- 1Department of Laboratory Sciences, Faculty of Public Health, Islamic University of Lebanon, Beirut, Lebanon
- 2Department of Biological Sciences, School of Arts and Sciences, Lebanese American University, Beirut, Lebanon
- 3Department of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Faculty of Agricultural and Food Sciences, American University of Beirut, Beirut, Lebanon
- 4Department of Nutrition and Food Science, School of Arts and Sciences, Lebanese American University, Beirut, Lebanon
Brucellosis is a recognized zoonotic disease caused by various Brucella species with significant economic and animal welfare ramifications worldwide. The spread of brucellosis from domestic livestock and wild animals, as well as its emergence in new regions, present novel epidemiological challenges. The consumption of unpasteurized milk and dairy products from unsanitary farms in endemic areas poses a serious risk to public health from brucellosis. Determining the accurate prevalence of brucellosis, particularly in regions with persistently high prevalence, basically requires careful and frequent surveillance. Furthermore, transmission and detection of the illness in non-endemic areas have become more complex due to global human and animal migration as well as the trade in animal products. This review presents an updated understanding of brucellosis, covering its classification and taxonomy, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment approaches, epidemiology, available control and prevention measures, antimicrobial resistance and the role of metal uptake in bacterial virulence. It highlights the consequences of brucellosis for global health and underscores the need for continuous research, knowledge sharing, and interdisciplinary cooperation for effective disease control and prevention.
1 Introduction
Brucellosis, frequently referred to as Malta fever, is a significant zoonotic infection that affects humans as well as domestic and wild animals. The infection can impact ungulates, marine mammals, rodents, carnivores, and primates. Bacteria of the genus Brucella were identified and named after David Bruce (1855–1931) as the primary cause of infertility and reproductive losses, with a tendency to induce mastitis, placentitis, and neonatal pneumonia (Gorvel, 2008). The classic or core Brucella species are Brucella abortus, Brucella canis, Brucella melitensis, Brucella neotomae, Brucella ovis, and Brucella suis. These are traditionally recognized as the main species within the genus Brucella. They are known for their host preferences and are often associated with specific animal populations (Occhialini et al., 2022). Brucella species are also recognized as zoonotic, meaning they could infect humans and cause serious illness (Adams, 2002). Recently, a group of taxonomists merged the brucellae with the primarily free-living, phylogenetically related Ochrobactrum spp. in the genus Brucella but Genetic comparison of Brucella spp. and Ochrobactrum spp. erroneously included into the genus Brucella confirms separate genera (De Figueiredo et al., 2015; Moreno et al., 2023). Despite significant advancements in scientific research and practical knowledge, in addition to almost a century of intensive research in many countries, brucellosis remains a persistent or reemerging zoonosis, causing significant economic losses, morbidity in humans, and prolonged poverty globally. Currently, the genus has ten species after new isolates from aquatic mammals (B. pinnipedialis and B. ceti), humans (B. inopinata), and common voles (B. microti) were identified. Although pseudogenes that affect host adaptability might play a role, the mechanisms underlying host preference are still unknown. The burden of Brucellosis on animals worldwide is significant. According to conservative estimates, more than 300 million of the 1.4 billion cattle globally are afflicted with the pathogen. Animals with brucellosis exhibit many clinical symptoms, including abortion (De Figueiredo et al., 2015). Various species of Brucella can infect humans unintentionally. Human illness typically arises via eating contaminated animal products, such as raw milk and cheese, or from direct contact with the tissues or blood of infected animals. Human brucellosis usually manifests as a high, wavy fever. However, chronic brucellosis can cause encephalomyelitis, endocarditis, hepatitis, arthritis, and orchitis, among other illnesses affecting numerous host organs (Dean et al., 2012; Young et al., 2014). The most frequent complication of Brucellosis is arthritis. The illness’s variety of symptoms makes diagnosis more difficult. Even in the majority of high-income countries, brucellosis has eluded systematic eradication efforts for over a century, and there remains no licensed human vaccine available (Bernués et al., 1997). Brucella species are classified as category B pathogens and possible bioterrorism agents due to their ability to aerosolize and the low infectious dose required for transmission. The estimated financial impact of a Brucella bioterrorism attack is second only to anthrax and tularemia, with an infectious dose of 10 to 100 organisms. Furthermore, the possibility of intentional release presents a direct threat to public health in metropolitan areas, one that cannot be addressed by the standard method of immunizing animals (Cutler et al., 2005). This review highlights all the aspects related to Brucella spp, including bacteriology, pathophysiology, diagnostics, treatment, control and prevention, virulence factors, and metal acquisition.
2 Classification and taxonomy
By comparing distinct sets of features, taxonomy, and nomenclature are examples of artificial systems designed to improve comprehension of the relationships between species. Due to the prior use of nonsystematic methodologies, such as common names, which led to unclear and erroneous nomenclature, early attempts at bacterial taxonomy were problematic. To address these issues, a decision was taken to move away from the taxonomic classification of higher organisms and begin a new framework for bacterial nomenclature. This was accomplished by creating new regulations intended to streamline classification and prevent pointless or confusing modifications.
The genus Brucella is a member of the class Alphaproteobacteria of the phylum Proteobacteria, belonging to the family Brucellaceae (family III), together with Mycoplana and Ochrobactrum, of the order Rhizobiales (Ruan, 2013). Families of organisms that are either plant or mammalian pathogens or symbionts are included in the class Alphaproteobacteria. The genera Ehrlichia, Rickettsia, and Bartonella are among the Alphaproteobacteria species that infect mammals; they are all transmitted through vectors. The small genome sizes of these organisms are compatible with their obligate intracellular survival, although this characteristic does not often characterize insect vector-based transmission, such as that of Coxiella. Brucella differs from most genera in the order Rhizobiales by having a streamlined genome in comparison to plant pathogens and the ability to infect mammalian cells—a characteristic that it shares only with Bartonella. However, there are significant differences between Brucella, a facultative intracellular pathogen, and Bartonella, an obligate intracellular pathogen. Firstly, compared to Bartonella spp., the genome of Brucella spp. is 50–100% larger and retains more metabolic processes commonly found in plant pathogens. The capacity to use plant-based compounds metabolically is consistent with the ability to persist in the soil for up to 10 weeks (Paulsen et al., 2002). The three genera share an environmental niche, as evidenced by the recent discovery of Brucella microti in soil (Scholz et al., 2008). The comparatively large genome size of Brucella species reflects their ability to exist in a variety of conditions, which may involve host adaptation. Variations in optimal growth conditions and cell surface structures (such as the cell wall) of different host species may also be reflected in the specific mechanisms for the uptake and intracellular growth of mammalian pathogens. Therefore, both Bartonella and Brucella may have acquired the ability to infect mammalian hosts, at least in part. As a result, it is possible that their nucleotide composition (i.e., G+C content) differs from that of genes conserved from progenitor organisms. Genes encoding secretion systems, adhesins, invasins, and polysaccharide biosynthesis are among the several candidates for this function (DelVecchio et al., 2002; Halling et al., 2005).
Nonetheless, it is likely that genes involved in the absorption or penetration of mammalian cells existed in ancestral species and were eliminated by plant diseases. In this scenario, the genes would not show characteristic nucleotide compositions and would need to be identified using more straightforward methods. An analysis of the genomes of several Brucella species reveals that during adaptation to an intracellular environment, genes lose their functionality due to the development of pseudogenes (Chain et al., 2005). More recently, it has been shown that adaptation to an intracellular lifestyle is linked to horizontal gene transfer specific to Brucella species, which is linked to significant virulence factors (Wattam et al., 2009). The most striking example is the suggestion that tissue tropism and host range in the nonzoonotic pathogen Brucella ovis were restricted by the inactivation of genes related to urease production, cell envelope construction, and nutrient uptake (Tsolis et al., 2009). These studies, however, do not distinguish between adaptation that occurs later in life and coevolution with a primary host.
The apparent adaptability of Brucella species to certain hosts has appropriately been the center of speculation regarding their origin. Based on currently observed host preferences, coevolution between Brucella species and their chosen hosts is a logical starting point. However, the minimal genetic variance found across Brucella species and the overall genetic variety seen between host species do not align with this straightforward conclusion. Although it is obvious that host and agent do not always evolve at the same rate, the general similarities found in Brucella species that have adapted to their hosts support either limited genetic flexibility or a more recent adaptation. Foster and colleagues concluded that most Brucella species diverged from a common ancestor (similar to B. ovis) within the past 86,000–296,000 years (Foster et al., 2009). This time frame unquestionably predates the domestication of livestock hosts, but it is by no means close to the time of host species divergence (Blair Hedges and Kumar, 2003). Their molecular clock, based on single nucleotide polymorphisms in 13 different Brucella genomes representing the original six species, supports this estimate. In conclusion, adaptation to and final preference for primary hosts do not appear to have played a significant role in the divergence of the Brucella spp.
It is important to note that the host preference of Brucella species is not as strict as it might seem. In vitro or in the wild, animals other than their primary host are susceptible to infection by Brucella bacteria. These infections, though, seem to be self-limiting. Furthermore, serious Brucella infections, including abortion storms, are exclusively caused by infection with the preferred species in regions where cattle and goats or cattle and swine overlap. The most well-studied example to date involves cattle that encountered feral pigs that were found to have contracted Brucella suis infection. Although bacteria were shed in the milk of infected animals, the infection was not transmissible, and infected cows gave birth to normal, healthy calves (Ewalt et al., 1997). Thus, the concept of host-specific adaptation is still a relevant area for further investigation.
Due to the seeming inability to reconcile genetic diversity with the wide range of phenotypes used to distinguish species and subspecies within the genus, there has been considerable interest in the taxonomy and nomenclature of Brucella (Whatmore, 2009). Brucella species have been identified since the late 19th and early 20th centuries, mostly from the host species from which they were isolated and in which they induce persistent and severe infection. David Bruce identified Brucella melitensis as the causative agent of illness in British soldiers stationed in Malta in 1887 (Ficht, 2010). But Themistocles Zammit deserves recognition for proving that goat milk was the cause of human illness (Wyatt, 2005). Brucella species were also discovered to be connected to other hosts in the following decades, such as Brucella abortus in cattle, Brucella suis in pigs, Brucella canis in dogs, Brucella ovis in sheep, and Brucella neotomae in the desert wood rat (Kurmanov et al., 2022). There are discernible variations in the severity of sickness caused by these agents when compared in a single host, such as humans, despite the fact that they have all been summarily categorized as class III biohazards. While B. ovis, B. neotomae, and B. canis are not classified as select agents, B. abortus, B. melitensis, and B. suis are regarded as significant public health hazards (Ficht, 2010).
3 Bacteriology
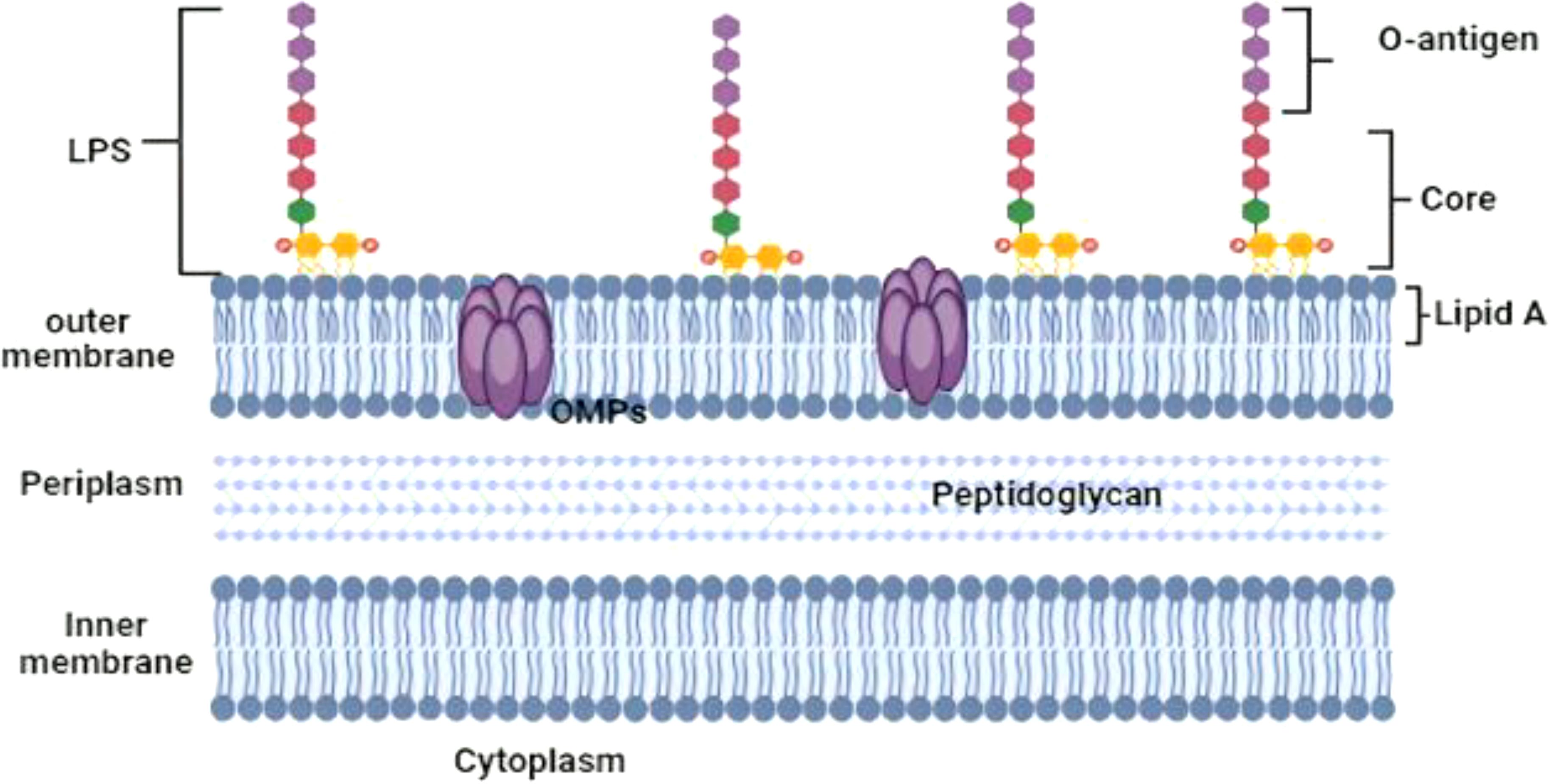
Brucella is a small Gram-negative, intracellular coccobacilli bacterium that lacks spores, flagella, and capsules (Al Dahouk et al., 2013). David Bruce discovered and isolated Brucella for the first time in 1886 from the spleens of soldiers who died from “Maltese fever” (Mantur et al., 2007). The cell wall of Brucella is made up of two membranes. Brucella’s outer membrane is composed of a phospholipid layer, outer membrane proteins, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The LPS of Brucella is made up of three components. First, the toxic component of the molecule is lipid A, a hydrophobic lipid moiety that is anchored in the membrane. Second, the non-repeated phosphorylated polysaccharide, known as the core, contributes to the outer membrane’s non-permeability. The core is divided into two distinct regions: the outer core, a branched pentasaccharide composed of glucose, galactose, and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine; and the inner core, which is characterized by sugars like L-glycero-D-manno-heptose and the essential eight-carbon sugar acid 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (Kdo). The third oligosaccharide is the O antigen, a repetitive oligosaccharide that varies significantly even among strains of the same species. It serves as a significant virulence factor for Brucella as well as an essential antigen that stimulates the body’s immunological response (Cardoso et al., 2006). Brucella primarily infects macrophages and trophoblast cells. It parasitizes host cells through a particular molecular mechanism and influences host cell death, which in turn facilitates host cell autophagy, establishing an environment that is conducive to its survival and propagation in the host cells (Weynants et al., 1996).
There are various structural variations between the enterobacteria frequently seen in alphaproteobacteria and the structure of Brucella lipid A. In addition to glucosamine, the presence of diaminoglucose implies that there are two populations of core lipid A molecules. Long saturated molecules (C16:0 to C18:0) and the exceptionally long-chain molecule 27-hydroxy-octacosanoate (27-OH-C28:0) are found in the fatty acid chains. The lack of phosphate, neutral carbohydrates, and ethanolamine is another feature. Additionally, the core region’s structure differs from that of the enterobacterial core. Mannose, glucose, quinovosamine (2-amino-2,6-dideoxy-D-glucose), non-substituted Kdo, and trace amounts of other sugars are the main constituents of the core region. The absence of the heptose region is another notable anomaly. All species of Brucella, except B. canis and B. ovis, have smooth LPS. The O-chain structure of Brucella species is a linear homopolymer of 4,6-dideoxy-4-formamido-α-D-mannose. Either 1,2 or 1,3 glycosidic links can be used to join individual units, and the proportion of these linkages in the O-polysaccharide varies between species of Brucella. Three primary epitopes—the A, M, and common epitopes—identified by monoclonal antibodies result from the specific arrangement of these connections and are present in all Brucella species. Numerous remarkable characteristics of the Brucella LPS envelope, including its permeability to hydrophobic substances and resistance to EDTA and cationic peptides such ad polymyxin, are caused by the bacterium’s unique chemical structure. Due to these structural variations, Brucella lipid A is significantly less toxic than enterobacterial lipid A, which is another notable effect. There are seven Brucella outer-membrane proteins (OMPs) that are exposed on the surface. These consist of the Ompl0, Ompl6, and Ompl9 lipoproteins, as well as the Omp25, Omp2b, and Omp31 proteins (Liu, 2015). The schematic illustration of the Brucella cell wall is shown in Figure 1.
3.1 Biology of Brucella
In vivo, Brucella rapidly propagate over the mucosal epithelial layer (Rossetti et al., 2013) and are taken up by dendritic cells (DCs) and mucosal macrophages. Through cellular tropism, Brucella is able to live and multiply inside competent phagocytic cells, avoid detection by the host immune system, and spread to target organs, such as the reproductive tract, fetal lungs, reticuloendothelial system, and placental trophoblasts in pregnant women (Adams, 2002). To comprehend the adhesion, internalization, intracellular trafficking, survival, and replication of Brucella in vulnerable hosts, in vitro investigations were employed as models. In order to internalize itself, Brucella initiate a zipper-like process on the surface of mucosal epithelial cells (Rossetti et al., 2012). Brucella binds to sialic acid and sulfated residue-containing binding molecules on the surface of epithelial cells, which are activated before and/or upon contact. However, these binding molecules are still not fully understood.
Binding stimulates small GTPase activity, which initiates a signaling cascade that reorganizes the actin cytoskeleton and induces a rearrangement of the host cell membrane along the pathogen’s surface, thereby enhancing invasion. Shortly after contact, entry occurs, necessitating the complete activation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascade. Brucella can live and multiply among inactivated phagocytic cells for up to 72 hours in vitro. In vivo, they can traverse the epithelium by undermining the function of the mucosal epithelial barrier, which enables Brucella to undergo transepithelial migration. This connection simultaneously triggers a minor innate immune response and modest proinflammatory activity (Barquero-Calvo et al., 2007). After being transferred across the epithelium, Brucella are taken up by mucosal phagocytic cells, where less than 10% of the phagocytized bacteria make it through a period of adaptation.
Brucella reduce, modify, or hide their pathogen-associated molecular patterns to evade immune recognition and trigger an immune response. On the other hand, some Toll-like receptors (TLRs; primarily TLR2, TLR4, and TLR9) start a limited intracellular signaling that activates the transcription factor NF-κB to control the expression of inflammatory cytokine genes (Oliveira et al., 2008) albeit at a 10-fold lower level than that seen with enterobacteria. Brucella live in a unique vacuole called the Brucella-containing vacuole (BCV) inside mononuclear phagocytic cells. They alter intracellular trafficking in this vacuole and convert it into a replicative compartment called a brucellosome. Research suggests that the BCV’s microenvironment has a restricted supply of nutrients12, to which Brucella quickly adjusts upon invasion (Köhler et al., 2002).
In order to adapt to low oxygen tension, the pathogen first increases amino acid catabolism, switches to alternative energy sources, and quantitatively reduces gene expression and protein synthesis involved in anabolic metabolism (Lamontagne et al., 2009). The development of a type IV secretion system (T4SS) early after infection is crucial for intracellular survival and multiplication inside mammalian cells in an in vitro brucellosis infection model. However, in vivo research has shown that while the T4SS is required for prolonged persistence, it is not necessary for invasion, systemic dispersion, or the development of the initial infection (Roux et al., 2007).
Invading Brucella that survive the adaptation phase during infection progressively restore the expression of important genes encoded by metabolic processes. This transcription-translation reactivation primarily affects cell membranes, transporters, and iron metabolism (Lamontagne et al., 2009). Brucella reproduce in tandem with the restoration of essential processes, such as the expression of virulence genes, which are occasionally strictly regulated by quorum-sensing molecules (Rambow-Larsen et al., 2008; Weeks et al., 2010). When an infection occurs, infected mononuclear phagocytic cells undergo significant transcriptional alterations during the adaptation stage. After 12 hours, when Brucella replication starts, the modifications return to normal. After adapting to the intramacrophage environment, Brucella prolongs its intracellular persistence indefinitely. This leads to the infection of desired targeted cells or tissues, including the reticuloendothelial system, endothelium, male genitalia, fetal lungs, skeletal tissues, and placental trophoblasts, as well as systemic metastasis. In order to give a more comprehensive systems biology description of the pathogenesis of brucellosis at the level of the entire host organism, there is currently a dearth of evidence describing the interaction of Brucella with these target cells and tissues (Carvalho Neta et al., 2008; Delpino et al., 2009).
4 Virulence factors and pathogenesis
4.1 Type IV secretion system
The type IV secretion system (T4SS) of Brucella has been the most extensively investigated factor influencing its virulence (DelVecchio et al., 2002). The 11 proteins that comprise the Brucella T4SS are a lytic transglycosylase (VirB1) that remodels the bacterial cell peptidoglycan layer during T4SS assembly, two ATPases (VirB4 and VirB11) that supply energy to drive effector secretion and eight proteins that comprise the core of the transporter (VirB2, VirB3, and VirB5 through VirB10) (Watarai et al., 2002c; Höppner et al., 2004; Carle et al., 2006). The operon that contains the T4SS genes is conserved in all strains of Brucella, and the virB mutants of B. abortus, B. melitensis, B. suis, B. canis, B. ovis, B. microti, and B. neotomae are significantly reduced in both natural and cultured hosts (Sieira et al., 2000; Patey et al., 2006; Sivanesan et al., 2010; Kang et al., 2019). Genes located outside of the virB operon also encode Brucella proteins that aid in the assembly and functionality of the T4SS. One such protein, VirJ, is a periplasmic protein whose exact role is still unknown, but it is necessary for the correct assembly of the T4SS and interacts directly with T4SS substrates that have a periplasmic intermediate during their export (Del Giudice et al., 2016). One of the main functions of the T4SS is to regulate the intracellular trafficking of the Brucella-containing vacuoles in host macrophages, preventing the bacteria from being killed and degraded in phagolysosomes (Comerci et al., 2001; Watarai et al., 2002a; Celli et al., 2003).
Initially, Brucella was identified as a facultative internal bacterial parasite that could multiply in phagocytes, such as granulocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells (DC), as well as epithelial, fibroblastic, and trophoblastic cells (Copin et al., 2012). Through lipid rafts, Brucella interacts with macrophage cell membranes and enters the host cell to produce Brucella-containing vacuoles (BCV), which are encircled by phagocytic vesicles (Köhler et al., 2003). Eight to twelve hours after entry, BCV matures into endosomes within the membrane-bound vacuoles, acidifies, and acquires host marker molecules through contact with lysosomes (Lys) and endosomes. Currently, the term “endosomal Brucella-containing vacuole” (eBCV) is used to refer to a BCV. The Type IV secretory system (T4SS) receives membranes derived from the Golgi apparatus and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by mediating the connection between the effector protein and the ER exit site as BCV grows and matures. The eBCV acquired Lys marker molecules (such as Rab7, LAMP-1, etc.) after losing the early host marker molecules (Von Bargen et al., 2012). When the BCV avoids Lys degradation, it will eventually reach the ER and fuse there in a way that depends on Rab2 and Sar1 (Celli et al., 2003). At this stage, the BCV is referred to as a replicative Brucella-containing vacuole, or rBCV. rBCV will change into autophagic Brucella-containing vacuole (aBCV) at a later stage of infection (Figure 2). The aBCV will not continue to develop and destroy cells at this time. At this point, Brucella has finished the intracellular circulation, and the organism uses lysis and nonlysis methods to release pathogens (Starr et al., 2012).
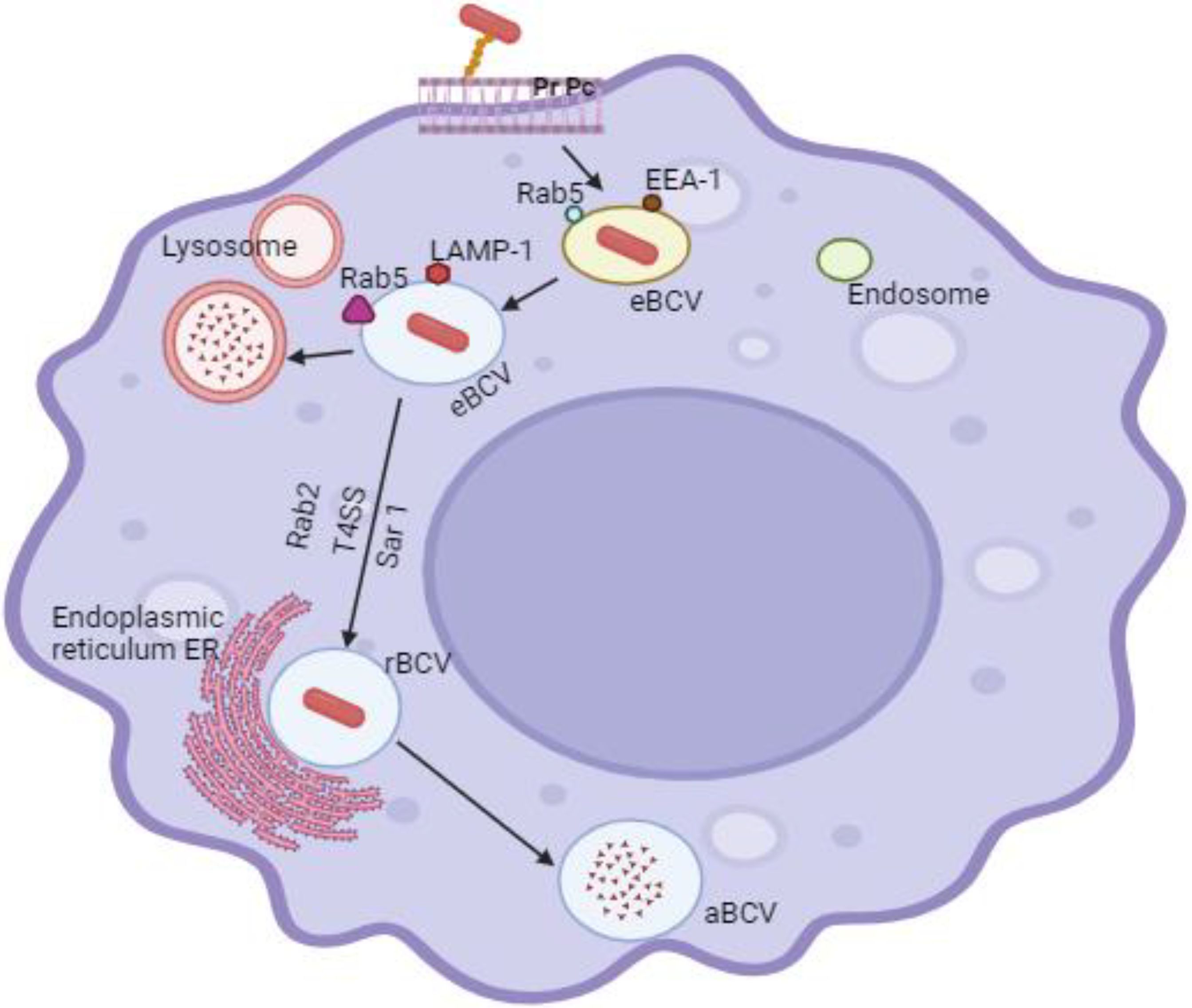
Figure 2. Through lipid rafts, Brucella interacts with macrophage cell membranes to penetrate host cells and produce Brucella-containing vacuoles (BCV), which are encircled by phagocytic vesicles. Eight to twelve hours after Brucella enters the cell, the virus (BCV) develops the endosomes in the membrane-bound vacuoles, creates acidified endosomes, and receives certain host marker molecules by contact with lysosomes (Lys) and endosomes. Currently, endosomal Brucella containing vacuole (eBCV) is the term used to refer to BCV. The Type IV secretory system (T4SS) receives membranes derived from the Golgi apparatus and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by mediating the connection between the effector protein and the ER exit site as BCV grows and matures. The eBCV acquired Lys marker molecules (such Rab7, LAMP-1, etc.) after losing the early host marker molecules.
