- 1Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Key Laboratory of Artificial Organs and Computational Medicine in Zhejiang Province, Shulan (Hangzhou) Hospital, Shulan International Medical College, Zhejiang Shuren University, Hangzhou, China
- 2School of Medicine, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
- 3Graduate School, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
- 4School of Clinical Medicine, Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou, China
- 5Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Shulan (Boao) Hospital, Boao, China
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has a global prevalence of 20%-33%, and has become the main cause of chronic liver disease. Apart from lifestyle modification therapy, there is currently no definitive pharmacological treatment, thus there is an urgent need to find effective intervention strategies to treat NAFLD. With the discovery of the important role of gut microbes in the pathogenesis of NAFLD, research on the prevention and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by probiotics is increasing. At present, many studies have confirmed the role of probiotic regulation in the treatment of NAFLD, which can reduce the level of transaminase and liver fibrosis in patients and protect the liver. The clinical application of probiotics includes single species such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria, as well as synbiotics with different compositions. This article reviews the therapeutic effects of probiotics on NAFLD and the mechanisms by which probiotics directly or indirectly affect the disease. Further research is needed to fully understand the specific underlying mechanisms between probiotics, gut microbes, and NAFLD, and more large-scale clinical trials are needed to evaluate probiotics for the treatment of NAFLD.
1 Introduction
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) refers to liver disease in which more than 5% of liver cells are infiltrated with liver fat on liver biopsy specimens and with no regard to excessive alcohol consumption or other clear liver injury factors (Roychowdhury et al., 2018). NAFLD can be divided into nonalcoholic simple fatty liver (NAFL) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). It is worth mentioning that since most NAFLD patients have one or more cardiometabolic risk factors, the existing name of NAFLD focuses on excluding excessive drinking as the cause. Thus, some international experts have reached a consensus and proposed using the new term metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), which refers to steatosis brought on by an unbalanced metabolic environment, along with potentially serious steatohepatitis lesions and accompanying fibrosis, to replace NAFLD (Eslam et al., 2020). NAFLD and MAFLD overlap significantly, and the two classifications generally have strong concordance, as indicated by a Cohen kappa value of up to 0.92. However, current research related to MAFLD are very limited (Alboraie et al., 2019). Currently, the global prevalence of NAFLD is increasing, with the incidence rate ranging from 30% to 32.4% (Riazi et al., 2022; Brennan et al., 2023; Younossi et al., 2023). Without timely treatment, NAFLD can progress to cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and even death (Friedman et al., 2018). However, there is no definite drug therapy for steatosis except lifestyle interventions. Therefore, it is urgent need to find effective treatment methods to alleviate NAFLD.
2 Application of probiotic therapy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
2.1 NAFLD and probiotic therapy
Recent studies have shown that regulation of gut microbiota can be a feasible strategy for preventing and treating NAFLD. Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host. Studies have found that probiotic therapy is an important means of regulating gut microbiota (O'flaherty and Klaenhammer, 2010). At present, many studies (Gao et al., 2016; Loman et al., 2018; Tang et al., 2019; Xiao et al., 2019; Pan et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2021; Huang et al., 2022) have confirmed the role of probiotics regulation in NAFLD treatment through meta-analysis, which can reduce the level of transaminase and liver fibrosis in patients and protect the liver (Khan et al., 2019; Sabirin et al., 2022). Therefore, the first part of the review focuses on the application of probiotic therapy in NAFLD, aiming to provide more and better ideas for the prevention and treatment of NAFLD. This review will provide an updated synthesis of the mechanisms of probiotic therapy in NAFLD and its therapeutic potential, with a focus on novel insights and future research directions.
2.2 The role of probiotics in NAFLD
2.2.1 Single probiotic
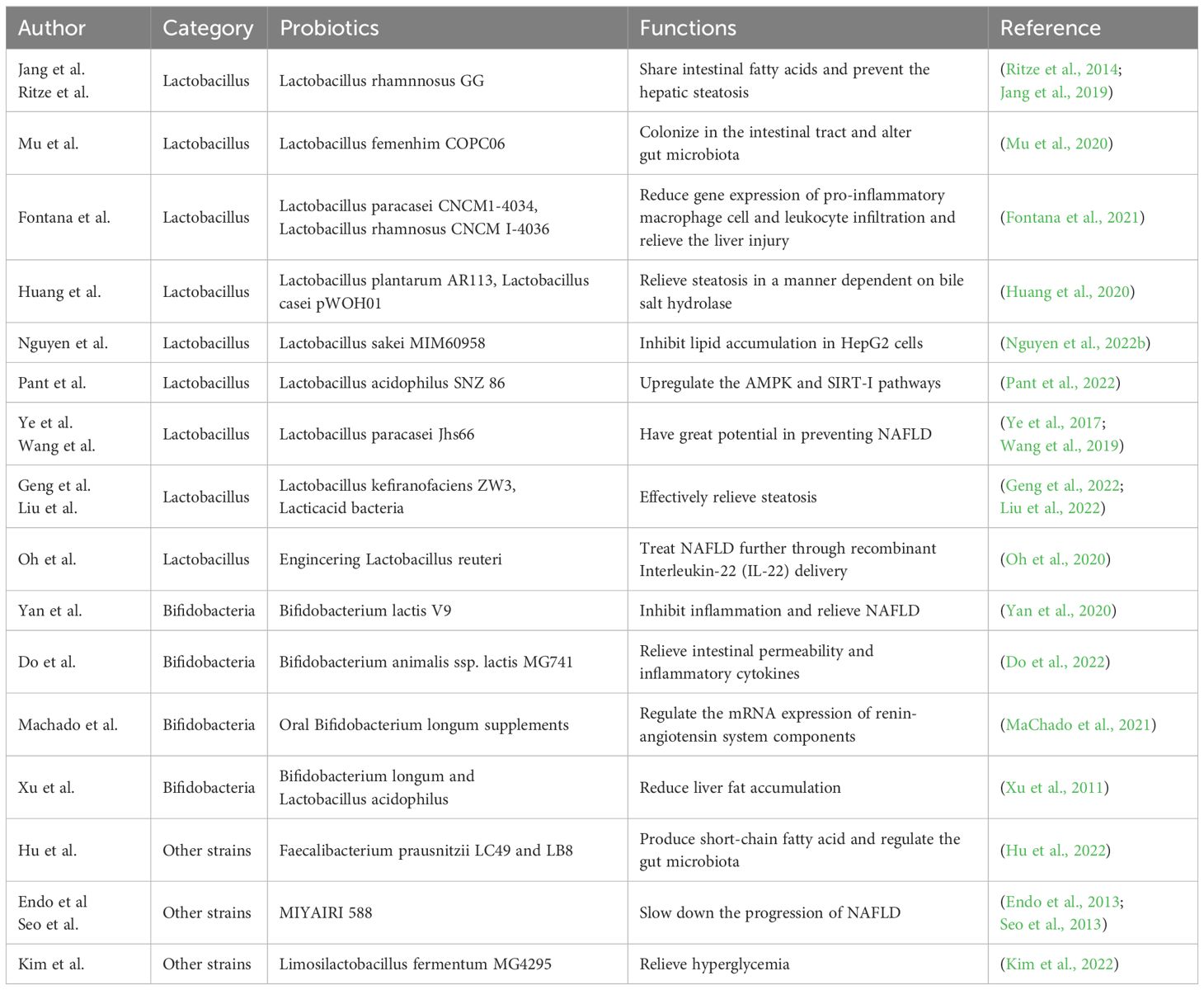
The protective and preventive function of Lactobacillus in NAFLD has been fully studied. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG has been confirmed to share intestinal fatty acids and prevent the development of diet-induced hepatic steatosis, thus effectively treating NAFLD (Jang et al., 2019). Ritze et al (Ritze et al., 2014). also showed that Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG can prevent NAFLD in mice. Mu et al (Mu et al., 2020). showed that Lactobacillus fermentum CQPC06 can colonize in the intestinal tract and alter gut microbiota in NAFLD mice. Lactobacillus paracasei CNCM I-4034 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-4036 can relieve the liver injury by reducing gene expression of pro-inflammatory macrophage cell and leukocyte infiltration of the liver in NAFLD rats (Fontana et al., 2021). Through the in vitro model, Lactobacillus plantarum AR113 and Lactobacillus casei pWQH01 relieved steatosis in a manner dependent on bile salt hydrolase (Huang et al., 2020). Similarly, Lactobacillus sakei MJM60958 can significantly inhibit lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells stimulated by oleic acid and cholesterol, reduce weight of both body and liver in NAFLD mice and control the level of NAFLD-related markers as well, indicating that Lactobacillus sakei MJM60958 can also effectively prevent and treat NAFLD (Nguyen et al., 2022b). Lactobacillus acidophilus SNZ 86 which can enrich selenium has also been confirmed to relieve hepatic steatosis by up-regulating the adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and silent information regulator 1 (SIRT-1) pathways (Pant et al., 2022). Lactobacillus paracasei Jlus66, isolated from natural fermented milk, also has great potential in preventing NAFLD (Ye et al., 2017), which was consistent with that of Wang et al (Wang et al., 2019). In addition, Geng et al (Geng et al., 2022). identified a new type of probiotic Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens ZW3 through zebrafish model and explored the its effect on lipid deposition. They proved that Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens ZW3 has a specific protective effect on NAFLD. Interestingly, engineering Lactobacillus reuteri, made by Oh et al., exerted the further therapeutic effect in NAFLD through recombinant Interleukin-22 (IL-22) delivery (Oh et al., 2020). Liu et al (Liu et al., 2022). made lactoferrin expressed by recombinant lactic acid bacteria, which was more effective in relieving steatosis.
