- 1Department of Urology, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 3Department of Medicine, Yanbian University, Yanbian, China
Periodontal disease (PD) is one of the most common chronic diseases in the oral cavity, typically referring to chronic inflammation caused by infection with pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity. PD primarily affects the tissues surrounding the teeth, leading to inflammation of the gums and periodontal tissues, destruction of the alveolar bone, and even loosening of the teeth. Numerous studies have shown that PD is not limited to the oral cavity but is also associated with the occurrence of diseases in multiple systems throughout the body. In recent years, increasing attention has been directed toward the interaction between PD and prostate diseases. This article reviews the potential associations between PD and prostate conditions such as chronic prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and prostate cancer (PCa). It explores the pathological mechanisms underlying this interaction and its clinical implications. Additionally, this article aims to identify potential pathogenic mechanisms and propose possible approaches for preventing and treating prostate diseases through the management of PD.
1 Introduction
Prostate diseases are common urological conditions, primarily including non-cancerous prostate conditions such as prostatitis and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), as well as prostate cancer (PCa). The global burden of prostate diseases is significant, particularly among middle-aged and older men (Gupta et al., 2017; Al-Ghazawi et al., 2023; Calderone et al., 2023). Prostate diseases impose a substantial economic burden on society and severely impact men’s quality of life and survival time (Calderone et al., 2023). Prostatitis can occur in men of all ages, with approximately 5–9% of adult men worldwide affected by prostatitis (Li et al., 2020; He et al., 2023). According to the classification system of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), prostatitis can be categorized into acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic prostatitis, chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), and asymptomatic prostatitis. Whether acute or chronic, patients with bacterial prostatitis may experience prominent lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and urinary discomfort (Lam and Stokes, 2024). Patients with acute bacterial prostatitis may present with systemic infection symptoms, such as high fever, chills, severe pain in the perineum or suprapubic region, and a swollen, tender prostate palpable during digital rectal examination (Schoeb et al., 2017; Lam and Stokes, 2024; Yang et al., 2024). Chronic bacterial prostatitis, on the other hand, is characterized by recurrent urinary tract infection symptoms, including dull pain in the lower abdomen, and may be accompanied by sexual dysfunction (Schoeb et al., 2017; Lam and Stokes, 2024). The primary clinical symptom of chronic pelvic pain syndrome is persistent pelvic pain lasting ≥3 months, often radiating to the lower back, and frequently accompanied by urinary and sexual dysfunction (Hervás-Pérez et al., 2020; Matsukawa et al., 2022; Stevens et al., 2023). The incidence of BPH increases significantly with age, affecting over half of men over 50 years old (Yu et al., 2020; Calderone et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2025). BPH primarily manifests as non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. The enlarged prostate gland compresses the urethra, causing bladder outlet obstruction and resulting in lower urinary tract symptoms such as weak urine flow, difficulty urinating, and a sensation of incomplete emptying (Sundaram et al., 2017; Zattoni et al., 2017; Dias et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2023; Kaltsas et al., 2025). In severe cases, it can lead to acute urinary retention and recurrent urinary tract infections (Kang et al., 2016; Zattoni et al., 2017; Kim EH. et al., 2018). PCa is the second most common malignant tumor in men globally, following lung cancer (Hussain et al., 2021). The incidence and mortality rates of prostate cancer have significantly increased in recent years, particularly among older men. Common clinical manifestations of PCa include increased nocturia, weakened urine flow, erectile dysfunction, and gross hematuria (Merriel et al., 2018). If PCa metastasizes to the spine and pelvis, it can cause metastatic bone pain (Yamashita et al., 2018). When it invades the spinal cord and nerves, it can lead to neurological symptoms (Viglialoro et al., 2021). However, due to the insidious nature of early symptoms, some cases are already at an advanced stage by the time of diagnosis, increasing treatment difficulty. Although prostate diseases have a high prevalence in the population and significantly impact men’s health, the factors influencing their occurrence and progression remain unclear.
Periodontal disease (PD) is a common, chronic inflammatory condition of the oral cavity, primarily comprising gingivitis or periodontitis (Zhao et al., 2024). PD often affects the supporting tissues surrounding the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligaments, cementum, and alveolar bone. The development of PD is triggered by a complex inflammatory response resulting from an imbalance of oral microorganisms, which is associated with the immune response to pathogenic microorganisms and their toxins (Zhang et al., 2025). The human oral cavity harbors a diverse array of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and protozoa, collectively referred to as the oral microbiota (Chattopadhyay et al., 2023). A normal microbiota maintains oral environmental stability, regulates oral pH levels, and stimulates the activation of immune-protective functions in the oral mucosa (Chattopadhyay et al., 2023). However, these microorganisms can also cause oral diseases; an increase in pathogenic bacteria and their metabolites may contribute to tooth destruction and oral tissue inflammation (Zhang et al., 2025). Additionally, oral microorganisms can enter the bloodstream and produce inflammatory factors, potentially triggering diseases in multiple systems throughout the body (Li et al., 2022). Recent studies have shown that PD caused by dysbiosis of the oral microbiota plays a significant role in the onset and progression of prostate diseases. In this review, we summarize epidemiological and pathophysiological studies on the relationship between PD and prostate diseases to explore potential methods for preventing and treating prostate diseases through PD intervention.
2 Observational and experimental evidence suggest a strong association between PD and prostate disease
Recent observational studies have shown that the oral health of male patients with prostate disease differs significantly from that of healthy males. This suggests that PD may play an essential role in the development, progression, and treatment outcomes of prostate disease. Additionally, several animal studies have reported similar findings (Table 1).
