- 1Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Shiyan Key Laboratory of Major Chronic Respiratory Disease, Hubei Provincial Clinical Research Center for Umbilical Cord Blood Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, Hubei, China
- 2Department of Laboratory, Shiyan Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, Hubei, China
- 3Department of Radiology, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, Hubei, China
- 4Department of Cardiothoracic surgery, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, Hubei, China
Background and Objective: Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PjP) remains an important cause of morbimortality worldwide, and differentiating Pneumocystis jirovecii (P. jirovecii) infection from P. jirovecii colonization (PjC) is crucial for guiding treatment strategies. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction-based targeted next-generation sequencing (mp-tNGS) is a promising tool for identifying lower respiratory tract infections, with a detectable pathogen spectrum that covers more than 95% of clinical infectious cases. This study evaluated mp-tNGS for P. jirovecii identification in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) samples combined with serum 1,3-β-D-glucan (BDG) level detection to differentiate PjP and PjC.
Methods: A total of 73 patients were enrolled and the final diagnosis was used as a reference criterion, and patients were divided into the PjP group and PjC group. The clinical data and detection performance of mp-tNGS/serum BDG were analyzed.
Results: The median fungal reads (normalized sequence counts) detected by mp-tNGS were 1522.00 (interquartile range [IQR], 581.5, 4898.0) in the PjP group versus 117.00 (IQR, 79.00, 257.00) in the PjC group (p <0.0001). Correspondingly, BDG levels were 122.5 (88.75,239.3) pg/ml in PjP patients compared to 59.00 (51.0,79.0) pg/ml in PjC patients (p <0.0001). Area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUROC) for discriminating PjP from colonization was 0.935 (95% CI: 0.88–0.99) for BALF mp-tNGS and 0.822 (95% CI: 0.72–0.93) for serum BDG. The optimal diagnostic thresholds were determined to be 355 reads for mp-tNGS (sensitivity: 89.1%; specificity: 85.2%) and 84.5 pg/ml for BDG (sensitivity: 85.2%; specificity: 80.4%).
Conclusion: BALF mp-tNGS and serum BDG serve as valuable adjunct diagnostic tools, providing reliable differentiation between P. jirovecii colonization and active infection.
1 Introduction
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PjP) is an acute and potentially fatal infection caused by the opportunistic fungal pathogen pneumocystis jirovecii, which predominantly affects immunocompromised individuals globally (Grønseth et al., 2021), with a particularly high prevalence among people living with HIV (PLWH) (Thomas and Limper, 2004). The incidence of PjP in PLWH has gradually decreased due to highly effective antiretroviral therapy and prophylactic treatment against P. jirovecii (Crothers et al., 2011; Salzer et al., 2018). However, with the extensive use of glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, radiotherapy and chemotherapy for tumors and organ transplantation, the incidence of PjP has risen significantly in non-HIV-infected populations (Bienvenu et al., 2016; Dunbar et al., 2020). Notably, non-HIV-infected immunocompromised individuals with PjP often exhibit a poor prognosis, characterized by severe clinical manifestations, an acute disease course, and rapid progression (Kanj et al., 2021). It has been reported that the mortality rate of PjP ranges from 10% to 20% in PLWH, whereas it significantly increases to 30%–60% in non-HIV-infected individuals (Morris and Norris, 2012; Stern et al., 2014; Kotani et al., 2017).
Traditionally, in the presence of clinical suspicion, PjP is diagnosed by the microscopic presence of pneumocysts in respiratory specimens by the use of staining methods, such as Giemsa, Gomori methenamine silver (GMS), calcofluor white, toluidine blue, and/or immunofluorescence antibody assay (Calderón et al., 2010). However, these methods are limited by suboptimal sensitivity and specificity, as well as prolonged turnaround times (TAT).
BDG, a highly conserved polysaccharide component of fungal cell walls, is synthesized during the biogenesis of the fungal cell wall in numerous pathogenic species. This immunogenic molecule has been established as a reliable biomarker for fungal infections, particularly pulmonary aspergillosis and invasive candidiasis (Obayashi et al., 1995). Although the assay lacks specificity for Pneumocystis jirovecii, quantitative detection of serum BDG levels has been established as an adjunctive tool for the diagnosis of PjP (Tasaka et al., 2007; Watanabe et al., 2009; Matsumura et al., 2012; Onishi et al., 2012). Previous studies have established varying diagnostic thresholds for serum BDG in Pneumocystis jirovecii detection. Tasaka et al (Tasaka et al., 2007). determined an optimal cut-off value of 31.1 pg/mL, demonstrating a negative predictive value of 0.980 and positive predictive value of 0.610. Notably, Matsumura et al (Matsumura et al., 2012). achieved a better area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.91 and a lower threshold of 15.6 pg/mL, maintaining 100% sensitivity while providing 80.0% specificity for definitive PjP diagnosis. Meta-analysis by Del Corpo et al (Del Corpo et al., 2020). revealed that serum BDG assay demonstrated limited diagnostic utility for PjP, with insufficient pooled sensitivity to exclude infection and inadequate specificity to confirm PjP diagnosis, particularly in high-prevalence populations. Consequently, we recommend that a comprehensive diagnostic strategy integrating serum BDG assay with complementary microbiological or molecular diagnostic modalities is essential for establishing reliable PjP diagnosis, especially in high-risk populations.
With the rapid advancements in molecular biology, techniques such as metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) and multiplex PCR-based targeted next-generation sequencing (mp-tNGS) are now widely employed to directly detect target organisms in respiratory samples (Sun et al., 2024; Yin et al., 2024; Hsu et al., 2025). A literature search conducted by X. Li et al (Li et al., 2023). identified 9 studies encompassing 1,343 patients, demonstrating that the pooled sensitivity and specificity of mNGS for diagnosing PjP were 0.974 (95% CI: 0.953–0.987) and 0.943 (95% CI: 0.926–0.957), respectively. A large-scale prospective study by Yin et al (Yin et al., 2024). demonstrated that tNGS outperformed mNGS in detecting pneumocystis jirovecii in BALF samples. Moreover, compared to mp-tNGS, mNGS has the limitations of high costs, long TAT, human gene interference, and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) must be separately detected (Miller et al., 2019). However, distinguishing colonization from active infection remains a challenge when using mNGS or tNGS, as positive results may be fungal colonization rather than infection; importantly, PjP is a life-threatening infection in the absence of specific treatment, whereas PjC is a less-severe presentation of asymptomatic colonization (Damiani et al., 2013).
However, the diagnostic performance of combining serum BDG assay and BALF mp-tNGS for differentiating between colonization and infection of pneumocystis jirovecii remains unexplored in current literature. In this study, we evaluated the diagnostic performance of BALF mp-tNGS combing with serum BDG for differentiating P. jirovecii infection between colonization.
2 Patients and methods
2.1 Participants and study design
Between January 2022 and December 2024, patients presenting with pulmonary infiltrates of undetermined etiology or clinical suspicion of PjP who received BALF mp-tNGS testing during the study period were enrolled at Taihe Hospital. Patients were excluded if the following criteria were met: (1) administered empiric treatment (therapeutic doses) for PjP prior to the mp-tNGS tests, (2) serum BDG assay were performed more than 7 days after mp-tNGS, (3) other pulmonary fungal infections are present, and (4) incomplete medical record. A complete medical records encompassing demographic characteristics, clinical parameters, radiologic and laboratory findings was collected before the end of the study for all enrolled patients, as follows: (1) underlying diseases (solid organ malignancy, hematologic malignancies, HIV/AIDS status, prolonged use of corticosteroids/immunosuppressants and autoimmune disease); (2) radiographic findings (chest X-ray and high-resolution computed tomography); (3) laboratory results (absolute count of leukocytes/lymphocyte, HIV viral load, hypersensitive-C-reactive protein [hs-CRP], erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), interleukin-6 [IL-6], procalcitonin [PCT] and lactate dehydrogenase [LDH]); and (4) clinical outcomes. Two independent senior clinicians who reviewed and evaluated the patients’ immune status, clinical manifestations, laboratory results, radiologic findings, the mp-tNGS report, and the response to anti-P. jirovecii treatment to determine the final diagnosis of PjP. The final diagnosis was used as a reference to which the mp-tNGS and serum BDG results were compared. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Taihe Hospital and informed written consent was obtained from each patient.
