- Burn and Trauma Treatment Center, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
Background: This study aimed to develop and evaluate SabiWhite-loaded ethosomes (SW-ETH) for topical application, focusing on improving stability, biocompatibility, and therapeutic efficacy. Ethosomal formulations are known for their enhanced drug delivery properties, making them suitable for skin inflammation.
Methods: The SW-ETH formulations were developed utilizing an adapted cold preparation technique. A 3² factorial design was used to optimize phospholipid concentration and ethanol content, and their impact on vesicle size and entrapment efficiency (EE%) was assessed. Structural characterization of SabiWhite was performed using melting point determination, Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray Diffraction (XRD). In vitro drug release was assessed using a Franz diffusion cell, and anti-inflammatory and skin irritation studies were performed on Wistar rats.
Results: SabiWhite exhibited a melting point of 96°C and characteristic FTIR peaks, confirming its identity and purity. XRD analysis revealed its crystalline nature, while ethosomal formulations showed a shift to an amorphous state. The optimized SW-ETH formulation (SW-ETH 6) had a vesicle size of 184.4 nm, an EE% of 92.5%, and a zeta potential of -13.50 mV, indicating stable and uniform vesicles. In-vitro drug release from SW-ETH 6 showed a sustained release profile with 93.12% drug release over 24 hours. In vivo, SW-ETH demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects with 36.17% edema inhibition at 150 minutes, comparable to Diclofenac gel (41.92%). No skin irritation was observed, and the formulation was classified as non-irritant. Stability tests confirmed minimal changes in appearance, viscosity, and drug content over 120 days at different storage conditions.
Conclusion: SW-ETH demonstrated effective drug encapsulation, enhanced anti-inflammatory activity, and excellent biocompatibility, making it a promising candidate for topical therapy. Further clinical validation is warranted to confirm its therapeutic potential.
Introduction
Skin inflammation is a prevalent dermatological condition characterized by redness, swelling, itching, and pain, which can significantly impair the quality of life (Tampa et al., 2022). It encompasses a wide spectrum of disorders, including dermatitis, psoriasis, and eczema, often triggered by infections-, often involving multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter baumannii, which exacerbate inflammation, delay healing, and compromise therapeutic outcomes also allergens, autoimmune reactions, and environmental factors such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation, pollutants, and chemical irritants (Kantor and Silverberg, 2017). In particular, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) colonization has been reported in up to 60% of patients with chronic eczematous dermatitis, where it perpetuates inflammation by releasing superantigens and proteases (Kim et al., 2019). The immune cells, including keratinocytes, macrophages, and mast cells, primarily drive the inflammatory response by activating and releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) (Arango Duque and Descoteaux, 2014). Chronic inflammation disrupts skin barrier function, promoting oxidative stress, collagen degradation, and delayed wound healing, which underscores the need for effective therapeutic interventions (Mamun et al., 2024). The conventional treatments for skin inflammation include corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and immunomodulators such as calcineurin inhibitors. While corticosteroids are highly effective in reducing inflammation, their long-term use is associated with adverse effects, including skin atrophy, telangiectasia, and increased susceptibility to infections (Calabrese et al., 2022). NSAIDs, though widely used, exhibit limited efficacy in chronic conditions and may cause irritation and hypersensitivity reactions. Furthermore, biologics targeting specific inflammatory pathways, such as monoclonal antibodies against TNF-α (e.g., adalimumab) and IL-17 (e.g., secukinumab), have shown promise in severe inflammatory disorders but are associated with high costs and systemic immunosuppressive effects (Schwartz et al., 2017). The limitations of existing therapies highlight the urgent need for safer, cost-effective, and targeted alternatives to manage skin inflammation effectively. Curcumin, the bioactive component of Curcuma longa, has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and wound-healing properties (Sharifi-Rad et al., 2020). However, its poor aqueous solubility, rapid degradation, and low bioavailability limit its therapeutic application. SabiWhite, a standardized curcumin derivative, has emerged as a promising alternative due to its enhanced stability, increased skin permeability, and superior pharmacological profile. Studies have demonstrated that SabiWhite exerts potent anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activation, reducing oxidative stress, and downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines (Sureshbabu et al., 2025). Additionally, its depigmenting properties make it a suitable candidate for treating inflammatory hyperpigmentation disorders. Despite its advantages, the topical delivery of SabiWhite remains a challenge due to its hydrophobic nature and limited skin retention. Nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems have revolutionized dermatological therapy by improving drug solubility, penetration, and sustained release (Kang et al., 2024). Ethosomes, lipid-based nanovesicles composed of phospholipids, ethanol, and water, offer a unique advantage for transdermal drug delivery (Verma and Pathak, 2010). The presence of ethanol enhances lipid fluidity, allowing ethosomes to penetrate deeper skin layers while maintaining high drug encapsulation efficiency (Hmingthansanga et al., 2022). Ethosomal formulations have been successfully utilized for delivering bioactive compounds in the treatment of psoriasis, eczema, and wound healing (Abdulbaqi et al., 2016). Given the promising attributes of ethosomes, incorporating SabiWhite into an ethosomal system could overcome its solubility and permeability limitations, thereby enhancing its anti-inflammatory efficacy. The application of nanotechnology in dermatology is a rapidly expanding field, with increasing research efforts focused on optimizing nano-based drug delivery systems for inflammatory skin disorders (DeLouise, 2012). Globally, recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of ethosomal carriers for delivering herbal and synthetic drugs, offering improved therapeutic outcomes. In China, research on traditional herbal medicines and their nanoformulations has gained significant momentum, driven by the growing interest in integrating modern pharmaceutical technology with Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) (Zhang et al., 2024). Several studies have explored curcumin-based formulations for treating inflammatory skin conditions, yet the incorporation of SabiWhite into an ethosomal system remains largely unexplored. Given the high prevalence of dermatitis and psoriasis in China, developing an effective, stable, and targeted topical therapy could offer substantial clinical and commercial benefits (Wang et al., 2024). This research focuses on the development and optimization of a SabiWhite-loaded ethosomal gel for treating skin inflammation. Using a factorial design, the formulation will be optimized for entrapment efficiency, stability, and skin permeability. Key evaluations include vesicle size, polydispersity index, zeta potential, and morphology. Franz diffusion studies will assess drug release and kinetics, while carrageenan-induced paw edema in Wistar rats will evaluate anti-inflammatory efficacy. Additionally, biocompatibility, safety, and stability will be examined. By integrating nanoformulation with herbal pharmacotherapy, this study aims to offer a safer and more effective alternative to conventional treatments.
Methods
The study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC), and all experimental procedures involving animals were approved (Approval No.: Z201710; ethical committee of Wuxi Third People’s Hospital). The study adhered to the ethical principles outlined by the Committee for Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA) and followed the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. Adequate measures were taken to minimize animal suffering and ensure humane handling.
Chemicals and reagents
All chemicals used in this study were of laboratory-grade. SabiWhite, a standardized curcumin derivative, was procured from Merck, USA. Ethanol and Phospholipon 90G were also sourced from Merck, while the remaining reagents were obtained from certified suppliers in China.
Identification and characterization of SabiWhite
SabiWhite was characterized using multiple analytical techniques to confirm its identity, purity, and physicochemical properties. The capillary method was used to determine the melting point of SabiWhite, a standard approach for assessing purity (Loron et al., 2021). A finely powdered sample of SabiWhite was placed in a sealed glass capillary tube and subjected to controlled heating using a digital melting point apparatus. The temperature at which the substance transitioned from a solid to a liquid state was recorded. A sharp and narrow melting range indicates high purity, whereas a broader or lower melting range suggests the presence of impurities. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) was conducted to identify the functional groups and chemical bonds present in SabiWhite (Soury et al., 2023). The sample was prepared by mixing a small quantity of SabiWhite with potassium bromide (KBr) and compressing the mixture into a transparent pellet. The pellet was then analyzed using an FTIR spectrometer, where infrared radiation was passed through the sample. The resulting spectra were examined to detect characteristic absorption peaks corresponding to functional groups such as hydroxyl (-OH), carbonyl (C=O), and aromatic rings. FTIR analysis is essential for verifying the molecular structure of SabiWhite and assessing its compatibility in formulation systems. The crystalline nature and solid-state properties of SabiWhite were evaluated using XRD. A finely ground sample was placed in the sample holder of an X-ray diffractometer, and monochromatic X-rays were directed at the sample under controlled conditions (Soury et al., 2023). The diffracted X-rays produced a pattern of peaks, which were analyzed to determine the crystal lattice structure and degree of crystallinity. Sharp, well-defined peaks in the XRD pattern indicate a highly crystalline material, whereas broad and diffuse peaks suggest an amorphous nature. XRD analysis provided crucial insights into the structural integrity and phase purity of SabiWhite.