Bifidobacteria also play an important role in the protection and prevention of NAFLD disease. Yan et al (Yan et al., 2020). evaluated the effect of Bifidobacterium lactis V9 on hepatic steatosis in NAFLD rats induced by high-fat diet. They found that Bifidobacterium lactis V9 could inhibit inflammation and relieve NAFLD. Do et al (Do et al., 2022). also found Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis MG741 could reduce weight and relieve NAFLD by relieving intestinal permeability and inflammatory cytokines. Oral Bifidobacterium longum supplements can prevent obesity and NAFLD by regulating the mRNA expression of renin-angiotensin system components (MaChado et al., 2021). Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus acidophilus can reduce liver fat accumulation, with the former being more effective (Xu et al., 2011).
Moreover, the therapeutic potential of other strains in NAFLD disease can’t be ignored. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii LC49 and LB8 were able to produce short-chain fatty acid and regulate the gut microbiota, indicating their potential role in NAFLD (Hu et al., 2022). MIYAIRI 588, as a probiotic that can enhance butyrate production, has been discovered to slow down the progression of NAFLD (Endo et al., 2013). Seo et al (Seo et al., 2013). also showed that MIYAIRI 588 had new potential to relieve NAFLD. In addition, Limosilactobacillus fermentum MG4295 has been proved to relieve hyperglycemia, a complication of NAFLD (Kim et al., 2022). (Table 1).
2.2.2 The combination of multi-strain probiotics
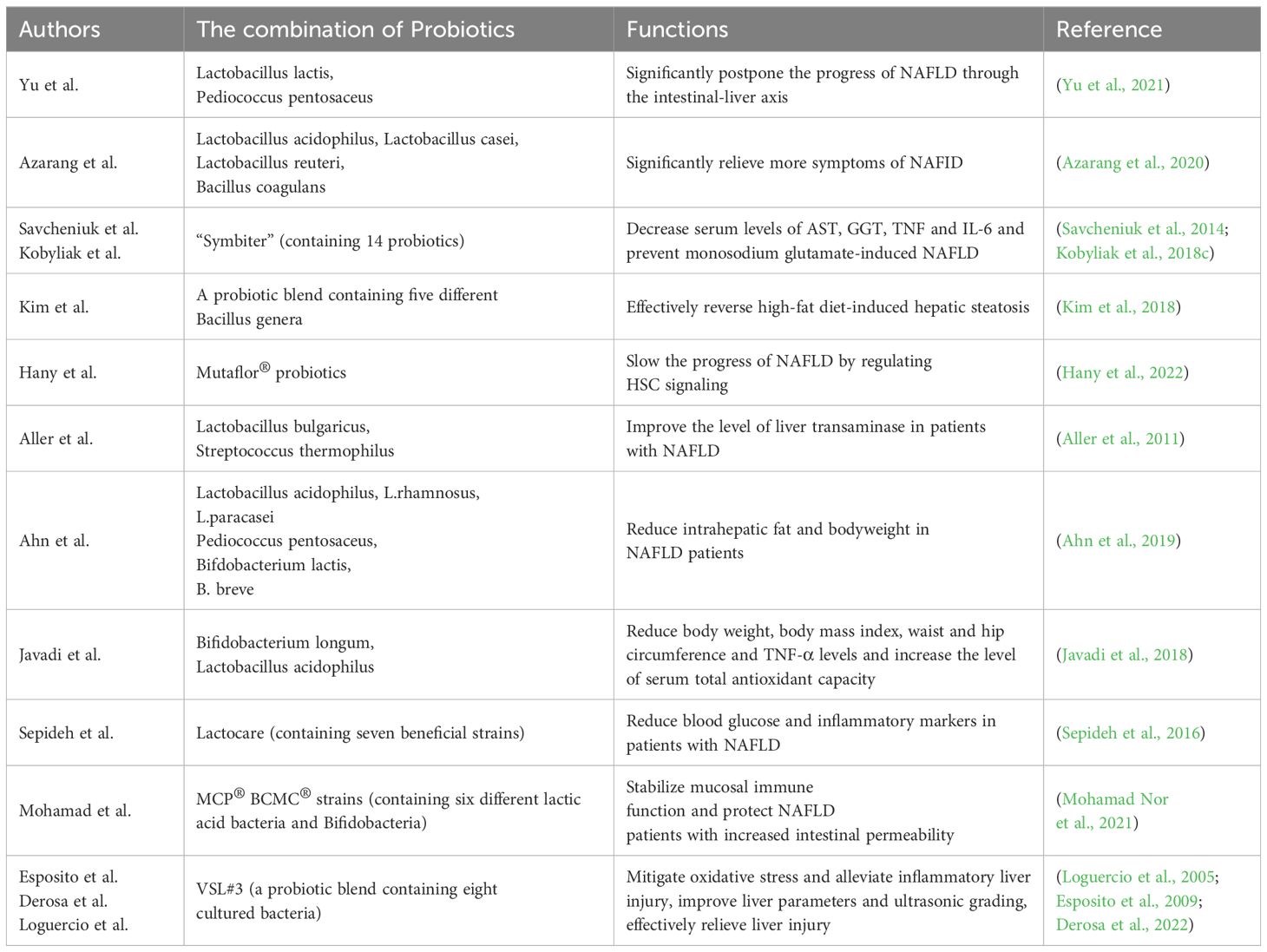
The use of single probiotics may not be satisfactory for the treatment of NAFLD. Therefore, many basic studies have focused on the research of the role of the combination of two or more probiotics. Yu et al (Yu et al., 2021). found that Lactobacillus lactis and Pediococcus pentosaceus could significantly postpone the progress of NAFLD through the intestinal-liver axis, especially through the tryptophan metabolic pathway. In the rat NAFLD model, Azarang et al (Azarang et al., 2020). showed that the utilization of single probiotics such as Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus reuteri and Bacillus coagulans could reduce oxidative stress markers and the combination of those four probiotics could significantly relieve more symptoms of NAFLD. Regular use of compound probiotics “Symbiter” has also been confirmed to prevent monosodium glutamate-induced NAFLD in mice (Savcheniuk et al., 2014). Furthermore, a probiotic blend containing five different Bacillus genera has been shown to effectively reverse high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis, highlighting the potential of Bacillus in treating NAFLD (Kim et al., 2018). Mutaflor® probiotics have also been shown to slow the progress of NAFLD by regulating HSC signaling (Hany et al., 2022).
Clinical trials investigating the role of combined probiotics in NAFLD have been successfully conducted, further enhancing the potential of probiotic combinations for clinical treatment of NAFLD. Tablets containing Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus was reported to be able to improve the level of liver transaminase in patients with NAFLD, thus having a better therapeutic effect on NAFLD (Aller et al., 2011). In a study conducted by Kobyliak et al (Kobyliak et al., 2018c), 58 patients with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD were enrolled and randomly assigned to receive either the polyprobiotic “Symbiter” or a placebo. The researchers discovered a significant reduction in the fatty liver index, accompanied by decreased serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), γ-glutamyl transpeptadase (GGT), tumor necrosis fator (TNF), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the probiotic group. These observations indicated the potential of “Symbiter” probiotics as a treatment for NAFLD.
Ahn et al (Ahn et al., 2019). treated obese NAFLD patients with a mixture of probiotics including six bacteria. They found that probiotic treatment for 12 weeks significantly reduced intrahepatic fat and body weight in NAFLD patients. Probiotic capsules composed of Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus acidophilus have been confirmed to significantly reduce body weight, body mass index, waist and hip circumference and TNF-α levels in patients with NAFLD, and increase the level of serum total antioxidant capacity (Javadi et al., 2018). Similarly, Lactocare, a probiotic capsule containing seven beneficial strains, significantly reduced blood glucose and inflammatory markers in patients with NAFLD (Sepideh et al., 2016). Multi-strain probiotics (MCP® BCMC® strains) containing six different lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria complement the treatment of NAFLD can stabilize mucosal immune function and protect NAFLD patients with increased intestinal permeability (Mohamad Nor et al., 2021). VSL#3, a probiotic blend containing eight cultured bacteria, has been utilized in the treatment of NAFLD in rats via its therapeutic effects involve the mitigation of oxidative stress and alleviation of inflammatory liver injury (Esposito et al., 2009). Derosa et al (Derosa et al., 2022). recruited 60 white adult suffering from NAFLD who were randomly assigned to receive VSL#3 or placebo. The results showed that VSL#3 probiotic therapy could significantly improve liver parameters and ultrasonic grading, and there was no difference between men and women. Loguercio et al (Loguercio et al., 2005). also found that probiotic VSL#3 can significantly improve liver injury caused by NAFLD through clinical cohort study. The capsule formed by probiotic combination has also been fully explored in pediatric NAFLD. Compared with children who received placebo, the level of liver function of children who received probiotic capsules exhibited remarkable enhancement (Famouri et al., 2017) (Table 2).
