- National Key Laboratory of Intelligent Tracking and Forecasting for Infectious Disease, National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Centre for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing, China
Introduction: Stenotrophomonas represents a group of bacteria that exhibit significant value in industrial and agricultural applications, while also posing pathogenic risks to humans. 704A1T was isolated from a patient with tuberculous pleurisy. Its 16S rRNA sequence showed the highest homology (99.72%) with a Stenotrophomonas strain without defined species classification. It is necessary to clarify the species 704A1T belonging to and its potential pathogenicity to humans.
Methods: Systematical evaluations including phenotypic and biochemical characteristics, antibiotic susceptibility, genomic sequencing were conducted. The pathogenicity and immunological characteristics were tested by intranasally inoculated C57BL/6J mice.
Results: 704A1T is Gram negative rod-shaped bacterium with flagella at single extreme. Showing highly similar with S. maltophilia, 704A1T also displayed distinct characteristic peaks in fatty acid profiling and MALDI-TOF analysis. 704A1T was resistance to 21 antibiotics, including four anti-tuberculosis drugs: rifampicin, streptomycin, rifabutin, and cycloserine. The average nucleotide identity (ANI) values of 704A1T compared to defined Stenotrophomonas species ranged from 80.03% to 89.6%, below than both the commonly accepted 95%-96% ANI threshold for prokaryote species and the 95% threshold suggested for Stenotrophomonas. Though no mortality was observed, 704A1T could cause severe consolidation in murine lung tissue and has the ability of hematogenous dissemination.
Conclusion: Results supported the classification of 704A1T (=GDMCC 1.4133T) as a novel species within the genus Stenotrophomonas, for which the name Stenotrophomonas tuberculopleuritidis sp. nov. is proposed. 704A1T is a multi-antibiotic resistance strain with potentially stronger pathogenicity than S. maltophilia and requires more clinical attention. The isolation of 704A1T underscored the importance of sustained surveillance and taxonomic clarity of Stenotrophomonas species emerging from clinical environments.
1 Introduction
Stenotrophomonas exhibits a wide range of habitats, including natural environment, patients, animals and plants. The common characteristics of Stenotrophomonas species are as follows: 1.Strong biofilm formation ability, enabling the formation of biofilms on various abiotic surfaces and tissues; 2. Extensive intrinsic and acquired multidrug resistance (mediated by efflux pumps, β-lactamases, and horizontal gene transfer), which confers resistance to clinically commonly used drugs such as cephalosporins and makes it as an emerging superbug (Sanchez, 2015; Brooke et al., 2017; Gil-Gil et al., 2020; Kumar et al., 2020); 3. High genotypic and phenotypic variability, even within the same species, which is the reason for the several changes in the taxonomic classification of the genus Stenotrophomonas and its species (Palleroni and Bradbury, 1993); 4. Possessing bacterial structures such as lipopolysaccharides, flagella, and pili, as well as type IV secretion systems; 5. Abundant extracellular enzymes, including proteases, esterases, phospholipases, extracellular nucleases, hyaluronidases, heparinases, hemolysins, and siderophores, etc (Trifonova and Strateva, 2019); 6. Capability to produce various active bactericidal factors, including proteolytic enzymes acting on Ralstonia solanacearum (Elhalag et al., 2016), antifungal substances Maltophilin (Jakobi et al., 1996) and Xanthobaccin (Nakayama et al., 1999), serine proteases against nematodes (Huang et al., 2009), broad-spectrum antibacterial R-type phage tail-like bacteriocins Maltocin P28 (Liu et al., 2013), S16 (Chen et al., 2019), and modular bacteriocins Stenocins (Paškevičius et al., 2022).
Therefore, Stenotrophomonas is a fascinating bacterium with a dual functional role. On the one hand, Stenotrophomonas has robust resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses, including plant pathogenic fungi and bacteria (Kumar et al., 2023). These bacteria engage in complex interactions with other microorganisms on plant surfaces and within soil through biofilm formation. They inhibit plant fungal pathogens and viruses while modulating rhizosphere microbial communities via mechanisms such as extracellular enzyme-mediated decomposition, iron nutrient competition, and more (Kumar et al., 2023). Against crop pests like Spodoptera litura, they trigger the accumulation of plant hormones (e.g., jasmonic acid) and upregulate jasmonic acid-responsive gene transcription (Ling et al., 2022). For plant growth promotion, they produce auxins and hydrogen cyanide, solubilize phosphorus/potassium salts, fix atmospheric nitrogen, and degrade compounds like geosmin, explosive pollutants (hexahydro-1, 3, 5-trinitro-1, 3, 5–triazine, RDX), keratin, macrocyclic hydrocarbons, and nitrophenols (Gao et al., 2013). These capabilities enable Stenotrophomonas to remediate agricultural soils by eliminating chemical pesticides, insecticides, and diverse environmental pollutants. Therefore, most Stenotrophomonas species are considered to have significant agronomic and industrial application values, established as plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), emerging biocatalysts for environmental biodegradation, and sustainable substitutes for synthetic fungicides.
While on the other hand, these common characteristics of Stenotrophomonas function as virulence factors in host colonization and infection. For instance, they degrade the extracellular matrix of tissue cells in the host respiratory system, connective tissues (especially collagen and fibronectin), neutrophil extracellular traps, serum immune proteins, etc., endowing Stenotrophomonas with high invasiveness to inactivate/evade the host immune defense system. They damage pulmonary epithelium, causing fulminant hemorrhagic pneumonia; induce intense inflammatory immune responses; mediate host tissue adhesion and form biofilms on abiotic surfaces like medical devices, enhancing the transmission of nosocomial infections; and synergistically exacerbate infections by other pathogens. Therefore, Stenotrophomonas, typified by S. maltophilia, is an emerging global opportunistic pathogen with growing clinical threat (Brooke, 2012). They can cause severe infections in multiple organs and tissues, including bloodstream and pneumonia. Notably, its bacteremia is associated with a mortality rate as high as 65% (Tan et al., 2014). S. maltophilia infection has be seen as a life-threatening disease in ICU patients, cancer patients, and immunocompromised individuals. Alongside Achromobacter xylosoxidans, it serves as a marker for the progression to severe lung diseases, holding comparable pathophysiological significance to Pseudomonas aeruginosa—the hallmark pathogen in cystic fibrosis patients (Menetrey et al., 2021). Consequently, the World Health Organization has classified S. maltophilia among the world’s most concerning emerging multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. Following extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae, carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, and refractory Pseudomonas aeruginosa, treatment guidelines from the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) list S. maltophilia alongside AmpC β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii as the three pathogens causing severe hospital-acquired infections with significant morbidity and mortality across U.S. healthcare settings (Tamma et al., 2022).
Among the definite Stenotrophomonas species, only seven species are considered to be human pathogens or have a history of isolation from human samples or clinical environments, namely S.maltophilia, S. sepilia (Gautam et al., 2021), S. pavanii (Iebba et al., 2018), S. acidaminiphila (Jezek et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2022), S. rhizophila (Chao et al., 2022), S. riyadhensis (Macori et al., 2024) and S. pigmentate (Li et al., 2024). Notably, in our prior study on the co-infection/co-isolation of Stenotrophomonas and Mycobacterium (Li et al., 2023), nine Stenotrophomonas isolates identified via 16S rRNA sequencing were assigned to three species: S. maltophilia, S. rhizophila, and S. pigmentate (Li et al., 2024). However, one strain, 704A1T, remained unassigned to a specific species. The 16S rRNA sequence of 704A1T exhibited the highest homology (99.72%) with Stenotrophomonas sp. strain DoB6 (JQ359085.1), and its recA gene showed the highest similarity (99.72%) to Stenotrophomonas sp. strain ZAC14D2_MKIMI4 (KX896038.1). Both strains have not a defined species annotation. Because this strain was also isolated from tuberculosis (TB) patient, indicating its potential pathogenicity and clinical importance to humans, it was evaluated systematically in this study to clarify its classification in the genus Stenotrophomonas and the main phenotypic, genetic and pathogenic characteristics.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Strain isolation and identification
Sputum sample was collected from the TB clinic of Chaoyang District Center for Disease Control and Prevention (39°89’ N, 116°40’ E) with traditional N-acetyl-1-cysteine-4% NaOH-phosphate alkaline decontamination treatment. The colonies on the 7H10 + 10% oleic acid-albumin-dextrose-catalase (OADC) agar plate were identified as Stenotrophomonas strains by amplification and sequencing with16S rRNA universal bacterial primers (16S-U: 5’AGA GTT TGA TCM TGG CTC AG 3’and 16S-L: 5’ CCG TCA ATT CMT TTR AGT TT 3’) (Li et al., 2023).
