values of 0.811(95%CI: 0.734-0.927), 0.793(95%CI: 0.705-0.857), and 0.764(95%CI: 0.699-0.839), respectively. Combined detection improved diagnostic efficacy, yielding an AUC of 0.855(95%CI: 0.814-0.984) (Table 5; Figure 1). Regarding prognosis prediction, serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels showed strong predictive value for DFI prognosis, with AUC values of 0.849(95%CI: 0.791-0.909), 0.834(95%CI: 0.743-0.898), and 0.809(95%CI: 0.715-0.873), respectively. The combined detection further enhanced predictive performance, achieving an AUC of 0.926(95%CI: 0.856-0.992) (Table 6; Figure 2).
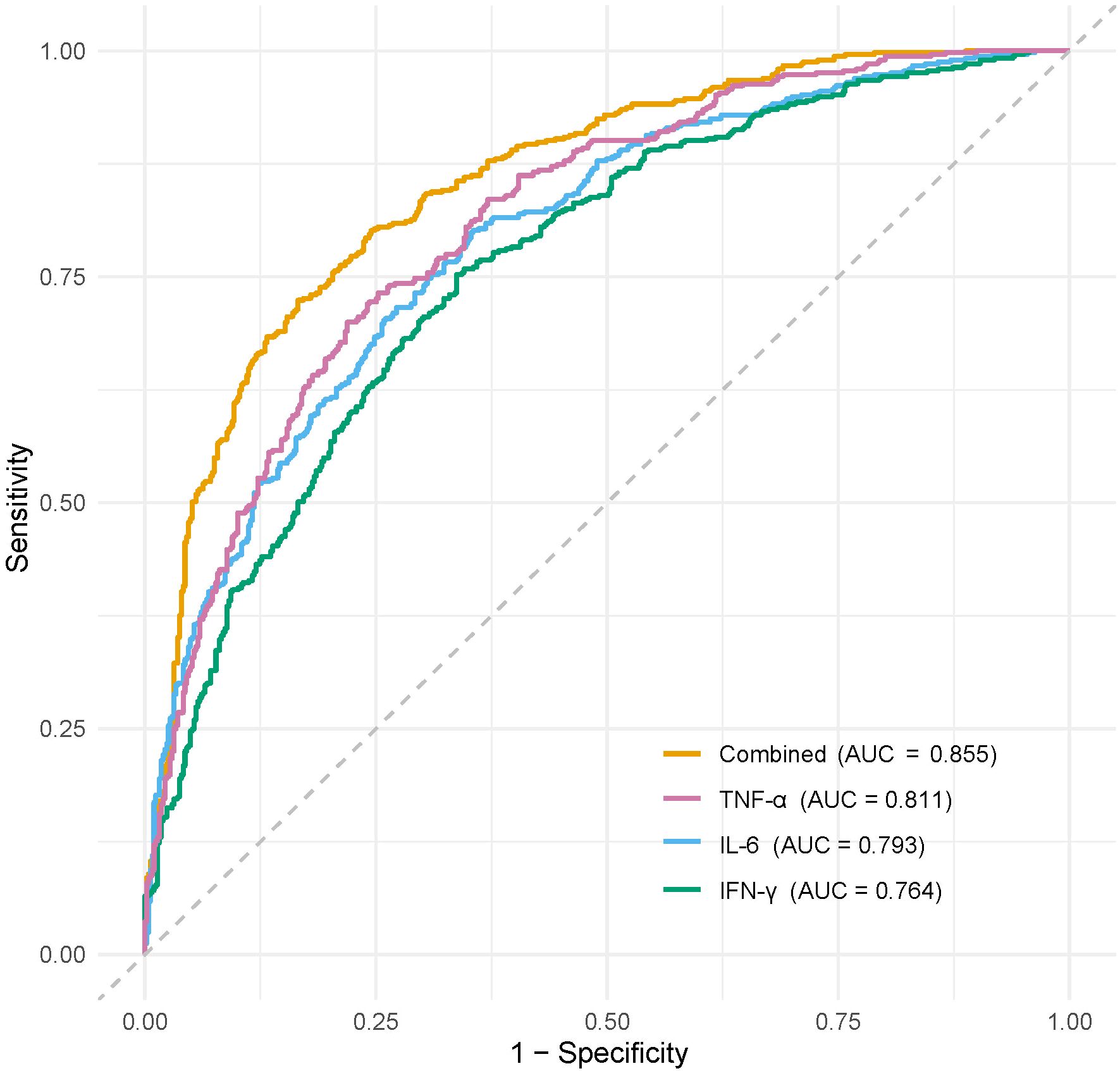
Figure 1. ROC curve of serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels in diagnosing the severity of DFI patients.