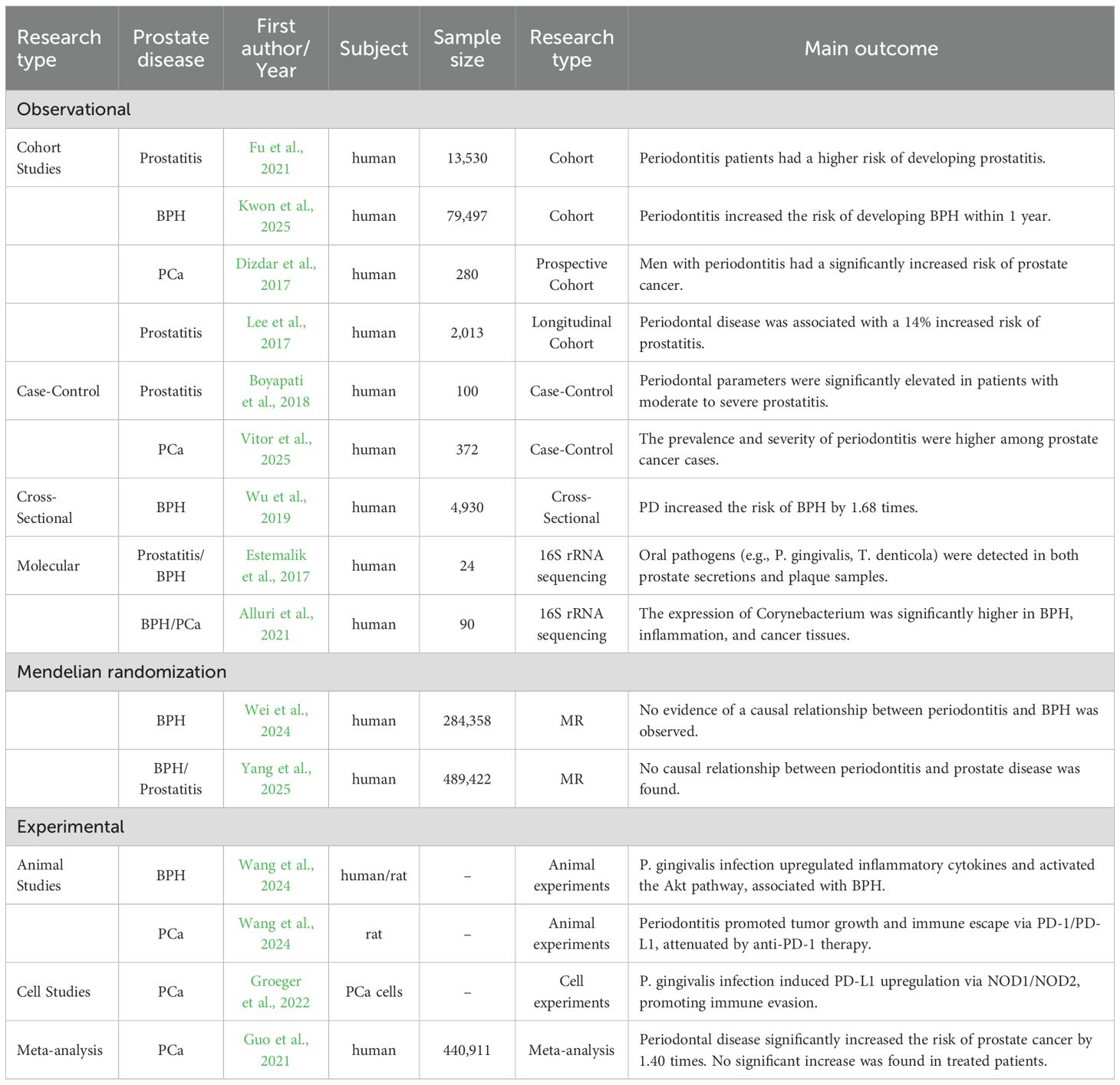
Table 1. Summary of evidence on the association between PD and prostate diseases, stratified by study design.
2.1 PD and prostatitis
PD is a chronic inflammatory disease, and its inflammatory mediators may affect distant organs through the bloodstream. For example, PD may influence the development of prostatitis. In a clinical study, 100 patients with both PD and chronic prostatitis were grouped, and periodontal parameters and serum PSA levels were recorded separately (Boyapati et al., 2018). It was found that periodontal parameters were significantly elevated in patients with moderate to severe prostatitis, indicating a pathological association between periodontitis and chronic prostatitis. In a cohort study in Taiwan comparing individuals with chronic periodontitis and healthy individuals, the risk of prostatitis was significantly higher in periodontitis patients than in those without periodontitis (Fu et al., 2021). Furthermore, John Estemalik et al. also identified similar DNA from Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola in prostate secretions and subgingival plaque from the same individuals with chronic prostatitis (Estemalik et al., 2017). These observational studies suggest that oral pathogens could potentially influence prostatitis through hematogenous spread or direct diffusion, confirming the association between PD and prostatitis.
2.2 PD and BPH
BPH is the most common urinary tract disease in elderly men, mainly manifested as cell proliferation in the prostate tissue, leading to an enlarged prostate. There may be a potential link between PD and the occurrence of BPH. A cross-sectional study of 4,930 men found that PD increased the risk of BPH by 1.68 times, with periodontitis patients having an even higher risk (Wu et al., 2019). In this study, the population was also grouped based on prostate volume, and PD was still found to increase the risk of BPH in different subgroups. However, individuals with a prostate volume >60g had a higher risk of PD (Wu et al., 2019). A cohort study in South Korea found that participants with a history of recurrent periodontitis had a higher incidence of BPH, indicating that chronic periodontitis is a risk factor for BPH (Kwon et al., 2025). Additionally, another study found that patients who underwent periodontal treatment had a reduced risk of BPH (Fu et al., 2021). In patients with both BPH and periodontitis, the same oral pathogens were detected in both prostate fluid and subgingival plaque (Estemalik et al., 2017). These studies suggest that PD may contribute to the development of BPH in men. However, other studies have yielded differing results, and Mendelian randomization studies on PD and BPH have not confirmed causal relationships at the genetic level (Wei et al., 2024; Yang L. et al., 2025). Future prospective cohort studies with larger sample sizes may be needed to clarify the true association between PD and BPH.
