- 1School of Clinical Medicine, Guilin Medical University, Guilin, China
- 2Precision Joint Inspection Centre, The People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuangzu Autonomous Region and Guangxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Nanning, China
- 3The First Clinical Medical College of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China
- 4Graduate College, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning, China
- 5Center for Reproductive Medicine and Genetics, The People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuangzu Autonomous Region and Guangxi Academic of Medical Sciences, Nanning, China
CRISPR technology, with its high specificity and programmability, has become an important tool for the detection of human pathogens. The timely and accurate detection of pathogens is crucial for public health. In recent years, significant progress has been made in the application of CRISPR technology for pathogen detection. However, several challenges remain, including detection sensitivity, specificity, and operational convenience. This review summarizes the latest advances in CRISPR technology for pathogen detection, with a focus on the principles and performance comparisons of amplification-based CRISPR (such as those combined with isothermal amplification techniques like RPA and LAMP) and amplification-free CRISPR (such as cascade CRISPR, sensor technologies, and digital droplet CRISPR). It also discusses their applications in pathogen detection. In addition, the article analyzes the advantages and limitations of CRISPR detection technology and looks forward to future development trends, providing a theoretical basis for the optimization of rapid diagnostic techniques for pathogens.
1 Introduction
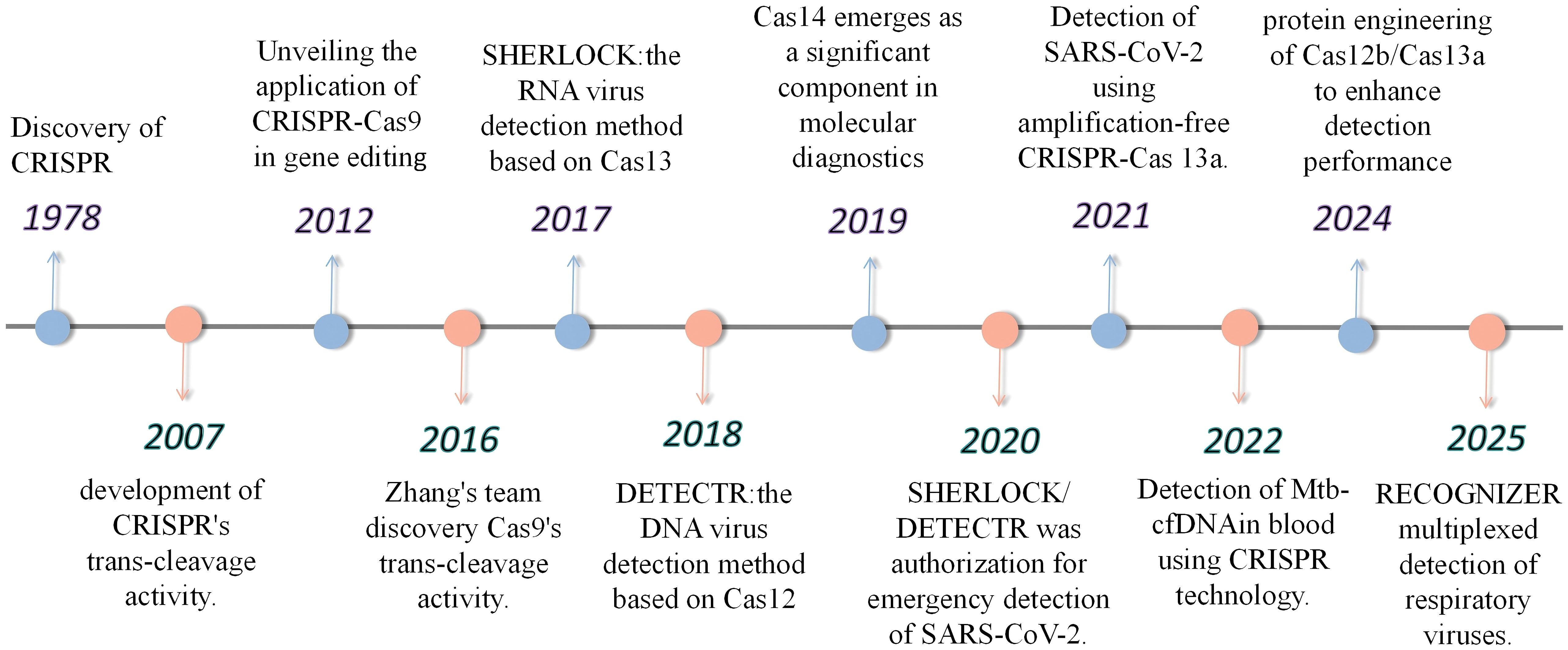
In the field of pathogen detection, various techniques have their own characteristics. Microbial culture, as the “gold standard” for laboratory detection, is capable of determining microbial viability and identifying low-abundance microbes. However, it is time-consuming (usually taking 2–10 days) (Shetty et al., 2003), and demands high technical skills and biosafety precautions, making it unsuitable for rapid detection needs. In immunological detection, antigen tests are mainly used in the early stages of infection, while antibody tests have a relatively low positive rate in the initial infection phase (approximately 27%-41%) (Deeks et al., 2020), which can increase to 78%–88% in the second to third week of infection. Traditional PCR-based detection techniques (such as qPCR) offer high sensitivity but require a long detection time and have high demands for equipment and technical personnel, making them unsuitable for point-of-care testing (POCT) during pathogen outbreaks. In recent years, isothermal amplification technologies (such as RPA and LAMP) have been successfully established to work at a constant temperature to eliminate the dependence on thermal cycles. However, isothermal amplification technologies usually have some disadvantages, such as non-specific. In recent years, the CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) system and its associated Cas proteins have been widely applied in the field of molecular diagnostics. Since its discovery in 1987, the CRISPR system has been identified as an adaptive immune mechanism in bacteria (Doudna and Charpentier, 2014). It enables recognition of specific nucleic acid sequences and achieving pathogens detection. CRISPR comprises six types (I–VI); II, V and VI are well characterized for gene editing and pathogen detection (Makarova et al., 2015; Shmakov et al., 2017) (Figure 1).
CRISPR detection methods are primarily categorized as amplification-based and amplification-free. Amplification-based approaches offer high sensitivity and specificity while requiring less complex instrumentation, making them an important advancement in molecular diagnostics. The application of CRISPR technology in the detection of various pathogens has also become increasingly widespread, including viruses (Miao et al., 2023), bacteria (Wu et al., 2021b), mycoplasma (Li et al., 2022b; Chen et al., 2022);, etc. Amplification-free CRISPR has gradually gained attention. Compared with traditional amplification-based methods, amplification-free CRISPR can eliminate the amplification step, reducing operational complexity and the risk of potential contamination. Researchers have explored a variety of amplification-free CRISPR detection strategies, which include innovative methods such as cascade CRISPR, sensor devices, and digital droplet CRISPR. These strategies are capable of sensitive pathogen detection without amplification. For example, an amplification-free CRISPR-Cas13a platform for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 was established, which can detect the virus down to 470 aM within 30 minutes, showing the potential of amplification-free strategies in pathogen detection (Shan et al., 2023).
Through continued refinement of CRISPR technology is anticipated to result in more efficient and convenient pathogen detection tools. This review delves into the principles of amplification-based and amplification-free CRISPR technologies, analyzes their advantages and limitations, introduces their applications in pathogen detection, and discusses their future prospects, aiming to offer a comprehensive reference for research in this field.
2 The principle of CRISPR immune activation cleavage
The CRISPR system is characterized by its excellent specificity and flexibility, which enables precise gene editing and regulation in a variety of organisms (Fang et al., 2023). It has not only played a significant role in basic research but also demonstrated broad prospects in applied research. In terms of applications, CRISPR technology has been involved in areas such as agriculture (Chen et al., 2019), biological research (Manghwar et al., 2019; Sanjana et al., 2014), environmental monitoring (Zhang et al., 2021), and disease treatment (Shokoohi et al., 2025a). In the field of molecular diagnostics, CRISPR technology has become an important tool.
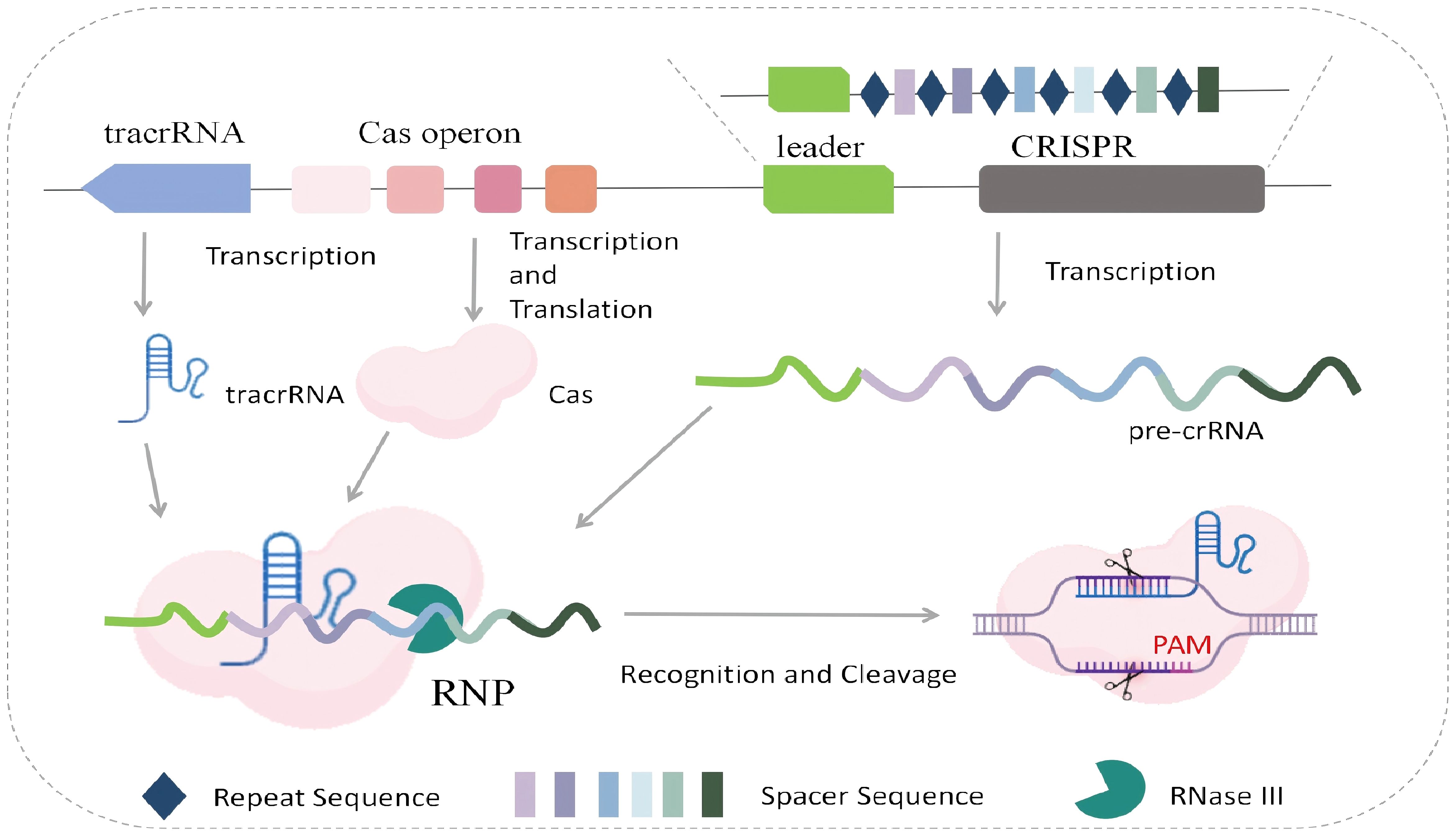
Taking Cas9 as an example, the immune activation mechanism of the CRISPR system is as follows: The CRISPR locus consists of spacer sequences and repeat sequences. When bacteria are first attacked by foreign material, the CRISPR system inserts a fragment of the foreign material’s gene into the spacer region. Upon re-infection by the same material, the repeat sequences and spacers in the CRISPR locus are transcribed into pre-crRNA, while the tracrRNA gene is transcribed into tracrRNA. Cas proteins (such as Cas9), tracrRNA, and pre-crRNA form an RNP complex. During this process, pre-crRNA matures and combines with tracrRNA to form crRNA. The crRNA guides the Cas protein complex to recognize the spacer sequence and PAM sequence in the target DNA. The Cas protein cleaves the double-strand of the target DNA at a specific position upstream of the PAM sequence, generating double-strand breaks (DSBs). In addition, after cleaving their targets, Cas9 (Hatada et al., 2023), Cas12a (Swarts and Jinek, 2019), and Cas14 (Cas12f) (Aquino-Jarquin, 2019) exhibit non-specific cleavage of single-strand DNA (ssDNA), while Cas13 shows non-specific cleavage activity against single-strand RNA (ssRNA). This phenomenon is known as trans-cleavage activity (Figure 2).