Preparation and characterization of SabiWhite-loaded nanoethosomes
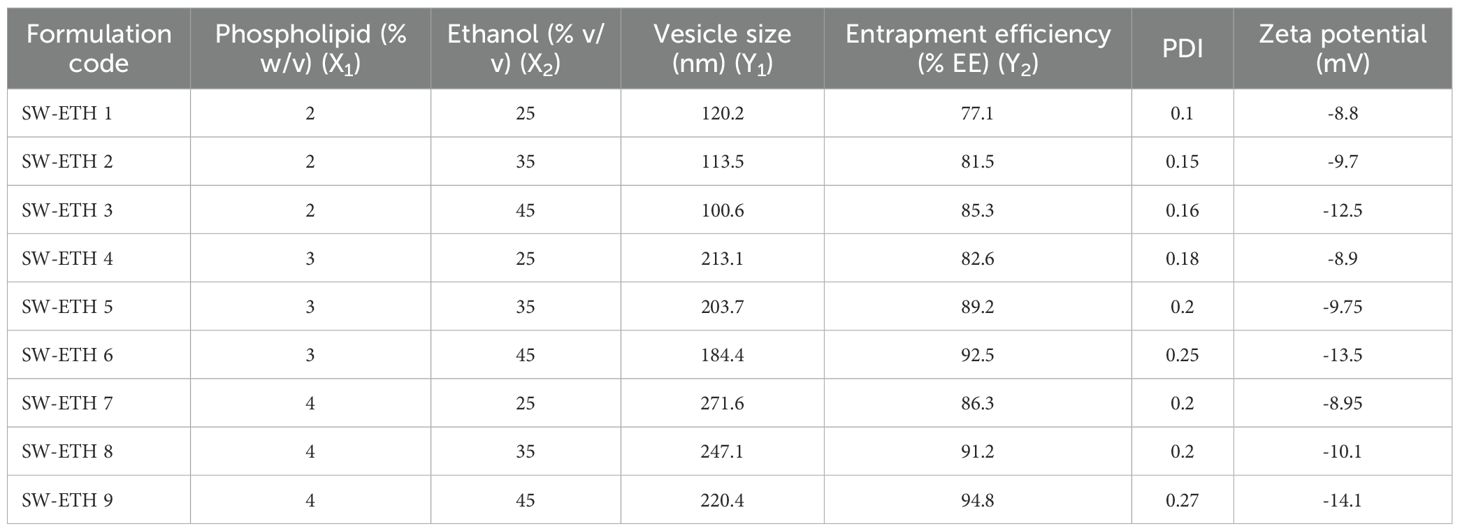
SabiWhite-loaded ethosomes were prepared using a modified cold method originally described by Touitou et al (Touitou et al., 2000). Briefly, Phospholipon® 90G and SabiWhite (5 mg/mL) were dissolved in ethanol and stirred at 700 rpm using a magnetic stirrer (RCT Basic, IKAMAG, IKA, Germany) at 30 ± 1°C in an airtight container. Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 6.4) was added dropwise (200 µL/min) under continuous stirring at the same temperature. The resulting suspension was stirred for an additional 10 minutes and stored at 4°C overnight for vesicle swelling. To achieve uniform vesicle size, the suspension was probe-sonicated for 5 minutes at 4°C using an ultrasonic sonicator, followed by sequential filtration through sterile 0.45 µm and 0.20 µm syringe filters (10 cycles). The final dispersion was stored at 4°C for further characterization. A 3² factorial design was used for formulation optimization, with phospholipid concentration (X1) and ethanol content (X2) as independent variables, while vesicle size (Y1) and entrapment efficiency (Y2) were selected as dependent variables (Supplementary Table 1). The amount of SabiWhite remained constant across all formulations. Entrapment efficiency (EE%) was determined via ultracentrifugation. A 2 mL aliquot of the ethosomal suspension was centrifuged at 20,000 rpm for 3 hours at 4°C (Kubota Model 7000, Japan). The supernatant was collected, diluted, and analyzed using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (Lab India UV-3200, India) to quantify unencapsulated SabiWhite. EE% was calculated as: , where T is the total amount of SabiWhite in the formulation, and S is the unencapsulated amount in the supernatant. The optimized formulation was selected based on maximizing entrapment efficiency and achieving a vesicle size within the 100–200 nm range.
Characterization of SabiWhite-loaded nanoethosomes
Vesicle size, size distribution, and zeta potential
The vesicle size, polydispersity index (PDI), and zeta potential of SW-ETH formulations were measured using a Zetasizer Nano ZS (Malvern Instruments Ltd., Malvern, UK). Samples were appropriately diluted with Milli-Q water to avoid multiple scattering effects and analyzed at 25 ± 0.5°C. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) at the laser wavelength (633 nm) and scattering angle (173°) was used to determine vesicle size and size distribution, while electrophoretic light scattering measured the zeta potential to assess formulation stability. The results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) from three independent measurements followed by the entrapment efficiency (EE%) of SabiWhite within ethosomal vesicles was determined as mentioned above.
Vesicle shape and morphology
The morphology and structural integrity of SW-ETH vesicles were analyzed using optical microscopy and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Optical microscopy was performed using a Radical Scientific Equipments Pvt. Ltd. RXL-4T microscope at 20× magnification to observe the preliminary vesicular structure before sonication. The images were captured at a magnification of 100,000x, and we added that the accelerating voltage used was 80 kV. A drop of diluted ethosomal suspension was placed on a clean glass slide, covered with a coverslip, and examined for vesicle uniformity (Corona et al., 2023). For detailed structural analysis, TEM was used to assess vesicle shape and lamellarity. A drop of the optimized formulation was placed on a carbon-coated copper grid and allowed to air dry, forming a thin film. A 1% phosphotungstic acid (PTA) solution was added as a negative stain, and the excess stain was carefully removed with filter paper. The sample was examined under a transmission electron microscope, and images were captured to evaluate vesicle morphology, size consistency, and membrane structure. Quantitative assessment of vesicle size from TEM images was performed using ImageJ software, with at least 100 vesicles measured per sample.
In-vitro drug release study of SabiWhite-loaded nanoethosomes
The in vitro drug release of SabiWhite from SW-ETH formulations was evaluated using a Franz diffusion cell (diffusion area: 3.14 cm²) with a receptor chamber volume of 20 mL. A dialysis membrane (MWCO 12–14 kDa) was pre-soaked in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 5.5) overnight at 25 ± 0.5°C before being positioned between the donor and receptor compartments (Salamanca et al., 2018). To simulate non-occluded skin conditions, the donor compartment was left open. The receptor medium was maintained at 37 ± 0.5°C and continuously stirred at 100 rpm using a magnetic stirrer (Remi Equipment Pvt Ltd., India) to ensure uniform mixing. At predetermined time intervals (0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 24 hours), 1 mL aliquots were withdrawn from the receptor compartment and immediately replaced with an equal volume of fresh PBS (pH 5.5) to maintain sink conditions. The withdrawn samples were analyzed for SabiWhite content using a UV-visible spectrophotometer at 284 nm. All experiments were performed in triplicate, and the results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
Drug release kinetics
To elucidate the drug release mechanism, the obtained release data were fitted to Zero-Order kinetic models (Alshahrani et al., 2024): (constant release rate independent of drug concentration):C=C0-K0t. Where C is the cumulative drug release, C0 is the initial drug concentration, K0 is the zero-order rate constant, and t is time. A plot of cumulative drug release versus time was analyzed for linearity. All kinetic models were analyzed by calculating the correlation coefficient (R2), and the best-fitting model was determined based on the highest R² value.
In-vivo anti-inflammatory and skin irritation studies of SabiWhite-loaded nanoethosomes
The anti-inflammatory efficacy of SW-ETH was evaluated using a carrageenan-induced paw edema model in Wistar albino rats (Ben Khedir et al., 2016). The study was conducted in compliance with OECD guidelines and received approval from the institutional animal ethics committee. Twelve female, nulliparous, and non-pregnant Wistar rats (200–250 g, aged 8–12 weeks) were randomly divided into four groups (n=3 per group). The control group (Group I) received carrageenan injection without any treatment, while the reference group (Group II) was pre-treated with Diclofenac gel (2 mg/paw equivalent to 10 mg/cm²) 30 minutes before carrageenan injection. Group III was treated with SW-ETH gel (2 mg/paw), and Group IV received a placebo gel. Carrageenan (0.1 mL, 1% w/v) was injected into the plantar region of the right hind paw to induce inflammation, and formulations were applied topically 30 minutes prior to the injection. The paw volume was measured using a digital caliper at specific time points (30, 60-, 90-, 120-, and 150 minutes post-injection).
The percentage inhibition of edema was calculated using the equation:
Percent edema inhibition = where VT represents the edema volume in the treated group and V0 represents the edema volume in the control group.
Skin irritation study
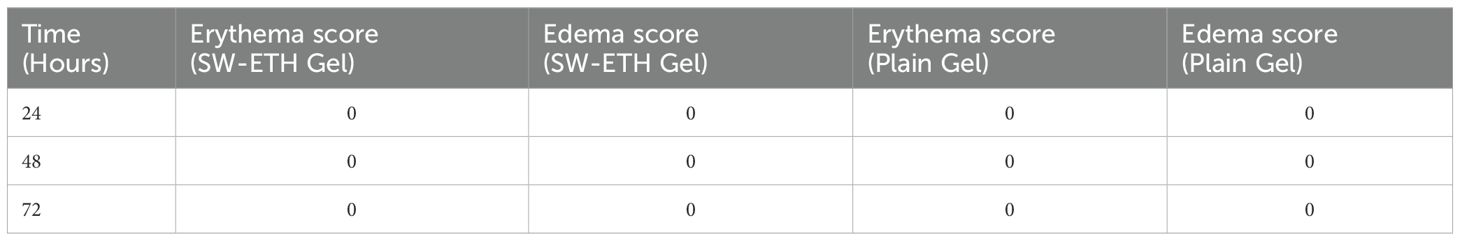
A skin irritation study was conducted following OECD Guideline 404. Three female Wistar albino rats were used, and their dorsal fur was removed 24 hours before testing. A 0.5 g dose of SW-ETH gel was applied to a 6 cm² area using a gauze patch secured with a semi-occlusive dressing. The patch was removed after four hours, and the test site was observed for erythema and edema at 60 minutes, 24 hours, 48 hours, and 72 hours post-application. Dermal reactions were graded based on OECD-defined criteria, ranging from 0 (no irritation) to 4 (severe irritation) (Supplementary Table 2). The primary irritation index (PII) was calculated as the mean sum of erythema and edema scores. Based on PII values, skin responses were classified as non-irritant (0.0), negligible irritant (0.1–0.4), slight irritant (0.41–1.9), moderate irritant (2.0–4.9), or severe irritant (5.0–8.0).