2.3 PD and PCa
Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the most common malignant tumors in men. The association between PD and PCa has been confirmed in numerous studies. In a case-control study involving 152 PCa patients and 220 control cases, periodontal examinations revealed a higher prevalence of PD among PCa patients, suggesting a link between periodontitis and the development of PCa (Vitor et al., 2025). In a 12-year longitudinal cohort study in South Korea, PD was found to increase the risk of PCa by 14%, with a significant positive correlation between PD and PCa (Lee et al., 2017). Additionally, Omer Dizdar et al. conducted a 12-year follow-up study on 280 participants with moderate to severe periodontitis, finding that periodontitis patients had a higher risk of developing PCa and blood cancer (Dizdar et al., 2017). A meta-analysis of cohort studies on the association between PD and PCa found that PD is associated with an increased risk of PCa. However, no significant association was observed in patients who received periodontal treatment (Guo et al., 2021). In another study, using 16S rRNA as primers, genomic DNA analysis of PCa glandular tissue identified specific periodontal pathogens, such as Fusobacterium nucleatum (Alluri et al., 2021). These study results support the view that PD is a risk factor for PCa. Middle-aged and older men should enhance their awareness of oral health and implement preventive and therapeutic measures for PD to reduce the risk of PCa.
3 Potential biological mechanisms linking PD and prostate disease
Although current observational studies have identified several associations between PD and prostate disease, and the differences described in these studies may become targets for the prevention and treatment of prostate disease, their specific mechanisms of action remain to be further clarified. This section will discuss in detail the potential mechanisms of action between PD and prostate disease, as well as how PD affects the development of prostate disease (Figure 1). It has been hypothesized that PD may directly or indirectly affect the onset and progression of prostate disease through the oral-prostate axis (Estemalik et al., 2017; Alluri et al., 2021; Wang SY. et al., 2024). One proposed mechanism suggests that oral pathogens may enter compromised periodontal tissues and subsequently enter and colonize the prostate via the blood or lymphatic systems (Estemalik et al., 2017; Alluri et al., 2021; Wang SY. et al., 2024). Moreover, PD is a chronic inflammatory disease, and the inflammatory factors it releases may affect prostate tissues through blood circulation, leading to a chronic inflammatory microenvironment, which in turn promotes the transformation of prostate disease from inflammation to hyperplasia or cancer. In recent years, with the advancement of biotechnology, researchers have gradually discovered the phenomenon of oral microbial transfer. In one study, 30 prostate tissue samples were selected from patients with inflammation, benign hyperplasia, and cancer (Alluri et al., 2021). Using 16S rRNA as primers, DNA from periodontal pathogens was detected in all these tissues (Alluri et al., 2021). Additionally, Wang et al. cultured subgingival plaque and prostate fluid from patients with BPH complicated by periodontitis, performed 16S rDNA sequencing, and detected oral pathogens such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, Streptococcus oralis, and Fusobacterium nucleatum (Wang SY. et al., 2024). In animal experiments, researchers established rat models of periodontitis and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), as well as their co-morbidities, to explore their interrelationships. Analysis of the gut microbiota by 16S rDNA sequencing and LC-MS/MS-based fecal metabolomics demonstrated that periodontitis may contribute to the pathogenesis of BPH by inducing dysbiosis of the gut flora and altering microbial-derived metabolites (Guo et al., 2023). When these periodontal pathogens colonize and infect the prostate, they may cause local inflammation and induce the onset of prostatitis. Infection of the prostate with Porphyromonas gingivalis upregulates the expression of inflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-6 receptor-α (IL-6Rα), and glycoprotein 130 (gp130) in the tissue. Its toxic factor, Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide (P.g-LPS), activates the Akt pathway through the IL-6/IL-6Rα/gp130 complex, significantly inhibiting prostate cell apoptosis and proliferation while promoting cell mitosis and proliferation, leading to BPH (Wang SY. et al., 2024). Additionally, Porphyromonas gingivalis and its LPS can upregulate PD-1/PD-L1 expression in PCa cells via the NOD1/NOD2 signaling pathway, promoting the increase in the proportion of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), regulatory T cells (Tregs), PD-L1 TAMs, and PD-1 CD8 Tregs, while reducing the proportion of CD8 Tregs (Groeger et al., 2022; Wang S. et al., 2024). This alters the tumor microenvironment to promote tumor immune escape and may contribute to the development and progression of PCa (Groeger et al., 2022; Wang S. et al., 2024).