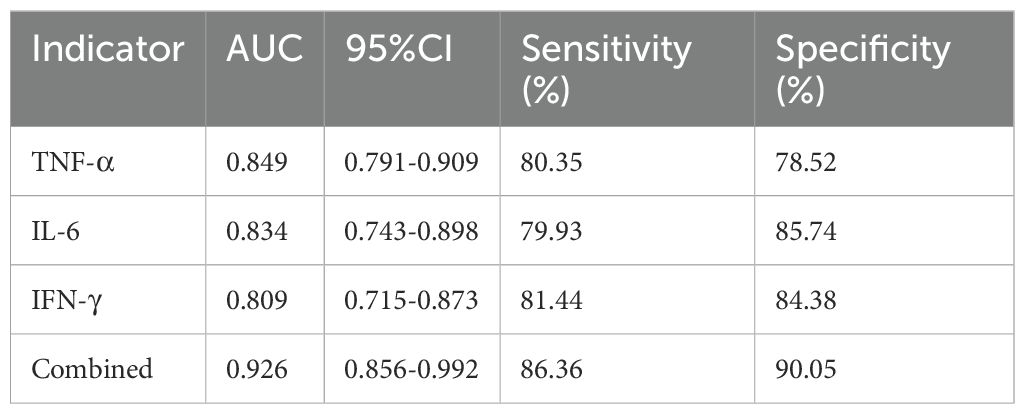
Table 6. Diagnostic value of serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ in predicting the prognosis of DFI patients.
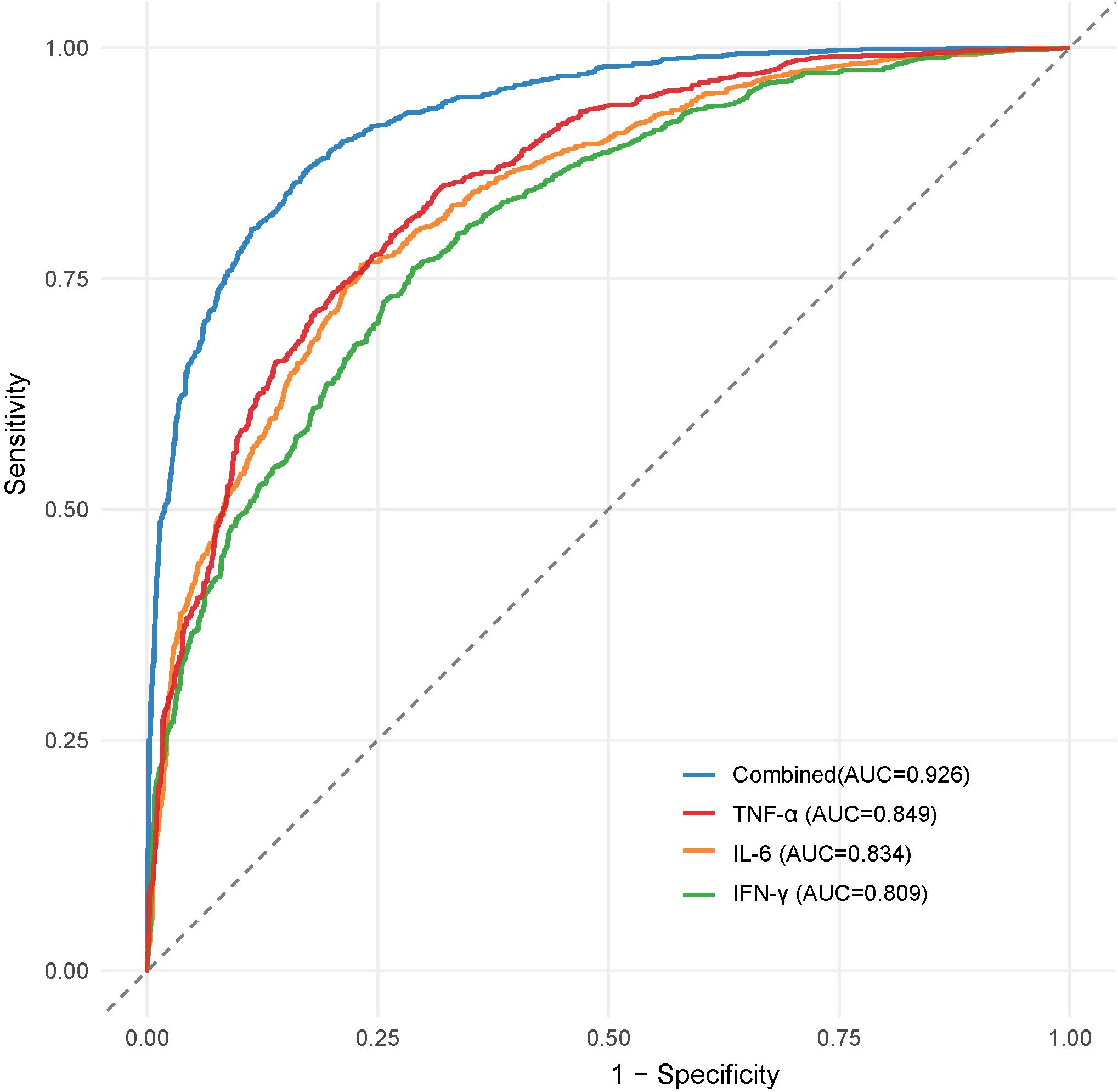
Figure 2. ROC curve of serum TNF-α, IL-6 and IFN-γ levels in diagnosing the prognosis of DFI patients.
4 Discussion
Due to impaired immune function in diabetic patients, vascular lesions can easily trigger ischemic necrosis. Additionally, sensory and motor neuropathy contribute to the development of diabetic foot. Once foot ulcers form, pathogenic microorganisms can readily invade deep tissues, leading to infections (Nauriyal and Byers, 2025). Infection is not only a crucial factor in exacerbating diabetic foot but also a leading cause of amputation. The hyperglycemic environment and malnutrition in diabetic patients create ideal conditions for bacterial growth and proliferation. Meanwhile, impaired leukocyte function further increases the risk of local soft tissue infections. Epidemiological studies indicate that the incidence of DFI has been rising annually and is projected to reach 7.7% by 2030 (Bakhtiyari et al., 2021). Therefore, accurately assessing DFI severity and implementing early intervention is essential for improving patient outcomes (Alvarez et al., 2020). Current conventional infection markers have limitations in assessing DFI severity, highlighting the importance of identifying new infection biomarkers and utilizing combined detection strategies for clinical applications. This study primarily investigates the correlation between inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ with DFI and further analyzes their relationship with infection severity, aiming to provide clinical guidance for early intervention, thereby improving patient prognosis and quality of life.