By interacting with lipid rafts on the plasma membrane, Brucella can mediate its internalization into phagocytes and to facilitate interaction with host cells. Glycosphingolipids and cholesterol found in lipid rafts have the ability to stimulate biological processes associated to membranes, including membrane fusion, transmembrane signaling, and the production of polybasic membrane complexes (Cutler et al., 2005). LPS can stop complement-mediated bacterial lysis and host cell apoptosis, and it is a crucial molecule in the interaction between Brucella and lipid rafts in the cell (Jiménez De Bagüés et al., 2004). Brucella invades cells through lipid rafts, and it has been demonstrated that the class A scavenger receptor (SR-A) and the prion protein (PrPc) are involved in this process (Watarai et al., 2003; Kim et al., 2004).
Specific lipid rafts contain prion proteins and SR-A, which are receptors for heat shock protein 60 (HSP60) and LPS. The early survival of Brucella in macrophages can be efficiently reduced by lipid raft destruction, suggesting that lipid raft introduction is a prerequisite for the early survival of bacteria (Naroeni and Porte, 2002). Brucella enters the cell to form a phagosome and take part in the endocytosis pathway, but it can be easily detached from the phagosome, suggesting that the lipid raft-mediated signaling pathway plays a role in Brucella’s early survival (Porte et al., 2003). aBCV is required by Brucella to finish its intracellular life cycle and cell-to-cell dissemination during intracellular circulation (Starr et al., 2008). The conversion of rBCV to aBCV starts when the ER Beclin1 and PI3K form a complex, although this process gradually slows down as ATG14L is consumed. The effector protein BspB interacts with the conserved oligomeric Golgi (COG) to regulate COG-dependent transport, reorient Golgi-generated vesicles to BCV, boost rBCV production, and enhance Brucella intracellular proliferation (Jiao et al., 2021).
Modulating the host immune response is another mechanism that the Brucella T4SS increases virulence (Rolán and Tsolis, 2007; Roux et al., 2007; Rolán and Tsolis, 2008). For example, the host cell ER chaperone BiP interacts with the T4SS effector VceC (De Jong et al., 2013). In Brucella-infected cells, this interaction results in ER stress and an unfolded protein response (UPR), which in turn promotes the production of the inflammatory cytokines interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). The synthesis of these cytokines by macrophages in response to VceC leads to the formation of granulomas, which promotes the persistence of infection. Researchers hypothesize that this T4SS effector may be crucial to transmission in natural hosts because VceC-mediated inflammatory cytokine release by placental trophoblasts also causes host cell death and fetal disease in the pregnant mice model (Keestra-Gounder et al., 2016; Byndloss et al., 2019).
The T4SS effectors BtpA and BtpB, in contrast to VceC, block dendritic cells’ ability to produce inflammatory cytokines by disrupting the TLR-Myd88-MAL signaling pathway (Salcedo et al., 2008; Sengupta et al., 2010; Alaidarous et al., 2014). It has been suggested that the T4SS effectors’ dual ability to stimulate and inhibit host immune responses enables Brucella to induce a response in the host that is beneficial to their long-term intracellular persistence. This balance ensures enough immunopathology to aid in their spread to other hosts, but not strong enough to cause sterilizing immunity and end the infection (De Jong et al., 2010).
4.2 Lipopolysaccharide
Brucella strains, like most Gram-negative bacteria, produce lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which is essential for maintaining the integrity of their cell envelope (Roop et al., 2021). They have a smooth LPS (S-LPS) composed of a polysaccharide O-chain, core, and lipid A, with two major exceptions: B. ovis and B. canis, which naturally produce a crude LPS lacking the O-chain. There is ample evidence to support the significance of the O-chain for the pathogenicity of naturally occurring smooth Brucella strains (Monreal et al., 2003; Roop et al., 2021). By shielding smooth Brucella strains from the complement’s bactericidal effects (González et al., 2008; Ouahrani-Bettache et al., 2019) and the antimicrobial peptides they encounter when interacting with host phagocytes, the LPS O-chain is one way that it contributes to virulence or by acting as an adhesin. Smooth Brucella strains can enter mammalian cells via an endocytic pathway that circumvents the broad fusion of BCVs with lysosomes, thanks to the interaction of the O-chain with lipid rafts on the surface of these cells (Porte et al., 2003). Before the involvement of the T4SS effectors, this entry point is the first necessary step in the replication of BCV by smooth strains (Naroeni and Porte, 2002; Watarai et al., 2002b).
Because this pathway of entry promotes modest levels of proinflammatory cytokine production in macrophages and dendritic cells, O-chain-mediated uptake of smooth Brucella strains also plays a significant role in immune evasion (Jiménez De Bagüés et al., 2004; Billard et al., 2007). In addition to being resistant to being broken down by macrophages, smooth LPS secreted by Brucella strains into BCVs also forms complexes with major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II), which prevents these phagocytes from presenting antigens to T lymphocytes (Forestier et al., 2000; Lapaque et al., 2006a). Inhibiting caspase 2-mediated cell death in these phagocytes is yet another mechanism whereby the O-chain-mediated entrance of smooth Brucella strains into macrophages adds to virulence (Gross et al., 2000; Fernandez-Prada et al., 2003; He et al., 2006). Although the exact processes underlying this suppression are unknown, smooth strains’ ability to prolong macrophage life expectancy probably improves the macrophages’ resistance to immunological clearance and ability to spread to many organs within their mammalian hosts (Pei et al., 2006; Chen and He, 2009).
Since lipid A is the part of LPS that the host pattern recognition receptor Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) recognizes, and since the lipid A of many Gram-negative bacteria generates potent inflammatory reactions, lipid A’s are sometimes referred to as “endotoxins” (Bryant et al., 2010). The production of low endotoxin activity lipopolysaccharides (LPS) by Brucella strains has long been reported (Duenas, 2004; Tumurkhuu et al., 2006). The fact that Brucella lipid A contains very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs), in contrast to its enteric counterparts, may be one reason for its reduced inflammatory response in certain strains of the bacteria (Velasco et al., 2000; Ferguson et al., 2004). These VLCFAs most likely stop the Brucella lipid A from interacting with TLR4 in the same potent ways as other bacterial lipid A molecules (Lapaque et al., 2006b). Remarkably, human neutrophils are similarly susceptible to early cell death caused by the Brucella lipid A. Macrophages and dendritic cells then consume dead neutrophils that harbor intracellular BrucellaBrucella through non-inflammatory mechanism. This has been suggested as one further tactic that Brucella strains may use to evade the host immune system’s recognition in the early phases of infection (Barquero-Calvo et al., 2015).
The primary structural function of the LPS core in many bacteria is to connect lipid A with the O-chain. It serves the same purpose in Brucella, but more recently, research has demonstrated that the LPS core is crucial in helping these bacteria evade recognition by the host immune system (Fontana et al., 2016; Salvador-Bescós et al., 2018). To be more precise, the Brucella generates a core structure with a side chain of lateral oligosaccharides that sterically covers lipid A and prevents it from binding to TLR4 on host dendritic cells and macrophages (Figure 3). The resistance of both smooth and rough Brucella strains to complement and bactericidal peptide killing appears to be influenced by this lateral side chain and the positive charge it provides on the LPS core (Soler-Lloréns et al., 2014).
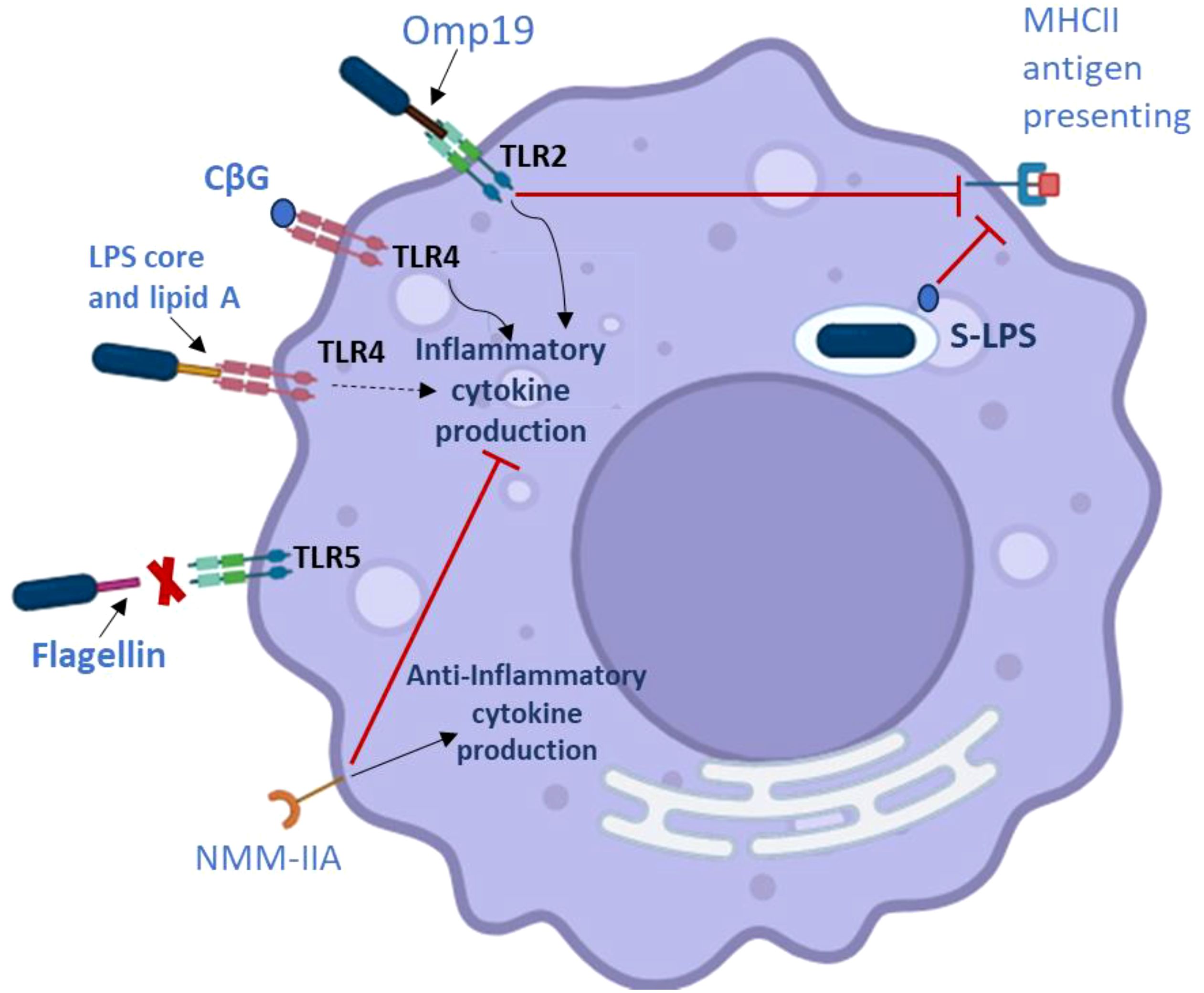
Figure 3. Factors related to Brucella virulence that affect macrophages’ ability to adjust the host immunological response. ∣, inhibition; →, activation. The dashed arrow shows that while the Brucella LPS produces a reduced inflammatory response, it does not signal through the TLR4 pathway robustly. The red X means that TLR5 does not identify the Brucella flagellin.
Brucella species that infect domestic animals, along with many strains that infect wildlife, share a highly conserved organization and composition of LPS biosynthesis genes. The absence of the O-chain from the LPS of B. ovis and B. canis is caused by well-documented genomic deletions (Zygmunt et al., 2009). However, some of the so-called early diverging Brucella strains that were isolated from human diseases and found in amphibians use the operon rmlABCD, which consists of four genes, to produce an LPS with an O-chain based on rhamnose rather than the perosamine O-side chain found in all other smooth Brucella strains (Wattam et al., 2012). It has been hypothesized that the acquisition of the genes encoding this latter kind of LPS O-chain was crucial to the evolution of Brucella strains as mammalian pathogens, given the proven significance of the perosamine O-chain in virulence (Wattam et al., 2009). It is interesting to note that serologic research indicates that the LPS cores of some early divergent strains might differ from those of the 200 typical Brucella strains.
4.3 Omp25/Omp31
Omp25, Omp25b, Omp25c, Omp25d, Omp31, Omb31p, and Omp22 are a family of highly conserved outer membrane proteins (OMPs) produced by Brucella strains that are crucial for preserving the integrity of their cell envelope (Cloeckaert et al., 2002). These β-barrel OMPs protect the bacteria against complement and other antimicrobial peptides found in the host when they function in tandem with the LPS O-chain. Their virulence contributions seem to be particularly significant for naturally occurring rough strains such as B. ovis (Edmonds et al., 2002; Martín-Martín et al., 2008). It has been demonstrated that B. abortus and B. melitensis omp25 mutants are attenuated in mice (Edmonds et al., 2002) and natural hosts (Edmonds et al., 2001), and that a B. melitensisomp31 mutant is attenuated in both mice and cultured mammalian cells (Verdiguel-Fernández et al., 2017; Fernández et al., 2020). The Brucella Omp25/Omp31 proteins have been shown to facilitate direct contacts between the Brucella and mammalian cells that are crucial for virulence, in addition to their structural roles in preserving cell envelope integrity. Some of the divergent phenotypes observed in virulence experiments for Brucella omp25 and omp31 mutants may be explained by these latter roles. In smooth strains (Manterola et al., 2007), where the LPS O-chain appears to be the predominant determinant in mammalian cell entry, there is no evidence that Omp25d and Omp22 perform this function. In contrast, Omp25d and Omp22 play significant roles in B. ovis entry into mammalian cells (Martín-Martín et al., 2008). The smooth strain B. abortus’s Omp25 protein also directly interacts with dendritic cells’ SLAMF1 protein on their surface, preventing them from maturing and releasing inflammatory cytokines (Degos et al., 2020) (Figure 4). Jubier-Maurin et al. (2001a) initially documented Omp25’s ability to suppress TNF-α production during Brucella infection; however, the molecular mechanisms of this function have only recently been determined. It is unclear exactly how these other hypothesized Omp25/Omp31 functions contribute to virulence, but there is evidence that the Brucella Omp25 and Omp31 proteins have the ability to modify other elements of host cell function during infection (Jubier-Maurin et al., 2001a; Zhang et al., 2016; Cui et al., 2017; Luo et al., 2018). The great degree of conservation of the Omp25/Omp31 proteins throughout the Rhizobiaceae family is one of its intriguing characteristics. The Omp25/Omp31 orthologs are also crucial for the productive relationships of other alphaproteobacteria with their respective eukaryotic hosts. For example, Agrobacterium tumefaciens’ wild-type pathogenicity in plants requires the Omp25 ortholog AopB (Jia et al., 2002). Bartonella henselae hbp knockdown strains are attenuated in endothelial cell cultures (Liu et al., 2012), and the Bartonella heme-binding proteins (Hbps) are likewise Omp25/Omp31 orthologs (Minnick et al., 2003). Remarkably, it has also been demonstrated that the Brucella Omp31b binds hemin in vitro, and the B. suis gene that codes for this protein is iron-controlled (Jubier-Maurin et al., 2001a).
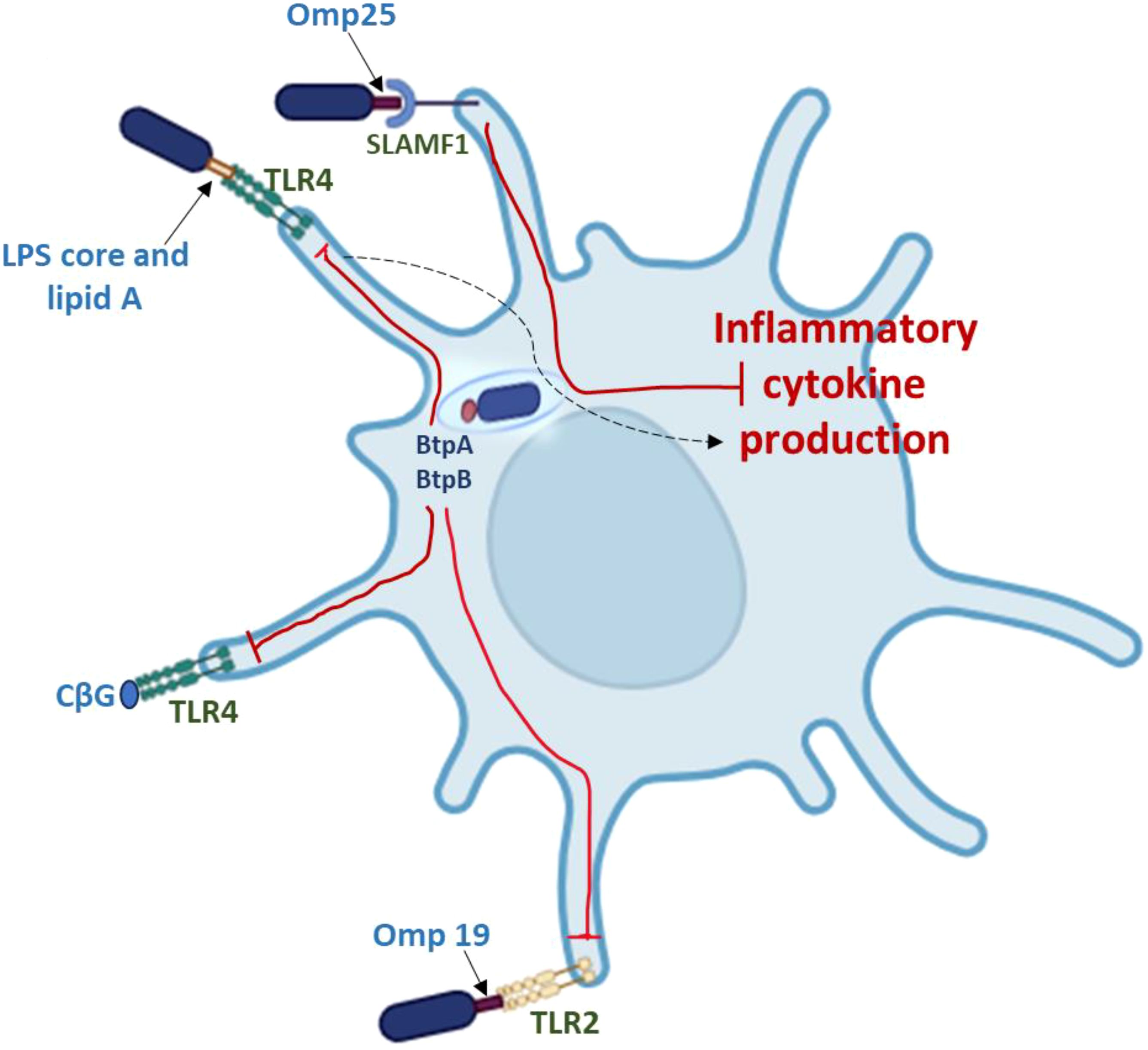
Figure 4. Factors associated with Brucella virulence that affect dendritic cells’ capacity to control the host immunological response. ∣, inhibition. The dashed arrow shows that while the Brucella LPS produces a reduced inflammatory response, it does not signal through the TLR4 pathway robustly.
It has not been demonstrated that any one Brucella species can synthesize all seven Omp25/Omp31 proteins (Martín-Martín et al., 2009). Large genomic deletions have resulted in the loss of genes encoding distinct Omp25/Omp31 proteins in some species, such as B. abortus and B. ovis (Pei et al., 2006). Other Brucella species have different patterns of Omp25/Omp31 production, which seem to be caused by smaller genetic abnormalities (Martín-Martín et al., 2009). The tight coordination of the expression of the omp25 and omp31 genes in response to environmental stimuli and physiological cues by the global regulators BvrRS, VjbR, and CtrA (Viadas et al., 2010) is consistent with the important function that this family of OMPs plays in the fundamental physiology and pathogenicity of Brucella strains.
4.4 Omp10, Omp16, and Omp19
Three outer membrane lipoproteins (Omp10, Omp16, and Omp19) are produced by different strains of Brucella (Tibor et al., 1999). The peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein (Pal), which is largely conserved in Gram-negative bacteria, has a homolog in Omp16 (Godlewska et al., 2009). These proteins interact with the constituents of the Tol complex and are essential for maintaining the structural integrity and functionality of the outer membrane. Omp16’s role as a pal homolog is consistent with the fact that it is an important gene in Brucella (Sidhu-Muñoz et al., 2016; Sternon et al., 2018; Zhi et al., 2020). Conversely, Omp19 is the most well-studied lipoprotein produced by Brucella. Through its interactions with TLR2, purified Omp19 has strong immunomodulatory activities that affect a wide range of host cells. These interactions have been linked to Brucella’s ability to evade host immune responses as well as their ability to induce immunopathology in specific tissues, including bone and the central nervous system (Coria et al., 2016; Velásquez et al., 2017) (Figures 3, 4). Furthermore, phenotypic analysis of an omp19 mutant B. abortus reveals that Omp19 shields the parental strain against lysosomal proteases encountered during intracellular residence in host macrophages and those encountered in the intestinal tract following oral infection (Pasquevich et al., 2019). Omp19 also shares significant amino acid homology with bacterial protease inhibitors (Ibañez et al., 2015), and it prevents proteases from degrading Omp25, another immunomodulatory protein. Omp10 homologs are only found in Brucella and a small number of other alphaproteobacteria (Cloeckaert et al., 1999), in contrast to Omp16 and Omp19, which exhibit homology to proteins from other bacteria. The biological role of this Omp is uncertain. Interestingly, the equivalent B. ovis mutants do not exhibit significant attenuation in mice (De Souza Filho et al., 2015), although B. abortus omp19 and omp10 mutants do (Sidhu-Muñoz et al., 2016). However, the inability to create double mutants of B. ovis omp10 omp19 raises the possibility that these proteins share a physiological role (Sidhu-Muñoz et al., 2016).
In addition to the previously mentioned proteins, Brucella species contains more proteins including Omp2a/2b, and BP26. The omp2a and omp2b gene products are homologous outer membrane proteins that function as porins, meaning they form channels in the outer membrane that allow small molecules to pass through. These proteins are crucial for the bacterial outer membrane, playing a role in nutrient and toxin transport. Variation in the omp2 locus, particularly in the omp2b gene, is linked to Brucella species identification and evolutionary adaptations (Paquet et al., 2001). Brucella BP26, also known as Omp28, is a 26 kDa periplasmic protein of Brucella species, a major immunodominant antigen that is widely used in diagnostic and vaccination efforts against brucellosis. BP26 is a target for antibodies in infected animals and humans, and its presence is a key indicator in the diagnosis of the disease (Kim D. et al., 2013).
4.5 Autotransporter adhesins
Autotransporter (AT) adhesins are of significant importance in facilitating the attachment of numerous bacterial pathogens to mammalian cells (Henderson et al., 2004). Brucella is known to possess five distinct AT adhesins. Among these, OmaA and BmaC are categorized as type I monomeric ATs (Posadas et al., 2012), whereas BtaE and BtaF fall under type II trimeric ATs (Muñoz González et al., 2019). Furthermore, BigA (264) showcases shared structural domains with the Escherichia coli adhesin intimin, representing an inverse AT adhesin (265). BmaC specifically binds to fibronectin present on the surface of host cells (260), while BtaE and BtaF have an affinity for hyaluronic acid (Ruiz-Ranwez et al., 2013). However, the specific receptors for OmaA and BigA remain unidentified. Interestingly, Brucella mutants lacking these AT adhesins demonstrate decreased attachment to epithelial cells, while still displaying wild-type intracellular replication in cultured macrophages. Moreover, these mutants exhibit attenuated virulence in mice when administered via intragastric or nasal routes, as opposed to intraperitoneal delivery. These experimental findings suggest that the primary role of AT adhesins is to enhance the attachment of Brucella to the host at mucosal surfaces during the initial phases of infection. Notably, BigA exhibits a preference for eukaryotic cell junctions (Leo et al., 2015; Czibener et al., 2016), a mechanism also employed by various bacterial pathogens to traverse mucosal barriers within the host (Ruch and Engel, 2017). Additionally, a double mutant of B. suis lacking btaE and btaF displays significantly higher attenuation in mice compared to single mutants of btaE or btaF, highlighting the complementary roles these adhesins play in virulence (Ruiz-Ranwez et al., 2013). Besides their attachment function, there is evidence suggesting that BtaF aids in protecting B. suis from the bactericidal effects of serum (Ruiz-Ranwez et al., 2013).
BmaC, BtaE, and BtaF are predominantly localized at a specific pole of the bacterial cell (Posadas et al., 2012). The concentration of these AT adhesins at the new pole, in conjunction with the observation that Brucella cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle are the predominant infectious form (Deghelt et al., 2014), has led researchers to propose that these adhesins collectively form an adhesive pole on the Brucella cell (Van Der Henst et al., 2013; De Bolle et al., 2015). Only a fraction of Brucella cells in planktonic cultures express these adhesins, indicating that the corresponding genes may only be optimally expressed upon exposure to a host-specific stimulus, such as interaction with mammalian cells. This observation aligns with the regulatory control of several AT-encoding genes by the quorum-sensing regulator VjbR (Uzureau et al., 2010) and the global regulator MucR (Pirone et al., 2018), as well as the intricate regulatory network known to govern btaE expression in B. abortus (Kleinman et al., 2017). The variability in the genes encoding AT-type adhesins within Brucella (Sieira et al., 2017) suggests functional overlap among these adhesins, as previously reported (Ruiz-Ranwez et al., 2013). Therefore, a comprehensive exploration of the roles of Brucella AT adhesins across different species and strains, utilizing mutants with multiple disrupted genes, is crucial for a precise evaluation of their contributions to virulence.