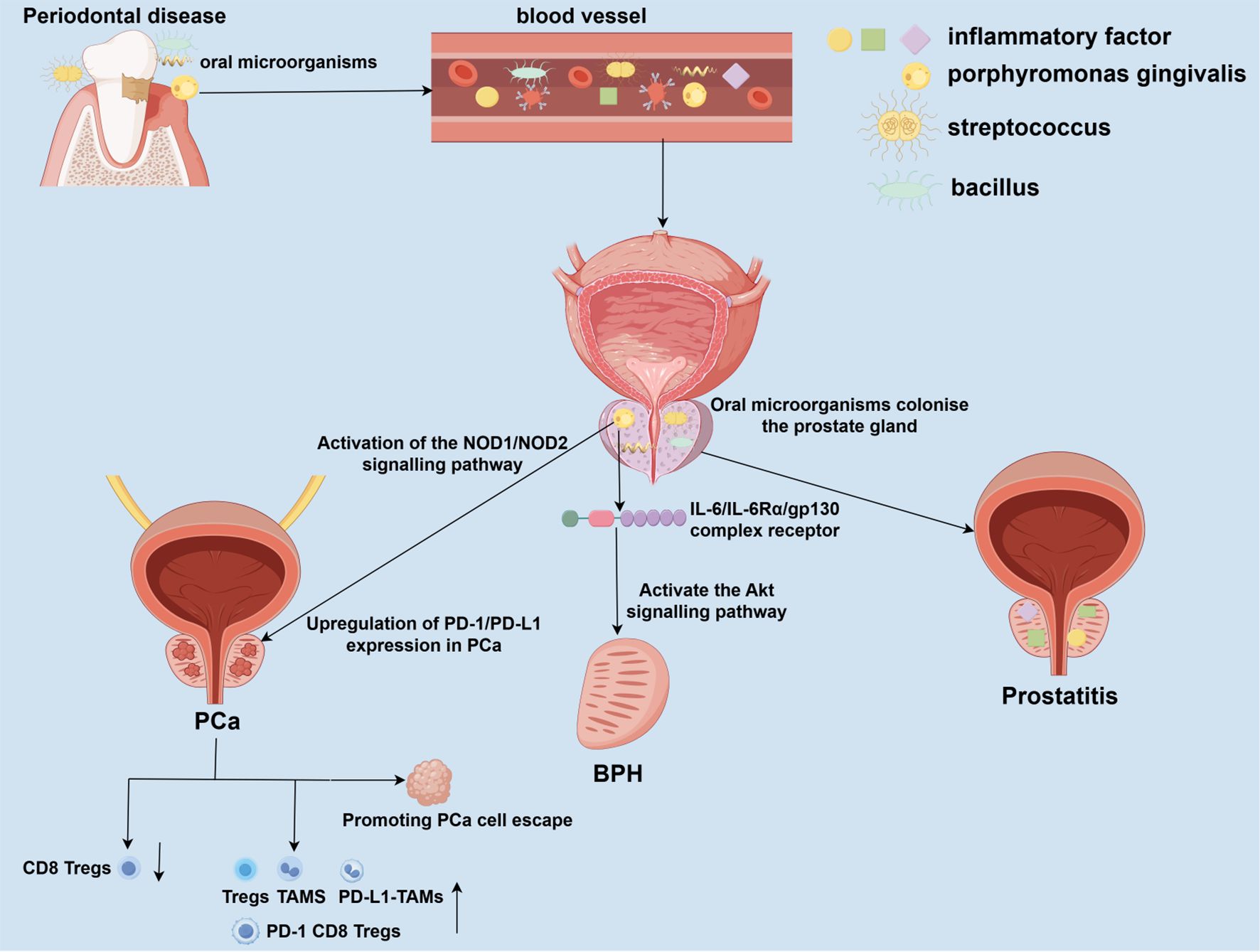
Figure 1. Potential mechanisms linking periodontal disease to prostate disease pathogenesis. Periodontal disease (PD), driven by oral dysbiosis, may impact prostate health through direct and indirect pathways. Oral pathogens from compromised periodontal pockets can enter the circulation and disseminate to the prostate gland. Colonization and infection by these pathogens can directly incite local inflammation, contributing to prostatitis. PD serves as a reservoir of chronic inflammation, releasing pro-inflammatory mediators and components of periodontal pathogens, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), into the bloodstream. This systemic inflammatory milieu can promote a pro-inflammatory microenvironment within the prostate. Infection with P. gingivalis and its LPS upregulates inflammatory cytokines, activates the IL-6/IL-6Rα/gp130 complex, and subsequently stimulates the Akt signaling pathway. This cascade disrupts the balance between cell proliferation and apoptosis, favoring prostate tissue hyperplasia. P. gingivalis infection, mediated through pattern recognition receptors, can upregulate immune checkpoint molecules like PD-L1 on tumor cells. This, along with the systemic inflammatory response, contributes to an immunosuppressive TME characterized by increased TAMs, regulatory Tregs, and exhausted CD8+ T cells, ultimately facilitating tumor immune evasion and progression. PD, periodontal disease; BPH, benign prostatic hyperplasia; PCa, prostate cancer; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-6Rα, interleukin-6 receptor alpha; gp130, glycoprotein 130; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; Akt, protein kinase B; NOD1/2, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 1/2; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; TME, tumor microenvironment; TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; Tregs, regulatory T cells.
4 Discussion
This review focuses on studies investigating the association between PD and prostate disease, as well as the potential mechanisms by which periodontal disease and its common oral pathogens influence the onset and progression of prostate disease (Figure 1). We propose that controlling PD may reduce the risk of developing prostate disease. This review primarily covers epidemiological studies on the association between PD and prostate disease, as well as a limited number of in vivo and in vitro studies. Epidemiological studies mainly include case-control studies and cross-sectional studies. In vivo studies primarily use rat or mouse animal models to simulate how PD-associated pathogens and inflammatory factors promote the development of prostate diseases. In vitro studies mainly involve microbiome and metabolome research, utilizing 16S rRNA sequencing of prostate-related tissues and subgingival exudate (Estemalik et al., 2017).
When interpreting the epidemiological association between PD and prostate diseases, it is essential to consider the influence of multiple potential confounding factors carefully. These confounding variables may partially drive the correlations observed in observational studies. Age represents the most clearly identified common risk factor shared by prostate diseases and PD. Advanced age is not only associated with prostate tissue hyperplasia and the accumulation of genetic mutations. Still, it is also closely linked to the physiological degeneration of periodontal tissues and prolonged microbial exposure (Tan et al., 2021; Fox et al., 2023; Bertolini and Clark, 2024). Furthermore, smoking is a well-established risk factor for periodontitis while also inducing systemic inflammation and oxidative stress (Mazurek-Mochol et al., 2017; Ehsan, 2025). Research indicates smoking may independently increase prostate cancer risk or influence its progression. Smokers typically exhibit poorer oral health and may face distinct prostate disease risks compared to non-smokers, making smoking a significant potential confounder (Tang et al., 2017; AlQobaly et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2024; Yang X. et al., 2025). Diabetes is also strongly associated with more severe and extensive periodontitis, exacerbating periodontal destruction through mechanisms such as advanced glycation end-product (AGEs) accumulation and immune dysfunction (Liu et al., 2018; Nonaka et al., 2018). Simultaneously, diabetes is recognized as a risk factor for BPH (Ozcan et al., 2017). The chronic inflammatory state accompanying diabetes may represent an upstream pathway linking PD to prostate diseases (Chen and Feng, 2023). Socioeconomic status (SES) is a multidimensional factor encompassing education, income, occupation, and access to healthcare. Lower SES is typically associated with poorer oral hygiene, reduced dental care utilization, higher smoking rates, unhealthy diets, and inadequate management of systemic diseases (Fowke et al., 2008; Kim HN. et al., 2018; Park et al., 2018; Tadakamadla et al., 2020; Mikami et al., 2023). These factors may contribute to the elevated burden of both PD and prostate disease in this population, introducing confounding into analyses (Fowke et al., 2008; Kim HN. et al., 2018; Park et al., 2018; Tadakamadla et al., 2020; Mikami et al., 2023). Although most observational studies attempt to control these variables through multivariate regression models, residual confounding may persist. Furthermore, Mendelian randomization studies have failed to establish a genetic-level causal relationship between PD and BPH, which partially weakens the causal inferences drawn from observational findings. This suggests that such associations may be influenced by the confounding factors or reverse causality.