2.2 Phenotypic and biochemical characteristics
Besides 7H10 + 10% OADC agar, the growth abilities of this strain on four kinds of medium, tryptone soy (TSA; Difco), Luria-Bertani (LB; Difco), columbia blood agar (OXOID) and Mueller-Hinton (MH; Difco), and under conditions of 15-37°C, pH range 5-10, and 0-5% NaCl concentration were tested. Cell modality was observed with optical microscope and transmission electron microscope (HT7700, Hitachi, Japan). Utilization of carbon sources and enzyme production were tested with the API 20NE, API ZYM and API 50 CH test kits (20050, 50300, 25200, BioMerier France, France) at 28°C and the endpoints were 48 h, 4 h and 48 h respectively according to the manufacturer’s manual.
2.3 Fatty acids analysis and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry
Cellular fatty acids were analysed using the Sherlock Microbial Identification System (MIDI) with the MIDI Sherlock software program (version 6.3) and RTSBA6 (6.21) library. MALDI-TOF was conducted on Autoflex speed TOF/TOF (Bruker Daltonics GmbH, Germany) and automatically interpreted by MALDI Biotype IVD2.3 (5989) analysis software. Identification score above 2.0 is cutoff value of intra species, and a score of 1.7-2.0 is intra genus.
2.4 Antibiotic susceptibility testing
The BD Phoenix™ NMIC 413 Panels on BD Phonenix-100 equipment (BD, Sparks, MD, USA), the customised AST plate for Chinese Pathogen Identification Net (CHNENF, Trek Diagnostic Systems Ltd, West Sussex, United Kingdom) and the Sensititre™ MYCOTB MIC plate (Trek Diagnostic Systems, Cleveland, OH, USA) were used to determine the strain’s sensitivity to drugs commonly used for Gram-negative strains and 12 anti-TB drugs. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) were judged according to the standards of the Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) (CLSI, 2018; CLSI, 2023) and manufacturer’s instructions.
2.5 Whole genome sequencing and gene function analysis
Genome of 704A1T was sequenced using a Pacbio sequel II and DNBSEQ platform under four SMRT cells Zero-Mode. Self-correction, single-base correction and gene prediction were performed sequentially by the program Canu, GATK and Glimmer3 with Hidden Markov model. Genome components were predicted using localized software, tRNAscan SE (version:1.3.1), Tandem Repeats Finder (version:4.04), PhiSpy (version: 4.2.21), etc. Gene function scanning was performed based on the databases listed below, KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes, http://www.kegg.jp), COG (Clusters of Orthologous Groups, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), NR (Non-Redundant Protein Database databases, ftp://ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/blast/db/FASTA/nr.gz), Swiss-Prot (http://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn), GO (Gene Ontology, http://www.geneontology.org), TrEMBL, EggNOG (http://eggnog.embl.de), VFDB (Virulence Factors of Pathogenic Bacteria, http://www.mgc.ac.cn), ARDB (Antibiotic Resistance Genes Database, http://www.argodb.org/), CAZy (Carbohydrate-Active enZYmes Database, http://www.cazy.org) and T3SS (Type III secretion system effector protein, http://effectivedb.org).
2.6 Pairwise average nucleotide identity comparison and phylogenetic analysis
16S rRNA gene sequence, ANI and core gene profiles of 704A1T were comprehensively compared with those of all 33 validated Stenotrophomonas species included in the Taxonomy up to 2024. 16S rRNA gene sequences of the type strains of each species were obtained from LPSN (https://lpsn.dsmz.de/) by their GenBank accessions, except for Stenotrophomonas muris, for which the 16S rRNA gene sequence was retrieved from its reference genome GCF_024621935.1 (gene locus NSA55_RS22000). Multiple sequence alignment was performed using Muscle v5.3 (https://drive5.com/muscle/) (Edgar, 2022). Reference genomes for each species were obtained from the NCBI database (except for S. panacihumi). The reference genome of Xanthomonas campestris (GCF_013388375.1) was used as an outgroup. Pairwise ANI calculations were performed using FastANI v1.34 (Jain et al., 2018) (https://github.com/ParBLiSS/FastANI), followed by average linkage hierarchical clustering through Python scripts, with results saved in Newick format. The valid value output threshold of FastANI is >78%. Single-copy orthologous protein sequences were identified using OrthoFinder v2.5.5 (Emms and Kelly, 2019) (https://github.com/davidemms/OrthoFinder) to obtain multiple sequence alignment files. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using IQtree v2.3.6 (Minh et al., 2020)(https://github.com/iqtree/iqtree2) with automatic model selection and 1000 bootstrap replicates. All trees were visualized and annotated using Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT) (Xie et al., 2023).
2.7 Animal infection experiment
Using a random number method, 6–7 weeks aged female C57BL/6J mice weighing 20–25 g were randomly divided into infection and control groups. Five mice in each infection group were intranasally inoculated with 25 μL of 1.5 × 108 CFU/mL of tested strains, and mice in the control groups were inoculated with PBS. At 4 h, 12 h, 1 day, 2 days and 3 days post-infection, the mice were sacrificed and the lung and spleen tissues were collected aseptically. The established Chinese reference strain of S. maltophilia strain 11066 was used as infection control in this experiment (Yue et al., 2023).
The left lobes of the lungs were fixed in 10% neutral formalin for 24 h, followed by tissue processing, paraffin embedding, sectioning and staining, and blindly examined by an expert in the field of laboratory animal pathology. Pulmonary clearance and occurrence of disseminated infection were monitored via quantitative bacteriology of the lung and spleen homogenates, respectively. Briefly, tissues were homogenised (1000 rpm) on ice in 1 mL of sterile normal saline by using a homogeniser (RZ-GR96A; Beijing Guoke Rongzhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China), 100 μL 10-fold serial dilutions of homogenates were spread on LB agar. The number of colonies was counted 24–48 h after incubation at 37°C. Bacterial colony counts were normalised according to the wet tissue weight and calculated as CFU/g.
2.8 Quantified cytokines tests
Remaining lung homogenates were used for quantified cytokines tests. Nine out of ten cytokines, namely tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), gamma interferon (IFN-γ), interleukin (IL)-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12p70, and IL-17A were quantified using Luminex technology (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) and reagents (12002798; BIO-RAD, USA). IL-22 was tested using RayBio® Mouse IL-22 ELISA Kit.
Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The t-test is used to compare the differences between the two groups. For the comparison between groups, the analysis of variance with Dunnett’s t-test is used. P<0.05 indicates that the difference is statistically significant.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Systematic phenotypic characteristics of the strain
The strain 704A1T was isolated from sputum samples of a 34-year-old female. The woman was clinically diagnosed as tuberculous pleurisy and under anti-TB treatment. The γ-interferon release assay test of this patient was positive, but the isolation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the sputum sample was negative.
704A1T is Gram- negative bacterium and grows well on tryptone soy (TSA; Difco), Luria-Bertani (LB; Difco), columbia blood agar (OXOID) and Mueller-Hinton (MH; Difco). Colorless, transparent, smooth and moist colonies on nutrient agar and grayish white, non-hemolytic colonies with ammonia odor on blood agar can be observed after 18–24 hours (Figures 1A, B). Growth of 704A1T on LB medium could be observed under conditions of 15-37 °C, pH range 5-10, and NaCl concentration of 0-5%. Under microscopes, 704A1T cells are Gram negative rod-shaped, 1.5-2 × 0.4-0.6 μM bodies with 1–5 flagella at the single extreme (Figure 1C).