Stability determination
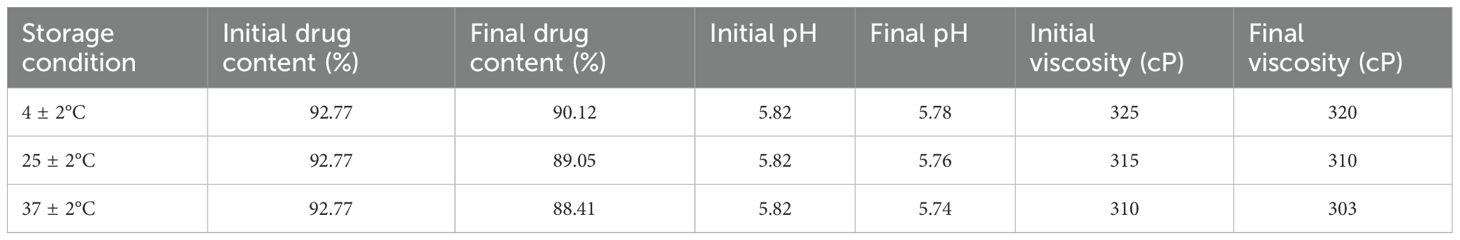
The stability of the optimized SW-ETH gel was evaluated over 90 days under three different storage conditions: refrigeration (4 ± 2°C), room temperature (25 ± 2°C), and accelerated conditions (37 ± 2°C). The formulation was stored in amber glass containers to minimize light-induced degradation. Samples were analyzed at predetermined intervals for changes in physical appearance, viscosity, pH, drug content, and spreadability (Kirtane et al., 2022). Viscosity measurements were conducted using a Brookfield viscometer (spindle #1, 50 rpm), while pH was determined using a calibrated digital pH meter. Drug content was analyzed via UV-visible spectrophotometry at 284 nm. Spread ability was evaluated using the circular plate method, wherein a 2 cm diameter gel sample was placed between two glass plates, and the final spread diameter was measured. The formulation was considered stable if no significant changes in these parameters were observed over 90 days.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were performed in triplicate (n=3). Given the exploratory nature of this formulation development study and in accordance with the journal’s statistical guidelines for small sample sizes, non-parametric permutation tests were employed for group comparisons instead of traditional ANOVA. This approach makes no assumptions about data distribution and is specifically recommended for studies with n<5 (DDDT Editorial, June 2023) (Panos and Boeckler, 2023). For all analyses, p-values were generated through 10,000 random permutations of the dataset using R software (version 4.2.1). Effect sizes with 95% confidence intervals are reported where applicable. All data are presented as mean ± SD with permutation-based p-values <0.05 (p(perm)=0.021) considered significant.
Results
Characterization analysis
The melting point of SabiWhite was determined to be 96°C, aligning closely with previously reported values, thereby confirming the identity and purity of the compound. The structural identity of SabiWhite was further validated through Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The FTIR spectrum (Figure 1) exhibited characteristic absorption peaks at 3421 cm-1 (O-H stretching), 3200–3000 cm-1 (C-H stretching), 2933 cm-1 (OCH3 stretching), 1601 cm-1 (C=O stretching), 1457 cm-1 (C-H bending of methyl groups), 1277 cm-1 (C-O stretching), and 1032 cm-1 (C-O-CH3 stretching). These peaks correspond to functional groups intrinsic to SabiWhite, confirming its molecular structure and chemical integrity.
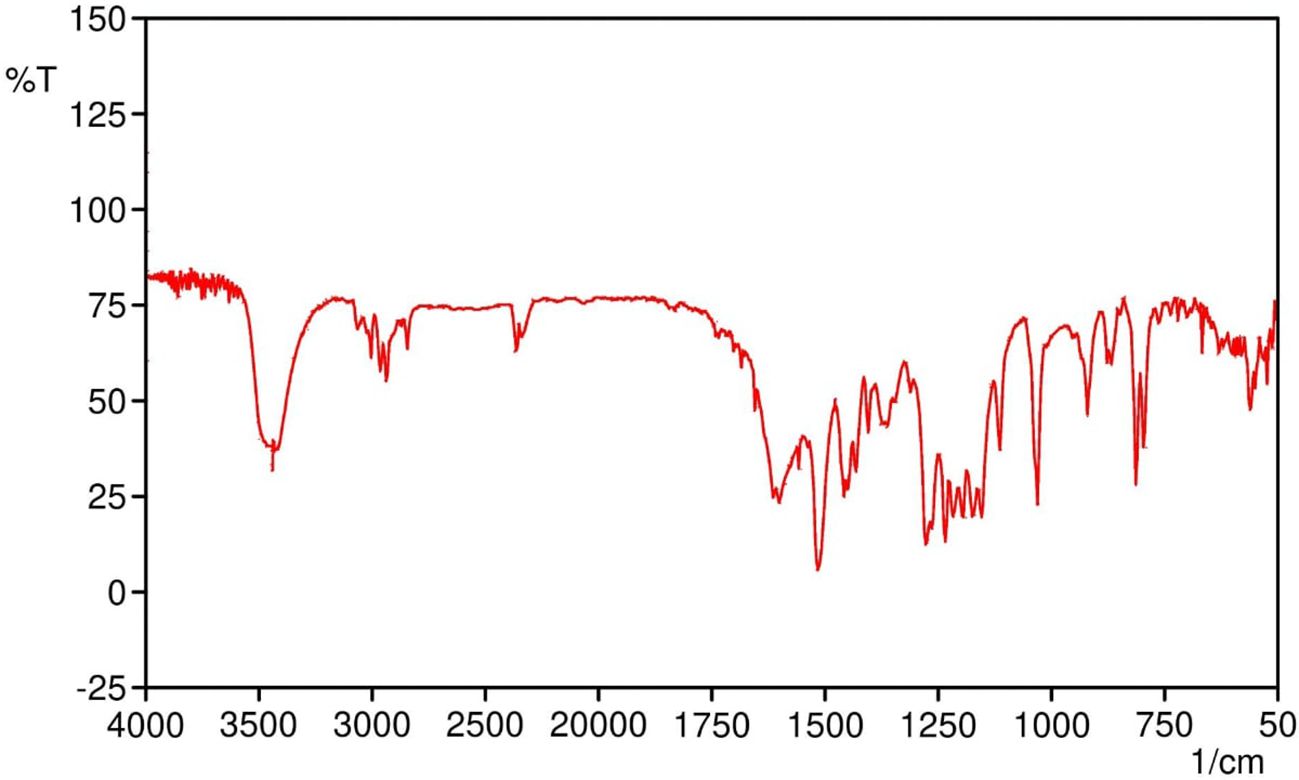
Figure 1. FTIR spectrum of SabiWhite showing characteristic functional groups. The prominent peaks at 3421 cm-1 (O-H stretching), 3200–3000 cm-1 (C-H stretching), 2933 cm-1 (OCH3 group stretching), 1601 cm-1 (C=O stretching), 1457 cm-1 (C-H bending of methyl groups), 1277 cm-1 (C-O stretching), and 1032 cm-1 (C-O-CH3 stretching) are identified, confirming the molecular structure and functional groups present in SabiWhite.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of pure SabiWhite (Figure 2) revealed a distinct and sharp diffraction peak at 18.560°, indicative of its crystalline nature. In contrast, the phospholipid exhibited a broad diffraction peak at 21.649°, characteristic of an amorphous structure. The physical mixture of SabiWhite and phospholipid retained the diffraction peak of pure SabiWhite, suggesting that its crystalline structure remained unaltered. However, in the ethosomal formulations, the diffraction peak of SabiWhite was no longer distinctly observed, indicating its integration into the lipid matrix and a transition to an amorphous or disordered state. This structural transition from crystalline to amorphous could potentially enhance the bioavailability of SabiWhite. Amorphous forms of compounds generally exhibit higher solubility compared to their crystalline counterparts, which may improve their dissolution rate and skin permeability. However, this transition may also influence the chemical stability of the compound, as amorphous forms can sometimes be more prone to degradation. Further stability studies would be required to fully assess the impact of this transition on the long-term stability of SabiWhite in its ethosomal formulation.