2.2 Definitions
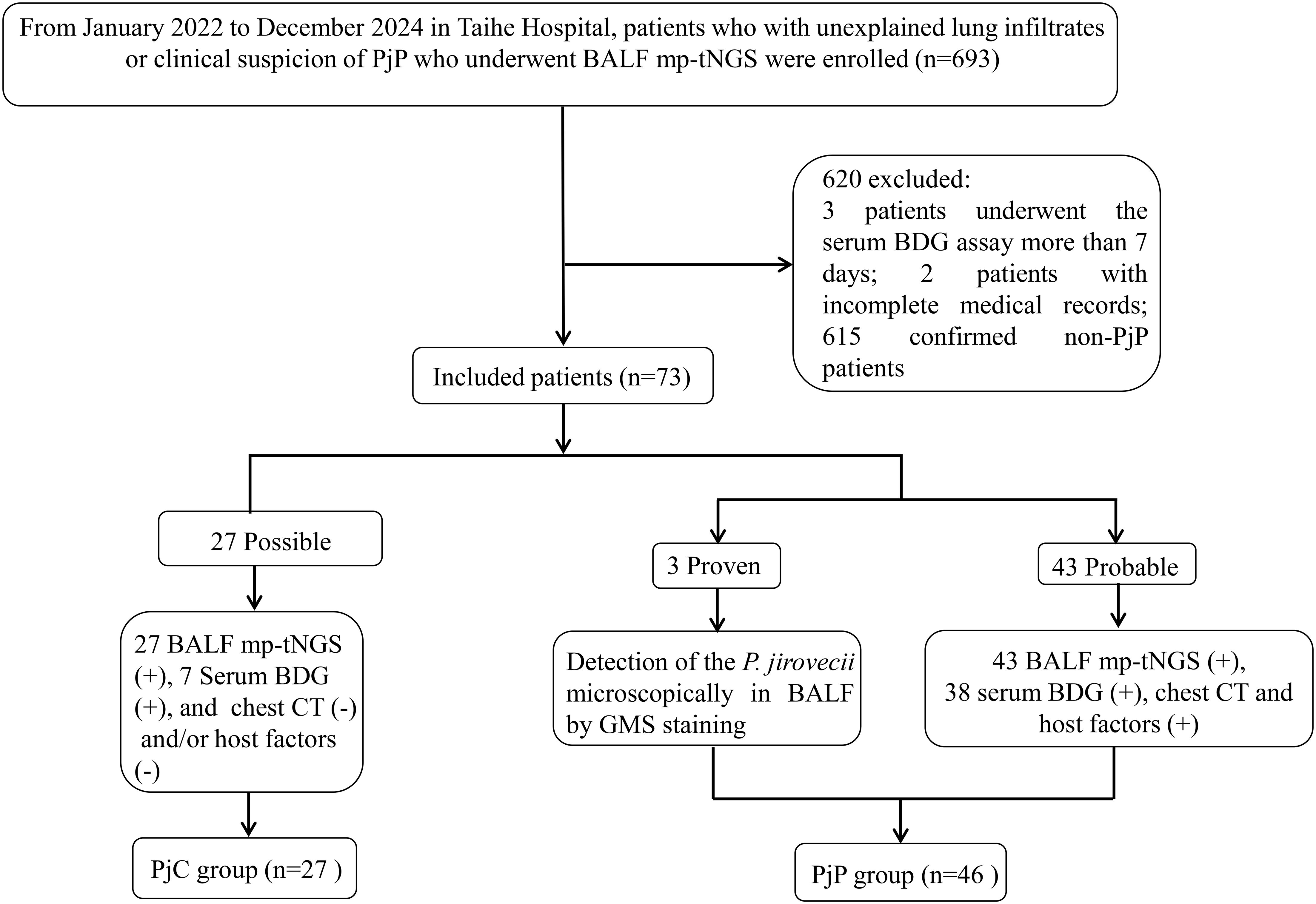
PjP classification followed modified EORTC/MSG consensus guidelines for invasive fungal diseases (Donnelly et al., 2020). Cases were categorized as: Proven/probable PjP: BALF demonstrating P. jirovecii via microscopy or mp-tNGS, plus clinical symptoms (fever >38°C, dyspnea, dry cough, or room-air SpO2 <90%) and characteristic CT findings (bilateral ground-glass opacities/diffuse infiltrates). PossiblePjP: BALF mp-tNGS-positive for P. jirovecii without corresponding clinical/radiological features. Non-PjP: Absence of microbiological and mp-tNGS evidence and clinical-radiological suspicion. As shown in Figure 1, the Proven and probable PjP cases were grouped into the PjP group; cases with a Possible PjP diagnosis were grouped into the PjC group.
2.3 Serum BDG tests
The (1–3)-β-D-glucan detection kit (Dynamiker Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China) was used to assess the levels of serum BDG following the manufacturer’s instructions with a chromogenic method (Yu et al., 2020). A serum BDG level ≥80 pg/ml was considered positive, as per the manufacturer’s recommended cut-off value.
2.5 mp-tNGS procedures and bioinformatics analysis
2.5.1 mp-tNGS workflow construction
Mp-tNGS workflow construction, including database integration and primer design, refer to the study of Zhang P et al (Zhang et al., 2024) YIN Y et al (Yin et al., 2024), the mp-tNGS panel covered 198 pathogen targets commonly encountered in clinical scenarios. A full list of the target species identified by the mp-tNGS panel is presented in Supplementary Table S1. Based on the integrated database in NCBI, target loci capable of precisely identifying species and strains were selected for primer design. Initially, target genes recommended by classical PCR methods in the literature were chosen, after which conserved and specific regions were assessed by bioinformatics evaluation. The primer design adheres to the following key principles: (1). The GC content (guanine - cytosine content) of primers is set within the range of 40% to 60%. (2). The length of primers is regulated between 18 base pairs and 26 base pairs. (3). The melting temperature (Tm value) of primers is designed to be around 60°C. (4). Self-dimers, hairpins, and cross-dimers must be avoided. Primer sets for over 300-plex amplification were designed, and additional primers (≥5) were designed for significant pathogens (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex [MTBC]) and those that require typing (e.g., SARS-CoV-2). A PCR process was developed and optimized to effectively amplify target signals with high sensitivity.
2.5.2 mp-tNGS nucleic acid extraction
DTT liquefaction reagent (0.1 M) in the same volume as the BALF sample was added to the sampling tube, which was subsequently vortexed, shaken, mixed well, and left for 3–5 min until the sample liquefied. A total of 1.3 mL of liquefied sample was added, 13 μL of exogenous endogenous reagent was added, the mixture was mixed well, the mixture was centrifuged at 12000 rpm for 5min, the supernatant was discarded, 500 μL of the sample was removed, the sample was mixed with a pipette, 500 μL of the sample was added to the bead mill tube of the extraction kit, 50 μL of SDS was added, and the mixture was placed into the sonicator (4700 rpm, oscillated for 45 s, with an intermittent pause of 20 s, and 2 intervals, with a total of 3 oscillations of 135 s) for sonication. The total time of 3 oscillations was 135 s for the wall-breaking treatment. After wall-breaking treatment, the mixture was centrifuged at 12000 rpm for 5min, and 400 μL (manual extraction) or 250 μL (automated extraction) of the supernatant was collected for nucleic acid extraction via the MetaPure DNA & RNA Extraction Kit (KingCreate, Guangzhou, China) and extracted according to the instructions of the kit.
2.5.3 mp-tNGS library construction
The target species covered by the mp-tNGS panel are listed in Supplementary Table S1. Library preparation was performed via the RP100™ Respiratory Pathogen Microorganisms Multiplex Testing Kit (KingCreate Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China). cDNA was synthesized via reverse transcription of the extracted nucleic acids, followed by steps such as target region enrichment, the first round of purification, junction ligation, and the second round of purification to complete library construction. Nuclease-free water (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) was used as a nontemplate control (NTC) to detect contamination. The generated libraries were quantified via an Equalbit DNA HS Assay Kit (Vazyme Biotech, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China) with an Invitrogen™ Qubit™ 3.0/4.0 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) fluorometer to ensure that all the samples had a library density ≥ 0.5 ng/μL or were subjected to library reconstruction. The constructed libraries were pooled according to the assayed concentrations in equal mass. The size of the library fragments was detected by a fully automated nucleic acid protein analyser (Qsep100) via a Standard Cartridge Kit (S2). The operation was carried out according to the instructions of the kit, and the size of the library fragments was approximately 250–350 bp. After library qualification, the pooled library was diluted and denatured according to the kit instructions to prepare a mixed library ready for sequencing, and 500 μL of the mixed library was added to the KM MiniSeqDx-CN Sequencing Kit on the KM MiniSeq Dx-CN Platform (KingCreate, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China).
2.5.4 Bioinformatics analysis
The sequencing data generated were analysed via a bioinformatic workflow. The raw sequencing read data were subjected to a quality control procedure. fastp v0.20.1 (Chen et al., 2018) was employed for adaptor trimming and low-quality filtering with default parameters, and Bowtie2 v2.4.1 (Langmead and Salzberg, 2012) was utilized to map the reads of each sample against the mp-tNGS special authoritatively classified database in very sensitive mode.
2.6 Statistical analysis
SPSS software version 26.0 was used for the statistical analysis. The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to assess whether continuous variables followed a normal or non-normal distribution. The continuous variables with normal distribution were expressed as the means ± standard deviations (means ± SDs), and a t test was used for comparison between two groups; non-normally distributed continuous variables were expressed as the median and interquartile range (25th–75th percentiles), and the Mann–Whitney U test was used for comparison between two groups. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were designed to assess the sensitivity, specificity, PPV (positive predictive value) () and NPV (negative predictive value) for the serum BDG and mp-tNGS. Categorical variables were expressed as n (%) and compared using the chi-square test. Probability values <5% (p<0.05) were considered statistically significant. The graphical were generated utilizing GraphPad Prism 9 software (GraphPad, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA). Optimal cutoffs of 355 reads for mp-tNGS and 84.5 pg/mL for BDG were derived from a mathematical assessment of the ROC curves using an optimization analysis of Youden’s J statistic.
3 Results
3.1 Demographic and clinical characteristics
During the 35-month study period, A total of 693 patients who underwent bronchoalveolar lavage for BALF sample collection and subsequent mp-tNGS testing were included in the study. Among them, seventy-eight patients with positive P. jirovecii mp-tNGS tests were divided into proven/probable PjP group (n=48), possible PjP group (n=30); and negative mp-tNGS in non-PjP group (n=615); serum BDG assay was performed more than 7 days after mp-tNGS in 3 patients, medical records were incomplete in 2 patients. Therefore, a total of 73 cases were ultimately included and classified into the PjP group (n=46) and the PjC group (n=27) based on the final diagnosis (Figure 1).