2.1 Principal of CRISPR detection
Researchers have leveraged the CRISPR-mediated principles of immune activation and cleavage to develop CRISPR-based in vitro diagnostic technologies, typically used for pathogen detection. Researchers design specific crRNAs to guide the CRISPR complex to bind and activate the target, thereby specifically cleaving the target and non-specifically cleaving the reporter molecule (a single-stranded nucleic acid fragment). By labeling the reporter molecule with fluorescent signals (such as FAM, ROX, etc.) and quenching groups (such as BHQ), to detection of pathogens. Additionally, biotin and FAM or digoxigenin (dig) can be labeled on the reporter molecule, and detection can be performed using lateral flow assay (LFA) strips. LFA does not require complex instruments, making the detection process more convenient and further expanding the application potential of CRISPR technology in POCT.
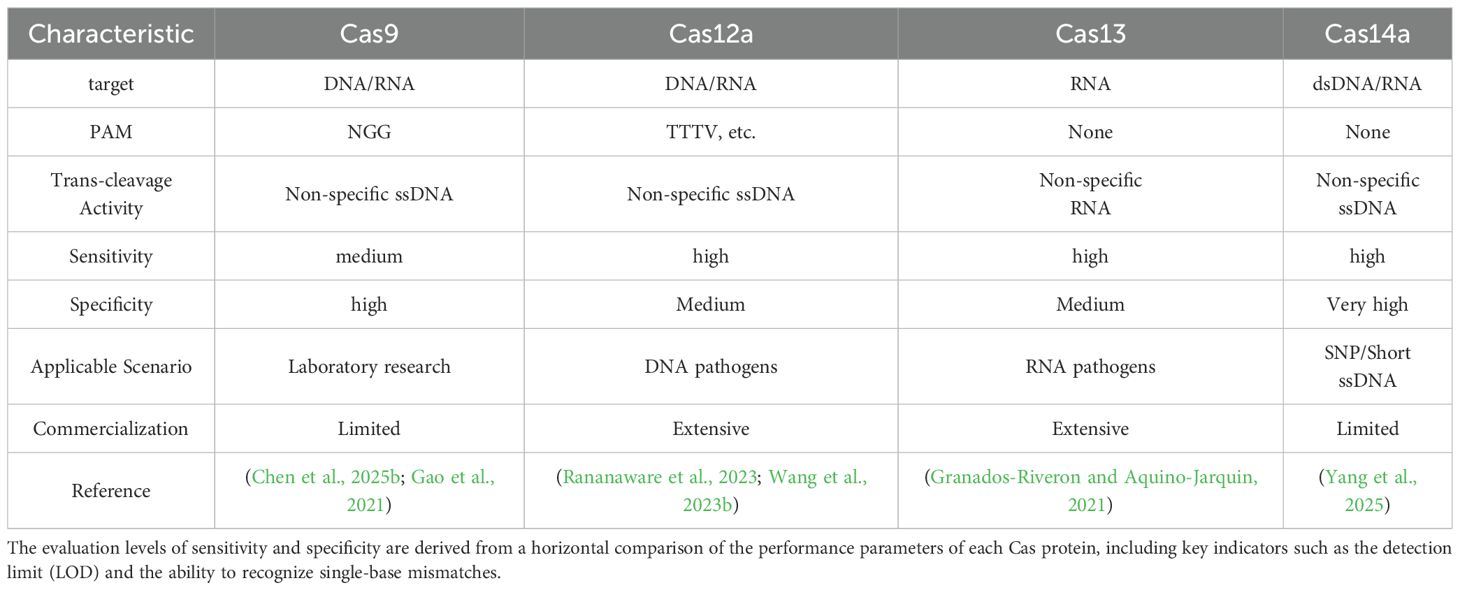
Commonly used Cas proteins include Cas9, Cas12a, Cas13, and Cas14 (Zhou et al., 2024a). In addition, other Cas proteins such as CasΦ (Cas12j) (Kang et al., 2024) and Cas14 (Cas12f) (He et al., 2024) have also been applied. Among them, Cas9, Cas12a, and Cas14 (Leung et al., 2022; Qiu et al., 2022) recognize and bind to DNA or RNA, while Cas13 (Abudayyeh et al., 2017; Cox et al., 2017) recognizes and binds to single-stranded RNA. The characteristics of main Cas protein in pathogen detection are shown in Table 1.
2.2 Classification of CRISPR detection
The application of CRISPR technology is becoming increasingly widespread in pathogen detection. Based on their application methods, CRISPR technologies can be divided into two major categories: amplification-based CRISPR and amplification-free CRISPR.
Amplification-based CRISPR technology relies on nucleic acid amplification techniques, such as RPA, LAMP, and multiple cross displacement amplification (MCDA), these techniques enhance the detection sensitivity for pathogens detection. For instance, the combination of RPA and CRISPR-Cas12a can achieve rapid detection of Mpox DNA within 30 minutes, and sensitive as low as 1 copy of (Zhao et al., 2023). Similarly, by combining LAMP with CRISPR-Cas12a has also shown good performance in detecting bacterial pathogens (Lee and Oh, 2022).
In contrast, amplification-free CRISPR emphasizes the direct detection of pathogens, which reduces the cumbersome amplification steps and decreases detection time. For instance, a CRISPR-Cas13a-based system can rapidly generate signals by directly binding to RNA targets, and achieving pathogen detection. Studies have shown that this method exhibits good specificity and sensitivity in detecting the HIV-1 virus (Zhang et al., 2025). Moreover, amplification-free CRISPR systems combined with novel sensor technologies (such as gFET, ECL, SERS) can directly monitor targets through signal transduction.
2.3 Principal of amplification-based CRISPR detection
Amplification-based CRISPR technology combines isothermal amplification techniques with the CRISPR system. The introduction of isothermal amplification significantly enhances detection sensitivity. Currently, amplification-based CRISPR methods are primarily categorized into two-step and one-step detection assays.
2.3.1 Principle of two-step amplification-based CRISPR detection
In the workflow of two-step amplification-based CRISPR, pathogens are first rapidly amplified using isothermal amplification techniques. After amplification is completed, the amplified products are manually introduced into the CRISPR reaction system.
The main application examples of amplification-based CRISPR technology include SHERLOCK (Kellner et al., 2019) and DETECTR (Broughton et al., 2020). SHERLOCK focuses on the CRISPR-Cas13 system and achieves sensitivity detection by RPA and transcribing DNA into RNA. The core of this process is the enzymatic activity of CRISPR-Cas13, which recognizes target sequences through crRNA and cleaves them after recognition. A significant advantage of this technology is 100% sensitivity and specificity demonstrated in clinical samples (Figure 3A). DETECTR is based on the CRISPR-Cas12 system and is primarily used for DNA detection. It combines RPA with CRISPR-Cas12 to achieve detection of DNA (Figure 3B). In two-step amplification-based CRISPR detection, the need to manually transfer amplified products into the CRISPR system not only increases operational complexity but also raises the risk of aerosol contamination.
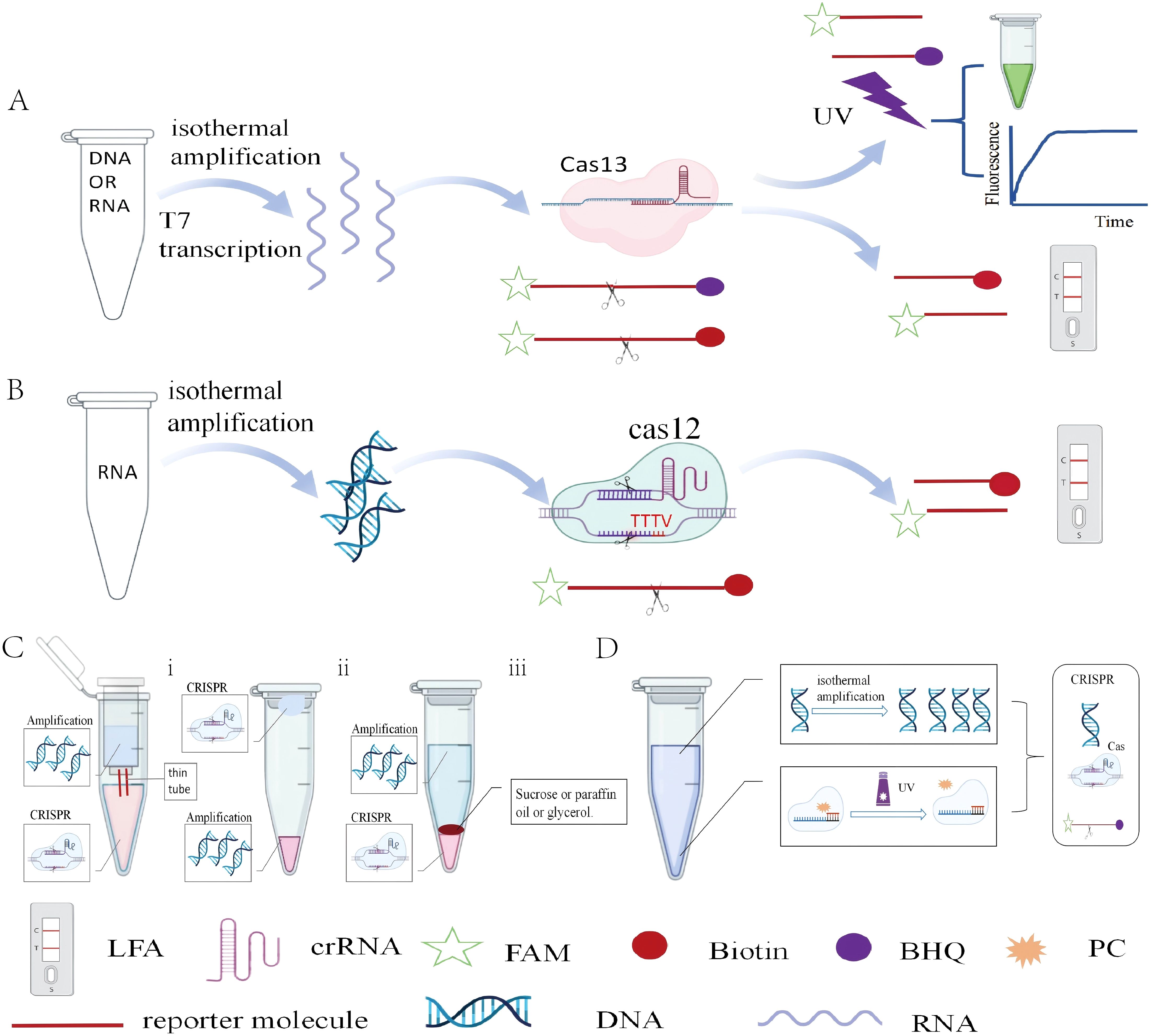
Figure 3. The principle of amplification-based CRISPR (A) SHERLOCK: RNA or DNA templates undergo isothermal amplification and T7-mediated reverse transcription, activating the CRISPR-Cas13 system to cleave reporter molecules for fluorescence or lateral flow assay (LFA) detection. (B) DETECTR: DNA templates are amplified isothermally to activate the CRISPR-Cas12 system, leading to reporter cleavage and fluorescent signal generation. (C) Physically segregated one-pot strategies: (I) Dual-chamber tubes connected by a narrow channel. (ii) Separate amplification (in cap) and CRISPR (in bottom) compartments, mixed by centrifugation. (iii) Layer-based isolation using high-density barriers (e.g., sucrose or mineral oil). (D) The photocleavable (PC) linker acts as a silencing factor. Its conjugation to the crRNA keeps the CRISPR system inactive. UV irradiation cleaves the linker, reverses the silencing effect, and activates the CRISPR system.