2.2.3 Incorporation of probiotics with other biological components
Since individual probiotic and combination of probiotics display have shown promising therapeutic potential, the incorporation of probiotics with other biological components has also attracted wide attention. Ahmed et al (Ahmed et al., 2020). showed that the combination of Lactobacillus reuteri and metronidazole could effectively regulate intestinal flora of NASH mice, resulting in improved therapeutic outcomes. Wang et al (Wang W. et al., 2020). found that the combination of probiotics Bifidobacterium bifidum V, Lactobacillus plantarum X and Salvia miltiorrhiza polysaccharide effectively alleviates hepatic steatosis by modulating gut microbiota and relieving insulin resistance in high-fat diet induced NAFLD mice. Importantly, the combined treatment showed potential benefits surpassing those of probiotics Bifidobacterium bifidum V and Lactobacillus plantarum X alone, indicating that Salvia miltiorrhiza polysaccharide can enhance the function of these probiotics. As the substrate of prebiotics, when combined with Bifidobacteria, it has the potential to improve the efficacy of NAFLD treatment. It is confirmed that the combination of Resveratrol and Bifidobacteria may be a potential drug for the treatment of NAFLD (Hu et al., 2021). In addition, in the NAFLD rat model, “Symbiter” combined with Omega-3 therapy could significantly relieve liver steatosis and liver conversion lipid accumulation compared with probiotics alone (Kobyliak et al., 2017). Furthermore, Kobyliak et al (Kobyliak et al., 2018a). incorporated 48 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with NAFLD and randomly assigned them to multi-strain “Symbiter” combined with Omega-3 (“Symbiter Omega” combination) and placebo respectively. They found that “Symbiter Omega” combination could reduce liver fat, improve blood lipids and metabolic characteristics, and reduce chronic systemic inflammation in NAFLD patients. Smectite is a natural silicate that binds to digestive mucus and has the ability to bind endotoxin and exotoxin. Studies have found that the combination of multi-probiotics “Symbiter” and Smectite gel “Symbiter Forte” can play a synergistically enhanced role in the effective treatment of NAFLD (Kobyliak et al., 2018b). In a clinical trial, 80 patients with NAFLD were given symbiotic supplements (including six probiotics and fructooligosaccharides) and placebos respectively. Symbiotic supplements have been found to relieve steatosis in patients with NAFLD (Asgharian et al., 2016). Probiotic mixtures have been found to act on lipid profiles, leptin and inflammatory biomarkers to treat fatty liver disease (Al-Muzafar and Amin, 2017). Similarly, Crommen et al (Crommen et al., 2022). have shown in clinical trials that a mixture of multi-strain probiotic powder and specific trace microelements can effectively improve NAFLD-related markers in obese patients undergoing miniature gastric bypass surgery.
2.2.4 Probiotics related products
The possible impact of probiotics-related products on NAFLD has garnered significant attention. Kefir is a probiotic beverage that contains a variety of lactic acid bacteria and yeast. In the NAFLD mouse model, the administration of Kefir has been shown to regulate the composition of intestinal microbiota and fungal flora, leading to effective treatment of the condition (Kim et al., 2017). Kombucha is a kind of natural nonalcoholic fermented beverage with probiotic characteristics produced by symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast. Moreira et al (Moreira et al., 2022). successfully confirmed that Kombucha can improve glucose tolerance and reduce liver steatosis in obese mice through NAFLD mouse experiments. Moreover, Konda et al (Konda et al., 2020). found that probiotics banana juice treated by pectinase can effectively deal with liver steatosis to effectively prevent NASH.
2.2.5 Probiotics plus lifestyle intervention
It is worth mentioning that probiotic supplements in conjunction with lifestyle interventions have also been confirmed to have positive effects on blood glucose parameters and leptin levels in patients with NAFLD (Behrouz et al., 2017). Lifestyle changes with multi-strain probiotic therapy can significantly improve liver histology, the levels of alanine aminotransferase and cytokine in patients with NAFLD (Duseja et al., 2019). Exercise training and probiotics are also recommended as effective treatments for NAFLD. Hosseini et al (Hosseini et al., 2022). proved that intensive interval training and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG can minimize damage to liver tissue cell and inflammation caused by NAFLD.
2.3 Future expectations
The aforementioned studies have consistently demonstrated the efficacy of probiotics and their associated products in the prevention and treatment of NAFLD. Furthermore, there is a growing trend in research towards the clinical application of these practical products. The application prospect of probiotics and its related products in NAFLD is worth anticipation and further promoting.
The mechanism underlying the therapeutic effects of probiotics in NAFLD treatment has consistently been a focal point of research. It is believed that distinct probiotic strains may exert their effects through different mediating mechanisms. Utilizing probiotics allows researchers to observe changes in the individual’s gut microbiota composition, while investigating how these changes impact disease progression remains a key area for exploration. With the continuous advancement of technical tools, an increasing number of research methods have been employed to investigate the mechanism underlying probiotic treatment of NAFLD. However, the current understanding of the precise mechanism by which probiotics exert their effects in NAFLD treatment remains limited. Only through the comprehensive utilization of various research techniques can a more comprehensive understanding of the mediating mechanisms be achieved. Researchers must devote further efforts to clarify the specific mechanism through which different probiotics play a role in NAFLD.
3 The mediating mechanism of probiotics in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Probiotic regulation offers an effective strategy for the treatment and prevention of NAFLD, particularly in the absence of clear pharmacological interventions for steatosis. Understanding the mediating mechanisms underlying probiotic therapy in NAFLD has remained a central focus of research focus of research. Probiotics have the ability to modulate the physiological function and metabolic status of patients with NAFLD by influencing the composition, abundance and balance of intestinal microflora. To investigate the mediating mechanism of probiotic therapy, it is essential to commence with a comprehensive exploration of the common pathogenesis and etiology of NAFLD.
The ecological imbalance of intestinal flora, alterations of intestinal cell permeability, liver injury, endoplasmic reticulum stress, abnormal activation of cellular signaling pathway, as well as dietary and genetic factors of patients, have all been implicated in the occurrence of NAFLD (Williams et al.,; Mouzaki and Allard, 2012; Goodwin et al., 2013). The second part of the review aims to comprehensively explore the intricate mediating mechanisms of probiotics in NAFLD treatment, contributing to the development of novel therapeutic approaches for the disease.
3.1 Maintaining the integrity of intestinal epithelial cells: anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation
3.1.1 Reactive oxygen species and Intestinal inflammation
Intestinal inflammation can influence the intestinal-liver axis, damaging the intestinal barrier, leading to bacterial translocation, activating the immune system response, and triggering a series of pro-inflammatory pathways in the liver, thereby accelerating the process of NAFLD (Pierantonelli and Svegliati-Baroni, 2019).
ROS in human body is mainly produced in endoplasmic reticulum, peroxisome, mitochondria and other organelles. Specially, Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production mainly occurs during the mitochondrial electron transport chain process (Novak and Mollen, 2015). However, excessive ROS can impede electron transfer, leading to mitochondrial damage and disruption of biological function of mitochondria and cell homeostasis, ultimately causing cell death (Kiffin et al., 2006; Scherz-Shouval and Elazar, 2007; Novak and Mollen, 2015).
The excessive accumulation of ROS in cells result in oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between ROS production and clearance in cells and tissues. In response to oxidative stress, cells activate various defense mechanisms or undergo cell death. Oxidative stress can induce intestinal mucosal damage, increase intestinal epithelial barrier permeability, facilitate bacterial invasion, stimulate immune response and initiate the pathological process of intestinal inflammation. The key manifestations of active intestinal inflammation include immune cell infiltration and neutrophilic granulocytosis (Goyette et al., 2007).
3.1.2 Probiotics prevent and treat NAFLD by preventing intestinal inflammation and antioxidation
3.1.2.1 Genetic engineering Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (ECN) is a genetically engineered oral probiotics with good safety and can assist in the treatment of many kinds of diseases (Lynch et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2022). ECN-pE, an oral probiotic, was genetically modified to enhance the expression of catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) for the treatment of intestinal inflammation. ZhouJ et al. evaluated the SOD competence of different ECN subtypes by assessing their ability to scavenge superoxide. Notably, ECN-pE(C/A)2 exhibited strong SOD activity, promoting significant colon tissue repair and alleviating intestinal inflammation (Zhou et al., 2022).
3.1.2.2 Bifidobacterium longum
Bifidobacterium longum have been demonstrated their ability to inhibit the development of intestinal inflammation by regulating immune system balance, enhancing acetate production and improving intestinal mucosal barrier function (Underwood et al., 2015; Chichlowski et al., 2020; Yao et al., 2021). In a study conducted by F.A.Abrantes et al., it was shown that Bifidobacterium longum B.longum51A effectively reverse colitis-induced increase of intestinal permeability and reduce the degree of colonic lesions (Abrantes et al., 2020). Its molecular biological mechanism is alleviating a series of changes during intestinal inflammation, such as decreased eosinophil peroxidase level, increase of IL-1β level, the significant increase of immunoglobulin concentration and the increase of inflammatory markers (Dvorak et al., 1994; Abrantes et al., 2020).
S. Yan et al. confirmed that the metabolites of B.longum YS108R contain antioxidant substances (Yao et al., 2021). Yusheng Wang et al. demonstrated that the supernatant from cultured B.longum CCFM752 exhibits antioxidant effect on cells, enhancing catalase activity and decreasing NADPH oxidase activity. In addition, it has been proved that Lactobacillus sake and other Lactobacillus probiotics can also relieve the symptoms of NAFLD through antioxidant mechanism (Wang et al., 2021).
Genetic engineering Escherichia coli and Bifidobacterium longum can improve the antioxidant level of cells and tissues, mitigate ROS-induced cell damage, protect intestinal mucosal barrier and effectively inhibit NAFLD triggered by intestinal inflammation. These findings highlight their significant clinical application value.
3.2 Regulating lipid metabolism to relieve NAFLD
3.2.1 Core pathological process
The main cause of NAFLD is the excessive accumulation of fat in the liver (Kanuri and Bergheim, 2013; Zeigerer, 2021). The fat accumulated in the liver can originate from various sources, including fatty acids digested and absorbed by intestinal epithelial cells from food, de novo synthesis of body fat, adipose tissue fat transport and conversion of other substances (Jones, 2016; Alves-Bezerra and Cohen, 2017; Carotti et al., 2020; Badmus et al., 2022). The liver, as the central organ of fatty acid metabolism, will experience fat accumulation when the production of fatty acids exceeds their consumption, including fat transport (Alves-Bezerra and Cohen, 2017). In the existing scientific research, it has been found that some probiotics can alleviate NAFLD symptoms by modulating lipid metabolism in the liver, offering potential avenues for clinical treatment of NAFLD.