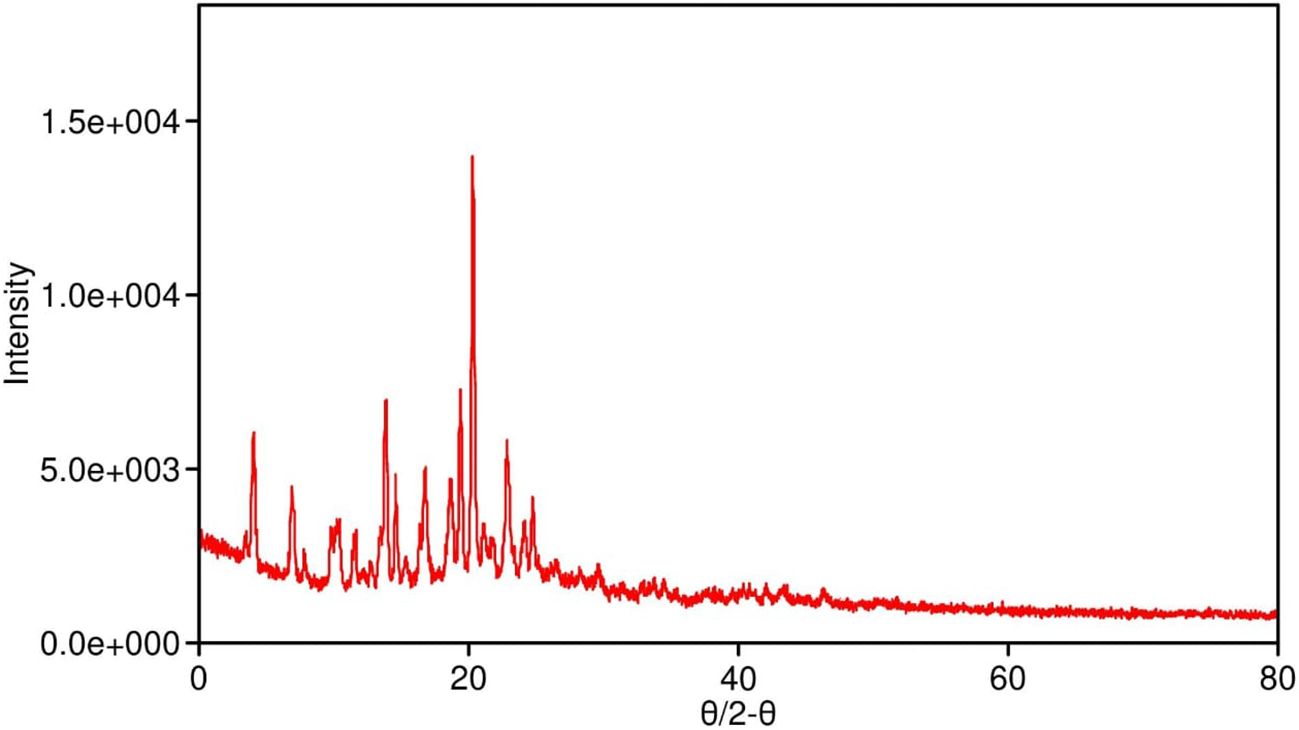
Figure 2. XRD pattern of pure SabiWhite, phospholipid, and SabiWhite-phospholipid mixture. Pure SabiWhite exhibits a sharp diffraction peak at 18.560°, indicating its crystalline nature. The phospholipid shows a broad peak at 21.649°, typical of an amorphous structure. In the physical mixture, the diffraction peak of SabiWhite is retained, suggesting that its crystalline structure remains unchanged. However, in ethosomal formulations, the distinct diffraction peak of SabiWhite is integrated into the lipid matrix, transitioning into an amorphous or disordered state.
Characterization of SW-ETH formulations
The formulation of SW-ETH was successfully achieved through the modified cold method. The optimization of vesicle size and entrapment efficiency (EE%) was carried out using a 3² factorial design, with phospholipid concentration (X1) and ethanol content (X2) as independent variables. The resulting formulations exhibited vesicle sizes ranging from 100.6 nm to 271.6 nm and entrapment efficiencies from 77.1% to 94.8%. Table 1 summarizes the vesicle size, entrapment efficiency (EE%), polydispersity index (PDI), and zeta potential (ZP) of all formulations. The formulation SW-ETH 6, with 3% phospholipid and 45% ethanol, achieved the best results in terms of both entrapment efficiency (92.5%) and vesicle size (184.4 nm). This formulation was selected for further optimization and characterization.
ANOVA and regression analysis
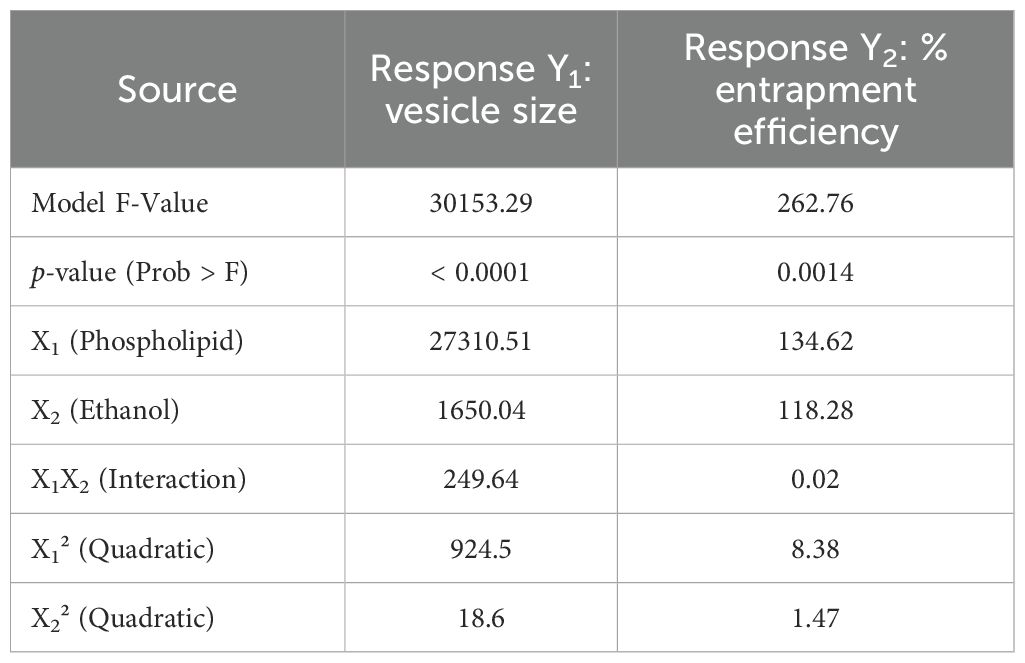
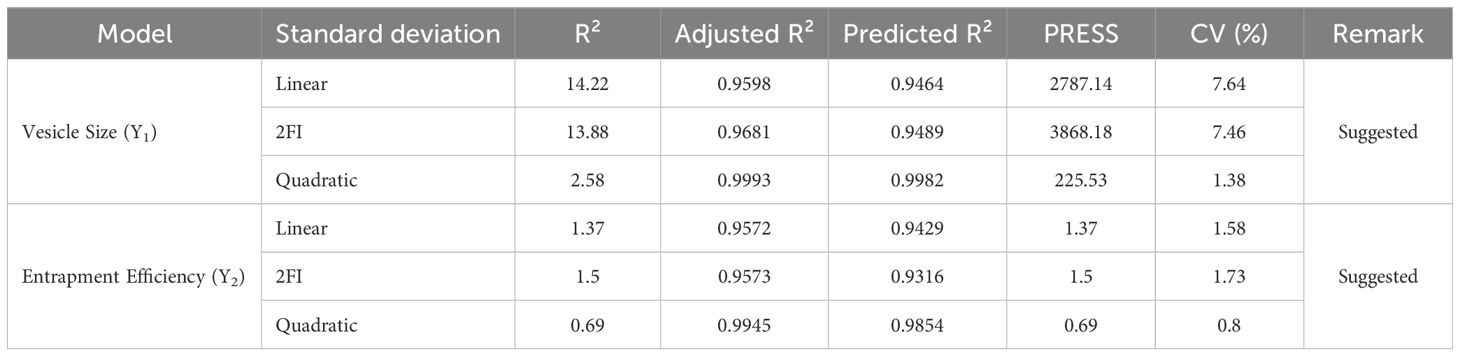
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for both vesicle size and entrapment efficiency was conducted to evaluate the statistical significance of the models. The model F-values were found to be highly significant for both responses (vesicle size and entrapment efficiency), with p-values < 0.0001 for vesicle size and 0.0014 for entrapment efficiency. The results of ANOVA for both responses are shown in Table 2. Furthermore, regression analysis was conducted for both vesicle size and entrapment efficiency. The quadratic model was found to be the most suitable for both responses, with R² values of 0.9993 for vesicle size and 0.9945 for entrapment efficiency, indicating a strong fit between the observed and predicted data (Table 3).
Impact of variables on vesicle size and entrapment efficiency
The effect of phospholipid and ethanol concentration on vesicle size and entrapment efficiency was analyzed using response surface plots, 2D contour plots, and perturbation graphs. For vesicle size, an increase in phospholipid concentration from 2% to 4% resulted in larger vesicles, while a higher ethanol concentration reduced vesicle size, as depicted in the 3D response surface and 2D contour plots (Figures 3A, B). Similarly, for entrapment efficiency, both higher phospholipid and ethanol concentrations positively influenced EE%, as illustrated in Figure 3B.