2.3.2 Principle of one-pot amplification-based CRISPR detection
To address these issues, researchers have explored various strategies to integrate amplification and CRISPR reactions into a single process. Currently, the main solutions include physically separating and optimizing reaction conditions to enabling one-pot reactions.
Firstly, the physically separation can be achieved by modifying the reaction tube design. For example, a double-layer reaction tube was designed, where the inner and outer layers are connected by a thin tube (Hu et al., 2022a). The inner layer is used for RPA and after completion, the amplified products are transferred to the outer layer containing the CRISPR reaction system through centrifugation, thus enabling one-pot detection. Additionally, the CRISPR reaction system was placed on the cap of the reaction tube (Sun et al., 2021). After amplification, the two systems are mixed by centrifugation. This optimized method can detect SARS-CoV-2 within 50 minutes, with a detection limit of 1 copy/μL. Secondly, physical separation can also be achieved by adding dense reagents (such as sucrose, mineral oil, and glycerol). A dynamic aqueous multiphase reaction system (DAMR) that exploits sucrose-density differences to compartmentalize two otherwise incompatible reactions in the same tube was developed (Yin et al., 2020). Paraffin was used to separate the RAA and CRISPR-Cas12a systems, ensuring that sufficient RAA amplicons diffuse to activate the CRISPR-Cas12a reaction (Tan et al., 2024). This method achieves a sensitivity of 2.5 × 10 copies/μL (Figure 3C).
Researchers have explored various innovative methods to efficiently integrate the two processes. LAMP and Cas12b-both active at 58°C-were combined to enable one-pot CRISPR detection (Gong et al., 2024). It was found that AacCas12b exhibits minimal cis-cleavage but robust trans-cleavage at 30-39°C, based on this, RPA and CRISPR/AacCas12b were integrated in a single tube to create the Rcod system (Lin et al., 2024). Additionally, a one-pot detection method utilizing suboptimal protospacer adjacent motifs (PAMs) for Cas12a, such as VTTV, TCTV, and TTVV, was developed (Lu et al., 2022). Compared to the traditional TTTV PAM, these suboptimal PAMs exhibit lower binding affinity, thereby reducing the cis-cleavage activity of Cas12a. This allows to more effectively accumulate amplified products, providing sufficient substrates for the Cas12a reaction and offering more flexible crRNA design. A photocontrolled one-pot CRISPR workflow was likewise established (Hu et al., 2022b). However, this inevitably entails low sensitivity and mutual interference between amplification and CRISPR. (Figure 3D).
2.4 Principal of amplification-free CRISPR detection
Amplification-free CRISPR technology is an emerging detection method whose key advantage lies in its ability to detection of pathogens without relying on traditional nucleic acid amplification techniques (Figure 4).
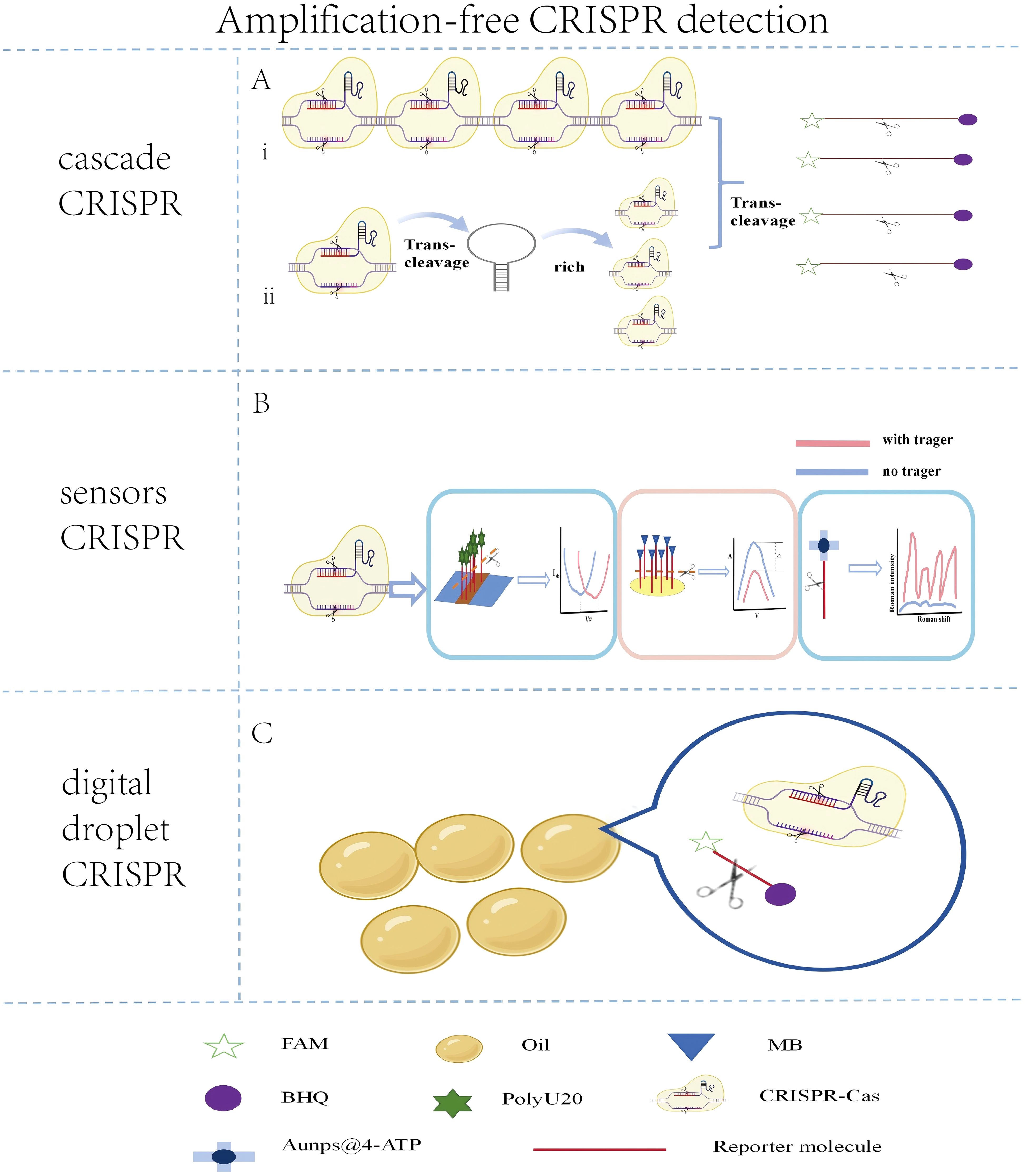
Figure 4. Schematic illustration of key amplification-free CRISPR detection strategies. (A) Cascade signal amplification approaches. (I) Multi-crRNA strategy: Simultaneous use of multiple crRNAs targeting a single pathogen enhances Cas protein activation and signal output. (ii) Nucleic acid circuit-based amplification: Autocatalytic reactions, such as the cleavage of a designed U-rich hairpin (URH) structure, generate secondary targets to activate additional Cas proteins for signal enhancement. (B) Sensor-integrated CRISPR platforms. Schematics of biosensors coupled with CRISPR for direct signal transduction, including gFET, ECL, and SERS sensors. (C) Digital droplet amplification-free CRISPR utilizes oil-phase droplets to achieve single-molecule detection.
2.4.1 Cascade CRISPR detection
In the CRISPR reaction system, crRNA scans and recognizes specific sequences to activate the Cas protein. The more crRNA species present, the more Cas proteins are activated, thereby enhancing the trans-cleavage activity. In amplification-free CRISPR detection strategies, to activate more Cas proteins and improve detection sensitivity, researchers have employed cascade methods, primarily including multi-protease cascade signal amplification and nucleic acid circuit signal amplification.
The multi-protease cascade signal amplification method mainly involves designing multiple crRNAs on the target. The detection limit for single crRNA was found to be around 80.52 pM, whereas for triple or quadruple crRNAs, the detection limit was between 6.92 and 1.25 pM. The detection limit for multiple crRNAs was 6 to 64 times higher than that for single crRNA (Zeng et al., 2022). Four crRNAs were designed on the target sequence, achieving a detection sensitivity of 0.16 pM (Yang et al., 2024). Similarly, a CRISPR-Cas12a system with multiple crRNAs was utilized to detect microsporidians (Zhang et al., 2024), which not only saved time but also reduced the risk of aerosol contamination, offering a new approach for detecting other pathogens.
Nucleic acid circuit signal amplification involves specially designed nucleic acid fragments to activate a secondary CRISPR reaction. A U-rich hairpin (URH) structure was be designed to replace the reporter molecule, with the loop part rich in uracil preferred for Cas13a cleavage and the stem part containing complementary bases to ensure the stability of the URH structure. In the presence of the target, the CRISPR system is activated, the URH structure is cleaved, and the released stem part serves as a target for secondary cleavage. Without amplification, this method can detect 100 copies/μL of SARS-CoV-2 within 5 minutes (Zeng et al., 2024). However, the method requires operation at low temperatures and is prone to false-positive results. Additionally, the DSAC detection system was developed by introducing circular nucleic acid sequences into the CRISPR reaction system (Zhou et al., 2024c). These sequences are cleaved into double strands by the trans-cleavage activity of Cas12a, thereby activating the CRISPR system. Furthermore, an amplification-free collateral cleavage-enhanced CRISPR-CasΦ method (TCC) was established, enabling pathogen detection with a sensitivity as low as 1.2 CFU/mL within 40 minutes (Chen et al., 2025a). This approach can also be extended for miRNA detection (Figure 3A).