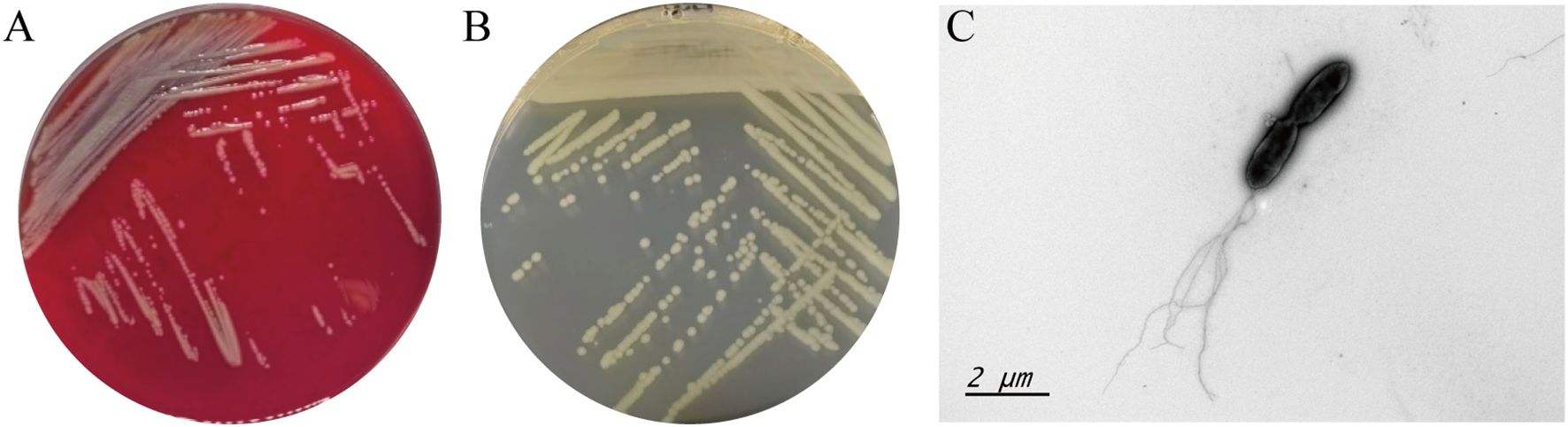
Figure 1. Growth morphology 704A1T on columbia blood agar (A), MH medium (B) and the bacterial image under the transmission electron microscopy (C).
Among a total of 84 reactions, 704A1T showed positive results for nitrate reduction, hydrolysis of heptavidin and gelatin, assimilation of β-galactosidase, glucose, mannose, N-acetylglucosamine, maltose, malic acid, and citric acid in API 20NE; it was positive for reactions of alkaline phosphatase, esterase lipase (C8), leucine arylamidase, acid phosphatase, and naphthol-AS-BI phosphate hydrolase in API ZYM. The only substrate that 704A1T could use as carbon source was esculin in API 50CH.
704A1T contains all 3 characteristic fatty acids of the genus Stenotrophomonas, iso-C11:0, iso-C11:03 3OH, and iso-C13:0 3OH (Heylen et al., 2007). Its predominant fatty acids were iso-C15:0, C15:0 anteiso, summed Feature 3(C16:1ω7c/16:1ω6c) and C16:0. The main peaks of 704A1T in the MALDI-TOF spectrum located at 4857.381Da, 5253.734Da, 6071.902Da and 4844.272Da. Both in terms of fatty acid and proteins composition, 704A1T has a high degree of similarity with S. maltophilia. The similarity index to S. maltophilia in the RTSBA6 library is 0.643, and the identification score in the Bruker_SSP library is 1.985.
3.2 Genetic characteristics and species classification
The complete genome of 704A1T was 4,686,432 bp in length and 63.77% GC content. The subreads N50 was 11,437 bp and N90 was 7,180 bp. Genome depth was 45.49%. The statistics of non-coding RNA were 73 tRNAs, 5 5S rRNAs, 4 16S rRNAs, 4 23S rRNAs and 22 sRNAs. A total of 4,214 CDSs, 315 tandem repeats, 214 minisatellite DNAs, and 16 microsatellite DNAs were predicted. Gene function annotation based on eleven databases showed that 704A1T has total 4128 functional genes, including 314 virulence factor genes in VFDB, 179 carbohydrate-active enzymes in CAZY, 3150 proteins in COG, 2548 genes in KEGG and 548 genes in T3SS. Scanning against COG, KEGG, NR, SWISSPROT and VFDB databases indicated that 704A1T has a membrane channel-forming protein YqfA of hemolysin III family on its genome, but no active haemolysin encoding gene like hlyB and hlyIII of 610A2T, the type strain of Stenotrophomonas pigmentate which was isolated from tuberculosis patients during the same period of 704A1T. The genotype of 704A1T was consistent with its phenotype that the 704A1T did not form hemolytic rings like 610A2T on the blood agar (Li et al., 2024).
16S rRNA gene sequencing is the most commonly used method for the preliminary identification of bacterial species. Although its resolution is insufficient to differentiate closely related Stenotrophomonas species (Yu and Wang, 2024), it still holds value in indicating potential novel taxa when sequence homology to known genomes is low. On the phylogenetic tree of 16S rRNA gene, 704A1Twas incorporated into a clade containing 12 species, including S. maltophilia, S. indicatrix, etc (Figure 2). ANI serves as the gold standard for defining prokaryotic species at the genomic level, with established threshold values validated for Stenotrophomonas species and complexes (Yu and Wang, 2024). The pairwise ANI comparisons between 704A1T and the 33 Stenotrophomonas species generated 18 valid ANI values, ranging from 89.66 and 83.77. with the highest value observed for S. indicatrix. Therefore, based on the 95% ANI threshold value suggested for Stenotrophomonas (Yu and Wang, 2024), 704A1T can be judged as new species of genus Stenotrophomonas. A total of 1,162 core genes were identified from the 33 genomes. On both the ANI clustering tree and single-copy orthologs phylogenetic tree, 704A1T formed a clade adjacent to the Stenotrophomonas maltophilia complex (Smc) together with S. indicatrix and S. lactitubi (Figure 2).
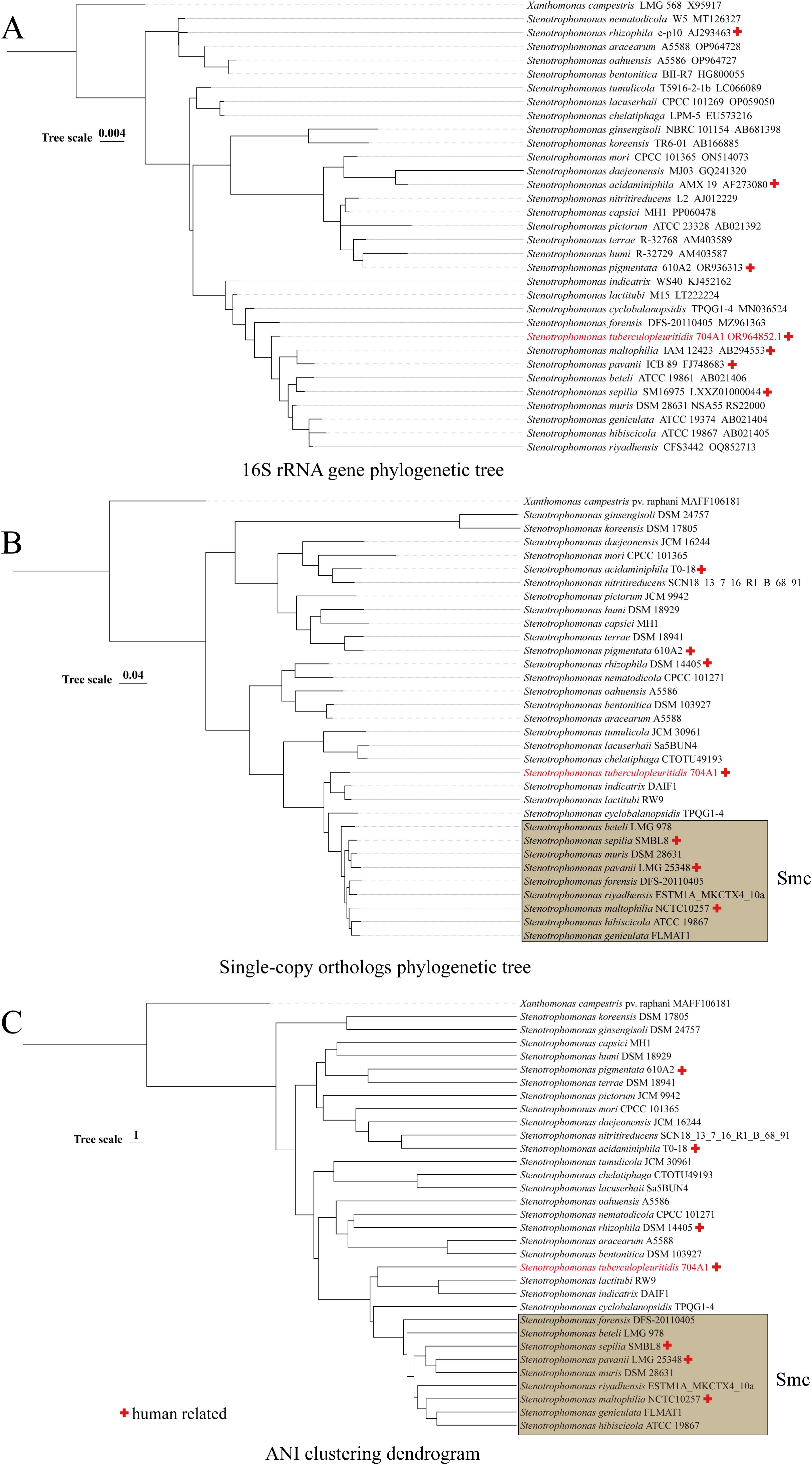
Figure 2. Phylogenetic/clustering tree constructed based on 16S rRNA gene (A), single-copy orthologs (B), and ANI (C).