As detailed in Table 1, the age was significantly younger in the PjP group, with a mean age of 61.5 ± 10.9 vs. 64.2 ± 10.3 in the PjC group (p = 0.000) and a higher proportion of male patients in PjP group (p = 0.02). No significant differences were noted between the two groups regarding smoking and drinking history (p = 0.41, p = 0.47). Compared with the PjC group, patients in the PjP group had a significantly higher incidence of fever (54.3% vs. 29.6%, p = 0.04) and hypoxemia (43.5% vs. 18.5%, p = 0.03). No significant differences were observed in the incidence of these underlying diseases between the PjP and PjC groups (p >0.05); but the proportion of patients with diabetes mellitus was significantly higher in the PjC group compared to the PjP group (25.9% vs. 6.5%, p = 0.02). Compared with the PjC group, bilateral ground glass opacities on chest CT were more common in the PjP group (50.0% vs. 11.1%, p = 0.001); typical chest CT findings are shown in Supplementary Figure A–D. Compared with the PjC group, patients in the PjP group had significantly lower levels of hemoglobin and albumin (p = 0.000). Notably, no significant differences were observed in inflammatory markers, including lymphocyte counts, ESR, LDH and PCT levels, between patients with PjP and those with PjC (Figures 2A–D, Table 1). In contrast, leukocyte counts, IL-6 and hs-CRP levels were significantly elevated in the PjP group compared to the PjC group (Figures 2E–G, Table 1). The fungal load was significantly higher in the PjP group, demonstrating a median mp-tNGS read of 1522.00 (581.5, 4898.0), compared to 117.00 (79.00, 257.00) in the PjC group (p < 0.0001, Figure 3A). Similarly, serum BDG levels were significantly elevated in the PjP group, with a median level of 122.5 (88.75,239.3) pg/ml, versus 59.00 (51.0,79.0) pg/ml in the PjC group (p <0.0001, Figure 3B).
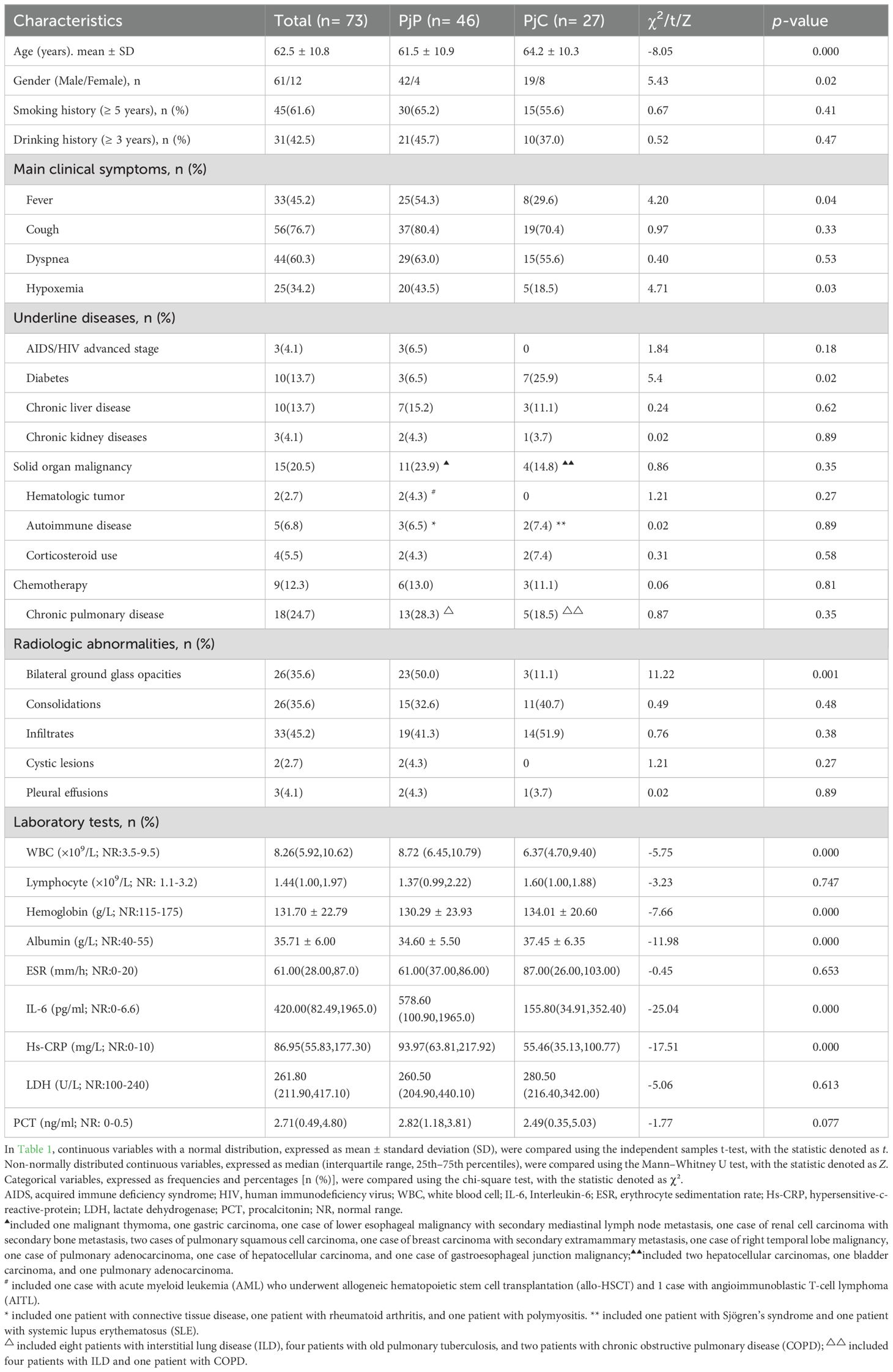
Table 1. Demographics and clinical characteristics of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PjP) and Pneumocystis jirovecii colonisation (PjC) patients (n=73).
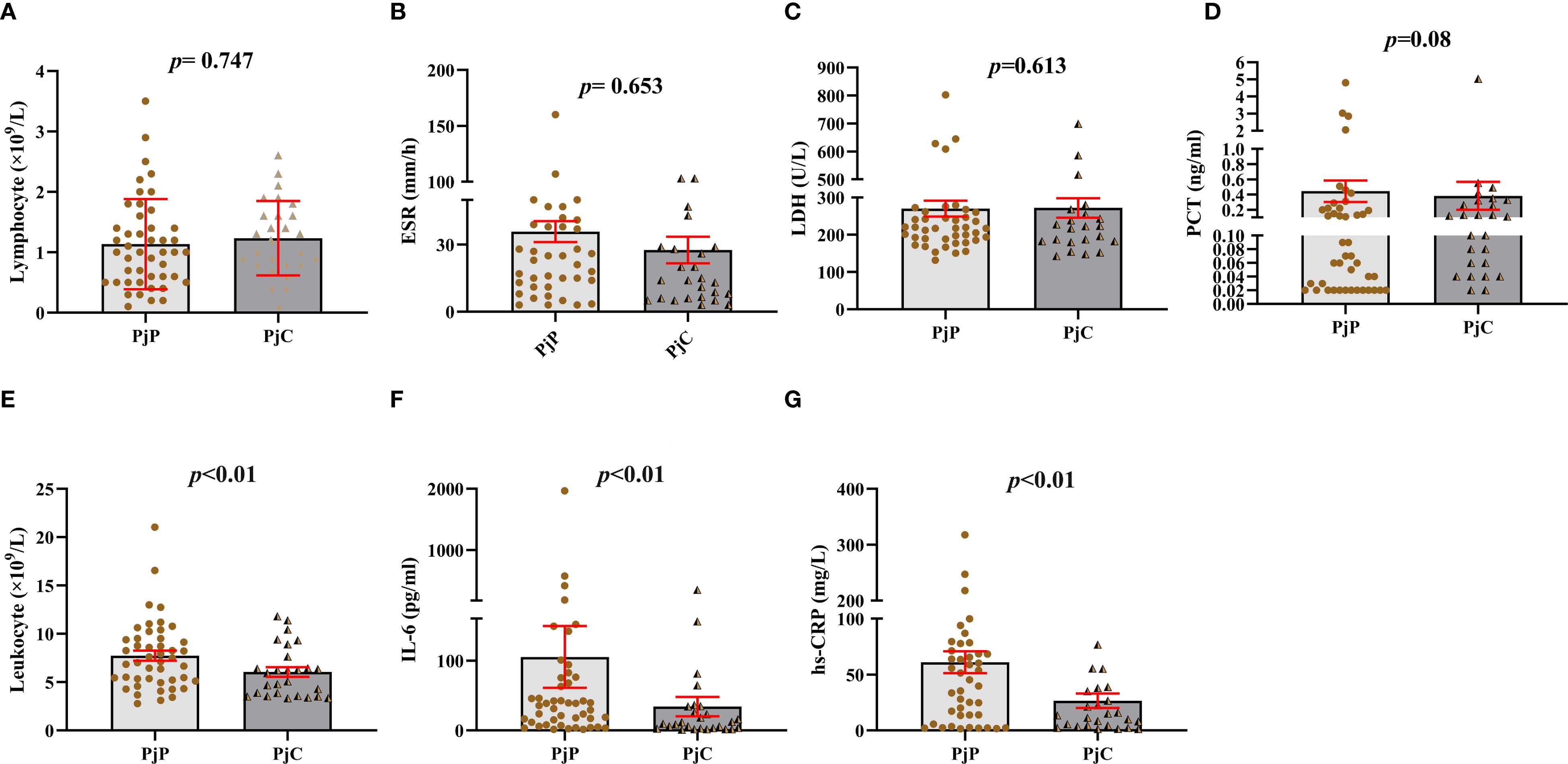
Figure 2. Blood analysis of leukocyte and lymphocyte counts, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), hypersensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels in Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PjP) and Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization (PjC) groups. (A) Comparison of the lymphocyte counts between PjP and PjC groups. (B) Comparison of the ESR levels between PjP and PjC groups. (C) Comparison of the LDH levels between PjP and PjC groups. (D) Comparison of the PCT levels between PjP and PjC groups. (E) Comparison of the leukocyte counts between PjP and PjC groups. (F) Comparison of the IL-6 levels between PjP and PjC groups. (G) Comparison of the hs-CRP levels between PjP and PjC groups.