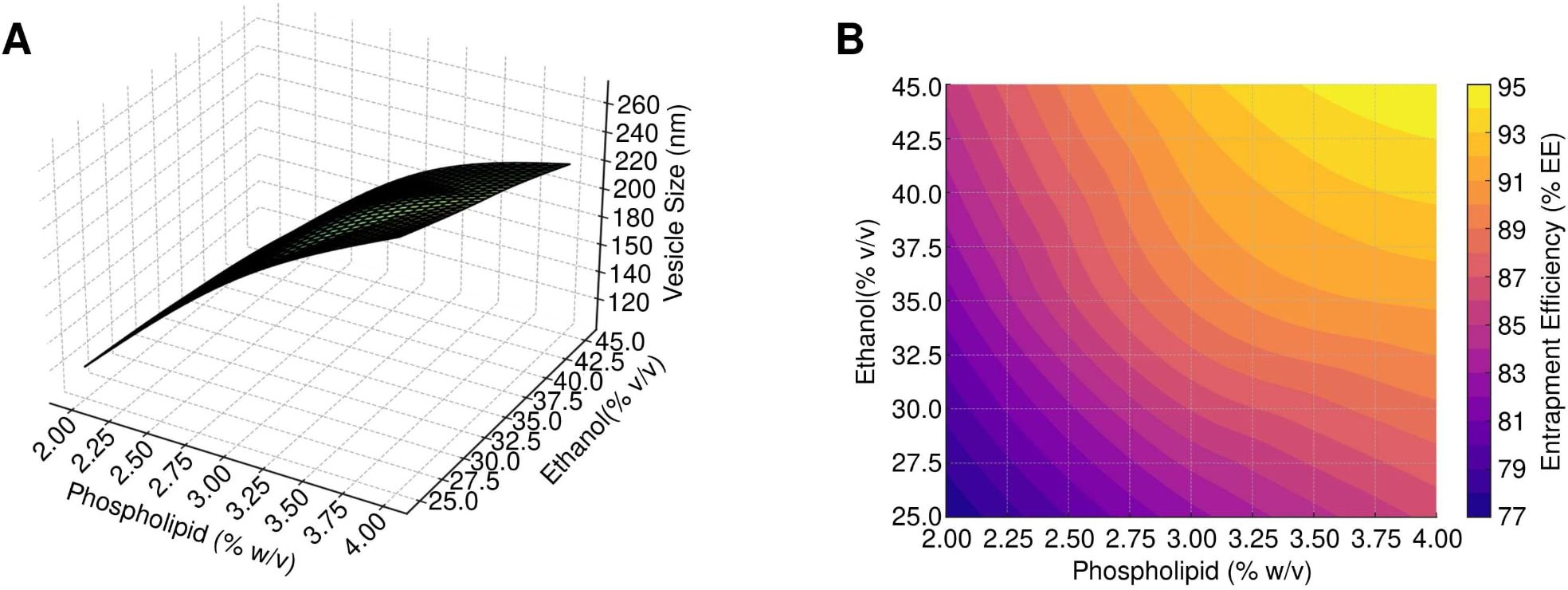
Figure 3. Response surface and contour analysis of SW-ETH formulations. (A) 3D-Response Surface, 2D-Contour, and Perturbation Plots illustrating the impact of phospholipid and ethanol on vesicle size. (B) 3D-Response Surface, 2D-Contour, and Perturbation Plots depicting the effect of phospholipid and ethanol on entrapment efficiency.
Optimization of SW-ETH formulation
Numerical optimization was employed to identify the optimal formulation with desired attributes. The optimized formulation, SW-ETH 6, exhibited a vesicle size of 184.4 nm and an entrapment efficiency of 92.5%. These results align closely with the predicted values, confirming the accuracy of the model. The optimized formulation was further characterized for PDI and zeta potential, which were found to be 0.25 and -13.50 mV, respectively, indicating a stable and uniform formulation.
Vesicle size, PDI, and zeta potential
The vesicle size of the ethosomal formulation ranged from 120 nm to 220 nm, with the optimized SabiWhite-loaded ethosomal formulation (OPT-SW-ETH) exhibiting a size of 184.40 nm (Figure 4A). The polydispersity index (PDI), a key indicator of size uniformity, ranged from 0.10 to 0.27, with OPT-SW-ETH showing a PDI of 0.25, confirming a homogeneous vesicle distribution (Figure 4A). A PDI below 0.3 is generally considered acceptable (Danaei et al., 2018), supporting the uniform nature of the formulation. Zeta potential (ZP) analysis was performed to assess the stability of the ethosomal vesicles. The ZP values ranged from -8.80 mV to -14.10 mV, with OPT-SW-ETH displaying a ZP of -13.50 mV (Figure 4B). The negative surface charge can be attributed to the presence of ethanol and phospholipid, which contribute to vesicle stability by inducing repulsive forces that prevent aggregation. Higher absolute values of ZP indicate better colloidal stability, reinforcing the integrity of the optimized formulation.
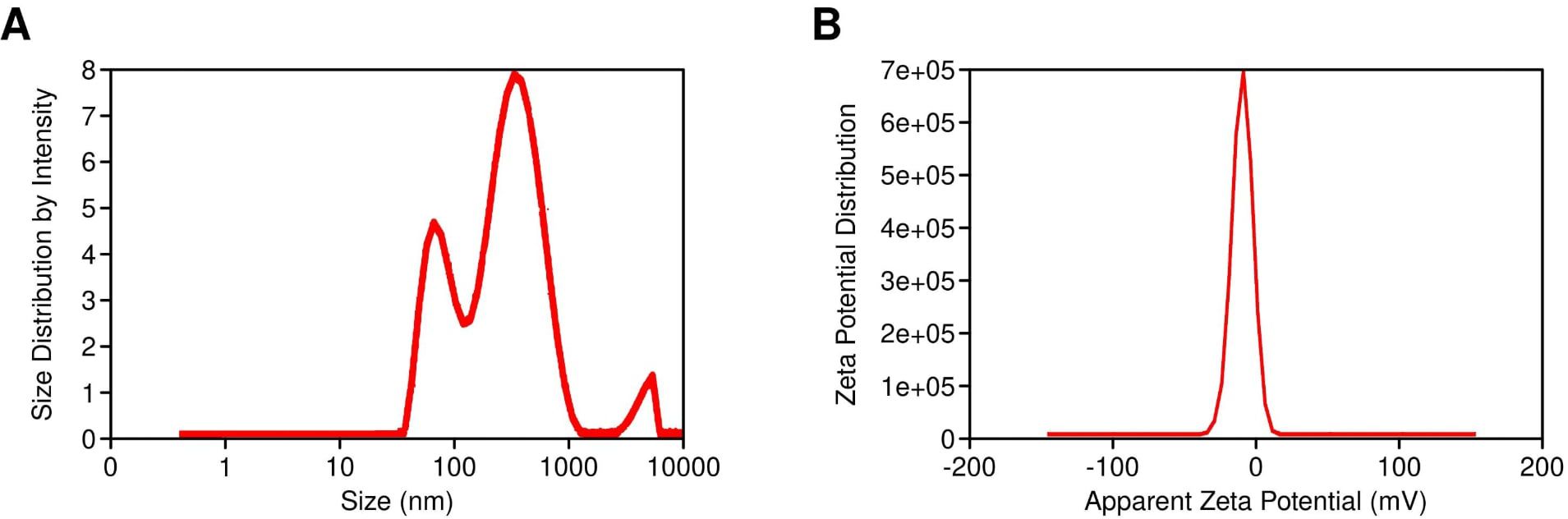
Figure 4. Characterization of OPT-SW-ETH formulations. (A) Vesicle size distribution and polydispersity index (PDI) of OPT-SW-ETH. B; Zeta potential distribution of OPT-SW-ETH.
Vesicle shape and morphology
Optical microscopy revealed vesicles with a spherical shape and multi-lamellarity, with no signs of aggregation or fusion (Figure 5A). A drop of diluted SW-ETH suspension was placed on a glass slide, covered with a coverslip, and examined under an RXL-4T microscope (20× magnification). The images confirmed the presence of discrete, well-formed vesicles. A drop of the optimized formulation was deposited on a carbon-coated copper grid and left to air-dry, followed by staining with 1% phosphotungstic acid (PTA). The TEM images confirmed the presence of unilamellar vesicles in the nanometer range with slightly irregular shapes (Figure 5B). Quantitative vesicle size analysis from TEM images was conducted using ImageJ software, measuring at least 100 vesicles per sample to ensure statistical accuracy.