3.3 Multi-antibiotic resistance
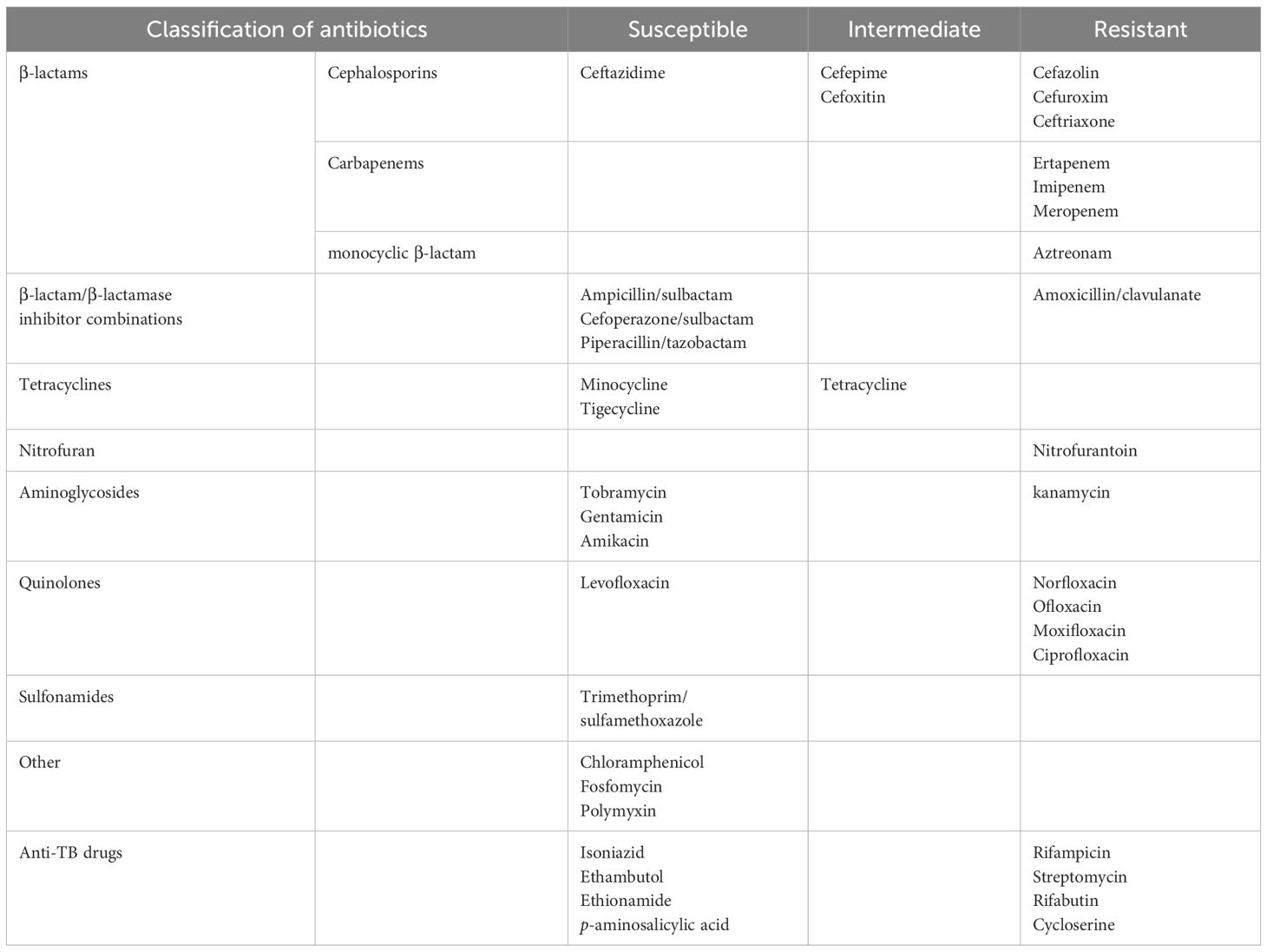
The AST results of the 39 drugs tested showed that 704A1T possessed the common characteristic of the genus Stenotrophomonas and is also a multidrug-resistant strain (Table 1). 704A1T is sensitivity to tetracyclines, aminoglycosides, and other antibiotics such as chloramphenicol, fosfomycin and polymyxin, but is generally resistant to β-lactam and quinolone antibiotics, while β-lactam inhibitors sulbactam and tazobactam can better increase the sensitivity of 704A1T to β-lactams than clavulanate. It is worth noting that 704A1 T is resistant to more than half of the anti-TB drugs, including rifampicin and rifabutin. Therefore, while the AST results for M. tuberculosis mixed with 704A1T will not be misjudged as MDR-TB like 610A2 T, it will just incorrectly be deemed as rifampicin-resistant (RR)-TB. The effect of its multidrug resistance on AST and treatment in cases of mixed infections stands out as a particularly notable aspect of Stenotrophomonas.
On the 704A1T genome, there are 85 antibiotic resistance genes matched in ARDB, CARD and KEGG, including 13 genes related to the resistance of the beta-lactam antibiotic (ampC, blaI, bl3_l, and bl2e_y56, et al), ksga gene related to kasugamycin, qnrb gene related to fluoroquinolone, aph6ic and aph3va related to aminoglycosides, dfra26 related to trimethoprim, and 22 multidrug resistance efflux pump genes. The drug resistance of 704A1T had good phenotype-genotype correlation.