4.6 Cyclic β-1,2- D-Glucan
Numerous Gram-negative bacteria synthesize polysaccharide polymers and release them into their periplasmic space, where they execute various physiological functions (Bontemps-Gallo and Lacroix, 2015). Brucella spp. and other alphaproteobacteria discharge a cyclic polymer comprised of 17 to 20 glucose units, referred to as cyclic β-1,2-glucan (CβG), into their periplasmic compartment (Iñón De Iannino et al., 1998). Within Sinorhizobium and Agrobacterium, the synthesis of CβG is controlled by osmotic conditions, indicating a potential function of this compound in osmotic protection (Breedveld and Miller, 1994). However, in Brucella, the production of CβG is not influenced by osmotic factors (De Iannino et al., 2000), and experimental data indicate that this polysaccharide has a minor impact as an osmoprotectant in these bacteria (Roset et al., 2014). Nonetheless, CβG plays a crucial function in the virulence of Brucella (Briones et al., 2001). Research utilizing B. abortus CβG synthase mutants and purified CβG has shown that this compound disrupts lipid rafts on the vacuoles containing Brucella, thereby impeding their interactions with lysosomes (Arellano-Reynoso et al., 2005) (Figure 5). Furthermore, CβG has been demonstrated to significantly affect the ability of macrophages and dendritic cells to generate both proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines (Martirosyan et al., 2012; Roset et al., 2014; Degos et al., 2015; Guidolin et al., 2018) (Figures 3, 4). The mechanism by which CβG is released from its periplasmic site in Brucella cells for these biological functions in vivo remains unclear. Nevertheless, CβG appears to possess dual roles in virulence. It is pivotal in the intracellular transportation of Brucella to their replicative environment within host macrophages, and it modulates the host immune response to facilitate their prolonged intracellular survival. Considering the suggested polar nature of the interaction of Brucella cells with their mammalian hosts (Van Der Henst et al., 2013; De Bolle et al., 2015), it is noteworthy that the CβG synthase (Cgs) and transporter (Cgt) exhibit polar distribution on the bacterial cell (Guidolin et al., 2015). The potential contribution of this polar distribution of the CβG biosynthesis and transport apparatus to virulence remains to be elucidated.
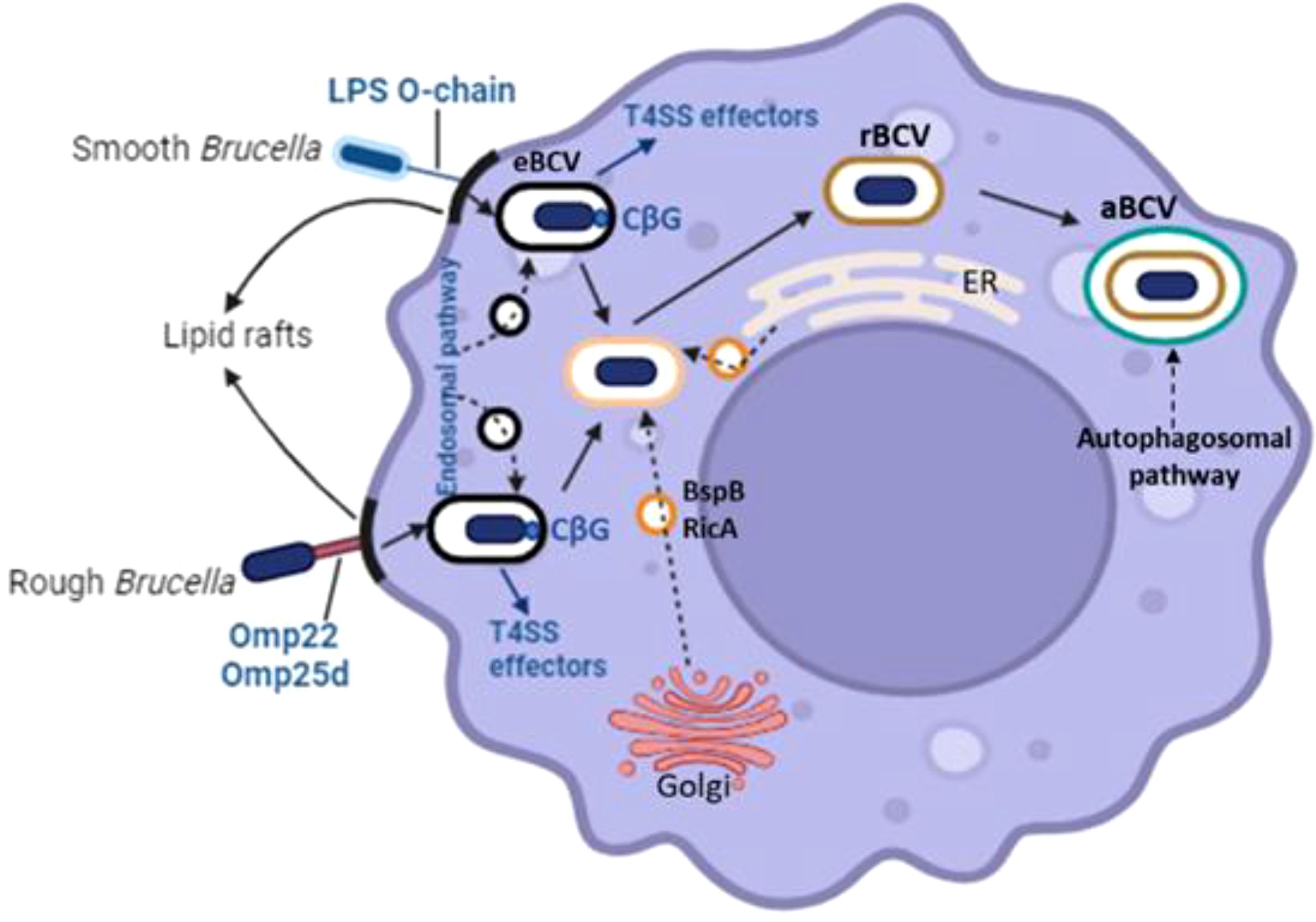
Figure 5. The contributions of various components such as the T4SS effectors, the LPS O-chain, Omp22, Omp25d, and cyclic β-1,2-Dglucan (CbG) are pivotal in the formation of the replicative Brucella-containing vacuole within host macrophages. The membrane vesicles, depicted as empty black and orange circles, are involved in trafficking from the endolysosomal pathway, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus towards the Brucella-containing vacuoles (BCVs).
4.7 Flagella
In 1998, Halling reported the identification of flagellar biosynthetic genes in B. abortus, even though the majority of Brucella strains are nonmotile (Halling, 1998). Subsequent research revealed that the majority of Brucella strains, if not all, have the genetic potential to create flagella (Fretin et al., 2005). However, only a small percentage of strains in the BO2 clade appear to be able to employ the flagella for motility, and they lack chemotaxis genes. Nevertheless, the discovery of B. melitensisfliF and flgF mutants in signature-tagged mutagenesis screens for attenuation in pregnant goats (Zygmunt et al., 2006) and mice (Lestrate et al., 2003) raised the possibility that these genes are involved in virulence. Studies have confirmed that flagellar biosynthesis genes are necessary for the wild-type virulence of B. melitensis and B. abortus strains in the mouse model. The Letesson group demonstrated that B. melitensis16M does, in fact, produce a single sheathed polar flagellum that is covered by an extension of the outer membrane (Al Dahouk et al., 2017). It is interesting to note that B. ovis mutants devoid of genes involved in flagellar biosynthesis exhibit full virulence in mice, indicating that the role played by flagella in pathogenesis may vary depending on the strain and, perhaps, the host (Sidhu-Muñoz et al., 2020).
Modulating the host immune response is one way that the flagella seem to contribute to pathogenicity (Terwagne et al., 2013). The Brucella flagellin is not detected by TLR5, in contrast to flagella from many other Gram-negative pathogens. This adds to the alleged stealthiness of infections caused by Brucella. However, data from experiments suggest that Brucella flagellin enters the cytoplasm of infected host cells and triggers an inflammatory response mediated by an inflammasome, which is crucial for “limiting” the extent of Brucella reproduction. Therefore, it has been suggested that the flagellum is an additional virulence factor that enables Brucella to modify the host immune response in a manner that facilitates the formation and persistence of chronic infections. It is also possible that these appendages, like those of other closely related alphaproteobacteria, have unidentified functions in pathogenesis, such as adhesins or surface attachment sensors (Hug et al., 2017). Furthermore, studies have revealed that sheathed flagella are involved in the release of outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) (Aschtgen et al., 2016), which is an intriguing relationship given the roles that OMVs have been suggested to play in host-pathogen interactions during Brucella infections (Pollak et al., 2012). Furthermore, sheathed flagella are relatively uncommon in bacteria.
While production of the polar flagellum in B. melitensis16M has only been observed in vitro, in bacterial cells grown to an early exponential phase in a rich medium, the genes involved in flagellar biosynthesis are tightly regulated in Brucella. These genes are readily expressed when this strain is replicating in mammalian cells (Fretin et al., 2005). A portion of the genes involved in flagellar biosynthesis in Brucella are expressed in phases; however, the regulatory networks governing the systematic temporal expression of these genes differ from those in other bacteria (Ferooz et al., 2011). Brucella flagellar gene expression is additionally regulated by the quorum-sensing regulators VjbR and BabR (also referred to as BlxR), the light-sensing regulator LovhK, the general stress response regulator RpoE1, and cyclic di-GMP-mediated signaling (Delrue et al., 2005; Kim HS. et al., 2013). Nearly all bacteria that use flagella for movement have chemotaxis genes, which enable them to regulate the direction of their flagellar rotation in response to environmental stimuli that vary in intensity (Wuichet and Zhulin, 2010). This enables them to swim away from harmful substances and toward nutrients. Given that the majority of Brucella strains do not appear to utilize their flagella for movement, the absence of chemotaxis genes in these bacteria is not particularly surprising. However, it does bring up some intriguing issues regarding how the motile BO2 strains navigate their native habitats.
4.8 Phosphatidylcholine
Prokaryotes typically lack the phospholipid phosphatidylcholine (PC), despite being a significant component of eukaryotic cell membranes (Wuichet and Zhulin, 2010). The discovery that some Brucella strains had PC in their cell envelopes occurred about 50 years ago (Thiele and Schwinn, 1973), which raised the possibility that the virulence of the outer membrane (OM) could be influenced by the presence of this “eukaryotic” phospholipid. Brucella strains use two distinct metabolic processes to produce PC: the Pcs system, which converts choline directly into PC, and the Pmt pathway, which methylates the phospholipid phosphatidylethanolamine to form PC (Herrmann et al., 2013). Independent research conducted in two distinct labs has verified that PC is crucial to Brucella pathogenicity. To obtain a comprehensive picture of how PC contributes to virulence, more research will be required as these investigations yielded inconsistent data about the relative contributions of the Pcs and Pmt pathways to virulence. However, the available experimental data generally indicates that the PC/PE ratio in Brucella strains’ outer membrane affects the bacteria’s resistance to complement and antimicrobial peptide killing, and that PC may also be involved in regulating the host’s response to infection (Bukata et al., 2008). It is also noteworthy that some other members of this group, like Agrobacterium and Rhizobia, interact with their respective plant hosts in a significant way due to PC’s incorporation into the outer membrane, which is a characteristic of alphaproteobacteria in general (Aktas et al., 2010).
4.9 Exopolysaccharides
Exopolysaccharides (EPSs) are polysaccharide polymers released by bacteria that are loosely linked with bacterial cells, generating an amorphous “slime layer” (Cuthbertson et al., 2009), or securely bound to the cell surface to form a capsule. EPSs are involved in several aspects of bacterial pathogenesis. They can act as adhesins and promote bacterial adhesion to eukaryotic cells (Tomlinson and Fuqua, 2009). Additionally, they can help bacteria avoid being recognized by the host’s innate and acquired immune responses (Muñoz et al., 2018), as well as shield them from the bactericidal effects of complement, neutrophils, and macrophages (Mishra et al., 2012). Furthermore, these polymers enable the formation of biofilms by bacteria, which adds to their ability to persist in the environment and mammalian hosts (Jones and Wozniak, 2017).
Genetically, Brucella strains are capable of producing extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) (Caswell et al., 2013), although experimental data indicate that the associated genes are highly regulated. For example, B. melitensis16M does not readily produce an EPS during routine in vitro cultivation; however, this strain produces an apparent EPS detected by calcofluor staining and forms “biofilm-like” bacterial cell aggregates in liquid culture upon disruption of a putative quorum-sensing pathway (Uzureau et al., 2007). Furthermore, a B. melitensisvirB mutant (Wang et al., 2010) and a B. abortus strain that overexpresses the glycosyltransferase WbkA (Dabral et al., 2015) have been reported to produce EPS and exhibit cellular aggregation. EPS production is also supported by reports of Brucella strains (Tang et al., 2019) forming “biofilms” and a B. melitensismucR mutant (Mirabella et al., 2013) exhibiting improved Congo red staining.
It is currently uncertain whether EPS is crucial for Brucella pathogenicity as the precise genes needed for EPS synthesis are still unclear. However, EPS synthesis is necessary for both the symbiotic and pathogenic relationships between rhizobia and agrobacteria and their respective plant hosts (Marczak et al., 2017; Thompson et al., 2018). The conservation of techniques used by alphaproteobacteria to maintain successful relationships with their eukaryotic hosts (Batut et al., 2004) raises the question of whether EPS synthesis contributes significantly to Brucella pathogenicity.
5 Epidemiology
5.1 Animal brucellosis
The incidence rate of brucellosis in developing Asian and African nations indicates that the disease is still a significant threat to both animal and human health in these areas. The prevalence of brucellosis in both Asia and African countries is 8% while it is 12% in the Indian livestock population (Suresh et al., 2022). Between 2010 and 2019, the prevalence of brucellosis in livestock ranged from 0.2% to 43.8% in cattle, 0.0% to 20.0% in goats, and 0.0% to 13.8% in sheep in many regions of the world, including sub-Saharan Africa (Djangwani et al., 2021). In Latin America, the seroprevalence of Brucella in bovine was 4%, with Venezuela having the highest prevalence (16%). Among regions, the highest seroprevalence is in Central America and the Caribbean islands (8% and 3%–15%, respectively) (Bonilla-Aldana et al., 2023).
B. canis primarily infects dogs and wild canids, but humans can also become infected. Globally, dog seroprevalence rates range from less than 1% to 15% or higher; greater rates are typically associated with stray dogs and poorer areas, most likely as a result of these communities’ higher numbers of intact canines and uncontrolled mating. In the US, B. suis biovars 1, 3, and 4 are detected. Biovars 1 through 3 have swine as their reservoir host; however, infections can also affect humans, dogs, cattle, and occasionally other species. Caribou and reindeer that inhabit Arctic locations, including Alaska, are infected by B. suis biovar 4. The eradication of B. suis from US commercial swine was achieved in 2011; however, the bacteria still exist in feral swine, especially in the Southern and Western Parts of the country, and it continues to pose a threat to commercial swine operations (Sandfoss et al., 2012).
Although endemic throughout Asia, the Middle East, South America, and Africa, B. melitensisis is not found in the United States. Three biovars and a smooth colony phenotype characterize B. melitensis. The reservoir hosts are sheep and goats, but it has also been reported in a wide range of other species. Similar to Brucella species in other host species, B. melitensis in small ruminants has similar clinical symptoms and modes of transmission (Garin-Bastuji et al., 2014).
Although B. abortus primarily affects cattle and bison, it has also been documented to affect yaks, as well as animals such as antelope, elk, sika deer, African buffalo, horses, camels, and South American camelids that encounter infected ruminants. B abortus biovar one has been eliminated from US cattle and domestic bison, but it was formerly thought to be the most serious livestock disease in the US, resulting in high rates of human infection through contact with sick animals or consumption of unpasteurized dairy products.
In parts of Europe, Africa, Asia, Central and South America, and Asia, B abortus is still enzootic. These locations also have high populations of cows, fewer economic resources, and lower implementation of control and surveillance measures (Pinn-Woodcock et al., 2023).
5.2 Human brucellosis
According to recent studies, there are 1.6–2.1 million new human cases worldwide each year, which is more significant than previously thought (Laine et al., 2023). High incidence rates are reported in areas with limited resources, including the Mediterranean, Middle East, Central Asia, and some parts of Africa. Among the nations with the highest documented rates of brucellosis are Iran, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Armenia, and Uzbekistan (Pal et al., 2017; Khurana et al., 2021).
Mexico and Peru have reported numerous occurrences in Latin America (Bano and Ahmad Lone, 2015). A study on the epidemiology of brucellosis in California by Fritz et al. found that the disease is most common among older Latino men and is significantly associated with the consumption of unpasteurized Mexican-style soft cheese. The most common species found in cases was B. melitensis. The 492 documented instances in California between 1993 and 2017 highlight the risks posed by brucellosis to human health (Fritz et al., 2021).
The yearly incidence rate for the 28 EU countries from 2017 to 2018 was 0.09 per 100,000 population (Uzunović et al., 2020). Successful intervention efforts were highlighted by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which reported a decrease in brucellosis cases from 735 in 2008 to 352 in 2011 (Bano and Ahmad Lone, 2015).
In Bosnia and Herzegovina, 263 instances were examined between 2008 and 2018, down from 102 in 2008 to only three in 2018. The evidence from other international research is consistent with the epidemiological characteristics found in this investigation. In particular, there was a noticeable male preponderance; patients were mostly from rural areas or had prior animal contact; the most affected age group was 25–49 years old (Bano and Ahmad Lone, 2015; Ali et al., 2018; Uzunović et al., 2020).
Since 1989, 80,000 instances of brucellosis have been documented annually, and the disease is found across much of Iran. Healthcare personnel in Iran have reportedly come into unintentional contact with Brucella strains while administering standard animal vaccinations (Alavi and Motlagh, 2012).
According to a study by Holt et al. (2021), brucellosis, a zoonotic illness caused by the Brucella species, is prevalent in rural India, with a seroprevalence rate of 15.1%. Due to close human-animal contact, this finding highlights the disease’s prevalence in areas with a high concentration of agriculture and livestock production, which facilitate disease transmission.
According to a study by Nawaz et al. on the epidemiology of brucellosis in Punjab, Pakistan, the seroprevalence was 13.13%, with higher rates in males aged 25 to 40 years (Sero-epidemiology, 2021).
With a national average annual incidence of 3.0 per 100,000, a four-year study found that the incidence of brucellosis varied throughout China. The rate more than doubled in Inner Mongolia, leading to a greater incidence rate in Northern China, while it significantly dropped in Xinjiang. Interestingly, men in this region aged between 45 and 64 are more than twice as likely to be impacted by women (Tao et al., 2021).
In many parts of the world, particularly sub-Saharan Africa, brucellosis is endemic. The prevalence of brucellosis in livestock varied from 0.2% to 43.8% in cattle, 0.0% to 20.0% in goats, and 0.0% to 13.8% in sheep, according to studies published between 2010 and 2019. Prevalence of human brucellosis in sub-Saharan Africa varies from 0% to 55.8%, indicating the substantial frequency of infection in this region (Djangwani et al., 2021).
A study performed in Algeria revealed that 15% of the veterinarians interviewed had contracted brucellosis during their professional practice. Direct, unprotected exposure to infected animals and/or their products, mainly during intervention for placental retention, recurrent encounters with brucellosis-infected farms, and unprotected handling of anti-Brucella vaccine appear to be the most common modes of contamination. The lack of protective equipment worn by veterinarians in their daily practice could be an important risk factor for brucellosis in these professionals. The lack of training in the handling of the antibrucellosis vaccine has made it a potential factor for brucellosis contamination, resulting in several cases of professional contamination (Lounes et al., 2022).
6 Antimicrobial resistance
The penetration of most antibiotics is restricted by the intracellular location of Brucella in reticuloendothelial cells and their preferred locations, such as bone. To treat brucellosis, antimicrobial regimens containing quinolones, doxycycline, rifampicin, streptomycin, and aminoglycosides are administered either alone or in combination (Ariza et al., 2007). There are several instances of brucellosis relapses after therapy, ranging from 5% to 15% in uncomplicated cases, and treatment failure occurs often (Del Pozo and Solera, 2015). In areas of the world where brucellosis is endemic, such as Egypt, Qatar, Iran, Malaysia, and China, antibiotic resistance in Brucella has recently been observed (Del Pozo and Solera, 2015).
Brucellosis in the Nile River Basin countries (Egypt, Sudan, Ethiopia, and Tanzania) is highly prevalent and endemic. There are several factors behind the failure of eradication of Brucella in these countries. In Ethiopia for example, brucellosis is one of the top five neglected zoonotic diseases in the country. According to several studies, the distribution and prevalence of bovine and human brucellosis in Ethiopia varies among regions in terms of animal production and management systems, community living standards and awareness levels. The disease has major zoonotic and economic implications for rural communities, particularly pastoralists (Erkyihun et al., 2022).The lack of cooperation between policymakers, health officials, veterinary sectors, and farmers is the key reason that impedes the control and prevention strategies in brucellosis endemic countries. The ‘test-and-slaughter’ strategy and the pasteurization of milk, which have been implemented successfully in the more economically developed countries, might not be the optimal control tools in most African countries due to scarcity of resources (Hikal et al., 2023).
Khan et al. studied antibiotic resistance of Brucella spp. isolated from animal populations in several locations in Egypt. In total, 34 Brucella isolates were discovered in the lymph nodes, milk, and fetal abomasal contents of sick cattle, buffaloes, sheep, and goats across nine regions. Chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, gentamicin, imipenem, rifampicin, streptomycin, and tetracycline were among the clinically used antimicrobial agents used for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Using molecular techniques, the genes and mutations linked to antibiotic resistance in Brucella isolates were verified. Eight B. abortus biovar 1 and twenty-one B. melitensis biovar 3 were among the 29 Brucella isolates that were identified and typed. The ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, imipenem, rifampicin, and streptomycin resistance rates of B. melitensiswere were 76.2%, 19.0%, 76.2%, 66.7%, and 4.8%, respectively. In contrast, 25.0%, 87.5%, 25.0%, and 37.5% of B. abortus were resistant to ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, imipenem, and rifampicin, respectively. All phenotypically resistant isolates have mutations in the rpoB gene linked to rifampicin resistance. Additionally, four isolates of B. melitensis that exhibited phenotypic resistance were found to have mutations in the gyrA and gyrB genes linked to ciprofloxacin resistance. In Egypt’s Brucella isolates, presence of these mutations reveals the molecular mechanisms underlying antibiotic resistance (Khan et al., 2019).
Another study by Dadar et al. used next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology and traditional phenotyping to assess AMR and virulence-associated variables in Brucella isolates obtained from people and animals in various parts of Iran. Their research identified B. melitensis as the most prevalent species among camels, small ruminants, and cows. There was only one human instance from which B. abortus was isolated.
For ampicillin-sulbactam, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, colistin, and rifampicin, probable intermediate or resistant phenotypic patterns were discovered. All isolates had mprF, bepG, bepF, bepC, bepE, and bepD as identified by whole-genome sequencing (WGS; however, other conventional AMR genes were not found. The genomes of all Brucella isolates contained 43 genes linked to five virulence factors, and there was no variation in the distribution of these genes. One gene encoded the Rab2-interacting conserved protein A (ricA), 12 genes were linked to a type IV secretion system (virB1-B12), two were linked to proteins that contain the toll-interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain (btpA, btpB), and 27 genes were linked to lipopolysaccharide (LPS). One gene was linked to the synthesis of cyclic β-1,2 glucans (cgs). This is the first study to disclose virulence factors and molecular-based AMR in Brucella isolated from humans and several animal hosts in Iran. Notably, most of the antibiotics used to treat human brucellosis still have the ability to in vitro affect Iranian isolates of B. abortus and B. melitensis. There was no variation in the distribution of virulence-associated genes across all isolates, and WGS was unable to identify traditional AMR genes. However, it remains unclear why the genomes of resistant strains lack traditional AMR genes. Further research is needed to investigate the proteomic and transcriptome mechanisms underlying phenotypic resistance (Dadar et al., 2023).
In India, Ayoub et al. explored the genetic basis of AMR in B. melitensis strains. Twenty-four isolates from humans and animals were subjected to antimicrobial susceptibility testing and whole-genome sequencing. The results showed resistance to ciprofloxacin (16.67%), doxycycline (20.80%), rifampicin (16.67%), and cotrimoxazole (4.17%). All isolates had efflux-related genes, including mprF, bepG, bepF, bepC, bepE, and bepD, according to genome analysis; however, no traditional AMR genes were found. Interestingly, both resistant and susceptible isolates have mutations in key AMR-associated genes like rpoB, gyrA, and folP, indicating a complex genotype–phenotype link in AMR among Brucella spp. Furthermore, it was observed that both resistant and some susceptible isolates had mutations in efflux genes, suggesting that these genes may play a part in resistance mechanisms. Nevertheless, phenotypic resistance did not always correspond with changes in AMR-associated genes, indicating a complex basis for resistance (Ayoub et al., 2024).
Moreover, In Ulanqab, Inner Mongolia, China, a total of 85 B. melitesis isolates were collected by Liu et al. from humans, assessing their resistance to nine antibiotics. The examined isolates were all sensitive to ciprofloxacin, gentamicin, levofloxacin, minocycline, sparfloxacin, doxycycline, and tetracycline. Of the isolates, 1.0% (1/85) and 7.0% (6/85) showed resistance to rifampin and cotrimoxazole, respectively. However, single isolates displaying rifampin resistance did not show alterations in the rpoB gene (Liu et al., 2018).
In Bosnia and Herzegovina, Arapović prospectively analyzed the rates of resistance among human Brucella melitensis strains. 108 B. melitensis isolates from 209 patients with diagnoses from five medical centers were included in this study. The B. melitensis isolates’ resistance patterns to the 13 most widely used antibiotics were examined. Blood cultures from 111 (53.1%) of the 209 patients tested positive for B. melitensis. 84.3% of the 108 isolates under investigation exhibited resistance to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. They found that B. melitensis was highly resistant to azithromycin. To comprehend the emergence of antibiotic resistance in human isolates of B. melitensis, further whole-genome sequencing research is required (Arapović et al., 2022).
A study performed in Norway provided a whole-genome sequencing and antimicrobial resistance in Brucella melitensis from a Norwegian perspective. The study analyzed the gene and protein sequences for seven known antibiotic resistance-associated genes (rpoB, folA, folP, gyrA, gyrB, parC, parE) and compared the sequenced isolates to the reference strain B. melitensis 16 M. Three different SNP variants were detected in rpoB, a gene associated with rifampicin resistance. The mutations detected in the rpoB gene in our data were located at nucleic acid position 1174 [392-Glu (GAG)◊Asp (GAC)], 1185 [629-Ala (GCG)◊Val (GTG)] and 2953 [985-Ala [GCC)◊Val (GTC)]. These alterations are different from mutations previously described as a cause of rifampicin resistance in Brucella. Additionally, the SNP alterations were not restricted to the four isolates phenotypically intermediate resistant to rifampicin based on gradient strip testing. The SNP changes therefore does not seem associated with rifampicin resistance. The observed SNP variants were however observed to be specific for certain lineages and sub-clusters based on WGS analysis; the SNP in position 1174 was detected in two related isolates within the Af clade, SNP in position 1185 was common for all isolates in the EM clade, and the SNP in position 2953 was restricted to the isolates in sub-cluster A in the EM clade. One mutation was detected in folA, a structural gene coding for dihydrofolate reductase and described to be involved in resistance mechanisms for trimethoprim. The detected SNP at position 73 [217-Arg (CGG)◊Leu (CTG)] was present in all isolates belonging to the Af clade in the current dataset. In folP, the gene coding for dihydrofolate synthase and associated with sulfamethoxazole resistance33, one SNP difference was detected compared to the reference strain at position 631 [211-Phe (TTC)◊Leu (CTC)].
Changes in the genes gyrA, gyrB, parC and parE were also detected. These genes are all known as fluoroquinolone-resistance determining genes, coding for DNA gyrase and DNA topoisomerase respectively. The described mutation in gyrA did not correspond with mutations related to fluoroqinolone resistance described earlier. The SNP detected in gyrA in position 1759 [599-Leu (CTG)◊Val (GTG)], was detected in all isolates in the EM clade, but was also detected in one isolate in the Af clade. The mutation in the gyrB gene was detected only in the reference strain B. abortus B19, and not in any B. melitensis isolates. Four SNP differences were detected in parC, of which two was only present in B. abortus (#21), and one SNP difference was detected in parE. The SNP difference in parE in position 27 [79-Asn (AAC)◊Ser (AGC)] was present in all isolates in the Af clade, and the SNP at position 799 [267-Arg (CGC)◊His (CAC)] in parC was present in a sub-cluster in the Af clade (Johansen et al., 2018).