However, Cascade CRISPR also bring many challenges. First, the complexity of crRNA design is increased. Second, nucleic acid circuit signal amplification is prone to false-positive results, which can affect the accuracy of detection.
2.4.2 Sensors combined with CRISPR detection
At present, amplification-free CRISPR technology can also use more sensitive sensor devices to efficiently output weak signals. Among them, graphene field-effect transistors (gFET), electrochemical biosensors (ECL), and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) are the three main types of sensor devices.
gFET achieve ultrasensitive nucleic acid detection by manipulating the conductivity of graphene. gFET consists of a graphene channel, source and drain electrodes connected to the graphene channel, and a gate electrode (Sun et al., 2024). The Cas13a was utilized in combination with a gFET, successfully enabling the detection of SARS-CoV-2 at the aM level within 30 minutes at 37°C (Li et al., 2022c). In this system, negatively charged RNA reporter molecules (such as PolyU20) are immobilized on the surface of the gFET via a molecular linker 1-pyrenebutyrate succinimide ester (PBASE). Upon activation of CRISPR Cas13a, the reporter molecules are cleaved, leading to a reduction in the electron-doping effect on the graphene surface and a positive shift in the charge neutrality point voltage (VCNP). The quantitative detection of target nucleic acids is achieved by measuring the change in VCNP. Further optimized this technology by designing reporter molecules (RP) with stronger electron-doping effects, significantly enhancing the specificity and sensitivity of detection (Sun et al., 2023). However, the stability of graphene in liquid environments remains a challenge. Although hydrophobic treatments (such as OTS coating) can enhance stability, the long-term stability of graphene in complex clinical samples still needs to be verified.
ECL are commonly used signal output devices in amplification-free CRISPR detection, consisting of an electrode system, an electrolyte solution, and an electrochemical indicator. The electrochemical CRISPR (E-CRISPR) method that uses methylene blue (MB)-modified reporter molecules. In the presence of the target, the trans-cleavage of the reporter molecules releases MB, altering the redox reactions on the electrode surface and generating a current signal. This method successfully detected HPV-16, PB-19, and TGF-β1 with a detection limit at the nanomolar (nM) level (Dai et al., 2019). Additionally, methylene blue (MB) and ferrocene (Fc) were employed as electrochemical indicators to detect the S gene and ORF1ab gene of SARS-CoV-2, utilizing the MB current signal in the negative potential range and the Fc current signal in the positive potential range (Kashefi-Kheyrabadi et al., 2023). Electrochemical biosensors offer sensitivity, rapid response, and ease of operation, making them suitable for rapid diagnosis and large-scale screening.
SERS is a spectroscopic technique based on the enhancement of Raman signals by metal nanostructures. SERS technology was utilized for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 without amplification, achieving a detection limit of 1 fM (Liang et al., 2021). This method involves attaching reporter molecules modified with biotin and thiol groups to streptavidin-coated magnetic beads and silver nanoparticles@4-ATP to form SERS probes. After activation of the CRISPR-Cas12 system, the reporter molecules are cleaved, causing the silver nanoparticles@4-ATP to dissociate and resulting in a decrease in Raman signals, with the signal change being proportional to the viral concentration. In addition to 4-ATP, commonly used Raman reporter molecules include 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (4-MBA). As demonstrated in one study, 4-MBA was conjugated to gold nanoparticles for this purpose (Ma et al., 2023). Furthermore, the operation process was significantly simplified by employing centrifugation or polyether sulfone (PES) membrane filtration for signal detection (Liang et al., 2021).
While gFET, ECL, and SERS technologies offer high sensitivity and specificity for amplification-free CRISPR detection, they differ in cost, stability, and operational complexity. gFET sensors require improvement in stability and remain in the laboratory research and development stage, making accurate estimation of their practical large-scale production costs challenging. ECL sensors strike a favorable balance between cost and performance, with relatively low instrument prices (approximately $5,000–$20,000), yet they still face background interference issues that require further optimization to improve the signal-to-noise ratio. In contrast, despite its outstanding detection performance, the high equipment acquisition cost of SERS technology (ranging from about $50,000 to $200,000 depending on configuration) limits its large-scale application in clinical settings. Future advancements in materials science and nanotechnology will drive the development of more stable, cost-effective, and user-friendly sensor devices, thereby laying a critical foundation for the practical application and widespread adoption of amplification-free CRISPR detection technology. (Figure 3B).
2.4.3 Digital droplet CRISPR detection
Digital droplet CRISPR technology is an emerging method for pathogen detection, utilizing microdroplet techniques to achieve quantitative detection of pathogens at the single-molecule level. The core of digital droplet CRISPR technology lies in the integration of the CRISPR system with droplet digital technology. The basic principle of droplet technology is to use microfluidics to divide sample liquids into micrometer-sized droplets, each of which can independently undergo a reaction. STAMP digital CRISPR-Cas13a technology to achieve quantitative detection of HIV-1 RNA, with a detection limit of 2000 copies/ml (Nouri et al., 2023). This technology uses commercial polycarbonate track-etched (PCTE) membranes to digitally partition the reaction mixture, utilizing its high-density and uniform-sized pores to divide the sample into tiny reaction units. Further proposed by combining the CRISPR system and target nucleic acids with an oil phase (90% isopropyl palmitate and 10% Abil EM 180) to generate polydisperse droplets with diameters of 10-100 μm through simple vertexing, with 90% having diameters less than 50 μm (Xue et al., 2023). This method significantly reduces the difficulty of droplet generation, eliminating the need for complex microfluidic devices and enhancing the convenience and accessibility of detection, making it particularly suitable for POCT and pathogen detection in resource-limited environments. By combining sample micro-segmentation with the CRISPR system, it may become a valuable tool for crisis response as the technology matures.(Figure 3C).
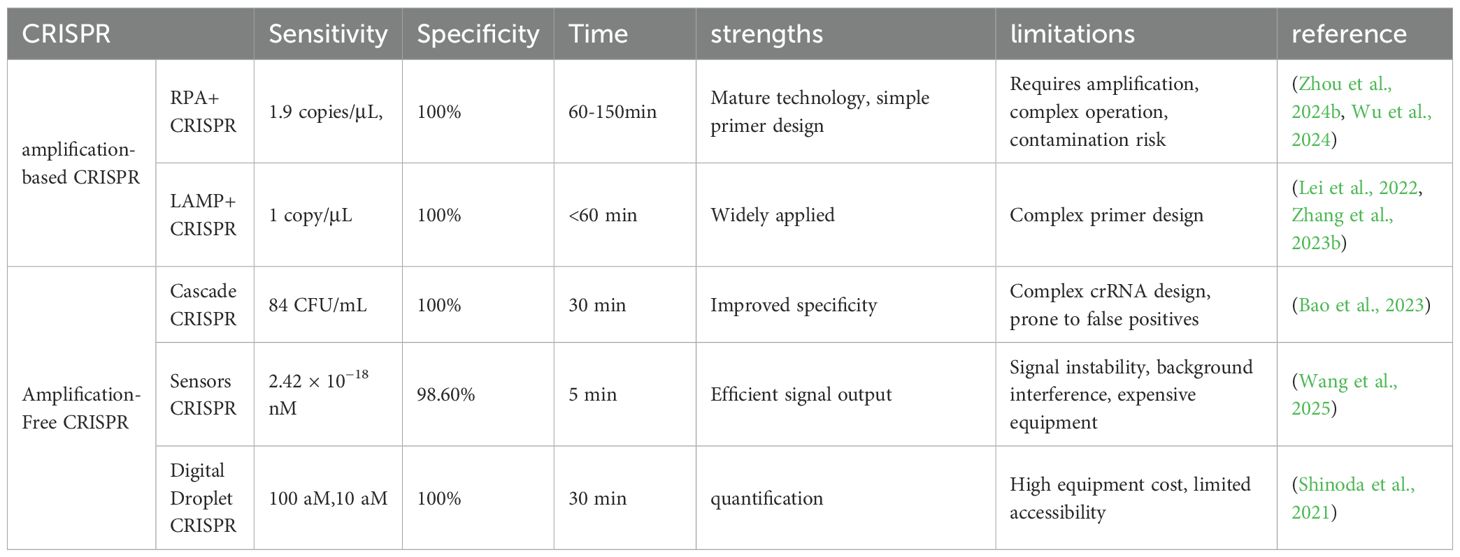
In brief, CRISPR-based nucleic acid detection has develop from amplification-dependent to amplification-free approaches. The two strategies differ in sensitivity, specificity, limitations, and strengths, as summarized in Table 2.
3 Applications of CRISPR in human pathogen detection
CRISPR technology serves as a molecular tool for detecting various pathogens. as shown in Figure 5.
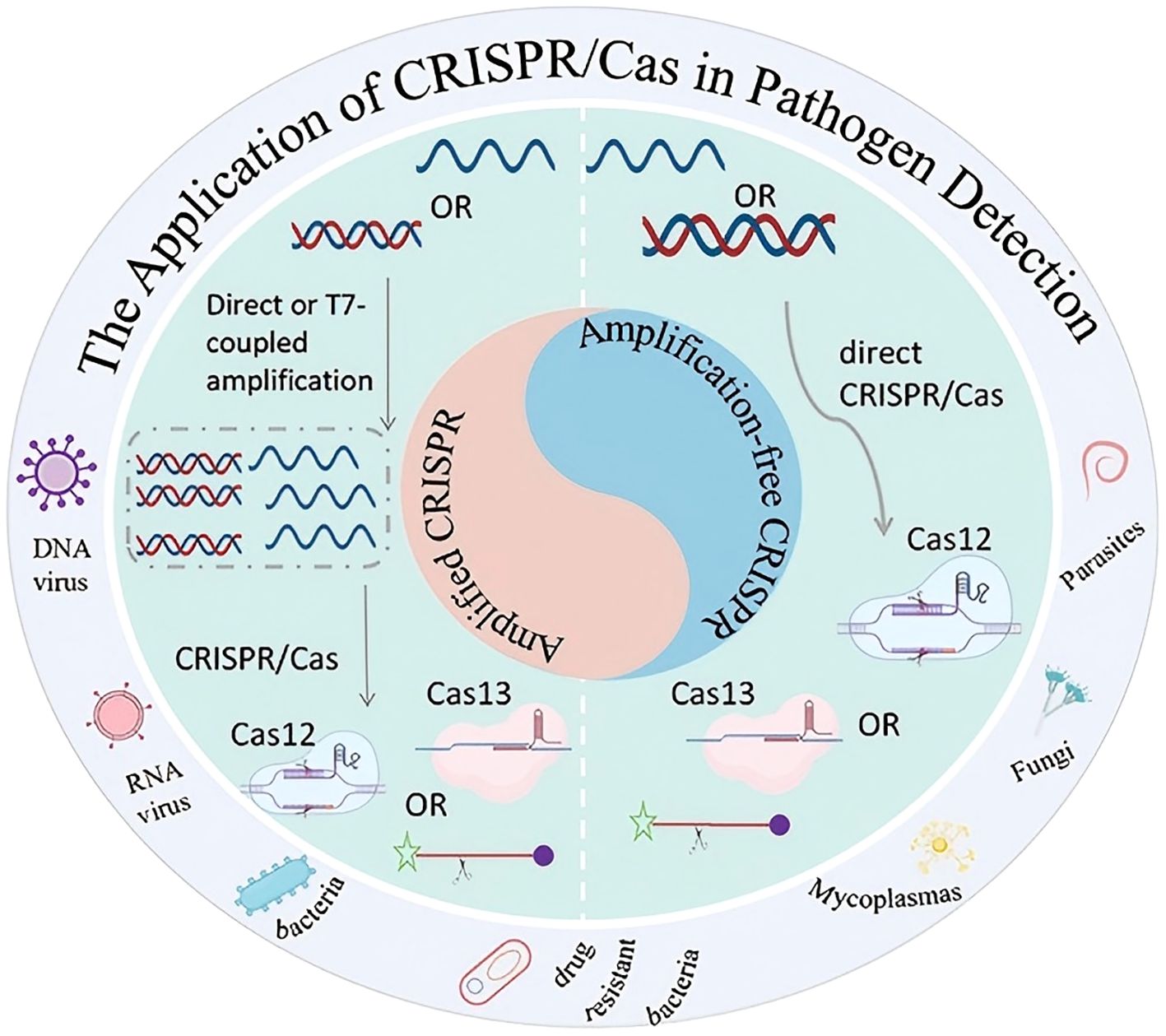
Figure 5. Application of CRISPR technology in pathogen detection: amplification and amplification-free strategies.