3.4 The virulence in mouse infection model
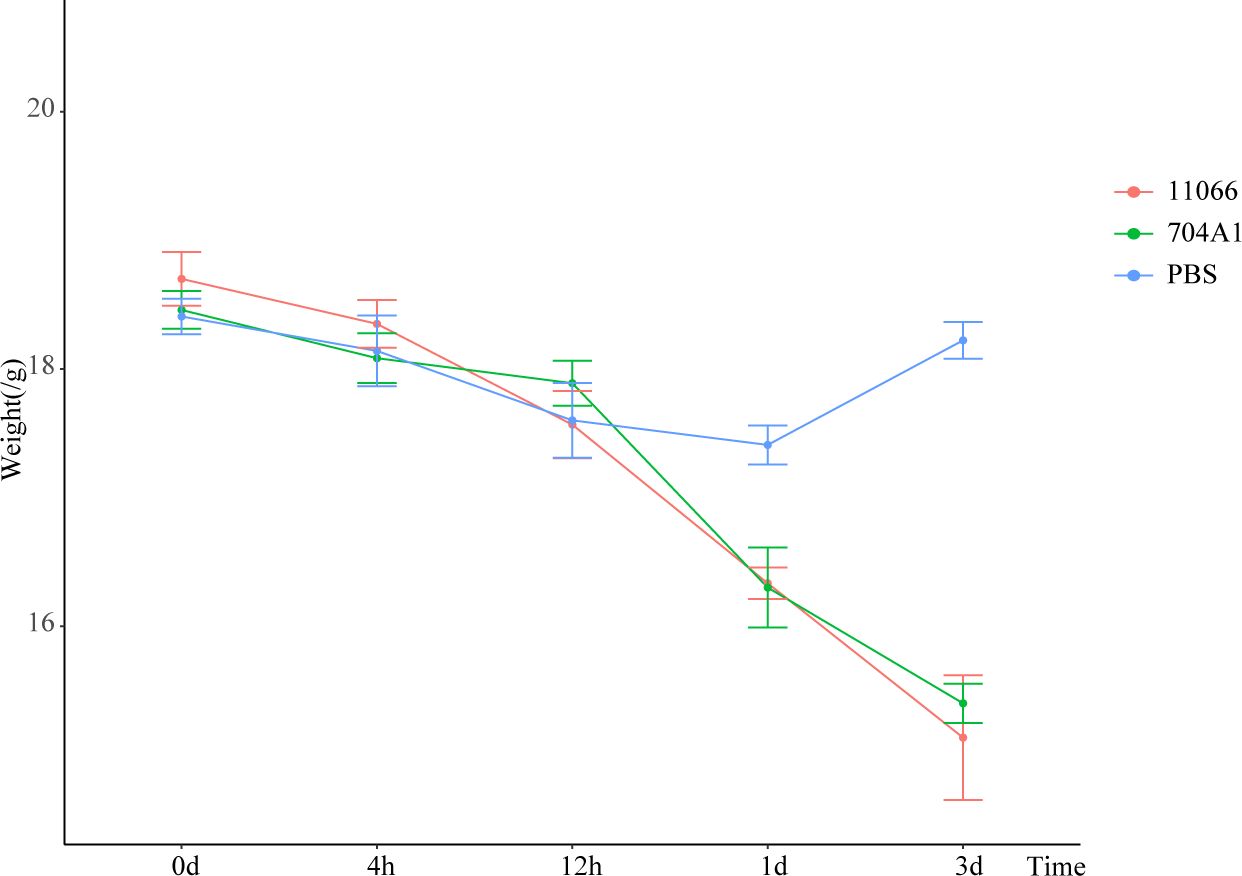
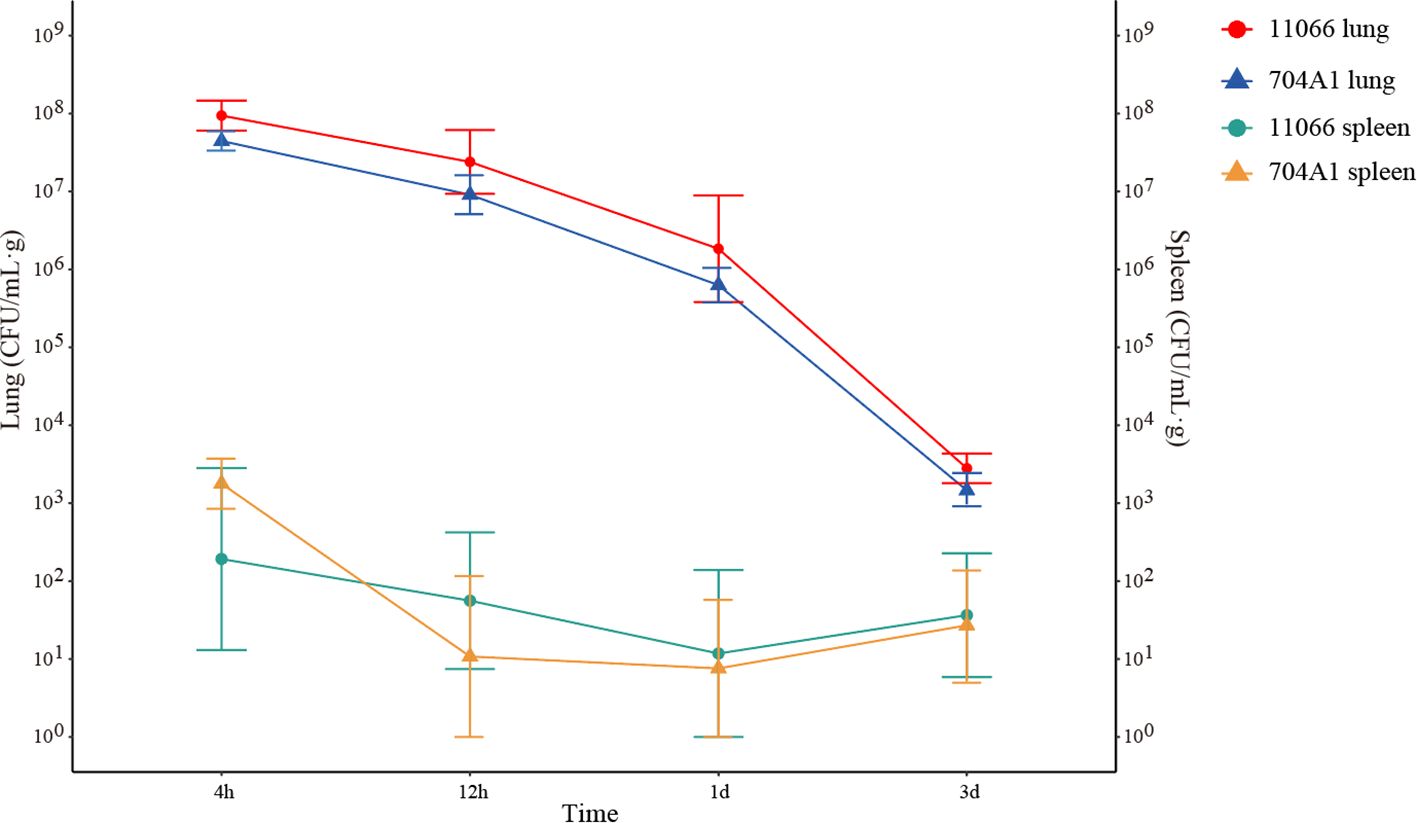
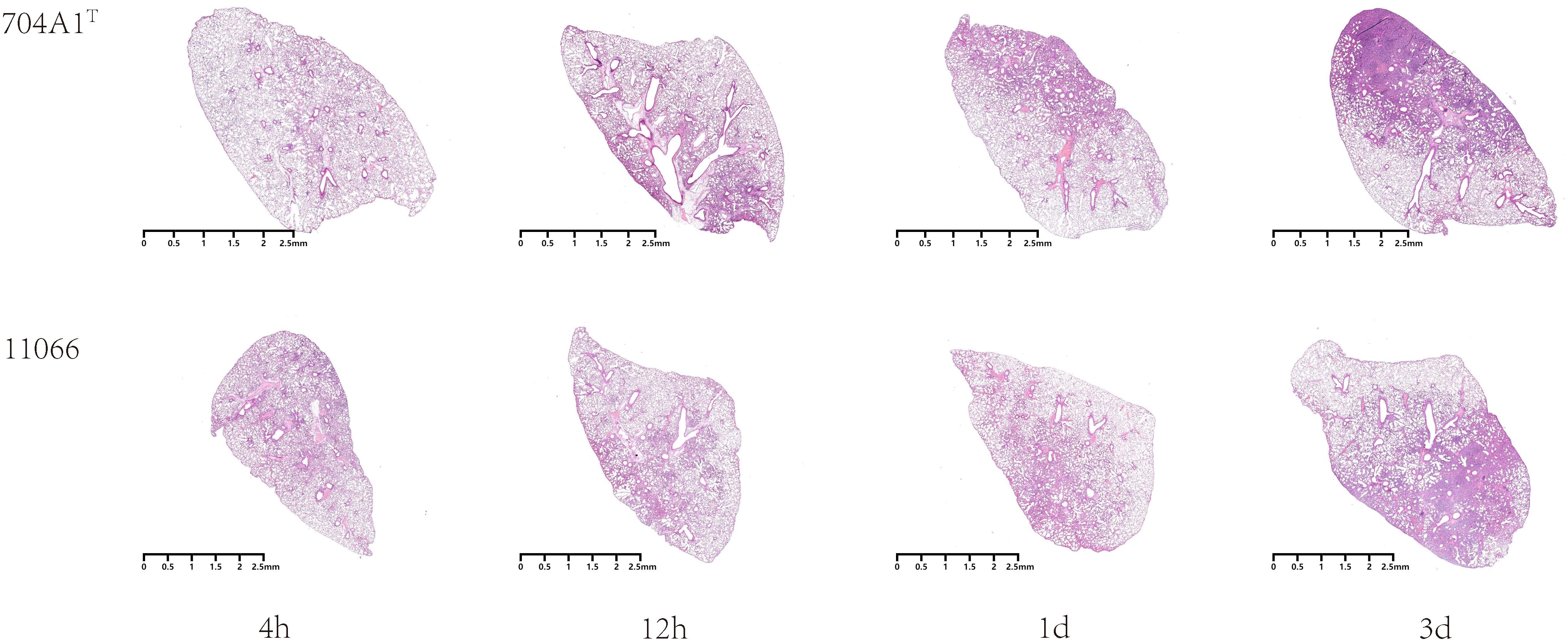
At the intranasal infection dose of 25 μL 1.5 × 108 CFU/mL, no mortality was observed. The body weights of the mice infected with 704A1T manifested a continuous downward trend. By the third day post-infection, the percentage of average weight loss had reached 16.5% (Figure 3). The bacterial load of 704A1T per tissue weight (g) in lung at four post-infection time points of 4h, 12h, 1d, and 3d infected were 4.84 ± 2.55×108 CFU/mL·g, 1.18 ± 0.85×107 CFU/mL·g, 7.76 ± 4.96×105 CFU/mL·g, and 1.80 ± 1.21×103 CFU/mL·g respectively (Figure 4). The strain could be isolated from the spleen homogenates at all four time points, indicating that 704A1T can invasive and spread in blood. Histological examination showed that pulmonary damage could be obviously observed starting from 12 hours after 704A1T infection. At the 3d post-infection, more than 50% of the lung tissue underwent consolidation (Figure 5).