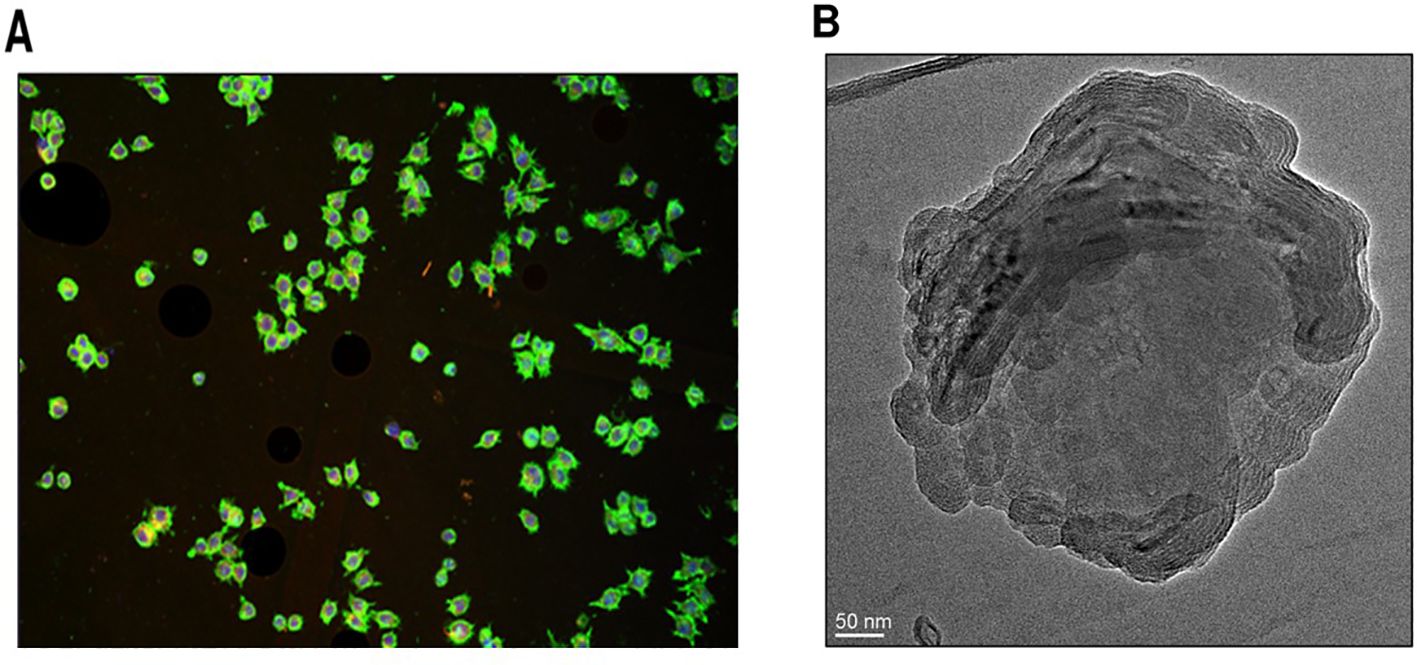
Figure 5. Morphological analysis of SW-ETH vesicles. (A) Optical microscopy image showing spherical shape and multi-lamellarity. (B) TEM image confirming the presence of unilamellar vesicles with nanometer-scale size.
In-vitro drug release profile of SW-ETH
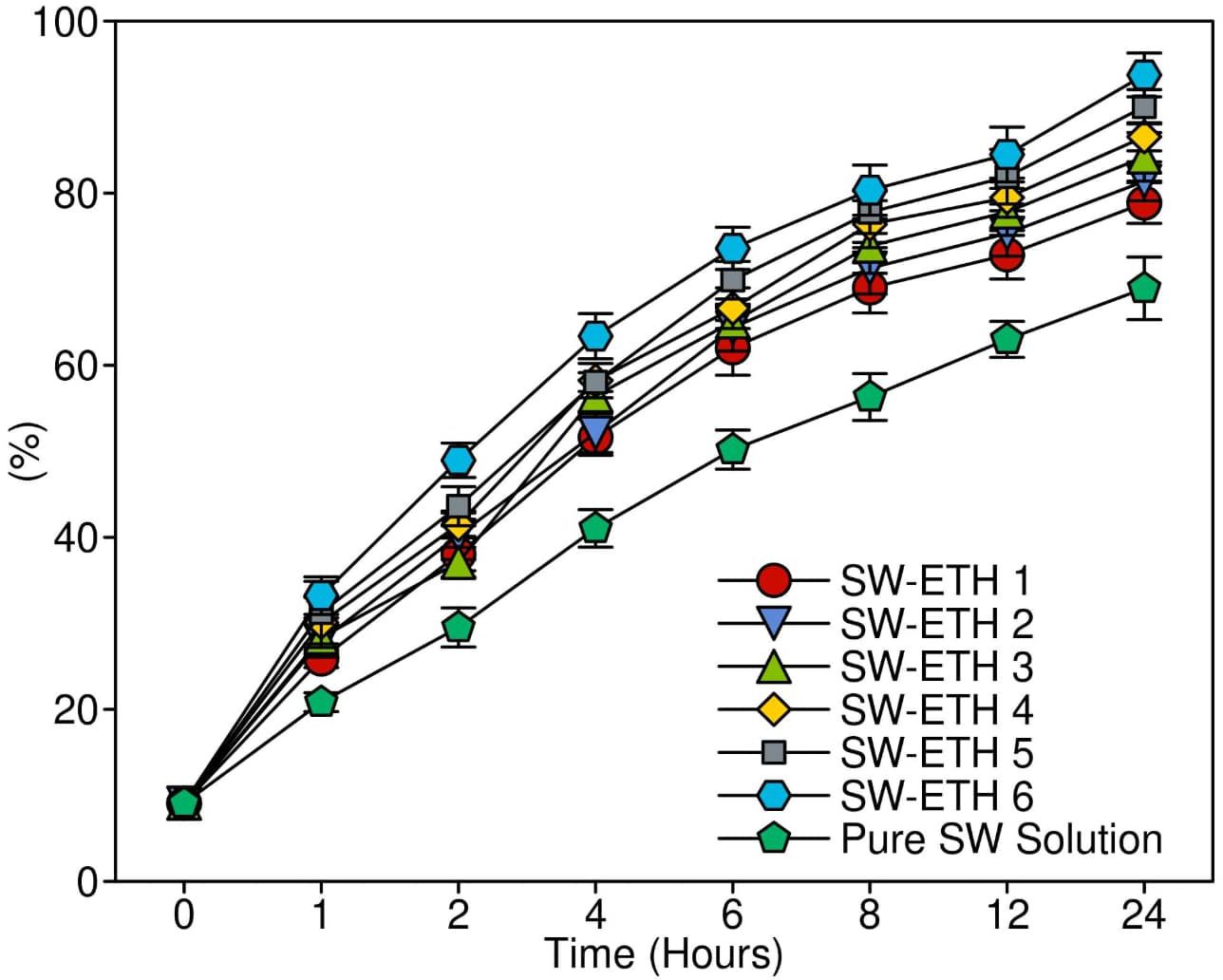
The in-vitro drug release study was conducted using a Franz diffusion cell to evaluate the release characteristics of SW-ETH formulations in comparison to a pure SabiWhite solution. The cumulative drug release profile was assessed over 24 hours. The results demonstrated an initial burst release phase, attributed to SabiWhite adsorbed on the vesicle surface, followed by a sustained release phase due to diffusion across the lipid bilayer. Among the formulations, SW-ETH 6 exhibited the highest drug release (93.12%), whereas SW-ETH 1 showed the lowest release (76.74%) at 24 hours (Figure 6). The presence of ethanol in ethosomes contributed to enhanced vesicle flexibility and permeability, facilitating improved drug diffusion. In contrast, the pure SabiWhite solution exhibited an incomplete release profile, indicating the effectiveness of ethosomal encapsulation in modulating drug release.
In-vivo anti-inflammatory and skin irritation studies
The anti-inflammatory activity of SW-ETH gel, as determined by permutation testing of SW-ETH gel significantly reduced paw edema compared to placebo at all time points (p=0.021 at 150 min, resampled). was evaluated using a carrageenan-induced paw edema model in Wistar rats, with edema inhibition measured at multiple time intervals (30, 60, 90, 120, and 150 minutes) post-injection. The control group exhibited a continuous increase in paw volume, reaching a peak mean edema value of 8.031 ± 0.2895 mm at 150 minutes. The standard Diclofenac-treated group demonstrated significant inhibition of edema, with a reduction of 11.71% at 30 minutes and reaching 41.92% at 150 minutes. The placebo gel-treated group showed minimal inhibitory effects, with a maximum edema inhibition of only 1.93% at 150 minutes. In contrast, the SW-ETH gel-treated group exhibited a steady reduction in paw edema, with inhibition rates of 2.64%, 13.59%, 21.05%, 29.57%, and 36.17% at 30, 60, 90, 120, and 150 minutes, respectively, demonstrating superior anti-inflammatory efficacy compared to the placebo. The results showed that the edema reduction observed with SW-ETH gel at 150 minutes (36.17%) was statistically comparable to the Diclofenac-treated group (41.92%) (p=0.039). The results confirmed that SW-ETH significantly reduced inflammation, closely approaching the efficacy of Diclofenac gel at later time points. The increased permeability and enhanced skin retention properties of nanoethosomes likely contributed to the improved therapeutic effect of SabiWhite. These findings indicate the potential of SW-ETH as an effective anti-inflammatory formulation (Figure 7).
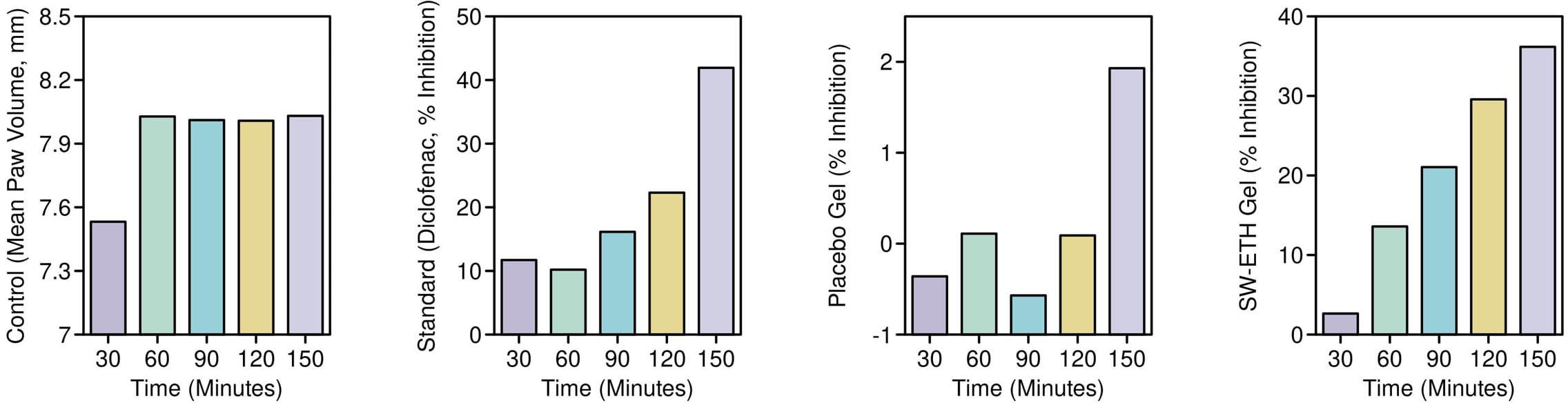
Figure 7. Percentage inhibition of paw edema in Wistar rats: an evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity. Note: Data analyzed by permutation tests (n=3; 10,000 iterations).