3.1 Viral pathogens
The outbreak of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, along with the persistent threat of other viral diseases, has made the development of rapid, sensitive, and specific viral detection methods particularly crucial. CRISPR systems have been successfully applied for rapid detection of various viruses, including influenza virus (Yoshimi et al., 2022), respiratory syncytial virus (Khamwut et al., 2025), SARS-CoV-2 (Nouri et al., 2021), and its variants (Y. Liang et al., 2021), which holds significant practical implications for responding to public health emergencies.
3.1.1 RNA viruses
Viruses are simple-structured, minuscule pathogens (Taylor and Leiman, 2020). During infection, they spread rapidly and widely, and are prone to mutation, especially RNA viruses, a trait that often affects the efficacy of vaccines and drug treatments. In 2020, the SHERLOCK detection technology was optimized, leading to the establishment of a one-pot CRISPR-Cas12b SARS-CoV-2 detection method known as STOPCovid.v1 (Joung et al., 2020). This method integrates magnetic bead extraction, LAMP and LFA, enabling virus detection within one hour. The sensitivity and specificity were 93.1% and 98.5%, respectively, as tested on 202 positive and 200 negative samples. In 2021, an amplification-free CRISPR-Cas13a SARS-CoV-2 detection method was developed, which enabled direct quantification of viral concentration using a mobile phone microscope (Fozouni et al., 2021). This technique, which employs triple crRNA to directly recognize and cleave reporter molecules, can detect the virus within 30–40 minutes, with a sensitivity of 30 copies/μL. The method established is a rapid POCT technology that could be adapted for portable detection, reducing reliance on specialized laboratories and personnel. SATORI (Iida et al., 2023) is an automated digital droplet CRISPR detection platform that can detect SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A/B viruses in just 9 minutes, with a sensitivity of 6.5 aM after magnetic bead enrichment. Mpox, a zoonotic virus (also known as monkeypox virus), has prompted researchers to develop a CRISPR-Cas12a-based detection system that can simultaneously detect mpox virus and other Ortho poxviruses, highlighting its importance in rapidly responding to outbreaks (Singh et al., 2023). Hepatitis D virus (HDV) can accelerate the progression of chronic hepatitis B virus infection and poses a health burden to patients. A CRISPR detection method based on RT-RAA was established, demonstrating a sensitivity of 10 copies/μL in positive samples. Ebola virus infection causes hemorrhagic fever, a disease with an extremely high mortality rate, for which there is currently no specific treatment. An amplification-free Cas-Roller method, which can detect Ebola virus down to 291 aM within 40 minutes at 37°C (Hang et al., 2022). In summary, the application of CRISPR technology, especially the Cas13a system, is gradually changing the way RNA viruses are detected, providing new solutions for viral detection.
3.1.2 DNA viruses
In the detection of DNA viruses, the CRISPR-Cas12a system has emerged as a unique and advantageous technology. HPV is considered a major cause of cervical cancer, and timely detection and typing of HPV are crucial for risk prediction and management. A POCT detection system that can detect six high-risk HPV types within 40 minutes, with a sensitivity of 1 copy/μl (Liu et al., 2024). Additionally, an amplification-free CRISPR platform can detect HPV16 (Yu et al., 2023). HBV is closely related to the occurrence of liver cancer and can be transmitted through mother-to-child, blood, and sexual contact. A CRISPR-Cas12a-mediated SERS detection method was established, enabling the detection of HBV DNA at 0.67 pM within 50 minutes (Du et al., 2023). The application of the CRISPR-Cas12a system in DNA virus detection, especially in the detection of HPV and HBV, offering important insights for the development of future pathogen detection technologies. It is worth noting that when using Cas13 to detect DNA, the amplified products need to be transcribed into RNA by T7 (Tian et al., 2022). In the study, DNA amplified by RPA was reverse transcribed into RNA using T7 prior to reaction with CRISPR-Cas13 (Xu et al., 2024). Separately, a CRISPR-Cas14a-based cascade colorimetric detection method was established, capable of detecting ASFV as low as 5 copies/μL and distinguishing mutant ASFV DNA with a 2-nt difference (X. Zhao et al., 2024).
In summary, the application of CRISPR technology in the detection of viral pathogens has demonstrated its superiority in sensitivity, specificity, and rapid response, providing significant technical support for clinical testing and public health (Shokoohi et al., 2025b). With continuous technological advancements and optimizations, future CRISPR detection platforms are expected to detection more viruses.
3.2 Bacterial pathogens
The detection of bacterial pathogens holds significant importance. Among them, the rapid diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is key to controlling the spread of tuberculosis. Recent studies have shown that combining CRISPR technology with isothermal amplification techniques can achieve rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. For example, the multiplex cross-displacement amplification technique (CRISPR-MCDA) with the CRISPR-Cas12b system can complete the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis within 70 minutes, with a detection limit of 5 fg/μL (Yang et al., 2023).
In the detection of drug-resistant bacteria, CRISPR technology also shows excellent potential. For the detection of MRSA, using an amplification-free CRISPR and ECL to detect the mecA gene in MRSA, modifying the reporter molecules with Ag to make the electrochemical signal changes between positive and negative more pronounced (Suea-Ngam et al., 2021). A multifunctional CRISPR biosensor based on colorimetric, photothermal, and fluorescent signals (CPF-CRISPR) was developed for detecting MRSA, overcoming the limitation of single-signal output in existing biosensors (Zheng et al., 2023). An interesting OR-gated logic was adopted to detect MSSA, MRSA, E. coli, and hepatitis B virus through a cascade positive feedback amplification-free CRISPR detection system (Lim et al., 2025). This method includes T1 and T2 reactions. In the T1 reaction, crRNAs corresponding to the four pathogens are added. Whether it is a single pathogen infection or a mixed infection, the T1-CRISPR system can be activated and the target BNA in the T2 reaction system can be released through trans-cleavage, thereby triggering the release of T2-gDNA and forming a positive feedback signal amplification mechanism. This design significantly reduces detection costs and sample requirements, providing an efficient and economical solution for multiplex pathogen detection. These technologies can provide information on bacterial drug resistance, aiding in drug selection and infection control.
CRISPR technology has shown unique advantages in the detection of bacterial pathogens. It is therefore relevant for both improving the timely management of infections and for inspiring new approaches in clinical diagnostics.
3.3 Others pathogens
The application of CRISPR technology in detecting fungi and parasites has garnered increasing attention from researchers, especially in public health and clinical diagnostics. CRISPR enables rapid and accurate detection of specific fungi and parasites, supporting early diagnosis and treatment.
In the field of fungal detection, a method with a sensitivity of 30 CFU/mL was developed for Candida albicans, demonstrating 100-fold higher sensitivity than microscopic staining (Shen et al., 2024). This approach is rapid, device-free, and suitable for resource-limited settings. For malaria detection, a CRISPR-Cas12-based method was established that enables rapid identification of Plasmodium species within 20 minutes (Wei et al., 2023). For Trichomonas vaginalis, which causes vaginitis or urethritis, a CRISPR-based detection platform was created (Li et al., 2022d). Regarding Mycoplasma pneumoniae, a common respiratory pathogen, the CRAFT platform was developed, integrating nucleic acid extraction, RPA, CRISPR reaction, and signal readout to achieve rapid, sensitive, and specific detection (Li et al., 2025).CRISPR technology, both amplification-based and amplification-free, has been applied for pathogen diagnostics, as summarized in Table 3.
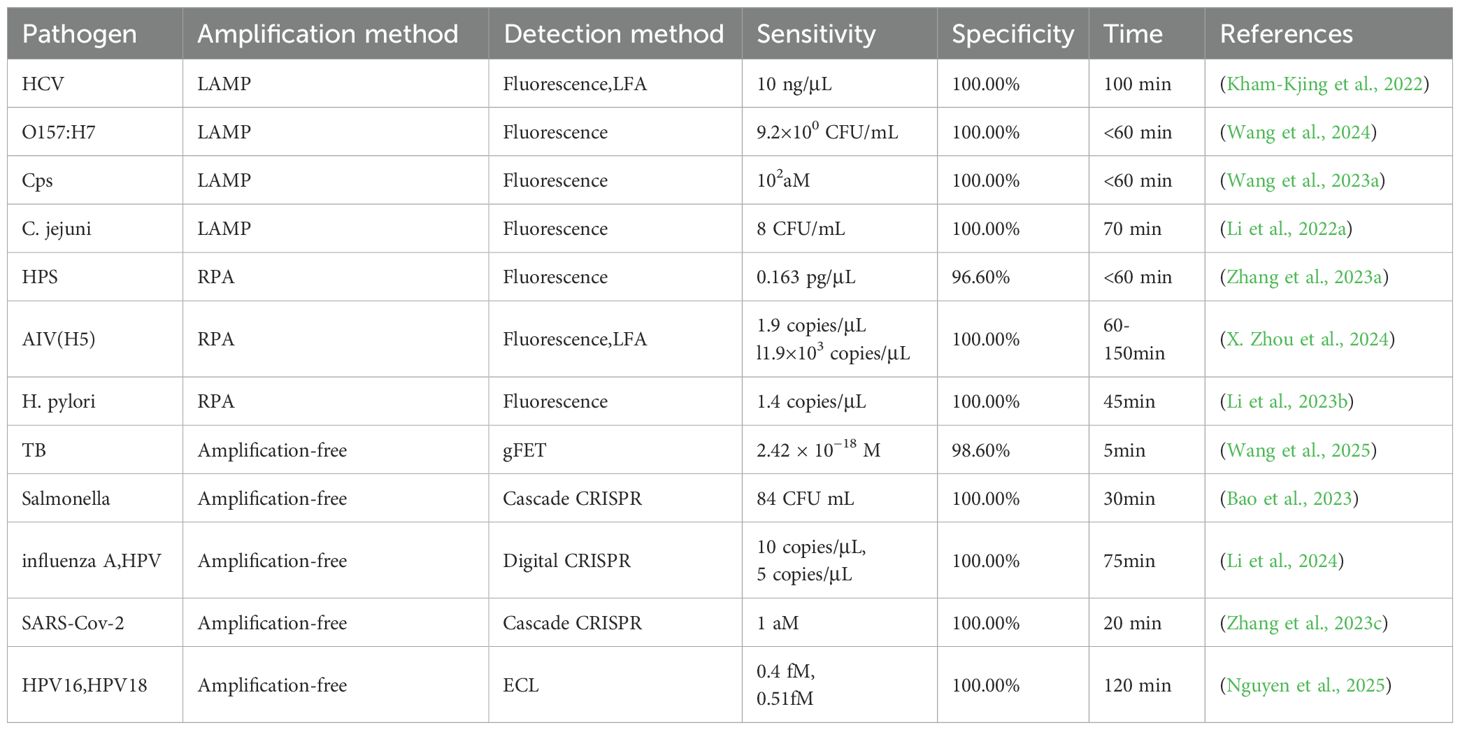
Table 3. Applications of amplification-based CRISPR and amplification-free CRISPR in the detection of different pathogens. .