Recent studies have shown that PD is closely associated with prostate diseases, including chronic prostatitis, BPH, and PCa. Research indicates that periodontal disease may affect prostate health through microbial transmission and systemic inflammation, highlighting the importance of oral health in preventing the risk of prostate diseases. Oral pathogens, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum, have been detected in prostate tissue, supporting the hypothesis that these pathogens may spread from the oral cavity to the prostate via the bloodstream or lymphatic system (Alluri et al., 2021). These pathogens may not only directly induce prostate inflammation but also promote cancer development by altering the local microenvironment. For example, Porphyromonas gingivalis has been shown to upregulate the expression of inflammatory cytokines and activate the Akt signaling pathway and the PD-1/PD-L1 receptor pathway, which are closely associated with the development of BPH and PCa (Groeger et al., 2022; Wang SY. et al., 2024). Furthermore, chronic inflammation caused by periodontal disease can exacerbate prostate lesions by releasing pro-inflammatory mediators such as IL-6 and reactive oxygen species into the bloodstream (Tonguç et al., 2022; Wang S. et al., 2024). This systemic response may sustain a pro-inflammatory environment within the prostate, thereby inducing tissue hyperplasia or malignant transformation (Groeger et al., 2022; Wang S. et al., 2024). The observed reduction in the risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia following periodontal treatment further underscores the critical role of inflammation in disease progression (Fu et al., 2021). Although most observational studies support a positive correlation between PD and prostate disease, considerable heterogeneity exists between studies, with inconsistent and even contradictory conclusions emerging, particularly in BPH research. For instance, cross-sectional and cohort studies by Wu et al. and Kwon et al. both indicated that PD significantly increases the risk of BPH, whereas studies by Wei et al. and Yang et al., based on Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis, failed to identify a genetic causal relationship between the two (Wu et al., 2019; Wei et al., 2024; Kwon et al., 2025; Yang L. et al., 2025). These inconsistencies may stem from several factors. Observational studies are susceptible to confounding variables, while MR analysis, although it reduces confounding, remains sensitive to weak instrumental variables or differences in population structure. Furthermore, inconsistencies in diagnostic criteria for BPH and severity classification of PD across studies may introduce bias. Some studies were based on Asian populations, while others utilized European databases; differences in genetic backgrounds, environmental factors, and healthcare accessibility may affect the generalizability of the findings.
This study has several limitations, primarily focused on epidemiological and in vitro experimental aspects, with limited involvement in vivo experiments. The specific molecular pathways by which bacterial translocation and oral pathogens induce prostatitis and carcinogenesis require further elucidation using advanced animal models and multi-omics approaches. Additionally, while the potential of PD management to alleviate the burden of prostate disease appears promising, it has not been fully explored. However, there is currently a complete lack of evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to substantiate that treating periodontal disease can alleviate symptoms of prostate conditions or alter their natural course. For instance, whether routine periodontal care for high-risk populations, such as elderly men, can reduce the incidence of PCa remains to be determined. Future research should utilize animal models that simulate the coexistence of PD and prostate disease to elucidate the molecular mechanisms and validate targeted therapeutic approaches. PD can facilitate the entry of oral pathogens into the bloodstream, causing transient bacteremia (Gualtero et al., 2023). While the existence of a resident blood microbiome in healthy individuals is debated and not supported by large-scale studies, it is plausible that during periods of active periodontal infection, these circulating pathogens could disseminate to and seed the prostate gland (Tan et al., 2023). Integrating multi-omics technologies, such as metagenomics and metabolomics, enables a systematic analysis of microbial characteristics and metabolite associations between oral and prostate dysbiosis. Furthermore, metagenomic sequencing of matched oral, blood, and prostate samples allows tracing the migration and colonization pathways of oral microbiota (Tan et al., 2023). Conducting additional randomized controlled trials to evaluate the impact of periodontal treatment on the severity of prostate symptoms or disease progression will provide stronger scientific evidence for clinical application.
5 Conclusion
The interplay between PD and prostate diseases highlights a potential shared pathophysiology centered on infection and inflammation. While current observational evidence suggests an association, it does not establish a causal relationship. Periodontitis may represent a novel, modifiable risk factor for prostate diseases. However, translating this association into clinical practice requires rigorous mechanistic studies to elucidate the causal pathways and, crucially, interventional trials to confirm that periodontal treatment can effectively improve prostate health outcomes. Enhancing oral health awareness and integrating dental care into urological health strategies may offer a promising avenue for the prevention and adjunctive therapy of prostate diseases, pending validation from future research.
Author contributions
SL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ML: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. WU JIEPING Medical Foundation (NO.3D4240299428).