3.2.2 Mechanism of Lactobacillus sake regulating lipid metabolism in liver
Lactobacillus sake has good antibacterial and antioxidant effects, exhibiting excellent antibacterial efficacy, safety and tolerance in the body (Schillinger and Lücke, 1989; Amanatidou et al., 2001; DÜz et al., 2020). Huong Thi Nguyen et al. evaluated the high anti-lipid effect of Lactobacillus sake MJM60958 in HepG2 cells and its therapeutic effect for high-fat diet induced NAFLD mouse model. Among different strains, MJM60958 showed the most pronounced effect in inhibiting lipid synthesis. It reduced lipid accumulation in hepatocytes, relieving NAFLD by decreasing serum level of AST, ALT, Triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TCHO), which serve as key markers of NAFLD (Nguyen et al., 2022a).
3.2.3 Mechanism of Lactobacillus salivarius regulating lipid metabolism in liver
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPAR) α, β/δ and γ regulate lipid homeostasis in the liver. Among them, PPARα is a key nuclear receptor, which controls the oxidation rate of fatty acids in mitochondria and is also related to carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1. Specifically, PPARα controls the oxidation of fatty acids in mitochondria, and PPARγ is involved in adipogenesis and lipid storage. Additionally, the AMPK pathway, which is activated in response to metabolic stress, plays a significant role in regulating lipid metabolism (Wang Y. et al., 2020).
In the study of Lihui Zhu et al., the probiotic strain Lactobacillus salivarius SNK-6 (L.salivarius SNK-6) demonstrated beneficial effects in a lying hen model of NAFLD. The findings revealed that the inhibition of miR-130a-5p significantly increased the expression of PPAR α, PPAR γ, fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4), SREBP1 and fatty acid synthase (FASN) related genes. Conversely, the administration of L.salivarius SNK6 up-regulate the expression of miR-130a-5p and down-regulate the expression of MBOAT2. Through the miR-130a-5p/MBOAT2 pathway, Lactobacillus salivary SNK-6 reduced the activity of ALT and AST and inhibited hepatic fat deposition, thus relieving the condition of NAFLD (Zhu et al., 2022).
3.2.4 Mechanism of Lactobacillus plantarum regulating lipid metabolism in liver
Studies conducted by Chuan Li et al. have shown that L.plantarum NCU116 alleviate hepatic fat accumulation by downregulating fat production and upregulating the expression of genes associated with fat decomposition and fatty acid oxidation. The experimental group treated with L.plantarum NCU116 showed increased expression of PPAR α, PPAR γ, PPAR δ, PGC1 α and CPT1 α, leading to effective reduction of hepatic fat accumulation (Li et al., 2014).
3.2.5 Mechanism of Lactobacillus reuteri regulating lipid metabolism in liver
Carmen Tenorio-Jim é nez et al. conducted the clinical evaluation trial of Lactobacillus reuteri V3401 on NAFLD. Sixty participants (aged 18 to 65 years) diagnosed with IRS were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either a daily dose of placebo or 5×109 colony-forming units of L. reuteri V3401. The study aimed to explore the mediating mechanism of L. reuteri in relieving NAFLD by detecting human serum level of LPS, insulin resistance and liver steatosis after the application of L. reuteri. Currently, the study is still in the stage of experiment and data analysis (Tenorio-Jiménez et al., 2018).
3.3 Probiotics relieve NAFLD by regulating the levels of different cytokines
3.3.1 Effect of Bifidobacterium on the level of related cytokines
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18) are the key cytokines in the pathogenesis of NAFLD (Stojsavljević et al., 2014; Ezquerro et al., 2019).
Experiments evidence has demonstrated that Lactobacillus sake MJM60958 relieved NAFLD by reducing the level of TNF-α (Carotti et al., 2020). In a Study by Moon Ho Do et al., mice fed with high-fat diet exhibited increased expression of genes encoding inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6. However, mice treated with a high dose of Bifidobacterium lactose MG741 reversed the expression trend of these genes, improving intestinal permeability and offering potential therapeutic benefits for NAFLD (Do et al., 2022).
3.3.2 Effect of multiple probiotics combination on the level of related cytokines
After clinical intervention with multiprobiotic “Symbiter” in patients with NAFLD, the levels of AST and GGT which are related with fat synthesis and the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and INF-γ decreased significantly. The fatty liver index (FLI) was significantly improved (Kobyliak et al., 2018a; Kobyliak et al., 2018c).
3.3.3 The function of IL-17
The regulation of cytokines and improvement of the tissue microenvironment are important for treating liver inflammation and alleviating autoimmune diseases. Interleukin-17 (IL-17) has shown promising potential in both research and application (Zhang et al., 2015). IL-17 serves as a key initiator of the inflammatory response, promoting the release of inflammatory cytokines and inducing an inflammatory cascade. Upon binding to its receptor, IL-17 can play its biological role through mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and activating transcription factors such as activator protein-1 (AP1), CCAAT-enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBPs) and nuclear transcription factor κB (NF-κB) (Monin and Gaffen, 2018).
The clinical studies of Chung-Hsing Wang et al. showed that the serum levels of IL-8, IL-17, MIP-1β and TNF-α in patients with type I diabetes treated with Bifidobacterium animalis, Akkermansia muciniphila and Lactobacillus salivarius were significantly lower than those without probiotics (Wang et al., 2022).
However, experimental study by Shuying He et al. has shown that IL-17 from Th17 cells can restore the function of intestinal epithelial tissue and barrier and maintain the integrity of intestinal barrier (He et al., 2022). To some extent, this finding highlighted the dual regulatory effect of IL-17 varing depending on the specific circumstances.
Currently, there is a scarcity of animal experiments and clinical trials investigating the correlation between IL-17 level changes and NAFLD improvement following probiotic use. Further research is needed to clucidate the relationship between IL-17 levels and NAFLD.
3.3.4 Blueberry combined with probiotics to regulate the level of cytokines
3.3.4.1 Effects of bioactive substances from blueberry on inflammation and oxidative stress
According to Felgus-Lavefve L et al., the bioactive molecules of blueberry inhibited inflammation and oxidative stress by downregulating NF-κB pathway, reducing ROS levels and attenuating lipid peroxidation. The understanding of the main molecular mechanisms of blueberry chemicals in the cell model is progressively advancing (Felgus-Lavefve et al., 2022).
Tarfa Albrahim et al. showed that the contents of antioxidant enzymes, glutathione and lipid peroxidation in rats fed blueberries increased, while the activities of inflammatory mediators (TNF-α, IL-6 and nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells) and fibrosis marker transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) in rat liver decreased significantly (Albrahim and Alonazi, 2022).
The studies above demonstrate the significant role of blueberry’s biological activity in anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation, leading to a notable reduction of inflammatory mediators-related cytokines. When blueberry is used in combination with probiotics, it exhibits distinct effects on the level of cytokines in NAFLD model.
3.3.4.2 Blueberry in combination with probiotics & important cytokine IL-22 and its molecular pathway
Studies by Juanjuan Zhu et al. have shown that blueberry combined with probiotics can alleviate NAFLD through IL-22-mediated Janus kinase 1 (JAK1)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)/Bcl-2-associated X protein (BAX) signal pathway (Zhu et al., 2018).
The expression of IL-22, JAK1 and STAT3 in NAFLD model significantly decreased, while the expression of apoptosis factor BAX showed a marked increase. However, the administration of probiotics resulted in a substantial increase in the levels of IL-22, JAK1 and STAT3 in NAFLD model, while decreased the level of BAX. Similarly, the suppression of IL-22 hindered the ability of probiotics to promote the expression of JAK1, STAT3 and BAX (Zhu et al., 2018). Probiotics can activate the JAK1/STAT3 signal pathway, inhibit the apoptosis factor BAX and reduce lipid deposition in vitro through IL-22 (Zenewicz, 2018; Zhu et al., 2018).
In addition, IL-22, acts as a key regulator of epithelial homeostasis, playing a critical role in preserving the function of epithelial barrier (Zenewicz, 2018; Patnaude et al., 2021).
3.3.4.3 Microflora secreting IL-22
IL-22 secreted by engineered Lactobacillus reuteri significantly reduced liver weight and triglyceride content in NAFLD model (Oh et al., 2020). It can be seen that IL-22 can alleviate the development of NAFLD.
IL-22, a member of the IL-20 subfamily, controls lipid metabolism in the liver by activating the above signaling pathways (Pan et al., 2014). As a therapeutic protein, IL-22 holds promising prospects for mitigating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
3.4 Probiotics relieve NAFLD by regulating intestinal microflora
3.4.1 Intestinal microbiota and imbalance
Intestinal microbiota encompasses the diverse microbial community residing in the human intestinal tract. These microorganisms are involved in the regulation of metabolism and physiological activities. Among the various microbial communities in intestinal tract, the bacterial community is of utmost importance (Pascale et al., 2018). Imbalance of intestinal microflora, or intestinal microecological dysbiosis, refers to disruptions in the composition, activity or distribution of microorganisms within the intestines. Such ecological disturbances or alterations in normal intestinal flora will affect intestinal permeability, intestinal mucosal barrier integrity and normal intestinal peristalsis, consequently resulting in a series of diseases (Canakis et al., 2020).
3.4.2 The relationship between intestinal microbiome and NAFLD and related mechanism
Changes in intestinal microflora composition can alleviate or aggravate NAFLD through a variety of mechanisms. The main mechanisms include affecting fat production, modulating dietary energy metabolism, impacting related gene expression in the cholic acid metabolism signal pathway, and altering intestinal permeability. However, further research is required to fully understand the relationship between these factors and the development or progress of NAFLD (Safari and Gérard, 2019).
In terms of dietary energy metabolism, researches by Bäckhed F et al. have shown that germ-free mice, compare to those with intestinal microbiota, are resistant to high-fat or high-sugar diet-induced obesity. Intestinal bacteria produce secretory bacterial enzymes that facilitate the breakdown and digestion of polysaccharides in food, enhancing the absorption of food nutrients (Bäckhed et al., 2004; Bäckhed et al., 2007).