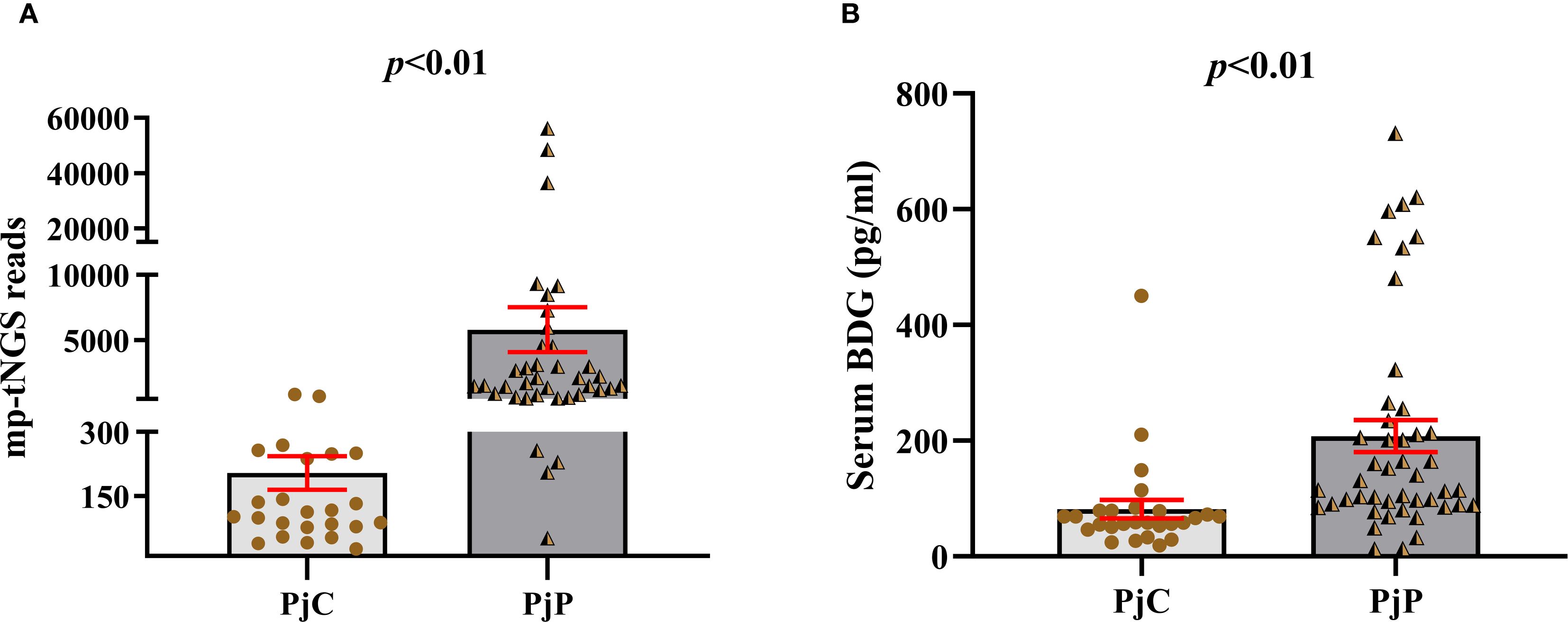
Figure 3. Number of multiplex PCR-based targeted next−generation sequencing (mp-tNGS) reads and levels of serum 1,3-β-D-glucan (BDG) between the Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PjP) and Pneumocystis jirovecii colonisation (PjC) groups. (A) Number of mp-tNGS reads between the PjP and PjC groups. (B) Level of serum BDG between the PjP and PjC groups.
3.2 Diagnostic efficacy of mp-tNGS and serum BDG for PjP
The AUROC of BALF mp-tNGS for discriminating PjP from colonization was 0.935 (95% CI: 0.88–0.99), whereas for serum BDG, it was 0.822 (95% CI: 0.72–0.93). The optimal cut-off values for distinguishing P. jirovecii infection from colonization were determined to be 355 reads for mp-tNGS (sensitivity: 89.1%; specificity: 85.2%; Figure 4A) and 84.5 pg/ml for serum BDG (sensitivity: 85.2%; specificity: 80.4%; Figure 4B). These optimal cut-off values were derived from a mathematical assessment of the ROC curves using an optimization analysis of Youden’s J statistic.
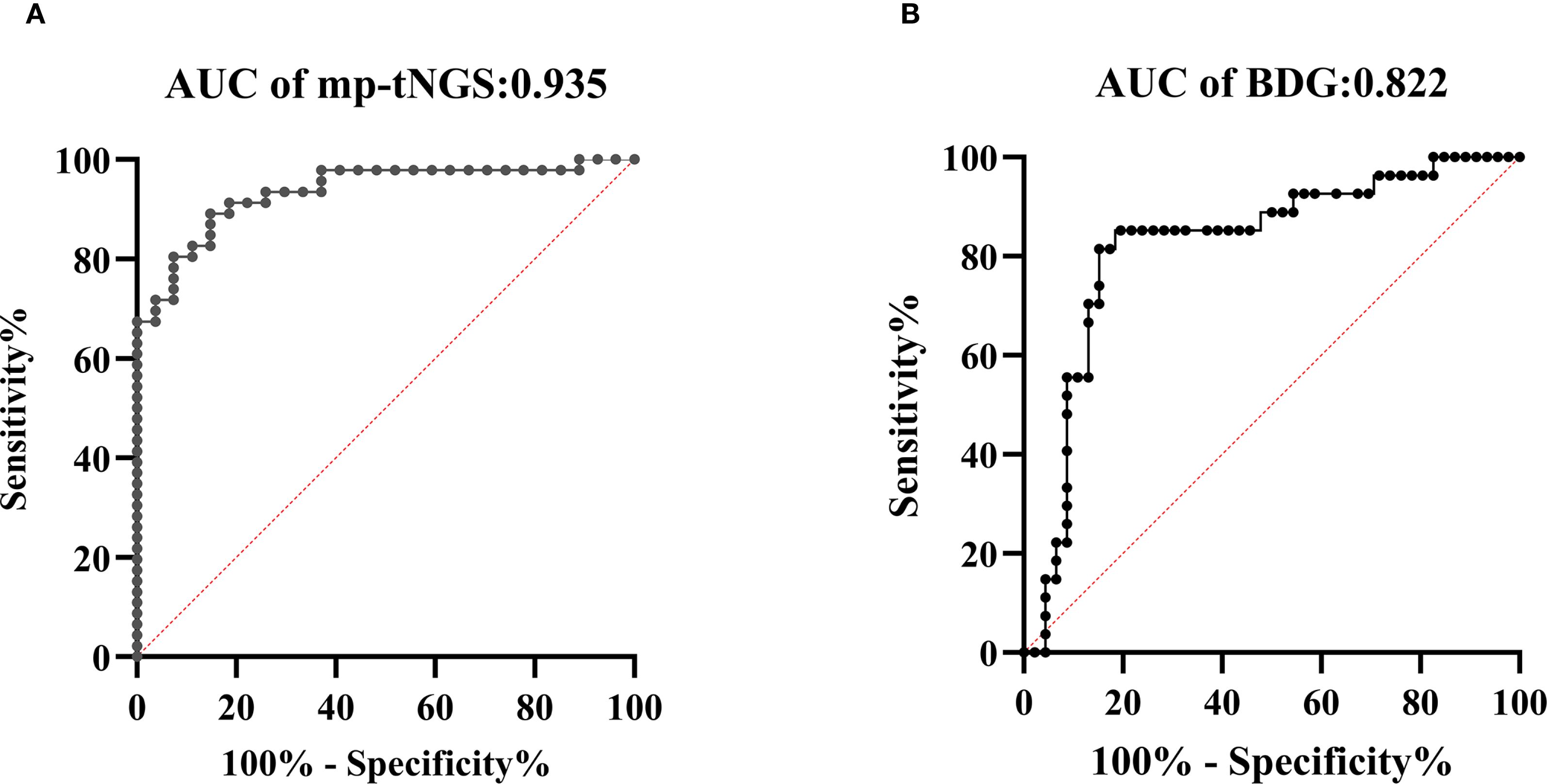
Figure 4. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated to evaluate the diagnostic performance of multiplex PCR-based targeted next−generation sequencing (mp-tNGS) and serum 1,3-β-D-glucan (BDG) assay in differentiating Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PjP) from Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization (PjC), (diagonal of ROC is usually referred to as the “no recognition rate line” or the “random guess line”). (A) The AUROC for mp-tNGS was 0.935 (A), (B) The AUROC for serum BDG assay was 0.822 (B).
3.3 The optimal threshold values for differentiating P. jirovecii infection from colonization
When mp-tNGS read counts were categorized into low (≤300), medium (300–1000), and high (≥1000) ranges, the proportions of patients diagnosed with PjP were 8.7% (4/46), 30.4% (14/46), and 60.9% (28/46), respectively (χ² =28.44, p = 0.000; Figure 5A). Conversely, among patients with PjC, the proportions were 81.5% (22/27), 18.5% (5/27), and 0% (0/27) in the low, medium, and high read count categories, respectively (χ² =44.33, p = 0.000; Figure 5B). When serum BDG levels were stratified into low (≤80 pg/ml), medium (80–200 pg/ml), and high (≥200 pg/ml) categories, the proportions of patients with PjP were 19.6% (9/46), 52.2% (24/46), and 28.3% (13/46), respectively (χ² =11.80, p = 0.003; Figure 5C). In contrast, among patients with PjC, the proportions were 81.5% (22/27), 11.1% (3/27), and 7.4% (2/27) in the low, medium, and high BDG categories, respectively (χ² =42.33, p = 0.000; Figure 5D). The scatterplot analysis revealed no significant correlation between mp-tNGS read counts and serum BDG levels in mp-tNGS-positive patients (r²=0.232, p = 0.06; Figure 6).