Acknowledgments
All figures in this article were drawn by Figdraw (https://www.figdraw.com/#/).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al-Ghazawi, M., Salameh, H., Amo-Afful, S., Khasawneh, S., and Ghanem, R. (2023). An in-depth look into the epidemiological and etiological aspects of prostate cancer: A literature review. Cureus. 15, e48252. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48252
Alluri, L. S. C., Paes Batista da Silva, A., Verma, S., Fu, P., Shen, D. L., MacLennan, G., et al. (2021). Presence of specific periodontal pathogens in prostate gland diagnosed with chronic inflammation and adenocarcinoma. Cureus. 13, e17742. doi: 10.7759/cureus.17742
AlQobaly, L., Abed, H., Alsahafi, Y., Sabbah, W., and Hakeem, F. F. (2022). Does smoking explain the association between use of e-cigarettes and self-reported periodontal disease? J. Dent. 122, 104164. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2022.104164
Bertolini, M. and Clark, D. (2024). Periodontal disease as a model to study chronic inflammation in aging. Geroscience. 46, 3695–3709. doi: 10.1007/s11357-023-00835-0
Boyapati, R., Swarna, C., Devulapalli, N., Sanivarapu, S., Katuri, K. K., and Kolaparthy, L. (2018). Unveiling the link between prostatitis and periodontitis. Contemp Clin. Dent. 9, 524–529. doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_746_18
Calderone, C. E., Turner, E. M., Hayek, O. E., Summerlin, D., West, J. T., Rais-Bahrami, S., et al. (2023). Contemporary review of multimodality imaging of the prostate gland. Diagnostics (Basel) 13, 1860. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13111860
Chattopadhyay, I., Lu, W., Manikam, R., Malarvili, M. B., Ambati, R. R., and Gundamaraju, R. (2023). Can metagenomics unravel the impact of oral bacteriome in human diseases? Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 39, 85–117. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2022.2102877
Chen, G. and Feng, L. (2023). Analysis of platelet and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio and diabetes mellitus with benign prostatic enlargement. Front. Immunol. 14, 1166265. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1166265
Dias, U. S., Jr., de Moura, M. R. L., Viana, P. C. C., de Assis, A. M., Marcelino, A. S. Z., Moreira, A. M., et al. (2021). Prostatic artery embolization: indications, preparation, techniques, imaging evaluation, reporting, and complications. Radiographics. 41, 1509–1530. doi: 10.1148/rg.2021200144
Dizdar, O., Hayran, M., Guven, D. C., Yılmaz, T. B., Taheri, S., Akman, A. C., et al. (2017). Increased cancer risk in patients with periodontitis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 33, 2195–2200. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2017.1354829
Ehsan, H. (2025). The influence of smoking on periodontal health: A case-control study in Afghanistan. J. Periodontol. 96, 817–825. doi: 10.1002/JPER.24-0693
Estemalik, J., Demko, C., Bissada, N. F., Joshi, N., Bodner, D., Shankar, E., et al. (2017). Simultaneous detection of oral pathogens in subgingival plaque and prostatic fluid of men with periodontal and prostatic diseases. J. Periodontol. 88, 823–829. doi: 10.1902/jop.2017.160477
Fowke, J. H., Murff, H. J., Signorello, L. B., Lund, L., and Blot, W. J. (2008). Race and socioeconomic status are independently associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia. J. Urol. 180, 2091–2096. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.07.059
Fox, J. J., Hashimoto, T., Navarro, H. I., Garcia, A. J., Shou, B. L., and Goldstein, A. S. (2023). Highly multiplexed immune profiling throughout adulthood reveals kinetics of lymphocyte infiltration in the aging mouse prostate. Aging (Albany NY). 15, 3356–3380. doi: 10.18632/aging.204708
Fu, E., Cheng, C. M., Chung, C. H., Lee, W. C., Chen, W. L., Sun, G. H., et al. (2021). Association of chronic periodontitis with prostatic hyperplasia and prostatitis: A population-based cohort study in Taiwan. J. Periodontol. 92, 72–86. doi: 10.1002/JPER.19-0706
Groeger, S., Wu, F., Wagenlehner, F., Dansranjav, T., Ruf, S., Denter, F., et al. (2022). PD-L1 up-regulation in prostate cancer cells by porphyromonas gingivalis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 12, 935806. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.935806
Gualtero, D. F., Lafaurie, G. I., Buitrago, D. M., Castillo, Y., Vargas-Sanchez, P. K., and Castillo, D. M. (2023). Oral microbiome mediated inflammation, a potential inductor of vascular diseases: a comprehensive review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 10, 1250263. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1250263
Guo, Z., Gu, C., Li, S., Gan, S., Li, Y., Xiang, S., et al. (2021). Periodontal disease and the risk of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 47, 1120–1130. doi: 10.1590/s1677-5538.ibju.2020.0333
Guo, X. P., Yang, J., Wu, L., Fang, C., Gu, J. M., Li, F., et al. (2023). Periodontitis relates to benign prostatic hyperplasia via the gut microbiota and fecal metabolome. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1280628. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1280628
Gupta, S., Gupta, A., Saini, A. K., Majumder, K., Sinha, K., and Chahal, A. (2017). Prostate cancer: how young is too young? Curr. Urol 9, 212–215. doi: 10.1159/000447143
He, H., Luo, H., Xu, H., Qian, B., Zou, X., Zhang, G., et al. (2023). Preclinical models and evaluation criteria of prostatitis. Front. Immunol. 14, 1183895. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1183895
Hervás-Pérez, J. P., Jiménez Díaz-Benito, V., Guodemar-Pérez, J., Ruiz-López, M., García-Fernández, P., Rodríguez-López, E. S., et al. (2020). The influence of physical activity as an alternative treatment to chronic prostatitis: A meta-analysis. Rev. Int. Androl. 18, 107–116. doi: 10.1016/j.androl.2018.12.001