4 Discussion
Compared to traditional pathogens detection methods, CRISPR technology offers advantages in sensitivity and specificity. Amplification-based CRISPR methods achieve detection sensitivities as low as 1 copy/μL through amplification but may introduce false-positive results due to contamination risks associated with amplification steps (Li et al., 2023a). In contrast, amplification-free CRISPR strategies, while slightly less sensitive, generally exhibit superior specificity and avoid cross-contamination risks inherent in amplification-based approaches. In terms of operational workflow, amplification-based methods typically require 30–60 minutes and involve relatively complex procedures, whereas amplification-free strategies significantly reduce detection time due to simplified steps, with some assays completing in as little as 5 minutes (Wang et al., 2025). Currently, amplification-based CRISPR has been widely applied for detecting various pathogens, while amplification-free approaches remain in early stages for detecting fungi, parasites, and mycoplasmas, with their potential yet to be fully explored.
Although CRISPR technology demonstrates excellent performance in laboratory settings, its stability, reproducibility, and diagnostic accuracy in real-world clinical scenarios require further validation through large-scale, multi-center clinical studies, particularly for complex sample matrices such as blood, sputum, and stool. In terms of regulatory approval and commercialization, only a few platforms (e.g., SHERLOCK and DETECTR) have received Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the U.S. FDA (Gupta et al., 2021), while most CRISPR-based diagnostic solutions remain in the research and early translation stages. In terms of cost, the two strategies differ significantly in their cost structures. The primary expense of amplification-based CRISPR lies in the nucleic acid pre-amplification step (for instance, the reagent cost for isothermal amplification such as RPA or LAMP is approximately $3–6 per sample), and the reactions can be performed on standard PCR instruments, resulting in a low equipment barrier. Studies have shown that the cost per test for amplification-based CRISPR can be as low as $0.84 (Shen et al., 2020), yet the amplification step remains the major cost component. In contrast, while amplification-free CRISPR saves on reagent costs, it may incur higher expenses in design and equipment. For example, cascade CRISPR requires the design and synthesis of multiple crRNAs, increasing both design complexity and cost. Meanwhile, sensor-based CRISPR (e.g., SERS sensors) and digital droplet CRISPR rely on more expensive specialized equipment. Moreover nucleic acid extraction, device integration, and result standardization remain critical challenges for large-scale implementation (Sultana et al., 2024).
Future development could focus on simplifying sample preprocessing, improving device portability and automation, and enabling multiplex detection. The integration of microfluidic technology with CRISPR holds promise for combining nucleic acid extraction, amplification, and detection into a unified system, enhancing throughput and applicability, as demonstrated in the detection of Vibrio parasympathetics (Wu et al., 2021a). Furthermore, the emergence of portable detection devices (e.g., CRISPR platforms integrated with thermometer (Liu et al., 2022), and fully automated digital droplet systems (e.g., SATORI (Iida et al., 2023)) has further advanced the application of CRISPR technology in POCT. CRISPR technology is well-suited for pathogen diagnostics in different contexts, such as resource-limited or rapid on-site testing scenarios.
Author contributions
XZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MX: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Validation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Validation, Writing – review & editing. XL: Validation, Writing – review & editing. JM: Validation, Writing – review & editing. JQ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZC: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The specific funding sources were the Guangxi Science and Technology Plan Project Fund (Grant No. GuiKeAB24010067) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U22A2092).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Guilin Medical University and the Precision United Laboratory Center of the People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region for their valuable suggestions on the original draft of this paper. We also thank my family and friends for their support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abudayyeh, O. O., Gootenberg, J. S., Essletzbichler, P., Han, S., Joung, J., Belanto, J. J., et al. (2017). RNA targeting with CRISPR-cas13. Nature 550, 280–284. doi: 10.1038/nature24049
Aquino-Jarquin, G. (2019). CRISPR-Cas14 is now part of the artillery for gene editing and molecular diagnostic. Nanomed.: Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 18, 428–431. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2019.03.006
Bao, Q., Sun, J., Fu, X., Sheng, L., Ye, Y., Ji, J., et al. (2023). A simplified amplification-free strategy with lyophilized CRISPR-ccrRNA system for drug-resistant salmonella detection. Small (Weinheim an Der Bergstrasse Germany) 19, e2207343. doi: 10.1002/smll.202207343
Broughton, J. P., Deng, X., Yu, G., Fasching, C. L., Servellita, V., Singh, J., et al. (2020). CRISPR-cas12-based detection of SARS-coV-2. Nat. Biotechnol. 38, 870–874. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0513-4
Chen, J., Chen, Y., Huang, L., Lin, X., Chen, H., Xiang, W., et al. (2025b). Trans-nuclease activity of Cas9 activated by DNA or RNA target binding. Nat. Biotechnol. 43, 558–568. doi: 10.1038/s41587-024-02255-7
Chen, J., Huang, Y., Xiao, B., Deng, H., Gong, K., Li, K., et al. (2022). Development of a RPA-CRISPR-cas12a assay for rapid, simple, and sensitive detection of mycoplasma hominis. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.842415
Chen, H., Song, F., Wang, B., Huang, H., Luo, Y., Han, X., et al. (2025a). Ultrasensitive detection of clinical pathogens through a target-amplification-free collateral-cleavage-enhancing CRISPR-CasΦ tool. Nat. Commun. 16, 3929. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59219-x
Chen, K., Wang, Y., Zhang, R., Zhang, H., and Gao, C. (2019). CRISPR/cas genome editing and precision plant breeding in agriculture. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 70, 667–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-100049
Cox, D. B. T., Gootenberg, J. S., Abudayyeh, O. O., Franklin, B., Kellner, M. J., Joung, J., et al. (2017). RNA editing with CRISPR-cas13. Sci. (New York N.Y.) 358, 1019–1027. doi: 10.1126/science.aaq0180
Dai, Y., Somoza, R. A., Wang, L., Welter, J. F., Li, Y., Caplan, A. I., et al. (2019). Exploring the trans-cleavage activity of CRISPR-cas12a (cpf1) for the development of a universal electrochemical biosensor. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. English) 58, 17399–17405. doi: 10.1002/anie.201910772
Deeks, J. J., Dinnes, J., Takwoingi, Y., Davenport, C., Spijker, R., Taylor-Phillips, S., et al. (2020). Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2. Cochrane Database Systematic Rev. 6, CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652
Doudna, J. A. and Charpentier, E. (2014). Genome editing. The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Sci. (New York N.Y.) 346, 1258096. doi: 10.1126/science.1258096
Du, Y., Ji, S., Dong, Q., Wang, J., Han, D., and Gao, Z. (2023). Amplification-free detection of HBV DNA mediated by CRISPR-Cas12a using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Analytica Chimica Acta 1245, 340864. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2023.340864
Fang, L., Yang, L., Han, M., Xu, H., Ding, W., and Dong, X. (2023). CRISPR-cas technology: A key approach for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Front. Bioengineering Biotechnol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1158672
Fozouni, P., Son, S., Díaz de León Derby, M., Knott, G. J., Gray, C. N., D’Ambrosio, M. V., et al. (2021). Amplification-free detection of SARS-CoV-2 with CRISPR-Cas13a and mobile phone microscopy. Cell 184, 323–333.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.001
Gao, J., Wu, L., Yang, D., Gong, W., and Wang, J. (2021). A one-pot CRISPR/cas9-typing PCR for DNA detection and genotyping. J. Mol. Diagnostics: JMD 23, 46–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2020.10.004
Gong, J., Jiang, Y., Zhang, D., Li, T., Fu, L., and Dou, X. (2024). One-tube detection of Salmonella Typhimurium using LAMP and CRISPR-Cas12b. Microbiol. Spectr. 12, e0127124. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01271-24
Granados-Riveron, J. T. and Aquino-Jarquin, G. (2021). CRISPR/cas13-based approaches for ultrasensitive and specific detection of microRNAs. Cells 10, 1655. doi: 10.3390/cells10071655
Gupta, R., Kazi, T. A., Dey, D., Ghosh, A., Ravichandiran, V., Swarnakar, S., et al. (2021). CRISPR detectives against SARS-CoV-2: A major setback against COVID-19 blowout. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 105, 7593–7605. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11583-6
Hang, X.-M., Liu, P.-F., Tian, S., Wang, H.-Y., Zhao, K.-R., and Wang, L. (2022). Rapid and sensitive detection of Ebola RNA in an unamplified sample based on CRISPR-Cas13a and DNA roller machine. Biosensors Bioelectronics 211, 114393. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114393
Hatada, I., Morita, S., and Horii, T. (2023). CRISPR/cas9. Methods Mol. Biol. (Clifton N.J.) 2637, 41–47. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3016-7_3
He, J., Hu, X., Weng, X., Wang, H., Yu, J., Jiang, T., et al. (2024). Efficient, specific and direct detection of double-stranded DNA targets using Cas12f1 nucleases and engineered guide RNAs. Biosensors Bioelectronics 260, 116428. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2024.116428
Hu, F., Liu, Y., Zhao, S., Zhang, Z., Li, X., Peng, N., et al. (2022a). A one-pot CRISPR/Cas13a-based contamination-free biosensor for low-cost and rapid nucleic acid diagnostics. Biosensors Bioelectronics 202, 113994. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.113994
Hu, M., Qiu, Z., Bi, Z., Tian, T., Jiang, Y., and Zhou, X. (2022b). Photocontrolled crRNA activation enables robust CRISPR-Cas12a diagnostics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 119, e2202034119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2202034119
Iida, T., Shinoda, H., and Watanabe, R. (2023). SATORI: Amplification-free digital RNA detection method for the diagnosis of viral infections. Biophysics Physicobiol. 20, e200031. doi: 10.2142/biophysico.bppb-v20.0031
Joung, J., Ladha, A., Saito, M., Kim, N.-G., Woolley, A. E., Segel, M., et al. (2020). Detection of SARS-coV-2 with SHERLOCK one-pot testing. New Engl. J. Med. 383, NEJMc2026172. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2026172
Kang, J.-E., Kim, H., Lee, Y.-H., Lee, H.-Y., Park, Y., Jang, H., et al. (2024). Unveiling cas12j trans-cleavage activity for CRISPR diagnostics: application to miRNA detection in lung cancer diagnosis. Advanced Sci. (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany) 11, e2402580. doi: 10.1002/advs.202402580