Compared with the infection of S. maltophilia strain 11066, there were no statistically significant differences in the changes of body weight, the bacterial loads in the lung and spleen of mice. The changes in histopathology were also quite similar. However, the mice in the group infected with 704A1T exhibited more severe clinical symptoms, including obviously decreased activity, listlessness, rapid shallow breathing and piloerection than those infected with 11066. The infections between 704A1T and 610A2T showed more significant differences than 11066. 610A2T could be cleared from the murine lungs two days after infection, and it could only be isolated from the spleen within four hours. The histopathological findings showed pulmonary hemorrhage without consolidation. Therefore, 704A1T persisted in the host for a longer time and caused more severe damage to the lung tissue than 610A2T.
On the 704A1T genome, 314 virulence factors were identified from VFDB, in which 26 factors were classified in level1 human diseases and Level2 infectious disease. Besides 548 genes identified in T3SS, annotation results showed that 704A1T possessed two types of secretion systems, consisting of 5 type IV secretion system genes (virB1- virB4 and virB11) and 7 type II secretion system HxcT pseudopilin genes (hxc Q, R, S, T, U, V, W). In addition to multiple chemotaxis factors, flagellar and pili related genes, biofilm-controlling response genes, it is worth noting that the 704A1T genome harbors a variety of virulence-related genes. For example, 704A1T harbors two mip genes, which encode the macrophage infectivity potentiator. This surface protein with peptidyl‐prolyl‐cis/trans isomerase activity is a kind of conserved virulence factor and plays a critical role in the effective infection of host cells. Its capacity to promote the parasitism of Legionella pneumophila within human macrophages and induce pneumonia in experimental models has been reported (Cianciotto et al., 1990; McChlery et al., 2009). The regulator of virulence determinants PhoP, belonging to the two-component system PhoPR, directly regulates the expression of genes such as moxR, which associated with the pathogenicity and bacterial load in various tissues of Riemerella anatipestifer, the causing bacterium of duck infectious serositis (Zhang et al., 2025). The transcriptional regulator RcsB on the 704A1Tgenome is a regulator that, like PhoP, is regulated by acetylation and involved in various processes such as biofilm formation and cell division (Qin et al., 2016; Lammers, 2021). Moreover, five Dot/Icm type IV secretion system effectors encoding genes were identified on the 704A1Tgenome. This is a system that can translocate more than 300 virulence factors (effectors) into host cells to facility intracellular survival and govern host cell interactions (Schroeder et al., 2010; Weber et al., 2014). 704A1T carries three thioredoxin 1 genes. Trx1 acts as reductases in redox regulation and protects proteins from oxidative aggregation and inactivation. Trx1 helps the cells to cope with various environmental stresses and inhibits programmed cell death. It also plays important roles in suppressing neurodegenerative disorders and resistance against oxidative stress-associated neuron damage (Awan et al., 2022). Some of these virulence genes are harbored by 704A, such as mip, but absent in 610A2T and 11066. It is speculated that this may be the reason that the pathogenicity of 704A showed in the mouse infection experiment are stronger than those of 610A2T and 11066, and its longer residence time in mice compared to the latter two.
3.5 The immune characteristics
After infection with 704A1, the overall immune response in mice was rapid (Figure 6). At 4 hours, among the 10 cytokines detected, GM-CSF, IL-17A, and IL-6 were significantly higher compared to the control group, suggesting that the host was in the early stage of the acute inflammatory response. In particular, the level of IL-6 was as high as 650.75 pg/mL, significantly higher than those in the infections with 11066 and 610A2T (which were 199.83 pg/mL and 115.78 pg/mL respectively). IL-6 has been reported to be related to the severity of many diseases (Schulte et al., 2013). The IL-6 levels in 704A1T are consistent with the fact that among infections by three Stenotrophomonas strains, it exhibited the most severe signs and pathological changes, even more severe than 11066, the representative clinical pathogenic species S. maltophilia. This result also suggested that IL-6 could serve as an early predictive indicator of the severity of the disease. At 12 hours, the levels of IL-6 and GM-CSF were significantly lower than those at 4 hours, and IL-12p70 began to increase significantly. IL-12p70 is a cytokine that promotes the differentiation of T cells into Th1 type, indicating that the immune system had shifted from the initial non-specific response to a more targeted adaptive immune response and the establishment of the Th1 immune response. One day after infection, the levels of most cytokines returned to normal, and only IL-12p70 and TNF-α were higher than those in the control group, indicating that the acute inflammation had been controlled. Three days after infection, only IL-17A among the cytokines was still higher than that in the control group. IL-17A is mainly produced by Th17 cells and plays an important role in tissue damage repair, which indicates that the acute inflammation has been controlled, and there is a transition to adaptive immunity and tissue damage repair. It is worth mentioning that the level of the cytokine IL-22, which is related to the mucosal barrier function, showed no significant change throughout the whole infection process (Dudakov et al., 2015). This may be because Stenotrophomonas strains can quickly invade the body and even spread through the blood, and it is not an infection mainly dominated by mucosal immunity.