Alterations in intestinal flora can impact the integrity of the intestinal mucosal barrier including the structure of intestinal mucous layer, antimicrobial peptides and tight junction proteins, leading to increased intestinal permeability. This association is closely linked to the severity, occurrence and progression of NAFLD (Giorgio et al., 2014).
Bile acid can not only promote fat absorption, but also play the role of signal molecules in self-metabolism (Jiang et al., 2015; Safari and Gérard, 2019). In terms of bile acid composition changes, intestinal flora changes can increase bile acid metabolites and reduce liver triglyceride accumulation by inhibiting intestinal farnesol X receptor (FXR) signal. These effects are primarily achieved through the down-regulation of liver sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1C (SREBP1C) and decrease of de novo synthesis of fat. Inhibition of intestinal FXR/ceramide axis can mediate the development of NAFLD related with intestinal microbiota (Jiang et al., 2015).
3.4.3 Potential probiotics in the treatment of NAFLD based on regulation of intestinal microbiota and its mechanism
In the study of Hu et al., F. prausnitzii strains (A2-165, LB8, ZF21, PL45 and LC49) could alleviate the symptoms related to glucose tolerance, liver steatosis, intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress in the NAFLD model (Hu et al., 2022). Notably, strains LC49 and LB8 were found to increase the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) and regulate the composition of intestinal flora. The core microflora related to NAFLD include Odoribacter, Roseburia, Erysipelatoclostridium, Tyzzerella, Faecalibaculum, Blautia and Acetatifactor. Among them, the effects of Erysipelatoclostridium, Tyzzerella, Faecalibaculum, Blautia and Acetatifactor on the progress of NAFLD could be reversed by F.prausnitzii LC49 and LB8.
Patients with NAFLD exhibited a significantly lower total bacterial load compared to normal subjects, accompanied by a reduction in the abundance of various normal bacteria in the intestinal wall, including Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, True bacillus and Propionibacterium (Vakhrushev et al., 2022).
F.prausnitzii LC49 and LB8 can enrich the abundance of Lactobacillus, Enterobacter ileum, Bacillus faecalis, Duboxi and Bifidobacterium, thus positively influences the metabolism of carbohydrates, amino acids and fatty acids. Moreover, F.prausnitzii LC49 and LB8 show significant anti-NAFLD effects and possess microbial regulatory properties, suggesting their potential as probiotic agents for the treatment of NAFLD (Hu et al., 2022; Shu et al., 2025).
4 Conclusions
While significant progress has been made in understanding the therapeutic potential of probiotics for NAFLD, several limitations persist in the current body of research. First, many studies lack long-term follow-up data, which is crucial to determine the sustainability of probiotic effects. Additionally, variations in probiotic strains and dosages across studies make it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about their optimal use. Most clinical trials have small sample sizes, limiting their generalizability. Furthermore, the mechanisms through which probiotics exert their therapeutic effects in NAFLD are not fully understood, with many studies relying on indirect markers of disease progression.
Despite promising therapeutic effects, challenges remain in probiotic application for MAFLD, such as the strain-specific nature of probiotics, host genetic and microbiota variability, and concerns regarding long-term safety and regulatory standardization. These issues underscore the need for rigorous clinical trials and mechanistic studies to validate efficacy and safety across diverse populations.
Future research should focus on large-scale, multicenter trials with longer follow-up periods. A more standardized approach to the selection and dosage of probiotic strains is essential for comparing results across studies. Furthermore, research into the specific molecular mechanisms by which probiotics modulate gut microbiota and influence liver function is crucial for developing targeted therapies. There is also a need for studies that explore the combined effects of probiotics with other therapeutic interventions, such as dietary modifications or pharmaceutical agents. Addressing these challenges will provide clearer insights into the role of probiotics in managing NAFLD (Figure 1).
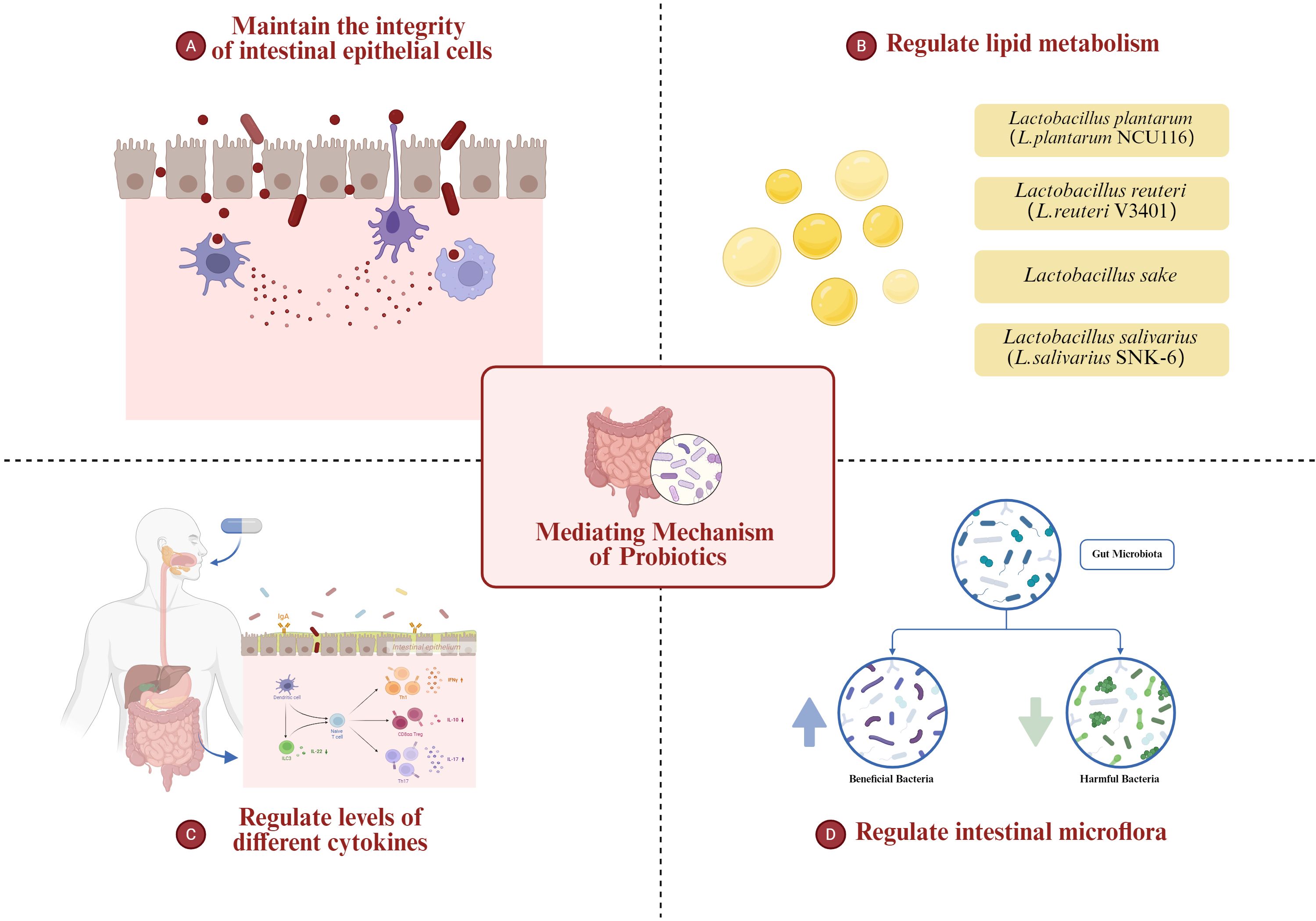
Figure 1. The role of probiotics in regulating the gut-liver axis in MAFLD, including modulation of intestinal microbiota, improvement of intestinal barrier integrity, alteration of lipid metabolism, and attenuation of inflammatory pathways.
Author contributions
XL: Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Validation, Investigation, Resources. WH: Software, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Formal analysis. CL: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Visualization, Investigation, Validation. ZF: Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Investigation, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis. SS: Formal analysis, Project administration, Data curation, Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. MC: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Project administration, Data curation. WG: Software, Investigation, Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. SZ: Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Investigation, Resources, Funding acquisition. ZY: Supervision, Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Resources, Visualization, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants from the Hainan Province Science and Technology Special Fund (ZDYF2025LCLH012), the National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFC2306800), the Key Research and Development Project of Zhejiang Province (2024C03149 and 2023C03046), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82470690 and 92159202), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2025ZFJH03).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abrantes, F. A., Nascimento, B. B., Andrade, M. E. R., de Barros, P. A. V., Cartelle, C. T., Martins, F. S., et al. (2020). Treatment with Bifidobacterium longum 51A attenuates intestinal damage and inflammatory response in experimental colitis. Benef Microbes 11, 47–57. doi: 10.3920/BM2019.0098
Ahmed, L. A., Salem, M. B., El-Din, S. H. S., Lakkany, N. M., Ahmed, H. O., and Nasr, S. M. (2020). Gut microbiota modulation as a promising therapy with metformin in rats with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Role of LPS/TLR4 and autophagy pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol 887, 173461. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173461
Ahn, S. B., Jun, D. W., Kang, B.-K., Lim, J. H., Lim, S., and Chung, M.-J. (2019). Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of a multispecies probiotic mixture in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep 9, 1–9. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42059-3
Alboraie, M., Youssef, N., Sherief, A. F., Afify, S., Wifi, M. N., Omran, D., et al. (2019). Egyptian liver library: an indexed database for liver disease evidence in Egypt. Arab J. Gastroenterol 20, 109–113. doi: 10.1016/j.ajg.2019.05.004
Albrahim, T. and Alonazi, M. (2022). Effect of blueberry extract on liver in aged rats. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev 2022, 3490776. doi: 10.1155/2022/3490776
Aller, R., De Luis, D., Izaola, O., Conde, R., Gonzalez Sagrado, M., and Primo, D. (2011). Effect of a probiotic on liver aminotransferases in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients: a double blind randomized clinical trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci 15, 1090–1095.