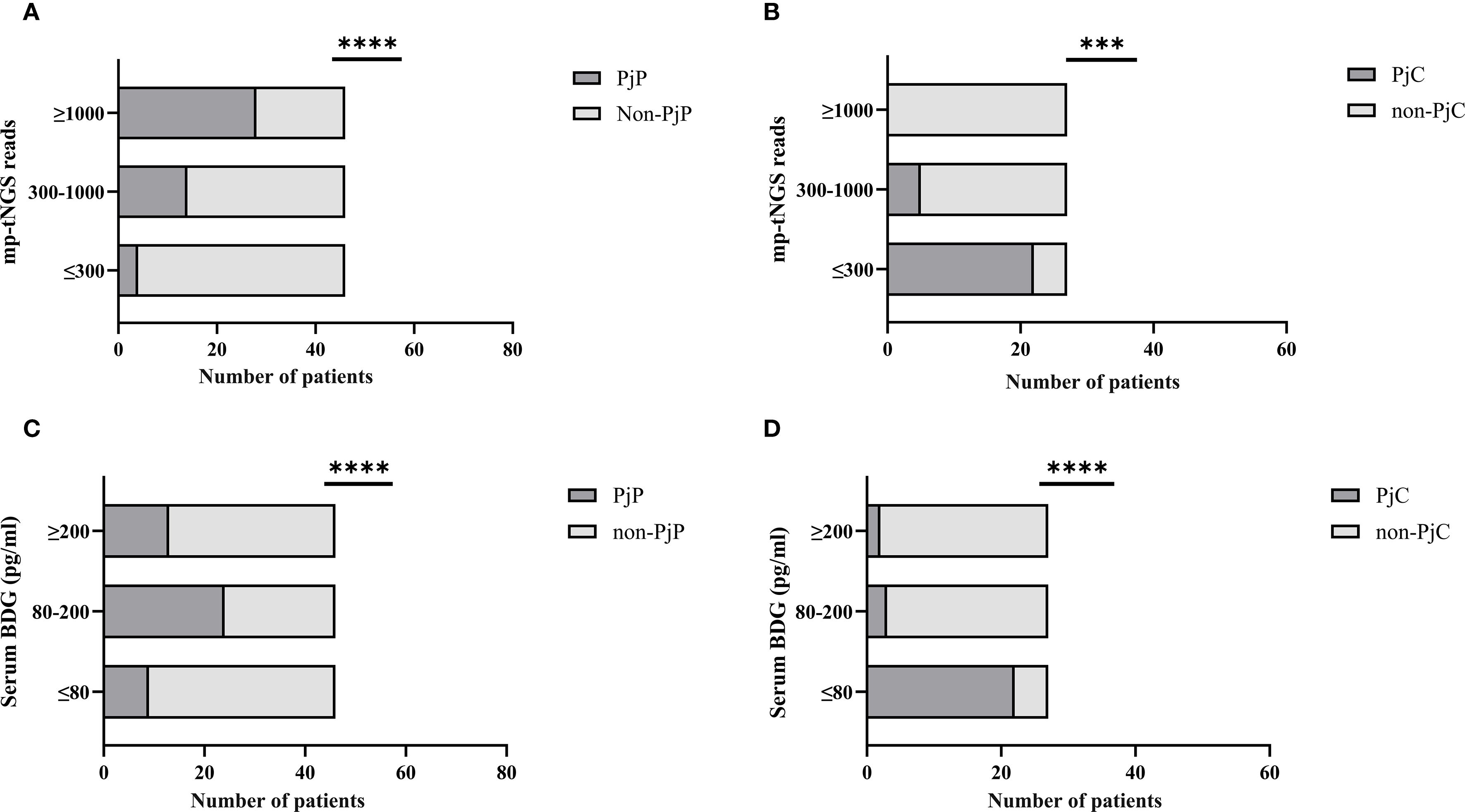
Figure 5. Proportion of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PjP) and Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization (PjC) patients across varying multiplex PCR-based targeted next−generation sequencing (mp-tNGS) read counts and serum 1,3-β-D-glucan (BDG) titers. (A) Proportion of PjP cases stratified by mp-tNGS read counts. (B) Proportion of PjC cases stratified by mp-tNGS read counts. (C) Proportion of PjP cases stratified by serum BDG titers. (D) Proportion of PjC cases stratified by serum BDG titers. ***p = 0.003; ****p = 0.000.
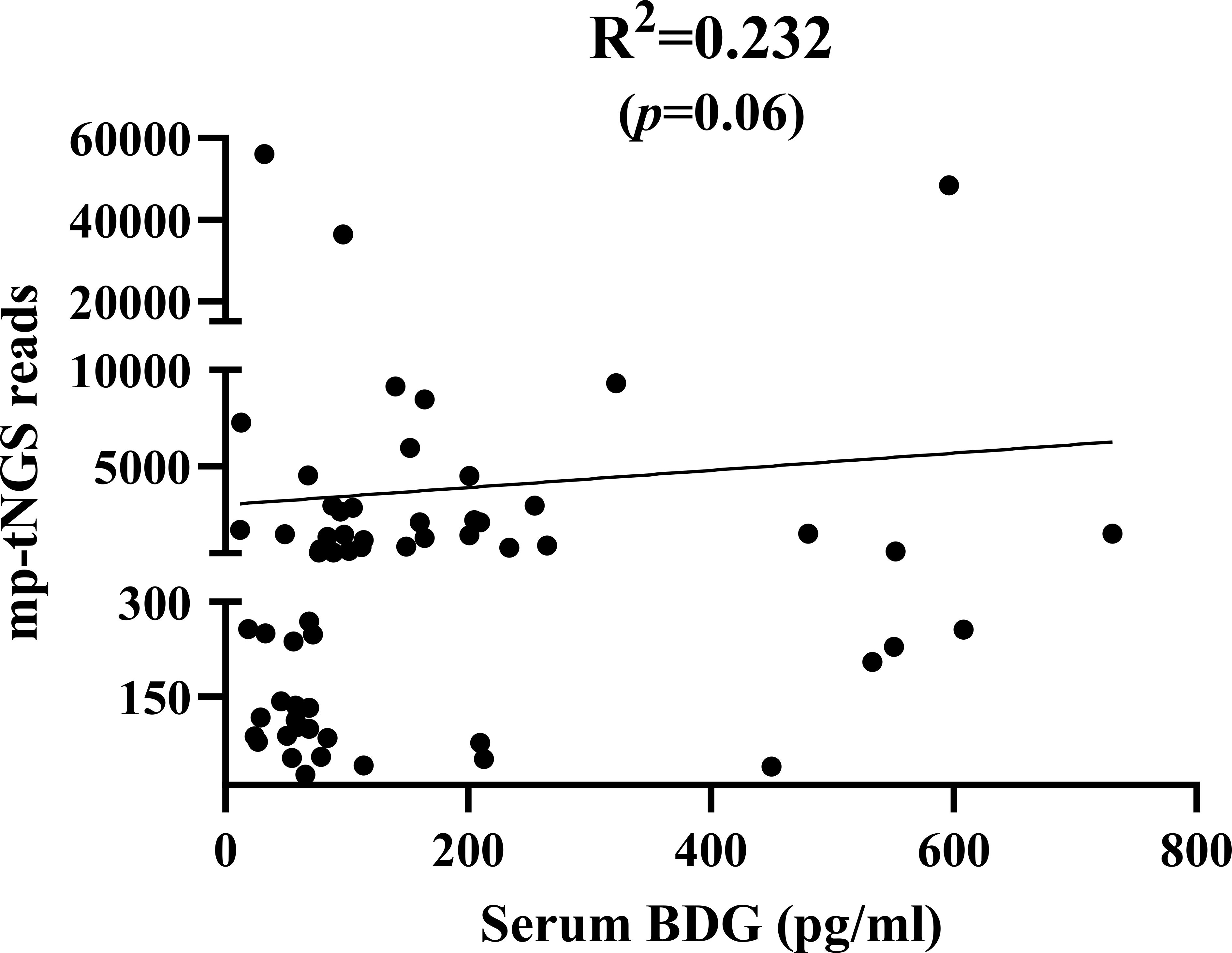
Figure 6. Scatterplot analysis of the correlation between multiplex PCR-based targeted next−generation sequencing (mp-tNGS) read counts and serum 1,3-β-D-glucan (BDG) levels in mp-tNGS-positive patients.
