- 1Department of Medical Microbiology and Parasitology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 2Division of Basic Medical Microbiology, State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 3Department of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
- 4Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of the Pacific, Arthur Dugoni School of Dentistry, San Francisco, CA, United States
- 5Institute of Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Guizhou Provincial Centre for Disease Control and Prevention, Guiyang, China
A Correction on
Bid-Induced Release of AIF/EndoG from Mitochondria Causes Apoptosis of Macrophages during Infection with Leptospira interrogans
By Hu W-L, Dong H-Y, Li Y, Ojcius DM, Li S-J and Yan J (2017). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 7:471. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00471
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 1E as published. The representative flow dot plots were misplaced. The corrected Figure 1 appears below.
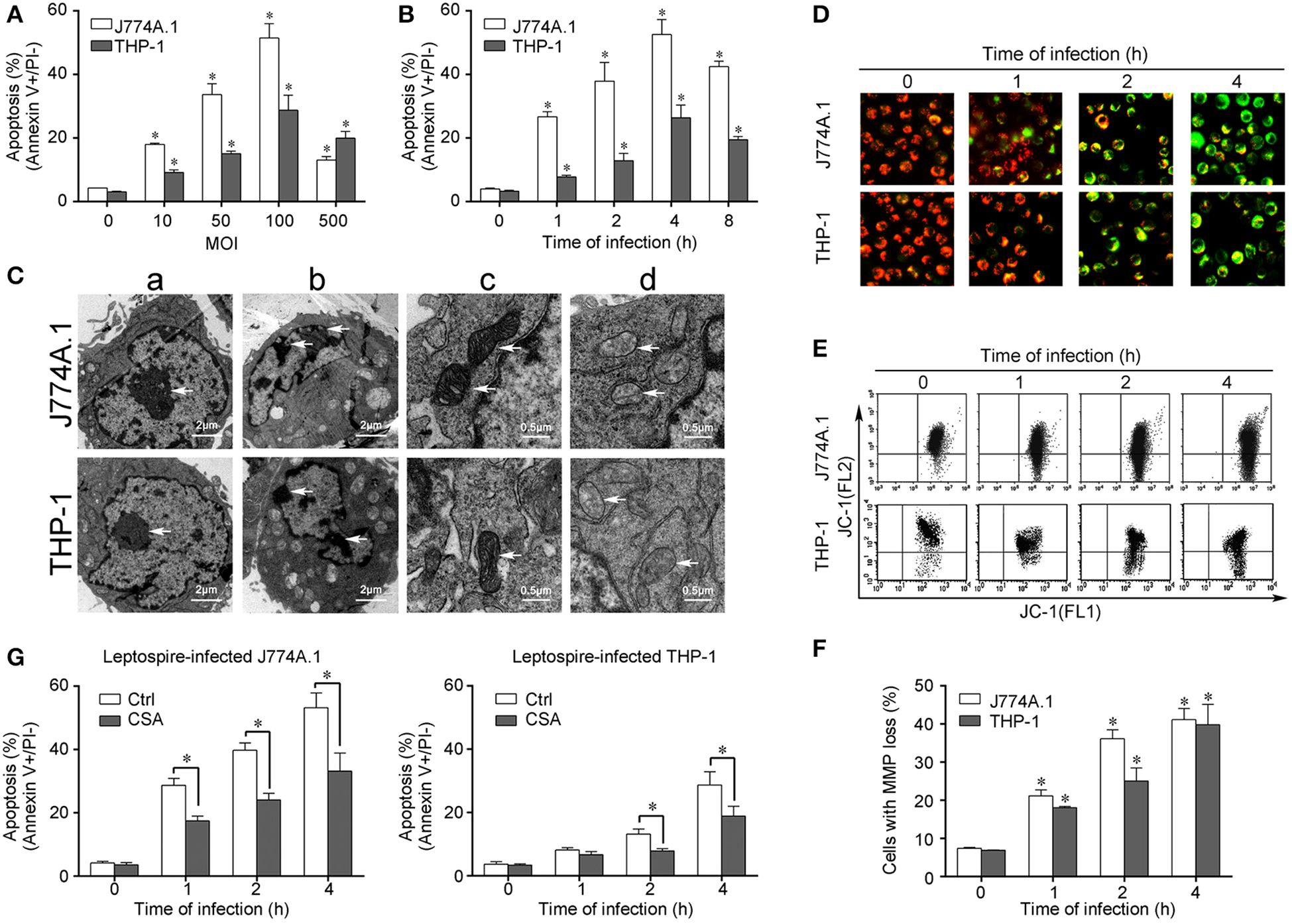
Figure 1. Apoptosis, pathological changes, and MMP decrease in leptospire-infected macrophages. (A) Apoptosis of macrophages infected with L. interrogans strain Lai at the optimal apoptosis-causing time for different MOIs. J774A.1 and THP-1 cells were infected with leptospires at 4 h. Bars show the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Five thousand cells were analyzed in each specimen. *p < 0.05 vs. apoptotic ratios in leptospire-infected macrophages with an MOI of 10, 50, 100, or 500. (B) Apoptosis of macrophages infected with L. interrogans strain Lai at the optimal apoptosis-causing MOI for different times. J774A.1 and THP-1 cells were infected at an MOI of 100. Bars show the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Five thousand cells were analyzed in each specimen. *p < 0.05 vs. apoptotic ratios in each macrophage type before infection. (C) The representative pathological changes in the nucleus and mitochondria in macrophages infected with L. interrogans strain Lai (MOI 100) for 4 h. a: healthly cells showed normal cellular morphology, b: chromatin margination in leptospire-infected macrophages crescent, c: mitochondrial shape in healthly macrophages, d: disappearance of mitochondrial cristae in leptospire-infected macrophages. (D) The representative MMP changes in macrophages during infection with L. interrogans strain Lai for the indicated times determined by fluorescence microscopy. The red cells have a high MMP while the green cells have a low MMP. (E) The representative MMP changes in macrophages during infection with L. interrogans strain Lai for the indicated times determined by flow cytometry. The FL2 channel indicates high MMP (red) while the FL1 channel shows low MMP (green). (F) Statistical summary of MMP changes by flow cytometry in leptospire-infected macrophages. Statistical data from experiments such as shown in (E). Bars show the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. The values at “0” h show the MMP values before infection. Five thousand cells were analyzed in each specimen. *p < 0.05 vs. MMP value of the macrophages before infection. (G) CSA blockage of the apoptosis in macrophages infected with L. interrogans strain Lai. Bars show the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Five thousand cells were analyzed in each specimen. *p < 0.05 vs. apoptotic ratios in each macrophage type unpretreated with CSA infected with the spirochetes.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: apoptosis, Leptospira, Bid, AIF, EndoG, macrophage
Citation: Hu W-L, Dong H-Y, Li Y, Ojcius DM, Li S-J and Yan J (2025) Correction: Bid-Induced Release of AIF/EndoG from Mitochondria Causes Apoptosis of Macrophages during Infection with Leptospira interrogans. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1635286. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1635286
Received: 27 May 2025; Accepted: 05 June 2025;
Published: 15 July 2025.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Alain Filloux, Nanyang Technological University, SingaporeCopyright © 2025 Hu, Dong, Li, Ojcius, Li and Yan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shi-Jun Li, emp1bWVkanVuQDE2My5jb20=; Jie Yan, bWVkX2JwQHpqdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Wei-Lin Hu
Wei-Lin Hu Hai-Yan Dong3†
Hai-Yan Dong3† Yang Li
Yang Li David M. Ojcius
David M. Ojcius Shi-Jun Li
Shi-Jun Li Jie Yan
Jie Yan