Al-Muzafar, H. M. and Amin, K. A. (2017). Probiotic mixture improves fatty liver disease by virtue of its action on lipid profiles, leptin, and inflammatory biomarkers. BMC complementary Altern. Med 17, 1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1540-z
Alves-Bezerra, M. and Cohen, D. E. (2017). Triglyceride metabolism in the liver. Compr. Physiol 8, 1–8. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c170012
Amanatidou, A., Smid, E. J., Bennik, M. H., and Gorris, L. G. (2001). Antioxidative properties of Lactobacillus sake upon exposure to elevated oxygen concentrations. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 203, 87–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10825.x
Asgharian, A., Askari, G., Esmailzade, A., Feizi, A., and Mohammadi, V. (2016). The effect of symbiotic supplementation on liver enzymes, C-reactive protein and ultrasound findings in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a clinical trial. . Int. J. Prev. Med 7, 59. doi: 10.4103/2008-7802.178533
Azarang, A., Farshad, O., Ommati, M. M., Jamshidzadeh, A., Heydari, R., and Abootalebi, S. N. (2020). Protective role of probiotic supplements in hepatic steatosis: a rat model study. . BioMed. Res. Int 2020, 1–15. doi: 10.1155/2020/5487659
Bäckhed, F., Ding, H., Wang, T., Hooper, L. V., Koh, G. Y., Nagy, A., et al. (2004). The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 101, 15718–15723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407076101
Bäckhed, F., Manchester, J. K., Semenkovich, C. F., and Gordon, J. I. (2007). Mechanisms underlying the resistance to diet-induced obesity in germ-free mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 104, 979–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605374104
Badmus, O. O., Hillhouse, S. A., Anderson, C. D., Hinds, T. D., and Stec, D. E. (2022). Molecular mechanisms of metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): functional analysis of lipid metabolism pathways. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 136, 1347–1366. doi: 10.1042/CS20220572
Behrouz, V., Jazayeri, S., Aryaeian, N., Zahedi, M. J., and Hosseini, F. (2017). Effects of probiotic and prebiotic supplementation on leptin, adiponectin, and glycemic parameters in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized clinical trial. Middle East J. Digestive Dis 9, 150. doi: 10.15171/mejdd.2017.66
Brennan, P. N., Elsharkawy, A. M., Kendall, T. J., Loomba, R., Mann, D. A., and Fallowfield, J. A. (2023). Antifibrotic therapy in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: time for a human-centric approach. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 2, 1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00796-x
Canakis, A., Haroon, M., and Weber, H. C. (2020). Irritable bowel syndrome and gut microbiota. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes 27, 28–35. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000523
Carotti, S., Aquilano, K., Valentini, F., Ruggiero, S., Alletto, F., Morini, S., et al. (2020). An overview of deregulated lipid metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with special focus on lysosomal acid lipase. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol 319, G469–G480. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00049.2020
Chichlowski, M., Shah, N., Wampler, J. L., Wu, S. S., and Vanderhoof, J. A. (2020). Bifidobacterium longum Subspecies infantis (B. infantis) in Pediatric Nutrition: Current State of Knowledge. Nutrients 12, 1581. doi: 10.3390/nu12061581
Crommen, S., Rheinwalt, K. P., Plamper, A., Simon, M.-C., Rösler, D., and Fimmers, R. (2022). A specifically tailored multistrain probiotic and micronutrient mixture affects nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—Related markers in patients with obesity after mini gastric bypass surgery. J. Nutr 152, 408–418. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxab392
Derosa, G., Guasti, L., D’angelo, A., Martinotti, C., Valentino, M. C., and Di Matteo, S. (2022). Probiotic therapy with VSL3® in patients with NAFLD: A randomized clinical trial. Front. Nutr 9.
Do, M. H., Oh, M.-J., Lee, H.-B., Kang, C.-H., Yoo, G., and Park, H.-Y. (2022). Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis MG741 Reduces Body Weight and Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Improving the Gut Permeability and Amelioration of Inflammatory Cytokines. . Nutrients 14, 1965. doi: 10.3390/nu14091965
Duseja, A., Acharya, S. K., Mehta, M., Chhabra, S., Shalimar Rana, S., and Das, A. (2019). High potency multistrain probiotic improves liver histology in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A randomised, double-blind, proof of concept study. BMJ Open Gastroenterol 6, e000315. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2019-000315
DÜz, M., DoĞan, Y. N., and DoĞan, İ. (2020). Antioxidant activitiy of Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus sake and Lactobacillus curvatus strains isolated from fermented Turkish Sucuk. Acad. Bras. Cienc 92, e20200105. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765202020200105
Dvorak, A. M., Estrella, P., and Ishizaka, T. (1994). Vesicular transport of peroxidase in human eosinophilic myelocytes. Clin. Exp. Allergy 24, 10–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1994.tb00910.x
Endo, H., Niioka, M., Kobayashi, N., Tanaka, M., and Watanabe, T. (2013). Butyrate-producing probiotics reduce nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression in rats: new insight into the probiotics for the gut-liver axis. PloS One 8, e63388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063388
Eslam, M., Newsome, P. N., Anstee, Q. M., Anstee, Q. M., Targher, G., and Romero-Gomez, M. (2020). A new definition for metabolic associated fatty liver disease: an international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 73(1):202–209. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.039
Esposito, E., Iacono, A., Bianco, G., Autore, G., Cuzzocrea, S., and Vajro, P. (2009). Probiotics reduce the inflammatory response induced by a high-fat diet in the liver of young rats. J. Nutr 139, 905–911. doi: 10.3945/jn.108.101808
Ezquerro, S., Mocha, F., Frühbeck, G., Guzmán-Ruiz, R., Valentí, V., Mugueta, C., et al. (2019). Ghrelin reduces TNF-α-induced human hepatocyte apoptosis, autophagy, and pyroptosis: role in obesity-associated NAFLD. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab 104, 21–37. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-01171
Famouri, F., Shariat, Z., Hashemipour, M., Keikha, M., and Kelishadi, R. (2017). Effects of probiotics on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr 64, 413–417. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001422
Felgus-Lavefve, L., Howard, L., Adams, S. H., and Baum, J. I. (2022). The effects of blueberry phytochemicals on cell models of inflammation and oxidative stress. Adv. Nutr 13, 1279–1309. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab137
Fontana, L., Plaza-Díaz, J., Robles-Bolívar, P., Valente-Godínez, H., Sáez-Lara, M. J., and Abadía-Molina, F. (2021). Bifidobacterium breve CNCM I-4035, Lactobacillus paracasei CNCM I-4034 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-4036 Modulate Macrophage Gene Expression and Ameliorate Damage Markers in the Liver of Zucker-Lepr fa/fa Rats. Nutrients 13, 202. doi: 10.3390/nu13010202
Friedman, S. L., Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A., Rinella, M., and Sanyal, A. J. (2018). Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med 24, 908–922. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9
Gao, X., Zhu, Y., Wen, Y., Liu, G., and Wan, C. (2016). Efficacy of probiotics in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adult and children: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hepatol. Res 46, 1226–1233. doi: 10.1111/hepr.12671
Geng, W., Zhang, Y., Yang, J., Zhang, J., Zhao, J., and Wang, J. (2022). Identification of a novel probiotic and its protective effects on NAFLD via modulating gut microbial community. J. Sci. Food Agric. 102 (11), 4620–4628. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11820
Giorgio, V., Miele, L., Principessa, L., Ferretti, F., Villa, M. P., Negro, V., et al. (2014). Intestinal permeability is increased in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and correlates with liver disease severity. Dig Liver Dis 46, 556–560. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2014.02.010
Goodwin, M., Herath, C., Jia, Z., Leung, C., Coughlan, M. T., Forbes, J., et al. (2013). Advanced glycation end products augment experimental hepatic fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 28, 369–376. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12042
Goyette, P., Labbé, C., Trinh, T. T., Xavier, R. J., and Rioux, J. D. (2007). Molecular pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: genotypes, phenotypes and personalized medicine. Ann. Med 39, 177–199. doi: 10.1080/07853890701197615
Hany, N. M., Eissa, S., Basyouni, M., Hasanin, A. H., Aboul-Ela, Y. M., and Abo Elmagd, N. M. (2022). Modulation of hepatic stellate cells by Mutaflor® probiotic in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease management. J. Trans. Med 20, 1–19. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03543-z
He, S., Cui, S., Song, W., Jiang, Y., Chen, H., Liao, D., et al. (2022). Interleukin-17 weakens the NAFLD/NASH process by facilitating intestinal barrier restoration depending on the gut microbiota. mBio 13, e0368821. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03688-21
Hosseini, H. M., Shirvani, H., Aghaei, F., Arabzadeh, E., and Hofmeister, M. (2022). Ameliorative effects of high intensity interval training and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG against tetracycline-induced fatty liver in rats: a gene expression profiling comparative study. EXCLI J 21, 991–1006. doi: 10.17179/excli2022-4791
Hu, W., Gao, W., Liu, Z., Fang, Z., Wang, H., and Zhao, J.. (2022). Specific strains of faecalibacterium prausnitzii ameliorate nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice in association with gut microbiota regulation. Nutrients 14, 2945. doi: 10.3390/nu14142945
Hu, D., Yang, W., Mao, P., and Cheng, M. (2021). Combined amelioration of prebiotic resveratrol and probiotic Bifidobacteria on obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr. Cancer 73, 652–661. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2020.1767166