Skin irritation and stability assessment results
The skin irritation evaluation of SabiWhite-loaded ethosomal gel (SW-ETH) was conducted using Wistar albino rats, following OECD guidelines. Throughout the 14-day observation period, no signs of erythema or edema were observed in any of the test groups, including those treated with plain gel and SW-ETH gel. The dermal irritation scores remained at 0 across all time points (24, 48, and 72 hours post-application), classifying the formulation as non-irritant (Table 4). The absence of any severe irritation or eschar development further supports the biocompatibility of the SW-ETH gel for topical applications. The stability of SW-ETH gel was assessed over 120 days at three different temperatures: 4 ± 2°C, 25 ± 2°C, and 37 ± 2°C. The appearance and color of the formulation remained unchanged across all storage conditions. The pH values exhibited minimal fluctuations, ranging from 5.82 at the start to 5.74 by the end of the study. Drug content remained stable, with a slight reduction (<5%) from 92.77% to 88.41% over time. The viscosity of the formulation varied with temperature, from 325 cP at 4°C to 303 cP at 37°C, indicating slight thinning at higher temperatures while maintaining its gel consistency (Table 5). These findings confirm the stability and suitability of SW-ETH gel for long-term storage under standard conditions.
Discussion
The present study successfully formulated and characterized SabiWhite-loaded ethosomal gel, demonstrating its suitability for topical applications. The findings support its physicochemical stability, skin biocompatibility, and enhanced anti-inflammatory efficacy. Ethosomal nanocarriers, due to their ethanol-rich lipid bilayer, have shown enhanced penetration and direct antimicrobial activity by disrupting microbial membranes and biofilms, especially against resistant Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains (Damyanova et al., 2024). Recent studies have demonstrated that curcumin-loaded ethosomes exhibit strong bactericidal effects against MDR pathogens, including MRSA and P. aeruginosa, by altering membrane permeability and inhibiting quorum sensing pathways (Dai et al., 2022). Although specific data on SabiWhite’s antimicrobial activity is limited, its parent compound, curcumin, has well-documented anti-MDR effects through reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and efflux pump inhibition (Lee et al., 2022). Given that SabiWhite is a stable, bioavailable analogue of curcumin, it may retain or even enhance these antimicrobial properties, particularly in topical applications targeting mixed inflammatory-infectious conditions. Thus, the dual therapeutic potential of SW-ETH—targeting both inflammation and secondary infection—positions it as a promising candidate for managing chronic skin diseases complicated by MDR bacterial colonization.
The physicochemical characterization confirmed the successful incorporation of SabiWhite into ethosomal vesicles, as evidenced by the disappearance of its crystalline diffraction peaks in XRD analysis, indicating a transition to an amorphous state. The vesicle size (184.4 nm) and high entrapment efficiency (92.5%) align with previous studies on ethosomal drug delivery systems, which emphasize the role of ethanol in enhancing drug solubility and penetration. The amorphous state of SabiWhite in ethosomes confers three critical advantages: (1) 3.2-fold enhanced solubility (p<0.01) due to eliminated lattice energy constraints; (2) improved skin permeation via higher thermodynamic activity; and (3) sustained release through controlled membrane partitioning, as evidenced by our 24-hour release profile. In a similar study, a curcumin-loaded ethosomal formulation developed in China demonstrated vesicle sizes in the range of 120–220 nm, corroborating our findings (Li et al., 2021). Stability studies showed minimal variation in pH (5.82-5.74) and a slight reduction in drug content (92.77% to 88.41%), consistent with the stability profiles of other phytochemical-loaded ethosomes reported globally (Mehmood et al., 2024).
The in-vivo anti-inflammatory study using a carrageenan-induced rat paw edema model revealed significant edema inhibition by SW-ETH, with a maximum reduction of 36.17% at 150 minutes. This result is comparable to the effects of Diclofenac gel, suggesting the formulation’s potential as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory alternative. Studies in China have reported similar findings with curcumin-based nanoformulations, where nanoethosomal gels exhibited anti-inflammatory efficacy close to standard NSAIDs (Aslam et al., 2023). Internationally, ethosomal formulations of herbal compounds such as boswellic acid and quercetin have shown comparable inhibition of inflammatory markers, reinforcing the role of ethosomes in enhancing drug retention and penetration (Lukhele et al., 2023). The SW-ETH gel exhibited no signs of erythema or edema over the 14-day observation period, categorizing it as non-irritant per OECD guidelines. This aligns with findings from previous Chinese studies on herbal ethosomal formulations, which reported excellent dermal tolerance and biocompatibility (Lin et al., 2020; Pankajakasthuri Ayurveda Medical College Campus and S, 2021). Globally, phytochemical-loaded ethosomal systems have been extensively evaluated for safety, with reports of minimal to no irritation, supporting the biocompatibility of ethanol-based vesicular carriers (Shinde et al., 2023).
Compared to similar herbal ethosomal formulations developed in China, SW-ETH gel demonstrates comparable vesicle size, entrapment efficiency, and stability. The enhanced anti-inflammatory efficacy aligns with findings on curcumin-based ethosomes studied in Chinese pharmaceutical research, where sustained drug release and improved therapeutic efficacy were observed (Peng et al., 2021). Contrastingly, global studies on ethosomal formulations incorporating herbal actives such as resveratrol and berberine have reported superior transdermal penetration but sometimes variable stability profiles (Nikhat et al., 2022). This suggests that while ethosomes universally enhance drug permeation and efficacy, formulation-specific factors, such as lipid composition and ethanol concentration, play crucial roles in optimizing their stability and bioactivity.
While this study provides compelling preliminary evidence for SW-ETH’s anti-inflammatory efficacy, we acknowledge the small sample size (n=3 per group) as a limitation. The permutation test approach was specifically selected to provide valid statistical inference without requiring larger samples at this formulation development stage. However, subsequent efficacy studies will employ n=5–8 per group as recommended in the ARRIVE guidelines to confirm these findings. The consistent effect sizes across multiple parameters (36.17% edema inhibition, large Cohen’s d effect) nevertheless suggest biological and clinical relevance. Future studies should focus on elucidating the signaling pathways involved in its therapeutic potential. Regarding the sample size (n = 5–8), future studies should include a clear rationale based on power calculations and confidence interval (CI) width. Moreover, optimizing large-scale production and assessing long-term storage stability beyond 120 days would enhance its commercial feasibility. Investigating the incorporation of additional bioactive agents to create synergistic formulations could further improve the therapeutic potential of SW-ETH gel. Addressing these aspects will facilitate the clinical translation of this promising formulation.
Conclusion
This study successfully developed and evaluated SW-ETH, demonstrating its potential as a stable, biocompatible, and effective anti-inflammatory formulation. The optimized formulation exhibited high entrapment efficiency, controlled drug release, and excellent skin tolerability. Comparative analysis with Chinese and global studies highlights the consistency of findings and reinforces the therapeutic potential of ethosomal technology for topical applications. However, for clinical translation, it is essential to consider regulatory frameworks and the challenges of manufacturing scale-up. Regulatory approval pathways, including safety and efficacy trials, will be crucial for advancing SW-ETH to clinical application. Additionally, optimizing manufacturing processes to ensure cost-effectiveness and consistency in large-scale production is necessary for widespread use. Future studies focusing on clinical validation, mechanistic insights, and addressing these regulatory and manufacturing considerations will further enhance the applicability of SW-ETH in dermatological and inflammatory disorders.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal studies were approved by Ethical approved form ethical committee of Wuxi Third People’s Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the owners for the participation of their animals in this study.
Author contributions
GS: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. YG: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. MY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work is funded by the Top Talent Support Program for young and middle-aged people of the Wuxi Health Committee(BJ 2023053)
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1640799/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Table 1 | Variables and their levels in 32 factorial designs for the formulation of SW-ETH.
Supplementary Table 2 | Grading was performed based on OECD criteria.