7 Diagnostic tools of brucellosis
The therapeutic management and control of infection depend heavily on prompt and accurate diagnosis. Bacterial culture techniques and other serological approaches are the primary means of detection. These methods also aid in monitoring programs, herd screening, and the planning, control, and eradication tactics in diverse global locations.
7.1 Bacterial isolation
Brucella species can be diagnosed using a variety of techniques, although the most reliable ones are isolation and culture of the organism (Al Dahouk et al., 2003). The use of a selective medium, such as Farrell’s medium, is recommended because all Brucella strains develop somewhat slowly, and the specimens from which isolations are typically conducted or attempted are frequently highly contaminated (Pappas et al., 2006). A negative diagnosis may not be made until after a week of incubation, which typically lasts 72 hours. Fetal stomach fluid, spleen, liver, placenta, lochia, milk (particularly colostrum or milk within a week of calving), semen, and lymph nodes (supramammary for chronic and latent infections, and retropharyngeal for early infections) are among the specimens that can be used for Brucella isolation. Brucella colonies are high, translucent, convex, with complete boundaries, smooth, and radiant surfaces (Bedore and Mustefa, 2019). Under transmitted light, the colonies seem honey-colored. The ideal pH range for culture is between 6.6 and 7.4, while the ideal temperature range is between 20°C and 40°C. CO2 is necessary for the growth of certain Brucella species. A culture can only be deemed negative if no colonies form after two to three weeks of incubation, while typical colonies emerge after two to thirty days (Ashenafi et al., 2007).
7.2 Serological tests
Since the majority of brucellosis control and eradication programs rely on serological testing, these tests are essential for laboratory diagnosis. They are classified into two main categories: screening tests and confirmatory tests. Although a number of serological tests have been utilized for laboratory testing of brucellosis, no single test is practical for all epidemiological studies because of issues with sensitivity and/or specificity (Mert et al., 2003). The Rose Bengal plate test, indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and serum agglutination test are the most often utilized serological assays for brucellosis (Luelseged, 2018). Due to its ease of use and apparent readability, the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT) is the most popular screening method for brucellosis in both humans and animals. Personal experience, however, may influence how the RBPT results are interpreted (Cho et al., 2010).
RBT’s shortcomings include limited specificity in endemic areas, low sensitivity, especially in chronic patients, and prozones that cause strongly positive sera to look negative (Díaz et al., 2011). Another effective screening test for dairy cattle is the Milk RingTest (MRT) (Mohamand et al., 2014). Although MRT is a straightforward and efficient serological technique, it is limited to usage with cow’s milk (Mohamand et al., 2014). In a glass or plastic tube, a drop of hematoxylin-stained antigen is combined with a tiny amount of milk. MRT is highly ambiguous at the individual animal level, but it is applicable to the entire herd and provides a basic picture of the infection status. Its shortcomings include its incapacity to male animals and its decreased dependability in large herds (Luelseged, 2018).
One popular confirmatory test for brucellosis is the complement fixation test (CFT). The Organization for Animal Health (WOAH) recommends CFT as the reference test for international animal transit due to its high accuracy. It is used as a confirmatory test for B. abortus, B. melitensis, and B. ovis infections (Sam et al., 2012). CFT is typically utilized on sera that test positive for RBPT, but like RBPT, it is also heavily impacted by the overuse of the strain 19 vaccine, especially when sexually mature cows and heifers have received recent or repeated immunizations. Strict cutoff readings that indicate infection are nearly impossible to prescribe, especially when S19 vaccine reactions are involved due to their potential for abuse. Occasionally negative results in the early stages of infections, high cost and technical complexity are some of CFT’s drawbacks. Additional limitations include the test’s incapacity to be used with hemolyzed serum samples and the subjectivity of interpreting the sporadic direct activation of complement by serum (anti-complementary activity). Animals infected with species antigenically similar to Brucella can also provide false-positive results. As a common test for brucellosis diagnosis, the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) has gained popularity (Al Dahouk and Nöckler, 2011). It is a valuable method for detecting Brucella antibodies in large populations and distinguishing between the acute and chronic stages of the illness. All four antibody classes (IgM, IgG1, IgG2, and IgA) can be identified with the ELISA method (Franco et al., 2007). The ELISA is an excellent control test in regions free of brucellosis and for survey testing in areas where vaccination has not been administered. However, it is difficult to use and cannot be used everywhere, particularly in areas where vaccination has been administered and is still not widely standardized (Al Dahouk and Nöckler, 2011).
One of the common serological assays for brucellosis diagnosis is the serum agglutination test (SAT) (Memish and Balkhy, 2004). It is straightforward to execute and does not require costly tools or extensive training. The total amount of IgM and IgG agglutinating antibodies is measured by SAT. The foundation of this test is the responsiveness of antibodies to Brucella’s smooth lipopolysaccharide. Applying a serial dilution of 1:2 through 1:64 to the blood samples can increase test specificity by removing excess antibodies that cause false-negative results due to the prozone effect (Al Dahouk and Nöckler, 2011). The incapacity to identify B. canis infections and the emergence of IgM immunoglobulin cross-reactions with Salmonella urbana, Escherichia coli O116 and O157, Francisella tularensis, and Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 are disadvantages of the serum agglutination test. By adding EDTA, 2-mercaptoethanol, or antihuman globulin, for example, some of these drawbacks can be addressed (Shemesh and Yagupsky, 2011).
7.3 Molecular tests
An in vitro method for amplifying nucleic acids, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is frequently employed in the diagnosis of infectious disorders. PCR is one of the most widely used tests for brucellosis diagnosis in humans nowadays (Queipo-Ortuño et al., 2008). The most widely used molecular methods for diagnosing brucellosis are PCR and/or its variations, which are based on the amplification of particular genomic sequences of the genus, species, or even biotypes of Brucella species (Dauphin et al., 2009). Compared with traditional PCR, real-time PCR is faster and more sensitive. Because PCR products do not require post-amplification handling, there is a reduced risk of contamination in the lab and false-positive results. Brucella cells can now be tested using real-time PCR techniques, according to recent studies (Al-Nakkas et al., 2005).
7.4 Nanotechnology methods
Flower-like gold nanoparticles labeled and silver deposition rapid vertical flow technology for highly sensitive detection of Brucella antibodies. The rapid vertical flow technique (RVFT) was discovered to identify brucellosis antibodies. It can successfully avoid the false negative problem in lateral flow assay. It is easy to use, with a quick time of 2–3 minutes visible to the naked eye and no special equipment. LPS were utilized to detect brucellosis antibodies to improve the procedure’s sensitivity. The advantages of the lateral flow immunoassay were kept while a single multipurpose buffer was developed in whole blood and other biological samples to enhance the sensitivity of serum antibody detection (Elrashedy et al., 2022).
8 Treatment of brucellosis
The stage of the disease (acute, subacute, or chronic), clinical severity, presence and types of focal disease (arthritis, epididymo-orchitis, spondylitis, endocarditis, neurobrucellosis, deep abscess, aortitis, etc.), targeted population groups (pregnant patients, lactating women, children under 8 years old), underlying conditions (immunosuppression, hepatic or renal failure), and the Brucella species (Alavi and Alavi, 2013; Tosatto et al., 2020) should all be taken into consideration when designing an anti-Brucella treatment regimen. Moreover, consideration should be given to antibiotic delivery techniques, drug availability, possible contraindications, and cost (Ariza et al., 2007).
Doxycycline, rifampin, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP–SMX), aminoglycosides (gentamicin or streptomycin, infrequently amikacin), and quinolones (ciprofloxacin or ofloxacin) are used to treat human brucellosis (Ariza et al., 2007). Ceftriaxone is currently a safe medication to use during pregnancy (Bosilkovski et al., 2019) and shows promise as a combination therapy for some Brucellar-related complications, such as neurobrucellosis, endocarditis, etc (Fatani et al., 2019). If there are no contraindications, doxycycline is the most successful treatment for brucellosis and forms a fundamental part of any therapeutic combination. Its MIC90 activity range is 0.004 to 1 mg/L. It is widely accessible, reasonably priced, and exhibits strong intracellular and exceptional activity in the acidic phagolysosomal environment (Solera, 2010).
In addition, rifampin is a first-line medication that has good bactericidal activity (MIC90:rifampin, 0.02–2.5 mg/L) (Bosilkovski et al., 2021) and great phagocytic cell penetration. Its anti-Brucella activity increases by 2–8 times at low pH (Akova et al., 1999). There have been reports of decreased susceptibility and even significant resistance to rifampin in Brucella over the past few decades (Hashim et al., 2014; Torkaman Asadi et al., 2017). When treating brucellosis, aminoglycosides are regarded as a significant class of antimicrobials. Their intracellular penetration is poor (Lecaroz, 2006), but their in vitro activity is good (MIC90: streptomycin, 0.125–8, average 2.5 mg/L; gentamicin, 0.25–2 mg/L) (Hall, 1990). In vitro, TMP-SMX exhibits excellent activity, adequate tissue, and intracellular penetration (MIC90: TMP-SMX, 0.38–8, average 1–2 mg/L) (Hall, 1990).
Though it can be used in alternate and three-drug regimens, TMP-SMX should not be the first line of treatment, except for pregnant women and children under the age of eight (Ariza et al., 2007). In certain parts of the world, Brucella have a high level of resistance to TMP-SMX (Irajian et al., 2016; Gu et al., 2020). Quinolones are alternative medications for the treatment of brucellosis because they have a low MIC90 (ofloxacin: 0.02–2.5 mg/L; ciprofloxacin: 0.06–2.0 mg/L), excellent intracellular penetration, and high tissue concentration (Falagas and Bliziotis, 2006). However, they have poor bactericidal activity in an acidic intracellular environment. Due to their high cost, lack of clinical experience, and the successful results seen with previous quinolones, newer fluoroquinolones, such as levofloxacin, are not advised for routine use in brucellosis (Ariza et al., 2007).
The doxycycline–streptomycin regimen, when compared with the doxycycline–gentamicin regimen, manifested equal efficacy and overall similar tolerability (Roushan et al., 2010). Fluoroquinolones, TMP-SMX, and their combinations with rifampin or doxycycline for six weeks are examples of alternative therapies (Skalsky et al., 2008). A combination regimen of rifampin and quinolones has shown encouraging outcomes in several studies for the treatment of brucellosis (Hashemi et al., 2012). When both were given for six weeks, the combination of doxycycline, rifampin, and levofloxacin produced a higher incidence of side effects and a much lower relapse rate than the doxycycline–rifampin regimen (Hasanain et al., 2016).
9 Brucellosis-related economic losses
Economic losses associated with brucellosis in livestock have been observed in different nations (Santos et al., 2013; Singh et al., 2015). All data indicate that brucellosis causes significant global economic losses in livestock health, production, and public health (cost of treatment and productivity loss in humans), even though estimates of the costs associated with brucellosis infections are still restricted to particular countries. For example, epidemiological surveys in India revealed that livestock brucellosis caused a median estimated economic loss of US $3.4 billion (Mantur and Amarnath, 2008; Singh et al., 2018).
According to another official report, bovine brucellosis causes about $600 million in annual economic damages in Latin America. It has been estimated that farms impacted by brucellosis see a 20–30% reduction in milk production (Herrera et al., 2008; Grace et al., 2020). However, only a few nations accurately report the losses they suffer from brucellosis. For example, Argentina loses up to US $60 million a year (Samartino, 2002), India loses a median of US $3.4 billion for cattle, sheep, and goats (Singh et al., 2015), Egypt loses US $9.8 million, the United States loses US $30 million, Brazil loses about US $448 million, and Kyrgyzstan loses about US $10.6 million (Dadar et al., 2021).
In Nigeria, brucellosis in small ruminants resulted in annual economic losses of US $3.2 million two decades ago. However, the brucellosis eradication programs may be quite expensive in developing countries (Zhang et al., 2018). For instance, the national brucellosis eradication program in the United States was estimated to have cost $3.5 billion between 1934 and 1997. Numerous economic ramifications for the livestock sector and public health prompted attempts to manage brucellosis in low-income and endemic nations using various strategies that will be covered in the following sections (Mcdermott et al., 2013).
10 Control and prevention measures against Brucella
According to Perez-Sancho et al. (2015), the World Health Organization (WHO) has identified brucellosis as one of the seven neglected zoonotic diseases that contribute significantly to poverty in poor nations. Furthermore, a brucellosis outbreak control program is beneficial for dairy herd maintenance. According to Olsen and Stoffregen (2005), brucellosis control programs can employ all or any of the following strategies: vaccination, testing and removal methods, and/or sanitation. Furthermore, the most cost-effective method of controlling brucellosis is to vaccinate cattle between the ages of 4 and 12 months and animals older than 12 months (Dadar et al., 2021). However, according to Olsen and Stoffregen (2005) (Olsen and Stoffregen, 2005), immunization alone is insufficient to eradicate brucellosis in any host species. The live vaccination strains of B. abortus currently used more frequently to prevent brucellosis in cattle include RB51 and S19 (Hou et al., 2019). Furthermore, the Brucellamelitensis REV-1 vaccination is the most efficient method for eliminating and controlling brucellosis in small ruminant animals, both young and adult. This method is the most effective when it comes to extended or nomadic husbandry and situations where small ruminants have a high frequency of brucellosis (Godfroid et al., 2013). The success of B. melitensis control programs seems to depend on vaccine efficacy and coverage, which are essential for preventing Brucella infections in small ruminants (Beauvais et al., 2016). Numerous elements must be assessed by the planned control program, including knowledge of local and regional differences in brucellosis epidemiological patterns in animals, cross-sectoral brucellosis epidemiological coordination and surveillance, husbandry practices, infrastructure support, community awareness, and social customs. A test-and-slaughter approach can be used to manage bovine brucellosis on dairy farms in nations with a low prevalence of the illness (Tesfaye et al., 2011). According to reports, other preventive measures including vaccinating female bovines and certifying herds free of brucellosis, are also successful methods for controlling the disease (Blasco and Molina-Flores, 2011; Avila-Granados et al., 2019). Strict national surveillance programs are therefore required to identify affected herds and enable the implementation of any ensuing preventative and remedial actions (Rivera et al., 2002). Ultimately, a combination of strategies is required for the effective control of brucellosis in animals, including animal surveillance using serological testing to identify infected animals, preventing the spread of brucellosis to herds of animals that are not infected, and removing animal carriers of the bacteria, such as dogs, cats, and mice, from the herd to eliminate the sources of infection (Kiros et al., 2016). For long-term eradication and control programs to be implemented, farmers’ cooperation and support are essential. Therefore, through ongoing education and training initiatives, veterinary organizations should raise farmers’ awareness of prevention tactics and transmission pathways. Other crucial prerequisites include the availability of resources for prevention and suitable veterinary care (Dadar et al., 2021).
11 Metal acquisition
Every form of life depends on metals. In biological processes such as DNA replication, transcription, respiration, precursor biosynthesis, and reactions to oxidative stress, metal cofactors have both structural and catalytic roles. The first-row transition metals—cobalt, nickel, copper, manganese, and iron—are necessary for most living things. Because of their homeostasis systems, organisms only accumulate the metals necessary to meet their physiological needs. These systems include efflux systems, chaperones, transfer, and storage proteins that keep these metals in non-toxic or unreactive forms, as well as transcriptional and translational regulators that strictly control the expression of the genes encoding these metal import, export, and storage (Summers, 2009; Palmer and Skaar, 2016).
Metal homeostasis mechanisms in mammals guard against metal toxicity and prevent invading microorganisms from establishing a productive infection. Iron sequestration, for example, is a well-documented technique used by mammals to inhibit microbial pathogen reproduction (Nairz et al., 2010). In the extracellular environment, iron-binding proteins such as transferrin and lactoferrin bind firmly to iron that has not been integrated into host proteins. Most iron is present as Fe3+ at physiological pH in this oxidizing environment. The amount of ‘free’ Fe3+ in blood and tissue fluids is believed to be <10–18 M. During infection, hepcidin inhibits ferroportin from releasing iron from nutritional sources and senescent or damaged erythrocytes into the bloodstream. This limits the availability of iron in the host’s extracellular environment. This so-called ‘hypoferremic response’ is considered a crucial component of innate immunity (Nemeth et al., 2004; Weiss, 2005).
Iron is present in the host’s intracellular environment as a dynamic equilibrium between Fe2+ and Fe3+. The ratio depends on the redox status, pH, and activity of cellular ferric reductases and ferroxidases (Anderson and Vulpe, 2009). Three mechanisms have been identified for mammals to deprive microbial pathogens such as Brucella, which dwell within phagosomal compartments in host macrophages, of iron. All three of these mechanisms are considered critical components of the host’s immunological response to infection. The first involves the natural resistance-associated macrophage protein (Nramp1) (Cellier et al., 2007). This protein enters macrophages’ phagosomal membranes and removes divalent cations like Fe2+ and Mn2+. Macrophages triggered by interferon γ (IFNγ) have lower numbers of transferrin receptors on their surface, reducing iron flow through the host cells. Finally, while iron release from host cells via ferroportin is often inhibited during the hypoferremic response, the activity of ferroportin in infected macrophages increases, resulting in active iron efflux from these cells (Nairz et al., 2007).
Brucella strains require iron, manganese, zinc, and magnesium transporters for wild-type virulence.
Brucella strains require iron, manganese, and magnesium for optimal growth in vitro. Phenotypic evaluations of defined mutants indicate that efficient zinc transport is also necessary for virulence in experimentally infected animals (Roop, 2012).
11.1 Iron transport
Iron is a co-factor for many different proteins because of its chemical flexibility. Iron is presumably necessary for the activity of a wide variety of Brucella proteins. Catalase, aldolase (Roop, 2012), and CobG, an enzyme involved in the production of cobalamin (vitamin B12), are a few examples of which this requirement has been experimentally confirmed (Schroeder et al., 2009).
11.1.1 The mammalian host is an Fe-deprived environment
Because Brucella strains live mostly near their mammalian hosts, they face a unique barrier in obtaining enough iron to meet their physiological requirements (Roop et al., 2009). This is due in part to the fact that the great majority of iron in mammals is not readily available because it is integrated into proteins as heme, Fe-S clusters, or mononuclear or dinuclear Fe centers (Corbin et al., 2008). Another factor to take into account is that the soluble and physiologically active form of iron, Fe2+, can combine with reactive oxygen species to produce harmful hydroxyl radicals (OH−). Consequently, mammals’ Fe homeostasis systems keep the amounts of “free” iron in their tissues at levels also referred to as siderocalin. This prevents the action of siderophores, which are small molecular weight chelators secreted into the environment by microbes to capture and transport iron (Yang et al., 2002; Sia et al., 2013). Furthermore, the liver generates the peptide hormone hepcidin (Hp), which causes ferroportin to degrade and stops iron from being released into the bloodstream from the liver and spleen (Michels et al., 2015). Thus, the already low quantities of free Fe accessible in the extracellular environment of mammals are further reduced by the combined actions of lactoferrin, calprotectin, and HP.
AAMs absorb large amounts of proteins, including iron and heme, due to their function in scavenging injured cells and tissue components (Cairo et al., 2011). Though greater ferroportin (Fp) activity in AAMs keeps intracellular Fe levels from becoming hazardous, AAMs have bigger intracellular labile Fe pools than CAMs. Additionally, less of this Fe is deposited in ferritin in AAMs than in CAMs, despite increased Fe flow through AAMs. It is yet unknown if the larger labile Fe pool in AAMs plays a role in Brucella strains choosing to inhabit these phagocytes during persistent infections. Regarding the possible sources of iron that Brucella strains in their mammalian hosts may access, three additional points are worth taking into account: (a) the recycling of iron from mammalian erythrocytes; (b) the increased uptake of heme-containing proteins by AAMs; and (c) the intracellular trafficking of Brucella strains in host cells.
11.1.2 Fe acquisition by Brucella
11.1.2.1 Siderophore production
Microbes release siderophores, which are low molecular weight chelators, into the surrounding environment in order to absorb iron (Raymond and Dertz, 2014). When exposed to iron deficiency, strains of Brucella create two catechol siderophores: brucebactin, which is a compound based on 2,3-DHBA, and 2,3 dihydroxybenzoic acid (2,3-DHBA) (González Carreró et al., 2002). The exact structure of brucebactin is currently unclear due to its instability in the lab. However, according to the molecular characteristics of the enzymes encoded by the genes responsible for these siderophores, brucebactin is most likely a monocatechol made up of 2,3-DHBA connected to either an amino acid or a polyamine (Bellaire et al., 2003b). Although siderophore synthesis is not necessary for the persistence of Brucella strains in host macrophages, experimental data indicates that it is crucial to the pathogenicity of these bacteria in the gravid ruminant reproductive tract. For example, pregnant goats (Bellaire et al., 1999) and cattle (Bellaire et al., 2003b) do not experience abortion when exposed to a B. abortus dhbC mutant, which does not produce 2,3-DHBA or brucebactin. However, in the mouse model of chronic infection, this mutant, along with isogenic B. abortus mutants that generate 2,3-DHBA but are unable to convert it to brucebactin, exhibits wild-type pathogenicity (González Carreró et al., 2002; Michelle et al., 2002). The structures of Brucella siderophores are shown in Figure 6.
The ability of B. abortus to use erythritol as its preferred carbon and energy source has been proposed as one reason for the apparent differential demand for siderophore formation in the bovine reproductive system. This four-carbon sugar alcohol is produced in large quantities by ruminant placental trophoblasts in the later stages of pregnancy. It has been suggested that the Brucella’s ability to effectively use this carbon source is connected to their virulence in pregnant ruminants. B. abortus 2308 exhibits a significantly higher requirement for iron while growing in the presence of erythritol than when growing with other easily utilizable carbon and energy sources, according to in vitro investigations (Bellaire et al., 2003a; Jain et al., 2011). It has been suggested that the formation of siderophores is crucial in providing this strain with the iron required to support the broad and quick bacterial reproduction in placental trophoblasts that results in abortion (Bellaire et al., 2003a).
When exposed to iron shortage in vitro, not all strains of B. abortus and B. melitensis produce catechol siderophores (Roop, 2012). Therefore, it will be crucial to clarify the relationship between siderophore synthesis and erythritol metabolism in Brucella strains and conduct conclusive research to ascertain whether or not this relationship accounts for the severe attenuation that the B. abortus dhbC mutant exhibits in pregnant ruminants. Determining whether or whether siderophore synthesis is necessary for the virulence of different Brucella strains in a range of natural hosts, both pregnant and non-pregnant, will also be crucial.
11.1.2.2 Siderophore transport systems in Brucella
Due to their size, Fe3+-siderophore complexes require energy to transport into the cytoplasm of bacteria. In Gram-negative bacteria, transport across the outer membrane is typically facilitated by ‘gated’ porins, which obtain the energy they need to drive this transport from the ExbBD-TonB system (Noinaj et al., 2010). These Fe3+-siderophore complexes are then bound by specific periplasmic binding proteins which direct them to cytoplasmic ABC-type permeases that mediate their passage across the cytoplasmic membrane (Figure 7). Once in the cytoplasm, Fe3+ is released from the siderophore by its reduction to Fe2+ and/or degradation of the siderophore (Harrington and Crumbliss, 2009). Two genetic loci involved in Fe3+-siderophore transport have been identified in Brucella—fatBDCE and exbBD-tonB. Published studies have shown that B. abortus fatB and B. melitensisfatC and exbB mutants cannot use brucebactin and 2,3-DHBA, respectively, as Fe sources in vitro (González Carreró et al., 2002; Danese et al., 2004). In contrast, the identity of the genes that encode the TonB-dependent OM protein that transports Fe3+-brucebactin across the outer membrane is presently unclear.
11.1.3 Heme as an Fe source for Brucella strains
It was demonstrated that exogenous heme could rescue the heme auxotrophy of a B. abortus hemH mutant, and the parental 2308 strain can transport the intact heme molecule (Roop Ii et al., 2017b). This was an important finding because as noted previously, the intracellular trafficking pattern of the Brucella in host macrophages places these bacteria in an environment where heme is conceivably a relevant Fe source.
One of the main roles of mammalian macrophages is the destruction of damaged and senescent erythrocytes and the recycling of the iron expelled from these cells (Bratosin et al., 1998). To provide the growing fetus with iron, ruminant placental trophoblasts also consume and break down maternal erythrocytes (Anderson et al., 1986). During both procedures, a significant amount of heme is delivered into these host phagocytes. In in vitro tests, B. melitensis16M and B. abortus 2308 may both use heme as an iron source (Bellaire et al., 2003a; Danese et al., 2004; Paulley et al., 2007). The periplasmic binding protein-dependent ABC-type transporter, which is made up of the proteins BhuT, U, and V, and the TonB-dependent outer membrane protein, BhuA, mediate heme transport (Figure 8). Brucella strains seem to have well-preserved genes that encode these proteins (Roop, 2012). Heme oxygenase is also present in Brucella strains (Puri and O’Brian, 2006). This enzyme, which we have designated BhuO (Roop, 2012), presumably degrades heme after it has been delivered into the cytoplasm, enabling the Brucella to exploit it as an iron source. In experimentally infected mice, an isogenic bhuA mutant derived from B. abortus 2308 exhibits notable attenuation (Paulley et al., 2007), indicating that the ability to transport heme is a crucial virulence factor.
It is yet to be experimentally established if heme consumption contributes significantly to the virulence of other Brucella strains or in wild hosts. The heme not integrated into cellular proteins in human cells is actively transported to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where heme oxygenase might destroy it due to its possible toxicity (Taketani, 2005). Numerous interactions between phagosomes and the host cell ER result in the membrane-bound vacuoles, often called replicative Brucella-containing vacuoles or rBCVs, in which the Brucella proliferate in host macrophages (Celli et al., 2003). After interacting with the ER exit sites, the rBCVs eventually fuse with the ER (Celli et al., 2005). Microscopically and in placental trophoblasts from experimentally infected ruminants, extensive contacts between rBCVs and the host cell ER have also been detected (Anderson et al., 1986). Therefore, it will also be crucial to ascertain how the interactions of the rBCVs with the host cell ER affects the availability of heme as an iron source for Brucella strains during their intracellular residence in macrophages and placental trophoblasts in order to better understand the host-pathogen interactions in brucellosis.
11.1.4 Siderophore-independent transport of Fe3+ in Brucella
Fe3+-siderophore complexes generally require energy for transport across the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria (Noinaj et al., 2010), but Fe3+ bound to low molecular weight chelators such as citrate can diffuse across the outer membrane via porins, where specialized Fe3+-specific periplasmic protein-dependent ABC transporters can capture this Fe3+ and transport it across the cytoplasmic membrane. Such transporters include the Sfu, Afu, and Yfu (Roop Ii et al., 2017b) systems described in Serratia, Actinobacillus, and Yersinia, respectively (Figure 9). Two sets of genes predicted to encode Sfu-type Fe3+ transporters have been described in Brucella (Jenner et al., 2009), but the corresponding gene products’ roles in Fe transport and/or virulence are unknown.
11.1.5 Detoxification of excess intracellular Fe by Brucella strains
Bacteria must not only be able to import enough Fe to meet their physiological needs but also have a means of maintaining cellular levels of unincorporated Fe below ‘toxic’ levels. One ‘indirect’ mechanism that they use is to tightly regulate the genes encoding their Fe import systems so that they only import Fe when cellular levels fall below a certain threshold. How Brucella strains employ this strategy to prevent toxicity will be discussed in detail in a subsequent section. The other two more ‘direct’ mechanisms that bacteria employ to prevent Fe toxicity are to (a) convert excess intracellular Fe2+ into a ‘non-toxic’ form (e.g., Fe3+) for storage in proteins such as bacterioferritin and Dps; and (b) to export excess intracellular Fe2+ from the cell.