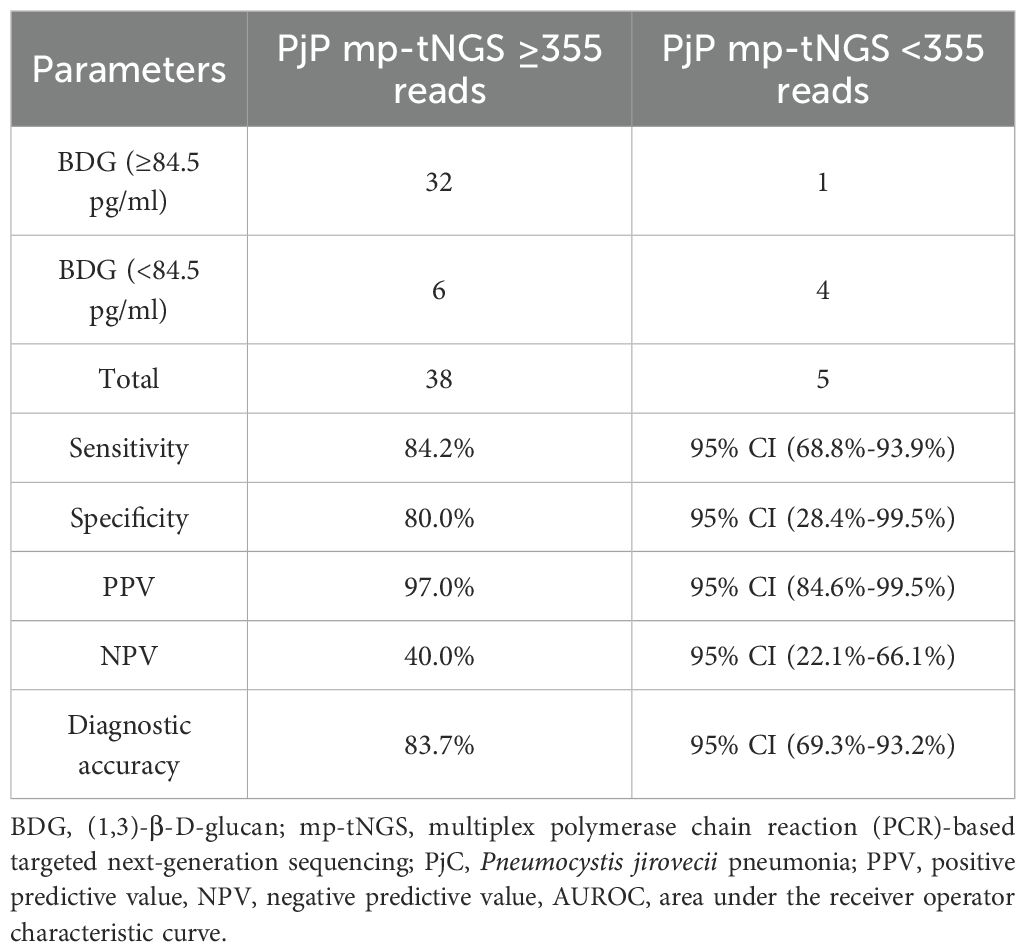
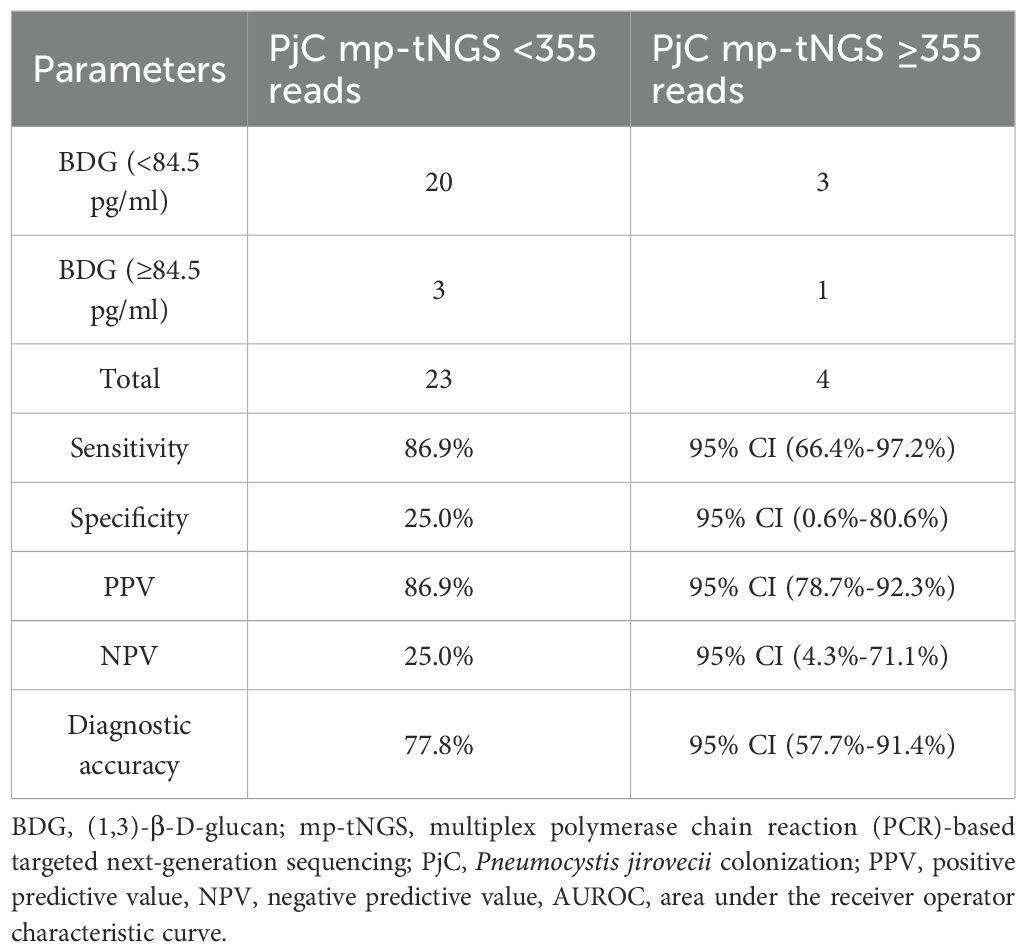
We evaluated a dual-tests approach for diagnosing PjP using combined thresholds: serum BDG ≥84.5 pg/mL AND mp-tNGS ≥355 reads. This strategy demonstrated 84.2% sensitivity (95% CI: 68.8%-93.9%), correctly identifying PjP cases, and 80.0% specificity (95% CI: 28.4%-99.5%), correctly identifying non-PjP cases. Positive results indicated 97.0% probability of true PjP (PPV; 95% CI: 84.6%-99.5%), while negative results excluded PjP in only 40.0% of cases (NPV; 95% CI: 22.1%-66.1%). Overall diagnostic accuracy ((true positives) + (true negatives))/((true positives + false positives + true negatives + false negatives)) was 83.7% (95% CI: 69.3%-93.2%; Table 2). For distinguishing PjC, we tested the inverse criteria: serum BDG <84.5 pg/mL AND mp-tNGS <355 reads. This combination achieved 86.9% sensitivity (95% CI: 66.4%-97.2%) for detecting PjC but only 25.0% specificity (95% CI: 0.6%-80.6%) for excluding non-PjC cases. Positive results indicated 86.9% probability of true PjC (PPV; 95% CI: 78.7%-92.3%), whereas negative results ruled out PjC in merely 25.0% of instances (NPV; 95% CI: 4.3%-71.1%). The overall accuracy was 77.8% (95% CI: 57.7%-91.4%; Table 3).
The clinical and radiological outcomes of patients with PjP showed varying degrees of improvement following treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) alone or in combination with other drugs, representative chest CT findings are shown in Supplementary Figure E–H.
4 Discussion
Pneumocystis jirovecii is a fungal pathogen that causes opportunistic pulmonary infections, particularly in immunocompromised individuals (Thomas and Limper, 2004; Grønseth et al., 2021). Notably, PjP is a life-threatening infection in the absence of specific treatment, whereas PjC is a less-severe presentation of Pneumocystis infection (Damiani et al., 2013). Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop novel diagnostic approaches to accurately distinguish between Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization and active infection. mp-tNGS is a highly sensitive method for detecting Pneumocystis jirovecii (Liu et al., 2024; Yin et al., 2024). However, it remains challenging to differentiate between colonization and true infection. Therefore, based on a comprehensive assessment of clinical features, the established cut-off value of mp-tNGS can be utilized to guide the initiation or discontinuation of anti-Pneumocystis jirovecii therapy.
In our study, 36.9% (n=27) of Pneumocystis jirovecii-positive patients were identified as colonization. This finding was consistent with previous reports, including a 40% colonization rate observed by Y. Jiang et al (Jiang et al., 2025). and 37.5% (24/64) documented by S. Tasaka et al (Tasaka et al., 2014); but differed from 11.7% (15/128) reported by Matsumura and colleagues (Matsumura et al., 2012), this differ is likely due to the inclusion of 60 pneumonia patients without colonization (non-colonization) in their overall sample, which expanded the sample size and consequently resulted in a lower colonization rate. Several populations have been considered as being colonized by Pneumocystis jirovecii, including immunocompromised individuals with varying degrees of immunodeficiency, patients with acute or chronic pulmonary diseases, pregnant women experiencing immunological changes, and healthcare workers frequently exposed to patients with PjP (Morris and Norris, 2012). In our study, the underlying diseases align with the reported risk factors predisposing individuals to colonization.
Various studies have investigated serum BDG as a noninvasive adjunct biomarker for diagnosing PjP in both PLWHand non-HIV-infected individuals, consistently demonstrating an elevated serum BDG levels in individuals with PjP (Tasaka et al., 2007; Cuétara et al., 2008; Pisculli and Sax, 2008; Watanabe et al., 2009; Held et al., 2011). And further studies have demonstrated that patients with active Pneumocystis jirovecii infection exhibit significantly higher serum BDG levels compared to those with P. jirovecii colonization (Matsumura et al., 2012; Damiani et al., 2013; Tasaka et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2021). Consistent with their observations, our study also found that serum BDG levels were significantly higher in the PjP group compared to the PjC group. Furthermore, we observed that PLWH with PjP had a higher serum BDG level than non-HIV-infected individuals with PjP, which is compatible with the observation by Tasaka and colleagues (Tasaka et al., 2014). This finding may be attributed to the higher fungal burden of Pneumocystis jirovecii in the lungs of PLWHwith PjP. Despite the high sensitivity of the BDG assay, false-positive results may occur in the presence of certain confounding factors, including other fungal infections, hemodialysis, Gram-negative bacteremia, severe mucositis, or the administration of intravenous immunoglobulin and the use of certain antibiotics (Onishi et al., 2012; Karageorgopoulos et al., 2013; Del Corpo et al., 2020). However, the high negative predictive value (NPV) of 96% for serum BDG suggests that levels below 80 pg/mL can almost rule out PjP, as previously concluded by Alanio et al (Alanio et al., 2016). Our findings are consistent with those of previous studies and indicate that the BDG assay is useful for excluding PjP. In our study, we established a serum BDG cut-off value of 84.5 pg/mL for distinguishing colonization from active infection; this threshold demonstrated a sensitivity of 85.2% and a specificity of 80.4%. Our findings are consistent with the results reported by Zhang et al (Zhang et al., 2025), who concluded that serum BDG showed high pooled sensitivity (0.83, 95% CI 0.77-0.88) but lower specificity (0.78, 95% CI 0.69-0.85).