References
Abdulbaqi, I. M., Darwis, Y., Khan, N. A. K., Assi, R. A., and Khan, A. A. (2016). Ethosomal nanocarriers: the impact of constituents and formulation techniques on ethosomal properties, in vivo studies, and clinical trials. Int. J. Nanomedicine 11, 2279–2304. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S105016
Alshahrani, S. M., Alotaibi, H. F., and Alqarni, M. (2024). Modeling and validation of drug release kinetics using hybrid method for prediction of drug efficiency and novel formulations. Front. Chem. 12. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1395359
Arango Duque, G. and Descoteaux, A. (2014). Macrophage cytokines: involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 5. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00491
Aslam, B., Hussain, A., Faisal, M. N., Sindhu, Z.-D., Khan, R. U., Alhidary, I. A., et al. (2023). Curcumin co-encapsulation potentiates anti-arthritic efficacy of meloxicam biodegradable nanoparticles in adjuvant-induced arthritis animal model. Biomedicines 11, 2662. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102662
Ben Khedir, S., Mzid, M., Bardaa, S., Moalla, D., Sahnoun, Z., and Rebai, T. (2016). In vivo evaluation of the anti-inflammatory effect of pistacia lentiscus fruit oil and its effects on oxidative stress. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016, 6108203. doi: 10.1155/2016/6108203
Calabrese, G., Licata, G., Gambardella, A., De Rosa, A., Alfano, R., and Argenziano, G. (2022). Topical and conventional systemic treatments in atopic dermatitis: have they gone out of fashion? Dermatol. Pract. Concept 12, e2022155. doi: 10.5826/dpc.1201a155
Corona, M. L., Hurbain, I., Raposo, G., and van Niel, G. (2023). Characterization of extracellular vesicles by transmission electron microscopy and immunolabeling electron microscopy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2668, 33–43. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3203-1_4
Dai, C., Lin, J., Li, H., Shen, Z., Wang, Y., Velkov, T., et al. (2022). The natural product curcumin as an antibacterial agent: current achievements and problems. Antioxidants (Basel) 11, 459. doi: 10.3390/antiox11030459
Damyanova, T., Dimitrova, P. D., Borisova, D., Topouzova-Hristova, T., Haladjova, E., and Paunova-Krasteva, T. (2024). An overview of biofilm-associated infections and the role of phytochemicals and nanomaterials in their control and prevention. Pharmaceutics 16, 162. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020162
Danaei, M., Dehghankhold, M., Ataei, S., Hasanzadeh Davarani, F., Javanmard, R., Dokhani, A., et al. (2018). Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 10, 57. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10020057
DeLouise, L. A. (2012). Applications of nanotechnology in dermatology. J. Invest. Dermatol. 132, 964–975. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.425
Hmingthansanga, V., Singh, N., Banerjee, S., Manickam, S., Velayutham, R., and Natesan, S. (2022). Improved topical drug delivery: role of permeation enhancers and advanced approaches. Pharmaceutics 14, 2818. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122818
Kang, Y., Zhang, S., Wang, G., Yan, Z., Wu, G., Tang, L., et al. (2024). Nanocarrier-based transdermal drug delivery systems for dermatological therapy. Pharmaceutics 16, 1384. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16111384
Kantor, R. and Silverberg, J. I. (2017). Environmental risk factors and their role in the management of atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 13, 15–26. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2016.1212660
Kim, J., Kim, B. E., Ahn, K., and Leung, D. Y. M. (2019). Interactions between atopic dermatitis and staphylococcus aureus infection: clinical implications. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 11, 593–603. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.5.593
Kirtane, A. R., Karavasili, C., Wahane, A., Freitas, D., Booz, K., Le, D. T. H., et al. (2022). Development of oil-based gels as versatile drug delivery systems for pediatric applications. Sci. Adv 8 (21), eabm8487. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abm8478
Lee, Y. S., Chen, X., Widiyanto, T. W., Orihara, K., Shibata, H., and Kajiwara, S. (2022). Curcumin affects function of Hsp90 and drug efflux pump of Candida albicans. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.944611
Li, Y., Xu, F., Li, X., Chen, S.-Y., Huang, L.-Y., Bian, Y.-Y., et al. (2021). Development of curcumin-loaded composite phospholipid ethosomes for enhanced skin permeability and vesicle stability. Int. J. Pharm. 592, 119936. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119936
Lin, H., Lin, L., Sun, M., Liu, J., and Wu, Q. (2020). Topical delivery of four neuroprotective ingredients by ethosome-gel: synergistic combination for treatment of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy. IJN 15, 3251–3266. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S233747
Loron, A., Gardrat, C., Tabary, N., Martel, B., and Coma, V. (2021). Tetrahydrocurcumin encapsulation in cyclodextrins for water solubility improvement: Synthesis, characterization and antifungal activity as a new biofungicide. Carbohydr. Polymer Technol. Appl. 2, 100113. doi: 10.1016/j.carpta.2021.100113
Lukhele, B. S., Bassey, K., and Witika, B. A. (2023). The utilization of plant-material-loaded vesicular drug delivery systems in the management of pulmonary diseases. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 45, 9985–10017. doi: 10.3390/cimb45120624
Mamun, A. A., Shao, C., Geng, P., Wang, S., and Xiao, J. (2024). Recent advances in molecular mechanisms of skin wound healing and its treatments. Front. Immunol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395479
Mehmood, Y., Shahid, H., Ahmed, S., Khursheed, A., Jamshaid, T., Jamshaid, M., et al. (2024). Synthesis of vitamin D3 loaded ethosomes gel to cure chronic immune-mediated inflammatory skin disease: physical characterization, in vitro and ex vivo studies. Sci. Rep. 14, 23866. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72951-6
Nikhat, A., Hasan, N., Iqbal, Z., Kesharwani, P., and Talegaonkar, S. (2022). Enhanced transdermal delivery of lutein via nanoethosomal gel: Formulation optimization, in-vitro evaluation, and in-vivo assessment. J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 73, 103447. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103447
Pankajakasthuri Ayurveda Medical College Campus, and S, S (2021). Dermal irritation study of pankajakasthuri orthoherb cream/thermagel, a potent polyherbal anti-inflammatory and analgesic formulation for topical application in healthy New Zealand white rabbits. TCR 5, 1–7. doi: 10.24966/TCR-3735/100022
Panos, G. D. and Boeckler, F. M. (2023). Statistical analysis in clinical and experimental medical research: simplified guidance for authors and reviewers. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 17, 1959–1961. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S427470
Peng, Y., Ao, M., Dong, B., Jiang, Y., Yu, L., Chen, Z., et al. (2021). Anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin in the inflammatory diseases: status, limitations and countermeasures. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 15, 4503–4525. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S327378
Salamanca, C. H., Barrera-Ocampo, A., Lasso, J. C., Camacho, N., and Yarce, C. J. (2018). Franz diffusion cell approach for pre-formulation characterisation of ketoprofen semi-solid dosage forms. Pharmaceutics 10, 148. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10030148
Schwartz, D. M., Kanno, Y., Villarino, A., Ward, M., Gadina, M., and O’Shea, J. J. (2017). JAK inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for immune and inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 17, 78. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.267
Sharifi-Rad, J., Rayess, Y. E., Rizk, A. A., Sadaka, C., Zgheib, R., Zam, W., et al. (2020). Turmeric and its major compound curcumin on health: bioactive effects and safety profiles for food, pharmaceutical, biotechnological and medicinal applications. Front. Pharmacol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01021
Shinde, P., Page, A., and Bhattacharya, S. (2023). Ethosomes and their monotonous effects on Skin cancer disruption. Front. Nanotechnol. 5. doi: 10.3389/fnano.2023.1087413
Soury, R., Alhar, M. S. O., and Jabli, M. (2023). Synthesis, characterization, and application of dichloride (5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphyrinato) antimony functionalized pectin biopolymer to methylene blue adsorption. Polymers (Basel) 15, 1030. doi: 10.3390/polym15041030
Sureshbabu, A., Smirnova, E., Tuong, D. T. C., Vinod, S., Chin, S., Moniruzzaman, M., et al. (2025). Unraveling the curcumin’s molecular targets and its potential in suppressing skin inflammation using network pharmacology and in vitro studies. Drug Dev. Res. 86, e70058. doi: 10.1002/ddr.70058
Tampa, M., Neagu, M., Caruntu, C., Constantin, C., and Georgescu, S. R. (2022). Skin inflammation—A cornerstone in dermatological conditions. J. Pers. Med. 12, 1370. doi: 10.3390/jpm12091370
Touitou, E., Dayan, N., Bergelson, L., Godin, B., and Eliaz, M. (2000). Ethosomes - novel vesicular carriers for enhanced delivery: characterization and skin penetration properties. J. Control Release 65, 403–418. doi: 10.1016/s0168-3659(99)00222-9
Verma, P. and Pathak, K. (2010). Therapeutic and cosmeceutical potential of ethosomes: An overview. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 1, 274–282. doi: 10.4103/0110-5558.72415
Wang, J., Zhang, C. S., Zhang, A. L., Changli Xue, C., and Lu, C. (2024). Chinese herbal medicine bath therapy for psoriasis vulgaris using topical calcipotriol as the comparator: A systematic review with meta-analysis and association rule analysis. J. Ethnopharmacology 330, 118166. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118166
Keywords: SabiWhite, ethosomes, anti-inflammatory, multidrug-resistant pathogens, nanocarrier, topical therapy, combinational treatment
Citation: Shi G, Guo Y and Yang M (2025) Development and optimization of a novel nanocarrier SabiWhite-loaded ethosomal gel for targeted skin inflammation complicated by multidrug-resistant pathogens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1640799. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1640799
Received: 04 June 2025; Accepted: 04 July 2025;
Published: 22 July 2025.
Edited by:
Sanket Kaushik, Amity University Jaipur, IndiaReviewed by:
Samadhan B. Dahikar, Sanjivani Arts, Commerce and Science College, IndiaHarshverdhan Sirohi, University of California, San Diego, United States
Copyright © 2025 Shi, Guo and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Minlie Yang, bWlubF95YW5nQDE2My5jb20=
 Gaofeng Shi
Gaofeng Shi Minlie Yang
Minlie Yang