11.1.6 Bacterioferritin and Dps
Bacterioferritins (Bfrs) are large, 24 subunit proteins that with 12 heme groups form hollow spheres in bacterial cells (Andrews, 2010). These proteins have distinctive ferroxidase centers that convert soluble Fe2+ to insoluble Fe3+, which is then stored as 2Fe(O)OH in the interior of these spherical proteins. Each Bfr can store up to 4500 atoms of Fe3+, and this Fe3+ can be converted to Fe2+ and released into the bacterial cytoplasm as needed to replenish depleted Fe levels. By converting the highly reactive Fe2+ to the less reactive Fe3+ and sequestering it away from the other cytoplasm components, Bfr serves as a depot for excess Fe and prevents this excess Fe from reaching toxic levels. Dps is another spherical protein found in bacteria that oxidizes Fe2+ to Fe3+ and stores the insoluble Fe3+ in its interior (Andrews, 2010). Although Dps, like Bfr, is considered a member of the ferritin-like superfamily of proteins, it has three important structural and functional differences when compared to Bfr. First, Dps is made up of 12 subunits, and is thus smaller than Bfr, and consequently can store less Fe (e.g., 500 atoms) than Bfr. The ferroxidase site in Dps is also different from that of Bfr, and Dps uses H2O2 instead of O2 to catalyze the oxidation of Fe2+. In addition, many, but not all bacterial Dps proteins, bind non-specifically to DNA. Based on these properties and the phenotypic analysis of bacterial dps mutants, it has been proposed that the major physiologic function of Dps is cellular defense against oxidative stress rather than Fe storage (Chiancone and Ceci, 2010). Brucella strains produce both Bfr (Almirón and Ugalde, 2010) and Dps (Kim et al., 2014). Phenotypical analysis of a defined mutant indicates that Bfr plays a role in Fe metabolism in B. abortus 2308. For instance, a bfr mutant is more sensitive to Fe deprivation and has reduced levels of intracellular Fe than the parent strain (Almirón and Ugalde, 2010). The biological function of Dps, on the other hand, is presently unclear. Although the dps gene is strongly regulated by the general stress response sigma factor RpoE1 in B. abortus 2308 (Kim et al., 2014), a B. abortus dps mutant exhibits wild-type resistance to H2O2 in vitro assays. Considering the possibility that Dps could conceivably play a compensatory role to Bfr in terms of Fe storage, it will be important to evaluate the Fe storage capabilities and virulence properties of Brucella bfr dps double mutants to adequately evaluate their respective biological functions.
11.2 Manganese transport
One high-affinity Mn transporter, MntH, is produced by Brucella strains, and the Mn-responsive transcriptional regulator Mur controls the expression of the related gene (Anderson et al., 2009). Mn-dependent enzymes are essential to Brucella strains’ fundamental physiology and pathogenicity, according to phenotypic examination of a range of mutations. These bacteria may also modify their cellular Mn level as a defense against oxidative stress (Roop Ii et al., 2017c). A B. abortus mntH mutant is significantly attenuated in the mouse model of chronic infection. It is yet unknown what causes this attenuation. The B. abortus mntH mutant has lower Mn superoxide dismutase activity than the parental strain, but an isogenic sodA mutant only shows mild attenuation in mice (Martin et al., 2012), suggesting that the mntH mutant’s severe attenuation is not caused by lower SodA activity. Although the relationship between Mn2+ transport and virB expression has not been studied, the B. abortus mntH mutant also shows aberrant expression of the genes encoding the Type IV secretion machinery (Anderson et al., 2009). One possible explanation for this relationship is that orthologs of the (p)ppGpp synthetase/hydrolase known as Rsh (Dozot et al., 2006), Manganese-dependent enzymes are necessary for both the induction of the stringent response in Brucella and the production of VirB (Pappas et al., 2006).
According to recent genetic and biochemical studies, E. coli can replace Fe2+ in important metabolic enzymes like ribulose-5-phosphate epimerase (Rpe), a key enzyme in the pentose-phosphate pathway, by increasing the intracellular ratio of Mn2+:Fe2+. Escherichia coli also shows increased mntH expression in response to exposure to H2O2 (Anjem et al., 2009). Since Mn2+ does not take part in Fenton reaction like Fe2+ does, this substitution shields Rpe from damage caused by H2O2. In vitro exposure of B. abortus 2308 to H2O2 also increases the expression of mntH, and in vitro experiments show that an isogenic mntH mutant is more sensitive to exposure to H2O2 than the original 2308 strain (Anderson et al., 2009). In order to protect these proteins from H2O2-mediated damage, it will be crucial to ascertain whether Brucella strains possess the same ability as E. coli to replace Fe2+ in metabolic enzymes with Mn2+.
11.3 Zinc transport
Many bacteria, including Brucella species, depend on zinc as a micronutrient. In Brucella strains, zinc is necessary for the correct operation of multiple critical enzymes involved in the production of amino acids and oxidative stress tolerance (Andreini et al., 2006). Zinc is also a crucial cofactor for the type IV secretion system effector protein RicA (Rab2 interacting conserved protein A) and the virulence-associated transcriptional regulatory protein MucR. Brucella strains have a high affinity zinc uptake mechanism termed ZnuABC that preferentially imports zinc because of its significance in their biology. On the other hand, the Brucella also encode a zinc export mechanism, ZntA, which aids in the intracellular detoxification of excess zinc due to the hazardous potential of free zinc cations (Sheehan et al., 2015). Zinc uptake and export systems are tightly regulated by two zinc-responsive regulatory proteins, Zur and ZntR, which regulate transcription of the znuABC and zntA genes, respectively (Clapp et al., 2011). Crucially, effective pathogenesis in animal models of Brucella infection depends on the appropriate homeostasis of zinc levels in the virus. The systems that control zinc uptake and export in Brucella strains will be described in this chapter, along with their function in virulence, the genetic control of zinc homeostasis, and zinc’s involvement as a cofactor for key enzymes in Brucella strains (Caswell, 2017). SodC is necessary for the Brucella’s complete pathogenicity and the bacteria’s high resistance to exogenous O2. In the periplasmic region of many Gram-negative bacteria, including several dangerous organisms, SodC, a periplasmic superoxide dismutase (SOD), is in charge of detoxifying exogenously produced superoxide (i.e., O2−). The SodC protein is frequently referred to as Cu-Zn SOD because bacterial SodC proteins require copper and zinc cofactors for proper enzymatic function, while the zinc cation appears to play a crucial structural role (Caswell, 2017).
11.4 Nickel transport
It has been demonstrated that urease is one of the few bacterial enzymes that needs nickel as a cofactor (Li and Zamble, 2009). According to Bandara et al. (2007) and Sangari et al. (2007), this enzyme is necessary for the pathogenicity of B. abortus 2308 and B. suis 1330 in mice when these strains are introduced orally, but not when they are given peritoneally. In mammalian cell cultures, B. suis and B. abortus urease mutants display wild-type pathogenicity. Urease is not necessary for intracellular survival in eukaryotic cells, but it helps the Brucella withstand the extremely low pH they experience during passage through the stomach and gastrointestinal tract following ingestion, according to the theory put up to explain these observations. Although NikABCDE and NikKMLQO, two nickel transporters, have been found in Brucella (Jubier-Maurin et al., 2001b; Sangari et al., 2010), how these transporters contribute to virulence is unclear. An isogenic nikA mutant generated from B. suis 1330 exhibits wild-type pathogenicity in the human monocytic cell line THP-1, even though nikA expression is increased in this strain during intracellular replication in J774 cells (Jubier-Maurin et al., 2001a). It will be crucial to evaluate the virulence characteristics of Brucella strains deficient in either the NikABCDE or NikKMLQO transporter, or both, in cultured macrophages and in mice infected by both the intraperitoneal and oral routes to better understand the necessity of nickel transport by Brucella strains in the host.
11.5 Magnesium transport
Bacterial cells contain large quantities of magnesium (mM). It is a structural and enzymatic co-factor for many cellular proteins and is crucial for preserving the structural integrity of ribosomes and cell membranes (Moomaw and Maguire, 2008). For example, Mg2+ is necessary for the activity of erythritol kinase, the enzyme that catalyzes the initial stage of erythritol catabolism in Brucella strains.
Virulence in Brucella strains has been genetically related to homologs of two genes involved in magnesium transport in other bacteria. Salmonella is the greatest example of the activity of the bacterial P-type ATPase MgtB as a magnesium transporter (Smith et al., 1993). During a screening of signature-tagged transposon mutants obtained from B. melitensis16M for attenuation in experimentally infected mice, a B. melitensis mgtB mutant was discovered (Lestrate et al., 2000). Remarkably, when cultivated in magnesium-limited media, this mutant showed no signs of growth defects. This implies that the Brucella have several magnesium transport mechanisms, just like other bacteria and as shown in Figure 10. A B. suis mgtC mutant does not grow well in a magnesium-restricted medium and exhibits significant attenuation in the murine macrophage-like J774 cell line (Lavigne et al., 2005), although the exact function of MgtC in magnesium transport has not been determined (Günzel et al., 2006; Alix and Blanc-Potard, 2007). Adding MgCl2 to the cell growth media can help mitigate this attenuation to some extent.
Figure 10. Nickel, zinc, manganese, magnesium and cobalt transporters in Brucella. OM, outer membrane; IM, inner membrane.
11.6 Cobalt transport
Many bacteria, including Brucella, require cobalt as a micronutrient because it is a necessary component of cobalamin (vitamin B12) (Warren et al., 2002). Additionally, cobalamin is necessary for the activity of several key bacterial enzymes, including the ribonucleotide reductase NrdJ (Taga and Walker, 2010) and the methionine synthase MetH (Roop Ii et al., 2017a). In mice and cultured mammalian cells, B. suis and B. melitensis mutants with defects in the cobalamin biosynthesis pathway are attenuated (Delrue et al., 2004). Brucella strains have an intact cobalamin biosynthesis pathway (Lundqvist et al., 2009). These infection models also attenuate a B. melitensis metH mutant (Lestrate et al., 2000). Between the cobalamin biosynthesis genes cobQ and cobU in Brucella are two genes that are anticipated to encode a CbtAB-type Cotransporter. The idea that the Brucella cbtA and B genes express a high-affinity Co transporter is supported by their location and the fact that they are located downstream of a cobalamin-responsive riboswitch (Rodionov et al., 2003), but this function has not been experimentally verified (Roop Ii et al., 2017a).
11.7 Metalloregulators and metal storage/detoxification proteins p
The prevention of toxicity resulting from the excessive buildup of these crucial micronutrients depends on proteins that directly contribute to metal homeostasis. Three transcriptional regulators—Irr (Martínez et al., 2005; Martínez et al., 2006), DhbR (Anderson et al., 2008), and Mur (Menscher et al., 2012)—have been identified as controlling the expression of Brucella metal acquisition genes. DhbR is an AraC-type transcriptional regulator that activates the transcription of the siderophore biosynthesis genes in B. abortus 2308 in response to Fe3+-siderophore levels in the external environment; Mur controls the expression of the gene encoding the Mn2+ transporter MntH in response to cellular Mn2+ levels; and Irr is an iron-responsive transcriptional regulator that governs the genes involved in iron acquisition and iron metabolism. Bacterioferritin (Bfr), a protein that accumulates and detoxifies intracellular iron, is also produced by certain strains of Brucella (Denoel et al., 1995; Almirón and Ugalde, 2010). Only Irr and Bfr have had their involvement in virulence investigated thus far. Though neither B. abortus nor B. melitensis-bfr mutants show attenuation in cultured human primary explant macrophages (Denoel et al., 1997), J774 or HeLa cells (Almirón and Ugalde, 2010), or experimentally infected mice (Denoel et al., 1997), a B. abortus irr mutant is attenuated in the mouse model (Anderson et al., 2011).
12 Vaccines
The most effective way to stop human infection is to control animal brucellosis. Research and scientific studies to develop brucellosis vaccines have been underway since the early 1900s. Inactivated, live-attenuated, and rough-attenuated vaccines are all part of the brucellosis vaccine development process. Inactivated vaccines were first developed as a disease prevention strategy. To prevent brucellosis, however, more immunologically effective live attenuated vaccines eventually took their place. The several kinds of brucellosis vaccinations and their effectiveness are listed below.
12.1 Live attenuated vaccines
In order to improve safety and immune responses, recent developments have concentrated on modified live attenuated vaccines with removed virulence genes. For instance, a mutant of the B. melitensis TcfSR promoter (Li et al., 2015) and the B. melitensis 16M hfq mutant strain (Zhang et al., 2013) showed considerable protection and minimal interference with serodiagnostic assays. Although they are sensitive to polymyxin B (Wang et al., 2014), other possible vaccines, including the M5-90ΔwboA mutant and 6MΔwzt, have shown decreased pathogenicity and enhanced defense mechanisms. Similar to the B. ovisabcBA (BoabcBA) vaccine (Costa et al., 2020), the 2308DNodVDNodW rough vaccine from the virulent B. abortus 2308 strain provides a strong immune response against the B. melitensis strain 16M. Brucella double gene knock-out vaccine strain MB6 Δbp26ΔwboA (RM6) was constructed and evaluated by Shi et al. the researchers have found that the RM6 strain had good proliferative ability and stable biological characteristics in vivo and in vitro. Moreover, it had a favorable safety profile and elicited specific immune responses in mice and sheep (Shi et al., 2022).
12.2 Subunit vaccines
Subunit vaccines exhibit promise in terms of non-infectious, non-viable, and safety. Nevertheless, they are not very good at simulating the spread of genuine illnesses (Ficht et al., 2009). Subunit vaccines have the advantage of being safe, but in order to produce strong immunity and protect cattle from brucellosis, they need to be administered in numerous booster doses and utilizing a variety of antigens, adjuvants, and delivery systems. However, due to associated expenditures, this strategy could not be commercially viable (Perkins et al., 2010). Regretfully, no viable subunit vaccination against brucellosis has been created in spite of countless attempts (Zimmermann and Curtis, 2019).
12.3 Vaccines based on nanoparticles
Oral vaccines containing nanoparticles and the Brucella vaccine produced antibody responses, including IgM, mucosal IgA, and IgG, in animal model studies. In animal investigations, these vaccinations have shown significant benefits, including a stronger Th1–Th17 immune response (Abkar et al., 2017). However, human brucellosis cannot be prevented by nanoparticle-based vaccinations because of the possible danger of disease transmission (Maleki et al., 2019). These vaccines’ primary disadvantages include their toxicity, limits in terms of antigen loading and manufacturing, and their less-than-ideal capacity to activate the immune system (Al-Halifa et al., 2019).
12.4 DNA vaccines
In the fight against brucellosis, DNA-based Brucella vaccines have proven to be both safe and effective. These vaccines’ capacity to produce antigens and integrate CpG patterns results in strong cellular immune responses. Simple storage conditions are another benefit of DNA-based vaccinations. They have important gene sequences that are essential to Brucella species’ intracellular survival (Hu et al., 2009). However, as compared to live-attenuated vaccines, DNA-based vaccines do not offer as much protection. Studies show no discernible changes in the expression of IL-4, IL-10, or IFN-γ, suggesting an immunological response to DNA-based vaccinations (Rosinha et al., 2002).
12.5 Vector vaccines
Using Brucella as a delivery vehicle, live vector-based vaccines have become a successful way to deliver a variety of antigens, both homologous and heterologous. By multiplying inside host cells and creating several copies of the Brucella antigen, these genetically engineered vaccines are designed to elicit an antigen-specific T-cell immune response (Al-Mariri et al., 2002).
12.6 Recombinant peptides
One promising strategy for preventing and controlling brucellosis is the use of recombinant peptides as vaccinations. Conventional vaccinations, such as the Rev-1 vaccine, have drawbacks, such as the potential to cause abortion in fetuses and disrupt diagnostic procedures. Recombinant peptides, on the other hand, provide safer and more precise substitutes (Cassataro et al., 2005).
13 Conclusion
In conclusion, a disease’s successful management, including individualized treatments and early detection, depends critically on understanding its biological components. Although the development of vaccines is informed by continuous research on disease processes, the length of time needed emphasizes the need of ongoing medication discovery. Additionally, more research is required using natural hosts and inoculation routes that resemble those seen in nature. In order to better understand the fundamental characteristics of Brucella pathogenicity, mice have proven invaluable. Brucella strains in their natural hosts may require different virulence determinants, and these determinants may be needed at different phases of the disease cycle in these hosts (e.g., chronic infection versus abortion and fetal pathology in ruminants). Finally, most research assessing the role of Brucella metal acquisition in virulence has been conducted in the mouse model of chronic infection, which is used to gauge the strains’ capacity to endure and proliferate in host macrophages. However, the mouse model results may not necessarily anticipate how a mutant would behave in the wild host, particularly in pregnant ruminants, as the experiments using B. abortus siderophore biosynthesis mutants clearly show. Whether or not these bacteria are living in macrophages, or placental trophoblasts may affect the sources of iron (such as Fe2+, Fe3+, and heme or heme-containing proteins) and other metals that are available as well as the metabolic needs of the intracellular Brucella for these metals. Future research must, therefore, evaluate the contribution of metal acquisition genes to virulence in a range of natural and experimental hosts, both pregnant and non-pregnant.
Author contributions
GG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Visualization, Project administration. HH: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Visualization, Project administration. ZE: Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Project administration. ST: Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CK: Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HK: Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JI: Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CI: Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out with the support of the Islamic University of Lebanon and Center of Research and Development.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abkar, M., Fasihi-Ramandi, M., Kooshki, H., and Sahebghadam Lotfi, A. (2017). Oral immunization of mice with Omp31-loaded N-trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles induces high protection against Brucella melitensis infection. Int. J. Nanomed. 12, 8769–8778. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S149774
Adams, L. G. (2002). The pathology of brucellosis reflects the outcome of the battle between the host genome and the Brucella genome. Vet. Microbiol. 90, 553–561. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1135(02)00235-3
Akova, M., Gür, D., Livermore, D. M., Kocagöz, T., and Akalin, H. E. (1999). In Vitro Activities of Antibiotics Alone and in Combination against Brucella melitensis at Neutral and Acidic pHs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43, 1298–1300. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.5.1298
Aktas, M., Wessel, M., Hacker, S., Klüsener, S., Gleichenhagen, J., and Narberhaus, F. (2010). Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and its significance in bacteria interacting with eukaryotic cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 89, 888–894. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.06.013
Alaidarous, M. A., Ve, T., Casey, L. W., Valkov, E., Ericsson, D. J., Ullah, M. O., et al. (2014). Mechanism of bacterial interference with TLR4 signaling by brucella toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing protein tcpB. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 654–668. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.523274
Alavi, S. M. and Alavi, L. (2013). Treatment of brucellosis: a systematic review of studies in recent twenty years. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 4, 636–641. doi: 10.22088/cjim.v4.n2.636
Alavi, S. M. and Motlagh, M. E. (2012). A review of epidemiology, diagnosis and management of brucellosis for general physicians working in the Iranian health network. Jundishapur. J. Microbiol. 5, 384–387. doi: 10.5812/jjm.3248
Al Dahouk, S., Köhler, S., Occhialini, A., Freddi, L., Damiano, M. A., Chaloin, L., et al. (2017). Brucella spp. of amphibians comprise genomically diverse motile strains competent for replication in macrophages and survival in mammalian hosts. Sci. Rep. 7, 44420. doi: 10.1038/srep44420
Al Dahouk, S. and Nöckler, K. (2011). Implications of laboratory diagnosis on brucellosis therapy. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 9, 833–845. doi: 10.1586/eri.11.55
Al Dahouk, S., Sprague, L. D., and Neubaeur, H. (2013). New developments in the diagnostic procedures for zoonotic brucellosis in humans: -EN- -FR- Nouveaux développements dans les procédures de diagnostic de la brucellose zoonotique chez l’homme -ES- Novedades en los procedimientos de diagnóstico de la brucelosis zoonótica en el ser humano. Rev. Sci. Tech. OIE 32, 177–188. doi: 10.20506/rst.32.1.2204
Al Dahouk, S., Tomaso, H., Nöckler, K., Neubauer, H., and Frangoulidis, D. (2003). Laboratory-based diagnosis of brucellosis–a review of the literature. Part II: serological tests for brucellosis. Clin. Lab. 49, 577–589. doi: 10.1515/KLINLAB.2003.49.11-12.577
Al-Halifa, S., Gauthier, L., Arpin, D., Bourgault, S., and Archambault, D. (2019). Nanoparticle-based vaccines against respiratory viruses. Front. Immunol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00022
Ali, S., Nawaz, Z., Akhtar, A., Aslam, R., Zahoor, M. A., and Ashraf, M. (2018). Epidemiological investigation of human brucellosis in Pakistan. Jundishapur. J. Microbiol. 11, e61764. doi: 10.5812/jjm.61764
Alix, E. and Blanc-Potard, A. B. (2007). MgtC: a key player in intramacrophage survival. Trends Microbiol. 15, 252–256. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2007.03.007
Al-Mariri, A., Tibor, A., Lestrate, P., Mertens, P., De Bolle, X., and Letesson, J. J. (2002). Yersinia enterocolitica as a Vehicle for a Naked DNA Vaccine Encoding Brucella abortus Bacterioferritin or P39 Antigen. Infect. Immun. 70, 1915–1923. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.1915-1923.2002
Almirón, M. A. and Ugalde, R. A. (2010). Iron homeostasis in Brucella abortus: the role of bacterioferritin. J. Microbiol. 48, 668–673. doi: 10.1007/s12275-010-0145-3
Al-Nakkas, A., Mustafa, A. S., and Wright, S. G. (2005). Large-scale evaluation of a single-tube nested PCR for the laboratory diagnosis of human brucellosis in Kuwait. J. Med. Microbiol. 54, 727–730. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.45772-0
Anderson, T. D., Meador, V. P., and Cheville, N. F. (1986). Pathogenesis of placentitis in the goat inoculated with brucella abortus. I. Gross and histologic lesions. Vet. Pathol. 23, 219–226. doi: 10.1177/030098588602300301
Anderson, E. S., Paulley, J. T., Gaines, J. M., Valderas, M. W., Martin, D. W., Menscher, E., et al. (2009). The manganese transporter mntH is a critical virulence determinant for brucella abortus 2308 in experimentally infected mice. Infect. Immun. 77, 3466–3474. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00444-09
Anderson, E. S., Paulley, J. T., Martinson, D. A., Gaines, J. M., Steele, K. H., and Roop, R. M. (2011). The iron-responsive regulator irr is required for wild-type expression of the gene encoding the heme transporter bhuA in brucella abortus 2308. J. Bacteriol. 193, 5359–5364. doi: 10.1128/JB.00372-11
Anderson, E. S., Paulley, J. T., and Roop, R. M. (2008). The araC-like transcriptional regulator dhbR is required for maximum expression of the 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid biosynthesis genes in brucella abortus 2308 in response to iron deprivation. J. Bacteriol. 190, 1838–1842. doi: 10.1128/JB.01551-07
Anderson, G. J. and Vulpe, C. D. (2009). Mammalian iron transport. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 66, 3241–3261. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0051-1
Andreini, C., Banci, L., Bertini, I., and Rosato, A. (2006). Zinc through the three domains of life. J. Proteome Res. 5, 3173–3178. doi: 10.1021/pr0603699
Andrews, S. C. (2010). The Ferritin-like superfamily: Evolution of the biological iron storeman from a rubrerythrin-like ancestor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 1800, 691–705. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2010.05.010
Anjem, A., Varghese, S., and Imlay, J. A. (2009). Manganese import is a key element of the OxyR response to hydrogen peroxide in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 72, 844–858. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06699.x
Arapović, J., Kompes, G., Dedić, K., Ostojić, M., Zvizdić, S., Nikolić, J., et al. (2022). Antimicrobial resistance profiles of human Brucella melitensis isolates in three different microdilution broths: the first multicentre study in Bosnia and Herzegovina. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 29, 99–104. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2022.02.005
Arellano-Reynoso, B., Lapaque, N., Salcedo, S., Briones, G., Ciocchini, A. E., Ugalde, R., et al. (2005). Cyclic β-1,2-glucan is a brucella virulence factor required for intracellular survival. Nat. Immunol. 6, 618–625. doi: 10.1038/ni1202
Ariza, J., Bosilkovski, M., Cascio, A., Colmenero, J. D., Corbel, M. J., Falagas, M. E., et al. (2007). Perspectives for the treatment of brucellosis in the 21st century: the ioannina recommendations. PloS Med. 4, e317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040317
Aschtgen, M. S., Lynch, J. B., Koch, E., Schwartzman, J., McFall-Ngai, M., and Ruby, E. (2016). Rotation of Vibrio fischeri Flagella Produces Outer Membrane Vesicles That Induce Host Development. Christie PJ, ed. J. Bacteriol. 198, 2156–2165. doi: 10.1128/JB.00101-16
Ashenafi, F., Teshale, S., Agga, G. E., Fikru, R., and Laikemariam, Y. (2007). Distribution of brucellosis among small ruminants in the pastoral region of Afar, eastern Ethiopia: -EN- Distribution of brucellosis among small ruminants in the pastoral region of Afar, eastern Ethiopia -FR- Distribution de la brucellose chez les petits ruminantsde la région pastorale d’Afar, Ethiopie orientale -ES- Distribución de la brucelosis de los pequeños rumiantes en la región pastoral de Afar, Etiopía oriental. Rev. Sci. Tech. OIE 26, 731–739. doi: 10.20506/rst.26.3.1781
Avila-Granados, L. M., Garcia-Gonzalez, D. G., Zambrano-Varon, J. L., and Arenas-Gamboa, A. M. (2019). Brucellosis in Colombia: current status and challenges in the control of an endemic disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 6. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00321
Ayoub, H., Kumar, M. S., Mehta, R., Thomas, P., Dubey, M., Dhanze, H., et al. (2024). Exploring genetic determinants of antimicrobial resistance in Brucella melitensis strains of human and animal origin from India. Front. Microbiol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1474957
Bandara, A. B., Contreras, A., Contreras-Rodriguez, A., Martins, A. M., Dobrean, V., Poff-Reichow, S., et al. (2007). Brucella suis urease encoded by ure 1 but not ure 2 is necessary for intestinal infection of BALB/c mice. BMC Microbiol. 7, 57. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-57
Bano, Y. and Ahmad Lone, S. (2015). Brucellosis: an economically important infection. J. Med. Microbiol. Diagn. 4, 208. doi: 10.4172/2161-0703.1000208
Barquero-Calvo, E., Chaves-Olarte, E., Weiss, D. S., Guzmán-Verri, C., Chacón-Díaz, C., Moriyón, I., et al. (2007). Brucella abortus Uses a Stealthy Strategy to Avoid Activation of the Innate Immune System during the Onset of Infection. Ojcius D, ed. PloS One 2, e631. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000631
Barquero-Calvo, E., Mora-Cartín, R., Arce-Gorvel, V., de Diego, J. L., Chacón-Díaz, C., Chaves-Olarte, E., et al. (2015). Brucella abortus Induces the Premature Death of Human Neutrophils through the Action of Its Lipopolysaccharide. Tsolis RM, ed. PloS Pathog. 11, e1004853. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004853
Batut, J., Andersson, S. G. E., and O’Callaghan, D. (2004). The evolution of chronic infection strategies in the α-proteobacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2, 933–945. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1044
Beauvais, W., Musallam, I., and Guitian, J. (2016). Vaccination control programs for multiple livestock host species: an age-stratified, seasonal transmission model for brucellosis control in endemic settings. Parasit Vectors 9, 55. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1327-6
Bedore, B. and Mustefa, M. (2019). Review on epidemiolgy and economic impact of small ruminant brucellosis in Ethiopian perspective. Vet. Med. Open J. 4, 77–86. doi: 10.17140/VMOJ-4-139. College of Veterinary Medicine, Haramaya University, P. O. BOX 301, Haramaya, Ethiopia.