Kashefi-Kheyrabadi, L., Nguyen, H. V., Go, A., and Lee, M.-H. (2023). Ultrasensitive and amplification-free detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using an electrochemical biosensor powered by CRISPR/Cas13a. Bioelectrochem. (Amsterdam Netherlands) 150, 108364. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2023.108364
Kellner, M. J., Koob, J. G., Gootenberg, J. S., Abudayyeh, O. O., and Zhang, F. (2019). SHERLOCK: Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR nucleases. Nat. Protoc. 14, 2986–3012. doi: 10.1038/s41596-019-0210-2
Kham-Kjing, N., Ngo-Giang-Huong, N., Tragoolpua, K., Khamduang, W., and Hongjaisee, S. (2022). Highly specific and rapid detection of hepatitis C virus using RT-LAMP-coupled CRISPR-cas12 assay. Diagnostics (Basel Switzerland) 12, 1524. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12071524
Khamwut, A., Nimnual, J., Chomta, N., Nimsamer, P., Mayuramart, O., Kaewsapsak, P., et al. (2025). Detection of respiratory syncytial virus based on RT-RPA and CRISPR-Cas12a. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood N.J.) 250. doi: 10.3389/ebm.2025.10387
Lee, S.-Y. and Oh, S.-W. (2022). Filtration-based LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12a system for the rapid, sensitive and visualized detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Talanta 241, 123186. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.123186
Lei, L., Liao, F., Tan, L., Duan, D., Zhan, Y., Wang, N., et al. (2022). LAMP coupled CRISPR-cas12a module for rapid, sensitive and visual detection of porcine circovirus 2. Animals: Open Access J. MDPI 12, 2413. doi: 10.3390/ani12182413
Leung, R. K.-K., Cheng, Q.-X., Wu, Z.-L., Khan, G., Liu, Y., Xia, H.-Y., et al. (2022). CRISPR-Cas12-based nucleic acids detection systems. Methods (San Diego Calif.) 203, 276–281. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2021.02.018
Li, C., Chen, X., Wen, R., Ma, P., Gu, K., Li, C., et al. (2022a). Immunocapture magnetic beads enhanced the LAMP-CRISPR/cas12a method for the sensitive, specific, and visual detection of campylobacter jejuni. Biosensors 12, 154. doi: 10.3390/bios12030154
Li, Y., Deng, F., Zhang, C., Lin, X., and Goldys, E. (2023b). “Integrated RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a system towards Point-of-Care H. pylori detection,” in Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Annual International Conference (Piscataway, NJ, USA: IEEE), Vol. 2023. 1–4. doi: 10.1109/EMBC40787.2023.10340749
Li, J., Huang, H., Song, Z., Chen, S., Xu, J., Yang, J., et al. (2025). Palm-sized CRISPR sensing platform for on-site Mycoplasma pneumoniae detection. Biosensors Bioelectronics 281, 117458. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2025.117458
Li, S., Wang, X., Yu, Y., Cao, S., Liu, J., Zhao, P., et al. (2022d). Establishment and application of a CRISPR-Cas12a-based RPA-LFS and fluorescence for the detection of Trichomonas vaginalis. Parasites Vectors 15, 350. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05475-5
Li, F., Xiao, J., Yang, H., Yao, Y., Li, J., Zheng, H., et al. (2022b). Development of a rapid and efficient RPA-CRISPR/cas12a assay for mycoplasma pneumoniae detection. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.858806
Li, H., Xie, Y., Chen, F., Bai, H., Xiu, L., Zhou, X., et al. (2023a). Amplification-free CRISPR/Cas detection technology: Challenges, strategies, and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 52, 361–382. doi: 10.1039/d2cs00594h
Li, H., Yang, J., Wu, G., Weng, Z., Song, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022c). Amplification-free detection of SARS-coV-2 and respiratory syncytial virus using CRISPR cas13a and graphene field-effect transistors. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. English) 61, e20220382. doi: 10.1002/anie.202203826
Li, S., Yin, H., Zheng, J., Wan, Y., Wang, K., Yang, C., et al. (2024). DECODE: contamination-free digital CRISPR platform for point-of-care detection of viral DNA/RNA. ACS Sensors 9, 4256–4264. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.4c01248
Liang, Y., Lin, H., Zou, L., Zhao, J., Li, B., Wang, H., et al. (2021). CRISPR-cas12a-based detection for the major SARS-coV-2 variants of concern. Microbiol. Spectr. 9, e0101721. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01017-21
Liang, J., Teng, P., Xiao, W., He, G., Song, Q., Zhang, Y., et al. (2021). Application of the amplification-free SERS-based CRISPR/Cas12a platform in the identification of SARS-CoV-2 from clinical samples. J. Nanobiotechnol. 19, 273. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01021-0
Lim, J., Van, A. B., Koprowski, K., Wester, M., Valera, E., and Bashir, R. (2025). Amplification-free, OR-gated CRISPR-Cascade reaction for pathogen detection in blood samples. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 122, e2420166122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2420166122
Lin, K., Yao, K., Li, X., Li, Q., Guo, X., You, W., et al. (2024). Rapid and sensitive detection of nucleic acids using an RAA-CRISPR/Cas12b one-pot detection assay (Rcod). Talanta 271, 125616. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2023.125616
Liu, Y., Chao, Z., Ding, W., Fang, T., Gu, X., Xue, M., et al. (2024). A multiplex RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a-based POCT technique and its application in human papillomavirus (HPV) typing assay. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 29, 34. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00548-y
Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Ma, L., Fu, R., Liu, H., Cui, Y., et al. (2022). CRISPR/Cas12a-based photothermal platform for the portable detection of citrus-associated Alternaria genes using a thermometer. Int. J. Biol. Macromolecules 222, 2661–2669. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.048
Lu, S., Tong, X., Han, Y., Zhang, K., Zhang, Y., Chen, Q., et al. (2022). Fast and sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using suboptimal protospacer adjacent motifs for Cas12a. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 6, 286–297. doi: 10.1038/s41551-022-00861-x
Ma, L., Zhang, W., Yin, L., Li, Y., Zhuang, J., Shen, L., et al. (2023). A SERS-signalled, CRISPR/Cas-powered bioassay for amplification-free and anti-interference detection of SARS-CoV-2 in foods and environmental samples using a single tube-in-tube vessel. J. Hazardous Materials 452, 131195. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131195
Makarova, K. S., Wolf, Y. I., Alkhnbashi, O. S., Costa, F., Shah, S. A., Saunders, S. J., et al. (2015). An updated evolutionary classification of CRISPR-Cas systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 13, 722–736. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3569
Manghwar, H., Lindsey, K., Zhang, X., and Jin, S. (2019). CRISPR/cas system: recent advances and future prospects for genome editing. Trends Plant Sci. 24, 1102–1125. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2019.09.006
Miao, J., Zuo, L., He, D., Fang, Z., Berthet, N., Yu, C., et al. (2023). Rapid detection of Nipah virus using the one-pot RPA-CRISPR/Cas13a assay. Virus Res. 332, 199130. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199130
Nguyen, H. V., Hwang, S., Lee, S. W., Jin, E., and Lee, M.-H. (2025). Detection of HPV 16 and 18 L1 genes by a nucleic acid amplification-free electrochemical biosensor powered by CRISPR/Cas9. Bioelectrochem. (Amsterdam Netherlands) 162, 108861. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2024.108861
Nouri, R., Jiang, Y., Politza, A. J., Liu, T., Greene, W. H., Zhu, Y., et al. (2023). STAMP-based digital CRISPR-cas13a for amplification-free quantification of HIV-1 plasma viral loads. ACS Nano 17, 10701–10712. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c01917
Nouri, R., Tang, Z., Dong, M., Liu, T., Kshirsagar, A., and Guan, W. (2021). CRISPR-based detection of SARS-CoV-2: A review from sample to result. Biosensors Bioelectronics 178, 113012. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113012
Qiu, M., Zhou, X.-M., and Liu, L. (2022). Improved strategies for CRISPR-cas12-based nucleic acids detection. J. Anal. Testing 6, 44–52. doi: 10.1007/s41664-022-00212-4
Rananaware, S. R., Vesco, E. K., Shoemaker, G. M., Anekar, S. S., Sandoval, L. S. W., Meister, K. S., et al. (2023). Programmable RNA detection with CRISPR-cas12a. Nat. Commun. 14, 5409. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41006-1
Sanjana, N. E., Shalem, O., and Zhang, F. (2014). Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat. Methods 11, 783–784. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3047
Shan, X., Gong, F., Yang, Y., Qian, J., Tan, Z., Tian, S., et al. (2023). Nucleic acid amplification-free digital detection method for SARS-coV-2 RNA based on droplet microfluidics and CRISPR-cas13a. Analytical Chem. 95, 16489–16495. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02007
Shen, S., Wang, W., Ma, Y., Wang, S., Zhang, S., Cai, X., et al. (2024). Affinity molecular assay for detecting Candida albicans using chitin affinity and RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a. Nat. Commun. 15, 9304. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53693-5
Shen, J., Zhou, X., Shan, Y., Yue, H., Huang, R., Hu, J., et al. (2020). Sensitive detection of a bacterial pathogen using allosteric probe-initiated catalysis and CRISPR-Cas13a amplification reaction. Nat. Commun. 11, 267. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14135-9
Shetty, A. K., Treynor, E., Hill, D. W., Gutierrez, K. M., Warford, A., and Baron, E. J. (2003). Comparison of conventional viral cultures with direct fluorescent antibody stains for diagnosis of community-acquired respiratory virus infections in hospitalized children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 22, 789–794. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000083823.43526.97
Shinoda, H., Taguchi, Y., Nakagawa, R., Makino, A., Okazaki, S., Nakano, M., et al. (2021). Amplification-free RNA detection with CRISPR-cas13. Commun. Biol. 4, 476. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02001-8
Shmakov, S., Smargon, A., Scott, D., Cox, D., Pyzocha, N., Yan, W., et al. (2017). Diversity and evolution of class 2 CRISPR-Cas systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 15, 169–182. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.184
Shokoohi, M., Ghaderi, M., Mokarami, M., Arian, H., Mohammadnabi, S., and Farokhi, A. (2025a). Targeted and epigenetic therapies for acute myeloid leukemia treatment. Discover Oncol. 16, 1711. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03534-8
Shokoohi, M., Sedaghatshoar, S., Arian, H., Mokarami, M., Habibi, F., and Bamarinejad, F. (2025b). Genetic advancements in breast cancer treatment: A review. Discover Oncol. 16, 127. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01884-x
Singh, M., Misra, C. S., Bindal, G., Rangu, S. S., and Rath, D. (2023). CRISPR-Cas12a assisted specific detection of mpox virus. J. Med. Virol. 95, e28974. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28974