Huang, W., Wang, G., Xia, Y., Xiong, Z., and Ai, L. (2020). Bile salt hydrolase-overexpressing Lactobacillus strains can improve hepatic lipid accumulation in vitro in an NAFLD cell model. Food Nutr. Res 64. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v64.3751
Huang, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, L., Zheng, K., Xiong, J., and Li, J. (2022). Effect of probiotics therapy on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. . Comput. Math. Methods Med 2022. doi: 10.1155/2022/7888076
Jang, H. R., Park, H.-J., Kang, D., Chung, H., Nam, M. H., Lee, Y., et al. (2019). A protective mechanism of probiotic Lactobacillus against hepatic steatosis via reducing host intestinal fatty acid absorption. Exp. Mol. Med 51, 1–14. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0352-x
Javadi, L., Khoshbaten, M., Safaiyan, A., Ghavami, M., Abbasi, M. M., and Gargari, B. P. (2018). Pro-and prebiotic effects on oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Asia Pacific J. Clin. Nutr 27, 1031–1039. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.042018.05
Jiang, C., Xie, C., Li, F., Zhang, L., Nichols, R. G., Krausz, K. W., et al. (2015). Intestinal farnesoid X receptor signaling promotes nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Invest 125, 386–402. doi: 10.1172/JCI76738
Jones, J. G. (2016). Hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetologia 59, 1098–1103. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-3940-5
Kanuri, G. and Bergheim, I. (2013). In vitro and in vivo models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Int. J. Mol. Sci 14, 11963–11980. doi: 10.3390/ijms140611963
Khan, M. Y., Mihali, A. B., Rawala, M. S., Aslam, A., and Siddiqui, W. J. (2019). The promising role of probiotic and synbiotic therapy in aminotransferase levels and inflammatory markers in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease–a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 31, 703–715. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001371
Kiffin, R., Bandyopadhyay, U., and Cuervo, A. M. (2006). Oxidative stress and autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal 8, 152–162. doi: 10.1089/ars.2006.8.152
Kim, D.-H., Kim, H., Jeong, D., Kang, I.-B., Chon, J.-W., Kim, H.-S., et al. (2017). Kefir alleviates obesity and hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet-fed mice by modulation of gut microbiota and mycobiota: targeted and untargeted community analysis with correlation of biomarkers. J. Nutr. Biochem 44, 35–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.02.014
Kim, B., Kwon, J., Kim, M.-S., Park, H., Ji, Y., and Holzapfel, W. (2018). Protective effects of Bacillus probiotics against high-fat diet-induced metabolic disorders in mice. PloS One 13, e0210120. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210120
Kim, J. E., Lee, J. Y., and Kang, C.-H. (2022). Limosilactobacillus fermentum MG4295 improves hyperglycemia in high-fat diet-induced mice. Foods 11, 231. doi: 10.3390/foods11020231
Kobyliak, N., Abenavoli, L., Falalyeyeva, T., Mykhalchyshyn, G., Boccuto, L., and Kononenko, L. (2018a). Beneficial effects of probiotic combination with omega-3 fatty acids in NAFLD: a randomized clinical study. Minerva Medica 109 (6), 418–428. doi: 10.23736/S0026-4806.18.05845-7
Kobyliak, N., Abenavoli, L., Falalyeyeva, T., and Beregova, T. (2018b). Efficacy of probiotics and smectite in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Hepatol 17, 153–161. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.7547
Kobyliak, N., Abenavoli, L., Mykhalchyshyn, G., Kononenko, L., Boccuto, L., and Kyriienko, D. (2018c). A multi-strain probiotic reduces the fatty liver index, cytokines and aminotransferase levels in NAFLD patients: evidence from a randomized clinical trial. doi: 10.15403/jgld.2014.1121.271.kby
Kobyliak, N., Falalyeyeva, T., Bodnar, P., and Beregova, T. (2017). Probiotics supplemented with omega-3 fatty acids are more effective for hepatic steatosis reduction in an animal model of obesity. Probiotics Antimicrobial Proteins 9, 123–130. doi: 10.1007/s12602-016-9230-1
Konda, P. Y., Poondla, V., Jaiswal, K. K., Dasari, S., Uyyala, R., and Surtineni, V. P. (2020). Pathophysiology of high fat diet induced obesity: impact of probiotic banana juice on obesity associated complications and hepatosteatosis. Sci. Rep 10, 1–17. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73670-4
Li, C., Nie, S. P., Zhu, K. X., Ding, Q., Li, C., Xiong, T., et al. (2014). Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 improves liver function, oxidative stress and lipid metabolism in rats with high fat diet induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Food Funct 5, 3216–3223. doi: 10.1039/C4FO00549J
Liu, Z.-S., Li, P.-L., Ku, Y.-W., and Chen, P.-W. (2022). Oral administration of recombinant lactoferrin-expressing probiotics ameliorates diet-induced lipid accumulation and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Microorganisms 10, 2215. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10112215
Loguercio, C., Federico, A., Tuccillo, C., Terracciano, F., D'Auria, M. V., and De Simone, C. (2005). Beneficial effects of a probiotic VSL3 on parameters of liver dysfunction in chronic liver diseases. J. Clin. Gastroenterol 39, 540–543. doi: 10.1097/01.mcg.0000165671.25272.0f
Loman, B. R., Hernández-Saavedra, D., An, R., and Rector, R. S. (2018). Prebiotic and probiotic treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev 76, 822–839. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuy031
Lynch, J. P., Goers, L., and Lesser, C. F. (2022). Emerging strategies for engineering Escherichia coli Nissle 1917-based therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci 43, 772–786. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2022.02.002
MaChado, A. S., Oliveira, J. R., Lelis, D. D. F., de Paula, A. M.B., Guimarães, A. L.S., and Andrade, J. M.O. (2021). Oral probiotic bifidobacterium longum supplementation improves metabolic parameters and alters the expression of the renin-angiotensin system in obese mice liver. Biol. Res. For Nurs 23, 100–108. doi: 10.1177/1099800420942942
Mohamad Nor, M. H., Ayob, N., Mokhtar, N. M., Raja Ali, R. A., Tan, G. C., and Wong, Z. (2021). The effect of probiotics (MCP® BCMC® Strains) on hepatic steatosis, small intestinal mucosal immune function, and intestinal barrier in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrients 13, 3192. doi: 10.3390/nu13093192
Monin, L. and Gaffen, S. L. (2018). Interleukin 17 family cytokines: signaling mechanisms, biological activities, and therapeutic implications. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol 10, a028522. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028522
Moreira, G. V., Araujo, L. C., Murata, G. M., Matos, S. L., and Carvalho, C. R.O. (2022). Kombucha tea improves glucose tolerance and reduces hepatic steatosis in obese mice. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy 155, 113660. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113660
Mouzaki, M. and Allard, J. P. (2012). The role of nutrients in the development, progression, and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol 46, 457–467. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31824cf51e
Mu, J., Tan, F., Zhou, X., and Zhao, X. (2020). Lactobacillus fermentum CQPC06 in naturally fermented pickles prevents non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by stabilizing the gut–liver axis in mice. Food Funct 11, 8707–8723. doi: 10.1039/D0FO01823F
Nguyen, H. T., Gu, M., Werlinger, P., Cho, J. H., Cheng, J., and Suh, J. W. (2022a). Lactobacillus sakei MJM60958 as a potential probiotic alleviated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice fed a high-fat diet by modulating lipid metabolism, inflammation, and gut microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci 23, 13436. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113436
Nguyen, H. T., Gu, M., Werlinger, P., Cho, J.-H., Cheng, J., and Suh, J.-W. (2022b). Lactobacillus sakei MJM60958 as a potential probiotic alleviated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice fed a high-fat diet by modulating lipid metabolism, inflammation, and gut microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci 23, 13436. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113436
Novak, E. A. and Mollen, K. P. (2015). Mitochondrial dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol 3, 62. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2015.00062
O'flaherty, S. and Klaenhammer, T. R. (2010). The role and potential of probiotic bacteria in the gut, and the communication between gut microflora and gut/host. Int. Dairy J 20, 262–268. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2009.11.011
Oh, J.-H., Schueler, K. L., Stapleton, D. S., Alexander, L. M., Yen, C.-L. E., and Keller, M. P. (2020). Secretion of recombinant interleukin-22 by engineered Lactobacillus reuteri reduces fatty liver disease in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. MSphere 5, e00183–e00120. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00183-20
Pan, C.-X., Tang, J., Wang, X.-Y., Wu, F.-R., Ge, J.-F., and Chen, F.-H. (2014). Role of interleukin-22 in liver diseases. Inflammation Res 63, 519–525. doi: 10.1007/s00011-014-0727-3
Pan, X., Wen, S. W., Kaminga, A. C., and Liu, A. (2020). Gut metabolites and inflammation factors in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep 10, 1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65051-8
Pant, R., Sharma, N., Kabeer, S. W., Sharma, S., and Tikoo, K. (2022). Selenium-enriched probiotic alleviates western diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats via modulation of autophagy through AMPK/SIRT-1 pathway. Biol. Trace Element Res 201 (3), 1–14. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03247-x
Pascale, A., Marchesi, N., Marelli, C., Coppola, A., Luzi, L., Govoni, S., et al. (2018). Microbiota and metabolic diseases. Endocrine 61, 357–371. doi: 10.1007/s12020-018-1605-5
Patnaude, L., Mayo, M., Mario, R., Wu, X., Knight, H., Creamer, K., et al. (2021). Mechanisms and regulation of IL-22-mediated intestinal epithelial homeostasis and repair. Life Sci 271, 119195. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119195
Pierantonelli, I. and Svegliati-Baroni, G. (2019). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: basic pathogenetic mechanisms in the progression from NAFLD to NASH. Transplantation 103, e1–e13. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002480