Bellaire, B. H., Elzer, P. H., Baldwin, C. L., and Roop, R. M. (1999). The Siderophore 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid Is Not Required for Virulence of Brucella abortus in BALB/c Mice. Moore RN, ed. Infect. Immun. 67, 2615–2618. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.5.2615-2618.1999
Bellaire, B. H., Elzer, P. H., Baldwin, C. L., and Roop, R. M. (2003a). Production of the Siderophore 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid Is Required for Wild-Type Growth of Brucella abortus in the Presence of Erythritol under Low-Iron Conditions In Vitro. Infect. Immun. 71, 2927–2932. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.5.2927-2932.2003
Bellaire, B. H., Elzer, P. H., Hagius, S., Walker, J., Baldwin, C. L., and Roop, R. M. (2003b). Genetic organization and iron-responsive regulation of the Brucella abortus 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid biosynthesis operon, a cluster of genes required for wild-type virulence in pregnant cattle. Infect. Immun. 71, 1794–1803. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.4.1794-1803.2003
Bernués, A., Manrique, E., and Maza, M. T. (1997). Economic evaluation of bovine brucellosis and tuberculosis eradication programmes in a mountain area of Spain. Prev. Vet. Med. 30, 137–149. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5877(96)01103-8
Billard, E., Dornand, J., and Gross, A. (2007). Interaction of Brucella suis and Brucella abortus Rough Strains with Human Dendritic Cells. Infect. Immun. 75, 5916–5923. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00931-07
Blair Hedges, S. and Kumar, S. (2003). Genomic clocks and evolutionary timescales. Trends Genet. 19, 200–206. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(03)00053-2
Blasco, J. M. and Molina-Flores, B. (2011). Control and eradication of brucella melitensis infection in sheep and goats. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 27, 95–104. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2010.10.003
Bonilla-Aldana, D. K., Trejos-Mendoza, A. E., Pérez-Vargas, S., Rivera-Casas, E., Muñoz-Lara, F., Zambrano, L. I., et al. (2023). A systematic review and meta-analysis of bovine brucellosis seroprevalence in Latin America and the Caribbean. New Microbes New Infect. 54, 101168. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101168
Bontemps-Gallo, S. and Lacroix, J. (2015). New insights into the biological role of the osmoregulated periplasmic glucans in pathogenic and symbiotic bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 7, 690–697. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12325
Bosilkovski, M., Arapović, J., and Keramat, F. (2019). Human brucellosis in pregnancy – an overview. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 20, 415–422. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2019.4499
Bosilkovski, M., Keramat, F., and Arapović, J. (2021). The current therapeutical strategies in human brucellosis. Infection 49, 823–832. doi: 10.1007/s15010-021-01586-w
Bratosin, D., Mazurier, J., Tissier, J. P., and Mazurier, C. (1998). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of senescent erythrocyte phagocytosis by macrophages. A review. Biochimie 80, 173–195. doi: 10.1016/S0300-9084(98)80024-2
Breedveld, M. W. and Miller, K. J. (1994). Cyclic beta-glucans of members of the family Rhizobiaceae. Microbiol. Rev. 58, 145–161. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.2.145-161.1994
Briones, G., Iñón De Iannino, N., Roset, M., Vigliocco, A., Paulo, P. S., and Ugalde, R. A. (2001). Brucella abortus Cyclic β-1,2-Glucan Mutants Have Reduced Virulence in Mice and Are Defective in Intracellular Replication in HeLa Cells. DiRita VJ, ed. Infect. Immun. 69, 4528–4535. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4528-4535.2001
Bryant, C. E., Spring, D. R., Gangloff, M., and Gay, N. J. (2010). The molecular basis of the host response to lipopolysaccharide. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 8, 8–14. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2266
Bukata, L., Altabe, S., De Mendoza, D., Ugalde, R. A., and Comerci, D. J. (2008). Phosphatidylethanolamine synthesis is required for optimal virulence of brucella abortus. J. Bacteriol. 190, 8197–8203. doi: 10.1128/JB.01069-08
Byndloss, M. X., Tsai, A. Y., Walker, G. T., Miller, C. N., Young, B. M., English, B. C., et al. (2019). Brucella abortus Infection of Placental Trophoblasts Triggers Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Cell Death and Fetal Loss via Type IV Secretion System-Dependent Activation of CHOP. Coyne CB, ed. mBio 10, e01538–e01519. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01538-19
Cairo, G., Recalcati, S., Mantovani, A., and Locati, M. (2011). Iron trafficking and metabolism in macrophages: contribution to the polarized phenotype. Trends Immunol. 32, 241–247. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.03.007
Cardoso, P. G., Macedo, G. C., Azevedo, V., and Oliveira, S. C. (2006). Brucella spp noncanonical LPS: structure, biosynthesis, and interaction with host immune system. Microb. Cell Factories 5, 13. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-5-13
Carle, A., Höppner, C., Ahmed Aly, K., Yuan, Q., den Dulk-Ras, A., Vergunst, A., et al. (2006). The Brucella suis Type IV Secretion System Assembles in the Cell Envelope of the Heterologous Host Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Increases IncQ Plasmid pLS1 Recipient Competence. Infect. Immun. 74, 108–117. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.1.108-117.2006
Carvalho Neta, A. V., Stynen, A. P. R., Paixão, T. A., Miranda, M., Costa, E. A., Sampaio, I. B. M., et al. (2008). Modulation of the bovine trophoblastic innate immune response by Brucella abortus. Infect. Immun. 76, 1897–1907. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01554-07
Cassataro, J., Estein, S. M., Pasquevich, K. A., Velikovsky, C. A., de la Barrera, S., Bowden, R., et al. (2005). Vaccination with the Recombinant Brucella Outer Membrane Protein 31 or a Derived 27-Amino-Acid Synthetic Peptide Elicits a CD4+ T Helper 1 Response That Protects against Brucella melitensis Infection. Infect. Immun. 73, 8079–8088. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.12.8079-8088.2005
Caswell, C. C. (2017). “The role of zinc in the biology and virulence of brucella strains,” in Metals and the Biology and Virulence of Brucella. Eds. Roop Ii, R. M. and Caswell, C. C. (Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing), 63–72. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53622-4_4
Caswell, C. C., Elhassanny, A. E. M., Planchin, E. E., Cornell, K. M., Ficht, T. A., and Tsolis, R. M. (2013). Diverse Genetic Regulon of the Virulence-Associated Transcriptional Regulator MucR in Brucella abortus 2308. Payne SM, ed. Infect. Immun. 81, 1040–1051. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01097-12
Celli, J., De Chastellier, C., Franchini, D. M., Pizarro-Cerda, J., Moreno, E., and Gorvel, J. P. (2003). Brucella evades macrophage killing via virB-dependent sustained interactions with the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Exp. Med. 198, 545–556. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030088
Celli, J., Salcedo, S. P., and Gorvel, J. P. (2005). Brucella coopts the small GTPase Sar1 for intracellular replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 102, 1673–1678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406873102
Cellier, M. F., Courville, P., and Campion, C. (2007). Nramp1 phagocyte intracellular metal withdrawal defense. Microbes Infect. 9, 1662–1670. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2007.09.006
Chain, P. S. G., Comerci, D. J., Tolmasky, M. E., Larimer, F. W., Malfatti, S. A., Vergez, L. M., et al. (2005). Whole-genome analyses of speciation events in pathogenic brucellae. Infect. Immun. 73, 8353–8361. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.12.8353-8361.2005
Chen, F. and He, Y. (2009). Caspase-2 Mediated Apoptotic and Necrotic Murine Macrophage Cell Death Induced by Rough Brucella abortus. May RC, ed. PloS One 4, e6830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006830
Chiancone, E. and Ceci, P. (2010). The multifaceted capacity of Dps proteins to combat bacterial stress conditions: Detoxification of iron and hydrogen peroxide and DNA binding. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 1800, 798–805. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2010.01.013
Cho, D., Nam, H., Kim, J., Heo, E., Cho, Y., Hwang, I., et al. (2010). Quantitative rose bengal test for diagnosis of bovine brucellosis. J. Immunoassay Immunochem. 31, 120–130. doi: 10.1080/15321811003617420
Clapp, B., Skyberg, J. A., Yang, X., Thornburg, T., Walters, N., and Pascual, D. W. (2011). Protective live oral brucellosis vaccines stimulate th1 and th17 cell responses. Morrison RP, ed. Infect. Immun. 79, 4165–4174. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05080-11
Cloeckaert, A., Tibor, A., and Zygmunt, M. S. (1999). Brucella outer membrane lipoproteins share antigenic determinants with bacteria of the family rhizobiaceae. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 6, 627–629. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.6.4.627-629.1999
Cloeckaert, A., Vizcaı́no, N., Paquet, J. Y., Bowden, R. A., and Elzer, P. H. (2002). Major outer membrane proteins of Brucella spp.: past, present and future. Vet. Microbiol. 90, 229–247. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1135(02)00211-0
Comerci, D. J., Martinez-Lorenzo, M. J., Sieira, R., Gorvel, J. P., and Ugalde, R. A. (2001). Essential role of the VirB machinery in the maturation of the Brucella abortus-containing vacuole. Cell Microbiol. 3, 159–168. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2001.00102.x
Copin, R., Vitry, M. A., Hanot Mambres, D., De Trez, C., Gorvel, J. P., Carlier, Y., et al. (2012). In Situ Microscopy Analysis Reveals Local Innate Immune Response Developed around Brucella Infected Cells in Resistant and Susceptible Mice. Roy CR, ed. PloS Pathog. 8, e1002575. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002575
Corbin, B. D., Seeley, E. H., Raab, A., Neal, R., Eisenach, K. D., Byrne, B. A., et al. (2008). Metal chelation and inhibition of bacterial growth in tissue abscesses. Science 319, 962–965. doi: 10.1126/science.1152449
Coria, L. M., Ibañez, A. E., Tkach, M., Delpino, M. V., Gorvel, J.-P., and Giambartolomei, G. H. (2016). A brucella spp. Protease inhibitor limits antigen lysosomal proteolysis, increases cross-presentation, and enhances CD8+ T cell responses. J. Immunol. 196, 4014–4029. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501188
Costa, L. F., Cabello, A. L., Batista, D. F. A., Oliveira, D. M., Santana, D. C. A., de Assis, A. D. S., et al. (2020). The candidate vaccine strain Brucella ovis Δ abcBA is protective against Brucella melitensis infection in mice. Microbiol. Immunol. 64, 730–736. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12850
Cui, B., Liu, W., Wang, X., Hou, Y., Ma, K., Wang, Y., et al. (2017). Brucella Omp25 Upregulates miR-155, miR-21-5p, and miR-23b to Inhibit Interleukin-12 Production via Modulation of Programmed Death-1 Signaling in Human Monocyte/Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00708
Cuthbertson, L., Mainprize, I. L., Naismith, J. H., and Whitfield, C. (2009). Pivotal roles of the outer membrane polysaccharide export and polysaccharide copolymerase protein families in export of extracellular polysaccharides in gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 73, 155–177. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00024-08
Cutler, S. J., Whatmore, A. M., and Commander, N. J. (2005). Brucellosis - new aspects of an old disease. J. Appl. Microbiol. 98, 1270–1281. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02622.x
Czibener, C., Merwaiss, F., Guaimas, F., Ibañez, A. E., Delpino, M. V., Spera, J. M., et al. (2016). BigA is a novel adhesin of Brucella that mediates adhesion to epithelial cells: Adhesion of Brucella to epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 18, 500–513. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12526
Dabral, N., Jain-Gupta, N., Seleem, M. N., Sriranganathan, N., and Vemulapalli, R. (2015). Overexpression of Brucella putative glycosyltransferase WbkA in B. abortus RB51 leads to production of exopolysaccharide. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 5. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00054
Dadar, M., Alamian, S., Brangsch, H., Elbadawy, M., Elkharsawi, A. R., Neubauer, H., et al. (2023). Determination of virulence-associated genes and antimicrobial resistance profiles in brucella isolates recovered from humans and animals in Iran using NGS technology. Pathogens 12, 82. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12010082
Dadar, M., Tiwari, R., Sharun, K., and Dhama, K. (2021). Importance of brucellosis control programs of livestock on the improvement of one health. Vet. Q. 41, 137–151. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2021.1894501
Danese, I., Haine, V., Delrue, R. M., Maquille, A., and Tibor, A. (2004). The ton system, an ABC transporter, and a universally conserved GTPase are involved in iron utilization by brucella melitensis 16M. Infect. Immun. 72, 5783–5790. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.5783-5790.2004
Dauphin, L. A., Hutchins, R. J., Bost, L. A., and Bowen, M. D. (2009). Evaluation of automated and manual commercial DNA extraction methods for recovery of brucella DNA from suspensions and spiked swabs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 47, 3920–3926. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01288-09
Dean, A. S., Crump, L., Greter, H., Hattendorf, J., Schelling, E., and Zinsstag, J. (2012). Clinical manifestations of human brucellosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Carabin H, ed. PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 6, e1929. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001929
De Bolle, X., Crosson, S., Matroule, J. Y., and Letesson, J. J. (2015). Brucella abortus cell cycle and infection are coordinated. Trends Microbiol. 23, 812–821. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2015.09.007
De Figueiredo, P., Ficht, T. A., Rice-Ficht, A., Rossetti, C. A., and Adams, L. G. (2015). Pathogenesis and immunobiology of brucellosis. Am. J. Pathol. 185, 1505–1517. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.03.003
Deghelt, M., Mullier, C., Sternon, J. F., Favier, A., Vandenhaute, J., and Letesson, J. J. (2014). G1-arrested newborn cells are the predominant infectious form of the pathogen Brucella abortus. Nat. Commun. 5, 4366. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5366
Degos, C., Gagnaire, A., Banchereau, R., Moriyón, I., and Gorvel, J. P. (2015). Brucella CβG induces a dual pro- and anti-inflammatory response leading to a transient neutrophil recruitment. Virulence 6, 19–28. doi: 10.4161/21505594.2014.979692
Degos, C., Hysenaj, L., Gonzalez-Espinoza, G., Arce-Gorvel, V., Gagnaire, A., Papadopoulos, A., et al. (2020). Omp25-dependent engagement of SLAMF1 by Brucella abortus in dendritic cells limits acute inflammation and favours bacterial persistence in vivo. Cell Microbiol. 22, e13164. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13164
De Iannino, N. I., Briones, G., Iannino, F., and Ugalde, R. A. (2000). Osmotic regulation of cyclic 1,2-β-glucan synthesis. Microbiology 146, 1735–1742. doi: 10.1099/00221287-146-7-1735
De Jong, M. F., Rolán, H. G., and Tsolis, R. M. (2010). Microreview: Innate immune encounters of the (Type) 4th kind: Brucella: Brucella T4SS and innate immunity. Cell Microbiol. 12, 1195–1202. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01498.x
De Jong, M. F., Starr, T., Winter, M. G., Byndloss, M. X., and Tsolis, R. M. (2013). Sensing of Bacterial Type IV Secretion via the Unfolded Protein Response. Roy C, Rikihisa Y, eds. mBio 4, e00418–e00412. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00418-12
Del Giudice, M. G., Döhmer, P. H., Spera, J. M., Laporte, F. T., Marchesini, M. I., Czibener, C., et al. (2016). VirJ is a brucella virulence factor involved in the secretion of type IV secreted substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 12383–12393. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.730994
Delpino, M. V., Fossati, C. A., and Baldi, P. C. (2009). Proinflammatory Response of Human Osteoblastic Cell Lines and Osteoblast-Monocyte Interaction upon Infection with Brucella spp. Infect. Immun. 77, 984–995. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01259-08
Del Pozo, J. S. G. and Solera, J. (2015). Treatment of human brucellosis — Review of evidence from clinical trials. In: baddour MM, ed. Updates Brucellosis. doi: 10.5772/61223. InTech.
Delrue, R. M., Deschamps, C., Leonard, S., Danese, I., Maquille, A., and Tibor, A. (2005). A quorum-sensing regulator controls expression of both the type IV secretion system and the flagellar apparatus of Brucella melitensis. Cell Microbiol. 7, 1151–1161. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00543.x
Delrue, R. M., Lestrate, P., Tibor, A., Letesson, J. J., and Bolle, X. (2004). Brucella pathogenesis, genes identified from random large-scale screens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 231, 1–12. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00963-7
DelVecchio, V. G., Kapatral, V., Redkar, R. J., Patra, G., Thimiri Kovvali, D. M., Tarek, M., et al. (2002). The genome sequence of the facultative intracellular pathogen. Brucella Melitensis Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99, 443–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.221575398
Denoel, P. A., Crawford, R. M., Zygmunt, M. S., Letesson, J. J., and Tibor, A. (1997). Survival of a bacterioferritin deletion mutant of Brucella melitensis 16M in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Infect. Immun. 65, 4337–4340. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.10.4337-4340.1997
Denoel, P. A., Zygmunt, M. S., Weynants, V., Tibor, A., and Letesson, J. J. (1995). Cloning and sequencing of the bacterioferritin gene of Brucella melitensis 16M strain. FEBS Lett. 361, 238–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00189-G
De Souza Filho, J. A., Martins, V. D. P., Campos, P. C., Alves-Silva, J., Santos, N. V., De Oliveira, F. S., et al. (2015). Mutant Brucella abortus Membrane Fusogenic Protein Induces Protection against Challenge Infection in Mice. Camilli A, ed. Infect. Immun. 83, 1458–1464. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02790-14
Díaz, R., Casanova, A., Ariza, J., and Moriyón, I. (2011). The rose bengal test in human brucellosis: A neglected test for the diagnosis of a neglected disease. Vinetz JM, ed. PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 5, e950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000950
Djangwani, J., Ooko Abong’, G., Gicuku Njue, L., and Kaindi, D. W. M. (2021). Brucellosis: Prevalence with reference to East African community countries – A rapid review. Vet. Med. Sci. 7, 851–867. doi: 10.1002/vms3.425
Dozot, M., Boigegrain, R. A., Delrue, R. M., Van Melderen, L., and Letesson, J. J. (2006). The stringent response mediator Rsh is required for Brucella melitensis and Brucella suis virulence, and for expression of the type IV secretion system virB. Cell Microbiol. 8, 1791–1802. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00749.x
Duenas, A. I. (2004). Interaction of endotoxins with Toll-like receptor 4 correlates with their endotoxic potential and may explain the proinflammatory effect of Brucella spp. LPS. Int. Immunol. 16, 1467–1475. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh148
Edmonds, M. D., Cloeckaert, A., Booth, N. J., Elzer, P. H., and Schurig, G. G. (2001). Attenuation of a Brucella abortus mutant lacking a major 25 kDa outer membrane protein in cattle. Am. J. Vet. Res. 62, 1461–1466. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.2001.62.1461
Edmonds, M. D., Cloeckaert, A., and Elzer, P. H. (2002). Brucella species lacking the major outer membrane protein Omp25 are attenuated in mice and protect against Brucella melitensis and Brucella ovis. Vet. Microbiol. 88, 205–221. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1135(02)00110-4
Elrashedy, A., Gaafar, M., Mousa, W., Nayel, M., Salama, A., Zaghawa, A., et al. (2022). Immune response and recent advances in diagnosis and control of brucellosis. Ger J. Vet. Res. 2, 10–24. doi: 10.51585/gjvr.2022.1.0033
Erkyihun, G. A., Gari, F. R., and Kassa, G. M. (2022). Bovine brucellosis and its public health significance in Ethiopia. Zoonoses 2, 965. doi: 10.15212/ZOONOSES-2022-0005
Ewalt, D. R., Payeur, J. B., Rhyan, J. C., and Geer, P. L. (1997). Brucella suis biovar 1 in naturally infected cattle: A bacteriological, serological, and histological study. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 9, 417–420. doi: 10.1177/104063879700900414
Falagas, M. E. and Bliziotis, I. A. (2006). Quinolones for treatment of human brucellosis: critical review of the evidence from microbiological and clinical studies. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50, 22–33. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.1.22-33.2006
Fatani, D. F., Alsanoosi, W. A., Badawi, M. A., and Thabit, A. K. (2019). Ceftriaxone use in brucellosis: A case series. IDCases 18, e00633. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2019.e00633
Ferguson, G. P., Datta, A., Baumgartner, J., Roop, R. M., Carlson, R. W., and Walker, G. C. (2004). Similarity to peroxisomal-membrane protein family reveals that Sinorhizobium and Brucella BacA affect lipid-A fatty acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 101, 5012–5017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307137101
Fernández, L. V., Oropeza-Navarro, R., Ortiz-Rico, A., Robles-Pesina, G., Ramírez-Lezama, J., Castañeda-Ramírez, A., et al. (2020). Brucella melitensis omp31 Mutant Is Attenuated and Confers Protection Against Virulent Brucella melitensis Challenge in BALB/c Mice. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 30, 497–504. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1908.08056
Fernandez-Prada, C. M., Zelazowska, E. B., Nikolich, M., Hadfield, T. L., Roop, R. M., Robertson, G. L., et al. (2003). Interactions between brucella melitensis and human phagocytes: bacterial surface O-polysaccharide inhibits phagocytosis, bacterial killing, and subsequent host cell apoptosis. Infect. Immun. 71, 2110–2119. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.4.2110-2119.2003
Ferooz, J., Lemaire, J., and Letesson, J. J. (2011). Role of FlbT in flagellin production in Brucella melitensis. Microbiology 157, 1253–1262. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.044867-0
Ficht, T. (2010). Brucella taxonomy and evolution. Future Microbiol. 5, 859–866. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.52
Ficht, T. A., Kahl-McDonagh, M. M., Arenas-Gamboa, A. M., and Rice-Ficht, A. C. (2009). Brucellosis: The case for live, attenuated vaccines. Vaccine 27, D40–D43. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.08.058
Fontana, C., Conde-Álvarez, R., Ståhle, J., Holst, O., Iriarte, M., Zhao, Y., et al. (2016). Structural studies of lipopolysaccharide-defective mutants from brucella melitensis identify a core oligosaccharide critical in virulence. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 7727–7741. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.701540
Forestier, C., Deleuil, F., Lapaque, N., Moreno, E., and Gorvel, J. P. (2000). Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharide in murine peritoneal macrophages acts as a down-regulator of T cell activation. J. Immunol. 165, 5202–5210. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.9.5202
Foster, J. T., Beckstrom-Sternberg, S. M., Pearson, T., Beckstrom-Sternberg, J. M., Chain, P. S. G., Roberto, F. F., et al. (2009). Whole-genome-based phylogeny and divergence of the genus. Brucella J. Bacteriol. 191, 2864–2870. doi: 10.1128/JB.01581-08
Franco, M. P., Mulder, M., Gilman, R. H., and Smits, H. L. (2007). Human brucellosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 7, 775–786. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70286-4
Fretin, D., Fauconnier, A., Köhler, S., Danese, I., Delrue, R. M., Lestrate, P., et al. (2005). The sheathed flagellum of Brucella melitensis is involved in persistence in a murine model of infection: B. melitensis flagellum is a virulence factor in mice. Cell Microbiol. 7, 687–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00502.x
Fritz, C. L., Nguyen, A., and Vugia, D. J. (2021). Epidemiology of brucellosis in california, 1993–2017: A continuing foodborne disease risk for older latinos. Clin. Infect. Dis. 73, 2023–2030. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab551
Garin-Bastuji, B., Hars, J., Drapeau, A., Ganière, J.-P., Cêtre-Sossah, C., and Moutou, F. (2014). Reemergence of brucella melitensis infection in wildlife, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 20, 1570–1571. doi: 10.3201/eid2009.131517
Godfroid, J., Al Dahouk, S., Pappas, G., Okono, D. O., Mantur, P. G., and Tibor, A. (2013). A “One Health” surveillance and control of brucellosis in developing countries: Moving away from improvisation. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 36, 241–248. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2012.09.001
Godlewska, R., WiÅniewska, K., Pietras, Z., and Jagusztyn-Krynicka, E. K. (2009). Peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein (Pal) of Gram-negative bacteria: function, structure, role in pathogenesis and potential application in immunoprophylaxis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 298, 1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01659.x
González, D., Grilló, M. J., De Miguel, M. J., Galán, J. C., Baroja, M. L., and Moriyón, I. (2008). Brucellosis Vaccines: Assessment of Brucella melitensis Lipopolysaccharide Rough Mutants Defective in Core and O-Polysaccharide Synthesis and Export. Nielsen K, ed. PloS One 3, e2760. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002760
González Carreró, M. I., Sangari, F. J., Agüero, J., and Garcı́a Lobo, J. M. (2002). Brucella abortus strain 2308 produces brucebactin, a highly efficient catecholic siderophore The GenBank accession number for the sequence reported in this paper is AF361942. Microbiology 148, 353–360. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-2-353
Gorvel, J. P. (2008). Brucella: a Mr “Hide” converted into Dr Jekyll. Microbes Infect. 10, 1010–1013. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2008.07.007
Grace, D., Wu, F., and Havelaar, A. H. (2020). MILK Symposium review: Foodborne diseases from milk and milk products in developing countries—Review of causes and health and economic implications. J. Dairy Sci. 103, 9715–9729. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-18323
Gross, A., Terraza, A., Ouahrani-Bettache, S., Liautard, J. P., and Dornand, J. (2000). In Vitro Brucella suis Infection Prevents the Programmed Cell Death of Human Monocytic Cells. Fischetti VA, ed. Infect. Immun. 68, 342–351. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.1.342-351.2000
Gu, J. Y., Liu, Y. J., Zhu, X. Q., Qiu, J. Y., and Sun, Y. (2020). Effects of endotoxin tolerance induced by porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide on inflammatory responses in neutrophils. Inflammation 43, 1692–1706. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01243-8
Guidolin, L. S., Arce-Gorvel, V., Ciocchini, A. E., Comerci, D. J., and Gorvel, J. P. (2018). Cyclic β-glucans at the bacteria-host cells interphase: One sugar ring to rule them all. Cell Microbiol. 20, e12850. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12850
Guidolin, L. S., Morrone Seijo, S. M., Guaimas, F. F., Comerci, D. J., and Ciocchini, A. E. (2015). Interaction Network and Localization of Brucella abortus Membrane Proteins Involved in the Synthesis, Transport, and Succinylation of Cyclic β-1,2-Glucans. Christie PJ, ed. J. Bacteriol. 197, 1640–1648. doi: 10.1128/JB.00068-15
Günzel, D., Kucharski, L. M., Kehres, D. G., Romero, M. F., and Maguire, M. E. (2006). The mgtC virulence factor of salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium activates na+,K+ -ATPase. J. Bacteriol. 188, 5586–5594. doi: 10.1128/JB.00296-06