To date, only two studies have analyzed the use of mp-tNGS for detecting pathogens in pulmonary infections, highlighting its superior performance in identifying Pneumocystis jiroveci (Liu et al., 2024; Yin et al., 2024). As reported by YIN Y et al (Yin et al., 2024). in a prospective cohort study comparing the detection rate of pathogens in 251 BALF samples between tNGS and mNGS, and found that mNGS performed better in detecting rare pathogens (such as Rhizobium budding, Aspergillus Niger complex, etc.), but missed a lot of P. jirovecii; while tNGS detected more viruses and P. jirovecii. Moreover, they demonstrated that the TAT for mp-tNGS was 10.3 hours, which was significantly shorter than the TAT of 16–24 h for mNGS. Importantly, compared to mp-tNGS, mNGS is limited by higher costs, interference from human genetic material, and the requirement for separate detection of DNA and RNA (Miller et al., 2019). Our results suggest that the combination of the mp-tNGS tests, applying cut-off values of 355 reads, and serum BDG detection, applying an 84.5 pg/ml threshold, can effectively differentiate Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia from colonization. However, five patients diagnosed with PjP revealed mp-tNGS reads below 355 (51, 205, 229, 256 and 349, respectively). Therefore, when mp-tNGS reads are fewer than 355, the results must be interpreted cautiously in conjunction with clinical manifestations and radiological features. The observed results—specifically, five non-HIV-infected immunocompromised patients with PjP showing mp-tNGS reads below 355 and four PjC case with read above 355—can be attributed to fungal burdens of P. jirovecii. As previously reported, the expression of PjP occurs with a lower fungal load in non-HIV-infected immunocompromised patients than PLWH (Limper et al., 1989; Fauchier et al., 2016). In our study, microscopic examination with GMS staining confirmed three cases of PjP, two of which were in PLWH, while none of the colonized or non-colonized patients had HIV infection. Consistent with previous reports, non-HIV-infected patients often develop PjP with a lower fungal load compared to PLWH (Limper et al., 1989), which can lead to false-negative results on microscopic examination (Azoulay et al., 2009).
Previous studies have suggested that serum BDG levels can be used to evaluate fungal load. However, Held et al (Held et al., 2011). demonstrated that BDG levels do not correlate with Pneumocystis jirovecii load. Consistent with these findings, our analysis revealed no correlation between mp-tNGS reads and BDG levels in mp-tNGS-positive patients, further supporting the notion that BDG may not reliably reflect P. jirovecii burden. A multicenter retrospective study by H. Sun et al (Sun et al., 2022). revealed that BALF-mNGS achieved a sensitivity of 97.40% and specificity of 85.12% for diagnosing PjP, which significantly outperforming blood BDG/LDH and BALF microscopy in sensitivity and BDG/LDH in specificity (p<0.05). Despite demonstrating good sensitivity, a notable limitation of their study is the lack of validation in distinguishing between colonization and infection. In this study, when using a combined diagnostic approach with a BDG threshold of 84.5 pg/mL and 355 mp-tNGS reads for the diagnosis of PjP, the sensitivity reached 84.2%, the PPV was 97.0%, and the diagnostic accuracy was 83.7%, which strongly support the diagnosis of PjP. Furthermore, the combination of BDG<84.5 pg/mL and mp-tNGS<355 reads for the diagnosis of PjC achieved a sensitivity of 86.9% and a PPV of 86.9%. These findings demonstrate that the combined use of serum BDG and BALF mp-tNGS provides excellent performance for distinguishing between colonization and infection with P jirovecii.
As previously reported, patients with PjP showed a high prevalence of mixed pulmonary infections (Jiang et al., 2021), we hypothesize that this may be attributed to varying degrees of immunosuppression in PjP patients. mp-tNGS has advantages in the identification of multiple microorganisms in respiratory samples, especially in the lower respiratory tract (Yin et al., 2024). In our study, BALF mp-tNGS detected one or more mixed microorganisms in 36 patients with PjP. Among these, cytomegalovirus (CMV) was the most frequently identified, followed by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), Streptococcus mitis, and influenza A virus (H1N1) and herpes simplex virus (HSV). Clinically, we consider these microorganisms less likely to be primary pathogens but rather potential colonizers. In this study, we did not perform a detailed evaluation of these patients, as the primary focus was to differentiate between colonization and infection by P jirovecii.
The application of tNGS encounters several substantial challenges, particularly in resource-limited settings. One of the primary barriers is the high upfront investment required for tNGS platforms, reagents, and bioinformatics infrastructure, which can be prohibitively expensive for many laboratories. Additionally, the tNGS workflow is inherently complex, involving multiple steps such as nucleic acid extraction, library preparation, sequencing, and data analysis (Yin et al., 2024); each of these steps introduces potential sources of error or variability, further complicating the process. Moreover, many laboratories, especially those in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), often lack the necessary infrastructure and resources to effectively implement tNGS, limiting its accessibility and utility in these regions. Our study has several limitations, including its retrospective, single-center design and the relatively small sample size. In the near future, we will provide a detailed report on the other detected mixed microorganisms in PjP.
In conclusion, the combination of BALF mp-tNGS results and serum BDG levels can effectively differentiate between P jirovecii. infection and colonization, potentially providing valuable guidance for clinical decision-making and therapeutic strategies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
This study has been approved by the ethics committee of the Taihe hospital, and performed in accordance with the principles of Good Clinical Practice following the Tri-Council guidelines. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for anonymized information to be published in this article.
Author contributions
HW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XC: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. XW: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. QC: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Software, Writing – review & editing. YWu: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft. FW: Data curation, Methodology, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YWa: Data curation, Methodology, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YT: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. TR: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. MW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Joint Fund Project for Innovative Development of Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2025AFD181).
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge all members of the Clinical Molecular Diagnosis Center, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine (Xiaofeng Wu, Yunyun Wang and Yanhui Zhou).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1611391/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure | Representative radiological characteristics of the chest in patients with PjP. Case 1: (A) Chest CT of a 62-year-old male revealed diffuse ground-glass opacities in both lungs, with significant improvement observed following treatment with sulfamethoxazole (E). Case 2: (B) Chest CT of a 61-year-old male demonstrated symmetrical perihilar high-density opacities and surrounding ground-glass opacities with indistinct margins; after sulfamethoxazole treatment, the lesions nearly resolved (F). Case 3: (C) Chest CT of a 44-year-old male showed consolidation in the left lower lobe with an air bronchogram sign, which significantly decreased after sulfamethoxazole therapy (G). Case 4: (D) Chest CT of a 61-year-old female revealed patchy opacities, ground-glass opacities, and partial consolidation in both lungs, with significant reduction in lesions following sulfamethoxazole treatment (H).