In recent years, the role of inflammation in diabetes and its complications has garnered increasing attention. Studies suggest that diabetic patients experience a chronic low-grade inflammatory state, and elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines are closely associated with the onset and progression of diabetes and its complications. For example, IL-6 levels are positively correlated with the severity of type 2 diabetes, and elevated IL-6 impairs tissue repair, leading to poor healing of diabetic foot ulcers. T lymphocytes play a crucial role in balancing inflammatory responses and microbial tolerance (Kronsteiner et al., 2019; Moura et al., 2019). TNF-α, a key cytokine in the Th1 signaling pathway, promotes the expression of intercellular adhesion molecules, facilitating the migration of activated neutrophils and T cells from the epidermis to the dermis. Additionally, TNF-α mediates the Th17 signaling pathway by interacting with dendritic and tissue cells, inducing IL-17 and IL-23 secretion to maintain tissue homeostasis. However, excessive TNF-α release may cause pathological damage, disrupting immune balance (Wang et al., 2021). Studies have shown that peripheral blood monocyte activity is enhanced in DFI patients, leading to increased TNF-α levels (Sayed and Mahmoud, 2016). IFN-γ, secreted by activated T cells, possesses antiviral and cell growth-inhibitory functions. In diabetic patients, major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) expression in pancreatic β-cells is upregulated, making them more susceptible to T-cell cytotoxicity. IFN-γ promotes diabetes development by inducing aberrant MHC expression. Moreover, IFN-γ directly inhibits β-cell proliferation and mediates pancreatic cell damage through multiple pathways (Samuel et al., 2019). Studies suggest that improvements in inflammatory biomarkers such as serum IFN-γ levels and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio are closely related to glycemic control (Abdel-Moneim et al., 2019). During the wound healing process of DFI, these inflammatory factors work synergistically, affecting immune defense in the early stages of inflammation and tissue repair in the later stages. The sustained high expression of TNF-α and IFN-γ may lead to delayed inflammation and the formation of chronic wounds, while the overexpression of IL-6 may promote the expression of chemokines, attracting macrophages to the infection site, thereby maintaining a chronic inflammatory state and delaying wound healing (Weigelt et al., 2009; Lee et al., 2019). Therefore, precisely regulating the levels of these inflammatory factors may be a key strategy for improving the treatment outcomes of DFI.
The results of this study indicate that serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ were significantly elevated in DFI patients compared to diabetic foot patients without infection, and their levels positively correlated with infection severity. In other words, the higher the levels of these inflammatory factors, the more severe the infection. Additionally, the expression levels of these cytokines significantly differed between patients with different prognoses. Patients in the good prognosis group had significantly lower serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels than those in the poor prognosis group. These findings suggest that abnormal elevations in TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels are closely associated with DFI severity and poor prognosis. Furthermore, ROC curve analysis demonstrated that serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels have good predictive value for DFI infection severity and prognosis, and their combined detection further improves predictive accuracy.
The levels of inflammatory factors have significant clinical application value in the early diagnosis, disease assessment, and personalized treatment of DFI. IL-6 is usually significantly elevated in DFI patients, and its sustained high levels may indicate a chronic inflammatory state, while excessive expression of TNF-α is associated with tissue necrosis and worsening of lesions (Falanga, 2005). In addition, IFN-γ plays a key role in assessing the severity of infection; its deficiency may reflect an immunosuppressive state, while overexpression may lead to uncontrolled inflammation and delayed wound healing (Donath, 2014; Abdel-Moneim et al., 2019). In the field of precision medicine, monitoring inflammatory factors can guide personalized treatment strategies. For example, anti-TNF-α drugs may be suitable for patients with excessive inflammation, while IL-6 antagonists can be used to reduce tissue damage caused by chronic inflammation (Donath, 2014). Moreover, biomarker-driven treatment models, such as the combined detection of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ, to optimize the use of antibiotics or immunomodulatory agents, help improve the precision of DFI diagnosis and treatment, avoiding over- or under-treatment. In the future, by integrating multi-omics data (such as genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics), predictive models or artificial intelligence algorithms based on individual inflammatory factor profiles may further enhance early screening and personalized intervention for DFI.
In the diagnosis and prognostic assessment of diabetic foot infections, inflammatory biomarkers such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ have been extensively studied and show promise in reflecting disease activity when compared to traditional biomarkers like CRP and WBC. Although traditional biomarkers are widely used in clinical practice due to their ease of detection and low cost, inflammatory markers such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ offer a more accurate reflection of both local and systemic immune responses, thus being considered of higher diagnostic and prognostic value in certain studies. However, the detection of these newer biomarkers involves higher costs and requires more sophisticated laboratory equipment and technical expertise, which may limit their widespread application in resource-limited settings. Given the feasibility of detection, the routine use of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ may face challenges, especially when integrated with existing clinical severity scoring systems, such as the Wagner score, which may provide more biological insight. Therefore, while these biomarkers have potential clinical applicability, their integration into routine diagnostic workflows needs further validation, particularly in low-resource environments, where combining them with traditional biomarkers may be more feasible to improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment decision-making.