Hall, W. H. (1990). Modern chemotherapy for brucellosis in humans. Clin. Infect. Dis. 12, 1060–1099. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.6.1060
Halling, S. M. (1998). On the presence and organization of open reading frames of the nonmotile pathogen brucella abortus similar to class II, III, and IV flagellar genes and to lcrD virulence superfamily. Microb. Comp. Genomics 3, 21–29. doi: 10.1089/omi.1.1998.3.21
Halling, S. M., Peterson-Burch, B. D., Bricker, B. J., et al. (2005). Completion of the Genome Sequence of Brucella abortus and Comparison to the Highly Similar Genomes of Brucella melitensis and Brucella suis. J. Bacteriol. 187, 2715–2726. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.8.2715-2726.2005
Harrington, J. M. and Crumbliss, A. L. (2009). The redox hypothesis in siderophore-mediated iron uptake. BioMetals 22, 679–689. doi: 10.1007/s10534-009-9233-4
Hasanain, A., Mahdy, R., Mohamed, A., and Ali, M. (2016). A randomized, comparative study of dual therapy (doxycycline–rifampin) versus triple therapy (doxycycline–rifampin–levofloxacin) for treating acute/subacute brucellosis. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 20, 250–254. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2016.02.004
Hashemi, S. H., Gachkar, L., Keramat, F., Mamani, M., Hajilooi, M., Janbakhsh, A., et al. (2012). Comparison of doxycycline–streptomycin, doxycycline–rifampin, and ofloxacin–rifampin in the treatment of brucellosis: a randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 16, e247–e251. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2011.12.003
Hashim, R., Ahmad, N., Mohamed Zahidi, J., and Nor-Masni, M. T. (2014). Identification and in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of brucella species isolated from human brucellosis. Int. J. Microbiol. 2014, 1–5. doi: 10.1155/2014/596245
He, Y., Reichow, S., Ramamoorthy, S., Paulley, J. T., Martin, D. W., and Roop II, R. M. (2006). Brucella melitensis triggers time-dependent modulation of apoptosis and down-regulation of mitochondrion-associated gene expression in mouse macrophages. Infect. Immun. 74, 5035–5046. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01998-05
Henderson, I. R., Navarro-Garcia, F., Desvaux, M., Fernandez, R. C., and Ala’Aldeen, D. (2004). Type V protein secretion pathway: the autotransporter story. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 68, 692–744. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.68.4.692-744.2004
Herrera, E., Palomares, G., and Díaz-Aparicio, E. (2008). Milk production increase in a dairy farm under a six-year brucellosis control program. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1149, 296–299. doi: 10.1196/annals.1428.011
Herrmann, C. K., Bukata, L., Melli, L., Marchesini, M. I., Caramelo, J. J., and Comerci, D. J. (2013). Identification and characterization of a high-affinity choline uptake system of brucella abortus. J. Bacteriol. 195, 493–501. doi: 10.1128/JB.01929-12
Hikal, A. F., Wareth, G., and Khan, A. (2023). Brucellosis: Why is it eradicated from domestic livestock in the United States but not in the Nile River Basin countries? Ger J. Microbiol. 3, 19–25. doi: 10.51585/gjm.2023.2.0026
Holt, H. R., Bedi, J. S., Kaur, P., Mangtani, P., Sharma, N. S., Gill, J. P. S., et al. (2021). Epidemiology of brucellosis in cattle and dairy farmers of rural Ludhiana, Punjab. Munoz-Zanzi C, ed. PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 15, e0009102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009102
Höppner, C., Liu, Z., Domke, N., Binns, A. N., and Baron, C. (2004). VirB1 Orthologs from Brucella suis and pKM101 Complement Defects of the Lytic Transglycosylase Required for Efficient Type IV Secretion from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J. Bacteriol. 186, 1415–1422. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.5.1415-1422.2004
Hou, H., Liu, X., and Peng, Q. (2019). The advances in brucellosis vaccines. Vaccine 37, 3981–3988. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.05.084
Hu, X. D., Yu, D. H., Chen, S. T., Li, S. X., and Cai, H. (2009). A Combined DNA Vaccine Provides Protective Immunity Against Mycobacterium bovis and Brucella abortus in Cattle. DNA Cell Biol. 28, 191–199. doi: 10.1089/dna.2008.0790
Hug, I., Deshpande, S., Sprecher, K. S., Pfohl, T., and Jenal, U. (2017). Second messenger–mediated tactile response by a bacterial rotary motor. Science 358, 531–534. doi: 10.1126/science.aan5353
Ibañez, A. E., Coria, L. M., Carabajal, M. V., Spera, J. M., Delpino, M. V., Czibener, C., et al. (2015). A bacterial protease inhibitor protects antigens delivered in oral vaccines from digestion while triggering specific mucosal immune responses. J. Controlled Release 220, 18–28. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.10.011
Iñón De Iannino, N., Briones, G., Tolmasky, M., and Ugalde, R. A. (1998). Molecular Cloning and Characterization of cgs, the Brucella abortus Cyclic β(1-2) Glucan Synthetase Gene: Genetic Complementation of Rhizobium meliloti ndvB and Agrobacterium tumefaciens chvB Mutants. J. Bacteriol. 180, 4392–4400. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.17.4392-4400.1998
Irajian, G. R., Masjedian Jazi, F., Mirnejad, R., Esmaeilzadeh, B., Amani, J., and Mostafaei, S. (2016). Species-specific PCR for the diagnosis and determination of antibiotic susceptibilities of brucella strains isolated from tehran, Iran. Iran J. Pathol. 11, 238–247. doi: 10.29252/ijp.11.3.238
Jain, N., Rodriguez, A. C., Kimsawatde, G., Seleem, M. N., Boyle, S. M., and Sriranganathan, N. (2011). Effect of entF deletion on iron acquisition and erythritol metabolism by Brucella abortus 2308: Role of entF gene in erythritol metabolism by Brucella. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 316, 1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.02186.x
Jenner, D. C., Dassa, E., Whatmore, A. M., and Atkins, H. S. (2009). ATP-binding cassette systems of brucella. Comp. Funct. Genomics 2009, 1–16. doi: 10.1155/2009/354649
Jia, Y. H., Li, L. P., Hou, Q. M., and Pan, S. Q. (2002). An Agrobacterium gene involved in tumorigenesis encodes an outer membrane protein exposed on the bacterial cell surface. Gene 284, 113–124. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(02)00385-2
Jiao, H., Zhou, Z., Li, B., Xiao, Y., Li, M., Zeng, H., et al. (2021). The mechanism of facultative intracellular parasitism of brucella. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 3673. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073673
Jiménez De Bagüés, M. P., Terraza, A., Gross, A., and Dornand, J. (2004). Different responses of macrophages to smooth and rough brucella spp.: relationship to virulence. Infect. Immun. 72, 2429–2433. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.4.2429-2433.2004
Johansen, T. B., Scheffer, L., Jensen, V. K., Bohlin, J., and Feruglio, S. L. (2018). Whole-genome sequencing and antimicrobial resistance in Brucella melitensis from a Norwegian perspective. Sci. Rep. 8, 8538. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26906-3
Jones, C. J. and Wozniak, D. J. (2017). Psl Produced by Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa Contributes to the Establishment of Biofilms and Immune Evasion. Goldberg JB, ed. mBio 8, e00864–e00817. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00864-17
Jubier-Maurin, V., Boigegrain, R. A., Cloeckaert, A., Gross, A., Alvarez-Martinez, M. T., and Terraza, A. (2001a). Major Outer Membrane Protein Omp25 of Brucella suis Is Involved in Inhibition of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Production during Infection of Human Macrophages. Tuomanen EI, ed. Infect. Immun. 69, 4823–4830. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.8.4823-4830.2001
Jubier-Maurin, V., Rodrigue, A., Ouahrani-Bettache, S., Layssac, M., Mandrand-Berthelot, M.-A., Köhler, S., et al. (2001b). Identification of the nik Gene Cluster of Brucella suis: Regulation and Contribution to Urease Activity. J. Bacteriol. 183, 426–434. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.2.426-434.2001
Kang, Y. S., Brown, D. A., and Kirby, J. E. (2019). Brucella neotomae Recapitulates Attributes of Zoonotic Human Disease in a Murine Infection Model. Roy CR, ed. Infect. Immun. 87, e00255–e00218. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00255-18
Keestra-Gounder, A. M., Byndloss, M. X., Seyffert, N., Young, B. M., Chávez-Arroyo, A., Tsai, A. Y., et al. (2016). NOD1 and NOD2 signalling links ER stress with inflammation. Nature 532, 394–397. doi: 10.1038/nature17631
Khan, A. U., Shell, W. S., Melzer, F., Sayour, A. E., Ramadan, E. S., Elschner, M. C., et al. (2019). Identification, genotyping and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of brucella spp. Isolated from livestock in Egypt. Microorganisms 7, 603. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7120603
Khurana, S. K., Sehrawat, A., Tiwari, R., Natesan, S., Dhama, K., and Kumar, M. (2021). Bovine brucellosis – a comprehensive review. Vet. Q. 41, 61–88. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2020.1868616
Kim, H. S., Caswell, C. C., Foreman, R., Roop, R. M., and Crosson, S. (2013). The brucella abortus general stress response system regulates chronic mammalian infection and is controlled by phosphorylation and proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 13906–13916. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.459305
Kim, D., Park, J., Kim, S. J., Soh, Y. M., Kim, H. M., and Oh, B. H. (2013). Brucella immunogenic BP26 forms a channel-like structure. J. Mol. Biol. 425, 1119–1126. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.01.015
Kim, S., Watarai, M., Suzuki, H., Makino, S., Kodama, T., and Shirahata, T. (2004). Lipid raft microdomains mediate class A scavenger receptor-dependent infection of Brucella abortus. Microb. Pathog. 37, 11–19. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2004.04.002
Kim, H., Willett, J. W., Jain-Gupta, N., Fiebig, A., and Crosson, S. (2014). The Brucella abortus virulence regulator, LovhK, is a sensor kinase in the general stress response signalling pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 94, 913–925. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12809
Kiros, A., Asgedom, H., and Abdi, R. D. (2016). A review on bovine brucellosis: epidemiology, diagnosis and control options. ARC J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2. doi: 10.20431/2455-2518.0203002
Kleinman, C. L., Sycz, G., Bonomi, H. R., Rodríguez, R. M., Zorreguieta, A., and Sieira, R. (2017). ChIP-seq analysis of the LuxR-type regulator VjbR reveals novel insights into the Brucella virulence gene expression network. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, 5757–5769. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx165
Köhler, S., Foulongne, V., Ouahrani-Bettache, S., Bourg, G., Teyssier, J., Ramuz, M., et al. (2002). The analysis of the intramacrophagic virulome of Brucella suis deciphers the environment encountered by the pathogen inside the macrophage host cell. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99, 15711–15716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.232454299
Köhler, S., Michaux-Charachon, S., Porte, F., Ramuz, M., and Liautard, J. P. (2003). What is the nature of the replicative niche of a stealthy bug named Brucella? Trends Microbiol. 11, 215–219. doi: 10.1016/S0966-842X(03)00078-7
Kurmanov, B., Zincke, D., Su, W., Niyazova, R., Akylbekova, D., Kydyrbayev, Z., et al. (2022). Assays for identification and differentiation of brucella species: A review. Microorganisms 10, 1584. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10081584
Laine, C. G., Johnson, V. E., Scott, H. M., and Arenas-Gamboa, A. M. (2023). Global estimate of human brucellosis incidence. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 29, 1825–1833. doi: 10.3201/eid2909.230052
Lamontagne, J., Forest, A., Marazzo, E., Denis, F., Butler, H., Michaud, J.-F., et al. (2009). Intracellular adaptation of brucella abortus. J. Proteome Res. 8, 1594–1609. doi: 10.1021/pr800978p
Lapaque, N., Forquet, F., De Chastellier, C., Mishal, Z., Jolly, G., Moreno, E., et al. (2006a). Characterization of Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharide macrodomains as mega rafts. Cell Microbiol. 8, 197–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00609.x
Lapaque, N., Takeuchi, O., Corrales, F., Akira, S., Moriyón, I., Howard, J. C., et al. (2006b). Differential inductions of TNF-alpha and IGTP, IIGP by structurally diverse classic and non-classic lipopolysaccharides. Cell Microbiol. 8, 401–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00629.x
Lavigne, J. P., O’Callaghan, D., and Blanc-Potard, A. B. (2005). Requirement of MgtC for Brucella suis Intramacrophage Growth: a Potential Mechanism Shared by Salmonella enterica and Mycobacterium tuberculosis for Adaptation to a Low-Mg2+ Environment. Infect. Immun. 73, 3160–3163. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.5.3160-3163.2005
Lecaroz, C. (2006). Intracellular killing of Brucella melitensis in human macrophages with microsphere-encapsulated gentamicin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 58, 549–556. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl257
Leo, J. C., Oberhettinger, P., Schütz, M., and Linke, D. (2015). The inverse autotransporter family: Intimin, invasin and related proteins. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 305, 276–282. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2014.12.011
Lestrate, P., Delrue, R.-M., Danese, I., Didembourg, C., Taminiau, B., Mertens, P., et al. (2000). Identification and characterization of in vivo attenuated mutants of Brucella melitensis. Mol. Microbiol. 38, 543–551. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02150.x
Lestrate, P., Dricot, A., Delrue, R. M., Danese, I., Maquille, A., Michaux, P., et al. (2003). Attenuated Signature-Tagged Mutagenesis Mutants of Brucella melitensis Identified during the Acute Phase ofInfection inMice. Infect. Immun. 71, 7053–7060. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.12.7053-7060.2003
Li, Y. and Zamble, D. B. (2009). Nickel homeostasis and nickel regulation: an overview. Chem. Rev. 109, 4617–4643. doi: 10.1021/cr900010n
Li, Z., Zhang, J., Zhang, K., Fu, Q., Wang, Z., Li, T., et al. (2015). Brucella melitensis 16MΔTcfSR as a potential live vaccine allows for the differentiation between natural and vaccinated infection. Exp. Ther. Med. 10, 1182–1188. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2619
Liu, D. (2015). “Brucella,” in Molecular Medical Microbiology (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 1781–1788. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-397169-2.00101-3
Liu, Z.-G., Di, D.-D., Wang, M., Piao, D.-R., Zhao, H.-Y., Cui, B.-Y., et al. (2018). In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility testing of human Brucella melitensis isolates from Ulanqab of Inner Mongolia, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 18, 43. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-2947-6
Liu, M., Ferrandez, Y., Bouhsira, E., Monteil, M., Franc, M., Boulouis, H.-J., et al. (2012). Heme Binding Proteins of Bartonella henselae Are Required when Undergoing Oxidative Stress During Cell and Flea Invasion. Bereswill S, ed. PloS One 7, e48408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048408
Lounes, N., Yahiaoui, D., Taftaf, D., and Zenia, S. (2022). A survey on the occupational exposure of veterinarians to brucellosis in Algeria. Ger J. Microbiol. 2, 28–35. doi: 10.51585/gjm.2022.2.0017
Luelseged, A. (2018). Review on molecular epidemiology and public health significance of brucellosis. Anim. Res. Vet. Sci. 2, 1–10. doi: 10.24966/ARVS-3751/100007. Addis Ababa University.
Lundqvist, J., Elmlund, D., Heldt, D., Deery, E., Söderberg, C. A. G., Hansson, M., et al. (2009). The AAA+ motor complex of subunits CobS and CobT of cobaltochelatase visualized by single particle electron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 167, 227–234. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2009.06.013
Luo, X., Zhang, X., Wu, X., Fan, Q., Song, X., Li, X., et al. (2018). Brucella downregulates tumor necrosis factor-α to promote intracellular survival via omp25 regulation of different microRNAs in porcine and murine macrophages. Front. Immunol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.02013
Maleki, M., Salouti, M., Shafiee Ardestani, M., and Talebzadeh, A. (2019). Preparation of a nanovaccine against Brucella melitensis M16 based on PLGA nanoparticles and oligopolysaccharide antigen. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 47, 4248–4256. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2019.1687490
Manterola, L., Guzmán-Verri, C., Chaves-Olarte, E., Barquero-Calvo, E., Moriyón, I., and López-Goñi, I. (2007). BvrR/bvrS-controlled outer membrane proteins omp3a and omp3b are not essential for brucella abortus virulence. Infect. Immun. 75, 4867–4874. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00439-07
Mantur, B. G. and Amarnath, S. K. (2008). Brucellosis in India — a review. J. Biosci. 33, 539–547. doi: 10.1007/s12038-008-0072-1
Mantur, B., Amarnath, S., and Shinde, R. (2007). Review of clinical and laboratory features of human. Brucellosis Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 25, 188. doi: 10.4103/0255-0857.34758
Marczak, M., Mazur, A., Koper, P., Żebracki, K., and Skorupska, A. (2017). Synthesis of rhizobial exopolysaccharides and their importance for symbiosis with legume plants. Genes 8, 360. doi: 10.3390/genes8120360
Martin, D. W., Baumgartner, J. E., Gee, J. M., Anderson, E. S., and Roop, R. M. (2012). SodA is a major metabolic antioxidant in Brucella abortus 2308 that plays a significant, but limited, role in the virulence of this strain in the mouse model. Microbiology 158, 1767–1774. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.059584-0
Martínez, M., Ugalde, R. A., and Almirón, M. (2005). Dimeric Brucella abortus Irr protein controls its own expression and binds haem. Microbiology 151, 3427–3433. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28213-0
Martínez, M., Ugalde, R. A., and Almirón, M. (2006). Irr regulates brucebactin and 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid biosynthesis, and is implicated in the oxidative stress resistance and intracellular survival of Brucella abortus. Microbiology 152, 2591–2598. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28782-0
Martín-Martín, A. I., Caro-Hernández, P., Orduña, A., Vizcaíno, N., and Fernández-Lago, L. (2008). Importance of the Omp25/Omp31 family in the internalization and intracellular replication of virulent B. ovis in murine macrophages and HeLa cells. Microbes Infect. 10, 706–710. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2008.02.013
Martín-Martín, A. I., Caro-Hernández, P., Sancho, P., Fernández-Lago, L., Moreno, E., and Moriyón, I. (2009). Analysis of the occurrence and distribution of the Omp25/Omp31 family of surface proteins in the six classical Brucella species. Vet. Microbiol. 137, 74–82. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.12.003
Martirosyan, A., Pérez-Gutierrez, C., Banchereau, R., Dutartre, H., Lecine, P., Dullaers, M., et al. (2012). Brucella β 1,2 cyclic glucan is an activator of human and mouse dendritic cells. Tsolis RM, ed. PloS Pathog. 8, e1002983. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002983
Mcdermott, J. J., Grace, D., and Zinsstag, J. (2013). Economics of brucellosis impact and control in low-income countries: -EN- -FR- -ES-. Rev. Sci. Tech. OIE 32, 249–261. doi: 10.20506/rst.32.1.2197
Memish, Z. A. and Balkhy, H. H. (2004). Brucellosis and international travel. J. Travel Med. 11, 49–55. doi: 10.2310/7060.2004.13551
Menscher, E. A., Caswell, C. C., Anderson, E. S., and Roop, R. M. (2012). Mur regulates the gene encoding the manganese transporter mntH in brucella abortus 2308. J. Bacteriol. 194, 561–566. doi: 10.1128/JB.05296-11
Mert, A., Ozaras, R., Tabak, F., Pekmezci, S., Yilmaz, Y., and Tahan, V. (2003). The sensitivity and specificity of Brucella agglutination tests. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 46, 241–243. doi: 10.1016/S0732-8893(03)00081-6
Michelle, A. P., Bryan, H. B., Erin, A. M., R. Martin, R., Phillip, H. E., and Cynthia, L. B. (2002). Brucella abortus siderophore2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHBA) facilitatesintracellular survival of the bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 32, 239–248. doi: 10.1006/mpat.2002.0500
Michels, K., Nemeth, E., Ganz, T., and Mehrad, B. (2015). Hepcidin and host defense against infectious diseases. Bliska JB Ed. PloS Pathog. 11, e1004998. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004998
Minnick, M. F., Sappington, K. N., Smitherman, L. S., Andersson, S. G. E., Karlberg, O., and Carroll, J. A. (2003). Five-member gene family of bartonella quintana. Infect. Immun. 71, 814–821. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.2.814-821.2003
Mirabella, A., Terwagne, M., Zygmunt, M. S., Cloeckaert, A., De Bolle, X., and Letesson, J. J. (2013). Brucella melitensis MucR, an Orthologue of Sinorhizobium meliloti MucR, Is Involved in Resistance to Oxidative, Detergent, and Saline Stresses and Cell Envelope Modifications. J. Bacteriol. 195, 453–465. doi: 10.1128/JB.01336-12
Mishra, M., Byrd, M. S., Sergeant, S., Azad, A. K., Parsek, M. R., McPhail, L., et al. (2012). Pseudomonas aeruginosa Psl polysaccharide reduces neutrophil phagocytosis and the oxidative response by limiting complement-mediated opsonization: Psl and the innate immune response towards P. aeruginosa. Cell Microbiol. 14, 95–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2011.01704.x
Mohamand, N., Gunaseelan, L., Sukumar, B., and Porteen, K. (2014). Milk Ring Test for spot identification of Brucella abortus infection in single cow herds. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 1, 70. doi: 10.5455/javar.2014.a8
Monreal, D., Grilló, M. J., González, D., Marín, C., and Moriyón, I. (2003). Characterization of Brucella abortus O-Polysaccharide and Core Lipopolysaccharide Mutants and Demonstration that a Complete Core Is Required for Rough Vaccines To Be Efficient against Brucella abortus and Brucella ovis in the Mouse Model. Infect. Immun. 71, 3261–3271. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.6.3261-3271.2003
Moomaw, A. S. and Maguire, M. E. (2008). The unique nature of mg2+ Channels. Physiology 23, 275–285. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00019.2008
Moreno, E., Middlebrook, E. A., Altamirano-Silva, P., Al Dahouk, S., Araj, G. F., Arce-Gorvel, V., et al. (2023). If you’re not confused, you’re not paying attention: ochrobactrum is not brucella. McAdam AJ, ed. J. Clin. Microbiol. 61, e00438–e00423. doi: 10.1128/jcm.00438-23
Muñoz, V. L., Porsch, E. A., and St. Geme, J. W. (2018). Kingella kingae Surface Polysaccharides Promote Resistance to Human Serum and Virulence in a Juvenile Rat Model. Payne SM, ed. Infect. Immun. 86, e00100–e00118. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00100-18
Muñoz González, F., Sycz, G., Alonso Paiva, I. M., Delpino, M. V., Spera, J. M., and Giambartolomei, G. H. (2019). The btaF adhesin is necessary for full virulence during respiratory infection by brucella suis and is a novel immunogen for nasal vaccination against brucella infection. Front. Immunol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01775
Nairz, M., Schroll, A., Sonnweber, T., and Weiss, G. (2010). The struggle for iron - a metal at the host-pathogen interface: Iron at the host-pathogen interface. Cell Microbiol. 12, 1691–1702. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01529.x
Nairz, M., Theurl, I., Ludwiczek, S., Theurl, M., Fritsch, P., Glaser, N., et al. (2007). The co-ordinated regulation of iron homeostasis in murine macrophages limits the availability of iron for intracellular Salmonella typhimurium. Cell Microbiol. 9, 2126–2140. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00942.x
Naroeni, A. and Porte, F. (2002). Role of cholesterol and the ganglioside GM 1 in entry and short-term survival of brucella suis in murine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 70, 1640–1644. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.3.1640-1644.2002
Nemeth, E., Tuttle, M. S., Powelson, J., Casey, M. E., Rodgers, J., Gary, A. S., et al. (2004). Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its internalization. Science 306, 2090–2093. doi: 10.1126/science.1104742
Noinaj, N., Guillier, M., Barnard, T. J., and Buchanan, S. K. (2010). TonB-dependent transporters: regulation, structure, and function. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 64, 43–60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.112408.134247
Occhialini, A., Hofreuter, D., Ufermann, C. M., Al Dahouk, S., and Köhler, S. (2022). The retrospective on atypical brucella species leads to novel definitions. Microorganisms 10, 813. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10040813
Oliveira, S. C., De Oliveira, F. S., Macedo, G. C., De Almeida, L. A., and Carvalho, N. B. (2008). The role of innate immune receptors in the control of Brucella abortus infection: Toll-like receptors and beyond. Microbes Infect. 10, 1005–1009. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2008.07.005
Olsen, S. C. and Stoffregen, W. S. (2005). Essential role of vaccines in brucellosis control and eradication programs for livestock. Expert Rev. Vaccines 4, 915–928. doi: 10.1586/14760584.4.6.915
Ouahrani-Bettache, S., Jiménez De Bagües, M. P., De La Garza, J., Freddi, L., Bueso, J. P., Lyonnais, S., et al. (2019). Lethality of Brucella microti in a murine model of infection depends on the wbkE gene involved in O-polysaccharide synthesis. Virulence 10, 868–878. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2019.1682762
Pal, M., Gizaw, F., Fekadu, G., Alemayehu, G., and Kandi, V. (2017). Public health and economic importance of bovine brucellosis: an overview. Am. J. Epidemiol. Infect. Dis. 5, 27–34. doi: 10.12691/ajeid-5-2-2
Palmer, L. D. and Skaar, E. P. (2016). Transition metals and virulence in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Genet. 50, 67–91. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120215-035146
Pappas, G., Papadimitriou, P., Akritidis, N., Christou, L., and Tsianos, E. V. (2006). The new global map of human brucellosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 6, 91–99. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70382-6
Paquet, J. Y., Diaz, M. A., Genevrois, S., Tibor, A., De Bolle, X., and Letesson, J. J. (2001). Molecular, antigenic, and functional analyses of omp2b porin size variants of brucella spp. J. Bacteriol. 183, 4839–4847. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.16.4839-4847.2001
Pasquevich, K. A., Carabajal, M. V., Guaimas, F. F., Zylberman, V., Spera, J. M., Delpino, M. V., et al. (2019). Omp19 enables brucella abortus to evade the antimicrobial activity from host’s proteolytic defense system. Front. Immunol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01436
Patey, G., Qi, Z., Bourg, G., Baron, C., and O’Callaghan, D. (2006). Swapping of Periplasmic Domains between Brucella suis VirB8 and a pSB102 VirB8 Homologue Allows Heterologous Complementation. Infect. Immun. 74, 4945–4949. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00584-06
Paulley, J. T., Anderson, E. S., and Roop, R. M. (2007). Brucella abortus requires the heme transporter bhuA for maintenance of chronic infection in BALB/c mice. Infect. Immun. 75, 5248–5254. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00460-07
Paulsen, I. T., Seshadri, R., Nelson, K. E., Eisen, J. A., Heidelberg, S. F. T. K. B., Read, T. D., et al. (2002). The Brucella suis genome reveals fundamental similarities between animal and plant pathogens and symbionts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99, 13148–13153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.192319099
Pei, J., Turse, J. E., Wu, Q., and Ficht, T. A. (2006). Brucella abortus rough mutants induce macrophage oncosis that requires bacterial protein synthesis and direct interaction with the macrophage. Infect. Immun. 74, 2667–2675. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.5.2667-2675.2006
Pérez-Sancho, M., García-Seco, T., Domínguez, L., and Álvarez, J. (2015). Control of animal brucellosis — The most effective tool to prevent human brucellosis. In: baddour MM, ed. Updates Brucellosis. doi: 10.5772/61222. InTech.