Suea-Ngam, A., Howes, P. D., and deMello, A. J. (2021). An amplification-free ultra-sensitive electrochemical CRISPR/Cas biosensor for drug-resistant bacteria detection. Chem. Sci. 12, 12733–12743. doi: 10.1039/d1sc02197d
Sultana, S., Azlan, A., Mohd Desa, M. N., Mahyudin, N. A., and Anburaj, A. (2024). A review of CRISPR-Cas and PCR-based methods for the detection of animal species in the food chain-current challenges and future prospects. Food Additives Contaminants Part A Chem. Analysis Control Exposure Risk Assess. 41, 213–227. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2024.2304577
Sun, M., Wang, S., Liang, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Liu, H., et al. (2024). Flexible graphene field-effect transistors and their application in flexible biomedical sensing. Nano-Micro Lett. 17, 34. doi: 10.1007/s40820-024-01534-x
Sun, Y., Yang, C., Jiang, X., Zhang, P., Chen, S., Su, F., et al. (2023). High-intensity vector signals for detecting SARS-CoV-2 RNA using CRISPR/Cas13a couple with stabilized graphene field-effect transistor. Biosensors Bioelectronics 222, 114979. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114979
Sun, Y., Yu, L., Liu, C., Ye, S., Chen, W., Li, D., et al. (2021). One-tube SARS-CoV-2 detection platform based on RT-RPA and CRISPR/Cas12a. J. Trans. Med. 19, 74. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02741-5
Swarts, D. C. and Jinek, M. (2019). Mechanistic Insights into the cis- and trans-Acting DNase Activities of Cas12a. Mol. Cell 73, 589–600.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.11.021
Tan, Q., Shi, Y., Duan, C., Li, Q., Gong, T., Li, S., et al. (2024). Simple, sensitive, and visual detection of 12 respiratory pathogens with one-pot-RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a assay. J. Med. Virol. 96, e29624. doi: 10.1002/jmv.29624
Taylor, N. M. I. and Leiman, P. G. (2020). Editorial overview: Virus structure and expression. Curr. Opin. Virol. 45, iii–iiv. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2020.11.005
Tian, T., Qiu, Z., Jiang, Y., Zhu, D., and Zhou, X. (2022). Exploiting the orthogonal CRISPR-Cas12a/Cas13a trans-cleavage for dual-gene virus detection using a handheld device. Biosensors Bioelectronics 196, 113701. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113701
Wang, Z., Chen, H., Hu, A., Cui, X., Shi, C., Lu, Z., et al. (2024). Establishment of LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12a for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and one-pot detection. Food Microbiol. 124, 104622. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2024.104622
Wang, W., Du, H., Dai, C., Ma, H., Luo, S., Wang, X., et al. (2025). Amplification-free detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis using CRISPR-Cas12a and graphene field-effect transistors. Nanoscale 17, 4603–4609. doi: 10.1039/d4nr03852e
Wang, Z., Huang, C., Wei, S., Zhu, P., Li, Y., Fu, W., et al. (2023). A CRISPR/cas12a-mediated sensitive DNA detection system for gene-edited rice. J. AOAC Int. 106, 558–567. doi: 10.1093/jaoacint/qsad022
Wang, R., Mao, X., Xu, J., Yao, P., Jiang, J., Li, Q., et al. (2023a). Engineering of the LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12b platform for Chlamydia psittaci detection. J. Med. Microbiol. 72. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001781
Wei, H., Li, J., Liu, Y., Cheng, W., Huang, H., Liang, X., et al. (2023). Rapid and Ultrasensitive Detection of Plasmodium spp. Parasites via the RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a Platform. ACS Infect. Dis. 9, 1534–1545. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00087
Wu, Y., Battalapalli, D., Hakeem, M. J., Selamneni, V., Zhang, P., Draz, M. S., et al. (2021b). Engineered CRISPR-Cas systems for the detection and control of antibiotic-resistant infections. J. Nanobiotechnol. 19, 401. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01132-8
Wu, H., Chen, Y., Yang, Q., Peng, C., Wang, X., Zhang, M., et al. (2021a). A reversible valve-assisted chip coupling with integrated sample treatment and CRISPR/Cas12a for visual detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Biosensors Bioelectronics 188, 113352. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113352
Wu, S., Yu, W., Fu, X., Yu, X., Ye, Z., Zhang, M., et al. (2024). Advances in virus detection techniques based on recombinant polymerase amplification. Molecules (Basel Switzerland) 29, 4972. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204972
Xu, Q., Zhang, Y., Sadigh, Y., Tang, N., Chai, J., Cheng, Z., et al. (2024). Specific and sensitive visual proviral DNA detection of major pathogenic avian leukosis virus subgroups using CRISPR-associated nuclease cas13a. Viruses 16, 1168. doi: 10.3390/v16071168
Xue, Y., Luo, X., Xu, W., Wang, K., Wu, M., Chen, L., et al. (2023). PddCas: A polydisperse droplet digital CRISPR/cas-based assay for the rapid and ultrasensitive amplification-free detection of viral DNA/RNA. Analytical Chem. 95, 966–975. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c03590
Yang, Y., Gong, F., Shan, X., Tan, Z., Zhou, F., Ji, X., et al. (2024). Amplification-free detection of Mpox virus DNA using Cas12a and multiple crRNAs. Mikrochimica Acta 191, 102. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06184-9
Yang, X., Huang, J., Chen, Y., Ying, X., Tan, Q., Chen, X., et al. (2023). Development of CRISPR/cas12b-based multiple cross displacement amplification technique for the detection of mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in clinical settings. Microbiol. Spectr. 11, e0347522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03475-22
Yang, X., Lu, L., Luo, Y., Wang, Q., Wang, J., Ren, Y., et al. (2025). Homemade isothermal amplification-initiated Cas14a assay for rapid quantitative detection of aquatic RNA virus gene with no PAM. Aquaculture 595, 741661. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2024.741661
Yin, K., Ding, X., Li, Z., Zhao, H., Cooper, K., and Liu, C. (2020). Dynamic aqueous multiphase reaction system for one-pot CRISPR-cas12a-based ultrasensitive and quantitative molecular diagnosis. Analytical Chem. 92, 8561–8568. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01459
Yoshimi, K., Takeshita, K., Yamayoshi, S., Shibumura, S., Yamauchi, Y., Yamamoto, M., et al. (2022). CRISPR-Cas3-based diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus. iScience 25, 103830. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103830
Yu, L., Peng, Y., Sheng, M., Wang, Q., Huang, J., and Yang, X. (2023). Sensitive and amplification-free electrochemiluminescence biosensor for HPV-16 detection based on CRISPR/cas12a and DNA tetrahedron nanostructures. ACS Sensors 8, 2852–2858. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.3c00806
Zeng, W., Chen, W., Liu, Y., Zhang, T., Zhai, C., Li, W., et al. (2024). Preamplification-free ultra-fast and ultra-sensitive point-of-care testing via LwaCas13a. Biosensors Bioelectronics 259, 116400. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2024.116400
Zeng, M., Ke, Y., Zhuang, Z., Qin, C., Li, L. Y., Sheng, G., et al. (2022). Harnessing multiplex crRNA in the CRISPR/cas12a system enables an amplification-free DNA diagnostic platform for ASFV detection. Analytical Chem. 94, 10805–10812. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c01588
Zhang, C., Chen, Y., Chen, X., Lin, X., Huang, Z., Zhang, L., et al. (2025). Single nanoparticle analysis-based CRISPR/Cas12 bioassay for amplification-free HIV detection. Chem. Commun. (Cambridge England) 61, 8759–8762. doi: 10.1039/d5cc01716e
Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, Q., Liu, Y., and Zhang, X. (2023c). An aM-level sensitive cascade CRISPR-Dx system (ASCas) for rapid detection of RNA without pre-amplification. Biosensors Bioelectronics 230, 115248. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2023.115248
Zhang, K., Sun, Z., Shi, K., Yang, D., Bian, Z., Li, Y., et al. (2023a). RPA-CRISPR/cas12a-based detection of haemophilus parasuis. Animals: Open Access J. MDPI 13, 3317. doi: 10.3390/ani13213317
Zhang, D., Zhang, Z., Unver, T., and Zhang, B. (2021). CRISPR/Cas: A powerful tool for gene function study and crop improvement. J. Advanced Res. 29, 207–221. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.10.003
Zhang, H., Zhao, H., Cao, L., Yu, B., Wei, J., Pan, G., et al. (2024). Harnessing multiplex crRNA enables an amplification-free/CRISPR-Cas12a-based diagnostic methodology for Nosema bombycis. Microbiol. Spectr. 12, e0301423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03014-23
Zhang, X., Zhao, Y., Zeng, Y., and Zhang, C. (2023b). Evolution of the probe-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assays in pathogen detection. Diagnostics (Basel Switzerland) 13, 1530. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13091530
Zhao, X., He, Y., Shao, S., Ci, Q., Chen, L., Lu, X., et al. (2024). CRISPR/cas14 and G-quadruplex DNAzyme-driven biosensor for paper-based colorimetric detection of African swine fever virus. ACS Sensors 9, 2413–2420. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.4c00090
Zhao, F., Hu, Y., Fan, Z., Huang, B., Wei, L., Xie, Y., et al. (2023). Rapid and sensitive one-tube detection of mpox virus using RPA-coupled CRISPR-Cas12 assay. Cell Rep. Methods 3, 100620. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100620
Zheng, L., Jiang, Y., Huang, F., Wu, Q., and Lou, Y. (2023). A colorimetric, photothermal, and fluorescent triple-mode CRISPR/cas biosensor for drug-resistance bacteria detection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 21, 493. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02262-x
Zhou, Z., Lau, C.-H., Wang, J., Guo, R., Tong, S., Li, J., et al. (2024c). Rapid and amplification-free nucleic acid detection with DNA substrate-mediated autocatalysis of CRISPR/cas12a. ACS Omega 9, 28866–28878. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c03413
Zhou, J., Li, Z., Seun Olajide, J., and Wang, G. (2024a). CRISPR/Cas-based nucleic acid detection strategies: Trends and challenges. Heliyon 10, e26179. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26179
Keywords: CRISPR technology, pathogen detection, amplification-based CRISPR, amplification-free CRISPR, isothermal amplification, sensor technology
Citation: Zhou X, Ye C, Xie M, Wei Y, Zhao Y, Liu X, Ma J, Qing J and Chen Z (2025) Advances in the application of CRISPR technology in pathogen detection: amplification-based and amplification-free strategies. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1645699. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1645699
Received: 12 June 2025; Accepted: 06 October 2025;
Published: 03 November 2025.
Edited by:
F-X Campbell-Valois, University of Ottawa, CanadaCopyright © 2025 Zhou, Ye, Xie, Wei, Zhao, Liu, Ma, Qing and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jilin Qing, aGVyb25kZ2lybEAxNjMuY29t; Zhizhong Chen, dGpjaGVuenpAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xiaoxing Zhou
Xiaoxing Zhou Chao Ye
Chao Ye Mengru Xie
Mengru Xie Yan Wei
Yan Wei Yilian Zhao
Yilian Zhao Xinchu Liu1
Xinchu Liu1 Jinghui Ma
Jinghui Ma Zhizhong Chen
Zhizhong Chen