Huang, Y. Q., Xu, J. N., Huang, Y., Xu, Y. D., Wang, H. L., Shi, W. T., et al. (2024). Independent and combined effects of smoking, drinking and depression on periodontal disease. BMC Oral. Health 24, 535. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04287-6
Hussain, Y., Mirzaei, S., Ashrafizadeh, M., Zarrabi, A., Hushmandi, K., Khan, H., et al. (2021). Quercetin and its nano-scale delivery systems in prostate cancer therapy: paving the way for cancer elimination and reversing chemoresistance. Cancers (Basel) 13, 1602. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071602
Kaltsas, A., Giannakodimos, I., Symeonidis, E. N., Deligiannis, D., Stavropoulos, M., Symeonidis, A., et al. (2025). To rezūm or not to rezūm: A narrative review of water vapor thermal therapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia. J. Clin. Med. 14, 4254. doi: 10.3390/jcm14124254
Kang, D. H., Cho, K. S., Ham, W. S., Choi, Y. D., and Lee, J. Y. (2016). A systematic review and meta-analysis of functional outcomes and complications following the photoselective vaporization of the prostate and monopolar transurethral resection of the prostate. World J. Mens Health 34, 110–122. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.2016.34.2.110
Kim, E. H., Brockman, J. A., and Andriole, G. L. (2018). The use of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Asian J. Urol. 5, 28–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2017.11.005
Kim, H. N., Jang, Y. E., Kim, C. B., and Kim, N. H. (2018). Socioeconomic status and self-reported periodontal symptoms in community-dwelling individuals: data from the Korea Community Health Surveys of 2011 and 2013. Int. Dent. J. 68, 411–419. doi: 10.1111/idj.12407
Kwon, M. J., Kang, H. S., Choi, H. G., Kim, J. H., Yoo, D. M., Lee, N. E., et al. (2025). Chronic periodontitis as a risk factor for benign prostatic hyperplasia: A cohort study. J. Clin. Med. 14, 1279. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041279
Lee, J. H., Kweon, H. H., Choi, J. K., Kim, Y. T., and Choi, S. H. (2017). Association between Periodontal disease and Prostate cancer: Results of a 12-year Longitudinal Cohort Study in South Korea. J. Cancer. 8, 2959–2965. doi: 10.7150/jca.20532
Li, G., Chang, D., Chen, D., Zhang, P., You, Y., Huang, X., et al. (2020). Efficacy of radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: A protocol for systematic review. Med. (Baltimore). 99, e22981. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022981
Li, Y., Zhu, M., Liu, Y., Luo, B., Cui, J., Huang, L., et al. (2022). The oral microbiota and cardiometabolic health: A comprehensive review and emerging insights. Front. Immunol. 13, 1010368. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1010368
Liu, Y., Yu, Y., Nickel, J. C., Iwasaki, L. R., Duan, P., Simmer-Beck, M., et al. (2018). Gender differences in the association of periodontitis and type 2 diabetes. Int. Dent. J. 68, 433–440. doi: 10.1111/idj.12399
Liu, J., Zhang, J., Fu, X., Yang, S., Li, Y., Liu, J., et al. (2023). The emerging role of cell adhesion molecules on benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 2870. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032870
Matsukawa, Y., Funahashi, Y., Ishida, S., Naito, Y., Yuba, T., Matsuo, K., et al. (2022). Clinical features and urodynamic findings in elderly men with chronic prostatitis. Int. J. Urol. 29, 441–445. doi: 10.1111/iju.14805
Mazurek-Mochol, M., Majorczyk, E., Banach, J., Dembowska, E., Kuśnierczyk, P., Safranow, K., et al. (2017). The influence of KIR gene presence/absence polymorphisms on the development of periodontal disease in smokers and non-smokers. Cent Eur. J. Immunol. 42, 347–353. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2017.72796
Merriel, S. W. D., Funston, G., and Hamilton, W. (2018). Prostate cancer in primary care. Adv. Ther. 35, 1285–1294. doi: 10.1007/s12325-018-0766-1
Mikami, R., Mizutani, K., Aoyama, N., Matsuura, T., Suda, T., Takeda, K., et al. (2023). Income-related inequalities in the association of smoking with periodontitis: a cross-sectional analysis in Tokyo Metropolitan Districts. Clin. Oral. Investig. 27, 519–528. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04747-9
Nonaka, K., Kajiura, Y., Bando, M., Sakamoto, E., Inagaki, Y., Lew, J. H., et al. (2018). Advanced glycation end-products increase IL-6 and ICAM-1 expression via RAGE, MAPK and NF-κB pathways in human gingival fibroblasts. J. Periodontal Res. 53, 334–344. doi: 10.1111/jre.12518
Ozcan, L., Besiroglu, H., Dursun, M., Polat, E. C., Otunctemur, A., and Ozbek, E. (2017). Comparison of the clinical parameters of benign prostate hyperplasia in diabetic and non diabetic patients. Arch. Ital Urol Androl. 89, 26–30. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2017.1.26
Park, M. B., Hyun, D. S., Song, J. M., Chung, H. C., Kwon, S. W., Kim, S. C., et al. (2018). Association between the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia and social disparities: Does social capital promote prostate health? Andrologia 50, e13125. doi: 10.1111/and.13125
Schoeb, D. S., Schlager, D., Boeker, M., Wetterauer, U., Schoenthaler, M., Herrmann, T. R. W., et al. (2017). Surgical therapy of prostatitis: a systematic review. World J. Urol. 35, 1659–1668. doi: 10.1007/s00345-017-2054-0
Stevens, R. H., Zhang, H., Kajsik, M., Płoski, R., Rydzanicz, M., Sabaka, P., et al. (2023). Successful use of a phage endolysin for treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome/chronic bacterial prostatitis. Front. Med. (Lausanne). 10, 1238147. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1238147
Sundaram, D., Sankaran, P. K., Raghunath, G., Vijayalakshmi, S., Vijayakumar, J., Yuvaraj, M. F., et al. (2017). Correlation of prostate gland size and uroflowmetry in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 11, Ac01–Aac4. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/26651.9835