Perkins, S. D., Smither, S. J., and Atkins, H. S. (2010). Towards a Brucella vaccine for humans. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 34, 379–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00211.x
Pinn-Woodcock, T., Frye, E., Guarino, C., Franklin-Guild, R., Newman, A., Bennett, J., et al. (2023). A one-health review on brucellosis in the United States. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 262, 1–12. doi: 10.2460/javma.23.01.0033
Pirone, L., Pitzer, J. E., D’Abrosca, G., Zola, A., Avella, P., Di Palma, A., et al. (2018). Identifying the region responsible for Brucella abortus MucR higher-order oligomer formation and examining its role in gene regulation. Sci. Rep. 8, 17238. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35432-1
Pollak, C. N., Delpino, M. V., Fossati, C. A., and Baldi, P. C. (2012). Outer Membrane Vesicles from Brucella abortus Promote Bacterial Internalization by Human Monocytes and Modulate Their Innate Immune Response. Oliveira SC, ed. PloS One 7, e50214. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050214
Porte, F., Naroeni, A., Ouahrani-Bettache, S., and Liautard, J. P. (2003). Role of the brucella suis lipopolysaccharide O antigen in phagosomal genesis and in inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion in murine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 71, 1481–1490. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.3.1481-1490.2003
Posadas, D. M., Ruiz-Ranwez, V., Bonomi, H. R., Martín, F. A., and Zorreguieta, A. (2012). BmaC, a novel autotransporter of Brucella suis, is involved in bacterial adhesion to host cells: Adherence of Brucella to host cells. Cell Microbiol. 14, 965–982. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01771.x
Puri, S. and O’Brian, M. R. (2006). The hmuQ and hmuD Genes from Bradyrhizobium japonicum Encode Heme-Degrading Enzymes. J. Bacteriol. 188, 6476–6482. doi: 10.1128/JB.00737-06
Queipo-Ortuño, M. I., Tena, F., Colmenero, J. D., and Morata, P. (2008). Comparison of seven commercial DNA extraction kits for the recovery of Brucella DNA from spiked human serum samples using real-time PCR. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 27, 109–114. doi: 10.1007/s10096-007-0409-y
Rambow-Larsen, A. A., Rajashekara, G., Petersen, E., and Splitter, G. (2008). Putative quorum-sensing regulator blxR of brucella melitensis regulates virulence factors including the type IV secretion system and flagella. J. Bacteriol. 190, 3274–3282. doi: 10.1128/JB.01915-07
Raymond, K. N. and Dertz, E. A. (2014). “Biochemical and physical properties of siderophores,” in Iron transport in bacteria. Eds. Crosa, J. H., Mey, A. R., and Payne, S. M. (Washington, D.C., USA: ASM Press), 1–17. doi: 10.1128/9781555816544.ch1
Rivera, S. A., Ramı́rez, M. C., and Lopetegui, I. P. (2002). Eradication of bovine brucellosis in the 10th Region de Los Lagos, Chile. Vet. Microbiol. 90, 45–53. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1135(02)00244-4
Rodionov, D. A., Vitreschak, A. G., Mironov, A. A., and Gelfand, M. S. (2003). Comparative genomics of the vitamin B12 metabolism and regulation in prokaryotes. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 41148–41159. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305837200
Rolán, H. G. and Tsolis, R. M. (2007). Mice Lacking Components of Adaptive Immunity Show Increased Brucella abortus virB Mutant Colonization. Infect. Immun. 75, 2965–2973. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01896-06
Rolán, H. G. and Tsolis, R. M. (2008). Inactivation of the type IV secretion system reduces the th1 polarization of the immune response to brucella abortus infection. Infect. Immun. 76, 3207–3213. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00203-08
Roop, R. M. (2012). Metal acquisition and virulence in Brucella. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 13, 10–20. doi: 10.1017/S1466252312000047
Roop, R. M., Barton, I. S., Hopersberger, D., and Martin, D. W. (2021). Uncovering the hidden credentials of brucella virulence. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 85, e00021–e00019. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00021-19
Roop, R. M., Gaines, J. M., Anderson, E. S., Caswell, C. C., and Martin, D. W. (2009). Survival of the fittest: how Brucella strains adapt to their intracellular niche in the host. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. (Berl). 198, 221–238. doi: 10.1007/s00430-009-0123-8
Roop Ii, R. M., Baumgartner, J. E., Pitzer, J. E., and Martin, D. W. (2017a). “Magnesium, copper and cobalt,” in Metals and the Biology and Virulence of Brucella. Eds. Roop Ii, R. M. and Caswell, C. C. (Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing), 81–94. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53622-4_6
Roop Ii, R. M., Elhassanny, A. E., Almirón, M. A., Anderson, E. S., and Atkinson, X. J. (2017b). “Iron,” in Metals and the Biology and Virulence of Brucella. Eds. Roop Ii, R. M. and Caswell, C. C. (Springer International Publishing), 9–39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53622-4_2
Roop Ii, R. M., Pitzer, J. E., Baumgartner, J. E., and Martin, D. W. (2017c). “Manganese,” in Metals and the Biology and Virulence of Brucella. Eds. Roop Ii, R. M. and Caswell, C. C. (Springer International Publishing), 41–61. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53622-4_3
Roset, M. S., Ibañez, A. E., De Souza Filho, J. A., Giambartolomei, G. H., and Delpino, M. V. (2014). Brucella cyclic β-1,2-glucan plays a critical role in the induction of splenomegaly in mice. Gorvel JP, ed. PloS One 9, e101279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101279
Rosinha, G. M. S., Leclerq, S., Harms, J. S., Oliveira, S. C., and Azevedo, V. (2002). Induction of a Th1-type of immune response but not protective immunity by intramuscular DNA immunisation with Brucella abortus GroEL heat-shock gene. J. Med. Microbiol. 51, 20–26. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-51-1-20
Rossetti, C. A., Drake, K. L., and Adams, L. G. (2012). Transcriptome analysis of HeLa cells response to Brucella melitensis infection: a molecular approach to understand the role of the mucosal epithelium in the onset of the Brucella pathogenesis. Microbes Infect. 14, 756–767. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2012.03.003
Rossetti, C. A., Drake, K. L., Siddavatam, P., Lawhon, S. D., Nunes, J. E. S., Gull, T., et al. (2013). Systems biology analysis of brucella infected peyer’s patch reveals rapid invasion with modest transient perturbations of the host transcriptome. Hensel M Ed. PloS One 8, e81719. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081719
Roushan, M. R. H., Amiri, M. J. S., Janmohammadi, N., and Pourmobasher, M. (2010). Comparison of the efficacy of gentamicin for 5 days plus doxycycline for 8 weeks versus streptomycin for 2 weeks plus doxycycline for 45 days in the treatment of human brucellosis: a randomized clinical trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 65, 1028–1035. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq064
Roux, C. M., Rolán, H. G., Santos, R. L., Beremand, P. D., Thomas, T. L., Adams, L. G., et al. (2007). Brucella requires a functional Type IV secretion system to elicit innate immune responses in mice. Cell Microbiol. 9, 1851–1869. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00922.x
Ruan, J. (2013). Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology (second edition) Volume 5 and the study of Actinomycetes systematic in China. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 53, 521–530. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.acta.2013.06.002
Ruch, T. R. and Engel, J. N. (2017). Targeting the mucosal barrier: how pathogens modulate the cellular polarity network. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 9, a027953. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a027953
Ruiz-Ranwez, V., Posadas, D. M., Estein, S. M., Abdian, P. L., Martin, F. A., and Zorreguieta, A. (2013). The BtaF Trimeric Autotransporter of Brucella suis Is Involved in Attachment to Various Surfaces, Resistance to Serum and Virulence. Ii RMR, ed. PloS One 8, e79770. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079770
Salcedo, S. P., Marchesini, M. I., Lelouard, H., Fugier, E., Jolly, G., Balor, S., et al. (2008). Brucella control of dendritic cell maturation is dependent on the TIR-containing protein btp1. Valdivia RH, ed. PloS Pathog. 4, e21. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0040021
Salvador-Bescós, M., Gil-Ramírez, Y., Zúñiga-Ripa, A., Mestre-Petrillo, F., and Moriyón, I. (2018). WadD, a new brucella lipopolysaccharide core glycosyltransferase identified by genomic search and phenotypic characterization. Front. Microbiol. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02293
Sam, I. C., Karunakaran, R., Kamarulzaman, A., Ponnampalavanar, S., Omar, S. F. S., Ng, K. P., et al. (2012). A large exposure to Brucella melitensis in a diagnostic laboratory. J. Hosp. Infect. 80, 321–325. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2011.12.004
Samartino, L. E. (2002). Brucellosis in Argentina. Vet. Microbiol. 90, 71–80. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1135(02)00247-X
Sandfoss, M. R., DePerno, C. S., Betsill, C. W., Palamar, M. B., Erickson, G., and Kennedy-Stoskopf, S. (2012). A Serosurvey for Brucella suis, Classical Swine Fever Virus, Porcine Circovirus Type 2, and Pseudorabies Virus in Feral Swine (Sus scrofa) of Eastern North Carolina. J. Wildl. Dis. 48, 462–466. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-48.2.462
Sangari, F. J., Cayón, A. M., Seoane, A., and García-Lobo, J. M. (2010). Brucella abortus ure2 region contains an acid-activated urea transporter and a nickel transport system. BMC Microbiol. 10, 107. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-107
Sangari, F. J., Seoane, A., Rodríguez, M. C., Agüero, J., and García Lobo, J. M. (2007). Characterization of the urease operon of brucella abortus and assessment of its role in virulence of the bacterium. Infect. Immun. 75, 774–780. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01244-06
Santos, R. L., Martins, T. M., Borges, Á. M, and Paixão, T. A. (2013). Economic losses due to bovine brucellosis in Brazil. Pesqui Veterinária Bras. 33, 759–764. doi: 10.1590/S0100-736X2013000600012
Scholz, H. C., Hubalek, Z., Nesvadbova, J., de Jong, A., Maquart, M., Tomaso, H., et al. (2008). Isolation of Brucella microti from soil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 14, 1316–1317. doi: 10.3201/eid1408.080286
Schroeder, S., Lawrence, A. D., Biedendieck, R., Rose, R. S., Deery, E., Graham, R. M., et al. (2009). Demonstration that cobG, the monooxygenase associated with the ring contraction process of the aerobic cobalamin (Vitamin B12) biosynthetic pathway, contains an fe-S center and a mononuclear non-heme iron center. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 4796–4805. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807184200
Sengupta, D., Koblansky, A., Gaines, J., Kingeter, L. M., Triplett, K., Sieling, P. A., et al. (2010). Subversion of innate immune responses by brucella through the targeted degradation of the TLR signaling adapter, MAL. J. Immunol. 184, 956–964. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902008
Sero-epidemiology, Z. N. (2021). and risk factor analysis of human brucellosis in Punjab, Pakistan: a cross sectional study. Trop. Biomed. 38, 413–419. doi: 10.47665/tb.38.3.084
Sheehan, L. M., Budnick, J. A., Roop, R. M., and Caswell, C. C. (2015). Coordinated Zinc Homeostasis Is Essential for the Wild-Type Virulence of Brucella abortus. Christie PJ, ed. J. Bacteriol. 197, 1582–1591. doi: 10.1128/JB.02543-14
Shemesh, A. A. and Yagupsky, P. (2011). Limitations of the standard agglutination test for detecting patients with brucella melitensis bacteremia. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 11, 1599–1601. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2011.0704
Shi, B., Li, X., Li, B., Zheng, N., Li, M., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). Construction and evaluation of the brucella double gene knock-out vaccine strain MB6 Δbp26ΔwboA (RM6). Zoonoses 2, 971. doi: 10.15212/ZOONOSES-2022-0031
Sia, A. K., Allred, B. E., and Raymond, K. N. (2013). Siderocalins: Siderophore binding proteins evolved for primary pathogen host defense. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 17, 150–157. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.11.014
Sidhu-Muñoz, R. S., Sancho, P., and Vizcaíno, N. (2016). Brucella ovis PA mutants for outer membrane proteins Omp10, Omp19, SP41, and BepC are not altered in their virulence and outer membrane properties. Vet. Microbiol. 186, 59–66. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.02.010
Sidhu-Muñoz, R. S., Tejedor, C., and Vizcaíno, N. (2020). The three flagellar loci of brucella ovis PA are dispensable for virulence in cellular models and mice. Front. Vet. Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00441
Sieira, R., Bialer, M. G., Roset, M. S., Martin, M. L., Coria, L. M., Ibañez, A. E., et al. (2017). Combinatorial control of adhesion of B rucella abortus 2308 to host cells by transcriptional rewiring of the trimeric autotransporter bta E gene. Mol. Microbiol. 103, 553–565. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13576
Sieira, R., Comerci, D. J., Sánchez, D. O., and Ugalde, R. A. (2000). A homologue of an operon required for DNA transfer in agrobacterium is required in brucella abortus for virulence and intracellular multiplication. J. Bacteriol. 182, 4849–4855. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.17.4849-4855.2000
Singh, B. B., Dhand, N. K., and Gill, J. P. S. (2015). Economic losses occurring due to brucellosis in Indian livestock populations. Prev. Vet. Med. 119, 211–215. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2015.03.013
Singh, B. B., Kostoulas, P., Gill, J. P. S., and Dhand, N. K. (2018). Cost-benefit analysis of intervention policies for prevention and control of brucellosis in India. Wunder E, ed. PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 12, e0006488. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006488
Sivanesan, D., Hancock, M. A., Villamil Giraldo, A. M., and Baron, C. (2010). Quantitative analysis of virB8–virB9–virB10 interactions provides a dynamic model of type IV secretion system core complex assembly. Biochemistry 49, 4483–4493. doi: 10.1021/bi902201y
Skalsky, K., Yahav, D., Bishara, J., Pitlik, S., Leibovici, L., and Paul, M. (2008). Treatment of human brucellosis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 336, 701–704. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39497.500903.25
Smith, D. L., Tao, T., and Maguire, M. E. (1993). Membrane topology of a P-type ATPase. The MgtB magnesium transport protein of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 22469–22479. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)41553-0
Solera, J. (2010). Update on brucellosis: therapeutic challenges. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 36, S18–S20. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.06.015
Soler-Lloréns, P., Gil-Ramírez, Y., Zabalza-Baranguá, A., Iriarte, M., and Moriyón, I. (2014). Mutants in the lipopolysaccharide of Brucella ovis are attenuated and protect against B. ovis infection in mice. Vet. Res. 45, 72. doi: 10.1186/s13567-014-0072-0
Starr, T., Child, R., Wehrly, T. D., Hansen, B., Hwang, S., Lopez-Otin, C., et al. (2012). Selective subversion of autophagy complexes facilitates completion of the brucella intracellular cycle. Cell Host Microbe 11, 33–45. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.12.002
Starr, T., Ng, T. W., Wehrly, T. D., Knodler, L. A., and Celli, J. (2008). Brucella intracellular replication requires trafficking through the late endosomal/lysosomal compartment. Traffic 9, 678–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00718.x
Sternon, J. F., Godessart, P., Gonçalves De Freitas, R., De Bolle, X., and Lestrate, P. (2018). Transposon Sequencing of Brucella abortus Uncovers Essential Genes for Growth In Vitro and Inside Macrophages. Bäumler AJ, ed. Infect. Immun. 86, e00312–e00318. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00312-18
Summers, A. O. (2009). Damage control: regulating defenses against toxic metals and metalloids. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 12, 138–144. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2009.02.003
Suresh, K. P., Patil, S. S., Nayak, A., Singh, B. R., Tiwari, R., Dhama, K., et al. (2022). Prevalence of brucellosis in livestock of African and Asian continents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Vet. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.923657
Taga, M. E. and Walker, G. C. (2010). Sinorhizobium meliloti requires a cobalamin-dependent ribonucleotide reductase for symbiosis with its plant host. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interactions® 23, 1643–1654. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-07-10-0151
Taketani, S. (2005). Aquisition, mobilization and utilization of cellular iron and heme: endless findings and growing evidence of tight regulation. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 205, 297–318. doi: 10.1620/tjem.205.297
Tang, T., Chen, G., Guo, A., Tang, F., Sun, J., Yu, S., et al. (2019). Comparative proteomic and genomic analyses of Brucella abortus biofilm and planktonic cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 21, 778–788. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10888
Tao, Z., Chen, Q., Chen, Y., Guo, Y., Du, L., Zhao, H., et al. (2021). Epidemiological characteristics of human brucellosis - China, 2016-2019. China CDC Wkly. 3, 114–119. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2021.030
Terwagne, M., Ferooz, J., Rolán, H. G., Delrue, R. M., Maquil, D., Ugalde, R. A., et al. (2013). Innate immune recognition of flagellin limits systemic persistence of B rucella: B rucella flagellin as innate immune signal. Cell Microbiol. 15, 942–960. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12088
Tesfaye, G., Tsegaye, W., Chanie, M., and Abinet, F. (2011). Seroprevalence and associated risk factors of bovine brucellosis in Addis Ababa dairy farms. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 43, 1001–1005. doi: 10.1007/s11250-011-9798-0
Thiele, O. W. and Schwinn, G. (1973). The Free Lipids of Brucella melitensis and Bordetella pertussis. Eur. J. Biochem. 34, 333–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02764.x
Thompson, M. A., Onyeziri, M. C., and Fuqua, C. (2018). Function and Regulation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Cell Surface Structures that Promote Attachment. In: Gelvin SB, ed. Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immunol. 418, 143–184. doi: 10.1007/82_2018_96. Springer International Publishing.
Tibor, A., Decelle, B., and Letesson, J. J. (1999). Outer Membrane Proteins Omp10, Omp16, and Omp19 of Brucella spp. Are Lipoproteins. Moore RN, ed. Infect. Immun. 67, 4960–4962. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.9.4960-4962.1999
Tomlinson, A. D. and Fuqua, C. (2009). Mechanisms and regulation of polar surface attachment in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 12, 708–714. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2009.09.014
Torkaman Asadi, F., Hashemi, S. H., Alikhani, M. Y., Moghimbeigi, A., and Naseri, Z. (2017). Clinical and diagnostic aspects of brucellosis and antimicrobial susceptibility of brucella isolates in hamedan, Iran. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 70, 235–238. doi: 10.7883/yoken.JJID.2016.133
Tosatto, V., Boattini, M., Nascimento, P., and Barata Moura, R. (2020). Lymphadenitis and aortitis due to Brucella melitensis infection. Infection 48, 313–314. doi: 10.1007/s15010-019-01385-4
Tsolis, R. M., Seshadri, R., Santos, R. L., Sangari, F. J., García Lobo, J. M., de Jong, M. F., et al. (2009). Genome Degradation in Brucella ovis Corresponds with Narrowing of Its Host Range and Tissue Tropism. Ahmed N, ed. PloS One 4, e5519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005519
Tumurkhuu, G., Koide, N., Takahashi, K., and Yoshida, T. (2006). Characterization of biological activities of brucella melitensis lipopolysaccharide. Microbiol. Immunol. 50, 421–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2006.tb03810.x
Uzunović, S., Skomorac, M., Bašić, F., Kamberović, F., Ibrahimagić, A., and Dizdarević, J. (2020). Human brucellosis as an epidemic zoonosis in zenica-doboj canton (Bosnia and herzegovina) during 2008-2018. Open Infect. Dis. J. 12, 1–6. doi: 10.2174/1874279302012010001
Uzureau, S., Godefroid, M., Deschamps, C., Lemaire, J., De Bolle, X., and Letesson, J. J. (2007). Mutations of the quorum sensing-dependent regulator vjbR lead to drastic surface modifications in brucella melitensis. J. Bacteriol. 189, 6035–6047. doi: 10.1128/JB.00265-07
Uzureau, S., Lemaire, J., Delaive, E., Van Der Henst, C., Deryckere, F., Wattiez, R., et al. (2010). Global analysis of quorum sensing targets in the intracellular pathogen brucella melitensis 16 M. J. Proteome Res. 9, 3200–3217. doi: 10.1021/pr100068p
Van Der Henst, C., De Barsy, M., Zorreguieta, A., Letesson, J. J., and De Bolle, X. (2013). The Brucella pathogens are polarized bacteria. Microbes Infect. 15, 998–1004. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2013.10.008
Velasco, J., Bengoechea, J. A., Brandenburg, K., Lindner, B., and Moriyón, I. (2000). Brucella abortus and Its Closest Phylogenetic Relative, Ochrobactrum spp., Differ in Outer Membrane Permeability and Cationic Peptide Resistance. Petri WA, ed. Infect. Immun. 68, 3210–3218. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.6.3210-3218.2000
Velásquez, L. N., Milillo, M. A., Delpino, M. V., Spera, J. M., Pasquevich, K. A., and Giambartolomei, G. H. (2017). Brucella abortus down-regulates MHC class II by the IL-6-dependent inhibition of CIITA through the downmodulation of IFN regulatory factor-1 (IRF-1). J. Leukoc. Biol. 101, 759–773. doi: 10.1189/jlb.4A0416-196R
Verdiguel-Fernández, L., Oropeza-Navarro, R., Basurto-Alcántara, F. J., Castañeda-Ramírez, A., and Verdugo-Rodríguez, A. (2017). Omp31 plays an important role on outer membrane properties and intracellular survival of Brucella melitensis in murine macrophages and HeLa cells. Arch. Microbiol. 199, 971–978. doi: 10.1007/s00203-017-1360-7
Viadas, C., Rodríguez, M. C., Sangari, F. J., Gorvel, J. P., García-Lobo, J. M., and López-Goñi, I. (2010). Transcriptome Analysis of the Brucella abortus BvrR/BvrS Two-Component Regulatory System. Bereswill S, ed. PloS One 5, e10216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010216
Von Bargen, K., Gorvel, J. P., and Salcedo, S. P. (2012). Internal affairs: investigating the Brucella intracellular lifestyle. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 36, 533–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2012.00334.x
Wang, Y., Chen, Z., Qiao, F., Lin, T., Zhao, H., Zhang, X., et al. (2010). The type IV secretion system affects the expression of Omp25/Omp31 and the outer membrane properties of Brucella melitensis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 303, 92–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01866.x
Wang, Z., Niu, J. R., Wang, X. L., Song, X. H., Li, T. C., Zhang, J., et al. (2014). Evaluation of a Brucella melitensis mutant deficient in O-polysaccharide export system ATP-binding protein as a rough vaccine candidate. Microbes Infect. 16, 633–639. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2014.06.013
Warren, M. J., Raux, E., Schubert, H. L., and Escalante-Semerena, J. C. (2002). The biosynthesis of adenosylcobalamin (vitamin B12). Nat. Prod. Rep. 19, 390–412. doi: 10.1039/b108967f
Watarai, M., Kim, S., Erdenebaatar, J., Haraguchi, M., Mao, J. H., Sato, M., et al. (2003). Cellular prion protein promotes brucella infection into macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 198, 5–17. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021980
Watarai, M., Makino, S., Fujii, Y., Okamoto, K., and Shirahata, T. (2002a). Modulation of Brucella-induced macropinocytosis by lipid rafts mediates intracellular replication. Cell Microbiol. 4, 341–355. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2002.00195.x
Watarai, M., Makino, S., Michikawa, M., Yanagisawa, K., Murakami, S., and Shirahata, T. (2002b). Macrophage plasma membrane cholesterol contributes to brucella abortus infection of mice. Infect. Immun. 70, 4818–4825. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.9.4818-4825.2002
Watarai, M., Makino, S., and Shirahata, T. (2002c). An essential virulence protein of Brucella abortus, VirB4, requires an intact nucleoside-triphosphate-binding domain. Microbiology 148, 1439–1446. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-5-1439
Wattam, A. R., Inzana, T. J., Williams, K. P., and O'Callaghan, D. (2012). Comparative genomics of early-diverging brucella strains reveals a novel lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis pathway. Keim PS, ed. mBio 3, e00388–e00312. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00388-12
Wattam, A. R., Williams, K. P., Snyder, E. E., Ficht, T. A., Tsolis, R. M., and Fraser, C. M. (2009). Analysis of ten brucella genomes reveals evidence for horizontal gene transfer despite a preferred intracellular lifestyle. J. Bacteriol. 191, 3569–3579. doi: 10.1128/JB.01767-08
Weeks, J. N., Galindo, C. L., Drake, K. L., Adams, G. L., Garner, H. R., and Ficht, T. A. (2010). Brucella melitensis VjbR and C12-HSL regulons: contributions of the N-dodecanoyl homoserine lactone signaling molecule and LuxR homologue VjbR to gene expression. BMC Microbiol. 10, 167. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-167
Weiss, G. (2005). Modification of iron regulation by the inflammatory response. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 18, 183–201. doi: 10.1016/j.beha.2004.09.001
Weynants, V., Tibor, A., Denoel, P. A., and Letesson, J. J. (1996). Infection of cattle with Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 a cause of the false positive serological reactions in bovine brucellosis diagnostic tests. Vet. Microbiol. 48, 101–112. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(95)00153-0
Whatmore, A. M. (2009). Current understanding of the genetic diversity of Brucella, an expanding genus of zoonotic pathogens. Infect. Genet. Evol. 9, 1168–1184. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2009.07.001
Wuichet, K. and Zhulin, I. B. (2010). Origins and diversification of a complex signal transduction system in prokaryotes. Sci. Signal. 3, ra50. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000724
Wyatt, H. V. (2005). How Themistocles Zammit found Malta Fever (Brucellosis) to be Transmitted by the Milk of Goats. J. R. Soc. Med. 98, 451–454. doi: 10.1177/014107680509801009
Yang, J., Goetz, D., Li, J.-Y., Wang, W., Mori, K., Setlik, D., et al. (2002). An iron delivery pathway mediated by a lipocalin. Mol. Cell. 10, 1045–1056. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00710-4
Young, E. J., Hasanjani Roushan, M. R., Shafae, S., Genta, R. M., and Taylor, S. L. (2014). Liver histology of acute brucellosis caused by Brucella melitensis. Hum. Pathol. 45, 2023–2028. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2014.07.007
Zhang, J., Guo, F., Chen, C., Wang, Z., Li, X., Shi, B., et al. (2013). Brucella melitensis 16 M Δ hfq attenuation confers protection against wild-type challenge in BALB/c mice. Microbiol. Immunol. 57, 502–510. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12065
Zhang, N., Huang, D., Wu, W., and Zhang, X. (2018). Animal brucellosis control or eradication programs worldwide: A systematic review of experiences and lessons learned. Prev. Vet. Med. 160, 105–115. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2018.10.002
Zhang, K., Wang, H., Guo, F., Li, Z., Wang, X., Wang, Y., et al. (2016). OMP31 of Brucella melitensis 16M impairs the apoptosis of macrophages triggered by TNF-α. Exp. Ther. Med. 12, 2783–2789. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3655
Zhi, F., Zhou, D., Li, J., Huang, D., Luo, X., Chen, Z., et al. (2020). Omp16, a conserved peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein, is involved in Brucella virulence in vitro. J. Microbiol. 58, 793–804. doi: 10.1007/s12275-020-0144-y
Zimmermann, P. and Curtis, N. (2019). Factors that influence the immune response to vaccination. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 32, e00084–e00018. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00084-18
Zygmunt, M. S., Blasco, J. M., Letesson, J. J., Cloeckaert, A., and Moriyon, I. (2009). DNA polymorphism analysis of Brucella lipopolysaccharide genes reveals marked differences in O-polysaccharide biosynthetic genes between smooth and rough Brucella species and novel species-specific markers. BMC Microbiol. 9, 92. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-92
Keywords: brucellosis, zoonotic disease, Brucella, livestock, public health threats
Citation: Ghssein G, Ezzeddine Z, Tokajian S, Khoury CA, Kobeissy H, Ibrahim J-N, Iskandar C and Hassan HF (2025) Brucellosis: Bacteriology, pathogenesis, epidemiology and role of the metallophores in virulence: a review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1621230. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1621230
Received: 02 May 2025; Accepted: 09 June 2025;
Published: 08 July 2025.
Edited by:
Ghassan M. Matar, American University of Beirut, LebanonReviewed by:
Hanwei Jiao, Southwest University, ChinaGamal Wareth, Friedrich Loeffler Institut, Germany
Copyright © 2025 Ghssein, Ezzeddine, Tokajian, Khoury, Kobeissy, Ibrahim, Iskandar and Hassan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hussein F. Hassan, aHVzc2Vpbi5oYXNzYW5AbGF1LmVkdS5sYg==
 Ghassan Ghssein
Ghassan Ghssein Zeinab Ezzeddine
Zeinab Ezzeddine Sima Tokajian2
Sima Tokajian2 Charbel Al Khoury
Charbel Al Khoury Jose-Noel Ibrahim
Jose-Noel Ibrahim Hussein F. Hassan
Hussein F. Hassan