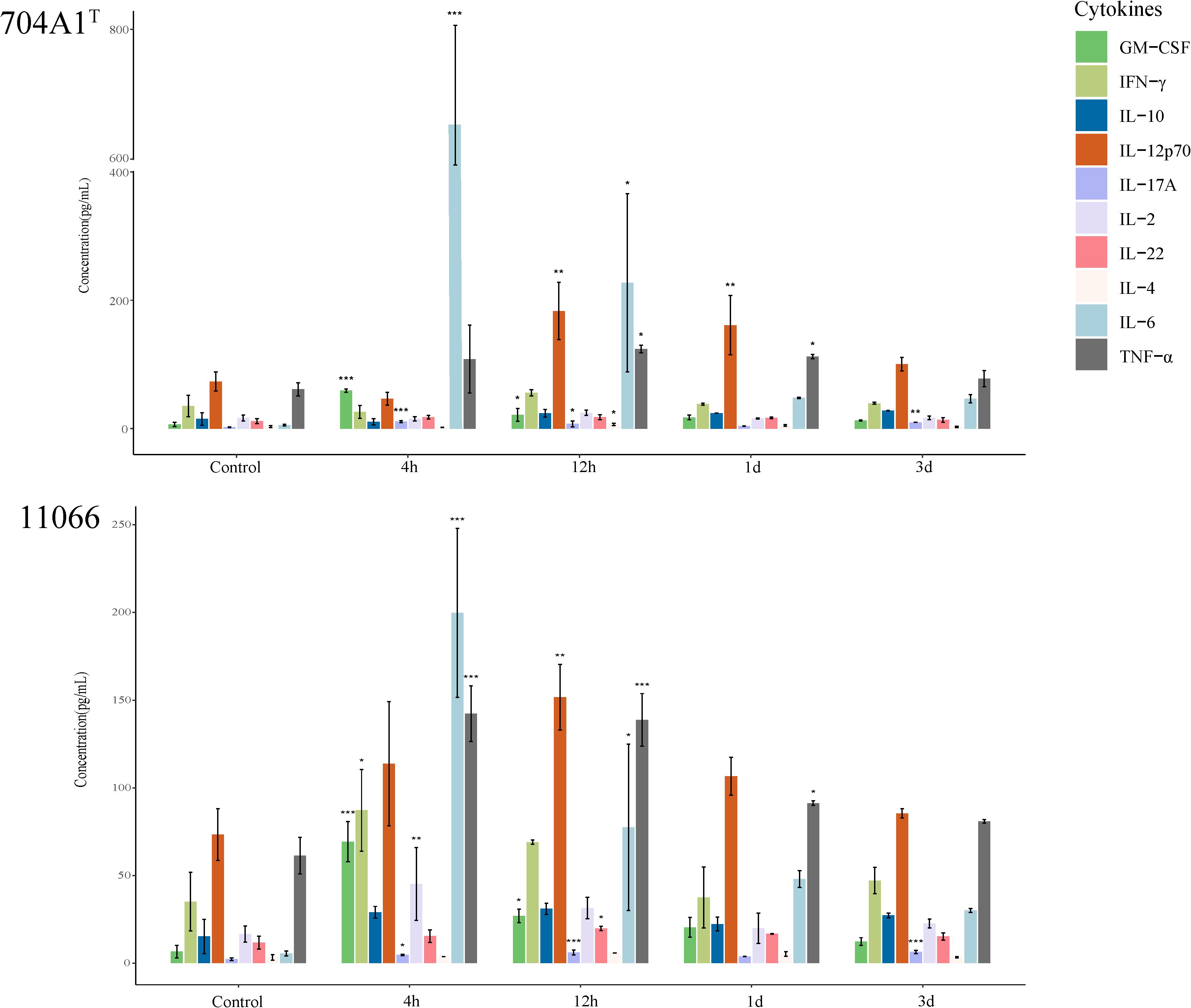
Figure 6. Immune response of 10 cytokines in the lung homogenates after infection of 704A1T and 11066. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
Description of Stenotrophomonas tuberculopleuritidis sp. nov.
Stenotrophomonas tuberculopleuritidis sp. nov. (tu.ber.cu.lo.pleu.ri’ti.dis. N.L. fem. n. tuberculopleuritis, tuberculous pleurisy; N.L. gen. n. tuberculopleuritidis, of a tuberculopleurisy patient).
The type strain 704A1T (=GDMCC 1.4133=JCM 36489) was first isolated from a tuberculous pleurisy patient. It is Gram-negative bacillus with 1–5 flagella at the single extreme, which can grow under conditions of 15-37 °C, pH range 5-10, and NaCl concentration of 0-5%. 704A1T showed positive results for nitrate reduction, hydrolysis of heptavidin and gelatin, assimilation of β-galactosidase, glucose, mannose, N-acetylglucosamine, maltose, malic acid, citric acid, alkaline phosphatase, esterase lipase (C8), leucine arylamidase, acid phosphatase, and naphthol-AS-BI phosphate hydrolase. Its predominant fatty acids were iso-C15:0, C15:0 anteiso, summed Feature 3(C16:1ω7c/16:1ω6c) and C16:0 and the main peaks of 704A1T in the MALDI-TOF spectrum located at 4857.381Da, 5253.734Da, 6071.902Da and 4844.272Da.
The ANI value of 704A1T compared to the defined species of genus Stenotrophomonas ranged between 80.03 and 89.6, with the highest for S. indicatrix and S. geniculata, and the lowest for S. ginsengisoli. The complete genome and 16S rRNA gene sequence of 704A1T have been deposited in GenBank under accession numbers CP130831.1 and OR964852, respectively.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, CP130831.1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, OR964852.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by The Laboratory Animal Welfare & Ethics Committee of the National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention (No. 2023-021). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
ZY: Visualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. BX: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. RW: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Resources, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the nomenclature reviewers Dr. Bernhard Schink and Dr. Aharon Oren of International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology for their assistance in nomenclature.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Awan, M. U. N., Yan, F., Mahmood, F., Bai, L., Liu, J., and Bai, J. (2022). The functions of thioredoxin 1 in neurodegeneration. Antioxid. Redox Signal 36, 1023–1036. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0186
Brooke, J. S. (2012). Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: an emerging global opportunistic pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 25, 2–41. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00019-11
Brooke, J. S., Di Bonaventura, G., Berg, G., and Martinez, J. L. (2017). Editorial: a multidisciplinary look at Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: an emerging multi-drug-resistant global opportunistic pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 8, 1511. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01511
Chao, A., Chao, A. S., Lin, C. Y., Weng, C. H., Wu, R. C., Yeh, Y. M., et al. (2022). Analysis of endometrial lavage microbiota reveals an increased relative abundance of the plastic-degrading bacteria Bacillus pseudofirmus and Stenotrophomonas rhizophila in women with endometrial cancer/endometrial hyperplasia. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 12, 1031967. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1031967
Chen, J., Zhu, Y., Yin, M., Xu, Y., Liang, X., and Huang, Y. P. (2019). Characterization of maltocin S16, a phage tail-like bacteriocin with antibacterial activity against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Escherichia coli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 127, 78–87. doi: 10.1111/jam.14294
Cianciotto, N. P., Bangsborg, J. M., Eisenstein, B. I., and Engleberg, N. C. (1990). Identification of mip-like genes in the genus Legionella. Infect. Immun. 58, 2912–2918. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2912-2918.1990
CLSI (2018). Performance standards for susceptibility tesing of Mycobacteria, Nocardia spp., and other aerobic actinomycetes, M64 (Wayne: The Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute).
CLSI (2023). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, CLSI M100, 33nd Edition (Wayne: The Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute).
Dudakov, J. A., Hanash, A. M., and van den Brink, M. R. (2015). Interleukin-22: immunobiology and pathology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 33, 747–785. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112123
Edgar, R. C. (2022). Muscle5: High-accuracy alignment ensembles enable unbiased assessments of sequence homology and phylogeny. Nat. Commun. 13, 6968. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34630-w
Elhalag, K. M., Messiha, N. A., Emara, H. M., and Abdallah, S. A. (2016). Evaluation of antibacterial activity of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia against Ralstonia solanacearum under different application conditions. J. Appl. Microbiol. 120, 1629–1645. doi: 10.1111/jam.13097
Emms, D. M. and Kelly, S. (2019). OrthoFinder: phylogenetic orthology inference for comparative genomics. Genome Biol. 20, 238. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1832-y
Gao, S., Seo, J. S., Wang, J., Keum, Y. S., Li, J., and Li, Q. X. (2013). Multiple degradation pathways of phenanthrene by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia C6. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 79, 98–104. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.01.012
Gautam, V., Patil, P. P., Bansal, K., Kumar, S., Kaur, A., Singh, A., et al. (2021). Description of Stenotrophomonas sepilia sp. nov., isolated from blood culture of a hospitalized patient as a new member of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia complex. New Microbes New Infect. 43, 100920. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100920
Gil-Gil, T., Martinez, J. L., and Blanco, P. (2020). Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: a review of current knowledge. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 18, 335–347. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2020.1730178
Heylen, K., Vanparys, B., Peirsegaele, F., Lebbe, L., and De Vos, P. (2007). Stenotrophomonas terrae sp. nov. and Stenotrophomonas humi sp. nov., two nitrate-reducing bacteria isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 2056–2061. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.65044-0
Huang, X., Liu, J., Ding, J., He, Q., Xiong, R., and Zhang, K. (2009). The investigation of nematocidal activity in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia G2 and characterization of a novel virulence serine protease. Can. J. Microbiol. 55, 934–942. doi: 10.1139/W09-045
Iebba, V., Guerrieri, F., Di Gregorio, V., Levrero, M., Gagliardi, A., Santangelo, F., et al. (2018). Combining amplicon sequencing and metabolomics in cirrhotic patients highlights distinctive microbiota features involved in bacterial translocation, systemic inflammation and hepatic encephalopathy. Sci. Rep. 8, 8210. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26509-y
Jain, C., Rodriguez, R. L., Phillippy, A. M., Konstantinidis, K. T., and Aluru, S. (2018). High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 9, 5114. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07641-9
Jakobi, M., Winkelmann, G., Kaiser, D., Kempler, C., Jung, G., Berg, G., et al. (1996). Maltophilin: a new antifungal compound produced by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia R3089. J. Antibiot. 49, 1101–1104. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.49.1101
Jezek, P., Safrankova, R., and Malisova, L. (2020). Unusual microbiological findings in bacteremia cases - three case reports. Klin Mikrobiol. Infekc. Lek. 26, 106–110.