Tadakamadla, S. K., Tadakamadla, J., Kroon, J., Lalloo, R., and Johnson, N. W. (2020). Effect of family characteristics on periodontal diseases in children and adolescents-A systematic review. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 18, 3–16. doi: 10.1111/idh.12398
Tan, J., Dai, A., Pan, L., Zhang, L., Wang, Z., Ke, T., et al. (2021). Inflamm-aging-related cytokines of IL-17 and IFN-γ Accelerate osteoclastogenesis and periodontal destruction. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 9919024. doi: 10.1155/2021/9919024
Tan, C. C. S., Ko, K. K. K., Chen, H., Liu, J., Loh, M., Chia, M., et al. (2023). No evidence for a common blood microbiome based on a population study of 9,770 healthy humans. Nat. Microbiol. 8, 973–985. doi: 10.1038/s41564-023-01350-w
Tang, B., Han, C. T., Gan, H. L., Zhang, G. M., Zhang, C. Z., Yang, W. Y., et al. (2017). Smoking increased the risk of prostate cancer with grade group ≥ 4 and intraductal carcinoma in a prospective biopsy cohort. Prostate. 77, 984–989. doi: 10.1002/pros.23354
Tonguç, M., Öztürk, C., Polat, G., Bobuşoğlu, O., Tek, S. A., Taşdelen, B., et al. (2022). Investigation of the relationship between periodontal and systemic inflammation in children with Sickle Cell Disease: A case- control study. Cytokine. 149, 155724. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155724
Viglialoro, R., Esposito, E., Zanca, R., Gessi, M., Depalo, T., Aghakhanyan, G., et al. (2021). What to trust, PSA or [(68)Ga]Ga-PSMA-11: learn from experience. Res. Rep. Urol. 13, 597–601. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S316446
Vitor, G. P., Carvalho, A. P., Esteves Lima, R. P., Miconi, W. G., Costa, F. O., and Cota, L. O. M. (2025). Association between periodontitis and prostate cancer: A case-control study. J. Periodontol. 96:1026–1034. doi: 10.1002/JPER.24-0440
Wang, S. Y., Cai, Y., Hu, X., Li, F., Qian, X. H., Xia, L. Y., et al. (2024). P. gingivalis in oral-prostate axis exacerbates benign prostatic hyperplasia via IL-6/IL-6R pathway. Mil Med. Res. 11, 30. doi: 10.1186/s40779-024-00533-8
Wang, S., Nie, F., Yin, Q., Tian, H., Gong, P., Ju, J., et al. (2024). Periodontitis promotes tumor growth and immune evasion via PD-1/PD-L1. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 74, 22. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03865-5
Wang, H., Tang, R., Luo, S., Hou, H., Liu, J., Liu, M., et al. (2025). Association of life’s crucial 9 score with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a cross-sectional study. J. Health Popul Nutr. 44, 163. doi: 10.1186/s41043-025-00925-z
Wei, H., Tian, G., Xu, S., Du, Y., Li, M., Wang, Y., et al. (2024). Evaluation of bi-directional causal association between periodontitis and benign prostatic hyperplasia: epidemiological studies and two-sample mendelian randomization analysis. Front. Genet. 15, 1326434. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1326434
Wu, L., Li, B. H., Wang, Y. Y., Wang, C. Y., Zi, H., Weng, H., et al. (2019). Periodontal disease and risk of benign prostate hyperplasia: a cross-sectional study. Mil Med. Res. 6, 34. doi: 10.1186/s40779-019-0223-8
Yamashita, K., Mizugishi, K., and Takaori-Kondo, A. (2018). Familial mediterranean fever mutations in a patient with periodic episodes of systemic pain deriving from cancer bone metastases. Intern. Med. 57, 2901–2904. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0431-17
Yang, X., Chen, H., Zhang, J., Zhang, S., Wu, Y. S., and Pang, J. (2025). Association of cigarette use with risk of prostate cancer among US males: a cross-sectional study from NHANES 1999-2020. BMC Public Health 25, 608. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21863-9
Yang, Y., Shigemura, K., Maeda, K., Moriwaki, M., Chen, K. C., Nakano, Y., et al. (2024). The harmful effects of overlooking acute bacterial prostatitis. Int. J. Urol. 31, 459–463. doi: 10.1111/iju.15390
Yang, L., Wang, L., Zheng, Y. B., Liu, Y., Bao, E. H., Wang, J. H., et al. (2025). Causal relationship between periodontitis and prostate diseases: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Clin. Oral. Investig. 29, 127. doi: 10.1007/s00784-025-06211-w
Yu, Z. J., Yan, H. L., Xu, F. H., Chao, H. C., Deng, L. H., Xu, X. D., et al. (2020). Efficacy and side effects of drugs commonly used for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 658. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00658
Zattoni, F., Ficarra, V., and Novara, G. (2017). Risk stratification for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urologia. 84, 153–157. doi: 10.5301/uro.5000220
Zhang, C., Fei, Y., Li, M., Li, J., Tang, M., Wang, G., et al. (2025). Chitosan-P407-PNIPAM hydrogel loaded with AgNPs/lipid complex for antibacterial, inflammation regulation and alveolar bone regeneration in periodontitis treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 307, 142080. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.142080
Keywords: periodontal disease, oral microbiota, prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostatitis, systemic inflammation, inflammatory factors
Citation: Li S, Cao H, Zhang Y, Yang T, Li M, Lv C and Lian X (2025) Association between periodontal disease and prostate disease: a mini review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1669490. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1669490
Received: 19 July 2025; Accepted: 26 September 2025;
Published: 08 October 2025.
Edited by:
Soumyadev Sarkar, Arizona State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Jungeun Park, Dankook University College of Public Health Sciences, Republic of KoreaCopyright © 2025 Li, Cao, Zhang, Yang, Li, Lv and Lian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xin Lian, bGlhbnhpbjYyMTYxNjNAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Shuxin Li
Shuxin Li Hongliang Cao
Hongliang Cao Yueqiu Zhang
Yueqiu Zhang Tong Yang1
Tong Yang1 Chensen Lv
Chensen Lv