References
Alanio, A., Hauser, P. M., Lagrou, K., Melchers, W. J., Helweg-Larsen, J., Matos, O., et al. (2016). ECIL guidelines for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with haematological Malignancies and stem cell transplant recipients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 71, 2386–2396. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw156
Azoulay, É., Bergeron, A., Chevret, S., Bele, N., Schlemmer, B., and Menotti, J. (2009). Polymerase chain reaction for diagnosing pneumocystis pneumonia in non-HIV immunocompromised patients with pulmonary infiltrates. Chest 135, 655–661. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-1309
Bienvenu, A. L., Traore, K., Plekhanova, I., Bouchrik, M., Bossard, C., and Picot, S. (2016). Pneumocystis pneumonia suspected cases in 604 non-HIV and HIV patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 46, 11–17. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2016.03.018
Calderón, E. J., Gutiérrez-Rivero, S., Durand-Joly, I., and Dei-Cas, E. (2010). Pneumocystis infection in humans: diagnosis and treatment. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 8, 683–701. doi: 10.1586/eri.10.42
Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y., and Gu, J. (2018). fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, i884–i890. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Crothers, K., Huang, L., Goulet, J. L., Goetz, M. B., Brown, S. T., Rodriguez-Barradas, M. C., et al. (2011). HIV infection and risk for incident pulmonary diseases in the combination antiretroviral therapy era. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 183, 388–395. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201006-0836OC
Cuétara, M. S., Alhambra, A., Chaves, F., Moragues, M. D., Pontón, J., and del Palacio, A. (2008). Use of a serum (1–>3)-beta-D-glucan assay for diagnosis and follow-up of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 47, 1364–1366. doi: 10.1086/592753
Damiani, C., Le Gal, S., Da Costa, C., Virmaux, M., Nevez, G., and Totet, A. (2013). Combined quantification of pulmonary Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA and serum (1->3)-β-D-glucan for differential diagnosis of pneumocystis pneumonia and Pneumocystis colonization. J. Clin. Microbiol. 51, 3380–3388. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01554-13
Del Corpo, O., Butler-Laporte, G., Sheppard, D. C., Cheng, M. P., McDonald, E. G., and Lee, T. C. (2020). Diagnostic accuracy of serum (1-3)-β-D-glucan for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 26, 1137–1143. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.05.024
Donnelly, J. P., Chen, S. C., Kauffman, C. A., Steinbach, W. J., Baddley, J. W., Verweij, P. E., et al. (2020). Revision and update of the consensus definitions of invasive fungal disease from the european organization for research and treatment of cancer and the mycoses study group education and research consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 71, 1367–1376. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz1008
Dunbar, A., Schauwvlieghe, A., Algoe, S., van Hellemond, J. J., Reynders, M., Vandecasteele, S., et al. (2020). Epidemiology of pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and (Non-)use of prophylaxis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 10, 224. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00224
Fauchier, T., Hasseine, L., Gari-Toussaint, M., Casanova, V., Marty, P. M., and Pomares, C. (2016). Detection of pneumocystis jirovecii by quantitative PCR to differentiate colonization and pneumonia in immunocompromised HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 54, 1487–1495. doi: 10.1128/JCM.03174-15
Grønseth, S., Rogne, T., Hannula, R., Åsvold, B. O., Afset, J. E., and Damås, J. K. (2021). Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of immunocompromised patients infected with Pneumocystis jirovecii in a twelve-year retrospective study from Norway. BMC Infect. Dis. 21, 659. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06144-1
Held, J., Koch, M. S., Reischl, U., Danner, T., and Serr, A. (2011). Serum (1 → 3)-β-D-glucan measurement as an early indicator of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and evaluation of its prognostic value. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 17, 595–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03318.x
Hsu, W. Y., Kao, T. W., Cho, H. C., Ruan, S. Y., Lee, T. F., Huang, Y. T., et al. (2025). Performance of a hybrid capture-based target enrichment next-generation sequencing for the identification of respiratory pathogens and resistance-associated genes in patients with severe pneumonia. Microbiol. Spectr. 13, e0213024. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02130-24
Jiang, J., Bai, L., Yang, W., Peng, W., An, J., Wu, Y., et al. (2021). Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for the diagnosis of pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in non-HIV-infected patients: A retrospective study. Infect. Dis. Ther. 10, 1733–1745. doi: 10.1007/s40121-021-00482-y
Jiang, Y., Huang, X., Zhou, H., Wang, M., Wang, S., Ren, X., et al. (2025). Clinical characteristics and prognosis of patients with severe pneumonia with pneumocystis jirovecii colonization: A multicenter, retrospective study. Chest 167, 54–66. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2024.07.140
Kanj, A., Samhouri, B., Abdallah, N., Chehab, O., and Baqir, M. (2021). Host factors and outcomes in hospitalizations for pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in the United States. Mayo Clin. Proc. 96, 400–407. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.07.029
Karageorgopoulos, D. E., Qu, J. M., Korbila, I. P., Zhu, Y. G., Vasileiou, V. A., and Falagas, M. E. (2013). Accuracy of β-D-glucan for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: a meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 19, 39–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03760.x
Kotani, T., Katayama, S., Miyazaki, Y., Fukuda, S., Sato, Y., and Ohsugi, K. (2017). Risk factors for the mortality of pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in non-HIV patients who required mechanical ventilation: A retrospective case series study. BioMed. Res. Int. 2017, 7452604. doi: 10.1155/2017/7452604
Langmead, B. and Salzberg, S. L. (2012). Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 9, 357–359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923
Li, X., Li, Z., Ye, J., and Ye, W. (2023). Diagnostic performance of metagenomic next-generation sequencing for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. BMC Infect. Dis. 23, 455. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08440-4
Limper, A. H., Offord, K. P., Smith, T. F., and Martin, W. J. 2. (1989). Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Differences in lung parasite number and inflammation in patients with and without AIDS. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis 140, 1204–1209. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.5.1204
Liu, Y., Wu, W., Xiao, Y., Zou, H., Hao, S., and Jiang, Y. (2024). Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing and targeted metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing pulmonary infections in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 14, 1439472. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1439472
Liu, L., Yuan, M., Shi, Y., and Su, X. (2021). Clinical Performance of BAL Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequence and Serum (1,3)-β-D-Glucan for Differential Diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia and Pneumocystis jirovecii Colonisation. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 11, 784236. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.784236
Matsumura, Y., Ito, Y., Iinuma, Y., Yasuma, K., Yamamoto, M., Matsushima, A., et al. (2012). Quantitative real-time PCR and the (1→3)-β-D-glucan assay for differentiation between Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and colonization. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 18, 591–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03605.x
Miller, S., Naccache, S. N., Samayoa, E., Messacar, K., Arevalo, S., Federman, S., et al. (2019). Laboratory validation of a clinical metagenomic sequencing assay for pathogen detection in cerebrospinal fluid. Genome Res. 29, 831–842. doi: 10.1101/gr.238170.118
Morris, A. and Norris, K. A. (2012). Colonization by Pneumocystis jirovecii and its role in disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 25, 297–317. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00013-12
Obayashi, T., Yoshida, M., Mori, T., Goto, H., Yasuoka, A., Iwasaki, H., et al. (1995). Plasma (1–>3)-beta-D-glucan measurement in diagnosis of invasive deep mycosis and fungal febrile episodes. Lancet 345, 17–20. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(95)91152-9
Onishi, A., Sugiyama, D., Kogata, Y., Saegusa, J., Sugimoto, T., Kawano, S., et al. (2012). Diagnostic accuracy of serum 1,3-β-D-glucan for pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, invasive candidiasis, and invasive aspergillosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 50, 7–15. doi: 10.1128/JCM.05267-11
Pisculli, M. L. and Sax, P. E. (2008). Use of a serum beta-glucan assay for diagnosis of HIV-related Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in patients with negative microscopic examination results. Clin. Infect. Dis. 46, 1928–1930. doi: 10.1086/588564
Salzer, H. J. F., Schäfer, G., Hoenigl, M., Günther, G., Hoffmann, C., Kalsdorf, B., et al. (2018). Clinical, diagnostic, and treatment disparities between HIV-infected and non-HIV-infected immunocompromised patients with pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. Respiration 96, 52–65. doi: 10.1159/000487713
Stern, A., Green, H., Paul, M., Vidal, L., and Leibovici, L. (2014). Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in non-HIV immunocompromised patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, Cd005590. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005590.pub3
Sun, H., Wang, F., Zhang, M., Xu, X., Li, M., Gao, W., et al. (2022). Diagnostic value of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid metagenomic next-generation sequencing in pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in non-HIV immunosuppressed patients. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 12, 872813. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.872813
Sun, L., Zhang, K., Liu, Y., Che, L., Zhang, P., Wang, B., et al. (2024). Metagenomic next-generation sequencing targeted and metagenomic next-generation sequencing for pulmonary infection in HIV-infected and non-HIV-infected individuals. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 14, 1438982. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1438982
Tasaka, S., Hasegawa, N., Kobayashi, S., Yamada, W., Nishimura, T., Takeuchi, T., et al. (2007). Serum indicators for the diagnosis of pneumocystis pneumonia. Chest 131, 1173–1180. doi: 10.1378/chest.06-1467
Tasaka, S., Kobayashi, S., Yagi, K., Asami, T., Namkoong, H., Yamasawa, W., et al. (2014). Serum (1 → 3) β-D-glucan assay for discrimination between Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and colonization. J. Infect. Chemother. 20, 678–681. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2014.07.001
Thomas, C. F., Jr and Limper, A. H. (2004). Pneumocystis pneumonia. N Engl. J. Med. 350, 2487–2498. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra032588
Watanabe, T., Yasuoka, A., Tanuma, J., Yazaki, H., Honda, H., Tsukada, K., et al. (2009). Serum (1–>3) beta-D-glucan as a noninvasive adjunct marker for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in patients with AIDS. Clin. Infect. Dis. 49, 1128–1131. doi: 10.1086/605579
Yin, Y., Zhu, P., Guo, Y., Li, Y., Chen, H., Liu, J., et al. (2024). Enhancing lower respiratory tract infection diagnosis: implementation and clinical assessment of multiplex PCR-based and hybrid capture-based targeted next-generation sequencing. EBioMedicine 107, 105307. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105307
Yu, Q., He, J., Xing, B., Li, X., Qian, H., Zhang, H., et al. (2020). Potential value of serum Aspergillus IgG antibody detection in the diagnosis of invasive and chronic pulmonary aspergillosis in non-agranulocytic patients. BMC Pulm Med. 20, 89. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-1125-y
Zhang, P., Liu, B., Zhang, S., Chang, X., Zhang, L., Gu, D., et al. (2024). Clinical application of targeted next-generation sequencing in severe pneumonia: a retrospective review. Crit. Care 28, 225. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-05009-8
Keywords: Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP), multiplex PCR-based targeted next generation sequencing (mp-tNGS), bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), 1, 3-β-D-glucan (BDG), colonization
Citation: Wang H, Chen X, Wu X, Cao Q, Wu Y, Wang F, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Tang Y, Ren T and Wang M (2025) Combined multiplex polymerase chain reaction-based targeted next−generation sequencing and serum 1, 3-β-D-glucan for differential diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia and Pneumocystis colonization. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1611391. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1611391
Received: 14 April 2025; Accepted: 28 August 2025;
Published: 18 September 2025.
Edited by:
Meng Qin, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Leland Shapiro, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, United StatesNina Stoyanova Yancheva-Petrova, Medical University Sofia, Bulgaria
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Chen, Wu, Cao, Wu, Wang, Wang, Zhou, Tang, Ren and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Meifang Wang, d21mcHBzMDJAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Tao Ren, ZG9jdG9ycmVudGFvQHNpbmEuY29t
 Hansheng Wang
Hansheng Wang Xiao Chen2
Xiao Chen2 Xiaofeng Wu
Xiaofeng Wu Meifang Wang
Meifang Wang