In conclusion, serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels are significantly elevated in DFI patients, and all three cytokines serve as potential biomarkers for assessing infection severity and prognosis. Moreover, combined detection enhances diagnostic accuracy. However, since this study only included single-center clinical data, the sample size and types of statistical data were limited, which may result in insufficient statistical power and make it difficult to generalize the findings to a broader population. Furthermore, as the study was conducted at a single research center, patient sources and treatment approaches may have regional or institution-specific biases, which could affect the external validity of the results. In the future, we plan to conduct multi-center studies, which will include a more diverse population, enhance the generalizability and reliability of the findings, and improve statistical power to draw more convincing conclusions. Additionally, we will further expand the sample size and continue to validate the reliability and practicality of the combined detection of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ in clinical practice, while exploring the specific mechanisms of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ in the development and progression of DFI to optimize diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for DFI.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Beijing Shijitan Hospital, Capital Medical University Ethical Review Approval Notice. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
SW: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. LG: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. XQ: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. TL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. JW: Writing – original draft. HX: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdel-Moneim, A., Semmler, M., Abdel-Reheim, E. S., Zanaty, M. I., and Addaleel, W. (2019). Association of glycemic status and interferon-gamma production with leukocytes and platelet indices alterations in type2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 13, 1963–1969. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2019.04.046
Alvarez, R., II, Castano-Tostado, E., Garcia-Gutierrez, D. G., Reynoso-Camacho, R., Elton-Puente, J. E., Barajas-Pozos, A., et al. (2020). Non-Targeted metabolomic analysis reveals serum phospholipid alterations in patients with early stages of diabetic foot ulcer. biomark. Insights 15, 1177271920954828. doi: 10.1177/1177271920954828
Amin, K., Qadr, S. H., Hassan Hussein, R., Ali, K. M., and Rahman, H. S. (2020). Levels of cytokines and GADA in type I and II diabetic patients. Prim Care Diabetes 14, 61–67. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2019.03.008
Bakhtiyari, A., Haghani, K., Bakhtiyari, S., Zaimy, M. A., Zahed, N., Gheysarzadeh, A., et al. (2021). Corrigendum to: association between ABCC8 ala1369Ser polymorphism (rs757110 T/G) and type 2 diabetes risk in an Iranian population: A case-control study. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 21, 1375. doi: 10.2174/187153032107210826095646
Castiglioni, S., Miranda, V., Cazzaniga, A., Campanella, M., Nichelatti, M., Andena, M., et al. (2017). Femtograms of interferon-gamma suffice to modulate the behavior of jurkat cells: A new light in immunomodulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18, 2715. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122715
Dhamodharan, U., Teena, R., Vimal Kumar, R., Changam, S. S., Ramkumar, K. M., and Rajesh, K. (2019). Circulatory levels of B-cell activating factor of the TNF family in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: Association with disease progression. Wound Repair Regener. 27, 442–449. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12720
Donath, M. Y. (2014). Targeting inflammation in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: time to start. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 13, 465–476. doi: 10.1038/nrd4275
Falanga, V. (2005). Wound healing and its impairment in the diabetic foot. Lancet 366, 1736–1743. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67700-8
Jeffcoate, W. J., Vileikyte, L., Boyko, E. J., Armstrong, D. G., and Boulton, A. J. M. (2018). Current challenges and opportunities in the prevention and management of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care 41, 645–652. doi: 10.2337/dc17-1836
Kronsteiner, B., Chaichana, P., Sumonwiriya, M., Jenjaroen, K., Chowdhury, F. R., Chumseng, S., et al. (2019). Diabetes alters immune response patterns to acute melioidosis in humans. Eur. J. Immunol. 49, 1092–1106. doi: 10.1002/eji.201848037
Lauri, C., Glaudemans, A., Campagna, G., Keidar, Z., Muchnik Kurash, M., Georga, S., et al. (2020). Comparison of white blood cell scintigraphy, FDG PET/CT and MRI in suspected diabetic foot infection: results of a large retrospective multicenter study. J. Clin. Med. 9, 1645. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061645