Kumar, S., Bansal, K., Patil, P. P., Kaur, A., Kaur, S., Jaswal, V., et al. (2020). Genomic insights into evolution of extensive drug resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia complex. Genomics 112, 4171–4178. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.06.049
Kumar, A., Rithesh, L., Kumar, V., Raghuvanshi, N., Chaudhary, K., Abhineet, et al. (2023). Stenotrophomonas in diversified cropping systems: friend or foe? Front. Microbiol. 14, 1214680. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1214680
Lammers, M. (2021). Post-translational lysine ac(et)ylation in bacteria: a biochemical, structural, and synthetic biological perspective. Front. Microbiol. 12, 757179. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.757179
Li, Y., Yu, Z., Fan, X., Xu, D., Liu, H., Zhao, X., et al. (2024). A novel pathogenic species of genus Stenotrophomonas: Stenotrophomonas pigmentata sp. nov. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 14, 1410385. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1410385
Li, Y., Zhao, A., Yu, Q., Yu, N., Cui, Y., Ma, X., et al. (2023). Effect of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia on tuberculosis. Microbiol. Spectr. 11, e0094423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00944-23
Ling, S., Zhao, Y., Sun, S., Zheng, D., Sun, X., Zeng, R., et al. (2022). Enhanced anti-herbivore defense of tomato plants against Spodoptera litura by their rhizosphere bacteria. BMC Plant Biol. 22, 254. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03644-3
Liu, J., Chen, P., Zheng, C., and Huang, Y. P. (2013). Characterization of maltocin P28, a novel phage tail-like bacteriocin from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 79, 5593–5600. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01648-13
Macori, G., Al-Qahtani, A. A., Koolman, L., Althawadi, S., Mutabaqani, M., Bashtawi, R., et al. (2024). Stenotrophomonas riyadhensis sp. nov., isolated from a hospital floor swab. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 74. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006250
McChlery, S., Ramage, G., and Bagg, J. (2009). Respiratory tract infections and pneumonia. Periodontol. 2000 49, 151–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2008.00278.x
Menetrey, Q., Sorlin, P., Jumas-Bilak, E., Chiron, R., Dupont, C., and Marchandin, H. (2021). Achromobacter xylosoxidans and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: emerging pathogens well-armed for life in the cystic fibrosis patients’ lung. Genes (Basel) 12(5):610–31. doi: 10.3390/genes12050610
Minh, B. Q., Schmidt, H. A., Chernomor, O., Schrempf, D., Woodhams, M. D., von Haeseler, A., et al. (2020). IQ-TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 37, 1530–1534. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa015
Nakayama, T., Homma, Y., Hashidoko, Y., Mizutani, J., and Tahara, S. (1999). Possible role of xanthobaccins produced by Stenotrophomonas sp. strain SB-K88 in suppression of sugar beet damping-off disease. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 4334–4339. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.10.4334-4339.1999
Palleroni, N. J. and Bradbury, J. F. (1993). Stenotrophomonas, a new bacterial genus for Xanthomonas maltophilia (Hugh 1980) Swings et al., 1983. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 43, 606–609. doi: 10.1099/00207713-43-3-606
Paškevičius, Š., Gleba, Y., and Ražanskienė, A. (2022). Stenocins: novel modular bacteriocins from opportunistic pathogen Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J. Biotechnol. 351, 9–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2022.04.006
Qin, R., Sang, Y., Ren, J., Zhang, Q., Li, S., Cui, Z., et al. (2016). The bacterial two-hybrid system uncovers the involvement of acetylation in regulating of lrp activity in Salmonella Typhimurium. Front. Microbiol. 7, 1864. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01864
Sanchez, M. B. (2015). Antibiotic resistance in the opportunistic pathogen Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Front. Microbiol. 6, 658. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00658
Schroeder, G. N., Petty, N. K., Mousnier, A., Harding, C. R., Vogrin, A. J., Wee, B., et al. (2010). Legionella pneumophila strain 130b possesses a unique combination of type IV secretion systems and novel Dot/Icm secretion system effector proteins. J. Bacteriol. 192, 6001–6016. doi: 10.1128/JB.00778-10
Schulte, W., Bernhagen, J., and Bucala, R. (2013). Cytokines in sepsis: potent immunoregulators and potential therapeutic targets–an updated view. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 165974. doi: 10.1155/2013/165974
Tamma, P. D., Aitken, S. L., Bonomo, R. A., Mathers, A. J., van Duin, D., and Clancy, C. J. (2022). Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidance on the treatment of ampC β-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales, carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis.: an Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. America 74, 2089–2114. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab1013
Tan, R., Liu, J., Li, M., Huang, J., Sun, J., and Qu, H. (2014). Epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance among commonly encountered bacteria associated with infections and colonization in intensive care units in a university-affiliated hospital in Shanghai. Wei mian yu gan ran za zhi 47, 87–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2012.11.006
Trifonova, A. and Strateva, T. (2019). Stenotrophomonas maltophilia - a low-grade pathogen with numerous virulence factors. Infect. Dis. (London England) 51, 168–178. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2018.1531145
Weber, S., Stirnimann, C. U., Wieser, M., Frey, D., Meier, R., Engelhardt, S., et al. (2014). A type IV translocated Legionella cysteine phytase counteracts intracellular growth restriction by phytate. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 34175–34188. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.592568
Xie, J., Chen, Y., Cai, G., Cai, R., Hu, Z., and Wang, H. (2023). Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT): a web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, W587–WW92. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad359
Yu, Z. and Wang, R. (2024). Revised taxonomic classification of the Stenotrophomonas genomes, providing new insights into the genus Stenotrophomonas. Front. Microbiol. 15, 1488674. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1488674
Yue, L., Yu, Z., and Wang, R. (2023). Establishment and evaluation of a reference strain of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Dis. Surveill. 38, 1484–1490.
Zhang, Y., Li, D., Yan, Q., Xu, P., Chen, W., Xin, H., et al. (2022). Genome-wide analysis reveals the emergence of multidrug resistant Stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila strain SINDOREI isolated from a patient with sepsis. Front. Microbiol. 13, 989259. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.989259
Keywords: stenotrophomonas, tuberculous pleurisy, multiple-drug-resistant, sputum, patient, pathogen
Citation: Yu Z, Xu B and Wang R (2025) Stenotrophomonas tuberculopleuritidis sp. nov., a novel pathogenic Stenotrophomonas species isolated from tuberculous pleurisy patient. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1629703. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1629703
Received: 16 May 2025; Accepted: 21 July 2025;
Published: 07 August 2025.
Edited by:
Dongsheng Zhou, Academy of Military Medical Science, ChinaReviewed by:
Kanika Bansal, Institute of Microbial Technology (CSIR), IndiaVikas Gautam, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), India
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Xu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ruibai Wang, d2FuZ3J1aWJhaUBpY2RjLmNu
†ORCID: Zelin Yu, orcid.org/0009-0003-7406-6053
Boqing Xu, orcid.org/0009-0004-5670-280X
Ruibai Wang, orcid.org/0000-0002-2258-3599
 Zelin Yu
Zelin Yu Boqing Xu†
Boqing Xu† Ruibai Wang
Ruibai Wang