Riazi, K., Azhari, H., Charette, J. H., Underwood, F. E., King, J. A., Afshar, E. E., et al. (2022). The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol 7, 851–861. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00165-0
Ritze, Y., Bárdos G, Claus, A., Ehrmann, V., Bergheim, I., and Schwiertz, A. (2014). Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. PloS One 9, e80169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080169
Roychowdhury, S., Selvakumar, P. C., and Cresci, G. A. (2018). The role of the gut microbiome in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Med. Sci 6, 47. doi: 10.3390/medsci6020047
Sabirin, F., Lim, S. M., Neoh, C. F., and Ramasamy, K. (2022). Hepatoprotection of probiotics against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in vivo: a systematic review. . Front. Nutr 524, 844374. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.844374
Safari, Z. and Gérard, P. (2019). The links between the gut microbiome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Cell Mol. Life Sci 76, 1541–1558. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03011-w
Savcheniuk, O., Kobyliak, N., Kondro, M., Virchenko, O., Falalyeyeva, T., and Beregova, T. (2014). Short-term periodic consumption of multiprobiotic from childhood improves insulin sensitivity, prevents development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and adiposity in adult rats with glutamate-induced obesity. BMC complementary Altern. Med 14, 1–17. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-247
Scherz-Shouval, R. and Elazar, Z. R. O. S. (2007). mitochondria and the regulation of autophagy. Trends Cell Biol 17, 422–427. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2007.07.009
Schillinger, U. and Lücke, F. K. (1989). Antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus sake isolated from meat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 55, 1901–1906. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.1901-1906.1989
Seo, M., Inoue, I., Tanaka, M., Matsuda, N., Nakano, T., and Awata, T. (2013). Clostridium butyricum MIYAIRI 588 improves high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Dig Dis. Sci 58, 3534–3544. doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2879-3
Sepideh, A., Karim, P., Hossein, A., Leila, R., Hamdollah, M., and Mohammad, G. E. (2016). Effects of multistrain probiotic supplementation on glycemic and inflammatory indices in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr 35, 500–505. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2015.1031355
Shu, J. Z., Huang, Y. H., He, X. H., Liu, F. Y., Liang, Q. Q., Yong, X. T., et al. (2025). Gut microbiota differences, metabolite changes, and disease intervention during metabolic - dysfunction - related fatty liver progression. World J. Hepatol 17, 103854. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.103854
Stojsavljević, S., Gomerčić Palčić, M., Virović Jukić, L., Smirčić Duvnjak, L., and Duvnjak, M. (2014). Adipokines and proinflammatory cytokines, the key mediators in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol 20, 18070–18091. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18070
Tang, Y., Huang, J., Zhang, W. Y., Qin, S., Yang, Y. X., and Ren, H. (2019). Effects of probiotics on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol 12, 1756284819878046. doi: 10.1177/1756284819878046
Tenorio-Jiménez, C., Martínez-Ramírez, M. J., Tercero-Lozano, M., Arraiza-Irigoyen, C., Del Castillo-Codes, I., Olza, J., et al. (2018). Evaluation of the effect of Lactobacillus reuteri V3401 on biomarkers of inflammation, cardiovascular risk and liver steatosis in obese adults with metabolic syndrome: a randomized clinical trial (PROSIR). BMC Complement Altern. Med 18, 306. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2371-x
Underwood, M. A., German, J. B., Lebrilla, C. B., and Mills, D. A. (2015). Bifidobacterium longum subspecies infantis: champion colonizer of the infant gut. Pediatr. Res 77, 229–235. doi: 10.1038/pr.2014.156
Vakhrushev, Y. M., Lukashevich, A. P., and Lyapina, M. V. (2022). The study of abdominal and parietal enteric microbiota in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ter Arkh 94, 188–193. doi: 10.26442/00403660.2022.02.201369
Wang, Y., Fang, Z., Zhai, Q., Cui, S., Zhao, J., Zhang, H., et al. (2021). Supernatants of bifidobacterium longum and lactobacillusplantarum strains exhibited antioxidative effects on A7R5 cells. Microorganisms 9, 452. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9020452
Wang, W., Li, Q., Chai, W., Sun, C., Zhang, T., and Zhao, C. (2019). Lactobacillus paracasei Jlus66 extenuate oxidative stress and inflammation via regulation of intestinal flora in rats with non alcoholic fatty liver disease. Food Sci. Nutr 7, 2636–2646. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1118
Wang, Y., Nakajima, T., Gonzalez, F. J., and Tanaka, N. (2020). PPARs as metabolic regulators in the liver: lessons from liver-specific PPAR-null mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci 21, 2061. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062061
Wang, W., Xu, A.-L., Li, Z.-C., Li, Y., Xu, S. F., and Sang, H. C. (2020). Combination of probiotics and Salvia miltiorrhiza polysaccharide alleviates hepatic steatosis via gut microbiota modulation and insulin resistance improvement in high fat-induced NAFLD mice. Diabetes Metab. J 44, 336–348. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0042
Wang, C. H., Yen, H. R., Lu, W. L., Ho, H. H., Lin, W. Y., Kuo, Y. W., et al. (2022). Adjuvant Probiotics of Lactobacillus salivarius subsp. salicinius AP-32, L. johnsonii MH-68, and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis CP-9 Attenuate Glycemic Levels and Inflammatory Cytokines in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 754401. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.754401
Williams, C. D., Stengel, J., Asike, M. I., Torres, D. M., Shaw, J., and Contreras, M. (2011). Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among a largely middle−aged population utilizing ultrasound and liver biopsy: a prospective study. Gastroenterology 140 (1), 124–31. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.09.038
Xiao, M.-W., Lin, S.-X., Shen, Z.-H., Luo, W.-W., and Wang, X.-Y. (2019). Systematic review with meta-analysis: the effects of probiotics in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. . Gastroenterol. Res. Pract 2019. doi: 10.1155/2019/1484598
Xu, R.-Y., Wan, Y.-P., Fang, Q.-Y., Lu, Q.-Y., Cai, W., and W. (2011). Supplementation with probiotics modifies gut flora and attenuates liver fat accumulation in rat nonalcoholic fatty liver disease model. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr 50 (1), 1108190104. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.11-38
Yan, Y., Liu, C., Zhao, S., Wang, X., Wang, J., and Zhang, H. (2020). Probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis V9 attenuates hepatic steatosis and inflammation in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. AMB Express 10, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13568-020-01038-y
Yang, R., Shang, J., Zhou, Y., Liu, W., Tian, Y., and Shang, H. (2021). Effects of probiotics on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 15, 1401–1409. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2022.2016391
Yao, S., Zhao, Z., Wang, W., and Liu, X. (2021). Bifidobacterium longum: protection against inflammatory bowel disease. J. Immunol. Res 2021, 8030297. doi: 10.1155/2021/8030297
Ye, H., Li, Q., Zhang, Z., Sun, M., Zhao, C., and Zhang, T. (2017). Effect of a novel potential probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei Jlus66 isolated from fermented milk on nonalcoholic fatty liver in rats. Food Funct 8, 4539–4546. doi: 10.1039/C7FO01108C
Younossi, Z. M., Golabi, P., Paik, J. M., Henry, A., Van Dongen, C., and Henry, L. (2023). The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): a systematic review. Hepatology 77, 1335–1347. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000004
Yu, J. S., Youn, G. S., Choi, J., Kim, C.-H., Kim, B. Y., and Yang, S.-J. (2021). Lactobacillus lactis and Pediococcus pentosaceus-driven reprogramming of gut microbiome and metabolome ameliorates the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Transl. Med 11, e634. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.634
Zeigerer, A. (2021). NAFLD - A rising metabolic disease. Mol. Metab 50, 101274. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101274
Zenewicz, L. A. (2018). IL-22: there is a gap in our knowledge. Immunohorizons 2, 198–207. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.1800006
Zhang, H., Bernuzzi, F., Lleo, A., Ma, X., and Invernizzi, P. (2015). Therapeutic potential of IL-17-mediated signaling pathway in autoimmune liver diseases. Mediators Inflamm 2015, 436450. doi: 10.1155/2015/436450
Zhou, J., Li, M., Chen, Q., Li, X., Chen, L., Dong, Z., et al. (2022). Programmable probiotics modulate inflammation and gut microbiota for inflammatory bowel disease treatment after effective oral delivery. Nat. Commun 13, 3432. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31171-0
Zhu, L., Liao, R., Huang, J., Xiao, C., Yang, Y., Wang, H., et al. (2022). Lactobacillus salivarius SNK-6 Regulates Liver Lipid Metabolism Partly via the miR-130a-5p/MBOAT2 Pathway in a NAFLD Model of Laying Hens. Cells 11, 4133. doi: 10.3390/cells11244133
Keywords: probiotic, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, application, mediating mechanism, future perspective
Citation: Luo X-Y, Huang W-B, Lu C-H, Gu W, Feng Z-X, Shen S, Chen M-Z, Zheng S-S and Yang Z (2025) Application of probiotic therapy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: mediating mechanism and future perspective. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1638372. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1638372
Received: 30 May 2025; Accepted: 12 August 2025;
Published: 15 September 2025.
Edited by:
Ren-Lei Ji, Harvard Medical School, United StatesReviewed by:
Lan Huang, Suzhou Municipal Hospital, ChinaXuesi Chen, The Affiliated People’s Hospital of Ningbo University, China
Copyright © 2025 Luo, Huang, Lu, Gu, Feng, Shen, Chen, Zheng and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhe Yang, eWFuZ3poZV8wMjAxNzMwQDE2My5jb20=; Shu-Sen Zheng, c2h1c2VuemhlbmdAemp1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xing-Yu Luo
Xing-Yu Luo Wei-Bin Huang
Wei-Bin Huang Chuang-Hui Lu1,3
Chuang-Hui Lu1,3 Sui Shen
Sui Shen Shu-Sen Zheng
Shu-Sen Zheng