Lavery, L. A., Oz, O. K., Bhavan, K., and Wukich, D. K. (2019). Diabetic foot syndrome in the twenty-first century. Clin. Podiatr Med. Surg. 36, 355–359. doi: 10.1016/j.cpm.2019.02.002
Lavery, L. A., Ryan, E. C., Ahn, J., Crisologo, P. A., Oz, O. K., La Fontaine, J., et al. (2020). The infected diabetic foot: re-evaluating the infectious diseases society of america diabetic foot infection classification. Clin. Infect. Dis. 70, 1573–1579. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz489
Lee, E. G., Luckett-Chastain, L. R., Calhoun, K. N., Frempah, B., Bastian, A., and Gallucci, R. M. (2019). Interleukin 6 function in the skin and isolated keratinocytes is modulated by hyperglycemia. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 5087847. doi: 10.1155/2019/5087847
Lipsky, B. A., Berendt, A. R., Deery, H. G., Embil, J. M., Joseph, W. S., Karchmer, A. W., et al. (2004). Infectious Diseases Society of, A. Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 39, 885–910. doi: 10.1086/424846
Lipsky, B. A., Senneville, E., Abbas, Z. G., Aragon-Sanchez, J., Diggle, M., Embil, J. M., et al. (2020). International Working Group on the Diabetic, F. Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of foot infection in persons with diabetes (IWGDF 2019 update). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 36 Suppl 1, e3280. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3280
Moura, J., Rodrigues, J., Goncalves, M., Amaral, C., Lima, M., and Carvalho, E. (2019). Imbalance in T-cell differentiation as a biomarker of chronic diabetic foot ulceration. Cell Mol. Immunol. 16, 833–834. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0233-1
Nauriyal, V. and Byers, K. (2025). Diabetic foot infections: Questions for an infectious disease consultant. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 38, 85–93. doi: 10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2025.01.009
Nicchio, I. G., Cirelli, T., da Costa Quil, L. C., Camilli, A. C., Scarel-Caminaga, R. M., and Manzolli Leite, F. R. (2025). Understanding the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-gamma) role in periodontitis and diabetes mellitus: A molecular perspective. Biochem. Pharmacol. 237 (7), 116908. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2025.116908
Pena-Duran, E., Garcia-Galindo, J. J., Lopez-Murillo, L. D., Huerta-Huerta, A., Balleza-Alejandri, L. R., Beltran-Ramirez, A., et al. (2025). Microbiota and inflammatory markers: A review of their interplay, clinical implications, and metabolic disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26, 1773. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041773
Pitocco, D., Spanu, T., Di Leo, M., Vitiello, R., Rizzi, A., Tartaglione, L., et al. (2019). Diabetic foot infections: a comprehensive overview. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 23, 26–37. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201904_17471
Samuel, R. O., Ervolino, E., de Azevedo Queiroz, I. O., Azuma, M. M., Ferreira, G. T., and Cintra, L. T. A. (2019). Th1/th2/th17/treg balance in apical periodontitis of normoglycemic and diabetic rats. J. Endod. 45, 1009–1015. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2019.05.003
Sayed, K. M. and Mahmoud, A. A. (2016). Heat shock protein-70 and hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients complicated with retinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol. 94, e361–e366. doi: 10.1111/aos.12919
Umapathy, D., Dornadula, S., Rajagopalan, A., Murthy, N., Mariappanadar, V., Kesavan, R., et al. (2018). Potential of circulatory procalcitonin as a biomarker reflecting inflammation among South Indian diabetic foot ulcers. J. Vasc. Surg. 67, 1283–1291.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.02.060
Wang, Y., Shao, T., Wang, J., Huang, X., Deng, X., Cao, Y., et al. (2021). An update on potential biomarkers for diagnosing diabetic foot ulcer at early stage. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy 133, 110991. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110991
Keywords: diabetic foot infection, TNF-α, IL-6, IFN-γ, severity, prognosis
Citation: Wang S, Gao L, Qin X, Li T, Wang J and Xie H (2025) The prognostic and diagnostic significance of inflammatory markers TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ in evaluating disease severity in diabetic foot infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1606612. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1606612
Received: 06 April 2025; Accepted: 20 June 2025;
Published: 03 July 2025.
Edited by:
Arindam Mitra, RV University, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Wang, Gao, Qin, Li, Wang and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huimin Xie, RW1pbHkwMzAyMThAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Shuo Wang
Shuo Wang Lei Gao1
Lei Gao1 Huimin Xie
Huimin Xie